PLINIAN AND SUBPLINIAN ERUPTIONS
|
|
|
- Gervase Nicholson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PLINIAN AND SUBPLINIAN ERUPTIONS A FIELD PERSPECTIVE RAFFAELLO CIONI DIP.TO SCIENZE DELLA TERRA UNIVERSITA DI FIRENZE THANKS TO: MAURO ROSI, MARCO PISTOLESI, COSTANZA BONADONNA, KATHY CASHMAN, LUCIA GURIOLI, BRUCE HOUGHTON, PAUL COLE, ANTONELLA BERTAGNINI, CLAUDIA D ORIANO, FILIPPO MUNDULA MeMoVolc workshop: The dynamics of volcanic explosive eruptions Geneva, January 2014
2 DEFINITION PLINIAN: explosive eruptions characterized by the sustained, quasi-steady, hours-lasting discharge into the atmosphere of a high-temperature, multiphase mixture (gas, solid and liquid particles), forming a convective vertical column that reaches heights of tens of kilometers before spreading laterally. DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PLINIAN AND SUBPLINIAN EVENTS IS GENERALLY CONSIDERED AS A MATTER OF SCALE AND A LARGER UNSTEADYNESS OF SUBPLINIAN EVENTS
3 MeMoVolc workshop: The dynamics of volcanic explosive eruptions Geneva, January 2014 Main features of Plinian-type eruptions From thinly stratified to massive!
4 MeMoVolc workshop: The dynamics of volcanic explosive eruptions Geneva, January 2014 Classification schemes
5 MeMoVolc workshop: The dynamics of volcanic explosive eruptions Geneva, January 2014 PLINIAN COLUMNS CORDON CAULLE 2011 (CHILE)
6 PLINIAN ERUPTIONS: main problems No serious problem of classification for plinian (s.s.) phases Classification based on dispersal of deposits (D index, Bt, Bc, etc.) Deposits can be studied and correlated over long distances MDR and other physical parameters can be estimated WHY TO DISCUSS ABOUT THEM?
7 DEFINITION COMPLEX EVENTS: although they always include a quasistationary phase, plinian (s.l.) eruptions may consist of a fairly rapid succession of volcanic pulses, in which phases of sustained convective plumes alternate with phases dominated by collapsing conditions and pulsatory explosive phases of different style, intensity and dynamics (vulcanian explosions, phases of prolonged ash emission, phreatomagmatic explosions, emission of lava flows or domes).
8 PLINIAN ERUPTIONS: how can be better describe them? Generally complex eruptions, with alternating phases of different style Deposits suggest different types of plinian pulses
9 PLINIAN ERUPTIONS: complex sequences ASKJA 1875 (Sparks et al., 1981) PINATUBO ka TAUPO (Houghton et al., 2010) (Paladio-Melosantos et al. 1995))
10 PLINIAN ERUPTIONS: complex sequences AD79 VESUVIUS OPLONTIS EXCAVATIONS
11 MeMoVolc workshop: The dynamics of volcanic explosive eruptions Geneva, January 2014 Can we better describe Plinian deposits? Based on vertical grain size variations, Plinian deposits can be subdivided into three main categories: simple stratified multiple Rosi (1996)
12 MeMoVolc workshop: The dynamics of volcanic explosive eruptions Geneva, January 2014 Simple Plinian fall deposits Result from the accumulation from stable convective columns From non-stratified to weakly stratified, grainsize grading possible Example: AD79 white,vesuvius; Minoan Plinian, Santorini Pinatubo C, Philippines
13 MeMoVolc workshop: The dynamics of volcanic explosive eruptions Geneva, January 2014 Stratified Plinian fall deposits Derive from an unsteady, oscillating eruptive column, often alternating convective and collapsing phases Different fall beds separated by sharp grain-size variations Examples: AD79 Grey, Vesuvius; Taupo Plinian
14 MeMoVolc workshop: The dynamics of volcanic explosive eruptions Geneva, January 2014 Multiple Plinian fall deposits Different fall beds produced by discrete, short-lived Plinian columns Beds can be deposited under different wind conditions Examples: El Chichon 1982, Mexico Askja 1875, Iceland
15 PLINIAN ERUPTIONS: how can be better describe them? SOME PARAMETERS ARE DIFFICULT TO ESTIMATE Problems with volume calculations volume from classical methods strongly differ from those used to estimate vitric ash lost (v.a.l. is about 60 wt% of the total!!) Problems with estimation of total grains size distribution Is TGSD strongly bimodal? Is a fine population totally missing from our estimations?
16 MeMoVolc workshop: The dynamics of volcanic explosive eruptions Geneva, January 2014 Plinian and Subplinian TGSD Woods and Bursik, 1991 VERY FEW DATA ON TGSD: STRONGLY POLIMODAL? WT. % AD 79 Redrawn from Rust and Cashman, 2011 PHI Cioni, unpublished
17 MeMoVolc workshop: The dynamics of volcanic explosive eruptions Geneva, January 2014 How can we better estimate TGSD (and volume)? Co-plinian ash Cotopaxi Layer 9 Barberi et al. 1995
18 MeMoVolc workshop: The dynamics of volcanic explosive eruptions Geneva, January 2014 Co-Plinian ash THE STUDY OF WELL PRESERVED DEPOSITS DISPERSED IN NO-WIND CONDITIONS COULD BE CRUCIAL FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF UNCERTAINTIES IN TGSD AND VOLUME ESTIMATIONS OF PLINIAN DEPOSITS The Pululahua (Ecuador) Basal Fall (BF) and the co-plinian ash (WA) Rosi and Papale (1993)
19 SUBPLINIAN ERUPTIONS LARGELY VARIABLE FEATURES OF THE DEPOSITS: MASSIVE, PUMICE- OR SCORIA-BEARING CORDON CAULLE 2011 (CHILE) AD472 POLLENA (VESUVIUS)
20 SUBPLINIAN ERUPTIONS LARGELY VARIABLE FEATURES OF THE DEPOSITS: MASSIVE, PUMICE- OR SCORIA-BEARING G.PICHICNHA 1660 (ECUADOR) AD1906 (VESUVIUS)
21 SUBPLINIAN ERUPTIONS LARGELY VARIABLE FEATURES OF THE DEPOSITS: STRATIFIED TO THINLY BEDDED 16 ka GREENISH (VESUVIUS)
22 SUBPLINIAN ERUPTIONS LARGELY VARIABLE FEATURES OF THE DEPOSITS: STRATIFIED TO THINLY BEDDED 512 AD (VESUVIUS)
23 MeMoVolc workshop: The dynamics of volcanic explosive eruptions Geneva, January 2014 SUBPLINIAN ERUPTIONS LARGELY VARIABLE FEATURES OF THE DEPOSITS: COMPLEX SEQUENCES AD 512 (VESUVIUS) EU1-2 opening phase EU3 stable subplinian EU5 oscillatory subplinian EU6 subplinian/violent strombolian Are all these the subplinian phases the result of similar processes? How should we describe and classify all these phases? Cioni et al., 2011
24 CLAST DENSITY AD 79 Vesuvius - PLINIAN Gurioli et al., 2004 AD 512Vesuvius - SUBPLINIAN Cioni et al., 2011 TEPHRI-PHONOLITE PHONOLITE TEPHRI-PHONOLITE Clast density of subplinian deposits is often polymodal
25 GROUNDMASS CRISTALLINITY AD 79 Vesuvius - PLINIAN AD 512Vesuvius - SUBPLINIAN Products from subplinan deposits are more crystalrich than plinian ones Gurioli et al., 2004
26 MeMoVolc workshop: The dynamics of volcanic explosive eruptions Geneva, January 2014 G.PICHINCHA 1660 VULCA NIAN C.CAULLE 2011 AD512 - VESUVIUS PLINIAN AD1906-VESUVIUS VIOLENT STROMBO LIAN SUBPLINIAN SUBPLINIAN DEPOSITS RECORD A LARGE RANGE OF ERUPTIVE STYLES
27 MeMoVolc workshop: The dynamics of volcanic explosive eruptions Geneva, January 2014 Time-scale of unsteadyness from deposits LOW FREQUENCY INSTABILITIES (HOURS?) Pre-minoan deposit Santorini
