Estimating vertical and horizontal resistivity of the overburden and the reservoir for the Alvheim Boa field. Folke Engelmark* and Johan Mattsson, PGS
|
|
|
- Allyson Phillips
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Estimating vertical and horizontal resistivity of the overburden and the reservoir for the Alvheim Boa field. Folke Engelmark* and Johan Mattsson, PGS Summary Towed streamer EM data was acquired in October 2012 over the Alvheim Boa Field located in the Norwegian sector of the North Sea. It is a challenging target consisting of a medium sized oil & gas field exhibiting an average transverse resistance located at 2,100 m below mudline. A depth model was defined for both the overburden and the reservoir interval based on an available well log, and the data was inverted as a series of 1D inversions for all common mid-points along two survey lines to form 2D resistivity sections. Both the vertical and horizontal resistivities were inverted for by minimizing the difference in the frequency responses between forward modeled data and the acquired towed streamer EM field data. Hence, the inversions were done with only a ten layer depth model as background information plus one value for the underburden. The reservoir interval itself displays high anisotropy as expected since the reservoir is a turbidite. It consists of high resistivity hydrocarbon-charged sands inter-bedded with low resistivity shales giving rise to an effective anisotropy ratio of around 5, whereas the proximal overburden layer exhibits an anisotropy of 2.6. When the anisotropy can be evaluated, the net-to-gross can be estimated facilitating a much improved quantitative estimate of the hydrocarbons in place. Further, when an anisotropic reservoir is located in proximity to or directly on top of basement it can be detected by means of the anisotropy alone. The basement is likely to be isotropic or even display inverse anisotropy due to vertical fractures being more abundant, wider and hence also better conducting than tight horizontal fractures. size and a depth of burial at 2,100 m below mudline. The reservoir is a turbidite. They are notoriously difficult to evaluate, even in wireline log data, and often show a rather low net-to-gross (N/G). A weak but consistent anomaly is seen in the towed streamer EM data next to the depocenter, and most significant is that a series of 1D cmp inversions along the survey lines results in a strong anisotropy to be assigned to the reservoir, in order for the inversion to converge properly. The anisotropy is not intrinsic to any lithology but arises as an effective anisotropy from the nature of turbidite reservoirs, where the highly resistive hydrocarbon-charged sands are inter-bedded with low resistivity shales. The towed streamer EM acquisition method The layout of the acquisition system is shown in Figure 1 below. The bi-pole source is 800 m long and towed at 10 m depth. The source-signal sequence is 120 s long with the source active the first 100 s followed by 20 s of no signal that is used for background noise estimation and noise reduction processing. The source runs at 1,500 amperes and the source signal is user selectable. Our current favorite is the so called Optimized Repeated Sequence (ORS). It can be viewed as a square-wave with twice the density of the discrete harmonics seen in a regular square-wave. The EM streamer has effectively 26 offsets varying from 0 7,700 m and it is towed at a nominal depth of 100 m. The maximum water depth is 400 m. Greater water depths are acceptable if the target is large, shallow below mudline, and highly resistive. The towing speed is 4 5 knots. Introduction Controlled source electro-magnetic (CSEM) marine methods have traditionally been node-based systems, where the receivers are placed as autonomous recording stations on the seafloor in a very sparse line or areal pattern. The source is then towed close to the seafloor emitting a constant source signal, which is typically a square-wave. The first available towed streamer EM system was tested in its final form in October The similarities to seismic acquisition are obvious, and the advantages are many including acquisition speed at 4-5 knots, fixed source - receiver geometry, dense common mid-point (cmp) sampling, real-time quality control and on-board processing facilitating a quick-look at the transverse resistance of the reservoir. The Alvheim Boa reservoir, known as the Alvheim sandstone, is a challenging target due to average Figure 1: The layout of the acquisition system is similar to 2D seismic. The 800 m long bi-pole source is towed at 10 m emitting a 1,500 A source signal. The streamer has offsets from 0-7,700 m and it is towed at a nominal depth of 100 m. The towing speed is 4 5 knots. Noise reduction is implemented in a number of different ways as described by Mattsson et al (2012). Stochastic
2 noise is attenuated by two methods. First the dense sampling both within the streamer and along the survey lines facilitates noise reduction by stacking which improves signal-to-noise by a factor N 1/2, where N is the number of stacked signals. The second method is the so-called low rank approximation based on singular value decomposition. It takes advantage of the fact that the signal occupies only discrete frequencies, whereas the stochastic noise is spread throughout the spectrum. By identifying the discrete signal frequencies, all noise between these frequencies can be removed. estimated resistivity based on a transform from velocity to resistivity for shales as described in Engelmark (2010). The two yellow fields highlight the Utsira sand ( m) and the Heimdal sandstone, which is the Alvheim Boa reservoir ( m). The resistivity log, in this case a deep induction log, measures horizontal resistivity. Modern tri-axial tools that simultaneously measure vertical and horizontal resistivity have been introduced, but are still rarely used. The survey lines and the Alvheim Boa field The two survey lines strike in the NNE direction in parallel over the Boa reservoir as seen in Figure 2. The locations of the lines are suboptimal due to permit constraints and existing infrastructure in the area, but they are traversing very close to the Boa depocenter as mapped from the seismic data and seen in warm colors to the left of the survey lines. Immediately to the right of these, there is a reference line showing the common distance for both lines from an arbitrary point outside the reservoir. The direction of sailing is also shown as South to North for line 201 and from North to South for line 202. Figure 3: Resistivity log (red) from a well penetrating the Boa reservoir (2,020 2,330 m below mudline) outside the hydrocarbon charged volume. The green curve is a shale-resistivity model based on the sonic log. Major sands are highlighted in yellow where the shale model deviates from the log as expected. The Utsira sand (shallow) and Heimdal reservoir (deep) are highlighted in yellow. Resistivity estimation Figure 2: The Alvheim Boa oil and gas field. The two survey lines are shown as magenta dotted lines. The Boa depocenter mapped from seismic is seen as the red anomaly immediately to the left of the lines. The color scale shows the reservoir thickness in meters. The solid magenta line is a reference line in meters common to both survey lines. Line 201 was shot from South to North, and Line 202 from North to South. Figure 3 below shows the deep induction resistivity log (red) from well 1 in the field. The green curve is the The vertical and horizontal resistivities below the mud-line were estimated along the two survey lines by means of 1D multi-trace anisotropic inversion. The 1D inversions were done individually for each common-mid-point (cmp) and then stitched together to form a 2D resistivity section along the survey lines. The inversion is formulated as a minimization problem using a trust-region-reflective algorithm based on the interior-reflective Newton method, described by Coleman and Li (1994, 1996). Each iteration involves the approximate solution of a large linear system using the method of preconditioned conjugate gradients. The objective function is defined as the L2-norm of the weighted differences between measured and modeled frequency response data. The associated frequency response uncertainties are used in the weights to downscale the noisy data. For both survey lines an eleven layer model has been estimated at each cmp. In this case, the seawater is approximated as one layer with a resistivity of ohmm taken from a conductivity, temperature & depth (CTD) measurements. The water depth is estimated from echo sounder measurements on board the vessel. The water depth varies in the model from 110 m in the north of the
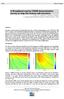
3 lines to 125 m in the south area. The subsea sediments were then divided into ten layers where the first two represent the overburden stretching from seafloor to the base of the Utsira sand for the first layer, and from the base of Utsira to the top of the Heimdal sandstone for the deeper layer. The Heimdal reservoir, also mapped in depth and thickness according to the well log, was then discretized into seven equally thick layers of 70 m followed by a half-space of under-burden. All subsurface layer thicknesses were kept fixed and equal for all cmps during the inversion and it is only the vertical and horizontal resistivities for each layer that are inverted for. Hence, in total ten vertical and ten horizontal resistivity values are estimated through inversion at each cmp. Six frequencies and eight offsets were used for all the inversions as listed below: Frequencies: 0.05, 0.015, 0.20, 0.25, 0.30, and 0.75 Hz. Offsets: 3550, 4000, 4450, 5050, 5650, 6250, 6850, and 7450 m. Even though shorter offsets are used in the streamer, they are neglected in the data going into the inversion. The reason is that a more finely resolved structure based on seismic data is needed to capture the variations in these short offsets. However, to characterize the deeper anomaly region and to roughly estimate the overburden, the set of offsets from m is sufficient. The selected frequency range from the ORS source sequence mentioned above is chosen to be sensitive to the anomaly region but also sufficient to be able to estimate both the vertical and horizontal resistivities in the two layer thick overburden model. Figure 5: The estimated horizontal resistivity for Line 201. Figure 6: The estimated vertical resistivity for Line 202. Figure 4: The estimated vertical resistivity for Line 201. The resulting vertical and horizontal resistivity cross sections are shown in Figures 4 & 5 respectively for Line 201 and in Figures 6 & 7 for Line 202. Line 201 is somewhat closer to the depocenter, hence also showing Figure 7: The estimated horizontal resistivity for Line 202 somewhat stronger anomalies. It can be concluded that the resistivity increase occurs at roughly the same lateral position and depth for both survey lines.
