Role of Data Analysis in fixing parameters for petrophysics & rockphysics modeling for effective seismic reservoir characterization A case study
|
|
|
- Gerard Alexander
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 145 Role of Data Analysis in fixing parameters for petrophysics & rockphysics modeling for effective seismic reservoir characterization A case study Summary Beena Jhaldiyal, Bisht, B.S., Chaudhury P.K.,Chetia, Binode The data which is recorded close to the reservoir by the measuring devices i.e. Well Log data and reservoir data play a vital role for understanding the reservoir and its behavior. The detail data analysis will lead to conceptual model for defining the reservoir properties through petrophysical modeling. The objective of the petrophysical interpretation is to transform well log measurements into reservoir properties i.e. porosity, saturation, permeability, mineral component volumes etc. These parameters are responsible for oil/gas estimation and production sustainability. Rock-physics transform petrophysical results into elastic properties that can be linked to seismic interpretation. This complementary nature of Petrophysics and Rock physics requires a tight integration for seismic reservoir characterization. Well log data and its analysis from various angles plays a crucial role in this process of integration. During drilling process log data are affected by borehole rugosity, invasion, mud cake formation, salinity, temperature & pressure etc. and sometimes logs could be entirely missing or not usable due to bad hole conditions. Thus log data needs to be conditioned before its evaluation. In general, most of the times petrophysical evaluation, petro-elastic modeling and synthetic to seismic tie are done independent of each other. This introduces uncertainty and inconsistency across the geoscientific data. Ideally, Petrophysics and Rock physics modeling should be an integrated process that can produce a greater consistency among different data. This paper highlights detail data analysis by various technique to firm up the rock model for petrophysical evaluation, rock physics modeling and the scenario modeling as applied in the study of a gas field in deep water offshore basin of ONGC, India. Key Words: Data Analysis, Log conditioning, Petrophysics, Rock-physics, Petro-elastic modeling, Seismic reservoir characterization Introduction The study area, is an offshore part of Mahanadi basin, is bounded in the southwest by 85 degree East Ridge whereas its structural separation with adjacent Bengal Basin is apparent by a deep throw of NW-SE trending fault. The major part of the present block encompasses the northeastern part of the Mahanadi basin. Bathymetry in the block varies from 800m to 2100m and the contours run more or less in northeast-southwest direction.fig.-1 Well log data provides a continuous record of a formation rock properties and its analysis helps in understanding the characteristics of reservoir. Petrophysical interpretation in turn provides a way to arrive at accurate values for the hydrocarbon saturation, movable and immovable hydrocarbon, water saturation, porosity, permeability and the lithology. Fig-1: Location Map For accurate determination of reservoir parameters in terms of petrophysical output (volume of shale & minerals, porosity and saturation) for any rock, identification of its constituents is of utmost importance. Knowledge of matrix GEOPIC, (ONGC Dehradun), India jhaldiyal_b@ongc.co.in
2 mineral, clay minerals and other mineral if present is beneficial to unravel complex reservoir and to arrive at more accurate petrophysical properties. equation depends upon the various situations of hydrocarbon accumulation and type of rock & its properties. The common problems faced by interpreter are the data sets of different service companies with different tool and vintage. Sometimes the wells are drilled with different drilling fluids and also it is possible that data could not be recorded in the zone of interest due to bad hole condition. To overcome these situations the data from the different sources need to be rescaled, normalized, synthesized and edited for erroneous values. This process is known as log conditioning. The data is then depth matched and corrected for the environmental effects. Data Analysis for Mineral Identification for Petrophysical Analysis The data after conditioning is now ready for the analysis. Crossplots are a convenient way to demonstrate how various combinations of logs respond to lithology and porosity. They also provide visual insight into the type of mixtures. Neutron porosity and density Crossplot is one of the strongest combination for identification of different lithology with fluid on linear scales with water-saturated pure lithologies (Sandstone, limestone, dolomite lines) graduated in porosity units. When the matrix lithology is a binary mixture (e.g., sandstone-lime or lime-dolomite or sandstone-dolomite) the point plotted from the log readings will fall between the corresponding lithology lines. Fig-2 Once the lithology has been identified and confirmed with the available core data, petrophysical analysis can be made. This requires selection of parameters to be used in the interpretation model for processing. The basic parameters which are applied throughout the interval covering different formations under study are the Temperature at the depth of computation (obtained from the surface and bottom hole temperatures), Mud density, Resistivity of mud, mud filtrate and mud cake (recorded in laboratory during drilling), Formation water salinity/ resistivity from Rt VS Phi Crossplot (Picket plot), Hydrocarbon type and its density from testing. The Petrophysical parameters a, m, n which are responsible for saturation estimation are generally obtained from laboratory. The selection of water saturation Fig-2: N-D Crossplot for lithology identification Petrophysical Analysis Although there are various techniques for processing but most widely used are deterministic and probabilistic approach. Now a days the latest technique for multimineral model is an Inverse optimisation technique which is adopted by almost all the oil companies. This technique also accounts for tool uncertainty and relative curve weightage with all the geological constraint for that formation. For any rock, petrophysical interpretation provides volume of minerals and shale, the porosity (both total and effective) and the hydrocarbon volume (movable and immovable). In order to carryout seismic reservoir characterisation we need to link petrophysical results i.e., the reservoir properties to the properties measured in seismic,i.e. elastic properties, through rock physics modeling. Data Analysis for Rockphysics modelling The elastic properties (Vp, Vs, RHOB) depend upon a number of reservoir properties like Facies, Fluids, Porosity, Saturation, Pressure, Stress, Temperature, etc. They depend most on the microstructure or the fabric or 2
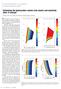
3 texture of the rock. Porosity plays an important role. Also the shape of the pores and the number and nature of the grain contacts affect the elastic properties of the rock. A Change in anyone of the reservoir properties e.g., shale content will lead to change in porosity. Thus the texture of the rock, and hence the reservoir properties, is created and controlled by depositional, sedimentological and diagenetic processes. The correct interpretation requires quantifying the connection between geology and seismic data. Rock physics models that relate velocity and impedance to porosity, saturation and mineralogy (e.g. minerals and shale volume, fluid content) form a critical part of seismic analysis. Elastic moduli is one of the key parameter for velocity estimation which is influenced by different factors of sedimentation process but falls within some permissible limits called bounds depending on porosity.fig-3 Fig-3 shows that before deposition, sediments exist as particles suspended in water (or air) and so their acoustic properties fall on the Reuss average of mineral and fluid. As the sediments deposit on the water bottom, their properties fall on (or near) the Reuss average, as long as they are weak and unconsolidated. Their porosity position along the Reuss average is determined by the geometry of the particle packing. Clean, well-sorted sands will be deposited with porosities around 40%. Poorly sorted sands (like sand-clay mixture and clay bearing sandstone Fig3) will be deposited along the Reuss average at lower porosities. Chalks will be deposited at high initial porosities. Upon burial, the various processes that give the sediment strength effective stress, compaction, and cementing move the sediments off the Reuss bound. It is observed that with increasing digenesis, the rock properties fall along steep trajectories that extend upward from the Reuss bound at critical porosity, toward the mineral end point at zero porosity. This analysis is essentially required for selecting suitable model and providing appropriate values of aspect ratio, compaction factor, effective bulk modulus(k) and shear modulus(µ) for estimation of elastic logs. Rockphysics Modeling : Fig-3: Upper and lower Elastic Bounds The upper and lower bounds of the elastic moduli of rocks provide a useful framework for velocity porosity relations. Theoretically the effective elastic moduli of rocks and sediments have been described through different effective-medium models. The inclusion based models approximate the