Sn-Modified Pt/SAPO-11 Catalysts for Selective Hydroisomerization of n-paraffins
|
|
|
- Chrystal Fox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1266 Energy & Fuels 2004, 18, Sn-Modified Pt/SAPO-11 Catalysts for Selective Hydroisomerization of n-paraffins Yunqi Liu,*, Chunying Liu, Chenguang Liu, Zhijian Tian, and Liwu Lin College of Chemistry & Chemical Engineering, University of Petroleum, Shandong , China, and Institute of Chemical Physics, The Chinese Academy of Science, Dalian , China Received January 28, Revised Manuscript Received May 6, 2004 The hydro of n-paraffins is a key reaction in hydrodewaxing of lubricating base oil. In this paper, we investigate the performance of Pt/SAPO-11 catalysts for isomerization of n-paraffins by the model compound of n-dodecane. Under this experimental condition, yields of feed isomers as well as cracking products are a function of the total n-dodecane. Primary products are methylundecane while multi-brancheds and cracking products are formed in successive reactions. The result shows that the addition of Sn increases the selectivity for isomerization reaction. The most ideal experimental data for hydro of n-dodecane is that the selectivity of isomerized products gets 90 when of n-dodecane is 90 for the Sn-promoted Pt/SAPO-11 catalyst. 1. Introduction Lubricating oils are being used under increasingly severe conditions. Meanwhile, the growing use of synthetic and unconventional base stocks make it more difficult to produce lube oils by simply modifying addition technology. 1 Hydroisomerization of n-paraffins over solid acid catalysts is used to produce high octane gasoline blending components, to increase the low temperature performance of diesel and to obtain high viscosity index lube oils. 2-4 These isomerization reactions are generally carried out over bifunctional catalysts containing metallic sites for hydrogenation/dehydrogenation and acid sites for skeletal isomerization via carbenium ions. Catalytic dewaxing is probably the first industrial application of selectivity properties of zeolite catalysts, which selectively crack long-chain n-paraffins contained in lube base oil. 5 The presence of acidic and the shape selective features of zeolites has spurred a widespread interest in new catalytic materials such as silicoaluminophosphate base catalysts for the hydroisomerization of paraffinic feedstocks. An attractive * Corresponding author. liuyq@mail.hdpu.edu.cn. University of Petroleum. The Chinese Academy of Science. (1) O Connor, C. T.; Steen, E. V.; Dry, M. E. New catalytic application of zeolites for petrochemicals. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1996, 102, (2) Calemma, V.; Peratello, S.; Perego, C. Hydroisomerization and hydrocracking of long-chain n-alkanes on Pt/amorphous SiO 2-Al 2O 3 catalysts. Appl. Catal., A: General 2000, 190, (3) Blomsma, E.; Martens, J. A.; Jacobs, P. A. Hydroisomerization and Hydrocracking of Heptane over Bimetallic Bifunctional Pt-Pd/ H-Beta and Pt-Pd/USY Zeolite catalysts. J. Catal. 1997, 165, (4) Martens, J. A.; Parton, R.; Uytterhoeven, L.; Jacobs, P. A. Selective of decane into branched isomers: A comparison of platinum/zsm-22, platinum/zsm-5 and platinum/usy zeolite catalysts. Appl. Catal., A: General 1991, 76, (5) Weitkamp, J.; Jacobs, P. A.; Martens, J. A.; Isomerization and Hydrocracking of C 9 through C 16 n-alkanes on Pt/HZSM-5 Zeolite. Appl. Catal. 