States of Matter in Food
|
|
|
- Noel Jacobs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Science Unit: Lesson 13: Matter States of Matter in Food Summary: Science skills: In this lesson, students explore the concept of state change, using various food and drink, in three activities: (1) Students observe ice, water and steam and then do a movement activity to illustrate water molecules in each state. (2) Students observe popcorn popping and discuss how a state change causes popcorn to pop. (3) Students add baking soda to orange juice to observe a gas and use a molecular model to visualize the chemical structure of baking soda. Close observation, careful observation, technical manipulation, comparison, inferring, concluding, verbally summarizing, reporting results. School Year: 2013/2014 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Notes: Champlain Heights Annex Elementary School, Vancouver School District Ingrid Sulston (scientist); Mona Francis and Ramona Smith (teachers) Presented to grades 2/3; appropriate for grades 2 7 with age appropriate modifications 1 hour and 20 minutes The popcorn activity is also in Lesson 3 (Physical Changes to Matter) in the Matter unit of the Scientist in Residence Program: Objectives: Students will be able to: Model the spacing and activity of the molecules in the three states of matter. View and understand state changes in a familiar context (food). Relate observed state changes to the underlying molecular changes. Background Information States of matter can be an abstract concept for many students. This lesson uses sensory experiences to approach the topic. Modeling the states of matter with their own bodies can help students visualize what is happening at the molecular level. Making snacks are fun and memorable activities on which to scaffold understanding the states of matter and state changes in molecular terms.
2 Vocabulary States of matter: Molecules and atoms: Model: Solid: Liquid: Gas: State change: The distinct physical forms that matter can take: solid, liquid or gas (plasma is also a state of matter, but not dealt with in this lesson). Tiny particles that make up everything around us. Molecules and atoms are too small to see individually, but with enough of them together they make objects we can see. Two or more atoms are bonded together to make a molecule. A representation of an object to help understand it. In this case the model (students themselves) are much larger than the real object (molecules), so that the arrangement and movement of molecules can be visualized. A state of matter. The molecules in a solid are packed tightly together. Solids keep their shape (even in a granular solid, the individual grains keep their shape). A state of matter. The molecules in liquids are free to move but remain close to each other. Liquids can change shape, but always take up the same amount of space. A state of matter. The molecules in gases are free to move apart from each other. Gases spread out to fill the container they are in. A change between any of the states of matter e.g. liquid to gas. Chemical reaction: A chemical reaction occurs when molecules break apart and their atoms rearrange to make new molecules. Sometimes the new molecules are a different state of matter, so the chemical reaction involves a state change. Materials Ice cube Small dixie cups, one per student Coffee stirrers, one per student, at each table in the baking soda cup Kettle to boil water, preferably with clear sides Materials to make popcorn Orange juice, about 40ml or half a Dixie cup per student; about one litre for a class Baking soda, distributed as about two Tbsp. in a Dixie cup per table Molecule model kit, one per student pair: Ziploc bag containing three red clay balls oxygen, two white clay balls hydrogen, one black clay ball carbon and six toothpick bonds. Clay balls should be about 1cm diameter. In the Classroom Introductory Discussion 1. Ask students if they are familiar with the states of matter (solid, liquid and gas). If they are not, introduce the states of matter using examples from around the classroom. Use ref. 1 to teach and review states of matter concepts. Inform students that they will model the states of matter with their own bodies, then explore states of matter in food. 2. Processes of science that the students will focus on: close observation, careful observation, technical manipulation, comparison, inferring, concluding, verbally summarizing, reporting results.
3 Safety guidelines: caution is required when handling boiling water. Science Activities (1) Activity Title: Modeling States of Matter Purpose of Activity: To model the relationships between the molecules in the different states of matter, while watching water change state. Set-up prior to experiment: boil a kettle of water, so that it is quick to boil again. Students work as one large group for this activity - space in the classroom (or gym) is needed. a. Tell students that they each represent a molecule. Molecules are way too small to see, so by making a model of molecules, we can visualize better what molecules are doing in solids, liquids and gases. b. Show students an ice cube and tell them that in a solid, like this ice cube, the molecules are packed tight, held together by strong bonds. Ask students to model a solid by linking arms with their neighbors, so that they are packed tight together in a group. The individuals can jiggle a little, but the group maintains its shape. c. Show students how as the solid ice cube gets energy from the air and a warm hand, it starts to melt and become a liquid. As the molecules gain energy, they are still bonded to each other, but more loosely, so they can move around more. Ask students to model a liquid by spreading apart and moving around more, but always touching at least one other student with an outstretched arm. The bonds between molecules break and form continuously, so that the group stays together but can move and change shape, as a liquid does. d. Show students water boiling in a kettle. As the liquid water gets even more energy the molecules gain enough energy to move completely apart and evaporate to a gas, which we see as bubbles in the liquid water. A gas fills the container it is in. Ask students to break all bonds with each other and run around the room, spreading out to fill the room. e. Students can be asked to become a liquid again condensation, then a solid freezing. (2) Activity Title: Popcorn Purpose of Activity: To show how state changes in water can produce a familiar snack food. Set-up prior to experiment: set up the hotplate, or microwave, ready for making popcorn. Students will do this activity as one group. a. Make popcorn on a hot plate, or make microwave popcorn. b. While the popcorn is popping, explain that there is a little water inside the popcorn kernel. As the kernel heats up, this water turns to a gas. The gas molecules inside the kernel move around more than the liquid water and bump against the inside of the kernel so hard that they exert pressure on it. Eventually the pressure is so high that the kernel bursts. Relate the activity of the molecules to the previous activity where the students modeled the states of matter. c. Students can examine popcorn kernels before and after popping, to see how the kernel turns inside out from the force of the explosion. The white part of popcorn was on the inside of the kernel. The remains of the brown husk can be found hidden inside. d. Optional: watch a video of what happens to popcorn in slow motion (ref. 2). This can be done while the popcorn is heating up if necessary.
