Chm 222 Spring 2015, Exercise Set 5 The Stereochemistry Pillar
|
|
|
- Alisha Nicholson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chm 222 Spring 2015, Exercise Set 5 The Stereochemistry Pillar Mr. Linck c Boniface Beebe Productions January 19, 2016 Version 3.0. NOTE: An asterisk in the problem title indicates that it is a continuing problem from the previous one. Two asterisk tells you the problem depends on the last two, etc Learning Organic Chemistry Review your notes from the last lecture. Summarize the subjects that were covered. Present that summary to another student in the class Ring Structure and Chemical Thinking If cyclopropane is strained, that is, has weaker than normal C-C bonds, and cyclohexane is not strained, which should have the most negative energy change for the reaction with Cl 2 to form a straight chain compounds with chlorine atoms on the ends? C n H 2n + Cl 2 = ClCH 2 (CH 2 ) n 2 CH 2 Cl HINTS: (1) Think through a series of reactions use Hess s law that starts with rupturing a C-C bond into two radicals, and proceed from there such that the sum of your reactions equals the desired overall result. (2) Be sure you understand your conclusion Ring Instability What hybridization would you have a carbon atom in cyclopropane use? Is anything wrong with the bonding given your choice of hybridization and the structure of cyclopropane? HINT: Think angles Another Ring Instability Issue* Draw a cyclopropane ring looking down a C-C bond and comment on any obvious instability.
2 Figure 1: Newman projection of a cyclohexane ring Ring Instability** State the two issue that affect ring instability Potential Ring Instability Draw a planar cyclohexane ring and then make a Newman projection looking down a C-C bond. Comment on any obvious instability The Cyclohexane Structure In Figure 1 is a Newman projection of a cyclohexane ring where each carbon is tetrahedrally coordinated. What is the relationship (gauche or antiperiplanar) of X and Y? 5.8. The Cyclohexane Structure* In Figure 1 is a Newman projection of a cyclohexane ring. What is the relationship (gauche or antiperiplanar) of X and the -CH 2 at the lower center (blue lines for those looking in color)? 5.9. The Cyclohexane Structure** In Figure 1 is a Newman projection of a cyclohexane ring. What is the relationship (gauche or antiperiplanar) of Y and the -CH 2 at the upper center (black lines for those looking in color)? The Cyclohexane Structure*** Again referencing Figure 1, if you were to put a large group at position X or Y, which would you choose for maximum stability? Why?
3 Figure 2: The flip of a cyclohexane ring within a Newman projection Stability in Cyclohexane Structures**** Imagine a motion where the front -CH 2 in Figure 1 is pulled down, causing X to rotate up, and, simultaneously, the rear -CH 2 is pulled up, causing Y to rotate down. The process is shown in Figure 2. Is X axial or equatorial in the starting material. Is X axial or equatorial in the product? What about Y? What can you say about a flip of the cyclohexane structure? Stability in Cyclohexane Structures If X is larger than Y (Figures 1 and 2), which of the two structures in Figure 2 is most stable? Three-Dimensional Ring Structure Draw a line structure representation of the cyclohexane ring in the chair form without any hydrogen atoms present Three-Dimensional Ring Structure* Draw a cyclohexane ring in the chair form with axial hydrogen atoms Three-Dimensional Ring Structure** Draw a cyclohexane ring in the chair form with equatorial hydrogen atoms Flipping the Chair Form Draw a flipped cyclohexane ring. This means, if the right hand carbon of your original drawing was up, make the right hand carbon now down Flipping the Chair Form* Convince yourself with your diagrams of the last problem that upon flipping all the axial hydrogen atoms becomes equatorial and all the equatorial ones become axial Top and Bottom of a Cyclohexane Ring Draw a cyclohexane ring with both the axial and equatorial hydrogen atoms on one of the carbons shown. Is one of those hydrogen atoms on top?
4 Isomers in Cyclohexane What is the fundamental reason why a cyclohexane ring has cis and trans isomers whereas hexane does not? Isomers in Cyclohexane Draw trans-1,3-dichlorocyclohexane where the cyclohexane ring is drawn flat Isomers in Cyclohexane Draw trans-1,3-dichlorocyclohexane in it stable conformation (3D drawing required) Isomers in Cyclohexane Draw the planar and 3D structures for cis-1,3-dichlorocyclohexane Stable Conformers in Rings Sketch the stable conformation of each of the following Conformers in Cyclohexane Can you show axial and equatorial substituents in a planar cyclohexane structure? Why or why not? Cyclohexane Conformations Draw the most stable conformer of cis-1-t-butyl-3-methylcyclohexane Cyclohexane Conformations A monosubstituted cyclohexane ring is more stable with the substituent in what position? Does that mean there is none of the other conformer? Explain Energy Difference in Cyclohexane Conformations The free energy difference, G(axial C 6 H 11 X) - G(eq C 6 H 11 X) is 7.3 kj/mole for X = CH 3. Calculate the ratio of equatorial species to axial. HINT: G = - R T ln([eq]/[ax]) where R is the universal gas constant, J/(K mole).
5 Energy Difference in Cyclohexane Conformations The ratio of the conformer of C 6 H 11 X, [eq]/[ax], when X is a phenyl group, is 110. What is the free energy difference between the two conformers. Which is more stable? HINT: See that of the last problem Cyclohexane Conformations Consider the two monosubstituted cyclohexane rings, C 6 H 11 X, where X is -CF 3 in one and -CCl 3 in the other. Which would you predict has the largest fraction of material with the X group axial? Explain Conformers in Cyclohexane Can you show the stable conformer of a substituted cyclohexane in a planar diagram? Why or why not? Isomers in Cyclohexane Can you show a cis isomer in a 3D structure of cyclohexane? Why or why not? Stable Isomers Is cis- or trans-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane more stable? Why? Isomers in Ring Structures Draw all of the isomers of dimethylcyclobutane Isomers in Ring Structures Draw the isomer cis-1-isopropyl-cis-5-methyl-cyclohexanol in the planar representation. HINT: The stereochemistry designation is relative to the position of the hydroxy group Isomers in Ring Structures* Draw the isomer cis-1-isopropyl-trans-5-methyl-cyclohexanol in the planar representation. HINT: The stereochemistry designation is relative to the position of the hydroxy group Conformers in Ring Structures** Draw the stable conformer of the compounds in the last two problems Stable Conformers Use the table of cyclohexane stabilities to guess (and draw) the stable conformation of trans-1- chloro-3-ethyl-cyclohexane Ring Stability and Reactions It is possible to imagine both 1 and 2 closing to make a lactones. Which is likely to occur most readily? Why? HINT: A lactone is a cyclic ester Ring Stability and Reactions Use epwa to describe any reaction that 3 might undergo in dilute aqueous acid. Why does your reaction occur?
6 X A (kcal/mole) X A (kcal/mole) F 0.15 CH Cl 0.43 CF Br 0.38 C 2 H CN 0.17 CCH 0.41 SH 0.9 SCH Table 1: The A values ( G o value) for the change from equatorial to axial conformer in kcal/mole for some X groups in C 6 H 11 X.
7 Stable Conformation Draw the stable conformation of cis-1-ethyl-2-isopropylcyclohexane Reactions and Stability Use 1,2-ethandiol to make the ketal of 4 and 5. Which is most stable? Why? HINT: Stability in ring compounds should make you think of (1) ring size and (2) conformation Isomer Drawing Lindane, an insecticide, is cis-(1,2,4,5)-trans-(3,6)-hexachlorocyclohexane. Draw the structure in the planar representation Stable Conformation* Draw the stable conformation of lindane Stable Conformation and Predictive Thinking The compound 5-hydroxy-1,3-dioxane (that nomenclature means a six membered ring with two oxygens replacing CH 2 groups in the 1 the 3 positions) is more stable in the axial conformation than in the equatorial, in contrast to hydroxycyclohexane. Why? HINT: Think about hydrogen bonding Conformers, Isomers, or the Same Thing How do you define each of the following terms: conformers, identical molecules, isomers? Conformers, Isomers, or the Same Thing Look at each of the following and indicate whether the relationship is: conformer, identical molecule, or isomer? Free Energy Difference and Equilibrium Constant The free energy change, G o, for conversion of the axial form of a monosubstituted cyclohexane to the equatorial form is kcal/mole when the substituent is COOH. What is the equilibrium constant for this conversion? HINT: See discussion in problem 27.
