Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of undoped and Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles
|
|
|
- Quentin Morris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 3 Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of undoped and Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles 3.1 Introduction Phosphors are substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence. Efficient phosphors for lighting applications, flat panel displays, etc have always been a goal for researchers. Phosphor materials are generally composed of a pure host matrix and a small amount of intentionally added impurity, so-called activator [54]. If the host material and the activator concentrations are fixed, the physical properties of phosphor materials such as the surface area, the crystallinity, the phase purity, and the distribution of activator in the host matrix play crucial roles in modulating luminescence 99
2 100 Undoped and Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles characteristics. Those material properties can be controlled by the preparation conditions: temperature, precursor concentration, and post annealing. Especially, the preparation and annealing temperatures greatly influence the luminescence intensity of phosphor particles since it directly affects the formation of crystal structure, crystallinity, the surface area of particles, and the distribution of activator. (Y,Gd)BO 3 :Eu [178] or Y 2 O 3 :Eu [179], Zn 2 SiO 4 :Mn [180], and BaMgAl 10 O 17 :Eu [181] are some phosphor materials which give red, green and blue emission respectively. Generally, most of the light emitting devices utilizes red, green, and blue colors for practical applications. The particle size of conventional phosphors are in micrometer scale, hence light scattering at grain boundaries is strong and it decreases the light output. Nanophosphors can be synthesized whose size varying from tens to hundreds of nanometers which itself are smaller than the incident light wavelength and this will reduce the scattering, thereby enhancing the luminescence efficiency. Synthesis of nanometre-size phosphors has attracted much attention owing to their size-dependent electrical and optical properties originating from the quantum confinement. Zinc gallium oxide, ZnGa 2 O 4, is a well-known low voltage oxide phosphor used in flat panel displays [ ]. This ternary oxide compound is a self activated phosphor, crystallizing in the normal spinel structure. The spinel unit cell belongs to the cubic space group Oh7 (Fd3m) with eight formula units per cell and contains two kinds of cation sites. The A site (Zn 2+ ) has tetrahedral coordination with full T d symmetry, while the B site (Ga 3+ ) has six fold distorted octahedral coordination belonging to the D 3d point group. The trigonal axis of the B site is, of course, coincident with the unit cell (111) axis, and the site has a center of inversion [185]. When undoped, ZnGa 2 O 4 provides a blue emission and rare earth doping
3 Introduction 101 gives the emission characteristics of rare earth ions and provides tunability over the whole visible spectra. Therefore zinc gallate is an excellent multi color phosphor material for flat panel displays. White light emitters have attracted special interest recently for a number of potential applications in cars, traffic information signs, displays and general illumination [ ]. White LEDs can be fabricated by several methods [133]. The first lies solely on combinations of LEDs with the three primary colors to produce bright white light sources which are significantly more efficient than incandescent bulbs and are more adaptable. Multiple semiconductor LEDs will not be competitive in the larger market for residential and commercial lighting. Moreover, the directional nature of LED output makes this approach not suitable for general illumination application. Another more practical method for producing white LEDs is upon absorption of blue or UV light, the phosphors convert the energy to visible radiation depending on the type of phosphors used. White light can be achieved either through several different colored phosphors, or utilizing the blue emission of the LED as the blue part of a multichromatic source. Ce 3+ doped Y 3 Al 5 O 12 nanophosphor absorbs light efficiently in the visible region of nm, and shows single broadband emission peaking at 560 nm and hence, it can be considered as a candidate for generating white light when coupled to a blue light-emitting diode [186]. Synthesis of ZnGa 2 O 4 spinel powders have been previously accomplished by solid state reaction between zinc oxide and gallium oxide or by flux method [106, 109, 184, ]. But this method requires heat treatment at higher temperatures for several hours and subsequent grinding. This may damage the phosphor surfaces, resulting in the loss of emission intensity. Various chemical syntheses have been developed to grow nanoparticles of
4 102 Undoped and Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles such ternary oxide materials [185, 190]. Hydrothermal method offers some advantages over the other techniques, such as low temperature synthesis, low cost, less hazardous and no need for the use of metal catalysts [ ]. Hirano et al. [192] studied the growth of undoped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles by hydrothermal method. Tas et al [193] prepared pure and Mn 2+ doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles by aging aqueous solutions of precursors and Takesada et al. [194] by glycothermal method. The effect of rare earth doping in the ZnGa 2 O 4 spinel structure is less studied. In the present study, undoped and Eu doped zinc gallium oxide (ZnGa 2 O 4 ) nanoparticles were synthesized via hydrothermal route using metallic precursors. The effect of temperature, Zn/Ga precursor ratio, dopant concentration and duration of growth on the structural and optical properties of nanoparticles were studied. 3.2 Experimental Fine powder of pure and Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 phosphors were prepared by the hydrothermal method. High-purity metals of gallium ( %, Alcan Electronic Materials) and zinc (99.995%, 5 mm dia, Qualigens) were dissolved in nitric acid (70%, Merck) separately and then diluted to appropriate concentrations with distilled water. The concentrations of the stock solutions were determined by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometric (ICP-AES) analysis (8440 PLASMALAB, LABTAM). The concentration of the gallium and zinc precursor solutions was determined to be 7.82 and gm/litre respectively. The gallium and zinc stock solutions were mixed in the 1:2 volume ratios with constant stirring. To prepare ZnGa 2 O 4 :Eu 3+ phosphor, appropriate amount of Eu 2 O 3 (99.99%,
5 Experimental 103 Alfa Aesar) was added to the mixed solution of parent cations. On constant stirring, a desired amount of aqueous ammonia (25%, Merck) was added to the clear solutions soon after dissolution to make ph of the solution as 8. The mixed solution was refluxed at room temperature in a magnetically stirred reactor for 30 minutes and then transferred into a teflon lined stainless steel autoclave. The tightly sealed autoclave was placed in oven and heated to a temperature of C for 3 h under autogenous pressure. The precipitates, which were formed under autogenously established hydrothermal conditions, were separated by filtering, then washed and dried in air at 50 0 C in air. The samples were washed with H 2 SO 4 so as to remove the residual ZnO phase, if any, present in them to obtain single phase zinc gallate spinel particles. Phase identification of the fine white zinc gallate powders was performed by x- ray powder diffraction (XRD) (Rigaku D max-c) using Cu-K α radiation ( Å). The morphology and size were examined by JEOL JEM- 3100F transmission electron microscope (TEM) operating at 200 kv. The sample for TEM was prepared by placing a drop of the synthesized powder suspension in methanol onto a standard carbon coated copper grid. The grids were dried before recording the micrographs. The elemental composition of Eu in the synthesized powders was determined by using 8440 PLAS- MALAB, LABTAM inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer (ICP-AES). Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) (Perkin Elmer) of the as prepared sample was carried out in the temperature range C at a heating rate of 10 0 C/min under nitrogen atmosphere. Horiba Jobin Yvon Fluoromax-3 spectrofluorimeter was used to investigate the photoluminescence properties of the phosphors at room temperature using Xe lamp as
