Analysis of Urban Surface Biophysical Descriptors and Land Surface Temperature Variations in Jimeta City, Nigeria
|
|
|
- Sheryl Owen
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Global Journal of Human Social Science Vol. 10 Issue 1 (Ver 1.0), April 2010 Page 19 Analysis of Urban Surface Biophysical Descriptors and Land Surface Temperature Variations in Jimeta City, Nigeria Ambrose A. Zemba GJHSS Classification (FOR) , , & Abstract:Land-use and land-cover (LULC) data are often employed for simple correlation analyses between LULC types and their thermal signatures in the studies of land surface temperature (LST) using remote sensing. This tends to slow down the development of remote sensing of land surface temperature. Hence, there is need for methodological shift to quantitative surface descriptors. Development of quantitative surface descriptors could improve our capabilities for modeling urban thermal landscapes and advance urban climate research. This study therefore adopted an analytical procedure based on a spectral derivation model for characterizing and quantifying the urban landscape in Jimeta, Nigeria. A Landsat Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+) image of the study area, acquired on 16 November 2008, was spectrally modeled into three fraction endmembers namely, green vegetation, soil, and impervious surface. A hybrid classification procedure was developed to classify the fraction images into six land-use and land-cover classes. Next, pixelbased LST measurements were related to urban surface biophysical descriptors derived from spectral mixture analysis (SMA). Correlation analyses were conducted to investigate land-cover based relationships between LST and impervious surface and green vegetation fractions for an analysis of the causes of LST variations. Results indicate that fraction images derived from SMA were effective for quantifying the urban morphology and for providing reliable measurements of biophysical variables such as vegetation abundance, soil and impervious surface. An examination of LST variations within the city and their relations with the composition of LULC types, biophysical descriptors, and other relevant spatial data shows that LST possessed a weak relation with the LULC compositions than with other variables (including urban biophysical descriptors, remote sensing biophysical variables, GIS-based impervious surface variables, and population density). Key words: Land surface temperature, urban surface biophysical descriptors, Land use, Land cover B I. INTRODUCTION ecause the receipt and loss of radiation of urban surfaces correspond closely to the distribution of landuse and land-cover (LULC) characteristics, there has always been a tendency to use thermatic LULC data, not quantitative surface descriptors, to describe urban thermal landscape. This has slowed down the development of remote sensing of land surface temperatures (LST) and thus surface About- Geography Department, Federal University of Technology, P.M.B. 2076, YolaContact no: , aazemba@yahoo.com temperature heat islands (Voogt and Oke, 2003). However, Clapham (2003) suggested using of a continuum-based classification for satellite imagery, which aims to provide continous data for the functional classes. The idea of continuum-based classification has long been pursued in urban landscape analysis. One of the major contributions is Ridd s (1995) vegetation-impervious surface-soil (V-I-S) model for characterizing urban environments. This model assumes that urban land-cover is a linear combination of three biophysical components: vegetation, impervious surface, and soil and has recently been successfully implemented by using the technique of spectral mixture analysis (Madhavan et al, 2001; Rasheed et al, 2001; Small, 2001; Phinn et al, 2002; Wu and Murray, 2003; and Lu and Weng, 2004). The Ridd model provides the potential for a link between remote sensing-derived urban biophysical components and LST, and may be applied to establish parameters for describing urban construction materials and fabrics to improve our understanding of urban surface energy budget and heat islands. The focus of this research is placed on the application of a methodology to examine the interplay between LST and urban morphology. A Landsat ETM+ image of 2008 that covers the City of Jimeta, Nigeria was used in conjunction with other types of spatial data for the analysis. The specific objectives were twofold: First, to employ spectral mixture modeling to derive urban surface biophysical attributes, and to apply spectrally unmixed results to characterize the urban landscape and secondly, to analyze the causes of LST variations, which were derived from Landsat thermal infrared data by linking LST with remotely sensed urban surface biophysical descriptors. II. STUDY AREA Jimeta, a twin city to Yola town, is the capital of Yola North Local Government and Adamawa State of Nigeria. The city is located at the bank of River Benue, between latitude to N and longitude to E. The area has a Sudan type of vegetation and a tropical climate marked by wet and dry seasons. The minimum temperature recorded is about 15 0 C and a maximum of about 40 0 C. The city has been experiencing an increasing population explosion since it assumed a status of Adamawa State capital in Like any other Nigerian cities, Jimeta comprises of so many land use types ranging from institutional, commercial, and residential. The city is clearly stratified in terms of population densities (Ilesanmi, 1999).
2 Page 20 Vol. 10 Issue 1 (Ver 1.0), April 2010 Global Journal of Human Social Science These are low, medium and high density areas. The low density areas are well planned units where government officials reside while medium and high density areas are made up of common people with little or unplanned streets and buildings.
3 Global Journal of Human Social Science Vol. 10 Issue 1 (Ver 1.0), April 2010 Page 21 In recent times, Jimeta has risen as the premier commercial, industrial and transportation urban area of the northeastern Nigeria. The rapid growth of Jimeta, particularly within the past 30 years, has made it one of the fastest growing metropolitan areas in Nigeria. For instance, the population of Jimeta increased significantly by 69% between 1973 and 1991 and 58% between 1991 and 2006 (NPC 2006). Concomitant with this high rate of population growth has been an explosive growth in retail, educational, commercial and administrative services within the area. This has resulted in tremendous land cover change dynamics within the metropolitan region, wherein urbanization has consumed vast acreages of land adjacent to the city proper and has pushed the urban fringe farther away from the original Jimeta urban core. An enormous transition of land from forest and agriculture to urban land uses has occurred in the area, the extent of which needs to be investigated for the sake of planning for the ever growing population. III. METHODS 1. Pre-processing of image Landsat 7-Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+) image with path/row of 185/54 dated 16 November 2008 was used in this research. The acquisition date has a highly clear atmospheric condition, and the image was acquired through the USGS Earth Resources Observation Systems Data Center, which has corrected radiometric and geometrical distortions of the image to a quality level of 1G before delivery. The major pre-processing on the image had to do with scan-line-off correction. The image was further rectified to a common Universal Traverse Mercator coordinate system based on 1:50, 000 scale topographic maps, and was resampled using the nearest neighbor algorithm with a pixel size of 30 m by 30 m for all bands including the thermal band. 2. Spectral mixture analysis Spectral mixture analysis was employed to estimate endmember fractions in the images. Endmembers are recognizable land-cover materials that have homogeneous spectral properties all over the image. Spectral mixture analysis assumes that the spectrum measured by a sensor is a linear combination of the spectra of all components within the pixel (Adams et al, 1995). The mathematical model of linear spectral mixture analysis is expressed as n R i = f k R ik + ER i Where, (1) k= i = 1,.... m (number of spectral bands), k = 1,.... n (number of end members) R i = Spectral reflectance of band i of a pixel which contains one or more endmembers; f k = Proportion or fraction of end member k within the pixel; R ik = Known spectral reflectance of end member k within the pixel on band i; and ER i = Error for band i or remainder between measured and modeled DN (band residuals). Estimation of endmembers was done using reference endmember fractions i.e. the laboratory spectra of the target materials in Erdas imagine software. 3. Estimation of impervious surface In this research, reference endmembers was applied. ERDAS Imagine GIS software has a collection of spectra libraries, from where the spectra that represent the materials used as endmembers (soil, vegetation and impervious surface) were selected. 4. Land-use and Land-cover classification The maximum likelihood classification algorithm was applied to classify the fraction image into ten classes. A distance threshold was selected for each class and was determined by examining interactively the histogram of each class in the distance image. Pixels with a distance value greater than the threshold were assigned a class value of zero in thematic image. A distance tree classifier was then applied to reclassify these pixels. The parameters required by the distance tree classifier were identified based on the mean and standard deviation from the sample points of each class. Finally, the accuracy of the classified image was checked with a stratified random sampling method against the reference data of 50 samples collected from a large-scale 2006 aerial photograph of the study area. Six land use/cover types were identified, including (i) built-up land (ii) bare surface (iii) natural vegetation or forest (iv) Marshy land (v) croplands and (vi) water bodies. An overall accuracy of 88% and a Kappa index of 0.84 were determined. 2. Estimation of Land Surface Temperature (LST) The Landsat TM and ETM+ thermal bands have different gain and offset values. Therefore, for the calculation of their radiance values, different formulas are used. In this study, for the calculation of radiance the formula in equation (2) was used: Radiance = ((L MAX L MIN ) / (DN MAX DN MIN )) * (DN DN MIN ) + L MIN where: (2) For band 6L and For band 6H L MAX = L MAX = L MIN = 0.0 L MIN = 3.2 DN MAX = 255 DN MAX = 255 DN MIN = 1 DN MIN = 1 The values for all these parameters were obtained from the data header files.
