Comparison between leached metakaolin and leached diatomaceous earth as raw materials for the synthesis of ZSM-5
|
|
|
- Laura Warner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Aguilar-Mamani et al. SpringerPlus 2014, 3:292 a SpringerOpen Journal RESEARCH Open Access Comparison between leached metakaolin and leached diatomaceous earth as raw materials for the synthesis of ZSM-5 Wilson Aguilar-Mamani 1,2*, Gustavo García 1,3, Jonas Hedlund 1 and Johanne Mouzon 1 Abstract Inexpensive raw materials have been used to prepare ZSM-5 zeolites with SiO 2 /Al 2 O 3 molar ratios in the range Kaolin or Bolivian diatomaceous earth was used as aluminosilicate raw materials and sodium hydroxide and n-butylamine were used as mineralizing agents and template. Dealumination of the raw materials by acid leaching made it possible to reach appropriate SiO 2 /Al 2 O 3 ratios and to reduce the amount of iron and other impurities. After mixing the components and aging, hydrothermal treatment was carried out and the products were recovered The results clearly show for the first time that well-crystallized ZSM-5 can be directly prepared from leached metakaolin or leached diatomaceous earth using sodium hydroxide and n-butylamine as mineralizing agents and template under appropriate synthesis conditions. A longer induction time prior to crystallization was observed for reaction mixtures prepared from leached diatomaceous earth, probably due to slower digestion of the fossilized diatom skeletons as compared with that for microporous leached metakaolin. The use of leached diatomaceous earth allowed higher yield of ZSM-5 crystals within comparable synthesis times. However, low amounts of Mordenite formed, which was related to the high calcium content of diatomaceous earth. Another considerable advantage of diatomaceous earth over kaolin is that diatomaceous earth does not require heat treatment at high temperature for metakaolinization. Keywords: Kaolin; Diatomaceous earth; n-butylamine; ZSM-5 zeolite Introduction The zeolite ZSM-5 (Zeolites Socony Mobil) is an aluminosilicate with high silica ratio with suitable properties for catalysis, adsorption and membrane applications (Jacobs 1981, Tavolaro and Drioli 1999, Weitkamp 2000). Researchers (Argauer and Landolt 1972) of Mobil Oil Corporation obtained the first patent on the synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite, in which they described that this zeolite can be formed with molar ratios of SiO 2 /Al 2 O 3 varying between 20 and 120. Depending on this ratio, the acidity and surface properties of ZSM-5 vary and therefore it is important to carefully control this parameter in the final product (Armaroli et al. 2006, Shirazi et al. 2008). Typical syntheses of ZSM-5 require sources of silicon and aluminium, a mineralizer (e.g. OH or F )andan * Correspondence: gonzalo316@gmail.com 1 Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, Luleå, Sweden 2 Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science and Technology, San Simon University, Cochabamba, Bolivia Full list of author information is available at the end of the article organic molecule as templating agent. Quaternary ammonium compounds like tetrapropyl ammonium bromide (TPA-Br) (Padovan et al. 1984, Shirazi et al. 2008) and tetrapropyl ammonium hydroxide (TPA-OH) (Kotasthane and Shiralkar 1986) are mostly used for the synthesis of ZSM-5. Unfortunately, these quaternary ammonium compounds are rather expensive. The molecule n-butylamine was reported (Sang et al. 2004, Zhao 2005, Martins et al. 2006, Feng et al. 2009) as an alternative templating agent to replace TPA-Br and TPA-OH and is about 100 times less expensive on a molar basis. In the past two decades, efforts have also been undertaken to identify inexpensive Si and Al sources to synthesize ZSM-5(Chareonpanich et al. 2004, Sanhueza et al. 2004, Mignoni et al. 2007, Aliev et al. 2011) and it has been shown that kaolin clay and diatomaceous earth are two suitable and inexpensive sources of silica and alumina. Kaolin clay contains kaolinite with a SiO 2 /Al 2 O 3 molar ratio close to 2 and therefore it is well suited for the preparation of low-silica zeolites such as zeolite A (Costa 2014 Aguilar-Mamani et al.; licensee Springer. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly credited.
2 Aguilar-Mamani et al. SpringerPlus 2014, 3:292 Page 2 of 10 et al. 1988, Murat et al. 1992, Chandrasekhar et al. 1997, Sanhueza et al. 1999). To obtain this zeolite from kaolin, two steps are necessary: first, a thermal treatment of kaolin to obtain an amorphous and reactive material denoted metakaolin. The second step is a hydrothermal treatment to convert metakaolin to zeolite in an alkaline aqueous medium. Preparation of zeolites with higher SiO 2 /Al 2 O 3 molarratiossuchaszeolitesx(delucas et al. 1992, Caballero et al. 2007, Colina and Llorens 2007) and Y (Bosch et al. 1983, Atta et al. 2007) from kaolinite has also been reported. However, the syntheses of these zeolites require either an increase of the amount of silica or partial removal of aluminium. The first alternative implies using an additional source of silica with high solubility, e.g. sodium silicate. The second alternative, i.e. dealumination, consists in either leaching kaolin in a solution of an inorganic acid (HCl, H 2 SO 4, HNO 3 ) (Ford 1992) or alternatively calcining the kaolin with an inorganic acid (H 2 SO 4 ) (Colina et al. 2001, Colina et al. 2002) The synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite from kaolin with additional sources of silica has been reported in patent (Reid 1982) and research papers (Khatamian and Irani 2009, Kovo et al. 2009). Dealumination of metakaolinite to synthesize ZSM-5 has also been investigated (Madhusoodana et al. 2005); (Zhang et al. 2007); (Madhusoodana et al. 2001). In all these studies, expensive tetrapropylamine was used as template. The synthesis of ZSM-5 with a high SiO 2 /Al 2 O 3 molar ratio from metakaolin and silica sol and less expensive n-butylamine has been reported (Feng et al. 2009). However, to the best of our knowledge, a combination of dealumination of metakaolin by acid treatment together with the use of n-butylamine as a template has not yet been reported. Diatomaceous earth is another inexpensive source of silica, which is a sedimentary rock comprised of fossilized skeletal remains of diatoms. It consists essentially of amorphous hydrated silica and a small amount of alumina and also impurities such as iron (Sanhueza et al. 2003). It can be used to produce mesoporous material such as MCM-41 (Sanhueza et al. 2006) and also both low and high silica zeolites such as A (Ghosh et al. 1994), P (Wajima et al. 2008) or NaP (Wajima et al. 2006), analcime (Chaisena and Rangsriwatananon 2005); (Rangsriwatananon et al. 2008), cancrinite (Chaisena and Rangsriwatananon 2005), hydroxisodalite (Chaisena and Rangsriwatananon 2005), NaY (Chi et al. 2011) and mordenite (Sanhueza et al. 2003). In most of these syntheses, the raw diatomaceous earth was acid treated to remove iron and other impurities. The conversion of diatomaceous earth to ZSM-5 was also studied in combination with other raw materials such as paper sludge ash (Wajima et al. 2008) or volcanic ash (Aliev et al. 2011). However, there are a few studies on the synthesis of ZSM-5 by using only diatomaceous earth as silica source. In these studies, diethanolamine(sanhueza et al. 2004) and expensive tetrapropylammonium bromide (Shan et al. 2004) were used as templates and these synthesis required quite long crystallization times from 40 hours to 6 days at a quite high temperature of 180 C. In the present work, we show for the first time that leached metakaolinite or diatomaceous earth in combination with sodium hydroxide and n-butylamine can be used as inexpensive raw materials for the synthesis of ZSM-5 without using an additional source of silica. However, both sources of alumino-silica are shown to behave differently during the course of synthesis and to lead to slightly different reaction products. In particular, we discuss these discrepancies in terms of composition, morphology, and porosity of the raw materials. Experimental Raw materials Kaolin (Riedel de Haen, pro analysi), diatomaceous earth (Murmuntani zone in the locality of Llica, Potosi, Bolivia), sodium hydroxide (Sigma Aldrich, reagent grade, 98%, anhydrous pellets), n-butylamine (Sigma Aldrich, 99.5%) and hydrochloric acid (Merk, pro analysi 37%) were used as reagents. Heat treatment Kaolin was first calcined in a porcelain crucible that was placed in a furnace and heated at a rate of 8 C/min in air. When the temperature reached 750 C, this temperature was maintained for 2 h to obtain metakaolin and the temperature in the furnace was then reduced to room temperature. It was not necessary to carry out the heat treatment for the diatomaceous earth in order to obtain ZSM-5, and consequently, this material was not heat treated. On the other hand, if the heat treatment of kaolin was omitted, no zeolite formed. Dealumination of raw materials Metakaolin and diatomaceous earth were acid leached in a spherical glass container under reflux conditions in a thermostated oil bath maintained at 115 C. Metakaolin or diatomaceous earth was stirred in hydrochloric acid (3 M) for 150 minutes. The metakaolin or diatomaceous earth to acid weight ratio was 1:17. Subsequently, the suspension was quenched and the acid leached product was washed with distilled water. Finally, the product was separated by filtration and the filter cake was washed with distilled water until the ph reached a value close to 7. Hydrothermal synthesis The synthesis mixtures were prepared by mixing the aluminosilicate sources with distilled water, n-butylamine