4 (3) Activity Title: Soda Drink Purpose of Activity: To observe a chemical reaction and understand the molecular mechanism underlying the reaction. Set-up prior to experiment: Pour a splash of juice into a Dixie cup for each student. Add the baking soda to one Dixie cup for each table. Give each student a coffee stirrer. Students will work individually to make the soda drink, then in pairs to assemble molecule models. 1. Introduce soda drink activity: we made popcorn by changing liquid water into a gas. Now we will make a gas in another way to make a soda drink. 2. Make soda: distribute a Dixie cup of orange juice to each student and a cup of baking soda and stir sticks to each table group. Ask the students to taste a little of the orange juice in their cup. Now ask the students to scoop some baking soda on the tip of a coffee stirrer, add it to their orange juice, and stir. 3. Ask students to watch and listen to what happens. (White with little bubbles; hear bubbles popping). 4. Ask students to taste the drink again. Ask students if the orange juice tastes different. (It should be fizzy on the tongue. Some students may also comment on it being sweeter or having another change in taste.) 5. Ask students about the states of matter and the state changes observed: Q. What states of matter did you start with? A solid (the baking soda) and a liquid (the orange juice). Q. What new state of matter was made? A gas (bubbles were observed). 6. Explain that a chemical reaction occurred between the solid and liquid, creating a new gas. Molecular modeling of the soda drink activity: 1. Distribute one molecule model kit to each pair of students. 2. Show students a model of HCO 3 (the molecule in baking soda). See photo and drawing. 3. Show students a model of hydrogen (H) - (the chemical in the juice that takes part in this chemical reaction). See photo and drawing. 4. Ask students to use the materials in their kits to make their own models of HCO 3 and H. 5. Tell students that when the baking soda (HCO 3 ) and juice (H) were mixed, their atoms rearranged as they chemically reacted. Explain that new molecules were formed as a result: One of the new molecules is a gas (seen and tasted as the bubbles and fizz in the soda). The other new molecule is water. 6. Ask students to pull apart their HCO 3 and reorganize the molecules to make the water molecule (H 2 O).
5 7. Then, ask students to use the remaining atoms (coloured balls) and bonds (toothpicks) to make the new gas molecule. They must combine the atoms according to the following rules (write rules on the board for reference): Each oxygen atom (red ball) must have two bonds (toothpicks) Each hydrogen atom (white ball) must have one bond only (toothpicks) Each carbon atom (black) must have four bonds (toothpicks) The angle of the bonds is not important. 8. Students should, given time, create the following two molecules: (1) H 2 O (water) (2) CO 2 (carbon dioxide), the new gas molecule 9. Discuss and summarize the soda activity: The baking soda and the orange juice chemically reacted. The reaction caused the molecules to reorganize. Two new molecules are created. One new molecule was water (which mixes in with the other water in the juice and disappears). The other new molecule was carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), which is a gas. You saw the CO 2 gas as little bubbles in the orange juice, heard the CO 2 gas bubbles popping, and also tasted the CO 2 gas as the fizz in your new drink. Closure Discussion This lesson involves a fair number of complex ideas, so review is maybe best done with the students taking turns to describe and explain parts of the lesson, with clarification by the teacher. References Bayrock, Fiona States of Matter: A question and Answer book. Capstone Press. < You tube video of popcorn popping slow motion. Accessed May. 12, 2014.
Lord Strathcona Elementary School, Vancouver School District. Ingrid Sulston (scientist); Reid McInnes and Phyllis Daly (teachers)
 Science Unit: Lesson 10: Space Rockets: Exploring the Solar System Summary: In part one of this two-part lesson, students make and launch Alka-seltzer rockets and learn about the chemical reaction causing
Science Unit: Lesson 10: Space Rockets: Exploring the Solar System Summary: In part one of this two-part lesson, students make and launch Alka-seltzer rockets and learn about the chemical reaction causing
Post-Show. Chemistry. Periodic Table of the Elements. After the Show. Traveling Science Shows
 Traveling Science Shows Post-Show Chemistry After the Show We recently presented a Chemistry show at your school, and thought you and your students might like to continue investigating this topic. The
Traveling Science Shows Post-Show Chemistry After the Show We recently presented a Chemistry show at your school, and thought you and your students might like to continue investigating this topic. The
Chapter 2, Lesson 5: Changing State Melting
 Chapter 2, Lesson 5: Changing State Melting Key Concepts Melting is a process that causes a substance to change from a solid to a liquid. Melting occurs when the molecules of a solid speed up enough that
Chapter 2, Lesson 5: Changing State Melting Key Concepts Melting is a process that causes a substance to change from a solid to a liquid. Melting occurs when the molecules of a solid speed up enough that
Chemical Change. Day 1: 70 minutes; Day 2: minutes
 Chemical Change Lesson Concept When one substance interacts with another substance, a chemical change may occur. There are five indicators that a chemical change has occurred: gas production (bubbles),
Chemical Change Lesson Concept When one substance interacts with another substance, a chemical change may occur. There are five indicators that a chemical change has occurred: gas production (bubbles),
Solids, liquids and gases
 Solids, liquids and gases Duration 60 minutes Lesson overview Students share what they know about the three states of matter solid, liquid and gas and consider some of their scientific properties. They
Solids, liquids and gases Duration 60 minutes Lesson overview Students share what they know about the three states of matter solid, liquid and gas and consider some of their scientific properties. They
INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 7
 INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 7 EXPLAINING MELTING AND SOLIDIFYING A. Lesson Cluster Goals and Lesson Objectives Goals Students should be able to explain melting and solidifying, by reference to the molecular
INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 7 EXPLAINING MELTING AND SOLIDIFYING A. Lesson Cluster Goals and Lesson Objectives Goals Students should be able to explain melting and solidifying, by reference to the molecular
Saturday Science Lesson Plan Fall 2008
 Saturday Science Lesson Plan Fall 2008 LEARNING OBJECTIVES STANDARDS 1.1.1 Observe, describe, draw, and sort objects carefully to learn about them. 1.2.6 Describe and compare objects in terms of number,
Saturday Science Lesson Plan Fall 2008 LEARNING OBJECTIVES STANDARDS 1.1.1 Observe, describe, draw, and sort objects carefully to learn about them. 1.2.6 Describe and compare objects in terms of number,
LESSON 6: Dew Drops ESTIMATED TIME Setup: 5 10 minutes Procedure: minutes
 LESSON 6: Dew Drops ESTIMATED TIME Setup: 5 10 minutes Procedure: 15 20 minutes DESCRIPTION Use jars of hot and cold water to demonstrate how water changes states. OBJECTIVE This lesson demonstrates the
LESSON 6: Dew Drops ESTIMATED TIME Setup: 5 10 minutes Procedure: 15 20 minutes DESCRIPTION Use jars of hot and cold water to demonstrate how water changes states. OBJECTIVE This lesson demonstrates the
MiSP CHEMICAL REACTIONS, L3 Teacher Guide. Introduction
 MiSP CHEMICAL REACTIONS, L3 Teacher Guide Introduction This weeklong unit should be included with other chemistry content teaching and learning. It is designed to follow Intermediate Level Science Core
MiSP CHEMICAL REACTIONS, L3 Teacher Guide Introduction This weeklong unit should be included with other chemistry content teaching and learning. It is designed to follow Intermediate Level Science Core
6th Grade: Great Salt Lake is Salty
 Curriculum written by Megan Black in partnership with The Great Salt Lake Institute at Westminster College. 6th Grade: Great Salt Lake is Salty Lesson Description: In this lesson students will compare
Curriculum written by Megan Black in partnership with The Great Salt Lake Institute at Westminster College. 6th Grade: Great Salt Lake is Salty Lesson Description: In this lesson students will compare
What is Science? Science is both a collection of knowledge and the process for building that knowledge.
