United States Patent (19) Maurer
|
|
|
- Lesley Herbert Cain
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
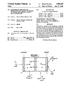
1 United States Patent (19) Maurer 54 OXIDATIVE DEGRADATION OF POLY WINYL ALCOHOL 75 Inventor: Hans W. Maurer, Paducah, Ky. 73) Assignee: Westvaco Corporation, New York, N.Y. 22 Filed: Sept. 28, Appl. No.: 1, U.S. C.... 2/91.3 VA, 2/29.6 WA 5 i Int. Cl.... C08f 3/34 58 Field of Search... 2/91.3 VA (56) References Cited FOREIGN PATENTS OR APPLICATIONS 398,383 5/1964 Japan OTHER PUBLICATIONS Polyvinyl Alcohol, Pritchard, (1970), pp. 85,86, Gor don and Breach Science Publishers. Primary Examiner-Paul Lieberman 57 ABSTRACT (11) () Jan. 7, 1975 Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) solutions are reduced in vis cosity in a predictable manner by reacting solutions of commercially available PVA with small amounts of hydrogen peroxide at high temperature in the pres cnce of a metallic ion catalyst. The viscosity reduc tions may be carried out using either a batch process or with a continuous cooking process, to produce film forming solutions of PVA having practical application in the paper industry as either a high speed surface or a coating binder. 3 Claims, 2 Drawing Figures OOO 90O -- REDUCTION OF BRABENDER VISCOSTY (33 C) I key A = ARCO 3 B = ARCO 205K C = ARCO - 6OO 5OO O O5 O.5 2.O 2.5 % OXDANT ADDED
2
3 1 OXIDATIVE DEGRADATION OF POLY WINYL ALCOHOL SUMMARY OF INVENTION The present invention relates generally to a treat ment for reducing the viscosity of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) solution in a predictable manner and particu larly to a process for degrading commercially available PVA in an oxidative reaction to produce PVA solu tion useful as a surface size or binder for a pigmented coating to be applied to the surface of paper. PVA is used in the paper industry principally as ei ther a surface sizing agent or as a binder in pigmented coatings. When used as a surface sizing agent, PVA yields grease resistance, smoothness, ink holdout, pick resistance and generally improved surface strength characteristics to the paper. When used as a binder in pigmented coatings, PVA is more effecient than starch, casien or other commonly known binders and thus per mits the application of a coating having a higher pig ment to binder ratio of the paper. However, it was found in a series of high speed sur face sizing trials with PVA that coat weights above 2 lb./side per ream could not be successfully applied to paper, and the reason for this lack of success was attrib uted to the rheology of the commercially available PVA grades used. Thus it was theorized that at high speeds and using in particular a gate roll size press, in creased pickup by the sheet might be attained by using a PVA solution of reduced viscosity. In addition it was also found during the trials that the commercially avail able PVA grades were being rejected in both the meter ing nip and the transfer nip of the gate roll size press at high speeds. The reason for this phenomena was sug gested to be a "balling up" of the PVA chains into coils which would not enter the nip. Accordingly, it was the orized that a PVA grade of lower molecular weight might reduce the curling tendency of the PVA chains and thus improve runnability. Hence the present invention was developed for the purpose of degrading and thereby reducing the viscos ity and molecular weight of some existing commercially available grades of PVA. It was known that PVA solu tions could be degraded by heating with hydrogen per oxide to reduce the viscosity of the solutions. However, it was also a requirement of the present invention that the PVA degradation should not be too severe or its film forming ability and the strength of its application to the paper surface might turn out to be unsatisfac tory. Thus even though it was known that PVA solu tions could be degraded by heating in the presence of hydrogen peroxide, there was no reference to a predict able and useful application of the reaction. Accord ingly, the present invention was developed to provide 55 a predictable process for the oxidative degradation of PVA solutions to reduce their viscosity through the mechanism of molecular degradation and thereby pro duce a product having particular utility in the paper in dustry as either a surface size treatment or a binder for paper coatings. DETAILED DESCRIPTION The present invention relates generally to the oxida tive degradation of PVA to produce a PVA solution particularly useful in the paper industry. The invention was developed with the following goals in mind: l. A predictable reduction of the viscosity of an aqueous solution of commercially available grade of PVA to improve its rheology and permit its use on high speed equipment for application to paper. 2. The preservation of the applicability of PVA as a binder for paper fibers and a coating pigment which could otherwise be destroyed by the exces sive oxidation and degradation of commercially available grades of PVA. 3. The generation of aldehydic groups on PVA to crosslink with hydroxyl groups during drying of a film of oxidized PVA on paper for the purpose of improving the strength of the surface film. Thus it was found that a satisfactory and predictable oxidation reaction, using commercially available grades of PVA, could be achieved for paper making ap plication by reacting an aqueous solution of PVA with small amounts of hydrogen peroxide in the presence of a transition metallic ion catalyst at temperatures in ex cess of 90 C. The successful application of the above noted procedure within the defined limits was found to be dependent on the presence within the PVA material of weak links (head-head, tail-tail) structures, a portion of which would be broken during the oxidation/degra dation reaction. In addition, it was discovered that the degradation of all of the weak links commonly present in commercially available PVA grades would produce an unwanted loss of the desirable rheological, adhesive and cohesive properties of the final product. Accord ingly, the success of the present invention was predi cated on the development of a process for oxidatively degrading a PVA sample having a known number of abnormal fractions in such a manner that some, but not all, of the fractions would be broken in the reaction. It will be recalled that the polymerization of the PVA precursor polyvinyl acetate (PVAc), occurs by a chain reaction mechanism, the majority of the steps in the growth of the PVAc chains are such that the head of one monomer is joined to the tail of another, thus head to-tail arrangement. However, a few additions occur to give head-to-head and tail-to-tail arrangements. The fraction of these abnormal additions depends on the temperature