Ultrasound-Enhanced Anodic Stripping Voltammetry Using Perfluorosulfonated Ionomer-Coated Mercury Thin-Film Electrodes
|
|
|
- Vivien Dickerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, Ultrasound-Enhanced Anodic Stripping Voltammetry Using Perfluorosulfonated Ionomer-Coated Mercury Thin-Film Electrodes Frank-Michael Matysik, Silke Matysik, Ana Maria Oliveira Brett,* and Christopher M. A. Brett* Departamento de Química, Universidade de Coimbra, 3049 Coimbra, Portugal The high mass transport caused by ultrasonic radiation in the preconcentration of trace metal species in anodic stripping voltammetry (ASV), leads to an order of magnitude enhancement in sensitivity. A Nafion-coated mercury thin-film working electrode is placed in a specially designed small-volume sonovoltammetric cell. The preparation and curing procedure for the Nafion film on a glassy carbon electrode substrate as well as ultrasound-enhanced mercury deposition through the Nafion film are optimized. The resulting electrode assembly is stable under ultrasonic irradiation. Optical microscopy observations show the formation of closely spaced mercury droplets of micrometer dimensions under the Nafion film. The performance characteristics of ultrasound-enhanced ASV at the Nafion-coated mercury thin-film electrode are studied in detail. The detection limit obtained for lead and cadmium test species is M (30 s preconcentration in the presence of ultrasound). A relative standard deviation of 1.2% is obtained for repetitive determinations of 10 nm Cd 2+ (n ) 9). Anodic stripping voltammetry (ASV) is well established as a powerful method for trace metal analysis. 1 Its inherent sensitivity results from preconcentrating the metal of interest into or onto an electrode followed by an anodic stripping step, usually using a differential pulse or square wave voltammetric scan. Potentially, the detection limit can be lowered via more efficient preconcentration. In other words, the higher the rate of mass transport during the deposition period the lower the attainable limit of detection. However, other prerequisites such as reproducibility of mass transport and stability of the electrode assembly under the preconcentration conditions have to be fulfilled. Several effective strategies have been described for preconcentrating the analyte in stripping voltammetric determinations. These include hydrodynamic systems such as the rotating disk electrode 2,3 and stationary electrodes in combination with flowing solutions, typically in wall-jet 4-6 configurations. Frequently, stirring is also used to impose convection in the electrolyte solution. In the case of microelectrodes, it has been demonstrated that sufficiently (1) Wang, J. Stripping Analysis: Principles, Instrumentation and Applications; VCH: Deerfield Beach, FL, (2) Florence, T. M. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1970, 26, (3) Brihaye, C.; Duyckaerts, G. Anal. Chim. Acta 1982, 143, (4) Gunasingham, H.; Ang, K. P.; Ngo, C. C. Anal. Chem. 1985, 57, (5) Omanovic, D.; Peharec, Z.; Magjer, T.; Lovric, M.; Branica, M. Electroanalysis 1994, 6, (6) Brett, C. M. A.; Lima, J. L. F. C; Garcia, M. B. Q. Analyst 1994, 119, effective preconcentration can be achieved in quiescent solution on the basis of (hemi)spherical diffusion. 7,8 Sonovoltammetry, i.e., the performance of voltammetry in the presence of ultrasound, has recently been established as a powerful tool for studying electrochemical processes The attractive features of ultrasound-enhanced voltammetry are as follows: (i) Ultrasonic irradiation leads to very high mass transport of electroactive species and their products to and from the electrode surface. 10,14 (ii) Ultrasound can influence the mechanism of chemical and electrochemical reactions via the action of highly reactive radicals such as OH and H formed during sonolysis of water. 15,16 (iii) The adsorption of species involved in an electrochemical reaction can be reduced in the presence of ultrasound. 17 (iv) Ultrasonic irradiation can provide continuous in situ activation of the electrode surface. 11,17 Among a variety of experimental strategies of introducing ultrasound into an electrochemical cell, direct-immersion sonicator probes are highly practicable. A suitable cell configuration contains the working electrode introduced from the bottom and placed directly below the tip of a vibrating titanium horn. One of the most attractive characteristics of this experimental configuration is the enormous enhancement of mass transport due to the high ultrasonic power intensity present in the vicinity of the electrode. Recently we have designed and evaluated a smallvolume cell, 1 order of magnitude smaller than previous sonoelectrochemical cell designs, 10,11 in which the coupling of ultrasound and voltammetry is particularly suitable for analytical studies. 18 The aim of the present work is to utilize the unique hydrodynamic characteristics that result from insonication of electrolyte solutions as an effective way to preconcentrate the analyte in anodic stripping voltammetry. A recent paper by Coury and co- (7) Wehmeyer, K. R.; Wightman, R. M. Anal. Chem. 1985, 57, (8) Matysik, F.-M.; Gläser, P.; Werner, G. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1994, 349, (9) Mason, T. J.; Lorimer, J. P.; Walton, D. J. Ultrasonics 1992, 28, (10) Hagan, C. R. S.; Coury, L. A., Jr. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, (11) Compton, R. G.; Eklund, J. C.; Page, S. D.; Sanders, G. H. W.; Booth, J. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, (12) Klíma, J.; Bernard, C.; Degrand, C. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1994, 367, (13) Reisse, J.; Francois, H.; Vandercammen, J.; Fabre, O.; Kirsch-de Mesmaeker, A.; Maerschalk, C; Delplancke, J.-L. Electrochim. Acta 1994, 39, (14) Walton, D. J.; Phull, S. S.; Chyla, A.; Lorimer, J. P.; Mason, T. J.; Burke, L. D.; Murphy, M.; Compton, R. G.; Eklund, J. C.; Page, S. D. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1995, 25, (15) Compton, R. G.; Eklund, J. C.; Page, S. D. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, (16) Compton, R. G.; Matysik, F.-M. Electroanalysis 1996, 8, (17) Oliveira Brett, A. M.; Matysik, F.-M. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg., in press. (18) Oliveira Brett, A. M.; Matysik, F.-M. Electrochim. Acta, in press. S (96) CCC: $ American Chemical Society Analytical Chemistry, Vol. 69, No. 8, April 15,
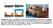
2 workers 19 also reported stripping voltammetric experiments in combination with ultrasound. However, the authors described sonochemical deposition of metal particles in organic suspensions onto a gold electrode followed by subsequent anodic stripping in a separate aqueous solution. In contrast to this, our investigationssformation of mercury thin-film and stripping voltammetry experimentssare performed entirely in the sonovoltammetric cell. This approach requires special attention regarding the stability of the working electrode, i.e., protecting the integrity of the mercury film, in the presence of ultrasound. Therefore, the preparation of perfluorosulfonated ionomer (Nafion)-coated mercury thin-film electrodes resistant to sonication and their characterization plays an important role in the present paper. The performance characteristics of the sonovoltammetric stripping procedure are studied and analytical utility is explored. EXPERIMENTAL SECTION Apparatus. Sonovoltammetric measurements were carried out in the cell arrangement illustrated in Figure 1. The jacketed glass cell, suitable for an electrolyte volume of 20 ml, was constructed such that the working electrode surface was facing the tip of the sonic horn probe. The horn was connected to a tapered microtip (3 mm diameter) which was fabricated from highgrade titanium alloy. The circulating coolant was water thermostated in a constant-temperature bath (25 C). Under optimized experimental conditions, the distance between the sonic horn and the working electrode was 6 ( 1 mm and an ultrasound power intensity of 30 ( 3Wcm -2 (calibrated according to the procedure of Mason et al. 20 ) was selected. The high-intensity ultrasonic processor was a Model VC501 (Sonics & Materials Inc.) rated by the manufacturer at 500 W when driven at 20 khz frequency. All voltammetric experiments were conducted using a PGSTAT 10 Autolab voltammetric analyzer (Eco Chemie, Utrecht, Netherlands). Microscopic studies were carried out with an Optiphot optical microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan). Photographs were taken with Kodak ASA 25 black and white or color films. Chemicals. Solutions were prepared from analytical grade chemical reagents and Millipore Milli-Q ultrapure water (resistivity g18 MΩ cm). Stock solutions of 10-3 MPb 2+ and Cd 2+ were prepared and diluted on the day as appropriate. A 5% solution of Nafion in low-weight alcohols (Aldrich) was diluted with ethanol (Merck, pro analysi) prior to application. Cellulose acetate (acetyl content 40%) was obtained from Sigma. N,N-Dimethylformamide (DMF) was of analytical grade (99.5%) and purchased from Fluka. The Standard Reference Material (SRM 1643c) was prepared at the facilities of the U.S. Geological Survey, Branch of Quality Assurance, Golden, CO, and obtained from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), Gaithersburg, MD. Procedures. Nafion-coated mercury thin-film electrodes (NC- MTFE) for ultrasound-enhanced stripping voltammetry were prepared according to the following procedure. First, the 6 mm diameter glassy carbon electrode (GCE), a gift from Prof. G. Jenkins, Alabama A&M University, Normal, AL, was polished using polishing foils with 0.3 µm alumina particles (Ehret Datentechnik, Emmendingen, Germany), rinsed with Milli-Q water and allowed to dry. Nafion coating was achieved by applying 10 µl (19) Madigan, N. A.; Murphy, T. J.; Fortune, J. M.; Hagan, C. R. S.; Coury, L. A., Jr. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, (20) Mason, T. J.; Lorimer, J. P.; Bates, D. M. Ultrasonics 1992, 30, Figure 1. Photograph and schematic representation of the sonovoltammetric cell: a, sonic horn with microtip; b, Ag/AgCl (3 M KCl) reference electrode; c, platinum coil counter electrode; d, coolant outlet; e, coolant inlet; f, cavitational plume; g, Nafion-coated mercury film; h, glassy carbon; i, O-ring seal; j, working electrode lead. of 0.5% (w/v) freshly prepared Nafion solution, followed immediately by 5 µl of DMF casting solvent, to the electrode surface with a micropipet. The solvents were evaporated in a warm airstream from an air gun while the electrode was rotated at 50 rpm. The polymer film was then cured for 60 s in a hot airstream ( 70 C), holding the gun just a few millimeters above the electrode surface. The Nafion-coated electrode was then placed in the sonovoltammetric cell containing 20 ml of 0.1 M acetate buffer (ph 4.60), and three cyclic voltammograms were performed in the potential range between -1.0 and 0.0 V to verify a low background current. Mercury deposition was done by adding 40 µl of a solution of 0.1 M Hg 2+ in 0.1 M KNO 3 /0.002 M HNO 3 to the actetate buffer solution and applying a similiar potential program as in square wave anodic stripping voltammetry, as specified below, utilizing ultrasonic enhancement of the deposition Analytical Chemistry, Vol. 69, No. 8, April 15, 1997