6 104 Undoped and Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles the excitation source. FT-IR (Thermo Nicolet) spectra were recorded in the range cm Results and discussion Figure 3.1: XRD pattern of (a) ICSD of ZnGa 2 O 4 (ICSD Card No ) (b) bulk ZnGa 2 O 4 (c) ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles (d) Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles Figure 3.1 shows the XRD pattern of the ZnGa 2 O 4 bulk powder (curve (b)) synthesized via solid state reaction by firing the mixture of ZnO and Ga 2 O 3 at C for 12 h. Curve (c) and (d) in figure 3.1 shows the XRD patterns of pure ZnGa 2 O 4 and Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles synthesized by hydrothermal technique at a growth temperature of C for 3 h. All the peaks in the x-ray diffraction pattern could be assigned to the typical spinel structure of ZnGa 2 O 4 (Figure 3.1(a)) [195]. There
7 Results and discussion 105 are no characteristic peaks of constituent oxides regardless of the dopant concentrations. Thus the spinel structure is not modified by the addition of Eu into the ZnGa 2 O 4 matrix. The broadening of the diffraction peaks shows that the synthesized materials are in nanometer regime. Figure 3.2: XRD pattern of Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles synthesized at various volume ratios of Zn/Ga precursor solutions at C for 3 h
8 106 Undoped and Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles Figure 3.3: XRD pattern of Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles synthesized at various temperature and duration of hydrothermal growth for a fixed volume ratio of 2 between Zn/Ga precursor solution Figure 3.2 shows the XRD profile of ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles synthesized by varying the volume ratio of Zn/Ga precursor solutions at a temperature of C for 3 h. It is observed that the FWHM of the (311) peak increases with the volume ratio of Zn/Ga precursors. When the volume ratio of Zn/Ga precursor solution is below 0.5, ZnO and Ga 2 O 3 phases were detected by XRD, but no spinel ZnGa 2 O 4 phase was found. Figure 3.3
9 Results and discussion 107 shows the XRD profile of ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles synthesized by varying the temperature and duration of growth by keeping the volume ratio of Zn/Ga precursor solutions as 2. The FWHM is found to be more or less same for hydrothermally grown samples for a duration of 3 h at C and C. The samples grown at C for a growth time of 6 h resulted in bigger particles (15.5 nm) where as at C for 6 h, the size of the particle remains almost same as that grown at 3 h. The exact mechanism of growth is not well understood. In the present study we have chosen the optimum values of volume ratio of Zn/Ga precursors, temperature and time of hydrothermal growth as 2, C and 3 h respectively. The average grain size (D) of the samples was estimated with the help of Scherrer equation [154] using the diffraction intensity of (311) peak. D = 0.9λ βcosθ (3.1) where, λ is the x-ray wavelength, β is the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the ZnGa 2 O 4 (311) line and θ is the diffraction angle. The grain size of the nanoparticles is in the range 8-17 nm and lattice parameter calculated were found to vary with the growth conditions and is in quite agreement with reported values. FT-IR spectra of the nanosized ZnGa 2 O 4 powders are shown in the figure 3.4. The peaks at 3318 cm 1 is due to the (O-H) vibration of H 2 O absorbed by the sample. The peaks at about 584 cm 1 and 409 cm 1 represent the characteristic metal-oxygen (Zn-O and Ga-O) vibrations respectively. The sharp peak at 1382 cm 1 corresponds to the adsorbed nitrate ions.
10 108 Undoped and Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles Figure 3.4: FTIR spectra of the nanoparticles of ZnGa 2 O 4 synthesized by hydrothermal method Figure 3.5 shows the TGA profile of the as-prepared undoped ZnGa 2 O 4 sample with a heating rate of 10 0 C/min and a nitrogen flow rate of 100 ml/min. It is observed that the powder undergoes two phase transitions in different temperature regions. The first occurs below the temperature of C which could be attributed to the loss of water molecules associated with the particles. The weight loss between 125 and C is due to the removal of nitrates. The evaporation of the adsorbed moisture contributed to the major weight loss of 8%. The pyrolytic condensation of residual metal salts or hydroxides in air involved a weight loss less than 5%.
11 Results and discussion 109 Figure 3.5: TGA spectra of the ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticle synthesized by hydrothermal method The diffuse reflectance spectrum of the bulk and nanosized ZnGa 2 O 4 powder in the visible region is shown in Figure 3.6. The diffuse reflectance spectroscopy measurements confirm the blue shift in the band gap of nanocrystals with respect to the bulk. The absorbance was calculated from the reflectance using Kubelka-Munk equation [168, 169]. Relative diffuse reflectance was measured with BaSO 4 powder as reference. The band gap 4.59 ev of nano ZnGa 2 O 4 particles was estimated from the plot of {(k/s)hν} 2 versus hν, [109, 168, 169] which is shown in the figure 3.7, where k and s denote absorption and scattering coefficients, hν the photon energy. The band gap of ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles is blue shifted from that of the bulk ZnGa 2 O 4 (4.52 ev). This increase in the band gap is due to the quantum confinement effects.
12 110 Undoped and Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles Figure 3.6: Diffuse reflectance spectra of bulk and nanosized ZnGa 2 O 4 powder Figure 3.7: Plot of [(k/s)hν] 2 vs energy of (a) bulk and (b) nanosized ZnGa 2 O 4 powder
13 Results and discussion 111 Figure 3.8: Room temperature photoluminescence emission spectra of bulk and ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles excited at λ ex = 254 nm Figure 3.8 shows the room temperature photoluminescence emission spectra of bulk and nano ZnGa 2 O 4. The room temperature photoluminescence measurements of the nanocrystals monitored at an excitation wavelength of 254 nm gave a broad spectrum [185]. The diffuse reflectance spectra (Figure 3.6) indicates that gallium is responsible for the photoluminescence excitation of the prepared nanopowders of ZnGa 2 O 4 [114]. However, the PL emission spectra shows some peaks at wavelengths of 399, 443, 453, 464, 470, 476, 484, and 493 nm when the nanophosphors were excited with the UV light of wavelength 254 nm. The excitation peak at
14 112 Undoped and Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles 254 nm corresponds to the charge transfer from O 2 to Ga 3+ at regular octahedral sites [196]. All the samples prepared at different volume ratio of Zn/Ga precursors exhibit broad emission spectra. These spectra exhibit certain peaks apart from the characteristic bell-shaped emission spectra of bulk ZnGa 2 O 4 phosphors as reported in literature [110, 114]. The isolated Ga 3+ ion exhibits spectral lines at wavelengths of , , , and nm in air [197]. Peaks observed in the emission spectra of the prepared ZnGa 2 O 4 nanophosphors may correspond to the electronic transitions of localized Ga 3+ ion in the octahedral Ga-O sites which induces the electronic energy levels to split. The quantum effects in nanophosphors prepared in this study are predominant because it have much smaller particle size than those of the powder prepared by the conventional solid-state reaction. [185]. This leads to splitting of electronic energy levels of Ga 3+ in the octahedral site of Ga-O resulting the peaks in the emission spectra. The blue emission band maximum at 470 nm corresponds to the self-activated luminescence of the host. The origin of the self activated blue emission around 437 nm in ZnGa 2 O 4 bulk is attributed to Ga 3+ at octahedrally coordinated site [110, 114]. Figure 3.9(a) shows the TEM image of Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 prepared with 0.02 mol Eu 2 O 3 in the precursor solution. TEM image confirms the formation of nanoparticles of the spinel phosphor material. The average size of the spherically shaped particles was determined to be 8 nm. This result is consistent with what we had obtained from XRD analysis. Figure 3.9(b) shows the HRTEM images of the Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles. The d value 2.1 Å corresponds to the (400) planes of the ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles. From the diffraction rings (Figure 3.9(c)) in the selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern, (220), (311), (400), (422), (511)
