EXERGY, ENERGY SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND OPTIMIZATION Vol. I - Graphic Exergy Analysis - Ishida M.
|
|
|
- Jason McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GRAPHIC EXERGY ANALYSIS Ishida M. Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama, Japan Keywords: first and second laws of thermodynamics, graphic thermodynamics, thermodynamics of a substance, thermodynamics of a process, thermodynamics of a system, energy utilization, exergy loss, exergy analysis, intermediary energy, heatequivalent energy, work-equivalent energy, quality of energy, energy level, thermodynamic compass, energy-utilization diagram Contents 1. Introduction 2. A New Approach to Thermodynamics 2.1. The Hierarchical Nature of Thermodynamics 2.2. Three Kinds of Thermodynamics 2.3. Thermodynamics of a Substance 2.4. Thermodynamics of a Process 2.5. Thermodynamics of a System 2.6. Characteristic Features of Intermediary Energy 3. Graphic Applications of Thermodynamic Compass 3.1. Introduction to Thermodynamic Compass 3.2. Classification of Processes on the Compass 3.3. Representation of Exergy Loss on Thermodynamic Compass 3.4. Application to Thermodynamics of Processes 4. Application of an Energy-Utilization Diagram (EUD) 4.1. Model System 4.2. The Second Law and Exergy Loss Analysis 4.3. The Second Law and Energy-Loss Analysis from the Viewpoint of the Energy- Utilization Diagram 4.4. Presentation of the Whole System 5. Conclusions Glossary Bibliography Biographical Sketch Summary The synthesis of chemical or energy systems is very creative work. It is thought that only a designer with special skill can accomplish it. In this section, I stress the importance of thermodynamics in creating new systems. Especially, I show that graphic methods can present the essence of thermodynamics very clearly. Several applications are also illustrated. 1. Introduction
2 Chemical process systems or energy systems are much more complicated than other systems. The number of the constituent parts in a system is generally large. The substances that are treated in them may often be composed of multiple components, and the mixture of those components show very peculiar properties that may not be predicted easily. Sometimes there are multiple phases. We can find in a system many kinds of processes such as chemical reactions, separation, heat exchange, and power-related processes taking place in a compressor or a turbine. Chemical reactions are investigated by chemists, and power-related processes by mechanical engineers, but the designer of process systems should cover all fields. Fortunately, by using the laws of thermodynamics, we can discuss all fields in a unified manner. 2. A New Approach to Thermodynamics 2.1. The Hierarchical Nature of Thermodynamics Figure 1 shows that there are three kinds of scale to which thermodynamics is applied. In (a), a phenomenon, for example a chemical reaction, takes place in a test tube or a reactor column. In (b), several to a few tens of phenomena proceed in a reactor with auxiliary mechanisms such as external cooling. In (c), scales of a few tens to a few hundred phenomena take place in cooperation with other phenomena in an entire chemical plant including reactors, separators, heat exchangers, and so on. Figure 1. Various scales of obects for application of thermodynamics The approach that has generally been taken in thermodynamics is to consider simple obects first. Hence, first a small-scale obect, say a test tube or a flask, is considered. Then we extend the applications to complicated obects of medium or large scale, such as a reactor with auxiliary mechanisms or an entire system. Although it seems reasonable to start from a simple case, we do not have a good method for extending the approach for simple obects to the level that it can be applied to complicated ones. Then we may be confused, because it is not possible to udge to what extent the results obtained for the simple obects can be applied to large-scale obects. Here we take the approach of considering all three scales in Figure 1 simultaneously from the beginning, and of developing thermodynamics that can be applied to not only
3 small-scale phenomena in a test tube or in a flask, but also medium, leading eventually to large-scale, phenomena. We do not need to change the method depending on the complexity of the application obect Three Kinds of Thermodynamics Let us try to extract the common elements from all of those three scales. In each scale of (a), (b), and (c), we find substances such as the reactant, the product, and the cooling medium. Hence, substance is common to the three scales. We also find a change in substances. The reaction in the test tube in (a) is a typical example. Hence, change of substances is the second common element. Furthermore, we find plural changes in substances. Even at the smallest scale, (a) in Figure 1, we can observe a rise in the temperature of the test tube. Hence we can find the change by the reaction, and the rise in the temperature of the test tube by the exothermic reaction taking place in the test tube. In other words, assembly of changes of substances is the third common element. Consequently, it may be a good idea to discuss thermodynamics based on these three common elements. This means that we can construct three kinds of thermodynamics. By dividing thermodynamics into these three kinds, we shall cover the full width of its applications Thermodynamics of a Substance When the number of phases, the quantity of each component in each phase, and the temperature and pressure, are specified, the energy H and entropy S of a substance can be determined independently from its production path. This is the thermodynamics of a substance. The energy of a substance is called internal energy or enthalpy depending on whether or not the process proceeds under constant volume Thermodynamics of a Process The circle in Figure 2 represents a change in a substance. The solid arrows going into and out of the circle show the input and output substances respectively. Since their energy H and entropy S can be determined, we can calculate the energy change ΔH and the entropy change ΔS for this change: out in Δ H = H H (1) Δ S = S S (2) out in When there are plural streams for input, say 1 and 2, H in and S in the above in equations can be replaced by ( H1,in + H2,in ) and ( S1,in + S2,in ), respectively. This is the thermodynamics of a process. This view can be applied to all changes in substances, such as chemical reactions or processes of heating, cooling, compression, expansion, and so on. We may call this change in substances a process.
