1. University of Ottawa 2. Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies 3. University of Texas at Austin
|
|
|
- Cecilia Burke
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figures: Azimuthal seismic anisotropy in the Earth s upper mantle and the thickness of tectonic plates A.J. Schaeffer 1, S. Lebedev 2 and T.W. Becker 3 Geophysical Journal International July University of Ottawa 2. Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies 3. University of Texas at Austin 1
2 Table S1: Level of significance between the radially averaged correlation coefficients contained in Table 1 for the depth range km, computed following the method of Becker et al. (2007). The upper half of the table is for r8 and the lower half is for r20. SL2016svA-YB13sv SL2016svAr-YB13sv SL2016svA-DR2012a SL2016svAr-DR2012a SL2016svA-3D Sva SL2016svAr-3D Sva YB13sv-DR2012a YB13sv-3D svA SL2016svA-YB13sv SL2016svAr-YB13sv SL2016svA-DR2012a SL2016svAr-DR2012a SL2016SvA-3D Sva SL2016SvAr-3D Sva YB13sv-DR2012a YB13sv-3D Sva
3 Table S2: Level of significance between the radially averaged correlation coefficients contained in Table 1 for the depth range km, computed following the method of Becker et al. (2007). The upper half of the table is for r8 and the lower half is for r20. SL2016svA-YB13sv SL2016svAr-YB13sv SL2016svA-DR2012a SL2016svAr-DR2012a SL2016svA-3D Sva SL2016svAr-3D Sva YB13sv-DR2012a YB13sv-3D svA SL2016svA-YB13sv SL2016svAr-YB13sv SL2016svA-DR2012a SL2016svAr-DR2012a SL2016SvA-3D Sva SL2016SvAr-3D Sva YB13sv-DR2012a YB13sv-3D Sva
4 Table S3: Level of significance between the radially averaged correlation coefficients contained in Table 1 for the depth range km, computed following the method of Becker et al. (2007). The upper half of the table is for r8 and the lower half is for r20. SL2016svA-YB13sv SL2016svAr-YB13sv SL2016svA-DR2012a SL2016svAr-DR2012a SL2016svA-3D Sva SL2016svAr-3D Sva YB13sv-DR2012a YB13sv-3D svA SL2016svA-YB13sv SL2016svAr-YB13sv SL2016svA-DR2012a SL2016svAr-DR2012a SL2016SvA-3D Sva SL2016SvAr-3D Sva YB13sv-DR2012a YB13sv-3D Sva
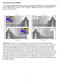
5 Figure S1: Comparison of isotropic component of SL2016svA (top row, SL2013sv; Schaeffer & Lebedev (2013)) with the isotropic component of SL2016svAr (bottom row) at depths of 100, 250 and 500 km. Below each pair of panels, the saturation limits in percent are indicated, followed by the difference in RMS perturbations between each set of panels. 5
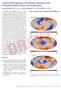
6 Figure S2: Synthetic tests illustrating the leakage between the isotropic and anisotropic model parameters. The results of two tests are illustrated at depths of 100, 250 and 500 km. The left panels illustrate the isotropic velocity anomalies that result from the inversion of a synthetic dataset generated from a purely anisotropic model, whereas the right panels show the anisotropic structure resulting from the inversion of a synthetic dataset derived from an isotropic model. Colour scales are indicated beneath each set of panels. Saturation limits for isotropic velocity are denoted top left of each map. For both isotropic and anisotropic maps, the RMS perturbation in percent is denoted at bottom right. 6
7 Figure S3: Angular misfit of SL2016svA compared with five other azimuthal anisotropy models: SL2016svAr, LH2008a (Lebedev & van der Hilst, 2008; Becker et al., 2012), YB13sv (Yuan & Beghein, 2013), 3D Sva (Debayle et al., 2016) and DR2012a (Debayle & Ricard, 2013), at depths of 50 km (left column), 100 km (centre column), and 200 km (right column). The colour scale indicates misfit in azimuthal anisotropy orientation between the models, with weighting based on the amplitude on SL2016svA. Global average angular misfit ( α ) is indicated at the lower left of each panel, with the continental ( α c ) and oceanic ( α o ) averages at lower right. 7
8 Figure S4: Average angular misfit α of fast-propagation directions in seismic anisotropy models as a function of depth, with respect to SL2016svAr, LH2008a (Lebedev & van der Hilst, 2008; Becker et al., 2012), DR2012a (Debayle & Ricard, 2013), 3D Sva (Debayle et al., 2016) and YB13sv (Yuan & Beghein, 2013). Solid curves: the global averages; dashed: for oceanic regions only; dash-dotted: continental regions only. Filled diamonds along the bottom axis indicate the depth-averaged global misfit for each model. Light grey line at α = 45 indicates a random average orientation between the two models. Note that the colours representing the different models change between the different panels. 8
9 Figure S5: Angular misfits between fast-propagation directions in tomographic models LH2008a (Lebedev & van der Hilst, 2008; Becker et al., 2012), YB13sv (Yuan & Beghein, 2013), 3D Sva (Debayle et al., 2016) and DR2012a (Debayle & Ricard, 2013) with the global spherical harmonic expansion of SKS splitting distribution from Becker et al. (2012), for depths of 125 km (left column) and 250 km (right column). For both the tomographic models and SKS splitting, anisotropy was expanded in generalized spherical harmonics up to maximum angular degree 20. The colour scale indicates misfit in azimuthal anisotropy orientation between the models, with weighting based on the amplitude of the tomography model. Global average angular misfit ( α ) is indicated at the lower left of each panel, with the continental ( α c ) and oceanic ( α o ) averages at the lower right. 9
10 Figure S6: Comparison of radially averaged inter-model correlations for global, upper-mantle anisotropy models, up to and including degree 8 ( r 8 ). The left panel illustrates correlations for the upper mantle at km depths; the right panel shows the correlations for the depth range km. In each panel, the models are sorted (left-right, bottom-up) by the decreasing total correlation (excluding auto-correlation, the white squares along the diagonal); these values are shown along the right vertical axis of each panel. Note that the sorting of the models differs between the two depth ranges. 10
11 References Becker, T. W., Ekström, G., Boschi, L., & Woodhouse, J. H., Length scales patterns, and origin of azimuthal seismic anisotropy in the upper mantle as mapped by Rayleigh waves, Geophys. J. Int., 171(1), Becker, T. W., Lebedev, S., & Long, M. D., On the relationship between azimuthal anisotropy from shear wave splitting and surface wave tomography, J. Geophys. Res., 117(B1), Debayle, E. & Ricard, Y., Seismic observations of large-scale deformation at the bottom of fast-moving plates, Earth Planet. Sc. Lett., pp Debayle, E., Kennett, B. L. N., & Priestley, K., Global azimuthal seismic anisotropy and the unique plate-motion deformation of Australia., Nature, 433(7025), Debayle, E., Dubuffet, F., & Durand, S., An automatically updated s-wavemodel of the upper mantle and the depth extent of azimuthal anisotropy, Geophys. Res. Lett., 43, 1 8. Lebedev, S. & van der Hilst, R. D., Global upper-mantle tomography with the automated multimode inversion of surface and S-wave forms, Geophys. J. Int., 173, Schaeffer, A. J. & Lebedev, S., Global shear speed structure of the upper mantle and transition zone, Geophys. J. Int., 194(1), Yuan, K. & Beghein, C., Seismic anisotropy changes across upper mantle phase transitions, Earth Planet. Sc. Lett., 374,
Supporting Information for An automatically updated S-wave model of the upper mantle and the depth extent of azimuthal anisotropy
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS Supporting Information for An automatically updated S-wave model of the upper mantle and the depth extent of azimuthal anisotropy Eric Debayle 1, Fabien Dubuffet 1 and Stéphanie
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS Supporting Information for An automatically updated S-wave model of the upper mantle and the depth extent of azimuthal anisotropy Eric Debayle 1, Fabien Dubuffet 1 and Stéphanie