15 Results and discussion 113 and (440) planes of ZnGa 2 O 4 could be identified. The particle size distribution of the Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles by counting the number of particles from the TEM image shown in figure 3.9(d) do assert the fact that most of the nanoparticles synthesized had the dimension 6-9 nm. Figure 3.9: (a) TEM image (b) HRTEM image (c) SAED pattern and (d) particle size distribution from the TEM image of Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles grown by hydrothermal method
16 114 Undoped and Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles Figure 3.10: Room temperature photoluminescence emission spectra of Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles excited at λ ex = 397 nm for different amount of Eu 2 O 3 in the precursor solution From the ICP-AES results it is found that Eu/(Eu+Ga) is about 3.38%. Figure 3.10 shows the room temperature photoluminescent emission spectra of Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles excited at 397 nm. The excitation energy almost coincides with the energy of 7 F 0 5 L 6 transitions of Eu 3+ ions, which is ev [198]. Excitation at 397 nm yields the characteristic emissions of Eu 3+ corresponding to 5 D j (j=0, 1) 7 F j (j=0, 1, 2, 3 and 4). The emission at 596 nm originates from the magnetic-dipole allowed 5 D 0 7 F 1 transition, indicating that Eu 3+ ions occupy a site with inversion symmetry. This is the only transition when Eu 3+ is situated at a site coinciding with a centre of symmetry. The emission at 619 nm corresponds
17 Results and discussion 115 to electric-dipole allowed 5 D 0 7 F 2 transition, which results in a large transition probability in the crystal field with inversion antisymmetry. The intensity of emission corresponds to the 5 D 0 7 F 2 transition is stronger than that of 5 D 0 7 F 1 transition. It is suggested that the Eu 3+ ions mainly occupy a site with inversion antisymmetry in the ZnGa 2 O 4 host. The emission at 701 nm is from 5 D 0 7 F 4 transition and at 653 nm is from 5 D 0 7 F 3 transition. The emission peaks at 583 nm corresponds to 5 D 0 7 F 0 transition. The observation of forbidden 5 D 0 7 F 0 transition indicates that some of the Eu ions are at low symmetry site. The detection of this transition suggests that Eu 3+ ions do not occupy a lattice site with inversion center. The emission at 543 nm is from 5 D 1 7 F 1 transition. Figure 3.11: Variation of PL integral intensity of Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles with amount of Eu 2 O 3 in the hydrothermal precursor solution
18 116 Undoped and Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles The luminescent intensity of Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles increases with increase of the amount of Eu 2 O 3 in the precursor solution up to 0.01 mol and then it decreases which is shown in the figure When the activator concentration increases above a certain level, luminescence begins to quench. Thus the emission intensity of 5 D 0 7 F j (j=0-4) depends on the amount of Eu 2 O 3. In this case, the pairing or aggregation of activator atoms at high concentration may change a fraction of the activators into quenchers and induce the quenching effect. The migration of excitation by resonant energy transfer between the Eu 3+ activators can sometimes be so efficient that it may carry the energy to a distant killer or to a quenching centre existing at the surface of the crystal. 3.4 Conclusion Undoped and Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanophosphors were synthesized by hydrothermal method by varying the process parameters such as temperature, time of growth, volume ratio of Zn/Ga precursor solutions and the amount of Eu 2 O 3 added to the precursor solution. The room temperature photoluminescence measurements of the nanocrystals monitored at an excitation wavelength of 254 nm gave a peak-shaped spectrum instead of the normally observed bell-shaped spectrum of bulk ZnGa 2 O 4. The band gap of the ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles is blue shifted compared with the bulk material due to quantum confinement effects. XRD and SAED results show Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles have spinel structure and the particle size 8 nm as confined by the TEM. Incorporation of Eu in the nanoparticles was confirmed by the ICP-AES studies. The red PL emissions from the intra-4f transition of Eu 3+ ions are observed in Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanophosphors
19 Conclusion 117 under an excitation of 397 nm. Luminescence quenching is observed in these nanophosphors as the amount of Eu 2 O 3 increases. These nanophosphors can be used as a blue to red converter for solid state lighting applications.
20 118 Undoped and Eu doped ZnGa 2 O 4 nanoparticles
CHAPTER 3. OPTICAL STUDIES ON SnS NANOPARTICLES
 42 CHAPTER 3 OPTICAL STUDIES ON SnS NANOPARTICLES 3.1 INTRODUCTION In recent years, considerable interest has been shown on semiconducting nanostructures owing to their enhanced optical and electrical
42 CHAPTER 3 OPTICAL STUDIES ON SnS NANOPARTICLES 3.1 INTRODUCTION In recent years, considerable interest has been shown on semiconducting nanostructures owing to their enhanced optical and electrical
Supporting Information. Solution-Based Growth of Monodisperse Cube-Like BaTiO 3 Colloidal Nanocrystals
 Supporting Information Solution-Based Growth of Monodisperse Cube-Like BaTiO 3 Colloidal Nanocrystals Shiva Adireddy, Baobao Cao, Cuikun Lin, Weilie Zhou and Gabriel Caruntu* Chemistry Department and the
Supporting Information Solution-Based Growth of Monodisperse Cube-Like BaTiO 3 Colloidal Nanocrystals Shiva Adireddy, Baobao Cao, Cuikun Lin, Weilie Zhou and Gabriel Caruntu* Chemistry Department and the
Department of Chemistry of The College of Staten Island and The Graduate Center, The City University of
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Fe 3 O 4 /Carbon quantum dots hybrid nanoflowers for highly active and
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Fe 3 O 4 /Carbon quantum dots hybrid nanoflowers for highly active and
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Dynamic Interaction between Methylammonium Lead Iodide and TiO 2 Nanocrystals Leads to Enhanced Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution from HI Splitting Xiaomei Wang,, Hong Wang,, Hefeng Zhang,,
Supporting Information Dynamic Interaction between Methylammonium Lead Iodide and TiO 2 Nanocrystals Leads to Enhanced Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution from HI Splitting Xiaomei Wang,, Hong Wang,, Hefeng Zhang,,
Visible-light Driven Plasmonic Photocatalyst Helical Chiral TiO 2 Nanofibers
 Visible-light Driven Plasmonic Photocatalyst Ag/AgCl @ Helical Chiral TiO 2 Nanofibers Dawei Wang, Yi Li*, Gianluca Li Puma, Chao Wang, Peifang Wang, Wenlong Zhang, and Qing Wang Fig. S1. The reactor of
Visible-light Driven Plasmonic Photocatalyst Ag/AgCl @ Helical Chiral TiO 2 Nanofibers Dawei Wang, Yi Li*, Gianluca Li Puma, Chao Wang, Peifang Wang, Wenlong Zhang, and Qing Wang Fig. S1. The reactor of
