Version 1.1 GIS Syllabus
|
|
|
- Domenic Owen
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CERTIFICATION Version 1.1 GIS Syllabus Endorsed 1
2 Version 1 January 2007 GIS Certification Programme 1. Target The GIS certification is aimed at: Those who wish to demonstrate a robust knowledge of basic principles governing GI techniques and their basic use through a specific software. Those who wish to have evidence that GIS users have certified basic skills. In the Italian situation certification is aimed at: those who wish to have officially recognised national and international certification of their skills in GIS in general and basic skills in the use of a specific software system; schools and study programmes that want to provide an additional professional and technical skill and a recognised professional qualification which can help job-seekers. public bodies and agencies that require an objective certification of the basic knowledge and practical skills of their employees working, at different levels (with different qualifications) and on different tasks, with GIS and spatial data. Private companies working in a range of sectors from GIS to IT networks, etc., that intend to employ people based on an objective evaluation of their knowledge. 2
3 2. Syllabus Module 1: Cartography The following is the syllabus for Module 1 of the GIS certification and provides the basis for the theory test in this module domain. Module goals Module 1 tests the candidate s knowledge of cartography starting with the basics of geodesy which are required in order to use data in a GIS. The candidate must be able to demonstrate knowledge of the most common reference systems, coordinate systems and cartographic projection systems. The candidate shall have a basic knowledge of map characteristics, map operations and on how real world objects can be represented. The candidate shall also be able to demonstrate knowledge of both digital and non-digital map typologies, in order to use them appropriately both outside and inside a GIS. The items with (*) suggest that they can be localized for each country. CATEGORY KNOWLEDGE AREA REF. KNOWLEDGE ITEM 1.1 General concepts 1.2 Classification of cartographic representations The shape of the Earth, physical and reference surfaces Reference systems and datums Coordinates on a curved and planar surface Classification by type of geometric distorsion Classification by scale Know the shapes by which the Earth is approximated and the relative key dimensions Know what is meant by topographic surface, geoid surface, ellipsoid surface and local spheroid Know what geodetic and vertical datums are Know the fundamental aspects of a geodetic reference system (rotational ellipsoid, survey reference point, deviation from the vertical) Know the fundamental aspects of a vertical reference system, understand orthometric height and ellipsoidal height Understand the meaning of latitude, longitude and height above sea level Understand the fundamental aspects and differences between the different coordinates on a curved surface (spherical, ellipsoidal, geoidal, astronomical and geocentric coordinates) Understand what equivalent (equal area), conformal and equidistant maps are Know what very large, large, medium, small and very small scale is. 3
4 CATEGORY KNOWLEDGE AREA REF. KNOWLEDGE ITEM 1.3 International, European and National cartography Classification by projection type Classification by source Classification by content (*) Know, with reference to the scale what technical, topographic, chorographic (intermediate-scale) geographical and cadastral maps are Understand the differences between perspective and conic, cylindrical and azimuthal projections Know the main kinds of projection systems Know what surveyed and derived maps are Understand the concept of cartographic generalisation Understand the difference between base and thematic maps Know how to distinguish the information content between a base and a thematic map Classification by use Understand the difference between a map, a plan and a chart, and distinguish the respective uses of each International cartography European cartography National cartography (*) Understand the key aspects of the UTM (Universal Transverse Mercator) system Understand the key aspects of the WGS84 system Understand the key aspects of ETRF89 (Terrestrial Reference Frame 1989) Understand the key aspects of the UTM ED50 reference system (ellipsoid and orientation) Know the national cartographic bodies Understand the key aspects of cadastral cartography (ellipsoid, orientation, Cassini- Soldner and Gauss-Boaga reference systems, ground control points) and map tiling Know the key aspects of the Roma40 Gauss- Boaga reference system (ellipsoid, orientation, Conformal Gauss cartographic parameters, ground control points) and map tiling Know the key aspects of the UTM ED50 Italian cartography (reference system: ellipsoid, orientation, cartographic coordinates and map tiling) Understand what is meant by the IGM95 network. 4
5 CATEGORY KNOWLEDGE AREA REF. KNOWLEDGE ITEM Cartographic coordinate transformation and conversion Measurement and positional elements, elevation points, contour lines Know what is meant by Regional Technical Map (Carta Tecnica Regionale - CTR) Know the term Coordinate Conversion Know the term Coordinate Transformation Know how to measure lengths and areas at different scales Know how to represent height (elevation points and contours). 1.4 Data quality Basic aspects Understand the terms completeness, logical consistency, positional accuracy, temporal accuracy, thematic accuracy and lineage. 1.5 Digital Elevation Models 1.6 Global Positioning System (GPS) Metadata for cartographic data Digital Elevation Models Global Positioning System (GPS) Know what metadata is and what the main contents should be Know the main metadata standard for GI Know what a Digital Elevation Model is and how it can be generated Know the basic operating principles of the Global Positioning System (GPS) and its use in GIS. 5
6 Module 2: GIS The following is the syllabus for Module 2 of the GIS certification and provides the basis for the theory and/or practical test in this module domain. Module goals Module 2 aims to test the candidate s knowledge of GIS components, data models for the appropriate representation of real world objects in a GIS, the concept of topology, and spatial analysis applied to both raster and vector data which describe both continuous fields and discrete real world entities. CATEGORY KNOWLEDGE AREA REF. KNOWLEDGE ITEM 2.1 Introduction to GIS Basic concepts Understand the term and concept of GIS Devices and file types specific of GIS GIS data and data sources Understand the difference between GIS and Information Systems in general Know the principal GIS application areas Understand and distinguish between the components of a GIS Understand the principal functions of a GIS Know the specific input devices used with GIS and the relevant technical characteristics that differentiate them (where applicable depending on the device: resolution, precision, colour range connector, management and use) Recognise the most common GIS file types and whether they are vector or raster format Distinguish the different types of data used in a GIS Identify the main data sources that can be used in GIS, such as: remotely sensed data, cadastral, paper and digital maps, socioeconomic data Understand the concept of spatial data Identify the different types of attributes (such as nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio) Know the main geographical data formats (such as coverage, geodatabase, shapefile, grid, dxf, dwg, geotiff, GML) Scale in GIS Understand the concept of scale in GIS Georeferencing Understand the concept of georeferencing Know how raster data can be georeferenced Know the function of a raster georeferencing file (World File). 6
7 CATEGORY KNOWLEDGE AREA REF. KNOWLEDGE ITEM 2.2 Data Models Modelling of the Real World Continuous and discrete modelling of the real world Know what a data model is Understand the process of creating a data model Understand the idea of conceptual, logical and physical models Understand the representation of the real world via a vector model Understand the representation of the real world via a raster model Topology Understand the concept of topology Understand the concepts of adjacency, connectivity and area (containment) Know how to differentiate between spaghetti (or CAD) vector data and topological vector data Understand the topological relationships of raster data ( essentially based on the concept of adjacency/nearness). 2.3 DBMS DBMS and GIS Know what a DBMS is Understand the logical structure of a DBMS within GIS Understand the principal operations to be carried out on data in a DBMS (selection, insertion, updating, deletion). 2.4 Data analysis Spatial Analysis Understand the main kinds of raster spatial analysis Attributes based analysis Understand the main kinds of single layer vector spatial analysis Understand the main kinds of multi-layer vector spatial analysis Know and differentiate the procedures for distance and area calculations in a vector and raster data modelling Understand how to choose objects based on their attributes Understand the use of relationships and links between tables Understand the key elements of statistics, such as, average, standard deviation, least squares, mean square deviation. 7
