A simple solution for georeferencing the Cassini map series of France
|
|
|
- Arlene Hodge
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gábor Timár, János Mészáros, Gábor Molnár A simple solution for georeferencing the Cassini map series of France Keywords: Cassini map; France; georeference; GIS; historic maps Summary: The Cassini map series of the 18th century France was geo-referred by other scientists several time. Their approach was to define as many control points (GCPs) as possible, to achieve an affordable fit to the modern cartographic products and coordinate systems, however this method claims a huge amount of work during the GCP selection. Here we suggest a different solution. The sheets have their own grid system, which is supposed to be a Cassini projection grid, centered at the Observatory of Paris (origin of projection: φ=48d 50m 10s ; λ=2d 20m 13.95s from Greenwich), which is based on a triangulation network (Ancienne Triangulation Francaise; ATF). Instead of an ellipsoid, a spheric base surface was used. Length of one degree along a meridian was set to 57,060 toises (cca. 111,213 meters), therefore the radius is 6,372,056 meters. Using the original and modern (WGS84) coordinates of the Paris Observatory, combined with the geoid undulation value of Paris, the datum shift coordinates from the ATF to the WGS84 are: dx= m; dy=+439 m; dz= m. Applying this GIS meta-data, just the four corners of each sheet can be applied as GCPs, and their grid coordinates are all indicated in toises (1 toise = meters). This georeference provides a good overview accuracy, which can be improved by the Bursa-Wolf type datum shift definition of the ATF, compiled using the original triangulation point list and the modern coordinates of these points. Introduction The Map of France by Cassini was one of the largest cartographic projects of the second part of the 18th century. Its result, the nice and picturesque series of 175 labeled and 7 auxiliary map sheets in 1:86400 scale is a unique data source, showing the geographical status of France around Its usage of the landscape historic analyses is traditional, just as examples, in the forest history (Dupuoey et al., 2007) and in coastline evolution analysis (Castaigns et al., 2011). Such a cartographic product can be analyzed and incorporated to GIS applications in georeferred form (Boutoura & Livieratos, 2006; Amoud, 2013; Cajthaml, 2011). As a result of the geo-reference, all pixels of the scanned maps or all vertices of the vectorized product have their own defined coordinates in a coordinate system, which is correctly defined in the GIS software environment. In the practice, this usually means that the geodetic datum (the base ellipsoid and its location/orientation) and the map projection (its type and projection parameters) are well defined (Timár & Molnár, 2013). If they are not known, it is also possible to seek ground control points (GCPs) to define the coordinates of all image elements in a commonly used coordinate Department of Geophysics and Space Science, Eötvös University, H-1117 Budapest, Pázmány Péter sétány 1/C, Hungary [timar@caesar.elte.hu] Department of Cartography and Geoinformatics, Eötvös University, H-1117 Budapest, Pázmány Péter sétány 1/A, Hungary MTA-ELTE Geological, Geophysical and Space Science Research Group, Hungarian Academy of Sciences at Eötvös University, H-1117 Budapest, Pázmány Péter sétány 1/C, Hungary
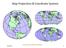
2 system, albeit not the original one, used for drawing the map. Usually the UTM or the modern national grids (e.g. the NTF/Lambert zones for France) are used for defining the geolocation of the GCPs, besides their image (pixel) coordinates. We have to underline that using a different coordinate system always causes a systematic error, which can be up to meters in horizontal accuracy for a map, showing an extent area of some ten kilometers. However, the georeference of the Cassini map can be considered as a solved problem, using several (altogether up to 200 thousands) GCPs and the rubber-sheet model (White & Griffin, 1985). This method is discussed by Grosso (2010), Costes et al. (2012) and finally, with a detailed analysis, by Herrault et al. (2013). The resulted geo-referred map sheets and even the whole Cassini mosaic are publicly available at the David Rumsay Map Collection, both in GeoTIFF (for GIS packages) and KMZ (Google Earth) formats (Fig. 1). Here we provide another solution, which is based on the true, exact original coordinate system of the Cassini map system. After the coordinate system definition, all we have to know is the extents of the map sheets and the location of the projection center in the sheet system. These pieces of information are sufficient to carry out the whole georeferencing of the Cassini map in a few days, by just defining the image (pixel-) and projected coordinates of all four corners of all sheets. Figure 1. The georeferenced mosaic of the 1:86400 Cassini sheets at the David Rumsey Map Collection; a result of defining of several tens of thousands control points. The native coordinate system of the Cassini map The map projection of these sheets are obviously the one, which is called Cassini projection afterwards of the project, defined by César-François Cassini de Thury in 1745, for spherical base surface. Later, it was extended to ellipsoidal base surfaces by the German mathematician Johann Georg von Soldner, therefore this projection of referred to as Cassini-Soldner projection in GIS
3 packages. In short, the spherical version is called Cassini while the ellipsoidal one is the Soldner or Cassini-Soldner projection. For the discussed maps, the base surface is a sphere, however we shall choose the Cassini-Soldner option with a spherical datum. The three-dimensional position of this sphere was defined by a geodetic basepoint set, which is now referred to as Ancienne Triangulation Francaise (ATF), however at the time of its creation it was called les principaux triangles qui servent de fondement a la description geometrique de la France (the principal triangles acting as the basis of the geometric description of France; Cassini & Maraldi, 1744). For the present study, it is a big luck that the map appendix of this latter work contains all of the information items, needed for defining both the ATF and the parameters of the used Cassini projection (Fig. 2); the radius of the base sphere and the latitude of the Paris Observatory (the projection center). Figure 2. Description of the used sphere base surface and the projection of geodetic origin of the Cassini mappation. The base surface is described as follows: en supposant la terre spherique et la grandeur du Degré moyen en France de toises (the spherical Earth is supposed and one degree [along the meridian] distance is toises. As one toise is meters, toises, one degree distance is cca. 111,213 meters, therefore the radius is 6,372,056 meters. It is also given, that the origin is the pole of the Paris Observatory, with the latitude of 48d 50m 10s. The longitudes of the triangulation points are given from the meridian of the Paris observatory, without indication of the eastern or western position from it. According to Mugnier (2001), the longitude difference between Paris and Greenwich, used for the ATF was 2d 20m 13.95s. This latitude-longitude pair can be used for the necessary parameters of the Cassini projection in any GIS software (latitude and longitude of the origin), while the false eastings and false northings can be simply set to zero. Also, we have to derive at least the abridging Molodensky-type datum shift parameters for the ATF sphere to realize its spatial position. Using the abovementioned old coordinates of the Paris
4 observatory and its modern ones in WGS84, as well as the geoid undulation value of Paris we obtain the following parameters for the ATF to WGS84 datum transformation: dx= m; dy=+439 m; dz= m. Note that the relatively high dx and dz values are the consequences of the spheric shape. We can define the native coordinate system by all of these parameters then we can proceed to GCP definition for the 187 sheets. Control points for geo-referencing the Cassini sheets The terrain covered by each Cassini sheet is 40,000 by 25,000 toises (77,962 * 48,727 meters). The grid (projected) coordinates are indicated at the sheet boundaries in toises, so after selecting a corner point by computer mouse, we can easily give the projected coordinates of the corner. All in all, for all sheets, 728 GCPs are needed to be defined. Moreover, these GCPs can be picked up semi- or full automatically (Rus et al., 2010), there is no need to seek identical points of the terrain in the old and new maps. Figure 3: Result of the simple geo-reference of the Cassini sheets around Reims, NE France on the Google Earth basis. Results of the geo-reference and possible improvements The accuracy of this simple georeferencing method is surprising. Even very far from the projection origin, the horizontal errors are no more than a few hundred meters (Figs. 3 & 4).