8 Free Energy Difference and Stability The value of G o (for a process such as described in the last problem) for a phenyl substituent is -2.9 kcal/mole. What is the stable conformation of cis-4-phenylcyclohexanoic acid? HINT: You need data from problem Ring Instability Chemists have been able to synthesize (with difficulty) cubane, C 8 H 8, 6. Why is this compound so unstable? D Drawing of Rings Here on the left is a planar perspective of a steroid ring. Put the substituents onto the proper positions with the proper geometric orientations in the chair form of that molecule, sketched without substituents on the right hand side Conformer Stability Draw the conformers (with respect to the cyclohexane ring) of menthol, 7, and indicate which is the most stable D Structure and NMR How many kinds of hydrogen atoms are present in bornane, 8? How would each be split in 1 H nmr? Conformational Energy and Explanations The difference in energy between the axial and equatorial conformers of the cyclohexylhalides (E axial - E equatorial ) is F, 0.15; Cl, 0.43; Br, 0.38;, I, 0.43, all in kcal/mole. Which of these data make sense to you on an initial look? Which don t? Is there any way you can account for the similarity of the last three? Reactions and Stereochemistry Review Progesterone, 9, is reacted with dimethylcuprate(i). Where will attack occur and what will be the stereochemistry of the product. Why? Isomeric Stability Which is more stable, cis- or trans-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane? Why?
9 Isomeric Stability Which is more stable, cis-(1,5)-trans-(2,4)- or cis-(1,4)-trans-(2,5)- tetramethylcyclohexane? HINT: The nomenclature here means, in the first case, for instance, that the methyl groups on atoms 1 and 5 are on the same side, and opposite that of the methyl groups on atoms 2 and Chirality How do you rigorously define a chiral molecule? HINT: There are two ways to state this, one of which involves mirror images. In my view, that is the hard way, especially in practice. Think i and σ Chirality* What works reasonably well (most of the time) to define a chiral molecule centered on a carbon atom? Chirality Which of the following are chiral molecules? HINT: Remember, in cases where there are two (or more) chiral centers, you have to have 3D drawing to assess stereochemistry. When you don t have it, you must generate it, even if you make assumptions in building your drawing Chirality Which of the following have a chiral (or stereogenic) center?
10 Superposition of Two Molecules If it is possible, show how you would rotate 9A to yield 9B. Specify the amount and your axes of rotation (i.e., 30 o about the C-Cl bond) Superposition of Two Molecules If it is possible, show how you would rotate 9C to yield 9D. Specify the amount and your axes of rotation (i.e., 30 o about the C-Cl bond) Reactions and Chirality Consider three reactions: Ethyl Grignard reacts with 2-pentanone, 3 hexanone, and 10, then with dilute acid, each separately. Which of these has a chiral center in the product? Review, Functional Groups What functional groups are in captopril, 11, a drug used to treat high blood pressure: Chirality* Identify the chiral centers in captopril, 11.
11 Chirality Which of the following have a stereogenic center(s)? Which are chiral molecules? R,S Nomenclature Determine whether each of the following is R or S Distinguishing Molecules For each of the pairs of compound, 12-17, classify them as a) identical, b) enantiomers, c) diastereomers, or d) constitutional isomers? Drawing Enantiomers and R,S Nomenclature Draw the enantiomer of 18 and 19. Also, determine whether the compound given is R or S Chiral Centers Find all the chirality centers in 20, streptimidone, an antibiotic, and determine for each whether it is R or S.
12
13 R,S Nomenclature Determine if 23A is R or S. How about 23B? Review of Reactions How would you convert 23A into 23B? Thinking About Stereochemistry* Would you really get 23B, and only 23B, in the last problem? Explain your reasoning Enantiomeric Pairs and Diastereomers Draw all possible structures for 1,2-dihydroxycyclopentane. Are there any enantiomeric pairs. Is there a meso compound? Are there any diastereomers? R,S Nomenclature In 21, 22, and 23 are drawings of 2-chlorobutane. For each compound, answer the question: Is this a drawing of the R or S enantiomer of 2-chlorobutane? Chirality Is 24 chiral? HINT: Tricky question Enantiomers and Diastereomers Draw stereorepresentations for all stereoisomers of 24. Label those that are meso compounds and those that are enantiomers Enantiomers and Diastereomers Draw stereorepresentations for all stereoisomers of 24A. Label those that are meso compounds and those that are enantiomers R,S Nomenclature Is compound 25 R or S (or neither)?
14 Isolating Enantiomers A chemist makes 2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetic acid (2-hydroxy-2-phenylethanoic acid). She reacts this acid with the natural enantiomer of cinchonine, a base (formula C 19 H 22 N 20 ) isolated from cinchona bark (and used to treat malaria) and carefully crystallizes the solution. The very first material to precipitate is separated from that which is the last to precipitate. When acidified, she finds the first material is (R)- 2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetic acid and the second is (S)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetic acid. Explain Enantiomer Ibuprofen has the structure 26, but only the S enantiomer is active as an antinflammatory. Draw it Chirality Does (1,3)-di-tert-butyl allene have an enantomeric pair? HINT: Allene is C double bond C double bond C R,S Nomenclature and Predictive Thinking Pretend those guys in Switzerland that developed the rules for R,S designation tried to name 27. Assume reasonable logic and decide if it is R or S. What is your logic? Chirality Is 28 chiral? Meso Compounds Is 29 a meso compound? Why or why not? Meso Compounds Is 30 a meso compound? Why or why not? R,S Nomenclature Assign R or S to each chiral (stereogenic) center in 31. HINT: Remember N inversion is fast (although P is not) R,S Nomenclature Is Useful Consider a general molecule with three chiral centers. How many isomers are possible? R,S Nomenclature Is Useful* Let the three centers in the molecule of the last problem be labeled consecutively as, for instance, RRS. What is the relationship between RRS and SRS? between RRS and SSR? between RSR and SRR? R,S Nomenclature and Predictive Thinking When (S)-1-chloro-2-methylbutane reacts with Cl 2 (by a mechanism that we have not covered) the product is 1,4-dichloro-2-methylbutane. Is the product R or S? What assumption(s) did you make, if any?
15
16 R,S Nomenclature Draw all possible structures of 2,3,4-tribromopentane and find the relationships between them. HINT: From a mathematical point of view, with all carbon atoms in the plane of the paper, the bromine atoms on C2, C3, and C4 can point either in or out: that gives 2 3 possible arrangements, all of which may not be distinguishable Chiral Compounds Is it true or false to say Every chiral compound has a diastereomer? Explain your answer S N 2 Attack and Stereochemistry Let CH 3 SC(H)(I)CH 3 be attacked in an S N 2 reaction with azide ion, N 3, as shown in 32. Is the product R or S? Did the configuration invert during the reaction? Did the name (that is, R or S) change? Why or why not? R, S, and Configuration Change Is it possible for that a substitution of X for Y in a molecule (where all other groups stay in the same absolute position) will lead to a change in name (R or S)? Is it possible for the name to not change with a change in configuration? Comment. HINT: Think about the rules for naming chiral centers D Shape Draw an accurate representation of the three dimensional shape of (S)-1,3-dichloropentane Reactions and Stereochemistry Treat 33 with AlH 4 followed by H +. What is the product? Pay attention to stereochemistry Reactions and Stereochemistry Treat 33 with dilute H + in ethanol. What is the product? Pay attention to stereochemistry Reactions and Stereochemistry If (R)-1-bromo-1-deutero-ethane is treated with triphenylphosphine to form the Wittig cation, what is the configuration (R or S) of that cation? HINT: Remember this is an S N 2 backside attack Chirality Is 34 chiral? Chirality Is 35 chiral? Chirality Is 36 chiral?