8 CATEGORY KNOWLEDGE AREA REF. KNOWLEDGE ITEM Distinguish between the main classification methods (such as quantile, standard deviation, natural breaks). 2.5 Thematic mapping Thematic representation Define the term thematic map List the key elements of a thematic map Distinguish between different types of thematic maps (such as choropleth, isopleth, proportional symbols, dot density) Understand the terms quantitative and qualitative maps. 8
9 Module 3: Use of a GIS software The following is the syllabus for Module 3 of the GIS certification and provides the basis for the practical test. Module aims Module 3 aims to check the candidate s knowledge in the use of specific GIS software which could be, in this phase, from ESRI and Intergraph. The themes and topics are independent of the actual software package and the specific software is used to test the skills of the candidate in GIS functionality common to all GIS software packages. CATEGORY SKILL SET REF. TASK ITEM 3.1 General concepts 3.2 GIS Data and attributes First steps with a GIS application Launch, close a GIS application Load vector and raster data in the GIS application Save a session Use the online help of the GIS application Modify the settings Display, hide the tool bars Use the zoom and pan tools Modify the data representation scale Modify the reference system Layer management Move between different layers Vector and raster data Attribute management Activate, disactivate a layer Change layer names Modify the visualisation properties of vector and raster data Open and close an attribute table Insert, remove a column from an attribute table Change an attribute value Define the values of a new attribute column via arithmetic operations on numerical values Define the values of a new attribute column via logical operations on attribute columns Use statistical functions on attributes Show statistical values on a graph Data operations Modify and create an object Create a new dataset from video digitizing on a raster base map. 9
10 CATEGORY SKILL SET REF. TASK ITEM 3.3 Data analysis Query and choose data 3.4 Thematic maps 3.5 Report preparation Calculate the area and the perimeter of a polygon Set the measurement units and find the distance between two objects Add attributes to a newly created data set Carry out a union between two tables Link two tables Identify, find and choose objects interactively Find objects via attributes Create a data subset Identify, find and choose objects via a query Create a new layer with objects chosen via a query Spatial data analysis Apply a buffer function Thematic data classification Thematic data Representaion Design of a thematic map Prepare data for printing Apply an overlay function Classify data using constant interval and standard deviation methods Classify data using the quantile method Classify data using the natural breaks method Represent the themes via dot density Represent the themes via graduated symbols Represent the themes via graduated colours Modify the colours, the texture, the layout and features of a thematic map Insert, modify and remove labels from a thematic map Set and modify the print layout properties (such as margins, page size) Create personalized symbols Modify layout components such as map, legend, scale, title, orientation Export the layout in different formats (such as jpeg, tiff, pdf). 10
EUROPEAN COMPUTER DRIVING LICENCE. GIS Cartography. Syllabus
 EUROPEAN COMPUTER DRIVING LICENCE GIS Cartography Syllabus Purpose This document details the syllabus for ECDL GIS Module 1 Cartography. The syllabus describes, through learning outcomes, the knowledge
EUROPEAN COMPUTER DRIVING LICENCE GIS Cartography Syllabus Purpose This document details the syllabus for ECDL GIS Module 1 Cartography. The syllabus describes, through learning outcomes, the knowledge
Overview key concepts and terms (based on the textbook Chang 2006 and the practical manual)
 Introduction Geo-information Science (GRS-10306) Overview key concepts and terms (based on the textbook 2006 and the practical manual) Introduction Chapter 1 Geographic information system (GIS) Geographically
Introduction Geo-information Science (GRS-10306) Overview key concepts and terms (based on the textbook 2006 and the practical manual) Introduction Chapter 1 Geographic information system (GIS) Geographically
Terms GIS GPS Vector Data Model Raster Data Model Feature Attribute Table Point Line Polygon Pixel RGB Overlay Function
 FINAL REVIEW FOR GIS (2016) PRACTICAL COMPONENT The first 40 mins of the exam will be open book and will require you to make a map using all the techniques learned over the semester. This map will be e-mailed
FINAL REVIEW FOR GIS (2016) PRACTICAL COMPONENT The first 40 mins of the exam will be open book and will require you to make a map using all the techniques learned over the semester. This map will be e-mailed
Lecture 2. A Review: Geographic Information Systems & ArcGIS Basics
 Lecture 2 A Review: Geographic Information Systems & ArcGIS Basics GIS Overview Types of Maps Symbolization & Classification Map Elements GIS Data Models Coordinate Systems and Projections Scale Geodatabases
Lecture 2 A Review: Geographic Information Systems & ArcGIS Basics GIS Overview Types of Maps Symbolization & Classification Map Elements GIS Data Models Coordinate Systems and Projections Scale Geodatabases
Fundamentals of ArcGIS Desktop Pathway
 Fundamentals of ArcGIS Desktop Pathway Table of Contents ArcGIS Desktop I: Getting Started with GIS 3 ArcGIS Desktop II: Tools and Functionality 5 Understanding Geographic Data 8 Understanding Map Projections
Fundamentals of ArcGIS Desktop Pathway Table of Contents ArcGIS Desktop I: Getting Started with GIS 3 ArcGIS Desktop II: Tools and Functionality 5 Understanding Geographic Data 8 Understanding Map Projections
What is a map? A simple representation of the real world Two types of maps
 Mapping with GIS What is a map? A simple representation of the real world Two types of maps Reference maps showing reference features such as roads, locations, political boundaries, cities etc. Thematic
Mapping with GIS What is a map? A simple representation of the real world Two types of maps Reference maps showing reference features such as roads, locations, political boundaries, cities etc. Thematic
Geographers Perspectives on the World
 What is Geography? Geography is not just about city and country names Geography is not just about population and growth Geography is not just about rivers and mountains Geography is a broad field that
What is Geography? Geography is not just about city and country names Geography is not just about population and growth Geography is not just about rivers and mountains Geography is a broad field that
GEOREFERENCING, PROJECTIONS Part I. PRESENTING DATA Part II
 Week 7 GEOREFERENCING, PROJECTIONS Part I PRESENTING DATA Part II topics of the week Georeferencing Coordinate systems Map Projections ArcMap and Projections Geo-referencing Geo-referencing is the process
Week 7 GEOREFERENCING, PROJECTIONS Part I PRESENTING DATA Part II topics of the week Georeferencing Coordinate systems Map Projections ArcMap and Projections Geo-referencing Geo-referencing is the process
Dr. ABOLGHASEM AKBARI Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources, University Malaysia Pahang (UMP)
 Workshop on : Dr. ABOLGHASEM AKBARI Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources, University Malaysia Pahang (UMP) 14-15 April 2016 Venue: Tehran, Iran GIS definitions GIS: A simplified view of the real
Workshop on : Dr. ABOLGHASEM AKBARI Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources, University Malaysia Pahang (UMP) 14-15 April 2016 Venue: Tehran, Iran GIS definitions GIS: A simplified view of the real
GIS CONCEPTS ARCGIS METHODS AND. 3 rd Edition, July David M. Theobald, Ph.D. Warner College of Natural Resources Colorado State University
 GIS CONCEPTS AND ARCGIS METHODS 3 rd Edition, July 2007 David M. Theobald, Ph.D. Warner College of Natural Resources Colorado State University Copyright Copyright 2007 by David M. Theobald. All rights
GIS CONCEPTS AND ARCGIS METHODS 3 rd Edition, July 2007 David M. Theobald, Ph.D. Warner College of Natural Resources Colorado State University Copyright Copyright 2007 by David M. Theobald. All rights
DATA SOURCES AND INPUT IN GIS. By Prof. A. Balasubramanian Centre for Advanced Studies in Earth Science, University of Mysore, Mysore
 DATA SOURCES AND INPUT IN GIS By Prof. A. Balasubramanian Centre for Advanced Studies in Earth Science, University of Mysore, Mysore 1 1. GIS stands for 'Geographic Information System'. It is a computer-based
DATA SOURCES AND INPUT IN GIS By Prof. A. Balasubramanian Centre for Advanced Studies in Earth Science, University of Mysore, Mysore 1 1. GIS stands for 'Geographic Information System'. It is a computer-based
The Elements of GIS. Organizing Data and Information. The GIS Database. MAP and ATRIBUTE INFORMATION
 GIS s Roots in Cartography Getting Started With GIS Chapter 2 Dursun Z. Seker MAP and ATRIBUTE INFORMATION Data (numbers and text) store as files refer to them collectively as a database gather inform.