4 Figure 2. Description of a process It should be noted that some energy, such as heat or work, is accepted or released by this change. The thick outlined arrows in Figure 2 represent this kind of energy. It is called intermediary energy, because the energy released by a process is generally accepted by another process, and the combination of acceptance and release of this energy comprises an energy transformation Thermodynamics of a System Figure 3 shows an assembly of processes. Figure 3(a) is called a system or a thermodynamic system, where the flow of substances (solid line arrows) may intersect the system boundary, but the flow of intermediary energy (thick outlined arrows) does not. Hence, Figure 3(b) is not a thermodynamic system, because intermediary energy released by process 4 intersects the system boundary. For a thermodynamic system, the following equations hold: ΔH = 0 (The first law of thermodynamics) (3) ΔS 0 (The second law of thermodynamics) (4) Figure 3. Assembly of processes
5 - - - TO ACCESS ALL THE 19 PAGES OF THIS CHAPTER, Visit: Bibliography Bean A., Tsatsaronis G., and Moran M. (1996). Thermal Design and Optimization. 542 pp. New York: John Wiley. [Exergy loss is called exergy destruction in this book.] Hohman E.C. (1971). Optimum Networks for Heat Exchange. Ph.D. Thesis, Chemical Engineering Department, University of Southern California, Los Angeles. [A Q T diagram is proposed.] Ishida M. (1983). Hierarchical structure analysis based on energy and exergy transformation of a process system. ACS Symposium Series 235, [The concepts of three kinds of thermodynamics and thermodynamic compass are proposed.] Ishida M. (1995). Thermodynamics: Its Perfect Comprehension and Applications. [in Japanese]. Tokyo: Baifukan. [This book deals with a new approach to thermodynamics explained in this article in detail. A process system synthesis based on thermodynamic compass is also discussed.] Ishida M. (1999). How can we ump in process system synthesis? Proceedings of ECOS 99, Ishida M. (2000). Hierarchical structure of thermodynamics. Applied Energy, 67, [The hierarchical structure of thermodynamics is discussed in detail.] Ishida M. and Chuang C.C. (1996). New approach to thermodynamics. Proceedings, ECOS'96, Stockholm, Sweden, pp Also in Energy Conversion and Management, 1997, 38, [A brief review is given of the new approach to thermodynamics explained in this article.] Ishida M. and Kawamura K. (1982). Energy and exergy analysis of a chemical process system based on enthalpy-direction factor diagram. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev., 21, [A diagram equivalent to the energy-utilization diagram is proposed.] Ishida M. and Nakagawa N. (1985). Exergy analysis of pervaporation system based on an energy utilization diagram. J. Membrane Sci., 24, [An energy-utilization analysis based on the energyutilization diagram was proposed.] Umeda T., Harada T. and Shiroko K. (1979) Umeda T. et al. (1979) A thermodynamic approach to the synthesis of heat integration systems in chemical processes. Comput. Chem. Eng. 3, [A Q (1 T/T 0 ) diagram is proposed.] Biographical Sketch Masaru Ishida is Director and Professor at the Chemical Resources Laboratory, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan. He received a Diploma in Chemical Engineering from Tokyo Institute of Technology in 1964, then performed graduate studies in chemical engineering with a maor in fluidization technology at Tokyo Institute of Technology, leading to the M.Sc. degree (1966) and Dr.Eng. degree (1969). He oined the Research Laboratory of Resources Utilization as a faculty member in 1969, and lectured on environmental process system design in undergraduate and graduate courses. His research activity is related to process system analysis and synthesis, evaluation of energy systems, design and operation of energy systems such as power plants and cogeneration systems, analysis of chemical plants, development of new separation systems such as sandwiched recycle chromatography,
6 and various works on the characteristic of fluidized beds and solid-gas reaction kinetics. He has received many awards such as the American Society of Mechanical Engineering Edward F. Obert Award (1999), the Excellent Research Award of the Chemical Engineering Society Japan (1998), and the Society Award of the Japan Institute of Energy (1998). Among his publications are more than 200 papers in ournals and for international conferences, and a book on thermodynamics (in Japanese).
CHEMICAL ENGINEEERING AND CHEMICAL PROCESS TECHNOLOGY Vol. III - Ideal Models Of Reactors - A. Burghardt
 IDEAL MODELS OF REACTORS A. Institute of Chemical Engineering, Polish Academy of Sciences, Poland Keywords: Thermodynamic state, conversion degree, extent of reaction, classification of chemical reactors,
IDEAL MODELS OF REACTORS A. Institute of Chemical Engineering, Polish Academy of Sciences, Poland Keywords: Thermodynamic state, conversion degree, extent of reaction, classification of chemical reactors,
Structured Process Energy-Exergy-Flow Diagram and Ideality Index for Analysis of Energy Transformation in Chemical Processes (Part 1)
 Structured Process Energy-Exergy-Flow Diagram and Ideality Index for Analysis of Energy Transformation in Chemical Processes (Part 1) Application to Unit Processes Hiroshi OAKI*, Masaru ISHIDA* and Tsuneo
Structured Process Energy-Exergy-Flow Diagram and Ideality Index for Analysis of Energy Transformation in Chemical Processes (Part 1) Application to Unit Processes Hiroshi OAKI*, Masaru ISHIDA* and Tsuneo
Entropy and Standard Free Energy:
 To ΔG or to ΔG 0 : Improving Conceptual Understanding in Thermodynamics A Presentation of the Flinn AP Chemistry Symposium CHEMED 2005 Paul D. Price Trinity Valley School Fort Worth, TX 76132 pricep@trinityvalleyschool.org
To ΔG or to ΔG 0 : Improving Conceptual Understanding in Thermodynamics A Presentation of the Flinn AP Chemistry Symposium CHEMED 2005 Paul D. Price Trinity Valley School Fort Worth, TX 76132 pricep@trinityvalleyschool.org
FUNDAMENTALS OF CHEMISTRY Vol. II - Irreversible Processes: Phenomenological and Statistical Approach - Carlo Cercignani
 IRREVERSIBLE PROCESSES: PHENOMENOLOGICAL AND STATISTICAL APPROACH Carlo Dipartimento di Matematica, Politecnico di Milano, Milano, Italy Keywords: Kinetic theory, thermodynamics, Boltzmann equation, Macroscopic
IRREVERSIBLE PROCESSES: PHENOMENOLOGICAL AND STATISTICAL APPROACH Carlo Dipartimento di Matematica, Politecnico di Milano, Milano, Italy Keywords: Kinetic theory, thermodynamics, Boltzmann equation, Macroscopic
AAE THERMOCHEMISTRY BASICS
 5.4 THERMOCHEMISTRY BASICS Ch5 23 Energies in Chemical Reactions Enthalpy of Combustion (Reactions): Q CV H in = H reactant H out = H product REACTANTS Stoichiometric fuel-oxidizer (air) mixture at standard
5.4 THERMOCHEMISTRY BASICS Ch5 23 Energies in Chemical Reactions Enthalpy of Combustion (Reactions): Q CV H in = H reactant H out = H product REACTANTS Stoichiometric fuel-oxidizer (air) mixture at standard
Process Design Decisions and Project Economics Prof. Dr. V. S. Moholkar Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Process Design Decisions and Project Economics Prof. Dr. V. S. Moholkar Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 2 Flowsheet Synthesis (Conceptual Design of
Process Design Decisions and Project Economics Prof. Dr. V. S. Moholkar Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 2 Flowsheet Synthesis (Conceptual Design of