5 Figure 4: Result of the simple geo-reference of the Cassini sheets around Le Verger, W France on the Google Earth basis. According to the results, the method is fully capable to build a mosaic for overview and coarse location purposes. Further improvement can be made by use a Bursa-Wolf type datum description, as Cassini & Maraldi (1744) published the coordinates of several terrain objects, whose modern coordinates are also available. Of course, a correction grid can be also compiled and applied, however this would need a lot of control points and, as it was mentioned in the Introduction, with a large sum of control points, the problem is already solved (Grosso, 2010; Costes et al., 2012; Herrault et al., 2013). References Amoud, J-L. (2013). Production of georeferenced data use, cost and accuracy. e-perimetron 8 (2): Boutoura, C. & E. Livieratos (2006). Some fundamentals for the study of the geometry of early maps by comparative methods. e-perimetron 1 (1): Cajthaml, J. (2011). Methods of georeferencing old maps ont he example of Czech early maps. In: Ruas, A. (ed.): Proceedings of the 25th International Cartographic Conference, Paris, France, 3-8 July, Cassini, C-F. & Maraldi, G. D. (1744). Nouvelle carte qui comprend les principaux triangles qui servent de fondement a la description geometrique de la France. Levee par ordre du Roy. Aubin & Heulland, Paris. Castaings, J., Dezileau, L., Fiandrino, A. & Verney, R. (2011). Evolution morphologique récente d un complexe lagunaire méditerranéen : le système des étangs Palavasiens (France). Revue Paralia 4:
6 Costes, B., Grosso, E. & Plumejeaud, C. (2012). Géoréférencement et appariement de données issues des cartes de Cassini : Intégration dans un référentiel topographique actuel. SAGEO12, Liège, Belgium. Dupouey, J.-L., J. Bachacou, R. Cosserat, S. Aberdam, D. Vallauri, G. Chappart & Corvisier De Villèle, M-A. (2007). Vers la réalisation d'une carte géoréférencée des forêts anciennes de France. Revue du Comité Français de Cartographie (CFC) 191: Grosso, E. (2010). Integration of historical geographic data into current georeferenced frameworks: A user-centered approach. e-perimetron 5 (3): Herrault, P-A., Sheeren, D., Fauvel, M., Monteil, C. & Paegelow, M. (2013). A comparative study of geometric transformation models for the historical Map of France registration. Geographia Technica 8 (1): Mugnier, C. J. (2001). Map grids & datums the French Republic. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing 67: 33 & 35. Rus, I., Balint, C., Crăciunescu, V., Constantunescu, S., Ovejanu, I. & Zs. Bartos-Elekes (2010). Automated georeference of the 1: Romanian maps under Lambert-Cholesky ( ) projection system. Acta Geodaetica et Geophysica Hungarica 45 (1): Timár, G.& G. Molnár (2013). Map grids & datums. University handout, Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest, 81 p. White, M.S. & P. Griffin (1985). Piecewise linear rubber-sheet map transformations. The American Cartographer 12 (3):
The Elements of GIS. Organizing Data and Information. The GIS Database. MAP and ATRIBUTE INFORMATION
 GIS s Roots in Cartography Getting Started With GIS Chapter 2 Dursun Z. Seker MAP and ATRIBUTE INFORMATION Data (numbers and text) store as files refer to them collectively as a database gather inform.
GIS s Roots in Cartography Getting Started With GIS Chapter 2 Dursun Z. Seker MAP and ATRIBUTE INFORMATION Data (numbers and text) store as files refer to them collectively as a database gather inform.
Working with georeferenced data. What is georeferencing? Coordinate Systems. Geographic and Projected Coordinate System
 GIS501 Fundamentals of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) Coordinate Systems Working with georeferenced data What is georeferencing? Geographically referenced data which is, in some way, referenced
GIS501 Fundamentals of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) Coordinate Systems Working with georeferenced data What is georeferencing? Geographically referenced data which is, in some way, referenced
SYSTEM OF THE 1: SCALE SHEETS OF THE SECOND MILITARY SURVEY IN TYROL AND SALZBURG
 Acta Geod. Geoph. Hung., Vol. 44(1), pp. 95 104 (2009) DOI: 10.1556/AGeod.44.2009.1.9 SYSTEM OF THE 1:28 800 SCALE SHEETS OF THE SECOND MILITARY SURVEY IN TYROL AND SALZBURG GTimár Department of Geophysics
Acta Geod. Geoph. Hung., Vol. 44(1), pp. 95 104 (2009) DOI: 10.1556/AGeod.44.2009.1.9 SYSTEM OF THE 1:28 800 SCALE SHEETS OF THE SECOND MILITARY SURVEY IN TYROL AND SALZBURG GTimár Department of Geophysics
Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections
 Organizing Data and Information Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections Map Scales Projections Information can be organized as lists, numbers, tables, text, pictures, maps, or indexes. Clusters of information
Organizing Data and Information Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections Map Scales Projections Information can be organized as lists, numbers, tables, text, pictures, maps, or indexes. Clusters of information
What Do You See? FOR 274: Forest Measurements and Inventory. Area Determination: Frequency and Cover
 What Do You See? Message of the Day: Many options exist to determine the size, area, or extent of a feature on a landscape FOR 274: Forest Measurements and Inventory Lecture 7: Measures of Land Area Frequency
What Do You See? Message of the Day: Many options exist to determine the size, area, or extent of a feature on a landscape FOR 274: Forest Measurements and Inventory Lecture 7: Measures of Land Area Frequency
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL. Lecture-1 Chapters 1 and 2
 Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-1 Chapters 1 and 2 What is GIS? A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer system for capturing, storing, querying, analyzing and
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-1 Chapters 1 and 2 What is GIS? A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer system for capturing, storing, querying, analyzing and
UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.97/6/IP. 33
 UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.97/6/IP. 33 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Seventeenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, 18-22 September 2006 Item 7 of the provisional
UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.97/6/IP. 33 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Seventeenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, 18-22 September 2006 Item 7 of the provisional
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: READS
 See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/259480162 Map grids and datums Book December 2013 DOI: 10.13140/2.1.2362.0167 CITATIONS 4 READS
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/259480162 Map grids and datums Book December 2013 DOI: 10.13140/2.1.2362.0167 CITATIONS 4 READS
Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts. -Coordinate Systems -Datum
 Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts -Map Projections -Coordinate Systems -Datum Map projection is "the process of systematically transforming positions on the Earth's spherical surface
Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts -Map Projections -Coordinate Systems -Datum Map projection is "the process of systematically transforming positions on the Earth's spherical surface
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2012
 WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2012 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Datums Datums A reference surface of the Earth Used as the
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2012 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Datums Datums A reference surface of the Earth Used as the
GPS Remote Sensing. GIS Photogrammetry. GEODESY Equipment (total station) CARTOGRAPHY Survey Software. Map Projection Coordinate Systems
 GPS Remote Sensing GIS Photogrammetry GEODESY Equipment (total station) CARTOGRAPHY Survey Software Map Projection Coordinate Systems 1 Coordinate Systems, Datum and Map Projection Dr. Maher A. El-Hallaq
GPS Remote Sensing GIS Photogrammetry GEODESY Equipment (total station) CARTOGRAPHY Survey Software Map Projection Coordinate Systems 1 Coordinate Systems, Datum and Map Projection Dr. Maher A. El-Hallaq
REFERENCING COORDINATE SYSTEMS MAP PROJECTIONS GEOREFERENCING
 GIS in Ecology SPATIAL REFERENCING COORDINATE SYSTEMS MAP PROJECTIONS GEOREFERENCING : :1 Where on earth? Early mapmakers recognized the need for a system that could locate features on the earth's surface.