Toward a generalized plate motion reference frame: Supplementary material
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.29/, Toward a generalized plate motion reference frame: Supplementary material T. W. Becker University of Southern California, Los Angeles CA, USA A. J.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.29/, Toward a generalized plate motion reference frame: Supplementary material T. W. Becker University of Southern California, Los Angeles CA, USA A. J.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 The major uncertainties in our model predictions arise from the input parameters, which include mantle density models (i.e. seismic tomography and choices about scaling velocities to temperature), crustal
The major uncertainties in our model predictions arise from the input parameters, which include mantle density models (i.e. seismic tomography and choices about scaling velocities to temperature), crustal
Auxiliary Material. Subduction of oceanic asthenosphere: evidence from sub-slab seismic anisotropy. Teh-Ru Alex Song, Hitoshi Kawakatsu
 Auxiliary Material Subduction of oceanic asthenosphere: evidence from sub-slab seismic anisotropy Teh-Ru Alex Song, Hitoshi Kawakatsu correspondence to: tehrusong@gmail.com 1 1. The effect of anisotropy
Auxiliary Material Subduction of oceanic asthenosphere: evidence from sub-slab seismic anisotropy Teh-Ru Alex Song, Hitoshi Kawakatsu correspondence to: tehrusong@gmail.com 1 1. The effect of anisotropy
Global anisotropic phase velocity maps for higher mode Love and Rayleigh waves
 Geophys. J. Int. (8) 7, 6 3 doi:./j.365-46x.7.3685.x Global anisotropic phase velocity maps for higher mode Love and Rayleigh waves K. Visser, J. Trampert and B. L. N. Kennett Department of Earth Sciences,
Geophys. J. Int. (8) 7, 6 3 doi:./j.365-46x.7.3685.x Global anisotropic phase velocity maps for higher mode Love and Rayleigh waves K. Visser, J. Trampert and B. L. N. Kennett Department of Earth Sciences,
On the relationship between azimuthal anisotropy from shear wave splitting and surface wave tomography
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008705, 2012 On the relationship between azimuthal anisotropy from shear wave splitting and surface wave tomography T. W. Becker, 1 S. Lebedev,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008705, 2012 On the relationship between azimuthal anisotropy from shear wave splitting and surface wave tomography T. W. Becker, 1 S. Lebedev,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Seismic evidence for a global low velocity layer within the Earth s upper mantle SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Benoît Tauzin 1, Eric Debayle 2 & Gérard Wittlinger 3 1 Department of Earth
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Seismic evidence for a global low velocity layer within the Earth s upper mantle SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Benoît Tauzin 1, Eric Debayle 2 & Gérard Wittlinger 3 1 Department of Earth
Global surface-wave tomography
 Global surface-wave tomography Lapo Boschi (lapo@erdw.ethz.ch) October 7, 2009 Love and Rayleigh waves, radial anisotropy Whenever an elastic medium is bounded by a free surface, coherent waves arise that
Global surface-wave tomography Lapo Boschi (lapo@erdw.ethz.ch) October 7, 2009 Love and Rayleigh waves, radial anisotropy Whenever an elastic medium is bounded by a free surface, coherent waves arise that
Supplementary Material for. Mantle induced subsidence and compression in SE Asia
 Supplementary Material for Mantle induced subsidence and compression in SE Asia Ting Yang 1 *, Michael Gurnis 1, Sabin Zahirovic 2 1 Seismological Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena,
Supplementary Material for Mantle induced subsidence and compression in SE Asia Ting Yang 1 *, Michael Gurnis 1, Sabin Zahirovic 2 1 Seismological Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena,
ANEWJOINTP AND S VELOCITY MODEL OF THE MANTLE PARAMETERIZED IN CUBIC B-SPLINES
 ANEWJOINTP AND S VELOCITY MODEL OF THE MANTLE PARAMETERIZED IN CUBIC B-SPLINES Michael Antolik, Göran Ekström, Adam M. Dziewonski, Yu J. Gu, Jian-feng Pan, and Lapo Boschi Department of Earth and Planetary
ANEWJOINTP AND S VELOCITY MODEL OF THE MANTLE PARAMETERIZED IN CUBIC B-SPLINES Michael Antolik, Göran Ekström, Adam M. Dziewonski, Yu J. Gu, Jian-feng Pan, and Lapo Boschi Department of Earth and Planetary
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (215) 23, 1832 1846 GJI Seismology doi: 1.193/gji/ggv41 A Bayesian approach to assess the importance of crustal corrections in global anisotropic surface
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (215) 23, 1832 1846 GJI Seismology doi: 1.193/gji/ggv41 A Bayesian approach to assess the importance of crustal corrections in global anisotropic surface
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1553 1 2 Supplementary Material: Exploration of geodynamic model parameters, seismological measurements, and additional tectonic constraints 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1553 1 2 Supplementary Material: Exploration of geodynamic model parameters, seismological measurements, and additional tectonic constraints 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Surface-wave studies of the Australian region
 Geol. Soc. Australia Spec. Publ. 22, and Geol. Soc. America Spec. Pap. 372 (2003), 25 40 Surface-wave studies of the Australian region E. DEBAYLE 1 * AND B. L. N. KENNETT 2 1 IPGS Ecole et Observatoire
Geol. Soc. Australia Spec. Publ. 22, and Geol. Soc. America Spec. Pap. 372 (2003), 25 40 Surface-wave studies of the Australian region E. DEBAYLE 1 * AND B. L. N. KENNETT 2 1 IPGS Ecole et Observatoire
3D IMAGING OF THE EARTH S MANTLE: FROM SLABS TO PLUMES
 3D IMAGING OF THE EARTH S MANTLE: FROM SLABS TO PLUMES Barbara Romanowicz Department of Earth and Planetary Science, U. C. Berkeley Dr. Barbara Romanowicz, UC Berkeley (KITP Colloquium 9/11/02) 1 Cartoon
3D IMAGING OF THE EARTH S MANTLE: FROM SLABS TO PLUMES Barbara Romanowicz Department of Earth and Planetary Science, U. C. Berkeley Dr. Barbara Romanowicz, UC Berkeley (KITP Colloquium 9/11/02) 1 Cartoon
Databases of surface wave dispersion
 submitted to Geophys. J. Int. Databases of surface wave dispersion Simona Carannante (1,2), Lapo Boschi (3) (1) Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche, Università Federico II, Naples, Italy (2) Istituto Nazionale
submitted to Geophys. J. Int. Databases of surface wave dispersion Simona Carannante (1,2), Lapo Boschi (3) (1) Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche, Università Federico II, Naples, Italy (2) Istituto Nazionale
Vertical coherence in mantle heterogeneity from global seismic data
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl049281, 2011 Vertical coherence in mantle heterogeneity from global seismic data L. Boschi 1,2 and T. W. Becker 3 Received 11 August 2011; revised
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl049281, 2011 Vertical coherence in mantle heterogeneity from global seismic data L. Boschi 1,2 and T. W. Becker 3 Received 11 August 2011; revised
Geophysical Journal International
 A Bayesian Method to Quantify Azimuthal Anisotropy Model Uncertainties: Application to Global Azimuthal Anisotropy in the Upper Mantle and Transition Zone Journal: Manuscript ID: Draft Manuscript Type:
A Bayesian Method to Quantify Azimuthal Anisotropy Model Uncertainties: Application to Global Azimuthal Anisotropy in the Upper Mantle and Transition Zone Journal: Manuscript ID: Draft Manuscript Type:
What does Seismic Anisotropy tell us about the Lithosphere-Asthenosphere Boundary?