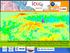
4 Page 22 Vol. 10 Issue 1 (Ver 1.0), April 2010 Global Journal of Human Social Science After the calculation of the radiance values, the temperature values were derived using the inverse of Planck function (equation 3), thus: T ( 0 C) = K 2-273, Where: (3) Ln{K 1 / CV R + 1} T ( 0 C) = Temperature in Degrees Celsius CV R = Cell (pixel) value as radiance K 1 = (for TM) or (for ETM and ETM+) in mw cm -2 sr -1 μm -1 K 2 = (for TM) or (foretm and ETM+) in Kelvin All the temperature derivations were modeled using a Model Maker in Erdas Imagine software. In examining the spatial relationship between land use/cover types and the surface energy response as measured by surface temperature, a classified image was overlaid to the surface temperature images. IV. RESULTS Urban Surface Biophysical Descriptors Fig 2 shows the three fraction images derived. This consists of Green vegetation, soil, and impervious surface fractions. Pixel values of these fraction images represent areal proportions of each biophysical descriptor within a pixel. Green vegetation fraction image showed a large dark area (low values) at the centre of the study area that corresponds to the central business district of the city. Bright areas of high green vegetation values are found in the surrounding areas. Though, various types of crops were at their maturity stage, the green vegetation fraction images in the northwestern to southwestern parts of the city were still conspicuous as evidenced by medium gray to dark tone. Column 3 of Table 1 displays green vegetation fraction values by land cover types. Forest/sparse trees (including natural/planted trees, bushes and grasses) apparently had the highest green vegetation fraction values (0.715). In contrast, built-up lands displayed the lowest green vegetation values (0.119). Little vegetation amount was also found in water bodies as indicated by the green vegetation fraction value (0.161). Bare surfaces or exposed soils, natural vegetated lands and cultivated or croplands put together yielded an intermediate green vegetation fraction values around Bare surfaces green vegetation standard deviation was slightly lower in value than that of cultivated land. Cultivated land standard deviation was the highest (0.33), suggesting that cultivated land may be characterized by various amounts of vegetation coverage. The least value of standard deviation for green vegetation was recorded in forest areas indicating that a variation in the amount of vegetation cover is minimal. The percentage of land covered by impervious surfaces may vary significantly with land use-land cover categories and sub-categories. This study reveals a substantially different estimate for each land use-land cover types. For example, a negative impervious a: Impervious suraface fraction image b: Vegetation fraction image c: Soil fraction image
5 Global Journal of Human Social Science Vol. 10 Issue 1 (Ver 1.0), April 2010 Page 23 Fig 2: Fraction images derived from spectral mixture analysis of the landsat ETM image A: Land surface temperature, 1986 B: Land Surface Temperature, 1998 Value Kilometers B: Land surface temperature, 2008 Value C: Land Surface Temperature, 2008 Fig 3: Land surface temperature variation in Jimeta in 1986 and Table 1: Descriptive Statistics of Biophysical Parameters of the Land Cover Types Land Use & land Mean LST Mean Mean Impervious Mean soil cover in 2008 ( 0 C) Vegetation surface fraction Built-up lands (3.10) (0.140) (0.226) (0.234) Bare soils (1.94) (0.155) (0.098) (0.144) Croplands (1.56) (0.333) (0.045) (0.252) Marshy lands (1.83) (0.151) (0.097) (0.184) Forest/bushy lands (1.37) (0.104) (0.030) 0.01 (0.077) Water (0.43) (0.178) (0.090) (0.156) Source: Derived from Landsat ETM+ Image. Values in brackets refer to standard deviations
6 Page 24 Vol. 10 Issue 1 (Ver 1.0), April 2010 Global Journal of Human Social Science Results are displayed in the last two columns of Table 2. For all land use and land cover types, land surface temperature values were negatively correlated with green vegetation fraction values, but were positively correlated with impervious fraction values. The strongest negative correlation existed between land surface temperature and green vegetation fraction values in croplands ( ) and forest (natural vegetation) ( ). The correlation coefficient values dropped slightly for bare surface ( ) and residential lands ( ), with a sharp decrease for marshy lands. The least correlation was found in water ( ). On the other hand, the strongest positive correlation between land surface temperature and impervious fraction values was found in crop lands (0.5558), followed by bare surfaces (0.5373). The weakest correlations ( and ) were observed in thick vegetation areas and water respectively. Table 2: Statistics of the Biophysical Descriptors by Land use-land cover types, and their Correlations with land surface temperature (significant at 0.05 level) Land Use-land Mean LST Mean Mean Impervious LST/Vegetation LST/Impervio cover Type Vegetation surface Fraction us surface Built-up lands (3.10) (0.140) (0.226) Bare surface (1.94) (0.155) (0.098) Croplands (1.56) (0.333) (0.045) Marshy lands (1.83) (0.151) (0.097) Natural vegetation (1.37) (0.104) (0.030) Water (0.43) (0.178) (0.090) Source: Derived from Landsat ETM+ Image (2008). Values in brackets are standard deviation V. CONCLUSION The use of thermal land use-land cover data is reported to have slowed down the development of remote sensing of land surface temperature and thus surface temperature heat island (Voogt and Oke, 2003). Hence, there has been a call to develop and apply quantitative surface descriptors to describe urban thermal landscapes in remote sensing studies. To make this happen, remote sensing techniques must enable parsimonious separation of urban land use/cover types into values directly related to their scale and signature (Phinn et al, 2002). This study has demonstrated that spectral mixture analysis (SMA), based on the V-I-S model, can provide a physically based solution for characterizing and quantifying urban landscape compositions, and that SMA-derived fraction estimates can be used as reliable urban surface biophysical descriptors. As a comparison, the study has examined the relationship between land surface temperature (LST) values and the compositions of LULC types within the city, as well as the relationships between LST and the urban biophysical descriptors derived from SMA, and other relevant spatial data. Results indicate that LST possessed a stronger relationship with these variables than the LULC compositions. The study also revealed that SMA provides a suitable model to decompose the spectral mixtures of L- resolution data such as Landsat TM/ETM+. The scene elements in the L-resolution data are smaller than the resolution cell of the sensor, and are therefore not detectable. Thus, a more realistic representation and quantification of urban surfaces are possible, in comparison to that provided by assignment of a single dominant class to every pixel by statistical models. With the availability of multi-temporal satellite images, stable and reliable fraction estimates derived from SMA may be more efficient for a LULC change detection than traditional pixel-by-pixel comparison methods, because the fractional characteristics of LULC types at one date are comparable with other dates of fraction images. Fraction images may also be translated into significant environmental variables such as impervious surface and vegetation abundance. By relating LST to changing fraction constituency over time with urban growth, the effect of urbanization on LST may be examined. VI. REFERENCES 1) Adams, J. B., Sabol, D. E., Kapos, V., Filho, R. A., Roberts, D. A., Smith, M. O. & Gillespie, A. R. (1995) Classification of multispectral images based on fractions of endmembers: Application to land cover changes in the Brazilian Amazon. Remote sensing of Environment, 52: ) Clapham, W.B. (2003) Continuum-based classification or remotely sensed imagery to describe urban sprawl on a watershed scale. Remote Sens Environs 86: ) Ilesanmi, F.A. (1999) Urban Settlements In Adebayo, A.A. and Tukur, A.L. (eds) Adamawa State in Maps, Department of Geography, FUTY and Paraclete Publishers, Yola. 4) Lu, D. and Weng, Q. (2004) Spectral Mixture Analysis of the Urban Landscapes in Indianapolis with Landsat ETM+. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 70, ) Madhavan, B.B., Kubo, S., Kurisaki, N. and Sivakumar, T.V.I.N. (2001) Appraising the Anatomy and Spatial Growth of the Bangkok Metropolitan Area Using a Vegetation-Impervious surface-soil Model through Remote Sensing,
7 Global Journal of Human Social Science Vol. 10 Issue 1 (Ver 1.0), April 2010 Page 25 International Journal of Remote Sensing, 22: ) National Population Commission (NPC, 2006) Details of the breakdown of the national and state provisional population totals 2006 census. 7) Phinn, S., Stanford, M., Scarth, P., Murray, A. T. & Shyy, P. T. (2002) Monitoring the composition of urban environments based on the vegetationimpervious surface-soil (VIS) model by subpixel analysis techniques. International Journal of Remote Sensing 23: ) Rasheed, T., Weeks, J. R., Gadalla, M. S. & Hill, A. G. (2001) Revealing the autonomy of cities through spectral mixture analysis of multispectral satellite imagery: A case study of the Greater Cairo region, Egypt, Geocarto International 16, ) Ridd, M.K. (1995) Exploring a V-I-S (vegetationimpervious surface-soil) model for urban ecosystem analysis through remote sensing: Comparative anatomy for cities. International Journal of Remote Sensing 16: ) Small, C. (2001) Estimation of urban vegetation abundance by spectral mixture analysis, International Journal of Remote Sensing, 22: ) Voogt, J.A. & Oke, T.R. (2003) Thermal Remote Sensing of Urban Climates. Remote Sensing of environment, 86, ) Weng, Q. (2001) A Remote Sensing-GIS Evaluation of Urban Expansion & Its Impact on Surface Temperature in the Zhujiang Delta, China. International Journal of Remote Sensing, ) Wu, C. & Murray, A.T. (2003) Estimating Impervious Surface Distribution by Spectral Mixture Analysis. Remote Sensing of Environment, 84,
1. Introduction. Chaithanya, V.V. 1, Binoy, B.V. 2, Vinod, T.R. 2. Publication Date: 8 April DOI: https://doi.org/ /cloud.ijarsg.
