Model Building Complexity in the Presence of a Rugose Water Bottom Gippsland Basin Australia
|
|
|
- Oscar Luke Roberts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Model Building Complexity in the Presence of a Rugose Water Bottom Gippsland Basin Australia Paul Bouloudas, Apache Energy, Juergen Fruehn, ION GX Technology
2 Introduction Situated offshore south-eastern Australia, the Gippsland Basin contains some 21 oil and gas fields currently in production, including Australia's largest oil discovery, the Kingfish field producing over a billion barrels of crude to date. Complex geology and extensive velocity anomalies lead to convoluted acoustic ray-paths, false seismic structures and limited imaging clarity of 3D seismic volumes. Time to depth conversion of apparent structural closures increase drilling risk due to velocity model uncertainties. Depth imaging has been performed by various contractors using a variety of sub-surface modelling tools and imaging algorithms. Trials have shown the extreme sensitivity of imaging clarity and structural closure to the derived velocity model. A rugose seafloor coupled with (a) a non-uniform water-layer velocity field, and (b) complex high velocity shallow carbonates, introduce small scale velocity anomalies that, if not captures during model-building, will compromise the image of deeper target levels. Recent model building and imaging efforts have seen extensive improvements in the worst affected areas, over and above previous imaging attempts. This paper highlights the model building techniques employed within a deep water complex structural setting. We aim to discuss the derivation and impact of a spatially variant water-layer model, an initial sediment model and the diverse nature of velocity-model building techniques. The knowledge gained at Gippsland may assist depth imaging in other deep water complex imaging environments. Initial Water And Sediment Velocity Model It has become standard practice to create an initial velocity model for depth imaging based on final pre-stack time migration RMS velocity volumes converted to interval velocity in depth. The water bottom is picked and gridded as a hard constraint, based on an initial migration (Jones et al. 2010). This may be appropriate in some geological settings. In Gippsland Basin multiple seismic surveys acquired over time in different seasons are used to image a steeply dipping rugose sea floor. Alternative approaches are required to define initial water layer and sediment layer velocity models separated by an accurate sea bottom horizon. The water column is a dynamic medium whose velocity response changes with depth due to properties such as salinity, temperature and density. These variations coupled with the physical limitations of measuring an accurate water depth during marine seismic acquisition combine to limit the validity of water depth maps in deep water settings with rugose steeply dipping sea beds. Empirical relationships have been defined that may model water velocity variations with depth in certain regions. In this study we treat the water column as a separate layer during the modelling process. All wells in the area are on the shelf region and cannot be used to verify the accuracy of the water model in minimising seafloor depth misties in the deeper water. In Gippsland Basin we use a data driven approach to model the water layer velocity both laterally and vertically. Time-depth water velocity readings taken during seismic acquisition at Gippsland are sparse and limited in depth extent. An initial depth variant water column velocity profile is created from publications released from the US Navy. Empirical curve fitting relationships are used to extend these profiles to maximum water depth. This depth variant, but laterally constant model drives an initial migration. Seabed RMO errors in the deeper areas are used to vertically update this model at regularised bin intervals of 25x25 metres. Additional smoothing produces an acceptable water layer model from which the initial migration is recomputed. A water bottom horizon is picked and gridded as a hard constraint before flooding with an initial sediment velocity model. To ensure accurate modelling of the incised canyons when moving into the deep water no smoothing is applied to the water bottom profile.
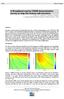
3 Figure 1: The final water layer velocity model is depth and laterally variant. Lateral variations are relatively minor over the shelf areas but increase dramatically over the steep bank moving into deeper water. An additional high resolution 3D pre-stack depth migration is used to define a seabed horizon inserted as a hard constraint between the water and sediment layer velocities of the initial interval velocity depth model. Figure 2: The water bottom rugosity over the survey area is displayed in this final gridded seafloor model. A large trench and incised canyons are clearly visible. The water depths range from 150 to 2580m. An accurate seafloor model is a prerequisite for shallow sediment model building. Building an accurate seafloor model is dependent upon an accurate water layer velocity representation. In Gippsland Basin a data driven approach is used in constructing the seafloor model. Shallow Sediment Velocity Model A wide variety of approaches are now used to build velocity models using pre stack depth migration imaging. These methods revolve around extracting detailed information about velocity errors from migrated data for input to subsequent tomographic inversion and model update. The pitfall in these methods is their ability to produce non-geological models, if not constrained adequately (Etgen et al, 2002). In this study area previous model building attempts had difficulty imaging structures below 2.5km in depth. A shallow high velocity carbonate sequence made velocity model update by tomographic inversion very unstable. The high velocity layer coupled with ray-path distortions from the rugose water bottom introduced unstable cyclic anomalies after tomographic update.
4 Figure 3: Shallow velocity model with seismic section overlain. The shallow carbonate sequence exhibits seismic velocities up to 4000m/sec which decrease over the next 1km of depth to 3000m/sec. Anomalous interval velocities are shown in this update which appear cyclic in nature on the right side of the section. These are believed to be caused by the tomography not handling the surfacechannelling features over a steep sea-bottom gradient (out of plane of the section). Inversion cell sizes are reduced to counter this effect however had little influence on the result. Hybrid Velocity Model Update A combination of manual velocity picking, model smoothing and hybrid model update helped to stabilise the velocity model in the carbonate sequence where interval velocities approached 4000m/sec. Over a vertical relief of less than 1km interval velocities reduce to 3000m/sec in the underlying sediments. Such rapid variations in vertical velocity are sometimes difficult to capture in a purely gridded tomographic approach. In contrast to a layer stripping approach for model building, gridded tomography removed the restrictions associated with using fixed vertical velocity gradients (Whitfield et al. 2008). The hybrid approach to model building differs from the purely gridded approach by introducing layer constraints at major velocity boundaries (Jones et al. 2007). At Gippsland solving the velocity model to the base of the carbonate sequence was imperative to avoid