4 The positions of the anomalies also coincide well with the maximum seismic amplitude according to Figure 2. The horizontal resistivity is also seen to increase where the maximum vertical resistivity occurs. Hence, even in a rather thin reservoir layer, there is still some sensitivity to the horizontal component in the inline data. Further, the thicknesses of the anomalies in the cross-sections agree well with expected values. The vertical resistivity is the volumetrically weighted arithmetic average of the oil/gas charged sand and shale resistivities, and the horizontal resistivity is the volumetrically weighted harmonic average of the two lithologies. The peak vertical resistivity along line 201 is around 50 ohm-m, whereas the horizontal resistivity increases to 10 ohm-m as shown in Figure 8 below. Assuming the average resistivity for the shales is 1.1 ohm-m, then the resistivity of the sands must be 55 ohm-m resulting in a N/G of A similar argument for line 202, located more distant from the depocenter than line 201, results in shale and sand resistivities of 1.1 and 24 ohm-m respectively and a N/G of Figure 9: Examples of the difference between measured and modeled frequency amplitude response. Figure 10: Examples of the difference between measured and modeled frequency phase response. Figure 8: The vertical and horizontal resistivities as a function of N/G for Line 201. At a N/G of 0.91 the two resistivities are in agreement with the inverted data. The relative difference, or misfit, between the measured and modeled frequency responses after inversion was plotted as a function of offset and frequency for both the amplitude and the phase. The result for the relative amplitude difference is largely below 4%, as shown in Figure 9, and the phase difference is below 2 % as seen in Figure 10. These values are at similar levels as the residual noise in the field data after processing. Conclusions The Alvheim Boa Field is a challenging target due to the combination of depth below mudline (2,100 m), limited lateral extension of the reservoir s depocenter (~2,000 m) and a low transverse resistance of the reservoir. The survey results and the inverted data show that we can use a data driven inversion to estimate both vertical and horizontal resistivity of the overburden as well as in the reservoir. Further, the reservoir is found to be anisotropic which in principle makes it possible to estimate net-to-gross (N/G) facilitating a better estimate of the hydrocarbons in place. Towed streamer EM data can hence be used to evaluate both the vertical and horizontal resistivity, facilitating an estimate of N/G resulting in improved estimates of hydrocarbon volumes in place. It is especially important when evaluating reservoirs close to or directly on top of the basement, a case that has been considered difficult for EM to resolve. The reservoir interval will show anisotropy due to a limited N/G, for example as in this case a turbidite sand, whereas the basement is likely to be isotropic or having a reversed anisotropy due to vertical fractures being more frequent and more conductive than horizontal fractures. The charged reservoir can then be convincingly detected based on anisotropy alone.
5 EDITED REFERENCES Note: This reference list is a copy-edited version of the reference list submitted by the author. Reference lists for the 2013 SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts have been copy edited so that references provided with the online metadata for each paper will achieve a high degree of linking to cited sources that appear on the Web. REFERENCES Coleman, T. F., and Y. Li, 1994, On the convergence of reflective newton methods for large-scale nonlinear minimization subject to bounds : Mathematical Programming, 67, no. 2, Coleman, T. F., and Y. Li, 1996, An interior, trust region approach for nonlinear minimization subject to bounds: SIAM Journal on Optimization, 6, no. 2, , Engelmark, F., 2010, Velocity to resistivity transform via porosity: Presented at the 80 th Annual International Meeting, SEG. Mattsson, J., P. Lindqvist, R. Juhasz, and E. Björnemo, 2012, Noise reduction and error analysis for a towed EM system: 82 nd Annual International Meeting, SEG, Expanded Abstracts, 1 5.
Modeling and interpretation of CSEM data from Bressay, Bentley and Kraken area of East Shetland Platform, North Sea
 from Bressay, Bentley and Kraken area of East Shetland Platform, North Sea Anwar Bhuiyan*, Rune Sakariassen, Øystein Hallanger and Allan McKay, PGS Summary The heavy oil reservoirs of the Bentley, Bressay
from Bressay, Bentley and Kraken area of East Shetland Platform, North Sea Anwar Bhuiyan*, Rune Sakariassen, Øystein Hallanger and Allan McKay, PGS Summary The heavy oil reservoirs of the Bentley, Bressay
Towed Streamer EM data from Barents Sea, Norway
 Towed Streamer EM data from Barents Sea, Norway Anwar Bhuiyan*, Eivind Vesterås and Allan McKay, PGS Summary The measured Towed Streamer EM data from a survey in the Barents Sea, undertaken in the Norwegian
Towed Streamer EM data from Barents Sea, Norway Anwar Bhuiyan*, Eivind Vesterås and Allan McKay, PGS Summary The measured Towed Streamer EM data from a survey in the Barents Sea, undertaken in the Norwegian
SEG Houston 2009 International Exposition and Annual Meeting
 The role of EM rock physics and seismic data in integrated 3D CSEM data analysis I. Brevik*, StatoilHydro, Pål T. Gabrielsen, Vestfonna and Jan Petter Morten, EMGS Summary An extensive 3D CSEM dataset
The role of EM rock physics and seismic data in integrated 3D CSEM data analysis I. Brevik*, StatoilHydro, Pål T. Gabrielsen, Vestfonna and Jan Petter Morten, EMGS Summary An extensive 3D CSEM dataset
Using seismic guided EM inversion to explore a complex geological area: An application to the Kraken and Bressay heavy oil discoveries, North Sea
 Using seismic guided EM inversion to explore a complex geological area: An application to the Kraken and Bressay heavy oil discoveries, North Sea Zhijun Du*, PGS Summary The integrated analysis of controlled
Using seismic guided EM inversion to explore a complex geological area: An application to the Kraken and Bressay heavy oil discoveries, North Sea Zhijun Du*, PGS Summary The integrated analysis of controlled
Anisotropic 2.5D Inversion of Towed Streamer EM Data from Three North Sea Fields Using Parallel Adaptive Finite Elements
 Anisotropic 2.5D Inversion of Towed Streamer EM Data from Three North Sea Fields Using Parallel Adaptive Finite Elements K. Key (Scripps Institution of Oceanography), Z. Du* (PGS), J. Mattsson (PGS), A.
Anisotropic 2.5D Inversion of Towed Streamer EM Data from Three North Sea Fields Using Parallel Adaptive Finite Elements K. Key (Scripps Institution of Oceanography), Z. Du* (PGS), J. Mattsson (PGS), A.
2011 SEG SEG San Antonio 2011 Annual Meeting 771. Summary. Method
 Geological Parameters Effecting Controlled-Source Electromagnetic Feasibility: A North Sea Sand Reservoir Example Michelle Ellis and Robert Keirstead, RSI Summary Seismic and electromagnetic data measure
Geological Parameters Effecting Controlled-Source Electromagnetic Feasibility: A North Sea Sand Reservoir Example Michelle Ellis and Robert Keirstead, RSI Summary Seismic and electromagnetic data measure
Detection, Delineation and Characterization of Shallow Anomalies Using Dual Sensor Seismic and Towed Streamer EM data
 Detection, Delineation and Characterization of Shallow Anomalies Using Dual Sensor Seismic and Towed Streamer EM data A.J. McKay* (Petroleum Geo-Services ASA), M. Widmaier (Petroleum Geo- Services ASA),
Detection, Delineation and Characterization of Shallow Anomalies Using Dual Sensor Seismic and Towed Streamer EM data A.J. McKay* (Petroleum Geo-Services ASA), M. Widmaier (Petroleum Geo- Services ASA),
Rock physics integration of CSEM and seismic data: a case study based on the Luva gas field.