GIS s Roots in Cartography Getting Started With GIS Chapter 2 Dursun Z. Seker MAP and ATRIBUTE INFORMATION Data (numbers and text) store as files refer to them collectively as a database gather inform.
12/26/2012. Geographic Information Systems * * * * GIS (... yrezaei
 ( - Geographic Information Systems ( ( 1 2 3 Information System Data base DB IS IS DB (Knowledge ( ( (System (Information System - (Georefrence Analysis Data + Knowledge ======== Information 4 5 ( < 10%
( - Geographic Information Systems ( ( 1 2 3 Information System Data base DB IS IS DB (Knowledge ( ( (System (Information System - (Georefrence Analysis Data + Knowledge ======== Information 4 5 ( < 10%
Performing Map Cartography. using Esri Production Mapping
 AGENDA Performing Map Cartography Presentation Title using Esri Production Mapping Name of Speaker Company Name Kannan Jayaraman Agenda Introduction What s New in ArcGIS 10.1 ESRI Production Mapping Mapping
AGENDA Performing Map Cartography Presentation Title using Esri Production Mapping Name of Speaker Company Name Kannan Jayaraman Agenda Introduction What s New in ArcGIS 10.1 ESRI Production Mapping Mapping
This week s topics. Week 6. FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications. Week 6
 FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 6 Week 6 Last week Chapter 8 Combining and splitting landscape features and merging GIS databases Chapter 11 Overlay processes Questions? Next week
FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 6 Week 6 Last week Chapter 8 Combining and splitting landscape features and merging GIS databases Chapter 11 Overlay processes Questions? Next week
Understanding Projections for GIS
 Presented by John Schaeffer Juniper GIS Services, Inc. This PowerPoint is available at JuniperGIS.com Presentation Objectives To understand basic concepts on projections and coordinate systems for the
Presented by John Schaeffer Juniper GIS Services, Inc. This PowerPoint is available at JuniperGIS.com Presentation Objectives To understand basic concepts on projections and coordinate systems for the
Mapping Census Data in ArcView 3.x
 Mapping Census Data in ArcView 3.x Nancy Lemay University of Ottawa Barbara Znamirowski Trent University Workshop Outline Defining certain concepts and terms: Map scale, coordinate systems, datum and projections.
Mapping Census Data in ArcView 3.x Nancy Lemay University of Ottawa Barbara Znamirowski Trent University Workshop Outline Defining certain concepts and terms: Map scale, coordinate systems, datum and projections.
Lecture 4. Coordinate Systems & Projections
 Lecture 4 Coordinate Systems & Projections Outline Geodesy Geoids Ellipsoids Geographic Coordinate Systems Magnetic North vs. True North Datums Projections Applying Coordinate Systems and Projections Why
Lecture 4 Coordinate Systems & Projections Outline Geodesy Geoids Ellipsoids Geographic Coordinate Systems Magnetic North vs. True North Datums Projections Applying Coordinate Systems and Projections Why
Introduction to Cartography GEOG 2016 E. Lecture-2 Geodesy and Projections
 Introduction to Cartography GEOG 2016 E Lecture-2 Geodesy and Projections What is Geodesy? The science of geodesy determines: Earth s shape and Interrelation of different points on earth s surface The
Introduction to Cartography GEOG 2016 E Lecture-2 Geodesy and Projections What is Geodesy? The science of geodesy determines: Earth s shape and Interrelation of different points on earth s surface The
REFERENCING COORDINATE SYSTEMS MAP PROJECTIONS GEOREFERENCING
 GIS in Ecology SPATIAL REFERENCING COORDINATE SYSTEMS MAP PROJECTIONS GEOREFERENCING : :1 Where on earth? Early mapmakers recognized the need for a system that could locate features on the earth's surface.
GIS in Ecology SPATIAL REFERENCING COORDINATE SYSTEMS MAP PROJECTIONS GEOREFERENCING : :1 Where on earth? Early mapmakers recognized the need for a system that could locate features on the earth's surface.
METADATA. Publication Date: Fiscal Year Cooperative Purchase Program Geospatial Data Presentation Form: Map Publication Information:
 METADATA CONTOURS Digital Geospatial Metadata: North Central Texas Orthophotography Identification Information Citation Originator: Publication Date: Fiscal Year 2001-2002 Title: Cooperative Purchase Program
METADATA CONTOURS Digital Geospatial Metadata: North Central Texas Orthophotography Identification Information Citation Originator: Publication Date: Fiscal Year 2001-2002 Title: Cooperative Purchase Program
Popular Mechanics, 1954
 Introduction to GIS Popular Mechanics, 1954 1986 $2,599 1 MB of RAM 2017, $750, 128 GB memory, 2 GB of RAM Computing power has increased exponentially over the past 30 years, Allowing the existence of
Introduction to GIS Popular Mechanics, 1954 1986 $2,599 1 MB of RAM 2017, $750, 128 GB memory, 2 GB of RAM Computing power has increased exponentially over the past 30 years, Allowing the existence of
Outline. Chapter 1. A history of products. What is ArcGIS? What is GIS? Some GIS applications Introducing the ArcGIS products How does GIS work?