 Introduction to Science Junior Science What is Science? Science is both a collection of knowledge and the process for building that knowledge. Science asks questions about the natural world and looks for
Introduction to Science Junior Science What is Science? Science is both a collection of knowledge and the process for building that knowledge. Science asks questions about the natural world and looks for
Chemical versus Physical Change
 Chemical versus Physical Change Overall Objective: By the end of the session pupils should understand the difference between a physical and chemical change and have a basic understanding of the states
Chemical versus Physical Change Overall Objective: By the end of the session pupils should understand the difference between a physical and chemical change and have a basic understanding of the states
Lord Strathcona Elementary School, Vancouver School District. Ingrid Sulston (scientist); Reid McInnes and Phyllis Daly (teachers)
 Science Unit: Lesson 14: Space Black Holes Summary: Students rotate through 4 stations that model phenomena scientists use to locate black holes: 1) gravity wells (marbles orbiting on spandex); 2) spinning
Science Unit: Lesson 14: Space Black Holes Summary: Students rotate through 4 stations that model phenomena scientists use to locate black holes: 1) gravity wells (marbles orbiting on spandex); 2) spinning
Chapter Preview. Improving Comprehension
 Chapter Preview Improving Comprehension Graphic Organizers are important visual tools that can help you organize information and improve your reading comprehension. The Graphic Organizer below is called
Chapter Preview Improving Comprehension Graphic Organizers are important visual tools that can help you organize information and improve your reading comprehension. The Graphic Organizer below is called
C1a The particulate nature of matter
 C1a The particulate nature of matter Introduction This topic may go back over ideas that students have already met, so it does not need to take up much teaching time. Nevertheless, it is important for
C1a The particulate nature of matter Introduction This topic may go back over ideas that students have already met, so it does not need to take up much teaching time. Nevertheless, it is important for
Matter and Its Changes
 Matter and Its Changes Matter: anything that has mass and occupies space (has volume) anything that has inertia and requires a force to start or stop it from moving Observation: gathering information using
Matter and Its Changes Matter: anything that has mass and occupies space (has volume) anything that has inertia and requires a force to start or stop it from moving Observation: gathering information using
Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy
 Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy By now you know that substances are made of atoms and molecules. These atoms and molecules are always in motion and have attractions to each other. When
Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy By now you know that substances are made of atoms and molecules. These atoms and molecules are always in motion and have attractions to each other. When
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan
 Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Presenter(s) Chemical Reactions Mercedes Taylor, Nick Settineri, Jessica Ziegler, Tyler Hurlburt, Parker Deal Grade Level 5 Standards Connection(s)
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Presenter(s) Chemical Reactions Mercedes Taylor, Nick Settineri, Jessica Ziegler, Tyler Hurlburt, Parker Deal Grade Level 5 Standards Connection(s)
Post-Show HOT AND COLD. Gases. Liquids. Solids. After the Show. Traveling Science Shows
 Traveling Science Shows Post-Show HOT AND COLD After the Show We recently presented a Hot and Cold show at your school, and thought you and your students might like to continue investigating this topic.
Traveling Science Shows Post-Show HOT AND COLD After the Show We recently presented a Hot and Cold show at your school, and thought you and your students might like to continue investigating this topic.
Unsaved Test, Version: 1 1
 Name: Key Concepts Select the term that best completes the statement. A. beam balance B. graduated cylinder C. scale D. matter E. mass F. newton G. volume H. height I. weight J. kilogram 1. Anything that
Name: Key Concepts Select the term that best completes the statement. A. beam balance B. graduated cylinder C. scale D. matter E. mass F. newton G. volume H. height I. weight J. kilogram 1. Anything that
Chapter 2, Lesson 1: Heat, Temperature, and Conduction
 Chapter 2, Lesson 1: Heat, Temperature, and Conduction Key Concepts Adding energy (heating) atoms and molecules increases their motion, resulting in an increase in temperature. Removing energy (cooling)
Chapter 2, Lesson 1: Heat, Temperature, and Conduction Key Concepts Adding energy (heating) atoms and molecules increases their motion, resulting in an increase in temperature. Removing energy (cooling)
STATES OF MATTER NOTES..
 STATES OF MATTER NOTES.. While you are reading, answer the following which will help you with the States of Matter Project. What is matter (definition): What are the states of matter and what are the characteristics/properties
STATES OF MATTER NOTES.. While you are reading, answer the following which will help you with the States of Matter Project. What is matter (definition): What are the states of matter and what are the characteristics/properties
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan
 Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Presenter(s) The Water Cycle UC Berkeley PhD students Grade Level 1 Standards Connection(s) Earth Sciences, physics sciences CA Science Content
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Presenter(s) The Water Cycle UC Berkeley PhD students Grade Level 1 Standards Connection(s) Earth Sciences, physics sciences CA Science Content
6.7 Design Your Own Experiment: Factors
 6.7 Design Your Own Experiment: Factors That Affect the Rate of Dissolving Page 158 PRESCRIBED LEARNING OUTCOMES measure substances and solutions according to ph, solubility, and concentration conduct
6.7 Design Your Own Experiment: Factors That Affect the Rate of Dissolving Page 158 PRESCRIBED LEARNING OUTCOMES measure substances and solutions according to ph, solubility, and concentration conduct
What Do You Think? Investigate GOALS
 Activity 2 More Chemical Changes GOALS In this activity you will: Observe several typical examples of evidence that a chemical change is occurring. Make generalizations about the combinations of materials
Activity 2 More Chemical Changes GOALS In this activity you will: Observe several typical examples of evidence that a chemical change is occurring. Make generalizations about the combinations of materials
Author(s): Prof. Eun-Ah Kim, Dr. Andrej Mesaros, Sarah Wharton, & Mark Walsh
 Liquid Crystals Author(s): Prof. Eun-Ah Kim, Dr. Andrej Mesaros, Sarah Wharton, & Mark Walsh Date Created: November, 2014 Subject: Chemistry Grade Level: K-2 & 3-5 Standards: N ext Generation Science Standards
Liquid Crystals Author(s): Prof. Eun-Ah Kim, Dr. Andrej Mesaros, Sarah Wharton, & Mark Walsh Date Created: November, 2014 Subject: Chemistry Grade Level: K-2 & 3-5 Standards: N ext Generation Science Standards
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan
 Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Presenter(s) Grade Level 3rd Melting, Freezing, and More!: Phase Transitions Steven Scroggins, Ailey Crow, Tom Holcombe, and Terence Choy California
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Presenter(s) Grade Level 3rd Melting, Freezing, and More!: Phase Transitions Steven Scroggins, Ailey Crow, Tom Holcombe, and Terence Choy California
Performance script for sixth graders By Thomas Kuo and Kimberly Kline LEAPS Fellows, University of California, Santa Barbara
 Performance script for sixth graders By Thomas Kuo and Kimberly Kline LEAPS Fellows, 2007-08 University of California, Santa Barbara [Remember to get answers from a wide variety of students in the audience.