introducing structural anomalies in the deeper sediments whose residual depth error is beyond the maximum acceptable range solvable by subsequent tomographic updates. Without adequate well control in the deeper sections, quantitative structural misties could not be evaluated. Residual depthcurvature on pre stack imaged gathers is used to judge the accuracy of the model update in the deep water. Figure 4: The hybrid approach to model building used during iteration 5. The shallow model is geologically plausible and is inserted to the base of the interpreted carbonate layer (bvhv). A gradient function is inserted below bvhv to the top of the interpreted Lakes Entrance (LE) formation. A smoothed version of previous model 3 is inserted below this constraint to 400m below the Top Latrobe (TOL) sequence. Extrapolation of faster velocities towards the trench is used to complete the update. This model is used to drive a final tomographic update. Imaging Examples Below A Deep Submarine Canon Huang et al. (2010) describe building an accurate velocity model (and using the optimum migration algorithm for the geology present) as a principal requirement in order to obtain high-quality and reliable subsurface images. In Gippsland we were able to build on the knowledge of previous
5 modelling and imaging studies. In this respect it is important to extend the lateral reach of the carbonate sequence on the left side of the section towards the sea-bottom trench to eliminate false structures being imaged below the trench. Vintage data from the 2008 pre stack depth migration effort show non-geologically plausible structures differing by up to 90m in vertical relief with the current dataset below the deep trench feature. Figure 5: Building on the knowledge from previous depth imaging efforts in this area enables the extension of the of the high velocity carbonate layer towards the sea-bottom trench (refer Figure 4). Without this extension the introduction of non-geologically plausible structures with large vertical relief are probable as shown in the 2008 vintage pre stack depth migration result (left). These apparent false structures are removed when using the current imaging model (right). (Scaling between the two sections is not balanced). Conclusions Gippsland Basin exhibits unique geological complexities that impact on seismic imaging quality and risk analysis. Model building strategies need to be adaptable and multi-faceted in their approach. We believe that a combination of layer stripping, gridded and hybrid model building coupled with focused tomographic inversion helps to produce a geologically plausible velocity model at Gippsland. Acknowledgements The authors thank Apache Energy and Kufpec for permission to publish this work. The authors are grateful to Stuart Greenwood and Noah Stevens of GXT Imaging Solutions and Chris Bullock (formerly GXT Imaging Solutions) for their contributions in processing these data. References Etgen, J.T., Billette, F.J., Sandschaper, R. and Rietveld, W. E. [2002] The key practical aspects of 3D tomography: data picking and model representation. 72 nd SEG International Exposition, Expanded Abstracts, 21, Huang, Y., Lin, D., Bai, B., Roby, S., and Ricardez, C. [2010] Challenges in presalt depth imaging of the deepwater Santos Basin, Brazil. The Leading Edge, 29 (7), Jones, I.F., Sugrue, M.J. and Hardy, P.B. [2007] Hybrid gridded tomography. First Break, 25 (4), Whitfield, P., Dazley, M., Santos-Luis, B., Nieuwland, F. and Lemaistre, L.[2008] Building velocity models for depth imaging in the presence of short-wavelength velocity variations: a North Sea case study. First Break, 26 (5),
Velocity Update Using High Resolution Tomography in Santos Basin, Brazil Lingli Hu and Jianhang Zhou, CGGVeritas
 Lingli Hu and Jianhang Zhou, CGGVeritas Summary The exploration interest in the Santos Basin offshore Brazil has increased with the large deep water pre-salt discoveries, such as Tupi and Jupiter. As the
Lingli Hu and Jianhang Zhou, CGGVeritas Summary The exploration interest in the Santos Basin offshore Brazil has increased with the large deep water pre-salt discoveries, such as Tupi and Jupiter. As the
H005 Pre-salt Depth Imaging of the Deepwater Santos Basin, Brazil
 H005 Pre-salt Depth Imaging of the Deepwater Santos Basin, Brazil Y. Huang* (CGGVeritas), D. Lin (CGGVeritas), B. Bai (CGGVeritas), S. Roby (CGGVeritas) & C. Ricardez (CGGVeritas) SUMMARY Several discoveries,
H005 Pre-salt Depth Imaging of the Deepwater Santos Basin, Brazil Y. Huang* (CGGVeritas), D. Lin (CGGVeritas), B. Bai (CGGVeritas), S. Roby (CGGVeritas) & C. Ricardez (CGGVeritas) SUMMARY Several discoveries,
A Southern North Sea Multi-Survey presdm using Hybrid Gridded Tomography
 A Southern North Sea Multi-Survey presdm using Hybrid Gridded Tomography Ian Jones* GX Technology, Egham, United Kingdom ijones@gxt.com Emma Evans and Darren Judd GX Technology, Egham, United Kingdom and
A Southern North Sea Multi-Survey presdm using Hybrid Gridded Tomography Ian Jones* GX Technology, Egham, United Kingdom ijones@gxt.com Emma Evans and Darren Judd GX Technology, Egham, United Kingdom and
Velocity model building challenges and solutions for seabed- and paleo-canyons: a case study in Campos Basin, Brazil
 Velocity model building challenges and solutions for seabed- and paleo-canyons: a case study in Campos Basin, Brazil Kai Zhang, Javier Subia, Chevron; Chanjuan Sun, Hao Shen, Nuree Han, CGG Summary The
Velocity model building challenges and solutions for seabed- and paleo-canyons: a case study in Campos Basin, Brazil Kai Zhang, Javier Subia, Chevron; Chanjuan Sun, Hao Shen, Nuree Han, CGG Summary The
Tu N Fault Shadow Removal over Timor Trough Using Broadband Seismic, FWI and Fault Constrained Tomography
 Tu N118 05 Fault Shadow Removal over Timor Trough Using Broadband Seismic, FWI and Fault Constrained Tomography Y. Guo* (CGG), M. Fujimoto (INPEX), S. Wu (CGG) & Y. Sasaki (INPEX) SUMMARY Thrust-complex
Tu N118 05 Fault Shadow Removal over Timor Trough Using Broadband Seismic, FWI and Fault Constrained Tomography Y. Guo* (CGG), M. Fujimoto (INPEX), S. Wu (CGG) & Y. Sasaki (INPEX) SUMMARY Thrust-complex
Summary. Introduction
 Multi-layer tomography and its application for improved depth imaging Patrice Guillaume, Steve Hollingworth*, Xiaoming Zhang, Anthony Prescott, Richard Jupp, Gilles Lambaré, Owen Pape, CGGVeritas Summary
Multi-layer tomography and its application for improved depth imaging Patrice Guillaume, Steve Hollingworth*, Xiaoming Zhang, Anthony Prescott, Richard Jupp, Gilles Lambaré, Owen Pape, CGGVeritas Summary
Tu N Estimation of Uncertainties in Fault Lateral Positioning on 3D PSDM Seismic Image - Example from the NW Australian Shelf
 Tu N118 06 Estimation of Uncertainties in Fault Lateral Positioning on 3D PSDM Seismic Image - Example from the NW Australian Shelf S. Birdus* (CGG), V. Ganivet (CGG), A. Artemov (CGG), R. Teakle (Chevron)
Tu N118 06 Estimation of Uncertainties in Fault Lateral Positioning on 3D PSDM Seismic Image - Example from the NW Australian Shelf S. Birdus* (CGG), V. Ganivet (CGG), A. Artemov (CGG), R. Teakle (Chevron)
Time vs depth in a North Sea case study of the ugly truth Abstract
 Time vs depth in a North Sea case study of the ugly truth Thomas Massip 1, Lauren Braidwood 1, Juergen Fruehn 1, Owen Isaac 1, Jonathan Denly 1, Robert Richardson 2, Phil Mollicone 3 1 ION Geophysical;
Time vs depth in a North Sea case study of the ugly truth Thomas Massip 1, Lauren Braidwood 1, Juergen Fruehn 1, Owen Isaac 1, Jonathan Denly 1, Robert Richardson 2, Phil Mollicone 3 1 ION Geophysical;