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2017, Volume 6, Issue 1, pp. 2088-2096 ISSN 2320 0243, Crossref: 10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.112 Research Article Open Access Estimation
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2017, Volume 6, Issue 1, pp. 2088-2096 ISSN 2320 0243, Crossref: 10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.112 Research Article Open Access Estimation
AssessmentofUrbanHeatIslandUHIusingRemoteSensingandGIS
 Global Journal of HUMANSOCIAL SCIENCE: B Geography, GeoSciences, Environmental Science & Disaster Management Volume 16 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal
Global Journal of HUMANSOCIAL SCIENCE: B Geography, GeoSciences, Environmental Science & Disaster Management Volume 16 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal
Comparison between Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Using Classification Based Emissivity and NDVI Based Emissivity
 Comparison between Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Using Classification Based Emissivity and NDVI Based Emissivity Isabel C. Perez Hoyos NOAA Crest, City College of New York, CUNY, 160 Convent Avenue,
Comparison between Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Using Classification Based Emissivity and NDVI Based Emissivity Isabel C. Perez Hoyos NOAA Crest, City College of New York, CUNY, 160 Convent Avenue,
Improvement of Urban Impervious Surface Estimation in Shanghai Using Landsat7 ETM+ Data
 Chin. Geogra. Sci. 2009 19(3) 283 290 DOI: 10.1007/s11769-009-0283-x www.springerlink.com Improvement of Urban Impervious Surface Estimation in Shanghai Using Landsat7 ETM+ Data (Department of Land Management,
Chin. Geogra. Sci. 2009 19(3) 283 290 DOI: 10.1007/s11769-009-0283-x www.springerlink.com Improvement of Urban Impervious Surface Estimation in Shanghai Using Landsat7 ETM+ Data (Department of Land Management,
URBAN CHANGE DETECTION OF LAHORE (PAKISTAN) USING A TIME SERIES OF SATELLITE IMAGES SINCE 1972
 URBAN CHANGE DETECTION OF LAHORE (PAKISTAN) USING A TIME SERIES OF SATELLITE IMAGES SINCE 1972 Omar Riaz Department of Earth Sciences, University of Sargodha, Sargodha, PAKISTAN. omarriazpk@gmail.com ABSTRACT
URBAN CHANGE DETECTION OF LAHORE (PAKISTAN) USING A TIME SERIES OF SATELLITE IMAGES SINCE 1972 Omar Riaz Department of Earth Sciences, University of Sargodha, Sargodha, PAKISTAN. omarriazpk@gmail.com ABSTRACT
Applications of GIS and Remote Sensing for Analysis of Urban Heat Island
 Chuanxin Zhu Professor Peter V. August Professor Yeqiao Wang NRS 509 December 15, 2016 Applications of GIS and Remote Sensing for Analysis of Urban Heat Island Since the last century, the global mean surface
Chuanxin Zhu Professor Peter V. August Professor Yeqiao Wang NRS 509 December 15, 2016 Applications of GIS and Remote Sensing for Analysis of Urban Heat Island Since the last century, the global mean surface
Remote sensing Based Assessment of Urban Heat Island Phenomenon in Nagpur Metropolitan Area
 International Journal of Information & Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 11 (2014), pp. 1069-1074 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com Remote sensing
International Journal of Information & Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 11 (2014), pp. 1069-1074 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com Remote sensing
Dynamic Expansion and Urbanization of Greater Cairo Metropolis, Egypt Ahmed Abdelhalim M. Hassan
 Ahmed Abdelhalim M. Hassan (MSc Ahmed Abdelhalim M. Hassan, Institue of Landscape Ecology, Muenster University, Robert-Koch Straße 28, D-48149 Münster, Germany, ahmedahalim@uni-muenster.de) 1 ABSTRACT
Ahmed Abdelhalim M. Hassan (MSc Ahmed Abdelhalim M. Hassan, Institue of Landscape Ecology, Muenster University, Robert-Koch Straße 28, D-48149 Münster, Germany, ahmedahalim@uni-muenster.de) 1 ABSTRACT
Urban Surface Biophysical Descriptors and Land Surface Temperature Variations
 Urban Surface Biophysical Descriptors and Land Surface Temperature Variations Qihao Weng, Dengsheng Lu, and Bingqing Liang Abstract In remote sensing studies of land surface temperatures (LST), thematic
Urban Surface Biophysical Descriptors and Land Surface Temperature Variations Qihao Weng, Dengsheng Lu, and Bingqing Liang Abstract In remote sensing studies of land surface temperatures (LST), thematic
Landuse and Landcover change analysis in Selaiyur village, Tambaram taluk, Chennai
 Landuse and Landcover change analysis in Selaiyur village, Tambaram taluk, Chennai K. Ilayaraja Department of Civil Engineering BIST, Bharath University Selaiyur, Chennai 73 ABSTRACT The synoptic picture
Landuse and Landcover change analysis in Selaiyur village, Tambaram taluk, Chennai K. Ilayaraja Department of Civil Engineering BIST, Bharath University Selaiyur, Chennai 73 ABSTRACT The synoptic picture
Monitoring Vegetation Growth of Spectrally Landsat Satellite Imagery ETM+ 7 & TM 5 for Western Region of Iraq by Using Remote Sensing Techniques.
 Monitoring Vegetation Growth of Spectrally Landsat Satellite Imagery ETM+ 7 & TM 5 for Western Region of Iraq by Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Fouad K. Mashee, Ahmed A. Zaeen & Gheidaa S. Hadi Remote
Monitoring Vegetation Growth of Spectrally Landsat Satellite Imagery ETM+ 7 & TM 5 for Western Region of Iraq by Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Fouad K. Mashee, Ahmed A. Zaeen & Gheidaa S. Hadi Remote
Research Article A Quantitative Assessment of Surface Urban Heat Islands Using Satellite Multitemporal Data over Abeokuta, Nigeria
 International Atmospheric Sciences Volume 2016, Article ID 3170789, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3170789 Research Article A Quantitative Assessment of Surface Urban Heat Islands Using Satellite
International Atmospheric Sciences Volume 2016, Article ID 3170789, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3170789 Research Article A Quantitative Assessment of Surface Urban Heat Islands Using Satellite
Urban Growth Analysis: Calculating Metrics to Quantify Urban Sprawl
 Urban Growth Analysis: Calculating Metrics to Quantify Urban Sprawl Jason Parent jason.parent@uconn.edu Academic Assistant GIS Analyst Daniel Civco Professor of Geomatics Center for Land Use Education
Urban Growth Analysis: Calculating Metrics to Quantify Urban Sprawl Jason Parent jason.parent@uconn.edu Academic Assistant GIS Analyst Daniel Civco Professor of Geomatics Center for Land Use Education
DEPENDENCE OF URBAN TEMPERATURE ELEVATION ON LAND COVER TYPES. Ping CHEN, Soo Chin LIEW and Leong Keong KWOH
 DEPENDENCE OF URBAN TEMPERATURE ELEVATION ON LAND COVER TYPES Ping CHEN, Soo Chin LIEW and Leong Keong KWOH Centre for Remote Imaging, Sensing and Processing, National University of Singapore, Lower Kent
DEPENDENCE OF URBAN TEMPERATURE ELEVATION ON LAND COVER TYPES Ping CHEN, Soo Chin LIEW and Leong Keong KWOH Centre for Remote Imaging, Sensing and Processing, National University of Singapore, Lower Kent
Preparation of LULC map from GE images for GIS based Urban Hydrological Modeling
 International Conference on Modeling Tools for Sustainable Water Resources Management Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad: 28-29 December 2014 Abstract Preparation
International Conference on Modeling Tools for Sustainable Water Resources Management Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad: 28-29 December 2014 Abstract Preparation
Digital Change Detection Using Remotely Sensed Data for Monitoring Green Space Destruction in Tabriz
 Int. J. Environ. Res. 1 (1): 35-41, Winter 2007 ISSN:1735-6865 Graduate Faculty of Environment University of Tehran Digital Change Detection Using Remotely Sensed Data for Monitoring Green Space Destruction
Int. J. Environ. Res. 1 (1): 35-41, Winter 2007 ISSN:1735-6865 Graduate Faculty of Environment University of Tehran Digital Change Detection Using Remotely Sensed Data for Monitoring Green Space Destruction
This is trial version
 Journal of Rangeland Science, 2012, Vol. 2, No. 2 J. Barkhordari and T. Vardanian/ 459 Contents available at ISC and SID Journal homepage: www.rangeland.ir Full Paper Article: Using Post-Classification
Journal of Rangeland Science, 2012, Vol. 2, No. 2 J. Barkhordari and T. Vardanian/ 459 Contents available at ISC and SID Journal homepage: www.rangeland.ir Full Paper Article: Using Post-Classification
Use of Corona, Landsat TM, Spot 5 images to assess 40 years of land use/cover changes in Cavusbasi
 New Strategies for European Remote Sensing, Olui (ed.) 2005 Millpress, Rotterdam, ISBN 90 5966 003 X Use of Corona, Landsat TM, Spot 5 images to assess 40 years of land use/cover changes in Cavusbasi N.
