Strain page 1. Strain. Paul Bons Mineralogie & Geodynamik, Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen
|
|
|
- Joanna Stafford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 page 1 Paul Bons Mineralogie & Geodynamik, Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen Figure 1. Population of Asaphus trilobites before and after a homogeneous deformation event. The amount of strain is visualised by a circle in the undeformed state, which has been deformed to the strain ellipse in the deformed state. Note that all deformed trilobites look different, although they all experienced exactly the same amount of deformation. Homogeneous strain is the change of shape resulting from stresses acting on a volume of material. Deformation involves four components 1. Rigid body translation 2. Rigid body rotation 3. Relative rotation of material lines with respect to each other 4. Stretching and shortening of material lines All of these four occur in the example of figure 1. The first two do not produce a change of shape of an object and are normally difficult to determine. The trilobites may have been incorporated on the shelf in front of one continent, which then drifted and rotated across the globe. This would already constitute a rigid body translation and rotation. So, when we speak about strain, we essentially only speak of the last two components of deformation. normally varies from point to point within a rock. However, we can also normally define a small area within the heterogeneous strain field, where we can approximately say that strain is homogeneous. Homogeneous strain in a volume means that all material points within that volume experienced the same amount of strain. Below, we look at the description of homogeneous strain, and will see that one can also use a Mohr circle construction here. Finite strain Finite strain Incremental strain rate Producing strain takes time, typically hundreds of thousands to millions of years in geology. We of course always see the end product of deformation in the rock record. Our task is to figure out what happened: we analyse the strain that we observe in the rock and try to quantify it. This way we can reconstruct the situation before deformation and in general get more insight into the events that produced the strain. A period of straining produces a certain amount of strain at the end, which we call the finite strain. The finite strain is the sum of many small increments of strain. The amount of strain accumulated during a small increment of time is the incremental strain. The strain rate is the rate of strain accumulation and has unit [s -1 ].
2 page 2 The position gradient tensor Figure 2 shows a general case of homogeneous deformation of a small volume of material. The position of material points in the undeformed state can be described by a vector (p). After deformation, each particle will have a new position in space, which can also be represented by a vector (q). As we already know, we can use a tensor to convert one vector into another. The same holds for position vectors during strain. If we do not have any rigid body translation, the particle in the origin of our reference system remains there: p = (0,0) goes to q = (0,0). Figure 2. Example of homogeneous deformation. Two vectors p 1 and p 2 deform to different vectors q 1 and q 2. The figure shows that in homogeneous deformation any straight line remains a straight line. Position gradient tensor If the above holds, i.e. we do not take rigid body translation into account, we can describe the relationship between p and q with a tensor multiplication: q i = F ij p j (1) Written out in full this means that we have 2 equations (in 2 dimensions): q x = F xx p x + F xy p y q y = F yx p x + F yy p y (2) The tensor F ij is called the position gradient tensor, which converts the position of a material point in the undeformed state to the one in the deformed state. Main types of strain There are four main types of strain, which each have their particular type of position gradient tensor. These are end-member types, meaning that in reality one usually has a combination of two or more of these types. The four types are described below for the 2-dimensional case: Pure shear " Pure shear: F ij = 2 0 % $ ' # 0 1/2& Simple shear " Simple shear: F ij = 1 1 % $ ' # 0 1& Area change (dilation) " Area change: F ij = 2 0 % $ ' # 0 2& Rotation # cos(30) sin(30) & Rotation: F ij = % ( $ "sin(30) cos(30) '
3 page 3 Stretching, shortening and rotation of lines Extension Rotation causes a change of length of lines. We can define the extension (e) of a line which had length l 0 before deformation and l 1 after deformation with: e = l 1 " l 0 l 0 (3) A line that does not change its length has e=1, a stretching line has e>1 and a shortening line has e<1. also causes a rotation! of lines, which is the difference between the orientation of a line in the undeformed and deformed state. Finite stretching axes Finite strain ellipse Finite stretching axes Finite strain ratio Plane strain A circle subjected to homogeneous strain always deforms to an ellipse (or a circle, which is also an ellipse). This ellipse we call the finite strain ellipse. In 3 dimensions the equivalent is the strain ellipsoid. As any ellipse, the strain ellipse has principal axes, perpendicular to each other. These axes represent the maximum and minimum extensions: e 1 and e 2 respectively in 2 dimensions. These axes we call the finite stretching axes (FSAs). The ratio of the maximum and minimum FSA we call the finite strain ratio (Rf or Rs), which is of course always equal or greater than one. In three dimensions we can measure two ratios of FSAs: e 1 /e 2 and e 2 /e 3. The ratio (k) between these two ratios again depends the shape of the finite strain ellipsoid. Here we can have three cases: k > 1 (e 1 /e 2 > e 2 /e 3 ): The strain ellipsoid is prolate (cigar-shaped) k < 1 (e 1 /e 2 < e 2 /e 3 ): The strain ellipsoid is oblate (pancake-shaped) k = 1 (e 1 /e 2 = e 2 /e 3 ): The strain ellipsoid is neither prolate nor oblate. If we have no volume change during deformation and there is zero stretching in the direction of the intermediate FSA (e 2 =1) we must have that e 3 =1/e 1, which means that k=1. This case is called plane strain. from passively deformed objects In an ideal world, all rocks would have spherical markers embedded in them. With those one could then determine the finite strain of each deformed rock. As always, the world is not ideal and we normally do not have such perfect markers. However, some rocks do have objects in them that can be used as strain markers. Some examples are: originally round (sand) grains, round worm burrows (Scolithus), reduction spots in shales, mafic enclaves in granitoids, ooids, etc. Under the assumption that these objects deformed just as much as the whole rock, we can use their deformed shape to determine the amount of strain. If the objects were originally spheres (like ooids), the method is straightforward: the finite elliptical shape is the finite strain ellipse. In many cases however, the objects were not spheres to start with. At the most one can assume they were originally roughly elliptical. Consider the population of elliptical objects in figure 2a. They have various shapes and orientations. After deformation (Fig. 2b) they have changed their shapes, but none of the objects has exactly the shape of the strain ellipse. It is then more difficult to determine the true amount of strain.