 What does Seismic Anisotropy tell us about the Lithosphere-Asthenosphere Boundary? Jean-Paul Montagner (1), Gael Burgos (1), Eric Beucler (2), Antoine Mocquet (2) and Yann Capdeville (2), Mathias Obrebski
What does Seismic Anisotropy tell us about the Lithosphere-Asthenosphere Boundary? Jean-Paul Montagner (1), Gael Burgos (1), Eric Beucler (2), Antoine Mocquet (2) and Yann Capdeville (2), Mathias Obrebski
Continent-sized anomalous zones with low seismic velocity at the base of Earth s mantle
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2733 Continent-sized anomalous zones with low seismic velocity at the base of Earth s mantle Edward J. Garnero 1, Allen K. McNamara 1, and Sang-Heon D. Shim 1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2733 Continent-sized anomalous zones with low seismic velocity at the base of Earth s mantle Edward J. Garnero 1, Allen K. McNamara 1, and Sang-Heon D. Shim 1
Global anisotropy and the thickness of continents
 1 Global anisotropy and the thickness of continents Yuancheng Gung, Barbara Romanowicz and Mark Panning Berkeley Seismological Laboratory and Department of Earth and Planetary Science, Berkeley, CA, 94720,USA.
1 Global anisotropy and the thickness of continents Yuancheng Gung, Barbara Romanowicz and Mark Panning Berkeley Seismological Laboratory and Department of Earth and Planetary Science, Berkeley, CA, 94720,USA.
boundaries with additional record sections, as emphasized in Fig. S2. The observations at the
 Data used to Sample African Anomaly. The great circle paths of the source-receiver combinations used in this study are shown in Fig. S1. The event information is given in Table S1. Abrupt Changes across
Data used to Sample African Anomaly. The great circle paths of the source-receiver combinations used in this study are shown in Fig. S1. The event information is given in Table S1. Abrupt Changes across
Anisotropy in the Australasian upper mantle from Love and Rayleigh waveform inversion
 Earth and Planetary Science Letters 184 (2000) 339^351 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Anisotropy in the Australasian upper mantle from Love and Rayleigh waveform inversion Eric Debayle a;b; *, B.L.N. Kennett
Earth and Planetary Science Letters 184 (2000) 339^351 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Anisotropy in the Australasian upper mantle from Love and Rayleigh waveform inversion Eric Debayle a;b; *, B.L.N. Kennett
The stratification of seismic azimuthal anisotropy in the western US
 The stratification of seismic azimuthal anisotropy in the western US Fan-Chi Lin 1, Michael H. Ritzwoller 1, Yingjie Yang 1, Morgan P. Moschetti 1, and Matthew J. Fouch 2 1 - Center for Imaging the Earth's
The stratification of seismic azimuthal anisotropy in the western US Fan-Chi Lin 1, Michael H. Ritzwoller 1, Yingjie Yang 1, Morgan P. Moschetti 1, and Matthew J. Fouch 2 1 - Center for Imaging the Earth's
Slabs, plumes and their interaction: new insights from global anisotropy tomography
 Slabs, plumes and their interaction: new insights from global anisotropy tomography Ana M G Ferreira Seismological Laboratory, Department of Earth Sciences University College London, UK Sung-Joon Chang,
Slabs, plumes and their interaction: new insights from global anisotropy tomography Ana M G Ferreira Seismological Laboratory, Department of Earth Sciences University College London, UK Sung-Joon Chang,
Figures S1 S4 show the measurements taken from the synthetic vespagrams where a)
 Figures S1 S4 show the measurements taken from the synthetic vespagrams where a) is the differential travel time versus the Dʺ discontinuity height, b) is the differential travel time versus δv S, c) is
Figures S1 S4 show the measurements taken from the synthetic vespagrams where a) is the differential travel time versus the Dʺ discontinuity height, b) is the differential travel time versus δv S, c) is
Databases of surface wave dispersion
 ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 48, N. 6, December 2005 Databases of surface wave dispersion Simona Carannante ( 1 ) and Lapo Boschi ( 2 ) ( 1 ) Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia, Sede di Bologna,
ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 48, N. 6, December 2005 Databases of surface wave dispersion Simona Carannante ( 1 ) and Lapo Boschi ( 2 ) ( 1 ) Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia, Sede di Bologna,
A three-dimensional radially anisotropic model of shear velocity in the whole mantle
 Geophys. J. Int. (2006) 167, 361 379 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03100.x A three-dimensional radially anisotropic model of shear velocity in the whole mantle Mark Panning and Barbara Romanowicz Berkeley
Geophys. J. Int. (2006) 167, 361 379 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03100.x A three-dimensional radially anisotropic model of shear velocity in the whole mantle Mark Panning and Barbara Romanowicz Berkeley
Whole Mantle Convection
 Whole Mantle Convection Overview 1. Evidence for whole mantle convection 2. Model of whole mantle convection reconciling geophysical and geochemical data Transition Zone Water Filter Model 3. Evidence
Whole Mantle Convection Overview 1. Evidence for whole mantle convection 2. Model of whole mantle convection reconciling geophysical and geochemical data Transition Zone Water Filter Model 3. Evidence
Contents of this file
 Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for Intraplate volcanism controlled by back-arc and continental structures in NE Asia inferred from trans-dimensional ambient noise tomography Seongryong
Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for Intraplate volcanism controlled by back-arc and continental structures in NE Asia inferred from trans-dimensional ambient noise tomography Seongryong
Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of seismic event locations determined using the final 3-D velocity model. We separate the crust-related
 Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of seismic event locations determined using the final 3-D velocity model. We separate the crust-related seismicity at depths of less than 40 km (panel A) from the deeper
Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of seismic event locations determined using the final 3-D velocity model. We separate the crust-related seismicity at depths of less than 40 km (panel A) from the deeper
Wide-band coupling of Earth s normal modes due to anisotropic inner core structure
 Geophys. J. Int. (28) 174, 919 929 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-246X.28.3824.x Wide-band coupling of Earth s normal modes due to anisotropic inner core structure J. C. E. Irving, A. Deuss and J. Andrews University
Geophys. J. Int. (28) 174, 919 929 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-246X.28.3824.x Wide-band coupling of Earth s normal modes due to anisotropic inner core structure J. C. E. Irving, A. Deuss and J. Andrews University