Summary. Introduction
 Detailed velocity model building in a carbonate karst zone and improving sub-karst images in the Gulf of Mexico Jun Cai*, Hao Xun, Li Li, Yang He, Zhiming Li, Shuqian Dong, Manhong Guo and Bin Wang, TGS
Detailed velocity model building in a carbonate karst zone and improving sub-karst images in the Gulf of Mexico Jun Cai*, Hao Xun, Li Li, Yang He, Zhiming Li, Shuqian Dong, Manhong Guo and Bin Wang, TGS
Downloaded 09/10/15 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 The role of legacy seismic in exploring new offshore hydrocarbon provinces or can you teach old data new tricks (technologies)? Howard Nicholls, Lauren Penn, Anna Marszalek, Paolo Esestime, Karyna Rodriguez,
The role of legacy seismic in exploring new offshore hydrocarbon provinces or can you teach old data new tricks (technologies)? Howard Nicholls, Lauren Penn, Anna Marszalek, Paolo Esestime, Karyna Rodriguez,
Dip-constrained tomography with weighting flow for paleo-canyons: a case study in Para- Maranhao Basin, Brazil Guang Chen and Lingli Hu, CGG
 Dip-constrained tomography with weighting flow for paleo-canyons: a case study in Para- Maranhao Basin, Brazil Guang Chen and Lingli Hu, CGG Summary Para-Maranhao Basin offshore Brazil is well-known for
Dip-constrained tomography with weighting flow for paleo-canyons: a case study in Para- Maranhao Basin, Brazil Guang Chen and Lingli Hu, CGG Summary Para-Maranhao Basin offshore Brazil is well-known for
P Edward Knight 1, James Raffle 2, Sian Davies 2, Henna Selby 2, Emma Evans 2, Mark Johnson 1. Abstract
 P1-3-10 De-risking Drill Decisions. A case study on the benefit of re-processing conventionally acquired seismic data with the latest broadband processing technology Edward Knight 1, James Raffle 2, Sian
P1-3-10 De-risking Drill Decisions. A case study on the benefit of re-processing conventionally acquired seismic data with the latest broadband processing technology Edward Knight 1, James Raffle 2, Sian
The seismic response to strong vertical velocity change
 10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P-073 The seismic response to strong vertical velocity change Ian F. Jones, ION GX Technology Summary Conventional seismic data processing, whether
10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P-073 The seismic response to strong vertical velocity change Ian F. Jones, ION GX Technology Summary Conventional seismic data processing, whether
Near surface velocity adjustments in presence of rugose water bottom A quantitative approach for Canyon Scaling
 10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 406 Near surface velocity adjustments in presence of rugose water bottom A quantitative approach for Canyon Scaling Himanshu Kumar*, Pramod Srivastava*,
10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 406 Near surface velocity adjustments in presence of rugose water bottom A quantitative approach for Canyon Scaling Himanshu Kumar*, Pramod Srivastava*,
Deep-Water Reservoir Potential in Frontier Basins Offshore Namibia Using Broadband 3D Seismic
 Deep-Water Reservoir Potential in Frontier Basins Offshore Namibia Using Broadband 3D Seismic E. Polyaeva* (Petroleum Geo-Services), I. Thomas (Chariot Oil and Gas), C. Reiser (Petroleum Geo-Services),
Deep-Water Reservoir Potential in Frontier Basins Offshore Namibia Using Broadband 3D Seismic E. Polyaeva* (Petroleum Geo-Services), I. Thomas (Chariot Oil and Gas), C. Reiser (Petroleum Geo-Services),
2010 SEG SEG Denver 2010 Annual Meeting
 Anisotropic model building with wells and horizons: Gulf of Mexico case study comparing different approaches Andrey Bakulin*, Olga Zdraveva, Yangjun (Kevin) Liu, Kevin Lyons, WesternGeco/Schlumberger Summary
Anisotropic model building with wells and horizons: Gulf of Mexico case study comparing different approaches Andrey Bakulin*, Olga Zdraveva, Yangjun (Kevin) Liu, Kevin Lyons, WesternGeco/Schlumberger Summary
J.A. Haugen* (StatoilHydro ASA), J. Mispel (StatoilHydro ASA) & B. Arntsen (NTNU)
 U008 Seismic Imaging Below "Dirty" Salt J.A. Haugen* (StatoilHydro ASA), J. Mispel (StatoilHydro ASA) & B. Arntsen (NTNU) SUMMARY Base and sub salt seismic imaging is still an unresolved issue. To solve
U008 Seismic Imaging Below "Dirty" Salt J.A. Haugen* (StatoilHydro ASA), J. Mispel (StatoilHydro ASA) & B. Arntsen (NTNU) SUMMARY Base and sub salt seismic imaging is still an unresolved issue. To solve
Th N Seismic Imaging in Gas Obscured Areas - Q Anomaly Detection and Q Migration Applied to Broadband Data
 Th N107 11 Seismic Imaging in Gas Obscured Areas - Q Anomaly Detection and Q Migration Applied to Broadband Data A. Castiello* (ION GXT), Y. Ren (ION GXT), S. Greenwood (ION GXT), T. Martin (ION GXT),
Th N107 11 Seismic Imaging in Gas Obscured Areas - Q Anomaly Detection and Q Migration Applied to Broadband Data A. Castiello* (ION GXT), Y. Ren (ION GXT), S. Greenwood (ION GXT), T. Martin (ION GXT),
Summary. Tomography with geological constraints
 : an alternative solution for resolving of carbonates Olga Zdraveva*, Saeeda Hydal, and Marta Woodward, WesternGeco Summary Carbonates are often present in close proximity to salt in the sedimentary basins
: an alternative solution for resolving of carbonates Olga Zdraveva*, Saeeda Hydal, and Marta Woodward, WesternGeco Summary Carbonates are often present in close proximity to salt in the sedimentary basins
COVER STORY LUKE TWIGGER, CGG, UK, EXAMINES RECENT ADVANCES IN SEISMIC TECHNOLOGY THAT REDUCE SUBSALT RISK.
 COVER STORY LUKE TWIGGER, CGG, UK, EXAMINES RECENT ADVANCES IN SEISMIC TECHNOLOGY THAT REDUCE SUBSALT RISK. O il and gas exploration, especially in areas of complex geology such as salt provinces, is a
COVER STORY LUKE TWIGGER, CGG, UK, EXAMINES RECENT ADVANCES IN SEISMIC TECHNOLOGY THAT REDUCE SUBSALT RISK. O il and gas exploration, especially in areas of complex geology such as salt provinces, is a
Velocity model building in complex media by multi-layer non-linear slope tomography. Summary Introduction Non-linear slope tomography
 Velocity model building in complex media by multi-layer non-linear slope tomography. Patrice Guillaume, Jean-Philippe Montel*, Xiaoming Zhang, Gilles Lambaré, Anthony Prescott, Matthieu Reinier, Richard
Velocity model building in complex media by multi-layer non-linear slope tomography. Patrice Guillaume, Jean-Philippe Montel*, Xiaoming Zhang, Gilles Lambaré, Anthony Prescott, Matthieu Reinier, Richard
Depth Imaging for Unconventional Reservoir Characterization: Canadian Plains Case Study
 Depth Imaging for Unconventional Reservoir Characterization: Canadian Plains Case Study Bill Goodway 1, Greg Purdue 1, Shiang Yong Looi 2, Lijuan (Kathy) Du 2, Mark Rowland 2 1 Apache Canada, 2 Schlumberger
Depth Imaging for Unconventional Reservoir Characterization: Canadian Plains Case Study Bill Goodway 1, Greg Purdue 1, Shiang Yong Looi 2, Lijuan (Kathy) Du 2, Mark Rowland 2 1 Apache Canada, 2 Schlumberger
C031 Quantifying Structural Uncertainty in Anisotropic Depth Imaging - Gulf of Mexico Case Study
 C031 Quantifying Structural Uncertainty in Anisotropic Depth Imaging - Gulf of Mexico Case Study K. Osypov* (WesternGeco), D. Nichols (WesternGeco), Y. Yang (WesternGeco), F. Qiao (WesternGeco), M. O'Briain
C031 Quantifying Structural Uncertainty in Anisotropic Depth Imaging - Gulf of Mexico Case Study K. Osypov* (WesternGeco), D. Nichols (WesternGeco), Y. Yang (WesternGeco), F. Qiao (WesternGeco), M. O'Briain
We A10 12 Common Reflection Angle Migration Revealing the Complex Deformation Structure beneath Forearc Basin in the Nankai Trough
