Hydronium or hydroxide ions can also be produced by a reaction of certain substances with water:
|
|
|
- Ethel Terry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chpter 14
2 1 ACIDS/BASES Acids hve tste, rect with most metls to produce, rect with most crbontes to produce, turn litmus nd phenolphthlein. Bses hve tste rect very well well with most metls or crbontes, turn litmus, nd phenolphthlein. Hydronium ion: An cid produces when mixed with wter; bse produces in wter. This is the Arrhenius definition. The hydroxide ions could be present in the originl compound: + - Soluble ionic compound: NOH (q) N (q) + OH (q) Hydronium or hydroxide ions cn lso be produced by rection of certin substnces with wter: HNO 3 (q) + H2 O(l) K = NH 3(q) + H2 O (l) K = The equilibrium constnts K nd K b lwys refer to the rection of some compound with to produce hydronium nd hydroxide ions respectively. The lrger the vlue of K the the cid. In similr wy the lrger the vlue of K b the stronger the bse. Strong cids hve K vlues tht re. All other cids re clssified s nd would hve K vlues tht re or. Exmple: Write the chemicl eqution tht represents the K for formic cid. How mny rrows should it hve?
3 2 1- Exmple: Write the chemicl eqution tht represents the K b for HCO 3. How mny rrows should it hve? BRONSTEAD-LOWRY DEFINITION OF ACID AND BASE + - HCHO 2 3 2(q) + HO 2 HO 3 (q) + CHO (q) HC2H3O 2 would be clssified s n cid becuse. During the rection is trnsferred from HC2H3O 2 to H2O. Another wy of defining cids nd bses is in terms of trnsfer of H. An cid is H nd bse would be H. In the reverse rection, hydronium ion would be clssified s /n nd cette ion s /n. HCHO + HO HO + CHO HC2H3O 2 nd C2H3O 2 re clled (CABP). Wht is the other CABP in the eqution: Exmple 1: Identify the conjugte cid-bse pirs in the following eqution. HSO + SO HSO + SO The cid in the CABP differs from the bse by conjugte cid conjugte bse mount of + chrge mount of - chrge number of H toms
4 3 Exmple 1: conjugte cid HCO HPO 4 conjugte bse HCO HPO 4 STRENGTH OF CONJUGATE ACIDS AND BASES In the chrt, the cid strength increses from to. Strong cids re nd bove. The bse strength increses from to. The strong bses re nd below. The stronger the cid the the bse its conjugte bse is. Any cid bove ** is n Arrhenius nd will usully produce when mixed with wter. Any bse ** tht is wter is n Arrhenius bse nd will usully produce when mixed with wter. ** If chemicl ppers in both columns you need to determine if it is better cid or better bse. Exmple: Which is the stronger cid: HCN or HNO 2 Exmple: Which is the stronger bse: HCO or CO ACID BASE REACTIONS When n cid rects with bse, the products re the. If the stronger cid nd bse re on the rectnt side, the vlue of K will be. If the stronger cid nd bse re on the product side, the vlue of K will be. In n queous solution the strongest bse thn cn exist is becuse sulfide nd oxide would rect with.
5 4 K For Acids t 25 C - Acid HA A K - 11 Hydriodic HI I 10-9 Hydrobromic HBr Br 10-7 Perchloric HClO4 ClO Hydrochloric HCl Cl 10-3 Chloric HClO3 ClO Sulfuric (1) H2SO4 HSO Nitric HNO3 NO Hydronium ion H3O H2O - -1 Iodic HIO3 IO3 1.6 x Oxlic (1) H2C2O4 HC2O4 5.9 x Sulfurous (1) H2SO3 HSO x Sulfuric (2) HSO4 SO4 1.2 x Chlorous HClO2 ClO2 1.1 x Phosphoric H3PO4 H2PO x Hydrofluoric HF F 6.6 x Nitrous HNO2 NO2 4.6 x Formic HCOOH HCOO 1.77 x Benzoic C6H5COOH C6H5COO 6.46 x Oxlic (2) HC2O4 C2O4 6.4 x Acetic CH3COOH CH3COO 1.76 x Crbonic (1) H2CO3 HCO3 4.3 x Sulfurous (2) HSO3 SO x Hydrosulfuric H2S HS 9.1 x Phosphoric (2) H2PO4 HPO x Hypochlorous HClO ClO 3.0 x Ammonium ion NH4 NH3 5.6 x Hydrocynic HCN CN 4.93 x Crbonic (2) HCO3 CO3 4.8 x Phosphoric (3) HPO4 PO4 2.2 x 10 Wter H2O OH hydroxide OH O - 2- hydrogen sulfide HS S
6 5 px px = where X is WARNING: This log is log bse. pk pk = EXAMPLE 1: Is formic cid strong or wek cid? Clculte pk for formic cid. EXAMPLE 2: The pk for benzoic cid is Clculte the vlue of K for benzoic cid. Is benzoic cid wek or strong cid?. Is it weker or stronger thn formic? cid K pk formic benzoic IMPORTANT POINT: The stronger the cid the the K nd the the pk ph ph = WARNING: ph is the log of the concentrtion of not the log of the concentrtion of.
7 6-5 Exmple: Wht re ph of 0.2 M HCl nd 0.2 M HC2H3O 2 (K = 1.8 x 10 )? IMPORTANT POINT: For the sme initil concentrtion, the stronger the cid the the ph. + Exmple: Clculte the [H3O ] in solution whose ph = 4.85 poh poh = - - Exmple: Clculte the poh of solution contining 0.25 M OH nd the [OH ] in - solution whose poh is 4.5. Which is the stronger bse (contins concentrtion of OH )? IMPORTANT POINT: The stronger the bse the the poh.
8 7 Exmple 1: Clculte the poh of 0.1 M B(OH) solution. 2-5 Exmple 2: Clculte the poh in 0.5 M NH 3 solution. K b = 1.8 x RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN [H3O ] AND [OH ] Whenever wter is present, this equilibrium is estblished very fst: H2 O (l) H3 O (q) + OH (q) K = K = [H3O ][OH ] TEMPERATURE ( C) K w x x x x x x x x Unless otherwise specified, the temperture should be ssumed to be nd K w is nd pk = w
9 8 - + In cid solutions there must be some OH nd in bse solutions there is some H3O. In n cidic solution the concentrtion of is greter thn. In bsic solution the concentrtion of is greter thn. - Exmple 1: Wht is the concentrtion of OH in 0.2 M cetic cid? Wht is the concentrtion + of H O in 0.1 M B(OH)? 3 2 solution + [H3O ] - [OH ] prents of H O M HC2H3O2 3 prents of OH - cidic or bsic? 0.1 M B(OH) 2 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ph AND poh ph + poh = Exmple 1: Wht is the ph of pure wter t 25 deg C? At 0 deg C?
10 9 Exmple 2: solution ph poh 0.2 M HC2H3O M B(OH) POLYPROTIC ACIDS - + H2SO 3 (q) + H2 O (l) HSO 3 (q) + H3 O (q) K = HSO 3 (q) + H2 O (l) SO 3 (q) + H3 O (q) K = Exmple 1: Clculte the ph of 0.1 M sulfurous cid solution.
11 IMPORTANT POINT Only the first rection in polyprotic cid needs to be used to find 3 the ph unless the second K is not smll nd t lest 10 times smller thn the first K. If you wnt to know the concentrtion of n ion not in the first rection you will need to solve the other equtions. 2- Exmple 2: Clculte the [SO 3 ] in 0.1 M sulfurous cid solution. 10 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN K AND K FOR A CONJUGATE ACID/BASE PAIR b HA + + K (q) - A (q) + + K b K x K = b = pk w These formuls re vlid only for Exmple 1: Look up the vlue of K for HClO nd clculte K b. This is K b for. Write the chemicl eqution tht belongs to this K. b Exmple 2: Clculte the vlue of K b for HCO Exmple 3: Is HCO 3 better s n cid or bse?