1983, 8, 123. dewaxing procedure 6,7 results through isomerization of the n-paraffins to branched isoparaffins, eliminating the yield loss associated with n-paraffin removal by cracking or solvent extraction. Shape-selective molecular sieves suppress formation of multibranched isomers which are more susceptible to hydrocracking, thereby leading to high isomerization selectivity. In the so-called isodewaxing process, the pour point is lowered by the introduction of a limited number of methyl branches in the long n-alkanes, while preserving the high quality associated with the paraffinic nature of the molecules. The framework of SAPO-11 is isotopic to that ALPO- 11, with AEL-type structure. The void volume consists of nonintersecting elliptic 10-membered ring pores of nm pore opening. Recently, evidence of selectivity in some hydrocarbon reactions using silicoaluminophosphate molecular sieves as solid catalysts has been reported, 8-12 indicating that s involving C 6 range hydrocarbons on SAPO-11 are potentially shape-selective. But little attention has been paid to metallic component. In this work, we have studied and compared the catalytic properties of the bifunctional (6) Miller, S. J. Three-step catalytic dewaxing and hydrofinishing. U.S. Patent 4,747,932, (7) Miller, R. J. Wax isomerization using catalyst of specific pore geometry [p]. U.S. Patent 5,135,638, (8) Larkspur, D. S.; Habib, M. M., et al. Use of Modified 5-7A pore molecular sieves for isomerization of hydrocarbons. U.S. Patent 5,282,958, (9) Campelo, J. M.; Lafont, F.; Marinas, J. M. Hydroisomerization and hydrocracking of n-heptane on Pt/SAPO-5 and Pt/SAPO-11 catalysts. J. Catal. 1995, 156, (10) Campelo, J. M.; Lafont, F.; Marinas, J. M. Hydroisomerization and hydrocracking of n-hexane on Pt/SAPO-5 and Pt/SAPO-11 catalysts. Zeolites 1995, 15, (11) Campelo, J. M.; Lafont, F.; Marinas, J. M. Pt/SAPO-5 and Pt/ SAPO-11 as Catalysts for Hydroisomerization and Hydrocracking of n-octane. J. Chem. Soc. Faradays 1995, 91 (10), (12) Campelo, J. M.; Lafont, F.; Marinas, J. M. Comparison of the activity and selectivity of Pt/SAPO-5 and Pt/SAPO-11 in n-heptane and hexane hydro. Appl. Catal., A: General 1997, 152, /ef049968x CCC: $ American Chemical Society Published on Web 07/07/2004
2 Sn-Modified Pt/SAPO-11 Catalysts Energy & Fuels, Vol. 18, No. 5, Figure 1. The X-ray diffraction pattern of the synthesized SAPO-11 molecular sieve. catalyst Sn-modified Pt/SAPO-11 with Pt/SAPO-11 in n-dodecane hydro. The result shows that the addition of Sn promotes the isomerization selectivity under n-dodecane deep. 2. Experimental Section 2.1. Catalyst Preparation. SAPO-11 is hydrothermally synthesized according to ref 13 and the typical gel composition is Al 2O 3/P 2O 5/SiO 2 is 1:1:0.3. The XRD of the crystal phase is shown in Figure 1. The main surface properties are surface area, 217 m 2 /g; pore volume, 0.24 cm 3 /g; median pore diameter, 0.59 nm. The catalysts employed in this work are SAPO-11 containing 0.5 wt of platinum or Tin-platinum as hydrogenating metal. In Pt-Sn/SAPO-11 catalyst, the atomic ratio of Sn to Pt is 1:1. The Pt and Sn were loaded on the SAPO-11 by wet impregnation with an aqueous solution of H 2PtCl 6 and SnCl 2. The resulting materials were dried at 393 K for 4 h and calcined at 823 K for 4hinair. Metal dispersions were measured using hydrogen chemisorption. Prior to the chemisorption experiment, the catalyst was pretreated at 400 C under flowing helium. Chemisorptions were carried out at room temperature. In the calculation of the metal dispersion, it was assumed that every surface atom of platinum chemisorbs one hydrogen atom. The dispersions, d(), were calculated as the number of platinum atoms at the surface divided by the total number of platinum atoms in the sample Catalytic Activity Measurements and Products Analysis. The measurements of reaction activities of catalysts for of n-dodecane were accomplished in a stainless steel microreactor at medium pressure (4.0 MPa). The reaction feed was introduced into the reactor by a pulseless pump. The liquid hourly space velocity (LHSV) was h -1 and the volume ratio of hydrogen to liquid was The reaction temperature was K. The products were collected and analyzed off-line by a Varian-3400 gas chromatograph equipped with a 0.32 mm 100 m HP CP-1 capillary column and a flame ionization detector, and the product identification was carried out by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). 