17 Chirality Is 37 chiral? Enantiomers, Diasteriomers, Same Molecule What is the relationship between the pairs of compounds, 38, 39, and 40? Choices are same molecule (which includes conformers), enantiomers, or diastereomers. HINT: Remember the easy way to answer this kind of question is to name the compounds.
a. Does the model have a plane of symmetry? Yes No The central carbon is said to be a stereocenter, stereogenic center, or chiral carbon.
 Name: TA Name Lab Section: Day Time OPTICAL ISOMERISM 1. Construct a model that has a central carbon atom with 4 different colored spheres attached to it, representing four different atoms or groups. Draw
Name: TA Name Lab Section: Day Time OPTICAL ISOMERISM 1. Construct a model that has a central carbon atom with 4 different colored spheres attached to it, representing four different atoms or groups. Draw
Chemistry 123: Physical and Organic Chemistry Topic 1: Organic Chemistry
 Concept Check: Topic 1: Conformation Winter 2009 Page 112 Concept Check: Topic 1: Conformation Winter 2009 Page 113 1 STEREOCHEMISTRY Winter 2009 Page 114 We have already covered two kinds of isomerism:
Concept Check: Topic 1: Conformation Winter 2009 Page 112 Concept Check: Topic 1: Conformation Winter 2009 Page 113 1 STEREOCHEMISTRY Winter 2009 Page 114 We have already covered two kinds of isomerism:
Chapter 7 Cyclic Compounds. Stereochemistry of Reactions
 Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 7 Cyclic Compounds. Stereochemistry of Reactions Solutions to In-Text Problems 7.3 Following the procedure in the
Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 7 Cyclic Compounds. Stereochemistry of Reactions Solutions to In-Text Problems 7.3 Following the procedure in the
Practice Hour Examination # 1-2
 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I Fall 2013 Practice Hour Examination # 1-2 Solutions Key Page 1 of 12 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Practice Hour Examination # 1-2 Monday,
CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I Fall 2013 Practice Hour Examination # 1-2 Solutions Key Page 1 of 12 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Practice Hour Examination # 1-2 Monday,
Copyright 2009 James K Whitesell
 Copyright 2009 James K Whitesell 5-1 These two molecules, cyclopropylcyclopentane and cyclobutycyclobutane have the same number of carbon and hydrogen atoms and thus they are constitutional isomers. 5-2
Copyright 2009 James K Whitesell 5-1 These two molecules, cyclopropylcyclopentane and cyclobutycyclobutane have the same number of carbon and hydrogen atoms and thus they are constitutional isomers. 5-2
B. A transition state represents a maximum on the reaction path diagram and can be isolated.
 Practice Hour Exam 2, Chemistry 2210, Organic Chemistry I 1. The most stable carbocation is: 2. Which of the following statements is true of transition states? A. A transition state represents a minimum
Practice Hour Exam 2, Chemistry 2210, Organic Chemistry I 1. The most stable carbocation is: 2. Which of the following statements is true of transition states? A. A transition state represents a minimum
Alkanes. Introduction
 Introduction Alkanes Recall that alkanes are aliphatic hydrocarbons having C C and C H bonds. They can be categorized as acyclic or cyclic. Acyclic alkanes have the molecular formula C n H 2n+2 (where
Introduction Alkanes Recall that alkanes are aliphatic hydrocarbons having C C and C H bonds. They can be categorized as acyclic or cyclic. Acyclic alkanes have the molecular formula C n H 2n+2 (where
CHAPTER 5. Stereoisomers
 CHAPTER 5 Stereoisomers We have already covered two kinds of isomerism: Constitutional Isomers (structural isomers) Stereoisomers Examples of Constitutional Isomers: Examples of Stereoisomers: Another
CHAPTER 5 Stereoisomers We have already covered two kinds of isomerism: Constitutional Isomers (structural isomers) Stereoisomers Examples of Constitutional Isomers: Examples of Stereoisomers: Another
CHAPTER 4 HW SOLUTIONS: ALKANES
 CAPTER W SOLUTONS: ALKANES CATEGORZATONS. assify each carbon atom pointed to below as,, or.. Draw an alkane that contains only: and carbon atoms carbon atoms and carbon atoms and carbon atoms or or or
CAPTER W SOLUTONS: ALKANES CATEGORZATONS. assify each carbon atom pointed to below as,, or.. Draw an alkane that contains only: and carbon atoms carbon atoms and carbon atoms and carbon atoms or or or
CHEM 241 ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES CHAP 3 ASSIGN H H
 CEM 241 ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES CAP 3 ASSIGN COMFORMATIONS AND cis-trans STEREOISOMERS 1. trans-1,2-dibromocyclohexane is represented by structure(s): D. II and III E. I and II 2. cis-1,3-dibromocyclohexane
CEM 241 ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES CAP 3 ASSIGN COMFORMATIONS AND cis-trans STEREOISOMERS 1. trans-1,2-dibromocyclohexane is represented by structure(s): D. II and III E. I and II 2. cis-1,3-dibromocyclohexane
Organic Chemistry Chapter 5 Stereoisomers H. D. Roth
 Organic Chemistry Chapter 5 Stereoisomers. D. Roth 11. Chirality of conformationally mobile systems ring compounds Monosubstituted cycloalkanes cannot have an asymmetric carbon in the ring, because there
Organic Chemistry Chapter 5 Stereoisomers. D. Roth 11. Chirality of conformationally mobile systems ring compounds Monosubstituted cycloalkanes cannot have an asymmetric carbon in the ring, because there
STEREOCHEMISTRY A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
 A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: STEREOCHEMISTRY 1. Determine the relationship between two given structures (which may be any of the kinds below). Also, define the following terms, and give examples of pairs
A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: STEREOCHEMISTRY 1. Determine the relationship between two given structures (which may be any of the kinds below). Also, define the following terms, and give examples of pairs
Full file at
 Chapter 2 - Alkanes: The Nature of Organic Compounds 1. Which of the following functional group classifications do not contain oxygen? A. ether B. thiol C. aldehyde D. ester E. amide 2. To which functional
Chapter 2 - Alkanes: The Nature of Organic Compounds 1. Which of the following functional group classifications do not contain oxygen? A. ether B. thiol C. aldehyde D. ester E. amide 2. To which functional
9. Stereochemistry: Introduction to Using Molecular Models
 9. Stereochemistry: Introduction to Using Molecular Models The first part of this document reviews some of the most important stereochemistry topics covered in lecture. Following the introduction, a number
9. Stereochemistry: Introduction to Using Molecular Models The first part of this document reviews some of the most important stereochemistry topics covered in lecture. Following the introduction, a number
CHAPTER 4 HW: ALKANES
 CAPTER 4 W: ALKANES CLASSES OF CARBON 1. assify each carbon atom pointed to below as 1, 2, 3 or 4. 2. Draw an alkane that contains only: 1 and 4 carbon atoms 2 carbon atoms 1 and 2 carbon atoms 1 and 3
CAPTER 4 W: ALKANES CLASSES OF CARBON 1. assify each carbon atom pointed to below as 1, 2, 3 or 4. 2. Draw an alkane that contains only: 1 and 4 carbon atoms 2 carbon atoms 1 and 2 carbon atoms 1 and 3
1. (3 pts) Circle the highest priority substituent of the following list:
 Ch 334 Midterm #3 November 17, 2006 Code 1. (3 pts) Circle the highest priority substituent of the following list: 2. (4 pts) Rank the following groups in order of increasing priority. Place the letter
Ch 334 Midterm #3 November 17, 2006 Code 1. (3 pts) Circle the highest priority substituent of the following list: 2. (4 pts) Rank the following groups in order of increasing priority. Place the letter
Chapter 3 AN INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC COMPOUNDS NOMENCLATURE, PHYSICAL PROPERTIES, REPRESENTATION OF STRUCTURE AND
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY, 2 ND EDITION PAULA YURKANIS BRUICE Chapter 3 AN INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC COMPOUNDS NOMENCLATURE, PHYSICAL PROPERTIES, AND REPRESENTATION OF STRUCTURE RAED M. AL-ZOUBI, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY, 2 ND EDITION PAULA YURKANIS BRUICE Chapter 3 AN INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC COMPOUNDS NOMENCLATURE, PHYSICAL PROPERTIES, AND REPRESENTATION OF STRUCTURE RAED M. AL-ZOUBI, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR
(1) Recall the different isomers mentioned in this tutorial.