 We A10 12 Common Reflection Angle Migration Revealing the Complex Deformation Structure beneath Forearc Basin in the Nankai Trough K. Shiraishi* (JAMSTEC), M. Robb (Emerson Paradigm), K. Hosgood (Emerson
We A10 12 Common Reflection Angle Migration Revealing the Complex Deformation Structure beneath Forearc Basin in the Nankai Trough K. Shiraishi* (JAMSTEC), M. Robb (Emerson Paradigm), K. Hosgood (Emerson
Dirty salt velocity inversion: The road to a clearer subsalt image
 GEOPHYSICS. VOL. 76, NO. 5 (SEPTEMBER-OCTOBER 2011); P. WB169 WB174, 8 FIGS. 10.1190/GEO2010-0392.1 Dirty salt velocity inversion: The road to a clearer subsalt image Shuo Ji 1, Tony Huang 1, Kang Fu 2,
GEOPHYSICS. VOL. 76, NO. 5 (SEPTEMBER-OCTOBER 2011); P. WB169 WB174, 8 FIGS. 10.1190/GEO2010-0392.1 Dirty salt velocity inversion: The road to a clearer subsalt image Shuo Ji 1, Tony Huang 1, Kang Fu 2,
Vertical and horizontal resolution considerations for a joint 3D CSEM and MT inversion
 Antony PRICE*, Total E&P and Don WATTS, WesternGeco Electromagnetics Summary To further explore the potential data content and inherent limitations of a detailed 3D Controlled Source ElectroMagnetic and
Antony PRICE*, Total E&P and Don WATTS, WesternGeco Electromagnetics Summary To further explore the potential data content and inherent limitations of a detailed 3D Controlled Source ElectroMagnetic and
EnQuest, 2 ION Geophysical
 De-risking Drill Decisions - A case study on the benefit of re-processing conventionally acquired seismic data with the latest broadband processing technology. Ed Knight 1, James Raffle 2, Sian Davies
De-risking Drill Decisions - A case study on the benefit of re-processing conventionally acquired seismic data with the latest broadband processing technology. Ed Knight 1, James Raffle 2, Sian Davies
Anisotropic Depth Migration and High-Resolution Tomography in Gulf of Mexico: A Case History
 Anisotropic Depth Migration and High-Resolution Tomography in Gulf of Mexico: A Case History Gary Rodriguez, Sherry Yang, Diane Yang, Quincy Zhang, Steve Hightower, TGS Summary We present a case study
Anisotropic Depth Migration and High-Resolution Tomography in Gulf of Mexico: A Case History Gary Rodriguez, Sherry Yang, Diane Yang, Quincy Zhang, Steve Hightower, TGS Summary We present a case study
Petroleum Prospectivity in the Namibe and Southern Benguela Basins, Offshore Angola
 Petroleum Prospectivity in the Namibe and Southern Benguela Basins, Offshore Angola C. Koch* (PGS), F. Pepe (PGS), R. Vasconcelos (PGS), F. Mathew (PGS), R. Borsato (PGS) & M.P.C. de Sá (Sonangol) SUMMARY
Petroleum Prospectivity in the Namibe and Southern Benguela Basins, Offshore Angola C. Koch* (PGS), F. Pepe (PGS), R. Vasconcelos (PGS), F. Mathew (PGS), R. Borsato (PGS) & M.P.C. de Sá (Sonangol) SUMMARY
G002 An Integrated Regional Framework for Seismic Depth Imaging in the Deepwater Gulf of Mexico
 G002 An Integrated Regional Framework for Seismic Depth Imaging in the Deepwater Gulf of Mexico M. Davidson (Fugro Multi Client Services), M. Leander (Fugro Multi Client Services), K. Mohn (Fugro Multi
G002 An Integrated Regional Framework for Seismic Depth Imaging in the Deepwater Gulf of Mexico M. Davidson (Fugro Multi Client Services), M. Leander (Fugro Multi Client Services), K. Mohn (Fugro Multi
Seismic imaging with multi-layer tomography
 first break volume 30, October 2012 Seismic imaging with multi-layer tomography Patrice Guillaume, 1* Jean-Philippe Montel, 1 Steve Hollingworth, 1 Xiaoming Zhang, 1 Anthony Prescott, 1 Mathieu Reinier,
first break volume 30, October 2012 Seismic imaging with multi-layer tomography Patrice Guillaume, 1* Jean-Philippe Montel, 1 Steve Hollingworth, 1 Xiaoming Zhang, 1 Anthony Prescott, 1 Mathieu Reinier,
APPENDIX C GEOLOGICAL CHANCE OF SUCCESS RYDER SCOTT COMPANY PETROLEUM CONSULTANTS
 APPENDIX C GEOLOGICAL CHANCE OF SUCCESS Page 2 The Geological Chance of Success is intended to evaluate the probability that a functioning petroleum system is in place for each prospective reservoir. The
APPENDIX C GEOLOGICAL CHANCE OF SUCCESS Page 2 The Geological Chance of Success is intended to evaluate the probability that a functioning petroleum system is in place for each prospective reservoir. The
W011 Full Waveform Inversion for Detailed Velocity Model Building
 W011 Full Waveform Inversion for Detailed Velocity Model Building S. Kapoor* (WesternGeco, LLC), D. Vigh (WesternGeco), H. Li (WesternGeco) & D. Derharoutian (WesternGeco) SUMMARY An accurate earth model
W011 Full Waveform Inversion for Detailed Velocity Model Building S. Kapoor* (WesternGeco, LLC), D. Vigh (WesternGeco), H. Li (WesternGeco) & D. Derharoutian (WesternGeco) SUMMARY An accurate earth model
Full-waveform inversion application in different geological settings Denes Vigh*, Jerry Kapoor and Hongyan Li, WesternGeco
 Full-waveform inversion application in different geological settings Denes Vigh*, Jerry Kapoor and Hongyan Li, WesternGeco Summary After the synthetic data inversion examples, real 3D data sets have been
Full-waveform inversion application in different geological settings Denes Vigh*, Jerry Kapoor and Hongyan Li, WesternGeco Summary After the synthetic data inversion examples, real 3D data sets have been
FloatSeis Technologies for Ultra-Deep Imaging Seismic Surveys
 FloatSeis Technologies for Ultra-Deep Imaging Seismic Surveys 25 th January, 2018 Aleksandr Nikitin a.nikitin@gwl-geo.com Geology Without Limits Overview 2011-2016 GWL Acquired over 43000 km 2D seismic
FloatSeis Technologies for Ultra-Deep Imaging Seismic Surveys 25 th January, 2018 Aleksandr Nikitin a.nikitin@gwl-geo.com Geology Without Limits Overview 2011-2016 GWL Acquired over 43000 km 2D seismic
B033 Improving Subsalt Imaging by Incorporating MT Data in a 3D Earth Model Building Workflow - A Case Study in Gulf of Mexico
 B033 Improving Subsalt Imaging by Incorporating MT Data in a 3D Earth Model Building Workflow - A Case Study in Gulf of Mexico E. Medina* (WesternGeco), A. Lovatini (WesternGeco), F. Golfré Andreasi (WesternGeco),
B033 Improving Subsalt Imaging by Incorporating MT Data in a 3D Earth Model Building Workflow - A Case Study in Gulf of Mexico E. Medina* (WesternGeco), A. Lovatini (WesternGeco), F. Golfré Andreasi (WesternGeco),
TOM 1.7. Sparse Norm Reflection Tomography for Handling Velocity Ambiguities
 SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 2554 Yonadav Sudman, Paradigm and Dan Kosloff, Tel-Aviv University and Paradigm Summary Reflection seismology with the normal range of offsets encountered in seismic surveys
SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 2554 Yonadav Sudman, Paradigm and Dan Kosloff, Tel-Aviv University and Paradigm Summary Reflection seismology with the normal range of offsets encountered in seismic surveys
Detection, Delineation and Characterization of Shallow Anomalies Using Dual Sensor Seismic and Towed Streamer EM data
 Detection, Delineation and Characterization of Shallow Anomalies Using Dual Sensor Seismic and Towed Streamer EM data A.J. McKay* (Petroleum Geo-Services ASA), M. Widmaier (Petroleum Geo- Services ASA),
Detection, Delineation and Characterization of Shallow Anomalies Using Dual Sensor Seismic and Towed Streamer EM data A.J. McKay* (Petroleum Geo-Services ASA), M. Widmaier (Petroleum Geo- Services ASA),
SeisLink Velocity. Key Technologies. Time-to-Depth Conversion
 Velocity Calibrated Seismic Imaging and Interpretation Accurate Solution for Prospect Depth, Size & Geometry Accurate Time-to-Depth Conversion was founded to provide geologically feasible solutions for