4 page 4 Figure 2. Population of elliptical objects with various shapes and orientations. (a) Undeformed state. (b) Deformed state. White ellipse shows the amount of strain (Rs=2.0). The Rf-" method The Rf-" method is used for populations of originally approximately elliptical objects, such as mafic enclaves in granitoids. The method yields the axial ratio (Rs) of the finite strain ellipse and the orientation of that ellipse. It cannot be used to determine any volume or area changes as it only gives the shape of the strain ellipse. The method is based on the idea that an object with an initial ellipticity (Ri) and orientation ("i) deforms together with the host rock to a different ellipticity (Rf) and orientation ("). Because initial ellipticities and orientations vary, so will the finite ellipticities and orientations. However, the finite distributions of Rf and " will not be random, but depend on the amount of strain (Rs). Take for example a population of objects with Ri=2 and variable orientations in figure 3. We can plot the angle " against the ellipticity Rf for all objects. Because all objects started with an ellipticity of 2, the data lie on the line Rf=2 in the undeformed state (Fig. 3a). After deformation, the distribution changes (Fig. 3b-c). In general points tend to wander towards a lower " and higher Rf. The Rf-" curves for different initial ellipticities can be calculated for different finite strains (Fig. 4). Measured data can be plotted on these graphs. One then looks which finite-strain graph fits the data best. The graphs also show a dashed line that encloses 50% of all data points. Figure 3. Population of objects with initial ellipticity of Ri=2 in the undeformed state (a) and after two stages of deformation (b & c). Bottom row: associated Rf-" plots.
5 page 5 Figure 4. Rf-f graphs for different finite strains.
6 page 6 The Fry method The Fry method does not directly use the shape of objects, but their spacing. In an isotropic, densely packed aggregate of objects (grains, ooids, etc.), the distances from the centres of objects to those of their neighbours is the same in all directions (Fig. 5a). If such an aggregate is deformed, some of the centres approach each other, while some move apart (Fig. 5b). This is used in the "Fry method". In the Fry method one plots all the distances between neighbours in a single graph. This done in the following way: Take a sheet of transparent paper and put a mark (small cross) in the middle. Put the mark on the centre of one object in an image of the deformed rock. Mark all the centres of the surrounding grains on the transparency Repeat this procedure for all grains in the image. After doing this, you have a graph that looks like figure 6a. When all the objects originally had an approximately equal distance, a blank ellipse should appear around the central marking: this is the strain ellipse (Fig. 6b). It should be stressed that this method only works when the object centres were originally equidistant, i.e. roughly the same everywhere. If this is not the case, you will not get a sharply bounded white ellipse and the method does not work. Figure 5. (a) Isotropic aggregate of roughly equal-sized objects (e.g. ooids). (b) Same aggregate, but deformed. Figure 6. Results of Fry analysis of aggregate of figure 5b. (a) Raw result. (b) Estimated strain ellipse, which has an axial ratio of 2.
7 Exercise page 7
Deformation and Strain
 Deformation and Strain Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 2/13/2017 15:13 We Discuss Deformation and Strain Deformation Components
Deformation and Strain Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 2/13/2017 15:13 We Discuss Deformation and Strain Deformation Components
lecture 6 Methods of Structural Geology W k = W R " F ij = $ W k and type of strain This lecture The Mohr circle for strain Vorticity
 Methods of Structural Geology lecture 6 Last lectures Mohr circle for strain This lecture This lecture Look at deformation history of individual lines/planes Different deformation histories: same result?
Methods of Structural Geology lecture 6 Last lectures Mohr circle for strain This lecture This lecture Look at deformation history of individual lines/planes Different deformation histories: same result?
Exercise: concepts from chapter 5
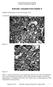 Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 5 1) Study the oöids depicted in Figure 1a and 1b. Figure 1a Figure 1b Figure 1. Nearly undeformed (1a) and significantly deformed (1b) oöids with spherulitic
Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 5 1) Study the oöids depicted in Figure 1a and 1b. Figure 1a Figure 1b Figure 1. Nearly undeformed (1a) and significantly deformed (1b) oöids with spherulitic
Ductile deformation - Finite strain
 327 Ductile deformation - Finite strain Deformation includes any process that results in a change in shape, size or location of a body. A solid body subjected to external forces tends to move or change
327 Ductile deformation - Finite strain Deformation includes any process that results in a change in shape, size or location of a body. A solid body subjected to external forces tends to move or change
= L 1 # L o = " L o. = L 1! L o
 GG303 Lab 9 10/20/09 1 STRAIN I Main Topics A General deformation B Homogeneous 2-D strain and the strain ellipse C Homogeneous 3-D strain and the strain ellipsoid (Flinn Diagrams) D Comments on measuring
GG303 Lab 9 10/20/09 1 STRAIN I Main Topics A General deformation B Homogeneous 2-D strain and the strain ellipse C Homogeneous 3-D strain and the strain ellipsoid (Flinn Diagrams) D Comments on measuring
Properties of surfaces II: Second moment of area
 Properties of surfaces II: Second moment of area Just as we have discussing first moment of an area and its relation with problems in mechanics, we will now describe second moment and product of area of
Properties of surfaces II: Second moment of area Just as we have discussing first moment of an area and its relation with problems in mechanics, we will now describe second moment and product of area of
Elements of Continuum Elasticity. David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II February 25, 2004
 Elements of Continuum Elasticity David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004 Solid Mechanics in 3 Dimensions: stress/equilibrium, strain/displacement, and intro to linear elastic
Elements of Continuum Elasticity David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004 Solid Mechanics in 3 Dimensions: stress/equilibrium, strain/displacement, and intro to linear elastic
GEL 3300 Lab #2: Measuring Strain
 GEL 3300 Lab #2: Measuring Strain The objective of this lab exercise is to use strain markers to determine the orientation of the finite strain ellipse for a deformed rock that contains deformed fossil
GEL 3300 Lab #2: Measuring Strain The objective of this lab exercise is to use strain markers to determine the orientation of the finite strain ellipse for a deformed rock that contains deformed fossil
Exercise solutions: concepts from chapter 5
 1) Stud the oöids depicted in Figure 1a and 1b. a) Assume that the thin sections of Figure 1 lie in a principal plane of the deformation. Measure and record the lengths and orientations of the principal
1) Stud the oöids depicted in Figure 1a and 1b. a) Assume that the thin sections of Figure 1 lie in a principal plane of the deformation. Measure and record the lengths and orientations of the principal
3D Elasticity Theory
 3D lasticity Theory Many structural analysis problems are analysed using the theory of elasticity in which Hooke s law is used to enforce proportionality between stress and strain at any deformation level.
3D lasticity Theory Many structural analysis problems are analysed using the theory of elasticity in which Hooke s law is used to enforce proportionality between stress and strain at any deformation level.