3 Aguilar-Mamani et al. SpringerPlus 2014, 3:292 Page 3 of 10 (NBA) and sodium hydroxide. The molar ratios in the synthesis mixtures were: Na 2 O/SiO 2 = 0.18; SiO 2 /Al 2 O 3 = X; SiO 2 /NBA = 7; H 2 O/SiO 2 = 30, where X = 33 and 44 for leached metakaolin and leached diatomaceous earth, respectively. The mixtures were aged under stirring for 24 hours at room temperature and were thereafter hydrothermally heated in Teflon lined stainless steel autoclaves kept for different times in an oil bath at 165 C. After hydrothermal treatment, the solids were recovered by filtration and washed with distilled water until the ph reached a value close to 7. The powders were dried at 100 C overnight and finally calcined at 550 C for 6 hours to remove the template. Characterization of the products The chemical compositions of kaolin, diatomaceous earth, leached aluminosilicates and the final products were determined using inductively coupled plasma-sector field mass spectrometry (ICP-SFMS). Samples of 0.1 g were fused with 0.4 g of LiBO 2 and dissolved in HNO 3. Crystallinity was examined by X-ray diffractometry (XRD) using a PANalytical Empyrean X-ray Diffractometer equipped with Cu LFF HR X-ray tube, a graphite monochromator, and a PIXcel3D detector. The X-ray tube was operated at 30 ma and 40 kv. The investigated 2θ range was from 5 to 50 with a step size of The degree of crystallinity was calculated by using the area of characteristic peaks of ZSM-5 between 22 and 25 after background removal following the equation by van Hooff (Vanhooff et al. 1991). ZSM-5 crystals with an average length of 10 μm synthesized from silicic acid and TPAOH by following the method reported by Lechert and Kleinwort (Robson and Lillerud 2001) were used as standard. The morphology of the ZSM-5 crystals was studied by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Magellan 400, FEI Company) without coating. The chemical composition of individual crystals was determined by energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS, 80 mm 2 X-max detector, Oxford Instruments) at an accelerating voltage of 10 kv. Nitrogen adsorption-desorption data were recorded with an ASAP 2010 equipment from Micrometrics to determine the BET specific surface area, total pore volume and micropore volume of the raw materials and reaction products, as well as the reference crystals. The weight percentage of solid retentate after aging was determined by filtration through a 1 μm filter paper and gravimetric method, while the filtrates were analyzed by ICP-SFMS. Results Characterization of the starting materials X-ray diffractograms of the raw aluminosilicates and dealuminated counterparts are shown in Figure 1. Kaolin of course contains mostly kaolinite (evidenced by reflections at 2θ = 12.33; 19.80; 20.40; and 35.11) but also traces of quartz (2θ = 20.85; 26.66) and muscovite (2θ = 8.83; 35.06). Kaolin after calcination and leaching was mostly an amorphous material with weak characteristic peaks of muscovite and quartz. On the other hand, raw diatomaceous earth shows the occurrence of halite NaCl (2θ = 27.41; 31.76; 45.53), muscovite (2θ = 8.83; 27.83; 35,06 ), albite (2θ = 22.03; 23.70) and quartz (2θ = 20.85; 26.66) in addition to amorphous material. After acid treatment and the subsequent washing, the amorphous material remained and NaCl was removed, but the other minor constituents were still present (muscovite, albite and quartz). The chemical compositions of the raw and leached materials measured by ICP-SFMS are given in Table 1. Raw kaolin and diatomaceous earth had a SiO 2 /Al 2 O 3 molar ratio of 2.2 and 15, respectively. This ratio was successfully increased by acid leaching to 33 and 44 for kaolin and diatomaceous earth, respectively. Acid leaching also reduced significantly the concentration of impurities in both materials. Finally, the leached materials had comparable compositions in terms of magnesium, potassium and iron. However, leached diatomaceous earth was approximately 4 times richer in sodium and calcium, which can be understood from the presence of NaCl and calcium compounds in the raw diatomaceous earth originating from a region close the salt lake Uyuni. Figure 2 shows the morphology of the raw materials and leached materials revealed by SEM. Kaolin is composed of stacks of platelets with hexagonal symmetry which is typical of natural kaolinites (Figure 2(a)). The leached metakaolin (Figure 2(b)) has very similar platelet morphology but the surface area increased from 12 to 288 m 2 /g as presented in Table 2. This is not surprising since acid-leached metakolin is known to form microporous silica (Madhusoodana et al. 2001); (Zhang et al. 2007). Raw diatomaceous earth (Figure 2(d)) exhibited large particles with typical shapes of diatomaceous biogenic sediments. Some diatomaceous earth particles were partially broken in smaller pieces by the mechanical action of stirring during the acid treatment but their characteristic shapes could still be distinguished (Figure 2(e)). Leaching of diatomaceous earth only caused a slight increase in specific surface area (from 38 to 55 m 2 /g; Table 2). Hydrothermal synthesis Hydrothermal synthesis in terms of composition of the synthesis mixture and synthesis time was first optimized to maximize the yield of ZSM-5 using leached metakaolin as a raw material. The composition used in this work was found to produce the highest yield of ZSM-5 crystals. Figure 3 shows the evolution of XRD crystallinity compared with a reference sample composed of 6 10 μm ZSM-5 crystals. It can be noticed in Figure 3(a) that samples prepared from leached metakaolin reached maximum crystallinity for synthesis times between 9
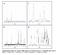
4 Aguilar-Mamani et al. SpringerPlus 2014, 3:292 Page 4 of 10 Figure 1 XRD diffractograms of the raw materials and acid-leached materials. and 12 hours before decreasing for prolonged hydrothermal treatments. The reaction parameters of the dealumination and hydrothermal treatments obtained on kaolin were employed for diatomaceous earth. As shown in Figure 3(b), the best crystallinity for leached diatomaceous earth was obtained for 12 hours of synthesis. Characterization of the crystalline products The diffractograms of the final reaction products obtained from both types of raw materials after 12 h synthesis are presented in Figure 4. The main characteristic peaks correspond to the MFI structure (2θ = 7.9; 8.7; 23.0 etc.) in good agreement with the reference pattern PDF The intensities of the main peak of quartz are similar in both samples and of the same order of magnitude as in the leached materials. Therefore, the quartz content is similar in both samples and originates from the raw materials. However, the reaction product obtained from diatomaceous earth contained traces of mordenite, approximately 5% of the intensity of the main peak of ZSM-5. The composition of the final products after 12 h synthesis was determined by ICP-SFMS analysis and the results were presented in Table 1. The average SiO 2 /Al 2 O 3 molar ratio was 23 and 40 for the reaction products obtained from leached metakaolin and diatomaceous earth, respectively. From these data, the reaction products could be considered as quite pure ZSM-5 with traces of mordenite formed during synthesis and of quartz remaining from the raw material. The morphology of the reaction products was studied by SEM and typical images were presented in Figure 5. Synthesis from leached metakaolin resulted in the formation of flat tablet shaped ZSM-5 crystals with a diameter of 5 6 μm, but also some smaller particles, as shown in Figure 5(a). In contrast, the ZSM-5 crystals obtained from leached diatomaceous earth were rounded with average Table 1 Compositions (in mole%) of kaolin, diatomaceous earth, leached metakaolin, leached diatomaceous earth and ZSM-5 products by ICP-SFMS Composition Kaolin Leached metakaolin ZSM-5 (K) Diatomaceous earth Leached diatomaceous earth ZSM-5 (D) SiO Al 2 O CaO Fe 2 O K 2 O MgO Na 2 O Mol SiO 2 /Al 2 O
5 Aguilar-Mamani et al. SpringerPlus 2014, 3:292 Page 5 of 10 Figure 2 Morphology of the raw materials and leached materials. (a) Kaolin (50000x magnification). (b) Leached metakaolin (LMK) (50000x magnification). (c) Solid part of LMK after aging (50000x magnification). (d) Diatomaceous earth (5000x magnification). (e) Leached diatomaceous earth (LD) (50000x magnification). (f) Solid part of LD after aging (50000x magnification). Table 2 Surface area and pore volumes derived from nitrogen adsorption data for the raw, leached materials, final products and standard sample Sample BET surface area (m 2 /g) Total pore volume (cm 3 /g) Micropore volume (cm 3 /g) Kaolin Leached metakaolin Diatomaceous earth Leached diatomaceous earth ZSM-5 (K) 255 (82%) (68%) ZSM-5 (D) 298 (96%) (82%) ZSM-5 standard
6 Aguilar-Mamani et al. SpringerPlus 2014, 3:292 Page 6 of 10 Figure 3 Crystallinity as a function of time of the reaction products prepared from acid leached materials. (a) Leached metakaolin. (b) Leached diatomaceous earth. diameter around 7 8 μm and aspect ratio close to 1 (Figure 5(b)). This sample also contained smaller particles and particularly small slabs as those encircled in Figure 5(b), which were attributed to mordenite. Discussion As shown above, the combination of both sodium hydroxide and n-butylamine together with leached metakaolin or leached diatomaceous earth was efficient to produce micron-sized ZSM-5 crystals within similar synthesis times. However, the reaction mechanism seems to differ depending on which alumino-silica source was used. Figure 3(a) clearly shows that crystal growth is triggered after an induction period of 2 h and slowly progresses until maximum crystallinity is reached after 9 h when leached metakaolin was used. In contrast, the induction Figure 4 XRD diffractograms of the products obtained after 12 hours of synthesis from acid leached materials. (a) Leached metakaolin. (b) Leached diatomaceous earth.