12 11 ** Go bck nd look t pge 4. Is solution of NHCO 3 cidic or bsic? ACID-BASE PROPERTIES OF SALTS compound color of phenolphthlein N3PO4 To simplify clcultions tht involve chemicl systems tht contin more thn one reversible rection, we will ttempt to find ONE equilibrium (the Principl Equilibrium) tht cn be used to determine concentrtions. When we hve series of cid/bse equilibri, we cn use the following rule: The principl rection will be rection tht rects the cid with the bse. The cid nd bse must be chosen from the chemicls dded. Write the principl rections occurring in ech of the following solutions: 1. NBr (q) Slts contining the ions tht re weker cids nd bses thn wter re. 2. NH4NO 3(q) Slts contining ions tht re stronger cids thn wter re 3. N2CO3(q) Slts tht contin ions tht re stronger bses thn wter re. Exmple: Would NHSO 3 (q) be cidic, bsic or neutrl?
13 12 METAL IONS slt (0.1 M) ph Cu(NO 3) 2 Slts tht contin highly chrged metl ions (especilly metls) re +. The higher the chrge/size rtio the cidic. Why would N not be expected to be very cidic? 2+ How cn Cu ct s n cid if it hs no H? In solution, most metl ions exist s complex ions with wter. The wters connected to the metl ion tend to be cidic thn wter not bonded to the metl ion. The rection is relly: HO + HO HO + OH where the * chemicls re bound to the metl ion. * + -* STRENGTH OF BINARY ACIDS As you go down column in the periodic tble, the strength of binry cids. STRENGTH OF OXY-ACIDS Within ech group rnk the following ccording to incresing cid strength:. HNO 3 HNO2 b. HClO 3 HClO HClO4 c. H2SO 4 H2SO3
14 13 Assign oxidtion numbers to N, Cl, nd S in ech cid. The stronger oxycid is the one with the oxidtion number Exmple: Which is stronger cid: HClO or HClO 2 ACID/BASE CHARACTERISTICS OF OXIDES The binry oxides cn be cidic (produces or rects with ), bsic (produces or rects with, or mphoteric (rects with nd ). Look t the Periodic Tble. The oxides of the non metls re when mixed with wter. For multiple oxides with the sme non-metl, the more cidic will be the one with the higher. The oxides of the lkli metls nd lkline erth metls re when mixed with wter. The oxides of the trnsitionl metls. Exmple 1: Exmple 2: Is CO cidic, bsic, neither, both when mixed with wter? When sulfur is burned, SO 2 is produced. Is SO 2 cidic, bsic, neither, both when mixed with wter? Is SO more or less cidic thn SO? 2 3 ANOTHER DEFINITION OF ACID AND BASE - LEWIS A Lewis cid is n electron pir. A Lewis bse is n electron pir.
1. Weak acids. For a weak acid HA, there is less than 100% dissociation to ions. The B-L equilibrium is:
 th 9 Homework: Reding, M&F, ch. 15, pp. 584-598, 602-605 (clcultions of ph, etc., for wek cids, wek bses, polyprotic cids, nd slts; fctors ffecting cid strength). Problems: Nkon, ch. 18, #1-10, 16-18,
th 9 Homework: Reding, M&F, ch. 15, pp. 584-598, 602-605 (clcultions of ph, etc., for wek cids, wek bses, polyprotic cids, nd slts; fctors ffecting cid strength). Problems: Nkon, ch. 18, #1-10, 16-18,
Chapter 16 Acid Base Equilibria
 Chpter 16 Acid Bse Equilibri 16.1 Acids & Bses: A Brief Review Arrhenius cids nd bses: cid: n H + donor HA(q) H(q) A(q) bse: n OH donor OH(q) (q) OH(q) Brønsted Lowry cids nd bses: cid: n H + donor HA(q)
Chpter 16 Acid Bse Equilibri 16.1 Acids & Bses: A Brief Review Arrhenius cids nd bses: cid: n H + donor HA(q) H(q) A(q) bse: n OH donor OH(q) (q) OH(q) Brønsted Lowry cids nd bses: cid: n H + donor HA(q)
Which of the following describes the net ionic reaction for the hydrolysis. Which of the following salts will produce a solution with the highest ph?
 95. Which of the following descries the net ionic rection for the hydrolysis of NH4Cl( s)? A. NH4 ( q) Cl & ( q) NH4Cl( s) B. NH Cl & 4 ( s) NH4 ( q) Cl ( q) C. Cl ( q) H O & 2 ( l) HCl( q) OH ( q) D.
95. Which of the following descries the net ionic rection for the hydrolysis of NH4Cl( s)? A. NH4 ( q) Cl & ( q) NH4Cl( s) B. NH Cl & 4 ( s) NH4 ( q) Cl ( q) C. Cl ( q) H O & 2 ( l) HCl( q) OH ( q) D.
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this mteril useful? You cn help our tem to keep this site up nd bring you even more content consider donting vi the link on our site. Still hving trouble understnding the mteril? Check out our Tutoring
Find this mteril useful? You cn help our tem to keep this site up nd bring you even more content consider donting vi the link on our site. Still hving trouble understnding the mteril? Check out our Tutoring
7/19/2011. Models of Solution Chemistry- III Acids and Bases
 Models of Solution Chemistry- III Acids nd Bses Ionic Atmosphere Model : Revisiting Ionic Strength Ionic strength - mesure of totl concentrtion of ions in the solution Chpter 8 1 2 i μ ( ) 2 c i z c concentrtion
Models of Solution Chemistry- III Acids nd Bses Ionic Atmosphere Model : Revisiting Ionic Strength Ionic strength - mesure of totl concentrtion of ions in the solution Chpter 8 1 2 i μ ( ) 2 c i z c concentrtion
Homework 04. Acids, Bases, and Salts
 HW04 - Acids, Bses, nd Slts! This is preview of the published version of the quiz Strted: Feb 21 t 8:59m Quiz Instruc!ons Homework 04 Acids, Bses, nd Slts Question 1 In the reversible rection HCN + H O
HW04 - Acids, Bses, nd Slts! This is preview of the published version of the quiz Strted: Feb 21 t 8:59m Quiz Instruc!ons Homework 04 Acids, Bses, nd Slts Question 1 In the reversible rection HCN + H O
Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry
 Homework Fundmentls of nlyticl hemistry hpter 9 0, 1, 5, 7, 9 cids, Bses, nd hpter 9(b) Definitions cid Releses H ions in wter (rrhenius) Proton donor (Bronsted( Lowry) Electron-pir cceptor (Lewis) hrcteristic
Homework Fundmentls of nlyticl hemistry hpter 9 0, 1, 5, 7, 9 cids, Bses, nd hpter 9(b) Definitions cid Releses H ions in wter (rrhenius) Proton donor (Bronsted( Lowry) Electron-pir cceptor (Lewis) hrcteristic
APEF Acids and Bases - Answers
 APEF Acids nd Bses - Answers 1. It requires 3.0 ml of 0.0500 mol/l NOH(q) to neutrlize 100.0 ml of gstric juice. We cn ssume tht HCl(q) is the only cid present in gstric juice. ) Clculte the concentrtion
APEF Acids nd Bses - Answers 1. It requires 3.0 ml of 0.0500 mol/l NOH(q) to neutrlize 100.0 ml of gstric juice. We cn ssume tht HCl(q) is the only cid present in gstric juice. ) Clculte the concentrtion
Chapter 17: Additional Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria
 1 Chpter 17: Additionl Aspects of Aqueous Equilibri Khoot! 1. Adding Br to sturted queous solution of decreses its solubility in wter. BSO 4, Li CO 3, PbS, AgBr. Which of the following mitures could be
1 Chpter 17: Additionl Aspects of Aqueous Equilibri Khoot! 1. Adding Br to sturted queous solution of decreses its solubility in wter. BSO 4, Li CO 3, PbS, AgBr. Which of the following mitures could be
30. a. Al(H 2 O) 6 + H 2 O Co(H 2 O) 5 (OH) 2+ + H 3 O + acid base conjugate base conjugate acid
 Chpter 14 : xx,3,40,4,xx,xx,47,50,54,55,xx,64,xx,83,85,91,93,95,10,11,134,138 xx.. HC H 3 O (q) H O(l) C H 3 O (q) H 3 O (q) = [H O ][C H O ] 3 3 [HC H O ] 3 b. Co(H O) 6 3 (q) H O(l) Co(H O) 5 (OH) (q)
Chpter 14 : xx,3,40,4,xx,xx,47,50,54,55,xx,64,xx,83,85,91,93,95,10,11,134,138 xx.. HC H 3 O (q) H O(l) C H 3 O (q) H 3 O (q) = [H O ][C H O ] 3 3 [HC H O ] 3 b. Co(H O) 6 3 (q) H O(l) Co(H O) 5 (OH) (q)
CHAPTER 08: MONOPROTIC ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIA
 Hrris: Quntittive Chemicl Anlysis, Eight Edition CHAPTER 08: MONOPROTIC ACIDBASE EQUILIBRIA CHAPTER 08: Opener A CHAPTER 08: Opener B CHAPTER 08: Opener C CHAPTER 08: Opener D CHAPTER 08: Opener E Chpter
Hrris: Quntittive Chemicl Anlysis, Eight Edition CHAPTER 08: MONOPROTIC ACIDBASE EQUILIBRIA CHAPTER 08: Opener A CHAPTER 08: Opener B CHAPTER 08: Opener C CHAPTER 08: Opener D CHAPTER 08: Opener E Chpter
Cu 3 (PO 4 ) 2 (s) 3 Cu 2+ (aq) + 2 PO 4 3- (aq) circle answer: pure water or Na 3 PO 4 solution This is the common-ion effect.