Provided by Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. for An Introduction to Structural Methods DVD-ROM
 Provided by Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. for An Introduction to Structural Methods DVD-ROM http://www.tasagraphicarts.com/progstruct.html AN INTRODUCTION TO STRUCTURAL METHODS - DETAILED CONTENTS: (Navigate
Provided by Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. for An Introduction to Structural Methods DVD-ROM http://www.tasagraphicarts.com/progstruct.html AN INTRODUCTION TO STRUCTURAL METHODS - DETAILED CONTENTS: (Navigate
Lecture Practical LECTURE 7 STRESS AND STRAIN
 LECTURE 7 STRESS AND STRAIN LECTURE PLAN ) STRESS a) The relationship between stress and force b) Stress Components c) Principle stresses d) Rock Failure 2) STRAIN a) Components of strain b) The strain
LECTURE 7 STRESS AND STRAIN LECTURE PLAN ) STRESS a) The relationship between stress and force b) Stress Components c) Principle stresses d) Rock Failure 2) STRAIN a) Components of strain b) The strain
lecture 8 Methods of Structural Geology This lecture Mas Rabassers de Dalt (Spain) Mas Rabassers de Dalt (Spain)
 This lecture Methods of Structural Geology lecture 8 Discuss the plotting exercise on Mas Rabassers de Dalt Look at folding related to shear zones Show an example of the application of new theory: Cap
This lecture Methods of Structural Geology lecture 8 Discuss the plotting exercise on Mas Rabassers de Dalt Look at folding related to shear zones Show an example of the application of new theory: Cap
Strain Transformation equations
 Strain Transformation equations R. Chandramouli Associate Dean-Research SASTRA University, Thanjavur-613 401 Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 8 Table of Contents 1. Stress transformation
Strain Transformation equations R. Chandramouli Associate Dean-Research SASTRA University, Thanjavur-613 401 Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 8 Table of Contents 1. Stress transformation
SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #2, Math 253
 SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #, Math 5. Find the equation of a sphere if one of its diameters has end points (, 0, 5) and (5, 4, 7). The length of the diameter is (5 ) + ( 4 0) + (7 5) = =, so the
SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #, Math 5. Find the equation of a sphere if one of its diameters has end points (, 0, 5) and (5, 4, 7). The length of the diameter is (5 ) + ( 4 0) + (7 5) = =, so the
Stress, Strain, Mohr s Circle
 Stress, Strain, Mohr s Circle The fundamental quantities in solid mechanics are stresses and strains. In accordance with the continuum mechanics assumption, the molecular structure of materials is neglected
Stress, Strain, Mohr s Circle The fundamental quantities in solid mechanics are stresses and strains. In accordance with the continuum mechanics assumption, the molecular structure of materials is neglected
CHAPTER THREE SYMMETRIC BENDING OF CIRCLE PLATES
 CHAPTER THREE SYMMETRIC BENDING OF CIRCLE PLATES * Governing equations in beam and plate bending ** Solution by superposition 1.1 From Beam Bending to Plate Bending 1.2 Governing Equations For Symmetric
CHAPTER THREE SYMMETRIC BENDING OF CIRCLE PLATES * Governing equations in beam and plate bending ** Solution by superposition 1.1 From Beam Bending to Plate Bending 1.2 Governing Equations For Symmetric
1. To analyze the deformation of a conical membrane, it is proposed to use a two-dimensional conical-polar coordinate system ( s,
 EN2210: Continuum Mechanics Homework 2: Kinematics Due Wed September 26, 2012 School of Engineering Brown University 1. To analyze the deformation of a conical membrane, it is proposed to use a two-dimensional
EN2210: Continuum Mechanics Homework 2: Kinematics Due Wed September 26, 2012 School of Engineering Brown University 1. To analyze the deformation of a conical membrane, it is proposed to use a two-dimensional
GG303 Lab 12 11/7/18 1
 GG303 Lab 12 11/7/18 1 DEFORMATION AROUND A HOLE This lab has two main objectives. The first is to develop insight into the displacement, stress, and strain fields around a hole in a sheet under an approximately
GG303 Lab 12 11/7/18 1 DEFORMATION AROUND A HOLE This lab has two main objectives. The first is to develop insight into the displacement, stress, and strain fields around a hole in a sheet under an approximately
PEAT SEISMOLOGY Lecture 2: Continuum mechanics
 PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 2: Continuum mechanics Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Strain Strain is the formal description of the change in shape of a
PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 2: Continuum mechanics Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Strain Strain is the formal description of the change in shape of a
Lecture 13: Tensors in paleomagnetism. What are tensors anyway? anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility (AMS) how to find it. what to do with it
 Lecture 13: Tensors in paleomagnetism What are tensors anyway? anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility (AMS) how to find it what to do with it anisotropy of magnetic remanence 1 What is a tensor? An array
Lecture 13: Tensors in paleomagnetism What are tensors anyway? anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility (AMS) how to find it what to do with it anisotropy of magnetic remanence 1 What is a tensor? An array
CHAPTER Va : CONTINUOUS HETEROGENEOUS DEFORMATION
 Va-1 INTRODUCTION Heterogeneous deformation results from mechanical instabilities (folding and boudinage) within an heterogeneous material or from strain localization in an homogeneous material (shear
Va-1 INTRODUCTION Heterogeneous deformation results from mechanical instabilities (folding and boudinage) within an heterogeneous material or from strain localization in an homogeneous material (shear
EAS MIDTERM EXAM
 Ave = 98/150, s.d. = 21 EAS 326-03 MIDTERM EXAM This exam is closed book and closed notes. It is worth 150 points; the value of each question is shown at the end of each question. At the end of the exam,
Ave = 98/150, s.d. = 21 EAS 326-03 MIDTERM EXAM This exam is closed book and closed notes. It is worth 150 points; the value of each question is shown at the end of each question. At the end of the exam,
Elements of Rock Mechanics
 Elements of Rock Mechanics Stress and strain Creep Constitutive equation Hooke's law Empirical relations Effects of porosity and fluids Anelasticity and viscoelasticity Reading: Shearer, 3 Stress Consider
Elements of Rock Mechanics Stress and strain Creep Constitutive equation Hooke's law Empirical relations Effects of porosity and fluids Anelasticity and viscoelasticity Reading: Shearer, 3 Stress Consider
Exercise: concepts from chapter 8
 Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 8 1) The following exercises explore elementary concepts associated with a linear elastic material that is isotropic and homogeneous with respect to elastic
Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 8 1) The following exercises explore elementary concepts associated with a linear elastic material that is isotropic and homogeneous with respect to elastic
Tensor Visualization. CSC 7443: Scientific Information Visualization
 Tensor Visualization Tensor data A tensor is a multivariate quantity Scalar is a tensor of rank zero s = s(x,y,z) Vector is a tensor of rank one v = (v x,v y,v z ) For a symmetric tensor of rank 2, its
Tensor Visualization Tensor data A tensor is a multivariate quantity Scalar is a tensor of rank zero s = s(x,y,z) Vector is a tensor of rank one v = (v x,v y,v z ) For a symmetric tensor of rank 2, its
Exercises for Multivariable Differential Calculus XM521
 This document lists all the exercises for XM521. The Type I (True/False) exercises will be given, and should be answered, online immediately following each lecture. The Type III exercises are to be done
This document lists all the exercises for XM521. The Type I (True/False) exercises will be given, and should be answered, online immediately following each lecture. The Type III exercises are to be done
Chapter 3: Stress and Equilibrium of Deformable Bodies
 Ch3-Stress-Equilibrium Page 1 Chapter 3: Stress and Equilibrium of Deformable Bodies When structures / deformable bodies are acted upon by loads, they build up internal forces (stresses) within them to
Ch3-Stress-Equilibrium Page 1 Chapter 3: Stress and Equilibrium of Deformable Bodies When structures / deformable bodies are acted upon by loads, they build up internal forces (stresses) within them to
GG612 Lecture 3. Outline
 GG61 Lecture 3 Strain and Stress Should complete infinitesimal strain by adding rota>on. Outline Matrix Opera+ons Strain 1 General concepts Homogeneous strain 3 Matrix representa>ons 4 Squares of line
GG61 Lecture 3 Strain and Stress Should complete infinitesimal strain by adding rota>on. Outline Matrix Opera+ons Strain 1 General concepts Homogeneous strain 3 Matrix representa>ons 4 Squares of line
c) Plot stability diagrams (Figure 11, p 10 of notes) for cases i) - iv), all on the same graph.
