OCN 201: Earth Structure
|
|
|
- Francis Berry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 OCN 201: Earth Structure Eric Heinen Eric H. De Carlo, Carlo: OCN 201, OCN Sp , Fall 2004
2 Early History of the Earth Rapid accretion of Earth and attendant dissipation of kinetic energy caused tremendous heating. Earth possibly melted completely. In molten state, differentiation would occur.
3 Core Formation Heavy elements (mainly Fe) would sink inward. Lighter elements would migrate outward. HOWEVER Heavy elements may have already been concentrated at the center because they fell inward during accretion. Thus the core may have formed by heterogenous accretion at Earth s formation or soon after if Earth formed by homogenous accretion. The latter would have been accompanied by extensive outgassing, the process that ultimately formed the oceans. Core formation was largely complete in <100 Ma.
4 Origin of Oceans/Atmosphere: I Accretion and differentiation of Earth would have created an atmosphere by outgassing Our atmosphere is thus of secondary origin: derived by outgassing of interior rather than directly from solar nebula Evidence: Earth is depleted in noble gases Alternate hypothesis: heterogeneous accretion of late veneer, possibly from asteroids (and small amount of comets) NOTE: we are simplifying the event sequence that led to the formation of the Earth and oceans
5 Origin of Oceans/Atmosphere: II Water as a volatile substance would have been outgassed from early Earth but retained by its gravity BUT the Earth surface was too hot for a liquid ocean Is Earth fully outgassed today??? Estimates range from 20% to nearly complete Outgassing was likely faster from early Earth Radioactive decay (causes heat) was 4-5 X greater than today, thus outgassing would have been commensurately faster
6 Origin of Oceans/Atmosphere: III Outgassing of Earth continues now... Evidence comes from 3 He in ocean near MOR 3 He released from Earth interior by volcanic processes, Sp2010
7 3 He in Pacific Ocean
8 Composition of Volcanic Gases TODAY. 80% H 2 O 10% CO 2 5% SO 2 1% H 2 Trace, N 2, HCl Major gases are in oxidized form now Only H 2 is reduced Early volcanic gases were likely in reduced form (H 2, CH 4, H 2 S, NH 3 ) Early atmosphere: Free O 2 would have been absent. CO 2 and CH 4 were probably abundant. The CO 2 would have eventually reacted with rocks (in water): (H 2 O) + CO 2 + CaSiO 3 CaCO 3 + SiO 2 + (H 2 O)
9 Early Atmosphere Free O 2 was absent Any O 2 was quickly used to oxidize reduced materials in rocks O 2 also used to oxidize reduced Fe (which was likely very abundant in early seawater)
10 Solar Luminosity Luminosity of Sun has increased by 30% over 4.5 Ga. Change in luminosity has altered Earth T Early Earth T = 248K (-13 o F, -25 o C) Current T = 288K (59 o F, 15 o C) Faint early sun paradox : why did Earth s early oceans not freeze over? CO 2 and CH 4 methane in the early atmosphere may be the answer., Sp2010
11 Structure of the Earth Inner core: solid Fe-Ni Outer core: liquid Fe-Ni Mantle: rocky: Mg-Fe silicate Crust: rocky: Mg-Fe-Al-Ca silicate Oceans: H 2 O with dissolved salts Atmosphere: N 2, O 2, Ar
12 Internal Structure of the Earth: I Mean density of Earth is 5.5 g/cm 3 (mass/vol) Density determined by shape, size, mass, and moment of inertia of Earth Earth structure determined in large part by physical measurements (seismic methods) Discontinuities in seismic velocities are due to changes in bulk density/composition
13 Seismic Waves: I Generated by earthquakes (or explosions) Two types: P and S waves
14 Seismic Waves: II P-waves Primary waves Faster than S waves Compressional Like a spring compressing and dilating Travel through solid or liquid
15 Seismic Waves: III S-waves Secondary waves Slower than P waves Shear Like undulation of string Do not propagate through a liquid No restoring force in liquid
16 Seismic Waves: IV
17 Seismic Waves: V Waves bend in response to changes in properties of material. S-wave shadow zone P-wave shadow zones, Sp2010
18 Internal Structure of the Earth: II (based on chemical properties) Inner Core: km, solid Fe + 6% Ni (16 g/cm 3 ) Outer Core: km, liquid Fe-Ni (12 g/cm 3 ) Core is 32% of Earth mass, 16% of its volume Mantle: ~ km, solid Mg-Fe-silicates (4.5 g/cm 3 ), 68% of Earth mass, 83% of its volume Crust: the skin of Earth: 0.4% of Earth mass and <1% of its volume.
19 Earth s Crust The crust represents only 0.4% of the mass of Earth, and <1% of its volume. There are two types: Oceanic and Continental Oceanic Only 6 km thick Made of basalt (like Hawaiian Islands) 2.9 g/cm 3 Continental 35 km thick Made of granite (really granodiorite or andesite) 2. 7 g/cm 3
20 Internal Structure of the Earth: III (based on physical properties) Use viscosity and strength to describe outer layers: Lithosphere: km = mantle + crust Asthenosphere: km = mantle Mesosphere: km = mantle
21 Internal Structure of the Earth: IV Lithosphere is cool, rigid, can support loads and includes the crust and uppermost mantle Asthenosphere is near its melting point, deforms plastically Upper asthenosphere ( km) is a low velocity zone thought to contain ~1% melt Upper asthenosphere is the zone of isostatic compensation and a zone of magma generation for igneous rocks The mesosphere (most of mantle) extends to the core and is more rigid than the asthenosphere
22 Bulk Composition of Earth (wt %) Elements are NOT distributed uniformly wt.% Fe 36.0 O 28.7 Mg 14.8 Si 13.6 Subtotal: 93.1% 85 ± 4 % of Fe is in the core (metallic) (Upper) Mantle: rocky: mainly Mg-silicates. Ni 2.0 Ca 1.7 S 1.7 Al 1.3 Most of the Ni is in the core Al is mostly in alumino-silicates TOTAL: 98-99%
23 Summary why do we have oceans? Lots of liquid water available but why? 1) rapid accretion of cold, icy, water rich planetesimals (allowed retention of volatile H 2 O after ice melted) 2) outgassing of interior of Earth brought H 2 O to surface 3) moderate distance from Sun moderate temperature allowed H 2 O to be present in liquid form Do other bodies in the Solar System have oceans? YES! Mars probably had oceans in the distant past. Europa (moon of Jupiter) may have oceans under thick ice. Titan, a moon of Saturn, may have liquid hydrocarbon oceans, with continents of rock, H 2 O ice, and CO 2 ice.
24 Earth and its nearest neighbors All 3 planets have similar noble gas abundance ratios, implying grossly similar composition and outgassing history.