rock as an elastic block of mineral perturbed by holes, while the granular-medium models or contact models describe the behavior of the separate elastic grains in contact. Whatsoever be the approach, the model should specify the volume fractions of the various constituents, the elastic moduli of the various phases, and the geometric details of how the phases are arranged relative to each other. The objective of the rock physics modelling is to provide link between the petrophysical properties and the elastic properties of the rock (Vp, Vs and RHOB).This link will allow the elastic properties of the rock determined through seismic inversion to be interpreted in terms of reservoir properties. Rockphysics makes use of the mineral and fluid volumes from petrophysics processed output. The total porosity and saturation are also obtained from log data processing. The Petrophysical analysis helps to identify the reservoir with fluid and the non reservoir. Selection of bulk and shear modulli is done according to the matrix reflected in the lithology crossplots. The Voigt and Reuss bounds help us to select the aspect ratio value for both the matrix and clay and the Effective Elastic modulli of the formation suitable for the model to estimatevp and Vs. Petrophysical Modelling of Well A: A critical part of establishing a predictive and consistent rock physics model is the generation of high quality and consistent petrophysical properties. The stratigraphic sequence encountered in Well#A has been subdivided into 3
4 various litho units, with reference to their age i.e. Pliocene, Mid-Miocene and Mid-Eocene. To evaluate the detailed composition of the rocks Neutron-Density crossplots are generated. Fig-4 shows different lithologies with fluids for the data from Pliocene formation to Mid-Eocene formation. The dominant lithology for Pliocene to Mid- Eocene top is sandstone and shale and that from Mid- Eocene to Log bottom is limestone and shale. Fig-5: Vp-PHIT cross plot for Bounds lower limit of Reuss bound for which the grain and clay aspect ratio are in lower range and the elastic constants K and µ will be an average of Reuss bound for Xu-White model. Fig-4: N-D Crossplot for lithology identification Log processing has been done accordingly for estimation of petrophysical properties like the volume of minerals and shale, the porosity (both total and effective) and the hydrocarbon volume. These volumes will be the input for rockphysics modeling. Rockphysics Modelling of Well A: A cross plot has been generated in acoustic domain Vp versus PHIT (Total porosity) for the rock model that has been identified by petrophysical analysis. Since the well logs yield information on constituents and their volume fractions and relatively little about grain and pore microstructure, the bounds turn out to be extremely valuable rock physics tools. Fig-5 shows that the Sediments of Pliocene and mid miocene formations are unconsolidated and loosely packed and hence fall in the Fig-6: Vp-PHIT Crossplot for Bounds Similarly, for Mid-Eocene age the sediments fall close to Ruess Bound but towards lower porosity range Fig-6. So accordingly the value of aspect ratio will be higher and values of K and µ will be different. These parameters and the volume obtained from petrophysics are incorporated in rockphysics workflow of Fugro Jason Powerelog RPM module to estimate the elastic logs (Vp, Vs & RHOB) 4
5 Petrophysics Rockphysics Output The well under study Well A had complete set of log suites (GR, CALI, LLD or RT, LLS, MSFL, RHOB, NPHI, DTCO and DTSM) Fig-7. Track- 1 to 4 shows the conditioned log data taken for petrophysical interpretation. Tracks- 5 and 6 show the output curves and the volumes generated respectively.track-7 describes the lithology along with the fluids. Tracks are the elastic logs generated through rockphysics modelling which are free from borehole effects and invasion effect of the borehole fluid into the reservoir. Conditioned Data Fig -8B: Crossplot of Simp Versus Vp/Vs Modelled Data Once these elastic logs have been generated by RPM they are subjected to well to seismic tie as shown in Fig-9 which shows a fairly good match with seismic. Fig-9: Well to Seismic tie shows good correlation Fig-7: Petrophysics- Rockphysics Output This data has been used for calibration of inversion results as shown in Fig-10. Well-A. There is a fair match between the recorded and modelled log where the borehole is in gauged condition. However the modeled logs have been generated throughout the interval and are free from the invasion and borehole effect. This has improved the quality of logs as shown in crossplot Fig-8A and 8B. Fig-10:Inverted P-impedance & Vp/VsThrough Well-A Conditioned Data Modelled Data Fig -8A:Crossplot of Pimp Versus Vp/Vs The gas charged Geobodies have been identified in acoustic impedance domain & calibrated with log data in 3D volume. 5
6 Conclusion The reservoir with desired fluid and non- reservoir are differentiated with the help of elastic properties of formation. These elastic properties are obtained from elastic logs i.e, RHOB, Vp and Vs, which are responsible for generating seismic response. The modelled logs (Vp, Vs, RHOB) are free from all perturbed effects (invasion, borehole, salinity, temperature) and are generated in situ conditions which provide the realistic picture of the seismic response in terms of lithology and fluid distribution. The petrophysical interpretation has been transferred into elastic domain to understand the corresponding seismic response in the entire area. This approach has given an effective lead to the Seismic reservoir characterization guided by rockphysics. Based on rockphysics analysis the identified gas charged geobodies have been delineated in 3D volume of the area as shown in Fig:10. This has given a lead for better seismic reservoir characterization. References An effective inclusion-based rock physics model for a sand shale sequence Mark Sams1* and Thomas Focht 2 Mavko, G., Mukerji,T. and Dvorkin, J. [2009] The rock physics handbook: tools for seismic analysis in porous media. Cambridge University Press. Joel Walls, Jack Dvorkin, Matt Carr,Well Logs and rock physics in seismic reservoir characterization Xu, S., and White, R.E., 1995, A new velocity model for clay-sand mixtures: Geophysical Prospecting 43, Jeff Baldwin, Tightly Integrating Petrophysics, Rock Physics in Single Model Generates Improved Results Sams, M. [2001] Geostatistical lithology modeling. ASEG 15th Geophysical Conference and Exhibition, Extended Abstracts Acknowledgements The authors are indebted to Shri Anil Sood, GGM-HOI- GEOPIC, Dehradun, India for providing the technical input and guidance for writing this paper and Shri S.K.Das, ED-BM-WON Vadodara for technical guidance and encouragement. Thanks are due to Shri AK Tandon Head-INTEG, GEOPIC, Dehradun, India for providing all kind of support for this work. We wish to express our thanks to CGG- Jason, India for providing technical help in Petrophysics and rock-physics modeling. The authors are grateful to the concern geoscientist of this domain for providing necessary input during the project work and writing this paper. We thank ONGC management for allowing us to submit this paper in SPG international conference The views expressed in this paper are solely of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the view of ONGC. 6
Evaluation of Rock Properties from Logs Affected by Deep Invasion A Case Study
 Evaluation of Rock Properties from Logs Affected by Deep Invasion A Case Study Jahan Zeb a, Reece Murrell b a CGG Australia, 1 Ord Street, West Perth, WA 6005 Contact email: Jahan.Zeb@cgg.com b Esso Australia,
Evaluation of Rock Properties from Logs Affected by Deep Invasion A Case Study Jahan Zeb a, Reece Murrell b a CGG Australia, 1 Ord Street, West Perth, WA 6005 Contact email: Jahan.Zeb@cgg.com b Esso Australia,
Generation of synthetic shear wave logs for multicomponent seismic interpretation
 10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 116 Generation of synthetic shear wave logs for multicomponent seismic interpretation Amit Banerjee* & A.K. Bakshi Summary Interpretation of Multicomponent
10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 116 Generation of synthetic shear wave logs for multicomponent seismic interpretation Amit Banerjee* & A.K. Bakshi Summary Interpretation of Multicomponent
Simultaneous Inversion of Clastic Zubair Reservoir: Case Study from Sabiriyah Field, North Kuwait
 Simultaneous Inversion of Clastic Zubair Reservoir: Case Study from Sabiriyah Field, North Kuwait Osman Khaled, Yousef Al-Zuabi, Hameed Shereef Summary The zone under study is Zubair formation of Cretaceous
Simultaneous Inversion of Clastic Zubair Reservoir: Case Study from Sabiriyah Field, North Kuwait Osman Khaled, Yousef Al-Zuabi, Hameed Shereef Summary The zone under study is Zubair formation of Cretaceous
Rock Physics Perturbational Modeling: Carbonate case study, an intracratonic basin Northwest/Saharan Africa
 Rock Physics Perturbational Modeling: Carbonate case study, an intracratonic basin Northwest/Saharan Africa Franklin Ruiz, Carlos Cobos, Marcelo Benabentos, Beatriz Chacon, and Roberto Varade, Luis Gairifo,
Rock Physics Perturbational Modeling: Carbonate case study, an intracratonic basin Northwest/Saharan Africa Franklin Ruiz, Carlos Cobos, Marcelo Benabentos, Beatriz Chacon, and Roberto Varade, Luis Gairifo,
Lithology prediction and fluid discrimination in Block A6 offshore Myanmar