of the polymerization reaction and varies with the known PVA grades from 1.23 percent at C. to 1.95 percent at 110 C. When the acetates are hydro lyzed, the head-to-head, tail-to-tail structures become 1,2-glycols which have hydroxyl substituents on adja cent carbons of the chain instead of the alternate car bons as usual. Of course, it was known that hydrogen peroxide alone would cleave the 1,2-glycols, however it was suspected that oxidation of PVA with hydrogen peroxide would also raise the possibility of forming many different organic radicals which could combine with one another or which could produce other radicals by a propogation procedure. Furthermore, it was known that the oxidation of PVA by hydrogen peroxide proceeded by a free radical mechanism and that the ini tial free radicals came from a decomposition of the hy drogen peroxide. However, experiments illustrated that oxidative degradation of PVA with hydrogen peroxide alone did not produce the desired reductions in viscos ity nor could the viscosity reductions be predicted. In addition, when hydrogen peroxide was used alone to degrade PVA samples, traces of excess peroxide could be found in the PVA solution even after the reaction was apparently completed. Accordingly, in an effort to achieve the desired reduction in viscosity of PVA in a
4 3 predictable manner while at the same time, carrying out the reaction in such a way that few if any under sired by-products would be produced, the combined treatment of the present invention was developed. Thus, in accordance with the present invention, the desired reduction in viscosity of a hydrolyzed PVA so lution was achieved by reacting the PVA solution with hydrogen peroxide in the presence of a metallic ion cat alyst. For the purposes of the present invention, it was suspected that the addition of a transition metallic ion catalyst to the PVA solution, such as Cutt, Cut, Fett or Fett", would aid the heat applied to the reaction products to decompose the hydrogen peroxide and pro duce the free radicals necessary for a predictable mo lecular degradation of the PVA. To prove the theory, copper ions (Cut) were used to produce the desired increase in viscosity reduction as compared with a sim ple hydrogen peroxide reaction, and achieve a predict able process. EXAMPLE I The oxidation degradation of a super-hydrolyzed, high viscosity grade of PVA (Airco 1, supplied by Airco Chemical Company) was performed first with hydrogen peroxide and secondly with hydrogen perox ide in the presence of a copper ion catalyst to demon strate the need for a transition metallic ion catalyst in the system to aid the breakdown of the peroxide. For these experiments, the reactions were carried out in a batch process using a Brabender Amylograph Viscograph. The concentration of the PVA solution was selected to obtain a viscosity reading for the unde graded sample of around 900 Brabender units (about 84% PVA to water by weight). The experiments were then carried out as follows: 38 minutes of heating at 1.5 C. per minute from C.; addition of oxidant; 15 minutes heating at 90 C.; 38 minutes to cool at 1.5 C. per minute to 33 C.; and, finally, 20 minutes at 33 C. Each of the oxidants were added to the PVA so lution as follows. 0. percent hydrogen peroxide (based on the weight of the PVA in solution) was added to the mixture in the form of 2 percent aqueous solution. For the hydrogen peroxide/copper catalyst sample, first, 0.05% CuSO4.5H2O (based on the weight of PVA in solution) was dissolved in 10 ml. of water and added to the solution. This was followed by about 1 minute of mild agitation and finally, the same amount of hydrogen peroxide used on the first sample was added. After the reactions, the degraded PVA samples collected, the reductions in viscosity were measured and the results recorded as set forth in Table I. TABLE Airco 1 - Oxidation Degradation Reactions Oxidant Brabender Brookfield Units, 33 C. Visc. C. (cps) None % HO % HO, 0.05% Cu.So.5HO A comparison between the first undegraded sample and the two oxidative reactions shows the utility of the metallic catalyst in the system to decompose the hydro gen peroxide and thereby produce the desired reduc tion in viscosity. For these experiments, a check for ex O cess peroxide was positive in the straight hydrogen per oxide reaction but negative for the reaction containing the copper ions. Another set of experiments were performed using three different commercially available PVA samples and with varying amounts of the hydrogen peroxide? copper oxidant disclosed herein to show the effective ness of the invention on different PVA grades and to illustrate the ranges of viscosity reduction obtainable. In each case, the same batch process employed in the first examples was used with a substantially 10 to 1 ratio of hydrogen peroxide to CuSo.5H2O being main tained. The results of the experiment are set forth below in Table II. Table I Batch Oxidation Reactions PWA Oxidant Brabender Brookfield Grade HOf Units Viscosity Solids (Airco) CuSO.5HO 33 C. (cps) 3 None %-0.03% %-0.06% %-0.3% %-0.26% None %-0.02% %-0.05% %-0.3% %-0.23% K None K 0.%-0.04% K 1.%-0.3% K 2.%-0.23% It may be seen from studying the results in Table II, and the curves in FIGS. 1 and 2 reproduced from the data taken, that the increments of viscosity reduction obtained by adding additional hydrogen peroxide and catalyst decreased as the amount of oxidant increased. Furthermore, since the samples chosen for the test, were each considered fully or super hydrolyzed, it would appear for these particular grades that an oxi dant level or about 1.3 percent hydrogen peroxide with 0.13%. CuSO4. SHO appears to be the maximum amount of oxidant for the effective viscosity reduction required. Later on, in an effort to establish a correlation be tween the actual viscosity measurements shown in Table II and the expected viscosity reduction, calcula tions were made to determine the predicted viscosity reduction using an oxidant level of 1.3 percent hydro gen peroxide with 0.13% CuSO. H.O. For the pur poses of the calculations certain assumptions were made. First the PVA samples were assumed to be monodisperse and the chain scission was assumed to occur at random sites throughout the chains. In addi tion, it was assumed that the cleaveage of 1,2-glycols was a predominant reaction in the oxidation of PVA. Thus, assuming that about 1.7 percent of the bonds in PVA are involved in 1,2-glycol structures and since these were thought to be the principal point of chain scissions, a degree of polymerization of was as sumed for the calculations. Furthermore, since the PVA samples were all used at identical concentrations and temperatures, it was assumed that a comparison would be possible relating viscosities to molecular weights.
