Grade Level: 6-8; Piloted at Grade 6
|
|
|
- Clifton Hampton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Julie Senka Science Teacher Piloted in Grade 6 Unit: Rock Cycle Rocks Grade Level: 6-8; Piloted at Grade 6 Modeling the Rock Cycle in a Diagram Aligned Lesson 4 Science Lesson for Unit: Rock Cycle Rocks About the author/teacher: 6 th - 8th grade science teacher jsenka@manhattan114.org Manhattan Junior High District 114 Manhattan, Illinois Lesson Length: 1 (45-minute) class period Related Unit: The Rock Cycle; Geologic Change WHST Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection, organization, and analysis of relevant content. (CCSS ELA) RST Integrate quantitative or technical information expressed in words in a text with a version of that information expressed visually (e.g., in a flowchart, diagram, model, graph, or table). (CCSS ELA) SL Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, teacher-led) with diverse partners on grade 6 topics, texts, and issues, building on others ideas and expressing their own clearly. (CCSS ELA)
2 Enduring Understandings Models can be used to represent systems and their interactions. Within a natural or designed system, the transfer of energy drives the motion and/or cycling of matter. Rocks and fossils tell the history of Earth and how environmental conditions have changed over time. The principle of uniformitarianism states that the processes that occurred in the past are the same as the processes occurring presently and will continue to occur in the future. The rock cycle is a slow, continuous, neverending recycling of rocks that changes Earth s surface. Energy from Earth s interior drives the rock cycle. Physical/Mechanical Weathering breaks down rocks into smaller pieces. Weathering changes rocks on Earth s surface. Erosion carries rocks away on Earth s surface. Melting of rocks can occur on or below Earth s surface. Igneous rocks can form aboveground from quick-cooling lava and underground from slow-cooling magma. Sedimentary rocks are made from cemented and compacted sediments. SS.IS MdC - Construct explanations using reasoning, correct sequence, examples and details, while acknowledging their strengths and weaknesses. (IL SS) SS.G2.6-8.MdC - Compare and contrast the cultural and environmental characteristics of different places or regions. (IL SS) MP.2 - Reason abstractly and quantitatively (CCSS Math) Essential Questions How does energy contribute to the formation of Earth materials, such as minerals, rocks, and ores? How can scientists determine what has happened in the past? How does energy affect Earth s landscapes? How do processes in the Rock Cycle affect earth s landscapes? How does change happen to Earth s landscapes? Changing Earth: What has the history of Earth looked like?
3 Metamorphic rocks are formed underground when a rock is exposed to intense heat and pressure. All rocks can weather and erode. All rocks can melt into magma. Geologic change on Earth is sudden, the result of catastrophic events (catastrophism), or slow and gradual (uniformitarianism). Geologic changes that occur today will affect resources and landscapes in the future. Transfer Goals Developing and using models Constructing explanations (for science) Identifying Patterns and Causes/Effects to make future predictions Using data and evidence of past events to make statistical predictions for future events Citing evidence that stability may be disturbed by sudden events or gradual changes over time Learning Objectives Use reasoning, along with the assumption that theories and laws that describe the natural world operate today as they did in the past and will continue to do so in the future, to connect the evidence and support an explanation for how the geologic time scale is used to construct a timeline of the Earth s history. Use evidence and reasoning to construct an explanation for the given phenomenon, which involves changes at Earth s surface. Identify and describe* the evidence necessary for constructing an explanation, including: o The slow and large-scale motion of the Earth s plates and the results of that motion. o Surface weathering, erosion, movement, and the deposition of sediment ranging from large to microscopic scales (e.g., sediment consisting of boulders and microscopic grains of sand, raindrops dissolving microscopic amounts of minerals). o Rapid catastrophic events (e.g., earthquakes, volcanoes, meteor impacts). Identify the corresponding timescales for each identified geoscience process. Use multiple valid and reliable sources, which may include students own investigations, evidence from data, and observations from conceptual models used to represent changes that occur on very large or small spatial and/or temporal scales (e.g., stream tables to illustrate erosion and deposition, maps and models to show the motion of tectonic plates). Use reasoning, along with the assumption that theories and laws that describe the natural world operate today as they did in the past and will
4 continue to do so in the future, to connect the evidence and support an explanation for how geoscience processes have changed the Earth s surface at a variety of temporal and spatial scales. Use reasoning, along with the assumption that theories and laws that describe the natural world operate today as they did in the past and will continue to do so in the future, to connect the evidence and support an explanation for how geoscience processes have changed the Earth s surface at a variety of temporal and spatial scales. Students describe the following chain of reasoning for their explanation: o Surface processes such as erosion, movement, weathering, and the deposition of sediment can modify surface features, such as mountains, or create new features, such as canyons. These processes can occur at spatial scales ranging from large to microscopic over time periods ranging from years to hundreds of millions of years. o Catastrophic changes can modify or create surface features over a very short period of time compared to other geoscience processes, and the results of those catastrophic changes are subject to further changes over time by processes that act on longer time scales (e.g., erosion of a meteor crater). o A given surface feature is the result of a broad range of geoscience processes occurring at different temporal and spatial scales. o Surface features will continue to change in the future as geoscience processes continue to occur. Students will be able to: Explain the changes that happened in Earth s 4.6 billion-year past are the same changes that occur in the present and will continue to occur in the future. Identify weathering as the force that breaks rocks down. Identify erosion as the force that move rocks from one place to another. Identify weathering and erosion as forces that work together to make and move sediment from one place to another. Identify compaction and cementation of sediments as the forces that create Sedimentary Rocks. Identify heat and pressure as the agents of metamorphism (Metamorphic Rocks.) Identify the cooling and hardening of magma and lava as the forces that create Igneous Rocks. Point to melting as the cause of any rock turning back into magma under the Earth s surface, or lava above. Identify Earth s internal energy as the driving force for the Rock Cycle. Identify the sun, water, and wind as agents of weathering and erosion on Earth s surface.
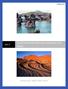
5 Classify the Rock Cycle as a slow and gradual process but identify counterexamples to explain when rocks can be changed suddenly, as seen in natural disasters. Explain the Rock Cycle and its processes verbally or in text. Communicate understanding of the Rock Cycle in a visual/graphical format. Library of Congress: Primary Sources Kiska Volcano in the Aleutian Islands Engage: How can I get students interested in this? See attached lesson for detailed plans. Materials/Supplies/Resources Pencil Rock Cycle Song from previous lessons The Rock Cycle Worksheet Smartboard or whiteboard with projector for students to record answers as a class (if possible) Random Name Picker from Classtools.net Students will sing the Rock Cycle Song from previous classes. The teacher will engage students with the image of Kiska Volcano in Alaska. Students will discuss what they know of volcanoes and the rocks they produce. Students will share whether igneous rocks are locally found within their own geographic region and construct an explanation as to why or why not. This particular volcano, Kiska Volcano, is located in the Aleutian Islands on the Ring of Fire. It is the most tectonically active region in the world. Students should be allowed some latitude in sharing their experiences with visiting a volcano. Furthermore, the teacher can allow some discussion on volcanoes seen in movies versus volcanoes in real life. Many movies portray volcanoes with impending doom and destruction. However, after an eruption, the soil is left with increased fertility and more nutrients for growing plants and crops. Students will independently complete the rock cycle diagram. As students finish, they should check their work, and on the back, explain why this rock cycle does/does not make sense. Students should be able to identify areas of weakness/struggle. When all students are done, the teacher can use a random name picker or student volunteers to place correct answers in their proper locations, along with an explanation of why the rock or process belongs there Metacognition. Students love writing answers on a Smart Board or whiteboard. Explore: What tasks/questions can I offer to help students puzzle through this?