 12.520 Problem Set 4 1) (100%) Consider a dry, noncohesive critical wedge, as discussed in class, as a model of snow in front of a snow plow. We will consider 4 cases: i) φ = 30, φ b = 10 ; ii) φ = 30,
12.520 Problem Set 4 1) (100%) Consider a dry, noncohesive critical wedge, as discussed in class, as a model of snow in front of a snow plow. We will consider 4 cases: i) φ = 30, φ b = 10 ; ii) φ = 30,
Rotational Motion. Chapter 4. P. J. Grandinetti. Sep. 1, Chem P. J. Grandinetti (Chem. 4300) Rotational Motion Sep.
 Rotational Motion Chapter 4 P. J. Grandinetti Chem. 4300 Sep. 1, 2017 P. J. Grandinetti (Chem. 4300) Rotational Motion Sep. 1, 2017 1 / 76 Angular Momentum The angular momentum of a particle with respect
Rotational Motion Chapter 4 P. J. Grandinetti Chem. 4300 Sep. 1, 2017 P. J. Grandinetti (Chem. 4300) Rotational Motion Sep. 1, 2017 1 / 76 Angular Momentum The angular momentum of a particle with respect
ELASTOPLASTICITY THEORY by V. A. Lubarda
 ELASTOPLASTICITY THEORY by V. A. Lubarda Contents Preface xiii Part 1. ELEMENTS OF CONTINUUM MECHANICS 1 Chapter 1. TENSOR PRELIMINARIES 3 1.1. Vectors 3 1.2. Second-Order Tensors 4 1.3. Eigenvalues and
ELASTOPLASTICITY THEORY by V. A. Lubarda Contents Preface xiii Part 1. ELEMENTS OF CONTINUUM MECHANICS 1 Chapter 1. TENSOR PRELIMINARIES 3 1.1. Vectors 3 1.2. Second-Order Tensors 4 1.3. Eigenvalues and
Surface force on a volume element.
 STRESS and STRAIN Reading: Section. of Stein and Wysession. In this section, we will see how Newton s second law and Generalized Hooke s law can be used to characterize the response of continuous medium
STRESS and STRAIN Reading: Section. of Stein and Wysession. In this section, we will see how Newton s second law and Generalized Hooke s law can be used to characterize the response of continuous medium
Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
 50 Module 4: Lecture 1 on Stress-strain relationship and Shear strength of soils Contents Stress state, Mohr s circle analysis and Pole, Principal stressspace, Stress pathsin p-q space; Mohr-Coulomb failure
50 Module 4: Lecture 1 on Stress-strain relationship and Shear strength of soils Contents Stress state, Mohr s circle analysis and Pole, Principal stressspace, Stress pathsin p-q space; Mohr-Coulomb failure
Ádx 1 + Áu 1 + u 1 ˆ
 Muddy Card Responses Lecture M16. The mud marked * is from the equivalent lecture (also M16) in 2000. I seem to have done a better job of explaining some of the derivations, as there were fewer questions
Muddy Card Responses Lecture M16. The mud marked * is from the equivalent lecture (also M16) in 2000. I seem to have done a better job of explaining some of the derivations, as there were fewer questions
Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017
 Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017 1. (10 points) Consider a body Ω that is assembled by gluing together two separate bodies along a flat interface. The normal vector to the interface is given by n
Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017 1. (10 points) Consider a body Ω that is assembled by gluing together two separate bodies along a flat interface. The normal vector to the interface is given by n
OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1
 OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1 (37) If a bug walks on the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + 2x 2y 4z 3 = 0 how close and how far can it get from the origin? Solution: Complete
OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1 (37) If a bug walks on the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + 2x 2y 4z 3 = 0 how close and how far can it get from the origin? Solution: Complete
Continuum mechanism: Stress and strain
 Continuum mechanics deals with the relation between forces (stress, σ) and deformation (strain, ε), or deformation rate (strain rate, ε). Solid materials, rigid, usually deform elastically, that is the
Continuum mechanics deals with the relation between forces (stress, σ) and deformation (strain, ε), or deformation rate (strain rate, ε). Solid materials, rigid, usually deform elastically, that is the
Macroscopic theory Rock as 'elastic continuum'
 Elasticity and Seismic Waves Macroscopic theory Rock as 'elastic continuum' Elastic body is deformed in response to stress Two types of deformation: Change in volume and shape Equations of motion Wave
Elasticity and Seismic Waves Macroscopic theory Rock as 'elastic continuum' Elastic body is deformed in response to stress Two types of deformation: Change in volume and shape Equations of motion Wave
Stress transformation and Mohr s circle for stresses
 Stress transformation and Mohr s circle for stresses 1.1 General State of stress Consider a certain body, subjected to external force. The force F is acting on the surface over an area da of the surface.
Stress transformation and Mohr s circle for stresses 1.1 General State of stress Consider a certain body, subjected to external force. The force F is acting on the surface over an area da of the surface.