5 5 Accordingly, based on the above assumptions and knowing that 1.3 percent hydrogen peroxide corre sponded closely to the theoretical mole requirement for oxidant cleavage of the estimated average 1.7%. 1,2- glycol bonds in the samples used, the Mark-Houwink Sakurada law (n)=km), relating intrinsic viscosity and molecular weight, was used to calculate the pre dicted final viscosities. For the purpose of the calcula tions, the value for a was selected as a =0.6 since for PVA at - C., the value of a ranges from The viscosity of the undegraded sample was substituted for K, and for M, the ratio of the calculated weight average degree of polymerization to the initial degree of polymerization of each sample was used. The data obtained is shown in Table III. TABLE II Comparison of Actual and Predicted Viscosities (1.3% HO-0.13% CuSO.5H2O) PWA Grade Initial Actual Predicted (Airco) Viscosity Viscosity Viscosity (cps) (cps) (cps) K The initial viscosities and the actual viscosities after reaction with the designated oxidant level were each measured using a Brookfield Viscometer at C. and 20 rpm. The deviations between the actual viscosities obtained and the predicted viscosities calculated var ied, but the variations were expected and were deemed to be reasonable considering the assumptions made. For instance, the extension of the Mark-Houwink Sakurada law relating the viscosity and molecular weight was probably not entirely valid from a theoreti cal standpoint. In addition, it was known that there was a possibility of aldehydes being formed during the hy drogen peroxide oxidation of PVA, which could cause the chains to crosslink by forming hemiacetals to show an increase in the actual viscosities measured. More over, the initial assumptions of monodisperse samples and random scission could not be applied strictly, but were only made to simplify the calculations. Therefore, considering the above factors, the predicted and actual viscosities cam out fairly close and gave at least some support to indicate that cleavage of 1,2-glycols was the predominant reaction in the oxidation of PVA, while establishing a utility for theoretical statistical equa tions. In addition to the batch oxidation experiments, a se ries of oxidative degradation experiments were carried out using a fully hydrolyzed PVA grade in a continuous starch cooking apparatus substantially as described in applicants U.S. Pat. No. 3,485,667 assigned to the pres ent assignee herein. The experiments were performed by preparing a PVA water slurry having an initial solids content of about 12% PVA by weight to which varying amounts of the preferred copper catalyst were added. Meanwhile, the starch cooker was prepared for use by adjusting the cooking conditions to about 1 C. at psig with water passing through. Before adding the PVA solution to the cooker, the hydrogen peroxide ox idant was added in amounts proportional to the amount of copper catalyst added (about a 10 to 1 ratio) and fi nally the slurry was passed through the starch cooker while maintaining the original operating conditions. O When oxidatively degraded PVA began coming out of the starch cooker, it was collected for measurements of viscosity. Viscosity measurements for the different samples were measured using a Brookfield viscometer at 20 rpm and at C. The results of these experiments are reproduced in Table IV. TABLE IV Continuous Oxidative Reactions (Airco 3) Oxidant Brabender Brookfield % HO/CuSO.5HO Units 33 C Viscosity (cps) Solids None %-0.03% %-0.06% %-0.3% %-0.20% A comparison of the data for the continuous oxida tion process, with the data in Table II for the same sam ple (Airco 3) in the batch oxidation process, shows that viscosity reductions in the starch cooker were less than those obtained with the batch process. However, these differences were attributed to the short retention time of the PVA product in the continuous cooker ap paratus. However, it is known that various retention de vices may be incorporated in a continuous cooking ap paratus, therefore the good viscosity reduction ob tained with the batch oxidation process could obviously be matched in the continuous oxidation process by sim ply incorporating a suitable retention chamber into the continuous cooking apparatus. Accordingly, the data reproduced in Table IV shows that a continuous high temperature starch cooking apparatus can be used for the oxidative degradation of an aqueous PVA solution to desired viscosity levels as a function of the amount of oxidant used. Of course, the purpose of the invention was directed primarily at obtaining a PVA product of reduced vis cosity for improved runnability on a high speed gate roll size press, however it was also recognized that too much degradation of the PVA material might produce a product that was undersirable for its intended use. Therefore, additional experiments were conducted to determine if the PVA samples, degraded according to the present invention, would maintain the desirable properties exhibited by unoxidized PVA when used as a sizing agent for paperboard, and whether or not the oxidized PVA would perform as a binder in a coating formulation in substantially the same manner as the un degraded PVA. Based on the above noted additional experiments, it was found that limited degradation of PVA did not ad versely effect the film forming properties of PVA when applied to paper and paperboard surfaces. The trials indicated that oxidant levels of up to 0.% HO, % CuSO. SHO based on dry PVA could be safely used. Furthermore, the reduced viscosity of the PVA solution at the same oxidant level improved the runna bility of the PVA at the size press. Similar data taken from experiments using a de graded PVA in a coating formulation showed that deg radation of the PVA with the same level of oxidant noted above did not produce a deleterious effect to the surface strength characteristics of the paper coated with the formulation.
6 7 Accordingly it may be seen that the present invention sets forth a novel process for predicting the reduction in viscosity of a PVA solution using either a batch or continuous process, wherein the reduction in viscosity is achieved through the oxidative degradation of the PVA solution with hydrogen peroxide in the presence of a transition metallic ion catalyst, such as copper (Cut). Thus it will be understood that even though only one preferred example has been disclosed in de tail, the invention is intended to cover all changes and modifications that might be made by one skilled in the art and which do not depart from the spirit and scope of the invention as defined in the appended claims. I claim: 1. The method of treating an aqueous polyvinyl alco hol solution to produce a predictable reduction in its viscosity which comprises oxidizing the polyvinyl alco hol solution at a temperature of from about 33 to C. with hydrogen peroxide in the presence of a Cut' metallic ion catalyst in the ratio of about 10 to 1 with the addition of by weight from about 0.20 percent -1. percent hydrogen peroxide and by weight 0.02 percent percent of the Cut" catalyst the weight of the hydrogen peroxide and the Cut" ion catalyst being based on the weight of poly vinyl alcohol in solution, and recovering the reduced in viscosity polyvinyl alco hol solution. 2. The method of claim 1 wherein the oxidation reac tion is carried out in a batch process at a temperature of from C. and for a period of about 2 hours. 3. The method of claim 1 wherein the oxidation reac tion is carried out in a continuous cooking process at a temperature of about 1 C. and a pressure of about psig, sk :k k k k 55
United States Patent (19) Kawana et al.
 - United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
- United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
: Y. ti- sk 22N. Sir S. United States Patent (19) Uhri 4,687,061. Aug. 18, Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4 g
 i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1
 USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080249323A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0249323 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2008 (54) SORBITOL CONVERSION PROCESS Publication Classification
US 20080249323A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0249323 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2008 (54) SORBITOL CONVERSION PROCESS Publication Classification
Method of modifying weather
 Page 1 of 8 Method of modifying weather Abstract ( 6 of 42 ) United States Patent 6,315,213 Cordani November 13, 2001 A method for artificially modifying the weather by seeding rain clouds of a storm with
Page 1 of 8 Method of modifying weather Abstract ( 6 of 42 ) United States Patent 6,315,213 Cordani November 13, 2001 A method for artificially modifying the weather by seeding rain clouds of a storm with
) USOO A. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994
 ) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
/1977 schroeder. only a one step exposure process.