 Outline Chapter 1 Introducing ArcGIS What is GIS? Some GIS applications Introducing the ArcGIS products How does GIS work? Basic data formats The ArcCatalog interface 1-1 1-2 A history of products Arc/Info
Outline Chapter 1 Introducing ArcGIS What is GIS? Some GIS applications Introducing the ArcGIS products How does GIS work? Basic data formats The ArcCatalog interface 1-1 1-2 A history of products Arc/Info
GIS CONCEPTS ARCGIS METHODS AND. 2 nd Edition, July David M. Theobald, Ph.D. Natural Resource Ecology Laboratory Colorado State University
 GIS CONCEPTS AND ARCGIS METHODS 2 nd Edition, July 2005 David M. Theobald, Ph.D. Natural Resource Ecology Laboratory Colorado State University Copyright Copyright 2005 by David M. Theobald. All rights
GIS CONCEPTS AND ARCGIS METHODS 2 nd Edition, July 2005 David M. Theobald, Ph.D. Natural Resource Ecology Laboratory Colorado State University Copyright Copyright 2005 by David M. Theobald. All rights
EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography
 EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography Lecture 3 Geodesy Map Projections, Datums, and Coordinate Systems 1 Geodesy The science of measuring and representing the shape and size of the earth, and
EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography Lecture 3 Geodesy Map Projections, Datums, and Coordinate Systems 1 Geodesy The science of measuring and representing the shape and size of the earth, and
Outline. Shape of the Earth. Geographic Coordinates (φ, λ, z) Ellipsoid or Spheroid Rotate an ellipse around an axis. Ellipse.
 Map Projections Outline Geodesy and map projections Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh Shape
Map Projections Outline Geodesy and map projections Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh Shape
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL. Lecture-1 Chapters 1 and 2
 Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-1 Chapters 1 and 2 What is GIS? A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer system for capturing, storing, querying, analyzing and
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-1 Chapters 1 and 2 What is GIS? A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer system for capturing, storing, querying, analyzing and
Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006
 I. Introduction and References Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006 The world is, approximately, a sphere. Maps are flat. Making maps requires some method of putting
I. Introduction and References Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006 The world is, approximately, a sphere. Maps are flat. Making maps requires some method of putting
Geodatabase Management Pathway
 Geodatabase Management Pathway Table of Contents ArcGIS Desktop II: Tools and Functionality 3 ArcGIS Desktop III: GIS Workflows and Analysis 6 Building Geodatabases 8 Data Management in the Multiuser Geodatabase
Geodatabase Management Pathway Table of Contents ArcGIS Desktop II: Tools and Functionality 3 ArcGIS Desktop III: GIS Workflows and Analysis 6 Building Geodatabases 8 Data Management in the Multiuser Geodatabase
GISc Technician model. Diploma in GISc / Geoinformatics NQF level 6. Minimum 240 credits
 GISc Technician model. Diploma in GISc / Geoinformatics NQF level. Minimum 20 credits The workforce and competency requirements of a GISc technicians is defined in terms of the Geomatics Act 19 of 2013,
GISc Technician model. Diploma in GISc / Geoinformatics NQF level. Minimum 20 credits The workforce and competency requirements of a GISc technicians is defined in terms of the Geomatics Act 19 of 2013,
Working with Projections and Datum Transformations in ArcGIS
 Werner Flacke / Birgit Kraus Working with Projections and Datum Transformations in ArcGIS Theory and Practical Examples First impression 2005 Points Verlag Norden*Halmstad VII Table of Contents Introduction
Werner Flacke / Birgit Kraus Working with Projections and Datum Transformations in ArcGIS Theory and Practical Examples First impression 2005 Points Verlag Norden*Halmstad VII Table of Contents Introduction
Projections & GIS Data Collection: An Overview
 Projections & GIS Data Collection: An Overview Projections Primary data capture Secondary data capture Data transfer Capturing attribute data Managing a data capture project Geodesy Basics for Geospatial
Projections & GIS Data Collection: An Overview Projections Primary data capture Secondary data capture Data transfer Capturing attribute data Managing a data capture project Geodesy Basics for Geospatial
Intro to GIS Fall 2010 Georeferencing & Map Projections
 Intro to GIS Fall 2010 Georeferencing & Map Projections SHAPE OF THE EARTH Earth's Shape Geoid: shape of earth minus topographic features (irregular due to local variations in gravity) Ellipsoid: elongated
Intro to GIS Fall 2010 Georeferencing & Map Projections SHAPE OF THE EARTH Earth's Shape Geoid: shape of earth minus topographic features (irregular due to local variations in gravity) Ellipsoid: elongated
CHAPTER 9 DATA DISPLAY AND CARTOGRAPHY
 CHAPTER 9 DATA DISPLAY AND CARTOGRAPHY 9.1 Cartographic Representation 9.1.1 Spatial Features and Map Symbols 9.1.2 Use of Color 9.1.3 Data Classification 9.1.4 Generalization Box 9.1 Representations 9.2
CHAPTER 9 DATA DISPLAY AND CARTOGRAPHY 9.1 Cartographic Representation 9.1.1 Spatial Features and Map Symbols 9.1.2 Use of Color 9.1.3 Data Classification 9.1.4 Generalization Box 9.1 Representations 9.2
2. GETTING STARTED WITH GIS
 2. GETTING STARTED WITH GIS What are geographic information systems and what are they used for? ArcGIS: ArcMap, ArcCatalog and ArcToolbox Vector data vs. raster data vs. attribute tables Polygons, polylines,
2. GETTING STARTED WITH GIS What are geographic information systems and what are they used for? ArcGIS: ArcMap, ArcCatalog and ArcToolbox Vector data vs. raster data vs. attribute tables Polygons, polylines,
INSPIRATION RESULTS AND BENEFITS ALBANIA
 INSPIRATION RESULTS AND BENEFITS ALBANIA By Eng. Besnik Çomo Paper prepared for E&I Workshop: Support to INSPIRE Implementation in enlargement and EWP Countries JRC ISPRA Central Office of Immovable Property
INSPIRATION RESULTS AND BENEFITS ALBANIA By Eng. Besnik Çomo Paper prepared for E&I Workshop: Support to INSPIRE Implementation in enlargement and EWP Countries JRC ISPRA Central Office of Immovable Property
Geometric Algorithms in GIS
 Geometric Algorithms in GIS GIS Software Dr. M. Gavrilova GIS System What is a GIS system? A system containing spatially referenced data that can be analyzed and converted to new information for a specific
Geometric Algorithms in GIS GIS Software Dr. M. Gavrilova GIS System What is a GIS system? A system containing spatially referenced data that can be analyzed and converted to new information for a specific
ENV101 EARTH SYSTEMS
 ENV101 EARTH SYSTEMS Practical Exercise 2 Introduction to ArcMap and Map Projections 1. OVERVIEW This practical is designed to familiarise students with the use of ArcMap for visualising spatial data and
ENV101 EARTH SYSTEMS Practical Exercise 2 Introduction to ArcMap and Map Projections 1. OVERVIEW This practical is designed to familiarise students with the use of ArcMap for visualising spatial data and
What is a Map Projection?