Supplementary Information for USArray Shear Wave Splitting Shows Seismic Anisotropy from Both Lithosphere and Asthenosphere
 GSA Data Repository 2015234 Supplementary Information for USArray Shear Wave Splitting Shows Seismic Anisotropy from Both Lithosphere and Asthenosphere Sutatcha Hongsresawat 1, Mark P. Panning 1, Raymond
GSA Data Repository 2015234 Supplementary Information for USArray Shear Wave Splitting Shows Seismic Anisotropy from Both Lithosphere and Asthenosphere Sutatcha Hongsresawat 1, Mark P. Panning 1, Raymond
Non-linear crustal corrections in high-resolution regional waveform seismic tomography
 Geophys. J. Int. (27) 17, 46 467 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-246X.27.3399.x Non-linear crustal corrections in high-resolution regional waveform seismic tomography Federica Marone and Barbara Romanowicz Berkeley
Geophys. J. Int. (27) 17, 46 467 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-246X.27.3399.x Non-linear crustal corrections in high-resolution regional waveform seismic tomography Federica Marone and Barbara Romanowicz Berkeley
PEAT SEISMOLOGY Lecture 9: Anisotropy, attenuation and anelasticity
 PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 9: Anisotropy, attenuation and anelasticity Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Anisotropy Introduction Most of the theoretical
PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 9: Anisotropy, attenuation and anelasticity Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Anisotropy Introduction Most of the theoretical
The Earth is Red; Dominance of large wavelength features in mantle boundary layers. Adam M. Dziewonski
 The Earth is Red; Dominance of large wavelength features in mantle boundary layers Adam M. Dziewonski KITP, EARTH08, July 2, 2008 Kircher, 1665 Imagining ca. Earth s 2005 Interior from E. Garnero s files
The Earth is Red; Dominance of large wavelength features in mantle boundary layers Adam M. Dziewonski KITP, EARTH08, July 2, 2008 Kircher, 1665 Imagining ca. Earth s 2005 Interior from E. Garnero s files
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (11) doi: 1.1111/j.1365-46X.11.531.x On the interpretation of SKS splitting measurements in the presence of several layers of anisotropy Barbara Romanowicz
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (11) doi: 1.1111/j.1365-46X.11.531.x On the interpretation of SKS splitting measurements in the presence of several layers of anisotropy Barbara Romanowicz
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Inability of additional parameters to resolve the Rayleigh-Love discrepancy Radial anisotropy is introduced to resolve the Rayleigh-Love misfit discrepancy that exists across large regions of the western
Inability of additional parameters to resolve the Rayleigh-Love discrepancy Radial anisotropy is introduced to resolve the Rayleigh-Love misfit discrepancy that exists across large regions of the western
Surface wave tomography for azimuthal anisotropy in a strongly reduced parameter space
 Geophys. J. Int. (2008) doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.03833.x Surface wave tomography for azimuthal anisotropy in a strongly reduced parameter space Mark P. Panning 1 and Guust Nolet 1,2 1 Department of
Geophys. J. Int. (2008) doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.03833.x Surface wave tomography for azimuthal anisotropy in a strongly reduced parameter space Mark P. Panning 1 and Guust Nolet 1,2 1 Department of
Data Repository Item
 Data Repository Item 2009003 An abrupt transition from magma-starved to magma-rich rifting in the eastern Black Sea Donna J. Shillington, Caroline L. Scott, Timothy A. Minshull, Rosemary A. Edwards, Peter
Data Repository Item 2009003 An abrupt transition from magma-starved to magma-rich rifting in the eastern Black Sea Donna J. Shillington, Caroline L. Scott, Timothy A. Minshull, Rosemary A. Edwards, Peter
Mantle flow and multistage melting beneath the Galápagos hotspot revealed by seismic imaging
 Mantle flow and multistage melting beneath the Galápagos hotspot revealed by seismic imaging Darwin R. Villagómez, Douglas R. Toomey, Dennis J. Geist, Emilie E. E. Hooft, & Sean C. Solomon Joint Inversion
Mantle flow and multistage melting beneath the Galápagos hotspot revealed by seismic imaging Darwin R. Villagómez, Douglas R. Toomey, Dennis J. Geist, Emilie E. E. Hooft, & Sean C. Solomon Joint Inversion
Rayleigh-wave dispersion reveals crust-mantle decoupling beneath eastern Tibet
 www.nature.com/scientificreports OPEN received: 23 April 2015 accepted: 16 October 2015 Published: 09 November 2015 Rayleigh-wave dispersion reveals crust-mantle decoupling beneath eastern Tibet Cédric
www.nature.com/scientificreports OPEN received: 23 April 2015 accepted: 16 October 2015 Published: 09 November 2015 Rayleigh-wave dispersion reveals crust-mantle decoupling beneath eastern Tibet Cédric
Ambient Noise Tomography in the Western US using Data from the EarthScope/USArray Transportable Array
 Ambient Noise Tomography in the Western US using Data from the EarthScope/USArray Transportable Array Michael H. Ritzwoller Center for Imaging the Earth s Interior Department of Physics University of Colorado
Ambient Noise Tomography in the Western US using Data from the EarthScope/USArray Transportable Array Michael H. Ritzwoller Center for Imaging the Earth s Interior Department of Physics University of Colorado
Constraints on lithosphere net rotation and asthenospheric viscosity from global mantle flow models and seismic anisotropy
 Article Volume 11, Number 5 13 May 2010 Q05W05, doi:10.1029/2009gc002970 ISSN: 1525 2027 Click Here for Full Article Constraints on lithosphere net rotation and asthenospheric viscosity from global mantle
Article Volume 11, Number 5 13 May 2010 Q05W05, doi:10.1029/2009gc002970 ISSN: 1525 2027 Click Here for Full Article Constraints on lithosphere net rotation and asthenospheric viscosity from global mantle
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2012) doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2012.05499.x Normal mode sensitivity to Earth s D layer and topography on the core mantle boundary: what we can and cannot
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2012) doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2012.05499.x Normal mode sensitivity to Earth s D layer and topography on the core mantle boundary: what we can and cannot
SURFACE WAVE GROUP VELOCITY MEASUREMENTS ACROSS EURASIA
 SURFACE WAVE GROUP VELOCITY MEASUREMENTS ACROSS EURASIA A. L. Levshin, M. H. Ritzwoller, and L. I. Ratnikova Department of Physics, University of Colorado at Boulder -Contract Number F49620-95-1-0139 Sponsored
SURFACE WAVE GROUP VELOCITY MEASUREMENTS ACROSS EURASIA A. L. Levshin, M. H. Ritzwoller, and L. I. Ratnikova Department of Physics, University of Colorado at Boulder -Contract Number F49620-95-1-0139 Sponsored
A. J. Schaeffer 1,2 & S. Lebedev 1 1 Geophysics Section, School of Cosmic Physics, Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies, Dublin, Ireland.
