GEL 3300 Lab #2: Measuring Strain
|
|
|
- Arron Roberts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GEL 3300 Lab #2: Measuring Strain The objective of this lab exercise is to use strain markers to determine the orientation of the finite strain ellipse for a deformed rock that contains deformed fossil brachiopods, let s call them spirex such as this: Since all of our fossils are deformed, we don t know a priori the original length of any of the sides, but we do know that the angle between the two axes of the fossil was originally 90, so we can evaluate angular strain and shear strain. You will need a protractor, a ruler, and a calculator to complete this exercise. 1) Eventually we will construct a Mohr Strain diagram, but first, let s make sure we all know what we re doing. A) In the drawing below, the un- deformed spirex is shown in gray, and after deformation is shown in black. The angle between lines A and B was 90 before deformation. Measure the angle between B0 (B before deformation) and B1 (B after deformation). This angle is the angular shear, Ψ, along line A. Remember there is a sign to this angle (+ / - ); the angular shear along line B is the same magnitude, opposite sign as the angular shear along line A. ΨA : B) Shear strain, γ, is the tangent of angular shear (γ = tan(ψ)). Using our above measurement will give us the shear strain in the A direction. γa : C) Recall from lecture that the stretching, S, is the change in length of a line after deformation. S is the ratio of L1/L0, or the length after deformation (L1) divided by the length before deformation (L0). Measure the stretching in the A and B directions by measuring the length of the fossil along lines A0, A1, B0, and B1 (A0 and A1 are parallel and right on top of one another).
2 LA0: LA1: SA: LB0: LB1: SB: D) Now recall that quadratic elongation, λ, is equal to S 2. And reciprocal quadratic elongation, λ, is equal to 1/λ. Calculate these in the A and B directions for our fossil. λa: λ A: λb: λ B: At this point, we have measured and calculated the variables used in the Mohr Strain diagram, but we have yet to identify the principal axes of our strain ellipse so we cannot yet use the strain equations, or create a Mohr Strain diagram. To do that we need to find a fossil that was oriented such that the A and B directions are perpendicular both before and after deformation (the definition of principal strain axes). 2. In real rocks we often are not so lucky to know the exact size of our original fossil (strain marker). On the final page of this lab are a bunch of fossils that were oriented in different directions before deformation. In order to do this exercise, we have to make a few assumptions. Simplifying assumptions are a very important part of how we develop a physical understanding of complex processes such as deformation. It is important to know what assumptions have been used. For this exercise we are going to use 4 assumptions: 1) Homogeneous deformation, 2) Plane strain or 2- dimensional deformation (this means we are assuming to have a plane that is parallel to the maximum and minimum stretching directions, and that no strain occurs in directions out of the plane. In a rock this could be thought of as a plane that is
3 perpendicular to the foliation and parallel to the lineation), 3) no change in volume (i.e. no dilation) and 4) All of these fossils started off the same size (this assumption is only for this exercise, and is not a commonly used or valid assumption). A) Measure the following on each of the fossils: Orientation of the fossil (e.g. measure the acute angle between the flat edge (line A) of the fossil and the long edge of the page. The grid on the page should make this easier); the angular shear along line A (the flat edge of the fossil. This is the same measurement you did on the above fossil when you measured the angle between line B0 and B1); the length of the flat edge of the fossil (length along line A); the length of the fossil along line B (this is the length of the middle petal of the fossils). Use a calculator to calculate the shear strain along line A for each fossil. Fossil # Orientation of line A ( ) Angular Shear, Ψ ( ) Length along A (cm) Length along B (cm) Shear Strain along A (γ = tan(ψ)) B) The fossils with the least shear strain along line A must be oriented with line A very close to the maximum, S1, or minimum, S3, stretching directions (principal strain axes). Using your measurements of fossil orientation, what are the orientations of S1 and S3? S1: S3: And the lengths of line A in these directions? LA1: LA3:
4 C) These lengths represent the lengths of the axes of our finite strain ellipse. From this we can calculate the original length of line A before deformation, because by definition the finite strain ellipse was a circle before deformation. Remember we made the assumption that all these fossils were the same size before deformation, so LA1 and LA3 were equal before deformation, and we can use the equations for area of a circle to calculate the original LA: L0A = (LA1*LA3) L0A: D) Use this value to calculate SA, λa, and λ A for each fossil. [SA = LA/L0A; λa = SA 2 ; λ A = 1/λA ] Now using the values of γ from above, calculate γa/λa. Fossil # SA λa λ A γa/λa E) Now you have everything you need to construct a Mohr Strain diagram. On a piece of graph paper, plot each of your fossils on a graph with λ A on the x- axis, and γa/λa on the y- axis. Do these points plot roughly in a circle? F) Using the strain equations, plot points on the graph for θd = ±15, ±30, ±45, ±60, ±75, and ±90. The strain equations are:
5 λ ' = λ ' 3+ λ ' 1 λ ' 3 λ ' γ λ = λ ' 3 λ ' 1 sin(2θ d ) 2 cos(2θ d ) The values for λ 1 and λ 3 are the values of λ A for the two fossils that are oriented nearly parallel to principal axes of finite strain ellipse. You calculated these in table 2.
6
Matrices and Deformation
 ES 111 Mathematical Methods in the Earth Sciences Matrices and Deformation Lecture Outline 13 - Thurs 9th Nov 2017 Strain Ellipse and Eigenvectors One way of thinking about a matrix is that it operates
ES 111 Mathematical Methods in the Earth Sciences Matrices and Deformation Lecture Outline 13 - Thurs 9th Nov 2017 Strain Ellipse and Eigenvectors One way of thinking about a matrix is that it operates
EAS MIDTERM EXAM
 Ave = 98/150, s.d. = 21 EAS 326-03 MIDTERM EXAM This exam is closed book and closed notes. It is worth 150 points; the value of each question is shown at the end of each question. At the end of the exam,
Ave = 98/150, s.d. = 21 EAS 326-03 MIDTERM EXAM This exam is closed book and closed notes. It is worth 150 points; the value of each question is shown at the end of each question. At the end of the exam,
LAB Exercise #4 - Answers The Traction Vector and Stress Tensor. Introduction. Format of lab. Preparation reading
 LAB Exercise #4 - Answers The Traction Vector and Stress Tensor Due: Thursday, 26 February 2009 (Special Thanks to D.D. Pollard who pioneered this exercise in 1991) Introduction Stress concentrations in
LAB Exercise #4 - Answers The Traction Vector and Stress Tensor Due: Thursday, 26 February 2009 (Special Thanks to D.D. Pollard who pioneered this exercise in 1991) Introduction Stress concentrations in
lecture 6 Methods of Structural Geology W k = W R " F ij = $ W k and type of strain This lecture The Mohr circle for strain Vorticity
 Methods of Structural Geology lecture 6 Last lectures Mohr circle for strain This lecture This lecture Look at deformation history of individual lines/planes Different deformation histories: same result?