 CHEM 1122011 NAME: ANSWER KEY Vining, Exm # SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS ============= 4 points ech ============ All work must be shown. 1. Wht re [H O ] nd [OH ] for solution tht hs ph of 9.0? Choose one. ()
CHEM 1122011 NAME: ANSWER KEY Vining, Exm # SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS ============= 4 points ech ============ All work must be shown. 1. Wht re [H O ] nd [OH ] for solution tht hs ph of 9.0? Choose one. ()
HONH 3 initial M - ~0 0 -x - +x +x equilibrium x - x x. ] (x)(x) x b. If you assume that x << 0.100, then x
![HONH 3 initial M - ~0 0 -x - +x +x equilibrium x - x x. ] (x)(x) x b. If you assume that x << 0.100, then x HONH 3 initial M - ~0 0 -x - +x +x equilibrium x - x x. ] (x)(x) x b. If you assume that x << 0.100, then x](/thumbs/72/67573254.jpg) Chpter 15 : xx, 4, 8, 0, 8, 44, 48, 50, 51, 55, 76, 8, 90, 96(90), 1(111) xx. NH 4 OH NH H O NH H O NH 4 H O 4.. HONH (q) H O(l) OH (q) HONH (q) HONH H O OH HONH initil 0.100 M ~0 0 x x x equilibrium 0.100
Chpter 15 : xx, 4, 8, 0, 8, 44, 48, 50, 51, 55, 76, 8, 90, 96(90), 1(111) xx. NH 4 OH NH H O NH H O NH 4 H O 4.. HONH (q) H O(l) OH (q) HONH (q) HONH H O OH HONH initil 0.100 M ~0 0 x x x equilibrium 0.100
Acid/Base Definitions
 Acids and Bases Acid/Base Definitions Arrhenius Model Acids produce hydrogen ions in aqueous solutions Bases produce hydroxide ions in aqueous solutions Bronsted-Lowry Model Acids are proton donors Bases
Acids and Bases Acid/Base Definitions Arrhenius Model Acids produce hydrogen ions in aqueous solutions Bases produce hydroxide ions in aqueous solutions Bronsted-Lowry Model Acids are proton donors Bases
FIRST EXAM. Answer any 4 of the following 5 questions. Please state any additional assumptions you made, and show all work.
 CEE 680 8 Mrch 018 FIRST EXAM Closed ook, one pge of notes llowed. Answer ny 4 of the following 5 questions. Plese stte ny dditionl ssumptions you mde, nd show ll work. Miscellneous Informtion: R = 1.987
CEE 680 8 Mrch 018 FIRST EXAM Closed ook, one pge of notes llowed. Answer ny 4 of the following 5 questions. Plese stte ny dditionl ssumptions you mde, nd show ll work. Miscellneous Informtion: R = 1.987
Problem 22: Buffer solutions 1. The equilibrium, which governs the concentration of H + within the solution is HCOOH! HCOO + H + + Hence K
 Problem : Buffer solutions. The equilibrium, hich governs the concentrtion of H ithin the solution is HCOOH! HCOO H [HCOO ] 4 Hence. [HCOOH] nd since [HCOOH] 0.00 M nd [HCOO ] 0.50 M -4 0.00 4..8 M 0.50
Problem : Buffer solutions. The equilibrium, hich governs the concentrtion of H ithin the solution is HCOOH! HCOO H [HCOO ] 4 Hence. [HCOOH] nd since [HCOOH] 0.00 M nd [HCOO ] 0.50 M -4 0.00 4..8 M 0.50
Acids and Bases. H + (aq) + Cl - (aq) 100 molecules HCl 100 H+ ions Cl- ions 100% HCl molecules dissociate in water.
 Acids nd Bses Acids: in generl cid is the substnce tht produces H ions when it is dissolved in wter. Acids cn be divided into two different clsses: Strong cid: is one tht completely dissocites into its
Acids nd Bses Acids: in generl cid is the substnce tht produces H ions when it is dissolved in wter. Acids cn be divided into two different clsses: Strong cid: is one tht completely dissocites into its
Chapter 16 Acid-Base Equilibria
 Chapter 16 Acid-Base Equilibria Learning goals and key skills: Understand the nature of the hydrated proton, represented as either H + (aq) or H 3 O + (aq) Define and identify Arrhenuis acids and bases.
Chapter 16 Acid-Base Equilibria Learning goals and key skills: Understand the nature of the hydrated proton, represented as either H + (aq) or H 3 O + (aq) Define and identify Arrhenuis acids and bases.
CHEMISTRY 16 HOUR EXAM III March 26, 1998 Dr. Finklea - Answer key
 CHEMISTRY 16 HOUR EXAM III Mrch 26, 1998 Dr. Finkle - Answer key 1. Phenol, lso known s crbolic cid, is wek monoprotic cid (HA). A 1.0 M solution of phenol hs ph of 4.95. Wht is the K of phenol? 1. 2.0
CHEMISTRY 16 HOUR EXAM III Mrch 26, 1998 Dr. Finkle - Answer key 1. Phenol, lso known s crbolic cid, is wek monoprotic cid (HA). A 1.0 M solution of phenol hs ph of 4.95. Wht is the K of phenol? 1. 2.0
[HCO ] log = M. + log = log = log [CH
![[HCO ] log = M. + log = log = log [CH [HCO ] log = M. + log = log = log [CH](/thumbs/75/72569575.jpg) Chpter 17: 7, 9, 11, 1, 15, 1, 7,, 9, 4, 49, 50, 51, 79, 81, 8, 87, 9, 99, 105, 11, 117 [HCO ] 7. ph = pk + log [H CO ] [HCO ] [H CO ] log = 1.6 [HCO ] = 0.04 [HCO ] [NH ] 0.15 M 9. ph = pk + log = 9.5
Chpter 17: 7, 9, 11, 1, 15, 1, 7,, 9, 4, 49, 50, 51, 79, 81, 8, 87, 9, 99, 105, 11, 117 [HCO ] 7. ph = pk + log [H CO ] [HCO ] [H CO ] log = 1.6 [HCO ] = 0.04 [HCO ] [NH ] 0.15 M 9. ph = pk + log = 9.5
Dr. Steward s CHM152 Exam #2 Review Spring 2014 (Ch ) KEY
 Dr. Stewrd s CHM152 Em #2 Review Spring 2014 (Ch. 16. 17) KEY 1. Eplin the commonion effect. Wek cid or wek bse s % dissocition will decrese if they re plced in solutions with one of the products of dissocition.
Dr. Stewrd s CHM152 Em #2 Review Spring 2014 (Ch. 16. 17) KEY 1. Eplin the commonion effect. Wek cid or wek bse s % dissocition will decrese if they re plced in solutions with one of the products of dissocition.