 Global heterogeneity of the lithosphere and underlying mantle: A seismological appraisal based on multimode surface-wave dispersion analysis, shear-velocity tomography, and tectonic regionalization A.
Global heterogeneity of the lithosphere and underlying mantle: A seismological appraisal based on multimode surface-wave dispersion analysis, shear-velocity tomography, and tectonic regionalization A.
Importance of crustal corrections in the development of a new global model of radial anisotropy
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010jb007520, 2010 Importance of crustal corrections in the development of a new global model of radial anisotropy M. P. Panning, 1 V. Lekić, 2,3
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010jb007520, 2010 Importance of crustal corrections in the development of a new global model of radial anisotropy M. P. Panning, 1 V. Lekić, 2,3
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/326/5949/112/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Global Surface Wave Tomography Using Seismic Hum Kiwamu Nishida,* Jean-Paul Montagner, Hitoshi Kawakatsu *To whom correspondence
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/326/5949/112/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Global Surface Wave Tomography Using Seismic Hum Kiwamu Nishida,* Jean-Paul Montagner, Hitoshi Kawakatsu *To whom correspondence
GEOL540: The Mantle System
 GEOL540: The Mantle System Instructor Prof. Thorsten Becker (ZHS269; (213)740-8365; twb@usc.edu) Times Two 1.5 hours, 3 units Objective This graduate class discusses the structure, dynamics, and evolution
GEOL540: The Mantle System Instructor Prof. Thorsten Becker (ZHS269; (213)740-8365; twb@usc.edu) Times Two 1.5 hours, 3 units Objective This graduate class discusses the structure, dynamics, and evolution
The Earth s Structure from Travel Times
 from Travel Times Spherically symmetric structure: PREM - Crustal Structure - Upper Mantle structure Phase transitions Anisotropy - Lower Mantle Structure D D - Structure of of the Outer and Inner Core
from Travel Times Spherically symmetric structure: PREM - Crustal Structure - Upper Mantle structure Phase transitions Anisotropy - Lower Mantle Structure D D - Structure of of the Outer and Inner Core
C3.4.1 Vertical (radial) variations in mantle structure
 C3.4 Mantle structure Mantle behaves as a solid on short time scales (seismic waves travel through it and this requires elastic behaviour). Over geological time scales the mantle behaves as a very viscous
C3.4 Mantle structure Mantle behaves as a solid on short time scales (seismic waves travel through it and this requires elastic behaviour). Over geological time scales the mantle behaves as a very viscous
Supplementary Online Material for. Seismic evidence for a chemically distinct thermochemical reservoir in Earth s deep mantle beneath Hawaii
 Supplementary Online Material for Seismic evidence for a chemically distinct thermochemical reservoir in Earth s deep mantle beneath Hawaii Authors: Chunpeng Zhao 1, Edward J. Garnero 1,*, Allen K. McNamara
Supplementary Online Material for Seismic evidence for a chemically distinct thermochemical reservoir in Earth s deep mantle beneath Hawaii Authors: Chunpeng Zhao 1, Edward J. Garnero 1,*, Allen K. McNamara
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2014) 199, 1395 1415 GJI Seismology doi: 10.1093/gji/ggu326 Shear-velocity structure, radial anisotropy and dynamics of the Tibetan crust Matthew R.
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2014) 199, 1395 1415 GJI Seismology doi: 10.1093/gji/ggu326 Shear-velocity structure, radial anisotropy and dynamics of the Tibetan crust Matthew R.
Structures Beneath California, Transpression, and Absolute Plate
 The Relationship Between Upper Mantle Anisotropic Structures Beneath California, Transpression, and Absolute Plate Motions Minoo Kosarian 1, Paul M. Davis 1, Toshiro Tanimoto 2 and Robert W. Clayton 3
The Relationship Between Upper Mantle Anisotropic Structures Beneath California, Transpression, and Absolute Plate Motions Minoo Kosarian 1, Paul M. Davis 1, Toshiro Tanimoto 2 and Robert W. Clayton 3
Rayleigh wave phase-velocity heterogeneity and multilayered azimuthal anisotropy of the Superior Craton, Ontario
 Geophys. J. Int. (2009) 176, 215 234 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.03982.x Rayleigh wave phase-velocity heterogeneity and multilayered azimuthal anisotropy of the Superior Craton, Ontario Fiona A. Darbyshire
Geophys. J. Int. (2009) 176, 215 234 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.03982.x Rayleigh wave phase-velocity heterogeneity and multilayered azimuthal anisotropy of the Superior Craton, Ontario Fiona A. Darbyshire
Internal deformation of the subducted Nazca slab inferred from seismic anisotropy
 1 Internal deformation of the subducted Nazca slab inferred from seismic anisotropy 2 3 4 Caroline M. Eakin 1,2*, Maureen D. Long 1, Alissa Scire 3, Susan L. Beck 3, Lara S. Wagner 4, George Zandt 3, Hernando
1 Internal deformation of the subducted Nazca slab inferred from seismic anisotropy 2 3 4 Caroline M. Eakin 1,2*, Maureen D. Long 1, Alissa Scire 3, Susan L. Beck 3, Lara S. Wagner 4, George Zandt 3, Hernando
Seismic tomography: Art or science?