Methods of Structural Geology lecture 6 Last lectures Mohr circle for strain This lecture This lecture Look at deformation history of individual lines/planes Different deformation histories: same result?
Deformation and Strain
 Deformation and Strain Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 2/13/2017 15:13 We Discuss Deformation and Strain Deformation Components
Deformation and Strain Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 2/13/2017 15:13 We Discuss Deformation and Strain Deformation Components
Transformation of functions
 Transformation of functions Translations Dilations (from the x axis) Dilations (from the y axis) Reflections (in the x axis) Reflections (in the y axis) Summary Applying transformations Finding equations
Transformation of functions Translations Dilations (from the x axis) Dilations (from the y axis) Reflections (in the x axis) Reflections (in the y axis) Summary Applying transformations Finding equations
Exercise: concepts from chapter 5
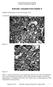 Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 5 1) Study the oöids depicted in Figure 1a and 1b. Figure 1a Figure 1b Figure 1. Nearly undeformed (1a) and significantly deformed (1b) oöids with spherulitic
Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 5 1) Study the oöids depicted in Figure 1a and 1b. Figure 1a Figure 1b Figure 1. Nearly undeformed (1a) and significantly deformed (1b) oöids with spherulitic
First Derivative Test
 MA 2231 Lecture 22 - Concavity and Relative Extrema Wednesday, November 1, 2017 Objectives: Introduce the Second Derivative Test and its limitations. First Derivative Test When looking for relative extrema
MA 2231 Lecture 22 - Concavity and Relative Extrema Wednesday, November 1, 2017 Objectives: Introduce the Second Derivative Test and its limitations. First Derivative Test When looking for relative extrema
Strain page 1. Strain. Paul Bons Mineralogie & Geodynamik, Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen
 page 1 Paul Bons Mineralogie & Geodynamik, Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen Figure 1. Population of Asaphus trilobites before and after a homogeneous deformation event. The amount of strain is visualised
page 1 Paul Bons Mineralogie & Geodynamik, Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen Figure 1. Population of Asaphus trilobites before and after a homogeneous deformation event. The amount of strain is visualised
lecture 8 Methods of Structural Geology This lecture Mas Rabassers de Dalt (Spain) Mas Rabassers de Dalt (Spain)
 This lecture Methods of Structural Geology lecture 8 Discuss the plotting exercise on Mas Rabassers de Dalt Look at folding related to shear zones Show an example of the application of new theory: Cap
This lecture Methods of Structural Geology lecture 8 Discuss the plotting exercise on Mas Rabassers de Dalt Look at folding related to shear zones Show an example of the application of new theory: Cap
= L 1 # L o = " L o. = L 1! L o
 GG303 Lab 9 10/20/09 1 STRAIN I Main Topics A General deformation B Homogeneous 2-D strain and the strain ellipse C Homogeneous 3-D strain and the strain ellipsoid (Flinn Diagrams) D Comments on measuring
GG303 Lab 9 10/20/09 1 STRAIN I Main Topics A General deformation B Homogeneous 2-D strain and the strain ellipse C Homogeneous 3-D strain and the strain ellipsoid (Flinn Diagrams) D Comments on measuring
Exam in : GEO-3104 Advanced Structural. Geology. Date : Time : Approved remedies : Ruler (linjal), Compasses (passer),
 Page 1 of 5 pages FINAL EXAM IN GEO-3104 Exam in : GEO-3104 Advanced Structural Geology Date : 28-02-2013 Time : 9.00 12.00 Place : Aud.Max. Approved remedies : Ruler (linjal), Compasses (passer), Protractor
Page 1 of 5 pages FINAL EXAM IN GEO-3104 Exam in : GEO-3104 Advanced Structural Geology Date : 28-02-2013 Time : 9.00 12.00 Place : Aud.Max. Approved remedies : Ruler (linjal), Compasses (passer), Protractor
Vectors Summary. can slide along the line of action. not restricted, defined by magnitude & direction but can be anywhere.
 Vectors Summary A vector includes magnitude (size) and direction. Academic Skills Advice Types of vectors: Line vector: Free vector: Position vector: Unit vector (n ): can slide along the line of action.
Vectors Summary A vector includes magnitude (size) and direction. Academic Skills Advice Types of vectors: Line vector: Free vector: Position vector: Unit vector (n ): can slide along the line of action.
MATH EVALUATION. What will you learn in this Lab?
 MATH EVALUATION What will you learn in this Lab? This exercise is designed to assess whether you have been exposed to the mathematical methods and skills necessary to complete the lab exercises you will
MATH EVALUATION What will you learn in this Lab? This exercise is designed to assess whether you have been exposed to the mathematical methods and skills necessary to complete the lab exercises you will
GG303 Lab 12 11/7/18 1
 GG303 Lab 12 11/7/18 1 DEFORMATION AROUND A HOLE This lab has two main objectives. The first is to develop insight into the displacement, stress, and strain fields around a hole in a sheet under an approximately
GG303 Lab 12 11/7/18 1 DEFORMATION AROUND A HOLE This lab has two main objectives. The first is to develop insight into the displacement, stress, and strain fields around a hole in a sheet under an approximately
Here is a sample problem that shows you how to use two different methods to add twodimensional
 LAB 2 VECTOR ADDITION-METHODS AND PRACTICE Purpose : You will learn how to use two different methods to add vectors. Materials: Scientific calculator, pencil, unlined paper, protractor, ruler. Discussion:
LAB 2 VECTOR ADDITION-METHODS AND PRACTICE Purpose : You will learn how to use two different methods to add vectors. Materials: Scientific calculator, pencil, unlined paper, protractor, ruler. Discussion:
CHAPTER 4 Stress Transformation
 CHAPTER 4 Stress Transformation ANALYSIS OF STRESS For this topic, the stresses to be considered are not on the perpendicular and parallel planes only but also on other inclined planes. A P a a b b P z
CHAPTER 4 Stress Transformation ANALYSIS OF STRESS For this topic, the stresses to be considered are not on the perpendicular and parallel planes only but also on other inclined planes. A P a a b b P z
9.7 Extension: Writing and Graphing the Equations
 www.ck12.org Chapter 9. Circles 9.7 Extension: Writing and Graphing the Equations of Circles Learning Objectives Graph a circle. Find the equation of a circle in the coordinate plane. Find the radius and
www.ck12.org Chapter 9. Circles 9.7 Extension: Writing and Graphing the Equations of Circles Learning Objectives Graph a circle. Find the equation of a circle in the coordinate plane. Find the radius and
MATH REFRESHER ANSWER SHEET (Note: Only this answer sheet and the following graph page will be evaluated)
 NAME: SCORE: /50 MATH REFRESHER ANSWER SHEET (Note: Only this answer sheet and the following graph page will be evaluated) 1. 23. 2. 24. 3. 25. 4. 26. 5. 27. 6. 28. 7. 29. 8. 30. 9. 31. 10. 32. 11. 33.