6 See attached lesson for detailed plans. To begin, the teacher should emphasize that students should start with what they know. Individually, the teacher can assist struggling students with the blank in the middle and walk students through the arrow leading from the middle. Individually, the teacher can point out the directionality of the arrows in the rock cycle. This makes that. For students who struggle, the teacher can also state that arrows indicate processes and rock images indicate Sedimentary, Igneous, or Metamorphic. The teacher can remind students to refer to their Rock Cycle Song. The teacher should tell students to look at other blanks that have been completed to assist them. It is imperative that the Teacher circulates and checks for student understanding while answering the questions. Again, the teacher can formatively assess students learning levels and mastery of the standard. Explain: How can I help students make sense of their observations? See attached lesson for detailed plans. To begin, the teacher should emphasize that students should start with what they know. Individually, the teacher can assist struggling students with the blank in the middle and walk students through the arrow leading from the middle. The teacher can remind students to refer to their Rock Cycle Song. Individually, the teacher can point out the directionality of the arrows in the rock cycle. This - makes that. For students who struggle, the teacher can also state that arrows indicate processes and rock images indicate Sedimentary, Igneous, or Metamorphic. The teacher should tell students to look at other blanks that have been completed to assist them. Upon completing the lab, students must summarize why their rock cycle makes sense. Before reviewing as a class, allow students to pair up with another student and compare answers. Students should explain why they answered as they did. As the students explain their rock cycle diagrams, the teacher should circulate and make note of students who are still struggling and where they are struggling.
7 Upon reviewing together, the teacher will use the random name picker at Classtools.net to allow students to complete the Rock Cycle Diagram on a Smart Board or White Board. THE TEACHER MUST CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING AND CLARIFY MISCONCEPTIONS AS THEY ARISE. Extend/Elaborate: How can my students apply their new knowledge to other situations? See attached lesson for detailed plans. A possible extension is for students to research current and historical uses for igneous rocks. (Granite Countertops, Obsidian Arrowheads, Pumice in Soap and Foot Stones; Lava Rocks for Grilling) As indicated by the Primary Source Analysis Tool, students can research Kiska Volcano, particularly where it is found. Upon researching, students will find that it is located in the Ring of Fire. The Ring of Fire is the most active tectonic plate in the world and has the most active volcanoes. This should transfer back/lead to future lessons involving Plate Tectonics. This activity should segue into a discussion on Earth s history, as the presence of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks give us a glimpse into how the areas have changed over time. Ex The presence of Granite indicates volcanic activity. Evaluate: How can I help my students self-evaluate and reflect on the learning? See attached lesson for detailed plans. Upon completing the activity, students must summarize why their rock cycle makes sense or why it does not.
8 Unit 2 Lesson 4 1 Class Period (45 minutes each) Modeling the Rock Cycle in a Diagram Julie M. Senka
9 This activity technically starts with the image from the LOC. The teacher displays an image of the Kiska Volcano in the Aleutian Islands. By this point, students should associate volcanoes with magma (underground) and lava (above ground). Lava and magma create igneous rocks. In the rock cycle SEP BIG IDEAS/DCI CCC Misconceptions This rock changes into that rock is shown by: this rock that rock.** Students may believe that volcanic eruptions are weather-dependent. diagram, the center, first place to start, is Magma. Once that is determined, all other pieces and processes should fall into place. Day 1 Part 1 Rock Cycle Song (2 minutes) Students should sing The Rock Cycle Song. Part 2 LOC Image (10-15 minutes) The teacher should display the LOC image and title (of Kiska Volcano) on a Smart Board or through students computers. Ask students to identify the rock type found around this landmark. Then ask students if they would be likely to find a large amount of this rock where they live. o Volcanoes are associated with magma and lava. Magma and lava create Igneous Rocks. o o Using a model to demonstrate phenomena Ask Questions Why are rocks different? How do rocks change? How are rocks made? Analyze and Interpret Data Why do rocks look the way they do? Constructing explanations Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information. Earth s features are the result of geological processes. Change on Earth is generally slow but can occur due to sudden events. There are 3 different types of rocks. Rocks form in different ways, and their appearances give us clues to their histories and what made them. The same changes that happened in the past will happen in the future. Stability and Change Identify factors that disrupt stability and lead to change over time. Cause and Effect An external (force) cause produces a predictable effect in rocks. Structure and Function Features of rocks determine their uses. Energy & Matter Rocks are changed due to the cycling of energy in the rock cycle. Scale Proportion & Quantity Model is too small to represent the depth of the Rock Cycle. Rocks are the same and come from the same places. Rocks are distributed evenly throughout the world. Metamorphic rocks are made from magma. Rocks are boring and tell us nothing about Earth. Change only occurs slowly. **Arrows in the Rock Cycle diagram indicate change and processes ONLY. Some areas may have more igneous rocks due to past or present volcanism. Regions such as the Ring of Fire will have a lot of igneous rocks. (The Aleutian Islands are on the Ring of Fire.)
10 o Spots on the ocean floor near sites of seafloor spreading have the newest Igneous Rocks. Part 3 Rock Cycle Diagram (15 minutes) The teacher should give students 10 minutes to complete The Rock Cycle Diagram independently. This should not be graded but assessed for understanding. By the end of this period, the teacher should have a firm grasp on who is meeting expectations and who is still emerging. The teacher should point out some clues that should, but may not, be obvious: o If the blank is on a rock, it should be igneous, metamorphic, or sedimentary. o Blanks above arrows indicate processes. o If students don t know how to read the diagram, they can t show the teacher what they know and complete it effectively. o Mnemonic devices again may help students. Mmmmmelting mmmmmakes. o Individually, the teacher can point out the directionality of the arrows in the rock cycle. This makes that. The teacher must circulate around the room and give the necessary hints from above to get students to where they need to be. For students who struggle, the teacher can suggest revisiting their Rock Cycle Song to guide them through a process or rock type. All students should complete a self-assessment that explains why the rock cycle makes sense or where they are still confused. Part 4 Rock Cycle Diagram Explained for students, by students (15 minutes) Students should pair up with someone around them and explain their answers to one another. The teacher should circulate around the room, paying attention to conversations and noting where misconceptions still arise. A Smart Board or other projector/whiteboard is really effective here. Kids love going up to the Smart Board. Using the random name picker at Classtools.net, or other randomizing device, the teacher should start with the answer in the middle. Have students fill in the blanks and explain why that makes sense. Allow students to give another explanation for why the answer is correct. Continue through the worksheet, with students explaining answers and the teacher asking questions where needed. Collect the Worksheet for a quick assessment and return it to students tomorrow. Part 5 Independent Practice (5 minutes) For additional practice, direct students back to the Guided Rock Cycle Notes from Lesson 1. At the bottom, students can draw a Rock Cycle. It can be simple or complex, but it has to be original. The teacher can do a quick check before students leave to make sure they are on the right track, or it can be checked in tomorrow. Differentiation For students who struggle, o The teacher can give them a Freebie a free space where the teacher should provide the type of rock and why that type of rock is the correct answer. o The teacher can allow them to check their answers against the Rock Cycle on Learner.org. For students who are nearing Mastery, o the teacher can allow them to complete the Further Investigation on the Primary Source Analysis Tool.