3 Figure 2. Potential-timewave form for ultrasound-enhanced SWASV. Preconcentration time varied between 30 and 120 s; ultrasound switched on 10 s before deposition period and switched off 5 s before end of deposition period. E cond and E dep represent the conditioning and deposition potentials, which are set at 0.0 and V, respectively. The NCMTFE was then ready for use in ASV measurements. The studies that led to this procedure are described in the next section. The ultrasound-enhanced ASV procedure is illustrated in Figure 2. Experiments were undertaken without deoxygenation and the square wave parameters were as follows: amplitude 50 mv, scan increment 2 mv, and frequency 50 Hz. The conditioning potential, E cond, was 0 V and the deposition potential, E dep, was V, which was also maintained under silent conditions for 5 s before starting the square wave scan. If not otherwise stated, the deposition time in the presence of ultrasound was 30 s. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Optimization of Preparing Nafion-Coated Mercury Thin- Film Electrodes. The stability of the thin mercury film under conditions of ultrasonic irradiation is the most important point for performing reliable ultrasound-enhanced ASV measurements. Several procedures for preparing mercury thin films with and without polymer coating were examined. It was found that mercury thin films formed onto glassy carbon electrodes without an additional polymer coating were not suitable for sonovoltammetric studies in the present cell configuration. This is not surprising because mercury shows only weak interactions with the glassy carbon surface 21 and the capability of high-intensity ultrasound to erode electrode material 11,22 is well-known. Consequently, further studies were directed to polymer-coated mercury films. Glassy carbon electrodes coated with cellulose acetate (prepared according to a procedure described in the literature 23 )or Nafion films were placed in the sonovoltammetric cell, and their stability in the presence of ultrasound was tested without mercury deposition. The adhesion of the cellulose acetate coatings on the glassy carbon substrate was not strong enough to be resistant to sonication. As a result, the whole film lifted off after sonication periods of less than 1 min. (21) Frenzel, W. Anal. Chim. Acta 1993, 273, (22) Madigan, N. A.; Hagan, C. R. S.; Coury, L. A., Jr. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1994, 141, L23-L24. (23) Dam, M. E. R.; Thomsen, K. N.; Pickup, P. G.; Schroder, K. H. Electroanalysis 1995, 7, The mechanical properties of Nafion films were found to be much better than those of cellulose acetate films. Nafion-coated electrodes were optimized in a similar way as described recently for the NCMTFE used in conjunction with batch injection analysis (BIA), 24 in which volumes in the microliter range are injected perpendicularly from a micropipet onto the center of the electrode. The use of DMF as casting solvent and heating during film formation improved the stability of the Nafion films under conditions of ultrasonic irradiation. In addition, preparation by spin-coating at a rotation speed of 50 rpm resulted in a more homogeneous polymer layer than under stationary conditions. Visually, the Nafion coating appeared transparent and uniform over the whole electrode surface. A typical optical micrograph of a Nafion-coated GCE is shown in Figure 3A, which also illustrates the roughness of the underlying glassy carbon surface. An appropriate procedure for in situ mercury deposition through the Nafion film was then elaborated. Initially the mercury thin film was formed using the BIA principle and the optimized procedure described in ref 24. To this end, 10 µl of0.1mhg 2+ in 0.1 M KNO 3 /0.002 M HNO 3 electrolyte solution was injected by micropipet on the top of the Nafion-coated GCE while a potential of -1.0 V was applied. Such a NCMTFE is stable under the hydrodynamic conditions of BIA and corresponding stripping voltammetric determinations. 24 However, in the presence of ultrasound this stability was not sufficientsafter a few seconds of ultrasonic irradiation the entire film or parts of it were lifted off. Lower concentrations of Hg 2+ were tried but led to insufficient mercury film formation since microliter volumes are employed in BIA mercury deposition. A much more suitable approach was found to be the in situ deposition of mercury from an acetate buffer solution containing Hg 2+, in the range of concentration normally used for mercury film formation on bare glassy carbon, in the presence of ultrasound. The potential program used was that of the square wave ASV (SWASV) procedure described in the Experimental Section, which involved a 30 s deposition period under ultrasonic irradiation; see Figure 2. High Hg 2+ concentrations in the 20 ml sonovoltammetric cell led to too rapid film formation and lifting off of the Nafion from the substrate; experiments showed that a concentration of MHg 2+ led to a good response. A stable background response was obtained with this electrode after the first or second scan, and the NCMTFE was then ready for ASV determinations. Trace metal determinations could be performed in the same solution by adding an appropriate amount of the analyte sample to the Hg 2+ /acetate buffer solution. There was good signal stability for repetitive measurements, to be quantified later, and the optical appearance of the Nafion/mercury assembly remained the same. Optical micrographs indicate that in representative central regions of the electrode small droplets of submicrometer size are formed (see Figure 3B). At the edge of the electrode, larger droplets can also be found as shown in Figure 3C and D, possibly due to the inhomogeneity of the ultrasonic field. The tendency for droplet formation has been observed previously for the widely used mercury films deposited on bare glassy carbon substrates, e.g., refs 21 and 25, where the formation of truly continuous thin films does not occur in practice. The electroanalytical behavior is little affected if procedures suggested (24) Brett, C. M. A.; Oliveira Brett, A. M.; Matysik, F.-M.; Matysik, S.; Kumbhat, S. Talanta 1996, 43, (25) Stulikova, M. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1973, 48, Analytical Chemistry, Vol. 69, No. 8, April 15,
4 Figure 3. Optical micrographs of (A) Nafion coating on glassy carbon substrate, (B) Nafion-coated mercury thin film electrode homogeneous inner region; (C) Nafion-coated mercury thin film electrode, edge of electrode; and (D) Nafion-coated mercury thin film electrode, edge of electrode. in the literature are followed. The mercury droplets are embedded in a compact, transparent Nafion matrix. Focusing the optical microscope through the film confirms that the droplets are formed on the glassy carbon substrate beneath the Nafion film. The thickness of this film can be estimated using data for the density of bulk Nafion 23 to be of the order of 1 µm. Thus the film is probably slightly lifted above where the drops form. Nevertheless, the ease of diffusion through such a thin film as demonstrated by the lack of limiting effects in square wave scans means that, effectively, linear diffusion still occurs. Optical micrographs were also taken from NCMTFE prepared using mercury deposition by BIA. These NCMTFE showed more closely arranged, larger droplets than found for the NCMTFE prepared in the presence of ultrasound. Thus, and in accordance with the above, the BIA-prepared Nafion film will be adherent over a lesser fraction of the substrate due to these larger droplets on the substrate and hence will be more prone to lift off. Additionally, it can be speculated that the greater mass of mercury in each droplet is also responsible for instability in the presence of ultrasound because the potential to cause mechanical destruction should be mass-dependent. For this reason, all of the following ASV experiments were done with NCMTFEs prepared by in situ deposition of mercury through the Nafion film as described in the Experimental Section. The ultrasound conditions, i.e., the horn tip-electrode separation and the power intensity, were also varied. The chosen parameters (horn tip-electrode separation 6 mm, power intensity 30Wcm -2 ) are a compromise between achieving high mass transport and ensuring stability of the NCMTFE. Under these Figure 4. Ultrasound-enhanced SWASV of 5 nm Pb 2+ at Nafioncoated mercury thin film electrode. Deposition times: (a) 30 (no ultrasound), (b) 30, (c) 60, (d) 90, and (e) 120 s. conditions the NCMTFE could be used for two days (4-5 h per day) without changes in the performance characteristics, whereas on the third day there was usually a decrease in sensitivity caused by the appearance of flaws in the Nafion coating. The NCMTFE was stored in air between experiments. Analytical Performance Characteristics. (i) Sensitivity and Limit of Detection. Figure 4 shows the SWASV response 1654 Analytical Chemistry, Vol. 69, No. 8, April 15, 1997