NAME: SCORE: /50 MATH REFRESHER ANSWER SHEET (Note: Only this answer sheet and the following graph page will be evaluated) 1. 23. 2. 24. 3. 25. 4. 26. 5. 27. 6. 28. 7. 29. 8. 30. 9. 31. 10. 32. 11. 33.
Math Refresher Answer Sheet (NOTE: Only this answer sheet and the following graph will be evaluated)
 Name: Score: / 50 Math Refresher Answer Sheet (NOTE: Only this answer sheet and the following graph will be evaluated) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. MAKE SURE CALCULATOR
Name: Score: / 50 Math Refresher Answer Sheet (NOTE: Only this answer sheet and the following graph will be evaluated) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. MAKE SURE CALCULATOR
Distance and Midpoint Formula 7.1
 Distance and Midpoint Formula 7.1 Distance Formula d ( x - x ) ( y - y ) 1 1 Example 1 Find the distance between the points (4, 4) and (-6, -). Example Find the value of a to make the distance = 10 units
Distance and Midpoint Formula 7.1 Distance Formula d ( x - x ) ( y - y ) 1 1 Example 1 Find the distance between the points (4, 4) and (-6, -). Example Find the value of a to make the distance = 10 units
Rotation of Axes. By: OpenStaxCollege
 Rotation of Axes By: OpenStaxCollege As we have seen, conic sections are formed when a plane intersects two right circular cones aligned tip to tip and extending infinitely far in opposite directions,
Rotation of Axes By: OpenStaxCollege As we have seen, conic sections are formed when a plane intersects two right circular cones aligned tip to tip and extending infinitely far in opposite directions,
Lecture 9: Measuring Strain and Mohr s Circle for Strain
 Lecture 9: Measuring Strain and Mohr s Circle for Strain The last lecture explained the basic ideas about strain and introduced the strain tensor. This lecture explores a few different ways to measure
Lecture 9: Measuring Strain and Mohr s Circle for Strain The last lecture explained the basic ideas about strain and introduced the strain tensor. This lecture explores a few different ways to measure
Provided by Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. for An Introduction to Structural Methods DVD-ROM
 Provided by Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. for An Introduction to Structural Methods DVD-ROM http://www.tasagraphicarts.com/progstruct.html AN INTRODUCTION TO STRUCTURAL METHODS - DETAILED CONTENTS: (Navigate
Provided by Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. for An Introduction to Structural Methods DVD-ROM http://www.tasagraphicarts.com/progstruct.html AN INTRODUCTION TO STRUCTURAL METHODS - DETAILED CONTENTS: (Navigate
Successful completion of the core function transformations unit. Algebra manipulation skills with squares and square roots.
 Extension A: Circles and Ellipses Algebra ; Pre-Calculus Time required: 35 50 min. Learning Objectives Math Objectives Students will write the general forms of Cartesian equations for circles and ellipses,
Extension A: Circles and Ellipses Algebra ; Pre-Calculus Time required: 35 50 min. Learning Objectives Math Objectives Students will write the general forms of Cartesian equations for circles and ellipses,
Lecture 38: Equations of Rigid-Body Motion
 Lecture 38: Equations of Rigid-Body Motion It s going to be easiest to find the equations of motion for the object in the body frame i.e., the frame where the axes are principal axes In general, we can
Lecture 38: Equations of Rigid-Body Motion It s going to be easiest to find the equations of motion for the object in the body frame i.e., the frame where the axes are principal axes In general, we can
σn -2α σ1= Maximum Principal Stress -2Θ
 The Mohr stress circle: Determining stress and stress states Seth C. Kruckenberg The goal of this lab is to reinforce concepts discussed in lecture on the topic of stress and give students a hands on intuition
The Mohr stress circle: Determining stress and stress states Seth C. Kruckenberg The goal of this lab is to reinforce concepts discussed in lecture on the topic of stress and give students a hands on intuition
Precalculus Review. Functions to KNOW! 1. Polynomial Functions. Types: General form Generic Graph and unique properties. Constants. Linear.
 Precalculus Review Functions to KNOW! 1. Polynomial Functions Types: General form Generic Graph and unique properties Constants Linear Quadratic Cubic Generalizations for Polynomial Functions - The domain
Precalculus Review Functions to KNOW! 1. Polynomial Functions Types: General form Generic Graph and unique properties Constants Linear Quadratic Cubic Generalizations for Polynomial Functions - The domain
PHYSICS 220 LAB #3: STATIC EQUILIBRIUM FORCES
 Lab Section M / T / W / Th /24 pts Name: Partners: PHYSICS 220 LAB #3: STATIC EQUILIBRIUM FORCES OBJECTIVES 1. To verify the conditions for static equilibrium. 2. To get practice at finding components
Lab Section M / T / W / Th /24 pts Name: Partners: PHYSICS 220 LAB #3: STATIC EQUILIBRIUM FORCES OBJECTIVES 1. To verify the conditions for static equilibrium. 2. To get practice at finding components
Combined Stresses and Mohr s Circle. General Case of Combined Stresses. General Case of Combined Stresses con t. Two-dimensional stress condition
 Combined Stresses and Mohr s Circle Material in this lecture was taken from chapter 4 of General Case of Combined Stresses Two-dimensional stress condition General Case of Combined Stresses con t The normal
Combined Stresses and Mohr s Circle Material in this lecture was taken from chapter 4 of General Case of Combined Stresses Two-dimensional stress condition General Case of Combined Stresses con t The normal
ALGEBRA 2 Summer Review Assignments Graphing
 ALGEBRA 2 Summer Review Assignments Graphing To be prepared for algebra two, and all subsequent math courses, you need to be able to accurately and efficiently find the slope of any line, be able to write
ALGEBRA 2 Summer Review Assignments Graphing To be prepared for algebra two, and all subsequent math courses, you need to be able to accurately and efficiently find the slope of any line, be able to write
Ductile deformation - Finite strain
 327 Ductile deformation - Finite strain Deformation includes any process that results in a change in shape, size or location of a body. A solid body subjected to external forces tends to move or change
327 Ductile deformation - Finite strain Deformation includes any process that results in a change in shape, size or location of a body. A solid body subjected to external forces tends to move or change
GG303 Lab 10 10/26/09 1. Stresses
 GG303 Lab 10 10/26/09 1 Stresses Eercise 1 (38 pts total) 1a Write down the epressions for all the stress components in the ' coordinate sstem in terms of the stress components in the reference frame.