Multiply twinned Pt Pd nanoicosahedrons as highly active electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation
 Supporting Information for Multiply twinned Pt Pd nanoicosahedrons as highly active electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation An-Xiang Yin, Xiao-Quan Min, Wei Zhu, Hao-Shuai Wu, Ya-Wen Zhang* and Chun-Hua
Supporting Information for Multiply twinned Pt Pd nanoicosahedrons as highly active electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation An-Xiang Yin, Xiao-Quan Min, Wei Zhu, Hao-Shuai Wu, Ya-Wen Zhang* and Chun-Hua
Supporting Information. CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient and stable photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient
Electronic Supplementary Information. Low-temperature Benchtop-synthesis of All-inorganic Perovskite Nanowires
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Low-temperature Benchtop-synthesis of All-inorganic Perovskite
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Low-temperature Benchtop-synthesis of All-inorganic Perovskite
Efficient Co-Fe layered double hydroxide photocatalysts for water oxidation under visible light
 Supplementary Information Efficient Co-Fe layered double hydroxide photocatalysts for water oxidation under visible light Sang Jun Kim, a Yeob Lee, a Dong Ki Lee, a Jung Woo Lee a and Jeung Ku Kang* a,b
Supplementary Information Efficient Co-Fe layered double hydroxide photocatalysts for water oxidation under visible light Sang Jun Kim, a Yeob Lee, a Dong Ki Lee, a Jung Woo Lee a and Jeung Ku Kang* a,b
The characterization of MnO nanostructures synthesized using the chemical bath deposition method
 The characterization of MnO nanostructures synthesized using the chemical bath deposition method LF Koao 1, F B Dejene 1* and HC Swart 2 1 Department of Physics, University of the Free State (Qwaqwa Campus),
The characterization of MnO nanostructures synthesized using the chemical bath deposition method LF Koao 1, F B Dejene 1* and HC Swart 2 1 Department of Physics, University of the Free State (Qwaqwa Campus),
College of Mechanical Engineering, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou , China; 2
 Proceedings Light-Assisted Room-Temperature NO2 Sensors Based on Black Sheet-Like NiO Xin Geng 1,2,3, Driss Lahem 4, Chao Zhang 1, *, Marie-Georges Olivier 3 and Marc Debliquy 3 1 College of Mechanical
Proceedings Light-Assisted Room-Temperature NO2 Sensors Based on Black Sheet-Like NiO Xin Geng 1,2,3, Driss Lahem 4, Chao Zhang 1, *, Marie-Georges Olivier 3 and Marc Debliquy 3 1 College of Mechanical
University of South Florida Development of a Smart Window for Green Buildings in Florida
 University of South Florida Development of a Smart Window for Green Buildings in Florida PI: Dr. Sarath Witanachchi Students: Marak Merlak, Ph.D Description: This proposal is aimed at developing a smart
University of South Florida Development of a Smart Window for Green Buildings in Florida PI: Dr. Sarath Witanachchi Students: Marak Merlak, Ph.D Description: This proposal is aimed at developing a smart
Synthesis of Colloidal Au-Cu 2 S Heterodimers via Chemically Triggered Phase Segregation of AuCu Nanoparticles
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Synthesis of Colloidal Au-Cu 2 S Heterodimers via Chemically Triggered Phase Segregation of AuCu Nanoparticles Nathan E. Motl, James F. Bondi, and Raymond E. Schaak* Department of
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Synthesis of Colloidal Au-Cu 2 S Heterodimers via Chemically Triggered Phase Segregation of AuCu Nanoparticles Nathan E. Motl, James F. Bondi, and Raymond E. Schaak* Department of
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 3, March-2014 ISSN
 156 Copper Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis Characterization Y.Suresh*1, S.Annapurna*2, G.Bhikshamaiah*3, A.K.Singh#4 Abstract Present work describes the synthesis nanoparticles using papaya extract as a
156 Copper Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis Characterization Y.Suresh*1, S.Annapurna*2, G.Bhikshamaiah*3, A.K.Singh#4 Abstract Present work describes the synthesis nanoparticles using papaya extract as a
Growth of silver nanocrystals on graphene by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and silver ions with a rapid and efficient one-step approach
 Growth of silver nanocrystals on graphene by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and silver ions with a rapid and efficient one-step approach Xiu-Zhi Tang, a Zongwei Cao, b Hao-Bin Zhang, a Jing Liu
Growth of silver nanocrystals on graphene by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and silver ions with a rapid and efficient one-step approach Xiu-Zhi Tang, a Zongwei Cao, b Hao-Bin Zhang, a Jing Liu
Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh
 Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh hierarchical superstructures for greatly fast removal of heavy metal ions with high efficiency Yong-Xing Zhang, a,b Yong
Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh hierarchical superstructures for greatly fast removal of heavy metal ions with high efficiency Yong-Xing Zhang, a,b Yong
Synthesis of 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted Nucleation for Plasmon-Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information A Generic Method for Rational Scalable Synthesis of Monodisperse Metal Sulfide Nanocrystals Haitao Zhang, Byung-Ryool Hyun, Frank W. Wise, Richard D. Robinson * Department of Materials
Supporting Information A Generic Method for Rational Scalable Synthesis of Monodisperse Metal Sulfide Nanocrystals Haitao Zhang, Byung-Ryool Hyun, Frank W. Wise, Richard D. Robinson * Department of Materials
Synthesis of nano-sized anatase TiO 2 with reactive {001} facets using lamellar protonated titanate as precursor
 Supporting Information Synthesis of nano-sized anatase TiO 2 with reactive {001} facets using lamellar protonated titanate as precursor Liuan Gu, Jingyu Wang *, Hao Cheng, Yunchen Du and Xijiang Han* Department
Supporting Information Synthesis of nano-sized anatase TiO 2 with reactive {001} facets using lamellar protonated titanate as precursor Liuan Gu, Jingyu Wang *, Hao Cheng, Yunchen Du and Xijiang Han* Department
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information High Performance Electrocatalyst: Pt-Cu Hollow Nanocrystals Xiaofei Yu, a Dingsheng, a Qing Peng a and Yadong Li* a a Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084
Supporting Information High Performance Electrocatalyst: Pt-Cu Hollow Nanocrystals Xiaofei Yu, a Dingsheng, a Qing Peng a and Yadong Li* a a Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084
Bright CuInS 2 /CdS Nanocrystal Phosphors for High-Gain Full-Spectrum Luminescent Solar Concentrators
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 215 Knowles et al. March 8, 215 Supplementary Information Bright Nanocrystal Phosphors for High-Gain
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 215 Knowles et al. March 8, 215 Supplementary Information Bright Nanocrystal Phosphors for High-Gain
High-Performance Semiconducting Polythiophenes for Organic Thin Film. Transistors by Beng S. Ong,* Yiliang Wu, Ping Liu and Sandra Gardner
 Supplementary Materials for: High-Performance Semiconducting Polythiophenes for Organic Thin Film Transistors by Beng S. Ong,* Yiliang Wu, Ping Liu and Sandra Gardner 1. Materials and Instruments. All
Supplementary Materials for: High-Performance Semiconducting Polythiophenes for Organic Thin Film Transistors by Beng S. Ong,* Yiliang Wu, Ping Liu and Sandra Gardner 1. Materials and Instruments. All
CHAPTER 4. SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION OF TiO 2 NANOTUBES AND THEIR APPLICATION IN DYE SENSITIZED SOLAR CELL
 93 CHAPTER 4 SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION OF TiO 2 NANOTUBES AND THEIR APPLICATION IN DYE SENSITIZED SOLAR CELL 4.1 INTRODUCTION TiO 2 -derived nanotubes are expected to be applicable for several applications,
93 CHAPTER 4 SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION OF TiO 2 NANOTUBES AND THEIR APPLICATION IN DYE SENSITIZED SOLAR CELL 4.1 INTRODUCTION TiO 2 -derived nanotubes are expected to be applicable for several applications,