 DAT Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 08: Conformational Analysis Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Isomers that differ by rotation about a single bond are called: Question #01 (A) Stereoisomers (B) Constitutional
DAT Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 08: Conformational Analysis Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Isomers that differ by rotation about a single bond are called: Question #01 (A) Stereoisomers (B) Constitutional
4. Stereochemistry of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 4. Stereochemistry of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 4 2003 Ronald Kluger Department of Chemistry University of Toronto The Shapes of Molecules! The
4. Stereochemistry of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 4 2003 Ronald Kluger Department of Chemistry University of Toronto The Shapes of Molecules! The
ch03 Student: A. anti B. gauche C. skewed D. eclipsed 2. What is the IUPAC name of the compound shown in the following Newman projection?
 ch03 Student: 1. Identify the conformation of butane shown below. A. anti B. gauche C. skewed D. eclipsed 2. What is the IUPAC name of the compound shown in the following Newman projection? A. 1,1,2,2-tetramethylethane
ch03 Student: 1. Identify the conformation of butane shown below. A. anti B. gauche C. skewed D. eclipsed 2. What is the IUPAC name of the compound shown in the following Newman projection? A. 1,1,2,2-tetramethylethane
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 Chapter 3 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Two types Saturated hydrocarbons Unsaturated hydrocarbons 3.1 Alkanes Also referred as aliphatic hydrocarbons General formula: CnH2n+2 (straight chain) and CnH2n (cyclic)
Chapter 3 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Two types Saturated hydrocarbons Unsaturated hydrocarbons 3.1 Alkanes Also referred as aliphatic hydrocarbons General formula: CnH2n+2 (straight chain) and CnH2n (cyclic)
(S)-(-)-Dopa, used to treat Parkinson's disease, and its medically ineffective (R)-(+) enantiomer
 C h a p t e r F i v e: Stereoisomerism N 2 2 N (S)-(-)-Dopa, used to treat Parkinson's disease, and its medically ineffective (R)-(+) enantiomer CM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter
C h a p t e r F i v e: Stereoisomerism N 2 2 N (S)-(-)-Dopa, used to treat Parkinson's disease, and its medically ineffective (R)-(+) enantiomer CM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter
STEREOCHEMISTRY OF ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES CONFORMATIONAL ISOMERS
 STEREOCHEMISTRY OF ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES CONFORMATIONAL ISOMERS 1 CONFORMATIONAL ISOMERS Stereochemistry concerned with the 3-D aspects of molecules Rotation is possible around C-C bonds in openchain
STEREOCHEMISTRY OF ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES CONFORMATIONAL ISOMERS 1 CONFORMATIONAL ISOMERS Stereochemistry concerned with the 3-D aspects of molecules Rotation is possible around C-C bonds in openchain
CHEMpossible. 261 Exam 1 Review
 CHEMpossible 261 Exam 1 Review A. Rank the following carboxylic acids from least acidic to most acidic: B. Draw the line-angle formulas for three acylic (non-cyclic) esters with the molecular formula C
CHEMpossible 261 Exam 1 Review A. Rank the following carboxylic acids from least acidic to most acidic: B. Draw the line-angle formulas for three acylic (non-cyclic) esters with the molecular formula C
Chapter 6 Principles of Stereochemistry
 6.1 (a) This compound is chiral. Methane is achiral. Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 6 Principles of Stereochemistry Solutions to In-Text Problems
6.1 (a) This compound is chiral. Methane is achiral. Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 6 Principles of Stereochemistry Solutions to In-Text Problems
Conformational Isomers. Isomers that differ as a result of sigma bond rotation of C-C bond in alkanes
 Conformational Isomers Isomers that differ as a result of sigma bond Isomers that differ as a result of sigma bond rotation of C-C bond in alkanes Bond Rotation and Newman Projections As carbon-carbon
Conformational Isomers Isomers that differ as a result of sigma bond Isomers that differ as a result of sigma bond rotation of C-C bond in alkanes Bond Rotation and Newman Projections As carbon-carbon
ORGANIC - EGE 5E CH. 5 - ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKANE NOMENCLATURE Before 1919, chemists literally had to memorize thousands of random (common) chemical names. IUPAC naming provides a systematic method to give every chemical
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKANE NOMENCLATURE Before 1919, chemists literally had to memorize thousands of random (common) chemical names. IUPAC naming provides a systematic method to give every chemical
KEY I. (28 points) i) NOTE: sp-hybridized carbanions make good nucleophiles for substitution reactions. Product A C C CH 3. Product B.
 I. (8 points) Page 1 A. omplete the following as necessary NT: sp-hybridized carbanions make good nucleophiles for substitution reactions NaN N Na Na (optional) i equivalents of Product A Product B a)
I. (8 points) Page 1 A. omplete the following as necessary NT: sp-hybridized carbanions make good nucleophiles for substitution reactions NaN N Na Na (optional) i equivalents of Product A Product B a)
Chem 201 Midterm Winter, 2013 Beauchamp
 hem 0 Midterm Winter, 0 Beauchamp Name Problems Points redit. Functional Group Nomenclature. Degrees of Unsaturation & Functional Groups or Various Nomenclature Terms. D structure, Functional Groups 0.
hem 0 Midterm Winter, 0 Beauchamp Name Problems Points redit. Functional Group Nomenclature. Degrees of Unsaturation & Functional Groups or Various Nomenclature Terms. D structure, Functional Groups 0.
Constitutional Isomers and Conformations of Alkanes & Cycloalkanes
 Discovering Molecular Models #1: Constitutional Isomers Conformations of Alkanes & Cycloalkanes There are no additional tutorial or laboratory notes. Read bring your course notes, as they provide all of
Discovering Molecular Models #1: Constitutional Isomers Conformations of Alkanes & Cycloalkanes There are no additional tutorial or laboratory notes. Read bring your course notes, as they provide all of
Constitutional Isomers and Conformations of Alkanes & Cycloalkanes
 Discovering Molecular Models #1: Constitutional Isomers Conformations of Alkanes & Cycloalkanes There are no additional tutorial or laboratory notes. Read bring your course notes, as they provide all of
Discovering Molecular Models #1: Constitutional Isomers Conformations of Alkanes & Cycloalkanes There are no additional tutorial or laboratory notes. Read bring your course notes, as they provide all of
Chapter 2 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes; Conformational and Geometrical Isomerism
 Chapter 2 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes; Conformational and Geometrical Isomerism Alkanes are hydrocarbons containing only single Bonds saturated General formula: CnH2n+2 Drawing chemical structures Several
Chapter 2 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes; Conformational and Geometrical Isomerism Alkanes are hydrocarbons containing only single Bonds saturated General formula: CnH2n+2 Drawing chemical structures Several
1. Discuss the the relative conformation analysis of 1,2-dimethylcyclohexane. H H H 3 C H H CH H 3 3 C H H
 1. Discuss the the relative conformation analysis of 1,2-dimethylcyclohexane. If we consider cis isomer of 1,2-dimethylcyclohexane, the e,a and a,e both conformer is optically active ads no element of
1. Discuss the the relative conformation analysis of 1,2-dimethylcyclohexane. If we consider cis isomer of 1,2-dimethylcyclohexane, the e,a and a,e both conformer is optically active ads no element of
1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound?