 Seismic tomography: Art or science? Frederik J Simons Princeton University What s inside the Earth? www.usgs.gov www.glencoe.com Dalton, Nature 2003 Only seismic waves have actually been there, done that
Seismic tomography: Art or science? Frederik J Simons Princeton University What s inside the Earth? www.usgs.gov www.glencoe.com Dalton, Nature 2003 Only seismic waves have actually been there, done that
Seismic tomography: Art or science? Frederik J Simons Princeton University
 Seismic tomography: Art or science? Frederik J Simons Princeton University What s inside the Earth? www.usgs.gov www.glencoe.com Dalton, Nature 2003 Only seismic waves have actually been there, done that
Seismic tomography: Art or science? Frederik J Simons Princeton University What s inside the Earth? www.usgs.gov www.glencoe.com Dalton, Nature 2003 Only seismic waves have actually been there, done that
Global upper-mantle tomography with the automated multimode inversion of surface and S-wave forms
 Geophys. J. Int. (28) 173, 55 518 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-246X.28.3721.x Global upper-mantle tomography with the automated multimode inversion of surface and S-wave forms Sergei Lebedev 1 and Rob D. van der
Geophys. J. Int. (28) 173, 55 518 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-246X.28.3721.x Global upper-mantle tomography with the automated multimode inversion of surface and S-wave forms Sergei Lebedev 1 and Rob D. van der
Multimode Rayleigh wave inversion for heterogeneity and azimuthal anisotropy of the Australian upper mantle
 Geophys. J. Int. (2002) 151, 738 754 Multimode Rayleigh wave inversion for heterogeneity and azimuthal anisotropy of the Australian upper mantle Frederik J. Simons, 1, Rob D. van der Hilst, 1 Jean-Paul
Geophys. J. Int. (2002) 151, 738 754 Multimode Rayleigh wave inversion for heterogeneity and azimuthal anisotropy of the Australian upper mantle Frederik J. Simons, 1, Rob D. van der Hilst, 1 Jean-Paul
Prevailing-frequency approximation of the coupling ray theory for S waves
 Prevailing-frequency approximation of the coupling ray theory for S waves Petr Bulant & Luděk Klimeš Department of Geophysics Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Charles University in Prague S EI S MIC
Prevailing-frequency approximation of the coupling ray theory for S waves Petr Bulant & Luděk Klimeš Department of Geophysics Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Charles University in Prague S EI S MIC
Velocity structure of the continental upper mantle: evidence from southern Africa
 Ž. Lithos 48 1999 45 56 Velocity structure of the continental upper mantle: evidence from southern Africa K. Priestley Department of Earth Sciences, Bullard Laboratories, UniÕersity of Cambridge, Cambridge
Ž. Lithos 48 1999 45 56 Velocity structure of the continental upper mantle: evidence from southern Africa K. Priestley Department of Earth Sciences, Bullard Laboratories, UniÕersity of Cambridge, Cambridge
Mantle and crust anisotropy in the eastern China region inferred from waveform
 Earth Planets Space, 53, 159 168, 2001 Mantle and crust anisotropy in the eastern China region inferred from waveform splitting of SKS and PpSms Takashi Iidaka 1 and Fenglin Niu 2 1 ERI, University of
Earth Planets Space, 53, 159 168, 2001 Mantle and crust anisotropy in the eastern China region inferred from waveform splitting of SKS and PpSms Takashi Iidaka 1 and Fenglin Niu 2 1 ERI, University of
Approximation to Cutoffs of Higher Modes of Rayleigh Waves for a Layered Earth Model
 Pure appl. geophys. 166 (2009) 339 351 Ó Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, 2009 0033 4553/09/030339 13 DOI 10.1007/s00024-008-0443-4 Pure and Applied Geophysics Approximation to Cutoffs of Higher Modes of Rayleigh
Pure appl. geophys. 166 (2009) 339 351 Ó Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, 2009 0033 4553/09/030339 13 DOI 10.1007/s00024-008-0443-4 Pure and Applied Geophysics Approximation to Cutoffs of Higher Modes of Rayleigh
Tomography of core-mantle boundary and lowermost mantle coupled by geodynamics: joint models of shear and compressional velocity
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tomography of core-mantle boundary and lowermost mantle coupled by geodynamics: joint models of shear and compressional velocity Gaia Soldati 1, Lapo Boschi 2,3, Steve Della
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tomography of core-mantle boundary and lowermost mantle coupled by geodynamics: joint models of shear and compressional velocity Gaia Soldati 1, Lapo Boschi 2,3, Steve Della
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors
 Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors 186 (2011) 59 69 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pepi Stratified
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors 186 (2011) 59 69 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pepi Stratified
Constraints on upper mantle viscosity from the flow induced pressure gradient across the Australian continental keel
 Article Volume 11, Number 6 4 June 2010 Q06004, doi:10.1029/2010gc003038 ISSN: 1525 2027 Click Here for Full Article Constraints on upper mantle viscosity from the flow induced pressure gradient across
Article Volume 11, Number 6 4 June 2010 Q06004, doi:10.1029/2010gc003038 ISSN: 1525 2027 Click Here for Full Article Constraints on upper mantle viscosity from the flow induced pressure gradient across
The geoid constraint in global geodynamics: viscosity structure, mantle heterogeneity models and boundary conditions
 Geophys. J. Znt. (1997) 131, 1-8 The geoid constraint in global geodynamics: viscosity structure, mantle heterogeneity models and boundary conditions Catherine Thoraval and Mark A. Richards Department
Geophys. J. Znt. (1997) 131, 1-8 The geoid constraint in global geodynamics: viscosity structure, mantle heterogeneity models and boundary conditions Catherine Thoraval and Mark A. Richards Department
Seismic Anisotropy and Mantle Flow in the Izu-Bonin-Mariana Subduction System
 Seismic Anisotropy and Mantle Flow in the Izu-Bonin-Mariana Subduction System Matthew J. Fouch (Department of Geological Sciences, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 85287, email: fouch@asu.edu) INTRODUCTION
Seismic Anisotropy and Mantle Flow in the Izu-Bonin-Mariana Subduction System Matthew J. Fouch (Department of Geological Sciences, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 85287, email: fouch@asu.edu) INTRODUCTION
Author's personal copy
 Earth and Planetary Science Letters 297 (2010) 341 354 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Earth and Planetary Science Letters journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Frontiers Mantle dynamics
Earth and Planetary Science Letters 297 (2010) 341 354 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Earth and Planetary Science Letters journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Frontiers Mantle dynamics
Seismic anisotropy in the lowermost mantle near the Perm Anomaly
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Seismic anisotropy in the lowermost mantle near the Perm Anomaly Maureen D. Long* and Colton Lynner Department of Geology and Geophysics, Yale
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Seismic anisotropy in the lowermost mantle near the Perm Anomaly Maureen D. Long* and Colton Lynner Department of Geology and Geophysics, Yale
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2012) 188, 293 300 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.05256.x An analysis of SS precursors using spectral-element method seismograms L. Bai, Y. Zhang and
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2012) 188, 293 300 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.05256.x An analysis of SS precursors using spectral-element method seismograms L. Bai, Y. Zhang and
Seismology 5: Body wave anisotropy
 Seismology 5: Body wave anisotropy what it is, how we study it, and what it can tell us about flow in the deep Earth Maureen D. Long, Yale University CIDER 7/8/16 Road map for today s talk Part I: Some
Seismology 5: Body wave anisotropy what it is, how we study it, and what it can tell us about flow in the deep Earth Maureen D. Long, Yale University CIDER 7/8/16 Road map for today s talk Part I: Some
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2011) 184, 1415 1427 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2010.04927.x The non-commutivity of shear wave splitting operators at low frequencies and implications
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2011) 184, 1415 1427 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2010.04927.x The non-commutivity of shear wave splitting operators at low frequencies and implications
Evidence of an axial magma chamber beneath the ultraslow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge
 GSA Data Repository 176 1 5 6 7 9 1 11 1 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL FOR: Evidence of an axial magma chamber beneath the ultraslow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge Hanchao Jian 1,, Satish C. Singh *, Yongshun
GSA Data Repository 176 1 5 6 7 9 1 11 1 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL FOR: Evidence of an axial magma chamber beneath the ultraslow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge Hanchao Jian 1,, Satish C. Singh *, Yongshun
Normal modes of the Earth
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Normal modes of the Earth To cite this article: Jean-Paul Montagner and Geneviève Roult 08 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 118 0104 View the article online for updates and enhancements.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Normal modes of the Earth To cite this article: Jean-Paul Montagner and Geneviève Roult 08 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 118 0104 View the article online for updates and enhancements.