9-1 (a) A weak electrolyte only partially ionizes when dissolved in water. NaHCO 3 is an
 Chpter 9 9- ( A ek electrolyte only prtilly ionizes hen dissolved in ter. NC is n exmple of ek electrolyte. (b A Brønsted-ory cid is cule tht dontes proton hen it encounters bse (proton cceptor. By this
Chpter 9 9- ( A ek electrolyte only prtilly ionizes hen dissolved in ter. NC is n exmple of ek electrolyte. (b A Brønsted-ory cid is cule tht dontes proton hen it encounters bse (proton cceptor. By this
AP Study Questions
 ID: A AP 16.4-16.7 Study Questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 What is the ph of an aqueous solution at 25.0 C in which [H + ] is 0.0025
ID: A AP 16.4-16.7 Study Questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 What is the ph of an aqueous solution at 25.0 C in which [H + ] is 0.0025
Organic Acids - Carboxylic Acids
 Orgnic Acids - rboxylic Acids Orgnic cids - crboxylic cid functionl group rboxylic cids re redily deprotonted by bses such s NO eg 3 O O - + O - + O 3 O O Acid Bse onjugte Bse onjugte Acid This rection
Orgnic Acids - rboxylic Acids Orgnic cids - crboxylic cid functionl group rboxylic cids re redily deprotonted by bses such s NO eg 3 O O - + O - + O 3 O O Acid Bse onjugte Bse onjugte Acid This rection
ACID BASE EQUILIBRIUM
 ACID BASE EQUILIBRIUM Part one: Acid/Base Theories Learning Goals: to identify acids and bases and their conjugates according to Arrhenius and Bronstead Lowry Theories. to be able to identify amphoteric
ACID BASE EQUILIBRIUM Part one: Acid/Base Theories Learning Goals: to identify acids and bases and their conjugates according to Arrhenius and Bronstead Lowry Theories. to be able to identify amphoteric
(for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes)
 www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) 1. chem10b 16.1-27 The ph of a 0.10 M solution of a weak base is 9.82. What is the K b for this base? A. 8.8 10-8 B. 2.1
www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) 1. chem10b 16.1-27 The ph of a 0.10 M solution of a weak base is 9.82. What is the K b for this base? A. 8.8 10-8 B. 2.1
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this mteil useful? You cn help ou tem to keep this site up nd bing you even moe content conside donting vi the link on ou site. Still hving touble undestnding the mteil? Check out ou Tutoing pge to
Find this mteil useful? You cn help ou tem to keep this site up nd bing you even moe content conside donting vi the link on ou site. Still hving touble undestnding the mteil? Check out ou Tutoing pge to
Acid and Base Definitions
 Chpter 8 AcidBse Equilibri Acid nd Bse Definitions 81 BrønstedLowry Acids nd Bses 8 Wter nd the p Scle 8 The Strengths of Acids nd Bses 84 Equilibri Involving Wek Acids nd Bses 85 Buffer Solutions 86 AcidBse
Chpter 8 AcidBse Equilibri Acid nd Bse Definitions 81 BrønstedLowry Acids nd Bses 8 Wter nd the p Scle 8 The Strengths of Acids nd Bses 84 Equilibri Involving Wek Acids nd Bses 85 Buffer Solutions 86 AcidBse
Honors Chemistry Study Guide for Acids and Bases. NH4 + (aq) + H2O(l) H3O + (aq) + NH3(aq) water. a)hno3. b) NH3
 Honors Chemistry Study Guide for Acids and Bases 1. Calculate the ph, poh, and [H3O + ] for a solution that has a [OH - ] = 4.5 x 10-5? 2. An aqueous solution has a ph of 8.85. What are the [H + ], [OH
Honors Chemistry Study Guide for Acids and Bases 1. Calculate the ph, poh, and [H3O + ] for a solution that has a [OH - ] = 4.5 x 10-5? 2. An aqueous solution has a ph of 8.85. What are the [H + ], [OH
First Exam December 19---Christmas Break begins December 21. Silberberg Chapter 17-18, Skoog 2-7, 11-13
 Announcements First Exam December 19---Christmas Break begins December 21. Silberberg Chapter 17-18, Skoog 2-7, 11-13 Please keep up with the work (lots of problems in this Chapter) and see me if you have
Announcements First Exam December 19---Christmas Break begins December 21. Silberberg Chapter 17-18, Skoog 2-7, 11-13 Please keep up with the work (lots of problems in this Chapter) and see me if you have
Experiment 9: DETERMINATION OF WEAK ACID IONIZATION CONSTANT & PROPERTIES OF A BUFFERED SOLUTION
 Experiment 9: DETERMINATION OF WEAK ACID IONIZATION CONSTANT & PROPERTIES OF A BUFFERED SOLUTION Purpose: Prt I: The cid ioniztion constnt of wek cid is to be determined, nd the cid is identified ccordingly.
Experiment 9: DETERMINATION OF WEAK ACID IONIZATION CONSTANT & PROPERTIES OF A BUFFERED SOLUTION Purpose: Prt I: The cid ioniztion constnt of wek cid is to be determined, nd the cid is identified ccordingly.
Aqueous Equilibria: Acids and Bases
 Slide 1 Chapter 14 Aqueous Equilibria: Acids and Bases Slide 2 Acid Base Concepts 01 Arrhenius Acid: A substance which dissociates to form hydrogen ions (H + ) in solution. HA(aq) H + (aq) + A (aq) Arrhenius
Slide 1 Chapter 14 Aqueous Equilibria: Acids and Bases Slide 2 Acid Base Concepts 01 Arrhenius Acid: A substance which dissociates to form hydrogen ions (H + ) in solution. HA(aq) H + (aq) + A (aq) Arrhenius
Chapter 15. Applications of Aqueous Equlibria. A bag of mostly water - Star Trek -
 Chpter 15. Applictions of Aqueous Equlibri A bg of mostly wter - Str Trek - Solutions of Acids or Bses Contining Common Ion Until now, we were concerned with the equilibrium of solution with n cid or bse.
Chpter 15. Applictions of Aqueous Equlibri A bg of mostly wter - Str Trek - Solutions of Acids or Bses Contining Common Ion Until now, we were concerned with the equilibrium of solution with n cid or bse.
Strong acids and bases. Strong acids and bases. Systematic Treatment of Equilibrium & Monoprotic Acid-base Equilibrium.
 Strong cids nd bses Systemtic Tretment of Equilibrium & Monoprotic cid-bse Equilibrium onc. (M) 0.0.00 -.00-5.00-8 p Strong cids nd bses onc. (M) p 0.0.0.00 -.0.00-5 5.0.00-8 8.0? We hve to consider utoprotolysis
Strong cids nd bses Systemtic Tretment of Equilibrium & Monoprotic cid-bse Equilibrium onc. (M) 0.0.00 -.00-5.00-8 p Strong cids nd bses onc. (M) p 0.0.0.00 -.0.00-5 5.0.00-8 8.0? We hve to consider utoprotolysis
Chem 130 Third Exam. Total /100
 Nme Chem 130 Third Exm On the following pges you will find eight questions covering vries topics rnging from precipittion solubility, cid bse, nd oxidtion reduction rections to metl lignd complexes nd
Nme Chem 130 Third Exm On the following pges you will find eight questions covering vries topics rnging from precipittion solubility, cid bse, nd oxidtion reduction rections to metl lignd complexes nd
Unit 6: ACIDS AND BASES
 Unit 6: Acids and Bases Honour Chemistry Unit 6: ACIDS AND BASES Chapter 16: Acids and Bases 16.1: Brønsted Acids and Bases Physical and Chemical Properties of Acid and Base Acids Bases Taste Sour (Citric
Unit 6: Acids and Bases Honour Chemistry Unit 6: ACIDS AND BASES Chapter 16: Acids and Bases 16.1: Brønsted Acids and Bases Physical and Chemical Properties of Acid and Base Acids Bases Taste Sour (Citric
Unit Nine Notes N C U9
 Unit Nine Notes N C U9 I. AcidBase Theories A. Arrhenius Acids and Bases 1. Acids contain hydronium ions (H O ) commonly referred to as hydrogen ions (H ) that dissociate in water a. Different acids release
Unit Nine Notes N C U9 I. AcidBase Theories A. Arrhenius Acids and Bases 1. Acids contain hydronium ions (H O ) commonly referred to as hydrogen ions (H ) that dissociate in water a. Different acids release
Chemistry 40S Acid-Base Equilibrium (This unit has been adapted from
 Chemistry 40S Acid-Base Equilibrium (This unit has been adapted from https://bblearn.merlin.mb.ca) Name: 1 Lesson 1: Defining Acids and Bases Goals: Outline the historical development of acid base theories.
Chemistry 40S Acid-Base Equilibrium (This unit has been adapted from https://bblearn.merlin.mb.ca) Name: 1 Lesson 1: Defining Acids and Bases Goals: Outline the historical development of acid base theories.