 CEM 331: Chapter 1/2: Structures (Atoms, Molecules, Bonding) 1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound? N C 2 C N C 2 C N 1 2 3 4 1: three sigma bonds and
CEM 331: Chapter 1/2: Structures (Atoms, Molecules, Bonding) 1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound? N C 2 C N C 2 C N 1 2 3 4 1: three sigma bonds and
(1) Check to see if the two compounds are identical. (2) Recall the definitions of stereoisomers, conformational isomers, and constitutional isomers.
 MCAT Organic Chemistry Problem Drill 04: Stereochemistry Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Determine the relationship of the molecules shown: O O Question #01 (A) Identical (B) Constitutional isomers (C)
MCAT Organic Chemistry Problem Drill 04: Stereochemistry Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Determine the relationship of the molecules shown: O O Question #01 (A) Identical (B) Constitutional isomers (C)
Conformational Analysis
 onformational Analysis Free Rotation about arbon-arbon Single Bonds A carbon carbon single bond is formed by the end-on overlap of cylindrically symmetrical sp 3 orbitals. Therefore, attached carbon atoms
onformational Analysis Free Rotation about arbon-arbon Single Bonds A carbon carbon single bond is formed by the end-on overlap of cylindrically symmetrical sp 3 orbitals. Therefore, attached carbon atoms
Organic Chemistry 1 CHM 2210 Exam 2 (October 10, 2001)
 Organic Chemistry 1 CM 2210 Exam 2 (October 10, 2001) Name (print): _ Signature: _ Student ID Number: _ There are 10 multiple choice problems (4 points each) on this exam. Record the answers to the multiple
Organic Chemistry 1 CM 2210 Exam 2 (October 10, 2001) Name (print): _ Signature: _ Student ID Number: _ There are 10 multiple choice problems (4 points each) on this exam. Record the answers to the multiple
Organic Chemistry 1 Lecture 6
 CEM 232 Organic Chemistry I Illinois at Chicago Organic Chemistry 1 Lecture 6 Instructor: Prof. Duncan Wardrop Time/Day: T & R, 12:30-1:45 p.m. January 28, 2010 1 Self Test Question Which form of strain
CEM 232 Organic Chemistry I Illinois at Chicago Organic Chemistry 1 Lecture 6 Instructor: Prof. Duncan Wardrop Time/Day: T & R, 12:30-1:45 p.m. January 28, 2010 1 Self Test Question Which form of strain
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition. Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i. Chapter 4 Alkanes
 Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 4 Alkanes Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 4 Alkanes Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Organic Chemistry, Fifth Edition
 Organic Chemistry, Fifth Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith Modified by Dr. Juliet Hahn Chapter 4 Alkanes Copyright 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without
Organic Chemistry, Fifth Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith Modified by Dr. Juliet Hahn Chapter 4 Alkanes Copyright 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without
Chapter 2. Alkanes and Cycloalkanes; Conformational and Geometrical Isomerism
 Chapter 2 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes; Conformational and Geometrical Isomerism Hydrocarbons are compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen. There are three main classes of hydrocarbons, based on the
Chapter 2 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes; Conformational and Geometrical Isomerism Hydrocarbons are compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen. There are three main classes of hydrocarbons, based on the
Exam 1 Chem 3045x Monday, October 1, 2001
 Exam 1 Chem 3045x Monday, October 1, 2001 Instructions: This is a closed book examination. Please print your name and social security number on the front page of the examination. Be sure to allot your
Exam 1 Chem 3045x Monday, October 1, 2001 Instructions: This is a closed book examination. Please print your name and social security number on the front page of the examination. Be sure to allot your
Lab Workshop 1: Alkane and cycloalkane conformations
 Lab Workshop : lkane and cycloalkane conformations ach student work group choose a Leader (reads activity out loud, poses questions to group), Facilitator (makes sure everyone is participating equally,
Lab Workshop : lkane and cycloalkane conformations ach student work group choose a Leader (reads activity out loud, poses questions to group), Facilitator (makes sure everyone is participating equally,
Why am I learning this, Dr. P?
 Chapter 4- Organic Compounds: Cycloalkanes and their Stereochemistry Ashley Piekarski, Ph.D. Why am I learning this, Dr. P? Cyclic compounds are commonly encountered in all classes of biomolecules: Proteins
Chapter 4- Organic Compounds: Cycloalkanes and their Stereochemistry Ashley Piekarski, Ph.D. Why am I learning this, Dr. P? Cyclic compounds are commonly encountered in all classes of biomolecules: Proteins
Dr. Steven Pedersen July 28, Chemistry 3A. Midterm 2
 Dr. Steven Pedersen July 28, 2015 hemistry A Midterm 2 Student name: ANSWER KEY Student signature: Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem Problem 4 Problem 5 Problem 6 Problem 7 Total Points (16 pts) (4 pts) (2 pts)
Dr. Steven Pedersen July 28, 2015 hemistry A Midterm 2 Student name: ANSWER KEY Student signature: Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem Problem 4 Problem 5 Problem 6 Problem 7 Total Points (16 pts) (4 pts) (2 pts)
Lesson 4. Molecular Geometry and Isomers II. Lesson 4 CH 3 HO H OH
 Lesson 4 Molecular Geometry and Isomers II 4 Lesson 4 3 O O 3 Organic Edge A. Structural Isomers (onstitutional Isomers) 1. Structural isomers are molecules that share the same molecular formula but differ
Lesson 4 Molecular Geometry and Isomers II 4 Lesson 4 3 O O 3 Organic Edge A. Structural Isomers (onstitutional Isomers) 1. Structural isomers are molecules that share the same molecular formula but differ
CHE 321 Summer 2010 Exam 2 Form Choose the structure(s) that represent cis-1-sec-butyl-4-methylcyclohexane. I II III
 CE 321 Summer 2010 Exam 2 orm 2 Multiple Choice Questions: 60 points 1. Choose the structure(s) that represent cis-1-sec-butyl-4-methylcyclohexane. I II III (A) I only (B) II only (C) I and II only II
CE 321 Summer 2010 Exam 2 orm 2 Multiple Choice Questions: 60 points 1. Choose the structure(s) that represent cis-1-sec-butyl-4-methylcyclohexane. I II III (A) I only (B) II only (C) I and II only II
Problems Points Credit
 hem 201 Final Fall, 2012 Beauchamp Name Problems Points redit 1. Functional Group Nomenclature (1 large structure) (R/S and E/Z too) 30 2. Types of Isomers, Degrees of Unsaturation 25 3. yclohexane onformations,
hem 201 Final Fall, 2012 Beauchamp Name Problems Points redit 1. Functional Group Nomenclature (1 large structure) (R/S and E/Z too) 30 2. Types of Isomers, Degrees of Unsaturation 25 3. yclohexane onformations,
ORGANIC - BRUICE 8E CH.3 - AN INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: INDEX OF HYDROGEN DEFICIENCY (STRUCTURAL) A saturated molecule is any molecule that has the maximum number of hydrogens possible for its chemical structure. The rule that
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: INDEX OF HYDROGEN DEFICIENCY (STRUCTURAL) A saturated molecule is any molecule that has the maximum number of hydrogens possible for its chemical structure. The rule that
Hour Examination # 1
 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I Fall 2013 Hour Examination # 1 Solutions Key Page 1 of 15 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Hour Examination # 1 Wednesday, September 25
CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I Fall 2013 Hour Examination # 1 Solutions Key Page 1 of 15 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Hour Examination # 1 Wednesday, September 25
1. The barrier to rotation around the C-C bonds for 2-methylpropane and 2,2-dimethylpropane are shown below.
 1. The barrier to rotation around the C-C bonds for 2-methylpropane and 2,2-dimethylpropane are shown below. E Rot = 14.2 kj/mol E Rot = 19.6 kj/mol a. Why does the potential energy of a molecule increase
1. The barrier to rotation around the C-C bonds for 2-methylpropane and 2,2-dimethylpropane are shown below. E Rot = 14.2 kj/mol E Rot = 19.6 kj/mol a. Why does the potential energy of a molecule increase
Stereochemistry. In organic chemistry, subtle differences in spatial arrangements can give rise to prominent effects.