Performance script for sixth graders By Thomas Kuo and Kimberly Kline LEAPS Fellows, 2007-08 University of California, Santa Barbara [Remember to get answers from a wide variety of students in the audience.
INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 5
 INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 5 EXPLAINING DISSOLVING A. Lesson Cluster Goals and Lesson Objectives Goals Students should be able to explain dissolving of solids in liquids in terms of molecules. Lesson
INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 5 EXPLAINING DISSOLVING A. Lesson Cluster Goals and Lesson Objectives Goals Students should be able to explain dissolving of solids in liquids in terms of molecules. Lesson
Recognizing Chemical_Reactions By Dr. Kathleen Vandiver
 Recognizing Chemical_Reactions By Dr. Kathleen Vandiver Hello. My name is Dr. Kathy Vandiver. And we're here at the Edgerton Center at MIT, a university in the United States. And the Edgerton Center is
Recognizing Chemical_Reactions By Dr. Kathleen Vandiver Hello. My name is Dr. Kathy Vandiver. And we're here at the Edgerton Center at MIT, a university in the United States. And the Edgerton Center is
The Changing Phases of Matter
 The Changing Phases of Matter Teacher's Guide Editors: Brian A. Jerome, Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome Assistant Editor: Louise Marrier Graphics: Lyndsey Canfield Dean Ladago Fred Thodal Lucy Rouse www.visuallearningco.com
The Changing Phases of Matter Teacher's Guide Editors: Brian A. Jerome, Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome Assistant Editor: Louise Marrier Graphics: Lyndsey Canfield Dean Ladago Fred Thodal Lucy Rouse www.visuallearningco.com
Unit 1 Lesson 6 Changes of State. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 The Fact of the Matter What happens when matter changes state? The three most familiar states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. A change of state is the change of a substance from one physical form
The Fact of the Matter What happens when matter changes state? The three most familiar states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. A change of state is the change of a substance from one physical form
Table of Contents. Diagnostic Pre-test... 5 Lesson 1: What Is an Atom? Lesson 5: Gases. Lesson 6: Melting and Freezing. Lesson 2: What Are Molecules?
 Table of Contents Diagnostic Pre-test................. 5 Lesson 1: What Is an Atom? What Can You See?................ 11 What Is Matter Made Of?........... 12 Describing the Atom............... 13 What
Table of Contents Diagnostic Pre-test................. 5 Lesson 1: What Is an Atom? What Can You See?................ 11 What Is Matter Made Of?........... 12 Describing the Atom............... 13 What
Objectives. Inertia. Is air matter? Is Light matter? Chapter 2. Chapter 2. Table of Contents. Chapter 2. Chapter 2. Section 1 What Is Matter?
 The Properties of Matter Section 1 What Is Matter? Table of Contents Section 1 What Is Matter? Section 2 Physical Properties Section 3 Chemical Properties Objectives Describe the two properties of all
The Properties of Matter Section 1 What Is Matter? Table of Contents Section 1 What Is Matter? Section 2 Physical Properties Section 3 Chemical Properties Objectives Describe the two properties of all
Characteristics of Chemical Change
 Section 2 Characteristics of Chemical Change What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section you will Observe several typical examples of evidence that a chemical change is occurring. Make generalizations
Section 2 Characteristics of Chemical Change What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section you will Observe several typical examples of evidence that a chemical change is occurring. Make generalizations
Changes of State. Thermal Energy: Changes of State 1
 Changes of State Last lesson we learned about thermal energy and temperature. Objects whose molecules are moving very quickly are said to have high thermal energy or high temperature. The higher the temperature,
Changes of State Last lesson we learned about thermal energy and temperature. Objects whose molecules are moving very quickly are said to have high thermal energy or high temperature. The higher the temperature,
Name: 1. Which of the following is probably true about 300 ml of sand and 300 ml of water?