 Rock physics integration of CSEM and seismic data: a case study based on the Luva gas field. Peter Harris*, Zhijun Du, Harald H. Soleng, Lucy M. MacGregor, Wiebke Olsen, OHM-Rock Solid Images Summary It
Rock physics integration of CSEM and seismic data: a case study based on the Luva gas field. Peter Harris*, Zhijun Du, Harald H. Soleng, Lucy M. MacGregor, Wiebke Olsen, OHM-Rock Solid Images Summary It
Towed Streamer EM Integrated interpretation for accurate characterization of the sub-surface. PETEX, Tuesday 15th of November 2016
 Towed Streamer EM Integrated interpretation for accurate characterization of the sub-surface. PETEX, Tuesday 15th of November 2016 Joshua May Sales and Marketing Manager Agenda Introduction to Towed Streamer
Towed Streamer EM Integrated interpretation for accurate characterization of the sub-surface. PETEX, Tuesday 15th of November 2016 Joshua May Sales and Marketing Manager Agenda Introduction to Towed Streamer
Vertical and horizontal resolution considerations for a joint 3D CSEM and MT inversion
 Antony PRICE*, Total E&P and Don WATTS, WesternGeco Electromagnetics Summary To further explore the potential data content and inherent limitations of a detailed 3D Controlled Source ElectroMagnetic and
Antony PRICE*, Total E&P and Don WATTS, WesternGeco Electromagnetics Summary To further explore the potential data content and inherent limitations of a detailed 3D Controlled Source ElectroMagnetic and
Seismic processing of numerical EM data John W. Neese* and Leon Thomsen, University of Houston
 Seismic processing of numerical EM data John W. Neese* and Leon Thomsen, University of Houston Summary The traditional methods for acquiring and processing CSEM data are very different from those for seismic
Seismic processing of numerical EM data John W. Neese* and Leon Thomsen, University of Houston Summary The traditional methods for acquiring and processing CSEM data are very different from those for seismic
We E Estimation of Induction Noise in a Towed EM Streamer
 We E108 07 Estimation of Induction Noise in a Towed EM Streamer A.L. Tcheheumeni Djanni* (The University of Edinburgh), A. Ziolkowski (The University of Edinburgh) & D. Wright (The University of Edinburgh)
We E108 07 Estimation of Induction Noise in a Towed EM Streamer A.L. Tcheheumeni Djanni* (The University of Edinburgh), A. Ziolkowski (The University of Edinburgh) & D. Wright (The University of Edinburgh)
Downloaded 09/09/15 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Reservoir properties estimation from marine broadband seismic without a-priori well information: A powerful de-risking workflow Cyrille Reiser*, Matt Whaley and Tim Bird, PGS Reservoir Limited Summary
Reservoir properties estimation from marine broadband seismic without a-priori well information: A powerful de-risking workflow Cyrille Reiser*, Matt Whaley and Tim Bird, PGS Reservoir Limited Summary
Downloaded 10/29/15 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 CSEM based Anisotropy trends in the Barents Sea. Slim Bouchrara *, Lucy MacGregor, Amanda Alvarez, Michelle Ellis, Rolf Ackermann, Paola Newton, Robert Keirstead, Alburto Rusic,Yijie Zhou and Hung-Wen
CSEM based Anisotropy trends in the Barents Sea. Slim Bouchrara *, Lucy MacGregor, Amanda Alvarez, Michelle Ellis, Rolf Ackermann, Paola Newton, Robert Keirstead, Alburto Rusic,Yijie Zhou and Hung-Wen
Downloaded 08/29/13 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 New approach to 3D inversion of MCSEM and MMT data using multinary model transform Alexander V. Gribenko and Michael S. Zhdanov, University of Utah and TechnoImaging SUMMARY Marine controlled-source electromagnetic
New approach to 3D inversion of MCSEM and MMT data using multinary model transform Alexander V. Gribenko and Michael S. Zhdanov, University of Utah and TechnoImaging SUMMARY Marine controlled-source electromagnetic
Downloaded 11/02/16 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at Summary.
 in thin sand reservoirs William Marin* and Paola Vera de Newton, Rock Solid Images, and Mario Di Luca, Pacific Exploración y Producción. Summary Rock Physics Templates (RPTs) are useful tools for well
in thin sand reservoirs William Marin* and Paola Vera de Newton, Rock Solid Images, and Mario Di Luca, Pacific Exploración y Producción. Summary Rock Physics Templates (RPTs) are useful tools for well
Case study: North Sea heavy oil reservoir characterization from integrated analysis of towed-streamer EM and dual-sensor seismic data
 Case study: North Sea heavy oil reservoir characterization from integrated analysis of towed-streamer EM and dual-sensor seismic data Zhijun Du 1 and Kerry Key 2 Downloaded 09/29/18 to 67.247.58.89. Redistribution
Case study: North Sea heavy oil reservoir characterization from integrated analysis of towed-streamer EM and dual-sensor seismic data Zhijun Du 1 and Kerry Key 2 Downloaded 09/29/18 to 67.247.58.89. Redistribution
IPTC PP Challenges in Shallow Water CSEM Surveying: A Case History from Southeast Asia
 IPTC-11511-PP Challenges in Shallow Water CSEM Surveying: A Case History from Southeast Asia Sandeep K. Chandola*, Rashidah Karim, Amy Mawarni, Russikin Ismail, Noreehan Shahud, Ramlee Rahman, Paul Bernabe
IPTC-11511-PP Challenges in Shallow Water CSEM Surveying: A Case History from Southeast Asia Sandeep K. Chandola*, Rashidah Karim, Amy Mawarni, Russikin Ismail, Noreehan Shahud, Ramlee Rahman, Paul Bernabe
Improved Exploration, Appraisal and Production Monitoring with Multi-Transient EM Solutions
 Improved Exploration, Appraisal and Production Monitoring with Multi-Transient EM Solutions Folke Engelmark* PGS Multi-Transient EM, Asia-Pacific, Singapore folke.engelmark@pgs.com Summary Successful as
Improved Exploration, Appraisal and Production Monitoring with Multi-Transient EM Solutions Folke Engelmark* PGS Multi-Transient EM, Asia-Pacific, Singapore folke.engelmark@pgs.com Summary Successful as
Summary. Introduction
 Noel Black*, Glenn A. Wilson, TechnoImaging, Alexander V. Gribenko and Michael S. Zhdanov, TechnoImaging and The University of Utah Summary Recent studies have inferred the feasibility of time-lapse controlled-source
Noel Black*, Glenn A. Wilson, TechnoImaging, Alexander V. Gribenko and Michael S. Zhdanov, TechnoImaging and The University of Utah Summary Recent studies have inferred the feasibility of time-lapse controlled-source
RC 1.3. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 1307
 from seismic AVO Xin-Gong Li,University of Houston and IntSeis Inc, De-Hua Han, and Jiajin Liu, University of Houston Donn McGuire, Anadarko Petroleum Corp Summary A new inversion method is tested to directly
from seismic AVO Xin-Gong Li,University of Houston and IntSeis Inc, De-Hua Han, and Jiajin Liu, University of Houston Donn McGuire, Anadarko Petroleum Corp Summary A new inversion method is tested to directly
TIV Contrast Source Inversion of mcsem data
 TIV Contrast ource Inversion of mcem data T. Wiik ( ), L. O. Løseth ( ), B. Ursin ( ), K. Hokstad (, ) ( )epartment for Petroleum Technology and Applied Geophysics, Norwegian University of cience and Technology
TIV Contrast ource Inversion of mcem data T. Wiik ( ), L. O. Løseth ( ), B. Ursin ( ), K. Hokstad (, ) ( )epartment for Petroleum Technology and Applied Geophysics, Norwegian University of cience and Technology
Summary. (a) (b) Introduction
 er well in AC 818, Gulf of Mexico Cam Kanhalangsy, Nick Golubev, Jurgen Johann Zach, Daniel Baltar*, EMGS Americas Summary We present anisotropic 2.5D inversion examples illustrating the possibility to
er well in AC 818, Gulf of Mexico Cam Kanhalangsy, Nick Golubev, Jurgen Johann Zach, Daniel Baltar*, EMGS Americas Summary We present anisotropic 2.5D inversion examples illustrating the possibility to
Enhancing the resolution of CSEM inversion using seismic constraints Peter Harris*, Rock Solid Images AS Lucy MacGregor, OHM Surveys Ltd
 Enhancing the resolution of CSEM inversion using seismic constraints Peter Harris*, Rock Solid Images AS Lucy MacGregor, OHM Surveys Ltd Summary The vertical resolution of inverted CSEM data remains an
Enhancing the resolution of CSEM inversion using seismic constraints Peter Harris*, Rock Solid Images AS Lucy MacGregor, OHM Surveys Ltd Summary The vertical resolution of inverted CSEM data remains an
Integrating rock physics and full elastic modeling for reservoir characterization Mosab Nasser and John B. Sinton*, Maersk Oil Houston Inc.