11 o A review on Quizlet or Quia.com Rags to Riches Game could be utilized. The teacher can go to either site and search for premade games or make one of her/his own. Quia.com requires a paid subscription, but Quizlet is free to teachers. Rubric & Assessment Based on teacher observations during the completion of the worksheet, peer-to-peer explanations, and student input on the paragraph, the teacher should assess student knowledge. Rubric Criterion I Can Mastery - 3 Getting There - 2 Needs Clarification - 1 Identify the types of rock (and magma) based on the processes that create the rocks. Correctly identifies all three types of rock (and magma) that were formed. Correctly identifies two types of rock (and magma) that were formed. Correctly identifies one type of rock that was formed. Identify processes that create rocks. In Notebook - Represent the Rock Cycle in a visual format Correctly identifies all 5 processes that form rocks. Correctly depicts the Rock Cycle, identifying all intermediate steps and processes. Correctly identifies 3-4 processes that form rocks. Correctly depicts the Rock Cycle, identifying most intermediate steps and processes. Correctly identifies 1-2 processes that form rocks. Cannot accurately draw a rock cycle diagram, or rock cycle diagram is missing major intermediate steps, rocks, and processes. Sample Remediation Based on the above rubric and teacher observations, students should be assigned further remediation if they are still struggling. Student Name Area that needs clarification? (Teacher will check) Igneous Rocks Sedimentary Rocks Metamorphic Rocks How can this be clarified? (student will decide) Brainpop Video Study Jams Video Classzone Animation Quizlet Game Quia.com review Other (specify) Brainpop Video Study Jams Video Classzone Animation Quizlet Game Quia.com review Other (specify) Brainpop Video Study Jams Video Classzone Animation Quizlet Game Quia.com review Other (specify) Student feedback after receiving help
Modeling the Rock Cycle with Play-Doh Aligned Lesson 3 Science Lesson for Unit: Rock Cycle Rocks
 Julie Senka Science Teacher Piloted in Grade 6 Unit: Rock Cycle Rocks Modeling the Rock Cycle with Play-Doh Aligned Lesson 3 Science Lesson for Unit: Rock Cycle Rocks Grade Level: 6-8; Piloted at Grade
Julie Senka Science Teacher Piloted in Grade 6 Unit: Rock Cycle Rocks Modeling the Rock Cycle with Play-Doh Aligned Lesson 3 Science Lesson for Unit: Rock Cycle Rocks Grade Level: 6-8; Piloted at Grade
Modeling the Rock Cycle with Crayons Aligned Lesson 6 Science Lesson for Unit: Rock Cycle Rocks
 Modeling the Rock Cycle with Crayons Aligned Lesson 6 Science Lesson for Unit: Rock Cycle Rocks Julie Senka Science Teacher Piloted in Grade 6 Unit: Rock Cycle Rocks Grade Level: 6-8; Piloted at Grade
Modeling the Rock Cycle with Crayons Aligned Lesson 6 Science Lesson for Unit: Rock Cycle Rocks Julie Senka Science Teacher Piloted in Grade 6 Unit: Rock Cycle Rocks Grade Level: 6-8; Piloted at Grade
Rocks Rock! Introduction to the Rock Cycle
 Rocks Rock! Introduction to the Rock Cycle Aligned Lesson 1 Science Lesson for Unit: Rock Cycle Rocks Julie Senka Science Teacher Piloted in Grade 6 Unit: Rock Cycle Rocks Grade Level: 6-8; Piloted at
Rocks Rock! Introduction to the Rock Cycle Aligned Lesson 1 Science Lesson for Unit: Rock Cycle Rocks Julie Senka Science Teacher Piloted in Grade 6 Unit: Rock Cycle Rocks Grade Level: 6-8; Piloted at
Back to the Big Question
 5.1 Understand the 5.4 Question Explore Learning Set 5 Back to the Big Question What processes within Earth cause geologic activity? You now know a lot about patterns of volcanoes in your region and around
5.1 Understand the 5.4 Question Explore Learning Set 5 Back to the Big Question What processes within Earth cause geologic activity? You now know a lot about patterns of volcanoes in your region and around
The performance expectation above was developed using the following elements from the NRC document A Framework for K-12 Science Education:
 MS-ESS2-1 Earth's Systems Students who demonstrate understanding can: MS-ESS2-1. Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth's materials and the flow of energy that drives this process. [Clarification
MS-ESS2-1 Earth's Systems Students who demonstrate understanding can: MS-ESS2-1. Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth's materials and the flow of energy that drives this process. [Clarification
EARTH S SYSTEMS: PROCESSES THAT SHAPE THE EARTH
 9 Week Unit UNIT 2 EARTH S SYSTEMS: PROCESSES THAT SHAPE THE EARTH Fourth Grade Rogers Public Schools : Earth s Systems: Processes that Shape the Earth 9 weeks In this unit, students develop understandings
9 Week Unit UNIT 2 EARTH S SYSTEMS: PROCESSES THAT SHAPE THE EARTH Fourth Grade Rogers Public Schools : Earth s Systems: Processes that Shape the Earth 9 weeks In this unit, students develop understandings
Geology Test Review Answers
 Name: Geology Test Review Answers Core: Fill in the blanks: 1. Sediments get compacted and cemented into sedimentary rock. 2. Igneous rocks can be intrusive or extrusive from a volcano. 3. Adding heat
Name: Geology Test Review Answers Core: Fill in the blanks: 1. Sediments get compacted and cemented into sedimentary rock. 2. Igneous rocks can be intrusive or extrusive from a volcano. 3. Adding heat
You Might Also Like. Thanks. Connect
 Thanks Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over at my blog
Thanks Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over at my blog
Version Date 6/26/17. Disciplinary Core Ideas (Framework)
 1 Earth Is Rock 1 What's the Story of This Place? Students consider the history of Earth and begin to think about rock and landforms as a source of for Earth s past. An Earth tour provides a sense of the
1 Earth Is Rock 1 What's the Story of This Place? Students consider the history of Earth and begin to think about rock and landforms as a source of for Earth s past. An Earth tour provides a sense of the
All instruction should be three-dimensional. NGSS Example Bundles. Page 1 of 14
 Middle School Topic Model Course II Bundle 3 Geologic Changes to the Earth This is the third bundle of the Middle School Topics Model Course II. Each bundle has connections to the other bundles in the
Middle School Topic Model Course II Bundle 3 Geologic Changes to the Earth This is the third bundle of the Middle School Topics Model Course II. Each bundle has connections to the other bundles in the
6.E E Rock Cycle/Weathering/Soil
 Name: Date: 1. A lake is surrounded by hills covered with trees and shrubs. Which statement correctly describes how a change to the plants in this area will affect this environment? A. Adding plants to
Name: Date: 1. A lake is surrounded by hills covered with trees and shrubs. Which statement correctly describes how a change to the plants in this area will affect this environment? A. Adding plants to
Rock Cycle Reader s Theater
 Rock Cycle Reader s Theater Characters Teacher1 Teacher 2 Student 1 Student 2 Student 3 Sedimentary Rock Crust Wind Water Ice Sediment 1 Sediment 2 Sediment 3 Metamorphic Rock The Rock Cycle Mantel Magma
Rock Cycle Reader s Theater Characters Teacher1 Teacher 2 Student 1 Student 2 Student 3 Sedimentary Rock Crust Wind Water Ice Sediment 1 Sediment 2 Sediment 3 Metamorphic Rock The Rock Cycle Mantel Magma
Processes That Shape the Earth Weather, Part I
 Grade 6 Science, Quarter 4, Unit 4.1 Processes That Shape the Earth Weather, Part I Overview Number of instructional days: 25 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to be learned Explain how condensation of water
Grade 6 Science, Quarter 4, Unit 4.1 Processes That Shape the Earth Weather, Part I Overview Number of instructional days: 25 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to be learned Explain how condensation of water
Rock Cycle. Presented by Kesler Science
 Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: What processes are involved in the formation and classification of metamorphic, sedimentary, and igneous rocks? Sediments A model that describes the formation,
Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: What processes are involved in the formation and classification of metamorphic, sedimentary, and igneous rocks? Sediments A model that describes the formation,
BRYCE CANYON NATIONAL PARK Earth s Dynamic Treasures Rocks & The Rock Cycle
 Grade Level: 4th-8th grades Subject Area: Earth Science Objectives: Introduce students to the rock cycle. Students will have an opportunity to categorize rocks from the three rock types. Students investigate
Grade Level: 4th-8th grades Subject Area: Earth Science Objectives: Introduce students to the rock cycle. Students will have an opportunity to categorize rocks from the three rock types. Students investigate
GCSE ready intervention tasks
 7. Earth 1 LEARNING CONTEXT AQA Big idea: 3.7 Earth AQA Strand: 3.7.1 Earth structure 3.7.2 Universe AQA Enquiry processes: 2.3 Draw conclusions 2.7 Critique claims How this provides GCSE readiness: The
7. Earth 1 LEARNING CONTEXT AQA Big idea: 3.7 Earth AQA Strand: 3.7.1 Earth structure 3.7.2 Universe AQA Enquiry processes: 2.3 Draw conclusions 2.7 Critique claims How this provides GCSE readiness: The
You Might Also Like. I look forward helping you focus your instruction while saving tons of time. Kesler Science Station Lab Activities 40%+ Savings!