28 MeMoVolc workshop: The dynamics of volcanic explosive eruptions Geneva, January 2014 Time-scale of unsteadyness from deposits LOW FREQUENCY INSTABILITIES (HOURS?) MINOAN ERUPTION - SANTORINI 8 ka BP MERCATO - VESUVIUS
29 MeMoVolc workshop: The dynamics of volcanic explosive eruptions Geneva, January 2014 Time-scale of unsteadyness from deposits INTERMEDIATE TO HIGH FREQUENCY INSTABILITIES (MINUTES?) AD VESUVIUS 19ka BP GREENISH- VESUVIUS 9 KA P.PRINCIPALI C. FLEGREI
30 SOME POINTS FOR DISCUSSION HOW CAN WE ADDRESS THE PROBLEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF DIFFERENT DEPOSITS WITH SIMILAR DISPERSAL (SUBPLINIAN S.L.)? WHICH ARE THE MOST IMPORTANT PARAMETERS TO BETTER DESCRIBE PLINIAN AND SUBPLINIAN ERUPTIONS? HOW CAN WE IMPROVE OUR CAPABILITY OF MEASURING VOLUME, TGSD, TIMESCALE OF UNSTEADYNESS
31 SOME POINTS FOR DISCUSSION PROBLEMS WITH CLASSIFYING COMPLEX ERUPTIONS: IS A PLINIAN ERUPTION A COMPLEX SEQUENCE FORMED BY DIFFERENT PULSES, OR SHOULD WE CLASSIFY SEPARATELY EACH DIFFERENT PULSE? HOW CAN WE DESCRIBE QUANTITATIVELY UNSTEADYNESS, AND WHICH ARE THE MAIN DRIVING PROCESSES?
32 MeMoVolc workshop: The dynamics of volcanic explosive eruptions Geneva, January 2014 POINTS FOR DISCUSSION: CAN A VOLCANO-BASED CLASSIFICATION HELP IMPROVING OUR UNDERSTANDING OF PL& SUBPL? PLINIAN Cioni et al., 2003 SUBPLINIAN I
33 PLINIAN ERUPTIONS Volcano based classification - Vesuvius Eruption style" Composition" SiO 2 (wt%)" Alkali" (wt %)" H 2 O " (wt %)" CO 2" ppm" Plinian" Trachyte" Phonolite to T-Phon." 54 61" 54 62" " 11-16" No data" 5-6(Avell)" 6 (AD 79)" No data" " bdl" Sub-Plinian I" T-Phon. to P-Tephrite " " " 11 16" (8 12 AD1631)" 2.5 (salic)" <5 (mafic)" 0 200" 2000" Sub-Plinian II" T-Phon. to P-Tephrite" " " 8-11 " No data" No data" Cioni et al., 2008
34 PLINIAN ERUPTIONS Volcano based classification - Vesuvius Eruption style " Column height" (km)" Total volume" (m 3 )" Accum. Rate " 10 km from vent)" Duration" Isopach 10 cm" (km 2 )" Density" " (kg/m 3 )" 100 kg/m 2" Distance" (km)" Plinian" > 20" 10 9" 10-20" hours" > 1500" " 100" Sub-" Plinian I" 15-20" 10 8" " 5-15" hours" " " 20-50" Sub-" Plinian II" 10-15" " 5-15" Hours - days" 200" " 15-25" Cioni et al., 2008
Pyroclastic Deposits I: Pyroclastic Fall Deposits
 Pyroclastic Deposits I: Pyroclastic Fall Deposits EAS 458 Volcanology Introduction We have seen that physics is useful in understanding volcanic processes, but physical models must be constrained by and
Pyroclastic Deposits I: Pyroclastic Fall Deposits EAS 458 Volcanology Introduction We have seen that physics is useful in understanding volcanic processes, but physical models must be constrained by and
Volcanic Plumes. JOHN WILEY & SONS Chichester New York Weinheim Brisbane Singapore Toronto
 Volcanic Plumes R. S. J. SPARKS University of Bristol, UK M. I. BURSIK State University of New York, USA S. N. CAREY University of Rhode Island, USA J. S. GILBERT Lancaster University, UK L. S. GLAZE NASA/Goddard
Volcanic Plumes R. S. J. SPARKS University of Bristol, UK M. I. BURSIK State University of New York, USA S. N. CAREY University of Rhode Island, USA J. S. GILBERT Lancaster University, UK L. S. GLAZE NASA/Goddard
IAVCEI Commission on Tephra Hazard Modelling
 IAVCEI Commission on Tephra Hazard Modelling FIELD WORKSHOP Field measurements for the characterization of tephra deposits (SALCEDO) Ecuador January 16-18, 2006 Table of content 1.0 INTRODUCTION page 2
IAVCEI Commission on Tephra Hazard Modelling FIELD WORKSHOP Field measurements for the characterization of tephra deposits (SALCEDO) Ecuador January 16-18, 2006 Table of content 1.0 INTRODUCTION page 2
Scarpati Claudio and Perrotta Annamaria
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2012292 Supplemental Information Scarpati Claudio (email:claudio.scarpati@unina.it) and Perrotta Annamaria Dipartimento di Scienze della Terra, Università di Napoli Federico II Erosional
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2012292 Supplemental Information Scarpati Claudio (email:claudio.scarpati@unina.it) and Perrotta Annamaria Dipartimento di Scienze della Terra, Università di Napoli Federico II Erosional
Assessing pyroclastic fall hazard through field data and numerical simulations: Example from Vesuvius
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B2, 2063, doi:10.1029/2001jb000642, 2003 Assessing pyroclastic fall hazard through field data and numerical simulations: Example from Vesuvius Raffaello Cioni,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B2, 2063, doi:10.1029/2001jb000642, 2003 Assessing pyroclastic fall hazard through field data and numerical simulations: Example from Vesuvius Raffaello Cioni,
External water and ice effect of wind - empirical findings
 External water and ice effect of wind - empirical findings Magnús T. Gudmundsson, Based on work and contributions from Björn Oddsson, Tobias Dürig, Þórdís Högnadóttir, Thor Thordarson, Ármann Höskuldsson,
External water and ice effect of wind - empirical findings Magnús T. Gudmundsson, Based on work and contributions from Björn Oddsson, Tobias Dürig, Þórdís Högnadóttir, Thor Thordarson, Ármann Höskuldsson,
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Intrusive and Effusive Rocks Effusive rocks: rapid cooling small crystalls or glas Lava & ash Magmatic
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Intrusive and Effusive Rocks Effusive rocks: rapid cooling small crystalls or glas Lava & ash Magmatic
The role of bubble formation in volcanic eruption
 The role of bubble formation in volcanic eruption Eyal Goldmann Division of Natural Sciences, El Camino College, Torrance, CA, 90506 Prepared for Geology 1 at El Camino College Fall 2009 1 1. Introduction
The role of bubble formation in volcanic eruption Eyal Goldmann Division of Natural Sciences, El Camino College, Torrance, CA, 90506 Prepared for Geology 1 at El Camino College Fall 2009 1 1. Introduction
Permeability controls on expansion and size distributions of pyroclasts
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008494, 2011 Permeability controls on expansion and size distributions of pyroclasts A. C. Rust 1 and K. V. Cashman 2 Received 3 May 2011;
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008494, 2011 Permeability controls on expansion and size distributions of pyroclasts A. C. Rust 1 and K. V. Cashman 2 Received 3 May 2011;
Numerical Simulations of Turbulent Flow in Volcanic Eruption Clouds
 Numerical Simulations of Turbulent Flow in Volcanic Eruption Clouds Project Representative Takehiro Koyaguchi Authors Yujiro Suzuki Takehiro Koyaguchi Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo
Numerical Simulations of Turbulent Flow in Volcanic Eruption Clouds Project Representative Takehiro Koyaguchi Authors Yujiro Suzuki Takehiro Koyaguchi Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo
What is the threat? Sue Loughlin and Julia Crummy British Geological Survey. NERC All rights reserved NERC All rights reserved
 What is the threat? Sue Loughlin and Julia Crummy British Geological Survey BATA Conference, London 15 th October 2013 What is a volcano? Where and how many? There are more than 1500 known potentially
What is the threat? Sue Loughlin and Julia Crummy British Geological Survey BATA Conference, London 15 th October 2013 What is a volcano? Where and how many? There are more than 1500 known potentially
Climate forcing volcanic eruptions: future extreme event occurrence likelihoods
 Climate Change and Extreme Events: Managing Tail Risks Workshop 2 3 February 2010 Washington DC Climate forcing volcanic eruptions: future extreme event occurrence likelihoods Willy Aspinall with apologies
Climate Change and Extreme Events: Managing Tail Risks Workshop 2 3 February 2010 Washington DC Climate forcing volcanic eruptions: future extreme event occurrence likelihoods Willy Aspinall with apologies
Probabilistic modelling of tephra dispersion
 Probabilistic modelling of tephra dispersion C. BONADONNA Department of Geology, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL 33620-5201, USA (e-mail: costanza@cas.usf.edu) Depending on their magnitude and location,
Probabilistic modelling of tephra dispersion C. BONADONNA Department of Geology, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL 33620-5201, USA (e-mail: costanza@cas.usf.edu) Depending on their magnitude and location,
LARGE-SCALE PLINIAN ERUPTIONS OF THE COLLI ALBANI AND THE CAMPI FLEGREI VOLCANOES: INSIGHTS FROM TEXTURAL AND RHEOLOGICAL STUDIES
 LARGE-SCALE PLINIAN ERUPTIONS OF THE COLLI ALBANI AND THE CAMPI FLEGREI VOLCANOES: INSIGHTS FROM TEXTURAL AND RHEOLOGICAL STUDIES SILVIA CAMPAGNOLA Dipartimento di Scienze sez.geologia, Università degli
LARGE-SCALE PLINIAN ERUPTIONS OF THE COLLI ALBANI AND THE CAMPI FLEGREI VOLCANOES: INSIGHTS FROM TEXTURAL AND RHEOLOGICAL STUDIES SILVIA CAMPAGNOLA Dipartimento di Scienze sez.geologia, Università degli
LECTURE #11: Volcanic Disasters: Lava Properties & Eruption Types
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #11: Volcanic Disasters: Lava Properties & Eruption Types Date: 13 February 2018 I. Exam I grades are posted on the class website (link at the bottom
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #11: Volcanic Disasters: Lava Properties & Eruption Types Date: 13 February 2018 I. Exam I grades are posted on the class website (link at the bottom
Sylvain Charbonnier. PASI Workshop About 60% of Indonesians live around 16 active volcanoes on the island of Java
 Numerical modelling of pyroclastic flows: a case study from the recent activity of Merapi Volcano, Central Java, Indonesia Sylvain Charbonnier PASI Workshop 2011 Case study: Merapi Volcano! About 60% of
Numerical modelling of pyroclastic flows: a case study from the recent activity of Merapi Volcano, Central Java, Indonesia Sylvain Charbonnier PASI Workshop 2011 Case study: Merapi Volcano! About 60% of
Statistics in Volcanology. TError: towards a better quantification of the uncertainty propagated during the characterization of tephra deposits
 Volume 1 November 18, 214 TError: towards a better quantification of the uncertainty propagated during the characterization of tephra deposits S. Biass 1, G. Bagheri 1, W. H. Aeberhard 2, C. Bonadonna
Volume 1 November 18, 214 TError: towards a better quantification of the uncertainty propagated during the characterization of tephra deposits S. Biass 1, G. Bagheri 1, W. H. Aeberhard 2, C. Bonadonna
Total Grain Size Distribution in Selected Icelandic Eruptions
 Total Grain Size Distribution in Selected Icelandic Eruptions Work for the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and the Icelandic Meteorological Office Authors: Ármann Höskuldsson, Maria Janebo,
Total Grain Size Distribution in Selected Icelandic Eruptions Work for the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and the Icelandic Meteorological Office Authors: Ármann Höskuldsson, Maria Janebo,
Tephra2. This module explains how to use TEPHRA2. Tephra2 Manual
 Tephra2 Manual Tephra2 Tephra2 uses the advection-diffusion equation to calculate tephra accumulation at locations about a volcano based on a pre-defined set of eruptive conditions. This module explains
Tephra2 Manual Tephra2 Tephra2 uses the advection-diffusion equation to calculate tephra accumulation at locations about a volcano based on a pre-defined set of eruptive conditions. This module explains
Applying Mass Eruption Rates in an Operational Dispersion Model
 Applying Mass Eruption Rates in an Operational Dispersion Model Frances Beckett, ADAQ, Met Office frances.beckett@metoffice.gov.uk MeMoVolc Workshop, University of Iceland, May 2016 The London Volcanic
Applying Mass Eruption Rates in an Operational Dispersion Model Frances Beckett, ADAQ, Met Office frances.beckett@metoffice.gov.uk MeMoVolc Workshop, University of Iceland, May 2016 The London Volcanic
Volcanic eruptions: Introduction to remote sensing techniques for fine ash and SO2 detection
 Volcanic eruptions: Introduction to remote sensing techniques for fine ash and SO2 detection Bernie Connell Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere Colorado State University USA Ash clouds
Volcanic eruptions: Introduction to remote sensing techniques for fine ash and SO2 detection Bernie Connell Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere Colorado State University USA Ash clouds
Tephra2 Users Manual
 Tephra2 Users Manual Spring 2011 Tephra2 uses the advection-diffusion equation to calculate tephra accumulation at locations about a volcano based on a pre-defined set of eruptive conditions. This manual
Tephra2 Users Manual Spring 2011 Tephra2 uses the advection-diffusion equation to calculate tephra accumulation at locations about a volcano based on a pre-defined set of eruptive conditions. This manual
Tephra sedimentation during the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull eruption (Iceland) from deposit, radar, and satellite observations
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008462, 2011 Tephra sedimentation during the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull eruption (Iceland) from deposit, radar, and satellite observations C. Bonadonna,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008462, 2011 Tephra sedimentation during the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull eruption (Iceland) from deposit, radar, and satellite observations C. Bonadonna,
Vulcanicity. Objectives to identify the basic structure of volcanoes and understand how they form.