 US00569.5218A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,695.218 Nicosia 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 1997 54 GLOW-N-THE-DARK BOOK 4,237,381 12/1980 Schroeder... 250/462 4.266,164 5/1981 Schroeder.. 315/169.1
US00569.5218A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,695.218 Nicosia 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 1997 54 GLOW-N-THE-DARK BOOK 4,237,381 12/1980 Schroeder... 250/462 4.266,164 5/1981 Schroeder.. 315/169.1
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Jongema 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF SODUM CHILORIDE 75) Inventor: Pieter Jongema, Brummen, Netherlands (73) Assignee: Akzo N.V., Netherlands (21) Appl. No.: 815,090 (22)
United States Patent (19) Jongema 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF SODUM CHILORIDE 75) Inventor: Pieter Jongema, Brummen, Netherlands (73) Assignee: Akzo N.V., Netherlands (21) Appl. No.: 815,090 (22)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
Sep. 2, 1993 (JP) Japan (51 int. Cl... GOR 33/02
 United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0087941A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0087941 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD OF PRODUCING CARBON NANOTUBE SPONGES (75)
(19) United States US 2013 0087941A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0087941 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD OF PRODUCING CARBON NANOTUBE SPONGES (75)
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
(12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1
 USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140238873A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0238873 A1 Li et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) MODIFIED BUBBLING TRANSFER METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. FOR
(19) United States US 20140238873A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0238873 A1 Li et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) MODIFIED BUBBLING TRANSFER METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. FOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,762,262 B1
 USOO6762262B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,762,262 B1 Wang et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 13, 2004 (54) PREPARATION OF ACRYLIC POLYOLS 5,480,943 A 1/1996 Guo... 5/330.5 5,5,693 A 6/1996
USOO6762262B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,762,262 B1 Wang et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 13, 2004 (54) PREPARATION OF ACRYLIC POLYOLS 5,480,943 A 1/1996 Guo... 5/330.5 5,5,693 A 6/1996
(19) Scott H. Stillinger, Los Gatos, Calif. Oddz0n Products, Campbell, Calif. 60,640 Jun. 11, 1987 Int. Cl'... A63B 37/14
 United States Patent Stillinger 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58 (56) (19) GENERALLY SPHERICAL OBJECT WITH FLOPPY FILAMENTS TO PROMOTE SURE CAPTURE Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Scott H. Stillinger,
United States Patent Stillinger 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58 (56) (19) GENERALLY SPHERICAL OBJECT WITH FLOPPY FILAMENTS TO PROMOTE SURE CAPTURE Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Scott H. Stillinger,
: X''' gy? î. * March 21, 1967 L. H. COOK ETA 3,310, ß. Filled Sept. 9, 1963 PROCESS FOR COMBINED PRODUCTION OF AMMONIA AND UREA
 s March 21, 1967 L. H. COOK ETA 3,310,376 PROCESS FOR COMBINED PRODUCTION OF AMMONIA AND UREA OF) O CN r) Filled Sept. 9, 1963 8 O C) LAO O 3 : X''' 8 8 ß LUCIEN H. COOK VO MAVROVIC INVENTORS. gy?47.244
s March 21, 1967 L. H. COOK ETA 3,310,376 PROCESS FOR COMBINED PRODUCTION OF AMMONIA AND UREA OF) O CN r) Filled Sept. 9, 1963 8 O C) LAO O 3 : X''' 8 8 ß LUCIEN H. COOK VO MAVROVIC INVENTORS. gy?47.244
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 200402369A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/023.6009 A1 Mafoti et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LW DENSITY ADHESIVES AND SEALANTS Publication Classification
US 200402369A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/023.6009 A1 Mafoti et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LW DENSITY ADHESIVES AND SEALANTS Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
MEET THE PRESENTERS. Ryan Connell - J.D. M.S. Jim Nelson - J.D., Ph.D.
 MEET THE PRESENTERS Jim Nelson - J.D., Ph.D. Registered Patent Attorney and Principal Over 40 years of IP experience in chemical, polymer, pharmaceutical, biotechnology, cosmetics and medical device fields.
MEET THE PRESENTERS Jim Nelson - J.D., Ph.D. Registered Patent Attorney and Principal Over 40 years of IP experience in chemical, polymer, pharmaceutical, biotechnology, cosmetics and medical device fields.
(51) Int. Cl."... C07C 209/00 The invention provides a novel process for producing a
 USOO5977412A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,977,412 Bremmer et al. () Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 1999 54 PROCESS FOR PREPARING 3,5-5,510,533 4/1996 Kobayashi et al.. DIFLUOROANILINE FOREIGN
USOO5977412A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,977,412 Bremmer et al. () Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 1999 54 PROCESS FOR PREPARING 3,5-5,510,533 4/1996 Kobayashi et al.. DIFLUOROANILINE FOREIGN
US 9,214,722 B2 Dec. 15, 2015
 I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
United States Patent (19) Ishikawa et al.
 United States Patent (19) Ishikawa et al. 54 NTCTHERMISTOR COMPOSITION BASED ON BARUMTTANATE 75) Inventors: Terunobu Ishikawa; Hideaki Niimi; Yasunobu Yoneda, all of 73 Assignee: Nagaokakyo, Japan Murata
United States Patent (19) Ishikawa et al. 54 NTCTHERMISTOR COMPOSITION BASED ON BARUMTTANATE 75) Inventors: Terunobu Ishikawa; Hideaki Niimi; Yasunobu Yoneda, all of 73 Assignee: Nagaokakyo, Japan Murata
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170139281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0139281 A1 Hou et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) ALIGNMENT METHOD OF FFS TYPE GO2F I/335 (2006.01)
(19) United States US 20170139281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0139281 A1 Hou et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) ALIGNMENT METHOD OF FFS TYPE GO2F I/335 (2006.01)
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Leonard 54 PREPARATION OF FORMIC ACID BY HYDROLYSIS OF METHYL FORMATE (76) Inventor: Jackson D. Leonard, 7002 Blvd. East, Guttenberg, N.J. 07093 (21) Appl. No. 912,189 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Leonard 54 PREPARATION OF FORMIC ACID BY HYDROLYSIS OF METHYL FORMATE (76) Inventor: Jackson D. Leonard, 7002 Blvd. East, Guttenberg, N.J. 07093 (21) Appl. No. 912,189 22 Filed:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
(12) United States Patent
 US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
Intelligent Hotspot Connection System
 (19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
(19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
United States Patent [19]
![United States Patent [19] United States Patent [19]](/thumbs/76/73521136.jpg) United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
in. ION SOURCE \, N. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1 (19) United States 1 N 4
 (19) United States US 20060219890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0219890 A1 Yamaguchi (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 5, 2006 (54) TIME OF FLIGHT MASS SPECTROMETER (75) Inventor: Shinichi
(19) United States US 20060219890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0219890 A1 Yamaguchi (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 5, 2006 (54) TIME OF FLIGHT MASS SPECTROMETER (75) Inventor: Shinichi
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. Hauge et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2011
 US 20110262772A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0262772 A1 Hauge et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCING ALIGNED NEAR Publication Classification
US 20110262772A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0262772 A1 Hauge et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2011 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCING ALIGNED NEAR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
BY ye; v P. April 29, 1969 C. S. KELLEY 3,441,626. TEMPERATURE CONTROL of EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS Filed March 6, 1967 INVENTOR. PRODUCT C. S.