 Thanks Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. Connect You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Thanks Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. Connect You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
MS.PS1.A: Structure and Properties of Matter
 MS.PS1.A: Structure and Properties of Matter Each pure substance has characteristic physical and chemical properties (for any bulk quantity under given conditions) that can be used to identify it. (MS
MS.PS1.A: Structure and Properties of Matter Each pure substance has characteristic physical and chemical properties (for any bulk quantity under given conditions) that can be used to identify it. (MS
11.4 The Rock Cycle. Rocks and Soils. Objective. Materials. Teacher Tip. Directed Instruction. Content. Introduction
 11.4 The Rock Cycle Rocks and Soils Objective Students will explain orally how rocks change form through the rock cycle. Materials Blackline Master 11.4A Discover: The Rock Cycle Blackline Master 11.4B
11.4 The Rock Cycle Rocks and Soils Objective Students will explain orally how rocks change form through the rock cycle. Materials Blackline Master 11.4A Discover: The Rock Cycle Blackline Master 11.4B
Modeling the Rock Cycle
 P a g e 1 Name Modeling the Rock Cycle Background Information: Like the Earth itself, rocks are in a constant state of change. Rocks are solids made up of different minerals. Scientists usually classify
P a g e 1 Name Modeling the Rock Cycle Background Information: Like the Earth itself, rocks are in a constant state of change. Rocks are solids made up of different minerals. Scientists usually classify
THE ROCK CYCLE & ROCKS. Subtitle
 THE ROCK CYCLE & ROCKS Subtitle 3. Three rocks that do not have minerals or are composed of nonmineral matter. Coal Pumuce Obsidian THE ROCK CYCLE Why do scientists study rocks? Rocks contain clues about
THE ROCK CYCLE & ROCKS Subtitle 3. Three rocks that do not have minerals or are composed of nonmineral matter. Coal Pumuce Obsidian THE ROCK CYCLE Why do scientists study rocks? Rocks contain clues about
SCI-5 KES 5.7 Geology Post-test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 SCI-5 KES 5.7 Geology Post-test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:1D5NLH 1 Earth's crust is made of plates that move slowly. This movement changes the appearance of the Earth's crust
SCI-5 KES 5.7 Geology Post-test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:1D5NLH 1 Earth's crust is made of plates that move slowly. This movement changes the appearance of the Earth's crust
Directed Reading. Section: Rocks and the Rock Cycle. made of a. inorganic matter. b. solid organic matter. c. liquid organic matter. d. chemicals.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Rocks and the Rock Cycle 1. The solid part of Earth is made up of material called a. glacial ice. b. lava. c. rock. d. wood. 2. Rock can be a collection of one
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Rocks and the Rock Cycle 1. The solid part of Earth is made up of material called a. glacial ice. b. lava. c. rock. d. wood. 2. Rock can be a collection of one
PENNSYLVANIA. Ordinary processes at Earth's surface and just below it cause rocks to change and soils to form. Page 1 of 3. S8.A.1.1.
 Know: Understand: Do: S8.D.1.1.1 -- Essential Explain the rock cycle as changes in the solid earth and rock types found in Pennsylvania (igneous - granite, basalt, obsidian, pumice, ; sedimentary - limestone,
Know: Understand: Do: S8.D.1.1.1 -- Essential Explain the rock cycle as changes in the solid earth and rock types found in Pennsylvania (igneous - granite, basalt, obsidian, pumice, ; sedimentary - limestone,
Igneous magma cools crystals, holes Metamorphic heat & pressure wavy layers, foliation Sedimentary straight layers, rough, dull, fossils
 First Semester Final Exam Study Guide Question Answer Illustration/Example List the three main types of rocks and draw a picture of each. Label the significant features. (Layers, crystals, holes, grains,
First Semester Final Exam Study Guide Question Answer Illustration/Example List the three main types of rocks and draw a picture of each. Label the significant features. (Layers, crystals, holes, grains,
Rocks: Stony Stalwarts: Adapted from:
 Rocks: Stony Stalwarts: Adapted from: http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/earth/inside-the-earth/rocks-article/ Rocks are so common that most of us take them for granted cursing when we hit them
Rocks: Stony Stalwarts: Adapted from: http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/earth/inside-the-earth/rocks-article/ Rocks are so common that most of us take them for granted cursing when we hit them
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Geologic Change over Time. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of uniformitarianism states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of uniformitarianism states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
4 th Grade PSI. Slide 1 / 107 Slide 2 / 107. Slide 3 / 107. Slide 4 / 107. Slide 5 / 107. Slide 6 / 107. The History of Planet Earth
 Slide 1 / 107 Slide 2 / 107 4 th Grade PSI The History of Planet Earth 2015-11-10 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 107 Slide 4 / 107 The History of Planet Earth The Structure of Earth Rock Layers Fossils and Relative
Slide 1 / 107 Slide 2 / 107 4 th Grade PSI The History of Planet Earth 2015-11-10 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 107 Slide 4 / 107 The History of Planet Earth The Structure of Earth Rock Layers Fossils and Relative
1. minerals - A naturally occurring substance that takes a solid Crystal form and is made of only a single (one) type of compound
 Science Name: Mr. G/Mrs. Kelly KEY Date: Study Guide - Lessons 5 and 6 Test Define the following terms: 1. minerals - A naturally occurring substance that takes a solid Crystal form and is made of only
Science Name: Mr. G/Mrs. Kelly KEY Date: Study Guide - Lessons 5 and 6 Test Define the following terms: 1. minerals - A naturally occurring substance that takes a solid Crystal form and is made of only
The Rocky Road Game. Sedimentary Rock. Igneous Rock. Start. Metamorphic Rock. Finish. Zone of Transportation. Weathering Way.