GIS in Ecology SPATIAL REFERENCING COORDINATE SYSTEMS MAP PROJECTIONS GEOREFERENCING : :1 Where on earth? Early mapmakers recognized the need for a system that could locate features on the earth's surface.
ch02.pdf chap2.pdf chap02.pdf
 Introduction to Geographic Information Systems 8th Edition Karl Solutions Manual Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/introduction-to-geographic-information-systems-8th-edition-karl-solutions-manu
Introduction to Geographic Information Systems 8th Edition Karl Solutions Manual Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/introduction-to-geographic-information-systems-8th-edition-karl-solutions-manu
DETAILED ANALYSIS OF THE MÜLLER S MAP OF BOHEMIA
 DETAILED ANALYSIS OF THE MÜLLER S MAP OF BOHEMIA Jiri Cajthaml Department of Mapping and Cartography Faculty of Civil Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague Thakurova 7, 166 29 Prague 6, Czech
DETAILED ANALYSIS OF THE MÜLLER S MAP OF BOHEMIA Jiri Cajthaml Department of Mapping and Cartography Faculty of Civil Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague Thakurova 7, 166 29 Prague 6, Czech
12/26/2012. Geographic Information Systems * * * * GIS (... yrezaei
 ( - Geographic Information Systems ( ( 1 2 3 Information System Data base DB IS IS DB (Knowledge ( ( (System (Information System - (Georefrence Analysis Data + Knowledge ======== Information 4 5 ( < 10%
( - Geographic Information Systems ( ( 1 2 3 Information System Data base DB IS IS DB (Knowledge ( ( (System (Information System - (Georefrence Analysis Data + Knowledge ======== Information 4 5 ( < 10%
Scientific project report
 Scientific project report Title of project: DIGITIZING, GEOREFERENCING AND PUBLISHING ON WEB OF THE MAP OF SOUTHERN ROMANIA ( CHARTA ROMÂNIEI MERIDIONALE ) Project number: PN-II-RU-TE-2011-3-0125 Project
Scientific project report Title of project: DIGITIZING, GEOREFERENCING AND PUBLISHING ON WEB OF THE MAP OF SOUTHERN ROMANIA ( CHARTA ROMÂNIEI MERIDIONALE ) Project number: PN-II-RU-TE-2011-3-0125 Project
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015
 WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Where is Boston? Introducing Geodesy, Ellipsoids & Geoids Geodesy
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Where is Boston? Introducing Geodesy, Ellipsoids & Geoids Geodesy
e-perimetron, Vol. 9, No. 3, 2014 [ ] ISSN
![e-perimetron, Vol. 9, No. 3, 2014 [ ] ISSN e-perimetron, Vol. 9, No. 3, 2014 [ ] ISSN](/thumbs/83/87610449.jpg) Gabor Timár *,**, Zsombor Bartos-Elekes **, Vasile Crăciunescu ***, C. Flueraru ***, Zoltán Imecs **, Zsolt Magyar-Sáska ** Danger doesn t vanish with the dikes: Comparison of the inundation pattern of
Gabor Timár *,**, Zsombor Bartos-Elekes **, Vasile Crăciunescu ***, C. Flueraru ***, Zoltán Imecs **, Zsolt Magyar-Sáska ** Danger doesn t vanish with the dikes: Comparison of the inundation pattern of
Introduction to Geographic Information Science. Updates/News. Last Lecture. Geography 4103 / Map Projections and Coordinate Systems
 Geography 4103 / 5103 Introduction to Geographic Information Science Map Projections and Coordinate Systems Updates/News Thursday s lecture Reading discussion 1 find the readings online open questions,
Geography 4103 / 5103 Introduction to Geographic Information Science Map Projections and Coordinate Systems Updates/News Thursday s lecture Reading discussion 1 find the readings online open questions,
Using of Old Maps within Landscape Changes Analysis
 Using of Old Maps within Landscape Changes Analysis Assoc. Prof. Jiri Cajthaml*, Dr. Jan Pacina** * Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Civil Engineering ** Jan Evangelista Purkyne University
Using of Old Maps within Landscape Changes Analysis Assoc. Prof. Jiri Cajthaml*, Dr. Jan Pacina** * Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Civil Engineering ** Jan Evangelista Purkyne University
Outline. Shape of the Earth. Geographic Coordinates (φ, λ, z) Ellipsoid or Spheroid Rotate an ellipse around an axis. Ellipse.