 April 29, 1969 C. S. KELLEY TEMPERATURE CONTROL of EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS Filed March 6, 1967 PRODUCT INVENTOR. C. S. KELLEY BY ye; v P. A 77OAPAWAYS United States Patent Office Patented Apr. 29, 1969 1.
April 29, 1969 C. S. KELLEY TEMPERATURE CONTROL of EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS Filed March 6, 1967 PRODUCT INVENTOR. C. S. KELLEY BY ye; v P. A 77OAPAWAYS United States Patent Office Patented Apr. 29, 1969 1.
Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions 7-6-2004 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Elvira Anoshkina University of Central
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions 7-6-2004 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Elvira Anoshkina University of Central
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
Experiment 5. Synthetic Polymers.
 Experiment 5. Synthetic Polymers. References: Brown & Foote, Chapters 24 INTRODUCTION: A polymer (Greek: polys + meros = many parts) is a giant or macromolecule made up of repeating structural units. The
Experiment 5. Synthetic Polymers. References: Brown & Foote, Chapters 24 INTRODUCTION: A polymer (Greek: polys + meros = many parts) is a giant or macromolecule made up of repeating structural units. The
United States Patent 19
 United States Patent 19 Anderson (54) 75 73) (21) 22) (51) 52) (58) BLENDS OF FUAN-ALDEHYDE ESINS WITH PHENOLIC ESINS AND MOLDED ATICLES PODUCED THEEFOM Inventor: Hugh C. Anderson, Palatine, Ill. Assignee:
United States Patent 19 Anderson (54) 75 73) (21) 22) (51) 52) (58) BLENDS OF FUAN-ALDEHYDE ESINS WITH PHENOLIC ESINS AND MOLDED ATICLES PODUCED THEEFOM Inventor: Hugh C. Anderson, Palatine, Ill. Assignee:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1
 US00782.5066B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1 Skaggs et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 2010 (54) RAPID FORMALDEHYDE (56) References Cited NEUTRALIZATION USING CHEMICALLY TREATED
US00782.5066B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1 Skaggs et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 2010 (54) RAPID FORMALDEHYDE (56) References Cited NEUTRALIZATION USING CHEMICALLY TREATED
United States Patent (19) Lahalih et al.
 United States Patent (19) Lahalih et al. 54 (75) (73 21) 22 (51) 52 (58) 56 METHOD FOR IMPROVING THE MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOIL, A POLYMERIC SOLUTION THEREFORE, AND A PROCESS FOR PREPARNG POLYMERIC
United States Patent (19) Lahalih et al. 54 (75) (73 21) 22 (51) 52 (58) 56 METHOD FOR IMPROVING THE MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOIL, A POLYMERIC SOLUTION THEREFORE, AND A PROCESS FOR PREPARNG POLYMERIC
(os) SSO. (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, (12) United States Patent (54) (75) (73)
 (12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
(12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
Science of Slime. Fig. 1 Structure of poly (vinyl alcohol)
 Name: Science of Slime Understanding the structure of a material and how it behaves is a large part of what chemists and materials scientists do for a living. Scientists and engineers cannot use new materials
Name: Science of Slime Understanding the structure of a material and how it behaves is a large part of what chemists and materials scientists do for a living. Scientists and engineers cannot use new materials
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7487686B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7487,686 B2 Feb. 10, 2009 (54) HIGH-PRECISION VORTEX FLOW METER (75) Inventors: An-Bang Wang, Taipei (TW); Ming-Hsun
USOO7487686B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7487,686 B2 Feb. 10, 2009 (54) HIGH-PRECISION VORTEX FLOW METER (75) Inventors: An-Bang Wang, Taipei (TW); Ming-Hsun
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,500,968 B2
 USOO6500968B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Zhou et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) PROCESS FOR SELECTIVE OXIDATION OF 4,824.976 A 4/1989 Clerici et al.... 549/531 ORGANIC FEEDSTOCKS
USOO6500968B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Zhou et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 31, 2002 (54) PROCESS FOR SELECTIVE OXIDATION OF 4,824.976 A 4/1989 Clerici et al.... 549/531 ORGANIC FEEDSTOCKS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013
 US 2013 OOO1573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0001573 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR AND METHOD OF Publication Classification
US 2013 OOO1573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0001573 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR AND METHOD OF Publication Classification
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
7" - seees / s (N 255 (N. Cases a1. C=s. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. es N? (19) United States.
 (19) United States US 20030085296A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085296A1 Waxmanski (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) HURRICANE AND TORNADO CONTROL DEVICE (76) Inventor: Andrew
(19) United States US 20030085296A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085296A1 Waxmanski (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) HURRICANE AND TORNADO CONTROL DEVICE (76) Inventor: Andrew
High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source.