 Stereochemistry This is study of the 3 dimensional arrangement in space of molecules. In organic chemistry, subtle differences in spatial arrangements can give rise to prominent effects. E.g. the isomers
Stereochemistry This is study of the 3 dimensional arrangement in space of molecules. In organic chemistry, subtle differences in spatial arrangements can give rise to prominent effects. E.g. the isomers
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Alkanes molecules consisting of carbons and hydrogens in the following ratio: C n H 2n+2 Therefore, an alkane having 4 carbons would have 2(4) + 2 hydrogens, which equals 10 hydrogens.
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Alkanes molecules consisting of carbons and hydrogens in the following ratio: C n H 2n+2 Therefore, an alkane having 4 carbons would have 2(4) + 2 hydrogens, which equals 10 hydrogens.
Chem 341 Organic Chemistry I Lecture Summary 10 September 14, 2007
 Chem 34 Organic Chemistry I Lecture Summary 0 September 4, 007 Chapter 4 - Stereochemistry of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Conformations of Cycloalkanes Cyclic compounds contain something we call Ring Strain.
Chem 34 Organic Chemistry I Lecture Summary 0 September 4, 007 Chapter 4 - Stereochemistry of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Conformations of Cycloalkanes Cyclic compounds contain something we call Ring Strain.
(2/94)(6,7,9/95)(8,9/97)(12/99)(1/00) Neuman Chapter 4
 4: Stereochemistry Tetrahedral Carbon Configurations Stereoisomers and R,S Assignments The Number and Types of Stereoisomers Drawing Structures of Stereoisomers Cyclic Molecules Optical Activity Preview
4: Stereochemistry Tetrahedral Carbon Configurations Stereoisomers and R,S Assignments The Number and Types of Stereoisomers Drawing Structures of Stereoisomers Cyclic Molecules Optical Activity Preview
When I lecture we will add more info, so leave spaces in your notes
 Title and Highlight Right side: NOTES! Topic: EQ: Date Date NOTES: Write out the notes from my website. Use different types of note-taking methods to help you recall info (different color pens/highlighters,
Title and Highlight Right side: NOTES! Topic: EQ: Date Date NOTES: Write out the notes from my website. Use different types of note-taking methods to help you recall info (different color pens/highlighters,
NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: Page 1 of 4
 NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: Page 1 of 4 Chemistry 2.339 Midterm Test Friday ctober 28, 2005 This test is worth 40 Marks. You must complete all work within the class period. Put all answers in the space provided.
NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: Page 1 of 4 Chemistry 2.339 Midterm Test Friday ctober 28, 2005 This test is worth 40 Marks. You must complete all work within the class period. Put all answers in the space provided.
Names. Chiral: A chiral object is not superimposable upon its mirror image. A chiral object contains the property of "handedness.
 CEM 241 IN-CLASS #3 MOLECULAR MODELS EXERCISE Names Stereoisomerism Construct a model containing a tetrahedral carbon (black ball) that is attached to four different atoms (use the green, orange, purple
CEM 241 IN-CLASS #3 MOLECULAR MODELS EXERCISE Names Stereoisomerism Construct a model containing a tetrahedral carbon (black ball) that is attached to four different atoms (use the green, orange, purple
Third Midterm Exam CHEM 255 Organic Chemistry I Prof. Bastin November 19, 2009
 Third Midterm Exam CEM 255 Organic Chemistry I Prof. Bastin November 19, 2009 Name Section Provide CLEAR, CONCISE answers using unambiguous, carefully drawn structures and arrows for all of the appropriate
Third Midterm Exam CEM 255 Organic Chemistry I Prof. Bastin November 19, 2009 Name Section Provide CLEAR, CONCISE answers using unambiguous, carefully drawn structures and arrows for all of the appropriate
CH 3 C 2 H 5. Tetrahedral Stereochemistry
 Ch 5 Tetrahedral Stereochemistry Enantiomers - Two non-superimposable mirror image molecules - They are stereoisomers with the same atoms and bonds, but different spatial geometries. - The two molecules
Ch 5 Tetrahedral Stereochemistry Enantiomers - Two non-superimposable mirror image molecules - They are stereoisomers with the same atoms and bonds, but different spatial geometries. - The two molecules
Chem 341 Jasperse Ch. 9 Handouts 1
 Chem 341 Jasperse Ch. 9 andouts 1 Ch. 9 Stereochemistry Stereoisomers have the same condensed formulas and basic bonding sequence, but have different 3-dimensional shape and cannot be interconverted 9.1,2
Chem 341 Jasperse Ch. 9 andouts 1 Ch. 9 Stereochemistry Stereoisomers have the same condensed formulas and basic bonding sequence, but have different 3-dimensional shape and cannot be interconverted 9.1,2
Departmental Final Examination. Organic Chemistry I Caffein
 Departmental Final Examination rganic Chemistry I 2423 Caffein Name CEMISTRY 2423 FINAL EXAM FALL, 2005 DIRECTINS: A periodic table is attached at the end of this exam. Please answer all questions as completely
Departmental Final Examination rganic Chemistry I 2423 Caffein Name CEMISTRY 2423 FINAL EXAM FALL, 2005 DIRECTINS: A periodic table is attached at the end of this exam. Please answer all questions as completely
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes
 Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
Chemistry 3719, Fall 2002 Exam 1 Name:
 Chemistry 3719, Fall 2002 Exam 1 Name: This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 600 points for Chemistry 3719/3719L. You have 50 minutes to complete the exam and you may use molecular models as
Chemistry 3719, Fall 2002 Exam 1 Name: This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 600 points for Chemistry 3719/3719L. You have 50 minutes to complete the exam and you may use molecular models as
comes forward STEREOISOMERS ISOMERS THAT ARE DIFFERENT BECAUSE OF THEIR ORIENTATION IN SPACE
 STEREOCEMISTRY SOME DEFINITIONS WIT EXAMPLES PRESENTING STEREO STRUCTURES CIRAL CENTER REPRESENTAITON goes back goes back in the plane of the paper comes forward comes forward DOTTED LINE - WEDGE goes
STEREOCEMISTRY SOME DEFINITIONS WIT EXAMPLES PRESENTING STEREO STRUCTURES CIRAL CENTER REPRESENTAITON goes back goes back in the plane of the paper comes forward comes forward DOTTED LINE - WEDGE goes
(a) (10 points) Fill in any hydrogens not shown and indicate the molecular formula of the compound in the box provided.