 Sedimentary Rock Deposition Depot Zone of Transportation Transported: Advance 3 Weathering Way The Rocky Road Game Uplift: Advance 5 Lithification Lane Crystallization Crossway Submerge Detour take the
Sedimentary Rock Deposition Depot Zone of Transportation Transported: Advance 3 Weathering Way The Rocky Road Game Uplift: Advance 5 Lithification Lane Crystallization Crossway Submerge Detour take the
Rock Cycle. Draw the Rock cycle on your remediation page OR use a sheet of notebook paper and staple
 Earth Science Test 8.ESS2.3) Describe the relationship between the processes and forces that create igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. I can develop and use models to explain how plate movements
Earth Science Test 8.ESS2.3) Describe the relationship between the processes and forces that create igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. I can develop and use models to explain how plate movements
Weathering and Erosion
 Unit abstract Overview In this unit of study, students are expected to develop understanding of the effects of weathering and the rate of erosion by water, ice, wind, or vegetation. The crosscutting concepts
Unit abstract Overview In this unit of study, students are expected to develop understanding of the effects of weathering and the rate of erosion by water, ice, wind, or vegetation. The crosscutting concepts
The Ohio State University School of Teaching and Learning Middle Childhood Education LESSON PLAN
 The Ohio State University School of Teaching and Learning Middle Childhood Education Intern: Jennifer Howes Mentor: Date: 3/14/11 Period: 1,6,7 Grade: 7 Subject: Science Topic: Plate Tectonics LESSON PLAN
The Ohio State University School of Teaching and Learning Middle Childhood Education Intern: Jennifer Howes Mentor: Date: 3/14/11 Period: 1,6,7 Grade: 7 Subject: Science Topic: Plate Tectonics LESSON PLAN
Science. Overview of Project: A new planet has just been discovered! Honors Project MP 4: New Planet s Core. DUE: June 4, 2013
 Science Honors Project MP 4: New Planet s Core DUE: June 4, 2013 Overview of Project: A new planet has just been discovered! It revolved around a nearby star, just outside our solar system. An unmanned
Science Honors Project MP 4: New Planet s Core DUE: June 4, 2013 Overview of Project: A new planet has just been discovered! It revolved around a nearby star, just outside our solar system. An unmanned
Fill in the blank with the word that completes the sentence. Then, find that work in the puzzle.
 Classwork #1 Name: 2 nd Grade PSI Fill in the blank with the word that completes the sentence. Then, find that work in the puzzle. 1. When the Earth is facing the sun, it is time. 2. Another word for spins
Classwork #1 Name: 2 nd Grade PSI Fill in the blank with the word that completes the sentence. Then, find that work in the puzzle. 1. When the Earth is facing the sun, it is time. 2. Another word for spins
4 th Grade Science Unit C: Earth Sciences Chapter 6: Minerals and Rocks Lesson 1: What are minerals?
 4 th Grade Science Unit C: Earth Sciences Chapter 6: Minerals and Rocks Lesson 1: What are minerals? mineral A mineral is a natural, nonliving, solid crystal that makes up rocks. All over the world, each
4 th Grade Science Unit C: Earth Sciences Chapter 6: Minerals and Rocks Lesson 1: What are minerals? mineral A mineral is a natural, nonliving, solid crystal that makes up rocks. All over the world, each
Grade 8 Learning Objectives MS-PS2-4.
 MS-PS2-4. Construct and present arguments using evidence to support the claim that gravitational interactions are attractive and depend on the masses of interacting objects. [Clarification Statement: Examples
MS-PS2-4. Construct and present arguments using evidence to support the claim that gravitational interactions are attractive and depend on the masses of interacting objects. [Clarification Statement: Examples
Rocks don't form into the three types of rocks and stay there. The Earth is constantly changing and in motion. The rock cycle demonstrates how a rock
 Rocks don't form into the three types of rocks and stay there. The Earth is constantly changing and in motion. The rock cycle demonstrates how a rock can start out as one type and change into another.
Rocks don't form into the three types of rocks and stay there. The Earth is constantly changing and in motion. The rock cycle demonstrates how a rock can start out as one type and change into another.
Lesson 4 Rocks Rock! Lesson Overview: Students will become familiar with rocks, minerals, and be introduced to the rock cycle.
 Lesson 4 Rocks Rock! Lesson Overview: Students will become familiar with rocks, minerals, and be introduced to the rock cycle. Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Explain the difference between rocks
Lesson 4 Rocks Rock! Lesson Overview: Students will become familiar with rocks, minerals, and be introduced to the rock cycle. Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Explain the difference between rocks
Changes in properties and states of matter provide evidence of the atomic theory of matter
 Science 8: Matter and Energy (1) Changes in properties and states of matter provide evidence of the atomic theory of matter Properties of objects and states of matter can change chemically and/or physically
Science 8: Matter and Energy (1) Changes in properties and states of matter provide evidence of the atomic theory of matter Properties of objects and states of matter can change chemically and/or physically
Earth Science Chapter 6 Rocks
 Earth Science Chapter 6 Rocks I. Rocks and the Rock Cycle * Material that makes up the solid part of the Earth. * Made of a variety of different combinations of minerals and organic matter. A. Three Major
Earth Science Chapter 6 Rocks I. Rocks and the Rock Cycle * Material that makes up the solid part of the Earth. * Made of a variety of different combinations of minerals and organic matter. A. Three Major
Science 2015 Earth Science. Study Guide
 Adult Basic Education Level II Science Science 2015 Earth Science Study Guide Resources: Discovering Science 7 Level II Science Courses Science 2011 Life Science Science 2012 Physical Science Science 2013
Adult Basic Education Level II Science Science 2015 Earth Science Study Guide Resources: Discovering Science 7 Level II Science Courses Science 2011 Life Science Science 2012 Physical Science Science 2013
MIDDLE SCHOOL CYCLING OF EARTH S MATERIALS
 3D Science Performance Assessment Tasks MIDDLE SCHOOL CYCLING OF EARTH S MATERIALS MS: ES: Earth s Materials and Energy Performance Task Task Title Cycling of Earth's Materials Standards Bundle Information
3D Science Performance Assessment Tasks MIDDLE SCHOOL CYCLING OF EARTH S MATERIALS MS: ES: Earth s Materials and Energy Performance Task Task Title Cycling of Earth's Materials Standards Bundle Information
Processes that Shape the Earth
 Grade 8 Science, Quarter 4, Unit 4.1 Processes that Shape the Earth Overview Number of instructional days: 20 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to be learned Explain the role of differential heating and convection
Grade 8 Science, Quarter 4, Unit 4.1 Processes that Shape the Earth Overview Number of instructional days: 20 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to be learned Explain the role of differential heating and convection
WHAT ARE ROCKS? ROCKS are a naturally occurring SOLID MIXTURE of one or more minerals and organic matter. Rocks are ALWAYS changing.
 WHAT ARE ROCKS? ROCKS are a naturally occurring SOLID MIXTURE of one or more minerals and organic matter. Rocks are ALWAYS changing. How do we classify Rocks? Formation (where and how the rock was formed)
WHAT ARE ROCKS? ROCKS are a naturally occurring SOLID MIXTURE of one or more minerals and organic matter. Rocks are ALWAYS changing. How do we classify Rocks? Formation (where and how the rock was formed)
The Cycling of Matter. Day 1
 The Cycling of Matter Day 1 Objective I will learn the rock cycle is the series of processes in which rock changes from one form to another. I will learn in the water cycle, water condenses, precipitates
The Cycling of Matter Day 1 Objective I will learn the rock cycle is the series of processes in which rock changes from one form to another. I will learn in the water cycle, water condenses, precipitates
TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology
 Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Edible Changing Rock (Starbursts)
 Name: Date: Hour: Lab Conduct Grade: 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Edible Changing Rock (Starbursts) Most rocks are made of minerals. All rock begin as igneous rock which is formed when magma or lava cools and
Name: Date: Hour: Lab Conduct Grade: 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Edible Changing Rock (Starbursts) Most rocks are made of minerals. All rock begin as igneous rock which is formed when magma or lava cools and
Earth s Plates, Part 1: What Are They, Where Are They and What Do They Do?