 Map Projections Outline Geodesy and map projections Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh Shape
Map Projections Outline Geodesy and map projections Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh Shape
Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910
 Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910 Where are you? 31UFT8361 174,7 441,2 51 58' NB 5 40' OL 2/60 Who are they? 3/60 Do geo data describe Earth s phenomena perfectly? Georeference systems ellipsoid
Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910 Where are you? 31UFT8361 174,7 441,2 51 58' NB 5 40' OL 2/60 Who are they? 3/60 Do geo data describe Earth s phenomena perfectly? Georeference systems ellipsoid
This week s topics. Week 6. FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications. Week 6
 FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 6 Week 6 Last week Chapter 8 Combining and splitting landscape features and merging GIS databases Chapter 11 Overlay processes Questions? Next week
FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 6 Week 6 Last week Chapter 8 Combining and splitting landscape features and merging GIS databases Chapter 11 Overlay processes Questions? Next week
Mapping coordinate systems
 Mapping coordinate systems 1. The Earth's Graticule Latitude and Longitude The graticule is the imaginary grid of lines running east-west (lines of latitude = parallels) and north-south lines of longitude
Mapping coordinate systems 1. The Earth's Graticule Latitude and Longitude The graticule is the imaginary grid of lines running east-west (lines of latitude = parallels) and north-south lines of longitude
Intro to GIS Fall 2010 Georeferencing & Map Projections
 Intro to GIS Fall 2010 Georeferencing & Map Projections SHAPE OF THE EARTH Earth's Shape Geoid: shape of earth minus topographic features (irregular due to local variations in gravity) Ellipsoid: elongated
Intro to GIS Fall 2010 Georeferencing & Map Projections SHAPE OF THE EARTH Earth's Shape Geoid: shape of earth minus topographic features (irregular due to local variations in gravity) Ellipsoid: elongated
Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910
 Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910 Where are you? 31UFT8361 174,7 441,2 51 58' NB 5 40' OL 2/60 Who are they? 3/60 Do geo data describe Earth s phenomena perfectly? Georeference systems ellipsoid
Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910 Where are you? 31UFT8361 174,7 441,2 51 58' NB 5 40' OL 2/60 Who are they? 3/60 Do geo data describe Earth s phenomena perfectly? Georeference systems ellipsoid
Shape e o f f the e Earth
 1 Coordinate Systems & Projections Coordinate Systems Two map layers are not going to register spatially unless they are based on the same coordinate system. 2 Contents Shape of the earth Datum Projections
1 Coordinate Systems & Projections Coordinate Systems Two map layers are not going to register spatially unless they are based on the same coordinate system. 2 Contents Shape of the earth Datum Projections
A PRIMER ON COORDINATE SYSTEMS Commonly Used in Michigan
 A PRIMER ON COORDINATE SYSTEMS Commonly Used in Michigan David P. Lusch, Ph.D., GISP Department of Geography Remote Sensing & GIS Research and Outreach Services Group Michigan State University September,
A PRIMER ON COORDINATE SYSTEMS Commonly Used in Michigan David P. Lusch, Ph.D., GISP Department of Geography Remote Sensing & GIS Research and Outreach Services Group Michigan State University September,
Georeferencing. Where on earth are we? Critical for importing and combining layers for mapping
 Georeferencing Where on earth are we? Critical for importing and combining layers for mapping 1. The Geoid Earth is not a perfect sphere, it is ellipsoidal.. earth is the 'Geoid'. The difference between
Georeferencing Where on earth are we? Critical for importing and combining layers for mapping 1. The Geoid Earth is not a perfect sphere, it is ellipsoidal.. earth is the 'Geoid'. The difference between
What is a Map Projection?
 What is a Map Projection? It is how we represent a three dimensional Earth on a flat piece of paper However The process of transferring information from the Earth to a map causes every projection to distort
What is a Map Projection? It is how we represent a three dimensional Earth on a flat piece of paper However The process of transferring information from the Earth to a map causes every projection to distort
Dr. ABOLGHASEM AKBARI Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources, University Malaysia Pahang (UMP)
 Workshop on : Dr. ABOLGHASEM AKBARI Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources, University Malaysia Pahang (UMP) 14-15 April 2016 Venue: Tehran, Iran GIS definitions GIS: A simplified view of the real
Workshop on : Dr. ABOLGHASEM AKBARI Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources, University Malaysia Pahang (UMP) 14-15 April 2016 Venue: Tehran, Iran GIS definitions GIS: A simplified view of the real
Projections & GIS Data Collection: An Overview
 Projections & GIS Data Collection: An Overview Projections Primary data capture Secondary data capture Data transfer Capturing attribute data Managing a data capture project Geodesy Basics for Geospatial
Projections & GIS Data Collection: An Overview Projections Primary data capture Secondary data capture Data transfer Capturing attribute data Managing a data capture project Geodesy Basics for Geospatial
GIS in Water Resources. Fall Homework #1
 GIS in Water Resources Fall 2015 Homework #1 Goal The goal of this homework is to reinforce the lecture material on Geodesy, Map Projections and Coordinate Systems by having you identify attributes and
GIS in Water Resources Fall 2015 Homework #1 Goal The goal of this homework is to reinforce the lecture material on Geodesy, Map Projections and Coordinate Systems by having you identify attributes and
Map Projections. Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps
 Map Projections Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps Map projections Define the spatial relationship between locations on earth and their relative locations on a flat map Are mathematical expressions
Map Projections Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps Map projections Define the spatial relationship between locations on earth and their relative locations on a flat map Are mathematical expressions
Coordinate Systems. Location on earth is defined by coordinates
 Coordinate Systems We think of the earth as a sphere It is actually a spheroid (ellipsoid), slightly larger in radius at the equator than at the poles Shape of the Earth Location on earth is defined by
Coordinate Systems We think of the earth as a sphere It is actually a spheroid (ellipsoid), slightly larger in radius at the equator than at the poles Shape of the Earth Location on earth is defined by
1/28/16. EGM101 Skills Toolbox. Oblate spheroid. The shape of the earth Co-ordinate systems Map projections. Geoid
 EGM101 Skills Toolbox Oblate spheroid The shape of the earth Co-ordinate systems Map projections The geoid is the shape that the surface of the oceans would take under the influence of Earth's gravitation
EGM101 Skills Toolbox Oblate spheroid The shape of the earth Co-ordinate systems Map projections The geoid is the shape that the surface of the oceans would take under the influence of Earth's gravitation
Version 1.1 GIS Syllabus
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CERTIFICATION Version 1.1 GIS Syllabus Endorsed 1 Version 1 January 2007 GIS Certification Programme 1. Target The GIS certification is aimed at: Those who wish to demonstrate
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CERTIFICATION Version 1.1 GIS Syllabus Endorsed 1 Version 1 January 2007 GIS Certification Programme 1. Target The GIS certification is aimed at: Those who wish to demonstrate
Referencing map features: Coordinate systems and map projections
 Referencing map features: Coordinate systems and map projections Coordinate systems and map projections if we want to integrate geographic data from many different sources, we need to use a consistent
Referencing map features: Coordinate systems and map projections Coordinate systems and map projections if we want to integrate geographic data from many different sources, we need to use a consistent
Lecture 4. Coordinate Systems & Projections
 Lecture 4 Coordinate Systems & Projections Outline Geodesy Geoids Ellipsoids Geographic Coordinate Systems Magnetic North vs. True North Datums Projections Applying Coordinate Systems and Projections Why
Lecture 4 Coordinate Systems & Projections Outline Geodesy Geoids Ellipsoids Geographic Coordinate Systems Magnetic North vs. True North Datums Projections Applying Coordinate Systems and Projections Why
Map Projections. What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL
 Map Projections What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL 1 CYLINDRICAL EQUAL AREA BONNE CRASTER PARABOLIC 2 ECKERT I ECKERT III ECKERT V There are many
Map Projections What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL 1 CYLINDRICAL EQUAL AREA BONNE CRASTER PARABOLIC 2 ECKERT I ECKERT III ECKERT V There are many
Georeferencing. Place names Postal addresses Postal codes Coordinate systems (lat/long, UTM, etc.)