25 Comparative Planetology Distance Surface Surface ATMOSPHERE: Mass Radius Density from Sun Temp. Press. H 2 O CO 2 N 2 O g km g/cm km (K) (atm) % % % % Venus Earth < Mars Inventory of CO 2, in units of moles: Earth, in crust, atmosphere, and oceans: 75 in mantle: 150 Venus, in atmosphere: 120 H 2 O + CO 2 + CaSiO 3 CaCO 3 + SiO 2 + H 2 O
26 Venus has outgassed a similar amount of CO 2 as Earth, but it stayed in the the atmosphere, causing a runaway greenhouse. On Earth this CO 2 is locked up in rocks! High temperatures caused Venus to lose all of its H 2 O (260 atm-worth!) by photodissociation followed by loss of H 2 to space. Venus would lose an Earth Oceans worth of H 2 O in 30 to 300 million years.
27 Comparison of Atmospheres: Venus vs. Earth N 2 has remained in atmosphere on Venus just like it has on Earth Low relative concentration on Venus results from dilution by the highly abundant CO 2 in the Venusian atmosphere., Sp2010
28 Comparison of Atmospheres: Mars vs. Earth Mars atmosphere is 1/150 that of Earth s. Mars is small and cold! N 2 was lost to space: ~1 atm in 4.5 billion years., Sp2010 H 2 O and CO 2 are frozen in the polar caps and regolith (soil).
29 SUMMARY Fate of Planetary Gases (volatile compounds) Earth Venus Mars H 2 O oceans H space ice O rocks (1 ocean in million years) CO 2 rocks atmosphere ice N 2 atmosphere atmosphere space (1 atm in 4.5 billion years) O 2 atmosphere none none
30 Evolution of Atmosphere-Ocean System, the Rise of Free Oxygen: I Earth is chemically reducing (much reduced Fe) To make free O 2 reducing material must be isolated/separated from oxidizing material Core formation did much but not enough Two theories for rise of O 2 in atmosphere: 2 H 2 O = 2 H 2 + O 2 Photodissociation of H 2 O and loss of H 2 to space (alone this would produce current levels in 4.5 Gy) CO 2 + H 2 O = CH 2 O + O 2 Photosynthesis combined with burial of 0.1% of OM (this would produce current levels in 4 My)
31 Evolution of Atmosphere-Ocean System, the Rise of Oxygen: II Before O 2 could accumulate in atmosphere enough needed to be produced to oxidize large surface reservoirs of reduced material, e.g., Fe 2+ dissolved in early oceans Free oxygen began accumulating about 2.4 Gy bp and present levels were likely reached around 800 My bp Multicellular organisms evolved later because of development of ozone layer, they eventually migrated from sea to land
32 Possible evolution of Earth s atmosphere over geologic time, Sp2010
33 Early Earth was a violent place, yet life originated there!, Sp2010
Early History of the Earth
 OCN 201 Earth Structure Early History of the Earth Rapid accretion of Earth and attendant dissipation of kinetic energy caused tremendous heating Earth possibly melted completely In molten state, differentiation
OCN 201 Earth Structure Early History of the Earth Rapid accretion of Earth and attendant dissipation of kinetic energy caused tremendous heating Earth possibly melted completely In molten state, differentiation
Formation of the Earth and Solar System
 Formation of the Earth and Solar System a. Supernova and formation of primordial dust cloud. NEBULAR HYPOTHESIS b. Condensation of primordial dust. Forms disk-shaped nubular cloud rotating counterclockwise.
Formation of the Earth and Solar System a. Supernova and formation of primordial dust cloud. NEBULAR HYPOTHESIS b. Condensation of primordial dust. Forms disk-shaped nubular cloud rotating counterclockwise.
Origin of the Solar System
 Origin of the Solar System Look for General Properties Dynamical Regularities Orbits in plane, nearly circular Orbit sun in same direction (CCW from N.P.) Rotation Axes to orbit plane (Sun & most planets;
Origin of the Solar System Look for General Properties Dynamical Regularities Orbits in plane, nearly circular Orbit sun in same direction (CCW from N.P.) Rotation Axes to orbit plane (Sun & most planets;
The Solar System consists of
 The Universe The Milky Way Galaxy, one of billions of other galaxies in the universe, contains about 400 billion stars and countless other objects. Why is it called the Milky Way? Welcome to your Solar
The Universe The Milky Way Galaxy, one of billions of other galaxies in the universe, contains about 400 billion stars and countless other objects. Why is it called the Milky Way? Welcome to your Solar
The History of the Earth
 The History of the Earth We have talked about how the universe and sun formed, but what about the planets and moons? Review: Origin of the Universe The universe began about 13.7 billion years ago The Big
The History of the Earth We have talked about how the universe and sun formed, but what about the planets and moons? Review: Origin of the Universe The universe began about 13.7 billion years ago The Big
The oldest rock: 3.96 billion yrs old: Earth was forming continental crust nearly 400 billion years ago!!
 Earth s vital statistics Shape: almost spherical Size: 6400km in radius Average density: 5.5gm/cc; surface: 3gm/cc or less; centre may be 10-15gm/cc 15gm/cc Temperature: core: 2200-2750 2750 o c Pressure:
Earth s vital statistics Shape: almost spherical Size: 6400km in radius Average density: 5.5gm/cc; surface: 3gm/cc or less; centre may be 10-15gm/cc 15gm/cc Temperature: core: 2200-2750 2750 o c Pressure:
Origin of the Solar System
 Origin of the Solar System Current Properties of the Solar System Look for General Properties Dynamical Regularities Orbits in plane, nearly circular Orbit sun in same direction (CCW from North pole) Rotation
Origin of the Solar System Current Properties of the Solar System Look for General Properties Dynamical Regularities Orbits in plane, nearly circular Orbit sun in same direction (CCW from North pole) Rotation
Important information from Chapter 1
 Important information from Chapter 1 Distinguish between: Natural hazard // Disaster // Catastrophe What role does human population play in these categories? Know how to read a Hazard Map, such as Figure
Important information from Chapter 1 Distinguish between: Natural hazard // Disaster // Catastrophe What role does human population play in these categories? Know how to read a Hazard Map, such as Figure
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark
 Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
PTYS 214 Spring Announcements. Next midterm 3/1!
 PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Next midterm 3/1! 1 Previously Solar flux decreases as radiation spreads out away from the Sun Planets are exposed to some small amount of the total solar radiation A
PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Next midterm 3/1! 1 Previously Solar flux decreases as radiation spreads out away from the Sun Planets are exposed to some small amount of the total solar radiation A
TODAY S FOCUS LAYERS OF THE EARTH
 TODAY S FOCUS LAYERS OF THE EARTH 8.6C investigate and describe applications of Newton s law of inertia, law of force and acceleration, and law of action-reaction such as in vehicle restraints, sports
TODAY S FOCUS LAYERS OF THE EARTH 8.6C investigate and describe applications of Newton s law of inertia, law of force and acceleration, and law of action-reaction such as in vehicle restraints, sports
GG101 Dynamic Earth Dr. Fletcher, POST 802A Text Fletcher, WileyPLUS
 GG101 Dynamic Earth Dr. Fletcher, POST 802A fletcher@soest.hawaii.edu 956-2582 Text Fletcher, 2011 WileyPLUS Three exams, 50% total 20 to 25 homeworks, 50% total All homeworks done on-line Assignments
GG101 Dynamic Earth Dr. Fletcher, POST 802A fletcher@soest.hawaii.edu 956-2582 Text Fletcher, 2011 WileyPLUS Three exams, 50% total 20 to 25 homeworks, 50% total All homeworks done on-line Assignments
Earth s Interior Earth - Chapter 12 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College
 Earth s Interior Earth - Chapter 12 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Probing Earth s Interior Most of our knowledge of Earth s interior comes from the study of earthquake waves. Travel times
Earth s Interior Earth - Chapter 12 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Probing Earth s Interior Most of our knowledge of Earth s interior comes from the study of earthquake waves. Travel times
The Terrestrial Planets
 The Terrestrial Planets Large Bodies: Earth (1 R E, 1 M E ) Venus (0.95 R E, 0.82 M E ) Small Bodies: Mars (0.53 R E, 0.11 M E ) Mercury (0.38 R E, 0.055 M E ) Moon (0.27 R E, 0.012 M E ) The surfaces
The Terrestrial Planets Large Bodies: Earth (1 R E, 1 M E ) Venus (0.95 R E, 0.82 M E ) Small Bodies: Mars (0.53 R E, 0.11 M E ) Mercury (0.38 R E, 0.055 M E ) Moon (0.27 R E, 0.012 M E ) The surfaces
Chapter 20 Earth: The Standard of Comparative Planetology
 Chapter 20 Earth: The Standard of Comparative Planetology Guidepost In the preceding chapter, you learned how our solar system formed as a by-product of the formation of the sun. You also saw how distance
Chapter 20 Earth: The Standard of Comparative Planetology Guidepost In the preceding chapter, you learned how our solar system formed as a by-product of the formation of the sun. You also saw how distance
EARTH TAKES SHAPE 1. Define all vocabulary words. Crust: The thin and solid outermost layer of the Earth above the mantle. Mantle: The layer of rock
 EARTH TAKES SHAPE 1. Define all vocabulary words. Crust: The thin and solid outermost layer of the Earth above the mantle. Mantle: The layer of rock between the Earth s crust and core Core: The central
EARTH TAKES SHAPE 1. Define all vocabulary words. Crust: The thin and solid outermost layer of the Earth above the mantle. Mantle: The layer of rock between the Earth s crust and core Core: The central
Importance of Solar System Objects discussed thus far. Interiors of Terrestrial Planets. The Terrestrial Planets
 Importance of Solar System Objects discussed thus far Interiors of Terrestrial Planets Chapter 9 Sun: Major source of heat for the surfaces of planets Asteroids: Provide possible insight to the composition
Importance of Solar System Objects discussed thus far Interiors of Terrestrial Planets Chapter 9 Sun: Major source of heat for the surfaces of planets Asteroids: Provide possible insight to the composition
Engineering Geology. Earth Structure. Hussien aldeeky
 Earth Structure Hussien aldeeky 1 Earth major spheres 1. Hydrosphere Ocean is the most prominent feature of the hydrosphere. - Is nearly 71% of Earth's surface - Holds about 97% of Earth's water Fresh
Earth Structure Hussien aldeeky 1 Earth major spheres 1. Hydrosphere Ocean is the most prominent feature of the hydrosphere. - Is nearly 71% of Earth's surface - Holds about 97% of Earth's water Fresh
Lecture 20. Origin of the atmosphere (Chap. 10) The carbon cycle and long-term climate (Chap. 8 of the textbook: p )
 Lecture 20 Origin of the atmosphere (Chap. 10) The carbon cycle and long-term climate (Chap. 8 of the textbook: p.158-170) end of last ice-age; begin civilization beginning of modern era of ice-ages asteroid
Lecture 20 Origin of the atmosphere (Chap. 10) The carbon cycle and long-term climate (Chap. 8 of the textbook: p.158-170) end of last ice-age; begin civilization beginning of modern era of ice-ages asteroid
Today. Solar System Formation. a few more bits and pieces. Homework due
 Today Solar System Formation a few more bits and pieces Homework due Pluto Charon 3000 km Asteroids small irregular rocky bodies Comets icy bodies Formation of the Solar System How did these things come
Today Solar System Formation a few more bits and pieces Homework due Pluto Charon 3000 km Asteroids small irregular rocky bodies Comets icy bodies Formation of the Solar System How did these things come
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics
 Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics Earthquakes Earthquake = vibration of the Earth produced by the rapid release of energy. Seismic Waves Focus = the place within the Earth where the rock breaks, producing an earthquake.
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics Earthquakes Earthquake = vibration of the Earth produced by the rapid release of energy. Seismic Waves Focus = the place within the Earth where the rock breaks, producing an earthquake.
Lecture 25: The Requirements for Life
 Lecture 25: The Requirements for Life Astronomy 141 Winter 2012 This lecture explores the requirements for life, and the factors affecting planetary habitability. The basic requirements are a source of
Lecture 25: The Requirements for Life Astronomy 141 Winter 2012 This lecture explores the requirements for life, and the factors affecting planetary habitability. The basic requirements are a source of
Outline 9: Origin of the Earth: solids, liquids, and gases. The Early Archean Earth
 Outline 9: Origin of the Earth: solids, liquids, and gases The Early Archean Earth Origin of Earth s Matter The earth is made of recycled elements formed in stars that existed prior to our Sun. Supernova
Outline 9: Origin of the Earth: solids, liquids, and gases The Early Archean Earth Origin of Earth s Matter The earth is made of recycled elements formed in stars that existed prior to our Sun. Supernova
Nature and Origin of Planetary Systems f p "
 Nature and Origin of Planetary Systems f p " Our Solar System as Example" We know far more about our solar system than about any other" It does have (at least) one planet suitable for life" Start with
Nature and Origin of Planetary Systems f p " Our Solar System as Example" We know far more about our solar system than about any other" It does have (at least) one planet suitable for life" Start with
Outline 9: Origin of the Earth: solids, liquids, and gases
 Outline 9: Origin of the Earth: solids, liquids, and gases The Early Archean Earth Origin of Earth s Matter The earth is made of recycled elements formed in stars that existed prior to our Sun. Supernova
Outline 9: Origin of the Earth: solids, liquids, and gases The Early Archean Earth Origin of Earth s Matter The earth is made of recycled elements formed in stars that existed prior to our Sun. Supernova
Why does the Earth have volcanoes? Why is there Earthquakes?