7 Aguilar-Mamani et al. SpringerPlus 2014, 3:292 Page 7 of 10 Figure 5 SEM images of ZSM-5 crystals from kaolin and diatomaceous earth. (a) Kaolin (5000x magnification). (b) Diatomaceous earth (5000x magnification). period was extended to 6 h before a sudden burst of crystal growth occurred between 8 and 9 h, if leached diatomaceous earth was used as alumino-silica source (Figure 3(b)). The differences in growth rates are not yet understood. However, the difference in induction period between both synthesis mixtures may be related to the state of the synthesis mixtures after 24 h aging and before hydrothermal treatment. After filtration through a1-μm filter paper, 26 and 80 wt.% of the original solid material remained from the aged synthesis mixtures prepared from leached metakaolin and leached diatomaceous earth, respectively. The filtrates were found to be silica-rich sols by ICP-SFMS (SiO 2 /Al 2 O 3 molar ratio ~ ). As shown in Figure 2(c), the solid retentate of the aged synthesis mixture prepared from leached metakaolin consisted of poorly defined platelets with a SiO 2 / Al 2 O 3 molar ratio of 7.5, which probably stem from undigested muscovite or other materials that did not become microporous or possibly sintered upon calcination. On the other hand in Figure 2(f), particles with typical morphology of fossilized diatom still comprised the main constituent of the diatomaceous earth synthesis mixture after aging, even though further communition occurred by mechanical mixing during aging. Therefore, the longer induction time encountered for the leached diatomaceous earth system can be imparted to the heavily condensed state still present after aging in comparison to the silicarich sol resulting from aging of the leached metakaolin mixture, the latter being more homogeneous and requiring less transformation for nucleation of zeolite crystals. Although induction time was longer, the maximum crystallinity was slightly higher for samples prepared from diatomaceous earth than from kaolin and amounts to 93 and 87%, respectively, as shown in Figure 3. By a normalization of the BET specific surface area and total micropore volume with respect to the ZSM-5 standard sample also used for determining crystallinity by XRD, we show that the crystallinity of the reaction product obtained from kaolin is in good agreement with the values given in Table 2 with a specific surface area of 82%. The total micropore volume (68%) value indicates that the final product prepared from kaolin contains approximately 30% of non-microporous material in addition to the ZSM-5 crystals. The same values calculated from the BET specific surface area and total micropore volume for the diatomaceous earth-derived product, 96 and 82% respectively, are higher than that obtained by XRD (93%). This can be attributed to the presence of mordenite as a by-product in addition to non-microporous materials. It was not possible to prevent the formation of mordenite by further optimization of the synthesis parameters. Instead, formation of mordenite occurred randomly, probably due to the variability of the diatomaceous earth raw material. Calcium was found to be concentrated in the mordenite crystals as revealed by the comparison of the EDS spectra between uncalcined ZSM-5 (Figure 6(a)) and mordenite (Figure 6(b)) crystals. Therefore, the higher calcium content in leached diatomaceous earth as compared to leached kaolin probably favored the formation of mordenite. The presence of n-butylamine as templating agent in the ZSM-5 crystals was also confirmed by EDS, as shown in Figure 6(a) with the characteristic peak of nitrogen and carbon, while that of sodium was quite weak. The BET specific surface area obtained in this work for the sample prepared from leached diatomaceous earth (298 m 2 /g)iscomparablewiththatobtainedinthestudy by Sang et al. 9 (294 m 2 /g), who employed water glass and aluminum sulfate as Si and Al sources, respectively. Therefore, Bolivian diatomaceous earth appears as a competitive source of inexpensive raw materials for the synthesis of ZSM-5 crystals. In addition to the higher crystallinity and BET specific surface area achieved in this work compared with kaolin, diatomaceous earth does not require heat treatment at high temperature for metakaolinization. Conclusions The inexpensive raw materials: kaolin, Bolivian diatomaceous earth, sodium hydroxide and n-butylamine have
8 Aguilar-Mamani et al. SpringerPlus 2014, 3:292 Page 8 of 10 Figure 6 EDS spectra of the final product obtained from leached diatomaceous earth. (a) ZSM-5 crystal. (b) Mordenite crystal. been used to prepare ZSM-5 zeolites with SiO 2 /Al 2 O 3 molar ratios in the range Dealumination of the raw materials by acid leaching made it possible to reach appropriate SiO 2 /Al 2 O 3 molar ratios and to reduce the amount of iron and other impurities in the raw materials. After mixing and aging for 24 hours, synthesis by hydrothermal treatment was carried out at165 C either using leached metakaolin or leached diatomaceous earth as source of alumino-silica. The results clearly show for the first time that well-crystallized ZSM-5 can be directly prepared from both materials in combination with sodium hydroxide and n-butylamine under appropriate synthesis conditions. Reaction mixtures prepared from leached diatomaceous earth showed longer induction period due to the slower digestion of the fossilized diatom skeletons compared with microporous leached metakaolin. However, the use of leached diatomaceous earth allowed higher yield in ZSM-5 crystals within comparable synthesis times
9 Aguilar-Mamani et al. SpringerPlus 2014, 3:292 Page 9 of 10 despite the formation of low contents of mordenite, which was related to the high calcium content of diatomaceous earth. Another considerable advantage of diatomaceous earth over kaolin is that diatomaceous earth does not require heat treatment at high temperature for metakaolinization. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions WAM carried out the experiments and drafted the manuscript under the supervision of JM and JH. GG assisted in the analysis of the experiments. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Acknowledgements Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (SIDA) is acknowledged for supporting the work financially. The Knut and Alice Wallenberg foundation is acknowledged for financially supporting the Magellan SEM instrument. Author details 1 Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, Luleå, Sweden. 2 Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science and Technology, San Simon University, Cochabamba, Bolivia. 3 Solid State and Theoretical Chemistry, Chemistry Research Institute, San Andres Mayor University, University Campus, Cota Cota, 27 Street, La Paz, Bolivia. Received: 10 April 2014 Accepted: 30 May 2014 Published: 10 June 2014 References Aliev AM, Mamedova UA, Samedov KR, Sarydzhanov AA, Agaeva RY (2011) Synthesis and physicochemical study of ZSM-5 high-silica zeolite from natural raw materials. Russ J Phys Chem A 85: Argauer RJ, Landolt GR (1972) Crystalline Zeolite Zsm-5 and Method of Preparing the same., 886A, 14 Nov 1972 Armaroli T, Simon LJ, Digne M, Montanari T, Bevilacqua M, Valtchev V, Patarin J, Busca G (2006) Effects of crystal size and Si/Al ratio on the surface properties of H-ZSM-5 zeolites. Appl Catal A Gen 306:78 84 Atta A, Ajayi O, Adefila S (2007) Synthesis of faujasite zeolites from Kankara kaolin clay. J Appl Sci Res 3: Bosch P, Ortiz L, Schifter I (1983) Synthesis of faujasite type zeolites from calcined kaolins. Ind Eng Chem Prod Res Dev 22: Caballero I, Colina FG, Costa J (2007) Synthesis of X-type zeolite from dealuminated kaolin by reaction with sulfuric acid at high temperature. Ind Eng Chem Prod Res 46: Chaisena A, Rangsriwatananon K (2005) Synthesis of sodium zeolites from natural and modified diatomite. Mater Lett 59: Chandrasekhar S, Raghavan P, Sebastian G, Damodaran AD (1997) Brightness improvement studies on kaolin based zeolite 4A. Appl Clay Sci 12: Chareonpanich M, Namto T, Kongkachuichay P, Limtrakul J (2004) Synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite from lignite fly ash and rice husk ash. Fuel Process Technol 85: Chi ZQ, Li JH, Chen HF (2011) Synthesis of NaY zeolite molecular sieves from calcined diatomite. Adv Mater Res 236: Colina FG, Llorens J (2007) Study of the dissolution of dealuminated kaolin in sodium potassium hydroxide during the gel formation step in zeolite X synthesis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 100: Colina FG, Esplugas S, Costa J (2001) High temperature reaction of kaolin with inorganic acids. Brit Ceram Trans 100: Colina FG, Esplugas S, Costa J (2002) High-temperature reaction of kaolin with sulfuric acid. Ind Eng Chem Res 41: Costa E, De Lucas A, Uguina MA, Ruiz JC (1988) Synthesis of 4A zeolite from calcined kaolins for use in detergents. Ind Eng Chem Res 27: De Lucas A, Uguina MA, Covian I, Rodriguez L (1992) Synthesis of 13X zeolite from calcined kaolins and sodium silicate for use in detergents. Ind Eng Chem Res 31: Feng H, Li C, Shan H (2009) In-situ synthesis and catalytic activity of ZSM-5 zeolite. Appl Clay Sci 42: Ford KJR (1992) Leaching of fine and pelletised Natal kaolin using sulphuric acid. Hydrometallurgy 29: Ghosh B, Agrawal DC, Bhatia S (1994) Synthesis of Zeolite AfromCalcined Diatomaceous Clay: Optimization Studies. Ind Eng Chem Res 33: Jacobs PA (1981) Properties of the end members in the