 Integrating rock physics and full elastic modeling for reservoir characterization Mosab Nasser and John B. Sinton*, Maersk Oil Houston Inc. Summary Rock physics establishes the link between reservoir properties,
Integrating rock physics and full elastic modeling for reservoir characterization Mosab Nasser and John B. Sinton*, Maersk Oil Houston Inc. Summary Rock physics establishes the link between reservoir properties,
Anisotropic tomography for TTI and VTI media Yang He* and Jun Cai, TGS
 media Yang He* and Jun Cai, TGS Summary A simultaneous anisotropic tomographic inversion algorithm is developed. Check shot constraints and appropriate algorithm preconditioning play an important role
media Yang He* and Jun Cai, TGS Summary A simultaneous anisotropic tomographic inversion algorithm is developed. Check shot constraints and appropriate algorithm preconditioning play an important role
D034 On the Effects of Anisotropy in Marine CSEM
 D034 On the Effects of Anisotropy in Marine CSEM L.O. Løseth* (Statoil ASA, formerly Dept. of Physics, NTNU), B. Ursin (Dept. of Appl. Geophys., NTNU) & L. Amundsen (Statoil ASA) SUMMARY In marine CSEM
D034 On the Effects of Anisotropy in Marine CSEM L.O. Løseth* (Statoil ASA, formerly Dept. of Physics, NTNU), B. Ursin (Dept. of Appl. Geophys., NTNU) & L. Amundsen (Statoil ASA) SUMMARY In marine CSEM
Tu B3 15 Multi-physics Characterisation of Reservoir Prospects in the Hoop Area of the Barents Sea
 Tu B3 15 Multi-physics Characterisation of Reservoir Prospects in the Hoop Area of the Barents Sea P. Alvarez (RSI), F. Marcy (ENGIE E&P), M. Vrijlandt (ENGIE E&P), K. Nichols (RSI), F. Bolivar (RSI),
Tu B3 15 Multi-physics Characterisation of Reservoir Prospects in the Hoop Area of the Barents Sea P. Alvarez (RSI), F. Marcy (ENGIE E&P), M. Vrijlandt (ENGIE E&P), K. Nichols (RSI), F. Bolivar (RSI),
Optimizing seismic repeatability at Ringhorne, Ringhorne East, Balder and Forseti with QC driven time-lapse processing
 with QC driven time-lapse processing Michael B Helgerud, Upendra Tiwari, Stephen Woods (ExxonMobil Exploration Company) Peter Homonko (ExxonMobil International Limited) Adam Bucki and Bernard Laugier (ExxonMobil
with QC driven time-lapse processing Michael B Helgerud, Upendra Tiwari, Stephen Woods (ExxonMobil Exploration Company) Peter Homonko (ExxonMobil International Limited) Adam Bucki and Bernard Laugier (ExxonMobil
Satish Singh* (IPG Paris, France, Tim Sears (British Gas, UK), Mark Roberts (IPG Paris, Summary. Introduction P - 92
 P - 92 Fine-Scale P- and S-Wave Velocities From Elastic Full Waveform Inversion of Multi-Component and Time-Lapse Data: Future of Quantitative Seismic Imaging Satish Singh* (IPG Paris, France, singh@ipgp.jussieu.fr),
P - 92 Fine-Scale P- and S-Wave Velocities From Elastic Full Waveform Inversion of Multi-Component and Time-Lapse Data: Future of Quantitative Seismic Imaging Satish Singh* (IPG Paris, France, singh@ipgp.jussieu.fr),
Downloaded 09/29/16 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Richard Wright*, James Carter, Ian Atkinson, Erin Gillis, Deric Cameron, and Leona Stead, Nalcor Energy Tom Neugebauer, TGS Jerry Witney, PGS Daniel Hughes and Michael Hall, Airbus Defence and Space Summary
Richard Wright*, James Carter, Ian Atkinson, Erin Gillis, Deric Cameron, and Leona Stead, Nalcor Energy Tom Neugebauer, TGS Jerry Witney, PGS Daniel Hughes and Michael Hall, Airbus Defence and Space Summary
THE USE OF SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES AND SPECTRAL DECOMPOSITION TO SUPPORT THE DRILLING PLAN OF THE URACOA-BOMBAL FIELDS
 THE USE OF SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES AND SPECTRAL DECOMPOSITION TO SUPPORT THE DRILLING PLAN OF THE URACOA-BOMBAL FIELDS Cuesta, Julián* 1, Pérez, Richard 1 ; Hernández, Freddy 1 ; Carrasquel, Williams 1 ; Cabrera,
THE USE OF SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES AND SPECTRAL DECOMPOSITION TO SUPPORT THE DRILLING PLAN OF THE URACOA-BOMBAL FIELDS Cuesta, Julián* 1, Pérez, Richard 1 ; Hernández, Freddy 1 ; Carrasquel, Williams 1 ; Cabrera,
The effect of anticlines on seismic fracture characterization and inversion based on a 3D numerical study
 The effect of anticlines on seismic fracture characterization and inversion based on a 3D numerical study Yungui Xu 1,2, Gabril Chao 3 Xiang-Yang Li 24 1 Geoscience School, University of Edinburgh, UK
The effect of anticlines on seismic fracture characterization and inversion based on a 3D numerical study Yungui Xu 1,2, Gabril Chao 3 Xiang-Yang Li 24 1 Geoscience School, University of Edinburgh, UK
G008 Advancing Marine Controlled Source Electromagnetics in the Santos Basin, Brazil
 G008 Advancing Marine Controlled Source Electromagnetics in the Santos Basin, Brazil M.P. Buonora* (Petrobras), A. Zerilli (WesternGeco Electromagnetics), T. Labruzzo (WesternGeco Electromagnetics) & L.F.
G008 Advancing Marine Controlled Source Electromagnetics in the Santos Basin, Brazil M.P. Buonora* (Petrobras), A. Zerilli (WesternGeco Electromagnetics), T. Labruzzo (WesternGeco Electromagnetics) & L.F.