EXERGY, ENERGY SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND OPTIMIZATION Vol. II - Design and Off-Design Simulation of Complex Energy Systems - Enrico Sciubba
 EXERGY, ENERGY SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND OPTIMIZATION Vol. II - Design and Off-Design Simulation of Complex DESIGN AND OFF-DESIGN SIMULATION OF COMPLEX ENERGY SYSTEMS Enrico Sciubba University of Roma 1 La Sapienza,
EXERGY, ENERGY SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND OPTIMIZATION Vol. II - Design and Off-Design Simulation of Complex DESIGN AND OFF-DESIGN SIMULATION OF COMPLEX ENERGY SYSTEMS Enrico Sciubba University of Roma 1 La Sapienza,
WASTEWATER RECYCLE, REUSE, AND RECLAMATION Vol. I - Membrane Separation Technologies - Takeshi Matsuura
 MEMBRANE SEPARATION TECHNOLOGIES Takeshi Matsuura Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Ont. Canada Keywords: membrane separation processes, pressure driven membrane processes,
MEMBRANE SEPARATION TECHNOLOGIES Takeshi Matsuura Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Ont. Canada Keywords: membrane separation processes, pressure driven membrane processes,
(g) + 2H 2. (g) CH [1] (g) H 2. Explain, with a calculation, whether this reaction is feasible at 25 C [3]
![(g) + 2H 2. (g) CH [1] (g) H 2. Explain, with a calculation, whether this reaction is feasible at 25 C [3] (g) + 2H 2. (g) CH [1] (g) H 2. Explain, with a calculation, whether this reaction is feasible at 25 C [3]](/thumbs/94/119401233.jpg) 1 This question looks at two reactions involving sulfur compounds (a) Hydrogen reacts with carbon disulfide as shown below 4H 2 + CS 2 CH 4 + 2H 2 S For this reaction, ΔH = 234 kj mol 1 and ΔS = 164 J
1 This question looks at two reactions involving sulfur compounds (a) Hydrogen reacts with carbon disulfide as shown below 4H 2 + CS 2 CH 4 + 2H 2 S For this reaction, ΔH = 234 kj mol 1 and ΔS = 164 J
Process design decisions and project economics Dr. V. S. Moholkar Department of chemical engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Process design decisions and project economics Dr. V. S. Moholkar Department of chemical engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 02 Flowsheet Synthesis (Conceptual Design of a Chemical
Process design decisions and project economics Dr. V. S. Moholkar Department of chemical engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 02 Flowsheet Synthesis (Conceptual Design of a Chemical
POINT SOURCES OF POLLUTION: LOCAL EFFECTS AND IT S CONTROL Vol. II - Contaminant Fate and Transport Process - Xi Yang and Gang Yu
 CONTAMINANT FATE AND TRANSPORT PROCESS Xi Yang and Gang Yu Department of Environmental Sciences and Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, P. R. China Keywords: chemical fate, physical transport, chemical
CONTAMINANT FATE AND TRANSPORT PROCESS Xi Yang and Gang Yu Department of Environmental Sciences and Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, P. R. China Keywords: chemical fate, physical transport, chemical
Turbomachinery. Hasan Ozcan Assistant Professor. Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering Karabuk University
 Turbomachinery Hasan Ozcan Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering Karabuk University Introduction Hasan Ozcan, Ph.D, (Assistant Professor) B.Sc :Erciyes University,
Turbomachinery Hasan Ozcan Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering Karabuk University Introduction Hasan Ozcan, Ph.D, (Assistant Professor) B.Sc :Erciyes University,
University of Engineering & Technology Lahore. (KSK Campus)
 Course File Session-2015 Semester: Fall 2016 MT-24: Thermodynamics for Technologists Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Engineering & Technology Lahore. (KSK Campus) Course File Contents
Course File Session-2015 Semester: Fall 2016 MT-24: Thermodynamics for Technologists Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Engineering & Technology Lahore. (KSK Campus) Course File Contents
Chemical Reaction Engineering Prof. Jayant Modak Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
 Chemical Reaction Engineering Prof. Jayant Modak Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture No. #40 Problem solving: Reactor Design Friends, this is our last session
Chemical Reaction Engineering Prof. Jayant Modak Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture No. #40 Problem solving: Reactor Design Friends, this is our last session
EXERGY, ENERGY SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND OPTIMIZATION Vol. II -Symbolic Thermoeconomic Analysis of Energy Systems - César Torres Cuadra
 SYMBOLIC THERMOECONOMIC ANALYSIS OF ENERGY SYSTEMS César Torres Cuadra Center of Research for Energy Resources and Consumption, Centro Politécnico Superior, Universidad de Zaragoza, Spain Keywords: Thermoeconomics,
SYMBOLIC THERMOECONOMIC ANALYSIS OF ENERGY SYSTEMS César Torres Cuadra Center of Research for Energy Resources and Consumption, Centro Politécnico Superior, Universidad de Zaragoza, Spain Keywords: Thermoeconomics,
REACTION EQUILIBRIUM
 REACTION EQUILIBRIUM A. REVERSIBLE REACTIONS 1. In most spontaneous reactions the formation of products is greatly favoured over the reactants and the reaction proceeds to completion (one direction). In
REACTION EQUILIBRIUM A. REVERSIBLE REACTIONS 1. In most spontaneous reactions the formation of products is greatly favoured over the reactants and the reaction proceeds to completion (one direction). In
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM COURSE TITLE: CHEMICAL REACTION ENGINEERING (COURSE CODE: )
 GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM COURSE TITLE: CHEMICAL REACTION ENGINEERING (COURSE CODE: 3360503) Diploma Programme in which this course is fered Chemical Engineering
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM COURSE TITLE: CHEMICAL REACTION ENGINEERING (COURSE CODE: 3360503) Diploma Programme in which this course is fered Chemical Engineering
(Refer Slide Time: 00:00:43 min) Welcome back in the last few lectures we discussed compression refrigeration systems.
 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Prof. M. Ramgopal Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 14 Vapour Absorption Refrigeration Systems (Refer Slide
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Prof. M. Ramgopal Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 14 Vapour Absorption Refrigeration Systems (Refer Slide
Lecture (9) Reactor Sizing. Figure (1). Information needed to predict what a reactor can do.
 Lecture (9) Reactor Sizing 1.Introduction Chemical kinetics is the study of chemical reaction rates and reaction mechanisms. The study of chemical reaction engineering (CRE) combines the study of chemical
Lecture (9) Reactor Sizing 1.Introduction Chemical kinetics is the study of chemical reaction rates and reaction mechanisms. The study of chemical reaction engineering (CRE) combines the study of chemical
Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S.K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S.K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 12 Second Law and Available Energy III Good morning. I welcome you to this session.
Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S.K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 12 Second Law and Available Energy III Good morning. I welcome you to this session.