5 Table 2. Analysis of a Standard Reference Material by Ultrasound-Enhanced ASV. Comparison between Certified Values and Experimental Results element certified concn (mg/ml) ((2σ) results obtained by US-ASV (mg/ml) ((2σ) Cd 12.2 ( ( 1.6 Pb 35.3 ( ( Figure 5. Ultrasound-enhanced SWASV of Cd and Pb at Nafioncoated mercury thin-film electrode. Concentrations: (a) [Cd 2+ ] ) 2 nm, [Pb 2+ ] ) 7 nm; (b) [Cd 2+ ] ) 7 nm, [Pb 2+ ] ) 12 nm; (c) [Cd 2+ ] ) 12 nm, [Pb 2+ ] ) 17 nm; (d) [Cd 2+ ] ) 17 nm, [Pb 2+ ] ) 22 nm. Preconcentration for 30 s in the presence of ultrasound. Table 1. Linear Regression of Calibration Data for Cadmium and Lead Determination by Ultrasound- Enhanced SWASV Using a Nafion-Coated Mercury Thin-Film Electrode a analyte slope ( σ (µa/nm) intercept ( σ (µa) regression coeff Cd ( ( (n ) 9) Pb ( ( (n ) 7) a Deposition time 30 s. obtained for the determination of 5 nm Pb 2+ using different preconcentration conditions: silent and ultrasound-enhanced. Increasing the deposition time with ultrasound-enhanced deposition in the range s leads to a linear increase in the ASV signal. It should be emphasized that curve a represents not just a background response but was obtained after a deposition period of 30 s under silent conditions for which the lead concentration tested is obviously below the detection limit. Comparison was also made with preconcentration in which the solution was agitated by magnetic stirring. It was found that the preconcentration efficiency in the presence of ultrasound was 5 times higher than that under magnetic stirring at the highest possible speed ( 500 rpm). As a consequence of the enhanced preconcentration due to ultrasound, quite short deposition times of 30 s were usually selected for ultrasound-assisted ASV measurements. Figure 5 illustrates the typical response obtained for the test species lead and cadmium present at concentrations in the lower nanomolar range. Calibration plots were linear within the concentration range from 5 to 50 nm; the results of linear regression are shown in Table 1. Higher concentrations can be measured but memory effects begin to appearsit is therefore advisable to dilute as appropriate. Detection limits were determined on the basis of the 3σ criterion where σ represents the standard deviation of the baseline noise. The limit of detection (30 s preconcentration) is M for both cadmium and lead. However, in practice the detection limit was 1 magnitude of order higher because trace metal impurities were encountered in the chemicals employed. (ii) Precision and Accuracy. The reproducibility of repetitive ultrasound-enhanced ASV experiments was characterized by performing successive determinations of 10 nm Cd 2+. As already mentioned, the in situ deposition of mercury requires one or two ASV determinations to establish stable electrode response. Thus, for statistical evaluation, the first measurement was not included. A relative standard deviation of 1.2% was obtained. Signal stability was also studied in the case of electrolyte exchange, i.e., after mercury deposition the cell electrolyte was replaced by an acetate buffer not containing Hg 2+. As a result, the SWASV signal obtained for 10 nm Cd 2+ showed a tendency to decrease slightly in successive experiments (between 3 and 7% after 10 measurements). Thus, most experiments were conducted in the presence of Hg 2+. However, care has to be taken because commercially available mercury(ii) salts often contain heavy metal impurities which can lead to blank values in the lower nanomolar range. Finally, the accuracy of ultrasound-enhanced ASV was examined. SRM 1643c (see Experimental Section), an aqueous solution containing 27 elements, was analyzed with respect to lead and cadmium content. The reference material was diluted by a factor of 20, and the determinations were done by the standard addition method. Comparison between the certified concentrations and those obtained with ultrasound-enhanced SWASV is shown in Table 2. The results obtained agree well with the certified values, taking the statistical uncertainty into consideration. The standard deviations given in Table 2 are significantly higher than those obtained for repetitive measurements with the same NCMTFE and without changing the electrolyte solution (see results above). Thus, the reproducibility has also to be associated with the preparation of the individual NCMTFEs and the handling of analyte solutions. CONCLUSIONS Ultrasound-enhanced SWASV has been demonstrated to be a reliable and accurate analytical method for highly sensitive trace metal determinations. The main effect of ultrasound is greatly enhanced mass transport, which can be exploited for effective preconcentration of analyte species in ASV. The in situ deposition of mercury through a Nafion film has resulted in a reliable electrode assembly which is resistant to ultrasonic irradiation. For practical applications, the Nafion coating has the additional advantage of reducing interferences from complex matrices. In particular, it appears to be attractive to direct future studies of ultrasound-enhanced ASV toward biological and environmental samples by utilizing other effects of ultrasound such as rapid cell disruption and homogenization of sample material. This approach Analytical Chemistry, Vol. 69, No. 8, April 15,
6 could lead to further simplification of real-life trace metal analysis with rapid response characteristics and a lesser risk of contamination in comparison with procedures involving separate sample pretreatment or digestion steps. ACKNOWLEDGMENT We thank the EU Human Capital and Mobility Programme for support under Contract CHRXCT and Junta Nacional de Investigação Científica e Tecnológica (JNICT), Portugal, under Contract PEAM/P/SEL/526/95. Received for review August 12, Accepted December 8, X AC960815J X Abstract published in Advance ACS Abstracts, March 1, Analytical Chemistry, Vol. 69, No. 8, April 15, 1997
Microelectrode arrays: application in batch-injection analysis
 Analytica Chimica Acta 385 (1999) 257±264 Microelectrode arrays: application in batch-injection analysis Denise A. Fungaro a,b, Christopher M.A. Brett a,* a Departamento de QuõÂmica, Universidade de Coimbra,
Analytica Chimica Acta 385 (1999) 257±264 Microelectrode arrays: application in batch-injection analysis Denise A. Fungaro a,b, Christopher M.A. Brett a,* a Departamento de QuõÂmica, Universidade de Coimbra,
Adsorption of Guanine, Guanosine, and Adenine at Electrodes Studied by Differential Pulse Voltammetry and Electrochemical Impedance
 2326 Langmuir 2002, 18, 2326-2330 Adsorption of Guanine, Guanosine, and Adenine at Electrodes Studied by Differential Pulse Voltammetry and Electrochemical Impedance Ana Maria Oliveira-Brett,* Luís Antônio
2326 Langmuir 2002, 18, 2326-2330 Adsorption of Guanine, Guanosine, and Adenine at Electrodes Studied by Differential Pulse Voltammetry and Electrochemical Impedance Ana Maria Oliveira-Brett,* Luís Antônio
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2011
 Supplementary Information for Selective adsorption toward toxic metal ions results in selective response: electrochemical studies on polypyrrole/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite Experimental Section
Supplementary Information for Selective adsorption toward toxic metal ions results in selective response: electrochemical studies on polypyrrole/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite Experimental Section
Specific Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide With A Catalase Biosensor Based on Mercury Thin Film Electrodes
 Turk J Chem 24 (2000), 95 99 c TÜBİTAK Specific Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide With A Catalase Biosensor Based on Mercury Thin Film Electrodes Nil ERTAŞ Ege University, Faculty of Science, Department
Turk J Chem 24 (2000), 95 99 c TÜBİTAK Specific Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide With A Catalase Biosensor Based on Mercury Thin Film Electrodes Nil ERTAŞ Ege University, Faculty of Science, Department
Voltammetric Comparison of the Electrochemical Oxidation of Toluene on Monolithic and Reticulated Glassy Carbon Electrodes in Aqueous Medium
 Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 2010, 28(6), 397-404 DOI: 10.4152/pea.201006397 PORTUGALIAE ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA ISSN 1647-1571 Voltammetric Comparison of the Electrochemical Oxidation of Toluene on Monolithic
Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 2010, 28(6), 397-404 DOI: 10.4152/pea.201006397 PORTUGALIAE ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA ISSN 1647-1571 Voltammetric Comparison of the Electrochemical Oxidation of Toluene on Monolithic
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Uniform and Rich Wrinkled Electrophoretic Deposited Graphene Film: A Robust Electrochemical Platform for TNT Sensing Longhua Tang, Hongbin Feng, Jinsheng Cheng and
Electronic Supplementary Information Uniform and Rich Wrinkled Electrophoretic Deposited Graphene Film: A Robust Electrochemical Platform for TNT Sensing Longhua Tang, Hongbin Feng, Jinsheng Cheng and
Anodic Stripping Voltammetry: An AFM Study of Some Problems and Limitations
 345 Full Paper Anodic Stripping Voltammetry: An AFM Study of Some Problems and Limitations Michael E. Hyde, Craig E. Banks, Richard G. Compton* Physical and Theoretical Chemistry Laboratory, University
345 Full Paper Anodic Stripping Voltammetry: An AFM Study of Some Problems and Limitations Michael E. Hyde, Craig E. Banks, Richard G. Compton* Physical and Theoretical Chemistry Laboratory, University
Electrochemical oxidation of bentazon at a glassy carbon electrode Application to the determination of a commercial herbicide
 Talanta 46 (1998) 1131 1135 Electrochemical oxidation of bentazon at a glassy carbon electrode Application to the determination of a commercial herbicide E. Manuela Garrido 1,a, José L. Costa Lima a, C.