INVESTIGATIONS OF Mn, Fe, Ni AND Pb DOPED
 INVESTIGATIONS OF Mn, Fe, Ni AND Pb DOPED ZINC SULPHIDE NANOPARTICLES A thesis submitted to the University of Pune FOR THE DEGREE OF DOCTOR of PHILOSOPHY IN PHYSICS by PRAMOD H. BORSE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS
INVESTIGATIONS OF Mn, Fe, Ni AND Pb DOPED ZINC SULPHIDE NANOPARTICLES A thesis submitted to the University of Pune FOR THE DEGREE OF DOCTOR of PHILOSOPHY IN PHYSICS by PRAMOD H. BORSE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS
One-pot Solvent-free Synthesis of Sodium Benzoate from the Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol over Novel Efficient AuAg/TiO 2 Catalysts
 Electronic Supplementary Information One-pot Solvent-free Synthesis of Sodium Benzoate from the Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol over Novel Efficient AuAg/TiO 2 Catalysts Ying Wang, Jia-Min Zheng, Kangnian
Electronic Supplementary Information One-pot Solvent-free Synthesis of Sodium Benzoate from the Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol over Novel Efficient AuAg/TiO 2 Catalysts Ying Wang, Jia-Min Zheng, Kangnian
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Facile synthesis of halogenated carbon quantum dots as an important intermediate for surface modification Jin Zhou, Pei Lin, Juanjuan Ma, Xiaoyue Shan, Hui Feng, Congcong
Electronic Supplementary Information Facile synthesis of halogenated carbon quantum dots as an important intermediate for surface modification Jin Zhou, Pei Lin, Juanjuan Ma, Xiaoyue Shan, Hui Feng, Congcong
Bandgap engineering through nanocrystalline magnetic alloy grafting on. graphene
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Bandgap engineering through nanocrystalline
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Bandgap engineering through nanocrystalline
Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties. and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
Catalytic Decomposition of Formaldehyde on Nanometer Manganese Dioxide
 Modern Applied Science April, 29 Catalytic Decomposition of Formaldehyde on Nanometer Manganese Dioxide Xiujuan Chu & Hua Zhang (Corresponding author) Tianjin Municipal Key Lab of Fibres Modification and
Modern Applied Science April, 29 Catalytic Decomposition of Formaldehyde on Nanometer Manganese Dioxide Xiujuan Chu & Hua Zhang (Corresponding author) Tianjin Municipal Key Lab of Fibres Modification and
Shape transition in ZnO nanostructures and its effect on blue-green photoluminescence
 Shape transition in ZnO nanostructures and its effect on blue-green photoluminescence Manoranjan Ghosh 1 and A.K. Raychaudhuri 2 DST Unit for Nanoscience, S.N.Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences, Block-JD,
Shape transition in ZnO nanostructures and its effect on blue-green photoluminescence Manoranjan Ghosh 1 and A.K. Raychaudhuri 2 DST Unit for Nanoscience, S.N.Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences, Block-JD,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Exploring the detection of metal ions by tailoring the coordination mode of V-shaped thienylpyridyl ligand in three MOFs Li-Juan Han,, Wei Yan, Shu-Guang Chen, Zhen-Zhen Shi, and
Supporting Information Exploring the detection of metal ions by tailoring the coordination mode of V-shaped thienylpyridyl ligand in three MOFs Li-Juan Han,, Wei Yan, Shu-Guang Chen, Zhen-Zhen Shi, and
Intensity (a.u.) 2Theta (degrees) Supplementary data O 3 BO 3. Sup-Figure 1: Room temperature XRD patterns of KCaBO 3 :Eu 3+ sample treated at 500 ºC.
 Supplementary data The following results and discussions are for the low-temperature (5 C) processed phosphors. 5 ºC Intensity (a.u.) KCaBO 3 Eu 2 O 3 H 3 BO 3 2 3 4 5 2Theta (degrees) 6 7 Sup-Figure 1:
Supplementary data The following results and discussions are for the low-temperature (5 C) processed phosphors. 5 ºC Intensity (a.u.) KCaBO 3 Eu 2 O 3 H 3 BO 3 2 3 4 5 2Theta (degrees) 6 7 Sup-Figure 1:
CHAPTER-2 SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF MODIFIED METAL OXIDES AND METAL SULPHIDES NANOPARTICLES
 CHAPTER-2 SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF MODIFIED METAL OXIDES AND METAL SULPHIDES NANOPARTICLES Nanoparticles have recently attracted significant attention from the science community. Nanoparticles
CHAPTER-2 SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF MODIFIED METAL OXIDES AND METAL SULPHIDES NANOPARTICLES Nanoparticles have recently attracted significant attention from the science community. Nanoparticles
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Visible Photocatalytic Water Splitting and Photocatalytic Two-Electron Oxygen Formation over Cu and Fe Doped g-c 3 N 4 Zhen Li a,b, Chao Kong a,b, Gongxuan Lu a* a State Key Laboratory
Supplementary Information Visible Photocatalytic Water Splitting and Photocatalytic Two-Electron Oxygen Formation over Cu and Fe Doped g-c 3 N 4 Zhen Li a,b, Chao Kong a,b, Gongxuan Lu a* a State Key Laboratory
Facile Synthesis and Catalytic Properties of CeO 2 with Tunable Morphologies from Thermal Transformation of Cerium Benzendicarboxylate Complexes
 Electronic Supplementary Information Facile Synthesis and Catalytic Properties of CeO 2 with Tunable Morphologies from Thermal Transformation of Cerium Benzendicarboxylate Complexes Yuhua Zheng, Kai Liu,
Electronic Supplementary Information Facile Synthesis and Catalytic Properties of CeO 2 with Tunable Morphologies from Thermal Transformation of Cerium Benzendicarboxylate Complexes Yuhua Zheng, Kai Liu,
SYNTHESIS OF CADMIUM SULFIDE NANOSTRUCTURES BY NOVEL PRECURSOR
 Nanomaterials: Applications and Properties (NAP-2011). Vol. 1, Part I 107 SYNTHESIS OF CADMIUM SULFIDE NANOSTRUCTURES BY NOVEL PRECURSOR M. Salavati Niasari 1,2* 1 Department of Inorganic Chemistry, Faculty
Nanomaterials: Applications and Properties (NAP-2011). Vol. 1, Part I 107 SYNTHESIS OF CADMIUM SULFIDE NANOSTRUCTURES BY NOVEL PRECURSOR M. Salavati Niasari 1,2* 1 Department of Inorganic Chemistry, Faculty
Photocatalytic degradation of dyes over graphene-gold nanocomposites under visible light irradiation
 Photocatalytic degradation of dyes over graphene-gold nanocomposites under visible light irradiation Zhigang Xiong, Li Li Zhang, Jizhen Ma, X. S. Zhao* Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering,
Photocatalytic degradation of dyes over graphene-gold nanocomposites under visible light irradiation Zhigang Xiong, Li Li Zhang, Jizhen Ma, X. S. Zhao* Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering,
CHAPTER 4. PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF Cr-DOPED, Co-DOPED AND Fe-DOPED NIO NANOPARTICLES
 59 CHAPTER 4 PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF Cr-DOPED, Co-DOPED AND Fe-DOPED NIO NANOPARTICLES 4.1 INTRODUCTION Extensive research has been carried out on transition metal ion doped semiconductors
59 CHAPTER 4 PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF Cr-DOPED, Co-DOPED AND Fe-DOPED NIO NANOPARTICLES 4.1 INTRODUCTION Extensive research has been carried out on transition metal ion doped semiconductors
Shape-selective Synthesis and Facet-dependent Enhanced Electrocatalytic Activity and Durability of Monodisperse Sub-10 nm Pt-Pd Tetrahedrons and Cubes
 Supporting Information Shape-selective Synthesis and Facet-dependent Enhanced Electrocatalytic Activity and Durability of Monodisperse Sub-10 nm Pt-Pd Tetrahedrons and Cubes An-Xiang Yin, Xiao-Quan Min,
Supporting Information Shape-selective Synthesis and Facet-dependent Enhanced Electrocatalytic Activity and Durability of Monodisperse Sub-10 nm Pt-Pd Tetrahedrons and Cubes An-Xiang Yin, Xiao-Quan Min,
Supporting Information
 1 Supporting Information Photoluminescent Carbogenic Dots A. B. Bourlinos, A. Stassinopoulos, D. Anglos, R. Zboril, V. Georgakilas, E. P. Giannelis *, Institute of Materials Science, NCSR Demokritos, Ag.
1 Supporting Information Photoluminescent Carbogenic Dots A. B. Bourlinos, A. Stassinopoulos, D. Anglos, R. Zboril, V. Georgakilas, E. P. Giannelis *, Institute of Materials Science, NCSR Demokritos, Ag.