In this lecture... Radial flow turbines Types of radial flow turbines Thermodynamics and aerodynamics Losses in radial flow turbines
 Lect- 35 1 In this lecture... Radial flow turbines Types of radial flow turbines Thermodynamics and aerodynamics Losses in radial flow turbines Radial turbines Lect-35 Development of radial flow turbines
Lect- 35 1 In this lecture... Radial flow turbines Types of radial flow turbines Thermodynamics and aerodynamics Losses in radial flow turbines Radial turbines Lect-35 Development of radial flow turbines
3/30/2017. Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Thermodynamics vs. Kinetics. Chapter 17. Spontaneity, Entropy, and Free Energy
 Chapter 17 Spontaneity, Entropy, and Thermodynamics vs. Kinetics Domain of Kinetics Rate of a reaction depends on the pathway from reactants to products. Thermodynamics tells us whether a reaction is spontaneous
Chapter 17 Spontaneity, Entropy, and Thermodynamics vs. Kinetics Domain of Kinetics Rate of a reaction depends on the pathway from reactants to products. Thermodynamics tells us whether a reaction is spontaneous
Thermodynamics. Thermodynamics of Chemical Reactions. Enthalpy change
 Thermodynamics 1 st law (Cons of Energy) Deals with changes in energy Energy in chemical systems Total energy of an isolated system is constant Total energy = Potential energy + kinetic energy E p mgh
Thermodynamics 1 st law (Cons of Energy) Deals with changes in energy Energy in chemical systems Total energy of an isolated system is constant Total energy = Potential energy + kinetic energy E p mgh
Chemical Reaction Engineering Prof. JayantModak Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
 Chemical Reaction Engineering Prof. JayantModak Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Module No. #05 Lecture No. #29 Non Isothermal Reactor Operation Let us continue
Chemical Reaction Engineering Prof. JayantModak Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Module No. #05 Lecture No. #29 Non Isothermal Reactor Operation Let us continue
In The Name Of God. Ali Hashempour. M.Sc. Student at School of Chemical Engineering, College of Engineering, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran.
 In The Name Of God Ali Hashempour M.Sc. Student at School of Chemical Engineering, College of Engineering,, Tehran, Iran. +98 910 876 3444 Ali.hashempour@ut.ac.ir Ali.hashempour71@gmail.com Research Interests
In The Name Of God Ali Hashempour M.Sc. Student at School of Chemical Engineering, College of Engineering,, Tehran, Iran. +98 910 876 3444 Ali.hashempour@ut.ac.ir Ali.hashempour71@gmail.com Research Interests
2013, 2011, 2009, 2008 AP
 Lecture 15 Thermodynamics I Heat vs. Temperature Enthalpy and Work Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions Average Bond Enthalpy Thermodynamics The relationship between chemical reactions and heat. What causes
Lecture 15 Thermodynamics I Heat vs. Temperature Enthalpy and Work Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions Average Bond Enthalpy Thermodynamics The relationship between chemical reactions and heat. What causes
CHEMISTRY 12 EQUILIBRIUM PROPERTIES & ENTROPY AND ENTHALPY WORKSHEET CHEMISTRY 12 EQUILIBRIUM PROPERTIES WORKSHEET
 CHEMISTRY 12 EQUILIBRIUM PROPERTIES & ENTROPY AND ENTHALPY WORKSHEET CHEMISTRY 12 EQUILIBRIUM PROPERTIES WORKSHEET 1) Write six statements that apply to all chemical equilibrium systems. (2 marks) System
CHEMISTRY 12 EQUILIBRIUM PROPERTIES & ENTROPY AND ENTHALPY WORKSHEET CHEMISTRY 12 EQUILIBRIUM PROPERTIES WORKSHEET 1) Write six statements that apply to all chemical equilibrium systems. (2 marks) System
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM. I. Multiple Choice 15 marks. 1. Reactions that can proceed in both the forward and reverse directions are said to be:
 Name: Unit Test CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM Date: _ 50 marks total I. Multiple Choice 15 marks 1. Reactions that can proceed in both the forward and reverse directions are said to be: A. complete B. reversible
Name: Unit Test CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM Date: _ 50 marks total I. Multiple Choice 15 marks 1. Reactions that can proceed in both the forward and reverse directions are said to be: A. complete B. reversible
wb Thermodynamics 2 Lecture 9 Energy Conversion Systems
 wb1224 - Thermodynamics 2 Lecture 9 Energy Conversion Systems Piero Colonna, Lecturer Prepared with the help of Teus van der Stelt 8-12-2010 Delft University of Technology Challenge the future Content
wb1224 - Thermodynamics 2 Lecture 9 Energy Conversion Systems Piero Colonna, Lecturer Prepared with the help of Teus van der Stelt 8-12-2010 Delft University of Technology Challenge the future Content
The reactions we have dealt with so far in chemistry are considered irreversible.
 1. Equilibrium Students: model static and dynamic equilibrium and analyse the differences between open and closed systems investigate the relationship between collision theory and reaction rate in order
1. Equilibrium Students: model static and dynamic equilibrium and analyse the differences between open and closed systems investigate the relationship between collision theory and reaction rate in order
Thermodynamic Analysis of Reforming Processes
 Thermodynamic Analysis of Reforming Processes Shareq Mohd Nazir a*, Schalk Cloete b, Shahriar Amini a,b, Olav Bolland a a. Department of Energy and Process Engineering, NTNU, Trondheim, Norway b. Sintef
Thermodynamic Analysis of Reforming Processes Shareq Mohd Nazir a*, Schalk Cloete b, Shahriar Amini a,b, Olav Bolland a a. Department of Energy and Process Engineering, NTNU, Trondheim, Norway b. Sintef
On Free Energy and Internal Combustion Engine Cycles. William D Harris rd Street Apt A Oakland, CA
 On Free Energy and Internal Combustion Engine Cycles. William D arris 548 43 rd Street Apt A Oakland, CA 94609 wdharris31416@gmail.com Abstract: The performance of one type of Internal Combustion Engine
On Free Energy and Internal Combustion Engine Cycles. William D arris 548 43 rd Street Apt A Oakland, CA 94609 wdharris31416@gmail.com Abstract: The performance of one type of Internal Combustion Engine
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit.