 10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 141 Lithology prediction and fluid discrimination in Block A6 offshore Myanmar Hanumantha Rao. Y *, Loic Michel, Hampson-Russell, Kyaw Myint, Ko Ko,
10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 141 Lithology prediction and fluid discrimination in Block A6 offshore Myanmar Hanumantha Rao. Y *, Loic Michel, Hampson-Russell, Kyaw Myint, Ko Ko,
Porosity. Downloaded 09/22/16 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Geostatistical Reservoir Characterization of Deepwater Channel, Offshore Malaysia Trisakti Kurniawan* and Jahan Zeb, Petronas Carigali Sdn Bhd, Jimmy Ting and Lee Chung Shen, CGG Summary A quantitative
Geostatistical Reservoir Characterization of Deepwater Channel, Offshore Malaysia Trisakti Kurniawan* and Jahan Zeb, Petronas Carigali Sdn Bhd, Jimmy Ting and Lee Chung Shen, CGG Summary A quantitative
ROCK PHYSICS DIAGNOSTICS OF NORTH SEA SANDS: LINK BETWEEN MICROSTRUCTURE AND SEISMIC PROPERTIES ABSTRACT
 ROCK PHYSICS DIAGNOSTICS OF NORTH SEA SANDS: LINK BETWEEN MICROSTRUCTURE AND SEISMIC PROPERTIES PER AVSETH, JACK DVORKIN, AND GARY MAVKO Department of Geophysics, Stanford University, CA 94305-2215, USA
ROCK PHYSICS DIAGNOSTICS OF NORTH SEA SANDS: LINK BETWEEN MICROSTRUCTURE AND SEISMIC PROPERTIES PER AVSETH, JACK DVORKIN, AND GARY MAVKO Department of Geophysics, Stanford University, CA 94305-2215, USA
Geological Classification of Seismic-Inversion Data in the Doba Basin of Chad*
 Geological Classification of Seismic-Inversion Data in the Doba Basin of Chad* Carl Reine 1, Chris Szelewski 2, and Chaminda Sandanayake 3 Search and Discovery Article #41899 (2016)** Posted September
Geological Classification of Seismic-Inversion Data in the Doba Basin of Chad* Carl Reine 1, Chris Szelewski 2, and Chaminda Sandanayake 3 Search and Discovery Article #41899 (2016)** Posted September
Calibration of the petro-elastic model (PEM) for 4D seismic studies in multi-mineral rocks Amini, Hamed; Alvarez, Erick Raciel
 Heriot-Watt University Heriot-Watt University Research Gateway Calibration of the petro-elastic model (PEM) for 4D seismic studies in multi-mineral rocks Amini, Hamed; Alvarez, Erick Raciel DOI: 10.3997/2214-4609.20132136
Heriot-Watt University Heriot-Watt University Research Gateway Calibration of the petro-elastic model (PEM) for 4D seismic studies in multi-mineral rocks Amini, Hamed; Alvarez, Erick Raciel DOI: 10.3997/2214-4609.20132136
Application of advance tools for reservoir characterization- EEI & Poisson s impedance: A Case Study
 P-272 Application of advance tools for reservoir characterization- EEI & Poisson s impedance: A Case Study Summary Puja Prakash*, S.K.Singh, Binode Chetia, P.K.Chaudhuri, Shyam Mohan, S.K.Das, ONGC Pore
P-272 Application of advance tools for reservoir characterization- EEI & Poisson s impedance: A Case Study Summary Puja Prakash*, S.K.Singh, Binode Chetia, P.K.Chaudhuri, Shyam Mohan, S.K.Das, ONGC Pore
Downloaded 11/02/16 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at Summary.
 in thin sand reservoirs William Marin* and Paola Vera de Newton, Rock Solid Images, and Mario Di Luca, Pacific Exploración y Producción. Summary Rock Physics Templates (RPTs) are useful tools for well
in thin sand reservoirs William Marin* and Paola Vera de Newton, Rock Solid Images, and Mario Di Luca, Pacific Exploración y Producción. Summary Rock Physics Templates (RPTs) are useful tools for well
Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Limited, 4th Floor GEOPIC, Dehradun , Uttarakhand
 Sedimentoical Core Samples A Case Study of Western Offshore Basin, India Ashok Soni*, Pradeep Kumar and B.S. Bisht Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Limited, 4th Floor GEOPIC, Dehradun-248195, Uttarakhand
Sedimentoical Core Samples A Case Study of Western Offshore Basin, India Ashok Soni*, Pradeep Kumar and B.S. Bisht Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Limited, 4th Floor GEOPIC, Dehradun-248195, Uttarakhand
Shaly Sand Rock Physics Analysis and Seismic Inversion Implication
 Shaly Sand Rock Physics Analysis and Seismic Inversion Implication Adi Widyantoro (IkonScience), Matthew Saul (IkonScience/UWA) Rock physics analysis of reservoir elastic properties often assumes homogeneity
Shaly Sand Rock Physics Analysis and Seismic Inversion Implication Adi Widyantoro (IkonScience), Matthew Saul (IkonScience/UWA) Rock physics analysis of reservoir elastic properties often assumes homogeneity
Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Ltd., VRC(Panvel), WOB, ONGC, Mumbai. 1
 P-259 Summary Data for identification of Porosity Behaviour in Oligocene Lime Stone of D18 Area Of Western Offshore, India V.K. Baid*, P.H. Rao, P.S. Basak, Ravi Kant, V. Vairavan 1, K.M. Sundaram 1, ONGC
P-259 Summary Data for identification of Porosity Behaviour in Oligocene Lime Stone of D18 Area Of Western Offshore, India V.K. Baid*, P.H. Rao, P.S. Basak, Ravi Kant, V. Vairavan 1, K.M. Sundaram 1, ONGC
GRAIN SORTING, POROSITY, AND ELASTICITY. Jack Dvorkin and Mario A. Gutierrez Geophysics Department, Stanford University ABSTRACT
 GRAIN SORTING, POROSITY, AND ELASTICITY Jack Dvorkin and Mario A. Gutierrez Geophysics Department, Stanford University July 24, 2001 ABSTRACT Grain size distribution (sorting) is determined by deposition.
GRAIN SORTING, POROSITY, AND ELASTICITY Jack Dvorkin and Mario A. Gutierrez Geophysics Department, Stanford University July 24, 2001 ABSTRACT Grain size distribution (sorting) is determined by deposition.
Integration of Rock Physics Models in a Geostatistical Seismic Inversion for Reservoir Rock Properties
 Integration of Rock Physics Models in a Geostatistical Seismic Inversion for Reservoir Rock Properties Amaro C. 1 Abstract: The main goal of reservoir modeling and characterization is the inference of
Integration of Rock Physics Models in a Geostatistical Seismic Inversion for Reservoir Rock Properties Amaro C. 1 Abstract: The main goal of reservoir modeling and characterization is the inference of
Shear Wave Velocity Estimation Utilizing Wireline Logs for a Carbonate Reservoir, South-West Iran
 Iranian Int. J. Sci. 4(2), 2003, p. 209-221 Shear Wave Velocity Estimation Utilizing Wireline Logs for a Carbonate Reservoir, South-West Iran Eskandari, H. 1, Rezaee, M.R., 2 Javaherian, A., 3 and Mohammadnia,
Iranian Int. J. Sci. 4(2), 2003, p. 209-221 Shear Wave Velocity Estimation Utilizing Wireline Logs for a Carbonate Reservoir, South-West Iran Eskandari, H. 1, Rezaee, M.R., 2 Javaherian, A., 3 and Mohammadnia,
Competing Effect of Pore Fluid and Texture -- Case Study
 Competing Effect of Pore Fluid and Texture -- Case Study Depth (m) Sw Sxo. m Poisson's Ratio.. GOC.1 5 7 8 9 P-Impedance OWC 15 GR.. RHOB.5 1 Saturation...5. 1. 1.5 Vs (km/s).. Poisson's Ratio 5 7 P-Impedance
Competing Effect of Pore Fluid and Texture -- Case Study Depth (m) Sw Sxo. m Poisson's Ratio.. GOC.1 5 7 8 9 P-Impedance OWC 15 GR.. RHOB.5 1 Saturation...5. 1. 1.5 Vs (km/s).. Poisson's Ratio 5 7 P-Impedance
Rock physics of a gas hydrate reservoir. Gas hydrates are solids composed of a hydrogen-bonded ROUND TABLE
 ROUND TABLE Rock physics of a gas hydrate reservoir JACK DVORKIN and AMOS NUR, Stanford University, California, U.S. RICHARD UDEN and TURHAN TANER, Rock Solid Images, Houston, Texas, U.S. Gas hydrates
ROUND TABLE Rock physics of a gas hydrate reservoir JACK DVORKIN and AMOS NUR, Stanford University, California, U.S. RICHARD UDEN and TURHAN TANER, Rock Solid Images, Houston, Texas, U.S. Gas hydrates
Estimating the hydrocarbon volume from elastic and resistivity data: A concept
 INTERPRETER S CORNER Coordinated by Rebecca B. Latimer Estimating the hydrocarbon volume from elastic and resistivity data: A concept CARMEN T. GOMEZ, JACK DVORKIN, and GARY MAVKO, Stanford University,
INTERPRETER S CORNER Coordinated by Rebecca B. Latimer Estimating the hydrocarbon volume from elastic and resistivity data: A concept CARMEN T. GOMEZ, JACK DVORKIN, and GARY MAVKO, Stanford University,
OTC OTC PP. Abstract
 OTC OTC-19977-PP Using Modern Geophysical Technology to Explore for Bypassed Opportunities in the Gulf of Mexico R.A. Young/eSeis; W.G. Holt, G. Klefstad/ Fairways Offshore Exploration Copyright 2009,
OTC OTC-19977-PP Using Modern Geophysical Technology to Explore for Bypassed Opportunities in the Gulf of Mexico R.A. Young/eSeis; W.G. Holt, G. Klefstad/ Fairways Offshore Exploration Copyright 2009,
Seismic reservoir and source-rock analysis using inverse rock-physics modeling: A Norwegian Sea demonstration
 66 Seismic reservoir and source-rock analysis using inverse rock-physics modeling: A Norwegian Sea demonstration Kenneth Bredesen 1, Erling Hugo Jensen 1, 2, Tor Arne Johansen 1, 2, and Per Avseth 3, 4
66 Seismic reservoir and source-rock analysis using inverse rock-physics modeling: A Norwegian Sea demonstration Kenneth Bredesen 1, Erling Hugo Jensen 1, 2, Tor Arne Johansen 1, 2, and Per Avseth 3, 4
Seismic Inversion and EMERGE Studies for Porosity distribution analysis in DCS area, Bombay Offshore Basin
 P-118 Seismic Inversion and EMERGE Studies for Porosity distribution analysis in DCS area, Summary Phukan, R.K*; Mishra, J; Lohani, N.C Oil Natural Gas Corporation Ltd, KDMIPE, Dehradun 248195, India Estimation
P-118 Seismic Inversion and EMERGE Studies for Porosity distribution analysis in DCS area, Summary Phukan, R.K*; Mishra, J; Lohani, N.C Oil Natural Gas Corporation Ltd, KDMIPE, Dehradun 248195, India Estimation
Integrating rock physics and full elastic modeling for reservoir characterization Mosab Nasser and John B. Sinton*, Maersk Oil Houston Inc.