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Black, Jr. et al. (54 75 73 21 22) 51 52) 58 (56) SELFACTIVATING FERROFLUD SEAL APPARATUS AND METHOD Inventors: Thomas J. Black, Jr., Lowell; Philip Stahl, Holliston, both of
United States Patent (19) Black, Jr. et al. (54 75 73 21 22) 51 52) 58 (56) SELFACTIVATING FERROFLUD SEAL APPARATUS AND METHOD Inventors: Thomas J. Black, Jr., Lowell; Philip Stahl, Holliston, both of
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USO0959882OB2 () Patent No.: Houze (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2017 (54) MIXTURES OF POLYVINYLAMINES AND (58) Field of Classification Search OF LIQUID COMPOSITIONS OF CATIONIC
(12) United States Patent USO0959882OB2 () Patent No.: Houze (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2017 (54) MIXTURES OF POLYVINYLAMINES AND (58) Field of Classification Search OF LIQUID COMPOSITIONS OF CATIONIC
TEPZZ Z 4A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2017/35
 (19) TEPZZ Z 4A_T (11) EP 3 211 024 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.08.17 Bulletin 17/3 (21) Application number: 171768.0 (22) Date of filing: 28.03.13 (1) Int Cl.: C08H 7/00
(19) TEPZZ Z 4A_T (11) EP 3 211 024 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.08.17 Bulletin 17/3 (21) Application number: 171768.0 (22) Date of filing: 28.03.13 (1) Int Cl.: C08H 7/00
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kramer et al. USOO661981 OB2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2003 (54) HALLOWEENTREAT CARRIER INCLUDING GLOW-IN-THE-DARK MATERIAL PUMPKIN DECORATING KIT, AND METHOD
(12) United States Patent Kramer et al. USOO661981 OB2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2003 (54) HALLOWEENTREAT CARRIER INCLUDING GLOW-IN-THE-DARK MATERIAL PUMPKIN DECORATING KIT, AND METHOD
SSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSS 22. 8a 1. United States Patent (19) Maru et al. 11 4,365,007 45) Dec. 21, 1982
 United States Patent (19) Maru et al. (54) FUEL CELL WITH INTERNAL REFORMING (75) Inventors: Hansraj C. Maru, Brookfield Center; Pinakin S. Patel, Danbury, both of Conn. 73 Assignee: Energy Research Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Maru et al. (54) FUEL CELL WITH INTERNAL REFORMING (75) Inventors: Hansraj C. Maru, Brookfield Center; Pinakin S. Patel, Danbury, both of Conn. 73 Assignee: Energy Research Corporation,
MODIFICATION WITH A SULFONATE MONOMER
 Thesis - MOLECULAR STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONAL MODIFICATIONS OF POLY(VINYL ALCOHOL) CHAPTER 8 BY TOHEI MORITANI MODIFICATION WITH A SULFONATE MONOMER A functional monomer containing sodium sulfonate group,
Thesis - MOLECULAR STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONAL MODIFICATIONS OF POLY(VINYL ALCOHOL) CHAPTER 8 BY TOHEI MORITANI MODIFICATION WITH A SULFONATE MONOMER A functional monomer containing sodium sulfonate group,
Yamamoto et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 11, 1995
 United States Patent 19) 11 USOO5431917A Patent Number: Yamamoto et al. Date of Patent: Jul. 11, 1995 54 HARD CAPSULE FOR PHARMACEUTICAL DRUGS AND METHOD FOR PRODUCING FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS THE SAME
United States Patent 19) 11 USOO5431917A Patent Number: Yamamoto et al. Date of Patent: Jul. 11, 1995 54 HARD CAPSULE FOR PHARMACEUTICAL DRUGS AND METHOD FOR PRODUCING FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS THE SAME
United States Patent (19) Amiet
 United States Patent (19) Amiet 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,879,407 Nov. 7, 1989 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF ETHYL TRFLUOROACETATE 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Louis Amiet, Lyons, France
United States Patent (19) Amiet 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,879,407 Nov. 7, 1989 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF ETHYL TRFLUOROACETATE 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Louis Amiet, Lyons, France
(54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited
 USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
Present State and Main Trends of Research on Liquid-Phase Oxidation of Organic Compounds
 1 Downloaded via 148.251.232.83 on July 10, 2018 at 19:07:56 (UTC). See https://pubs.acs.org/sharingguidelines for options on how to legitimately share published articles. Present State and Main Trends
1 Downloaded via 148.251.232.83 on July 10, 2018 at 19:07:56 (UTC). See https://pubs.acs.org/sharingguidelines for options on how to legitimately share published articles. Present State and Main Trends
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent NO.: US 6,371,384 ~1 Garcia (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16,2002
 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent NO.: US 6,371,384 ~1 Garcia (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16,2002 (54) AQUEOUS FOAM GENERATING SYSTEM 4,802,630 A * 211989 Kromrey... 2391428 AND METHOD FOR GENERATING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent NO.: US 6,371,384 ~1 Garcia (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 16,2002 (54) AQUEOUS FOAM GENERATING SYSTEM 4,802,630 A * 211989 Kromrey... 2391428 AND METHOD FOR GENERATING
Document 11 discloses aqueous colloidal solutions of hydrated oxides of copper which are highly suitable for use as fungicides.
 The present invention relates to a method for metallising dielectric substrates, the use of aqueous colloidal solutions in such methods, aqueous colloidal solutions and aqueous developer solutions and
The present invention relates to a method for metallising dielectric substrates, the use of aqueous colloidal solutions in such methods, aqueous colloidal solutions and aqueous developer solutions and
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2. Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007
 USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 2012.0034542A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0034542 A1 Martin et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SEAL FOR SOLID POLYMER Related U.S. Application Data ELECTROLYTE
US 2012.0034542A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0034542 A1 Martin et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SEAL FOR SOLID POLYMER Related U.S. Application Data ELECTROLYTE
(54) (75) (73) (Us) (21) (22) (63) 1, 2007, provisional application No. 60/997,142,?led
 US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7470,444 B2
 USOO747044.4B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 7470,444 B2 McKinzie et al. () Date of Patent: Dec., 2008 (54) TRIPE-BLEACHING COMPOSITION 3,0, 166 A 3, 1962 Smith (75) Inventors: Michael D.
USOO747044.4B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 7470,444 B2 McKinzie et al. () Date of Patent: Dec., 2008 (54) TRIPE-BLEACHING COMPOSITION 3,0, 166 A 3, 1962 Smith (75) Inventors: Michael D.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,229,054 B1. Dai et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 8, THEREFOR 3,644,534 2/1972 Reabe.