Velocity Calibrated Seismic Imaging and Interpretation Accurate Solution for Prospect Depth, Size & Geometry Accurate Time-to-Depth Conversion was founded to provide geologically feasible solutions for
3D Converted Wave Data Processing A case history
 P-290 3D Converted Wave Data Processing A case history N. B. R. Prasad, ONGC Summary In recent years, there has been a growing interest in shear- wave exploration for hydrocarbons as it facilitates to
P-290 3D Converted Wave Data Processing A case history N. B. R. Prasad, ONGC Summary In recent years, there has been a growing interest in shear- wave exploration for hydrocarbons as it facilitates to
2012 SEG DOI SEG Las Vegas 2012 Annual Meeting Page 1
 Full-azimuth towed-streamer seismic: An exploration tool for pre-salt hydrocarbon exploration offshore Brazil Alex Cooke*, Franck Le Diagon, Ricardo De Marco, Daniela Amazonas, Timothy Bunting, Nick Moldoveanu,
Full-azimuth towed-streamer seismic: An exploration tool for pre-salt hydrocarbon exploration offshore Brazil Alex Cooke*, Franck Le Diagon, Ricardo De Marco, Daniela Amazonas, Timothy Bunting, Nick Moldoveanu,
Plane-wave migration in tilted coordinates
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 124, April 4, 2006, pages 1 16 Plane-wave migration in tilted coordinates Guojian Shan and Biondo Biondi ABSTRACT Plane-wave migration in tilted coordinates is powerful
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 124, April 4, 2006, pages 1 16 Plane-wave migration in tilted coordinates Guojian Shan and Biondo Biondi ABSTRACT Plane-wave migration in tilted coordinates is powerful
SEG Houston 2009 International Exposition and Annual Meeting
 Salt interpretation validated by salt tectonic study in the offshore Gulf of Mexico Li Li *, Itze Chang and Quincy Zhang, TGS-NOPEC Geophysical Company Summary To identify and define a complex salt body
Salt interpretation validated by salt tectonic study in the offshore Gulf of Mexico Li Li *, Itze Chang and Quincy Zhang, TGS-NOPEC Geophysical Company Summary To identify and define a complex salt body
Downloaded 09/16/16 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Data Using a Facies Based Bayesian Seismic Inversion, Forties Field, UKCS Kester Waters* (Ikon Science Ltd), Ana Somoza (Ikon Science Ltd), Grant Byerley (Apache Corp), Phil Rose (Apache UK) Summary The
Data Using a Facies Based Bayesian Seismic Inversion, Forties Field, UKCS Kester Waters* (Ikon Science Ltd), Ana Somoza (Ikon Science Ltd), Grant Byerley (Apache Corp), Phil Rose (Apache UK) Summary The
Downloaded 10/02/18 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Multi-scenario, multi-realization seismic inversion for probabilistic seismic reservoir characterization Kester Waters* and Michael Kemper, Ikon Science Ltd. Summary We propose a two tiered inversion strategy
Multi-scenario, multi-realization seismic inversion for probabilistic seismic reservoir characterization Kester Waters* and Michael Kemper, Ikon Science Ltd. Summary We propose a two tiered inversion strategy
A 3D illumination study to investigate fault shadow effects over the Hoop Fault Complex Anthony Hardwick* and Litty Rajesh, TGS
 A 3D illumination study to investigate fault shadow effects over the Hoop Fault Complex Anthony Hardwick* and Litty Rajesh, TGS Summary Fault shadows represent zones of unreliable seismic imaging in the
A 3D illumination study to investigate fault shadow effects over the Hoop Fault Complex Anthony Hardwick* and Litty Rajesh, TGS Summary Fault shadows represent zones of unreliable seismic imaging in the
Tomography for Static Corrections and Prestack Depth Imaging
 Tomography for Static Corrections and Prestack Depth Imaging Xianhuai Zhu, Ph.D. Fusion Petroleum Technologies Inc. 25231 Grogan's Mill Road, Suite 175 The Woodlands, TX 77380, USA Summary Turning-ray
Tomography for Static Corrections and Prestack Depth Imaging Xianhuai Zhu, Ph.D. Fusion Petroleum Technologies Inc. 25231 Grogan's Mill Road, Suite 175 The Woodlands, TX 77380, USA Summary Turning-ray
Downloaded 11/20/12 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 AVO crossplot analysis in unconsolidated sediments containing gas hydrate and free gas: Green Canyon 955, Gulf of Mexico Zijian Zhang* 1, Daniel R. McConnell 1, De-hua Han 2 1 Fugro GeoConsulting, Inc.,
AVO crossplot analysis in unconsolidated sediments containing gas hydrate and free gas: Green Canyon 955, Gulf of Mexico Zijian Zhang* 1, Daniel R. McConnell 1, De-hua Han 2 1 Fugro GeoConsulting, Inc.,
Anisotropic 2.5D Inversion of Towed Streamer EM Data from Three North Sea Fields Using Parallel Adaptive Finite Elements
 Anisotropic 2.5D Inversion of Towed Streamer EM Data from Three North Sea Fields Using Parallel Adaptive Finite Elements K. Key (Scripps Institution of Oceanography), Z. Du* (PGS), J. Mattsson (PGS), A.
Anisotropic 2.5D Inversion of Towed Streamer EM Data from Three North Sea Fields Using Parallel Adaptive Finite Elements K. Key (Scripps Institution of Oceanography), Z. Du* (PGS), J. Mattsson (PGS), A.
Tu SRS2 07 A Full-waveform Inversion Case Study from Offshore Gabon
 Tu SRS2 07 A Full-waveform Inversion Case Study from Offshore Gabon A. Privitera (CGG), A. Ratcliffe* (CGG) & N. Kotova (CGG) SUMMARY We applied full waveform inversion to a seismic dataset from offshore
Tu SRS2 07 A Full-waveform Inversion Case Study from Offshore Gabon A. Privitera (CGG), A. Ratcliffe* (CGG) & N. Kotova (CGG) SUMMARY We applied full waveform inversion to a seismic dataset from offshore
3D beam prestack depth migration with examples from around the world
 A Publication of Petroleum Geo-Services Vol. 8 No. 8 August 2008 3D beam prestack depth migration with examples from around the world Introduction In 1999 AGS specialized in 2D seismic depth processing.
A Publication of Petroleum Geo-Services Vol. 8 No. 8 August 2008 3D beam prestack depth migration with examples from around the world Introduction In 1999 AGS specialized in 2D seismic depth processing.
RAYFRACT IN MARINE SURVEYS. The data provided by the contractor needed total re-picking and reinterpretation.
 RAYFRACT IN MARINE SURVEYS As part of a geotechnical assessment and feasibility planning of channel improvement a shallow marine seismic refraction survey was undertaken. The data was initially processed
RAYFRACT IN MARINE SURVEYS As part of a geotechnical assessment and feasibility planning of channel improvement a shallow marine seismic refraction survey was undertaken. The data was initially processed
Combining Velocity Model Building and Interpretation Techniques to Reduce Uncertainty in Pre-salt Imaging
 Combining Velocity Model Building and Interpretation Techniques to Reduce Uncertainty in Pre-salt Imaging A. Lewis* (PGS), F. Mathem SUMMARY There is ever increasing interest in exploring pre-salt provinces
Combining Velocity Model Building and Interpretation Techniques to Reduce Uncertainty in Pre-salt Imaging A. Lewis* (PGS), F. Mathem SUMMARY There is ever increasing interest in exploring pre-salt provinces
Shear wave statics in 3D-3C : An alternate approach
 P-157 C. B. Yadava*, M Singh, Kuldeep Prakash, Kunal Niyogi GEOPIC, Oil & Natural Gas Corporation Ltd, Dehradun Summary 3D-3C data was acquired in Sayan-Tadkeshwar area of Cambay basin to bring out sand
P-157 C. B. Yadava*, M Singh, Kuldeep Prakash, Kunal Niyogi GEOPIC, Oil & Natural Gas Corporation Ltd, Dehradun Summary 3D-3C data was acquired in Sayan-Tadkeshwar area of Cambay basin to bring out sand