Supporting Information. Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of BaY 2
 Supporting Information Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of BaY 2 F 8 :Yb 3+ /Er 3+ Nanobelts 5 Guofeng Wang, Qing Peng, and Yadong Li* Department of Chemistry and State Key Laboratory of New Ceramics
Supporting Information Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of BaY 2 F 8 :Yb 3+ /Er 3+ Nanobelts 5 Guofeng Wang, Qing Peng, and Yadong Li* Department of Chemistry and State Key Laboratory of New Ceramics
Supporting Information s for
 Supporting Information s for # Self-assembling of DNA-templated Au Nanoparticles into Nanowires and their enhanced SERS and Catalytic Applications Subrata Kundu* and M. Jayachandran Electrochemical Materials
Supporting Information s for # Self-assembling of DNA-templated Au Nanoparticles into Nanowires and their enhanced SERS and Catalytic Applications Subrata Kundu* and M. Jayachandran Electrochemical Materials
CHAPTER IV SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF METAL IONS DOPED ZINC SELENIDE NANOPARTICLES
 132 CHAPTER IV SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF METAL IONS DOPED ZINC SELENIDE NANOPARTICLES 4.1 Introduction Introducing impurity atoms into a semiconductor host leads to an increase in the free-carrier
132 CHAPTER IV SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF METAL IONS DOPED ZINC SELENIDE NANOPARTICLES 4.1 Introduction Introducing impurity atoms into a semiconductor host leads to an increase in the free-carrier
photo-mineralization of 2-propanol under visible light irradiation
 Electronic Supplementary Information for WO 3 modified titanate network film: highly efficient photo-mineralization of 2-propanol under visible light irradiation Experimental Preparation of STN, and WO
Electronic Supplementary Information for WO 3 modified titanate network film: highly efficient photo-mineralization of 2-propanol under visible light irradiation Experimental Preparation of STN, and WO
Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification
 Electronic Supporting Informations (ESI): Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification Jun Kim, Yu-Ri Lee and Wha-Seung
Electronic Supporting Informations (ESI): Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification Jun Kim, Yu-Ri Lee and Wha-Seung
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Reductive dismantling and functionalization of carbon nanohorns
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Reductive dismantling and functionalization of carbon nanohorns
Electronic supplementary information. A longwave optical ph sensor based on red upconversion
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic supplementary information A longwave optical ph sensor based on red upconversion
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic supplementary information A longwave optical ph sensor based on red upconversion
Supramolecular Self-Assembly of Morphology-dependent Luminescent Ag Nanoclusters
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information for Supramolecular Self-Assembly of Morphology-dependent Luminescent Ag
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information for Supramolecular Self-Assembly of Morphology-dependent Luminescent Ag
Synthesis of Pt-Ni-Graphene via in situ Reduction and its Enhanced Catalyst Activity for the Methanol Oxidation
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) available: Synthesis of Pt-Ni-Graphene via in situ Reduction and its Enhanced Catalyst Activity for the Methanol Oxidation Lihong Li, Yuen Wu, Jun Lu, Caiyun
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) available: Synthesis of Pt-Ni-Graphene via in situ Reduction and its Enhanced Catalyst Activity for the Methanol Oxidation Lihong Li, Yuen Wu, Jun Lu, Caiyun
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Phenyl-Modified Carbon Nitride Quantum Dots with Distinct Photoluminescence Behavior Qianling Cui, Jingsan Xu,* Xiaoyu Wang, Lidong Li,* Markus Antonietti, and Menny Shalom anie_201511217_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf
Supporting Information Phenyl-Modified Carbon Nitride Quantum Dots with Distinct Photoluminescence Behavior Qianling Cui, Jingsan Xu,* Xiaoyu Wang, Lidong Li,* Markus Antonietti, and Menny Shalom anie_201511217_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf
Supporting Information
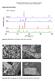 Supporting Information Figure S1. XRD patterns of ZnGa 2 O 4, GaN, ZnO, and Ga 2 O 3. Figure S2. SEM micrographs for ZnO (A), Ga 2 O 3 (B), GaN (C), ZnGa 2 O 4 (D). Figure S3A. Raman shifts associated
Supporting Information Figure S1. XRD patterns of ZnGa 2 O 4, GaN, ZnO, and Ga 2 O 3. Figure S2. SEM micrographs for ZnO (A), Ga 2 O 3 (B), GaN (C), ZnGa 2 O 4 (D). Figure S3A. Raman shifts associated
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Ultrathin Spinel-Structured Nanosheets Rich in Oxygen Deficiencies for Enhanced Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation** Jian Bao, Xiaodong Zhang,* Bo Fan, Jiajia Zhang, Min Zhou, Wenlong
Supporting Information Ultrathin Spinel-Structured Nanosheets Rich in Oxygen Deficiencies for Enhanced Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation** Jian Bao, Xiaodong Zhang,* Bo Fan, Jiajia Zhang, Min Zhou, Wenlong
The CdS and CdMnS nanocrystals have been characterized using UV-visible spectroscopy, TEM, FTIR, Particle Size Measurement and Photoluminiscence.
 Synthesis of CdS and CdMns Nanocrystals in Organic phase Usha Raghavan HOD, Dept of Information Technology VPM s Polytechnic, Thane Maharashtra Email id: usharagha@gmail.com Abstract: The present work
Synthesis of CdS and CdMns Nanocrystals in Organic phase Usha Raghavan HOD, Dept of Information Technology VPM s Polytechnic, Thane Maharashtra Email id: usharagha@gmail.com Abstract: The present work
Supporting information for:
 Supporting information for: CdTe/CdS Core/Shell Quantum Dots co-catalyzed by Sulfur Tolerant [Mo 3 S 13 ] 2- Nanoclusters for Efficient Visible Light-driven Hydrogen Evolution Dongting Yue, Xufang Qian,
Supporting information for: CdTe/CdS Core/Shell Quantum Dots co-catalyzed by Sulfur Tolerant [Mo 3 S 13 ] 2- Nanoclusters for Efficient Visible Light-driven Hydrogen Evolution Dongting Yue, Xufang Qian,
Supporting Information. Synthesis of Mg/ Al Layered Double Hydroxides for Adsorptive Removal of. Fluoride from Water: A Mechanistic and Kinetic Study
 Supporting Information Synthesis of Mg/ Al Layered Double Hydroxides for Adsorptive Removal of Fluoride from Water: A Mechanistic and Kinetic Study Gautam Kumar Sarma and Md. Harunar Rashid* Department
Supporting Information Synthesis of Mg/ Al Layered Double Hydroxides for Adsorptive Removal of Fluoride from Water: A Mechanistic and Kinetic Study Gautam Kumar Sarma and Md. Harunar Rashid* Department
Novel fluorescent matrix embedded carbon quantum dots enrouting stable gold and silver hydrosols
 Novel fluorescent matrix embedded carbon quantum dots enrouting stable gold and silver hydrosols Shouvik Mitra a, Sourov Chandra b, Prasun Patra a, Panchanan Pramanik b *, Arunava Goswami a * a AERU, Biological
Novel fluorescent matrix embedded carbon quantum dots enrouting stable gold and silver hydrosols Shouvik Mitra a, Sourov Chandra b, Prasun Patra a, Panchanan Pramanik b *, Arunava Goswami a * a AERU, Biological
Photonic structuring improves colour purity of rare-earth. nanophosphors
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Materials Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Photonic structuring improves colour purity of rare-earth nanophosphors
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Materials Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Photonic structuring improves colour purity of rare-earth nanophosphors