 USOO6229054B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,229,054 B1 Dai et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 8, 2001 (54) DERIVATIVE OF CARDANOLAND USES 3,283,030 11/1966 Bean et al.... 568/630 THEREFOR
USOO6229054B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,229,054 B1 Dai et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 8, 2001 (54) DERIVATIVE OF CARDANOLAND USES 3,283,030 11/1966 Bean et al.... 568/630 THEREFOR
Introduction to Polymerization Processes
 Introduction to Polymerization Processes Reference: Aspen Polymers: Unit Operations and Reaction Models, Aspen Technology, Inc., 2013. 1- Polymer Definition A polymer is a macromolecule made up of many
Introduction to Polymerization Processes Reference: Aspen Polymers: Unit Operations and Reaction Models, Aspen Technology, Inc., 2013. 1- Polymer Definition A polymer is a macromolecule made up of many
MATERIALS SCIENCE POLYMERS
 POLYMERS 1) Types of Polymer (a) Plastic Possibly the largest number of different polymeric materials come under the plastic classification. Polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene,
POLYMERS 1) Types of Polymer (a) Plastic Possibly the largest number of different polymeric materials come under the plastic classification. Polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Taniguchi et al. (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURING FERULIC ACD 75 Inventors: Hisaji Taniguchi; Eisaku Nomura; Takuo Tsuno; Seiko Minami, all of Wakayama; Koji Kato, Hashimoto; Chieko
United States Patent (19) Taniguchi et al. (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURING FERULIC ACD 75 Inventors: Hisaji Taniguchi; Eisaku Nomura; Takuo Tsuno; Seiko Minami, all of Wakayama; Koji Kato, Hashimoto; Chieko
ACRYSOL TT-615 Rheology Modifier
 Technical Data Sheet ACRYSOL TT-615 Rheology Modifier Description Typical Physical Properties ACRYSOL TT-615 Rheology Modifier is an alkali swellable acrylic polymer emulsion used as either a primary or
Technical Data Sheet ACRYSOL TT-615 Rheology Modifier Description Typical Physical Properties ACRYSOL TT-615 Rheology Modifier is an alkali swellable acrylic polymer emulsion used as either a primary or
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Shioyama et al. 54 (75) 73) (21) 22 (51) (52) 58) 56 PROCESS FOR PRODUCING ALUMINUM CTRATE SOLUTIONS Inventors: Tod K. Shioyama; Robert A. Little, both of Bartlesville, Okla.
United States Patent (19) Shioyama et al. 54 (75) 73) (21) 22 (51) (52) 58) 56 PROCESS FOR PRODUCING ALUMINUM CTRATE SOLUTIONS Inventors: Tod K. Shioyama; Robert A. Little, both of Bartlesville, Okla.
United States Patent (19) Gudmundsen et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gudmundsen et al. 54 RECOVERY OF ANHYDROUS HCL GAS BY EXTRACTIVE DISTILLATION WITH A HALDE SALT (75 Inventors: Sigmund Gudmundsen, Saetre I Hurum; Egil Ronaess, Porsgrunn; Sver
United States Patent (19) Gudmundsen et al. 54 RECOVERY OF ANHYDROUS HCL GAS BY EXTRACTIVE DISTILLATION WITH A HALDE SALT (75 Inventors: Sigmund Gudmundsen, Saetre I Hurum; Egil Ronaess, Porsgrunn; Sver
ACRYSOL TT-935 Rheology Modifier
 Technical Data Sheet ACRYSOL TT-935 Rheology Modifier Description ACRYSOL TT-935 Rheology Modifier offers a low cost/high performance alternative to cellulosic thickeners in interior flat to semigloss
Technical Data Sheet ACRYSOL TT-935 Rheology Modifier Description ACRYSOL TT-935 Rheology Modifier offers a low cost/high performance alternative to cellulosic thickeners in interior flat to semigloss
United States Patent (19) Sumikawa et al.
 United States Patent (19) Sumikawa et al. 11 3,983,170 (45) Sept. 28, 1976 (54) (75) 73 22 21 52) 51 58) PROCESS FOR THE PURIFICATION OF MALIC ACID Inventors: Shozo Sumikawa, Hofu, Rikichi Maida; Yuriaki
United States Patent (19) Sumikawa et al. 11 3,983,170 (45) Sept. 28, 1976 (54) (75) 73 22 21 52) 51 58) PROCESS FOR THE PURIFICATION OF MALIC ACID Inventors: Shozo Sumikawa, Hofu, Rikichi Maida; Yuriaki
III. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,143,451 (45. Date of Patent: Sep. 1, Millgard
 United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
(19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070268651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0268651 A1 TAKASHIMA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 22, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CERAMIC CAPACITOR May 22, 2006 (JP)...
(19) United States US 20070268651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0268651 A1 TAKASHIMA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 22, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CERAMIC CAPACITOR May 22, 2006 (JP)...
- X. (bka III IIII. United States Patent (19) Sobata et al e (2. o
 United States Patent (19) Sobata et al. 54 ACTIVITY CONTROL APPARATUS FOR ZINC PHOSPHATE TREATMENT SOLUTION 75) Inventors: Tamotsu Sobata, Ibaraki; Katsuhiro Takeshita, Hirakata, both of Japan 73) Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Sobata et al. 54 ACTIVITY CONTROL APPARATUS FOR ZINC PHOSPHATE TREATMENT SOLUTION 75) Inventors: Tamotsu Sobata, Ibaraki; Katsuhiro Takeshita, Hirakata, both of Japan 73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ishihara USOO68033B2 (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: US 6,803,3 B2 Oct. 12, 2004 (54) POLYMEREMULSION (75) Inventor: Takamasa Ishihara, Takatsuki (JP) (73) Assignee: Shinto
(12) United States Patent Ishihara USOO68033B2 (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: US 6,803,3 B2 Oct. 12, 2004 (54) POLYMEREMULSION (75) Inventor: Takamasa Ishihara, Takatsuki (JP) (73) Assignee: Shinto
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0286850 A1 Peterson et al. US 20140286850A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) METHOD OF MAKING SODIUM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0286850 A1 Peterson et al. US 20140286850A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) METHOD OF MAKING SODIUM
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Kreuz et al. (11) 4,426,253 45) Jan. 17, 1984 (54) 75 73) (21) 22 (51) (52) 58) HIGH SPEED ETCHING OF POLYMIDE FILM Inventors: John A. Kreuz, Columbus; Christopher M. Hawins,
United States Patent (19) Kreuz et al. (11) 4,426,253 45) Jan. 17, 1984 (54) 75 73) (21) 22 (51) (52) 58) HIGH SPEED ETCHING OF POLYMIDE FILM Inventors: John A. Kreuz, Columbus; Christopher M. Hawins,
I IIIII IIIII lll (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2. (45) Date of Patent:
 I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9633947B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant:
USOO9633947B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant:
He'? United States Patent (19) Foer. 11) Patent Number: 4,595,469 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 17, 1986 NOOH /6. PRODUCT NaCl + H2O FEED (54)
 United States Patent (19) Foer 11) Patent Number: 4,595,469 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 17, 1986 (54) I75 (73) 21 22 63 (51) (52) 58 ELECTROLYTIC PROCESS FOR PRODUCTION OF GASEOUS HYDROGEN CHLORIDE AND AOUEOUS
United States Patent (19) Foer 11) Patent Number: 4,595,469 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 17, 1986 (54) I75 (73) 21 22 63 (51) (52) 58 ELECTROLYTIC PROCESS FOR PRODUCTION OF GASEOUS HYDROGEN CHLORIDE AND AOUEOUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050O25974A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0025974 A1 Lennhoff (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 3, 2005 (54) CARBON AND ELECTROSPUN Publication Classification NANOSTRUCTURES
(19) United States US 20050O25974A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0025974 A1 Lennhoff (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 3, 2005 (54) CARBON AND ELECTROSPUN Publication Classification NANOSTRUCTURES
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
United States Patent Office
 United States Patent Office 2,84,461 NON-CATALYTIC LIQUED PHASE ISOBUTANE OXDATION De Loss E. Winkler, Orinda, and George W. Hearne, Lafayette, Calif., assignors to Shell Development Com pany, New York,
United States Patent Office 2,84,461 NON-CATALYTIC LIQUED PHASE ISOBUTANE OXDATION De Loss E. Winkler, Orinda, and George W. Hearne, Lafayette, Calif., assignors to Shell Development Com pany, New York,
USE OF RHEOLOGY AS A DEVELOPING AND TROUBLESHOOTING TOOL FOR PSA APPLICATIONS.