CHAPTER 4 Stress Transformation
 CHAPTER 4 Stress Transformation ANALYSIS OF STRESS For this topic, the stresses to be considered are not on the perpendicular and parallel planes only but also on other inclined planes. A P a a b b P z
CHAPTER 4 Stress Transformation ANALYSIS OF STRESS For this topic, the stresses to be considered are not on the perpendicular and parallel planes only but also on other inclined planes. A P a a b b P z
Sheet metal forming with six components of strain
 Sheet metal forming with six components of strain Julian Allwood Micromechanics Seminar Friday 8 May 2009 Department of Engineering University of Cambridge jma42@cam.ac.uk 1 A question from the 1960 s
Sheet metal forming with six components of strain Julian Allwood Micromechanics Seminar Friday 8 May 2009 Department of Engineering University of Cambridge jma42@cam.ac.uk 1 A question from the 1960 s
Matrices and Deformation
 ES 111 Mathematical Methods in the Earth Sciences Matrices and Deformation Lecture Outline 13 - Thurs 9th Nov 2017 Strain Ellipse and Eigenvectors One way of thinking about a matrix is that it operates
ES 111 Mathematical Methods in the Earth Sciences Matrices and Deformation Lecture Outline 13 - Thurs 9th Nov 2017 Strain Ellipse and Eigenvectors One way of thinking about a matrix is that it operates
Numerical Modelling in Geosciences. Lecture 6 Deformation
 Numerical Modelling in Geosciences Lecture 6 Deformation Tensor Second-rank tensor stress ), strain ), strain rate ) Invariants quantities independent of the coordinate system): - First invariant trace:!!
Numerical Modelling in Geosciences Lecture 6 Deformation Tensor Second-rank tensor stress ), strain ), strain rate ) Invariants quantities independent of the coordinate system): - First invariant trace:!!
Soil Mechanics Prof. B.V.S. Viswanathan Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture 51 Earth Pressure Theories II
 Soil Mechanics Prof. B.V.S. Viswanathan Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture 51 Earth Pressure Theories II Welcome to lecture number two on earth pressure theories.
Soil Mechanics Prof. B.V.S. Viswanathan Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture 51 Earth Pressure Theories II Welcome to lecture number two on earth pressure theories.
both an analytical approach and the pole method, determine: (a) the direction of the
 Quantitative Problems Problem 4-3 Figure 4-45 shows the state of stress at a point within a soil deposit. Using both an analytical approach and the pole method, determine: (a) the direction of the principal
Quantitative Problems Problem 4-3 Figure 4-45 shows the state of stress at a point within a soil deposit. Using both an analytical approach and the pole method, determine: (a) the direction of the principal
c) Plot stability diagrams (Figure 11, p 10 of notes) for cases i) - iv), all on the same graph.
 12.520 Problem Set 4 Due 10/25/06 1) (90%) Consider a dry, noncohesive critical wedge, as discussed in class, as a model of snow in front of a snow plow. We will consider 4 cases: i) φ = 30, φ b = 10 ;
12.520 Problem Set 4 Due 10/25/06 1) (90%) Consider a dry, noncohesive critical wedge, as discussed in class, as a model of snow in front of a snow plow. We will consider 4 cases: i) φ = 30, φ b = 10 ;
Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Lecture Slides
 Lecture Slides Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner.
Lecture Slides Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner.
MATH 1020 WORKSHEET 12.1 & 12.2 Vectors in the Plane
 MATH 100 WORKSHEET 1.1 & 1. Vectors in the Plane Find the vector v where u =, 1 and w = 1, given the equation v = u w. Solution. v = u w =, 1 1, =, 1 +, 4 =, 1 4 = 0, 5 Find the magnitude of v = 4, 3 Solution.
MATH 100 WORKSHEET 1.1 & 1. Vectors in the Plane Find the vector v where u =, 1 and w = 1, given the equation v = u w. Solution. v = u w =, 1 1, =, 1 +, 4 =, 1 4 = 0, 5 Find the magnitude of v = 4, 3 Solution.
TWO THEOREMS ON THE FOCUS-SHARING ELLIPSES: A THREE-DIMENSIONAL VIEW
 TWO THEOREMS ON THE FOCUS-SHARING ELLIPSES: A THREE-DIMENSIONAL VIEW ILYA I. BOGDANOV Abstract. Consider three ellipses each two of which share a common focus. The radical axes of the pairs of these ellipses
TWO THEOREMS ON THE FOCUS-SHARING ELLIPSES: A THREE-DIMENSIONAL VIEW ILYA I. BOGDANOV Abstract. Consider three ellipses each two of which share a common focus. The radical axes of the pairs of these ellipses
GPS, Strain & Earthquakes Unit 2: Strain reading for students
 GPS, Strain & Earthquakes Unit 2: Strain reading for students Nancy West, Beth Pratt-Sitaula, and Shelley Olds (UNAVCO) expanded from work by Vince Cronin (Baylor University) Earth s crust is deforming.
GPS, Strain & Earthquakes Unit 2: Strain reading for students Nancy West, Beth Pratt-Sitaula, and Shelley Olds (UNAVCO) expanded from work by Vince Cronin (Baylor University) Earth s crust is deforming.
Mechanics of materials Lecture 4 Strain and deformation
 Mechanics of materials Lecture 4 Strain and deformation Reijo Kouhia Tampere University of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Design Wednesday 3 rd February, 206 of a continuum
Mechanics of materials Lecture 4 Strain and deformation Reijo Kouhia Tampere University of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Design Wednesday 3 rd February, 206 of a continuum
Brittle Deformation. Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm
 Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
Suusamyr, Kyrgyzstan Structural-geological Report
 Suusamyr, Kyrgyzstan Structural-geological Report by David Fossati fossatid@student.ethz.ch Contents 1 Introduction... 2 2 Field work area... 2 3 Field work methods... 5 4 Analysis methods... 7 5 Maps
Suusamyr, Kyrgyzstan Structural-geological Report by David Fossati fossatid@student.ethz.ch Contents 1 Introduction... 2 2 Field work area... 2 3 Field work methods... 5 4 Analysis methods... 7 5 Maps
8.1. What is meant by the shear strength of soils? Solution 8.1 Shear strength of a soil is its internal resistance to shearing stresses.