 Vulcanicity Objectives to identify the basic structure of volcanoes and understand how they form. Some key terms to start.. Viscosity how well a substance (lava) flows. Acid lavas have a high viscosity,
Vulcanicity Objectives to identify the basic structure of volcanoes and understand how they form. Some key terms to start.. Viscosity how well a substance (lava) flows. Acid lavas have a high viscosity,
PUBLICATIONS. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth
 PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth RESEARCH ARTICLE This article is a companion to Tadini et al. [2017] doi:10.1002/2016jb013860. Key Points: A new geodatabase for Somma Vesuvio
PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth RESEARCH ARTICLE This article is a companion to Tadini et al. [2017] doi:10.1002/2016jb013860. Key Points: A new geodatabase for Somma Vesuvio
WET EXPLOSIVE ERUPTIONS. Hawaii Photograph: Dorian Weisel
 WET EXPLOSIVE ERUPTIONS Hawaii Photograph: Dorian Weisel WET EXPLOSIVE ERUPTIONS mechanisms hot magma/ hot rock + water pyroclasts + steam rapid expansion of gas fragmentation of magma + wall rock external
WET EXPLOSIVE ERUPTIONS Hawaii Photograph: Dorian Weisel WET EXPLOSIVE ERUPTIONS mechanisms hot magma/ hot rock + water pyroclasts + steam rapid expansion of gas fragmentation of magma + wall rock external
Topic 1: Modeling SFU: (JVGR 1992)
 Topic 1: Modeling SFU: (JVGR 1992) 1. Were different chamber top shapes used other than flat, i.e. convex, concave, convoluted / ridged? What is the sensitivity of your models to this? Also, was there
Topic 1: Modeling SFU: (JVGR 1992) 1. Were different chamber top shapes used other than flat, i.e. convex, concave, convoluted / ridged? What is the sensitivity of your models to this? Also, was there
IVATF/2-WP/09 10/06/11. International PAPER WORKING TESTING. (Presented DISCUSSION. 2.1 presented. this working. paper, some.
 International Civil Aviation Organization IVATF/2-WP/09 10/06/11 WORKING PAPER INTERNATIONAL VOLCANIC ASH TASK FORCE (IVATF) SECOND MEETING Montréal, 11 to 15 July 2011 Agenda Item 2: Report of the Science
International Civil Aviation Organization IVATF/2-WP/09 10/06/11 WORKING PAPER INTERNATIONAL VOLCANIC ASH TASK FORCE (IVATF) SECOND MEETING Montréal, 11 to 15 July 2011 Agenda Item 2: Report of the Science
Volcanoes. volcanic hazards. Image courtesy of USGS.
 Volcanoes volcanic hazards Volcanic hazards Pyroclastic flows and surges Pyroclastic flows and surges PYROCLAST: all solid fragments ejected from volcanoes PYROCLASTIC FLOW: A flow of hot gas and volcanic
Volcanoes volcanic hazards Volcanic hazards Pyroclastic flows and surges Pyroclastic flows and surges PYROCLAST: all solid fragments ejected from volcanoes PYROCLASTIC FLOW: A flow of hot gas and volcanic
Igneous petrology EOSC 321 Laboratory 8: Intermediate and Felsic Volcanic Rocks. Pyroclastic Rocks
 321 Lab 8 Instructor: L. Porritt - 1 - Igneous petrology EOSC 321 Laboratory 8: Intermediate and Felsic Volcanic Rocks. Pyroclastic Rocks Learning Goals. After this Lab, you should be able: Identify fine-grained
321 Lab 8 Instructor: L. Porritt - 1 - Igneous petrology EOSC 321 Laboratory 8: Intermediate and Felsic Volcanic Rocks. Pyroclastic Rocks Learning Goals. After this Lab, you should be able: Identify fine-grained
University of Bristol - Explore Bristol Research. Peer reviewed version. Link to published version (if available): 10.
 Eychenne, J., Cashman, K. V., Rust, A. C., & Durant, A. (2015). Impact of the lateral blast on the spatial pattern and grain size characteristics of the 18 May 1980 Mount St. Helens fallout deposit. Journal
Eychenne, J., Cashman, K. V., Rust, A. C., & Durant, A. (2015). Impact of the lateral blast on the spatial pattern and grain size characteristics of the 18 May 1980 Mount St. Helens fallout deposit. Journal
Probabilistic evaluation of the physical impact of future tephra fallout events for the Island of Vulcano, Italy
 Bulletin of Volcanology manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Probabilistic evaluation of the physical impact of future tephra fallout events for the Island of Vulcano, Italy Sebastien Biass
Bulletin of Volcanology manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Probabilistic evaluation of the physical impact of future tephra fallout events for the Island of Vulcano, Italy Sebastien Biass
Limitations of the advection-diffusion equation for modeling tephra fallout: 1992 eruption of Cerro Negro Volcano, Nicaragua.