 Name: Jaguar Review #2 Physical Sciences Benchmark A: Relate uses, properties and chemical processes to the behavior and/or arrangement of the small particles that compose matter. 1. Which of the following
Name: Jaguar Review #2 Physical Sciences Benchmark A: Relate uses, properties and chemical processes to the behavior and/or arrangement of the small particles that compose matter. 1. Which of the following
2/22/2019 NEW UNIT! Chemical Interactions. Atomic Basics #19
 NEW UNIT! Chemical Interactions Atomic Basics #19 1 Vocabulary: Matter: Anything that has mass and takes up space. Atom: the smallest particle of matter. Element: A pure substance made up of only one type
NEW UNIT! Chemical Interactions Atomic Basics #19 1 Vocabulary: Matter: Anything that has mass and takes up space. Atom: the smallest particle of matter. Element: A pure substance made up of only one type
5.4 The Kinetic Molecular Theory and Changes of State
 5.4 The Kinetic Molecular Theory and Changes of State Chemists know that they will probably never be able to observe exactly what is happening in a chemical reaction. Observation is a powerful tool of
5.4 The Kinetic Molecular Theory and Changes of State Chemists know that they will probably never be able to observe exactly what is happening in a chemical reaction. Observation is a powerful tool of
Predict the effect of increased competition for abiotic and biotic resources on a food web. colored pencils graph paper ruler
 Edit File QUICK LAB Effect of Abiotic and Biotic Factors No organism exists in isolation. Organisms depend on and compete for the abiotic, or non-living, factors in its environment. For example, organisms
Edit File QUICK LAB Effect of Abiotic and Biotic Factors No organism exists in isolation. Organisms depend on and compete for the abiotic, or non-living, factors in its environment. For example, organisms
Chapter Review USING VOCABULARY UNDERSTANDING CONCEPTS. Skills Worksheet
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING VOCABULARY 1. Academic Vocabulary Which of the following words means a set of steps or events? a. reaction b. process c. principle d. role For each pair of terms,
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING VOCABULARY 1. Academic Vocabulary Which of the following words means a set of steps or events? a. reaction b. process c. principle d. role For each pair of terms,
INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 8 Explaining Evaporation and Boiling
 INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 8 Explaining Evaporation and Boiling A. Lesson Cluster Goals and Lesson Objectives Goals: Students should be able to explain evaporation and boiling, both in macroscopic
INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 8 Explaining Evaporation and Boiling A. Lesson Cluster Goals and Lesson Objectives Goals: Students should be able to explain evaporation and boiling, both in macroscopic
States of Matter 1 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016
 States of Matter 1 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 States of Matter 2 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are the three states of matter? 3 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 At any given temperature, all substances exist
States of Matter 1 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 States of Matter 2 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are the three states of matter? 3 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 At any given temperature, all substances exist
Section 1: Four States of Matter (pages 60-67)
 Name: Sci Number: Period: Parent Signature: My little book of: Word: Pg found States of matter Solid Four States of Matter: Section 1 definitions: (pg60) My definition Chp 3 Draw/paste examples of all
Name: Sci Number: Period: Parent Signature: My little book of: Word: Pg found States of matter Solid Four States of Matter: Section 1 definitions: (pg60) My definition Chp 3 Draw/paste examples of all
Matter and Its Properties. Unit 2
 Matter and Its Properties Unit 2 Lesson 1: Physical & Chemical Properties & Changes Unit 2: Matter and Its Properties Section 1: Physical Properties & Change Lesson 1: Physical & Chemical Properties &
Matter and Its Properties Unit 2 Lesson 1: Physical & Chemical Properties & Changes Unit 2: Matter and Its Properties Section 1: Physical Properties & Change Lesson 1: Physical & Chemical Properties &
TEACHER NOTES: ICE CUBE POSTER
 TEACHER NOTES: NATIONAL CURRICULUM LINKS THE PARTICULATE NATURE OF MATTER the properties of the different states of matter (solid, liquid and gas) in terms of the particle model, including gas pressure
TEACHER NOTES: NATIONAL CURRICULUM LINKS THE PARTICULATE NATURE OF MATTER the properties of the different states of matter (solid, liquid and gas) in terms of the particle model, including gas pressure
What Do You Think? Investigate GOALS. Part A: Freezing Water
 Activity 5 Freezing Water GOALS In this activity you will: Determine the freezing point of water. Show graphically what happens to the temperature as water is cooled to freezing and while it is freezing.
Activity 5 Freezing Water GOALS In this activity you will: Determine the freezing point of water. Show graphically what happens to the temperature as water is cooled to freezing and while it is freezing.
3.3 Phase Changes 88 A NATURAL APPROACH TO CHEMISTRY. Section 3.3 Phase Changes
 Section 3.3 Phase Changes 3.3 Phase Changes Solid, liquid and gas During a phase change, a substance rearranges the order of its particles (atoms or molecules). Examples of phase change include melting
Section 3.3 Phase Changes 3.3 Phase Changes Solid, liquid and gas During a phase change, a substance rearranges the order of its particles (atoms or molecules). Examples of phase change include melting
Transformation of Matter: Physical and Chemical Changes
 Transformation of Matter: Physical and Chemical Changes What does it mean to transform? Transform: change in form, appearance, or makeup What kinds of things transform? How can it be transformed? How
Transformation of Matter: Physical and Chemical Changes What does it mean to transform? Transform: change in form, appearance, or makeup What kinds of things transform? How can it be transformed? How
Category V Physical Science Examples
 Category V Physical Science Examples Guiding student interpretation and reasoning Chemistry That Applies Chemistry That Applies contains numerous questions to guide students interpretation of and reasoning
Category V Physical Science Examples Guiding student interpretation and reasoning Chemistry That Applies Chemistry That Applies contains numerous questions to guide students interpretation of and reasoning
CO 2. Lesson 1. Production of a gas
 Lesson 1 Production of a gas T E A C H E R G U I D E CO 2 Lesson summary Students meet volcanologist Victor Helguson, who is studying the gases released by volcanoes in Iceland. Students conduct a chemical
Lesson 1 Production of a gas T E A C H E R G U I D E CO 2 Lesson summary Students meet volcanologist Victor Helguson, who is studying the gases released by volcanoes in Iceland. Students conduct a chemical
Standards 8.5.c. I know chemical reactions usually liberate or absorbs heat.
 6 March 2013 Give an example of a physical change and a chemical change, and then describe how they are different from the other. Explain your answer in 2-3 sentences. Standards 8.5.c. I know chemical
6 March 2013 Give an example of a physical change and a chemical change, and then describe how they are different from the other. Explain your answer in 2-3 sentences. Standards 8.5.c. I know chemical
KINETIC PARTICLE THEORY
 KINETIC PARTICLE THEORY IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS: The mixing process in gases or solutions due to the random motion of particles is called Diffusion. The process by which a liquid changes into a vapour at
KINETIC PARTICLE THEORY IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS: The mixing process in gases or solutions due to the random motion of particles is called Diffusion. The process by which a liquid changes into a vapour at
TEACHER S NOTES FOR UNIT 1: KAI/OCEAN (SCIENTIFIC METHOD PLUS)
 TEACHER S NOTES FOR UNIT 1: KAI/OCEAN (SCIENTIFIC METHOD PLUS) After introducing/reviewing the scientific method (see 2 handouts), try this sequence of lessons to allow students to experiment themselves,
TEACHER S NOTES FOR UNIT 1: KAI/OCEAN (SCIENTIFIC METHOD PLUS) After introducing/reviewing the scientific method (see 2 handouts), try this sequence of lessons to allow students to experiment themselves,
1 Three States of Matter
 CHAPTER 3 1 Three States of Matter SECTION States of Matter BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is matter made of? What are the three most common
CHAPTER 3 1 Three States of Matter SECTION States of Matter BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is matter made of? What are the three most common
Chapter 8. Chapter 8. Preview. Bellringer. Chapter 8. Particles of Matter. Objectives. Chapter 8. Particles of Matter, continued
 States of Matter Preview Bellringer Section 2 Behavior of Gases In the kitchen, you might find three different forms of water. What are these three forms of water, and where exactly in the kitchen would
States of Matter Preview Bellringer Section 2 Behavior of Gases In the kitchen, you might find three different forms of water. What are these three forms of water, and where exactly in the kitchen would
Students will have practical experience of how to set up an experiment, obtain results and interpret those results.