 8.1. What is meant by the shear strength of soils? Solution 8.1 Shear strength of a soil is its internal resistance to shearing stresses. 8.2. Some soils show a peak shear strength. Why and what type(s)
8.1. What is meant by the shear strength of soils? Solution 8.1 Shear strength of a soil is its internal resistance to shearing stresses. 8.2. Some soils show a peak shear strength. Why and what type(s)
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS For Marker s Use Only LAST NAME (printed): FIRST
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS For Marker s Use Only LAST NAME (printed): FIRST
CONSTITUTIVE RELATIONS FOR LINEAR ELASTIC SOLIDS
 Chapter 9 CONSTITUTIV RLATIONS FOR LINAR LASTIC SOLIDS Figure 9.1: Hooke memorial window, St. Helen s, Bishopsgate, City of London 211 212 CHAPTR 9. CONSTITUTIV RLATIONS FOR LINAR LASTIC SOLIDS 9.1 Mechanical
Chapter 9 CONSTITUTIV RLATIONS FOR LINAR LASTIC SOLIDS Figure 9.1: Hooke memorial window, St. Helen s, Bishopsgate, City of London 211 212 CHAPTR 9. CONSTITUTIV RLATIONS FOR LINAR LASTIC SOLIDS 9.1 Mechanical
Structural Geology. Part 1: Continuum mechanics and rheology
 12.113 Structural Geology Part 1: Continuum mechanics and rheology Fall 2005 2 Contents 1 Stress and strain 5 1.1 Stress (T&M pp.128 164)........................... 5 1.1.1 Introduction...............................
12.113 Structural Geology Part 1: Continuum mechanics and rheology Fall 2005 2 Contents 1 Stress and strain 5 1.1 Stress (T&M pp.128 164)........................... 5 1.1.1 Introduction...............................
Exercise: mechanics of dike formation at Ship Rock
 Exercise: mechanics of dike formation at Ship Rock Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch. 8, p. 87 95, 319-33 Delaney & Pollard, 1981, Deformation of host rocks and flow of magma during growth
Exercise: mechanics of dike formation at Ship Rock Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch. 8, p. 87 95, 319-33 Delaney & Pollard, 1981, Deformation of host rocks and flow of magma during growth
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
Exam in : GEO-3104 Advanced Structural. Geology. Date : Time : Approved remedies : Ruler (linjal), Compasses (passer),
 Page 1 of 5 pages FINAL EXAM IN GEO-3104 Exam in : GEO-3104 Advanced Structural Geology Date : 28-02-2013 Time : 9.00 12.00 Place : Aud.Max. Approved remedies : Ruler (linjal), Compasses (passer), Protractor
Page 1 of 5 pages FINAL EXAM IN GEO-3104 Exam in : GEO-3104 Advanced Structural Geology Date : 28-02-2013 Time : 9.00 12.00 Place : Aud.Max. Approved remedies : Ruler (linjal), Compasses (passer), Protractor
3 2 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) 3. a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1
 Math Problem a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1 3 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) = Au( t) with u (0) =. 3 1 u 1 =, u 1 3 = b- True or false and why 1. if A is
Math Problem a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1 3 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) = Au( t) with u (0) =. 3 1 u 1 =, u 1 3 = b- True or false and why 1. if A is
Dynamic analysis. 1. Force and stress
 Dynamic analysis 1. Force and stress Dynamics is the part of structural geology that involves energy, force, stress, and strength. It's very important to distinguish dynamic concepts from kinematic ones.
Dynamic analysis 1. Force and stress Dynamics is the part of structural geology that involves energy, force, stress, and strength. It's very important to distinguish dynamic concepts from kinematic ones.
(Relatively) Painless Stress Tensors
 (Relatively) Painless Stress Tensors Colin A. Shaw, University of Wisconsin, Eau Claire shawca@uwec.edu A graphical approach to introducing tensors Adapted from Means (1976) Context Presentation: The activity
(Relatively) Painless Stress Tensors Colin A. Shaw, University of Wisconsin, Eau Claire shawca@uwec.edu A graphical approach to introducing tensors Adapted from Means (1976) Context Presentation: The activity
Mechanical Properties of Materials
 Mechanical Properties of Materials Strains Material Model Stresses Learning objectives Understand the qualitative and quantitative description of mechanical properties of materials. Learn the logic of
Mechanical Properties of Materials Strains Material Model Stresses Learning objectives Understand the qualitative and quantitative description of mechanical properties of materials. Learn the logic of
The Sphere OPTIONAL - I Vectors and three dimensional Geometry THE SPHERE
 36 THE SPHERE You must have played or seen students playing football, basketball or table tennis. Football, basketball, table tennis ball are all examples of geometrical figures which we call "spheres"
36 THE SPHERE You must have played or seen students playing football, basketball or table tennis. Football, basketball, table tennis ball are all examples of geometrical figures which we call "spheres"
Tensor Transformations and the Maximum Shear Stress. (Draft 1, 1/28/07)
 Tensor Transformations and the Maximum Shear Stress (Draft 1, 1/28/07) Introduction The order of a tensor is the number of subscripts it has. For each subscript it is multiplied by a direction cosine array
Tensor Transformations and the Maximum Shear Stress (Draft 1, 1/28/07) Introduction The order of a tensor is the number of subscripts it has. For each subscript it is multiplied by a direction cosine array
STRAIN. Normal Strain: The elongation or contractions of a line segment per unit length is referred to as normal strain denoted by Greek symbol.
 STRAIN In engineering the deformation of a body is specified using the concept of normal strain and shear strain whenever a force is applied to a body, it will tend to change the body s shape and size.
STRAIN In engineering the deformation of a body is specified using the concept of normal strain and shear strain whenever a force is applied to a body, it will tend to change the body s shape and size.
Basic Equations of Elasticity
 A Basic Equations of Elasticity A.1 STRESS The state of stress at any point in a loaded bo is defined completely in terms of the nine components of stress: σ xx,σ yy,σ zz,σ xy,σ yx,σ yz,σ zy,σ zx,andσ
A Basic Equations of Elasticity A.1 STRESS The state of stress at any point in a loaded bo is defined completely in terms of the nine components of stress: σ xx,σ yy,σ zz,σ xy,σ yx,σ yz,σ zy,σ zx,andσ
Force and Stress. Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics. Ben van der Pluijm. WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/9/ :35 PM
 Force and Stress Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/9/2017 12:35 PM We Discuss Force and Stress Force and Units (Trigonometry) Newtonian
Force and Stress Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/9/2017 12:35 PM We Discuss Force and Stress Force and Units (Trigonometry) Newtonian
GEOL 309 Laboratory Activity: Euler Poles. Name
 GEOL 309 Laboratory Activity: Euler Poles Name Instructions: Follow the directions given. Take a picture (with your phone) of your work showing final pole locations on the globe. Print pictures and turn
GEOL 309 Laboratory Activity: Euler Poles Name Instructions: Follow the directions given. Take a picture (with your phone) of your work showing final pole locations on the globe. Print pictures and turn
Chapter 4. Electric Fields in Matter
 Chapter 4. Electric Fields in Matter 4.1.2 Induced Dipoles What happens to a neutral atom when it is placed in an electric field E? The atom now has a tiny dipole moment p, in the same direction as E.