 Integrating rock physics and full elastic modeling for reservoir characterization Mosab Nasser and John B. Sinton*, Maersk Oil Houston Inc. Summary Rock physics establishes the link between reservoir properties,
Integrating rock physics and full elastic modeling for reservoir characterization Mosab Nasser and John B. Sinton*, Maersk Oil Houston Inc. Summary Rock physics establishes the link between reservoir properties,
The role of seismic modeling in Reservoir characterization: A case study from Crestal part of South Mumbai High field
 P-305 The role of seismic modeling in Reservoir characterization: A case study from Crestal part of South Mumbai High field Summary V B Singh*, Mahendra Pratap, ONGC The objective of the modeling was to
P-305 The role of seismic modeling in Reservoir characterization: A case study from Crestal part of South Mumbai High field Summary V B Singh*, Mahendra Pratap, ONGC The objective of the modeling was to
ROCK PHYSICS MODELING FOR LITHOLOGY PREDICTION USING HERTZ- MINDLIN THEORY
 ROCK PHYSICS MODELING FOR LITHOLOGY PREDICTION USING HERTZ- MINDLIN THEORY Ida Ayu PURNAMASARI*, Hilfan KHAIRY, Abdelazis Lotfy ABDELDAYEM Geoscience and Petroleum Engineering Department Universiti Teknologi
ROCK PHYSICS MODELING FOR LITHOLOGY PREDICTION USING HERTZ- MINDLIN THEORY Ida Ayu PURNAMASARI*, Hilfan KHAIRY, Abdelazis Lotfy ABDELDAYEM Geoscience and Petroleum Engineering Department Universiti Teknologi
Methane hydrate rock physics models for the Blake Outer Ridge
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 307 Methane hydrate rock physics models for the Blake Outer Ridge Christine Ecker 1 ABSTRACT Seismic analyses of methane hydrate data from
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 307 Methane hydrate rock physics models for the Blake Outer Ridge Christine Ecker 1 ABSTRACT Seismic analyses of methane hydrate data from
Researcher 2015;7(9)
 4D Seismic Feasibility Study using well Logs in Sienna gas Field, West Delta Deep Marine concession, Egypt Helal, A., Shebl, A. 1, ElNaggar, S. 2 and Ezzat, A. 3 1 Faculty of Science, Ain Shams University,
4D Seismic Feasibility Study using well Logs in Sienna gas Field, West Delta Deep Marine concession, Egypt Helal, A., Shebl, A. 1, ElNaggar, S. 2 and Ezzat, A. 3 1 Faculty of Science, Ain Shams University,
SPE These in turn can be used to estimate mechanical properties.
 SPE 96112 Pressure Effects on Porosity-Log Responses Using Rock Physics Modeling: Implications on Geophysical and Engineering Models as Reservoir Pressure Decreases Michael Holmes, SPE, Digital Formation,
SPE 96112 Pressure Effects on Porosity-Log Responses Using Rock Physics Modeling: Implications on Geophysical and Engineering Models as Reservoir Pressure Decreases Michael Holmes, SPE, Digital Formation,
Sections Rock Physics Seminar Alejandra Rojas
 Sections 1.1 1.3 Rock Physics Seminar Alejandra Rojas February 6 th, 2009 Outline Introduction Velocity Porosity relations for mapping porosity and facies Fluid substitution analysis 1.1 Introduction Discovering
Sections 1.1 1.3 Rock Physics Seminar Alejandra Rojas February 6 th, 2009 Outline Introduction Velocity Porosity relations for mapping porosity and facies Fluid substitution analysis 1.1 Introduction Discovering
Comparison of Classical Archie s Equation with Indonesian Equation and Use of Crossplots in Formation Evaluation: - A case study
 P-310 Summary Comparison of Classical Archie s Equation and Use of Crossplots in Formation Evaluation: - A case study Nitin Sharma In petroleum Exploration and Development Formation Evaluation is done
P-310 Summary Comparison of Classical Archie s Equation and Use of Crossplots in Formation Evaluation: - A case study Nitin Sharma In petroleum Exploration and Development Formation Evaluation is done
SRC software. Rock physics modelling tools for analyzing and predicting geophysical reservoir properties
 SRC software Rock physics modelling tools for analyzing and predicting geophysical reservoir properties Outline About SRC software. Introduction to rock modelling. Rock modelling program structure. Examples
SRC software Rock physics modelling tools for analyzing and predicting geophysical reservoir properties Outline About SRC software. Introduction to rock modelling. Rock modelling program structure. Examples
23855 Rock Physics Constraints on Seismic Inversion
 23855 Rock Physics Constraints on Seismic Inversion M. Sams* (Ikon Science Ltd) & D. Saussus (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Seismic data are bandlimited, offset limited and noisy. Consequently interpretation of
23855 Rock Physics Constraints on Seismic Inversion M. Sams* (Ikon Science Ltd) & D. Saussus (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Seismic data are bandlimited, offset limited and noisy. Consequently interpretation of
Rock Physics of Shales and Source Rocks. Gary Mavko Professor of Geophysics Director, Stanford Rock Physics Project
 Rock Physics of Shales and Source Rocks Gary Mavko Professor of Geophysics Director, Stanford Rock Physics Project 1 First Question: What is Shale? Shale -- a rock composed of mud-sized particles, such
Rock Physics of Shales and Source Rocks Gary Mavko Professor of Geophysics Director, Stanford Rock Physics Project 1 First Question: What is Shale? Shale -- a rock composed of mud-sized particles, such
Reservoir Characteristics of a Quaternary Channel: Incorporating Rock Physics in Seismic and DC Resistivity Surveys
 Reservoir Characteristics of a Quaternary Channel: Incorporating Rock Physics in Seismic and DC Resistivity Surveys Jawwad Ahmad* University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada jahmad@phys.ualberta.ca
Reservoir Characteristics of a Quaternary Channel: Incorporating Rock Physics in Seismic and DC Resistivity Surveys Jawwad Ahmad* University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada jahmad@phys.ualberta.ca
Practical Gassmann fluid substitution in sand/shale sequences
 first break volume 25, December 2007 tutorial Practical Gassmann fluid substitution in sand/shale sequences Rob Simm * Introduction When performing fluid substitution on log data Gassmann s (1951) model
first break volume 25, December 2007 tutorial Practical Gassmann fluid substitution in sand/shale sequences Rob Simm * Introduction When performing fluid substitution on log data Gassmann s (1951) model
The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe
 Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Primary funding is provided by The SPE Foundation through member donations and a contribution from Offshore Europe The Society is grateful to those companies that allow their professionals to serve as
Th LHR2 08 Towards an Effective Petroelastic Model for Simulator to Seismic Studies
 Th LHR2 08 Towards an Effective Petroelastic Model for Simulator to Seismic Studies A. Briceno* (Heriot-Watt University), C. MacBeth (Heriot-Watt University) & M.D. Mangriotis (Heriot-Watt University)
Th LHR2 08 Towards an Effective Petroelastic Model for Simulator to Seismic Studies A. Briceno* (Heriot-Watt University), C. MacBeth (Heriot-Watt University) & M.D. Mangriotis (Heriot-Watt University)
Theoretical Approach in Vp/Vs Prediction from Rock Conductivity in Gas Saturating Shaly Sand
 Modern Applied Science; Vol. 13, No. 1; 2019 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-1852 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Theoretical Approach in Vp/Vs Prediction from Rock Conductivity in Gas
Modern Applied Science; Vol. 13, No. 1; 2019 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-1852 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Theoretical Approach in Vp/Vs Prediction from Rock Conductivity in Gas
We apply a rock physics analysis to well log data from the North-East Gulf of Mexico
 Rock Physics for Fluid and Porosity Mapping in NE GoM JACK DVORKIN, Stanford University and Rock Solid Images TIM FASNACHT, Anadarko Petroleum Corporation RICHARD UDEN, MAGGIE SMITH, NAUM DERZHI, AND JOEL
Rock Physics for Fluid and Porosity Mapping in NE GoM JACK DVORKIN, Stanford University and Rock Solid Images TIM FASNACHT, Anadarko Petroleum Corporation RICHARD UDEN, MAGGIE SMITH, NAUM DERZHI, AND JOEL
Rock Physics and Quantitative Wavelet Estimation. for Seismic Interpretation: Tertiary North Sea. R.W.Simm 1, S.Xu 2 and R.E.