 Earth s Plates, Part 1: What Are They, Where Are They and What Do They Do? A scientist named Alfred Wegener believed that, at one time, all of the continents were one landmass. Although he had no real
Earth s Plates, Part 1: What Are They, Where Are They and What Do They Do? A scientist named Alfred Wegener believed that, at one time, all of the continents were one landmass. Although he had no real
CURRICULUM FOR SCIENCE GRADE 8
 CURRICULUM FOR SCIENCE GRADE 8 This curriculum is part of the Educational Program of Studies of the Rahway Public Schools. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Dr. Kevin K. Robinson, Program Supervisor of STEM The Board acknowledges
CURRICULUM FOR SCIENCE GRADE 8 This curriculum is part of the Educational Program of Studies of the Rahway Public Schools. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Dr. Kevin K. Robinson, Program Supervisor of STEM The Board acknowledges
Rocks are made from Minerals
 Rocks and Minerals Rocks are made from Minerals Rocks are nothing more than a mixture of different mineral crystals. ***All three minerals are combined in a Granite rock Granite Quartz + Biotite + Feldspar
Rocks and Minerals Rocks are made from Minerals Rocks are nothing more than a mixture of different mineral crystals. ***All three minerals are combined in a Granite rock Granite Quartz + Biotite + Feldspar
Can Rocks Gain Weight?
 We have been investigating properties of common rocks and minerals. Now it is your turn to design and conduct your own investigation to answer the question, Would rocks gain weight if they were soaked
We have been investigating properties of common rocks and minerals. Now it is your turn to design and conduct your own investigation to answer the question, Would rocks gain weight if they were soaked
2nd Grade Changing of Earth
 Slide 1 / 133 Slide 2 / 133 2nd Grade Changing of Earth 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 133 Table of Contents: Changing of Earth Earth and Moon Cycles Weather Cycles The Rock Cycle Defined Events Gradual
Slide 1 / 133 Slide 2 / 133 2nd Grade Changing of Earth 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 133 Table of Contents: Changing of Earth Earth and Moon Cycles Weather Cycles The Rock Cycle Defined Events Gradual
A PowerPoint has also been developed for use with this lesson plan
 Unit B: Components of Soil Lesson 3: Understanding the Properties of Rocks Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in the students achieving the following objectives: 1. Identify
Unit B: Components of Soil Lesson 3: Understanding the Properties of Rocks Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in the students achieving the following objectives: 1. Identify
GEOLOGY. What is geology?
 GEOLOGY What is geology? It is essentially the study of the earth and it s dynamic processes. Features and processes of rocks, the earth s interior and surface. Structure of the Earth Made up of three
GEOLOGY What is geology? It is essentially the study of the earth and it s dynamic processes. Features and processes of rocks, the earth s interior and surface. Structure of the Earth Made up of three
Relative Dating. The Rock Cycle. Key Concept Scientists can interpret the sequence of events in Earth s history by studying rock layers.
 2 What You Will Learn The rock cycle includes the formation and recycling of rock. Relative dating establishes the order in which rocks formed or events took place. The principle of superposition states
2 What You Will Learn The rock cycle includes the formation and recycling of rock. Relative dating establishes the order in which rocks formed or events took place. The principle of superposition states
TEACHER BACKGROUND KNOWEDGE. Minerals, Rocks and the Rock Cycle
 TEACHER BACKGROUND KNOWEDGE Minerals, Rocks and the Rock Cycle Core Concepts Rocks in the Earth s crust vary in their form and structure based on process that made them. The constant changing of the form
TEACHER BACKGROUND KNOWEDGE Minerals, Rocks and the Rock Cycle Core Concepts Rocks in the Earth s crust vary in their form and structure based on process that made them. The constant changing of the form
2nd Grade. Earth and Moon Cycles. Slide 1 / 133 Slide 2 / 133. Slide 3 / 133. Slide 4 / 133. Slide 5 / 133. Slide 6 / 133.
 Slide 1 / 133 Slide 2 / 133 2nd Grade Changing of Earth 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 133 Slide 4 / 133 Table of Contents: Changing of Earth Earth and Moon Cycles Click on the topic to go to that
Slide 1 / 133 Slide 2 / 133 2nd Grade Changing of Earth 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 133 Slide 4 / 133 Table of Contents: Changing of Earth Earth and Moon Cycles Click on the topic to go to that
PHILIP MORANT SCHOOL AND COLLEGE. Catastrophe. Autumn term homework 1H
 PHILIP MORANT SCHOOL AND COLLEGE Catastrophe Autumn term homework 1H Unit: Catastrophe Homework tasks 1. Self- Assessment - What do I already know? 2. LAT - "Explaining the Rock cycle" Level 2-5 + Level
PHILIP MORANT SCHOOL AND COLLEGE Catastrophe Autumn term homework 1H Unit: Catastrophe Homework tasks 1. Self- Assessment - What do I already know? 2. LAT - "Explaining the Rock cycle" Level 2-5 + Level
Science Is A Verb! Part 1 LET S DO IT! ISBN
 LET S DO IT! Science Is A Verb! Part 1 ISBN 978-1-847003-56-0 Contents INTRODUCTION Lab Title How bright can you make the light bulbs? Students know how to design and build simple series and parallel circuits
LET S DO IT! Science Is A Verb! Part 1 ISBN 978-1-847003-56-0 Contents INTRODUCTION Lab Title How bright can you make the light bulbs? Students know how to design and build simple series and parallel circuits
THE CHANGING SURFACE OF THE EARTH
 THE CHANGING SURFACE OF THE EARTH Key words Drain geological agent weathering erosion Sediment deposition transport The landscape is a consequence of the action of two types of geological processes; internal
THE CHANGING SURFACE OF THE EARTH Key words Drain geological agent weathering erosion Sediment deposition transport The landscape is a consequence of the action of two types of geological processes; internal
DO NOW: HW DUE FRIDAY!!!
 DO NOW: HW DUE FRIDAY!!! 1. What is a sedimentary rock? 2. How are sedimentary rocks formed? 3. What are the characteristics of sedimentary rock? 4. What are metamorphic rocks? 5. How are metamorphic rocks
DO NOW: HW DUE FRIDAY!!! 1. What is a sedimentary rock? 2. How are sedimentary rocks formed? 3. What are the characteristics of sedimentary rock? 4. What are metamorphic rocks? 5. How are metamorphic rocks
Lesson 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle
 Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 8 Content Vocabulary 9 Lesson Outline 10 MiniLab 12 Content Practice A 13 Content Practice B 14 School to Home 15 Key Concept Builders 16 Enrichment
Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 8 Content Vocabulary 9 Lesson Outline 10 MiniLab 12 Content Practice A 13 Content Practice B 14 School to Home 15 Key Concept Builders 16 Enrichment
Name Class Date. Study Guide for 7 th Grade Final Exam (Semester One)
 Name Class Date Study Guide for 7 th Grade Final Exam (Semester One) 1. What are the steps of the scientific method? Define the problem or question Form a hypothesis (MUST BE TESTABLE) o (identify variables)
Name Class Date Study Guide for 7 th Grade Final Exam (Semester One) 1. What are the steps of the scientific method? Define the problem or question Form a hypothesis (MUST BE TESTABLE) o (identify variables)
Grade 8 Science Proficiency Scale Quarter 1
 (EDP) Grade 8 Science Proficiency Scale Quarter 1 Have been exposed to and are working towards being able to complete the steps of the Engineering Design Process when solving a problem. complete some but
(EDP) Grade 8 Science Proficiency Scale Quarter 1 Have been exposed to and are working towards being able to complete the steps of the Engineering Design Process when solving a problem. complete some but
Exploring Geography. Chapter 1. Chapter 1, Section
 Chapter 1, Section World Geography Chapter 1 Exploring Geography Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 1, Section
Chapter 1, Section World Geography Chapter 1 Exploring Geography Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 1, Section
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA
 UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
Background Knowledge: Students should be familiar with characteristics and formation of sedimentary, metamorphic and igneous rocks.