3D VTI traveltime tomography for near-surface imaging Lina Zhang*, Jie Zhang, Wei Zhang, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC)
 Downloaded 01/03/14 to 16.01.198.34. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/ 3D VTI traveltime tomography for near-surface imaging Lina Zhang*, Jie
Downloaded 01/03/14 to 16.01.198.34. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/ 3D VTI traveltime tomography for near-surface imaging Lina Zhang*, Jie
Downloaded 03/06/15 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Integration of seismic, CSEM and well data in the Perdido basin, Gulf of Mexico Philippe Nivlet, Luis Sánchez Pérez, EMGS Services México, José Antonio Escalera Alcocer, José Trinidad Martínez Vázquez,
Integration of seismic, CSEM and well data in the Perdido basin, Gulf of Mexico Philippe Nivlet, Luis Sánchez Pérez, EMGS Services México, José Antonio Escalera Alcocer, José Trinidad Martínez Vázquez,
Downloaded 09/16/16 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Data Using a Facies Based Bayesian Seismic Inversion, Forties Field, UKCS Kester Waters* (Ikon Science Ltd), Ana Somoza (Ikon Science Ltd), Grant Byerley (Apache Corp), Phil Rose (Apache UK) Summary The
Data Using a Facies Based Bayesian Seismic Inversion, Forties Field, UKCS Kester Waters* (Ikon Science Ltd), Ana Somoza (Ikon Science Ltd), Grant Byerley (Apache Corp), Phil Rose (Apache UK) Summary The
Downloaded 10/29/15 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Electrical anisotropy drivers in the Snøhvit region of the Barents Sea Michelle Ellis*, Lucy MacGregor, Rolf Ackermann, Paola Newton, Robert Keirstead, Alberto Rusic, Slim Bouchrara, Amanda Geck Alvarez,
Electrical anisotropy drivers in the Snøhvit region of the Barents Sea Michelle Ellis*, Lucy MacGregor, Rolf Ackermann, Paola Newton, Robert Keirstead, Alberto Rusic, Slim Bouchrara, Amanda Geck Alvarez,
Elastic full waveform inversion for near surface imaging in CMP domain Zhiyang Liu*, Jie Zhang, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC)
 Elastic full waveform inversion for near surface imaging in CMP domain Zhiyang Liu*, Jie Zhang, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) Summary We develop an elastic full waveform inversion
Elastic full waveform inversion for near surface imaging in CMP domain Zhiyang Liu*, Jie Zhang, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) Summary We develop an elastic full waveform inversion
Downloaded 10/02/18 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Multi-scenario, multi-realization seismic inversion for probabilistic seismic reservoir characterization Kester Waters* and Michael Kemper, Ikon Science Ltd. Summary We propose a two tiered inversion strategy
Multi-scenario, multi-realization seismic inversion for probabilistic seismic reservoir characterization Kester Waters* and Michael Kemper, Ikon Science Ltd. Summary We propose a two tiered inversion strategy
Feasibility and design study of a multicomponent seismic survey: Upper Assam Basin
 P-276 Summary Feasibility and design study of a multicomponent seismic survey: Upper Assam Basin K.L.Mandal*, R.K.Srivastava, S.Saha, Oil India Limited M.K.Sukla, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
P-276 Summary Feasibility and design study of a multicomponent seismic survey: Upper Assam Basin K.L.Mandal*, R.K.Srivastava, S.Saha, Oil India Limited M.K.Sukla, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
2010 SEG SEG Denver 2010 Annual Meeting
 Anisotropic model building with wells and horizons: Gulf of Mexico case study comparing different approaches Andrey Bakulin*, Olga Zdraveva, Yangjun (Kevin) Liu, Kevin Lyons, WesternGeco/Schlumberger Summary
Anisotropic model building with wells and horizons: Gulf of Mexico case study comparing different approaches Andrey Bakulin*, Olga Zdraveva, Yangjun (Kevin) Liu, Kevin Lyons, WesternGeco/Schlumberger Summary
Lithology-based model transform. Summary
 cdf( ) pdf( ) 3D lithological inversion of geophysical data Leif H. Cox*, Glenn A. Wilson, TechnoImaging, Michael S. Zhdanov, University of Utah and TechnoImaging, and Julian Vrbancich, Defense Science
cdf( ) pdf( ) 3D lithological inversion of geophysical data Leif H. Cox*, Glenn A. Wilson, TechnoImaging, Michael S. Zhdanov, University of Utah and TechnoImaging, and Julian Vrbancich, Defense Science
Full-waveform inversion application in different geological settings Denes Vigh*, Jerry Kapoor and Hongyan Li, WesternGeco
 Full-waveform inversion application in different geological settings Denes Vigh*, Jerry Kapoor and Hongyan Li, WesternGeco Summary After the synthetic data inversion examples, real 3D data sets have been
Full-waveform inversion application in different geological settings Denes Vigh*, Jerry Kapoor and Hongyan Li, WesternGeco Summary After the synthetic data inversion examples, real 3D data sets have been
Pluto 1.5 2D ELASTIC MODEL FOR WAVEFIELD INVESTIGATIONS OF SUBSALT OBJECTIVES, DEEP WATER GULF OF MEXICO*
 Pluto 1.5 2D ELASTIC MODEL FOR WAVEFIELD INVESTIGATIONS OF SUBSALT OBJECTIVES, DEEP WATER GULF OF MEXICO* *This paper has been submitted to the EAGE for presentation at the June 2001 EAGE meeting. SUMMARY
Pluto 1.5 2D ELASTIC MODEL FOR WAVEFIELD INVESTIGATIONS OF SUBSALT OBJECTIVES, DEEP WATER GULF OF MEXICO* *This paper has been submitted to the EAGE for presentation at the June 2001 EAGE meeting. SUMMARY
Reducing Uncertainty through Multi-Measurement Integration: from Regional to Reservoir scale
 Reducing Uncertainty through Multi-Measurement Integration: from Regional to Reservoir scale Efthimios Tartaras Data Processing & Modeling Manager, Integrated Electromagnetics CoE, Schlumberger Geosolutions
Reducing Uncertainty through Multi-Measurement Integration: from Regional to Reservoir scale Efthimios Tartaras Data Processing & Modeling Manager, Integrated Electromagnetics CoE, Schlumberger Geosolutions
Keywords. CSEM, Inversion, Resistivity, Kutei Basin, Makassar Strait
 Noor Jehan Ashaari Muhamad* (EMGS Asia Pacific), Ritesh Mohan Joshi (EMGS Asia Pacific), Muhamad Afifie Chan Mahadie Chan (EMGS Asia Pacific) mmuhamad@emgs.com Keywords CSEM, Inversion, Resistivity, Kutei
Noor Jehan Ashaari Muhamad* (EMGS Asia Pacific), Ritesh Mohan Joshi (EMGS Asia Pacific), Muhamad Afifie Chan Mahadie Chan (EMGS Asia Pacific) mmuhamad@emgs.com Keywords CSEM, Inversion, Resistivity, Kutei
X004 3D CSEM Inversion Strategy - An Example Offshore West of Greenland
 X004 3D CSEM Inversion Strategy - An Example Offshore West of Greenland A. Lovatini* (WesternGeco EM - Geosystem), M.D. Watts (WesternGeco EM - Geosystem), K. Umbach (EnCana Corp.) & A. Ferster (EnCana
X004 3D CSEM Inversion Strategy - An Example Offshore West of Greenland A. Lovatini* (WesternGeco EM - Geosystem), M.D. Watts (WesternGeco EM - Geosystem), K. Umbach (EnCana Corp.) & A. Ferster (EnCana
23855 Rock Physics Constraints on Seismic Inversion
 23855 Rock Physics Constraints on Seismic Inversion M. Sams* (Ikon Science Ltd) & D. Saussus (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Seismic data are bandlimited, offset limited and noisy. Consequently interpretation of
23855 Rock Physics Constraints on Seismic Inversion M. Sams* (Ikon Science Ltd) & D. Saussus (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Seismic data are bandlimited, offset limited and noisy. Consequently interpretation of
Summary. Introduction
 Detailed velocity model building in a carbonate karst zone and improving sub-karst images in the Gulf of Mexico Jun Cai*, Hao Xun, Li Li, Yang He, Zhiming Li, Shuqian Dong, Manhong Guo and Bin Wang, TGS
Detailed velocity model building in a carbonate karst zone and improving sub-karst images in the Gulf of Mexico Jun Cai*, Hao Xun, Li Li, Yang He, Zhiming Li, Shuqian Dong, Manhong Guo and Bin Wang, TGS
Downloaded 11/20/12 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 AVO crossplot analysis in unconsolidated sediments containing gas hydrate and free gas: Green Canyon 955, Gulf of Mexico Zijian Zhang* 1, Daniel R. McConnell 1, De-hua Han 2 1 Fugro GeoConsulting, Inc.,