 Rock Physics and Quantitative Wavelet Estimation for Seismic Interpretation: Tertiary North Sea R.W.Simm 1, S.Xu 2 and R.E.White 2 1. Enterprise Oil plc, Grand Buildings, Trafalgar Square, London WC2N
Rock Physics and Quantitative Wavelet Estimation for Seismic Interpretation: Tertiary North Sea R.W.Simm 1, S.Xu 2 and R.E.White 2 1. Enterprise Oil plc, Grand Buildings, Trafalgar Square, London WC2N
*Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Limited, 4th Floor GEOPIC, Dehradun , Uttarakhand # Roxar, Emerson Process Management
 Generation of regional trend from Boolean log of lithofacies for building a realistic fine scale geological model using stochastic facies modelling A case study BS Bisht, Ajeet Pandey*, SP Singh, Samir
Generation of regional trend from Boolean log of lithofacies for building a realistic fine scale geological model using stochastic facies modelling A case study BS Bisht, Ajeet Pandey*, SP Singh, Samir
P314 Anisotropic Elastic Modelling for Organic Shales
 P314 Anisotropic Elastic Modelling for Organic Shales X. Wu* (British Geological Survey), M. Chapman (British Geological Survey), X.Y. Li (British Geological Survey) & H. Dai (British Geological Survey)
P314 Anisotropic Elastic Modelling for Organic Shales X. Wu* (British Geological Survey), M. Chapman (British Geological Survey), X.Y. Li (British Geological Survey) & H. Dai (British Geological Survey)
Quantitative Interpretation
 Quantitative Interpretation The aim of quantitative interpretation (QI) is, through the use of amplitude analysis, to predict lithology and fluid content away from the well bore. This process should make
Quantitative Interpretation The aim of quantitative interpretation (QI) is, through the use of amplitude analysis, to predict lithology and fluid content away from the well bore. This process should make
F003 Geomodel Update Using 4-D Petrophysical Seismic Inversion on the Troll West Field
 F003 Geomodel Update Using 4-D Petrophysical Seismic Inversion on the Troll West Field K. Gjerding* (Statoil), N. Skjei (Statoil), A. Norenes Haaland (Statoil), I. Machecler (CGGVeritas Services) & T.
F003 Geomodel Update Using 4-D Petrophysical Seismic Inversion on the Troll West Field K. Gjerding* (Statoil), N. Skjei (Statoil), A. Norenes Haaland (Statoil), I. Machecler (CGGVeritas Services) & T.
Quick Look : Rule Of Thumb of Rock Properties in Deep Water, Krishna-Godavari Basin
 5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 576-581 Quick Look : Rule Of Thumb of Rock Properties in Deep Water, Krishna-Godavari Basin Acharya M. N. 1, Biswal A. K. 1
5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 576-581 Quick Look : Rule Of Thumb of Rock Properties in Deep Water, Krishna-Godavari Basin Acharya M. N. 1, Biswal A. K. 1
Rock Physics Modeling in Montney Tight Gas Play
 Rock Physics Modeling in Montney Tight Gas Play Ayato Kato 1, Kunio Akihisa 1, Carl Wang 2 and Reona Masui 3 1 JOGMEC-TRC, Chiba, Japan, kato-ayato@jogmec.go.jp 2 Encana, Calgary, Alberta 3 Mitsubishi
Rock Physics Modeling in Montney Tight Gas Play Ayato Kato 1, Kunio Akihisa 1, Carl Wang 2 and Reona Masui 3 1 JOGMEC-TRC, Chiba, Japan, kato-ayato@jogmec.go.jp 2 Encana, Calgary, Alberta 3 Mitsubishi
Generation of Pseudo-Log Volumes from 3D Seismic Multi-attributes using Neural Networks: A case Study
 5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 541-549 Multi-attributes using Neural Networks: A case Study V.B.Singh, S.P.S.Negi, D.Subrahmanyam, S.Biswal & V.K.Baid G&G
5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 541-549 Multi-attributes using Neural Networks: A case Study V.B.Singh, S.P.S.Negi, D.Subrahmanyam, S.Biswal & V.K.Baid G&G
Integration of rock attributes to discriminate Miocene reservoirs for heterogeneity and fluid variability
 P 397 Integration of rock attributes to discriminate Miocene reservoirs for heterogeneity and fluid variability Debajyoti Guha*, Ashok Yadav, Santan Kumar, Naina Gupta, Ashutosh Garg *Reliance Industries
P 397 Integration of rock attributes to discriminate Miocene reservoirs for heterogeneity and fluid variability Debajyoti Guha*, Ashok Yadav, Santan Kumar, Naina Gupta, Ashutosh Garg *Reliance Industries
Well Logging Importance in Oil and Gas Exploration and Production
 Well Logging Importance in Oil and Gas Exploration and Production Dr. R. Giri Prasad 1 1 Associate Professor, Dept. of Petroleum Engineering, Aditya Engineering College, hod_pt@aec.edu.in I. INTRODUCTION
Well Logging Importance in Oil and Gas Exploration and Production Dr. R. Giri Prasad 1 1 Associate Professor, Dept. of Petroleum Engineering, Aditya Engineering College, hod_pt@aec.edu.in I. INTRODUCTION
Petrophysical Rock Typing: Enhanced Permeability Prediction and Reservoir Descriptions*
 Petrophysical Rock Typing: Enhanced Permeability Prediction and Reservoir Descriptions* Wanida Sritongthae 1 Search and Discovery Article #51265 (2016)** Posted June 20, 2016 *Adapted from oral presentation
Petrophysical Rock Typing: Enhanced Permeability Prediction and Reservoir Descriptions* Wanida Sritongthae 1 Search and Discovery Article #51265 (2016)** Posted June 20, 2016 *Adapted from oral presentation
4D stress sensitivity of dry rock frame moduli: constraints from geomechanical integration
 Title 4D stress sensitivity of dry rock frame moduli: constraints from geomechanical integration Authors Bloomer, D., Ikon Science Asia Pacific Reynolds, S., Ikon Science Asia Pacific Pavlova, M., Origin
Title 4D stress sensitivity of dry rock frame moduli: constraints from geomechanical integration Authors Bloomer, D., Ikon Science Asia Pacific Reynolds, S., Ikon Science Asia Pacific Pavlova, M., Origin
Tu P8 08 Modified Anisotropic Walton Model for Consolidated Siliciclastic Rocks: Case Study of Velocity Anisotropy Modelling in a Barents Sea Well
 Tu P8 08 Modified Anisotropic Walton Model for Consolidated Siliciclastic Rocks: Case Study of Velocity Anisotropy Modelling in a Barents Sea Well Y. Zhou (Rock Solid Images), F. Ruiz (Repsol), M. Ellis*
Tu P8 08 Modified Anisotropic Walton Model for Consolidated Siliciclastic Rocks: Case Study of Velocity Anisotropy Modelling in a Barents Sea Well Y. Zhou (Rock Solid Images), F. Ruiz (Repsol), M. Ellis*
QUANTITATIVE INTERPRETATION
 QUANTITATIVE INTERPRETATION THE AIM OF QUANTITATIVE INTERPRETATION (QI) IS, THROUGH THE USE OF AMPLITUDE ANALYSIS, TO PREDICT LITHOLOGY AND FLUID CONTENT AWAY FROM THE WELL BORE This process should make
QUANTITATIVE INTERPRETATION THE AIM OF QUANTITATIVE INTERPRETATION (QI) IS, THROUGH THE USE OF AMPLITUDE ANALYSIS, TO PREDICT LITHOLOGY AND FLUID CONTENT AWAY FROM THE WELL BORE This process should make
Bikashkali Jana*, Sudhir Mathur, Sudipto Datta
 10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 354 Facies characterization of a low permeability Cretaceous clastic reservoir to understand reservoir spatial distribution in the Nagayalanka Field,
10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 354 Facies characterization of a low permeability Cretaceous clastic reservoir to understand reservoir spatial distribution in the Nagayalanka Field,
IDENTIFYING PATCHY SATURATION FROM WELL LOGS Short Note. / K s. + K f., G Dry. = G / ρ, (2)