Talanta 46 (1998) 1131 1135 Electrochemical oxidation of bentazon at a glassy carbon electrode Application to the determination of a commercial herbicide E. Manuela Garrido 1,a, José L. Costa Lima a, C.
In a typical routine, the pristine CNT (purchased from Bill Nanotechnology, Inc.) were
 Supplementary Information Pd induced Pt(Ⅳ) reduction to form Pd@Pt/CNT core-shell catalyst for a more complete oxygen reduction Preparation of SH- functionalized CNT In a typical routine, the pristine
Supplementary Information Pd induced Pt(Ⅳ) reduction to form Pd@Pt/CNT core-shell catalyst for a more complete oxygen reduction Preparation of SH- functionalized CNT In a typical routine, the pristine
In situ bismuth film modified carbon fiber microelectrode for nanomolar detection of cadmium and lead
 Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 51A, May 2012, pp. 699-703 In situ bismuth film modified carbon fiber microelectrode for nanomolar detection of cadmium and lead S Anandhakumar, J Mathiyarasu* & K L N
Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 51A, May 2012, pp. 699-703 In situ bismuth film modified carbon fiber microelectrode for nanomolar detection of cadmium and lead S Anandhakumar, J Mathiyarasu* & K L N
Nanomaterials and Chemistry Key Laboratory, Wenzhou University, Wenzhou, (P. R. China).
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale Synergistically enhanced activity of graphene quantum dot/multi-walled carbon nanotube composites as metal-free catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale Synergistically enhanced activity of graphene quantum dot/multi-walled carbon nanotube composites as metal-free catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction
Voltammetry. Voltammetry and Polarograph. Chapter 23. Polarographic curves -- Voltammograms
 Chapter 23 Voltammetry Voltammetry and Polarograph Electrochemistry techniques based on current (i) measurement as function of voltage (E appl ) Voltammetry Usually when the working electrode is solid,
Chapter 23 Voltammetry Voltammetry and Polarograph Electrochemistry techniques based on current (i) measurement as function of voltage (E appl ) Voltammetry Usually when the working electrode is solid,
Current based methods
 Current based methods Amperometric and voltammetric sensors More significant influence on analytical parameters (sensitivity, selectivity, interferences elimination) kind of method, potential range, electrode
Current based methods Amperometric and voltammetric sensors More significant influence on analytical parameters (sensitivity, selectivity, interferences elimination) kind of method, potential range, electrode
Chapter 2. Materials and Methods
 Chapter 2 Materials and Methods 2. Materials and Methods This chapter describes the chemicals, reagents and instruments used for carrying out this study. A brief discussion of the methods used for the
Chapter 2 Materials and Methods 2. Materials and Methods This chapter describes the chemicals, reagents and instruments used for carrying out this study. A brief discussion of the methods used for the
Simultaneous Detection of Cd (II), Pb (II), Cu (II), and Hg (II) Ions in Dye Waste Water Using a Boron Doped Diamond Electrode with DPASV
 140 Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, Vol. 31, No. 1 Jang-Hee Yoon et al. DOI 10.5012/bkcs.2010.31.01.140 Simultaneous Detection of (II), (II), (II), and (II) Ions in Dye Waste Water Using a Boron Doped Diamond
140 Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, Vol. 31, No. 1 Jang-Hee Yoon et al. DOI 10.5012/bkcs.2010.31.01.140 Simultaneous Detection of (II), (II), (II), and (II) Ions in Dye Waste Water Using a Boron Doped Diamond
Supporting Information
 Gold Nanoparticle-Modified ITO Electrode for Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence: Well-Preserved Transparency and Highly-Enhanced Activity Zuofeng Chen and Yanbing Zu * Department of Chemistry, The University
Gold Nanoparticle-Modified ITO Electrode for Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence: Well-Preserved Transparency and Highly-Enhanced Activity Zuofeng Chen and Yanbing Zu * Department of Chemistry, The University
CEINT/NIST PROTOCOL REPORTING GUIDELINES FOR THE PREPARATION OF AQUEOUS NANOPARTICLE DISPERSIONS FROM DRY MATERIALS. Ver. 2.0
 CEINT/NIST PROTOCOL REPORTING GUIDELINES FOR THE PREPARATION OF AQUEOUS NANOPARTICLE DISPERSIONS FROM DRY MATERIALS Ver. 2.0 July 8, 2010 Protocol Contributors: J. S. Taurozzi 1, V. A. Hackley 1, M. R.
CEINT/NIST PROTOCOL REPORTING GUIDELINES FOR THE PREPARATION OF AQUEOUS NANOPARTICLE DISPERSIONS FROM DRY MATERIALS Ver. 2.0 July 8, 2010 Protocol Contributors: J. S. Taurozzi 1, V. A. Hackley 1, M. R.
Supporting Information for. Highly durable Pd metal catalysts for the oxygen. reduction reaction in fuel cells; Coverage of Pd metal with.
 Supporting Information for Highly durable Pd metal catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction in fuel cells; Coverage of Pd metal with silica Sakae Takenaka 1 *, Naoto Susuki 1, Hiroaki Miyamoto 1, Eishi
Supporting Information for Highly durable Pd metal catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction in fuel cells; Coverage of Pd metal with silica Sakae Takenaka 1 *, Naoto Susuki 1, Hiroaki Miyamoto 1, Eishi
Unit 2 B Voltammetry and Polarography
 Unit 2 B Voltammetry and Polarography Voltammetric methods of Analysis What is Voltammetry? A time-dependent potential is applied to an electrochemical cell, and the current flowing through the cell is
Unit 2 B Voltammetry and Polarography Voltammetric methods of Analysis What is Voltammetry? A time-dependent potential is applied to an electrochemical cell, and the current flowing through the cell is
Supporting information:
 Supporting information: The Role of Anisotropic Structure and Its Aspect Ratio: High-Loading Carbon Nanospheres Supported Pt Nanowires and Their High Performance Toward Methanol Electrooxidation Feng-Zhan
Supporting information: The Role of Anisotropic Structure and Its Aspect Ratio: High-Loading Carbon Nanospheres Supported Pt Nanowires and Their High Performance Toward Methanol Electrooxidation Feng-Zhan
Electronic Supplementary Information. Facile synthesis of polypyrrole coated copper nanowire: new concept to engineered core-shell structures
 Electronic Supplementary Information Facile synthesis of polypyrrole coated copper nanowire: new concept to engineered core-shell structures Yang Liu, a Zhen Liu, a Ning Lu, b Elisabeth Preiss, a Selcuk
Electronic Supplementary Information Facile synthesis of polypyrrole coated copper nanowire: new concept to engineered core-shell structures Yang Liu, a Zhen Liu, a Ning Lu, b Elisabeth Preiss, a Selcuk
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Bamboo-Like Carbon Nanotube/Fe 3 C Nanoparticle Hybrids and Their Highly Efficient Catalysis for Oxygen Reduction Wenxiu Yang a,b, Xiangjian Liu a,b, Xiaoyu Yue a,b, Jianbo Jia,
Supporting Information Bamboo-Like Carbon Nanotube/Fe 3 C Nanoparticle Hybrids and Their Highly Efficient Catalysis for Oxygen Reduction Wenxiu Yang a,b, Xiangjian Liu a,b, Xiaoyu Yue a,b, Jianbo Jia,
Sieving Behaviour of Nanoscopic Pores by. Hydrated Ions
 Sieving Behaviour of Nanoscopic Pores by Hydrated Ions Joohan Lee a and Juhyoun Kwak* a Department of Chemistry, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), 373-1 Guseong-dong, Yuseong-gu,
Sieving Behaviour of Nanoscopic Pores by Hydrated Ions Joohan Lee a and Juhyoun Kwak* a Department of Chemistry, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), 373-1 Guseong-dong, Yuseong-gu,
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Digital Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence Biosensor for the Determination of Multiple Proteins Based on Boolean Logic Gate Honglan Qi*, Xiaoying Qiu, Chen Wang, Qiang Gao, Chengxiao
Supplementary Material Digital Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence Biosensor for the Determination of Multiple Proteins Based on Boolean Logic Gate Honglan Qi*, Xiaoying Qiu, Chen Wang, Qiang Gao, Chengxiao
Supplementary Information. For. A Universal Method for Preparing Functional ITO Electrodes with Ultrahigh Stability