 Georeferencing Georeferencing Used to describe the act of assigning locations to data or information Certain requirements include that they are: unique, have shared meaning, and are persistent through
Georeferencing Georeferencing Used to describe the act of assigning locations to data or information Certain requirements include that they are: unique, have shared meaning, and are persistent through
SPOT DEM Product Description
 SPOT DEM Product Description Version 1.1 - May 1 st, 2004 This edition supersedes previous versions Acronyms DIMAP DTED DXF HRS JPEG, JPG DEM SRTM SVG Tiff - GeoTiff XML Digital Image MAP encapsulation
SPOT DEM Product Description Version 1.1 - May 1 st, 2004 This edition supersedes previous versions Acronyms DIMAP DTED DXF HRS JPEG, JPG DEM SRTM SVG Tiff - GeoTiff XML Digital Image MAP encapsulation
EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography
 EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography Lecture 3 Geodesy Map Projections, Datums, and Coordinate Systems 1 Geodesy The science of measuring and representing the shape and size of the earth, and
EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography Lecture 3 Geodesy Map Projections, Datums, and Coordinate Systems 1 Geodesy The science of measuring and representing the shape and size of the earth, and
What is Geodesy? Types of Geodesy terrestrial or classical geodesy space geodesy theoretical geodesy
 What is Geodesy? Geodesy is the study of: The size, shape and motion of the earth The measurement of the position and motion of points on the earth's surface, and The study of the earth's gravity field
What is Geodesy? Geodesy is the study of: The size, shape and motion of the earth The measurement of the position and motion of points on the earth's surface, and The study of the earth's gravity field
NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections
 NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections From http://www.or.blm.gov/gis/ 1 Geographic coordinates Coordinates are expressed as Latitude and Longitude in Degrees, Minutes, Seconds
NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections From http://www.or.blm.gov/gis/ 1 Geographic coordinates Coordinates are expressed as Latitude and Longitude in Degrees, Minutes, Seconds
The Wildlife Society Meet and Greet. Come learn about what the UNBC Student Chapter of TWS is all about!
 Georeferencing I GEOG 300, Lecture 4 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 The Wildlife Society Meet and Greet Quiz Come learn about what the UNBC Student Chapter of TWS is all about! 5:30 7:30 PM, Wednesday September
Georeferencing I GEOG 300, Lecture 4 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 The Wildlife Society Meet and Greet Quiz Come learn about what the UNBC Student Chapter of TWS is all about! 5:30 7:30 PM, Wednesday September
GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATE SYSTEMS
 GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATE SYSTEMS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015 What is Georeferencing? Used to establish a location on the Earth s surface 1 st order polynomial transformation Georeferencing toolbar What
GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATE SYSTEMS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015 What is Georeferencing? Used to establish a location on the Earth s surface 1 st order polynomial transformation Georeferencing toolbar What
Positional Accuracy of the Google Earth Imagery In The Gaza Strip
 Positional Accuracy of the Google Earth Imagery In The Gaza Strip Maher A. El-Hallaq Associate Professor of Surveying Civil Engineering Department The Islamic University of Gaza, Palestine mhallaq@iugaza.edu.ps
Positional Accuracy of the Google Earth Imagery In The Gaza Strip Maher A. El-Hallaq Associate Professor of Surveying Civil Engineering Department The Islamic University of Gaza, Palestine mhallaq@iugaza.edu.ps
SECTION 4 PARCEL IDENTIFIERS 4.1 LONGITUDE AND LATITUDE
 SECTION 4 PARCEL IDENTIFIERS 4.1 LONGITUDE AND LATITUDE Most maps must be drawn in such a way that points and areas can be located accurately on the earth's surface and described objectively. A uniform
SECTION 4 PARCEL IDENTIFIERS 4.1 LONGITUDE AND LATITUDE Most maps must be drawn in such a way that points and areas can be located accurately on the earth's surface and described objectively. A uniform
4 Survey Datums. 4.1 Horizontal Datum Policy SURVEY DATUMS SEPTEMBER 2006
 4 Survey Datums Today s multi-organizational Project Development efforts require the use of common, accurate horizontal and vertical survey datums and consistent, precise control-survey procedures to ensure
4 Survey Datums Today s multi-organizational Project Development efforts require the use of common, accurate horizontal and vertical survey datums and consistent, precise control-survey procedures to ensure
Scott A. True Project Scientist Geodesy & Geophysics Division Basic and Applied Research Office InnoVision Directorate
 EGM96 Variable Resolution Geoid Implementation Error in GEOTRANS 2.3 Scott A. True Project Scientist Geodesy & Geophysics Division Basic and Applied Research Office InnoVision Directorate Introduction
EGM96 Variable Resolution Geoid Implementation Error in GEOTRANS 2.3 Scott A. True Project Scientist Geodesy & Geophysics Division Basic and Applied Research Office InnoVision Directorate Introduction
Catchment Delineation Workflow
 Catchment Delineation Workflow Slide 1 Given is a GPS point (Lat./Long.) for an outlet location. The outlet could be a proposed Dam site, a storm water drainage culvert on a rural highway, or any other
Catchment Delineation Workflow Slide 1 Given is a GPS point (Lat./Long.) for an outlet location. The outlet could be a proposed Dam site, a storm water drainage culvert on a rural highway, or any other
Data acquisition and integration 1.
 Data acquisition and integration 1. Ferenc Végső Data acquisition and integration 1.: Ferenc Végső Lector: Árpád Barsi This module was created within TÁMOP - 4.1.2-08/1/A-2009-0027 "Tananyagfejlesztéssel
Data acquisition and integration 1. Ferenc Végső Data acquisition and integration 1.: Ferenc Végső Lector: Árpád Barsi This module was created within TÁMOP - 4.1.2-08/1/A-2009-0027 "Tananyagfejlesztéssel
How does an ellipsoid differ from a sphere in approximating the shape and size of the Earth?
 Chapter 02 Test Bank Worksheet Questions 1. What is a map projection? Topic: Map Projection 2. How does an ellipsoid differ from a sphere in approximating the shape and size of the Earth? Topic: Ellipsoid
Chapter 02 Test Bank Worksheet Questions 1. What is a map projection? Topic: Map Projection 2. How does an ellipsoid differ from a sphere in approximating the shape and size of the Earth? Topic: Ellipsoid
Understanding Projections for GIS
 Presented by John Schaeffer Juniper GIS Services, Inc. This PowerPoint is available at JuniperGIS.com Presentation Objectives To understand basic concepts on projections and coordinate systems for the
Presented by John Schaeffer Juniper GIS Services, Inc. This PowerPoint is available at JuniperGIS.com Presentation Objectives To understand basic concepts on projections and coordinate systems for the
Spatial locations. Spatial locations. Spatial locations. Spatial locations
 Where am I? sounds simple, but definitely not huge amount of picky detail Cartographers make a career from the details focus on the minimum you need to know c Philip M. Dixon (Iowa State Univ.) Spatial
Where am I? sounds simple, but definitely not huge amount of picky detail Cartographers make a career from the details focus on the minimum you need to know c Philip M. Dixon (Iowa State Univ.) Spatial
Data acquisition and integration 1.