 What is a Map Projection? It is how we represent a three dimensional Earth on a flat piece of paper However The process of transferring information from the Earth to a map causes every projection to distort
What is a Map Projection? It is how we represent a three dimensional Earth on a flat piece of paper However The process of transferring information from the Earth to a map causes every projection to distort
NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections
 NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections From http://www.or.blm.gov/gis/ 1 Geographic coordinates Coordinates are expressed as Latitude and Longitude in Degrees, Minutes, Seconds
NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections From http://www.or.blm.gov/gis/ 1 Geographic coordinates Coordinates are expressed as Latitude and Longitude in Degrees, Minutes, Seconds
Lower Density Growth Management Metadata
 Products > BYTES of the BIG APPLE TM Lower Density Growth Management Metadata nyldgma Data Format: Shapefile File or table name: nyldgma Data Projection: NAD_1983_StatePlane_New_York_Long_Island_FIPS_3104_Feet
Products > BYTES of the BIG APPLE TM Lower Density Growth Management Metadata nyldgma Data Format: Shapefile File or table name: nyldgma Data Projection: NAD_1983_StatePlane_New_York_Long_Island_FIPS_3104_Feet
ARMY ITAM GIS: Automating Standard Army Training Map Production
 ARMY ITAM GIS: Automating Standard Army Training Map Production Douglas Willets ITAM Western Regional Support Center, Center for Environmental Management of Military Lands, Colorado State University, Fort
ARMY ITAM GIS: Automating Standard Army Training Map Production Douglas Willets ITAM Western Regional Support Center, Center for Environmental Management of Military Lands, Colorado State University, Fort
Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts. -Coordinate Systems -Datum
 Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts -Map Projections -Coordinate Systems -Datum Map projection is "the process of systematically transforming positions on the Earth's spherical surface
Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts -Map Projections -Coordinate Systems -Datum Map projection is "the process of systematically transforming positions on the Earth's spherical surface
Digital Topographic Map 1 : DTK1000
 Digital Topographic Map 1 : 1 DTK Documentation as of: 14.8.217 Federal Agency for Cartography and Geodesy DTK page 1 Digital Topographic Map 1 : 1 DTK Contents DTK Page 1 Index of data sets 3 2 Description
Digital Topographic Map 1 : 1 DTK Documentation as of: 14.8.217 Federal Agency for Cartography and Geodesy DTK page 1 Digital Topographic Map 1 : 1 DTK Contents DTK Page 1 Index of data sets 3 2 Description
Introduction to ArcMap
 Introduction to ArcMap ArcMap ArcMap is a Map-centric GUI tool used to perform map-based tasks Mapping Create maps by working geographically and interactively Display and present Export or print Publish
Introduction to ArcMap ArcMap ArcMap is a Map-centric GUI tool used to perform map-based tasks Mapping Create maps by working geographically and interactively Display and present Export or print Publish
ch02.pdf chap2.pdf chap02.pdf
 Introduction to Geographic Information Systems 8th Edition Karl Solutions Manual Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/introduction-to-geographic-information-systems-8th-edition-karl-solutions-manu
Introduction to Geographic Information Systems 8th Edition Karl Solutions Manual Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/introduction-to-geographic-information-systems-8th-edition-karl-solutions-manu
ENV208/ENV508 Applied GIS. Week 2: Making maps, data visualisation, and GIS output
 ENV208/ENV508 Applied GIS Week 2: Making maps, data visualisation, and GIS output Overview GIS Output Map Making Types of Maps Key Elements GIS Output Formats Table Graph Statistics Maps Map Making Maps
ENV208/ENV508 Applied GIS Week 2: Making maps, data visualisation, and GIS output Overview GIS Output Map Making Types of Maps Key Elements GIS Output Formats Table Graph Statistics Maps Map Making Maps
ARCGIS PRO COURSE, APPLIED TO ENVIROMENTAL MANAGEMENT GIS. Course. Training. .com
 ARC PRO COURSE, APPLIED TO ENVIROMENTAL MANAGEMENT TYC Training Course.com TRAINING OVERVIEW This Arc Pro online course will provide a great deal of information about the link between earth s ecosystems
ARC PRO COURSE, APPLIED TO ENVIROMENTAL MANAGEMENT TYC Training Course.com TRAINING OVERVIEW This Arc Pro online course will provide a great deal of information about the link between earth s ecosystems
Hydrology and Floodplain Analysis, Chapter 10
 Hydrology and Floodplain Analysis, Chapter 10 Hydrology and Floodplain Analysis, Chapter 10.1 Introduction to GIS GIS Geographical Information System Spatial Data Data linked with geographical location
Hydrology and Floodplain Analysis, Chapter 10 Hydrology and Floodplain Analysis, Chapter 10.1 Introduction to GIS GIS Geographical Information System Spatial Data Data linked with geographical location
Overview. GIS Data Output Methods
 Overview GIS Output Formats ENV208/ENV508 Applied GIS Week 2: Making maps, data visualisation, and GIS output GIS Output Map Making Types of Maps Key Elements Table Graph Statistics Maps Map Making Maps
Overview GIS Output Formats ENV208/ENV508 Applied GIS Week 2: Making maps, data visualisation, and GIS output GIS Output Map Making Types of Maps Key Elements Table Graph Statistics Maps Map Making Maps
ArcGIS Pro: Essential Workflows STUDENT EDITION
 ArcGIS Pro: Essential Workflows STUDENT EDITION Copyright 2018 Esri All rights reserved. Course version 6.0. Version release date August 2018. Printed in the United States of America. The information contained
ArcGIS Pro: Essential Workflows STUDENT EDITION Copyright 2018 Esri All rights reserved. Course version 6.0. Version release date August 2018. Printed in the United States of America. The information contained
Coordinate Systems. Location on earth is defined by coordinates
 Coordinate Systems We think of the earth as a sphere It is actually a spheroid (ellipsoid), slightly larger in radius at the equator than at the poles Shape of the Earth Location on earth is defined by
Coordinate Systems We think of the earth as a sphere It is actually a spheroid (ellipsoid), slightly larger in radius at the equator than at the poles Shape of the Earth Location on earth is defined by
Canadian Board of Examiners for Professional Surveyors Core Syllabus Item C 5: GEOSPATIAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 Study Guide: Canadian Board of Examiners for Professional Surveyors Core Syllabus Item C 5: GEOSPATIAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS This guide presents some study questions with specific referral to the essential
Study Guide: Canadian Board of Examiners for Professional Surveyors Core Syllabus Item C 5: GEOSPATIAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS This guide presents some study questions with specific referral to the essential
Georeferencing. Place names Postal addresses Postal codes Coordinate systems (lat/long, UTM, etc.)