 I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
Collision Theory. and I 2
 Collision Theory To explain why chemical reactions occur, chemists have proposed a model, known as collision theory, which states that molecules must collide in order to react. These collisions can involve
Collision Theory To explain why chemical reactions occur, chemists have proposed a model, known as collision theory, which states that molecules must collide in order to react. These collisions can involve
EXPERIMENT 3 THE IODINE CLOCK
 EXPERIMENT 3 THE IODINE CLOCK Introduction The Rates of Chemical Reactions Broadly defined, chemical kinetics is the study of the rates at which chemical reactions proceed. Oftentimes, reaction rate data
EXPERIMENT 3 THE IODINE CLOCK Introduction The Rates of Chemical Reactions Broadly defined, chemical kinetics is the study of the rates at which chemical reactions proceed. Oftentimes, reaction rate data
Thermodynamic Third class Dr. Arkan J. Hadi
 5.5 ENTROPY CHANGES OF AN IDEAL GAS For one mole or a unit mass of fluid undergoing a mechanically reversible process in a closed system, the first law, Eq. (2.8), becomes: Differentiation of the defining
5.5 ENTROPY CHANGES OF AN IDEAL GAS For one mole or a unit mass of fluid undergoing a mechanically reversible process in a closed system, the first law, Eq. (2.8), becomes: Differentiation of the defining
Chapter 17. Free Energy and Thermodynamics. Chapter 17 Lecture Lecture Presentation. Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University
 Chapter 17 Lecture Lecture Presentation Chapter 17 Free Energy and Thermodynamics Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University First Law of Thermodynamics You can t win! The first law of thermodynamics
Chapter 17 Lecture Lecture Presentation Chapter 17 Free Energy and Thermodynamics Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University First Law of Thermodynamics You can t win! The first law of thermodynamics
Spontaneous Change.! Although exothermic processes tend to be spontaneous, spontaneous reactions can be exothermic or endothermic:
 Spontaneous Change! Any process, once initiated, that continues without further intervention is spontaneous.! Although exothermic processes tend to be spontaneous, spontaneous reactions can be exothermic
Spontaneous Change! Any process, once initiated, that continues without further intervention is spontaneous.! Although exothermic processes tend to be spontaneous, spontaneous reactions can be exothermic
CM 3230 Thermodynamics, Fall 2016 Lecture 16
 CM 3230 Thermodynamics, Fall 2016 Lecture 16 1. Joule-Thomsom Expansion - For a substance flowing adiabatically through a throttle (valve or pourous plug): in > out and negligible change in kinetic and
CM 3230 Thermodynamics, Fall 2016 Lecture 16 1. Joule-Thomsom Expansion - For a substance flowing adiabatically through a throttle (valve or pourous plug): in > out and negligible change in kinetic and
Charles Cao. Growth. Properties. Bio-analytical Applications. Assembly. 226 Leigh hall. 20 nm
 Charles Cao (cao@chem.ufl.edu), 226 Leigh hall. 20 nm Growth Properties Assembly Bio-analytical Applications CHM 6154 (Spring, 2015) Chemical Separations Instructor: Charles Cao (cao@chem.ufl.edu), 226
Charles Cao (cao@chem.ufl.edu), 226 Leigh hall. 20 nm Growth Properties Assembly Bio-analytical Applications CHM 6154 (Spring, 2015) Chemical Separations Instructor: Charles Cao (cao@chem.ufl.edu), 226
DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS METHODS FOR DATA FROM FIELD EXPERIMENTS
 DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS METHODS FOR DATA FROM FIELD EXPERIMENTS S. Shibusawa and C. Haché Faculty of Agriculture, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, Japan Keywords: Field experiments,
DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS METHODS FOR DATA FROM FIELD EXPERIMENTS S. Shibusawa and C. Haché Faculty of Agriculture, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, Japan Keywords: Field experiments,
BCIT Fall Chem Exam #2
 BCIT Fall 2017 Chem 3310 Exam #2 Name: Attempt all questions in this exam. Read each question carefully and give a complete answer in the space provided. Part marks given for wrong answers with partially
BCIT Fall 2017 Chem 3310 Exam #2 Name: Attempt all questions in this exam. Read each question carefully and give a complete answer in the space provided. Part marks given for wrong answers with partially
AP CHEMISTRY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 AP CHEMISTRY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 1 A sample of solid U O 8 is placed in a rigid 1.500 L flask. Chlorine gas, Cl 2 (g), is added, and the flask is heated to 862 C. The equation for
AP CHEMISTRY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 1 A sample of solid U O 8 is placed in a rigid 1.500 L flask. Chlorine gas, Cl 2 (g), is added, and the flask is heated to 862 C. The equation for
Hydrogen addition to the Andrussow process for HCN synthesis
 Applied Catalysis A: General 201 (2000) 13 22 Hydrogen addition to the Andrussow process for HCN synthesis A.S. Bodke, D.A. Olschki, L.D. Schmidt Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science,
Applied Catalysis A: General 201 (2000) 13 22 Hydrogen addition to the Andrussow process for HCN synthesis A.S. Bodke, D.A. Olschki, L.D. Schmidt Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science,
Exergy. What s it all about? Thermodynamics and Exergy
 Exergy What s it all about? Thermodynamics and Exergy Quality of Energy General recognition that some forms of energy are more useful than others Electricity can be used for light, heat, cooling, mechanical
Exergy What s it all about? Thermodynamics and Exergy Quality of Energy General recognition that some forms of energy are more useful than others Electricity can be used for light, heat, cooling, mechanical
1. Describe the changes in reactant and product concentration as equilibrium is approached.
 Web Review 1. Describe the changes in reactant and product concentration as equilibrium is approached. 2. Describe the changes in the forward and the reverse rates as equilibrium is approached. 3. State
Web Review 1. Describe the changes in reactant and product concentration as equilibrium is approached. 2. Describe the changes in the forward and the reverse rates as equilibrium is approached. 3. State
ME 200 Final Exam December 14, :00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 11:30 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae 2:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 200 Final Exam December 14, 2015
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 11:30 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae 2:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 200 Final Exam December 14, 2015
Chapter Two. Basic Thermodynamics, Fluid Mechanics: Definitions of Efficiency. Laith Batarseh
 Chapter Two Basic Thermodynamics, Fluid Mechanics: Definitions of Efficiency Laith Batarseh The equation of continuity Most analyses in this book are limited to one-dimensional steady flows where the velocity
Chapter Two Basic Thermodynamics, Fluid Mechanics: Definitions of Efficiency Laith Batarseh The equation of continuity Most analyses in this book are limited to one-dimensional steady flows where the velocity
ES 202 Fluid and Thermal Systems
 ES Fluid and Thermal Systems Lecture : Power Cycles (/4/) Power cycle Road Map of Lecture use Rankine cycle as an example the ideal Rankine cycle representation on a T-s diagram divergence of constant
ES Fluid and Thermal Systems Lecture : Power Cycles (/4/) Power cycle Road Map of Lecture use Rankine cycle as an example the ideal Rankine cycle representation on a T-s diagram divergence of constant
Chemistry 1A, Spring 2007 Midterm Exam 3 April 9, 2007 (90 min, closed book)
 Chemistry 1A, Spring 2007 Midterm Exam 3 April 9, 2007 (90 min, closed book) Name: KEY SID: TA Name: 1.) Write your name on every page of this exam. 2.) This exam has 34 multiple choice questions. Fill
Chemistry 1A, Spring 2007 Midterm Exam 3 April 9, 2007 (90 min, closed book) Name: KEY SID: TA Name: 1.) Write your name on every page of this exam. 2.) This exam has 34 multiple choice questions. Fill
Scheme G. Sample Test Paper-I
 Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time: 1 hour 1) All questions are compulsory 2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary 3) Figures to the right indicate full marks 4) Assume suitable
Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time: 1 hour 1) All questions are compulsory 2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary 3) Figures to the right indicate full marks 4) Assume suitable
CHEMISTRY 202 Practice Hour Exam II. Dr. D. DeCoste T.A (60 pts.) 21 (40 pts.) 22 (20 pts.)