Chem 1046 Lecture Notes Chapter 17
 Chem 1046 Lecture Notes Chapter 17 Updated 01-Oct-2012 The Chemistry of Acids and Bases These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text, They do NOT Replace reading the Text Book Material. Additional material that
Chem 1046 Lecture Notes Chapter 17 Updated 01-Oct-2012 The Chemistry of Acids and Bases These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text, They do NOT Replace reading the Text Book Material. Additional material that
CH 15 Summary. Equilibrium is a balance between products and reactants
 CH 15 Summary Equilibrium is a balance between products and reactants Use stoichiometry to determine reactant or product ratios, but NOT reactant to product ratios. Capital K is used to represent the equilibrium
CH 15 Summary Equilibrium is a balance between products and reactants Use stoichiometry to determine reactant or product ratios, but NOT reactant to product ratios. Capital K is used to represent the equilibrium
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM. Cato Maximilian Guldberg and his brother-in-law Peter Waage developed the Law of Mass Action
 CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM Cato Maximilian Guldberg and his brother-in-law Peter Waage developed the Law of Mass Action Chemical Equilibrium Reversible Reactions: A chemical reaction in which the products can
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM Cato Maximilian Guldberg and his brother-in-law Peter Waage developed the Law of Mass Action Chemical Equilibrium Reversible Reactions: A chemical reaction in which the products can
Properties of Acids and Bases
 Chapter 15 Aqueous Equilibria: Acids and Bases Properties of Acids and Bases Generally, an acid is a compound that releases hydrogen ions, H +, into water. Blue litmus is used to test for acids. Blue litmus
Chapter 15 Aqueous Equilibria: Acids and Bases Properties of Acids and Bases Generally, an acid is a compound that releases hydrogen ions, H +, into water. Blue litmus is used to test for acids. Blue litmus
is considered acid 1, identify the other three terms as acid 2, base 1, and base 2 to indicate the conjugate acid-base pairs.
 18.1 Introduction to Acids and Bases 1. Name the following compounds as acids: a. H2SO4 d. HClO4 b. H2SO3 e. HCN c. H2S 2. Which (if any) of the acids mentioned in item 1 are binary acids? 3. Write formulas
18.1 Introduction to Acids and Bases 1. Name the following compounds as acids: a. H2SO4 d. HClO4 b. H2SO3 e. HCN c. H2S 2. Which (if any) of the acids mentioned in item 1 are binary acids? 3. Write formulas
INTRODUCTION TO ACIDS AND BASES
 INTRODUCTION TO ACIDS AND BASES ALIGNED STANDARDS S.C. 912.P.8.11 Relate acidity and basicity to hydronium and hydroxide concentration and ph. S.C.912.N.1.2 Describe and explain what characterizes science
INTRODUCTION TO ACIDS AND BASES ALIGNED STANDARDS S.C. 912.P.8.11 Relate acidity and basicity to hydronium and hydroxide concentration and ph. S.C.912.N.1.2 Describe and explain what characterizes science
Week 6 AB Strength, ph, Kw, Acids
 Week 6 AB Strength, ph, Kw, Acids Q UEST IO N 1 A 0.1 M solution of an electrolyte has a ph of 4.0. What is the electrolyte? A. a strong acid B. a strong base C. a weak acid D. a weak base E. a salt of
Week 6 AB Strength, ph, Kw, Acids Q UEST IO N 1 A 0.1 M solution of an electrolyte has a ph of 4.0. What is the electrolyte? A. a strong acid B. a strong base C. a weak acid D. a weak base E. a salt of
Acids and Bases. Unit 10
 Acids and Bases Unit 10 1 Properties of Acids and Bases Acids Bases Taste Sour Turns Litmus Dye Red Reacts with Metals to give H 2 (g) Taste Bitter Turns Litmus Dye Blue Do Not React with Metals Reacts
Acids and Bases Unit 10 1 Properties of Acids and Bases Acids Bases Taste Sour Turns Litmus Dye Red Reacts with Metals to give H 2 (g) Taste Bitter Turns Litmus Dye Blue Do Not React with Metals Reacts
CHEMGURU.ORG YOUTUBE ; CHEMGURU. Syllabus. Acids and Bases, ph, Common ion effect, Buffer solutions, Hydrolysis of salts and Solubility Product.
 Syllbus Acids nd Bses, ph, Common ion effect, Buffer solutions, Hydrolysis of slts nd Solubility Product. Acids nd Bses Here we discuss some importnt definitions of cids nd bses. Arrhenius Definition Arrhenius
Syllbus Acids nd Bses, ph, Common ion effect, Buffer solutions, Hydrolysis of slts nd Solubility Product. Acids nd Bses Here we discuss some importnt definitions of cids nd bses. Arrhenius Definition Arrhenius
Chapter 16 - Acids and Bases
 Chapter 16 - Acids and Bases 16.1 Acids and Bases: The Brønsted Lowry Model 16.2 ph and the Autoionization of Water 16.3 Calculations Involving ph, K a and K b 16.4 Polyprotic Acids 16.1 Acids and Bases:
Chapter 16 - Acids and Bases 16.1 Acids and Bases: The Brønsted Lowry Model 16.2 ph and the Autoionization of Water 16.3 Calculations Involving ph, K a and K b 16.4 Polyprotic Acids 16.1 Acids and Bases:
ACIDS, BASES, AND SALTS
 ACIDS, BASES, AND SALTS Chapter Quiz Choose the best answer and write its letter on the line. 1. A solution in which the hydroxide-ion concentration is 1 10 2 is a. acidic. c. neutral. b. basic. d. none
ACIDS, BASES, AND SALTS Chapter Quiz Choose the best answer and write its letter on the line. 1. A solution in which the hydroxide-ion concentration is 1 10 2 is a. acidic. c. neutral. b. basic. d. none
AP Chemistry: Acids & Bases Notes
 AP Chemistry: Acids & Bases Notes Objectives Definition of Acids-Bases Acid Strength Base Strength ph-poh Scale Calculating ph of Strong Acids-Bases Calculating ph of Weak Acids-Bases Calculating Ka from
AP Chemistry: Acids & Bases Notes Objectives Definition of Acids-Bases Acid Strength Base Strength ph-poh Scale Calculating ph of Strong Acids-Bases Calculating ph of Weak Acids-Bases Calculating Ka from
EXAM 2 PRACTICE KEY. Leaders: Deborah Course: CHEM 178
 Leaders: Deborah Course: CHEM 178 EXAM 2 PRACTICE KEY Instructor: Bonaccorsi/Vela Date: 3/6/18 Make sure you (also) know: Acid-base definitions Arrhenius Bronsted-Lowry Lewis Autoionization process of
Leaders: Deborah Course: CHEM 178 EXAM 2 PRACTICE KEY Instructor: Bonaccorsi/Vela Date: 3/6/18 Make sure you (also) know: Acid-base definitions Arrhenius Bronsted-Lowry Lewis Autoionization process of
CHEMISTRY - BROWN 13E CH.16 - ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIA - PART 2.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ph and poh To deal with incredibly small concentration values of [H + ] and [OH - ] we can use the ph scale. Under normal conditions, the ph scale operates within the range
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ph and poh To deal with incredibly small concentration values of [H + ] and [OH - ] we can use the ph scale. Under normal conditions, the ph scale operates within the range
Chapter 10 - Acids & Bases
 Chapter 10 - Acids & Bases 10.1-Acids & Bases: Definitions Arrhenius Definitions Acids: substances that produce hydrogen ions when dissolved in H 2 O Common Strong Acids: Common Weak acids: Organic carboxylic
Chapter 10 - Acids & Bases 10.1-Acids & Bases: Definitions Arrhenius Definitions Acids: substances that produce hydrogen ions when dissolved in H 2 O Common Strong Acids: Common Weak acids: Organic carboxylic
A) Arrhenius Acids produce H+ and bases produce OH not always used because it only IDs X OH as basic species
 3 ACID AND BASE THEORIES: A) Arrhenius Acids produce H+ and bases produce OH not always used because it only IDs X OH as basic species B) Bronsted and Lowry Acid = H + donor > CB = formed after H + dissociates
3 ACID AND BASE THEORIES: A) Arrhenius Acids produce H+ and bases produce OH not always used because it only IDs X OH as basic species B) Bronsted and Lowry Acid = H + donor > CB = formed after H + dissociates
CHEMISTRY - BROWN 14E CH.16 - ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIA.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ACID IDENTIFICATION The most common feature of an acid is that many possess an H + ion called the. When it comes to acids there are 2 MAJOR TYPES that exist: are acids where