GG303 Lab 10 10/26/09 1 Stresses Eercise 1 (38 pts total) 1a Write down the epressions for all the stress components in the ' coordinate sstem in terms of the stress components in the reference frame.
ME 230 Kinematics and Dynamics
 ME 230 Kinematics and Dynamics Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Washington Lecture 6: Particle Kinetics Kinetics of a particle (Chapter 13) - 13.4-13.6 Chapter 13: Objectives
ME 230 Kinematics and Dynamics Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Washington Lecture 6: Particle Kinetics Kinetics of a particle (Chapter 13) - 13.4-13.6 Chapter 13: Objectives
Math Section 4.3 Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Pure Math 30: Explained! 81
 4 www.puremath30.com 81 Part I: General Form General Form of a Conic: Ax + Cy + Dx + Ey + F = 0 A & C are useful in finding out which conic is produced: A = C Circle AC > 0 Ellipse A or C = 0 Parabola
4 www.puremath30.com 81 Part I: General Form General Form of a Conic: Ax + Cy + Dx + Ey + F = 0 A & C are useful in finding out which conic is produced: A = C Circle AC > 0 Ellipse A or C = 0 Parabola
Mathematics Trigonometry: Unit Circle
 a place of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagog Mathematics Trigonometr: Unit Circle Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported b UBC Teaching and
a place of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagog Mathematics Trigonometr: Unit Circle Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported b UBC Teaching and
Determining strain graphically
 Nancy West, Beth Pratt-Sitaula, and Shelley Olds, expanded from work by Vince Cronin, Baylor University and Anne Egger, Central Washington University. We have ample evidence that Earth deforms deformed
Nancy West, Beth Pratt-Sitaula, and Shelley Olds, expanded from work by Vince Cronin, Baylor University and Anne Egger, Central Washington University. We have ample evidence that Earth deforms deformed
Taylor Polynomials. James K. Peterson. Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University
 James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University September 24, 2013 Outline 1 First Order Approximation s Second Order Approximations 2 Approximation
James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University September 24, 2013 Outline 1 First Order Approximation s Second Order Approximations 2 Approximation
Systems of Nonlinear Equations and Inequalities: Two Variables
 Systems of Nonlinear Equations and Inequalities: Two Variables By: OpenStaxCollege Halley s Comet ([link]) orbits the sun about once every 75 years. Its path can be considered to be a very elongated ellipse.
Systems of Nonlinear Equations and Inequalities: Two Variables By: OpenStaxCollege Halley s Comet ([link]) orbits the sun about once every 75 years. Its path can be considered to be a very elongated ellipse.
LESSON EII.F ABSOLUTE VALUE 89
 LESSON EII.F ABSOLUTE VALUE LESSON EII.F ABSOLUTE VALUE 89 OVERVIEW Here s what you ll learn in this lesson: Solving Equations a. Solving x = a b. Solving Ax + B = a c. Solving Ax + B = Cx + D Solving
LESSON EII.F ABSOLUTE VALUE LESSON EII.F ABSOLUTE VALUE 89 OVERVIEW Here s what you ll learn in this lesson: Solving Equations a. Solving x = a b. Solving Ax + B = a c. Solving Ax + B = Cx + D Solving
Lecture 38: Equations of Rigid-Body Motion
 Lecture 38: Equations of Rigid-Body Motion It s going to be easiest to find the equations of motion for the object in the body frame i.e., the frame where the axes are principal axes In general, we can
Lecture 38: Equations of Rigid-Body Motion It s going to be easiest to find the equations of motion for the object in the body frame i.e., the frame where the axes are principal axes In general, we can
8.3 GRAPH AND WRITE EQUATIONS OF CIRCLES
 8.3 GRAPH AND WRITE EQUATIONS OF CIRCLES What is the standard form equation for a circle? Why do you use the distance formula when writing the equation of a circle? What general equation of a circle is
8.3 GRAPH AND WRITE EQUATIONS OF CIRCLES What is the standard form equation for a circle? Why do you use the distance formula when writing the equation of a circle? What general equation of a circle is
Lab: Vectors. You are required to finish this section before coming to the lab. It will be checked by one of the lab instructors when the lab begins.