 8 th grade Standard III, Objective 2 Title: Rock Cycle Activity Description: Students will follow a rock as it travels through the rock cycle. They will model the movement of earth materials by rolling
8 th grade Standard III, Objective 2 Title: Rock Cycle Activity Description: Students will follow a rock as it travels through the rock cycle. They will model the movement of earth materials by rolling
Demonstrate knowledge of Earth Science. US (v5), 2 credits
 GEOLOGY UNIT STANDARD Demonstrate knowledge of Earth Science US 18982 (v5), 2 credits UNIT STANDARD Title: Demonstrate knowledge of Earth science Level: 1 Credits: 2 Purpose: People credited with this
GEOLOGY UNIT STANDARD Demonstrate knowledge of Earth Science US 18982 (v5), 2 credits UNIT STANDARD Title: Demonstrate knowledge of Earth science Level: 1 Credits: 2 Purpose: People credited with this
Chapter Test C. Rocks: Mineral Mixtures MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Assessment Chapter Test C Rocks: Mineral Mixtures MULTIPLE CHOICE Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. 1. Which rock was used to construct the pyramids at Giza? a. granite RCKs2 b. marble
Assessment Chapter Test C Rocks: Mineral Mixtures MULTIPLE CHOICE Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. 1. Which rock was used to construct the pyramids at Giza? a. granite RCKs2 b. marble
Earth s Changing Surface
 Earth s Changing Surface Fourth grade scientists are introduced to the scope of geologic time and learn about forces that change our Earth s surface. During their study, students use scientific modeling
Earth s Changing Surface Fourth grade scientists are introduced to the scope of geologic time and learn about forces that change our Earth s surface. During their study, students use scientific modeling
Topics. Nuclear waste storage, risk analysis, evidence and tradeoffs, Groundwater, aquifer, aquitard. literacy
 UNIT OVERVIEW GEOLOGICAL PROCESSES Listed below is a summary of the activities in this unit. Note that the total teaching time is listed as 26 32 periods of approximately 45 50 minutes (approximately 6
UNIT OVERVIEW GEOLOGICAL PROCESSES Listed below is a summary of the activities in this unit. Note that the total teaching time is listed as 26 32 periods of approximately 45 50 minutes (approximately 6
GEOLOGY CURRICULUM. Unit 1: Introduction to Geology
 Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 GEOLOGY CURRICULUM Unit 1: Introduction to Geology OVERVIEW Summary In this unit students will be introduced to the field of geology.
Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 GEOLOGY CURRICULUM Unit 1: Introduction to Geology OVERVIEW Summary In this unit students will be introduced to the field of geology.
Non-fiction: Dig This! Want to know what the world was like millions of years ago? Look to the rocks.
 Non-fiction: Dig This! Dig This! Fossil Find Want to know what the world was like millions of years ago? Look to the rocks. One hundred and fifty million years ago, one of the very first birds appeared
Non-fiction: Dig This! Dig This! Fossil Find Want to know what the world was like millions of years ago? Look to the rocks. One hundred and fifty million years ago, one of the very first birds appeared
The Official CA State Science Education Standards for Earth Science K 8
 The Official CA State Science Education Standards for Earth Science K 8 Kindergarten The Earth is composed of land, air and water. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. characteristics
The Official CA State Science Education Standards for Earth Science K 8 Kindergarten The Earth is composed of land, air and water. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. characteristics
Materials needed: ISNs (students & teacher), document camera, self-reflection pages, corrected tests
 Science April 6-10 L.HE.05.11 Explain that the traits of an individual are influenced by both the environment and the genetics of the individual. L.HE.05.12 Distinguish between inherited and acquired traits.
Science April 6-10 L.HE.05.11 Explain that the traits of an individual are influenced by both the environment and the genetics of the individual. L.HE.05.12 Distinguish between inherited and acquired traits.
Weathering and Erosion Board Game Directions
 Weathering and Erosion Board Game Directions 1. Divide the class into teams of three. Two of the groups will be the players and one will hold the answer sheet and tell players if answers are correct or
Weathering and Erosion Board Game Directions 1. Divide the class into teams of three. Two of the groups will be the players and one will hold the answer sheet and tell players if answers are correct or
Benchmark 3 Science Study Guide S6E5 A-Crust, Mantle, Core 1. What happens to the temperature as you travel to the center of the Earth?
 Benchmark 3 Science Study Guide S6E5 A-Crust, Mantle, Core 1. What happens to the temperature as you travel to the center of the Earth? IT GETS HOTTER. 2. What happens to the density as you travel to the
Benchmark 3 Science Study Guide S6E5 A-Crust, Mantle, Core 1. What happens to the temperature as you travel to the center of the Earth? IT GETS HOTTER. 2. What happens to the density as you travel to the
Potential short answer questions: What is Pangea? Describe at least 4 pieces of evidence that led Wegener to suggest the theory of Continental Drift.
 6th Grade Earth Science Fall Semester Mid-Term Study Guide The mid-term may include: 4 short answer questions,1-2 sketches to draw and/or label, 4 partially filled charts which you should complete, 30
6th Grade Earth Science Fall Semester Mid-Term Study Guide The mid-term may include: 4 short answer questions,1-2 sketches to draw and/or label, 4 partially filled charts which you should complete, 30
Lesson 5. Weathering Competition. Summary. Suggested Timeline. Materials. Objective. Teacher Background Knowledge. Page 1 of 6
 Page 1 of 6 Weathering Instructional Case: A series of student-centered science lessons Suggested Timeline Two 45-minute periods with one 24-hour period in between for soaking overnight. Materials Plastic,
Page 1 of 6 Weathering Instructional Case: A series of student-centered science lessons Suggested Timeline Two 45-minute periods with one 24-hour period in between for soaking overnight. Materials Plastic,
3. [ES 3] 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change?
![3. [ES 3] 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change? 3. [ES 3] 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change?](/thumbs/89/98260180.jpg) Science 8 SCIENCE QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT 2 3. [ES 3] S 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change? A. Glaciers melt
Science 8 SCIENCE QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT 2 3. [ES 3] S 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change? A. Glaciers melt
Earth s Changing Surface Chapter 4
 Name Hour Due Date Earth s Changing Surface Chapter (You do not need your book) Page 1 Fossils Summary Page 2 Traces of Tracks Page 3 Finding the Relative Age of Rocks Summary. Page - Finding the Relative
Name Hour Due Date Earth s Changing Surface Chapter (You do not need your book) Page 1 Fossils Summary Page 2 Traces of Tracks Page 3 Finding the Relative Age of Rocks Summary. Page - Finding the Relative
B) color B) Sediment must be compacted and cemented before it can change to sedimentary rock. D) igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks
 1. Which characteristic of nonsedimentary rocks would provide the least evidence about the environment in which the rocks were formed? A) structure B) color C) crystal size D) mineral composition 2. Which
1. Which characteristic of nonsedimentary rocks would provide the least evidence about the environment in which the rocks were formed? A) structure B) color C) crystal size D) mineral composition 2. Which
TO GO TO ANY OF THE PAGES LISTED BELOW, CLICK ON ITS TITLE
 TO GO TO ANY OF THE PAGES LISTED BELOW, CLICK ON ITS TITLE CHAPTER 6 Plate Tectonics 1 6-1 What is continental drift? 2 6-2 Why is the seafloor spreading? 3 6-3 What evidence supports seafloor spreading?