Interval anisotropic parameters estimation in a least squares sense Case histories from West Africa
 P-263 Summary Interval anisotropic parameters estimation in a least squares sense Patrizia Cibin*, Maurizio Ferla Eni E&P Division (Milano, Italy), Emmanuel Spadavecchia - Politecnico di Milano (Milano,
P-263 Summary Interval anisotropic parameters estimation in a least squares sense Patrizia Cibin*, Maurizio Ferla Eni E&P Division (Milano, Italy), Emmanuel Spadavecchia - Politecnico di Milano (Milano,
Anisotropic tomography for TTI and VTI media Yang He* and Jun Cai, TGS
 media Yang He* and Jun Cai, TGS Summary A simultaneous anisotropic tomographic inversion algorithm is developed. Check shot constraints and appropriate algorithm preconditioning play an important role
media Yang He* and Jun Cai, TGS Summary A simultaneous anisotropic tomographic inversion algorithm is developed. Check shot constraints and appropriate algorithm preconditioning play an important role
Imaging complex structure with crosswell seismic in Jianghan oil field
 INTERPRETER S CORNER Coordinated by Rebecca B. Latimer Imaging complex structure with crosswell seismic in Jianghan oil field QICHENG DONG and BRUCE MARION, Z-Seis, Houston, Texas, U.S. JEFF MEYER, Fusion
INTERPRETER S CORNER Coordinated by Rebecca B. Latimer Imaging complex structure with crosswell seismic in Jianghan oil field QICHENG DONG and BRUCE MARION, Z-Seis, Houston, Texas, U.S. JEFF MEYER, Fusion
Rough sea estimation for phase-shift de-ghosting Sergio Grion*, Rob Telling and Seb Holland, Dolphin Geophysical
 Rough sea estimation for phase-shift de-ghosting Sergio Grion*, Rob Telling and Seb Holland, Dolphin Geophysical Summary This paper discusses rough-sea de-ghosting for variabledepth streamer data. The
Rough sea estimation for phase-shift de-ghosting Sergio Grion*, Rob Telling and Seb Holland, Dolphin Geophysical Summary This paper discusses rough-sea de-ghosting for variabledepth streamer data. The
We LHR3 06 Detecting Production Effects and By-passed Pay from 3D Seismic Data Using a Facies Based Bayesian Seismic Inversion
 We LHR3 06 Detecting Production Effects and By-passed Pay from 3D Seismic Data Using a Facies Based Bayesian Seismic Inversion K.D. Waters* (Ikon Science Ltd), A.V. Somoza (Ikon Science Ltd), G. Byerley
We LHR3 06 Detecting Production Effects and By-passed Pay from 3D Seismic Data Using a Facies Based Bayesian Seismic Inversion K.D. Waters* (Ikon Science Ltd), A.V. Somoza (Ikon Science Ltd), G. Byerley
Identifying faults and gas chimneys using multiattributes and neural networks
 CORNER INTERPRETER S Coordinated by Linda R. Sternbach Identifying faults and gas chimneys using multiattributes and neural networks PAUL MELDAHL and ROAR HEGGLAND, Statoil, Stavanger, Norway BERT BRIL
CORNER INTERPRETER S Coordinated by Linda R. Sternbach Identifying faults and gas chimneys using multiattributes and neural networks PAUL MELDAHL and ROAR HEGGLAND, Statoil, Stavanger, Norway BERT BRIL
Adding Value with Broadband Seismic and Inversion in the Central North Sea Seagull Area
 H2-2-1 Adding Value with Broadband Seismic and Inversion in the Central North Sea Seagull Area Marnix Vermaas, Andy Lind Apache North Sea, Aberdeen, UK Introduction The merits of modern broadband seismic
H2-2-1 Adding Value with Broadband Seismic and Inversion in the Central North Sea Seagull Area Marnix Vermaas, Andy Lind Apache North Sea, Aberdeen, UK Introduction The merits of modern broadband seismic
Hybrid Gridded Tomography. Ian F. Jones Mick Sugrue Pierre Hardy. GX Technology, 180 High Street, Egham, Surrey TW20 9DN, UK
 Hybrid Gridded Tomography By Ian F. Jones Mick Sugrue Pierre Hardy GX Technology, 8 High Street, Egham, Surrey TW 9DN, UK First Break V 5 April 7 P5- Corresponding Author Ian F. Jones ijones@gxt.com Hybrid
Hybrid Gridded Tomography By Ian F. Jones Mick Sugrue Pierre Hardy GX Technology, 8 High Street, Egham, Surrey TW 9DN, UK First Break V 5 April 7 P5- Corresponding Author Ian F. Jones ijones@gxt.com Hybrid
Residual Moveout Correction; its impact on PSTM Processed data: A Case Study
 P - 130 Residual Moveout Correction; its impact on PSTM Processed data: A Case Study Anand Prakash*, S.K.Bora, Anil Kumar, Regional Computer Centre,P-32 Transport Deport Road, Kolkata 700088 a_prakash999@hotmail.com
P - 130 Residual Moveout Correction; its impact on PSTM Processed data: A Case Study Anand Prakash*, S.K.Bora, Anil Kumar, Regional Computer Centre,P-32 Transport Deport Road, Kolkata 700088 a_prakash999@hotmail.com
Improving Resolution with Spectral Balancing- A Case study
 P-299 Improving Resolution with Spectral Balancing- A Case study M Fatima, Lavendra Kumar, RK Bhattacharjee, PH Rao, DP Sinha Western Offshore Basin, ONGC, Panvel, Mumbai Summary: The resolution limit
P-299 Improving Resolution with Spectral Balancing- A Case study M Fatima, Lavendra Kumar, RK Bhattacharjee, PH Rao, DP Sinha Western Offshore Basin, ONGC, Panvel, Mumbai Summary: The resolution limit
IPTC PP Challenges in Shallow Water CSEM Surveying: A Case History from Southeast Asia
 IPTC-11511-PP Challenges in Shallow Water CSEM Surveying: A Case History from Southeast Asia Sandeep K. Chandola*, Rashidah Karim, Amy Mawarni, Russikin Ismail, Noreehan Shahud, Ramlee Rahman, Paul Bernabe
IPTC-11511-PP Challenges in Shallow Water CSEM Surveying: A Case History from Southeast Asia Sandeep K. Chandola*, Rashidah Karim, Amy Mawarni, Russikin Ismail, Noreehan Shahud, Ramlee Rahman, Paul Bernabe
Use of Traveltime Tomographic velocity model beyond imaging: Estimating 3D pore pressure & effective stress volumes
 10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 324 Summary Use of Traveltime Tomographic velocity model beyond imaging: Estimating 3D pore pressure & effective stress volumes Kanharol K Hari*,
10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 324 Summary Use of Traveltime Tomographic velocity model beyond imaging: Estimating 3D pore pressure & effective stress volumes Kanharol K Hari*,
ANGLE-DEPENDENT TOMOSTATICS. Abstract
 ANGLE-DEPENDENT TOMOSTATICS Lindsay M. Mayer, Kansas Geological Survey, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS Richard D. Miller, Kansas Geological Survey, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS Julian Ivanov,
ANGLE-DEPENDENT TOMOSTATICS Lindsay M. Mayer, Kansas Geological Survey, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS Richard D. Miller, Kansas Geological Survey, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS Julian Ivanov,
Chapter 1. Introduction EARTH MODEL BUILDING
 Chapter 1 Introduction Seismic anisotropy in complex earth subsurface has become increasingly important in seismic imaging due to the increasing offset and azimuth in modern seismic data. To account for
Chapter 1 Introduction Seismic anisotropy in complex earth subsurface has become increasingly important in seismic imaging due to the increasing offset and azimuth in modern seismic data. To account for
2011 SEG SEG San Antonio 2011 Annual Meeting 771. Summary. Method
 Geological Parameters Effecting Controlled-Source Electromagnetic Feasibility: A North Sea Sand Reservoir Example Michelle Ellis and Robert Keirstead, RSI Summary Seismic and electromagnetic data measure
Geological Parameters Effecting Controlled-Source Electromagnetic Feasibility: A North Sea Sand Reservoir Example Michelle Ellis and Robert Keirstead, RSI Summary Seismic and electromagnetic data measure
Vertical Hydrocarbon Migration at the Nigerian Continental Slope: Applications of Seismic Mapping Techniques.