 University of West Hungary, Faculty of Geoinformatics Ferenc Végső Data acquisition and integration 1. module DAI1 The basics of positioning SZÉKESFEHÉRVÁR 2010 The right to this intellectual property
University of West Hungary, Faculty of Geoinformatics Ferenc Végső Data acquisition and integration 1. module DAI1 The basics of positioning SZÉKESFEHÉRVÁR 2010 The right to this intellectual property
CHAPTER EXIT CHAPTER. Models of Earth. 3.1 Modeling the Planet. 3.2 Mapmaking and Technology. 3.3 Topographic Maps CHAPTER OUTLINE
 EXIT CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet.2 Mapmaking and Technology. Topographic Maps CHAPTER OUTLINE CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet A flat of Earth is a convenient tool, but it can distort the shape, distance,
EXIT CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet.2 Mapmaking and Technology. Topographic Maps CHAPTER OUTLINE CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet A flat of Earth is a convenient tool, but it can distort the shape, distance,
A methodology for image matching of historical maps
 Mohamed S. El-Hussainy *, Moustafa A. Baraka **, Maher A. El-Hallaq *** A methodology for image matching of historical maps Keywords: Historic Maps, Modern Maps, Image Processing, Transformation, Correlation
Mohamed S. El-Hussainy *, Moustafa A. Baraka **, Maher A. El-Hallaq *** A methodology for image matching of historical maps Keywords: Historic Maps, Modern Maps, Image Processing, Transformation, Correlation
Modern Navigation. Thomas Herring
 12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Today s Class Latitude and Longitude Simple spherical definitions Geodetic definition: For an ellipsoid Astronomical definition: Based on direction of gravity Relationships
12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Today s Class Latitude and Longitude Simple spherical definitions Geodetic definition: For an ellipsoid Astronomical definition: Based on direction of gravity Relationships
The Nature of Spatial Data. Keith C. Clarke Geography UCSB
 The Nature of Spatial Data Keith C. Clarke Geography UCSB Geographic primitives G = g (x, y, z, s, A, t) [x, y, z] = f(λ, φ, d) Geography also highly dependent upon model First, the datum (d) Models of
The Nature of Spatial Data Keith C. Clarke Geography UCSB Geographic primitives G = g (x, y, z, s, A, t) [x, y, z] = f(λ, φ, d) Geography also highly dependent upon model First, the datum (d) Models of
Lab #3 Map Projections.
 Lab #3 Map Projections http://visual.merriam-webster.com/images/earth/geography/cartography/map-projections.jpg Map Projections Projection: a systematic arrangement of parallels and meridians on a plane
Lab #3 Map Projections http://visual.merriam-webster.com/images/earth/geography/cartography/map-projections.jpg Map Projections Projection: a systematic arrangement of parallels and meridians on a plane
Analysis of European Topographic Maps for Monitoring Settlement Development
 Analysis of European Topographic Maps for Monitoring Settlement Development Ulrike Schinke*, Hendrik Herold*, Gotthard Meinel*, Nikolas Prechtel** * Leibniz Institute of Ecological Urban and Regional Development,
Analysis of European Topographic Maps for Monitoring Settlement Development Ulrike Schinke*, Hendrik Herold*, Gotthard Meinel*, Nikolas Prechtel** * Leibniz Institute of Ecological Urban and Regional Development,
Precise Hong Kong Geoid HKGEOID-2000
 Yong-Qi Chen 1, Zhicai Luo 1 and Simon Kwok 2 1.Department of Land Surveying and Geo-Informatics, The Hong Kong olytechnic University 2 Geodetic Survey Section, Lands Department, HKSAR Abstract: This paper
Yong-Qi Chen 1, Zhicai Luo 1 and Simon Kwok 2 1.Department of Land Surveying and Geo-Informatics, The Hong Kong olytechnic University 2 Geodetic Survey Section, Lands Department, HKSAR Abstract: This paper
DATA SOURCES AND INPUT IN GIS. By Prof. A. Balasubramanian Centre for Advanced Studies in Earth Science, University of Mysore, Mysore
 DATA SOURCES AND INPUT IN GIS By Prof. A. Balasubramanian Centre for Advanced Studies in Earth Science, University of Mysore, Mysore 1 1. GIS stands for 'Geographic Information System'. It is a computer-based
DATA SOURCES AND INPUT IN GIS By Prof. A. Balasubramanian Centre for Advanced Studies in Earth Science, University of Mysore, Mysore 1 1. GIS stands for 'Geographic Information System'. It is a computer-based
GPS Surveying Dr. Jayanta Kumar Ghosh Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee. Lecture 06 GPS Position
 GPS Surveying Dr. Jayanta Kumar Ghosh Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Lecture 06 GPS Position Friends! Welcome you to sixth class on GPS surveying. Today, I am going
GPS Surveying Dr. Jayanta Kumar Ghosh Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Lecture 06 GPS Position Friends! Welcome you to sixth class on GPS surveying. Today, I am going
When the Earth Was Flat. Measurements were made using a plumb bob, a spirit level, and a stick. Also, the Stars.