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information For A Universal Method for Preparing Functional ITO Electrodes with Ultrahigh
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information For A Universal Method for Preparing Functional ITO Electrodes with Ultrahigh
An extraordinarily stable catalyst: Pt NPs supported on two-dimensional Ti 3 C 2 X 2 (X=OH, F) nanosheets for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
 An extraordinarily stable catalyst: Pt NPs supported on two-dimensional Ti 3 X 2 (X=OH, F) nanosheets for Oxygen Reduction Reaction Xiaohong Xie, Siguo Chen*, Wei Ding, Yao Nie, and Zidong Wei* Experimental
An extraordinarily stable catalyst: Pt NPs supported on two-dimensional Ti 3 X 2 (X=OH, F) nanosheets for Oxygen Reduction Reaction Xiaohong Xie, Siguo Chen*, Wei Ding, Yao Nie, and Zidong Wei* Experimental
Electrocatalysis by Subcellular Liver Fractions Bound to Carbon Nanostructures for Stereoselective Green Drug Metabolite Synthesis
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Electrocatalysis by Subcellular Liver Fractions Bound to Carbon Nanostructures
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Electrocatalysis by Subcellular Liver Fractions Bound to Carbon Nanostructures
Determination of Zinc, Cadmium, Lead and Copper in Effluent Sample
 Determination of Zinc, Cadmium, Lead and Copper in Effluent Sample Branch: General analytical chemistry, water, waste water, environmental protection Key Words 797 / polarography / VA / 8 / Zn / Cd / Pb
Determination of Zinc, Cadmium, Lead and Copper in Effluent Sample Branch: General analytical chemistry, water, waste water, environmental protection Key Words 797 / polarography / VA / 8 / Zn / Cd / Pb
Single Catalyst Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO 2 in Water to H 2 :CO Syngas Mixtures with Water Oxidation to O 2
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Single Catalyst Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO 2
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Single Catalyst Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO 2
Electrochemical detection of phenol in aqueous solutions
 Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 11, November 2004, pp. 797-803 Electrochemical detection of phenol in aqueous solutions J Mathiyarasu*, James Joseph, K L N Phani & V Yegnaraman Electrodics &
Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 11, November 2004, pp. 797-803 Electrochemical detection of phenol in aqueous solutions J Mathiyarasu*, James Joseph, K L N Phani & V Yegnaraman Electrodics &
Lithium-ion Batteries Based on Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotubes and Ionic Liquid
 Electronic Supplementary Information Lithium-ion Batteries Based on Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotubes and Ionic Liquid Electrolytes Wen Lu, * Adam Goering, Liangti Qu, and Liming Dai * 1. Synthesis of
Electronic Supplementary Information Lithium-ion Batteries Based on Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotubes and Ionic Liquid Electrolytes Wen Lu, * Adam Goering, Liangti Qu, and Liming Dai * 1. Synthesis of
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 215 Electronic Supplementary Information Redox cycling-amplified enzymatic Ag deposition
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 215 Electronic Supplementary Information Redox cycling-amplified enzymatic Ag deposition
sensors ISSN by MDPI
 Sensors 003, 3, 3-50 sensors ISSN 1-80 003 by MDPI http://www.mdpi.net/sensors Determination of Dopamine in the Presence of Ascorbic Acid using Poly (Acridine red) Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode Yuzhong
Sensors 003, 3, 3-50 sensors ISSN 1-80 003 by MDPI http://www.mdpi.net/sensors Determination of Dopamine in the Presence of Ascorbic Acid using Poly (Acridine red) Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode Yuzhong
Electrochemical Detection of 2-Naphthol at a Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with Tosflex Film
 1315 Full Paper Electrochemical Detection of 2-Naphthol at a Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with Tosflex Film Ming-Chih Tsai, Po-Yu Chen* Faculty of Medicinal and Applied Chemistry, Kaohsiung Medical
1315 Full Paper Electrochemical Detection of 2-Naphthol at a Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with Tosflex Film Ming-Chih Tsai, Po-Yu Chen* Faculty of Medicinal and Applied Chemistry, Kaohsiung Medical
Air Quality 2 - Determination of Cd and Pb by Anodic Stripping Voltammetry
 Air Quality 2 - Determination of Cd and Pb by Anodic Stripping Voltammetry Introduction: In the first experiment of this set, you measured the concentration of benzene in gasoline, and it is a reasonable
Air Quality 2 - Determination of Cd and Pb by Anodic Stripping Voltammetry Introduction: In the first experiment of this set, you measured the concentration of benzene in gasoline, and it is a reasonable
Homogeneous Electrochemical Assay for Protein Kinase Activity
 Homogeneous Electrochemical Assay for Protein Kinase Activity Ik-Soo Shin,,, Rohit Chand, Sang Wook Lee, Hyun-Woo Rhee, Yong-Sang Kim, * and Jong-In Hong* Corresponding Author *Prof. Dr. J.-I. Hong, Department
Homogeneous Electrochemical Assay for Protein Kinase Activity Ik-Soo Shin,,, Rohit Chand, Sang Wook Lee, Hyun-Woo Rhee, Yong-Sang Kim, * and Jong-In Hong* Corresponding Author *Prof. Dr. J.-I. Hong, Department
Preparation of Prussian blue-modified screen-printed electrodes via a chemical deposition for mass production of stable hydrogen peroxide sensors
 Procedure 7 Preparation of Prussian blue-modified screen-printed electrodes via a chemical deposition for mass production of stable hydrogen peroxide sensors Francesco Ricci, Danila Moscone and Giuseppe
Procedure 7 Preparation of Prussian blue-modified screen-printed electrodes via a chemical deposition for mass production of stable hydrogen peroxide sensors Francesco Ricci, Danila Moscone and Giuseppe
Electro Chemical Comparative Studies Of Ortho, Meta and Para Nitro Phenols
 International journal of Emerging Trends in Science and Technology Electro Chemical Comparative Studies Of Ortho, Meta and Para Nitro Phenols Authors M. S. Selvakumar 1*, Dr. N. Xavier 2, Dr. V. Jeyabal
International journal of Emerging Trends in Science and Technology Electro Chemical Comparative Studies Of Ortho, Meta and Para Nitro Phenols Authors M. S. Selvakumar 1*, Dr. N. Xavier 2, Dr. V. Jeyabal
Amplified electrochemiluminescent immunosensing using apoferritin-templated poly(ethylenimine) nanoparticles as co-reactant
 Amplified electrochemiluminescent immunosensing using apoferritin-templated poly(ethylenimine) nanoparticles as co-reactant Ni Liao, Ying Zhuo, Yaqin Chai, Yun Xiang, Yaling Cao, Ruo Yuan, Jing Han Education
Amplified electrochemiluminescent immunosensing using apoferritin-templated poly(ethylenimine) nanoparticles as co-reactant Ni Liao, Ying Zhuo, Yaqin Chai, Yun Xiang, Yaling Cao, Ruo Yuan, Jing Han Education
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence of Single Conjugated Polymer Nanoparticles Ya-Lan Chang, Rodrigo E. Palacios, Fu-Ren F. Fan, Allen J. Bard, and Paul F. Barbara Department of Chemistry
Supporting Information Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence of Single Conjugated Polymer Nanoparticles Ya-Lan Chang, Rodrigo E. Palacios, Fu-Ren F. Fan, Allen J. Bard, and Paul F. Barbara Department of Chemistry
Supporting Information. Temperature dependence on charge transport behavior of threedimensional
 Supporting Information Temperature dependence on charge transport behavior of threedimensional superlattice crystals A. Sreekumaran Nair and K. Kimura* University of Hyogo, Graduate School of Material
Supporting Information Temperature dependence on charge transport behavior of threedimensional superlattice crystals A. Sreekumaran Nair and K. Kimura* University of Hyogo, Graduate School of Material
Mobility and Reactivity of Oxygen Adspecies on Platinum Surface
 Mobility and Reactivity of Oxygen Adspecies on Platinum Surface Wei Wang, Jie Zhang, Fangfang Wang, Bing-Wei Mao, Dongping Zhan*, Zhong-Qun Tian State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces,