Pentasil-family of zeolites: characterization as adsorbents. Zeolites 1: Khatamian M, Irani M (2009) Preparation and characterization of nanosized ZSM-5 zeolite using kaolin and investigation of kaolin content, crystallization time and temperature changes on the size and crystallinity of products. J Iran Chem Soc 6: Kotasthane AN, Shiralkar VP (1986) Thermoanalytical studies of high silica ZSM-5 zeolites containing organic templates. Thermochimica Acta 102:37 45 Kovo AS, Hernandez O, Holmes SM (2009) Synthesis and characterization of zeolite Y and ZSM-5 from Nigerian Ahoko Kaolin using a novel, lower temperature, metakaolinization technique. J Mater Chem 19: Madhusoodana CD, Kameshima Y, Yasumori A, Okada K (2001) Fast formation of ZSM-5 zeolite using microporous silica obtained from selective leaching of metakaolinite. Clay Sci 11: Madhusoodana C, Das R, Kameshima Y, Okada K (2005) Preparation of ZSM-5 zeolite honeycomb monoliths using microporous silica obtained from metakaolinite. J Porous Mat 12: Martins L, Peguin RPS, Urquiet-González EA (2006) Cu and Co exchanged ZSM-5 zeolites: activity towards no reduction and hydrocarbon oxidation. Quimica Nova 29: Mignoni ML, Detoni C, Pergher SBC (2007) Estudo da síntese da zeólita ZSM-5 a partir de argilas naturais. Quimica Nova 30:45 48 Murat M, Amokrane A, Bastide J, Montanaro L (1992) Synthesis of zeolites from thermally activated kaolinite. Some observations on nucleation and growth. Clay Min 27: Padovan M, Leofanti G, Solari M, Moretti E (1984) Studies on the ZSM 5 zeolite formation. Zeolites 4: Rangsriwatananon K, Chaisena A, Thongkasam C (2008) Thermal and acid treatment on natural raw diatomite influencing in synthesis of sodium zeolites. J Porous Mater 15: Reid (1982) Manufacture of zeolites. European Patent Office :68817, 24 June 1982 Robson H, Lillerud KP (2001) In Chapter 62 - MFI High-Alumina ZSM-5 Si(93), Al(7). Vol. pp. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam Sang S, Chang F, Liu Z, He C, He Y, XU L (2004) Difference of ZSM-5 zeolites synthesized with various templates. Catal Today 93 95: Sanhueza V, Kelm U, Cid R (1999) Synthesis of molecular sieves from Chilean kaolinites: 1. Synthesis of NaA type zeolites. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 74: Sanhueza V, Kelm U, Cid R (2003) Synthesis of mordenite from diatomite: a case of zeolite synthesis from natural material. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 78: Sanhueza V, Kelm U, Cid R, López-Escobar L (2004) Synthesis of ZSM-5 from diatomite: a case of zeolite synthesis from a natural material. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 79: Sanhueza V, López-Escobar L, Kelm U, Cid R (2006) Synthesis of a mesoporous material from two natural sources. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81: Shan W, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Xia J, Tang Y (2004) Synthesis of Meso-/Macroporous Zeolite (Fe, Al)-ZSM-5 Microspheres from Diatomite. Chem Lett 33: Shirazi L, Jamshidi E, Ghasemi MR (2008) The effect of Si/Al ratio of ZSM-5 zeolite on its morphology, acidity and crystal size. Cryst Res Technol 43: Tavolaro A, Drioli E (1999) Zeolite membranes. Adv Mater 11: Van Hooff JHC, Roelofsen JW (1991) Chapter 7 Techniques of Zeolite Characterization. In: van Bekkum EMF H, Jansen JC (eds) In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, Vol. 58. Elsevier, pp Wajima T, Haga M, Kuzawa K, Ishimoto H, Tamada O, Ito K, Nishiyama T, Downs RT, Rakovan JF (2006) Zeolite synthesis from paper sludge ash at low temperature (90 C) with addition of diatomite. J Hazard Mater 132: Wajima T, Shimizu T, Ikegami Y (2008) Zeolite synthesis from paper sludge ash with addition of diatomite. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 83: Weitkamp J (2000) Zeolites and catalysis. Solid State Ionics 131:
10 Aguilar-Mamani et al. SpringerPlus 2014, 3:292 Page 10 of 10 Zhang Y, Gao W, Cui L (2007) In-situ Growth of ZSM-5 Zeolite on Acid-Activated Metakaolin. In: Ruren Xu ZGJC, Wenfu Y (eds) Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, Volume 17. Elsevier, pp Zhao H (2005) The difference between ZSM-5 zeolites manufactured from various synthesis systems and their catalytic performances. J China Petroleum Petrochem Technology 3:49 55 doi: / Cite this article as: Aguilar-Mamani et al.: Comparison between leached metakaolin and leached diatomaceous earth as raw materials for the synthesis of ZSM-5. SpringerPlus :292. Submit your manuscript to a journal and benefit from: 7 Convenient online submission 7 Rigorous peer review 7 Immediate publication on acceptance 7 Open access: articles freely available online 7 High visibility within the field 7 Retaining the copyright to your article Submit your next manuscript at 7 springeropen.com
Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment
 Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment Ming Zhou,* Ali A. Rownaghi, and Jonas Hedlund,* *Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, SE-971 87 Luleå,
Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment Ming Zhou,* Ali A. Rownaghi, and Jonas Hedlund,* *Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, SE-971 87 Luleå,
Synthesis of Zeolite A Membrane from Rice Husk Ash
 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol.19 No.2 pp.79-83, 2009 Chayakorn BHAVORNTHANAYOD and Pesak RUNGROJCHAIPON * Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, King Mongkut s Institute of Technology
Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol.19 No.2 pp.79-83, 2009 Chayakorn BHAVORNTHANAYOD and Pesak RUNGROJCHAIPON * Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, King Mongkut s Institute of Technology
Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous α-al 2 O 3 Supports
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous
ASIAN JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY
 Asian Journal of Chemistry; Vol. 28, No. 1 (2016), 211-215 ASIAN JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY http://dx.doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2016.19348 Synthesis of ZSM-5 Directly from Kaolin without Organic Template: Part-1:
Asian Journal of Chemistry; Vol. 28, No. 1 (2016), 211-215 ASIAN JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY http://dx.doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2016.19348 Synthesis of ZSM-5 Directly from Kaolin without Organic Template: Part-1:
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Cu-SSZ-39, an active and hydrothermally stable catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx Manuel Moliner, *a Cristina Franch, a Eduardo Palomares,
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Cu-SSZ-39, an active and hydrothermally stable catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx Manuel Moliner, *a Cristina Franch, a Eduardo Palomares,
Direct synthesis of mordenite from kaolin and rice husk ash
 BC.97 Proceedings of the IConSSE FSM SWCU (2015), pp. BC.97 102 ISBN: 978-602-1047-21-7 Direct synthesis of mordenite from kaolin and rice husk ash Sari Rahmawati *, Ratna Ediati, Didik Prasetyoko Chemistry
BC.97 Proceedings of the IConSSE FSM SWCU (2015), pp. BC.97 102 ISBN: 978-602-1047-21-7 Direct synthesis of mordenite from kaolin and rice husk ash Sari Rahmawati *, Ratna Ediati, Didik Prasetyoko Chemistry
Synthesis of the zeolite ZSM-5 by using seed crystals
 Synthesis of the zeolite ZSM-5 by using seed crystals 'D. MRAVEC, a D. RIEČANOVÁ, a J. ILAVSKÝ, and b J. MAJLING 11 Department of Organic Technology, Faculty of Chemical Technology, Slovak Technical University,
Synthesis of the zeolite ZSM-5 by using seed crystals 'D. MRAVEC, a D. RIEČANOVÁ, a J. ILAVSKÝ, and b J. MAJLING 11 Department of Organic Technology, Faculty of Chemical Technology, Slovak Technical University,
CONVERSION OF ETHANOL TO OLEFINS OVER HZSM-5 CATALYSTS
 CONVERSION OF ETHANOL TO OLEFINS OVER HZSM-5 CATALYSTS P. R. S. SALBEGO *1, G. S. N. M. CENTENARO 1, R. KLAIC 1, N. I. CANABARRO 1, T. K. MULLER 1, M. A. MAZUTTI 1, E. L. FOLETTO 1, S. L. JAHN 1 1 Universidade
CONVERSION OF ETHANOL TO OLEFINS OVER HZSM-5 CATALYSTS P. R. S. SALBEGO *1, G. S. N. M. CENTENARO 1, R. KLAIC 1, N. I. CANABARRO 1, T. K. MULLER 1, M. A. MAZUTTI 1, E. L. FOLETTO 1, S. L. JAHN 1 1 Universidade
Utilization of Rice Husk Ash Silica in Controlled Releasing Application
 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol.9 No.2 pp.6-65, 29 Utilization of Rice Husk Ash Silica in Controlled Releasing Application Piyawan PRAWINGWONG, Chaiyan CHAIYA 2, Prasert REUBROYCHAROEN 3
Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol.9 No.2 pp.6-65, 29 Utilization of Rice Husk Ash Silica in Controlled Releasing Application Piyawan PRAWINGWONG, Chaiyan CHAIYA 2, Prasert REUBROYCHAROEN 3
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Engineering Growth Defects: A New Route Towards Hierarchical
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Engineering Growth Defects: A New Route Towards Hierarchical
PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 11, No. 1, January - March 2016, p. 271-276 PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 11, No. 1, January - March 2016, p. 271-276 PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL
Science & Technologies SYNTHESIS AND SPECTROSCOPIC STUDY OF ZEOLITE A TYPE AND X TYPE
 SYNTHESIS AND SPECTROSCOPIC STUDY OF ZEOLITE A TYPE AND X TYPE B. Bogdanov 1, D. Benev 2 and D.Georgiev 3 1 Department Technology of Water, Inorg. compounds and silicates, 2 Central Research Laboratory