 Science Unit: Lesson 11: Temperate Forest The Way a Tree Works School year: 2006/2007 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Notes: Lord Selkirk Annex Elementary School, Vancouver
Science Unit: Lesson 11: Temperate Forest The Way a Tree Works School year: 2006/2007 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Notes: Lord Selkirk Annex Elementary School, Vancouver
Unit 6M.3: Changing materials
 Unit 6M.3: Adding materials to water. Chemical reactions Skill you will use: Classifying Observing Predicting By the end of this unit you should: Know that when substances are added to water, some will
Unit 6M.3: Adding materials to water. Chemical reactions Skill you will use: Classifying Observing Predicting By the end of this unit you should: Know that when substances are added to water, some will
17B: Distilling Aromatic Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 17 17B: Distilling Aromatic Hydrocarbons Key Question: How are aromatic compounds isolated? What do they have in common? Aromatic hydrocarbon molecules were originally discovered in spices and
Chapter 17 17B: Distilling Aromatic Hydrocarbons Key Question: How are aromatic compounds isolated? What do they have in common? Aromatic hydrocarbon molecules were originally discovered in spices and
States of Matter: A Solid Lesson where Liquids Can be a Gas!
 TEACHER GUIDE STATES OF MATTER 60 Minute Physical Science Lesson Science- to- Go! Program Grades: 1-3 States of Matter: A Solid Lesson where Liquids Can be a Gas! Description Your classroom will be converted
TEACHER GUIDE STATES OF MATTER 60 Minute Physical Science Lesson Science- to- Go! Program Grades: 1-3 States of Matter: A Solid Lesson where Liquids Can be a Gas! Description Your classroom will be converted
Chemistry #3 Notebook States of Matter
 Name Hour Test Date Group # Chemistry #3 Notebook States of Matter LEARNING TARGETS I CAN model the motion and arrangement of particles in typical solids, liquids and gasses. I CAN describe how the motion
Name Hour Test Date Group # Chemistry #3 Notebook States of Matter LEARNING TARGETS I CAN model the motion and arrangement of particles in typical solids, liquids and gasses. I CAN describe how the motion
THIRD GRADE WATER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 THIRD GRADE WATER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF THIRD GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing the different components of the water cycle. LAB: Contrasting water with hydrogen peroxide.
THIRD GRADE WATER 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES WATER CYCLE OVERVIEW OF THIRD GRADE WATER WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing the different components of the water cycle. LAB: Contrasting water with hydrogen peroxide.
Weather Tanks. NC Standards 5.E.1, 5.P.2.1 Page 3. Grade 5 Earth Science, Physical Science. Activity Description & Estimated Class Time.
 Weather Tanks NC Standards 5.E.1, 5.P.2.1 Page 3 Grade 5 Earth Science, Physical Science Throughout the guide, teaching tips are in red. Activity Description & Estimated Class Time Objectives This activity
Weather Tanks NC Standards 5.E.1, 5.P.2.1 Page 3 Grade 5 Earth Science, Physical Science Throughout the guide, teaching tips are in red. Activity Description & Estimated Class Time Objectives This activity
Chemistry: classifying chemical and physical changes in various materials/substances
 Chemistry: classifying chemical and physical changes in various materials/substances Nikki Schilling, Ames, St. Paul Mn Based on original activity from Cool Chemistry Concoctions by Joe Rhatigan and Veronika
Chemistry: classifying chemical and physical changes in various materials/substances Nikki Schilling, Ames, St. Paul Mn Based on original activity from Cool Chemistry Concoctions by Joe Rhatigan and Veronika
Creative Classroom Lessons
 Matter, Matter Everywhere! Solids, Liquids and Gases Unit Creative Classroom Lessons Contents: 1. Solids, Liquids and gases student folder cover 2. Introduction Activity: Mystery Box 3. Solids, Liquids
Matter, Matter Everywhere! Solids, Liquids and Gases Unit Creative Classroom Lessons Contents: 1. Solids, Liquids and gases student folder cover 2. Introduction Activity: Mystery Box 3. Solids, Liquids
Oobleck: A Program about States of Matter Presented by the Sciencenter in Ithaca, NY. Program Overview
 Oobleck: A Program about States of Matter Presented by the Sciencenter in Ithaca, NY Program Overview Oobleck introduces students to states of matter and scientific observation. The program is designed
Oobleck: A Program about States of Matter Presented by the Sciencenter in Ithaca, NY Program Overview Oobleck introduces students to states of matter and scientific observation. The program is designed
Chapter 3. Preview. Section 1 Three States of Matter. Section 2 Behavior of Gases. Section 3 Changes of State. States of Matter.
 States of Matter Preview Section 1 Three States of Matter Section 2 Behavior of Gases Section 3 Changes of State Concept Mapping Section 1 Three States of Matter Bellringer In the kitchen, you might find
States of Matter Preview Section 1 Three States of Matter Section 2 Behavior of Gases Section 3 Changes of State Concept Mapping Section 1 Three States of Matter Bellringer In the kitchen, you might find
Chapter 6, Lesson 7: Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions
 Chapter 6, Lesson 7: Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions Key Concepts If two substances react and the temperature of the mixture decreases, the reaction is endothermic. If two substances react and the
Chapter 6, Lesson 7: Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions Key Concepts If two substances react and the temperature of the mixture decreases, the reaction is endothermic. If two substances react and the
Solids (cont.) Describe the movement of particles in a solid and the forces between them.