 Lab: Vectors Lab Section (circle): Day: Monday Tuesday Time: 8:00 9:30 1:10 2:40 Name Partners Pre-Lab You are required to finish this section before coming to the lab. It will be checked by one of the
Lab: Vectors Lab Section (circle): Day: Monday Tuesday Time: 8:00 9:30 1:10 2:40 Name Partners Pre-Lab You are required to finish this section before coming to the lab. It will be checked by one of the
COURSE STRUCTURE CLASS -X
 COURSE STRUCTURE CLASS -X Units Unit Name Marks I NUMBER SYSTEMS 06 II ALGEBRA 20 III COORDINATE GEOMETRY 06 IV GEOMETRY 15 V TRIGONOMETRY 12 VI MENSURATION 10 VII STATISTICS & PROBABILTY 11 Total 80 UNIT
COURSE STRUCTURE CLASS -X Units Unit Name Marks I NUMBER SYSTEMS 06 II ALGEBRA 20 III COORDINATE GEOMETRY 06 IV GEOMETRY 15 V TRIGONOMETRY 12 VI MENSURATION 10 VII STATISTICS & PROBABILTY 11 Total 80 UNIT
Recognise the Equation of a Circle. Solve Problems about Circles Centred at O. Co-Ordinate Geometry of the Circle - Outcomes
 1 Co-Ordinate Geometry of the Circle - Outcomes Recognise the equation of a circle. Solve problems about circles centred at the origin. Solve problems about circles not centred at the origin. Determine
1 Co-Ordinate Geometry of the Circle - Outcomes Recognise the equation of a circle. Solve problems about circles centred at the origin. Solve problems about circles not centred at the origin. Determine
Experiment 3 Forces are Vectors
 Name Partner(s): Experiment 3 Forces are Vectors Objectives Preparation Pre-Lab Understand that some quantities in physics are vectors, others are scalars. Be able to perform vector addition graphically
Name Partner(s): Experiment 3 Forces are Vectors Objectives Preparation Pre-Lab Understand that some quantities in physics are vectors, others are scalars. Be able to perform vector addition graphically
Lecture Practical LECTURE 7 STRESS AND STRAIN
 LECTURE 7 STRESS AND STRAIN LECTURE PLAN ) STRESS a) The relationship between stress and force b) Stress Components c) Principle stresses d) Rock Failure 2) STRAIN a) Components of strain b) The strain
LECTURE 7 STRESS AND STRAIN LECTURE PLAN ) STRESS a) The relationship between stress and force b) Stress Components c) Principle stresses d) Rock Failure 2) STRAIN a) Components of strain b) The strain
Technische Universität München Zentrum Mathematik
 Technische Universität München Zentrum Mathematik Prof. Dr. Dr. Jürgen Richter-Gebert, Bernhard Werner Projective Geometry SS 8 https://www-m.ma.tum.de/bin/view/lehre/ss8/pgss8/webhome Solutions for Worksheet
Technische Universität München Zentrum Mathematik Prof. Dr. Dr. Jürgen Richter-Gebert, Bernhard Werner Projective Geometry SS 8 https://www-m.ma.tum.de/bin/view/lehre/ss8/pgss8/webhome Solutions for Worksheet
Section 6.1 Sinusoidal Graphs
 Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and related to points on a circle We noticed how the x and y values
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and related to points on a circle We noticed how the x and y values
Orthogonality. Orthonormal Bases, Orthogonal Matrices. Orthogonality
 Orthonormal Bases, Orthogonal Matrices The Major Ideas from Last Lecture Vector Span Subspace Basis Vectors Coordinates in different bases Matrix Factorization (Basics) The Major Ideas from Last Lecture
Orthonormal Bases, Orthogonal Matrices The Major Ideas from Last Lecture Vector Span Subspace Basis Vectors Coordinates in different bases Matrix Factorization (Basics) The Major Ideas from Last Lecture
SECTION NUMBER: LAB PARTNERS: VECTORS (FORCE TABLE) LAB II
 Physics 8/18 NAME: TA: LAB PARTNERS: SECTION NUMBER: VECTORS (FORCE TABLE) LAB II Introduction In the Vectors I lab last week we used force tables to introduce the concept of vectors and how they are used
Physics 8/18 NAME: TA: LAB PARTNERS: SECTION NUMBER: VECTORS (FORCE TABLE) LAB II Introduction In the Vectors I lab last week we used force tables to introduce the concept of vectors and how they are used
GEOL 309 Laboratory Activity: Euler Poles. Name
 GEOL 309 Laboratory Activity: Euler Poles Name Instructions: Follow the directions given. Take a picture (with your phone) of your work showing final pole locations on the globe. Print pictures and turn
GEOL 309 Laboratory Activity: Euler Poles Name Instructions: Follow the directions given. Take a picture (with your phone) of your work showing final pole locations on the globe. Print pictures and turn
SUMMER ASSIGNMENT - AP PHYSICS 1 & 2
 Welcome to AP Physics! SUMMER ASSIGNMENT - AP PHYSICS 1 & 2 Please follow the instructions carefully. The assignment consists of 3 parts as detailed below. The first two parts require you to buy supplies
Welcome to AP Physics! SUMMER ASSIGNMENT - AP PHYSICS 1 & 2 Please follow the instructions carefully. The assignment consists of 3 parts as detailed below. The first two parts require you to buy supplies
Vectors and Matrices Lecture 2
 Vectors and Matrices Lecture 2 Dr Mark Kambites School of Mathematics 13/03/2014 Dr Mark Kambites (School of Mathematics) COMP11120 13/03/2014 1 / 20 How do we recover the magnitude of a vector from its
Vectors and Matrices Lecture 2 Dr Mark Kambites School of Mathematics 13/03/2014 Dr Mark Kambites (School of Mathematics) COMP11120 13/03/2014 1 / 20 How do we recover the magnitude of a vector from its
Lecture Notes 5
 1.5 Lecture Notes 5 Quantities in Different Coordinate Systems How to express quantities in different coordinate systems? x 3 x 3 P Direction Cosines Axis φ 11 φ 3 φ 1 x x x x 3 11 1 13 x 1 3 x 3 31 3
1.5 Lecture Notes 5 Quantities in Different Coordinate Systems How to express quantities in different coordinate systems? x 3 x 3 P Direction Cosines Axis φ 11 φ 3 φ 1 x x x x 3 11 1 13 x 1 3 x 3 31 3
GRAPHICAL PRESENTATION AND STATISTICAL ORIENTATION OF STRUCTURAL DATA PRESENTED WITH STEREOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS FOR 3-D ANALYSES.
 GRAPHICAL PRESENTATION AND STATISTICAL ORIENTATION OF STRUCTURAL DATA PRESENTED WITH STEREOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS FOR 3-D ANALYSES. COMMONLY USED PLOTTING AND CONTOURING TOOLS CAN BE DOWNLOADED FOR VARIOUS
GRAPHICAL PRESENTATION AND STATISTICAL ORIENTATION OF STRUCTURAL DATA PRESENTED WITH STEREOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS FOR 3-D ANALYSES. COMMONLY USED PLOTTING AND CONTOURING TOOLS CAN BE DOWNLOADED FOR VARIOUS
The hitch in all of this is figuring out the two principal angles and which principal stress goes with which principal angle.
 Mohr s Circle The stress basic transformation equations that we developed allowed us to determine the stresses acting on an element regardless of its orientation as long as we know the basic stresses σx,
Mohr s Circle The stress basic transformation equations that we developed allowed us to determine the stresses acting on an element regardless of its orientation as long as we know the basic stresses σx,
Name: Lab Partner: Section: In this experiment vector addition, resolution of vectors into components, force, and equilibrium will be explored.