SYNTHESIS AND SPECTROSCOPIC STUDY OF ZEOLITE A TYPE AND X TYPE B. Bogdanov 1, D. Benev 2 and D.Georgiev 3 1 Department Technology of Water, Inorg. compounds and silicates, 2 Central Research Laboratory
MISCELLANEOUS SOLID-STATE COMPOUNDS
 Inorganic Syntheses, Volume 30 Edited by Donald W. Murphy, Leonard V. Interrante Copyright 1995 by Inorganic Syntheses, Inc. Chapter Six MISCELLANEOUS SOLID-STATE COMPOUNDS 43. ZEOLITE MOLECULAR SIEVES
Inorganic Syntheses, Volume 30 Edited by Donald W. Murphy, Leonard V. Interrante Copyright 1995 by Inorganic Syntheses, Inc. Chapter Six MISCELLANEOUS SOLID-STATE COMPOUNDS 43. ZEOLITE MOLECULAR SIEVES
Preparation of Silica Gel from Rice Husk Ash Using Microwave Heating
 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol.19 No.2 pp.45-50, 2009. Preparation of Silica Gel from Rice Husk Ash Using Microwave Heating Supitcha RUNGRODNIMITCHAI *, Wachira PHOKHANUSAI and Natthapong
Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol.19 No.2 pp.45-50, 2009. Preparation of Silica Gel from Rice Husk Ash Using Microwave Heating Supitcha RUNGRODNIMITCHAI *, Wachira PHOKHANUSAI and Natthapong
Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of Phenol
 http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.952 2015, 4(2), 438-442 RESEARCH ARTICLE Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of
http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.952 2015, 4(2), 438-442 RESEARCH ARTICLE Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information 1. Thermodynamic data The isomerization of glucose into fructose using can be represented as: The equilibrium constant K eq and equilibrium conversion were calculated as follows:
Supplementary Information 1. Thermodynamic data The isomerization of glucose into fructose using can be represented as: The equilibrium constant K eq and equilibrium conversion were calculated as follows:
Crystallization of NBA-ZSM-5 from Kaolin
 DOCTORAL T H E SIS Crystallization of NBA-ZSM-5 from Kaolin Wilson Aguilar-Mamani Chemical Technology Crystallization of NBA-ZSM-5 from kaolin Wilson Aguilar-Mamani Luleå University of Technology Department
DOCTORAL T H E SIS Crystallization of NBA-ZSM-5 from Kaolin Wilson Aguilar-Mamani Chemical Technology Crystallization of NBA-ZSM-5 from kaolin Wilson Aguilar-Mamani Luleå University of Technology Department
A test reaction for titanium silicalite catalysts
 A test reaction for titanium silicalite catalysts Kraushaar, B.; van Hooff, J.H.C. Published in: Catalysis Letters DOI: 10.1007/BF00765329 Published: 01/01/1989 Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known
A test reaction for titanium silicalite catalysts Kraushaar, B.; van Hooff, J.H.C. Published in: Catalysis Letters DOI: 10.1007/BF00765329 Published: 01/01/1989 Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known
Synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite from lignite fly ash and rice husk ash
 Fuel Processing Technology 85 (2004) 1623 1634 www.elsevier.com/locate/fuproc Synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite from lignite fly ash and rice husk ash Metta Chareonpanich a, *, Teerapong Namto a, Paisan Kongkachuichay
Fuel Processing Technology 85 (2004) 1623 1634 www.elsevier.com/locate/fuproc Synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite from lignite fly ash and rice husk ash Metta Chareonpanich a, *, Teerapong Namto a, Paisan Kongkachuichay
Asian Journal on Energy and Environment
 As. J. Energy Env. 2006, 7(01), 241-245 Asian Journal on Energy and Environment ISSN 1513-4121 Available online at www.asian-energy-journal.info Hydrogen Production from Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane
As. J. Energy Env. 2006, 7(01), 241-245 Asian Journal on Energy and Environment ISSN 1513-4121 Available online at www.asian-energy-journal.info Hydrogen Production from Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane
Supporting Information. Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with. Controlled Mesoporosity and Size
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Isotherm study on adsorption removal of Pb (II) by MCM-41 zeolite synthesized from biomass ash TAN Gang1,a, XUE Yongjie2,b and CAI Jun3,c
 214 International Conference on Computer Science and Electronic Technology (ICCSET 214) Isotherm study on adsorption removal of Pb (II) by MCM-41 zeolite synthesized from biomass ash TAN Gang1,a, XUE Yongjie2,b
214 International Conference on Computer Science and Electronic Technology (ICCSET 214) Isotherm study on adsorption removal of Pb (II) by MCM-41 zeolite synthesized from biomass ash TAN Gang1,a, XUE Yongjie2,b
Rapid and Mass Production of Porous Materials Using a Continuous Microwave Equipment
 Rapid and Mass Production of Porous Materials Using a Continuous Microwave Equipment Dae Sung Kim, Ji Man Kim, Jong-San Chang, and Sang-Eon Park* Catalysis Center for Molecular Engineering, Korea Research
Rapid and Mass Production of Porous Materials Using a Continuous Microwave Equipment Dae Sung Kim, Ji Man Kim, Jong-San Chang, and Sang-Eon Park* Catalysis Center for Molecular Engineering, Korea Research
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx applications
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx
SYNTHESIS OF FAUJASITE WITH HIGH THERMAL STABILITY FROM FLY ASH
 26 SYNTHESIS OF FAUJASITE WITH HIGH THERMAL STABILITY FROM FLY ASH Sutarno and Yateman Arryanto Chemistry Department, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta ABSTRACT
26 SYNTHESIS OF FAUJASITE WITH HIGH THERMAL STABILITY FROM FLY ASH Sutarno and Yateman Arryanto Chemistry Department, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta ABSTRACT
Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Substituted Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves with AEL Structure
 Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)231 237 Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Substituted Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves with AEL Structure Benjing Xu, Ling Qian, Xinmei Liu, Chunmin
Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)231 237 Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Substituted Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves with AEL Structure Benjing Xu, Ling Qian, Xinmei Liu, Chunmin
Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties. and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
INVESTIGATING DOPED MESOPROUS ZSM-5 FOR CASCADE CATALYSIS
 INVESTIGATING DOPED MESOPROUS ZSM-5 FOR CASCADE CATALYSIS Introduction With the recent innovations and progress in the nanotechnology industry, a family of microporous catalysts and adsorbents known as
INVESTIGATING DOPED MESOPROUS ZSM-5 FOR CASCADE CATALYSIS Introduction With the recent innovations and progress in the nanotechnology industry, a family of microporous catalysts and adsorbents known as
Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique
 Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique Zhou Ying, Yao Qimei, Qiu Jieshan *, Guo Hongchen, Sun Zongwei Carbon Research Laboratory, Center for Nano Materials and Science, School
Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique Zhou Ying, Yao Qimei, Qiu Jieshan *, Guo Hongchen, Sun Zongwei Carbon Research Laboratory, Center for Nano Materials and Science, School
Supporting information
 Supporting information Hierarchical Macro-meso-microporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Hollow Fibers With Highly Efficient Catalytic Cracking Capability Jia Liu, a Guiyuan Jiang,* a Ying Liu, a Jiancheng Di, b Yajun
Supporting information Hierarchical Macro-meso-microporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Hollow Fibers With Highly Efficient Catalytic Cracking Capability Jia Liu, a Guiyuan Jiang,* a Ying Liu, a Jiancheng Di, b Yajun
Precious Metal-free Electrode Catalyst for Methanol Oxidations
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
Electronic supplementary information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information Heterogeneous nucleation and growth of highly crystalline
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information Heterogeneous nucleation and growth of highly crystalline
PREPARATION OF SYNTHETIC ZEOLITES FROM COAL FLY ASH. Shamsul Kamal Sulaiman
 Solid State Science and Technology, Vol. 16, No 1 (28) 17-113 ISSN 128-7389 PREPARATION OF SYNTHETIC ZEOLITES FROM COAL FLY ASH Shamsul Kamal Sulaiman Mineral Research Centre, Minerals and Geoscience Department,
Solid State Science and Technology, Vol. 16, No 1 (28) 17-113 ISSN 128-7389 PREPARATION OF SYNTHETIC ZEOLITES FROM COAL FLY ASH Shamsul Kamal Sulaiman Mineral Research Centre, Minerals and Geoscience Department,
Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different Proportions
 2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO
 Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nanocrystalline Zeolite using Clear Solution
 Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nanocrystalline Zeolite using Clear Solution Syaifullah Muhammad 1 *, Izarul Machdar 1, Sofyana 1, Aris Munandar 1, Tuty Emilia Agustina 3 Edy Saputra 2, Shaobin Wang 4 and Moses
Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nanocrystalline Zeolite using Clear Solution Syaifullah Muhammad 1 *, Izarul Machdar 1, Sofyana 1, Aris Munandar 1, Tuty Emilia Agustina 3 Edy Saputra 2, Shaobin Wang 4 and Moses