Mobility and Reactivity of Oxygen Adspecies on Platinum Surface Wei Wang, Jie Zhang, Fangfang Wang, Bing-Wei Mao, Dongping Zhan*, Zhong-Qun Tian State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces,
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information The electrochemical discrimination of pinene enantiomers by
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information The electrochemical discrimination of pinene enantiomers by
Biotinyl moiety-selective polymer films with highly ordered macropores
 Supporting information Biotinyl moiety-selective polymer films with highly ordered macropores Subramanian Suriyanarayanan, a Luigi Petrone, b Thomas Ederth b and Ian A. Nicholls a,c* a Bioorganic & Biophysical
Supporting information Biotinyl moiety-selective polymer films with highly ordered macropores Subramanian Suriyanarayanan, a Luigi Petrone, b Thomas Ederth b and Ian A. Nicholls a,c* a Bioorganic & Biophysical
Supplementary Information. Seeding Approach to Noble Metal Decorated Conducting Polymer Nanofiber Network
 Supplementary Information Seeding Approach to Noble Metal Decorated Conducting Polymer Nanofiber Network Zhen Liu, Selcuk Poyraz, Yang Liu, Xinyu Zhang* Department of Polymer and Fiber Engineering, Auburn
Supplementary Information Seeding Approach to Noble Metal Decorated Conducting Polymer Nanofiber Network Zhen Liu, Selcuk Poyraz, Yang Liu, Xinyu Zhang* Department of Polymer and Fiber Engineering, Auburn
Electrogenerated Upconverted Emission from Doped Organic Nanowires
 Electrogenerated Upconverted Emission from Doped Organic Nanowires Qing Li, Chuang Zhang, Jian Yao Zheng, Yong Sheng Zhao*, Jiannian Yao* Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) 1 Experimental details
Electrogenerated Upconverted Emission from Doped Organic Nanowires Qing Li, Chuang Zhang, Jian Yao Zheng, Yong Sheng Zhao*, Jiannian Yao* Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) 1 Experimental details
Electrochemiluminescence detection of near single DNA molecule with quantum dots-dendrimer nanocomposite for signal amplification
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry 2011 Electrochemiluminescence detection of near single DNA molecule with quantum
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry 2011 Electrochemiluminescence detection of near single DNA molecule with quantum
Supplementary Information:
 Supplementary Information: One-Step and Rapid Synthesis of Clean and Monodisperse Dendritic Pt Nanoparticles and Their High Performance Toward Methanol Oxidation and p-nitrophenol Reduction Jun Wang, Xin-Bo
Supplementary Information: One-Step and Rapid Synthesis of Clean and Monodisperse Dendritic Pt Nanoparticles and Their High Performance Toward Methanol Oxidation and p-nitrophenol Reduction Jun Wang, Xin-Bo
ANALYSIS OF LEAD IN SEAWATER
 ANALYSIS OF LEAD IN SEAWATER BY DIFFERENTIAL PULSE POLAROGRAPHY Introduction Electrochemical methods of analysis can be used for the quantitative analysis of any electroactive species any species that
ANALYSIS OF LEAD IN SEAWATER BY DIFFERENTIAL PULSE POLAROGRAPHY Introduction Electrochemical methods of analysis can be used for the quantitative analysis of any electroactive species any species that
Pt-Cu Hierarchical Quasi Great Dodecahedrons with Abundant
 Electronic Supplementary Material Material (ESI) for (ESI) Chemical for ChemComm. Science. This journal is is The The Royal Royal Society Society of Chemistry of Chemistry 2017 2017 Supporting Information
Electronic Supplementary Material Material (ESI) for (ESI) Chemical for ChemComm. Science. This journal is is The The Royal Royal Society Society of Chemistry of Chemistry 2017 2017 Supporting Information
Supporting Information. Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide on Nitrogen-Doped Carbons: Insights from Isotopic Labeling Studies
 Supporting Information Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide on Nitrogen-Doped Carbons: Insights from Isotopic Labeling Studies Dorottya Hursán 1,2 and Csaba Janáky 1,2* 1 Department of Physical
Supporting Information Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide on Nitrogen-Doped Carbons: Insights from Isotopic Labeling Studies Dorottya Hursán 1,2 and Csaba Janáky 1,2* 1 Department of Physical
Highly efficient hydrogen evolution of platinum via tuning the interfacial dissolved-gas concentration
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information for Highly efficient hydrogen evolution of platinum via tuning
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information for Highly efficient hydrogen evolution of platinum via tuning
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Engineering Cu 2 O/NiO/Cu 2 MoS 4 Hybrid Photocathode for H 2 Generation in Water Chen Yang, a,b
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Engineering Cu 2 O/NiO/Cu 2 MoS 4 Hybrid Photocathode for H 2 Generation in Water Chen Yang, a,b
Supporting Information for
 Supporting Information for Electrodeposition of Isolated Platinum Atoms and Clusters on Bismuth Characterization and Electrocatalysis Min Zhou, Jeffrey E. Dick, and Allen J. Bard Center for Electrochemistry,
Supporting Information for Electrodeposition of Isolated Platinum Atoms and Clusters on Bismuth Characterization and Electrocatalysis Min Zhou, Jeffrey E. Dick, and Allen J. Bard Center for Electrochemistry,
Electrochemically-assisted self-assembly of mesoporous silica thin films SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION A. WALCARIUS, E. SIBOTTIER, M. ETIENNE, J.
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Electrochemically-assisted self-assembly of mesoporous silica thin films A. WALCARIUS, E. SIBOTTIER, M. ETIENNE, J. GHANBAJA 50 nm Fig. S1. TEM image of an electrodeposited surfactant-templated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Electrochemically-assisted self-assembly of mesoporous silica thin films A. WALCARIUS, E. SIBOTTIER, M. ETIENNE, J. GHANBAJA 50 nm Fig. S1. TEM image of an electrodeposited surfactant-templated
Full Paper. Full Paper. 1. Introduction. Z. M. Wang, H. W. Guo, E. Liu,* G. C. Yang, N. W. Khun
 Full Paper Bismuth/Polyaniline/Glassy Carbon Electrodes Prepared with Different Protocols for Stripping Voltammetric Determination of Trace Cd and Pb in Solutions Having Surfactants Z. M. Wang, H. W. Guo,
Full Paper Bismuth/Polyaniline/Glassy Carbon Electrodes Prepared with Different Protocols for Stripping Voltammetric Determination of Trace Cd and Pb in Solutions Having Surfactants Z. M. Wang, H. W. Guo,
Boron-doped diamond as the new electrode material for determination of heavy metals
 Boron-doped diamond as the new electrode material for determination of heavy metals Zuzana Chomisteková, Jozef Sochr, Jana Svítková, Ľubomír Švorc Institute of Analytical Chemistry, Faculty of Chemical
Boron-doped diamond as the new electrode material for determination of heavy metals Zuzana Chomisteková, Jozef Sochr, Jana Svítková, Ľubomír Švorc Institute of Analytical Chemistry, Faculty of Chemical
CHAPTER-5 CYCLIC VOLTAMETRIC STUDIES OF NOVEL INDOLE ANALOGUES PREPARED IN THE PRESENT STUDY
 CHAPTER-5 CYCLIC VOLTAMETRIC STUDIES OF NOVEL INDOLE ANALOGUES PREPARED IN THE PRESENT STUDY Page No. 175-187 5.1 Introduction 5.2 Theoretical 5.3 Experimental 5.4 References 5. 1 Introduction Electrochemical
CHAPTER-5 CYCLIC VOLTAMETRIC STUDIES OF NOVEL INDOLE ANALOGUES PREPARED IN THE PRESENT STUDY Page No. 175-187 5.1 Introduction 5.2 Theoretical 5.3 Experimental 5.4 References 5. 1 Introduction Electrochemical
Facile and Gram-scale Synthesis of Metal-free Catalysts: Toward Realistic Applications for Fuel Cells
 Supplementary Information Facile and Gram-scale Synthesis of Metal-free Catalysts: Toward Realistic Applications for Fuel Cells Ok-Hee Kim 1, Yong-Hun Cho 2, Dong Young Chung 3,4, Minjeong Kim 3,4, Ji
Supplementary Information Facile and Gram-scale Synthesis of Metal-free Catalysts: Toward Realistic Applications for Fuel Cells Ok-Hee Kim 1, Yong-Hun Cho 2, Dong Young Chung 3,4, Minjeong Kim 3,4, Ji
Table S1. Electrocatalyst plating conditions Metal Anode (foil) Plating Potential (V versus Ag/AgCl) Rh Pt 1 M HCl/HPLC.