 Why does the Earth have volcanoes? Why is there Earthquakes? Turn to your neighbor and review: How and when did the Earth form? How old are the first traces of life on Earth? Logical? * 1.5Ga (1 st multicellular
Why does the Earth have volcanoes? Why is there Earthquakes? Turn to your neighbor and review: How and when did the Earth form? How old are the first traces of life on Earth? Logical? * 1.5Ga (1 st multicellular
Terrestrial Planets: The Earth as a Planet
 Terrestrial Planets: The Earth as a Planet In today s class, we want to look at those characteristics of the Earth that are also important in our understanding of the other terrestrial planets. This is
Terrestrial Planets: The Earth as a Planet In today s class, we want to look at those characteristics of the Earth that are also important in our understanding of the other terrestrial planets. This is
Chapter Outline. Earth and Other Planets. The Formation of the Solar System. Clue #1: Planetary Orbits. Clues to the Origin of the Solar System
 Chapter Outline Earth and Other Planets The Formation of the Solar System Exploring the Solar System Chapter 16 Great Idea: Earth, one of the planets that orbit the Sun, formed 4.5 billion years ago from
Chapter Outline Earth and Other Planets The Formation of the Solar System Exploring the Solar System Chapter 16 Great Idea: Earth, one of the planets that orbit the Sun, formed 4.5 billion years ago from
Evolution of the Atmosphere: The Biological Connection
 Evolution of the Atmosphere: The Biological Connection The Earth s Four Spheres How It All Began Or At Least How We Think It Began O.k. it s a good guess Egg of energy The Big Bang splattered radiation
Evolution of the Atmosphere: The Biological Connection The Earth s Four Spheres How It All Began Or At Least How We Think It Began O.k. it s a good guess Egg of energy The Big Bang splattered radiation
The Earth Fast Facts. Outline. The Solar System is Ours! Astronomy 210. Section 1 MWF Astronomy Building
 Astronomy 210 Section 1 MWF 1500-1550 134 Astronomy Building This Class (Lecture 19): The Earth Night Observations! Next Class: The Earth-Moon System Music: Amy Hit the Atmosphere Counting Crows The Solar
Astronomy 210 Section 1 MWF 1500-1550 134 Astronomy Building This Class (Lecture 19): The Earth Night Observations! Next Class: The Earth-Moon System Music: Amy Hit the Atmosphere Counting Crows The Solar
Standard 2, Objective 1: Evaluate the source of Earth s internal heat and the evidence of Earth s internal structure.
 Standard 2: Students will understand Earth s internal structure and the dynamic nature of the tectonic plates that form its surface. Standard 2, Objective 1: Evaluate the source of Earth s internal heat
Standard 2: Students will understand Earth s internal structure and the dynamic nature of the tectonic plates that form its surface. Standard 2, Objective 1: Evaluate the source of Earth s internal heat
How do we know about the different layers of Earth's interior when we've never been there?
 Layers of the Earth Layers of the Earth How do we know about the different layers of Earth's interior when we've never been there? Oct 11 6:41 AM Make a note: These layers are inferred based on seismic
Layers of the Earth Layers of the Earth How do we know about the different layers of Earth's interior when we've never been there? Oct 11 6:41 AM Make a note: These layers are inferred based on seismic
Differentiation 1: core formation OUTLINE
 Differentiation 1: core formation Reading this week: White Ch 12 OUTLINE Today 1.Finish some slides 2.Layers 3.Core formation 1 Goldschmidt Classification/Geochemical Periodic Chart Elements can be assigned
Differentiation 1: core formation Reading this week: White Ch 12 OUTLINE Today 1.Finish some slides 2.Layers 3.Core formation 1 Goldschmidt Classification/Geochemical Periodic Chart Elements can be assigned
Lab 5: An Investigation of Meteorites Geology 202: Earth s Interior
 Lab 5: An Investigation of Meteorites Geology 202: Earth s Interior Asteroids and Meteorites: What is the difference between asteroids and meteorites? Asteroids are rocky and metallic objects that orbit
Lab 5: An Investigation of Meteorites Geology 202: Earth s Interior Asteroids and Meteorites: What is the difference between asteroids and meteorites? Asteroids are rocky and metallic objects that orbit
The Interior of the Earth. The Interior of the Earth. Chapter 30. Merry Christmas. Quick Quiz
 Chapter 30 The Interior of the Earth The Interior of the Earth Yesterday: The main features of the earth s surface are continents and ocean basins. Today: What are the main features of the earth s interior?
Chapter 30 The Interior of the Earth The Interior of the Earth Yesterday: The main features of the earth s surface are continents and ocean basins. Today: What are the main features of the earth s interior?
The Solar System. Earth as a Planet
 The Solar System Earth as a Planet Earth s Interior Core: Highest density; nickel and iron Mantle: Moderate density; silicon, oxygen, etc. Crust: Lowest density; granite, basalt, etc. Differentiation Gravity
The Solar System Earth as a Planet Earth s Interior Core: Highest density; nickel and iron Mantle: Moderate density; silicon, oxygen, etc. Crust: Lowest density; granite, basalt, etc. Differentiation Gravity
Week Five: Earth s Interior/Structure
 Week Five: Earth s Interior/Structure The Earth s Interior/Structure Cut a planet in half See layers Most dense material (metals) at bottom Medium density material (rocks) in middle Even less dense (liquids
Week Five: Earth s Interior/Structure The Earth s Interior/Structure Cut a planet in half See layers Most dense material (metals) at bottom Medium density material (rocks) in middle Even less dense (liquids
OCN 201: Origin of the Earth and Oceans. Waimea Bay, Jan 2002
 OCN 201: Origin of the Earth and Oceans Waimea Bay, Jan 2002 Periodic Table of the Elements Noble IA IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA VIIIA IB IIB IIIB IVB VB VIB VIIB gases H He Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si
OCN 201: Origin of the Earth and Oceans Waimea Bay, Jan 2002 Periodic Table of the Elements Noble IA IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA VIIIA IB IIB IIIB IVB VB VIB VIIB gases H He Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si
Chapter 9. ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Class 26: Planetary Geology [3/23/07] Announcements.
![Chapter 9. ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Class 26: Planetary Geology [3/23/07] Announcements. Chapter 9. ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Class 26: Planetary Geology [3/23/07] Announcements.](/thumbs/87/96235120.jpg) ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 26: Planetary Geology [3/23/07] Announcements Planetary Geology Planetary
ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 26: Planetary Geology [3/23/07] Announcements Planetary Geology Planetary
What are terrestrial planets like on the inside? Chapter 9 Planetary Geology: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds. Seismic Waves.