TO GO TO ANY OF THE PAGES LISTED BELOW, CLICK ON ITS TITLE CHAPTER 6 Plate Tectonics 1 6-1 What is continental drift? 2 6-2 Why is the seafloor spreading? 3 6-3 What evidence supports seafloor spreading?
for EDC Earth Science EDC Earth Science features the following design components:
 LAB- AIDS Correlations to Georgia Science Standards of Excellence 2016 for EDC Earth Science ABOUT EDC EARTH SCIENCE EDC Earth Science is a full year, activity- driven high school earth science course
LAB- AIDS Correlations to Georgia Science Standards of Excellence 2016 for EDC Earth Science ABOUT EDC EARTH SCIENCE EDC Earth Science is a full year, activity- driven high school earth science course
Benchmark A: Describe how the positions and motions of the objects in the universe cause predictable and cyclic events.
 Earth and Space Sciences Students demonstrate an understanding about how Earth systems and processes interact in the geosphere resulting in the habitability of Earth. This includes demonstrating an understanding
Earth and Space Sciences Students demonstrate an understanding about how Earth systems and processes interact in the geosphere resulting in the habitability of Earth. This includes demonstrating an understanding
GEOMORPHOLOGY WHAT AM I EXECTED TO LEARN?
 GEOMORPHOLOGY WHAT AM I EXECTED TO LEARN? Define rock. List and recognize clear examples of the three primary rocks types. Explain the difference between the three different ways sedimentary rocks are
GEOMORPHOLOGY WHAT AM I EXECTED TO LEARN? Define rock. List and recognize clear examples of the three primary rocks types. Explain the difference between the three different ways sedimentary rocks are
Grade 7 Science Revision Sheet for third term final exam
 Grade 7 Science Revision Sheet for third term final exam Material for the final exam : 1- Chapter 4 sections 1+2+3+4 [rock cycle + igneous rocks + sedimentary rocks + metamorphic rocks ] pages from the
Grade 7 Science Revision Sheet for third term final exam Material for the final exam : 1- Chapter 4 sections 1+2+3+4 [rock cycle + igneous rocks + sedimentary rocks + metamorphic rocks ] pages from the
Classify Rock (rock1)
 Name: Date: 1. Cleavage of a mineral is related to a mineral's A. chemical composition. B. streak color. C. luster. D. crystalline structure. 2. Which is not part of the definition of a mineral? A. naturally
Name: Date: 1. Cleavage of a mineral is related to a mineral's A. chemical composition. B. streak color. C. luster. D. crystalline structure. 2. Which is not part of the definition of a mineral? A. naturally
Earth Science Unit 1 Review
 Name: Date: 1. The picture below shows a model of the rock cycle. 2. rock cycle diagram is shown below. During which part of the rock cycle does water break rocks apart?. part 1 B. part 2. part 3 D. part
Name: Date: 1. The picture below shows a model of the rock cycle. 2. rock cycle diagram is shown below. During which part of the rock cycle does water break rocks apart?. part 1 B. part 2. part 3 D. part
L wave Lahar Lava Magma
 Very large collapsed volcanic crater, often containing a lake eg. Lake Taupo The process which provides the force to move the tectonic plates Innermost part of the Earth, made of a liquid outer core and
Very large collapsed volcanic crater, often containing a lake eg. Lake Taupo The process which provides the force to move the tectonic plates Innermost part of the Earth, made of a liquid outer core and
Plate Tectonics: Our Dynamic Planet. Description
 TEACHER GUIDE Plate Tectonics: Our Dynamic Planet 90 Minute Earth Science Lesson Gallery Program Grades: 4-8 Plate Tectonics: Our Dynamic Planet Description Journey to the interior of the Earth and discover
TEACHER GUIDE Plate Tectonics: Our Dynamic Planet 90 Minute Earth Science Lesson Gallery Program Grades: 4-8 Plate Tectonics: Our Dynamic Planet Description Journey to the interior of the Earth and discover
INTRODUCTION. MRT to magma chamber: field inquiry on plate tectonics and the rock cycle at Little Guilin, Singapore. Field inquiry approach
 MRT to magma chamber: field inquiry on plate tectonics and the rock cycle at Little Guilin, Singapore Education and Outreach INTRODUCTION Field inquiry approach This site and the suggested questions and
MRT to magma chamber: field inquiry on plate tectonics and the rock cycle at Little Guilin, Singapore Education and Outreach INTRODUCTION Field inquiry approach This site and the suggested questions and
EARTH/SPACE SCIENCE. Earth Materials and Changes
 EARTH/SPACE SCIENCE This Earth/Space science course is designed to continue student investigations of the earth sciences that began in grades K-8 while providing students the experiences and necessary
EARTH/SPACE SCIENCE This Earth/Space science course is designed to continue student investigations of the earth sciences that began in grades K-8 while providing students the experiences and necessary
S6E5: we will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. b. Investigate the contribution of minerals to rock composition
 S6E5: we will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. b. Investigate the contribution of minerals to rock composition c. Classify rocks by their process of formation d. Describe
S6E5: we will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. b. Investigate the contribution of minerals to rock composition c. Classify rocks by their process of formation d. Describe
Conceptual narrative Science: The Earth s surface
 Year 9 Conceptual narrative Science: The Earth s surface In the Earth and space sciences sub-strand, there are two main conceptual threads being developed from Foundation through to Year 10, Earth in space
Year 9 Conceptual narrative Science: The Earth s surface In the Earth and space sciences sub-strand, there are two main conceptual threads being developed from Foundation through to Year 10, Earth in space
Sediment Fossil Surprise Activity
 Sediment Fossil Surprise Activity Name: 4th grade PSI Science - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Activity Question How are fossils deposited
Sediment Fossil Surprise Activity Name: 4th grade PSI Science - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Activity Question How are fossils deposited
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 1, Week 8, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 1, Week 8, Day 1 1 Outcomes for Today Standard focus: Earth Sciences 3.c Students know how to explain the properties of rocks based on physical and chemical conditions
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 1, Week 8, Day 1 1 Outcomes for Today Standard focus: Earth Sciences 3.c Students know how to explain the properties of rocks based on physical and chemical conditions
Our Planet Earth. I nteractions of Earth Systems
 CHAPTER 3 LESSON 2 Our Planet Earth I nteractions of Earth Systems Key Concepts How does the water cycle show interactions of Earth systems? How does weather show interactions of Earth systems? How does
CHAPTER 3 LESSON 2 Our Planet Earth I nteractions of Earth Systems Key Concepts How does the water cycle show interactions of Earth systems? How does weather show interactions of Earth systems? How does
6 th Grade Earth Science
 6 th Grade Earth Science Scranton School District Scranton, PA 6 th Grade Earth Science Prerequisite: Completion of Fifth Grade Science The 6th Grade Earth Science curriculum provides students with the
6 th Grade Earth Science Scranton School District Scranton, PA 6 th Grade Earth Science Prerequisite: Completion of Fifth Grade Science The 6th Grade Earth Science curriculum provides students with the