 CHEMISTRY 202 Practice Hour Exam II Fall 2016 Dr. D. DeCoste Name Signature T.A. This exam contains 22 questions on 7 numbered pages. Check now to make sure you have a complete exam. You have two hours
CHEMISTRY 202 Practice Hour Exam II Fall 2016 Dr. D. DeCoste Name Signature T.A. This exam contains 22 questions on 7 numbered pages. Check now to make sure you have a complete exam. You have two hours
B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M Science AP Chemistry
 B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M Science AP Chemistry ORGANIZING THEME/TOPIC UNIT 1: ATOMIC STRUCTURE Atomic Theory Electron configuration Periodic Trends Big Idea 1: The chemical
B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M Science AP Chemistry ORGANIZING THEME/TOPIC UNIT 1: ATOMIC STRUCTURE Atomic Theory Electron configuration Periodic Trends Big Idea 1: The chemical
CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS. Nature of Energy. ΔE = q + w. w = PΔV
 CHEMICAL HERMODYNAMICS Nature of Energy hermodynamics hermochemistry Energy (E) Work (w) Heat (q) Some Definitions Study the transformation of energy from one form to another during physical and chemical
CHEMICAL HERMODYNAMICS Nature of Energy hermodynamics hermochemistry Energy (E) Work (w) Heat (q) Some Definitions Study the transformation of energy from one form to another during physical and chemical
Chapter 2 Thermodynamics
 Chapter 2 Thermodynamics 2.1 Introduction The First Law of Thermodynamics is a statement of the existence of a property called Energy which is a state function that is independent of the path and, in the
Chapter 2 Thermodynamics 2.1 Introduction The First Law of Thermodynamics is a statement of the existence of a property called Energy which is a state function that is independent of the path and, in the
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Entropy and free energy
 Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Entropy and free energy Learning goals and key skills: Explain and apply the terms spontaneous process, reversible process, irreversible process, and isothermal process.
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Entropy and free energy Learning goals and key skills: Explain and apply the terms spontaneous process, reversible process, irreversible process, and isothermal process.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Second Law of Thermodynamics First Law: the total energy of the universe is a constant Second Law: The entropy of the universe increases in a spontaneous process, and remains unchanged in a process at
Second Law of Thermodynamics First Law: the total energy of the universe is a constant Second Law: The entropy of the universe increases in a spontaneous process, and remains unchanged in a process at
The Laws of Thermodynamics
 Entropy I. This, like enthalpy, Thus, II. A reaction is ( more on this later) if: (H, enthalpy) (S, entropy) III. IV. Why does entropy happen? Probability It s harder to keep things in order (look at my
Entropy I. This, like enthalpy, Thus, II. A reaction is ( more on this later) if: (H, enthalpy) (S, entropy) III. IV. Why does entropy happen? Probability It s harder to keep things in order (look at my
Unit 4: Thermochemistry
 Unit 4: Thermochemistry The making and breaking of bonds only happen as a result of energy being exchanged. Some reactions give off energy and some take in energy. This unit is all about the energy of
Unit 4: Thermochemistry The making and breaking of bonds only happen as a result of energy being exchanged. Some reactions give off energy and some take in energy. This unit is all about the energy of
ADVANCED PLACEMENT CHEMISTRY
 AP Chemistry is a second year chemistry for students planning to pursue a science or technology-related college curriculum or for those desiring college chemistry credit. BIG IDEA 1: The chemical elements
AP Chemistry is a second year chemistry for students planning to pursue a science or technology-related college curriculum or for those desiring college chemistry credit. BIG IDEA 1: The chemical elements
Science Department-High School
 Science Department-High School Course Description SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY I GRADE LEVEL: 11 DURATION: 1 ACADEMIC YEAR of 250 min per Week NUMBER OF CREDITS: 1.25 BOOK : MODERN CHEMISTRY (HOLT) - To cover part
Science Department-High School Course Description SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY I GRADE LEVEL: 11 DURATION: 1 ACADEMIC YEAR of 250 min per Week NUMBER OF CREDITS: 1.25 BOOK : MODERN CHEMISTRY (HOLT) - To cover part
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Kinetics How fast a rxn. proceeds Equilibrium How far a rxn proceeds towards completion Thermodynamics Study of energy relationships & changes which occur during chemical
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Kinetics How fast a rxn. proceeds Equilibrium How far a rxn proceeds towards completion Thermodynamics Study of energy relationships & changes which occur during chemical
The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that brings the system into equilibrium with aheat reservoir. (4.
 Energy Equation Entropy equation in Chapter 4: control mass approach The second law of thermodynamics Availability (exergy) The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that
Energy Equation Entropy equation in Chapter 4: control mass approach The second law of thermodynamics Availability (exergy) The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that
Chemistry 103 Spring Announcements 1. Ch. 16 OWL homework is active. 2. Next midterm exam on May 17 or 19.
 Today 1. More on entropy. Announcements 1. Ch. 16 OWL homework is active. 2. Next midterm exam on May 17 or 19. 3. CSULA closure on May 21 (furlough). 4. CSULA closure on May 31 (holiday). 5. Bring textbook
Today 1. More on entropy. Announcements 1. Ch. 16 OWL homework is active. 2. Next midterm exam on May 17 or 19. 3. CSULA closure on May 21 (furlough). 4. CSULA closure on May 31 (holiday). 5. Bring textbook
Equilibrium Written Response
 Equilibrium Written Response January 1998 2. Consider the following equilibrium: CS2 (g) + 3Cl2 (g) CCl4 (g) + S2Cl2 (g) ΔH = -238 kj a) Sketch a potential energy diagram for the reaction above and label
Equilibrium Written Response January 1998 2. Consider the following equilibrium: CS2 (g) + 3Cl2 (g) CCl4 (g) + S2Cl2 (g) ΔH = -238 kj a) Sketch a potential energy diagram for the reaction above and label
Clausius Clapeyron Equation
 Course - BSc. Applied Physical Science (Computer Science) Year & Semester - Ist, IInd Subject - Physics Paper No. - 6 Paper Title - Thermal Physics Lecture No. 18 Clausius Clapeyron Equation Hello friends,
Course - BSc. Applied Physical Science (Computer Science) Year & Semester - Ist, IInd Subject - Physics Paper No. - 6 Paper Title - Thermal Physics Lecture No. 18 Clausius Clapeyron Equation Hello friends,
Blue Marble University
 Blue Marble University B.S./D.Sc. 5 year Fast Track Combination Program, featuring a Bachelor Degree in Chemical Engineering and a Doctoral Degree in Chemical Engineering. (5 Year Program You Can Complete
Blue Marble University B.S./D.Sc. 5 year Fast Track Combination Program, featuring a Bachelor Degree in Chemical Engineering and a Doctoral Degree in Chemical Engineering. (5 Year Program You Can Complete
Thermochemistry. Energy and Chemical Change
 Thermochemistry Energy and Chemical Change Energy Energy can change for and flow, but it is always conserved. The Nature of Energy Energy the ability to do work or produce heat Potential energy Kinetic
Thermochemistry Energy and Chemical Change Energy Energy can change for and flow, but it is always conserved. The Nature of Energy Energy the ability to do work or produce heat Potential energy Kinetic
POE Concepts and Learning Objectives
 POE Concepts and Learning Objectives Unit 1 Energy and Power Time Days: 49 days Lesson 1.1 Mechanisms (15 days): 1. Engineers and engineering technologists apply math, science, and disciplinespecific skills
POE Concepts and Learning Objectives Unit 1 Energy and Power Time Days: 49 days Lesson 1.1 Mechanisms (15 days): 1. Engineers and engineering technologists apply math, science, and disciplinespecific skills
Physics 1501 Lecture 37
 Physics 1501: Lecture 37 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Midterm 2 in class Wednesday Friday: review session bring your questions Todays topics Chap.18: Heat and Work»
Physics 1501: Lecture 37 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Midterm 2 in class Wednesday Friday: review session bring your questions Todays topics Chap.18: Heat and Work»
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, Chapter 7 ENTROPY
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Gibb s Free Energy. This value represents the maximum amount of useful work (non PV-work) that can be obtained by a system.