 1. Fundamentals (a) (10 points) Fill in any hydrogens not shown and indicate the molecular formula of the compound in the box provided. (b) (10 points) Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following
1. Fundamentals (a) (10 points) Fill in any hydrogens not shown and indicate the molecular formula of the compound in the box provided. (b) (10 points) Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following
Organic Chemistry Unit #2: Structure of Alkanes, Cycloalkanes, and Alkenes
 Organic hemistry Unit #2: Structure of Alkanes, ycloalkanes, and Alkenes Bring your model kits to class we will to learn to use them! Objectives: by the end of this unit, you should be able to... Interconvert
Organic hemistry Unit #2: Structure of Alkanes, ycloalkanes, and Alkenes Bring your model kits to class we will to learn to use them! Objectives: by the end of this unit, you should be able to... Interconvert
Enantiomers. nonsuperimposable mirror image Both Configuration will be opposite. Both Configuration will be opposite
 Optical Isomerism Isomerism of Organic Molecules: Two chiral centers Many organic compounds have more than one asymmetric carbon. The more asymmetric carbons a compound has, the more number of stereoisomers
Optical Isomerism Isomerism of Organic Molecules: Two chiral centers Many organic compounds have more than one asymmetric carbon. The more asymmetric carbons a compound has, the more number of stereoisomers
CHEM1902/ N-9 November 2014
 CEM1902/4 2014-N-9 November 2014 The elimination of 2 O from alcohol A can form the isomeric alkenes B and C. Elimination of Br from the alkyl halide D can generate the same two alkenes. 7 Assign the absolute
CEM1902/4 2014-N-9 November 2014 The elimination of 2 O from alcohol A can form the isomeric alkenes B and C. Elimination of Br from the alkyl halide D can generate the same two alkenes. 7 Assign the absolute
Stereochemistry CHAPTER SUMMARY
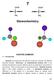 2 7 2 7. Introduction APTER SUMMARY Isomers are compounds with identical molecular formulas but different structural formulas. Structural or constitutional isomers differ in the bonding arrangement of
2 7 2 7. Introduction APTER SUMMARY Isomers are compounds with identical molecular formulas but different structural formulas. Structural or constitutional isomers differ in the bonding arrangement of
A. Structure and Nomenclature. Introduction of Organic Chemistry. Unit 2: Structure of Alkanes, Cycloalkanes, and Alkenes
 Organic hemistry #2 1 Introduction of Organic hemistry. Unit 2: Structure of Alkanes, ycloalkanes, and Alkenes Bring your model kits to class we will to learn to use them! Objectives: by the end of this
Organic hemistry #2 1 Introduction of Organic hemistry. Unit 2: Structure of Alkanes, ycloalkanes, and Alkenes Bring your model kits to class we will to learn to use them! Objectives: by the end of this
Problems Points Credit
 Chem 201 Midterm Winter, 2018 Beauchamp ame Problems Points Credit 1. Functional Group omenclature (1 large structure) 30 2. Resonance, Formal Charge, Arrows 18 3. Properties of Atoms, Logic Arguments
Chem 201 Midterm Winter, 2018 Beauchamp ame Problems Points Credit 1. Functional Group omenclature (1 large structure) 30 2. Resonance, Formal Charge, Arrows 18 3. Properties of Atoms, Logic Arguments
Chemistry 123: Physical and Organic Chemistry Topic 1: Organic Chemistry
 Topic 1: Mechanisms and Curved Arrows etc Reactions of Alkenes:.Similar functional groups react the same way. Why? Winter 2009 Page 73 Topic 1: Mechanisms and Curved Arrows etc Reactivity:.Electrostatic
Topic 1: Mechanisms and Curved Arrows etc Reactions of Alkenes:.Similar functional groups react the same way. Why? Winter 2009 Page 73 Topic 1: Mechanisms and Curved Arrows etc Reactivity:.Electrostatic
STEREOGENIC CENTER (Chiral Center,Asymmetric Center) Atom (usually carbon) to which 4 different groups are attached: W Z C X Y
 STEREOGENI ENTER (hiral enter,asymmetric enter) Atom (usually carbon) to which 4 different groups are attached: W Z X Y Many, but not all, molecules which contain a stereogenic center are chiral. (A molecule
STEREOGENI ENTER (hiral enter,asymmetric enter) Atom (usually carbon) to which 4 different groups are attached: W Z X Y Many, but not all, molecules which contain a stereogenic center are chiral. (A molecule
CHEMISTRY 112A FALL 2015 EXAM 1 SEPTEMBER 27, 2016 NAME- WRITE BIG STUDENT ID: SECTION AND/OR GSI IF YOU ARE IN THE LABORATORY COURSE:
 CHEMISTRY 112A FALL 2015 EXAM 1 SEPTEMBER 27, 2016 NAME- WRITE BIG STUDENT ID: SECTIN AND/R GSI IF YU ARE IN THE LABRATRY CURSE: You will have 75 minutes in which to work. BE NEAT! Non-legible structure
CHEMISTRY 112A FALL 2015 EXAM 1 SEPTEMBER 27, 2016 NAME- WRITE BIG STUDENT ID: SECTIN AND/R GSI IF YU ARE IN THE LABRATRY CURSE: You will have 75 minutes in which to work. BE NEAT! Non-legible structure
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY CHEM 2210 SECOND REVIEW EXAM FALL *A*
 ORGANI EMISTRY EM 2210 SEOND REVIEW EXAM ALL 1999 - *A* 1. What is the IUPA name of the compound shown? O A. cis-1-chloro-4-cyclohexanol B. cis-4-chlorocyclohexanol. trans-1-chloro-4-cyclohexanol trans-4-chlorocyclohexanol
ORGANI EMISTRY EM 2210 SEOND REVIEW EXAM ALL 1999 - *A* 1. What is the IUPA name of the compound shown? O A. cis-1-chloro-4-cyclohexanol B. cis-4-chlorocyclohexanol. trans-1-chloro-4-cyclohexanol trans-4-chlorocyclohexanol
13. Free Radical Chemistry
 hem 201 Study Session Final Beauchamp ame Problems Points redit 1. Functional Group omenclature (1 large structure) 2. Various possibilities: Types of Isomers, Degrees of Unsaturation, common nomenclature,
hem 201 Study Session Final Beauchamp ame Problems Points redit 1. Functional Group omenclature (1 large structure) 2. Various possibilities: Types of Isomers, Degrees of Unsaturation, common nomenclature,
2. 2D Lewis structure (large structure with possible formal charge) 20
 hem 201 Final Fall, 2017 Beauchamp ame Problems Points redit 1. Functional Group omenclature (1 large structure) 30 2. 2D Lewis structure (large structure with possible formal charge) 20 3. yclohexane
hem 201 Final Fall, 2017 Beauchamp ame Problems Points redit 1. Functional Group omenclature (1 large structure) 30 2. 2D Lewis structure (large structure with possible formal charge) 20 3. yclohexane
Please provide clear and concise answers to all of the following questions. Use equations and/or drawings to support your answers where appropriate.
 Organic hemistry I (230-001) Examination II October 27, 2004 Key Name (PINT LEGIBLY): Please provide clear and concise answers to all of the following questions. Use equations and/or drawings to support
Organic hemistry I (230-001) Examination II October 27, 2004 Key Name (PINT LEGIBLY): Please provide clear and concise answers to all of the following questions. Use equations and/or drawings to support
Chapter 2: An Introduction to Organic Compounds
 Chapter : An Introduction to Organic Compounds I. FUNCTIONAL GROUPS: Functional groups with similar structure/reactivity may be "grouped" together. A. Functional Groups With Carbon-Carbon Multiple Bonds.
Chapter : An Introduction to Organic Compounds I. FUNCTIONAL GROUPS: Functional groups with similar structure/reactivity may be "grouped" together. A. Functional Groups With Carbon-Carbon Multiple Bonds.
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2
 C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
CHEM 231 (Davis) Organic Chemistry FINAL EXAM May 15, YOUR NAME (Last, First, M.I.) DISCUSSION SECTION #53 (5 Points)
 CHEM 231 (Davis) rganic Chemistry FINAL EXAM May 15, 2006 YUR NAME (Last, First, M.I.) DISCUSSIN SECTIN #53 (5 Points) Initial of last name Instructions Please fill in your name in the space above and
CHEM 231 (Davis) rganic Chemistry FINAL EXAM May 15, 2006 YUR NAME (Last, First, M.I.) DISCUSSIN SECTIN #53 (5 Points) Initial of last name Instructions Please fill in your name in the space above and
1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound?