 1 Materials and Methods Electrode Preparation All chemicals and supplies were high purity (> 999%) and supplied from Alfa Aesar or Fisher Scientific For anodic catalyst selection, 5 cm 2 titanium foil
1 Materials and Methods Electrode Preparation All chemicals and supplies were high purity (> 999%) and supplied from Alfa Aesar or Fisher Scientific For anodic catalyst selection, 5 cm 2 titanium foil
Cyclic Voltammetry. Objective: To learn the basics of cyclic voltammetry with a well-behaved echem system
 Cyclic Voltammetry Objective: To learn the basics of cyclic voltammetry with a well-behaved echem system Introduction Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is a popular electroanalytical technique for its relative simplicity
Cyclic Voltammetry Objective: To learn the basics of cyclic voltammetry with a well-behaved echem system Introduction Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is a popular electroanalytical technique for its relative simplicity
Cyclic Voltammetry. Fundamentals of cyclic voltammetry
 Cyclic Voltammetry Cyclic voltammetry is often the first experiment performed in an electrochemical study of a compound, biological material, or an electrode surface. The effectiveness of cv results from
Cyclic Voltammetry Cyclic voltammetry is often the first experiment performed in an electrochemical study of a compound, biological material, or an electrode surface. The effectiveness of cv results from
Evidence for Covalent Bonding of Aryl Groups to MnO 2 Nanorods from Diazonium-Based Grafting
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information for Evidence for Covalent Bonding of Aryl Groups to MnO 2 Nanorods from
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information for Evidence for Covalent Bonding of Aryl Groups to MnO 2 Nanorods from
Investigation of DNA methylation by direct electrocatalytic oxidation
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Chemical Communications Investigation of DNA methylation by direct electrocatalytic oxidation Po Wang, Zhibin Mai, Zong Dai * and Xiaoyong Zou * School of
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Chemical Communications Investigation of DNA methylation by direct electrocatalytic oxidation Po Wang, Zhibin Mai, Zong Dai * and Xiaoyong Zou * School of
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Corrosion of Self-Propelled Catalytic Microengines Guanjia Zhao a, Bahareh Khezri a, Samuel Sanchez b, Oliver G. Schmidt b, Richard D. Webster a, Martin Pumera a * Experimental Section Materials The cyclopore
Corrosion of Self-Propelled Catalytic Microengines Guanjia Zhao a, Bahareh Khezri a, Samuel Sanchez b, Oliver G. Schmidt b, Richard D. Webster a, Martin Pumera a * Experimental Section Materials The cyclopore
Supplementary Figure 1 a) Scheme of microfluidic device fabrication by photo and soft lithography,
 a b 1 mm Supplementary Figure 1 a) Scheme of microfluidic device fabrication by photo and soft lithography, (a1, a2) 50nm Pd evaporated on Si wafer with 100 nm Si 2 insulating layer and 5nm Cr as an adhesion
a b 1 mm Supplementary Figure 1 a) Scheme of microfluidic device fabrication by photo and soft lithography, (a1, a2) 50nm Pd evaporated on Si wafer with 100 nm Si 2 insulating layer and 5nm Cr as an adhesion
The challenges of field sensors for trace metal detection. Chris Searle Product Manager Trace2o Ltd
 The challenges of field sensors for trace metal detection Chris Searle Product Manager Trace2o Ltd What is a heavy metal and why is it necessary to determine concentration? Tends to be categorised as Metallic
The challenges of field sensors for trace metal detection Chris Searle Product Manager Trace2o Ltd What is a heavy metal and why is it necessary to determine concentration? Tends to be categorised as Metallic
Supporting Information
 Platinum-Gold Nanoparticles: A Highly Active Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Rechargeable Lithium-Air Batteries Yi-Chun Lu, Zhichuan Xu, Hubert A. Gasteiger, Shuo Chen, Kimberly Hamad- Schifferli and
Platinum-Gold Nanoparticles: A Highly Active Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Rechargeable Lithium-Air Batteries Yi-Chun Lu, Zhichuan Xu, Hubert A. Gasteiger, Shuo Chen, Kimberly Hamad- Schifferli and
Dual redox catalysts for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions: towards a redox flow Li-O 2 battery
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Dual redox catalysts for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions:
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Dual redox catalysts for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions:
Hydrodynamic Electrodes and Microelectrodes
 CHEM465/865, 2004-3, Lecture 20, 27 th Sep., 2004 Hydrodynamic Electrodes and Microelectrodes So far we have been considering processes at planar electrodes. We have focused on the interplay of diffusion
CHEM465/865, 2004-3, Lecture 20, 27 th Sep., 2004 Hydrodynamic Electrodes and Microelectrodes So far we have been considering processes at planar electrodes. We have focused on the interplay of diffusion
Tunable nitrogen-doped carbon aerogels as sustainable electrocatalysts in the oxygen. reduction reaction Electronic Supplementary information (ESI)
 Tunable nitrogen-doped carbon aerogels as sustainable electrocatalysts in the oxygen reduction reaction Electronic Supplementary information (ESI) Stephanie-Angelika Wohlgemuth,* a Tim-Patrick Fellinger
Tunable nitrogen-doped carbon aerogels as sustainable electrocatalysts in the oxygen reduction reaction Electronic Supplementary information (ESI) Stephanie-Angelika Wohlgemuth,* a Tim-Patrick Fellinger
Supplementary Information. Unusual High Oxygen Reduction Performance in All-Carbon Electrocatalysts
 Supplementary Information Unusual High Oxygen Reduction Performance in All-Carbon Electrocatalysts Wei Wei 1, 4,, Ying Tao 1, 4,, Wei Lv 2,, Fang-Yuan Su 2, Lei Ke 2, Jia Li 2, Da-Wei Wang 3, *, Baohua
Supplementary Information Unusual High Oxygen Reduction Performance in All-Carbon Electrocatalysts Wei Wei 1, 4,, Ying Tao 1, 4,, Wei Lv 2,, Fang-Yuan Su 2, Lei Ke 2, Jia Li 2, Da-Wei Wang 3, *, Baohua
Electrochemical study and applications of the selective electrodeposition of silver on quantum dots
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Electrochemical study and applications of the selective electrodeposition of silver on quantum dots Daniel Martín-Yerga*, Estefanía Costa Rama and Agustín Costa-García Department
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Electrochemical study and applications of the selective electrodeposition of silver on quantum dots Daniel Martín-Yerga*, Estefanía Costa Rama and Agustín Costa-García Department
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information 1 2-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)-1H-benzimidazole-manganese oxide hybrid as a promising structural model for Tyrosine 161/Histidine 190-manganese cluster in Photosystem II Mohammad Mahdi
Supplementary Information 1 2-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)-1H-benzimidazole-manganese oxide hybrid as a promising structural model for Tyrosine 161/Histidine 190-manganese cluster in Photosystem II Mohammad Mahdi
Correlating Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Activity in Alkaline Electrolyte to Hydrogen Binding Energy on Monometallic Surfaces
 Supplemental Materials for Correlating Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Activity in Alkaline Electrolyte to Hydrogen Binding Energy on Monometallic Surfaces Wenchao Sheng, a MyatNoeZin Myint, a Jingguang G.
Supplemental Materials for Correlating Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Activity in Alkaline Electrolyte to Hydrogen Binding Energy on Monometallic Surfaces Wenchao Sheng, a MyatNoeZin Myint, a Jingguang G.
DIFFERENTIAL PULSE ANODIC STRIPPING VOLTAMMETRIC DETERMINATION OF SELENIUM(IV) AT A GOLD ELECTRODE MODIFIED WITH 3, 3 -DIAMINOBENZIDINE.
 Innovare Academic Sciences International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 0975-1491 Vol 6, Issue 3, 2014 Original Article DIFFERENTIAL PULSE ANODIC STRIPPING VOLTAMMETRIC DETERMINATION
Innovare Academic Sciences International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 0975-1491 Vol 6, Issue 3, 2014 Original Article DIFFERENTIAL PULSE ANODIC STRIPPING VOLTAMMETRIC DETERMINATION
Electrochemical behaviour of cytochrome c at electrically heated microelectrodes
 Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 19 (1999) 127 133 Electrochemical behaviour of cytochrome c at electrically heated microelectrodes T. Voss a, P. Gründler a, C.M.A. Brett b, A.M. Oliveira
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 19 (1999) 127 133 Electrochemical behaviour of cytochrome c at electrically heated microelectrodes T. Voss a, P. Gründler a, C.M.A. Brett b, A.M. Oliveira
ELECTROCHEMICAL DETERMINATION OF DOPAMINE WITH GRAPHENE-MODIFIED GLASSY CARBON ELECTRODES
 STUDIA UBB CHEMIA, LXI, 3, Tom I, 216 (p. 135-144) (RECOMMENDED CITATION) Dedicated to Professor Luminița Silaghi-Dumitrescu on the occasion of her 65 th anniversary ELECTROCHEMICAL DETERMINATION OF DOPAMINE
STUDIA UBB CHEMIA, LXI, 3, Tom I, 216 (p. 135-144) (RECOMMENDED CITATION) Dedicated to Professor Luminița Silaghi-Dumitrescu on the occasion of her 65 th anniversary ELECTROCHEMICAL DETERMINATION OF DOPAMINE
Facile synthesis and application of highly luminescent CdTe quantum dots with an electrogenerated precursor
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Chemical Communications Facile synthesis and application of highly luminescent CdTe quantum dots with an electrogenerated precursor Cunwang Ge, Min Xu, Jing
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Chemical Communications Facile synthesis and application of highly luminescent CdTe quantum dots with an electrogenerated precursor Cunwang Ge, Min Xu, Jing
Modified Electrode Voltammetric Sensors for Trace Metals in Environmental Samples
 298 J. Braz. Chem. Soc., Vol. 11, No. 3, 298-303, 2000. Brett & Fungaro c 2000 J. Soc. Braz. Bras. Chem. Química Soc Printed in Brazil 0103-5053 $6.00+0.00 Article Modified Electrode Voltammetric Sensors