 University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2004 Limitations of the advection-diffusion equation for modeling tephra fallout: 1992 eruption of Cerro Negro
University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2004 Limitations of the advection-diffusion equation for modeling tephra fallout: 1992 eruption of Cerro Negro
ERTH 456 / GEOL 556 Volcanology. Lecture 06: Conduits
 1 / 28 ERTH 456 / GEOL 556 Volcanology Lecture 06: Conduits Ronni Grapenthin rg@nmt.edu MSEC 356, x5924 hours: TR 3-4PM or appt. September 12, 2016 2 / 28 How does magma get from source to surface? What
1 / 28 ERTH 456 / GEOL 556 Volcanology Lecture 06: Conduits Ronni Grapenthin rg@nmt.edu MSEC 356, x5924 hours: TR 3-4PM or appt. September 12, 2016 2 / 28 How does magma get from source to surface? What
1/31/2013 BASALTIC BASALTIC ANDESITIC RHYOLITIC
 Can you predict the location of volcanoes? What is causing this eruption? What factors influence its character? A volcano is any landform from which lava, gas, or ashes, escape from underground or have
Can you predict the location of volcanoes? What is causing this eruption? What factors influence its character? A volcano is any landform from which lava, gas, or ashes, escape from underground or have
Probabilistic modeling of tephra dispersion: hazard assessment of a multi-phase eruption at Tarawera Volcano, New Zealand
 Probabilistic modeling of tephra dispersion: hazard assessment of a multi-phase eruption at Tarawera Volcano, New Zealand C. Bonadonna 1, C.B. Connor 2, B.F. Houghton 1, L. Connor 2, M. Byrne 3, A. Laing
Probabilistic modeling of tephra dispersion: hazard assessment of a multi-phase eruption at Tarawera Volcano, New Zealand C. Bonadonna 1, C.B. Connor 2, B.F. Houghton 1, L. Connor 2, M. Byrne 3, A. Laing
Tephra dispersal and eruption dynamics of wet and dry phases of the 1875 eruption of. Askja Volcano
 Tephra dispersal and eruption dynamics of wet and dry phases of the 1875 eruption of Askja Volcano R.J. Carey a,*, B.F. Houghton a, T. Thordarson b a Department of Geology and Geophysics, SOEST, University
Tephra dispersal and eruption dynamics of wet and dry phases of the 1875 eruption of Askja Volcano R.J. Carey a,*, B.F. Houghton a, T. Thordarson b a Department of Geology and Geophysics, SOEST, University
Visualizing Earth Science. Chapter Overview. Volcanoes and Eruption Types. By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner. Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other
 Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
GLY July Ms. Nelda Breedt. Plates move slowly and eventually.
 GLY 162 Tectonic Processes: Volcanism Ms. Nelda Breedt GLY 162 Environmental Geology Plate Tectonics Plates move slowly and eventually. 2 Spread apart (divergent plates) Dive beneath one another (converging
GLY 162 Tectonic Processes: Volcanism Ms. Nelda Breedt GLY 162 Environmental Geology Plate Tectonics Plates move slowly and eventually. 2 Spread apart (divergent plates) Dive beneath one another (converging
NSF-MARGINS Expedition to Anatahan Volcano March 2005
 1 NSF-MARGINS Expedition to Anatahan Volcano March 2005 According to the Emergency Management Office (EMO) report distributed in February 2005, the third historical eruption of Anatahan began on January
1 NSF-MARGINS Expedition to Anatahan Volcano March 2005 According to the Emergency Management Office (EMO) report distributed in February 2005, the third historical eruption of Anatahan began on January
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
Hawaiian Submarine Volcanism. Stages of Hawaiian Volcanoes:
 Hawaiian Submarine Volcanism November 1, 2011 Mary Tardona GG 711 Stages of Hawaiian Volcanoes: Typically, three main stages: Pre shield Shield Post shield Sometimes followed by: Rejuvenation Stage GG
Hawaiian Submarine Volcanism November 1, 2011 Mary Tardona GG 711 Stages of Hawaiian Volcanoes: Typically, three main stages: Pre shield Shield Post shield Sometimes followed by: Rejuvenation Stage GG
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann
 17.04.2010 Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on Iceland Phreatomagmatic eruption 1 Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on Iceland Phreatomagmatic eruption Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on
17.04.2010 Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on Iceland Phreatomagmatic eruption 1 Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on Iceland Phreatomagmatic eruption Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on
! Profile of Mauna Loa in Hawaii. Mauna Loa is one of five huge shield volcanoes that make up the island of Hawaii.
 - Shield Volcanoes - Low, rounded profiles; slope angles 2-10 ; composed of numerous flows of mafic composition and little explosive activity - Largest of all volcanoes! Shield volcanoes consist of numerous
- Shield Volcanoes - Low, rounded profiles; slope angles 2-10 ; composed of numerous flows of mafic composition and little explosive activity - Largest of all volcanoes! Shield volcanoes consist of numerous
Magma vs. Lava. Molten rock below Earth s surface is called magma. The magma that reaches the surface and erupts out of a volcano is called lava.
 CH. 10.1 Be able to Explain the factors that determine the type of volcanic eruption. List the 3 types of volcanoes Describe the features of a volcano. What is a Volcano? Volcanoes are sites where molten
CH. 10.1 Be able to Explain the factors that determine the type of volcanic eruption. List the 3 types of volcanoes Describe the features of a volcano. What is a Volcano? Volcanoes are sites where molten
EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4
 Name: EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4 Introduction In the previous lab, we learned about mineral characteristics, properties and identities as well as the three basic rock
Name: EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4 Introduction In the previous lab, we learned about mineral characteristics, properties and identities as well as the three basic rock
INTRODUCTION TO TEPHROCHRONOLOGY
 ENEGeol 2017 - PART 1 INTRODUCTION TO TEPHROCHRONOLOGY Eruption of Chaiten, 2008 Tephra is an all-embracing term for the explosively erupted, loose fragmental (pyroclastic) products of a volcanic eruption,
ENEGeol 2017 - PART 1 INTRODUCTION TO TEPHROCHRONOLOGY Eruption of Chaiten, 2008 Tephra is an all-embracing term for the explosively erupted, loose fragmental (pyroclastic) products of a volcanic eruption,
Earth Science Chapter 6 Rocks
 Earth Science Chapter 6 Rocks I. Rocks and the Rock Cycle * Material that makes up the solid part of the Earth. * Made of a variety of different combinations of minerals and organic matter. A. Three Major
Earth Science Chapter 6 Rocks I. Rocks and the Rock Cycle * Material that makes up the solid part of the Earth. * Made of a variety of different combinations of minerals and organic matter. A. Three Major
Volcanism Activity. Choose one of the options below to complete for tomorrow. You may work with a partner on this activity. Be creative and realistic!