Nanoporous TiO 2 Nanoparticle Assemblies with Mesoscale Morphologies: Nano-Cabbage versus Sea-Anemone
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplemental Documents Nanoporous TiO 2 Nanoparticle Assemblies with Mesoscale Morphologies: Nano-Cabbage
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplemental Documents Nanoporous TiO 2 Nanoparticle Assemblies with Mesoscale Morphologies: Nano-Cabbage
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets Lan Wang, a Ling Zang, b Jincai Zhao c and Chuanyi Wang*
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets Lan Wang, a Ling Zang, b Jincai Zhao c and Chuanyi Wang*
Supporting Information. Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with. Controlled Mesoporosity and Size
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Shape Effect of Ag-Ni Binary Nanoparticles on Catalytic Hydrogenation Aided by Surface Plasmon
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Shape Effect of Ag-Ni Binary Nanoparticles on Catalytic Hydrogenation
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Shape Effect of Ag-Ni Binary Nanoparticles on Catalytic Hydrogenation
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Plasmonics-enhanced metal-organic frameworks nanofilms
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Plasmonics-enhanced metal-organic frameworks nanofilms
A triazine-based covalent organic polymer for efficient CO 2 adsorption
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information A triazine-based covalent organic polymer for efficient CO
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information A triazine-based covalent organic polymer for efficient CO
Supporting Information. Graphene Oxide-Palladium Modified Ag-AgBr: A Novel Visible-Light- Responsive Photocatalyst for the Suzuki Coupling Reaction**
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Graphene Oxide-Palladium Modified Ag-AgBr: A Novel Visible-Light- Responsive
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Graphene Oxide-Palladium Modified Ag-AgBr: A Novel Visible-Light- Responsive
Synthesis of 12 nm iron oxide nanoparticles
 Electronic Supporting Information for Dendronized iron oxide nanoparticles as contrast agent for MRI Brice Basly, a Delphine Felder-Flesch,* a Pascal Perriat, b Claire Billotey, c Jacqueline Taleb, c Geneviève
Electronic Supporting Information for Dendronized iron oxide nanoparticles as contrast agent for MRI Brice Basly, a Delphine Felder-Flesch,* a Pascal Perriat, b Claire Billotey, c Jacqueline Taleb, c Geneviève
A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON CHARACTERIZATION AND PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITIES OF PbS AND Co DOPED PbS NANOPARTICLES
 Chalcogenide Letters Vol. 9, No. 7, July 2012, p. 299-306 A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON CHARACTERIZATION AND PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITIES OF PbS AND Co DOPED PbS NANOPARTICLES A.V.BORHADE a*, B.K.UPHADE b a Department
Chalcogenide Letters Vol. 9, No. 7, July 2012, p. 299-306 A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON CHARACTERIZATION AND PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITIES OF PbS AND Co DOPED PbS NANOPARTICLES A.V.BORHADE a*, B.K.UPHADE b a Department
Instantaneous reduction of graphene oxide at room temperature
 Instantaneous reduction of graphene oxide at room temperature Barun Kuma Burman, Pitamber Mahanandia and Karuna Kar Nanda Materials Research Centre, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore-560012, India
Instantaneous reduction of graphene oxide at room temperature Barun Kuma Burman, Pitamber Mahanandia and Karuna Kar Nanda Materials Research Centre, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore-560012, India
SUPPORTING INFORMATION. a) Anorganische Chemie I-Festkörperchemie und Materialien, Ruhr-Universität Bochum, D Bochum,
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Facile preparation of quantum cutting GdF 3 :Eu 3+ nanoparticles from ionic liquids Chantal Lorbeer a, Joanna Cybinska a,b, Anja-Verena Mudring a * a) Anorganische Chemie I-Festkörperchemie
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Facile preparation of quantum cutting GdF 3 :Eu 3+ nanoparticles from ionic liquids Chantal Lorbeer a, Joanna Cybinska a,b, Anja-Verena Mudring a * a) Anorganische Chemie I-Festkörperchemie
Supporting Information for. Size-Dependent Oxidation State and CO Oxidation Activity of Tin
 Supporting Information for Size-Dependent Oxidation State and CO Oxidation Activity of Tin Oxide Clusters Yusuke Inomata, Ken Albrecht,, Kimihisa Yamamoto *,, Laboratory for Chemistry and Life Science,
Supporting Information for Size-Dependent Oxidation State and CO Oxidation Activity of Tin Oxide Clusters Yusuke Inomata, Ken Albrecht,, Kimihisa Yamamoto *,, Laboratory for Chemistry and Life Science,
Supporting Information. a Department of Chemistry, University of California, Riverside, California 92521,
 Supporting Information Assembly of Supertetrahedral T 5 Copper-Indium Sulfide Clusters into Super-Supertetrahedron of Infinite Order Le Wang a, Tao Wu a, Fan Zuo a,, Xiang Zhao a, Xianhui Bu b, Jianzhong
Supporting Information Assembly of Supertetrahedral T 5 Copper-Indium Sulfide Clusters into Super-Supertetrahedron of Infinite Order Le Wang a, Tao Wu a, Fan Zuo a,, Xiang Zhao a, Xianhui Bu b, Jianzhong
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information A difunctional metal organic framework with Lewis
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information A difunctional metal organic framework with Lewis
Supporting Information:
 Supporting Information: Columnar Self-assembly of Cu 2 S Hexagonal Nanoplates Induced by Tin (IV)-X Complex Inorganic Surface Ligand Xiaomin Li, Huaibin Shen, Jinzhong Niu, Sen Li, Yongguang Zhang, Hongzhe
Supporting Information: Columnar Self-assembly of Cu 2 S Hexagonal Nanoplates Induced by Tin (IV)-X Complex Inorganic Surface Ligand Xiaomin Li, Huaibin Shen, Jinzhong Niu, Sen Li, Yongguang Zhang, Hongzhe
CHAPTER 3 EFFECT OF COBALT DOPING ON THE OPTICAL AND MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF CADMIUM SULFIDE NANOCRYSTALS
 49 CHAPTER 3 EFFECT OF COBALT DOPING ON THE OPTICAL AND MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF CADMIUM SULFIDE NANOCRYSTALS 3.1 INTRODUCTION 3.1.1 Diluted Magnetic Semiconductor Diluted magnetic semiconductors (DMSs)
49 CHAPTER 3 EFFECT OF COBALT DOPING ON THE OPTICAL AND MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF CADMIUM SULFIDE NANOCRYSTALS 3.1 INTRODUCTION 3.1.1 Diluted Magnetic Semiconductor Diluted magnetic semiconductors (DMSs)
Graphene Quantum Dots based systems as HIV. Inhibitors
 Supporting Information to Graphene Quantum Dots based systems as HIV Inhibitors Daniela Iannazzo, *, Alessandro Pistone, Stefania Ferro, Laura De Luca, Anna Maria Monforte, Roberto Romeo, Maria Rosa Buemi
Supporting Information to Graphene Quantum Dots based systems as HIV Inhibitors Daniela Iannazzo, *, Alessandro Pistone, Stefania Ferro, Laura De Luca, Anna Maria Monforte, Roberto Romeo, Maria Rosa Buemi
Supplementary Figure 1: (a) Upconversion emission spectra of the NaYF 4 4 core shell shell nanoparticles as a function of Tm
 Supplementary Figure 1: (a) Upconversion emission spectra of the NaYF 4 @NaYbF 4 :Tm(x%) @NaYF 4 core shell shell nanoparticles as a function of Tm 3+ content in the inner shell layer. The spectra were
Supplementary Figure 1: (a) Upconversion emission spectra of the NaYF 4 @NaYbF 4 :Tm(x%) @NaYF 4 core shell shell nanoparticles as a function of Tm 3+ content in the inner shell layer. The spectra were
Supporting Information Detailed Experiments Materials: All the reagents were analytical grate and used without further purification.