298 J. Braz. Chem. Soc., Vol. 11, No. 3, 298-303, 2000. Brett & Fungaro c 2000 J. Soc. Braz. Bras. Chem. Química Soc Printed in Brazil 0103-5053 $6.00+0.00 Article Modified Electrode Voltammetric Sensors
[Supplementary Information] One-Pot Synthesis and Electrocatalytic Activity of Octapodal Au-Pd Nanoparticles
![[Supplementary Information] One-Pot Synthesis and Electrocatalytic Activity of Octapodal Au-Pd Nanoparticles [Supplementary Information] One-Pot Synthesis and Electrocatalytic Activity of Octapodal Au-Pd Nanoparticles](/thumbs/78/77448401.jpg) [Supplementary Information] One-Pot Synthesis and Electrocatalytic Activity of Octapodal Au-Pd Nanoparticles Jong Wook Hong, Young Wook Lee, Minjung Kim, Shin Wook Kang, and Sang Woo Han * Department of
[Supplementary Information] One-Pot Synthesis and Electrocatalytic Activity of Octapodal Au-Pd Nanoparticles Jong Wook Hong, Young Wook Lee, Minjung Kim, Shin Wook Kang, and Sang Woo Han * Department of
Short Communication Electrochemical Polymerization of Methylene Blue on Glassy Carbon Electrode
 Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 12 (2017) 9907 9913, doi: 10.20964/2017.10.49 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Short Communication Electrochemical Polymerization of Methylene
Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 12 (2017) 9907 9913, doi: 10.20964/2017.10.49 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Short Communication Electrochemical Polymerization of Methylene
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information A fishnet electrochemical Hg 2+ sensing strategy based on gold nanopartical-bioconjugate and thymine-hg 2+ -thymine coordination chemistry Xuemei Tang 1, Huixiang Liu 1, Binghua
Supporting Information A fishnet electrochemical Hg 2+ sensing strategy based on gold nanopartical-bioconjugate and thymine-hg 2+ -thymine coordination chemistry Xuemei Tang 1, Huixiang Liu 1, Binghua
Supporting Information. Synthesis of Metallic Magnesium Nanoparticles by Sonoelectrochemistry. Iris Haas and Aharon Gedanken*
 Supporting Information Synthesis of Metallic Magnesium Nanoparticles by Sonoelectrochemistry Iris Haas and Aharon Gedanken* Experimental Materials and chemical preparation The Gringard reagents, ethyl-mgcl
Supporting Information Synthesis of Metallic Magnesium Nanoparticles by Sonoelectrochemistry Iris Haas and Aharon Gedanken* Experimental Materials and chemical preparation The Gringard reagents, ethyl-mgcl
Electrochemistry and Detection of Organic and Biological Molecules Such as Catechol and Ascorbic Acid at Conducting Poly (2,2-bithiophene) Electrode
 Electrochemistry and Detection of Organic and Biological Molecules Such as Catechol and Ascorbic Acid at Conducting Poly (2,2-bithiophene) Electrode Suzanne K. Lunsford a*, Jelynn Stinson a, and Justyna
Electrochemistry and Detection of Organic and Biological Molecules Such as Catechol and Ascorbic Acid at Conducting Poly (2,2-bithiophene) Electrode Suzanne K. Lunsford a*, Jelynn Stinson a, and Justyna
Electrochemical Techniques: Anodic Stripping Voltammetry
 Electrochemical Techniques: Anodic Stripping Voltammetry Quantitative Determination of Copper, Lead and Cadmium in Tap Water at a Thin Mercury Film Electrode. 1. Aim To use a standard additions method
Electrochemical Techniques: Anodic Stripping Voltammetry Quantitative Determination of Copper, Lead and Cadmium in Tap Water at a Thin Mercury Film Electrode. 1. Aim To use a standard additions method
Surfactant-free exfoliation of graphite in aqueous solutions
 Surfactant-free exfoliation of graphite in aqueous solutions Karen B. Ricardo, Anne Sendecki, and Haitao Liu * Department of Chemistry, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA 15260, U.S.A 1. Materials
Surfactant-free exfoliation of graphite in aqueous solutions Karen B. Ricardo, Anne Sendecki, and Haitao Liu * Department of Chemistry, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA 15260, U.S.A 1. Materials
A Chitosan-Multiwall Carbon Nanotube Modified Electrode for Simultaneous Detection of Dopamine and Ascorbic Acid
 2004 The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry 1055 A Chitosan-Multiwall Carbon Nanotube Modified Electrode for Simultaneous Detection of Dopamine and Ascorbic Acid Lingyan JIANG,* Chuanyin LIU,* Liping
2004 The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry 1055 A Chitosan-Multiwall Carbon Nanotube Modified Electrode for Simultaneous Detection of Dopamine and Ascorbic Acid Lingyan JIANG,* Chuanyin LIU,* Liping
Carbon nanotubes and conducting polymer composites
 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections University of Wollongong Thesis Collection University of Wollongong Year 4 Carbon nanotubes and conducting polymer composites May Tahhan University of Wollongong
University of Wollongong Thesis Collections University of Wollongong Thesis Collection University of Wollongong Year 4 Carbon nanotubes and conducting polymer composites May Tahhan University of Wollongong
Carbon powder modification. Preparation of NS1, NS2, NS3 and NS4.
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL SECTION Reagents. Carbon powder (Norit-S50) was purchased from Norit, 4-aminobenzene sulfonic acid (99%), lithium perchlorate (99%, potassium ferricyanide (99%) and
SUPPORTING INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL SECTION Reagents. Carbon powder (Norit-S50) was purchased from Norit, 4-aminobenzene sulfonic acid (99%), lithium perchlorate (99%, potassium ferricyanide (99%) and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2633 Mechanically controlled radical polymerization initiated by ultrasound Hemakesh Mohapatra, Maya Kleiman, Aaron P. Esser-Kahn Contents 1. Materials and methods 2 2. Procedure for
DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2633 Mechanically controlled radical polymerization initiated by ultrasound Hemakesh Mohapatra, Maya Kleiman, Aaron P. Esser-Kahn Contents 1. Materials and methods 2 2. Procedure for
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Journal Name Chemicals Electronic Supplementary Information Two kinds of commercial anion exchange
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Journal Name Chemicals Electronic Supplementary Information Two kinds of commercial anion exchange
Supporting Information. Single Particle Detection by Area Amplification Single Wall Carbon Nanotube Attachment to a Nanoelectrode
 Supporting Information Single Particle Detection by Area Amplification Single Wall Carbon Nanotube Attachment to a Nanoelectrode Jun Hui Park, Scott N. Thorgaard, Bo Zhang, Allen J. Bard * Center for Electrochemistry,
Supporting Information Single Particle Detection by Area Amplification Single Wall Carbon Nanotube Attachment to a Nanoelectrode Jun Hui Park, Scott N. Thorgaard, Bo Zhang, Allen J. Bard * Center for Electrochemistry,
Test Procedure for ItalSens IS-1 Graphite Sensors
 Test Procedure for ItalSens IS-1 Graphite Sensors Using Naphthol Oxidation to Check the Electrode Stability or Detect Naphthol Last revision: December 16, 2015 2015 PalmSens BV www.palmsens.com Contents
Test Procedure for ItalSens IS-1 Graphite Sensors Using Naphthol Oxidation to Check the Electrode Stability or Detect Naphthol Last revision: December 16, 2015 2015 PalmSens BV www.palmsens.com Contents
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2018. Supporting Information for Small, DOI: 10.1002/smll.201801523 Ultrasensitive Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Detection Based
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2018. Supporting Information for Small, DOI: 10.1002/smll.201801523 Ultrasensitive Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Detection Based
Reagents and equipments. All DNA sequences were all synthesized by Sangon
 Supporting Information Experimental Section Reagents and equipments. All DA sequences were all synthesized by Sangon (Shanghai, China). The sequences are as follows: DA-(AG 3 ): 5 - H -(CH ) 6 -AGGGTTAGGGTTAGGGTTAGGG-(CH
Supporting Information Experimental Section Reagents and equipments. All DA sequences were all synthesized by Sangon (Shanghai, China). The sequences are as follows: DA-(AG 3 ): 5 - H -(CH ) 6 -AGGGTTAGGGTTAGGGTTAGGG-(CH
Supporting Information Design and characterization of an electrochemical peptide-based sensor fabricated via click chemistry
 Electronic upplementary Material (EI) for Chemical Communications This journal is The Royal ociety of Chemistry 2011 upporting Information Design and characterization of an electrochemical peptide-based
Electronic upplementary Material (EI) for Chemical Communications This journal is The Royal ociety of Chemistry 2011 upporting Information Design and characterization of an electrochemical peptide-based
Solution-processable graphene nanomeshes with controlled
 Supporting online materials for Solution-processable graphene nanomeshes with controlled pore structures Xiluan Wang, 1 Liying Jiao, 1 Kaixuan Sheng, 1 Chun Li, 1 Liming Dai 2, * & Gaoquan Shi 1, * 1 Department
Supporting online materials for Solution-processable graphene nanomeshes with controlled pore structures Xiluan Wang, 1 Liying Jiao, 1 Kaixuan Sheng, 1 Chun Li, 1 Liming Dai 2, * & Gaoquan Shi 1, * 1 Department
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Selective Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide to Ethylene and Ethanol on Copper (I) Oxide Catalysts Dan Ren, Yilin Deng, Albertus Denny Handoko, Chung Shou Chen, Souradip
Supporting Information Selective Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide to Ethylene and Ethanol on Copper (I) Oxide Catalysts Dan Ren, Yilin Deng, Albertus Denny Handoko, Chung Shou Chen, Souradip
A stable dual-functional system of visible-light-driven Ni(II) reduction to a nickel nanoparticle catalyst and robust in situ hydrogen production
 Electronic Supporting Information A stable dual-functional system of visible-light-driven Ni(II) reduction to a nickel nanoparticle catalyst and robust in situ hydrogen production Chuanjun Wang, a Shuang
Electronic Supporting Information A stable dual-functional system of visible-light-driven Ni(II) reduction to a nickel nanoparticle catalyst and robust in situ hydrogen production Chuanjun Wang, a Shuang