 Solids A solid is matter that has a definite shape and a definite volume. The attractive forces between the particles in a solid are strong and pull them close together. Solids (cont.) Describe the movement
Solids A solid is matter that has a definite shape and a definite volume. The attractive forces between the particles in a solid are strong and pull them close together. Solids (cont.) Describe the movement
A simple equation of what happens when you add baking soda to vinegar:
 What s the Matter? Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. Mass is the stuff that matter is made of, or the amount of particles in a substance or object. Matter has physical and chemical properties
What s the Matter? Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. Mass is the stuff that matter is made of, or the amount of particles in a substance or object. Matter has physical and chemical properties
Science 14 Unit A: Investigating Properties of Matter Chapter 3 Mixtures and Their Uses pp WORKBOOK Name:
 Science 14 Unit A: Investigating Properties of Matter Chapter 3 Mixtures and Their Uses pp. 40-57 WORKBOOK Name: 3.1 Two Kinds of Mixtures pp. 42-44 Read pp. 42-43 Mixtures are represented on the right
Science 14 Unit A: Investigating Properties of Matter Chapter 3 Mixtures and Their Uses pp. 40-57 WORKBOOK Name: 3.1 Two Kinds of Mixtures pp. 42-44 Read pp. 42-43 Mixtures are represented on the right
1. Read the following article and fill in the vocabulary crossword. An Atom Apart: by Leslie Cargile
 Grade 6 Science Summer Work International School of Arts and Sciences ISAS 2012 2013 Name: 1. Read the following article and fill in the vocabulary crossword. An Atom Apart: by Leslie Cargile Have you
Grade 6 Science Summer Work International School of Arts and Sciences ISAS 2012 2013 Name: 1. Read the following article and fill in the vocabulary crossword. An Atom Apart: by Leslie Cargile Have you
1 Compounds and Molecules
 CAPTER 6 1 Compounds and Molecules SECTION The Structure of Matter KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What holds compounds and substances together? What determines the properties
CAPTER 6 1 Compounds and Molecules SECTION The Structure of Matter KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What holds compounds and substances together? What determines the properties
5 th Grade Lesson Plan: Matter and Chemical Reactions
 5 th Grade Lesson Plan: Matter and Chemical Reactions Objective: Teach students that matter is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction, rather, it is transformed. Identify evidence that
5 th Grade Lesson Plan: Matter and Chemical Reactions Objective: Teach students that matter is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction, rather, it is transformed. Identify evidence that
SNC1D CHEMISTRY 2/8/2013. ATOMS, ELEMENTS, & COMPOUNDS L Chemical Properties (P ) Chemical Properties. Chemical Properties
 SNC1D CHEMISTRY ATOMS, ELEMENTS, & COMPOUNDS L (P.152-155) When we watch a fireworks display we are, in scientific terminology, seeing the chemical properties of the fireworks. A chemical property is a
SNC1D CHEMISTRY ATOMS, ELEMENTS, & COMPOUNDS L (P.152-155) When we watch a fireworks display we are, in scientific terminology, seeing the chemical properties of the fireworks. A chemical property is a
Lesson Plan: Stearic Acid
 Lesson Plan: Stearic Acid Created by: In this lesson, students investigate how stearic acid undergoes a 2014 AACT Middle School phase change from solid to liquid and back from liquid to solid. Content
Lesson Plan: Stearic Acid Created by: In this lesson, students investigate how stearic acid undergoes a 2014 AACT Middle School phase change from solid to liquid and back from liquid to solid. Content
States of Matter. Changes in State
 CHAPTER 8 States of Matter LESSON 2 Changes in State What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
CHAPTER 8 States of Matter LESSON 2 Changes in State What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
OK, you ve probably seen the Bill Nye video and have learned that matter is everything and all stuff. That s right. Everything around you is matter.
 Matter & Chemistry OK, you ve probably seen the Bill Nye video and have learned that matter is everything and all stuff. That s right. Everything around you is matter. In fact, anything that has weight
Matter & Chemistry OK, you ve probably seen the Bill Nye video and have learned that matter is everything and all stuff. That s right. Everything around you is matter. In fact, anything that has weight
4 th Grade Science Unit: Matter Matters Conservation of Matter Unit Snapshot
 4 th Grade Science Unit: Matter Matters Conservation of Matter Unit Snapshot Grade Level: 4 Topic: Electricity, Heat and Matter Duration: 14 days Summary This series of activities is for students to develop
4 th Grade Science Unit: Matter Matters Conservation of Matter Unit Snapshot Grade Level: 4 Topic: Electricity, Heat and Matter Duration: 14 days Summary This series of activities is for students to develop
The Big Drip - Key Stage 2
 The Big Drip - Key Stage 2 INTRODUCTION THE BIG DRIP is based on Attainment Target 3 of the National Curriculum for Science and these notes are intended as a guide to the scientific content of the play
The Big Drip - Key Stage 2 INTRODUCTION THE BIG DRIP is based on Attainment Target 3 of the National Curriculum for Science and these notes are intended as a guide to the scientific content of the play
Today is: Monday, October 17th
 Today is: Monday, October 17th Get out your homework! 10/17/2016 #motivationmonday (This is Week 11 Warm Ups!) 1. It s a new quarter, which means a fresh start! What can you do to stay motivated this quarter?
Today is: Monday, October 17th Get out your homework! 10/17/2016 #motivationmonday (This is Week 11 Warm Ups!) 1. It s a new quarter, which means a fresh start! What can you do to stay motivated this quarter?
Lesson 1 Solids, Liquids, and Gases
 Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 8 Content Vocabulary 9 Lesson Outline 10 MiniLab 12 Content Practice A 13 Content Practice B 14 School to Home 15 Key Concept Builders 16 Enrichment
Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 8 Content Vocabulary 9 Lesson Outline 10 MiniLab 12 Content Practice A 13 Content Practice B 14 School to Home 15 Key Concept Builders 16 Enrichment
Matter and Its Changes
 Lesson 2 Matter and Its Changes 6.NS.3, 6.NS.5, 6.NS.6, 6.NS.7, 6.NS.10, 6.1.1, 6.1.2, 6.1.3 Skim or scan the heading, boldfaced words, and pictures in the lesson. Identify or predict three facts you will
Lesson 2 Matter and Its Changes 6.NS.3, 6.NS.5, 6.NS.6, 6.NS.7, 6.NS.10, 6.1.1, 6.1.2, 6.1.3 Skim or scan the heading, boldfaced words, and pictures in the lesson. Identify or predict three facts you will
The Can Demonstration
 The Can Demonstration With your table, make a prediction as to what will happen to the can. Discuss why you think that the can imploded. What are some reasons? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xg5niowf_zw&t=28s
The Can Demonstration With your table, make a prediction as to what will happen to the can. Discuss why you think that the can imploded. What are some reasons? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xg5niowf_zw&t=28s
Changing States of Matter By Cindy Grigg
 By Cindy Grigg 1 On Earth, almost all matter exists in just three states. Matter is usually a solid, a liquid, or a gas. Plasma, the fourth state of matter, is rare on Earth. It sometimes can be found
By Cindy Grigg 1 On Earth, almost all matter exists in just three states. Matter is usually a solid, a liquid, or a gas. Plasma, the fourth state of matter, is rare on Earth. It sometimes can be found
4. Every CHANGE in matter includes a change in, which is conserved in a chemical reaction and. TRANSFORMED from one form to another.