 USE OF RHEOLOGY AS A DEVELOPING AND TROUBLESHOOTING TOOL FOR PSA APPLICATIONS. Michael DeFrancisis, Applications Engineer, Henkel, Bridgewater, NJ Yayun Liu, Senior Development Scientist, Henkel, Bridgewater,
USE OF RHEOLOGY AS A DEVELOPING AND TROUBLESHOOTING TOOL FOR PSA APPLICATIONS. Michael DeFrancisis, Applications Engineer, Henkel, Bridgewater, NJ Yayun Liu, Senior Development Scientist, Henkel, Bridgewater,
June 9, R. C. DATIN ETAL SYNTHESIS OF NITROSODIMETHYLAMINE Filed Jan. 7, ,136,821
 June 9, 1964 R. C. DATIN ETAL SYNTHESIS OF NITROSODIMETHYLAMINE Filed Jan. 7, 19 United States Patent Office Patented June 9, 1964 SYNTHESS OF NTROSO/IETHYLAMINE Richard C. Datin and George A. Eliott,
June 9, 1964 R. C. DATIN ETAL SYNTHESIS OF NITROSODIMETHYLAMINE Filed Jan. 7, 19 United States Patent Office Patented June 9, 1964 SYNTHESS OF NTROSO/IETHYLAMINE Richard C. Datin and George A. Eliott,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014O124381A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0124381 A1 FAN (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2014 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCING METHANOL (52) U.S. Cl. FROMMETHANE CPC...
(19) United States US 2014O124381A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0124381 A1 FAN (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2014 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCING METHANOL (52) U.S. Cl. FROMMETHANE CPC...
Method of producing cumulus clouds
 1 of 6 6/16/2012 11:15 PM ( 7 of 7 ) United States Patent 4,653,690 St. Amand, et al. March 31, 1987 Method of producing cumulus clouds Abstract The disruption of a thermal inversion and formation of cumulus
1 of 6 6/16/2012 11:15 PM ( 7 of 7 ) United States Patent 4,653,690 St. Amand, et al. March 31, 1987 Method of producing cumulus clouds Abstract The disruption of a thermal inversion and formation of cumulus
? Ns 54 F2 44. al-f2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
Si-iö, TH". ()SSS N I. 6-7 Zaf (54) United States Patent (19) Cuff (11 3,968,700. (45) July 13, (21) Appl. No.: 493,748
 United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
Techniques for effluent treatment. Lecture 5
 Techniques for effluent treatment Lecture 5 Techniques for effluent treatment Dye effluent treatment methods are classified into three main categories: 1. Physical treatment method 2. Chemical treatment
Techniques for effluent treatment Lecture 5 Techniques for effluent treatment Dye effluent treatment methods are classified into three main categories: 1. Physical treatment method 2. Chemical treatment
United States Patent (19) Lin et al.
 United States Patent (19) Lin et al. (54) (75) (73) (21) 22) 51 (52) 58) (56) PROCESS FOR PRODUCING SS-ETHYLENEDIAMENE-N,N'-DISUCCINIC ACID Inventors: Ronny W. Lin, Baton Rouge; Eldon E. Atkinson, Jr.,
United States Patent (19) Lin et al. (54) (75) (73) (21) 22) 51 (52) 58) (56) PROCESS FOR PRODUCING SS-ETHYLENEDIAMENE-N,N'-DISUCCINIC ACID Inventors: Ronny W. Lin, Baton Rouge; Eldon E. Atkinson, Jr.,
LAB. FACTORS INFLUENCING ENZYME ACTIVITY
 AP Biology Date LAB. FACTORS INFLUENCING ENZYME ACTIVITY Background Enzymes are biological catalysts capable of speeding up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy. One benefit of enzyme catalysts
AP Biology Date LAB. FACTORS INFLUENCING ENZYME ACTIVITY Background Enzymes are biological catalysts capable of speeding up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy. One benefit of enzyme catalysts
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 2007 O190148A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0190148A1 Cronin et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) GEL COMPOSITIONS, APPARATUSES AND Publication Classification
US 2007 O190148A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0190148A1 Cronin et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) GEL COMPOSITIONS, APPARATUSES AND Publication Classification
ZZZZZZZZZZYZZZZZZZZZZZZZz6
 USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
Mathis. 58) Field of Search /603 56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 2,826,610 3/1958 Morris et al /603
 United States Patent (19) Correia et al. US00540 1876A 11 Patent Number: Date of Patent: Mar. 28, 1995 (54 SYNTHESIS F CHLRACETIC ACIDS 75 Inventors: Yves Correia, Chateau Arnoux; Daniel Pellegrin, Grenoble,
United States Patent (19) Correia et al. US00540 1876A 11 Patent Number: Date of Patent: Mar. 28, 1995 (54 SYNTHESIS F CHLRACETIC ACIDS 75 Inventors: Yves Correia, Chateau Arnoux; Daniel Pellegrin, Grenoble,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,763,928 B2
 USOO7763928B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) MULTI-TIME PROGRAMMABLE MEMORY (58) Field of Classification Search... 257/314321, 257/E29.129,
USOO7763928B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) MULTI-TIME PROGRAMMABLE MEMORY (58) Field of Classification Search... 257/314321, 257/E29.129,