 Volcanism Activity Choose one of the options below to complete for tomorrow. You may work with a partner on this activity. Be creative and realistic! Option 1 Option 2 Option 3 Create a comic strip or
Volcanism Activity Choose one of the options below to complete for tomorrow. You may work with a partner on this activity. Be creative and realistic! Option 1 Option 2 Option 3 Create a comic strip or
Augustine Volcano, Calculating Ash Fallout
 Augustine Volcano, 1986 - Calculating Fallout -What controls the fallout of particles through the atmosphere? -Can we predict when and where an erupted ash cloud will fall out on the Earth? Summit: 1260
Augustine Volcano, 1986 - Calculating Fallout -What controls the fallout of particles through the atmosphere? -Can we predict when and where an erupted ash cloud will fall out on the Earth? Summit: 1260
3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts
 3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts Think about What happens when a volcano erupts? Volcanoes erupt many types of material Earth s thin outer layer is, but most of Earth is extremely hot rock
3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts Think about What happens when a volcano erupts? Volcanoes erupt many types of material Earth s thin outer layer is, but most of Earth is extremely hot rock
Chapter 18. Volcanism
 Chapter 18 Volcanism Ring of fire contains 66% of world s active volcanoes Convergent : Divergent: Icelandic Eruption Mount Etna Different Kinds of eruptions: Volcanic activity is controlled by plate tectonics,
Chapter 18 Volcanism Ring of fire contains 66% of world s active volcanoes Convergent : Divergent: Icelandic Eruption Mount Etna Different Kinds of eruptions: Volcanic activity is controlled by plate tectonics,
Calderas. Myojin Knoll Submarine Caldera m. 500 m. 5 km. (after Kennedy and Stix, 2003)
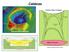 Calderas Myojin Knoll Submarine Caldera 1400 m 500 m 5 km (after Kennedy and Stix, 2003) Definition Outline Relationships to Eruption Volume and VEI Structural Components Types Caldera Genetic Models and
Calderas Myojin Knoll Submarine Caldera 1400 m 500 m 5 km (after Kennedy and Stix, 2003) Definition Outline Relationships to Eruption Volume and VEI Structural Components Types Caldera Genetic Models and
GY 111: Physical Geology
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 9: Extrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) The chemical composition of the crust 2) Crystallization of molten
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 9: Extrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) The chemical composition of the crust 2) Crystallization of molten
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 4 22 January 2004 Turn in Homework #1 Any Questions? IMPORTANT Big Island Field Trip We need a $162 payment for airfare BEFORE January 29 th Description of logistics,
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 4 22 January 2004 Turn in Homework #1 Any Questions? IMPORTANT Big Island Field Trip We need a $162 payment for airfare BEFORE January 29 th Description of logistics,
THE VESUVIAN VOLCANIC SYSTEM
 -200- the volcano, the required interdisciplinary research efforts leading to the development of the simulator will be discussed. It will be concluded that the development of a Global Volcanic Simulator
-200- the volcano, the required interdisciplinary research efforts leading to the development of the simulator will be discussed. It will be concluded that the development of a Global Volcanic Simulator
WHEN IS A SURGE NOT A SURGE? THAT IS THE PERPLEXING QUESTION. (for emergency managers)
 WHEN IS A SURGE NOT A SURGE? THAT IS THE PERPLEXING QUESTION (for emergency managers) Mount St Helens, May 18, 1980 37 years, 5 months, and 6 days ago.. Eyewitnesses there were many! Rosenbaum and Waitt,
WHEN IS A SURGE NOT A SURGE? THAT IS THE PERPLEXING QUESTION (for emergency managers) Mount St Helens, May 18, 1980 37 years, 5 months, and 6 days ago.. Eyewitnesses there were many! Rosenbaum and Waitt,
Efficient Forecasting of Volcanic Ash Clouds. Roger P Denlinger Hans F Schwaiger US Geological Survey
 Efficient Forecasting of Volcanic Ash Clouds Roger P Denlinger Hans F Schwaiger US Geological Survey Two basic questions addressed in this talk: 1. How does uncertainty affect forecasts of volcanic ash
Efficient Forecasting of Volcanic Ash Clouds Roger P Denlinger Hans F Schwaiger US Geological Survey Two basic questions addressed in this talk: 1. How does uncertainty affect forecasts of volcanic ash
Sensitivity analysis and uncertainty estimation for tephra dispersal models
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2006jb004864, 2008 Sensitivity analysis and uncertainty estimation for tephra dispersal models Simona Scollo, 1 Stefano Tarantola, 2 Costanza Bonadonna,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2006jb004864, 2008 Sensitivity analysis and uncertainty estimation for tephra dispersal models Simona Scollo, 1 Stefano Tarantola, 2 Costanza Bonadonna,
Engineering Geology. Igneous rocks. Hussien Al - deeky
 Igneous rocks Hussien Al - deeky 1 The Geology Definition of Rocks In Geology Rock is defined as the solid material forming the outer rocky shell or crust of the earth. There are three major groups of
Igneous rocks Hussien Al - deeky 1 The Geology Definition of Rocks In Geology Rock is defined as the solid material forming the outer rocky shell or crust of the earth. There are three major groups of
Debris Avalanches. Debris avalanche deposits on a volcano in Chile. All of the area in the foreground is buried by a thick debris avalanche.
 Debris Avalanches Volcanoes are not very stable structures. From time to time, they collapse producing large rock and ash avalanches that travel at high speeds down valleys. Collapse maybe caused by an
Debris Avalanches Volcanoes are not very stable structures. From time to time, they collapse producing large rock and ash avalanches that travel at high speeds down valleys. Collapse maybe caused by an
Lecture 3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Dr. Shwan Omar
 Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark
 Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
J. Mangas and F.J. Perez-Torrado. Departamento de Física. Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria Las Palmas de Gran Canaria.
 Magmatic processes in the oceanic lithosphere: characterization of the ultramafic and mafic materials from the Holocene volcanic centers of Bandama and La Caldera de Pinos de Gáldar (Gran Canaria, Canary
Magmatic processes in the oceanic lithosphere: characterization of the ultramafic and mafic materials from the Holocene volcanic centers of Bandama and La Caldera de Pinos de Gáldar (Gran Canaria, Canary
Data Repository Item 1
 GSA DR 2006031 Burgisser, p. 1 Data Repository Item 1 of Burgisser, A., and Gardner. J., Using Hydraulic Equivalence to Discriminate Transport Processes of Volcanic Flows This Electronic Supplement contains
GSA DR 2006031 Burgisser, p. 1 Data Repository Item 1 of Burgisser, A., and Gardner. J., Using Hydraulic Equivalence to Discriminate Transport Processes of Volcanic Flows This Electronic Supplement contains
WHAT IS A MAGMA. Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth.
 UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research
 Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 195 (2010) 31 47 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jvolgeores
Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 195 (2010) 31 47 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jvolgeores
3/7/17. #16 - Case Studies of Volcanoes II. Announcements Monday 2/27
 Announcements Monday 2/27 Exam #1: Monday Feb. 27 th, 7:15-8:15 (see web site) Last Names A - N Loomis 141 Last Names O - Z Loomis 151 Bring your student ID An old exam is posted in Compass If you are
Announcements Monday 2/27 Exam #1: Monday Feb. 27 th, 7:15-8:15 (see web site) Last Names A - N Loomis 141 Last Names O - Z Loomis 151 Bring your student ID An old exam is posted in Compass If you are
SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH AND EDUCATION IN THE AIR FORCE AFASES2017
 SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH AND EDUCATION IN THE AIR FORCE AFASES2017 PROBABILITY ASSESSMENT OF POSSIBLE VOLCANIC ASH CONTAMINATION FOR THE BULGARIAN AIRSPACE BY DEVELOPING OF EVENT TREE AND RISK MATRIX FOR HYPOTHETICAL
SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH AND EDUCATION IN THE AIR FORCE AFASES2017 PROBABILITY ASSESSMENT OF POSSIBLE VOLCANIC ASH CONTAMINATION FOR THE BULGARIAN AIRSPACE BY DEVELOPING OF EVENT TREE AND RISK MATRIX FOR HYPOTHETICAL
Why was this eruption important?