New Strategies for European Remote Sensing, Olui (ed.) 2005 Millpress, Rotterdam, ISBN 90 5966 003 X Use of Corona, Landsat TM, Spot 5 images to assess 40 years of land use/cover changes in Cavusbasi N.
Analysis of Landuse, Landcover Change and Urban Expansion in Akure, Nigeria (pp )
 Journal of Innovative Research in Engineering and Sciences 2(4), June, 2011. ISSN : 2141-8225. http://www.grpjournal.org. Printed in Nigeria. All rights researved. Global Research Publishing, 2011. Analysis
Journal of Innovative Research in Engineering and Sciences 2(4), June, 2011. ISSN : 2141-8225. http://www.grpjournal.org. Printed in Nigeria. All rights researved. Global Research Publishing, 2011. Analysis
CHANGES IN VIJAYAWADA CITY BY REMOTE SENSING AND GIS
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 8, Issue 5, May 2017, pp.217 223, Article ID: IJCIET_08_05_025 Available online at http://www.ia aeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtyp
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 8, Issue 5, May 2017, pp.217 223, Article ID: IJCIET_08_05_025 Available online at http://www.ia aeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtyp
STUDY OF NORMALIZED DIFFERENCE BUILT-UP (NDBI) INDEX IN AUTOMATICALLY MAPPING URBAN AREAS FROM LANDSAT TM IMAGERY
 STUDY OF NORMALIZED DIFFERENCE BUILT-UP (NDBI) INDEX IN AUTOMATICALLY MAPPING URBAN AREAS FROM LANDSAT TM IMAGERY Dr. Hari Krishna Karanam Professor, Civil Engineering, Dadi Institute of Engineering &
STUDY OF NORMALIZED DIFFERENCE BUILT-UP (NDBI) INDEX IN AUTOMATICALLY MAPPING URBAN AREAS FROM LANDSAT TM IMAGERY Dr. Hari Krishna Karanam Professor, Civil Engineering, Dadi Institute of Engineering &
A COMPARISON OF SPECTRAL MIXTURE ANALYSIS METHODS FOR URBAN LANDSCAPE USING LANDSAT ETM+ DATA: LOS ANGELES, CA
 A COMPARISO OF SPECTRAL MIXTURE AALYSIS METHODS FOR URBA LADSCAPE USIG LADSAT ETM+ DATA: LOS AGELES, CA Xianfeng Chen a and Lin Li b a Slippery Rock University of Pennsylvania, Slippery Rock, PA 657, USA
A COMPARISO OF SPECTRAL MIXTURE AALYSIS METHODS FOR URBA LADSCAPE USIG LADSAT ETM+ DATA: LOS AGELES, CA Xianfeng Chen a and Lin Li b a Slippery Rock University of Pennsylvania, Slippery Rock, PA 657, USA
Quantifying Land Use/Cover Dynamics of Nainital Town (India) Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques
 Quantifying Land Use/Cover Dynamics of Nainital Town (India) Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques Jiwan Rawat 1*, Vivekananda Biswas 1 and Manish Kumar 1 1 Centre of Excellence for NRDMS in Uttarakhand,
Quantifying Land Use/Cover Dynamics of Nainital Town (India) Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques Jiwan Rawat 1*, Vivekananda Biswas 1 and Manish Kumar 1 1 Centre of Excellence for NRDMS in Uttarakhand,
Contents. Introduction Study area Data and Methodology Results Conclusions
 Modelling Spatial Changes in Suburban Areas of Istanbul Using Landsat 5 TM Data Şinasi Kaya(Assoc. Prof. Dr. ITU) Elif Sertel(Assoc. Prof. Dr. ITU) Dursun Z. Şeker(Prof. Dr. ITU) 1 Contents Introduction
Modelling Spatial Changes in Suburban Areas of Istanbul Using Landsat 5 TM Data Şinasi Kaya(Assoc. Prof. Dr. ITU) Elif Sertel(Assoc. Prof. Dr. ITU) Dursun Z. Şeker(Prof. Dr. ITU) 1 Contents Introduction
Urban Tree Canopy Assessment Purcellville, Virginia
 GLOBAL ECOSYSTEM CENTER www.systemecology.org Urban Tree Canopy Assessment Purcellville, Virginia Table of Contents 1. Project Background 2. Project Goal 3. Assessment Procedure 4. Economic Benefits 5.
GLOBAL ECOSYSTEM CENTER www.systemecology.org Urban Tree Canopy Assessment Purcellville, Virginia Table of Contents 1. Project Background 2. Project Goal 3. Assessment Procedure 4. Economic Benefits 5.
Overview of Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping
 Overview of Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping What is remote sensing? Why remote sensing? Examples of remote sensing in natural resources mapping Class goals What is Remote Sensing A remote sensing
Overview of Remote Sensing in Natural Resources Mapping What is remote sensing? Why remote sensing? Examples of remote sensing in natural resources mapping Class goals What is Remote Sensing A remote sensing
Spatial Geotechnologies and GIS tools for urban planners applied to the analysis of urban heat island. Case Caracas city, Venezuela Contribution 115.
 planners applied to the analysis of urban heat island. Case Caracas city, Venezuela Contribution 115. Fig.1 The city of Caracas, as many others Latin-American cities, has experimented a fast growth in
planners applied to the analysis of urban heat island. Case Caracas city, Venezuela Contribution 115. Fig.1 The city of Caracas, as many others Latin-American cities, has experimented a fast growth in
URBAN heating and the formation of urban heat islands
 IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN APPLIED EARTH OBSERVATIONS AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 6, NO. 3, JUNE 2013 1749 Examining Urban Heat Island Relations to Land Use and Air Pollution: Multiple Endmember Spectral
IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN APPLIED EARTH OBSERVATIONS AND REMOTE SENSING, VOL. 6, NO. 3, JUNE 2013 1749 Examining Urban Heat Island Relations to Land Use and Air Pollution: Multiple Endmember Spectral
Abstract. TECHNOFAME- A Journal of Multidisciplinary Advance Research. Vol.2 No. 2, (2013) Received: Feb.2013; Accepted Oct.
 Vol.2 No. 2, 83-87 (2013) Received: Feb.2013; Accepted Oct. 2013 Landuse Pattern Analysis Using Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Morar Block, of Gwalior District, M.P. Subhash Thakur 1 Akhilesh Singh 2
Vol.2 No. 2, 83-87 (2013) Received: Feb.2013; Accepted Oct. 2013 Landuse Pattern Analysis Using Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Morar Block, of Gwalior District, M.P. Subhash Thakur 1 Akhilesh Singh 2
VISUALIZATION URBAN SPATIAL GROWTH OF DESERT CITIES FROM SATELLITE IMAGERY: A PRELIMINARY STUDY
 CO-439 VISUALIZATION URBAN SPATIAL GROWTH OF DESERT CITIES FROM SATELLITE IMAGERY: A PRELIMINARY STUDY YANG X. Florida State University, TALLAHASSEE, FLORIDA, UNITED STATES ABSTRACT Desert cities, particularly
CO-439 VISUALIZATION URBAN SPATIAL GROWTH OF DESERT CITIES FROM SATELLITE IMAGERY: A PRELIMINARY STUDY YANG X. Florida State University, TALLAHASSEE, FLORIDA, UNITED STATES ABSTRACT Desert cities, particularly
GIS GIS ETM+
 GIS 1388 Vol.1, No.1, Spring 2009 39-56 GIS Iranian Remote Sensing & GIS ETM+ *4 3 2 1 GIS -1-2 -3 GIS -4 88/8/9 : 88/4/30 :.. ). (.... ( ). ETM+. (LSU)...V_I_S : Email: soodabeh_namdari@yahoo.com 22431788
GIS 1388 Vol.1, No.1, Spring 2009 39-56 GIS Iranian Remote Sensing & GIS ETM+ *4 3 2 1 GIS -1-2 -3 GIS -4 88/8/9 : 88/4/30 :.. ). (.... ( ). ETM+. (LSU)...V_I_S : Email: soodabeh_namdari@yahoo.com 22431788
MAPPING LAND USE/ LAND COVER OF WEST GODAVARI DISTRICT USING NDVI TECHNIQUES AND GIS Anusha. B 1, Sridhar. P 2
 MAPPING LAND USE/ LAND COVER OF WEST GODAVARI DISTRICT USING NDVI TECHNIQUES AND GIS Anusha. B 1, Sridhar. P 2 1 M. Tech. Student, Department of Geoinformatics, SVECW, Bhimavaram, A.P, India 2 Assistant
MAPPING LAND USE/ LAND COVER OF WEST GODAVARI DISTRICT USING NDVI TECHNIQUES AND GIS Anusha. B 1, Sridhar. P 2 1 M. Tech. Student, Department of Geoinformatics, SVECW, Bhimavaram, A.P, India 2 Assistant
Characterizing fractional vegetation cover and land surface temperature based on sub- pixel fractional impervious surfaces from Landsat TM/ETM+
 1 2 Characterizing fractional vegetation cover and land surface temperature based on sub- pixel fractional impervious surfaces from Landsat TM/ETM+ 3 4 Youshui Zhang a, b, *, Angela Harris a, Heiko Balzter
1 2 Characterizing fractional vegetation cover and land surface temperature based on sub- pixel fractional impervious surfaces from Landsat TM/ETM+ 3 4 Youshui Zhang a, b, *, Angela Harris a, Heiko Balzter
Remote sensing of sealed surfaces and its potential for monitoring and modeling of urban dynamics
 Remote sensing of sealed surfaces and its potential for monitoring and modeling of urban dynamics Frank Canters CGIS Research Group, Department of Geography Vrije Universiteit Brussel Herhaling titel van
Remote sensing of sealed surfaces and its potential for monitoring and modeling of urban dynamics Frank Canters CGIS Research Group, Department of Geography Vrije Universiteit Brussel Herhaling titel van
7.1 INTRODUCTION 7.2 OBJECTIVE
 7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered as an essential element for modeling and
7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered as an essential element for modeling and
Urban Mapping & Change Detection. Sebastian van der Linden Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Germany