 Georeferencing Georeferencing Used to describe the act of assigning locations to data or information Certain requirements include that they are: unique, have shared meaning, and are persistent through
Georeferencing Georeferencing Used to describe the act of assigning locations to data or information Certain requirements include that they are: unique, have shared meaning, and are persistent through
GPS Remote Sensing. GIS Photogrammetry. GEODESY Equipment (total station) CARTOGRAPHY Survey Software. Map Projection Coordinate Systems
 GPS Remote Sensing GIS Photogrammetry GEODESY Equipment (total station) CARTOGRAPHY Survey Software Map Projection Coordinate Systems 1 Coordinate Systems, Datum and Map Projection Dr. Maher A. El-Hallaq
GPS Remote Sensing GIS Photogrammetry GEODESY Equipment (total station) CARTOGRAPHY Survey Software Map Projection Coordinate Systems 1 Coordinate Systems, Datum and Map Projection Dr. Maher A. El-Hallaq
Dr.Weerakaset Suanpaga (D.Eng RS&GIS)
 The Analysis of Discrete Entities i in Space Dr.Weerakaset Suanpaga (D.Eng RS&GIS) Aim of GIS? To create spatial and non-spatial database? Not just this, but also To facilitate query, retrieval and analysis
The Analysis of Discrete Entities i in Space Dr.Weerakaset Suanpaga (D.Eng RS&GIS) Aim of GIS? To create spatial and non-spatial database? Not just this, but also To facilitate query, retrieval and analysis
DATA 301 Introduction to Data Analytics Geographic Information Systems
 DATA 301 Introduction to Data Analytics Geographic Information Systems Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca DATA 301: Data Analytics (2) Why learn Geographic
DATA 301 Introduction to Data Analytics Geographic Information Systems Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca DATA 301: Data Analytics (2) Why learn Geographic
GEOGRAPHY 350/550 Final Exam Fall 2005 NAME:
 1) A GIS data model using an array of cells to store spatial data is termed: a) Topology b) Vector c) Object d) Raster 2) Metadata a) Usually includes map projection, scale, data types and origin, resolution
1) A GIS data model using an array of cells to store spatial data is termed: a) Topology b) Vector c) Object d) Raster 2) Metadata a) Usually includes map projection, scale, data types and origin, resolution
GIS Data Production and Editing Pathway
 GIS Data Production and Editing Pathway Table of Contents ArcGIS Desktop II: Tools and Functionality 3 ArcGIS Desktop III: GIS Workflows and Analysis 6 Building Geodatabases 8 Creating and Maintaining
GIS Data Production and Editing Pathway Table of Contents ArcGIS Desktop II: Tools and Functionality 3 ArcGIS Desktop III: GIS Workflows and Analysis 6 Building Geodatabases 8 Creating and Maintaining
Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections
 Organizing Data and Information Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections Map Scales Projections Information can be organized as lists, numbers, tables, text, pictures, maps, or indexes. Clusters of information
Organizing Data and Information Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections Map Scales Projections Information can be organized as lists, numbers, tables, text, pictures, maps, or indexes. Clusters of information
An Information Model for Maps: Towards Cartographic Production from GIS Databases
 An Information Model for s: Towards Cartographic Production from GIS Databases Aileen Buckley, Ph.D. and Charlie Frye Senior Cartographic Researchers, ESRI Barbara Buttenfield, Ph.D. Professor, University
An Information Model for s: Towards Cartographic Production from GIS Databases Aileen Buckley, Ph.D. and Charlie Frye Senior Cartographic Researchers, ESRI Barbara Buttenfield, Ph.D. Professor, University
Acknowledgments xiii Preface xv. GIS Tutorial 1 Introducing GIS and health applications 1. What is GIS? 2
 Acknowledgments xiii Preface xv GIS Tutorial 1 Introducing GIS and health applications 1 What is GIS? 2 Spatial data 2 Digital map infrastructure 4 Unique capabilities of GIS 5 Installing ArcView and the
Acknowledgments xiii Preface xv GIS Tutorial 1 Introducing GIS and health applications 1 What is GIS? 2 Spatial data 2 Digital map infrastructure 4 Unique capabilities of GIS 5 Installing ArcView and the
Performing Advanced Cartography with Esri Production Mapping
 Esri International User Conference San Diego, California Technical Workshops July 25, 2012 Performing Advanced Cartography with Esri Production Mapping Tania Pal & Madhura Phaterpekar Agenda Outline generic
Esri International User Conference San Diego, California Technical Workshops July 25, 2012 Performing Advanced Cartography with Esri Production Mapping Tania Pal & Madhura Phaterpekar Agenda Outline generic
Map projections. Rüdiger Gens
 Rüdiger Gens Coordinate systems Geographic coordinates f a: semi-major axis b: semi-minor axis Geographic latitude b Geodetic latitude a f: flattening = (a-b)/a Expresses as a fraction 1/f = about 300
Rüdiger Gens Coordinate systems Geographic coordinates f a: semi-major axis b: semi-minor axis Geographic latitude b Geodetic latitude a f: flattening = (a-b)/a Expresses as a fraction 1/f = about 300
Geomatics: Geotechnologies in Action, Grade 12, University/College Expectations
 Geographic Foundations: Space and Systems SSV.01 explain how the earth is modelled for scientific and mapping purposes; SSV.02 demonstrate an understanding of basic spatial concepts; Page 1 SSV.03 explain
Geographic Foundations: Space and Systems SSV.01 explain how the earth is modelled for scientific and mapping purposes; SSV.02 demonstrate an understanding of basic spatial concepts; Page 1 SSV.03 explain
Shape e o f f the e Earth
 1 Coordinate Systems & Projections Coordinate Systems Two map layers are not going to register spatially unless they are based on the same coordinate system. 2 Contents Shape of the earth Datum Projections
1 Coordinate Systems & Projections Coordinate Systems Two map layers are not going to register spatially unless they are based on the same coordinate system. 2 Contents Shape of the earth Datum Projections
Lab #3 Map Projections.
 Lab #3 Map Projections http://visual.merriam-webster.com/images/earth/geography/cartography/map-projections.jpg Map Projections Projection: a systematic arrangement of parallels and meridians on a plane
Lab #3 Map Projections http://visual.merriam-webster.com/images/earth/geography/cartography/map-projections.jpg Map Projections Projection: a systematic arrangement of parallels and meridians on a plane
GIS in Water Resources Midterm Exam Fall 2008 There are 4 questions on this exam. Please do all 4.
 Page 1 of 8 Name: GIS in Water Resources Midterm Exam Fall 2008 There are 4 questions on this exam. Please do all 4. 1. Basic Concepts [20 points] Find the letter with the best answer for each term: 1.
Page 1 of 8 Name: GIS in Water Resources Midterm Exam Fall 2008 There are 4 questions on this exam. Please do all 4. 1. Basic Concepts [20 points] Find the letter with the best answer for each term: 1.