 Chapter 9 Planetary Geology: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What are terrestrial planets like on the inside? Seismic Waves Vibrations that travel through Earth s interior tell us what Earth is
Chapter 9 Planetary Geology: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds What are terrestrial planets like on the inside? Seismic Waves Vibrations that travel through Earth s interior tell us what Earth is
Lecture 31. Planetary Accretion the raw materials and the final compositions
 Lecture 31 Planetary Accretion the raw materials and the final compositions Reading this week: White Ch 11 (sections 11.1-11.4) Today 1. Boundary conditions for Planetary Accretion Growth and Differentiation
Lecture 31 Planetary Accretion the raw materials and the final compositions Reading this week: White Ch 11 (sections 11.1-11.4) Today 1. Boundary conditions for Planetary Accretion Growth and Differentiation
The Ocean as a stratified body of water
 The Ocean as a stratified body of water Density = f (salt content, T, pressure) Γ 35,25,1 = 1.02335 g cm -3 (= 1023 kg m -3 ) σ S,t,P = (Γ S,t,P -1) x 1000 σ 35,25,1 = 23.25 g cm -3 (= 23.25 kg m -3 )
The Ocean as a stratified body of water Density = f (salt content, T, pressure) Γ 35,25,1 = 1.02335 g cm -3 (= 1023 kg m -3 ) σ S,t,P = (Γ S,t,P -1) x 1000 σ 35,25,1 = 23.25 g cm -3 (= 23.25 kg m -3 )
 http://eps.mcgill.ca/~courses/c201_winter/ http://eps.mcgill.ca/~courses/c201_winter/ Neutron Proton Nucleosynthesis neutron!! electron!+!proton!!=!!é!!+!h +!! t 1/2 =!12!minutes H + +!neutron!! Deuterium!(D)
http://eps.mcgill.ca/~courses/c201_winter/ http://eps.mcgill.ca/~courses/c201_winter/ Neutron Proton Nucleosynthesis neutron!! electron!+!proton!!=!!é!!+!h +!! t 1/2 =!12!minutes H + +!neutron!! Deuterium!(D)
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version E of the exam. Please fill in (E). A) This
ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version E of the exam. Please fill in (E). A) This
The History of the Earth
 The History of the Earth Origin of the Universe The universe began about 13.9 billion years ago According to Big Bang theory almost all matter was in the form of energy E = MC 2 E = energy, M = mass and
The History of the Earth Origin of the Universe The universe began about 13.9 billion years ago According to Big Bang theory almost all matter was in the form of energy E = MC 2 E = energy, M = mass and
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version B of the exam. Please fill in (B). A) This
ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version B of the exam. Please fill in (B). A) This
EARTH S ENERGY SOURCES
 EARTH S ENERGY SOURCES The geological processes that shape the Earth s surface are powered by two major sources of energy; geothermal heat from the Earth s interior and external energy from the sun. The
EARTH S ENERGY SOURCES The geological processes that shape the Earth s surface are powered by two major sources of energy; geothermal heat from the Earth s interior and external energy from the sun. The
Astr 1050 Fri., Feb. 24, 2017
 Astr 1050 Fri., Feb. 24, 2017 Chapter 7 & 8: Overview & Formation of the Solar System Reading: Chapters 7 on Solar System Chapter 8: Earth & Terrestrial Planets Reminders: New homework on MA up this afternoon,
Astr 1050 Fri., Feb. 24, 2017 Chapter 7 & 8: Overview & Formation of the Solar System Reading: Chapters 7 on Solar System Chapter 8: Earth & Terrestrial Planets Reminders: New homework on MA up this afternoon,
Chapter 12 Lecture. Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology. Eleventh Edition. Earth s Interior. Tarbuck and Lutgens Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 12 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Eleventh Edition Earth s Interior Tarbuck and Lutgens Earth s Internal Structure Earth s interior can be divided into three major layers defined
Chapter 12 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Eleventh Edition Earth s Interior Tarbuck and Lutgens Earth s Internal Structure Earth s interior can be divided into three major layers defined
Last Name First Name. OCEANOGRAPHY 201 Spring, 2011 Exam #1: Section #2
 Last Name First Name Student ID# I hereby authorize the use of the last 5 digits of my bar code number for the purpose of posting my grades in OCN 201. (Please sign above; your grades cannot be posted
Last Name First Name Student ID# I hereby authorize the use of the last 5 digits of my bar code number for the purpose of posting my grades in OCN 201. (Please sign above; your grades cannot be posted
The Main Point. Other Properties Earth has one large Moon. Earth has a strong Magnetic Field. Lecture #11: Earth: Geology and Interior
 Lecture #11: Earth: Geology and Interior Overview of Earth's basic properties. Earth's Interior and Surface: Composition and Structure. Surface Geologic Processes. Evolution of the Surface. Reading: Chapters
Lecture #11: Earth: Geology and Interior Overview of Earth's basic properties. Earth's Interior and Surface: Composition and Structure. Surface Geologic Processes. Evolution of the Surface. Reading: Chapters
Any Questions? 99.9 % of mass is in the Sun; 99 % of angular momentum is in the planets. Planets in two groups:
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 2 15 January 2004 Any Questions? Origin of solar system Pick a theory, any theory, but it must be consistent with these facts: Planets all revolve around the Sun in
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 2 15 January 2004 Any Questions? Origin of solar system Pick a theory, any theory, but it must be consistent with these facts: Planets all revolve around the Sun in
Next opportunity to observe the Moon and Venus close together: Dec. 31, Announcements
 Announcements Last OWL homework: due 12/15 before midnight Study guide for final exam is up on the class webpage Practice exam up Thursday afternoon Final exam: Monday, Dec. 15, 10:30 AM, Hasbrouck 20
Announcements Last OWL homework: due 12/15 before midnight Study guide for final exam is up on the class webpage Practice exam up Thursday afternoon Final exam: Monday, Dec. 15, 10:30 AM, Hasbrouck 20
Origin of solar system. Origin of solar system. Geology of the Hawaiian Islands. Any Questions? Class 2 15 January 2004
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 2 15 January 2004 Any Questions? Origin of solar system Pick a theory, any theory, but it must be consistent with these facts: Planets all revolve around the Sun in
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 2 15 January 2004 Any Questions? Origin of solar system Pick a theory, any theory, but it must be consistent with these facts: Planets all revolve around the Sun in
Chapter 7 Earth and the Terrestrial Worlds
 Chapter 7 Earth and the Terrestrial Worlds Guest Lecture by Chris Kelso Please pick up one notecard of each color (5 total) Outline The Earth s Interior The Earth s Surface The Earth s Atmosphere Concept
Chapter 7 Earth and the Terrestrial Worlds Guest Lecture by Chris Kelso Please pick up one notecard of each color (5 total) Outline The Earth s Interior The Earth s Surface The Earth s Atmosphere Concept
FORCES ON EARTH UNIT 3.2. An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth.