 Urban Mapping & Change Detection Sebastian van der Linden Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Germany Introduction - The urban millennium Source: United Nations Introduction Text Source: Google Earth Introduction
Urban Mapping & Change Detection Sebastian van der Linden Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Germany Introduction - The urban millennium Source: United Nations Introduction Text Source: Google Earth Introduction
Residential Development Dynamics in Port Harcourt Metropolis: Implication for Efficient Urban Planning
 Residential Development Dynamics in Port Harcourt Metropolis: Implication for Efficient Urban Planning Collins H. Wizor (Ph.D) Department of Geography and Environmental Management, University of Port Harcourt,
Residential Development Dynamics in Port Harcourt Metropolis: Implication for Efficient Urban Planning Collins H. Wizor (Ph.D) Department of Geography and Environmental Management, University of Port Harcourt,
APPLICATION OF LAND CHANGE MODELER FOR PREDICTION OF FUTURE LAND USE LAND COVER A CASE STUDY OF VIJAYAWADA CITY
 APPLICATION OF LAND CHANGE MODELER FOR PREDICTION OF FUTURE LAND USE LAND COVER A CASE STUDY OF VIJAYAWADA CITY K. Sundara Kumar 1, Dr. P. Udaya Bhaskar 2, Dr. K. Padmakumari 3 1 Research Scholar, 2,3
APPLICATION OF LAND CHANGE MODELER FOR PREDICTION OF FUTURE LAND USE LAND COVER A CASE STUDY OF VIJAYAWADA CITY K. Sundara Kumar 1, Dr. P. Udaya Bhaskar 2, Dr. K. Padmakumari 3 1 Research Scholar, 2,3
International Journal of Intellectual Advancements and Research in Engineering Computations
 ISSN:2348-2079 Volume-5 Issue-2 International Journal of Intellectual Advancements and Research in Engineering Computations Agricultural land investigation and change detection in Coimbatore district by
ISSN:2348-2079 Volume-5 Issue-2 International Journal of Intellectual Advancements and Research in Engineering Computations Agricultural land investigation and change detection in Coimbatore district by
Urban Growth Analysis In Akure Metropolis
 Urban Growth Analysis In Akure Metropolis Olaoluwa A. Idayat, Samson A. Samuel, Muibi K.H, Ogbole John, Alaga A, T., Ajayi Victoria Abstract: Urban Land use changes, quantification and the analysis of
Urban Growth Analysis In Akure Metropolis Olaoluwa A. Idayat, Samson A. Samuel, Muibi K.H, Ogbole John, Alaga A, T., Ajayi Victoria Abstract: Urban Land use changes, quantification and the analysis of
INVESTIGATION LAND USE CHANGES IN MEGACITY ISTANBUL BETWEEN THE YEARS BY USING DIFFERENT TYPES OF SPATIAL DATA
 INVESTIGATION LAND USE CHANGES IN MEGACITY ISTANBUL BETWEEN THE YEARS 1903-2010 BY USING DIFFERENT TYPES OF SPATIAL DATA T. Murat Celikoyan, Elif Sertel, Dursun Zafer Seker, Sinasi Kaya, Uğur Alganci ITU,
INVESTIGATION LAND USE CHANGES IN MEGACITY ISTANBUL BETWEEN THE YEARS 1903-2010 BY USING DIFFERENT TYPES OF SPATIAL DATA T. Murat Celikoyan, Elif Sertel, Dursun Zafer Seker, Sinasi Kaya, Uğur Alganci ITU,
Land cover/land use mapping and cha Mongolian plateau using remote sens. Title. Author(s) Bagan, Hasi; Yamagata, Yoshiki. Citation Japan.
 Title Land cover/land use mapping and cha Mongolian plateau using remote sens Author(s) Bagan, Hasi; Yamagata, Yoshiki International Symposium on "The Imp Citation Region Specific Systems". 6 Nove Japan.
Title Land cover/land use mapping and cha Mongolian plateau using remote sens Author(s) Bagan, Hasi; Yamagata, Yoshiki International Symposium on "The Imp Citation Region Specific Systems". 6 Nove Japan.
THE REVISION OF 1:50000 TOPOGRAPHIC MAP OF ONITSHA METROPOLIS, ANAMBRA STATE, NIGERIA USING NIGERIASAT-1 IMAGERY
 I.J.E.M.S., VOL.5 (4) 2014: 235-240 ISSN 2229-600X THE REVISION OF 1:50000 TOPOGRAPHIC MAP OF ONITSHA METROPOLIS, ANAMBRA STATE, NIGERIA USING NIGERIASAT-1 IMAGERY 1* Ejikeme, J.O. 1 Igbokwe, J.I. 1 Igbokwe,
I.J.E.M.S., VOL.5 (4) 2014: 235-240 ISSN 2229-600X THE REVISION OF 1:50000 TOPOGRAPHIC MAP OF ONITSHA METROPOLIS, ANAMBRA STATE, NIGERIA USING NIGERIASAT-1 IMAGERY 1* Ejikeme, J.O. 1 Igbokwe, J.I. 1 Igbokwe,
Monitoring and Change Detection along the Eastern Side of Qena Bend, Nile Valley, Egypt Using GIS and Remote Sensing
 Advances in Remote Sensing, 2013, 2, 276-281 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ars.2013.23030 Published Online September 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ars) Monitoring and Change Detection along the Eastern
Advances in Remote Sensing, 2013, 2, 276-281 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ars.2013.23030 Published Online September 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ars) Monitoring and Change Detection along the Eastern
SSRG International Journal of Geo informatics and Geological Science (SSRG-IJGGS) Volume 4 Issue 3 Sep to Dec 2017
 Evaluation of the Relationship between Land Use/Land Cover Dynamics and Land Surface Temperature across the Niger Delta Region of Nigeria Aniekan Eyoh 1, Francis Okeke 2 Department of Geoinformatics &
Evaluation of the Relationship between Land Use/Land Cover Dynamics and Land Surface Temperature across the Niger Delta Region of Nigeria Aniekan Eyoh 1, Francis Okeke 2 Department of Geoinformatics &
Spatiotemporal Analysis of Noida, Greater Noida and Surrounding Areas (India) Using Remote Sensing and GIS Approaches
 Spatiotemporal Analysis of Noida, Greater Noida and Surrounding Areas (India) Using Remote Sensing and GIS Approaches Gopal Krishna* Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi, India ABSTRACT Spatiotemporal
Spatiotemporal Analysis of Noida, Greater Noida and Surrounding Areas (India) Using Remote Sensing and GIS Approaches Gopal Krishna* Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi, India ABSTRACT Spatiotemporal
Application of Remote Sensing Techniques for Change Detection in Land Use/ Land Cover of Ratnagiri District, Maharashtra
 IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 3, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov. - Dec. 2015), PP 55-60 www.iosrjournals.org Application of Remote Sensing
IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 3, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov. - Dec. 2015), PP 55-60 www.iosrjournals.org Application of Remote Sensing
Impact of Landuse Change on Surface Temperature in Ibadan, Nigeria Abegunde Linda, Adedeji Oluwatola
 Impact of Landuse Change on Surface Temperature in Ibadan, Nigeria Abegunde Linda, Adedeji Oluwatola Abstract It has become an increasing evident that large development influences the climate. There are
Impact of Landuse Change on Surface Temperature in Ibadan, Nigeria Abegunde Linda, Adedeji Oluwatola Abstract It has become an increasing evident that large development influences the climate. There are
Critical Assessment of Land Use Land Cover Dynamics Using Multi-Temporal Satellite Images
 Environments 2015, 2, 61-90; doi:10.3390/environments2010061 OPEN ACCESS environments ISSN 2076-3298 www.mdpi.com/journal/environments Article Critical Assessment of Land Use Land Cover Dynamics Using
Environments 2015, 2, 61-90; doi:10.3390/environments2010061 OPEN ACCESS environments ISSN 2076-3298 www.mdpi.com/journal/environments Article Critical Assessment of Land Use Land Cover Dynamics Using
Mapping and Assessing Urban Impervious Areas Using Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis: A Case Study in the City of Tampa, Florida
 University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School January 2012 Mapping and Assessing Urban Impervious Areas Using Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis:
University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School January 2012 Mapping and Assessing Urban Impervious Areas Using Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis:
Yanbo Huang and Guy Fipps, P.E. 2. August 25, 2006
 Landsat Satellite Multi-Spectral Image Classification of Land Cover Change for GIS-Based Urbanization Analysis in Irrigation Districts: Evaluation in Low Rio Grande Valley 1 by Yanbo Huang and Guy Fipps,
Landsat Satellite Multi-Spectral Image Classification of Land Cover Change for GIS-Based Urbanization Analysis in Irrigation Districts: Evaluation in Low Rio Grande Valley 1 by Yanbo Huang and Guy Fipps,
PREDICTION OF FUTURE LAND USE LAND COVER CHANGES OF VIJAYAWADA CITY USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS
 PREDICTION OF FUTURE LAND USE LAND COVER CHANGES OF VIJAYAWADA CITY USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS K. Sundara Kumar 1 *, N V A Sai Sankar Valasala 2, J V Subrahmanyam V 3, Mounika Mallampati 4 Kowsharajaha
PREDICTION OF FUTURE LAND USE LAND COVER CHANGES OF VIJAYAWADA CITY USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS K. Sundara Kumar 1 *, N V A Sai Sankar Valasala 2, J V Subrahmanyam V 3, Mounika Mallampati 4 Kowsharajaha
EVALUATION OF URBANIZATION INFLUENCES ON URBAN CLIMATE WITH REMOTE SENSING AND CLIMATE OBSERVATIONS. George Xian 1 and Mike Crane 2.