Supporting Information:
 Supporting Information: In Situ Synthesis of Magnetically Recyclable Graphene Supported Pd@Co Core-Shell Nanoparticles as Efficient Catalysts for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane Jun Wang,
Supporting Information: In Situ Synthesis of Magnetically Recyclable Graphene Supported Pd@Co Core-Shell Nanoparticles as Efficient Catalysts for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane Jun Wang,
and their Maneuverable Application in Water Treatment
 Hierarchical Films of Layered Double Hydroxides by Using a Sol-Gel Process and their Maneuverable Application in Water Treatment Yufei Zhao, Shan He, Min Wei,* David G. Evans, Xue Duan State Key Laboratory
Hierarchical Films of Layered Double Hydroxides by Using a Sol-Gel Process and their Maneuverable Application in Water Treatment Yufei Zhao, Shan He, Min Wei,* David G. Evans, Xue Duan State Key Laboratory
The GO was synthesized by oxidation of purified natural small graphite and graphite
 Jing-He Yang, a,b Geng Sun, a Yongjun Gao, a Huabo Zhao, a Pei Tang, a Juan Tan, b Lu b and Ding Ma*,a An-Hui a Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering,
Jing-He Yang, a,b Geng Sun, a Yongjun Gao, a Huabo Zhao, a Pei Tang, a Juan Tan, b Lu b and Ding Ma*,a An-Hui a Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering,
Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for production of hydrogen from methanol steam reforming
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for
Recycling of Municipal Solid Waste Ash through an Innovative Technology to Produce Commercial Zeolite material of High Cation Exchange Capacity
 Proceedings of NAWTEC16 16th Annual North American Waste-to-Energy Conference May 19-21, 2008, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA NAWTEC16-1919 Recycling of Municipal Solid Waste Ash through an Innovative
Proceedings of NAWTEC16 16th Annual North American Waste-to-Energy Conference May 19-21, 2008, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA NAWTEC16-1919 Recycling of Municipal Solid Waste Ash through an Innovative
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets Lan Wang, a Ling Zang, b Jincai Zhao c and Chuanyi Wang*
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets Lan Wang, a Ling Zang, b Jincai Zhao c and Chuanyi Wang*
PREPARATION, CHARACTERISATION AND PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITY OF TERNARY GRAPHENE-Fe 3 O 4 :TiO 2 NANOCOMPOSITES
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 13, No. 2, April - June 2018, p. 499-504 PREPARATION, CHARACTERISATION AND PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITY OF TERNARY GRAPHENE-Fe 3 O 4 :TiO 2 NANOCOMPOSITES
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 13, No. 2, April - June 2018, p. 499-504 PREPARATION, CHARACTERISATION AND PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITY OF TERNARY GRAPHENE-Fe 3 O 4 :TiO 2 NANOCOMPOSITES
Supplementary Information for Efficient catalytic conversion of fructose into hydroxymethylfurfural by a novel carbon based solid acid
 Supplementary Information for Efficient catalytic conversion of fructose into hydroxymethylfurfural by a novel carbon based solid acid Jianjian Wang, Wenjie Xu, Jiawen Ren*, Xiaohui Liu, Guanzhong Lu,
Supplementary Information for Efficient catalytic conversion of fructose into hydroxymethylfurfural by a novel carbon based solid acid Jianjian Wang, Wenjie Xu, Jiawen Ren*, Xiaohui Liu, Guanzhong Lu,
ICTR 2004 CONGRESSO BRASILEIRO DE CIÊNCIA E TECNOLOGIA EM RESÍDUOS E DESENVOLVIMENTO SUSTENTÁVEL Costão do Santinho Florianópolis Santa Catarina
 ICTR 2004 CONGRESSO BRASILEIRO DE CIÊNCIA E TECNOLOGIA EM RESÍDUOS E DESENVOLVIMENTO SUSTENTÁVEL Costão do Santinho Florianópolis Santa Catarina A LOW COST ZSM-5 ZEOLITE OBTAINED FROM RICE HULL ASH A.
ICTR 2004 CONGRESSO BRASILEIRO DE CIÊNCIA E TECNOLOGIA EM RESÍDUOS E DESENVOLVIMENTO SUSTENTÁVEL Costão do Santinho Florianópolis Santa Catarina A LOW COST ZSM-5 ZEOLITE OBTAINED FROM RICE HULL ASH A.
Synthesis of Zeolite Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation
 Synthesis of Zeolite Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation April. 10. 2003 Sang Hoon Hyun, Dong Wook Shin, Young Eun Lee, Moon Hee Han*, and Churl Hee Cho* School of Materials Science & Engineering Yonsei
Synthesis of Zeolite Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation April. 10. 2003 Sang Hoon Hyun, Dong Wook Shin, Young Eun Lee, Moon Hee Han*, and Churl Hee Cho* School of Materials Science & Engineering Yonsei
Synthesis of a Zeolite Column with a Monolithic Microhoneycomb Structure Using the Ice Template Method
 Synthesis of a Zeolite Column with a Monolithic Microhoneycomb Structure Using the Ice Template Method Shin R. Mukai, Shinya Murata, Kazufusa Onodera and Izumi Yamada *1 Graduate School of Engineering,
Synthesis of a Zeolite Column with a Monolithic Microhoneycomb Structure Using the Ice Template Method Shin R. Mukai, Shinya Murata, Kazufusa Onodera and Izumi Yamada *1 Graduate School of Engineering,
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
enzymatic cascade system
 Electronic Supplementary Information Fe 3 O 4 -Au@mesoporous SiO 2 microsphere: an ideal artificial enzymatic cascade system Xiaolong He, a,c Longfei Tan, a Dong Chen,* b Xiaoli Wu, a,c Xiangling Ren,
Electronic Supplementary Information Fe 3 O 4 -Au@mesoporous SiO 2 microsphere: an ideal artificial enzymatic cascade system Xiaolong He, a,c Longfei Tan, a Dong Chen,* b Xiaoli Wu, a,c Xiangling Ren,
Highly active and reusable catalyst from Fe-Mg-hydrotalcite anionic clay for Friedel Crafts type benzylation reactions
 J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 117, No. 6, November 2005, pp. 635 639. Indian Academy of Sciences. Highly active and reusable catalyst from Fe-Mg-hydrotalcite anionic clay for Friedel Crafts type benzylation reactions
J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 117, No. 6, November 2005, pp. 635 639. Indian Academy of Sciences. Highly active and reusable catalyst from Fe-Mg-hydrotalcite anionic clay for Friedel Crafts type benzylation reactions
Solution-processable graphene nanomeshes with controlled
 Supporting online materials for Solution-processable graphene nanomeshes with controlled pore structures Xiluan Wang, 1 Liying Jiao, 1 Kaixuan Sheng, 1 Chun Li, 1 Liming Dai 2, * & Gaoquan Shi 1, * 1 Department
Supporting online materials for Solution-processable graphene nanomeshes with controlled pore structures Xiluan Wang, 1 Liying Jiao, 1 Kaixuan Sheng, 1 Chun Li, 1 Liming Dai 2, * & Gaoquan Shi 1, * 1 Department
Effect of acid modification on physicochemical characteristics of Kpautagi clay
 Leonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 28, January-June 2016 p. 87-94 Effect of acid modification on physicochemical characteristics of Kpautagi clay Matthew A. ONU 1,*, Joseph O. OKAFOR 1,
Leonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 28, January-June 2016 p. 87-94 Effect of acid modification on physicochemical characteristics of Kpautagi clay Matthew A. ONU 1,*, Joseph O. OKAFOR 1,
Min Bum Park, Sang Hyun Ahn, Nak Ho Ahn and Suk Bong Hong*
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 S1 Supplementary Information for Charge density mismatch synthesis of MEI- and BPH-type zeolites
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 S1 Supplementary Information for Charge density mismatch synthesis of MEI- and BPH-type zeolites
Clean synthesis of propylene carbonate from urea and 1,2-propylene glycol over zinc iron double oxide catalyst
 Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:794 798 (2006) DOI: 10.1002/jctb.1412 Clean synthesis of propylene carbonate from urea and 1,2-propylene glycol over zinc iron
Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:794 798 (2006) DOI: 10.1002/jctb.1412 Clean synthesis of propylene carbonate from urea and 1,2-propylene glycol over zinc iron
Research on Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis for Ion Exchange of Molecular Sieves
 Scientific Research China Petroleum Processing and Petrochemical Technology 2018, Vol. 20, No. 2, pp 1-5 June 30, 2018 Research on Bipolar Membrane for Ion Exchange of Molecular Sieves Chen Beiyan 1 ;
Scientific Research China Petroleum Processing and Petrochemical Technology 2018, Vol. 20, No. 2, pp 1-5 June 30, 2018 Research on Bipolar Membrane for Ion Exchange of Molecular Sieves Chen Beiyan 1 ;
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
Sodium silicate as source of silica for synthesis of mesoporous SBA-15
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Sodium silicate as source of silica for synthesis of mesoporous SBA-15 To cite this article: Norhasyimi Rahmat et al 2016 IOP
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Sodium silicate as source of silica for synthesis of mesoporous SBA-15 To cite this article: Norhasyimi Rahmat et al 2016 IOP
Report on Preparation of Nanotemplates for mab Crystallization
 Deliverable number D2.1 Due date 30/09/2017 Deliverable title Report on Preparation of Nanotemplates for mab Crystallization Issue date 21/09/2017 WP number WP2 Author(s) J. Heng, W. Chen, H. Yang Lead
Deliverable number D2.1 Due date 30/09/2017 Deliverable title Report on Preparation of Nanotemplates for mab Crystallization Issue date 21/09/2017 WP number WP2 Author(s) J. Heng, W. Chen, H. Yang Lead
Nanoporous TiO 2 Nanoparticle Assemblies with Mesoscale Morphologies: Nano-Cabbage versus Sea-Anemone