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ACID IDENTIFICATION The most common feature of an acid is that many possess an H + ion called the. When it comes to acids there are 2 MAJOR TYPES that exist: are acids where
Experiment 9: WEAK ACID IONIZATION CONSTANT & PROPERTIES OF A BUFFERED SOLUTION
 Experiment 9: WEAK ACID IONIZATION CONSTANT & PROPERTIES OF A BUFFERED SOLUTION Purpose: Prt I: The cid ioniztion constnt of wek cid is to be determined, nd the cid is identified ccordingly. Prt II: The
Experiment 9: WEAK ACID IONIZATION CONSTANT & PROPERTIES OF A BUFFERED SOLUTION Purpose: Prt I: The cid ioniztion constnt of wek cid is to be determined, nd the cid is identified ccordingly. Prt II: The
Chem12 Acids : Exam Questions M.C.-100
 Chem12 Acids : Exam Questions M.C.-100 1) Given : HPO 4 2- (aq) + NH 4 + (aq) H 2 PO 4 - (aq) + NH 3 (aq), the strongest acid in the above equation is : a) NH 4 + b) HPO 4 2- c) NH 3 d) H 2 PO 4-2)
Chem12 Acids : Exam Questions M.C.-100 1) Given : HPO 4 2- (aq) + NH 4 + (aq) H 2 PO 4 - (aq) + NH 3 (aq), the strongest acid in the above equation is : a) NH 4 + b) HPO 4 2- c) NH 3 d) H 2 PO 4-2)
Indicator Color in acid (ph < 7) Color at ph = 7 Color in base (ph > 7) Phenolphthalein Bromothymol Blue Red Litmus Blue Litmus
 Unit 9: Acids and Bases Notes Introduction and Review 1. Define Acid: 2. Name the following acids: HCl H2SO4 H2SO3 H2S 3. Bases usually contain 4. Name the following bases: NaOH Ca(OH)2 Cu(OH)2 NH4OH Properties
Unit 9: Acids and Bases Notes Introduction and Review 1. Define Acid: 2. Name the following acids: HCl H2SO4 H2SO3 H2S 3. Bases usually contain 4. Name the following bases: NaOH Ca(OH)2 Cu(OH)2 NH4OH Properties
CEE 370 Environmental Engineering Principles
 Updated: 29 September 2015 Print version CEE 370 Environmental Engineering Principles Lecture #7 Environmental Chemistry V: Thermodynamics, Henry s Law, Acids-bases II Reading: Mihelcic & Zimmerman, Chapter
Updated: 29 September 2015 Print version CEE 370 Environmental Engineering Principles Lecture #7 Environmental Chemistry V: Thermodynamics, Henry s Law, Acids-bases II Reading: Mihelcic & Zimmerman, Chapter
CHEMICAL KINETICS
 CHEMICAL KINETICS Long Answer Questions: 1. Explin the following terms with suitble exmples ) Averge rte of Rection b) Slow nd Fst Rections c) Order of Rection d) Moleculrity of Rection e) Activtion Energy
CHEMICAL KINETICS Long Answer Questions: 1. Explin the following terms with suitble exmples ) Averge rte of Rection b) Slow nd Fst Rections c) Order of Rection d) Moleculrity of Rection e) Activtion Energy
CHEMISTRY - CLUTCH CH.15 - ACID AND BASE EQUILIBRIUM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ACID IDENTIFICATION The most common feature of an acid is that many possess an H + ion called the. When it comes to acids there are 2 MAJOR TYPES that exist: are acids where
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ACID IDENTIFICATION The most common feature of an acid is that many possess an H + ion called the. When it comes to acids there are 2 MAJOR TYPES that exist: are acids where
temperature is known as ionic product of water. It is designated as K w. Value of K w
 Ionic product of ter The product of concentrtions of H nd OH ions in ter t prticulr temperture is knon s ionic product of ter. It is designted s K. H O H 1 OH ; H 57.3 kjm The vlue of [H ][OH ] K ; K[HO]
Ionic product of ter The product of concentrtions of H nd OH ions in ter t prticulr temperture is knon s ionic product of ter. It is designted s K. H O H 1 OH ; H 57.3 kjm The vlue of [H ][OH ] K ; K[HO]
Cu 2+ (aq) + 4NH 3(aq) = Cu(NH 3) 4 2+ (aq) I (aq) + I 2(aq) = I 3 (aq) Fe 3+ (aq) + 6H 2O(l) = Fe(H 2O) 6 3+ (aq) Strong acids
 There are three definitions for acids and bases we will need to understand. Arrhenius Concept: an acid supplies H + to an aqueous solution. A base supplies OH to an aqueous solution. This is the oldest
There are three definitions for acids and bases we will need to understand. Arrhenius Concept: an acid supplies H + to an aqueous solution. A base supplies OH to an aqueous solution. This is the oldest
Chapter 14: Acids and Bases
 Chapter 14: Acids and Bases Properties of Acids and Bases What is an acid? Some examples of common items containing acids: Vinegar contains acetic acid; lemons and citrus fruits contain citric acid; many
Chapter 14: Acids and Bases Properties of Acids and Bases What is an acid? Some examples of common items containing acids: Vinegar contains acetic acid; lemons and citrus fruits contain citric acid; many
Chap 16 Chemical Equilibrium HSU FUYIN
 Chap 16 Chemical Equilibrium HSU FUYIN 1 Definitions: Arrhenius & Brønsted Lowry acid and base Arrhenius theory: An acid is a substance that, when dissolved in water, increases the concentration of hydrogen
Chap 16 Chemical Equilibrium HSU FUYIN 1 Definitions: Arrhenius & Brønsted Lowry acid and base Arrhenius theory: An acid is a substance that, when dissolved in water, increases the concentration of hydrogen
CEE 370 Environmental Engineering Principles
 Updated: 29 September 2015 Print version CEE 370 Environmental Engineering Principles Lecture #7 Environmental Chemistry V: Thermodynamics, Henry s Law, Acidsbases II Reading: Mihelcic & Zimmerman, Chapter
Updated: 29 September 2015 Print version CEE 370 Environmental Engineering Principles Lecture #7 Environmental Chemistry V: Thermodynamics, Henry s Law, Acidsbases II Reading: Mihelcic & Zimmerman, Chapter
Calorimetry, Heat and ΔH Problems
 Calorimetry, Heat and ΔH Problems 1. Calculate the quantity of heat involved when a 70.0g sample of calcium is heated from 22.98 C to 86.72 C. c Ca= 0.653 J/g C q = 2.91 kj 2. Determine the temperature
Calorimetry, Heat and ΔH Problems 1. Calculate the quantity of heat involved when a 70.0g sample of calcium is heated from 22.98 C to 86.72 C. c Ca= 0.653 J/g C q = 2.91 kj 2. Determine the temperature
AP Chemistry CHAPTER 16 STUDY GUIDE Acid-Base Equilibrium
 AP Chemistry CHAPTER 16 STUDY GUIDE AcidBase Equilibrium 16.1 Acids and Bases: A Brief Review Acids taste sour and cause certain dyes to change color. Bases taste bitter and feel soapy. Arrhenius concept
AP Chemistry CHAPTER 16 STUDY GUIDE AcidBase Equilibrium 16.1 Acids and Bases: A Brief Review Acids taste sour and cause certain dyes to change color. Bases taste bitter and feel soapy. Arrhenius concept
Unit 10: Acids and Bases
 Unit 10: Acids and Bases PROPERTIES OF ACIDS & BASES Properties of an Acid: a Tastes sour substance which dissociates (ionizes, breaks apart in solution) in water to form hydrogen ions Turns blue litmus
Unit 10: Acids and Bases PROPERTIES OF ACIDS & BASES Properties of an Acid: a Tastes sour substance which dissociates (ionizes, breaks apart in solution) in water to form hydrogen ions Turns blue litmus
Acid Base Equilibrium Review
 Acid Bse Equilirium Review Proof of true understnding of cid se equilirium culmintes in the ility to find ph of ny solution or comintion of solutions. The ility to determine ph of multitude of solutions
Acid Bse Equilirium Review Proof of true understnding of cid se equilirium culmintes in the ility to find ph of ny solution or comintion of solutions. The ility to determine ph of multitude of solutions
Mr. Storie 40S Chemistry Student Acid and bases Unit. Acids and Bases
 Acids and Bases 1 UNIT 4: ACIDS & BASES OUTCOMES All important vocabulary is in Italics and bold. Outline the historical development of acid base theories. Include: Arrhenius, BronstedLowry, Lewis. Write
Acids and Bases 1 UNIT 4: ACIDS & BASES OUTCOMES All important vocabulary is in Italics and bold. Outline the historical development of acid base theories. Include: Arrhenius, BronstedLowry, Lewis. Write
Acids and Bases. Essential Practice for success on the exam!