Chapter 4. Electric Fields in Matter 4.1.2 Induced Dipoles What happens to a neutral atom when it is placed in an electric field E? The atom now has a tiny dipole moment p, in the same direction as E.
Eigen decomposition for 3D stress tensor
 Eigen decomposition for 3D stress tensor by Vince Cronin Begun September 13, 2010; last revised September 23, 2015 Unfinished Dra ; Subject to Revision Introduction If we have a cubic free body that is
Eigen decomposition for 3D stress tensor by Vince Cronin Begun September 13, 2010; last revised September 23, 2015 Unfinished Dra ; Subject to Revision Introduction If we have a cubic free body that is
Chapter 6: Plastic Theory
 OHP Mechanical Properties of Materials Chapter 6: Plastic Theory Prof. Wenjea J. Tseng 曾文甲 Department of Materials Engineering National Chung Hsing University wenjea@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Reference: W. F.
OHP Mechanical Properties of Materials Chapter 6: Plastic Theory Prof. Wenjea J. Tseng 曾文甲 Department of Materials Engineering National Chung Hsing University wenjea@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Reference: W. F.
Getting Started with Communications Engineering
 1 Linear algebra is the algebra of linear equations: the term linear being used in the same sense as in linear functions, such as: which is the equation of a straight line. y ax c (0.1) Of course, if we
1 Linear algebra is the algebra of linear equations: the term linear being used in the same sense as in linear functions, such as: which is the equation of a straight line. y ax c (0.1) Of course, if we
ELASTICITY (MDM 10203)
 LASTICITY (MDM 10203) Lecture Module 5: 3D Constitutive Relations Dr. Waluyo Adi Siswanto University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Generalised Hooke's Law In one dimensional system: = (basic Hooke's law) Considering
LASTICITY (MDM 10203) Lecture Module 5: 3D Constitutive Relations Dr. Waluyo Adi Siswanto University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Generalised Hooke's Law In one dimensional system: = (basic Hooke's law) Considering
Combined Stresses and Mohr s Circle. General Case of Combined Stresses. General Case of Combined Stresses con t. Two-dimensional stress condition
 Combined Stresses and Mohr s Circle Material in this lecture was taken from chapter 4 of General Case of Combined Stresses Two-dimensional stress condition General Case of Combined Stresses con t The normal
Combined Stresses and Mohr s Circle Material in this lecture was taken from chapter 4 of General Case of Combined Stresses Two-dimensional stress condition General Case of Combined Stresses con t The normal
Determination of Locally Varying Directions through Mass Moment of Inertia Tensor
 Determination of Locally Varying Directions through Mass Moment of Inertia Tensor R. M. Hassanpour and C.V. Deutsch Centre for Computational Geostatistics Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
Determination of Locally Varying Directions through Mass Moment of Inertia Tensor R. M. Hassanpour and C.V. Deutsch Centre for Computational Geostatistics Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
Hydraulic properties of porous media
 PART 5 Hydraulic properties of porous media Porosity Definition: Void space: n V void /V total total porosity e V void /V solid Primary porosity - between grains Secondary porosity - fracture or solution
PART 5 Hydraulic properties of porous media Porosity Definition: Void space: n V void /V total total porosity e V void /V solid Primary porosity - between grains Secondary porosity - fracture or solution
Exercise: concepts from chapter 6
 Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Chapter 6 1) The definition of the traction vector (6.7) relies upon the approximation of rock as a continuum, so the ratio of resultant force to surface area
Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Chapter 6 1) The definition of the traction vector (6.7) relies upon the approximation of rock as a continuum, so the ratio of resultant force to surface area
GEO E1050 Finite Element Method Mohr-Coulomb and other constitutive models. Wojciech Sołowski
 GEO E050 Finite Element Method Mohr-Coulomb and other constitutive models Wojciech Sołowski To learn today. Reminder elasticity 2. Elastic perfectly plastic theory: concept 3. Specific elastic-perfectly
GEO E050 Finite Element Method Mohr-Coulomb and other constitutive models Wojciech Sołowski To learn today. Reminder elasticity 2. Elastic perfectly plastic theory: concept 3. Specific elastic-perfectly
Summary so far. Geological structures Earthquakes and their mechanisms Continuous versus block-like behavior Link with dynamics?
 Summary so far Geodetic measurements velocities velocity gradient tensor (spatial derivatives of velocity) Velocity gradient tensor = strain rate (sym.) + rotation rate (antisym.) Strain rate tensor can
Summary so far Geodetic measurements velocities velocity gradient tensor (spatial derivatives of velocity) Velocity gradient tensor = strain rate (sym.) + rotation rate (antisym.) Strain rate tensor can
VYSOKÁ ŠKOLA BÁŇSKÁ TECHNICKÁ UNIVERZITA OSTRAVA
 VYSOKÁ ŠKOLA BÁŇSKÁ TECHNICKÁ UNIVERZITA OSTRAVA FAKULTA METALURGIE A MATERIÁLOVÉHO INŽENÝRSTVÍ APPLIED MECHANICS Study Support Leo Václavek Ostrava 2015 Title:Applied Mechanics Code: Author: doc. Ing.
VYSOKÁ ŠKOLA BÁŇSKÁ TECHNICKÁ UNIVERZITA OSTRAVA FAKULTA METALURGIE A MATERIÁLOVÉHO INŽENÝRSTVÍ APPLIED MECHANICS Study Support Leo Václavek Ostrava 2015 Title:Applied Mechanics Code: Author: doc. Ing.
Constitutive models: Incremental plasticity Drücker s postulate
 Constitutive models: Incremental plasticity Drücker s postulate if consistency condition associated plastic law, associated plasticity - plastic flow law associated with the limit (loading) surface Prager
Constitutive models: Incremental plasticity Drücker s postulate if consistency condition associated plastic law, associated plasticity - plastic flow law associated with the limit (loading) surface Prager
Lecture 11: Differential Geometry
 Lecture 11: Differential Geometry c Bryan S. Morse, Brigham Young University, 1998 2000 Last modified on February 28, 2000 at 8:45 PM Contents 11.1 Introduction..............................................
Lecture 11: Differential Geometry c Bryan S. Morse, Brigham Young University, 1998 2000 Last modified on February 28, 2000 at 8:45 PM Contents 11.1 Introduction..............................................