Lecture 2. Map Projections and GIS Coordinate Systems. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
 Lecture 2 Map Projections and GIS Coordinate Systems Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Map Projections Map projections are mathematical formulas
Lecture 2 Map Projections and GIS Coordinate Systems Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Map Projections Map projections are mathematical formulas
Map Projections. Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps
 Map Projections Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps Map projections Define the spatial relationship between locations on earth and their relative locations on a flat map Are mathematical expressions
Map Projections Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps Map projections Define the spatial relationship between locations on earth and their relative locations on a flat map Are mathematical expressions
GED 554 IT & GIS. Lecture 6 Exercise 5. May 10, 2013
 GED 554 IT & GIS Lecture 6 Exercise 5 May 10, 2013 Free GIS data sources ******************* Mapping numerical data & Symbolization ******************* Exercise: Making maps for presentation GIS DATA SOFTWARE
GED 554 IT & GIS Lecture 6 Exercise 5 May 10, 2013 Free GIS data sources ******************* Mapping numerical data & Symbolization ******************* Exercise: Making maps for presentation GIS DATA SOFTWARE
a system for input, storage, manipulation, and output of geographic information. GIS combines software with hardware,
 Introduction to GIS Dr. Pranjit Kr. Sarma Assistant Professor Department of Geography Mangaldi College Mobile: +91 94357 04398 What is a GIS a system for input, storage, manipulation, and output of geographic
Introduction to GIS Dr. Pranjit Kr. Sarma Assistant Professor Department of Geography Mangaldi College Mobile: +91 94357 04398 What is a GIS a system for input, storage, manipulation, and output of geographic
Problems and Challenges
 2018 Esri Petroleum GIS Conference Problems and Challenges May 9 10, 2018 Houston, Texas George R. Brown Convention Center Disunity of drawing standards and format Large amount of work in Cartography,
2018 Esri Petroleum GIS Conference Problems and Challenges May 9 10, 2018 Houston, Texas George R. Brown Convention Center Disunity of drawing standards and format Large amount of work in Cartography,
Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910
 Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910 Where are you? 31UFT8361 174,7 441,2 51 58' NB 5 40' OL 2/60 Who are they? 3/60 Do geo data describe Earth s phenomena perfectly? Georeference systems ellipsoid
Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910 Where are you? 31UFT8361 174,7 441,2 51 58' NB 5 40' OL 2/60 Who are they? 3/60 Do geo data describe Earth s phenomena perfectly? Georeference systems ellipsoid
Geographic Systems and Analysis
 Geographic Systems and Analysis New York University Robert F. Wagner Graduate School of Public Service Instructor Stephanie Rosoff Contact: stephanie.rosoff@nyu.edu Office hours: Mondays by appointment
Geographic Systems and Analysis New York University Robert F. Wagner Graduate School of Public Service Instructor Stephanie Rosoff Contact: stephanie.rosoff@nyu.edu Office hours: Mondays by appointment
Geog Lecture 29 Mapping and GIS Continued
 Geog 1000 - Lecture 29 Mapping and GIS Continued http://scholar.ulethbridge.ca/chasmer/classes/ Today s Lecture (Pgs 13-25, 28-29) 1. Hand back Assignment 3 2. Review of Dr. Peddle s lecture last week
Geog 1000 - Lecture 29 Mapping and GIS Continued http://scholar.ulethbridge.ca/chasmer/classes/ Today s Lecture (Pgs 13-25, 28-29) 1. Hand back Assignment 3 2. Review of Dr. Peddle s lecture last week
Spatial Data Analysis with ArcGIS Desktop: From Basic to Advance
 Spatial Data Analysis with ArcGIS Desktop: From Basic to Advance 1. Course overview Modern environmental, energy as well as resource modeling and planning require huge amount of geographically located
Spatial Data Analysis with ArcGIS Desktop: From Basic to Advance 1. Course overview Modern environmental, energy as well as resource modeling and planning require huge amount of geographically located
What should you consider concerning colors in maps in order to illustrate qualitative data, and quantitative data, respectively? Exemplify.
 1, Cartography, 10 p (HA) _ When doing a map based on quantitative data you have for example to decide upon the classification. Three common classifications are Equal interval, Quantiles (percentiles)
1, Cartography, 10 p (HA) _ When doing a map based on quantitative data you have for example to decide upon the classification. Three common classifications are Equal interval, Quantiles (percentiles)
ArcMap - EXPLORING THE DATABASE Part I. SPATIAL DATA FORMATS Part II
 Week 5 ArcMap - EXPLORING THE DATABASE Part I SPATIAL DATA FORMATS Part II topics of the week Exploring the Database More on the Table of Contents Exploration tools Identify, Find, Measure, Map tips, Hyperlink,
Week 5 ArcMap - EXPLORING THE DATABASE Part I SPATIAL DATA FORMATS Part II topics of the week Exploring the Database More on the Table of Contents Exploration tools Identify, Find, Measure, Map tips, Hyperlink,
GIS for Surveyors: Wetland Studies and Solutions, Inc.
 GIS for Surveyors: Concepts, Solutions, and Applications ` New Jersey Society of Professional Land Surveyors (NJSPLS) SurvCon 2013, Atlantic City, New Jersey Presented by John Cooke and Yeoanny A. Venetsanos,
GIS for Surveyors: Concepts, Solutions, and Applications ` New Jersey Society of Professional Land Surveyors (NJSPLS) SurvCon 2013, Atlantic City, New Jersey Presented by John Cooke and Yeoanny A. Venetsanos,
Charlene Nielsen, MSc.
 GIS Project Issues Charlene Nielsen, MSc charlene.nielsen@ualberta.ca 492-93979397 B414 BioSci Building www.biology.ualberta.ca/facilities/gis Introduction to GIS in Ecology What a GIS is not What is a
GIS Project Issues Charlene Nielsen, MSc charlene.nielsen@ualberta.ca 492-93979397 B414 BioSci Building www.biology.ualberta.ca/facilities/gis Introduction to GIS in Ecology What a GIS is not What is a
Lab 1: Importing Data, Rectification, Datums, Projections, and Output (Mapping)
 Lab 1: Importing Data, Rectification, Datums, Projections, and Output (Mapping) Topics covered in this lab: i. Importing spatial data to TAS ii. Rectification iii. Conversion from latitude/longitude to
Lab 1: Importing Data, Rectification, Datums, Projections, and Output (Mapping) Topics covered in this lab: i. Importing spatial data to TAS ii. Rectification iii. Conversion from latitude/longitude to
Map Projections. What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL
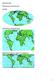 Map Projections What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL 1 CYLINDRICAL EQUAL AREA BONNE CRASTER PARABOLIC 2 ECKERT I ECKERT III ECKERT V There are many
Map Projections What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL 1 CYLINDRICAL EQUAL AREA BONNE CRASTER PARABOLIC 2 ECKERT I ECKERT III ECKERT V There are many
Introduction to Spatial Data Resources and Analysis for research in Urban Design and Planning
 Introduction to Spatial Data Resources and Analysis for research in Urban Design and Planning 2-day workshop notes 27-28 September 2004 Introductions please put on a name tag to help me know who you are
Introduction to Spatial Data Resources and Analysis for research in Urban Design and Planning 2-day workshop notes 27-28 September 2004 Introductions please put on a name tag to help me know who you are
The Geodatabase Working with Spatial Analyst. Calculating Elevation and Slope Values for Forested Roads, Streams, and Stands.