 IDENTIFYING PATCHY SATURATION FROM WELL LOGS Short Note JACK DVORKIN, DAN MOOS, JAMES PACKWOOD, AND AMOS NUR DEPARTMENT OF GEOPHYSICS, STANFORD UNIVERSITY January 5, 2001 INTRODUCTION Gassmann's (1951)
IDENTIFYING PATCHY SATURATION FROM WELL LOGS Short Note JACK DVORKIN, DAN MOOS, JAMES PACKWOOD, AND AMOS NUR DEPARTMENT OF GEOPHYSICS, STANFORD UNIVERSITY January 5, 2001 INTRODUCTION Gassmann's (1951)
RESERVOIR CHARACTERIZATION USING SEISMIC AND WELL LOGS DATA (A CASE STUDY OF NIGER DELTA)
 RESERVOIR CHARACTERIZATION USING SEISMIC AND WELL LOGS DATA (A CASE STUDY OF NIGER DELTA) * ESHIMOKHAI, S. and AKHIREVBULU, O.E. http://dx.doi.org/10.4314/ejesm.v5i4.s20 Received 19th June 2012; accepted
RESERVOIR CHARACTERIZATION USING SEISMIC AND WELL LOGS DATA (A CASE STUDY OF NIGER DELTA) * ESHIMOKHAI, S. and AKHIREVBULU, O.E. http://dx.doi.org/10.4314/ejesm.v5i4.s20 Received 19th June 2012; accepted
Comparative Study of AVO attributes for Reservoir Facies Discrimination and Porosity Prediction
 5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-004, India PP 498-50 Comparative Study of AVO attributes for Reservoir Facies Discrimination and Porosity Prediction Y. Hanumantha Rao & A.K.
5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-004, India PP 498-50 Comparative Study of AVO attributes for Reservoir Facies Discrimination and Porosity Prediction Y. Hanumantha Rao & A.K.
Abstract. Introduction to Area
 Petro physical analysis of Habib Rahi Limestone of Mari Gas Field using open hole wire line logs of well Mari Deep -06 Central Indus Basin Pakistan (A Case Study) 1a Quaid Khan Jadoon, 1a Muhammad Zahid
Petro physical analysis of Habib Rahi Limestone of Mari Gas Field using open hole wire line logs of well Mari Deep -06 Central Indus Basin Pakistan (A Case Study) 1a Quaid Khan Jadoon, 1a Muhammad Zahid
Petrophysical Charaterization of the Kwale Field Reservoir Sands (OML 60) from Wire-line Logs, Niger Delta, Nigeria. EKINE, A. S.
 JASEM ISSN 1119-8362 All rights reserved Full-text Available Online at wwwbiolineorgbr/ja J Appl Sci Environ Manage December, 2009 Vol 13(4) 81-85 Petrophysical Charaterization of the Kwale Field Reservoir
JASEM ISSN 1119-8362 All rights reserved Full-text Available Online at wwwbiolineorgbr/ja J Appl Sci Environ Manage December, 2009 Vol 13(4) 81-85 Petrophysical Charaterization of the Kwale Field Reservoir
The Marrying of Petrophysics with Geophysics Results in a Powerful Tool for Independents Roger A. Young, eseis, Inc.
 The Marrying of Petrophysics with Geophysics Results in a Powerful Tool for Independents Roger A. Young, eseis, Inc. While the application of new geophysical and petrophysical technology separately can
The Marrying of Petrophysics with Geophysics Results in a Powerful Tool for Independents Roger A. Young, eseis, Inc. While the application of new geophysical and petrophysical technology separately can
Hydrocarbon Volumetric Analysis Using Seismic and Borehole Data over Umoru Field, Niger Delta-Nigeria
 International Journal of Geosciences, 2011, 2, 179-183 doi:10.4236/ijg.2011.22019 Published Online May 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijg) Hydrocarbon Volumetric Analysis Using Seismic and Borehole
International Journal of Geosciences, 2011, 2, 179-183 doi:10.4236/ijg.2011.22019 Published Online May 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijg) Hydrocarbon Volumetric Analysis Using Seismic and Borehole
Reservoir properties inversion from AVO attributes
 Reservoir properties inversion from AVO attributes Xin-gang Chi* and De-hua Han, University of Houston Summary A new rock physics model based inversion method is put forward where the shaly-sand mixture
Reservoir properties inversion from AVO attributes Xin-gang Chi* and De-hua Han, University of Houston Summary A new rock physics model based inversion method is put forward where the shaly-sand mixture
The elastic properties such as velocity, density, impedance,
 SPECIAL SECTION: Rr ock Physics physics Lithology and fluid differentiation using rock physics template XIN-GANG CHI AND DE-HUA HAN, University of Houston The elastic properties such as velocity, density,
SPECIAL SECTION: Rr ock Physics physics Lithology and fluid differentiation using rock physics template XIN-GANG CHI AND DE-HUA HAN, University of Houston The elastic properties such as velocity, density,
C002 Petrophysical Seismic Inversion over an Offshore Carbonate Field
 C002 Petrophysical Seismic Inversion over an Offshore Carbonate Field T. Coleou* (CGGVeritas), F. Allo (CGGVeritas), O. Colnard (CGGVeritas), I. Machecler (CGGVeritas), L. Dillon (Petrobras), G. Schwedersky
C002 Petrophysical Seismic Inversion over an Offshore Carbonate Field T. Coleou* (CGGVeritas), F. Allo (CGGVeritas), O. Colnard (CGGVeritas), I. Machecler (CGGVeritas), L. Dillon (Petrobras), G. Schwedersky
Rock physics and AVO applications in gas hydrate exploration
 Rock physics and AVO applications in gas hydrate exploration ABSTRACT Yong Xu*, Satinder Chopra Core Lab Reservoir Technologies Division, 301,400-3rd Ave SW, Calgary, AB, T2P 4H2 yxu@corelab.ca Summary
Rock physics and AVO applications in gas hydrate exploration ABSTRACT Yong Xu*, Satinder Chopra Core Lab Reservoir Technologies Division, 301,400-3rd Ave SW, Calgary, AB, T2P 4H2 yxu@corelab.ca Summary
Evaluation of Low Resistivity Laminated Shaly Sand Reservoirs
 Evaluation of Low Resistivity Laminated Shaly Sand Reservoirs Summary Dr S S Prasad, C S Sajith & S S Bakshi Sub Surface Team, Mehsana Asset, ONGC, Palavasna, Mehsana, Gujarat E-mail : shivshankarp@gmailcom
Evaluation of Low Resistivity Laminated Shaly Sand Reservoirs Summary Dr S S Prasad, C S Sajith & S S Bakshi Sub Surface Team, Mehsana Asset, ONGC, Palavasna, Mehsana, Gujarat E-mail : shivshankarp@gmailcom
From loose grains to stiff rocks The rock-physics "life story" of a clastic sediment, and its significance in QI studies
 From loose grains to stiff rocks The rock-physics "life story" of a clastic sediment, and its significance in QI studies Prof. Per Avseth, NTNU/G&G Resources Burial depth/temp. Elastic Modulus The rock
From loose grains to stiff rocks The rock-physics "life story" of a clastic sediment, and its significance in QI studies Prof. Per Avseth, NTNU/G&G Resources Burial depth/temp. Elastic Modulus The rock
THE ROCK PHYSICS HANDBOOK
 THE ROCK PHYSICS HANDBOOK TOOLS FOR SEISMIC ANALYSIS IN POROUS MEDIA Gary Mavko Tapan Mukerji Jack Dvorkin Stanford University Stanford University Stanford University CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS
THE ROCK PHYSICS HANDBOOK TOOLS FOR SEISMIC ANALYSIS IN POROUS MEDIA Gary Mavko Tapan Mukerji Jack Dvorkin Stanford University Stanford University Stanford University CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS
Pre Stack Imaging To Delineate A New Hydrocarbon Play A Case History
 5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 375-379 Pre Stack Imaging To Delineate A New Hydrocarbon Play A Case History D. Srinivas, T.R. Murali Mohan, Ashwani Lamba,
5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 375-379 Pre Stack Imaging To Delineate A New Hydrocarbon Play A Case History D. Srinivas, T.R. Murali Mohan, Ashwani Lamba,
Feasibility and design study of a multicomponent seismic survey: Upper Assam Basin