 Chapter 3 Vectors Name: Lab Partner: Section: 3.1 Purpose In this experiment vector addition, resolution of vectors into components, force, and equilibrium will be explored. 3.2 Introduction A vector is
Chapter 3 Vectors Name: Lab Partner: Section: 3.1 Purpose In this experiment vector addition, resolution of vectors into components, force, and equilibrium will be explored. 3.2 Introduction A vector is
Solving Equations by Factoring. Solve the quadratic equation x 2 16 by factoring. We write the equation in standard form: x
 11.1 E x a m p l e 1 714SECTION 11.1 OBJECTIVES 1. Solve quadratic equations by using the square root method 2. Solve quadratic equations by completing the square Here, we factor the quadratic member of
11.1 E x a m p l e 1 714SECTION 11.1 OBJECTIVES 1. Solve quadratic equations by using the square root method 2. Solve quadratic equations by completing the square Here, we factor the quadratic member of
TRAINING LAB BLOOD AS EVIDENCE ANALYZING BLOOD SPATTER NAME
 TRAINING LAB BLOOD AS EVIDENCE ANALYZING BLOOD SPATTER NAME Background: You have learned how to analyze individual blood drops to determine the height a passive drop fell, the direction a moving drop was
TRAINING LAB BLOOD AS EVIDENCE ANALYZING BLOOD SPATTER NAME Background: You have learned how to analyze individual blood drops to determine the height a passive drop fell, the direction a moving drop was
Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
 50 Module 4: Lecture 1 on Stress-strain relationship and Shear strength of soils Contents Stress state, Mohr s circle analysis and Pole, Principal stressspace, Stress pathsin p-q space; Mohr-Coulomb failure
50 Module 4: Lecture 1 on Stress-strain relationship and Shear strength of soils Contents Stress state, Mohr s circle analysis and Pole, Principal stressspace, Stress pathsin p-q space; Mohr-Coulomb failure
Instructions. Do not open your test until instructed to do so!
 st Annual King s College Math Competition King s College welcomes you to this year s mathematics competition and to our campus. We wish you success in this competition and in your future studies. Instructions
st Annual King s College Math Competition King s College welcomes you to this year s mathematics competition and to our campus. We wish you success in this competition and in your future studies. Instructions
Force Vectors and Static Equilibrium
 Force Vectors 1 Force Vectors and Static Equilibrium Overview: In this experiment you will hang weights from pulleys over the edge of a small round force table, to exert various forces on a metal ring
Force Vectors 1 Force Vectors and Static Equilibrium Overview: In this experiment you will hang weights from pulleys over the edge of a small round force table, to exert various forces on a metal ring
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Advanced Math A Units and s Advanced Math A Unit 1 Functions and Math Models (7 days) 10% of grade s 1. I can make connections between the algebraic equation or description
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Advanced Math A Units and s Advanced Math A Unit 1 Functions and Math Models (7 days) 10% of grade s 1. I can make connections between the algebraic equation or description
Exercise solutions: concepts from chapter 5
 1) Stud the oöids depicted in Figure 1a and 1b. a) Assume that the thin sections of Figure 1 lie in a principal plane of the deformation. Measure and record the lengths and orientations of the principal
1) Stud the oöids depicted in Figure 1a and 1b. a) Assume that the thin sections of Figure 1 lie in a principal plane of the deformation. Measure and record the lengths and orientations of the principal
8 Eigenvectors and the Anisotropic Multivariate Gaussian Distribution
 Eigenvectors and the Anisotropic Multivariate Gaussian Distribution Eigenvectors and the Anisotropic Multivariate Gaussian Distribution EIGENVECTORS [I don t know if you were properly taught about eigenvectors
Eigenvectors and the Anisotropic Multivariate Gaussian Distribution Eigenvectors and the Anisotropic Multivariate Gaussian Distribution EIGENVECTORS [I don t know if you were properly taught about eigenvectors
Chapter 7 INTERNAL FORCES
 Chapter 7 INTERNAL FORCES READING QUIZ 1. In a multiforce member, the member is generally subjected to an internal. A) normal force B) shear force C) bending moment D) All of the above. 2. In mechanics,
Chapter 7 INTERNAL FORCES READING QUIZ 1. In a multiforce member, the member is generally subjected to an internal. A) normal force B) shear force C) bending moment D) All of the above. 2. In mechanics,
Otterbein University Department of Physics Physics Laboratory Partner s Name: EXPERIMENT D FORCE VECTORS
 Name: Partner s Name: EXPERIMENT 1500-7 2D FORCE VECTORS INTRODUCTION A vector is represented by an arrow: it has a direction and a magnitude (or length). Vectors can be moved around the page without changing
Name: Partner s Name: EXPERIMENT 1500-7 2D FORCE VECTORS INTRODUCTION A vector is represented by an arrow: it has a direction and a magnitude (or length). Vectors can be moved around the page without changing
Unit 3 Trigonometry Note Package. Name:
 MAT40S Unit 3 Trigonometry Mr. Morris Lesson Unit 3 Trigonometry Note Package Homework 1: Converting and Arc Extra Practice Sheet 1 Length 2: Unit Circle and Angles Extra Practice Sheet 2 3: Determining
MAT40S Unit 3 Trigonometry Mr. Morris Lesson Unit 3 Trigonometry Note Package Homework 1: Converting and Arc Extra Practice Sheet 1 Length 2: Unit Circle and Angles Extra Practice Sheet 2 3: Determining
Section 2.6 Solving Linear Inequalities
 Section 2.6 Solving Linear Inequalities INTRODUCTION Solving an inequality is much like solving an equation; there are, though, some special circumstances of which you need to be aware. In solving an inequality
Section 2.6 Solving Linear Inequalities INTRODUCTION Solving an inequality is much like solving an equation; there are, though, some special circumstances of which you need to be aware. In solving an inequality
Graphs. 1. Graph paper 2. Ruler
 Graphs Objective The purpose of this activity is to learn and develop some of the necessary techniques to graphically analyze data and extract relevant relationships between independent and dependent phenomena,
Graphs Objective The purpose of this activity is to learn and develop some of the necessary techniques to graphically analyze data and extract relevant relationships between independent and dependent phenomena,
MAE 322 Machine Design Lecture 2. Dr. Hodge Jenkins Mercer University
 MAE 322 Machine Design Lecture 2 Dr. Hodge Jenkins Mercer University Statics Load Failure Theories to Understand Maximum Normal Stress (MNS) Maximum Shear Stress (MSS) Distortion Energy (DE) Coulomb-Mohr
MAE 322 Machine Design Lecture 2 Dr. Hodge Jenkins Mercer University Statics Load Failure Theories to Understand Maximum Normal Stress (MNS) Maximum Shear Stress (MSS) Distortion Energy (DE) Coulomb-Mohr
Mathematics for Graphics and Vision
 Mathematics for Graphics and Vision Steven Mills March 3, 06 Contents Introduction 5 Scalars 6. Visualising Scalars........................ 6. Operations on Scalars...................... 6.3 A Note on
Mathematics for Graphics and Vision Steven Mills March 3, 06 Contents Introduction 5 Scalars 6. Visualising Scalars........................ 6. Operations on Scalars...................... 6.3 A Note on
Lesson 9 Exploring Graphs of Quadratic Functions
 Exploring Graphs of Quadratic Functions Graph the following system of linear inequalities: { y > 1 2 x 5 3x + 2y 14 a What are three points that are solutions to the system of inequalities? b Is the point
Exploring Graphs of Quadratic Functions Graph the following system of linear inequalities: { y > 1 2 x 5 3x + 2y 14 a What are three points that are solutions to the system of inequalities? b Is the point
Student Exploration: Vectors
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Vectors Vocabulary: component, dot product, magnitude, resultant, scalar, unit vector notation, vector Prior Knowledge Question (Do this BEFORE using the Gizmo.) An airplane
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Vectors Vocabulary: component, dot product, magnitude, resultant, scalar, unit vector notation, vector Prior Knowledge Question (Do this BEFORE using the Gizmo.) An airplane