 FORCES ON EARTH UNIT 3.2 An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth. USE THESE NOTES: OUR HOME PLANET EARTH: What do you know about our planet? SO.HOW
FORCES ON EARTH UNIT 3.2 An investigation into how Newton s Laws of Motion are applied to the tectonic activity on Earth. USE THESE NOTES: OUR HOME PLANET EARTH: What do you know about our planet? SO.HOW
PLATO - 5. Planetary atmospheres
 PLATO - 5 Planetary atmospheres 1 Mercury Smallest planet! 0.38 Earth radii! 0.055 Earth masses! 0.39 AU orbit (eccentric)! 350K surface temperature (ranges from 100K-700K)! Slow 59 day rotation (2/3 orbital
PLATO - 5 Planetary atmospheres 1 Mercury Smallest planet! 0.38 Earth radii! 0.055 Earth masses! 0.39 AU orbit (eccentric)! 350K surface temperature (ranges from 100K-700K)! Slow 59 day rotation (2/3 orbital
Nebular Hypothesis (Kant, Laplace 1796) - Earth and the other bodies of our solar system (Sun, moons, etc.) formed from a vast cloud of dust and
 Plate Tectonics Origin of Universe Big Bang model (Hubble, 1929) - The universe began with an explosive e expansion of matter, which later became what we know as stars, planets, moons, etc. This event
Plate Tectonics Origin of Universe Big Bang model (Hubble, 1929) - The universe began with an explosive e expansion of matter, which later became what we know as stars, planets, moons, etc. This event
Lecture #11: Plan. Terrestrial Planets (cont d) Jovian Planets
 Lecture #11: Plan Terrestrial Planets (cont d) Jovian Planets Mercury (review) Density = 5.4 kg / liter.. ~ Earth s Rocky mantle + iron/nickel core Slow spin: 59 days (orbital period = 88 days) No satellites
Lecture #11: Plan Terrestrial Planets (cont d) Jovian Planets Mercury (review) Density = 5.4 kg / liter.. ~ Earth s Rocky mantle + iron/nickel core Slow spin: 59 days (orbital period = 88 days) No satellites
Shape and Size of the Earth
 Planet Earth Shape and Size of the Earth Gravity is what gives Earth its spherical shape Only effective if the body is of a critical size Critical radius is about 350 km Shape and Size of the Earth Earth
Planet Earth Shape and Size of the Earth Gravity is what gives Earth its spherical shape Only effective if the body is of a critical size Critical radius is about 350 km Shape and Size of the Earth Earth
General Introduction. The Earth as an evolving geologic body
 General Introduction The Earth as an evolving geologic body Unique/important attributes of Planet Earth 1. Rocky planet w/ strong magnetic field Mercury has a weak field, Mars has a dead field 1 Unique/important
General Introduction The Earth as an evolving geologic body Unique/important attributes of Planet Earth 1. Rocky planet w/ strong magnetic field Mercury has a weak field, Mars has a dead field 1 Unique/important
ASTR-101 Section 004 Lecture 9 Rare Earth? John T. McGraw, Professor
 ASTR-101 Section 004 Lecture 9 Rare Earth? John T. McGraw, Professor Rare Earth Long-lived sun Rocky world C, O, Si, materials for soil, tools and subsistence Near circular orbit Not too warm not too cold
ASTR-101 Section 004 Lecture 9 Rare Earth? John T. McGraw, Professor Rare Earth Long-lived sun Rocky world C, O, Si, materials for soil, tools and subsistence Near circular orbit Not too warm not too cold
Astronomy. physics.wm.edu/~hancock/171/ A. Dayle Hancock. Small 239. Office hours: MTWR 10-11am
 Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Planetology II Key characteristics Chemical elements and planet size Radioactive dating Solar system formation Solar nebula
Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Planetology II Key characteristics Chemical elements and planet size Radioactive dating Solar system formation Solar nebula
Structure of the Earth
 Structure of the Earth What is the earth like below its surface? Inside the Earth 1:34 What makes up the interior of our planet? Compiled by Susan Weidkamp Chapter 22 Objectives To observe how change is
Structure of the Earth What is the earth like below its surface? Inside the Earth 1:34 What makes up the interior of our planet? Compiled by Susan Weidkamp Chapter 22 Objectives To observe how change is
Today. Events. Terrestrial Planet Geology. Fall break next week - no class Tuesday
 Today Terrestrial Planet Geology Events Fall break next week - no class Tuesday When did the planets form? We cannot find the age of a planet, but we can find the ages of the rocks that make it up. We
Today Terrestrial Planet Geology Events Fall break next week - no class Tuesday When did the planets form? We cannot find the age of a planet, but we can find the ages of the rocks that make it up. We
Last Name First Name. OCEANOGRAPHY 201 Fall, 2013 Exam #1: Section #1
 Last Name First Name Student ID# Signature I hereby authorize the use of the last 5 digits of my bar code number for the purpose of posting my grades in OCN 201. (Please sign above; your grades cannot
Last Name First Name Student ID# Signature I hereby authorize the use of the last 5 digits of my bar code number for the purpose of posting my grades in OCN 201. (Please sign above; your grades cannot
Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System. Chapter Eight
 Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System Chapter Eight ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 07 Oct. 15, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6)
Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System Chapter Eight ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 07 Oct. 15, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6)
The Planets, Asteroids, Moons, etc.