 GIS LAB 7 The Geodatabase Working with Spatial Analyst. Calculating Elevation and Slope Values for Forested Roads, Streams, and Stands. This lab will ask you to work with the Spatial Analyst extension.
GIS LAB 7 The Geodatabase Working with Spatial Analyst. Calculating Elevation and Slope Values for Forested Roads, Streams, and Stands. This lab will ask you to work with the Spatial Analyst extension.
The European Surveying Plot A surveying map of land property: A proposal and it s perspectives
 The European Surveying Plot A surveying map of land property: A proposal and it s perspectives Nikolaos KALAMAKIS, Greece Key words: INSPIRE, Interoperability, National Geographic Organizations, technical
The European Surveying Plot A surveying map of land property: A proposal and it s perspectives Nikolaos KALAMAKIS, Greece Key words: INSPIRE, Interoperability, National Geographic Organizations, technical
Esri UC2013. Technical Workshop.
 Esri International User Conference San Diego, California Technical Workshops July 9, 2013 CAD: Introduction to using CAD Data in ArcGIS Jeff Reinhart & Phil Sanchez Agenda Overview of ArcGIS CAD Support
Esri International User Conference San Diego, California Technical Workshops July 9, 2013 CAD: Introduction to using CAD Data in ArcGIS Jeff Reinhart & Phil Sanchez Agenda Overview of ArcGIS CAD Support
INTRODUCTION TO GIS. Practicals Guide. Chinhoyi University of Technology
 INTRODUCTION TO GIS Practicals Guide Chinhoyi University of Technology Lab 1: Basic Visualisation You have been requested to make a map of Zimbabwe showing the international boundary and provinces. The
INTRODUCTION TO GIS Practicals Guide Chinhoyi University of Technology Lab 1: Basic Visualisation You have been requested to make a map of Zimbabwe showing the international boundary and provinces. The
When the Earth Was Flat. Measurements were made using a plumb bob, a spirit level, and a stick. Also, the Stars.
 ABSTRACT Defining the shape of the Earth geoid. Mathematical models spheroid or ellipsoid Mathematical projection of geodetic systems GIS/GPS technology The need for a unified projection systems World
ABSTRACT Defining the shape of the Earth geoid. Mathematical models spheroid or ellipsoid Mathematical projection of geodetic systems GIS/GPS technology The need for a unified projection systems World
ARCGIS PRO COURSE, BEGINNER LEVEL ONLINE TRAINING GIS. Course. Training. .com
 ARC PRO COURSE, BEGINNER LEVEL ONLINE TRAINING Course.com TYC TRAINING OVERVIEW This course will provide a basic introduction in Arc PRO, the new Arc Desktop release. The training material will be focused
ARC PRO COURSE, BEGINNER LEVEL ONLINE TRAINING Course.com TYC TRAINING OVERVIEW This course will provide a basic introduction in Arc PRO, the new Arc Desktop release. The training material will be focused
NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources
 NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 1 Introduction to GIS Eva Strand, University of Idaho Map of the Pacific Northwest from http://www.or.blm.gov/gis/ Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in
NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 1 Introduction to GIS Eva Strand, University of Idaho Map of the Pacific Northwest from http://www.or.blm.gov/gis/ Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in
These modules are covered with a brief information and practical in ArcGIS Software and open source software also like QGIS, ILWIS.
 Online GIS Training and training modules covered are: 1. ArcGIS, Analysis, Fundamentals and Implementation 2. ArcGIS Web Data Sharing 3. ArcGIS for Desktop 4. ArcGIS for Server These modules are covered
Online GIS Training and training modules covered are: 1. ArcGIS, Analysis, Fundamentals and Implementation 2. ArcGIS Web Data Sharing 3. ArcGIS for Desktop 4. ArcGIS for Server These modules are covered
Geographic Information Systems class # 1 February 19, Coordinate reference systems in GIS: geodetic coordinates
 Geographic Information Systems class # 1 February 19, 2013 Coordinate reference systems in GIS: geodetic coordinates Manuel Campagnolo ISA Manuel Campagnolo (ISA) GIS/SIG 2012 2013 February 19, 2013 1
Geographic Information Systems class # 1 February 19, 2013 Coordinate reference systems in GIS: geodetic coordinates Manuel Campagnolo ISA Manuel Campagnolo (ISA) GIS/SIG 2012 2013 February 19, 2013 1
Introduction to Geographic Information Systems
 Introduction to Geographic Information Systems Lynn_Carlson@brown.edu 401-863-9917 The Environmental And Remote TecHnologies Lab MacMillan Hall, Room 105 http://www.brown.edu/research/earthlab/ Outline
Introduction to Geographic Information Systems Lynn_Carlson@brown.edu 401-863-9917 The Environmental And Remote TecHnologies Lab MacMillan Hall, Room 105 http://www.brown.edu/research/earthlab/ Outline
ISO Swift Current LiDAR Project 2009 Data Product Specifications. Revision: A
 ISO 19131 Swift Current LiDAR Project 2009 Data Product Specifications Revision: A Data product specifications: Swift Current LiDAR Project 2009 - Table of Contents- 1. Overview... 4 1.1. Informal description...
ISO 19131 Swift Current LiDAR Project 2009 Data Product Specifications Revision: A Data product specifications: Swift Current LiDAR Project 2009 - Table of Contents- 1. Overview... 4 1.1. Informal description...
The Nature of Spatial Data. Keith C. Clarke Geography UCSB
 The Nature of Spatial Data Keith C. Clarke Geography UCSB Geographic primitives G = g (x, y, z, s, A, t) [x, y, z] = f(λ, φ, d) Geography also highly dependent upon model First, the datum (d) Models of
The Nature of Spatial Data Keith C. Clarke Geography UCSB Geographic primitives G = g (x, y, z, s, A, t) [x, y, z] = f(λ, φ, d) Geography also highly dependent upon model First, the datum (d) Models of
400_scale_tiles(poly)(sp_nad83)
 400_scale_tiles(poly)(sp_nad83) Identification_Information Data_Quality_Information Spatial_Data_Organization_Information Spatial_Reference_Information Entity_and_Attribute_Information Distribution_Information
400_scale_tiles(poly)(sp_nad83) Identification_Information Data_Quality_Information Spatial_Data_Organization_Information Spatial_Reference_Information Entity_and_Attribute_Information Distribution_Information
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015
 WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Where is Boston? Introducing Geodesy, Ellipsoids & Geoids Geodesy
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Where is Boston? Introducing Geodesy, Ellipsoids & Geoids Geodesy
Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems.
 Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems. A GIS without coordinates would simply be a database like Microsoft Excel
Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems. A GIS without coordinates would simply be a database like Microsoft Excel
GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS. GIS Foundation Capacity Building Course. Introduction
 GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS. GIS Foundation Capacity Building Course. Introduction In recent times digital mapping has become part and parcel of our daily lives with experience from Google Maps on
GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS. GIS Foundation Capacity Building Course. Introduction In recent times digital mapping has become part and parcel of our daily lives with experience from Google Maps on