AVO crossplot analysis in unconsolidated sediments containing gas hydrate and free gas: Green Canyon 955, Gulf of Mexico Zijian Zhang* 1, Daniel R. McConnell 1, De-hua Han 2 1 Fugro GeoConsulting, Inc.,
A new model for pore pressure prediction Fuyong Yan* and De-hua Han, Rock Physics Lab, University of Houston Keyin Ren, Nanhai West Corporation, CNOOC
 A new model for pore pressure prediction Fuyong Yan* and De-hua Han, Rock hysics Lab, University of Houston Keyin Ren, Nanhai West Corporation, CNOOC Summary Eaton s equation is the most popularly used
A new model for pore pressure prediction Fuyong Yan* and De-hua Han, Rock hysics Lab, University of Houston Keyin Ren, Nanhai West Corporation, CNOOC Summary Eaton s equation is the most popularly used
A Broadband marine CSEM demonstration survey to map the Uranus salt structure
 A Broadband marine CSEM demonstration survey to map the Uranus salt structure M. Vöge ( 1 ), A. A. Pfaffhuber ( 1 ), K. Hokstad ( 2 ), B. Fotland( 2 ) ( 1 ) Norwegian Geotechnical Institute, Sognsveien
A Broadband marine CSEM demonstration survey to map the Uranus salt structure M. Vöge ( 1 ), A. A. Pfaffhuber ( 1 ), K. Hokstad ( 2 ), B. Fotland( 2 ) ( 1 ) Norwegian Geotechnical Institute, Sognsveien
Imaging complex structure with crosswell seismic in Jianghan oil field
 INTERPRETER S CORNER Coordinated by Rebecca B. Latimer Imaging complex structure with crosswell seismic in Jianghan oil field QICHENG DONG and BRUCE MARION, Z-Seis, Houston, Texas, U.S. JEFF MEYER, Fusion
INTERPRETER S CORNER Coordinated by Rebecca B. Latimer Imaging complex structure with crosswell seismic in Jianghan oil field QICHENG DONG and BRUCE MARION, Z-Seis, Houston, Texas, U.S. JEFF MEYER, Fusion
Geophysical model response in a shale gas
 Geophysical model response in a shale gas Dhananjay Kumar and G. Michael Hoversten Chevron USA Inc. Abstract Shale gas is an important asset now. The production from unconventional reservoir like shale
Geophysical model response in a shale gas Dhananjay Kumar and G. Michael Hoversten Chevron USA Inc. Abstract Shale gas is an important asset now. The production from unconventional reservoir like shale
The role of seismic modeling in Reservoir characterization: A case study from Crestal part of South Mumbai High field
 P-305 The role of seismic modeling in Reservoir characterization: A case study from Crestal part of South Mumbai High field Summary V B Singh*, Mahendra Pratap, ONGC The objective of the modeling was to
P-305 The role of seismic modeling in Reservoir characterization: A case study from Crestal part of South Mumbai High field Summary V B Singh*, Mahendra Pratap, ONGC The objective of the modeling was to
An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks
 An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks YONGYI LI, Paradigm Geophysical, Calgary, Alberta, Canada Clastic sediments, particularly shale, exhibit transverse isotropic
An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks YONGYI LI, Paradigm Geophysical, Calgary, Alberta, Canada Clastic sediments, particularly shale, exhibit transverse isotropic
Velocity Update Using High Resolution Tomography in Santos Basin, Brazil Lingli Hu and Jianhang Zhou, CGGVeritas
 Lingli Hu and Jianhang Zhou, CGGVeritas Summary The exploration interest in the Santos Basin offshore Brazil has increased with the large deep water pre-salt discoveries, such as Tupi and Jupiter. As the
Lingli Hu and Jianhang Zhou, CGGVeritas Summary The exploration interest in the Santos Basin offshore Brazil has increased with the large deep water pre-salt discoveries, such as Tupi and Jupiter. As the
Oil and Gas Research Institute Seismic Analysis Center Faults Detection Using High-Resolution Seismic Reflection Techniques
 Oil and Gas Research Institute Seismic Analysis Center Faults Detection Using High-Resolution Seismic Reflection Techniques Ghunaim T. Al-Anezi (KACST) March 2013 1 Objectives The objective of the survey
Oil and Gas Research Institute Seismic Analysis Center Faults Detection Using High-Resolution Seismic Reflection Techniques Ghunaim T. Al-Anezi (KACST) March 2013 1 Objectives The objective of the survey
Using high-density OBC seismic data to optimize the Andrew satellites development
 Using high-density OBC seismic data to optimize the Andrew satellites development Leendert Padmos, 1* Daniel Davies, 1 Merv Davies 1 and John McGarrity 1 Abstract The processed data from conventional towed-streamer
Using high-density OBC seismic data to optimize the Andrew satellites development Leendert Padmos, 1* Daniel Davies, 1 Merv Davies 1 and John McGarrity 1 Abstract The processed data from conventional towed-streamer
Achieving depth resolution with gradient array survey data through transient electromagnetic inversion
 Achieving depth resolution with gradient array survey data through transient electromagnetic inversion Downloaded /1/17 to 128.189.118.. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of
Achieving depth resolution with gradient array survey data through transient electromagnetic inversion Downloaded /1/17 to 128.189.118.. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of
Statics preserving projection filtering Yann Traonmilin*and Necati Gulunay, CGGVeritas
 Yann Traonmilin*and Necati Gulunay, CGGVeritas Summary Projection filtering has been used for many years in seismic processing as a tool to extract a meaningful signal out of noisy data. We show that its
Yann Traonmilin*and Necati Gulunay, CGGVeritas Summary Projection filtering has been used for many years in seismic processing as a tool to extract a meaningful signal out of noisy data. We show that its
Improved Interpretability via Dual-sensor Towed Streamer 3D Seismic - A Case Study from East China Sea
 Improved Interpretability via Dual-sensor Towed Streamer 3D Seismic - A Case Study from East China Sea S. Rongfu (CNOOC Shanghai), C. Hua (CNOOC Shanghai), W. Yun (CNOOC Shanghai), Z. Yabin (CNOOC Shanghai),
Improved Interpretability via Dual-sensor Towed Streamer 3D Seismic - A Case Study from East China Sea S. Rongfu (CNOOC Shanghai), C. Hua (CNOOC Shanghai), W. Yun (CNOOC Shanghai), Z. Yabin (CNOOC Shanghai),
Deep-Water Reservoir Potential in Frontier Basins Offshore Namibia Using Broadband 3D Seismic
 Deep-Water Reservoir Potential in Frontier Basins Offshore Namibia Using Broadband 3D Seismic E. Polyaeva* (Petroleum Geo-Services), I. Thomas (Chariot Oil and Gas), C. Reiser (Petroleum Geo-Services),
Deep-Water Reservoir Potential in Frontier Basins Offshore Namibia Using Broadband 3D Seismic E. Polyaeva* (Petroleum Geo-Services), I. Thomas (Chariot Oil and Gas), C. Reiser (Petroleum Geo-Services),
Downloaded 01/06/15 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Application of wide-azimuth 3D seismic attributes to predict the microfractures in Block MA area for shale gas exploration in South China Yusheng Zhang* 1, Gang Yu 1, Ximing Wang 1, Xing Liang 2, and Li
Application of wide-azimuth 3D seismic attributes to predict the microfractures in Block MA area for shale gas exploration in South China Yusheng Zhang* 1, Gang Yu 1, Ximing Wang 1, Xing Liang 2, and Li
Available online Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research, 2016, 3(2):1-7. Research Article
 Available online www.jsaer.com, 2016, 3(2):1-7 Research Article ISSN: 2394-2630 CODEN(USA): JSERBR Assessment of the Reliability of Magnetic Method to Delineate Geologic Features in a Basement Complex:
Available online www.jsaer.com, 2016, 3(2):1-7 Research Article ISSN: 2394-2630 CODEN(USA): JSERBR Assessment of the Reliability of Magnetic Method to Delineate Geologic Features in a Basement Complex:
6298 Stress induced azimuthally anisotropic reservoir - AVO modeling
 6298 Stress induced azimuthally anisotropic reservoir - AVO modeling M. Brajanovski* (Curtin University of Technology), B. Gurevich (Curtin University of Technology), D. Nadri (CSIRO) & M. Urosevic (Curtin
6298 Stress induced azimuthally anisotropic reservoir - AVO modeling M. Brajanovski* (Curtin University of Technology), B. Gurevich (Curtin University of Technology), D. Nadri (CSIRO) & M. Urosevic (Curtin