 DATE DUE: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 305 Name: Section: The Planets, Asteroids, Moons, etc. Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer or option. Use GEOLOGIC vocabulary
DATE DUE: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 305 Name: Section: The Planets, Asteroids, Moons, etc. Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer or option. Use GEOLOGIC vocabulary
Last Name First Name OCEANOGRAPHY 201. Fall, 2015 Exam #1: Section #1
 Last Name First Name Student ID# Signature I hereby authorize the use of the last 5 digits of my bar code number for the purpose of posting my grades in OCN 201. (Please sign above; your grades cannot
Last Name First Name Student ID# Signature I hereby authorize the use of the last 5 digits of my bar code number for the purpose of posting my grades in OCN 201. (Please sign above; your grades cannot
The Earth. Part II: Solar System. The Earth. 1a. Interior. A. Interior of Earth. A. The Interior. B. The Surface. C. Atmosphere
 Part II: Solar System The Earth The Earth A. The Interior B. The Surface C. Atmosphere 2 Updated: July 14, 2007 A. Interior of Earth 1. Differentiated Structure 2. Seismography 3. Composition of layers
Part II: Solar System The Earth The Earth A. The Interior B. The Surface C. Atmosphere 2 Updated: July 14, 2007 A. Interior of Earth 1. Differentiated Structure 2. Seismography 3. Composition of layers
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 2 THE EARTH Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College of Education
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 2 THE EARTH Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College of Education
10/11/2010. Acceleration due to gravity, a. Bulk Properties Mass = 6 x kg Diameter = 12,756 km Density = 5515 kg/m 3 (mix of rock and iron)
 Acceleration due to gravity, a Bulk Properties Mass = 6 x 10 24 kg Diameter = 12,756 km Density = 5515 kg/m 3 (mix of rock and iron) Escape Velocity, v e Albedo Amount of sunlight reflected back into space
Acceleration due to gravity, a Bulk Properties Mass = 6 x 10 24 kg Diameter = 12,756 km Density = 5515 kg/m 3 (mix of rock and iron) Escape Velocity, v e Albedo Amount of sunlight reflected back into space
Petrology. Petrology: the study of rocks, especially aspects such as physical, chemical, spatial and chronoligic. Associated fields include:
 Petrology Petrology: the study of rocks, especially aspects such as physical, chemical, spatial and chronoligic. Associated fields include: Petrography: study of description and classification of rocks
Petrology Petrology: the study of rocks, especially aspects such as physical, chemical, spatial and chronoligic. Associated fields include: Petrography: study of description and classification of rocks
What is it like? When did it form? How did it form. The Solar System. Fall, 2005 Astronomy 110 1
 What is it like? When did it form? How did it form The Solar System Fall, 2005 Astronomy 110 1 Fall, 2005 Astronomy 110 2 The planets all orbit the sun in the same direction. The Sun spins in the same
What is it like? When did it form? How did it form The Solar System Fall, 2005 Astronomy 110 1 Fall, 2005 Astronomy 110 2 The planets all orbit the sun in the same direction. The Sun spins in the same
Last Name First Name
 Last Name First Name Student ID# Signature I hereby authorize the use of the last 5 digits of my bar code number for the purpose of posting my grades in OCN 201. (Please sign above; your grades cannot
Last Name First Name Student ID# Signature I hereby authorize the use of the last 5 digits of my bar code number for the purpose of posting my grades in OCN 201. (Please sign above; your grades cannot
Climate Regulation. - What stabilizes the climate - Greenhouse effect
 Climate Regulation - What stabilizes the climate - Greenhouse effect Last time! Processes that shaped Earth: Volcanism, tectonics! How we retain atmospheric molecules ( escape speed )! A magnetic field
Climate Regulation - What stabilizes the climate - Greenhouse effect Last time! Processes that shaped Earth: Volcanism, tectonics! How we retain atmospheric molecules ( escape speed )! A magnetic field
Composition and the Early History of the Earth
 Composition and the Early History of the Earth Sujoy Mukhopadhyay CIDER 2006 What we will cover in this lecture Composition of Earth Short lived nuclides and differentiation of the Earth Atmosphere and
Composition and the Early History of the Earth Sujoy Mukhopadhyay CIDER 2006 What we will cover in this lecture Composition of Earth Short lived nuclides and differentiation of the Earth Atmosphere and
1 The Earth as a Planet
 General Astronomy (29:61) Fall 2012 Lecture 27 Notes, November 5, 2012 1 The Earth as a Planet As we start studying the planets, we begin with Earth. To begin with, it gives us a different perspective
General Astronomy (29:61) Fall 2012 Lecture 27 Notes, November 5, 2012 1 The Earth as a Planet As we start studying the planets, we begin with Earth. To begin with, it gives us a different perspective
The Role of Biology in the Climate System: Long Term Climate Regulation. Earth History, Gaia and Human Perturbations of Biological Systems
 The Role of Biology in the Climate System: Long Term Climate Regulation Earth History, Gaia and Human Perturbations of Biological Systems How would the Earth differ if Life had not evolved or expanded?
The Role of Biology in the Climate System: Long Term Climate Regulation Earth History, Gaia and Human Perturbations of Biological Systems How would the Earth differ if Life had not evolved or expanded?
Structure of the Earth EARTH ( ) - need a solid, will not go through a liquid
 EARTH ( ) Structure of the Earth Deep Wells: - deepest is 12 km (7.5 miles) in Russia - temp at bottom = 190oC or 375oF! Seismology - science of shock waves - caused by earthquakes, volcanoes, etc. - shows
EARTH ( ) Structure of the Earth Deep Wells: - deepest is 12 km (7.5 miles) in Russia - temp at bottom = 190oC or 375oF! Seismology - science of shock waves - caused by earthquakes, volcanoes, etc. - shows
Can t t wait to take Exam 4!
 Can t t wait to take Exam 4! Really can t wait to study for the final exam! 1 2 Housekeeping Exam 4: study glossaries, chapter questions TA lab closed after Tues. How to study for exam 4 Make lists for
Can t t wait to take Exam 4! Really can t wait to study for the final exam! 1 2 Housekeeping Exam 4: study glossaries, chapter questions TA lab closed after Tues. How to study for exam 4 Make lists for
EASC100: EXAM1 (07) Lithosphere and Hydrosphere
 EASC100: EXAM1 (07) Lithosphere and Hydrosphere Name: 1. Why do Mercury and the Moon lack an atmosphere? A) They formed after all the gas had been used up. B) They are so cold that all their gases have
EASC100: EXAM1 (07) Lithosphere and Hydrosphere Name: 1. Why do Mercury and the Moon lack an atmosphere? A) They formed after all the gas had been used up. B) They are so cold that all their gases have
Birth Date of a Planet?