 Gibb s Free Energy 1. What is Gibb s free energy? What is its symbol? This value represents the maximum amount of useful work (non PV-work) that can be obtained by a system. It is symbolized by G. We only
Gibb s Free Energy 1. What is Gibb s free energy? What is its symbol? This value represents the maximum amount of useful work (non PV-work) that can be obtained by a system. It is symbolized by G. We only
KEY for CHEM 116 EXAM #2 PRACTICE
 Circle the correct answers ( points each) KEY for CHEM 6 EXAM # PRACTICE. If the half-life of a reaction depends on the concentration of the reactant, then the reaction cannot be order. a. second b. zero
Circle the correct answers ( points each) KEY for CHEM 6 EXAM # PRACTICE. If the half-life of a reaction depends on the concentration of the reactant, then the reaction cannot be order. a. second b. zero
2/18/2013. Spontaneity, Entropy & Free Energy Chapter 16
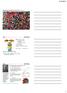 Spontaneity, Entropy & Chapter 16 G = H T S G is Gibbs free energy H is enthalpy T is temperture in Kelvin S is entropy Refers to the system Proved on p. 760 from S = H/T S univ = - G T at constant T &
Spontaneity, Entropy & Chapter 16 G = H T S G is Gibbs free energy H is enthalpy T is temperture in Kelvin S is entropy Refers to the system Proved on p. 760 from S = H/T S univ = - G T at constant T &
(1)5. Which of the following equations is always valid for a fixed mass system undergoing an irreversible or reversible process:
 Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
2. Fundamental Concepts
 2. Fundamental Concepts 2-1. The System 2-2. Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Systems 2-3. Components, Constituents, and Pure Substances 2-4. Equilibrium 2-5. Property, State, and Process 2-6. The Zeroth
2. Fundamental Concepts 2-1. The System 2-2. Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Systems 2-3. Components, Constituents, and Pure Substances 2-4. Equilibrium 2-5. Property, State, and Process 2-6. The Zeroth
 Vapour Absorption Refrigeration Systems Based On Ammonia- Water Pair Nagendra M CBM Engineer, Hindusthan Zink.Ltd The specific objectives of this lesson are to: 1. Introduce ammonia-water based vapour
Vapour Absorption Refrigeration Systems Based On Ammonia- Water Pair Nagendra M CBM Engineer, Hindusthan Zink.Ltd The specific objectives of this lesson are to: 1. Introduce ammonia-water based vapour
first law of ThermodyNamics
 first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
Energy is the capacity to do work
 1 of 10 After completing this chapter, you should, at a minimum, be able to do the following. This information can be found in my lecture notes for this and other chapters and also in your text. Correctly
1 of 10 After completing this chapter, you should, at a minimum, be able to do the following. This information can be found in my lecture notes for this and other chapters and also in your text. Correctly
Chemical Kinetics and Reaction Engineering
 Chemical Kinetics and Reaction Engineering MIDTERM EXAMINATION II Friday, April 9, 2010 The exam is 100 points total and 20% of the course grade. Please read through the questions carefully before giving
Chemical Kinetics and Reaction Engineering MIDTERM EXAMINATION II Friday, April 9, 2010 The exam is 100 points total and 20% of the course grade. Please read through the questions carefully before giving
ENTROPY. Chapter 7. Mehmet Kanoglu. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition. Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles.
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 1, Issue 8, 2013 ISSN (online):
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 1, Issue 8, 2013 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Development and theoretical analysis of mathematical expressions for change of entropy
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 1, Issue 8, 2013 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Development and theoretical analysis of mathematical expressions for change of entropy
Complex Compounds Background of Complex Compound Technology
 Complex Compounds For more than 20 years, Rocky Research has been a pioneer in the field of sorption refrigeration utilizing complex compounds. Our technology earned special recognition from NASA in 1999.
Complex Compounds For more than 20 years, Rocky Research has been a pioneer in the field of sorption refrigeration utilizing complex compounds. Our technology earned special recognition from NASA in 1999.
Equilibrium Written Response
 Equilibrium Written Response January 1998 2. Consider the following equilibrium: CS2 (g) + 3Cl2 (g) CCl4 (g) + S2Cl2 (g) H = -238 kj a) Sketch a potential energy diagram for the reaction above and label
Equilibrium Written Response January 1998 2. Consider the following equilibrium: CS2 (g) + 3Cl2 (g) CCl4 (g) + S2Cl2 (g) H = -238 kj a) Sketch a potential energy diagram for the reaction above and label
THIS LAB IS CHAOS! 2. In liquids or gases? Explain.
 THIS LAB IS CHAOS! PRELAB INTRODUCTION Part 1 We are already familiar with the Enthalpy (H) for a reaction. We know that if a reaction gives off heat, that it is considered exothermic and has a negative
THIS LAB IS CHAOS! PRELAB INTRODUCTION Part 1 We are already familiar with the Enthalpy (H) for a reaction. We know that if a reaction gives off heat, that it is considered exothermic and has a negative
Thermochemistry Lecture
 Thermochemistry Lecture Jennifer Fang 1. Enthalpy 2. Entropy 3. Gibbs Free Energy 4. q 5. Hess Law 6. Laws of Thermodynamics ENTHALPY total energy in all its forms; made up of the kinetic energy of the
Thermochemistry Lecture Jennifer Fang 1. Enthalpy 2. Entropy 3. Gibbs Free Energy 4. q 5. Hess Law 6. Laws of Thermodynamics ENTHALPY total energy in all its forms; made up of the kinetic energy of the
Ammonia Synthesis with Aspen Plus V8.0
 Ammonia Synthesis with Aspen Plus V8.0 Part 1 Open Loop Simulation of Ammonia Synthesis 1. Lesson Objectives Become comfortable and familiar with the Aspen Plus graphical user interface Explore Aspen Plus
Ammonia Synthesis with Aspen Plus V8.0 Part 1 Open Loop Simulation of Ammonia Synthesis 1. Lesson Objectives Become comfortable and familiar with the Aspen Plus graphical user interface Explore Aspen Plus
SKMM 2413 Thermodynamics
 SKMM 2413 Thermodynamics Md. Mizanur Rahman, PhD Department of Thermo-Fluids Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia UTM Office: C23-228 mizanur@fkm.utm.my Semester I, 2016-2017
SKMM 2413 Thermodynamics Md. Mizanur Rahman, PhD Department of Thermo-Fluids Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia UTM Office: C23-228 mizanur@fkm.utm.my Semester I, 2016-2017
and mol of Cl 2 was heated in a vessel of fixed volume to a constant temperature, the following reaction reached equilibrium.