 Part C: Lesson 1.4 - Read pages 20-29 to answer these questions. Add to notes - 1. A physical change alters the form or appearance of matter, such as Change in size, a change in SIZE or. SHAPE shape, or
Part C: Lesson 1.4 - Read pages 20-29 to answer these questions. Add to notes - 1. A physical change alters the form or appearance of matter, such as Change in size, a change in SIZE or. SHAPE shape, or
Science in the Kitchen
 Program Support Notes by: Margaret Bishop B.Ed, Dip T Produced by: VEA Pty Ltd Commissioning Editor: Sandra Frerichs B.Ed, M.Ed. Executive Producer: Simon Garner B.Ed, Dip Management Davis Film and Video
Program Support Notes by: Margaret Bishop B.Ed, Dip T Produced by: VEA Pty Ltd Commissioning Editor: Sandra Frerichs B.Ed, M.Ed. Executive Producer: Simon Garner B.Ed, Dip Management Davis Film and Video
5 th GRADE PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL TESTS
 5 th GRADE PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL TESTS Summary: Students investigate 5 unknown white powders. They gather clues by observing the physical and chemical changes of the powders. At the end of the activity,
5 th GRADE PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL TESTS Summary: Students investigate 5 unknown white powders. They gather clues by observing the physical and chemical changes of the powders. At the end of the activity,
Reactions that Produce Heat
 Chemical Dominoes Activity 7 Reactions that Produce Heat GOALS In this activity you will: Explain the effect of particle size and use of a catalyst on reaction rate. Represent energy changes graphically.
Chemical Dominoes Activity 7 Reactions that Produce Heat GOALS In this activity you will: Explain the effect of particle size and use of a catalyst on reaction rate. Represent energy changes graphically.
Matter, Atoms & Molecules
 Matter, Atoms & Molecules Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. All matter is made of tiny particles called atoms, which are too small to see with the naked eye. Matter Matter is anything
Matter, Atoms & Molecules Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. All matter is made of tiny particles called atoms, which are too small to see with the naked eye. Matter Matter is anything
States of Matter. What physical changes and energy changes occur as matter goes from one state to another?
 Name States of Matter Date What physical changes and energy changes occur as matter goes from one state to another? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about states of
Name States of Matter Date What physical changes and energy changes occur as matter goes from one state to another? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about states of
Changing States of Matter
 Matter is the Stuff Around You Matter is everything around you. Matter is anything made of atoms and molecules. Matter is anything that has a mass. Matter is also related to light and electromagnetic radiation.
Matter is the Stuff Around You Matter is everything around you. Matter is anything made of atoms and molecules. Matter is anything that has a mass. Matter is also related to light and electromagnetic radiation.
Matter: Properties and Changes
 Matter: Properties and Changes Matter and Its Changes What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
Matter: Properties and Changes Matter and Its Changes What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
The physical state of a substance can be changed by increasing or decreasing its temperature.
 Chemistry Lecture #63: Changes of State The physical state of a substance can be changed by increasing or decreasing its temperature. For example, a solid substance can be converted into a liquid by heating
Chemistry Lecture #63: Changes of State The physical state of a substance can be changed by increasing or decreasing its temperature. For example, a solid substance can be converted into a liquid by heating
Matter. Gas. Solid Liquid. Both shape and volume are not fixed. It has a fixed shape and a fixed volume.
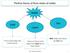 Matter Solid Liquid Gas It has a fixed shape and a fixed volume. It does not have a fixed shape, but it does have a fixed volume. Both shape and volume are not fixed. Felix Yung and John Polias 1 Matter
Matter Solid Liquid Gas It has a fixed shape and a fixed volume. It does not have a fixed shape, but it does have a fixed volume. Both shape and volume are not fixed. Felix Yung and John Polias 1 Matter
3. Watch video All About Solids, Liquids, & Gases. Watch first eight minutes.
 Structure and Transformation of Matter Original (2008) Lesson Plan I can classify matter into different categories. I can describe the differences between solid, liquid, and gas. Lesson 1: Search for Matter
Structure and Transformation of Matter Original (2008) Lesson Plan I can classify matter into different categories. I can describe the differences between solid, liquid, and gas. Lesson 1: Search for Matter
6.1. How Compounds Form. Chemicals Everywhere. Hydrogen peroxide. Compounds
 6.1 How Compounds Form Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Compounds are composed of two or more elements that combine in a specific ratio. Ionic compounds form when metallic and
6.1 How Compounds Form Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Compounds are composed of two or more elements that combine in a specific ratio. Ionic compounds form when metallic and
Chemical Formulas and Equations
 Part I: The Big Picture Chemical Formulas and Equations Reminder: H is the element symbol for Hydrogen. H 2 is the chemical formula for hydrogen. The subscript 2 after the H means that two atoms of hydrogen
Part I: The Big Picture Chemical Formulas and Equations Reminder: H is the element symbol for Hydrogen. H 2 is the chemical formula for hydrogen. The subscript 2 after the H means that two atoms of hydrogen
MS-PS1 Matter and Its Interactions
 MS-PS1 Matter and Its Interactions Key Ideas and Common Student Misconceptions This document compiles Key Ideas and developed by AAAS Project 2061 and the National Science Foundation. For additional information
MS-PS1 Matter and Its Interactions Key Ideas and Common Student Misconceptions This document compiles Key Ideas and developed by AAAS Project 2061 and the National Science Foundation. For additional information
By All INdICATIONS (2 Hours)
 By All INdICATIONS (2 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 5 Grade Range: 6-8 OVERVIEW In this activity, students create an acid-base indicator using red cabbage extract. Students then use this indicator
By All INdICATIONS (2 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 5 Grade Range: 6-8 OVERVIEW In this activity, students create an acid-base indicator using red cabbage extract. Students then use this indicator