 Mount St. Helens Mount St. Helens has a long geological history (>3,000 yrs) of explosive eruptions. The 1980 Events: Initial relatively mild steam and ash (Vulcanian) eruptions. Sustained plinian eruption
Mount St. Helens Mount St. Helens has a long geological history (>3,000 yrs) of explosive eruptions. The 1980 Events: Initial relatively mild steam and ash (Vulcanian) eruptions. Sustained plinian eruption
Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research
 Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 178 (2008) 94 103 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research journal homepage: www. elsevier. com/ locate/ jvolgeores
Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 178 (2008) 94 103 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research journal homepage: www. elsevier. com/ locate/ jvolgeores
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Fires Within: Igneous Activity Foundations, 6e - Chapter 7 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The nature of volcanic eruptions Characteristics
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Fires Within: Igneous Activity Foundations, 6e - Chapter 7 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The nature of volcanic eruptions Characteristics
Overview of Ch. 4. I. The nature of volcanic eruptions 9/19/2011. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5
 Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Statistics in Volcanology: Uncertainty in Volcanology Data and Models
 : Data and Models School of Geosciences University of South Florida February 2017 Volcanic s... Eruption of Shinmoe-dake volcano, Kirishima volcano complex, Japan. Major research questions Tolbachik, Kamchatka,
: Data and Models School of Geosciences University of South Florida February 2017 Volcanic s... Eruption of Shinmoe-dake volcano, Kirishima volcano complex, Japan. Major research questions Tolbachik, Kamchatka,
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
Physical Volcanology Lecture 1. USGS Photo. May 12, 1991 Mount Pinatubo, Philippines. Instructor: Joe Dufek
 Physical Volcanology Lecture 1 USGS Photo. May 12, 1991 Mount Pinatubo, Philippines Instructor: Joe Dufek Email: dufek@gatech.edu Physical Volcanology: - Normally meets MW, but we will have some earlier
Physical Volcanology Lecture 1 USGS Photo. May 12, 1991 Mount Pinatubo, Philippines Instructor: Joe Dufek Email: dufek@gatech.edu Physical Volcanology: - Normally meets MW, but we will have some earlier
Grain size, areal thickness distribution and controls on sedimentation of the 1991 Mount Pinatubo tephra layer in the South China Sea
 Bull Volcanol (2005) 67:490 495 DOI 10.1007/s00445-005-0421-y ERRATUM Martin G. Wiesner Andreas Wetzel Sandra G. Catane Eddie L. Listanco Hannah T. Mirabueno Grain size, areal thickness distribution and
Bull Volcanol (2005) 67:490 495 DOI 10.1007/s00445-005-0421-y ERRATUM Martin G. Wiesner Andreas Wetzel Sandra G. Catane Eddie L. Listanco Hannah T. Mirabueno Grain size, areal thickness distribution and
REFERENCE: The Blue Planet An Introduction to Earth System Science. Brian J. Skinner and Barbara W. Murck (2011) Third Edition. John Wiley and Sons
 REFERENCE: The Blue Planet An Introduction to Earth System Science. Brian J. Skinner and Barbara W. Murck (2011) Third Edition. John Wiley and Sons Inc. PLATE BOUNDARIES OCEAN FLOOR SEISMIC ACTIVITY WORLD'S
REFERENCE: The Blue Planet An Introduction to Earth System Science. Brian J. Skinner and Barbara W. Murck (2011) Third Edition. John Wiley and Sons Inc. PLATE BOUNDARIES OCEAN FLOOR SEISMIC ACTIVITY WORLD'S
Introduction to Planetary Volcanism
 Introduction to Planetary Volcanism SUB G&ttlngen 204459 028 Gregory Mursky University of Wisconsin Milwaukee 96 A11088 Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 ' Preface Introduction 1 Historical
Introduction to Planetary Volcanism SUB G&ttlngen 204459 028 Gregory Mursky University of Wisconsin Milwaukee 96 A11088 Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 ' Preface Introduction 1 Historical
Recognising Igneous Rocks Teacher Notes
 Minerals are the building blocks of rocks Minerals are inorganic crystals with constant structure and composition Classification of igneous rocks Igneous (Latin ig = fire, neous = born) rocks are formed
Minerals are the building blocks of rocks Minerals are inorganic crystals with constant structure and composition Classification of igneous rocks Igneous (Latin ig = fire, neous = born) rocks are formed
Thursday, October 4 th
 Thursday, October 4 th Objective: We will use and define the different ways to classify igneous rocks. Warm-up: 1. Which type of lava is most viscous? 2. Which type of lava has the least amount of silicate?
Thursday, October 4 th Objective: We will use and define the different ways to classify igneous rocks. Warm-up: 1. Which type of lava is most viscous? 2. Which type of lava has the least amount of silicate?