 EVALUATION OF URBANIZATION INFLUENCES ON URBAN CLIMATE WITH REMOTE SENSING AND CLIMATE OBSERVATIONS George Xian 1 and Mike Crane 2 1 SAIC/ 2 USGS National Center for Earth Resources Observation and Science,
EVALUATION OF URBANIZATION INFLUENCES ON URBAN CLIMATE WITH REMOTE SENSING AND CLIMATE OBSERVATIONS George Xian 1 and Mike Crane 2 1 SAIC/ 2 USGS National Center for Earth Resources Observation and Science,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Spatio-Temporal changes of Land
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Spatio-Temporal changes of Land
Progress and Land-Use Characteristics of Urban Sprawl in Busan Metropolitan City using Remote sensing and GIS
 Progress and Land-Use Characteristics of Urban Sprawl in Busan Metropolitan City using Remote sensing and GIS Homyung Park, Taekyung Baek, Yongeun Shin, Hungkwan Kim ABSTRACT Satellite image is very usefully
Progress and Land-Use Characteristics of Urban Sprawl in Busan Metropolitan City using Remote sensing and GIS Homyung Park, Taekyung Baek, Yongeun Shin, Hungkwan Kim ABSTRACT Satellite image is very usefully
The relationship between land cover changes and spatial-temporal dynamics of land surface temperature
 76 The relationship between land cover changes and spatial-temporal dynamics of land surface temperature Samereh Falahatkar 1, Seyed Mohsen Hosseini 2 and Ali Reza Soffianian 3 1 Academic center for education,
76 The relationship between land cover changes and spatial-temporal dynamics of land surface temperature Samereh Falahatkar 1, Seyed Mohsen Hosseini 2 and Ali Reza Soffianian 3 1 Academic center for education,
Abstract: Introduction: 10 th ESRI India User Conference 2009 Geography in Action
 Mitigation of Thermal Pollution to enhance urban air quality through Remote Sensing and GIS Anshu Gupta, Lecturer, Centre of Remote Sensing and GIS, MANIT, Bhopal, E- mail: anshugupta20002001@gmail.com
Mitigation of Thermal Pollution to enhance urban air quality through Remote Sensing and GIS Anshu Gupta, Lecturer, Centre of Remote Sensing and GIS, MANIT, Bhopal, E- mail: anshugupta20002001@gmail.com
DETECTION AND ANALYSIS OF LAND-USE/LAND-COVER CHANGES IN NAY PYI TAW, MYANMAR USING SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING IMAGES
 DETECTION AND ANALYSIS OF LAND-USE/LAND-COVER CHANGES IN NAY PYI TAW, MYANMAR USING SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING IMAGES Kay Khaing Oo 1, Eiji Nawata 1, Kiyoshi Torii 2 and Ke-Sheng Cheng 3 1 Division of Environmental
DETECTION AND ANALYSIS OF LAND-USE/LAND-COVER CHANGES IN NAY PYI TAW, MYANMAR USING SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING IMAGES Kay Khaing Oo 1, Eiji Nawata 1, Kiyoshi Torii 2 and Ke-Sheng Cheng 3 1 Division of Environmental
Comparison of Spectral Analysis Techniques for Impervious Surface Estimation Using Landsat Imagery
 Comparison of Spectral Analysis Techniques for Impervious Surface Estimation Using Landsat Imagery Fei Yuan, Changshan Wu, and Marvin E. Bauer Abstract Various methodologies have been used to estimate
Comparison of Spectral Analysis Techniques for Impervious Surface Estimation Using Landsat Imagery Fei Yuan, Changshan Wu, and Marvin E. Bauer Abstract Various methodologies have been used to estimate
Vegetation Change Detection of Central part of Nepal using Landsat TM
 Vegetation Change Detection of Central part of Nepal using Landsat TM Kalpana G. Bastakoti Department of Geography, University of Calgary, kalpanagb@gmail.com Abstract This paper presents a study of detecting
Vegetation Change Detection of Central part of Nepal using Landsat TM Kalpana G. Bastakoti Department of Geography, University of Calgary, kalpanagb@gmail.com Abstract This paper presents a study of detecting
MONITORING THE SURFACE HEAT ISLAND (SHI) EFFECTS OF INDUSTRIAL ENTERPRISES
 MONITORING THE SURFACE HEAT ISLAND (SHI) EFFECTS OF INDUSTRIAL ENTERPRISES A. Şekertekin a, *, Ş. H. Kutoglu a, S. Kaya b, A. M. Marangoz a a BEU, Engineering Faculty, Geomatics Engineering Department
MONITORING THE SURFACE HEAT ISLAND (SHI) EFFECTS OF INDUSTRIAL ENTERPRISES A. Şekertekin a, *, Ş. H. Kutoglu a, S. Kaya b, A. M. Marangoz a a BEU, Engineering Faculty, Geomatics Engineering Department
Improving urban classification through fuzzy supervised classification and spectral mixture analysis
 International Journal of Remote Sensing Vol. 28, No. 18, 20 September 2007, 4047 4063 Improving urban classification through fuzzy supervised classification and spectral mixture analysis J. TANG*{, L.
International Journal of Remote Sensing Vol. 28, No. 18, 20 September 2007, 4047 4063 Improving urban classification through fuzzy supervised classification and spectral mixture analysis J. TANG*{, L.
Abstract: About the Author:
 REMOTE SENSING AND GIS IN LAND USE PLANNING Sathees kumar P 1, Nisha Radhakrishnan 2 1 1 Ph.D Research Scholar, Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli- 620015,
REMOTE SENSING AND GIS IN LAND USE PLANNING Sathees kumar P 1, Nisha Radhakrishnan 2 1 1 Ph.D Research Scholar, Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli- 620015,
Land Use/Cover Changes & Modeling Urban Expansion of Nairobi City
 Land Use/Cover Changes & Modeling Urban Expansion of Nairobi City Overview Introduction Objectives Land use/cover changes Modeling with Cellular Automata Conclusions Introduction Urban land use/cover types
Land Use/Cover Changes & Modeling Urban Expansion of Nairobi City Overview Introduction Objectives Land use/cover changes Modeling with Cellular Automata Conclusions Introduction Urban land use/cover types
The Road to Data in Baltimore
 Creating a parcel level database from high resolution imagery By Austin Troy and Weiqi Zhou University of Vermont, Rubenstein School of Natural Resources State and local planning agencies are increasingly
Creating a parcel level database from high resolution imagery By Austin Troy and Weiqi Zhou University of Vermont, Rubenstein School of Natural Resources State and local planning agencies are increasingly
Estimation of Land Surface Temperature of Kumta Taluk Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques
 Estimation of Land Surface Temperature of Kumta Taluk Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques Dr. A.G Koppad 1 and Malini P.J 2 Research Associate, NISAR Project (NRM) COF SIRSI, UAS Dharwad Professor
Estimation of Land Surface Temperature of Kumta Taluk Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques Dr. A.G Koppad 1 and Malini P.J 2 Research Associate, NISAR Project (NRM) COF SIRSI, UAS Dharwad Professor
LAND USE LAND COVER, CHANGE DETECTION OF FOREST IN KARWAR TALUK USING GEO-SPATIAL TECHNIQUES
 LAND USE LAND COVER, CHANGE DETECTION OF FOREST IN KARWAR TALUK USING GEO-SPATIAL TECHNIQUES Dr. A.G Koppad 1, Malini P.J 2 Professor and University Head (NRM) COF SIRSI, UAS DHARWAD Research Associate,
LAND USE LAND COVER, CHANGE DETECTION OF FOREST IN KARWAR TALUK USING GEO-SPATIAL TECHNIQUES Dr. A.G Koppad 1, Malini P.J 2 Professor and University Head (NRM) COF SIRSI, UAS DHARWAD Research Associate,
Mapping and Spatial Characterisation of Major Urban Centres in Parts of South Eastern Nigeria with Nigeriasat-1 Imagery
 Mapping and Spatial Characterisation of Major Urban Centres in Parts of South Eastern Nigeria with Joel I. IGBOKWE, Nigeria Key words: Urban Planning, Urban growth, Urban Infrastructure, Landuse, Satellite
Mapping and Spatial Characterisation of Major Urban Centres in Parts of South Eastern Nigeria with Joel I. IGBOKWE, Nigeria Key words: Urban Planning, Urban growth, Urban Infrastructure, Landuse, Satellite
IMPROVING REMOTE SENSING-DERIVED LAND USE/LAND COVER CLASSIFICATION WITH THE AID OF SPATIAL INFORMATION
 IMPROVING REMOTE SENSING-DERIVED LAND USE/LAND COVER CLASSIFICATION WITH THE AID OF SPATIAL INFORMATION Yingchun Zhou1, Sunil Narumalani1, Dennis E. Jelinski2 Department of Geography, University of Nebraska,
IMPROVING REMOTE SENSING-DERIVED LAND USE/LAND COVER CLASSIFICATION WITH THE AID OF SPATIAL INFORMATION Yingchun Zhou1, Sunil Narumalani1, Dennis E. Jelinski2 Department of Geography, University of Nebraska,
Object-based classification of residential land use within Accra, Ghana based on QuickBird satellite data
 International Journal of Remote Sensing Vol. 28, No. 22, 20 November 2007, 5167 5173 Letter Object-based classification of residential land use within Accra, Ghana based on QuickBird satellite data D.