 Supporting Information Detailed Experiments Materials: All the reagents were analytical grate and used without further purification. Synthesis of the Steep Rhombohedra MnCO 3 : In a typical synthesis,
Supporting Information Detailed Experiments Materials: All the reagents were analytical grate and used without further purification. Synthesis of the Steep Rhombohedra MnCO 3 : In a typical synthesis,
Supporting Information. Synthesis of Metallic Magnesium Nanoparticles by Sonoelectrochemistry. Iris Haas and Aharon Gedanken*
 Supporting Information Synthesis of Metallic Magnesium Nanoparticles by Sonoelectrochemistry Iris Haas and Aharon Gedanken* Experimental Materials and chemical preparation The Gringard reagents, ethyl-mgcl
Supporting Information Synthesis of Metallic Magnesium Nanoparticles by Sonoelectrochemistry Iris Haas and Aharon Gedanken* Experimental Materials and chemical preparation The Gringard reagents, ethyl-mgcl
In situ formation of metal Cd x Zn 1-x S nanocrystals on graphene surface: A novel method to synthesis sulfide-graphene nanocomposites
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 In situ formation of metal Cd x Zn 1-x S nanocrystals on graphene surface: A novel method to
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 In situ formation of metal Cd x Zn 1-x S nanocrystals on graphene surface: A novel method to
Room-temperature method for coating ZnS shell on semiconductor quantum dots
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic supplementary information Room-temperature method for coating
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic supplementary information Room-temperature method for coating
A Highly efficient Iron doped BaTiO 3 nanocatalyst for the catalytic reduction of nitrobenzene to azoxybenzene
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 A Highly efficient Iron doped BaTiO 3 nanocatalyst for the catalytic reduction of nitrobenzene
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 A Highly efficient Iron doped BaTiO 3 nanocatalyst for the catalytic reduction of nitrobenzene
Facile synthesis of polymer and carbon spheres decorated with highly dispersed metal nanoparticles
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 1 Facile synthesis of polymer and carbon spheres decorated with highly dispersed metal nanoparticles
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 1 Facile synthesis of polymer and carbon spheres decorated with highly dispersed metal nanoparticles
Confined Synthesis of CdSe Quantum Dots in the Pores of Metal-Organic Frameworks
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Confined Synthesis of CdSe Quantum Dots in the Pores
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Confined Synthesis of CdSe Quantum Dots in the Pores
A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with. Aliphatic Alcohols in the Presence of Molecular Oxygen. Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with Aliphatic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with Aliphatic
Supporting Information:
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information: Single Component Mn-doped Perovskite-related CsPb 2 Cl x Br 5-x Nanoplatelets
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information: Single Component Mn-doped Perovskite-related CsPb 2 Cl x Br 5-x Nanoplatelets
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (ESI) variable light emission created via direct ultrasonic exfoliation of
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (ESI) High quantum-yield luminescent MoS 2 quantum dots
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (ESI) High quantum-yield luminescent MoS 2 quantum dots
Facile bulk production of highly blue fluorescent
 Electronic Supplementary Information for Facile bulk production of highly blue fluorescent graphitic carbon nitride quantum dots and its application as a highly selective and sensitive sensor for the detection
Electronic Supplementary Information for Facile bulk production of highly blue fluorescent graphitic carbon nitride quantum dots and its application as a highly selective and sensitive sensor for the detection
Biomimetic Structure Design and Construction of Cactus-like MoS2/Bi19Cl3S27 Photocatalyst for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Biomimetic Structure Design
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Biomimetic Structure Design
Supporting Information for. Selectivity and Activity in Catalytic Methanol Oxidation in the Gas Phase
 1 / 5 Supporting Information for The Influence of Size-Induced Oxidation State of Platinum Nanoparticles on Selectivity and Activity in Catalytic Methanol Oxidation in the Gas Phase Hailiang Wang, Yihai
1 / 5 Supporting Information for The Influence of Size-Induced Oxidation State of Platinum Nanoparticles on Selectivity and Activity in Catalytic Methanol Oxidation in the Gas Phase Hailiang Wang, Yihai
Trapping Lithium into Hollow Silica Microspheres. with a Carbon Nanotube Core for Dendrite-Free
 Supporting Information Trapping Lithium into Hollow Silica Microspheres with a Carbon Nanotube Core for Dendrite-Free Lithium Metal Anodes Tong-Tong Zuo,, Ya-Xia Yin,, Shu-Hua Wang, Peng-Fei Wang,, Xinan
Supporting Information Trapping Lithium into Hollow Silica Microspheres with a Carbon Nanotube Core for Dendrite-Free Lithium Metal Anodes Tong-Tong Zuo,, Ya-Xia Yin,, Shu-Hua Wang, Peng-Fei Wang,, Xinan
Supplementary Information for
 Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
CHAPTER III. ORGANIC LIGANDS PASSIVATED ZnSe NANOSTRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONAL PROPERTIES
 82 CHAPTER III ORGANIC LIGANDS PASSIVATED ZnSe NANOSTRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONAL PROPERTIES 3.1 INTRODUCTION Semiconductor nanocrystals have size tunable optical properties that open up possibilities for revolutionary
82 CHAPTER III ORGANIC LIGANDS PASSIVATED ZnSe NANOSTRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONAL PROPERTIES 3.1 INTRODUCTION Semiconductor nanocrystals have size tunable optical properties that open up possibilities for revolutionary
Division of Fuel Cells, Dalian National Laboratory for Clean Energy, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting information Tuned Depositing Ag clusters on ZrO 2 Nanocrystals from Silver Mirror
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting information Tuned Depositing Ag clusters on ZrO 2 Nanocrystals from Silver Mirror
Supporting Information. Modulating the photocatalytic redox preferences between
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Modulating the photocatalytic redox preferences between anatase TiO 2 {001}
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Modulating the photocatalytic redox preferences between anatase TiO 2 {001}
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary Information Multifunctional Fe 2 O 3 /CeO 2 Nanocomposites for Free Radical Scavenging
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary Information Multifunctional Fe 2 O 3 /CeO 2 Nanocomposites for Free Radical Scavenging
O-Allylation of phenols with allylic acetates in aqueous medium using a magnetically separable catalytic system
 Supporting information for -Allylation of phenols with allylic acetates in aqueous medium using a magnetically separable catalytic system Amit Saha, John Leazer* and Rajender S. Varma* Sustainable Technology
Supporting information for -Allylation of phenols with allylic acetates in aqueous medium using a magnetically separable catalytic system Amit Saha, John Leazer* and Rajender S. Varma* Sustainable Technology
Sub-10-nm Au-Pt-Pd Alloy Trimetallic Nanoparticles with. High Oxidation-Resistant Property as Efficient and Durable
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Sub-10-nm Au-Pt-Pd Alloy Trimetallic Nanoparticles with High
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Sub-10-nm Au-Pt-Pd Alloy Trimetallic Nanoparticles with High
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information All inorganic cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals for photodetector
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information All inorganic cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals for photodetector
Supporting information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information Cube-like anatase TiO 2 single crystal with enhanced photocatalytic CO 2
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information Cube-like anatase TiO 2 single crystal with enhanced photocatalytic CO 2
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Tunable Phase and Visible-Light Photocatalytic Activity
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Metallic-Zinc Assistant Synthesis of Ti 3+ Self-Doped TiO 2 with Tunable Phase and Visible-Light Photocatalytic Activity Zhaoke Zheng, a Baibiao Huang,* a Xiaodong
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Metallic-Zinc Assistant Synthesis of Ti 3+ Self-Doped TiO 2 with Tunable Phase and Visible-Light Photocatalytic Activity Zhaoke Zheng, a Baibiao Huang,* a Xiaodong