 EM 331: hapter 1/2: Structures (Atoms, Molecules, Bonding) 1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound? N 2 N 2 N 1 2 3 4 2. What hybrid orbitals are used to
EM 331: hapter 1/2: Structures (Atoms, Molecules, Bonding) 1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound? N 2 N 2 N 1 2 3 4 2. What hybrid orbitals are used to
Chemistry M11 Spring 2010 Examination #3 ANSWER KEY pp. 1
 Chemistry M11 Spring 2010 Examination #3 ASWER KEY pp. 1 or Questions 1 2, consider the hydrogenation of trans-3-methyl-2-pentene in the presence of a transition metal catalyst. 1. C Determine the major
Chemistry M11 Spring 2010 Examination #3 ASWER KEY pp. 1 or Questions 1 2, consider the hydrogenation of trans-3-methyl-2-pentene in the presence of a transition metal catalyst. 1. C Determine the major
CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Text Sections (N0 1.9, 9-11) Homework: Chapter 1:
 CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Atomic Structure - Valence Electrons Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule - Ionic bond - Covalent bond How to write Lewis
CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Atomic Structure - Valence Electrons Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule - Ionic bond - Covalent bond How to write Lewis
unsaturated (one or more pi bonds) alkanes alkenes alkynes benzene naming alkanes C 4 H 10 C 5 H 12 C 6 H 14 C 7 H 16 C 8 H 18 C 9 H 20 C 10 H 22
 hapter 4: Alkanes and ycloalkanes [Sections: 4.1-4.14] Basic Organic ompound Nomenclature hydrocarbons: comprised of just carbon and hydrogen saturated (no pi bonds) unsaturated (one or more pi bonds)
hapter 4: Alkanes and ycloalkanes [Sections: 4.1-4.14] Basic Organic ompound Nomenclature hydrocarbons: comprised of just carbon and hydrogen saturated (no pi bonds) unsaturated (one or more pi bonds)
EXAMINATION 1 Chemistry 3A. Making up an I Grade If you are, please indicate the semester during which you took previous Chem 3A and the Instructor
 1 EXAMINATION 1 Chemistry 3A Key Name: Print first name before second! Use capital letters! SID #: Peter Vollhardt February 28, 2017 GSI (if you are taking Chem 3AL): Please provide the following information
1 EXAMINATION 1 Chemistry 3A Key Name: Print first name before second! Use capital letters! SID #: Peter Vollhardt February 28, 2017 GSI (if you are taking Chem 3AL): Please provide the following information
California State Polytechnic University, Pomona Nomenclature (one structure) 25
 alifornia State Polytechnic University, Pomona 1 hem 314 Final Exam Spring, 2005 Beauchamp ame Problem Points redit 1. omenclature (one structure) 25 2. 2D Lewis structure (large structure with 20 possible
alifornia State Polytechnic University, Pomona 1 hem 314 Final Exam Spring, 2005 Beauchamp ame Problem Points redit 1. omenclature (one structure) 25 2. 2D Lewis structure (large structure with 20 possible
Please read and sign the Honor Code statement below:
 CHEM 3311 Exam #2 Name Dr. Minger June 22, 2015 Please read and sign the Honor Code statement below: I pledge that on my honor, as a University of Colorado at Boulder student, I have neither given nor
CHEM 3311 Exam #2 Name Dr. Minger June 22, 2015 Please read and sign the Honor Code statement below: I pledge that on my honor, as a University of Colorado at Boulder student, I have neither given nor
STEREOCHEMISTRY. 2. Define the following, and tell whether or not a given compound or structure fits the description or possesses the feature.
 A STUDENT SOULD BE ABLE TO: STEREOEMISTRY 1. Determine the relationship between two given structures (which may be any of the kinds below). Also, define each of the following terms, and give examples of
A STUDENT SOULD BE ABLE TO: STEREOEMISTRY 1. Determine the relationship between two given structures (which may be any of the kinds below). Also, define each of the following terms, and give examples of
Stereochemistry. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition
 Stereochemistry Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition Stereochemistry! Some objects are not the same as their mirror images (technically, they have no plane of symmetry)! A right-hand glove
Stereochemistry Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition Stereochemistry! Some objects are not the same as their mirror images (technically, they have no plane of symmetry)! A right-hand glove
Part I. Multiple choice. (4 points each.) Choose the one best answer and mark your answer on the ScanTron sheet.
 Test 3 Chemistry 2321 April 25, 2003 McMurry, Chapters 9-11 103 Total Points Name Please Print Part I. Multiple choice. (4 points each.) Choose the one best answer and mark your answer on the ScanTron
Test 3 Chemistry 2321 April 25, 2003 McMurry, Chapters 9-11 103 Total Points Name Please Print Part I. Multiple choice. (4 points each.) Choose the one best answer and mark your answer on the ScanTron
Alkanes 3/27/17. Hydrocarbons: Compounds made of hydrogen and carbon only. Aliphatic (means fat ) - Open chain Aromatic - ring. Alkane Alkene Alkyne
 Alkanes EQ 1. How will I define Hydrocarbons? 2. Compare and contrast the 3 types of hydrocarbons (Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes). Hydrocarbons: Compounds made of hydrogen and carbon only. Aliphatic (means
Alkanes EQ 1. How will I define Hydrocarbons? 2. Compare and contrast the 3 types of hydrocarbons (Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes). Hydrocarbons: Compounds made of hydrogen and carbon only. Aliphatic (means
STEREOGENIC CENTER (Chiral Center,Asymmetric Center)
 STEREOGENI ENTER (hiral enter,asymmetric enter) Atom (usually carbon) to which 4 different groups are attached: W Z X Y Many, but not all, molecules which contain a stereogenic center are chiral. (A molecule
STEREOGENI ENTER (hiral enter,asymmetric enter) Atom (usually carbon) to which 4 different groups are attached: W Z X Y Many, but not all, molecules which contain a stereogenic center are chiral. (A molecule
More Tutorial at
 1. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question (50 pts). 1) Which of the following statements about propene, CH3CH CH2, is 1) correct? A) There
1. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question (50 pts). 1) Which of the following statements about propene, CH3CH CH2, is 1) correct? A) There
Form 0 CHE321 Exam 1 9/26/2006
 CE321 Exam 1 9/26/2006 Multiple Choice Questions. 60 points 1. Draw the two best contributing structures for methylimidate. To get you started a partial structure is given. C C C Choose the incorrect statement.
CE321 Exam 1 9/26/2006 Multiple Choice Questions. 60 points 1. Draw the two best contributing structures for methylimidate. To get you started a partial structure is given. C C C Choose the incorrect statement.
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 201/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry CHE1502/201/1/2016
 CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
Loudon Chapter 7 Review: Cyclic Compounds Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 8/24/2017
 Compounds with a single ring are monocyclic. For example: Assuming they have no double or triple bonds, they each have one degree of unsaturation. This means that their formulas follow the pattern C nh
Compounds with a single ring are monocyclic. For example: Assuming they have no double or triple bonds, they each have one degree of unsaturation. This means that their formulas follow the pattern C nh
EXAMINATION 1 Chemistry 3A SID #:
 EXAMINATION hemistry A Name: Print first name before second! Use capital letters! SID #: Peter Vollhardt February, 08 GSI (if you are taking hem AL): Please provide the following information if applicable.
EXAMINATION hemistry A Name: Print first name before second! Use capital letters! SID #: Peter Vollhardt February, 08 GSI (if you are taking hem AL): Please provide the following information if applicable.
OChem1 Old Exams. Chemistry 3719 Practice Exams
 OChem1 Old Exams Chemistry 3719 Practice Exams Fall 2017 Chemistry 3719 Practice Exam A1 This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 600 points for Chemistry 3719/3719L. You have 50 minutes to complete
OChem1 Old Exams Chemistry 3719 Practice Exams Fall 2017 Chemistry 3719 Practice Exam A1 This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 600 points for Chemistry 3719/3719L. You have 50 minutes to complete