3. Results and Discussion 3.1. Identification of the Products from Hydro of n-dodecane. The high resolution GC-MS analysis shows that the mixture of isododecane was formed mainly of mono-branched isomers in different positions of the paraffinic chain at lower levels, which consist of 2-methylundecane, 3-methylundecane, 4-methylundecane, and 5- or 6-methylundecane (unresolved). At higher degrees, a decrease in the relative concentration of mono-branched isomers and an increase in the di-branched isomers were observed. There are scarcely any tri-branched isomers in the products. The typical chromatograms of the products from hydro of n-dodecane on Pt(Sn)/ SAPO-11 catalysts were shown in Figure 2b. In the dibranched isomers, the composition of the fraction of dimethyl isomers slightly varies with the global (specially 2,3-dimethyl-, 2,4-dimethyl-, 2,5-dimethyl-, and 2,6-dimethyldecane), and it substantially deviates from that observed in selective SAPO-11 zeolites The Relationship of Conversion with Selectivity of Isomerized Products. In the hydro reaction of n-dodecane, the products include monobranched isomers, multi-branched isomers, and cracked products. In the multi-branched products, the dibranched isomers are the main products and the tribranched isomers hardly exist in the isomer products. In cracked products, which indicated the molecules with carbon number less than dodecane, there is scarcely any methane. These are benefit to iso-waxing processing. So, the isomer selectivity is defined as the percentage of isomers (including mono-branched and multi-branched isomers) in the total products. Table 1 and Table 2 show the percentage of different kinds of products vs n- dodecane. The results indicate that the isomerization of n-dodecane over Pt/SAPO-11 or Pt-Sn/SAPO-11 is a unique function of the total. Initially, the into isododecane is more than 94, reaching the highest isomer selectivity, but on continuing to increase the n-dodecane the selectivity decreases. Over the Pt-Sn/SAPO-11 catalyst, we obtained more than 90 isomerization selectivity at 90 n- dodecane. Meanwhile, only 85 isomerization selectivity at 87 n-dodecane over Pt/ SAPO-11 has been obtained. When the of n-dodecane is more than the 87, the isomerization selectivity obviously decreases. The better catalytic
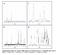
3 1268 Energy & Fuels, Vol. 18, No. 5, 2004 Liu et al. Figure 2. (a) Chromatogram of typical products of hydro of n-dodecane on Pt(Sn)/SAPO : C 4-C 9 alkane and their isomers; 12-15: 2,3-dimethyl-, 2,4-dimethyl-, 2,5-dimethyl-, and 2,6-dimethyldecane; 16: 5(6)-methyldodecane; 17: 4-methyldodecane; 18: 2-methyldodecane; 19: 3-methyldodecane; 20; dodecane. (b) The reaction network of hydro of n-dodecane on Pt/SAPO-11 catalysts. Table 1. Isomer Selectivity vs Conversion of n-dodecane on Pt-Sn/SAPO-11 Catalyst mono-branched products multi-branched products cracked products selectivity Table 2. Isomer Selectivity vs Conversion of n-dodecane on Pt/SAPO-11 Catalyst mono-branched products multi-branched products cracked products isomerized selectivity performance may be attributed to the addition of a second metal to the metallic catalyst composition The Effects from Different Composition of Molecular Sieve. In Table 3, we present the products distribution on different compositions of molecular sieves. The results show that the activity and selectivity is strongly affected by the silica content in gel composition of synthesized zeolites. As we know, the acidity of SAPO molecular sieves is attributed to the substitution Si for Al or P in the skeleton of the microporous wall. With the addition of silica in gel composition, the silicon content in the skeleton of the microporous wall and acidity will increase, so the higher acidity of as-synthesied zeolite contributes to the increase in n-dodecane hydro on Pt/SAPO-11 catalysts. However the selectivity of isomerized products decreases when the content of silica reaches a certain value, so it is necessary to control the acidity or acidity distribution in the skeleton of the zeolite microporous wall.