Downloaded 02/06/15 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Vertical and horizontal resistivity analysis by an electrical anisotropy template Zakir Hossain, Paola Vera de Newton* ock Solid Images Inc, 2600 South Gessner oad, Houston, TX 77063, USA Summary Analysis
Vertical and horizontal resistivity analysis by an electrical anisotropy template Zakir Hossain, Paola Vera de Newton* ock Solid Images Inc, 2600 South Gessner oad, Houston, TX 77063, USA Summary Analysis
SACS Internal report Note on the seismic data
 Netherlands Institute of Applied Geoscience TNO - National Geological Survey TNO-report NITG 00-237-B SACS Internal report Note on the seismic data Restricted for SACS-members Date October 2000 Author(s)
Netherlands Institute of Applied Geoscience TNO - National Geological Survey TNO-report NITG 00-237-B SACS Internal report Note on the seismic data Restricted for SACS-members Date October 2000 Author(s)
TOM 2.6. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 2581
 Oz Yilmaz* and Jie Zhang, GeoTomo LLC, Houston, Texas; and Yan Shixin, PetroChina, Beijing, China Summary PetroChina conducted a multichannel large-offset 2-D seismic survey in the Yumen Oil Field, Northwest
Oz Yilmaz* and Jie Zhang, GeoTomo LLC, Houston, Texas; and Yan Shixin, PetroChina, Beijing, China Summary PetroChina conducted a multichannel large-offset 2-D seismic survey in the Yumen Oil Field, Northwest
Time-Lapse Seismic: A Geophysicist s Perspective. Rob Staples Shell E & P Europe. SPE / EAGE workshop Copenhagen, March 2004
 Time-Lapse Seismic: A Geophysicist s Perspective Rob Staples Shell E & P Europe SPE / EAGE workshop Copenhagen, March 2004 1. What do we observe? 2. Noise and detectability 3. Resolution, scale, interference
Time-Lapse Seismic: A Geophysicist s Perspective Rob Staples Shell E & P Europe SPE / EAGE workshop Copenhagen, March 2004 1. What do we observe? 2. Noise and detectability 3. Resolution, scale, interference
Envelope of Fracture Density
 Dragana Todorovic-Marinic* Veritas DGC Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada dragant@veritasdgc.com Dave Gray, Ye Zheng Veritas DGC Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada Glenn Larson and Jean Pelletier Devon Canada
Dragana Todorovic-Marinic* Veritas DGC Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada dragant@veritasdgc.com Dave Gray, Ye Zheng Veritas DGC Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada Glenn Larson and Jean Pelletier Devon Canada
Interval anisotropic parameters estimation in a least squares sense Case histories from West Africa
 P-263 Summary Interval anisotropic parameters estimation in a least squares sense Patrizia Cibin*, Maurizio Ferla Eni E&P Division (Milano, Italy), Emmanuel Spadavecchia - Politecnico di Milano (Milano,
P-263 Summary Interval anisotropic parameters estimation in a least squares sense Patrizia Cibin*, Maurizio Ferla Eni E&P Division (Milano, Italy), Emmanuel Spadavecchia - Politecnico di Milano (Milano,
Reservoir properties inversion from AVO attributes
 Reservoir properties inversion from AVO attributes Xin-gang Chi* and De-hua Han, University of Houston Summary A new rock physics model based inversion method is put forward where the shaly-sand mixture
Reservoir properties inversion from AVO attributes Xin-gang Chi* and De-hua Han, University of Houston Summary A new rock physics model based inversion method is put forward where the shaly-sand mixture
PART A: Short-answer questions (50%; each worth 2%)
 PART A: Short-answer questions (50%; each worth 2%) Your answers should be brief (just a few words) and may be written on these pages if you wish. Remember to hand these pages in with your other exam pages!
PART A: Short-answer questions (50%; each worth 2%) Your answers should be brief (just a few words) and may be written on these pages if you wish. Remember to hand these pages in with your other exam pages!
Observations of Azimuthal Anisotropy in Prestack Seismic Data
 Observations of Azimuthal Anisotropy in Prestack Seismic Data David Gray* CGGVeritas, Calgary, AB, Canada dave.gray@cggveritas.com Summary A method for displaying prestack seismic data that highlights
Observations of Azimuthal Anisotropy in Prestack Seismic Data David Gray* CGGVeritas, Calgary, AB, Canada dave.gray@cggveritas.com Summary A method for displaying prestack seismic data that highlights
X040 Buried Sources and Receivers in a Karsted Desert Environment
 X040 Buried Sources and Receivers in a Karsted Desert Environment C. Berron* (CGGVeritas Services S.A.), E. Forgues (CGGVeritas Services S. A.), M. Jervis (Saudi Aramco), A. Bakulin (Saudi Aramco) & R.
X040 Buried Sources and Receivers in a Karsted Desert Environment C. Berron* (CGGVeritas Services S.A.), E. Forgues (CGGVeritas Services S. A.), M. Jervis (Saudi Aramco), A. Bakulin (Saudi Aramco) & R.
Tu A4 01 Shooting Over the Streamer Spread; a Novel Approach in Seismic Marine Acquisition and Imaging
 Tu A4 01 Shooting Over the Streamer Spread; a Novel Approach in Seismic Marine Acquisition and Imaging V. Vinje* (CGG), J.E. Lie (Lundin Norway), V. Danielsen (Lundin Norway), P.E. Dhelie (Lundin Norway),
Tu A4 01 Shooting Over the Streamer Spread; a Novel Approach in Seismic Marine Acquisition and Imaging V. Vinje* (CGG), J.E. Lie (Lundin Norway), V. Danielsen (Lundin Norway), P.E. Dhelie (Lundin Norway),
2012 SEG DOI SEG Las Vegas 2012 Annual Meeting Page 1
 Full-azimuth towed-streamer seismic: An exploration tool for pre-salt hydrocarbon exploration offshore Brazil Alex Cooke*, Franck Le Diagon, Ricardo De Marco, Daniela Amazonas, Timothy Bunting, Nick Moldoveanu,
Full-azimuth towed-streamer seismic: An exploration tool for pre-salt hydrocarbon exploration offshore Brazil Alex Cooke*, Franck Le Diagon, Ricardo De Marco, Daniela Amazonas, Timothy Bunting, Nick Moldoveanu,
RC 2.7. Main Menu. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 1355
 Thierry Coléou, Fabien Allo and Raphaël Bornard, CGG; Jeff Hamman and Don Caldwell, Marathon Oil Summary We present a seismic inversion method driven by a petroelastic model, providing fine-scale geological
Thierry Coléou, Fabien Allo and Raphaël Bornard, CGG; Jeff Hamman and Don Caldwell, Marathon Oil Summary We present a seismic inversion method driven by a petroelastic model, providing fine-scale geological
Net-to-gross from Seismic P and S Impedances: Estimation and Uncertainty Analysis using Bayesian Statistics
 Net-to-gross from Seismic P and S Impedances: Estimation and Uncertainty Analysis using Bayesian Statistics Summary Madhumita Sengupta*, Ran Bachrach, Niranjan Banik, esterngeco. Net-to-gross (N/G ) is
Net-to-gross from Seismic P and S Impedances: Estimation and Uncertainty Analysis using Bayesian Statistics Summary Madhumita Sengupta*, Ran Bachrach, Niranjan Banik, esterngeco. Net-to-gross (N/G ) is
Anisotropic velocity changes in seismic time-lapse data Jorg Herwanger*, Ed Palmer (WesternGeco), Christian Rau Schiøtt (Hess)
 Anisotropic velocity changes in seismic time-lapse data Jorg Herwanger*, Ed Palmer (WesternGeco), Christian Rau Schiøtt (Hess) Summary Reservoir production causes subsurface deformations and changes in
Anisotropic velocity changes in seismic time-lapse data Jorg Herwanger*, Ed Palmer (WesternGeco), Christian Rau Schiøtt (Hess) Summary Reservoir production causes subsurface deformations and changes in
Rock physics and AVO analysis for lithofacies and pore fluid prediction in a North Sea oil field
 Rock physics and AVO analysis for lithofacies and pore fluid prediction in a North Sea oil field Downloaded 09/12/14 to 84.215.159.82. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use
Rock physics and AVO analysis for lithofacies and pore fluid prediction in a North Sea oil field Downloaded 09/12/14 to 84.215.159.82. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use
F. Bacciotti K. D Amore J. Seguin
 The Role of 4D Seismic Interpretation and Dynamic Modelling in the Successful Drilling of a Late Stage Development Well in the West Brae Field, North Sea F. Bacciotti K. D Amore J. Seguin Introduction