Sources of Unsteady Column Dynamics in Pyroclastic Flow Eruptions
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 96, NO. B13, PAGES 21,887-21,892, DECEMBER 10, 1991 Sources of Unsteady Column Dynamics in Pyroclastic Flow Eruptions GREG A. VALENTINE AND KENNETH H. WOHLETZ Earth
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 96, NO. B13, PAGES 21,887-21,892, DECEMBER 10, 1991 Sources of Unsteady Column Dynamics in Pyroclastic Flow Eruptions GREG A. VALENTINE AND KENNETH H. WOHLETZ Earth
Upward migration of Vesuvius magma chamber over the past 20 thousand years
 Upward migration of Vesuvius magma chamber over the past 20 thousand years Bruno Scaillet, Michel Pichavant, R. Cioni To cite this version: Bruno Scaillet, Michel Pichavant, R. Cioni. Upward migration
Upward migration of Vesuvius magma chamber over the past 20 thousand years Bruno Scaillet, Michel Pichavant, R. Cioni To cite this version: Bruno Scaillet, Michel Pichavant, R. Cioni. Upward migration
Title: Basaltic scoria textures from a zoned conduit as precursors to violent Strombolian activity
 Editorial Manager(tm) for Geology Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: G30720R1 Title: Basaltic scoria textures from a zoned conduit as precursors to violent Strombolian activity Short Title: Basaltic scoria
Editorial Manager(tm) for Geology Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: G30720R1 Title: Basaltic scoria textures from a zoned conduit as precursors to violent Strombolian activity Short Title: Basaltic scoria
Estimates of the dynamics of volcano eruption column using real-time AVHRR data
 Estimates of the dynamics of volcano eruption column using real-time AVHRR data Ignacio Galindo Centro Universitario de Investigaciones en Ciencias del Ambiente (CUICA) UNIVERSIDAD DE COLIMA, Colima, México
Estimates of the dynamics of volcano eruption column using real-time AVHRR data Ignacio Galindo Centro Universitario de Investigaciones en Ciencias del Ambiente (CUICA) UNIVERSIDAD DE COLIMA, Colima, México
The caldera-forming eruption of Volcµn Ceboruco, Mexico
 Bull Volcanol (2000) 62 : 20±33 Springer-Verlag 2000 RESEARCH ARTICLE J. E. Gardner S. Tait The caldera-forming eruption of Volcµn Ceboruco, Mexico Received: 18 November 1998 / Accepted: 23 October 1999
Bull Volcanol (2000) 62 : 20±33 Springer-Verlag 2000 RESEARCH ARTICLE J. E. Gardner S. Tait The caldera-forming eruption of Volcµn Ceboruco, Mexico Received: 18 November 1998 / Accepted: 23 October 1999
Daniel Frost & Stefan Lachowycz
 Daniel Frost & Stefan Lachowycz Studying the Colima active volcano, Mexico 2009 Daniel and Stefan studied Earth Science at Oxford University. For their project they went to Mexico to work as field assistants
Daniel Frost & Stefan Lachowycz Studying the Colima active volcano, Mexico 2009 Daniel and Stefan studied Earth Science at Oxford University. For their project they went to Mexico to work as field assistants
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
INFORMATION TO USERS U M I
 INFORMATION TO USERS This manuscript has been reproduced from the microfilm master. UMI films the text directly from the original or copy submitted. Thus, some thesis and dissertation copies are in typewriter
INFORMATION TO USERS This manuscript has been reproduced from the microfilm master. UMI films the text directly from the original or copy submitted. Thus, some thesis and dissertation copies are in typewriter
Tephra2 Tutorial Scripts By Leah Courtland
 Tephra2 Tutorial Scripts By Leah Courtland Tephra2 Tutorial 1: An Introduction This video will introduce you to the concepts behind the tephra2 online simulation tool. Tephra2 uses the advection diffusion
Tephra2 Tutorial Scripts By Leah Courtland Tephra2 Tutorial 1: An Introduction This video will introduce you to the concepts behind the tephra2 online simulation tool. Tephra2 uses the advection diffusion
WHAT YOU WILL LEARN. Key Concepts: TitleTitle Volcanoes and Global Warming. Carbon dioxide Sulfur dioxide Sulfate aerosols Greenhouse effect
 TitleTitle Volcanoes and Global Warming Key Concepts: Carbon dioxide Sulfur dioxide Sulfate aerosols Greenhouse effect WHAT YOU WILL LEARN 1. You will identify materials ejected by volcanic activity. 2.
TitleTitle Volcanoes and Global Warming Key Concepts: Carbon dioxide Sulfur dioxide Sulfate aerosols Greenhouse effect WHAT YOU WILL LEARN 1. You will identify materials ejected by volcanic activity. 2.
Volcanic Hazards: Airborne Debris
 Activity 4 Volcanic Hazards: Airborne Debris Goals In this activity you will: Understand why ash from volcanic eruptions can affect a much larger region than lava, pyroclastic flows, or lahars. Define
Activity 4 Volcanic Hazards: Airborne Debris Goals In this activity you will: Understand why ash from volcanic eruptions can affect a much larger region than lava, pyroclastic flows, or lahars. Define
A. What is a volcano?
 VOLCANISM THE ROCK CYCLE I. Introduction From: Roman god of fire, Vulcan A. What is a volcano? A conical mountain formed around a vent where lava, pyroclastic materials, and gases are erupted. I. Introduction
VOLCANISM THE ROCK CYCLE I. Introduction From: Roman god of fire, Vulcan A. What is a volcano? A conical mountain formed around a vent where lava, pyroclastic materials, and gases are erupted. I. Introduction
Igneous Rocks. Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members:
 Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Estimates of the Dynamics of Volcano Eruption Column Using Real-time AVHRR Data
 Estimates of the Dynamics of Volcano Eruption Column Using Real-time AVHRR Data Ignacio Galindo Centro Universitario de Investigaciones en Ciencias del Ambiente (CUICA) UNIVERSIDAD DE COLIMA, Colima, México
Estimates of the Dynamics of Volcano Eruption Column Using Real-time AVHRR Data Ignacio Galindo Centro Universitario de Investigaciones en Ciencias del Ambiente (CUICA) UNIVERSIDAD DE COLIMA, Colima, México
A computer model for volcanic ashfallout and assessment of subsequent hazard $
 Computers & Geosciences 31 (2005) 837 845 www.elsevier.com/locate/cageo A computer model for volcanic ashfallout and assessment of subsequent hazard $ G. Macedonio a, A. Costa b,,1, A. Longo c a Osservatorio
Computers & Geosciences 31 (2005) 837 845 www.elsevier.com/locate/cageo A computer model for volcanic ashfallout and assessment of subsequent hazard $ G. Macedonio a, A. Costa b,,1, A. Longo c a Osservatorio
Probabilistic tephra hazard maps for the Neapolitan area: Quantitative volcanological study of Campi Flegrei eruptions
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:1.129/27jb4954, 28 Probabilistic tephra hazard maps for the Neapolitan area: Quantitative volcanological study of Campi Flegrei eruptions G. Mastrolorenzo,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:1.129/27jb4954, 28 Probabilistic tephra hazard maps for the Neapolitan area: Quantitative volcanological study of Campi Flegrei eruptions G. Mastrolorenzo,
EAS 116 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 EAS 116 Earthquakes and Volcanoes J. Haase Forecasting Volcanic Eruptions Assessment of Volcanic Hazard Is that volcano active? Mount Lassen: 12000 BP and 1915 Santorini, IT: 180,000 BP, 70,000 BP, 21000
EAS 116 Earthquakes and Volcanoes J. Haase Forecasting Volcanic Eruptions Assessment of Volcanic Hazard Is that volcano active? Mount Lassen: 12000 BP and 1915 Santorini, IT: 180,000 BP, 70,000 BP, 21000
Coupling of turbulent and non-turbulent flow
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2794 Coupling of turbulent and non-turbulent flow Eric C. P. Breard, Gert Lube, Jim R. Jones, Josef Dufek, Shane J. Cronin, Greg A. Valentine and Anja Moebis
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2794 Coupling of turbulent and non-turbulent flow Eric C. P. Breard, Gert Lube, Jim R. Jones, Josef Dufek, Shane J. Cronin, Greg A. Valentine and Anja Moebis
Station 2 2. Identify the type of each sample (i.e. rock type, mineral class) 3. Samples A and B have a very similar appearance. What key characterist
 Station 1 2. Identify the type of each sample (i.e. rock type, mineral class) 3. What is an important economic use of sample 1B? Station 2 2. Identify the type of each sample (i.e. rock type, mineral class)
Station 1 2. Identify the type of each sample (i.e. rock type, mineral class) 3. What is an important economic use of sample 1B? Station 2 2. Identify the type of each sample (i.e. rock type, mineral class)