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplemental Documents Nanoporous TiO 2 Nanoparticle Assemblies with Mesoscale Morphologies: Nano-Cabbage
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplemental Documents Nanoporous TiO 2 Nanoparticle Assemblies with Mesoscale Morphologies: Nano-Cabbage
Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite from
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite from
Supporting Information. Graphene Oxide-Palladium Modified Ag-AgBr: A Novel Visible-Light- Responsive Photocatalyst for the Suzuki Coupling Reaction**
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Graphene Oxide-Palladium Modified Ag-AgBr: A Novel Visible-Light- Responsive
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Graphene Oxide-Palladium Modified Ag-AgBr: A Novel Visible-Light- Responsive
Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with HCl and H 2 O 2 to Produce. Dichloropropanols Catalyzed by Hollow TS-1 Zeolite
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 216 Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with and 2 O 2 to Produce Dichloropropanols Catalyzed
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 216 Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with and 2 O 2 to Produce Dichloropropanols Catalyzed
A high-efficient monoclinic BiVO 4 adsorbent for selective capture toxic selenite
 Supporting Online Materials for A high-efficient monoclinic BiVO 4 adsorbent for selective capture toxic selenite Huan Ouyang, Yuanyuan Sun*, and Jianqiang Yu* Collaborative Innovation Center for Marine
Supporting Online Materials for A high-efficient monoclinic BiVO 4 adsorbent for selective capture toxic selenite Huan Ouyang, Yuanyuan Sun*, and Jianqiang Yu* Collaborative Innovation Center for Marine
Growth and characterization of hydrothermally-grown zeolite crystals
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 5, No. 1, March 1983, pp. i3-19 @ Printed in India. Growth and characterization of hydrothermally-grown zeolite crystals M S JOSHI and B T BHOSKAR* Department of Physics, Sardar
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 5, No. 1, March 1983, pp. i3-19 @ Printed in India. Growth and characterization of hydrothermally-grown zeolite crystals M S JOSHI and B T BHOSKAR* Department of Physics, Sardar
SNRU Jou r n al of Sc ien ce an d T ech n olo gy 8 ( 3 ) S ep tem ber D ec em be r ( ) SNRU Journal of Science and Technology
 SNRU Jou r n al of Sc ien ce an d T ech n olo gy 8 ( 3 ) S ep tem ber D ec em be r ( 2 01 6 ) 3 20 32 6 SNRU Journal of Science and Technology J ou rn al h om e pa ge : sn r u j st. s n r u. ac. t h Synthesis
SNRU Jou r n al of Sc ien ce an d T ech n olo gy 8 ( 3 ) S ep tem ber D ec em be r ( 2 01 6 ) 3 20 32 6 SNRU Journal of Science and Technology J ou rn al h om e pa ge : sn r u j st. s n r u. ac. t h Synthesis
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 3, March-2014 ISSN
 156 Copper Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis Characterization Y.Suresh*1, S.Annapurna*2, G.Bhikshamaiah*3, A.K.Singh#4 Abstract Present work describes the synthesis nanoparticles using papaya extract as a
156 Copper Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis Characterization Y.Suresh*1, S.Annapurna*2, G.Bhikshamaiah*3, A.K.Singh#4 Abstract Present work describes the synthesis nanoparticles using papaya extract as a
Supplementary Information. Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information of Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information of Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite) catalyst
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Titanium Dioxide: Modification with Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide Xuandong Li,* Meirong Kang, Xijiang Han, Jingyu Wang, and Ping Xu
Supporting Information Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Titanium Dioxide: Modification with Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide Xuandong Li,* Meirong Kang, Xijiang Han, Jingyu Wang, and Ping Xu
FORMATION OF CRYSTAL STRUCTURES DURING ACTIVATED CARBON PRODUCTION FROM TURKISH ELBISTAN LIGNITE
 FORMATION OF CRYSTAL STRUCTURES DURING ACTIVATED CARBON PRODUCTION FROM TURKISH ELBISTAN LIGNITE Billur Sakintuna 1, Sevil Çetinkaya 2, and Yuda Yürüm 1 1 Sabanci University Faculty of Engineering and
FORMATION OF CRYSTAL STRUCTURES DURING ACTIVATED CARBON PRODUCTION FROM TURKISH ELBISTAN LIGNITE Billur Sakintuna 1, Sevil Çetinkaya 2, and Yuda Yürüm 1 1 Sabanci University Faculty of Engineering and
Multi-stage synthesis of nanopore NaA zeolite membranes for separation of water/ethanol mixtures
 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Innovation Vol-1, Issue-6 (2017), 42-46 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Innovation (IJREI) journal home page: http://www.ijrei.com
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Innovation Vol-1, Issue-6 (2017), 42-46 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Innovation (IJREI) journal home page: http://www.ijrei.com
Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylene oxide) templated nickel oxide nanofibers for dye degradation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Environmental Science: Nano. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylene
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Environmental Science: Nano. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylene
Quantitative measurement of a mixture of mesophases cubic MCM-48 and hexagonal MCM-41 by 13C CP/MAS NMR
 University Technology Malaysia From the SelectedWorks of Hadi Nur May, 2004 Quantitative measurement of a mixture of mesophases cubic MCM-48 and hexagonal MCM-41 by 13C CP/MAS NMR Hadi Nur, University
University Technology Malaysia From the SelectedWorks of Hadi Nur May, 2004 Quantitative measurement of a mixture of mesophases cubic MCM-48 and hexagonal MCM-41 by 13C CP/MAS NMR Hadi Nur, University
Synthesis of renewable diesel with hydroxyacetone and 2-methyl-furan
 Supporting Information Synthesis of renewable diesel with hydroxyacetone and 2-methyl-furan Guangyi Li, a,b Ning Li, a Shanshan Li, a,b Aiqin Wang, a Yu Cong, a Xiaodong Wang a and Tao Zhang a * a State
Supporting Information Synthesis of renewable diesel with hydroxyacetone and 2-methyl-furan Guangyi Li, a,b Ning Li, a Shanshan Li, a,b Aiqin Wang, a Yu Cong, a Xiaodong Wang a and Tao Zhang a * a State
Supplementary Information for
 Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Fabrication of SiO 2, Al 2 O 3, and TiO 2 Microcapsules with Hollow Core and Mesoporous Shell Structure
 Fabrication of SiO 2, Al 2 O 3, and TiO 2 Microcapsules with Hollow Core and Mesoporous Shell Structure Xiao-Feng Guo, Yong-Suk Kim, and Geon-Joong Kim Department of Chemical Engineering, Inha UniVersity,
Fabrication of SiO 2, Al 2 O 3, and TiO 2 Microcapsules with Hollow Core and Mesoporous Shell Structure Xiao-Feng Guo, Yong-Suk Kim, and Geon-Joong Kim Department of Chemical Engineering, Inha UniVersity,
Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR
 a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
Solvent-free Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Raw Materials
 Solvent-free Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Raw Materials Limin Ren, Qinming Wu, Chengguang Yang, Longfeng Zhu, Caijin Li, Pengling Zhang, Haiyan Zhang, Xiangju Meng,*, Feng-Shou Xiao*, Department of
Solvent-free Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Raw Materials Limin Ren, Qinming Wu, Chengguang Yang, Longfeng Zhu, Caijin Li, Pengling Zhang, Haiyan Zhang, Xiangju Meng,*, Feng-Shou Xiao*, Department of
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using
 Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Characterization of NaA Zeolite Oxygen Permeable Membrane on TiO 2 / -Al 2 O 3 Composite Support
 Characterization of NaA Zeolite Oxygen Permeable Membrane on TiO 2 / -Al 2 Composite Support ZHU Mengfu 1,a*, SU Hongbo 1,b, DENG Cheng 1,c, YUWEN Linlin 1,d and JIANG Mingming 1,e 1 Institute of Medical
Characterization of NaA Zeolite Oxygen Permeable Membrane on TiO 2 / -Al 2 Composite Support ZHU Mengfu 1,a*, SU Hongbo 1,b, DENG Cheng 1,c, YUWEN Linlin 1,d and JIANG Mingming 1,e 1 Institute of Medical
SYNTHESIS OF NaA ZEOLITE
 Proceedings of a 12 th International Conference MTCM 2009 September 22-24, 2009, Varna, Bulgaria SYNTHESIS OF NaA ZEOLITE Dimitar Georgiev, Bogdan Bogdanov*, Yancho Hristov, Irena Markovska*, Krasimira
Proceedings of a 12 th International Conference MTCM 2009 September 22-24, 2009, Varna, Bulgaria SYNTHESIS OF NaA ZEOLITE Dimitar Georgiev, Bogdan Bogdanov*, Yancho Hristov, Irena Markovska*, Krasimira
Synthesis of highly b-oriented zeolite MFI films by suppressing. twin crystal growth during the secondary growth
 Supplementary Information Synthesis of highly b-oriented zeolite MFI films by suppressing twin crystal growth during the secondary growth Xianming Li, a Yong Peng, a Zhengbao Wang,* a and Yushan Yan a,
Supplementary Information Synthesis of highly b-oriented zeolite MFI films by suppressing twin crystal growth during the secondary growth Xianming Li, a Yong Peng, a Zhengbao Wang,* a and Yushan Yan a,
Photodecomposition of Water Catalyzed by Zr- and Ti-MCM-41
 ESO 25(6) #7759 Energy Sources, 25:591 596, 2003 Copyright 2003 Taylor & Francis 0090-8312/03 $12.00 +.00 DOI: 10.1080/00908310390195651 Photodecomposition of Water Catalyzed by Zr- and Ti-MCM-41 S.-H.