 P-276 Summary Feasibility and design study of a multicomponent seismic survey: Upper Assam Basin K.L.Mandal*, R.K.Srivastava, S.Saha, Oil India Limited M.K.Sukla, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
P-276 Summary Feasibility and design study of a multicomponent seismic survey: Upper Assam Basin K.L.Mandal*, R.K.Srivastava, S.Saha, Oil India Limited M.K.Sukla, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
A021 Petrophysical Seismic Inversion for Porosity and 4D Calibration on the Troll Field
 A021 Petrophysical Seismic Inversion for Porosity and 4D Calibration on the Troll Field T. Coleou* (CGG), A.J. van Wijngaarden (Hydro), A. Norenes Haaland (Hydro), P. Moliere (Hydro), R. Ona (Hydro) &
A021 Petrophysical Seismic Inversion for Porosity and 4D Calibration on the Troll Field T. Coleou* (CGG), A.J. van Wijngaarden (Hydro), A. Norenes Haaland (Hydro), P. Moliere (Hydro), R. Ona (Hydro) &
water L v i Chapter 4 Saturation
 4. Resistivity The presence of hydrocarbons is identified by the electrical resistance of the formation. These electrical properties of rocks depend on the pore geometry and fluid distribution. That is,
4. Resistivity The presence of hydrocarbons is identified by the electrical resistance of the formation. These electrical properties of rocks depend on the pore geometry and fluid distribution. That is,
Downloaded 10/25/16 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Facies modeling in unconventional reservoirs using seismic derived facies probabilities Reinaldo J. Michelena*, Omar G. Angola, and Kevin S. Godbey, ireservoir.com, Inc. Summary We present in this paper
Facies modeling in unconventional reservoirs using seismic derived facies probabilities Reinaldo J. Michelena*, Omar G. Angola, and Kevin S. Godbey, ireservoir.com, Inc. Summary We present in this paper
Mechanical Properties Log Processing and Calibration. R.D. Barree
 Mechanical Properties Log Processing and Calibration R.D. Barree Logging for Mechanical Properties Acoustic logs Measure compressional and shear velocity or slowness (1/v) Can be affected by fractures,
Mechanical Properties Log Processing and Calibration R.D. Barree Logging for Mechanical Properties Acoustic logs Measure compressional and shear velocity or slowness (1/v) Can be affected by fractures,
So I have a Seismic Image, But what is in that Image?
 P-513 So I have a Seismic Image, But what is in that Image? Dr. Nader C. Dutta, Schlumberger Introduction and background Migration involves repositioning of returned signals in a seismic experiment to
P-513 So I have a Seismic Image, But what is in that Image? Dr. Nader C. Dutta, Schlumberger Introduction and background Migration involves repositioning of returned signals in a seismic experiment to
Downloaded 10/29/15 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Electrical anisotropy drivers in the Snøhvit region of the Barents Sea Michelle Ellis*, Lucy MacGregor, Rolf Ackermann, Paola Newton, Robert Keirstead, Alberto Rusic, Slim Bouchrara, Amanda Geck Alvarez,
Electrical anisotropy drivers in the Snøhvit region of the Barents Sea Michelle Ellis*, Lucy MacGregor, Rolf Ackermann, Paola Newton, Robert Keirstead, Alberto Rusic, Slim Bouchrara, Amanda Geck Alvarez,
Uncertainties in rock pore compressibility and effects on time lapse seismic modeling An application to Norne field
 Uncertainties in rock pore compressibility and effects on time lapse seismic modeling An application to Norne field Amit Suman and Tapan Mukerji Department of Energy Resources Engineering Stanford University
Uncertainties in rock pore compressibility and effects on time lapse seismic modeling An application to Norne field Amit Suman and Tapan Mukerji Department of Energy Resources Engineering Stanford University
Rock physics integration of CSEM and seismic data: a case study based on the Luva gas field.
 Rock physics integration of CSEM and seismic data: a case study based on the Luva gas field. Peter Harris*, Zhijun Du, Harald H. Soleng, Lucy M. MacGregor, Wiebke Olsen, OHM-Rock Solid Images Summary It
Rock physics integration of CSEM and seismic data: a case study based on the Luva gas field. Peter Harris*, Zhijun Du, Harald H. Soleng, Lucy M. MacGregor, Wiebke Olsen, OHM-Rock Solid Images Summary It
PETROLEUM GEOSCIENCES GEOLOGY OR GEOPHYSICS MAJOR
 PETROLEUM GEOSCIENCES GEOLOGY OR GEOPHYSICS MAJOR APPLIED GRADUATE STUDIES Geology Geophysics GEO1 Introduction to the petroleum geosciences GEO2 Seismic methods GEO3 Multi-scale geological analysis GEO4
PETROLEUM GEOSCIENCES GEOLOGY OR GEOPHYSICS MAJOR APPLIED GRADUATE STUDIES Geology Geophysics GEO1 Introduction to the petroleum geosciences GEO2 Seismic methods GEO3 Multi-scale geological analysis GEO4
Poisson's Ration, Deep Resistivity and Water Saturation Relationships for Shaly Sand Reservoir, SE Sirt, Murzuq and Gadames Basins, Libya (Case study)
 Journal of Geography and Geology; Vol. 7, No. 1; 2015 ISSN 1916-9779 E-ISSN 1916-9787 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Poisson's Ration, Deep Resistivity and Water Saturation Relationships
Journal of Geography and Geology; Vol. 7, No. 1; 2015 ISSN 1916-9779 E-ISSN 1916-9787 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Poisson's Ration, Deep Resistivity and Water Saturation Relationships
BPM37 Linking Basin Modeling with Seismic Attributes through Rock Physics
 BPM37 Linking Basin Modeling with Seismic Attributes through Rock Physics W. AlKawai* (Stanford University), T. Mukerji (Stanford University) & S. Graham (Stanford University) SUMMARY In this study, we
BPM37 Linking Basin Modeling with Seismic Attributes through Rock Physics W. AlKawai* (Stanford University), T. Mukerji (Stanford University) & S. Graham (Stanford University) SUMMARY In this study, we
Rock physics and AVO analysis for lithofacies and pore fluid prediction in a North Sea oil field
 Rock physics and AVO analysis for lithofacies and pore fluid prediction in a North Sea oil field Downloaded 09/12/14 to 84.215.159.82. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use
Rock physics and AVO analysis for lithofacies and pore fluid prediction in a North Sea oil field Downloaded 09/12/14 to 84.215.159.82. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use
Seismic characterization of Montney shale formation using Passey s approach
 Seismic characterization of Montney shale formation using Passey s approach Ritesh Kumar Sharma*, Satinder Chopra and Amit Kumar Ray Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary Summary Seismic characterization of
Seismic characterization of Montney shale formation using Passey s approach Ritesh Kumar Sharma*, Satinder Chopra and Amit Kumar Ray Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary Summary Seismic characterization of
Recent advances in application of AVO to carbonate reservoirs: case histories
 Recent advances in application of AVO to reservoirs: case histories Yongyi Li, Bill Goodway*, and Jonathan Downton Core Lab Reservoir Technologies Division *EnCana Corporation Summary The application of
Recent advances in application of AVO to reservoirs: case histories Yongyi Li, Bill Goodway*, and Jonathan Downton Core Lab Reservoir Technologies Division *EnCana Corporation Summary The application of
Multiple horizons mapping: A better approach for maximizing the value of seismic data