Surface wave higher-mode phase velocity measurements using a roller-coaster-type algorithm
 Geophys. J. Int. (2003) 155, 289 307 Surface wave higher-mode phase velocity measurements using a roller-coaster-type algorithm Éric Beucler, Éléonore Stutzmann and Jean-Paul Montagner Laboratoire de sismologie
Geophys. J. Int. (2003) 155, 289 307 Surface wave higher-mode phase velocity measurements using a roller-coaster-type algorithm Éric Beucler, Éléonore Stutzmann and Jean-Paul Montagner Laboratoire de sismologie
Observations of long period Rayleigh wave ellipticity
 Geophys. J. Int. (), doi:./j.-x...x Observations of long period Rayleigh wave ellipticity Ana M. G. Ferreira and John H. Woodhouse Department of Earth Sciences, University of Oxford, Parks Road, Oxford
Geophys. J. Int. (), doi:./j.-x...x Observations of long period Rayleigh wave ellipticity Ana M. G. Ferreira and John H. Woodhouse Department of Earth Sciences, University of Oxford, Parks Road, Oxford
A Systematic Comparison of the Transverse Energy Minimization and Splitting Intensity Techniques for Measuring Shear-Wave Splitting Parameters
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 15, No. 1, pp. 23 239, February 215, doi: 1.1785/121418 E A Systematic Comparison of the Transverse Energy Minimization and Splitting Intensity Techniques
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 15, No. 1, pp. 23 239, February 215, doi: 1.1785/121418 E A Systematic Comparison of the Transverse Energy Minimization and Splitting Intensity Techniques
Minor-arc and major-arc global surface wave diffraction tomography
 Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors 149 (2005) 205 223 Minor-arc and major-arc global surface wave diffraction tomography Anatoli L. Levshin a,, Michael P. Barmin a, Michael H. Ritzwoller a, Jeannot
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors 149 (2005) 205 223 Minor-arc and major-arc global surface wave diffraction tomography Anatoli L. Levshin a,, Michael P. Barmin a, Michael H. Ritzwoller a, Jeannot
Robust Normal Mode Constraints on Inner Core Anisotropy From Model Space Search
 Robust Normal Mode Constraints on Inner Core Anisotropy From Model Space Search Caroline Beghein, Jeannot Trampert, Faculty of Earth Sciences, Utrecht University, Post Office Box 821, 358 TA utrecht, Netherlands
Robust Normal Mode Constraints on Inner Core Anisotropy From Model Space Search Caroline Beghein, Jeannot Trampert, Faculty of Earth Sciences, Utrecht University, Post Office Box 821, 358 TA utrecht, Netherlands
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Patterns of intraplate volcanism controlled by asthenospheric shear Clinton P. Conrad 1,,*, Todd A. Bianco 1,, Eugene I. Smith 2, and Paul Wessel 1 1 Department of Geology & Geophysics,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Patterns of intraplate volcanism controlled by asthenospheric shear Clinton P. Conrad 1,,*, Todd A. Bianco 1,, Eugene I. Smith 2, and Paul Wessel 1 1 Department of Geology & Geophysics,
Peer Reviewed Publications
 Peer Reviewed Publications Moucha, R., A. M. Forte, D. B. Rowley, J. X. Mitrovica, N. A. Simmons, and S. P. Grand (2009),Deep mantle forces and the uplift of the Colorado Plateau,Geophys. Res. Lett., doi:10.1029/2009gl039778,
Peer Reviewed Publications Moucha, R., A. M. Forte, D. B. Rowley, J. X. Mitrovica, N. A. Simmons, and S. P. Grand (2009),Deep mantle forces and the uplift of the Colorado Plateau,Geophys. Res. Lett., doi:10.1029/2009gl039778,
Seismic interferometry with antipodal station pairs
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 4, 1 5, doi:1.12/grl.597, 213 Seismic interferometry with antipodal station pairs Fan-Chi Lin 1 and Victor C. Tsai 1 Received 25 June 213; revised 19 August 213; accepted
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 4, 1 5, doi:1.12/grl.597, 213 Seismic interferometry with antipodal station pairs Fan-Chi Lin 1 and Victor C. Tsai 1 Received 25 June 213; revised 19 August 213; accepted
Investigating the S Wave Velocity Structure in front Region of Subduction Zone by Seismogram Analysis of Sumatra's Earthquakes in UGM Station
 Geosciences 2012, 2(4): 93-100 DOI: 10.5923/j.geo.20120204.04 Investigating the S Wave Velocity Structure in front Region of Subduction Zone by Seismogram Analysis of Sumatra's Earthquakes in UGM Station
Geosciences 2012, 2(4): 93-100 DOI: 10.5923/j.geo.20120204.04 Investigating the S Wave Velocity Structure in front Region of Subduction Zone by Seismogram Analysis of Sumatra's Earthquakes in UGM Station
2.1 Introduction. 16 Chapter2
 Chapter 2 Surface wave tomography of North America and the Caribbean using global and regional broadband networks: phase velocity maps and limitations of ray theory Abstract We present phase velocity maps
Chapter 2 Surface wave tomography of North America and the Caribbean using global and regional broadband networks: phase velocity maps and limitations of ray theory Abstract We present phase velocity maps
Estimation of S-wave scattering coefficient in the mantle from envelope characteristics before and after the ScS arrival
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 30, NO. 24, 2248, doi:10.1029/2003gl018413, 2003 Estimation of S-wave scattering coefficient in the mantle from envelope characteristics before and after the ScS arrival
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 30, NO. 24, 2248, doi:10.1029/2003gl018413, 2003 Estimation of S-wave scattering coefficient in the mantle from envelope characteristics before and after the ScS arrival
Global variation of body wave attenuation in the upper mantle from teleseismic P wave and S wave spectra
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl046812, 2011 Global variation of body wave attenuation in the upper mantle from teleseismic P wave and S wave spectra Y. K. Hwang, 1 J. Ritsema,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl046812, 2011 Global variation of body wave attenuation in the upper mantle from teleseismic P wave and S wave spectra Y. K. Hwang, 1 J. Ritsema,