ESO 25(6) #7759 Energy Sources, 25:591 596, 2003 Copyright 2003 Taylor & Francis 0090-8312/03 $12.00 +.00 DOI: 10.1080/00908310390195651 Photodecomposition of Water Catalyzed by Zr- and Ti-MCM-41 S.-H.
DICP Course - Dalian, 2012 Preparation of solid catalysts Part 8 Supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences
 DICP Course - Dalian, 2012 Preparation of solid catalysts Part 8 Supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences Charles Kappenstein, Professor Emeritus, University of Poitiers, France Preparation of catalysts
DICP Course - Dalian, 2012 Preparation of solid catalysts Part 8 Supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences Charles Kappenstein, Professor Emeritus, University of Poitiers, France Preparation of catalysts
Supports, Zeolites, Mesoporous Materials - Chapter 9
 Supports, Zeolites, Mesoporous Materials - Chapter 9 Krijn P. de Jong Inorganic Chemistry and Catalysis Utrecht University NIOK CAIA Course, Schiermonnikoog, December 4 th, 2009 1 Overview of lecture Introduction
Supports, Zeolites, Mesoporous Materials - Chapter 9 Krijn P. de Jong Inorganic Chemistry and Catalysis Utrecht University NIOK CAIA Course, Schiermonnikoog, December 4 th, 2009 1 Overview of lecture Introduction
MOHAMED R. BERBER Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Tanta University, Tanta 31527, Egypt.
 Advanced Materials Development and Performance (AMDP211) International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 6 (212) 133-137 World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 1.1142/S21194512366 CONTROL
Advanced Materials Development and Performance (AMDP211) International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 6 (212) 133-137 World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 1.1142/S21194512366 CONTROL
IGCSE (9-1) Edexcel - Chemistry
 IGCSE (9-1) Edexcel - Chemistry Principles of Chemistry Chemical Formulae, Equations and Calculations NOTES 1.25: Write word equations and balanced chemical equations (including state symbols): For reactions
IGCSE (9-1) Edexcel - Chemistry Principles of Chemistry Chemical Formulae, Equations and Calculations NOTES 1.25: Write word equations and balanced chemical equations (including state symbols): For reactions
Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts
 Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts N.D. Charisiou 1,2, A. Baklavaridis 1, V.G. Papadakis 2, M.A. Goula 1 1 Department of Environmental
Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts N.D. Charisiou 1,2, A. Baklavaridis 1, V.G. Papadakis 2, M.A. Goula 1 1 Department of Environmental
Pioneering In Situ Recrystallization during Bead Milling: A Top-down Approach to Prepare Zeolite A Nanocrystals
 Supporting Information Pioneering In Situ Recrystallization during Bead Milling: A Top-down Approach to Prepare Zeolite A Nanocrystals Chokkalingam Anand 1, Yudai Yamaguchi 1, Zhendong Liu 1, Sayoko Ibe
Supporting Information Pioneering In Situ Recrystallization during Bead Milling: A Top-down Approach to Prepare Zeolite A Nanocrystals Chokkalingam Anand 1, Yudai Yamaguchi 1, Zhendong Liu 1, Sayoko Ibe
SBA-15-functionalized sulfonic acid confined acidic ionic liquid: a powerful and water-tolerant catalyst for solvent-free esterifications
 SBA-15-functionalized sulfonic acid confined acidic ionic liquid: a powerful and water-tolerant catalyst for solvent-free esterifications Babak Karimi* a, Majid Vafaeezadeh a a Department of Chemistry,
SBA-15-functionalized sulfonic acid confined acidic ionic liquid: a powerful and water-tolerant catalyst for solvent-free esterifications Babak Karimi* a, Majid Vafaeezadeh a a Department of Chemistry,
Sintering behavior of feldspar rocks
 Research Inventy: International Journal Of Engineering And Science Vol.4, Issue 10 (October2014), PP 49-55 Issn (e): 2278-4721, Issn (p):2319-6483, www.researchinventy.com Sintering behavior of feldspar
Research Inventy: International Journal Of Engineering And Science Vol.4, Issue 10 (October2014), PP 49-55 Issn (e): 2278-4721, Issn (p):2319-6483, www.researchinventy.com Sintering behavior of feldspar
Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh
 Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh hierarchical superstructures for greatly fast removal of heavy metal ions with high efficiency Yong-Xing Zhang, a,b Yong
Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh hierarchical superstructures for greatly fast removal of heavy metal ions with high efficiency Yong-Xing Zhang, a,b Yong
SYNTHESIS OF ZEOLITE FROM
 SYNTHESIS OF ZEOLITE FROM COAL FLY ASH: ITS APPLICATION AS WATER SORBENT Thepparat Klamrassamee 1, Prasert Pavasant 2 and Navadol Laosiripojana 1 * 1 The Joint Graduate School of Energy and Environment,
SYNTHESIS OF ZEOLITE FROM COAL FLY ASH: ITS APPLICATION AS WATER SORBENT Thepparat Klamrassamee 1, Prasert Pavasant 2 and Navadol Laosiripojana 1 * 1 The Joint Graduate School of Energy and Environment,
Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification
 Electronic Supporting Informations (ESI): Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification Jun Kim, Yu-Ri Lee and Wha-Seung
Electronic Supporting Informations (ESI): Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification Jun Kim, Yu-Ri Lee and Wha-Seung
Electronic Supplementary Material
 Electronic Supplementary Material Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous Si MCM-41 materials and their application as solid acid catalysts in some esterification reactions by Tarun F Parangi (pp
Electronic Supplementary Material Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous Si MCM-41 materials and their application as solid acid catalysts in some esterification reactions by Tarun F Parangi (pp
Role of iron in preparation and oxygen reduction reaction activity of nitrogen-doped carbon
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Role of iron in preparation and oxygen reduction reaction
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Role of iron in preparation and oxygen reduction reaction
Catalytic Decomposition of Formaldehyde on Nanometer Manganese Dioxide
 Modern Applied Science April, 29 Catalytic Decomposition of Formaldehyde on Nanometer Manganese Dioxide Xiujuan Chu & Hua Zhang (Corresponding author) Tianjin Municipal Key Lab of Fibres Modification and
Modern Applied Science April, 29 Catalytic Decomposition of Formaldehyde on Nanometer Manganese Dioxide Xiujuan Chu & Hua Zhang (Corresponding author) Tianjin Municipal Key Lab of Fibres Modification and
A General Synthesis of Discrete Mesoporous Carbon Microspheres through a Confined Self- Assembly Process in Inverse Opals
 A General Synthesis of Discrete Mesoporous Carbon Microspheres through a Confined Self- Assembly Process in Inverse Opals Zhenkun Sun,, Yong Liu, Bin Li, Jing Wei, Minghong Wang, Qin Yue, Yonghui Deng,
A General Synthesis of Discrete Mesoporous Carbon Microspheres through a Confined Self- Assembly Process in Inverse Opals Zhenkun Sun,, Yong Liu, Bin Li, Jing Wei, Minghong Wang, Qin Yue, Yonghui Deng,
Having a High Mg/Al Molar Ratio
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION High-Temperature CO 2 Sorption on Hydrotalcite Having a High Mg/Al Molar Ratio Suji Kim, Sang Goo Jeon, and Ki Bong Lee*, Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Korea
SUPPORTING INFORMATION High-Temperature CO 2 Sorption on Hydrotalcite Having a High Mg/Al Molar Ratio Suji Kim, Sang Goo Jeon, and Ki Bong Lee*, Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Korea