International Journal of Remote Sensing Vol. 28, No. 22, 20 November 2007, 5167 5173 Letter Object-based classification of residential land use within Accra, Ghana based on QuickBird satellite data D.
Accuracy Assessment of Land Cover Classification in Jodhpur City Using Remote Sensing and GIS
 Accuracy Assessment of Land Cover Classification in Jodhpur City Using Remote Sensing and GIS S.L. Borana 1, S.K.Yadav 1 Scientist, RSG, DL, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India 1 Abstract: A This study examines
Accuracy Assessment of Land Cover Classification in Jodhpur City Using Remote Sensing and GIS S.L. Borana 1, S.K.Yadav 1 Scientist, RSG, DL, Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India 1 Abstract: A This study examines
Urban Hydrology - A Case Study On Water Supply And Sewage Network For Madurai Region, Using Remote Sensing & GIS Techniques
 RESEARCH INVENTY: International Journal of Engineering and Science ISBN: 2319-6483, ISSN: 2278-4721, Vol. 1, Issue 8 (November 2012), PP 07-12 www.researchinventy.com Urban Hydrology - A Case Study On
RESEARCH INVENTY: International Journal of Engineering and Science ISBN: 2319-6483, ISSN: 2278-4721, Vol. 1, Issue 8 (November 2012), PP 07-12 www.researchinventy.com Urban Hydrology - A Case Study On
Use of Satellite Data to Study the Impact of Land-Cover/Land-Use Change in Madison County Alabama
 American Journal of Applied Sciences 6 (4): 656-660, 2009 ISSN 1546-9239 2009 Science Publications Use of Satellite Data to Study the Impact of Land-Cover/Land-Use Change in Madison County Alabama Tomas
American Journal of Applied Sciences 6 (4): 656-660, 2009 ISSN 1546-9239 2009 Science Publications Use of Satellite Data to Study the Impact of Land-Cover/Land-Use Change in Madison County Alabama Tomas
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 12, December-2013 ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 12, December-2013 144 Assessment of Seasonal Variation of Land Surface Temperature (LST) in an Urban Area Arun Mondal1, Deepak
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 12, December-2013 144 Assessment of Seasonal Variation of Land Surface Temperature (LST) in an Urban Area Arun Mondal1, Deepak
Land Use Changing Scenario at Kerniganj Thana of Dhaka District Using Remote Sensing and GIS
 Research Paper Land Use Changing Scenario at Kerniganj Thana of Dhaka District Using Remote Sensing and GIS Farzana Raihan 1 * and Nowrine Kaiser 1 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Forestry and Environment
Research Paper Land Use Changing Scenario at Kerniganj Thana of Dhaka District Using Remote Sensing and GIS Farzana Raihan 1 * and Nowrine Kaiser 1 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Forestry and Environment
Monitoring of Forest Cover Change in Sundarban mangrove forest using Remote sensing and GIS
 Monitoring of Forest Cover Change in Sundarban mangrove forest using Remote sensing and GIS By Mohammed Monirul Alam April 2008 Content 1: INTRODUCTION 2: OBJECTIVES 3: METHODOLOGY 4: RESULTS & DISCUSSION
Monitoring of Forest Cover Change in Sundarban mangrove forest using Remote sensing and GIS By Mohammed Monirul Alam April 2008 Content 1: INTRODUCTION 2: OBJECTIVES 3: METHODOLOGY 4: RESULTS & DISCUSSION
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 11, November ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 11, November-2015 180 Quantifying Land use/cover change of Oredo, Egor, Ikpoba-Okha LGA, Benin City, Edo State, Nigeria from
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 11, November-2015 180 Quantifying Land use/cover change of Oredo, Egor, Ikpoba-Okha LGA, Benin City, Edo State, Nigeria from
An Internet-based Agricultural Land Use Trends Visualization System (AgLuT)
 An Internet-based Agricultural Land Use Trends Visualization System (AgLuT) Prepared for Missouri Department of Natural Resources Missouri Department of Conservation 07-01-2000-12-31-2001 Submitted by
An Internet-based Agricultural Land Use Trends Visualization System (AgLuT) Prepared for Missouri Department of Natural Resources Missouri Department of Conservation 07-01-2000-12-31-2001 Submitted by
Impact of the Human Activities on the Local Climate and Environment of the Suez City in Egypt
 International Journal of Geosciences, 2014, 5, 700-709 Published Online June 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijg http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ijg.2014.57063 Impact of the Human Activities on
International Journal of Geosciences, 2014, 5, 700-709 Published Online June 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijg http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ijg.2014.57063 Impact of the Human Activities on
IMPACT OF URBAN EVOLUTION ON LAND-USE CHANGE OF SARGODHA CITY, PAKISTAN
 Impact of Urban Evolution on Land-Use Change of Sargodha City in Pakistan J. Sc. & Tech. Univ. Peshawar, 2015, 39 (2), 29-36. IMPACT OF URBAN EVOLUTION ON LAND-USE CHANGE OF SARGODHA CITY, PAKISTAN SAJJAD
Impact of Urban Evolution on Land-Use Change of Sargodha City in Pakistan J. Sc. & Tech. Univ. Peshawar, 2015, 39 (2), 29-36. IMPACT OF URBAN EVOLUTION ON LAND-USE CHANGE OF SARGODHA CITY, PAKISTAN SAJJAD
URBAN GROWTH AND LAND USE/LAND COVER MODELING IN SEMARANG, CENTRAL JAVA, INDONESIA
 URBAN GROWTH AND LAND USE/LAND COVER MODELING IN SEMARANG, CENTRAL JAVA, INDONESIA Firman Hadi 1, Rajesh B. Thapa 2, M. Helmi 3, Manzul K. Hazarika 1, Sasanka Madawalagama 1, Lakmal N. Deshapriya 1 1 Geoinformatics
URBAN GROWTH AND LAND USE/LAND COVER MODELING IN SEMARANG, CENTRAL JAVA, INDONESIA Firman Hadi 1, Rajesh B. Thapa 2, M. Helmi 3, Manzul K. Hazarika 1, Sasanka Madawalagama 1, Lakmal N. Deshapriya 1 1 Geoinformatics
URBAN MAPPING AND CHANGE DETECTION
 URBAN MAPPING AND CHANGE DETECTION Sebastian van der Linden with contributions from Akpona Okujeni Humboldt-Unveristät zu Berlin, Germany Introduction Introduction The urban millennium Source: United Nations,
URBAN MAPPING AND CHANGE DETECTION Sebastian van der Linden with contributions from Akpona Okujeni Humboldt-Unveristät zu Berlin, Germany Introduction Introduction The urban millennium Source: United Nations,
Land Use and Land Cover Detection by Different Classification Systems using Remotely Sensed Data of Kuala Tiga, Tanah Merah Kelantan, Malaysia
 Land Use and Land Cover Detection by Different Classification Systems using Remotely Sensed Data of Kuala Tiga, Tanah Merah Kelantan, Malaysia Wani Sofia Udin*, Zuhaira Nadhila Zahuri Faculty of Earth
Land Use and Land Cover Detection by Different Classification Systems using Remotely Sensed Data of Kuala Tiga, Tanah Merah Kelantan, Malaysia Wani Sofia Udin*, Zuhaira Nadhila Zahuri Faculty of Earth
1. Introduction. S.S. Patil 1, Sachidananda 1, U.B. Angadi 2, and D.K. Prabhuraj 3
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2014, Volume 3, Issue 1, pp. 525-531, Article ID Tech-249 ISSN 2320-0243 Research Article Open Access Machine Learning Technique
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2014, Volume 3, Issue 1, pp. 525-531, Article ID Tech-249 ISSN 2320-0243 Research Article Open Access Machine Learning Technique
AN INVESTIGATION OF AUTOMATIC CHANGE DETECTION FOR TOPOGRAPHIC MAP UPDATING
 AN INVESTIGATION OF AUTOMATIC CHANGE DETECTION FOR TOPOGRAPHIC MAP UPDATING Patricia Duncan 1 & Julian Smit 2 1 The Chief Directorate: National Geospatial Information, Department of Rural Development and
AN INVESTIGATION OF AUTOMATIC CHANGE DETECTION FOR TOPOGRAPHIC MAP UPDATING Patricia Duncan 1 & Julian Smit 2 1 The Chief Directorate: National Geospatial Information, Department of Rural Development and