 Multiple horizons mapping: A better approach for maximizing the value of seismic data Das Ujjal Kumar *, SG(S) ONGC Ltd., New Delhi, Deputed in Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Govt. of India Email:
Multiple horizons mapping: A better approach for maximizing the value of seismic data Das Ujjal Kumar *, SG(S) ONGC Ltd., New Delhi, Deputed in Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Govt. of India Email:
Rock Physics Interpretation of microstructure Chapter Jingqiu Huang M.S. Candidate University of Houston
 Rock Physics Interpretation of microstructure Chapter2.1 2.2 2.3 Jingqiu Huang M.S. Candidate University of Houston Introduction Theory and models Example in North Sea Introduction Theoretical models Inclusion
Rock Physics Interpretation of microstructure Chapter2.1 2.2 2.3 Jingqiu Huang M.S. Candidate University of Houston Introduction Theory and models Example in North Sea Introduction Theoretical models Inclusion
Pre-Stack Seismic Inversion and Amplitude Versus Angle Modeling Reduces the Risk in Hydrocarbon Prospect Evaluation
 Advances in Petroleum Exploration and Development Vol. 7, No. 2, 2014, pp. 30-39 DOI:10.3968/5170 ISSN 1925-542X [Print] ISSN 1925-5438 [Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org Pre-Stack Seismic Inversion
Advances in Petroleum Exploration and Development Vol. 7, No. 2, 2014, pp. 30-39 DOI:10.3968/5170 ISSN 1925-542X [Print] ISSN 1925-5438 [Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org Pre-Stack Seismic Inversion
New Frontier Advanced Multiclient Data Offshore Uruguay. Advanced data interpretation to empower your decision making in the upcoming bid round
 New Frontier Advanced Multiclient Data Offshore Uruguay Advanced data interpretation to empower your decision making in the upcoming bid round Multiclient data interpretation provides key deliverables
New Frontier Advanced Multiclient Data Offshore Uruguay Advanced data interpretation to empower your decision making in the upcoming bid round Multiclient data interpretation provides key deliverables
Pressure and Compaction in the Rock Physics Space. Jack Dvorkin
 Pressure and Compaction in the Rock Physics Space Jack Dvorkin June 2002 0 200 Compaction of Shales Freshly deposited shales and clays may have enormous porosity of ~ 80%. The speed of sound is close to
Pressure and Compaction in the Rock Physics Space Jack Dvorkin June 2002 0 200 Compaction of Shales Freshly deposited shales and clays may have enormous porosity of ~ 80%. The speed of sound is close to
INTRODUCTION TO LOGGING TOOLS
 BY: MUHAMMAD ZAHID INTRODUCTION TO LOGGING TOOLS 1- SPONTANEOUS POTENTIAL (SP) The Spontaneous potential survey, (sp) was one of the first measurements, which was carried out, in a well bore. The SP log
BY: MUHAMMAD ZAHID INTRODUCTION TO LOGGING TOOLS 1- SPONTANEOUS POTENTIAL (SP) The Spontaneous potential survey, (sp) was one of the first measurements, which was carried out, in a well bore. The SP log
J.V. Herwanger* (Ikon Science), A. Bottrill (Ikon Science) & P. Popov (Ikon Science)
 29829. One 4D geomechanical model and its many applications J.V. Herwanger* (Ikon Science), A. Bottrill (Ikon Science) & P. Popov (Ikon Science) Main objectives (i) Field case study demonstrating application
29829. One 4D geomechanical model and its many applications J.V. Herwanger* (Ikon Science), A. Bottrill (Ikon Science) & P. Popov (Ikon Science) Main objectives (i) Field case study demonstrating application
Keywords. PMR, Reservoir Characterization, EEI, LR
 Enhancing the Reservoir Characterization Experience through Post Migration Reprocessed (PMR) Data A case study Indrajit Das*, Ashish Kumar Singh, Shakuntala Mangal, Reliance Industries Limited, Mumbai
Enhancing the Reservoir Characterization Experience through Post Migration Reprocessed (PMR) Data A case study Indrajit Das*, Ashish Kumar Singh, Shakuntala Mangal, Reliance Industries Limited, Mumbai
Log Ties Seismic to Ground Truth
 26 GEOPHYSICALCORNER Log Ties Seismic to Ground Truth The Geophysical Corner is a regular column in the EXPLORER, edited by R. Randy Ray. This month s column is the first of a two-part series titled Seismic
26 GEOPHYSICALCORNER Log Ties Seismic to Ground Truth The Geophysical Corner is a regular column in the EXPLORER, edited by R. Randy Ray. This month s column is the first of a two-part series titled Seismic
MUDLOGGING, CORING, AND CASED HOLE LOGGING BASICS COPYRIGHT. Coring Operations Basics. By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES MUDLOGGING, CORING, AND CASED HOLE LOGGING BASICS Coring Operations Basics By the end of this lesson, you will be able to: Understand why cores are justified and who needs core data
LEARNING OBJECTIVES MUDLOGGING, CORING, AND CASED HOLE LOGGING BASICS Coring Operations Basics By the end of this lesson, you will be able to: Understand why cores are justified and who needs core data
FORMATION EVALUATION OF SIRP FIELD USING WIRELINE LOGS IN WESTERN DEPOBELT OF NIGER DELTA
 FORMATION EVALUATION OF SIRP FIELD USING WIRELINE LOGS IN WESTERN DEPOBELT OF NIGER DELTA 1 Obioha C, ²Adiela U. P and ³*Egesi N 1,3 Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, University of Port Harcourt,
FORMATION EVALUATION OF SIRP FIELD USING WIRELINE LOGS IN WESTERN DEPOBELT OF NIGER DELTA 1 Obioha C, ²Adiela U. P and ³*Egesi N 1,3 Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, University of Port Harcourt,
S.P.S.Negi, Ajai Kumar, D. Subrahmanyam, V.K.Baid, V.B.Singh & S.Biswal Mumbai High Asset, SPIC, ONGC, Mumbai INTRODUCTION
 5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 837-842 Geological Prognosis of Horizontal Wells Using 3D Geocellular Model-An Aid to Develop the Complex Carbonate Reservoir
5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 837-842 Geological Prognosis of Horizontal Wells Using 3D Geocellular Model-An Aid to Develop the Complex Carbonate Reservoir
Objective Oriented Reprocessing of 3D data - A Case Study of Cambay Basin
 10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 223 Objective Oriented Reprocessing of 3D data - A Case Study of Cambay Basin Viswaja Devalla* S.K.Choudhary and M.S.Rawat Summary The 3D seismic
10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 223 Objective Oriented Reprocessing of 3D data - A Case Study of Cambay Basin Viswaja Devalla* S.K.Choudhary and M.S.Rawat Summary The 3D seismic
Rock Physics & Formation Evaluation. Special Topic
 Volume 30 Issue 5 May 2012 Special Topic Technical Articles Dual representation of multiscale fracture network modelling for UAE carbonate field AVO and spectral decomposition for derisking Palaeogene
Volume 30 Issue 5 May 2012 Special Topic Technical Articles Dual representation of multiscale fracture network modelling for UAE carbonate field AVO and spectral decomposition for derisking Palaeogene
Stochastic Modeling & Petrophysical Analysis of Unconventional Shales: Spraberry-Wolfcamp Example
 Stochastic Modeling & Petrophysical Analysis of Unconventional Shales: Spraberry-Wolfcamp Example Fred Jenson and Howard Rael, Fugro-Jason Introduction Recent advances in fracture stimulation techniques
Stochastic Modeling & Petrophysical Analysis of Unconventional Shales: Spraberry-Wolfcamp Example Fred Jenson and Howard Rael, Fugro-Jason Introduction Recent advances in fracture stimulation techniques