 ABSTRACT Defining the shape of the Earth geoid. Mathematical models spheroid or ellipsoid Mathematical projection of geodetic systems GIS/GPS technology The need for a unified projection systems World
ABSTRACT Defining the shape of the Earth geoid. Mathematical models spheroid or ellipsoid Mathematical projection of geodetic systems GIS/GPS technology The need for a unified projection systems World
1. Geospatial technology rarely links geospatial data to nonspatial data. a. True *b. False
 Chapter 2 Where in the Geospatial World Are You? 1. Geospatial technology rarely links geospatial data to nonspatial data. 2. For geospatial technology to work, every location on Earth must be: a. inhabited
Chapter 2 Where in the Geospatial World Are You? 1. Geospatial technology rarely links geospatial data to nonspatial data. 2. For geospatial technology to work, every location on Earth must be: a. inhabited
Lecture 2. Map Projections and GIS Coordinate Systems. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
 Lecture 2 Map Projections and GIS Coordinate Systems Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Map Projections Map projections are mathematical formulas
Lecture 2 Map Projections and GIS Coordinate Systems Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Map Projections Map projections are mathematical formulas
Comparative analysis of historical maps of the Canton of Zurich - Switzerland in an interactive online platform
 Comparative analysis of historical maps of the Canton of Zurich - Switzerland in an interactive online platform Angeliki Tsorlini, Ionut Iosifescu, Lorenz Hurni ETH Zurich, Institute of Cartography and
Comparative analysis of historical maps of the Canton of Zurich - Switzerland in an interactive online platform Angeliki Tsorlini, Ionut Iosifescu, Lorenz Hurni ETH Zurich, Institute of Cartography and
Geographic Information Systems class # 1 February 19, Coordinate reference systems in GIS: geodetic coordinates
 Geographic Information Systems class # 1 February 19, 2013 Coordinate reference systems in GIS: geodetic coordinates Manuel Campagnolo ISA Manuel Campagnolo (ISA) GIS/SIG 2012 2013 February 19, 2013 1
Geographic Information Systems class # 1 February 19, 2013 Coordinate reference systems in GIS: geodetic coordinates Manuel Campagnolo ISA Manuel Campagnolo (ISA) GIS/SIG 2012 2013 February 19, 2013 1
Overview key concepts and terms (based on the textbook Chang 2006 and the practical manual)
 Introduction Geo-information Science (GRS-10306) Overview key concepts and terms (based on the textbook 2006 and the practical manual) Introduction Chapter 1 Geographic information system (GIS) Geographically
Introduction Geo-information Science (GRS-10306) Overview key concepts and terms (based on the textbook 2006 and the practical manual) Introduction Chapter 1 Geographic information system (GIS) Geographically
Geographers Perspectives on the World
 What is Geography? Geography is not just about city and country names Geography is not just about population and growth Geography is not just about rivers and mountains Geography is a broad field that
What is Geography? Geography is not just about city and country names Geography is not just about population and growth Geography is not just about rivers and mountains Geography is a broad field that
The Gauss Conform Coordinate
 Surveying The South African Coordinate Reference System (Part 2) by Aslam Parker, Chief Directorate: National Geo-spatial Information Part 1 of this article (see PositionIT Nov/Dec 2011) focused on the
Surveying The South African Coordinate Reference System (Part 2) by Aslam Parker, Chief Directorate: National Geo-spatial Information Part 1 of this article (see PositionIT Nov/Dec 2011) focused on the
2. GETTING STARTED WITH GIS
 2. GETTING STARTED WITH GIS What are geographic information systems and what are they used for? ArcGIS: ArcMap, ArcCatalog and ArcToolbox Vector data vs. raster data vs. attribute tables Polygons, polylines,
2. GETTING STARTED WITH GIS What are geographic information systems and what are they used for? ArcGIS: ArcMap, ArcCatalog and ArcToolbox Vector data vs. raster data vs. attribute tables Polygons, polylines,
Georeferencing. Geography is the key to linking attributes. Georeferencing is the key to geography.
 Georeferencing Geography is the key to linking attributes. Georeferencing is the key to geography. Why georeferencing? Many reasons for having georeferences Many different approaches to georeferencing
Georeferencing Geography is the key to linking attributes. Georeferencing is the key to geography. Why georeferencing? Many reasons for having georeferences Many different approaches to georeferencing
EUROPEAN COMPUTER DRIVING LICENCE. GIS Cartography. Syllabus
 EUROPEAN COMPUTER DRIVING LICENCE GIS Cartography Syllabus Purpose This document details the syllabus for ECDL GIS Module 1 Cartography. The syllabus describes, through learning outcomes, the knowledge
EUROPEAN COMPUTER DRIVING LICENCE GIS Cartography Syllabus Purpose This document details the syllabus for ECDL GIS Module 1 Cartography. The syllabus describes, through learning outcomes, the knowledge
EXPLANATION OF G.I.S. PROJECT ALAMEIN FOR WEB PUBLISHING
 EXPLANATION OF G.I.S. PROJECT ALAMEIN FOR WEB PUBLISHING Compilato: Andrea De Felici Rivisto: Approvato: Daniele Moretto ARIDO S President Versione: 1.0 Distribuito: 28/06/2013 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION..3
EXPLANATION OF G.I.S. PROJECT ALAMEIN FOR WEB PUBLISHING Compilato: Andrea De Felici Rivisto: Approvato: Daniele Moretto ARIDO S President Versione: 1.0 Distribuito: 28/06/2013 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION..3
KURSUS COORDINATED CADASTRAL SYSTEM (CCS) INSTITUT TANAH & UKUR NEGARA BEHRANG, PERAK
 KURSUS COORDINATED CADASTRAL SYSTEM (CCS) INSTITUT TANAH & UKUR NEGARA BEHRANG, PERAK TECHNIQUES FOR INTEGRATING THE DIGITAL COORDINATED CADASTRAL DATA WITH MAPPING DATA (MODULE C) OLEH: ASSOC.PROF DR
KURSUS COORDINATED CADASTRAL SYSTEM (CCS) INSTITUT TANAH & UKUR NEGARA BEHRANG, PERAK TECHNIQUES FOR INTEGRATING THE DIGITAL COORDINATED CADASTRAL DATA WITH MAPPING DATA (MODULE C) OLEH: ASSOC.PROF DR
Module 2: Mapping Topic 2 Content: Determining Latitude and Longitude Notes
 Introduction In order to more easily locate points on a globe or map, cartographers designed a system of imaginary vertical lines (also called parallels) and horizontal lines (also called meridians) that
Introduction In order to more easily locate points on a globe or map, cartographers designed a system of imaginary vertical lines (also called parallels) and horizontal lines (also called meridians) that
GIST 3300 / Geographic Information Systems. Last Time. Today
 GIST 3300 / 5300 Last Time Ellipsoids and Datums Today Map Projections Map Projections Today we will build on the concepts of Geographic Coordinate Systems, Ellipsoids and Datums and add the concepts of
GIST 3300 / 5300 Last Time Ellipsoids and Datums Today Map Projections Map Projections Today we will build on the concepts of Geographic Coordinate Systems, Ellipsoids and Datums and add the concepts of
Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006
 I. Introduction and References Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006 The world is, approximately, a sphere. Maps are flat. Making maps requires some method of putting
I. Introduction and References Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006 The world is, approximately, a sphere. Maps are flat. Making maps requires some method of putting
Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems.
 Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems. A GIS without coordinates would simply be a database like Microsoft Excel
Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems. A GIS without coordinates would simply be a database like Microsoft Excel
Map projections. Rüdiger Gens
 Rüdiger Gens Coordinate systems Geographic coordinates f a: semi-major axis b: semi-minor axis Geographic latitude b Geodetic latitude a f: flattening = (a-b)/a Expresses as a fraction 1/f = about 300
Rüdiger Gens Coordinate systems Geographic coordinates f a: semi-major axis b: semi-minor axis Geographic latitude b Geodetic latitude a f: flattening = (a-b)/a Expresses as a fraction 1/f = about 300
Introduction to GIS - 2
 Introduction to GIS - 2 Outline Using GIS Representation of spatial objects in GIS Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh
Introduction to GIS - 2 Outline Using GIS Representation of spatial objects in GIS Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh
Monitoring vegetation activity in Hungary using Direct Broadcast MODIS data
 Monitoring vegetation activity in Hungary using Direct Broadcast MODIS data Anikó Kern1 Contributors: Szilárd Pásztor1, Péter Bognár1, Zoltán Barcza2, Gábor Timár1, János Lichtenberger1, Péter Steinbach3,
Monitoring vegetation activity in Hungary using Direct Broadcast MODIS data Anikó Kern1 Contributors: Szilárd Pásztor1, Péter Bognár1, Zoltán Barcza2, Gábor Timár1, János Lichtenberger1, Péter Steinbach3,
Evaluation of GPS in Orthometric Heights Determination in Khartoum State (Sudan)
 Evaluation of GPS in Orthometric Heights Determination in Khartoum State (Sudan) Dr. Nagi Zomrawi Mohammed 1, Dr. Abd Elrahim Elgizouli Mohammed 2 and Engineer Osman Bakry 3 1 Sudan University of Science
Evaluation of GPS in Orthometric Heights Determination in Khartoum State (Sudan) Dr. Nagi Zomrawi Mohammed 1, Dr. Abd Elrahim Elgizouli Mohammed 2 and Engineer Osman Bakry 3 1 Sudan University of Science
Lecture 10-14: Map Projections and Coordinate System
 URP 1281 Surveying and Cartography Lecture 10-14: Map Projections and Coordinate System December 27, 2015 Course Teacher: Md. Esraz-Ul-Zannat Assistant Professor Department of Urban and Regional Planning
URP 1281 Surveying and Cartography Lecture 10-14: Map Projections and Coordinate System December 27, 2015 Course Teacher: Md. Esraz-Ul-Zannat Assistant Professor Department of Urban and Regional Planning
DATA 301 Introduction to Data Analytics Geographic Information Systems
 DATA 301 Introduction to Data Analytics Geographic Information Systems Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca DATA 301: Data Analytics (2) Why learn Geographic
DATA 301 Introduction to Data Analytics Geographic Information Systems Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca DATA 301: Data Analytics (2) Why learn Geographic
USAGE OF OLD MAPS AND THEIR DISTRIBUTION WITHIN THE FRAME OF WEB MAP SERVICES
 USAGE OF OLD MAPS AND THEIR DISTRIBUTION WITHIN THE FRAME OF WEB MAP SERVICES Jiri Cajthaml, Jiri Krejci Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department of Mapping and Cartography,
USAGE OF OLD MAPS AND THEIR DISTRIBUTION WITHIN THE FRAME OF WEB MAP SERVICES Jiri Cajthaml, Jiri Krejci Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department of Mapping and Cartography,
The Earth is a Rotating Sphere
 The Earth is a Rotating Sphere The Shape of the Earth Earth s Rotation ( and relative movement of the Sun and Moon) The Geographic Grid Map Projections Global Time The Earth s Revolution around the Sun
The Earth is a Rotating Sphere The Shape of the Earth Earth s Rotation ( and relative movement of the Sun and Moon) The Geographic Grid Map Projections Global Time The Earth s Revolution around the Sun
2. Which geometric model has been used at some time to describe the earth? a. Sphere b. Oblate ellipsoid c. Flat disk. d. Geoid e.
 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 Geography 12 Sample Mid-Term Examination Before you
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 Geography 12 Sample Mid-Term Examination Before you
Geog Lecture 29 Mapping and GIS Continued
 Geog 1000 - Lecture 29 Mapping and GIS Continued http://scholar.ulethbridge.ca/chasmer/classes/ Today s Lecture (Pgs 13-25, 28-29) 1. Hand back Assignment 3 2. Review of Dr. Peddle s lecture last week
Geog 1000 - Lecture 29 Mapping and GIS Continued http://scholar.ulethbridge.ca/chasmer/classes/ Today s Lecture (Pgs 13-25, 28-29) 1. Hand back Assignment 3 2. Review of Dr. Peddle s lecture last week
FlexiCadastre User Conference 2013 GIS Data Verification & Challenges
 FlexiCadastre User Conference 2013 GIS Data Verification & Challenges May 7, 2013 Amanda Blackmore GIS Specialist OVERVIEW GIS Definitions & Terminology Spatial Data Common Issues or Concerns Data Verification
FlexiCadastre User Conference 2013 GIS Data Verification & Challenges May 7, 2013 Amanda Blackmore GIS Specialist OVERVIEW GIS Definitions & Terminology Spatial Data Common Issues or Concerns Data Verification
Map Projections & Coordinate Systems
 Map Projections & Coordinate Systems 9/7/2017 1 Why? Laying the Earth Flat Need convenient means of measuring and comparing distances, directions, areas, shapes. Traditional surveying instruments measure
Map Projections & Coordinate Systems 9/7/2017 1 Why? Laying the Earth Flat Need convenient means of measuring and comparing distances, directions, areas, shapes. Traditional surveying instruments measure
GEOIDS FAQ. November
 GEOIDS FAQ 1. What is a geoid? A geoid is a representation of the equipotential surface of the Earth s gravity field. It can be thought of as a surface coinciding with the undisturbed mean sea level extended
GEOIDS FAQ 1. What is a geoid? A geoid is a representation of the equipotential surface of the Earth s gravity field. It can be thought of as a surface coinciding with the undisturbed mean sea level extended
Spatial Data, 16 th Century Dutchmen, GPS and GIS. Martin Charlton, National Centre for Geocomputation National University of Ireland Maynooth
 Spatial Data, 16 th Century Dutchmen, GPS and GIS Martin Charlton, National Centre for Geocomputation National University of Ireland Maynooth Maps as truth Maps are cultural artifacts, comparable in history
Spatial Data, 16 th Century Dutchmen, GPS and GIS Martin Charlton, National Centre for Geocomputation National University of Ireland Maynooth Maps as truth Maps are cultural artifacts, comparable in history
Coordinate Systems and Map James Frew ESM 263 Winter
 Coordinate Systems and Map Projec@ons 1 Outline Introduc@on La@tude and longitude Projec@ons and coordinate systems Placenames Postal addresses and postal codes Linear referencing systems Cadasters Conver@ng
Coordinate Systems and Map Projec@ons 1 Outline Introduc@on La@tude and longitude Projec@ons and coordinate systems Placenames Postal addresses and postal codes Linear referencing systems Cadasters Conver@ng
Analytical and Computer Cartography Lecture 3: Review: Coordinate Systems
 Analytical and Computer Cartography Lecture 3: Review: Coordinate Systems Geographic Coordinates NAD83 NAD27 remained in use until the earthcentered international GRS80 was complete (Geodetic Reference
Analytical and Computer Cartography Lecture 3: Review: Coordinate Systems Geographic Coordinates NAD83 NAD27 remained in use until the earthcentered international GRS80 was complete (Geodetic Reference
Height systems. Rudi Gens Alaska Satellite Facility
 Rudi Gens Alaska Satellite Facility Outline Why bother about height systems? Relevant terms Coordinate systems Reference surfaces Geopotential number 2 Why bother about height systems? give a meaning to
Rudi Gens Alaska Satellite Facility Outline Why bother about height systems? Relevant terms Coordinate systems Reference surfaces Geopotential number 2 Why bother about height systems? give a meaning to