Using Geographic Information Systems and Remote Sensing Technology to Analyze Land Use Change in Harbin, China from 2005 to 2015
 Using Geographic Information Systems and Remote Sensing Technology to Analyze Land Use Change in Harbin, China from 2005 to 2015 Yi Zhu Department of Resource Analysis, Saint Mary s University of Minnesota,
Using Geographic Information Systems and Remote Sensing Technology to Analyze Land Use Change in Harbin, China from 2005 to 2015 Yi Zhu Department of Resource Analysis, Saint Mary s University of Minnesota,
ANALYSIS OF VEGETATION DISTRIBUTION IN URBAN AREAS: SPATIAL ANALYSIS APPROACH ON A REGIONAL SCALE
 ANALYSIS OF VEGETATION DISTRIBUTION IN URBAN AREAS: SPATIAL ANALYSIS APPROACH ON A REGIONAL SCALE Kiichiro Kumagai Department of Civil and Environmental System Engineering, Setsunan University 17-8 Ikedanakamachi,
ANALYSIS OF VEGETATION DISTRIBUTION IN URBAN AREAS: SPATIAL ANALYSIS APPROACH ON A REGIONAL SCALE Kiichiro Kumagai Department of Civil and Environmental System Engineering, Setsunan University 17-8 Ikedanakamachi,
CHAPTER 1 THE UNITED STATES 2001 NATIONAL LAND COVER DATABASE
 CHAPTER 1 THE UNITED STATES 2001 NATIONAL LAND COVER DATABASE Collin Homer*, Jon Dewitz, Joyce Fry, and Nazmul Hossain *U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) Center for Earth Resources Observation and Science
CHAPTER 1 THE UNITED STATES 2001 NATIONAL LAND COVER DATABASE Collin Homer*, Jon Dewitz, Joyce Fry, and Nazmul Hossain *U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) Center for Earth Resources Observation and Science
DETECTION OF CHANGES IN FOREST LANDCOVER TYPE AFTER FIRES IN PORTUGAL
 DETECTION OF CHANGES IN FOREST LANDCOVER TYPE AFTER FIRES IN PORTUGAL Paulo M. Barbosa, Mário R. Caetano, and Teresa G. Santos Centro Nacional de Informação Geográfica (CNIG), Portugal barp@cnig.pt, mario@cnig.pt,
DETECTION OF CHANGES IN FOREST LANDCOVER TYPE AFTER FIRES IN PORTUGAL Paulo M. Barbosa, Mário R. Caetano, and Teresa G. Santos Centro Nacional de Informação Geográfica (CNIG), Portugal barp@cnig.pt, mario@cnig.pt,
ASSESSING THE IMPACT OF URBANIZATION ON URBAN CLIMATE BY REMOTE SENSING PERSPECTIVE: A CASE STUDY IN DANANG CITY, VIETNAM
 ASSESSING THE IMPACT OF URBANIZATION ON URBAN CLIMATE BY REMOTE SENSING PERSPECTIVE: A CASE STUDY IN DANANG CITY, VIETNAM Nguyen Hoang Khanh Linh a,*, Huynh Van Chuong a a Faculty of Land Resources and
ASSESSING THE IMPACT OF URBANIZATION ON URBAN CLIMATE BY REMOTE SENSING PERSPECTIVE: A CASE STUDY IN DANANG CITY, VIETNAM Nguyen Hoang Khanh Linh a,*, Huynh Van Chuong a a Faculty of Land Resources and
Spatio-temporal dynamics of the urban fringe landscapes
 Spatio-temporal dynamics of the urban fringe landscapes Yulia Grinblat 1, 2 1 The Porter School of Environmental Studies, Tel Aviv University 2 Department of Geography and Human Environment, Tel Aviv University
Spatio-temporal dynamics of the urban fringe landscapes Yulia Grinblat 1, 2 1 The Porter School of Environmental Studies, Tel Aviv University 2 Department of Geography and Human Environment, Tel Aviv University
Land Use/Land Cover Mapping in and around South Chennai Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques ABSTRACT
 Land Use/Land Cover Mapping in and around South Chennai Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques *K. Ilayaraja, Abhishek Singh, Dhiraj Jha, Kriezo Kiso, Amson Bharath institute of Science and Technology
Land Use/Land Cover Mapping in and around South Chennai Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques *K. Ilayaraja, Abhishek Singh, Dhiraj Jha, Kriezo Kiso, Amson Bharath institute of Science and Technology
A Method to Improve the Accuracy of Remote Sensing Data Classification by Exploiting the Multi-Scale Properties in the Scene
 Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Spatial Accuracy Assessment in Natural Resources and Environmental Sciences Shanghai, P. R. China, June 25-27, 2008, pp. 183-188 A Method to Improve the
Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Spatial Accuracy Assessment in Natural Resources and Environmental Sciences Shanghai, P. R. China, June 25-27, 2008, pp. 183-188 A Method to Improve the
A comparison of pixel and object-based land cover classification: a case study of the Asmara region, Eritrea
 Geo-Environment and Landscape Evolution III 233 A comparison of pixel and object-based land cover classification: a case study of the Asmara region, Eritrea Y. H. Araya 1 & C. Hergarten 2 1 Student of
Geo-Environment and Landscape Evolution III 233 A comparison of pixel and object-based land cover classification: a case study of the Asmara region, Eritrea Y. H. Araya 1 & C. Hergarten 2 1 Student of
A METHOD TO MAP LAND-USE CHANGE AND URBAN GROWTH IN NORTH RHINE-WESTPHALIA (GERMANY)
 Proceedings of the 2 nd Workshop of the EARSeL SIG on Land Use and Land Cover A METHOD TO MAP LAND-USE CHANGE AND URBAN GROWTH IN NORTH RHINE-WESTPHALIA (GERMANY) Roland Goetzke, Martin Over and Matthias
Proceedings of the 2 nd Workshop of the EARSeL SIG on Land Use and Land Cover A METHOD TO MAP LAND-USE CHANGE AND URBAN GROWTH IN NORTH RHINE-WESTPHALIA (GERMANY) Roland Goetzke, Martin Over and Matthias
Spatiotemporal Monitoring of Urban Vegetation
 Spatiotemporal Monitoring of Urban Vegetation Christopher Small Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory, Columbia University, USA small@ldeo.columbia.edu Roberta Balstad Miller CIESIN Columbia University, USA
Spatiotemporal Monitoring of Urban Vegetation Christopher Small Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory, Columbia University, USA small@ldeo.columbia.edu Roberta Balstad Miller CIESIN Columbia University, USA
Environmental Impact Assessment Land Use and Land Cover CISMHE 7.1 INTRODUCTION
 7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered an essential element for modeling and understanding
7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered an essential element for modeling and understanding
Change Detection Analysis By Using Ikonos And Quick Bird Imageries
 Change Detection Analysis By Using Ikonos And Quick Bird Imageries Eltahir Mohamed Elhadi 12 and Nagi Zomrawi 2 1-China University of Geosciences Faculty of Resources, Wuhan, 430074, China, 2-Sudan University
Change Detection Analysis By Using Ikonos And Quick Bird Imageries Eltahir Mohamed Elhadi 12 and Nagi Zomrawi 2 1-China University of Geosciences Faculty of Resources, Wuhan, 430074, China, 2-Sudan University
Quick Response Report #126 Hurricane Floyd Flood Mapping Integrating Landsat 7 TM Satellite Imagery and DEM Data
 Quick Response Report #126 Hurricane Floyd Flood Mapping Integrating Landsat 7 TM Satellite Imagery and DEM Data Jeffrey D. Colby Yong Wang Karen Mulcahy Department of Geography East Carolina University
Quick Response Report #126 Hurricane Floyd Flood Mapping Integrating Landsat 7 TM Satellite Imagery and DEM Data Jeffrey D. Colby Yong Wang Karen Mulcahy Department of Geography East Carolina University
IMAGE CLASSIFICATION TOOL FOR LAND USE / LAND COVER ANALYSIS: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD AND MINIMUM DISTANCE METHOD
 IMAGE CLASSIFICATION TOOL FOR LAND USE / LAND COVER ANALYSIS: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD AND MINIMUM DISTANCE METHOD Manisha B. Patil 1, Chitra G. Desai 2 and * Bhavana N. Umrikar 3 1 Department
IMAGE CLASSIFICATION TOOL FOR LAND USE / LAND COVER ANALYSIS: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD AND MINIMUM DISTANCE METHOD Manisha B. Patil 1, Chitra G. Desai 2 and * Bhavana N. Umrikar 3 1 Department