 Acids and Bases AP Chemistry Review 1. If 50 ml of 0.025 M NaOH is mixed with 50 ml of 0.05 M HCl, what is the resulting ph of the mixture closest to? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 2. What is the ph of a 0.1
Acids and Bases AP Chemistry Review 1. If 50 ml of 0.025 M NaOH is mixed with 50 ml of 0.05 M HCl, what is the resulting ph of the mixture closest to? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 2. What is the ph of a 0.1
Initial Change x +x +x Equilibrium x x x
 Chpter 8 Homework Solutions 8.1 () n(h ) 0.144 mol/l x 0.05 L 3.60x10-3 mol n(oh - ) 0.15 mol/l x 0.05 L 3.1x10-3 mol After neutrliztion, excess n(h ) 3.6x10-3 mol - 3.1x10-3 mol 4.8x10-4 mol [ H n( H
Chpter 8 Homework Solutions 8.1 () n(h ) 0.144 mol/l x 0.05 L 3.60x10-3 mol n(oh - ) 0.15 mol/l x 0.05 L 3.1x10-3 mol After neutrliztion, excess n(h ) 3.6x10-3 mol - 3.1x10-3 mol 4.8x10-4 mol [ H n( H
Types of Ka Calculation problems
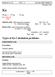 Chemistry 12 UNIT 4 ACIDS AND BASES PACKAGE #3 Ka HB (aq) H + (aq) + B - (aq) Ka = [ H + ] [ B - ] [HB] STRONG ACID: 100% dissociation (ionization) HCl à H + + Cl - Ka ~ infinity since [large] Equil: ~0
Chemistry 12 UNIT 4 ACIDS AND BASES PACKAGE #3 Ka HB (aq) H + (aq) + B - (aq) Ka = [ H + ] [ B - ] [HB] STRONG ACID: 100% dissociation (ionization) HCl à H + + Cl - Ka ~ infinity since [large] Equil: ~0
Chapter 15 - Acids and Bases Fundamental Concepts
 Chapter 15 - Acids and Bases Fundamental Concepts Acids and Bases: Basic Definitions Properties of Acids Sour Taste React with active metals (Al, Zn, Fe) to yield H 2 gas: Corrosive React with carbonates
Chapter 15 - Acids and Bases Fundamental Concepts Acids and Bases: Basic Definitions Properties of Acids Sour Taste React with active metals (Al, Zn, Fe) to yield H 2 gas: Corrosive React with carbonates
Duncan. UNIT 14 - Acids & Bases. COMMON ACIDS NOTES lactic acetic phosphoric NAMING ACIDS NOTES
 COMMON ACIDS NOTES lactic acetic phosphoric citric malic PROPERTIES OF ACIDS 1. 1. PROPERTIES OF BASES 2. 2. 3. 3. 4. 4. 5. 5. NAMING ACIDS NOTES Binary acids (H + one element) 1. hydro- - HF 2. root of
COMMON ACIDS NOTES lactic acetic phosphoric citric malic PROPERTIES OF ACIDS 1. 1. PROPERTIES OF BASES 2. 2. 3. 3. 4. 4. 5. 5. NAMING ACIDS NOTES Binary acids (H + one element) 1. hydro- - HF 2. root of
HA(aq) H + (aq) + A (aq) We can write an equilibrium constant expression for this dissociation: [ ][ ]
![HA(aq) H + (aq) + A (aq) We can write an equilibrium constant expression for this dissociation: [ ][ ] HA(aq) H + (aq) + A (aq) We can write an equilibrium constant expression for this dissociation: [ ][ ]](/thumbs/87/96059823.jpg) 16.6 Weak Acids Weak acids are only partially ionized in aqueous solution. There is a mixture of ions and un-ionized acid in solution. Therefore, weak acids are in equilibrium: Or: HA(aq) + H 2 O(l) H
16.6 Weak Acids Weak acids are only partially ionized in aqueous solution. There is a mixture of ions and un-ionized acid in solution. Therefore, weak acids are in equilibrium: Or: HA(aq) + H 2 O(l) H
FIRST EXAM. Miscellaneous Information: R = cal/mole K = J/mole K Absolute zero = C 1 joule = calories -20 C = wicked cold
 CEE 680 16 October 2012 FIRS EXAM Closed book, one page of notes allowed. Answer question #1 and #4, and either #2 or #3. Please state any additional assumptions you made, and show all work. You are welcome
CEE 680 16 October 2012 FIRS EXAM Closed book, one page of notes allowed. Answer question #1 and #4, and either #2 or #3. Please state any additional assumptions you made, and show all work. You are welcome
Acids. Names of Acids. Naming Some Common Acids. Solution. Learning Check Acids and Bases. Arrhenius acids Produce H + ions in water.
 Chapter 10 Acids and Bases Acids 10.1 Acids and Bases Arrhenius acids Produce H + ions in water. H 2 O HCl(g) H + (aq) + Cl (aq) Are electrolytes. Have a sour taste. Turn litmus red. Neutralize bases.
Chapter 10 Acids and Bases Acids 10.1 Acids and Bases Arrhenius acids Produce H + ions in water. H 2 O HCl(g) H + (aq) + Cl (aq) Are electrolytes. Have a sour taste. Turn litmus red. Neutralize bases.
OWL Assignment #2 Study Sheet
 OWL Assignment #2 Study Sheet Binary Acid Nomenclature Binary compounds are composed of two elements. When one of the elements is a binary acid can be formed. Examples of this are HCl or H 2 S. When put
OWL Assignment #2 Study Sheet Binary Acid Nomenclature Binary compounds are composed of two elements. When one of the elements is a binary acid can be formed. Examples of this are HCl or H 2 S. When put
Chapters 15 & 16 ACIDS & BASES ph & Titrations
 PROPERTIES OF ACIDS Chapters 15 & 16 ACIDS & BASES ph & Titrations There are 5 main properties of acids: 1. sour taste 2. change the color of acidbase indicators 3. react with metals to produce H2 gas
PROPERTIES OF ACIDS Chapters 15 & 16 ACIDS & BASES ph & Titrations There are 5 main properties of acids: 1. sour taste 2. change the color of acidbase indicators 3. react with metals to produce H2 gas
-a base contains an OH group and ionizes in solutions to produce OH - ions: Neutralization: Hydrogen ions (H + ) in solution form
 NOTES Acids, Bases & Salts Arrhenius Theory of Acids & Bases: an acid contains hydrogen and ionizes in solutions to produce H+ ions: a base contains an OH group and ionizes in solutions to produce OH ions:
NOTES Acids, Bases & Salts Arrhenius Theory of Acids & Bases: an acid contains hydrogen and ionizes in solutions to produce H+ ions: a base contains an OH group and ionizes in solutions to produce OH ions:
CEE November 2012 SECOND EXAM. Answer all questions. Please state any additional assumptions you made, and show all work.