 ROAR HEGGLAND, Statoil ASA, N-4035 Stavanger, Norway Vertical Hydrocarbon Migration at the Nigerian Continental Slope: Applications of Seismic Mapping Techniques. Summary By the use of 3D seismic data,
ROAR HEGGLAND, Statoil ASA, N-4035 Stavanger, Norway Vertical Hydrocarbon Migration at the Nigerian Continental Slope: Applications of Seismic Mapping Techniques. Summary By the use of 3D seismic data,
E014 4D Case Study at Ringhorne, Ringhorne East, Balder and Forseti - Integrating OBC with Streamer Data
 E014 4D Case Study at Ringhorne, Ringhorne East, Balder and Forseti - Integrating OBC with Streamer Data M.B. Helgerud* (ExxonMobil E&P), U.K. Tiwari (ExxonMobil E&P), S.G. Woods (ExxonMobil E&P), P. Homonko
E014 4D Case Study at Ringhorne, Ringhorne East, Balder and Forseti - Integrating OBC with Streamer Data M.B. Helgerud* (ExxonMobil E&P), U.K. Tiwari (ExxonMobil E&P), S.G. Woods (ExxonMobil E&P), P. Homonko
VELOCITY REDUCTION - A POINT IN VELOCITY MODEL BUILDING FOR PRE-STACK KIRCHOFF DEPTH MIGRATION
 Physical Geography; Cartography; Geographic Information Systems & Spatial Planing VELOCITY REDUCTION - A POINT IN VELOCITY MODEL BUILDING FOR PRE-STACK KIRCHOFF DEPTH MIGRATION Dr. Maya Grigorova University
Physical Geography; Cartography; Geographic Information Systems & Spatial Planing VELOCITY REDUCTION - A POINT IN VELOCITY MODEL BUILDING FOR PRE-STACK KIRCHOFF DEPTH MIGRATION Dr. Maya Grigorova University
Airborne gravity gradiometer surveying of petroleum systems under Lake Tanganyika, Tanzania
 Airborne gravity gradiometer surveying of petroleum systems under Lake Tanganyika, Tanzania D. Roberts Beach Energy P. Roy Chowdhury CGG S. J. Lowe CGG A. N. Christensen CGG Outline Introduction Geology
Airborne gravity gradiometer surveying of petroleum systems under Lake Tanganyika, Tanzania D. Roberts Beach Energy P. Roy Chowdhury CGG S. J. Lowe CGG A. N. Christensen CGG Outline Introduction Geology
Multiattributes and Seismic Interpretation of Offshore Exploratory Block in Bahrain A Case Study
 Multiattributes and Seismic Interpretation of Offshore Exploratory Block in Bahrain A Case Study Suresh Thampi, Aqeel Ahmed, Yahya Al-Ansari, Ali Shehab, Ahmed Fateh, Anindya Ghosh, Ghada Almoulani. The
Multiattributes and Seismic Interpretation of Offshore Exploratory Block in Bahrain A Case Study Suresh Thampi, Aqeel Ahmed, Yahya Al-Ansari, Ali Shehab, Ahmed Fateh, Anindya Ghosh, Ghada Almoulani. The
MUHAMMAD S TAMANNAI, DOUGLAS WINSTONE, IAN DEIGHTON & PETER CONN, TGS Nopec Geological Products and Services, London, United Kingdom
 Geological and Geophysical Evaluation of Offshore Morondava Frontier Basin based on Satellite Gravity, Well and regional 2D Seismic Data Interpretation MUHAMMAD S TAMANNAI, DOUGLAS WINSTONE, IAN DEIGHTON
Geological and Geophysical Evaluation of Offshore Morondava Frontier Basin based on Satellite Gravity, Well and regional 2D Seismic Data Interpretation MUHAMMAD S TAMANNAI, DOUGLAS WINSTONE, IAN DEIGHTON
Using seismic guided EM inversion to explore a complex geological area: An application to the Kraken and Bressay heavy oil discoveries, North Sea
 Using seismic guided EM inversion to explore a complex geological area: An application to the Kraken and Bressay heavy oil discoveries, North Sea Zhijun Du*, PGS Summary The integrated analysis of controlled
Using seismic guided EM inversion to explore a complex geological area: An application to the Kraken and Bressay heavy oil discoveries, North Sea Zhijun Du*, PGS Summary The integrated analysis of controlled
Hydrocarbon Trap Classification Based on Associated Gas Chimneys
 Chapter 14 Hydrocarbon Trap Classification Based on Associated Gas Chimneys Roar Heggland 1 Abstract Oil seeps, shallow gas, and surface features such as seabed pockmarks and mud volcanoes are historically
Chapter 14 Hydrocarbon Trap Classification Based on Associated Gas Chimneys Roar Heggland 1 Abstract Oil seeps, shallow gas, and surface features such as seabed pockmarks and mud volcanoes are historically
Summary. Introduction
 with constrained iterative tomography: Methodology and application Hans Kristian Helgesen* (Statoil), Jun Tang (WesternGeco), Jinjun Liu (Statoil), Antoun Salama, Randolph Pepper, Sam Madden, Marta Woodward,
with constrained iterative tomography: Methodology and application Hans Kristian Helgesen* (Statoil), Jun Tang (WesternGeco), Jinjun Liu (Statoil), Antoun Salama, Randolph Pepper, Sam Madden, Marta Woodward,
Seismic Inversion on 3D Data of Bassein Field, India
 5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 526-532 Seismic Inversion on 3D Data of Bassein Field, India K.Sridhar, A.A.K.Sundaram, V.B.G.Tilak & Shyam Mohan Institute
5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 526-532 Seismic Inversion on 3D Data of Bassein Field, India K.Sridhar, A.A.K.Sundaram, V.B.G.Tilak & Shyam Mohan Institute
The 2D/3D i-stats Workflow for Image-Based Near-Surface Modeling for Statics Corrections
 The 2D/3D i-stats Workflow for Image-Based Near-Surface Modeling for Statics Corrections Öz Yilmaz CTO, GeoTomo LLC With the i-stats workflow, you no longer need first-break picking as for traveltime tomography,
The 2D/3D i-stats Workflow for Image-Based Near-Surface Modeling for Statics Corrections Öz Yilmaz CTO, GeoTomo LLC With the i-stats workflow, you no longer need first-break picking as for traveltime tomography,
Absorption related velocity dispersion below a possible gas hydrate geobody. Ian F. Jones, ION GX Technology, UK
 Ian F. Jones, ION GX Technology, UK Abstract Velocity dispersion is not usually a problem in surface seismic data processing, as the seismic bandwidth is relatively narrow, and thus for most Q values,
Ian F. Jones, ION GX Technology, UK Abstract Velocity dispersion is not usually a problem in surface seismic data processing, as the seismic bandwidth is relatively narrow, and thus for most Q values,
SCEC Community Fault and Velocity Models and how they might contribute to the DCPP seismic hazard assessment. Andreas Plesch Harvard University
 SCEC Community Fault and Velocity Models and how they might contribute to the DCPP seismic hazard assessment Andreas Plesch Harvard University SCEC Unified Structural Representation (USR) The SCEC USR
SCEC Community Fault and Velocity Models and how they might contribute to the DCPP seismic hazard assessment Andreas Plesch Harvard University SCEC Unified Structural Representation (USR) The SCEC USR
Depth Imaging through Surface Carbonates: A 2D example from the Canadian Rocky Mountains
 Depth Imaging through Surface Carbonates: A 2D example from the Canadian Rocky Mountains Yong Hua* University of Calgary, Calgary, AB yhua@ucalgary.ca and Don Lawton University of Calgary, Calgary, AB,
Depth Imaging through Surface Carbonates: A 2D example from the Canadian Rocky Mountains Yong Hua* University of Calgary, Calgary, AB yhua@ucalgary.ca and Don Lawton University of Calgary, Calgary, AB,
SUMMARY ANGLE DECOMPOSITION INTRODUCTION. A conventional cross-correlation imaging condition for wave-equation migration is (Claerbout, 1985)
 Comparison of angle decomposition methods for wave-equation migration Natalya Patrikeeva and Paul Sava, Center for Wave Phenomena, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY Angle domain common image gathers offer
Comparison of angle decomposition methods for wave-equation migration Natalya Patrikeeva and Paul Sava, Center for Wave Phenomena, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY Angle domain common image gathers offer
Salt Geology and New Plays in Deep-Water Gulf of Mexico* By Abu Chowdhury 1 and Laura Borton 1