4 Sn-Modified Pt/SAPO-11 Catalysts Energy & Fuels, Vol. 18, No. 5, catalysts Table 3. The Effects on Product Distribution from Different Gel Composition of Molecular Sieve a gel composition SiO 2/Al 2O 3/P 2O 5 cracked products isomerized products isomer selectivity Pt/SAPO-11(1) 0.1:1:1: Pt/SAPO-11(2) 0.2:1:1: Pt/SAPO-11(3) 0.3:1:1: Pt/SAPO-11(4) 0.4:1:1: a The reaction conditions: T ) 360 C, P ) 4.0 MPa, LHVS ) 1h -1. catalysts Table 4. The Effects on Products Distribution with Varied Ratios of Sn/Pt a metal dispersion D micropore (nm) cracked products isomerized products isomer selectivity 0.5Pt-0.0Sn Pt-0.5Sn Pt-1.0Sn Pt-2.0Sn a The reaction conditions: T ) 360 C, P ) 4.0 MPa, LHVS ) 1h -1 ; micropore indicates the pore diameter of Pt(Sn)/SAPO-11 catalysts corresponding to loading volume The Effect of Sn Promoter on Pt(Sn)/SAPO- 11 with Varied Ratios of Sn/Pt. To obtain information about the beneficial effect of Sn as a promoter if there is a truly synergistic phenomenon, we investigated the effect of varying the ratio of Sn/Pt and the result is listed in Table 4. The selectivity of isomerized products increases with the addition of Sn promoter in the range of lower than 1 of Sn/Pt ratio. When the ratio of Sn/Pt goes beyond the limits of 1:1, the decreases with the increase of the ratio of Sn/Pt, but the selectivity of isomerized products has hardly any decrease in trend but has an increase in trend. The decrease in may be attributed to the cover of acidity on the porous surface of zeolite, while the increased selectivity of isomerized products may be attributed to high metal dispersion and the modification to the pore mouth of the molecular sieve from the Sn promoter The Mechanism of Hydro of n- Dodecane on Bifunctional Catalyst. If an n-alkane is converted on a bifunctional catalyst in the presence of hydrogen, two principal reactions take place: 14 isomerization into isoalkanes, and hydrocracked into products with a lower carbon atom number than the feed. A simplified reaction network of long-chain n-alkane hydro over bifunctional catalysts is that in which hydroisomerization and hydrocracking occur in series. In the first step, the n-alkane is isomerized to a set of its isomers with single branches. In a consecutive step, these isomers are again isomerized, whereby dibranched isoalkanes are produced. If further isomerization occurs, however, the tri-branched species is produced under a very rapid hydrocracking referred to as type A β-scission. In addition to this main pathway of hydrocracking via tri-branched species, there is some contribution to hydrocracking reactions starting from di-branched species referred to as type B β-scission. Figure 2 shows the reaction network from hydro of n-dodecane on Pt/SAPO-11 catalysts. Due to the selective effect of the SAPO-11 molecular sieve, the tri-branched species hardly form in this catalytic reaction. Figure 3, parts a and b, give the composition of the isododecane and cracked products from n-dodecane (13) Yu, Z.; Yan, A.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Q. Synthesis and crystal morphology of SAPO-11. J. Inorg. Chem. 1989, 5 (4), (14) Taylor, R. J.; Petty, R. H. Selective Hydroisomerization of longchain normal paraffins. Appl. Catal., A: General 1994, 119, hydro over Pt/SAPO-11 and Pt-Sn/SAPO-11 catalysts. The results indicate that the isododecanes obtained through isomerization of n-dodecane can be either mono-branched or di-branched; the tri-branched isomers do not appear with the two catalysts in the experimental range studied. These results also indicate the isomer distribution is a function of the total and di-branched isomers are formed in successive reaction from methylundecane and only appear at high values of n-dodecane and in small quantities. The multi-branched isomers obvious increase at levels more than 60. On Pt/SAPO-11 and Pt-Sn/ SAPO-11 catalysts, even at 90 n-dodecane, the cracking yields are limited and amount to lower than 10 on Sn-modified Pt/SAPO-11 catalyst. Much higher reaction severities are necessary to crack the isododecane molecules on the two catalysts. This is attributed to the feature of 10-membered ring zeolite. The key feature of the SAPO-11 is the limited penetration of branched molecules into this zeolite. According to pore mouth catalysis and key-lock catalysis concepts, the product distribution from the n-dodecane hydro can be explained as follows. The catalytic of alkane on SAPO-11 base catalysts does not involve diffusion transportation through the micropores. Skeletal isomerization occurs on molecules absorbed in pore mouths and on the external surfaces of the zeolite crystals. 