 CEE 680 20 November 2012 SECOND EXAM Closed book, two pages of notes allowed. Answer all questions. Please state any additional assumptions you made, and show all work. Some useful constants: P CO2 = 10
CEE 680 20 November 2012 SECOND EXAM Closed book, two pages of notes allowed. Answer all questions. Please state any additional assumptions you made, and show all work. Some useful constants: P CO2 = 10
Dynamic equilibrium: rate of evaporation = rate of condensation II. In a closed system a solid obtains a dynamic equilibrium with its dissolved state
 CHEMISTRY 111 LECTURE EXAM III Material PART 1 CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM Chapter 14 I Dynamic Equilibrium I. In a closed system a liquid obtains a dynamic equilibrium with its vapor state Dynamic equilibrium:
CHEMISTRY 111 LECTURE EXAM III Material PART 1 CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM Chapter 14 I Dynamic Equilibrium I. In a closed system a liquid obtains a dynamic equilibrium with its vapor state Dynamic equilibrium:
(Label the Conjugate Pairs) Water in the last example acted as a Bronsted-Lowry base, and here it is acting as an acid. or
 Chapter 16 - Acid-Base Equilibria Arrhenius Definition produce hydrogen ions in aqueous solution. produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in water. Limits to aqueous solutions. Only one kind of base. NH
Chapter 16 - Acid-Base Equilibria Arrhenius Definition produce hydrogen ions in aqueous solution. produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in water. Limits to aqueous solutions. Only one kind of base. NH
CEE March FIRST EXAM (Solutions)
 CEE 680 5 March 015 FIRST EXAM (Solutions) Closed book, one page of notes allowed. Answer any 4 of the following 5 questions. Please state any additional assumptions you made, and show all work. You are
CEE 680 5 March 015 FIRST EXAM (Solutions) Closed book, one page of notes allowed. Answer any 4 of the following 5 questions. Please state any additional assumptions you made, and show all work. You are
Chemistry I Notes Unit 10: Acids and Bases
 Chemistry I Notes Unit 10: Acids and Bases Acids 1. Sour taste. 2. Acids change the color of acid- base indicators (turn blue litmus red). 3. Some acids react with active metals and release hydrogen gas,
Chemistry I Notes Unit 10: Acids and Bases Acids 1. Sour taste. 2. Acids change the color of acid- base indicators (turn blue litmus red). 3. Some acids react with active metals and release hydrogen gas,
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 14 Outline Acids and Bases
 Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 14 Outline Acids and Bases The Nature of Acids and Bases Svante Arrhenius was the first to recognize the nature of acids and bases. He postulated that acids produce hydrogen ions(h
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 14 Outline Acids and Bases The Nature of Acids and Bases Svante Arrhenius was the first to recognize the nature of acids and bases. He postulated that acids produce hydrogen ions(h
Unit 2 Acids and Bases
 Unit 2 Acids and Bases 1 Topics Properties / Operational Definitions Acid-Base Theories ph & poh calculations Equilibria (Kw, K a, K b ) Indicators Titrations STSE: Acids Around Us 2 Operational Definitions
Unit 2 Acids and Bases 1 Topics Properties / Operational Definitions Acid-Base Theories ph & poh calculations Equilibria (Kw, K a, K b ) Indicators Titrations STSE: Acids Around Us 2 Operational Definitions
I. The Dissociation of Water
 AP Chem Unit #12 I. The Dissociation of Water A. What is the process known as the autoionization of water? B. K w = C. What are the [H + ] and [OH ] in pure distilled water? D. Compare and contrast the
AP Chem Unit #12 I. The Dissociation of Water A. What is the process known as the autoionization of water? B. K w = C. What are the [H + ] and [OH ] in pure distilled water? D. Compare and contrast the
ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIA. Chapter 16
 P a g e 1 Chapter 16 ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIA Nature of Acids and Bases Before we formally define acids and bases, let s examine their properties. Properties of Acids Sour taste Ability to dissolve many metals
P a g e 1 Chapter 16 ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIA Nature of Acids and Bases Before we formally define acids and bases, let s examine their properties. Properties of Acids Sour taste Ability to dissolve many metals
X212F Which of the following is a weak base in aqueous solution? A) H 2 CO 3 B) B(OH) 3 C) N 2 H 4 D) LiOH E) Ba(OH) 2
 PX212SP14 Practice Exam II / Spring 2014 1. Which of the following statements are characteristic of acids? 1. They are proton donors. 2. They react with bases to produce a salt and water. 3. They taste
PX212SP14 Practice Exam II / Spring 2014 1. Which of the following statements are characteristic of acids? 1. They are proton donors. 2. They react with bases to produce a salt and water. 3. They taste
Acid-Base Equilibria
 Acid-Base Equilibria 1. Classify each of the following species as an acid, a base, or amphoteric in aqueous solution: (a) H 2 O; (b) CH 3 CH 2 ; (c) PO 4 3 ; (d) C 6 H 5 NH 3 2. Write the proton transfer
Acid-Base Equilibria 1. Classify each of the following species as an acid, a base, or amphoteric in aqueous solution: (a) H 2 O; (b) CH 3 CH 2 ; (c) PO 4 3 ; (d) C 6 H 5 NH 3 2. Write the proton transfer
Acids - Bases in Water
 more equilibrium Dr. Fred Omega Garces Chemistry, Miramar College 1 Acids-Bases Characteristics Acids (Properties) Taste Sour Dehydrate Substances Neutralizes bases Dissolves metals Examples: Juices: TJ,
more equilibrium Dr. Fred Omega Garces Chemistry, Miramar College 1 Acids-Bases Characteristics Acids (Properties) Taste Sour Dehydrate Substances Neutralizes bases Dissolves metals Examples: Juices: TJ,
Lecture 10. Professor Hicks Inorganic Chemistry II (CHE152) Scale of [H 3 O + ] (or you could say [H + ]) concentration
![Lecture 10. Professor Hicks Inorganic Chemistry II (CHE152) Scale of [H 3 O + ] (or you could say [H + ]) concentration Lecture 10. Professor Hicks Inorganic Chemistry II (CHE152) Scale of [H 3 O + ] (or you could say [H + ]) concentration](/thumbs/91/106142196.jpg) Lecture 10 Professor Hicks Inorganic Chemistry II (CHE152) ph Scale of [H 3 O + ] (or you could say [H + ]) concentration More convenient than scientific notation ph = log [H 3 O + ] still not sure? take
Lecture 10 Professor Hicks Inorganic Chemistry II (CHE152) ph Scale of [H 3 O + ] (or you could say [H + ]) concentration More convenient than scientific notation ph = log [H 3 O + ] still not sure? take
Chem 106 Thursday, March 10, Chapter 17 Acids and Bases
 Chem 106 Thursday, March 10, 2011 Chapter 17 Acids and Bases K a and acid strength Acid + base reactions: Four types (s +s, s + w, w + s, and w + w) Determining K from concentrations and ph ph of aqueous
Chem 106 Thursday, March 10, 2011 Chapter 17 Acids and Bases K a and acid strength Acid + base reactions: Four types (s +s, s + w, w + s, and w + w) Determining K from concentrations and ph ph of aqueous
Acids and Bases. Slide 1 / 208. Slide 2 / 208. Slide 3 / 208. Table of Contents: Acids and Bases
 Slide 1 / 208 Slide 2 / 208 Acids and Bases Table of Contents: Acids and Bases Click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 208 Properties of Acids and Bases Conjugate Acid and Base Pairs Amphoteric
Slide 1 / 208 Slide 2 / 208 Acids and Bases Table of Contents: Acids and Bases Click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 208 Properties of Acids and Bases Conjugate Acid and Base Pairs Amphoteric
Chapter 16 Acid Base Equilibria
 Chapter 16 Acid Base Equilibria 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Acid Base Equilibria 16.1 : A Brief Review 16.2 Brønsted Lowry 16.3 The Autoionization of Water 16.4 The ph Scale 16.5 Strong Balsamic Vinegar
Chapter 16 Acid Base Equilibria 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Acid Base Equilibria 16.1 : A Brief Review 16.2 Brønsted Lowry 16.3 The Autoionization of Water 16.4 The ph Scale 16.5 Strong Balsamic Vinegar
Part 01 - Assignment: Introduction to Acids &Bases
 Part 01 - Assignment: Introduction to Acids &Bases Classify the following acids are monoprotic, diprotic, or triprotic by writing M, D, or T, respectively. 1. HCl 2. HClO4 3. H3As 4. H2SO4 5. H2S 6. H3PO4
Part 01 - Assignment: Introduction to Acids &Bases Classify the following acids are monoprotic, diprotic, or triprotic by writing M, D, or T, respectively. 1. HCl 2. HClO4 3. H3As 4. H2SO4 5. H2S 6. H3PO4
Chapter 14. Objectives
 Section 1 Properties of Acids and Bases Objectives List five general properties of aqueous acids and bases. Name common binary acids and oxyacids, given their chemical formulas. List five acids commonly
Section 1 Properties of Acids and Bases Objectives List five general properties of aqueous acids and bases. Name common binary acids and oxyacids, given their chemical formulas. List five acids commonly