Chemical Heterogeneity in the Mantle: Inferences from Seismology, Mineral Physics and Geodynamics
 Chemical Heterogeneity in the Mantle: Inferences from Seismology, Mineral Physics and Geodynamics Jeannot Trampert (Utrecht University), Frederic Deschamps (ETH Zurich), Paul Tackley (ETH Zurich) Probabilistic
Chemical Heterogeneity in the Mantle: Inferences from Seismology, Mineral Physics and Geodynamics Jeannot Trampert (Utrecht University), Frederic Deschamps (ETH Zurich), Paul Tackley (ETH Zurich) Probabilistic
Three-dimensional structure of the African superplume from waveform modelling
 Geophys. J. Int. (5) 161, 283 294 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-X.5.258.x Three-dimensional structure of the African superplume from waveform modelling Sidao Ni, 1,2 Don V. Helmberger 2 and Jeroen Tromp 2 1 School
Geophys. J. Int. (5) 161, 283 294 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-X.5.258.x Three-dimensional structure of the African superplume from waveform modelling Sidao Ni, 1,2 Don V. Helmberger 2 and Jeroen Tromp 2 1 School
Crustal structure beneath the Indochina peninsula from teleseismic receiver functions
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044874, 2010 Crustal structure beneath the Indochina peninsula from teleseismic receiver functions Ling Bai, 1 Xiaobo Tian, 2 and Jeroen Ritsema
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044874, 2010 Crustal structure beneath the Indochina peninsula from teleseismic receiver functions Ling Bai, 1 Xiaobo Tian, 2 and Jeroen Ritsema
24th Seismic Research Review Nuclear Explosion Monitoring: Innovation and Integration
 A REFERENCE DATA SET FOR VALIDATING 3-D MODELS E. R. Engdahl, Eric A. Bergman, Michael H. Ritzwoller, Nikolai M. Shapiro and Anatoli L. Levshin University of Colorado, Boulder Sponsored by Defense Threat
A REFERENCE DATA SET FOR VALIDATING 3-D MODELS E. R. Engdahl, Eric A. Bergman, Michael H. Ritzwoller, Nikolai M. Shapiro and Anatoli L. Levshin University of Colorado, Boulder Sponsored by Defense Threat
The use of crustal higher modes to constrain crustal structure across Central Asia
 Geophys. J. Int. (2) 16, 961 972 doi: 1.1111/j.16-26X.2.2.x The use of crustal higher modes to constrain crustal structure across Central Asia A. L. Levshin, M. H. Ritzwoller and N. M. Shapiro Department
Geophys. J. Int. (2) 16, 961 972 doi: 1.1111/j.16-26X.2.2.x The use of crustal higher modes to constrain crustal structure across Central Asia A. L. Levshin, M. H. Ritzwoller and N. M. Shapiro Department
Comparison of azimuthal seismic anisotropy from surface waves and finite strain from global mantle-circulation models
 Geophys. J. Int. (23) 155, 696 714 Comparison of azimuthal seismic anisotropy from surface waves and finite strain from global mantle-circulation models Thorsten W. Becker, 1 James B. Kellogg, 2 Göran
Geophys. J. Int. (23) 155, 696 714 Comparison of azimuthal seismic anisotropy from surface waves and finite strain from global mantle-circulation models Thorsten W. Becker, 1 James B. Kellogg, 2 Göran
S-Wave Velocity Structure beneath Southwest North America from Seismogram Comparisons of the Mexico Earthquake on 22 June 1997
 ITB J. Sci Vol. 40 A, No. 2, 2008, 109-129 109 S-Wave Velocity Structure beneath Southwest North America from Seismogram Comparisons of the Mexico Earthquake on 22 June 1997 Bagus Jaya Santosa Prodi Geofisika,
ITB J. Sci Vol. 40 A, No. 2, 2008, 109-129 109 S-Wave Velocity Structure beneath Southwest North America from Seismogram Comparisons of the Mexico Earthquake on 22 June 1997 Bagus Jaya Santosa Prodi Geofisika,
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2013) 194, 1042 1049 Advance Access publication 2013 May 3 doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt144 Finite-frequency sensitivity kernels for two-station surface wave
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2013) 194, 1042 1049 Advance Access publication 2013 May 3 doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt144 Finite-frequency sensitivity kernels for two-station surface wave
COMPUTATION OF REGIONAL TRAVEL TIMES AND STATION CORRECTIONS FROM THREE-DIMENSIONAL VELOCITY MODELS
 COMPUTATION OF REGIONAL TRAVEL TIMES AND STATION CORRECTIONS FROM THREE-DIMENSIONAL VELOCITY MODELS A. Villaseñor 1,2, M.P. Barmin 1, M.H. Ritzwoller 1, and A.L. Levshin 1 1 Department of Physics, University
COMPUTATION OF REGIONAL TRAVEL TIMES AND STATION CORRECTIONS FROM THREE-DIMENSIONAL VELOCITY MODELS A. Villaseñor 1,2, M.P. Barmin 1, M.H. Ritzwoller 1, and A.L. Levshin 1 1 Department of Physics, University
Some aspects of seismic tomography
 Some aspects of seismic tomography Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego September 7, 2009 Earthquake Research Institute Part 1: Global Tomography P velocity perturbations 200 km 1000 km 2700 km MIT 2006
Some aspects of seismic tomography Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego September 7, 2009 Earthquake Research Institute Part 1: Global Tomography P velocity perturbations 200 km 1000 km 2700 km MIT 2006
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2013) 194, 401 416 Advance Access publication 2013 April 5 doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt092 Normal mode splitting function measurements of anelasticity and attenuation
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2013) 194, 401 416 Advance Access publication 2013 April 5 doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt092 Normal mode splitting function measurements of anelasticity and attenuation
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1131692/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Localized Temporal Change of the Earth s Inner Core Boundary This PDF file includes: Materials and Methods Figs. S1 to S3
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1131692/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Localized Temporal Change of the Earth s Inner Core Boundary This PDF file includes: Materials and Methods Figs. S1 to S3