 Save the whales. Collect the whole set Plan to be spontaneous tomorrow Life is too short not to be in a hurry Oceanography Lecture 4 Defining Boundaries: 2) Plate Tectonics I 1. Review 2. Intro to Plate
Save the whales. Collect the whole set Plan to be spontaneous tomorrow Life is too short not to be in a hurry Oceanography Lecture 4 Defining Boundaries: 2) Plate Tectonics I 1. Review 2. Intro to Plate
The Earth - Surface and Interior
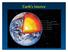 Earth's Interior The Earth - Surface and Interior Basic Data Diameter 12,756 km (equator) Mass 6 x 10 24 kg Density 5.5 g/cm 3 5500 kg/m 3 Escape velocity 11.2 km/s Temp -130 F to 140 F 183K to 333K Albedo
Earth's Interior The Earth - Surface and Interior Basic Data Diameter 12,756 km (equator) Mass 6 x 10 24 kg Density 5.5 g/cm 3 5500 kg/m 3 Escape velocity 11.2 km/s Temp -130 F to 140 F 183K to 333K Albedo
Lecture 2: The Solar System
 Lecture 2: The Solar System 1) WileyPLUS (online) registration? homework? 2) Final Exam scheduled Tuesday, December 15 (12-2) 3) iclickers assigned on Tuesday 4) Big Island Field Trip Fall 2015 Big Island
Lecture 2: The Solar System 1) WileyPLUS (online) registration? homework? 2) Final Exam scheduled Tuesday, December 15 (12-2) 3) iclickers assigned on Tuesday 4) Big Island Field Trip Fall 2015 Big Island
Evidence of Earth s Interior Direct and Indirect Evidence
 Into Which Layer Have We Drilled? Evidence of Earth s Interior Direct and Indirect Evidence 1. Crust 2. Mantle 3. Outer Core 4. Inner Core Why?? How Many Types of Crust Exist? Which of the following is
Into Which Layer Have We Drilled? Evidence of Earth s Interior Direct and Indirect Evidence 1. Crust 2. Mantle 3. Outer Core 4. Inner Core Why?? How Many Types of Crust Exist? Which of the following is
For the next few weeks: Terrestrial Planets, their Moons, and the Sun. Planetary Surfaces and Interiors 2/20/07
 For the next few weeks: Terrestrial Planets, their Moons, and the Sun Announcements Reading Assignment Section 9-1 (pp 186-189), 9-5 and 9-6 (pp 199-203) 3 rd Homework is now posted on the course website
For the next few weeks: Terrestrial Planets, their Moons, and the Sun Announcements Reading Assignment Section 9-1 (pp 186-189), 9-5 and 9-6 (pp 199-203) 3 rd Homework is now posted on the course website
Our Planetary System. Chapter 7
 Our Planetary System Chapter 7 Key Concepts for Chapter 7 and 8 Inventory of the Solar System Origin of the Solar System What does the Solar System consist of? The Sun: It has 99.85% of the mass of the
Our Planetary System Chapter 7 Key Concepts for Chapter 7 and 8 Inventory of the Solar System Origin of the Solar System What does the Solar System consist of? The Sun: It has 99.85% of the mass of the
Section 1: Earth s Interior and Plate Tectonics Section 2: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Section 3: Minerals and Rocks Section 4: Weathering and Erosion
 Section 1: Earth s Interior and Plate Tectonics Section 2: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Section 3: Minerals and Rocks Section 4: Weathering and Erosion Key Terms Crust Mantle Core Lithosphere Plate Tectonics
Section 1: Earth s Interior and Plate Tectonics Section 2: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Section 3: Minerals and Rocks Section 4: Weathering and Erosion Key Terms Crust Mantle Core Lithosphere Plate Tectonics
Today we begin with. Water is everywhere on and in Earth It is the only substance that exists in all 3 phases (solid, liquid, gas) on the surface!
 Water is everywhere on and in Earth It is the only substance that exists in all 3 phases (solid, liquid, gas) on the surface! Today we begin with Water Origin of Earth s water Properties of water Water
Water is everywhere on and in Earth It is the only substance that exists in all 3 phases (solid, liquid, gas) on the surface! Today we begin with Water Origin of Earth s water Properties of water Water
Class Announcements. Solar System. Objectives for today. Will you read Chap 32 before Wed. class? Chap 32 Beyond the Earth
 Class Announcements Please fill out an evaluation for this class. If you release your name I ll I give you quiz credit. Will you read Chap 32 before Wed. class? a) Yes b) No Chap 32 Beyond the Earth Objectives
Class Announcements Please fill out an evaluation for this class. If you release your name I ll I give you quiz credit. Will you read Chap 32 before Wed. class? a) Yes b) No Chap 32 Beyond the Earth Objectives
9/22/ A Brief Tour of the Solar System. Chapter 6: Formation of the Solar System. What does the solar system look like?
 9/22/17 Lecture Outline 6.1 A Brief Tour of the Solar System Chapter 6: Formation of the Solar System What does the solar system look like? Our goals for learning: What does the solar system look like?
9/22/17 Lecture Outline 6.1 A Brief Tour of the Solar System Chapter 6: Formation of the Solar System What does the solar system look like? Our goals for learning: What does the solar system look like?
For thought: Excess volatiles
 For thought: Excess volatiles Term coined by William Rubey (circa 1955) Definition: Compounds present at Earth s surface that were not derived from converting igneous rock to sedimentary rock Rubey and
For thought: Excess volatiles Term coined by William Rubey (circa 1955) Definition: Compounds present at Earth s surface that were not derived from converting igneous rock to sedimentary rock Rubey and
Formation of Planets and Earth Structure. Big Bang Theory. What is the shape of our solar system?
 Formation of Planets and Earth Structure From work of Einstein and Hubble Big Bang Theory ~14 Ga All matter in one point Exploded Expanding still Food for thought What is the shape of our solar system?
Formation of Planets and Earth Structure From work of Einstein and Hubble Big Bang Theory ~14 Ga All matter in one point Exploded Expanding still Food for thought What is the shape of our solar system?
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999
 Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
Earthquakes. Earthquakes and Earth s Interior Earth Science, 13e Chapter 8. Elastic rebound. Earthquakes. Earthquakes 11/19/2014.
 and Earth s Interior Earth Science, 13e Chapter 8 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College General features Vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Associated with movements
and Earth s Interior Earth Science, 13e Chapter 8 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College General features Vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Associated with movements
Chapter 15: The Origin of the Solar System
 Chapter 15: The Origin of the Solar System The Solar Nebula Hypothesis Basis of modern theory of planet formation: Planets form at the same time from the same cloud as the star. Planet formation sites
Chapter 15: The Origin of the Solar System The Solar Nebula Hypothesis Basis of modern theory of planet formation: Planets form at the same time from the same cloud as the star. Planet formation sites
Earth. Interior Crust Hydrosphere Atmosphere Magnetosphere Tides
 Earth Interior Crust Hydrosphere Atmosphere Magnetosphere Tides Semi-major Axis 1 A.U. Inclination 0 Orbital period 1.000 tropical year Orbital eccentricity 0.017 Rotational period 23 h 56 min 4.1 s Tilt
Earth Interior Crust Hydrosphere Atmosphere Magnetosphere Tides Semi-major Axis 1 A.U. Inclination 0 Orbital period 1.000 tropical year Orbital eccentricity 0.017 Rotational period 23 h 56 min 4.1 s Tilt
Recall Hypsometric Curve?
 Structure and Composition of the Earth (Why?) Recall Hypsometric Curve? Continental crust is very different from oceanic crust. To understand this, we need to know more about the structure & composition
Structure and Composition of the Earth (Why?) Recall Hypsometric Curve? Continental crust is very different from oceanic crust. To understand this, we need to know more about the structure & composition
see disks around new stars in Orion nebula where planets are probably being formed 3
 Planet Formation contracting cloud forms stars swirling disk of material around forming star (H, He, C, O, heavier elements, molecules, dust ) form planets New born star heats up material, blows away solar
Planet Formation contracting cloud forms stars swirling disk of material around forming star (H, He, C, O, heavier elements, molecules, dust ) form planets New born star heats up material, blows away solar