PEAT SEISMOLOGY Lecture 9: Anisotropy, attenuation and anelasticity
 PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 9: Anisotropy, attenuation and anelasticity Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Anisotropy Introduction Most of the theoretical
PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 9: Anisotropy, attenuation and anelasticity Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Anisotropy Introduction Most of the theoretical
Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
 56 Module 4: Lecture 7 on Stress-strain relationship and Shear strength of soils Contents Stress state, Mohr s circle analysis and Pole, Principal stressspace, Stress pathsin p-q space; Mohr-Coulomb failure
56 Module 4: Lecture 7 on Stress-strain relationship and Shear strength of soils Contents Stress state, Mohr s circle analysis and Pole, Principal stressspace, Stress pathsin p-q space; Mohr-Coulomb failure
Mathematics AQA Advanced Subsidiary GCE Core 1 (MPC1) January 2010
 Link to past paper on AQA website: http://store.aqa.org.uk/qual/gce/pdf/aqa-mpc1-w-qp-jan10.pdf These solutions are for your personal use only. DO NOT photocopy or pass on to third parties. If you are
Link to past paper on AQA website: http://store.aqa.org.uk/qual/gce/pdf/aqa-mpc1-w-qp-jan10.pdf These solutions are for your personal use only. DO NOT photocopy or pass on to third parties. If you are
Flin Flon Mining Belt
 EOSC433: Geotechnical Engineering Practice & Design Lecture 7: Stress Analysis around Underground Openings 1 of 40 Erik Eberhardt UBC Geological Engineering EOSC 433 (2007) Flin Flon Mining Belt Since
EOSC433: Geotechnical Engineering Practice & Design Lecture 7: Stress Analysis around Underground Openings 1 of 40 Erik Eberhardt UBC Geological Engineering EOSC 433 (2007) Flin Flon Mining Belt Since
3. The linear 3-D elasticity mathematical model
 3. The linear 3-D elasticity mathematical model In Chapter we examined some fundamental conditions that should be satisfied in the modeling of all deformable solids and structures. The study of truss structures
3. The linear 3-D elasticity mathematical model In Chapter we examined some fundamental conditions that should be satisfied in the modeling of all deformable solids and structures. The study of truss structures
GG611 Structural Geology Sec1on Steve Martel POST 805
 GG611 Structural Geology Sec1on Steve Martel POST 805 smartel@hawaii.edu Lecture 5 Mechanics Stress, Strain, and Rheology 11/6/16 GG611 1 Stresses Control How Rock Fractures hkp://hvo.wr.usgs.gov/kilauea/update/images.html
GG611 Structural Geology Sec1on Steve Martel POST 805 smartel@hawaii.edu Lecture 5 Mechanics Stress, Strain, and Rheology 11/6/16 GG611 1 Stresses Control How Rock Fractures hkp://hvo.wr.usgs.gov/kilauea/update/images.html
3.22 Mechanical Properties of Materials Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 3.22 Mechanical Properties of Materials Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Quiz #1 Example
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 3.22 Mechanical Properties of Materials Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Quiz #1 Example
MLC Practice Final Exam
 Name: Section: Recitation/Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 13. Show all your work on the standard
Name: Section: Recitation/Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 13. Show all your work on the standard
Taylor Series and stationary points
 Chapter 5 Taylor Series and stationary points 5.1 Taylor Series The surface z = f(x, y) and its derivatives can give a series approximation for f(x, y) about some point (x 0, y 0 ) as illustrated in Figure
Chapter 5 Taylor Series and stationary points 5.1 Taylor Series The surface z = f(x, y) and its derivatives can give a series approximation for f(x, y) about some point (x 0, y 0 ) as illustrated in Figure
Lecture 8. Stress Strain in Multi-dimension
 Lecture 8. Stress Strain in Multi-dimension Module. General Field Equations General Field Equations [] Equilibrium Equations in Elastic bodies xx x y z yx zx f x 0, etc [2] Kinematics xx u x x,etc. [3]
Lecture 8. Stress Strain in Multi-dimension Module. General Field Equations General Field Equations [] Equilibrium Equations in Elastic bodies xx x y z yx zx f x 0, etc [2] Kinematics xx u x x,etc. [3]
By drawing Mohr s circle, the stress transformation in 2-D can be done graphically. + σ x σ y. cos 2θ + τ xy sin 2θ, (1) sin 2θ + τ xy cos 2θ.
 Mohr s Circle By drawing Mohr s circle, the stress transformation in -D can be done graphically. σ = σ x + σ y τ = σ x σ y + σ x σ y cos θ + τ xy sin θ, 1 sin θ + τ xy cos θ. Note that the angle of rotation,
Mohr s Circle By drawing Mohr s circle, the stress transformation in -D can be done graphically. σ = σ x + σ y τ = σ x σ y + σ x σ y cos θ + τ xy sin θ, 1 sin θ + τ xy cos θ. Note that the angle of rotation,
Prestress stability. Lecture VI. Session on Granular Matter Institut Henri Poincaré. R. Connelly Cornell University Department of Mathematics
 Prestress stability Lecture VI Session on Granular Matter Institut Henri Poincaré R. Connelly Cornell University Department of Mathematics 1 Potential functions How is the stability of a structure determined
Prestress stability Lecture VI Session on Granular Matter Institut Henri Poincaré R. Connelly Cornell University Department of Mathematics 1 Potential functions How is the stability of a structure determined
D1. A normally consolidated clay has the following void ratio e versus effective stress σ relationship obtained in an oedometer test.
 (d) COMPRESSIBILITY AND CONSOLIDATION D1. A normally consolidated clay has the following void ratio e versus effective stress σ relationship obtained in an oedometer test. (a) Plot the e - σ curve. (b)
(d) COMPRESSIBILITY AND CONSOLIDATION D1. A normally consolidated clay has the following void ratio e versus effective stress σ relationship obtained in an oedometer test. (a) Plot the e - σ curve. (b)
Lecture Triaxial Stress and Yield Criteria. When does yielding occurs in multi-axial stress states?
 Lecture 5.11 Triaial Stress and Yield Criteria When does ielding occurs in multi-aial stress states? Representing stress as a tensor operational stress sstem Compressive stress sstems Triaial stresses:
Lecture 5.11 Triaial Stress and Yield Criteria When does ielding occurs in multi-aial stress states? Representing stress as a tensor operational stress sstem Compressive stress sstems Triaial stresses:
7. STRESS ANALYSIS AND STRESS PATHS
 7-1 7. STRESS ANALYSIS AND STRESS PATHS 7.1 THE MOHR CIRCLE The discussions in Chapters and 5 were largely concerned with vertical stresses. A more detailed examination of soil behaviour requires a knowledge
7-1 7. STRESS ANALYSIS AND STRESS PATHS 7.1 THE MOHR CIRCLE The discussions in Chapters and 5 were largely concerned with vertical stresses. A more detailed examination of soil behaviour requires a knowledge