 Q1. When a mixture of 0.45 mol of PCl and 0.68 mol of Cl was heated in a vessel of fixed volume to a constant temperature, the following reaction reached equilibrium. PCl + Cl PCl 5 H = 9 kj mol 1 At equilibrium,
Q1. When a mixture of 0.45 mol of PCl and 0.68 mol of Cl was heated in a vessel of fixed volume to a constant temperature, the following reaction reached equilibrium. PCl + Cl PCl 5 H = 9 kj mol 1 At equilibrium,
7.2. Thermodynamics and Equilibrium. What Conditions Favour a Change? 328 MHR Unit 4 Chemical Systems and Equilibrium
 7.2 Thermodynamics and Equilibrium Section Preview/ Specific Expectations In this section, you will identify qualitatively entropy changes that are associated with physical and chemical processes describe
7.2 Thermodynamics and Equilibrium Section Preview/ Specific Expectations In this section, you will identify qualitatively entropy changes that are associated with physical and chemical processes describe
Introduction to Chemical Engineering
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering EIT Micro-Course Series Every two weeks we present a 35 to 45 minute interactive course Practical, useful with Q & A throughout PID loop Tuning / Arc Flash Protection,
Introduction to Chemical Engineering EIT Micro-Course Series Every two weeks we present a 35 to 45 minute interactive course Practical, useful with Q & A throughout PID loop Tuning / Arc Flash Protection,
Energy Optimization in Process Systems. Warsaw University of TechnoLogy, Facuity of Chemical and Process Engineering, Warsaw, Poland ELSEVIER
 Energy Optimization in Process Systems First Edition Stanistaw Sieniutycz Warsaw University of TechnoLogy, Facuity of Chemical and Process Engineering, Warsaw, Poland Jacek Jekowski Rzeszöw University
Energy Optimization in Process Systems First Edition Stanistaw Sieniutycz Warsaw University of TechnoLogy, Facuity of Chemical and Process Engineering, Warsaw, Poland Jacek Jekowski Rzeszöw University
Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts
 Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1-1 Thermodynamics and Energy Application Areas of Thermodynamics 1-2 Importance of Dimensions and Units Some SI and English Units Dimensional Homogeneity Unity
Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1-1 Thermodynamics and Energy Application Areas of Thermodynamics 1-2 Importance of Dimensions and Units Some SI and English Units Dimensional Homogeneity Unity
first later later still successful collision ( reaction ) low conc. both high conc. blue high conc. both low conc. red
 Collision theory Basic idea (basic premise) http://www.chem.iastate.edu/group/greenbowe/sections/projectfolder/animations/no+o3singlerxn.html - before molecules can react, they must collide. H 2 + I 2
Collision theory Basic idea (basic premise) http://www.chem.iastate.edu/group/greenbowe/sections/projectfolder/animations/no+o3singlerxn.html - before molecules can react, they must collide. H 2 + I 2
Principles Of Engineering Detailed Outline
 Principles Of Engineering Detailed Outline Unit 1 Energy and Power Time Days: 115 days Lesson 1.0 Introduction to POE (15 days) 1. Introduction to classroom expectations, Engineering notebook, Pretest
Principles Of Engineering Detailed Outline Unit 1 Energy and Power Time Days: 115 days Lesson 1.0 Introduction to POE (15 days) 1. Introduction to classroom expectations, Engineering notebook, Pretest
Classroom: 318 Subject: AP Chemistry Quarter 2 Teacher: van Balveren, Suzanne
 Livingston American School Quarterly Lesson Plan Concept / Topic To Teach: Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Equilibrium Equilibrium Acids and Bases Acids and Bases Standards Addressed: College Board canbe formed
Livingston American School Quarterly Lesson Plan Concept / Topic To Teach: Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Equilibrium Equilibrium Acids and Bases Acids and Bases Standards Addressed: College Board canbe formed
Engineering Thermodynamics
 Basic Engineering Thermodynamics A Venkatesh Professor Emeritus, Mechanical Engineering Department East West Institute of Technology, Bangalore, India (Formerly Professor of Mechanical Engineering, IIT
Basic Engineering Thermodynamics A Venkatesh Professor Emeritus, Mechanical Engineering Department East West Institute of Technology, Bangalore, India (Formerly Professor of Mechanical Engineering, IIT
Exergy Losses Relation with Driving Forces for Heat Transfer Process on Hot Plates Using Mathematical Programming
 Proceedings of the 3 rd International Conference on Fluid Flow, Heat and Mass Transfer (FFHMT 16) Ottawa, Canada May 2 3, 2016 Paper No. 103 Exergy Losses Relation with Driving Forces for Heat Transfer
Proceedings of the 3 rd International Conference on Fluid Flow, Heat and Mass Transfer (FFHMT 16) Ottawa, Canada May 2 3, 2016 Paper No. 103 Exergy Losses Relation with Driving Forces for Heat Transfer
Jeff Brown Hope College, Department of Engineering, 27 Graves Pl., Holland, Michigan, USA UNESCO EOLSS
 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Jeff Brown Hope College, Department of Engineering, 27 Graves Pl., Holland, Michigan, USA Keywords: Solid mechanics, stress, strain, yield strength Contents 1. Introduction 2. Stress
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Jeff Brown Hope College, Department of Engineering, 27 Graves Pl., Holland, Michigan, USA Keywords: Solid mechanics, stress, strain, yield strength Contents 1. Introduction 2. Stress
Chapter Seventeen Thermodynamics: Spontaneity, Entropy, and Free Energy
 1 Thermodynamics: Spontaneity, Entropy, and Free Energy 2 Introductory Concepts Thermodynamics examines the relationship between heat (q) and work (w) Spontaneity is the notion of whether or not a process
1 Thermodynamics: Spontaneity, Entropy, and Free Energy 2 Introductory Concepts Thermodynamics examines the relationship between heat (q) and work (w) Spontaneity is the notion of whether or not a process