 Salt Geology and New Plays in Deep-Water Gulf of Mexico* By Abu Chowdhury 1 and Laura Borton 1 Search and Discovery Article #10131 (2007) Posted August 25, 2007 *Adapted from extended abstract prepared
Salt Geology and New Plays in Deep-Water Gulf of Mexico* By Abu Chowdhury 1 and Laura Borton 1 Search and Discovery Article #10131 (2007) Posted August 25, 2007 *Adapted from extended abstract prepared
Seismic Attributes and Their Applications in Seismic Geomorphology
 Academic article Seismic Attributes and Their Applications in Seismic Geomorphology Sanhasuk Koson, Piyaphong Chenrai* and Montri Choowong Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University,
Academic article Seismic Attributes and Their Applications in Seismic Geomorphology Sanhasuk Koson, Piyaphong Chenrai* and Montri Choowong Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University,
Seismic Guided Drilling: Near Real Time 3D Updating of Subsurface Images and Pore Pressure Model
 IPTC 16575 Seismic Guided Drilling: Near Real Time 3D Updating of Subsurface Images and Pore Pressure Model Chuck Peng, John Dai and Sherman Yang, Schlumberger WesternGeco Copyright 2013, International
IPTC 16575 Seismic Guided Drilling: Near Real Time 3D Updating of Subsurface Images and Pore Pressure Model Chuck Peng, John Dai and Sherman Yang, Schlumberger WesternGeco Copyright 2013, International
Earth s Continents and Seafloors. GEOL100 Physical Geology Ray Rector - Instructor
 Earth s Continents and Seafloors GEOL100 Physical Geology Ray Rector - Instructor OCEAN BASINS and CONTINENTAL PLATFORMS Key Concepts I. Earth s rocky surface covered by of two types of crust Dense, thin,
Earth s Continents and Seafloors GEOL100 Physical Geology Ray Rector - Instructor OCEAN BASINS and CONTINENTAL PLATFORMS Key Concepts I. Earth s rocky surface covered by of two types of crust Dense, thin,
From PZ summation to wavefield separation, mirror imaging and up-down deconvolution: the evolution of ocean-bottom seismic data processing
 From PZ summation to wavefield separation, mirror imaging and up-down deconvolution: the evolution of ocean-bottom seismic data processing Sergio Grion, CGGVeritas Summary This paper discusses present
From PZ summation to wavefield separation, mirror imaging and up-down deconvolution: the evolution of ocean-bottom seismic data processing Sergio Grion, CGGVeritas Summary This paper discusses present
SEG Houston 2009 International Exposition and Annual Meeting
 The role of EM rock physics and seismic data in integrated 3D CSEM data analysis I. Brevik*, StatoilHydro, Pål T. Gabrielsen, Vestfonna and Jan Petter Morten, EMGS Summary An extensive 3D CSEM dataset
The role of EM rock physics and seismic data in integrated 3D CSEM data analysis I. Brevik*, StatoilHydro, Pål T. Gabrielsen, Vestfonna and Jan Petter Morten, EMGS Summary An extensive 3D CSEM dataset
F003 Geomodel Update Using 4-D Petrophysical Seismic Inversion on the Troll West Field
 F003 Geomodel Update Using 4-D Petrophysical Seismic Inversion on the Troll West Field K. Gjerding* (Statoil), N. Skjei (Statoil), A. Norenes Haaland (Statoil), I. Machecler (CGGVeritas Services) & T.
F003 Geomodel Update Using 4-D Petrophysical Seismic Inversion on the Troll West Field K. Gjerding* (Statoil), N. Skjei (Statoil), A. Norenes Haaland (Statoil), I. Machecler (CGGVeritas Services) & T.
Towed Streamer EM data from Barents Sea, Norway
 Towed Streamer EM data from Barents Sea, Norway Anwar Bhuiyan*, Eivind Vesterås and Allan McKay, PGS Summary The measured Towed Streamer EM data from a survey in the Barents Sea, undertaken in the Norwegian
Towed Streamer EM data from Barents Sea, Norway Anwar Bhuiyan*, Eivind Vesterås and Allan McKay, PGS Summary The measured Towed Streamer EM data from a survey in the Barents Sea, undertaken in the Norwegian
Sub Basalt Imaging Using Low Frequency Processing and Angle stack In Saurashtra Region, Western India
 5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 90-94 Sub Basalt Imaging Using Low Frequency Processing and Angle stack In Saurashtra Region, Western India A.K.Sarkar & R.Mohan
5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 90-94 Sub Basalt Imaging Using Low Frequency Processing and Angle stack In Saurashtra Region, Western India A.K.Sarkar & R.Mohan
Improving the quality of Velocity Models and Seismic Images. Alice Chanvin-Laaouissi
 Improving the quality of Velocity Models and Seismic Images Alice Chanvin-Laaouissi 2015, 2015, PARADIGM. PARADIGM. ALL RIGHTS ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. RESERVED. Velocity Volumes Challenges 1. Define sealed
Improving the quality of Velocity Models and Seismic Images Alice Chanvin-Laaouissi 2015, 2015, PARADIGM. PARADIGM. ALL RIGHTS ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. RESERVED. Velocity Volumes Challenges 1. Define sealed
Optimizing seismic repeatability at Ringhorne, Ringhorne East, Balder and Forseti with QC driven time-lapse processing
 with QC driven time-lapse processing Michael B Helgerud, Upendra Tiwari, Stephen Woods (ExxonMobil Exploration Company) Peter Homonko (ExxonMobil International Limited) Adam Bucki and Bernard Laugier (ExxonMobil
with QC driven time-lapse processing Michael B Helgerud, Upendra Tiwari, Stephen Woods (ExxonMobil Exploration Company) Peter Homonko (ExxonMobil International Limited) Adam Bucki and Bernard Laugier (ExxonMobil
A Broadband marine CSEM demonstration survey to map the Uranus salt structure
 A Broadband marine CSEM demonstration survey to map the Uranus salt structure M. Vöge ( 1 ), A. A. Pfaffhuber ( 1 ), K. Hokstad ( 2 ), B. Fotland( 2 ) ( 1 ) Norwegian Geotechnical Institute, Sognsveien
A Broadband marine CSEM demonstration survey to map the Uranus salt structure M. Vöge ( 1 ), A. A. Pfaffhuber ( 1 ), K. Hokstad ( 2 ), B. Fotland( 2 ) ( 1 ) Norwegian Geotechnical Institute, Sognsveien
Pre Stack Imaging To Delineate A New Hydrocarbon Play A Case History
 5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 375-379 Pre Stack Imaging To Delineate A New Hydrocarbon Play A Case History D. Srinivas, T.R. Murali Mohan, Ashwani Lamba,
5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 375-379 Pre Stack Imaging To Delineate A New Hydrocarbon Play A Case History D. Srinivas, T.R. Murali Mohan, Ashwani Lamba,
HORDA SURVEY HERALDS NEW STRATEGY
 HORDA SURVEY HERALDS NEW STRATEGY CGG sets sights on multi-client market leadership in Norway BY IDAR HORSTAD, ERLING FRANTZEN AND JO FIRTH, CGG 12 seismic profile Figure 1: Reprocessing of the Cornerstone
HORDA SURVEY HERALDS NEW STRATEGY CGG sets sights on multi-client market leadership in Norway BY IDAR HORSTAD, ERLING FRANTZEN AND JO FIRTH, CGG 12 seismic profile Figure 1: Reprocessing of the Cornerstone
Imaging challenges and processing solutions in the Brazilian Equatorial Margin: A case study in the Barreirinhas Basin
 Imaging challenges and processing solutions in the Brazilian Equatorial Margin: A case study in the Barreirinhas Basin Karine Pereira 1, Yamen Belhassen 1, Erick Tomaz 1, Sonia Domont 1, and Diego Carotti
Imaging challenges and processing solutions in the Brazilian Equatorial Margin: A case study in the Barreirinhas Basin Karine Pereira 1, Yamen Belhassen 1, Erick Tomaz 1, Sonia Domont 1, and Diego Carotti
Prestack Depth Migration - An ultimate aspiration for subsurface imaging in geologically complex area.
 P-119 Prestack Depth Migration - An ultimate aspiration for subsurface imaging in geologically complex area. R. L. Basak*, A. K. Rao, and S. S. Rawat, ONGC, India. Summary Over the last decade, it is predominantly
P-119 Prestack Depth Migration - An ultimate aspiration for subsurface imaging in geologically complex area. R. L. Basak*, A. K. Rao, and S. S. Rawat, ONGC, India. Summary Over the last decade, it is predominantly