The Role of 4D Seismic Interpretation and Dynamic Modelling in the Successful Drilling of a Late Stage Development Well in the West Brae Field, North Sea F. Bacciotti K. D Amore J. Seguin Introduction
We A Multi-Measurement Integration Case Study from West Loppa Area in the Barents Sea
 We-16-12 A Multi-Measurement ntegration Case Study from West Loppa Area in the Barents Sea. Guerra* (WesternGeco), F. Ceci (WesternGeco), A. Lovatini (WesternGeco), F. Miotti (WesternGeco), G. Milne (WesternGeco),
We-16-12 A Multi-Measurement ntegration Case Study from West Loppa Area in the Barents Sea. Guerra* (WesternGeco), F. Ceci (WesternGeco), A. Lovatini (WesternGeco), F. Miotti (WesternGeco), G. Milne (WesternGeco),
Downloaded 09/10/15 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 The role of legacy seismic in exploring new offshore hydrocarbon provinces or can you teach old data new tricks (technologies)? Howard Nicholls, Lauren Penn, Anna Marszalek, Paolo Esestime, Karyna Rodriguez,
The role of legacy seismic in exploring new offshore hydrocarbon provinces or can you teach old data new tricks (technologies)? Howard Nicholls, Lauren Penn, Anna Marszalek, Paolo Esestime, Karyna Rodriguez,
AVAZ and VVAZ practical analysis to estimate anisotropic properties
 AVAZ and VVAZ practical analysis to estimate anisotropic properties Yexin Liu*, SoftMirrors Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada yexinliu@softmirrors.com Summary Seismic anisotropic properties, such as orientation
AVAZ and VVAZ practical analysis to estimate anisotropic properties Yexin Liu*, SoftMirrors Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada yexinliu@softmirrors.com Summary Seismic anisotropic properties, such as orientation
Summary. 2D potential field migration of gravity fields and their gradients. For a 2D gravity field, we can define the complex intensity:
 Michael S. Zhdanov*, The University of Utah and TechnoImaging, Xiaojun Liu, The University of Utah, and Glenn A. Wilson, TechnoImaging Summary We introduce 2D potential field migration for the interpretation
Michael S. Zhdanov*, The University of Utah and TechnoImaging, Xiaojun Liu, The University of Utah, and Glenn A. Wilson, TechnoImaging Summary We introduce 2D potential field migration for the interpretation
Tu N Fault Shadow Removal over Timor Trough Using Broadband Seismic, FWI and Fault Constrained Tomography
 Tu N118 05 Fault Shadow Removal over Timor Trough Using Broadband Seismic, FWI and Fault Constrained Tomography Y. Guo* (CGG), M. Fujimoto (INPEX), S. Wu (CGG) & Y. Sasaki (INPEX) SUMMARY Thrust-complex
Tu N118 05 Fault Shadow Removal over Timor Trough Using Broadband Seismic, FWI and Fault Constrained Tomography Y. Guo* (CGG), M. Fujimoto (INPEX), S. Wu (CGG) & Y. Sasaki (INPEX) SUMMARY Thrust-complex
AVAZ inversion for fracture orientation and intensity: a physical modeling study
 AVAZ inversion for fracture orientation and intensity: a physical modeling study Faranak Mahmoudian*, Gary F. Margrave, and Joe Wong, University of Calgary. CREWES fmahmoud@ucalgary.ca Summary We present
AVAZ inversion for fracture orientation and intensity: a physical modeling study Faranak Mahmoudian*, Gary F. Margrave, and Joe Wong, University of Calgary. CREWES fmahmoud@ucalgary.ca Summary We present
Integrated Fracture Identification with Z-VSP and Borehole Images: A study from Cambay Basin
 P-124 Integrated Fracture Identification with Z-VSP and Borehole Images: A study from Cambay Basin Sattwati Dey, Jubilant Energy; Chandramani Shrivastva, Schlumberger; Sreemanti Gijare*, Schlumberger;
P-124 Integrated Fracture Identification with Z-VSP and Borehole Images: A study from Cambay Basin Sattwati Dey, Jubilant Energy; Chandramani Shrivastva, Schlumberger; Sreemanti Gijare*, Schlumberger;
Reservoir Characterization using AVO and Seismic Inversion Techniques
 P-205 Reservoir Characterization using AVO and Summary *Abhinav Kumar Dubey, IIT Kharagpur Reservoir characterization is one of the most important components of seismic data interpretation. Conventional
P-205 Reservoir Characterization using AVO and Summary *Abhinav Kumar Dubey, IIT Kharagpur Reservoir characterization is one of the most important components of seismic data interpretation. Conventional
Seismic wavepropagation concepts applied to the interpretation of marine controlled-source electromagnetics
 Seismic wavepropagation concepts applied to the interpretation of marine controlled-source electromagnetics Rune Mittet, EMGS SUMMARY are very useful for the interpretation of seismic data. Moreover, these
Seismic wavepropagation concepts applied to the interpretation of marine controlled-source electromagnetics Rune Mittet, EMGS SUMMARY are very useful for the interpretation of seismic data. Moreover, these
3D Converted Wave Data Processing A case history
 P-290 3D Converted Wave Data Processing A case history N. B. R. Prasad, ONGC Summary In recent years, there has been a growing interest in shear- wave exploration for hydrocarbons as it facilitates to
P-290 3D Converted Wave Data Processing A case history N. B. R. Prasad, ONGC Summary In recent years, there has been a growing interest in shear- wave exploration for hydrocarbons as it facilitates to
Tu SRS3 02 Data Reconstruction and Denoising of Different Wavefield Components Using Green s Theorem
 Tu SRS3 02 Data Reconstruction and Denoising of Different Wavefield Components Using Green s Theorem N. Kazemi* (University of Alberta) & A.C. Ramirez (Statoil) SUMMARY Multicomponent technology is likely
Tu SRS3 02 Data Reconstruction and Denoising of Different Wavefield Components Using Green s Theorem N. Kazemi* (University of Alberta) & A.C. Ramirez (Statoil) SUMMARY Multicomponent technology is likely
TOM 1.7. Sparse Norm Reflection Tomography for Handling Velocity Ambiguities
 SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 2554 Yonadav Sudman, Paradigm and Dan Kosloff, Tel-Aviv University and Paradigm Summary Reflection seismology with the normal range of offsets encountered in seismic surveys
SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 2554 Yonadav Sudman, Paradigm and Dan Kosloff, Tel-Aviv University and Paradigm Summary Reflection seismology with the normal range of offsets encountered in seismic surveys
Main Menu RC 1.5. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 1315
 : Onshore Nigeria Processing, Interpretation and Drilling Case History. Charles Ojo, Piero Licalsi, and Serafino Gemelli, Nigerian Agip Oil Company, Mike Atkins* and Tue Larsen, Veritas DGC Summary During
: Onshore Nigeria Processing, Interpretation and Drilling Case History. Charles Ojo, Piero Licalsi, and Serafino Gemelli, Nigerian Agip Oil Company, Mike Atkins* and Tue Larsen, Veritas DGC Summary During
Time-frequency analysis of seismic data using synchrosqueezing wavelet transform a
 Time-frequency analysis of seismic data using synchrosqueezing wavelet transform a a Published in Journal of Seismic Exploration, 23, no. 4, 303-312, (2014) Yangkang Chen, Tingting Liu, Xiaohong Chen,
Time-frequency analysis of seismic data using synchrosqueezing wavelet transform a a Published in Journal of Seismic Exploration, 23, no. 4, 303-312, (2014) Yangkang Chen, Tingting Liu, Xiaohong Chen,
Compensating visco-acoustic effects in anisotropic resverse-time migration Sang Suh, Kwangjin Yoon, James Cai, and Bin Wang, TGS
 Compensating visco-acoustic effects in anisotropic resverse-time migration Sang Suh, Kwangjin Yoon, James Cai, and Bin Wang, TGS SUMMARY Anelastic properties of the earth cause frequency dependent energy
Compensating visco-acoustic effects in anisotropic resverse-time migration Sang Suh, Kwangjin Yoon, James Cai, and Bin Wang, TGS SUMMARY Anelastic properties of the earth cause frequency dependent energy
2012 SEG SEG Las Vegas 2012 Annual Meeting Page 1
 3D full-waveform inversion at Mariner a shallow North Sea reservoir Marianne Houbiers 1 *, Edward Wiarda 2, Joachim Mispel 1, Dmitry Nikolenko 2, Denes Vigh 2, Bjørn-Egil Knudsen 1, Mark Thompson 1, and
3D full-waveform inversion at Mariner a shallow North Sea reservoir Marianne Houbiers 1 *, Edward Wiarda 2, Joachim Mispel 1, Dmitry Nikolenko 2, Denes Vigh 2, Bjørn-Egil Knudsen 1, Mark Thompson 1, and