1. Background: The SVD and the best basis (questions selected from Ch. 6- Can you fill in the exercises?)
 Math 35 Exam Review SOLUTIONS Overview In this third of the course we focused on linear learning algorithms to model data. summarize: To. Background: The SVD and the best basis (questions selected from
Math 35 Exam Review SOLUTIONS Overview In this third of the course we focused on linear learning algorithms to model data. summarize: To. Background: The SVD and the best basis (questions selected from
STRAIN. Normal Strain: The elongation or contractions of a line segment per unit length is referred to as normal strain denoted by Greek symbol.
 STRAIN In engineering the deformation of a body is specified using the concept of normal strain and shear strain whenever a force is applied to a body, it will tend to change the body s shape and size.
STRAIN In engineering the deformation of a body is specified using the concept of normal strain and shear strain whenever a force is applied to a body, it will tend to change the body s shape and size.
Solution. Using the point-slope form of the equation we have the answer immediately: y = 4 5 (x ( 2)) + 9 = 4 (x +2)+9
 Chapter Review. Lines Eample. Find the equation of the line that goes through the point ( 2, 9) and has slope 4/5. Using the point-slope form of the equation we have the answer immediately: y = 4 5 ( (
Chapter Review. Lines Eample. Find the equation of the line that goes through the point ( 2, 9) and has slope 4/5. Using the point-slope form of the equation we have the answer immediately: y = 4 5 ( (
Structural Geology, GEOL 330 Fold mapping lab: Even folds get parasites Spring, 2012
 Structural Geology, GEOL 330 Name: Fold mapping lab: Even folds get parasites Spring, 2012 This exercise is meant to mimic a field experience in which you, the student, will measure beddingcleavage relationships
Structural Geology, GEOL 330 Name: Fold mapping lab: Even folds get parasites Spring, 2012 This exercise is meant to mimic a field experience in which you, the student, will measure beddingcleavage relationships
Name Date: Course number: MAKE SURE TA & TI STAMPS EVERY PAGE BEFORE YOU START. Grade: EXPERIMENT 4
 Laboratory Section: Last Revised on June 18, 2018 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 4 Moment of Inertia & Oscillations 0 Pre-Laboratory Work [20 pts] 1 a) In Section 31, describe briefly the steps you
Laboratory Section: Last Revised on June 18, 2018 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 4 Moment of Inertia & Oscillations 0 Pre-Laboratory Work [20 pts] 1 a) In Section 31, describe briefly the steps you
OSWAAL BOOKS MARCH 2019 EXAM LEARNING MADE SIMPLE. Published by : FOR CBSE
 OSWAAL BOOKS LEARNING MADE SIMPLE FOR CBSE MARCH 2019 EXAM SOLVED PAPER 2018 MATHEMATICS CLASS 10 Published by : OSWAAL BOOKS 1/11, Sahitya Kunj, M.G. Road, Agra - 282002, UP (India) Ph.: 0562 2857671,
OSWAAL BOOKS LEARNING MADE SIMPLE FOR CBSE MARCH 2019 EXAM SOLVED PAPER 2018 MATHEMATICS CLASS 10 Published by : OSWAAL BOOKS 1/11, Sahitya Kunj, M.G. Road, Agra - 282002, UP (India) Ph.: 0562 2857671,
MA 1128: Lecture 08 03/02/2018. Linear Equations from Graphs And Linear Inequalities
 MA 1128: Lecture 08 03/02/2018 Linear Equations from Graphs And Linear Inequalities Linear Equations from Graphs Given a line, we would like to be able to come up with an equation for it. I ll go over
MA 1128: Lecture 08 03/02/2018 Linear Equations from Graphs And Linear Inequalities Linear Equations from Graphs Given a line, we would like to be able to come up with an equation for it. I ll go over
5.3 GRAPHICAL VELOCITY ANALYSIS Instant Center Method
 ME GRHL VELOTY NLYSS GRHL VELOTY NLYSS nstant enter Method nstant center of velocities is a simple graphical method for performing velocity analysis on mechanisms The method provides visual understanding
ME GRHL VELOTY NLYSS GRHL VELOTY NLYSS nstant enter Method nstant center of velocities is a simple graphical method for performing velocity analysis on mechanisms The method provides visual understanding
Lecture 18. In other words, if you double the stress, you double the resulting strain.
 Lecture 18 Stress and Strain and Springs Simple Harmonic Motion Cutnell+Johnson: 10.1-10.4,10.7-10.8 Stress and Strain and Springs So far we ve dealt with rigid objects. A rigid object doesn t change shape
Lecture 18 Stress and Strain and Springs Simple Harmonic Motion Cutnell+Johnson: 10.1-10.4,10.7-10.8 Stress and Strain and Springs So far we ve dealt with rigid objects. A rigid object doesn t change shape
The No Calculators Pages
 Trigonometry Summer 2005 Name: The No Calculators Pages Instructions: See front page for general instructions. Finish this page before going to the rest. You may not return to this page once you turn on
Trigonometry Summer 2005 Name: The No Calculators Pages Instructions: See front page for general instructions. Finish this page before going to the rest. You may not return to this page once you turn on
9. Stress Transformation
 9.7 ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM SHEAR STRESS A pt in a body subjected to a general 3-D state of stress will have a normal stress and shear-stress components acting on each of its faces. We can develop stress-transformation
9.7 ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM SHEAR STRESS A pt in a body subjected to a general 3-D state of stress will have a normal stress and shear-stress components acting on each of its faces. We can develop stress-transformation
Interactive 3D Sketchupbook
 THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY - SCHOOL OF GEOSCIENCES Interactive 3D Sketchupbook Patrice F. Rey CHAPTER 1 Orienting Planes and Lines 1 Interactive 1.1 Strike, dip and dip direction In a 3D space, planar surfaces
THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY - SCHOOL OF GEOSCIENCES Interactive 3D Sketchupbook Patrice F. Rey CHAPTER 1 Orienting Planes and Lines 1 Interactive 1.1 Strike, dip and dip direction In a 3D space, planar surfaces
Summary of Derivative Tests
 Summary of Derivative Tests Note that for all the tests given below it is assumed that the function f is continuous. Critical Numbers Definition. A critical number of a function f is a number c in the
Summary of Derivative Tests Note that for all the tests given below it is assumed that the function f is continuous. Critical Numbers Definition. A critical number of a function f is a number c in the
both an analytical approach and the pole method, determine: (a) the direction of the
 Quantitative Problems Problem 4-3 Figure 4-45 shows the state of stress at a point within a soil deposit. Using both an analytical approach and the pole method, determine: (a) the direction of the principal
Quantitative Problems Problem 4-3 Figure 4-45 shows the state of stress at a point within a soil deposit. Using both an analytical approach and the pole method, determine: (a) the direction of the principal
Example 2.1. Draw the points with polar coordinates: (i) (3, π) (ii) (2, π/4) (iii) (6, 2π/4) We illustrate all on the following graph:
 Section 10.3: Polar Coordinates The polar coordinate system is another way to coordinatize the Cartesian plane. It is particularly useful when examining regions which are circular. 1. Cartesian Coordinates
Section 10.3: Polar Coordinates The polar coordinate system is another way to coordinatize the Cartesian plane. It is particularly useful when examining regions which are circular. 1. Cartesian Coordinates
Math 120: Precalculus Autumn 2017 A List of Topics for the Final
 Math 120: Precalculus Autumn 2017 A List of Topics for the Final Here s a fairly comprehensive list of things you should be comfortable doing for the final. Really Old Stuff 1. Unit conversion and rates
Math 120: Precalculus Autumn 2017 A List of Topics for the Final Here s a fairly comprehensive list of things you should be comfortable doing for the final. Really Old Stuff 1. Unit conversion and rates
IYGB. Special Extension Paper A. Time: 3 hours 30 minutes. Created by T. Madas. Created by T. Madas
 IYGB Special Extension Paper A Time: 3 hours 30 minutes Candidates may NOT use any calculator Information for Candidates This practice paper follows the Advanced Level Mathematics Core and the Advanced
IYGB Special Extension Paper A Time: 3 hours 30 minutes Candidates may NOT use any calculator Information for Candidates This practice paper follows the Advanced Level Mathematics Core and the Advanced
Math Precalculus I University of Hawai i at Mānoa Spring
 Math 135 - Precalculus I University of Hawai i at Mānoa Spring - 2013 Created for Math 135, Spring 2008 by Lukasz Grabarek and Michael Joyce Send comments and corrections to lukasz@math.hawaii.edu Contents
Math 135 - Precalculus I University of Hawai i at Mānoa Spring - 2013 Created for Math 135, Spring 2008 by Lukasz Grabarek and Michael Joyce Send comments and corrections to lukasz@math.hawaii.edu Contents
SANDERSON HIGH SCHOOL AP CALCULUS AB/BC SUMMER REVIEW PACKET
 SANDERSON HIGH SCHOOL AP CALCULUS AB/BC SUMMER REVIEW PACKET 017-018 Name: 1. This packet is to be handed in on Monday August 8, 017.. All work must be shown on separate paper attached to the packet. 3.
SANDERSON HIGH SCHOOL AP CALCULUS AB/BC SUMMER REVIEW PACKET 017-018 Name: 1. This packet is to be handed in on Monday August 8, 017.. All work must be shown on separate paper attached to the packet. 3.
4 The Trigonometric Functions
 Mathematics Learning Centre, University of Sydney 8 The Trigonometric Functions The definitions in the previous section apply to between 0 and, since the angles in a right angle triangle can never be greater
Mathematics Learning Centre, University of Sydney 8 The Trigonometric Functions The definitions in the previous section apply to between 0 and, since the angles in a right angle triangle can never be greater
Section 1.5. Solution Sets of Linear Systems
 Section 1.5 Solution Sets of Linear Systems Plan For Today Today we will learn to describe and draw the solution set of an arbitrary system of linear equations Ax = b, using spans. Ax = b Recall: the solution
Section 1.5 Solution Sets of Linear Systems Plan For Today Today we will learn to describe and draw the solution set of an arbitrary system of linear equations Ax = b, using spans. Ax = b Recall: the solution
Equilibrium of Deformable Body
 Equilibrium of Deformable Body Review Static Equilibrium If a body is in static equilibrium under the action applied external forces, the Newton s Second Law provides us six scalar equations of equilibrium
Equilibrium of Deformable Body Review Static Equilibrium If a body is in static equilibrium under the action applied external forces, the Newton s Second Law provides us six scalar equations of equilibrium
EAS FINAL EXAM
 EAS 326-03 FINAL EXAM This exam is closed book and closed notes. It is worth 150 points; the value of each question is shown at the end of each question. At the end of the exam, you will find two pages
EAS 326-03 FINAL EXAM This exam is closed book and closed notes. It is worth 150 points; the value of each question is shown at the end of each question. At the end of the exam, you will find two pages
Trigonometry LESSON SIX - Trigonometric Identities I Lesson Notes
 LESSON SIX - Trigonometric Identities I Example Understanding Trigonometric Identities. a) Why are trigonometric identities considered to be a special type of trigonometric equation? Trigonometric Identities
LESSON SIX - Trigonometric Identities I Example Understanding Trigonometric Identities. a) Why are trigonometric identities considered to be a special type of trigonometric equation? Trigonometric Identities