15,16 In the mono-branching reaction of n-alkane, only part of the molecule penetrates into a micropore opening. The skeletal rearrangement takes place in the pore mouth where there is less steric hindrance (pore mouth catalysis). Further branching in the carbon skeleton is introduced when the monobranched molecule is stretched across the external crystal surface. With the first branching pinned into one pore mouth, additional branchings are generated at positions where the carbon chain faces neighboring pore mouths (key-lock concept). In di-branched isomers, the content of 2-methylundecane is relatively less than other methylundecane product, but the content of 2-methyl (including 2,3-dimethyl-, 2,4-dimethyl-, 2,5- (15) Souverijns, W.; Martens, J. A.; Uytterhoeven, L., et al. Selective key-lock catalysis in dimethyl branching of alkanes on TON zeolites. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1997, 105, (16) Martens, J. A.; Parton, R.; Uytterhoeven, L.; Jacobs, P. A. Selective of decane into branched isomers: A comparison of platinum/zsm-22, platinum/zsm-5 and platinum/usy zeolite catalysts. Appl. Catal., A: General 1991, 76,
5 1270 Energy & Fuels, Vol. 18, No. 5, 2004 Liu et al. Figure 3. (a) Composition of the reaction products (wt ) lumped as mono- and multi-branched isododecane, cracked products vs n-dodecane on Pt/SAPO-11. (b) Composition of the reaction products (wt ) lumped as mono- and multi-branched isododecane, cracked products vs n-dodecane on Pt-Sn/SAPO-11. dimethyl-, and 2,6-dimethyldecane) in di-branched isomers obviously increased, which substantiates the keylock reaction mechanism. According to the reaction pathway, although the selectivity of isomers depends mainly on the properties of zeolite, but the balance of acidic vs metallic function in the catalyst is also an important factor. Owing to the as-synthesized zeolite having an appropriate porous mouth, we obtained better isomer selectivity in two catalysts. Considering that we have used the same molecular sieve in two different catalysts, the improved selectivity should be ascribed to the Sn promoter. The promoter may modify the acidity or porous pathway in the synthesized molecular sieve, which helps to avoid the deep isomerization and cracking reaction in the surface of the molecular sieve Product Composition and Cracking Reaction Mechanism. In Tables 1 and 2, we list the content of cracking products on Pt/SAPO-11 and Pt(Sn)/SAPO- 11, respectively. The results show that cracking products exclusively consisted of alkane and both n-alkane and isoalkane with one methyl branching were obtained, which substantially deviates from that observed in selective SAPO-11 zeolites with a key-lock mechanism. In cracked products, which indicated the molecules with carbon number less than dodecane, there is scarcely any methane. The carbon-number distribution of cracked products is shown in Figure 4. On the SAPO-11 base catalysts, linear fragments predominated in the cracked products of lower carbon number. This suggests that cracking occurs according to B1-, B2-, and C-type mechanisms. The content of branched isomer in the cracked products increases with increasing carbon number of the fraction. Souverijns et al. 17 have investigated the hydro of heptadecane on Pt/ZSM- (17) Souverijns, W.; Martens, J. A.; Froment, G. F.; Jacobs, P. A. Hydrocracking of isoheptadecanes on Pt/H-ZSM-22: An example of pore mouth catalysis. J. Catal. 1998, 174, ,
6 Sn-Modified Pt/SAPO-11 Catalysts Energy & Fuels, Vol. 18, No. 5, more than four carbon number atom, whereas the type B and C mechanisms yield propane and larger linear and branched fragments. According to the pore mouth catalysis model, mechanism C appears to be the most likely mechanism for β-scission on SAPO-11 base catalysts. This is due to the fact that the parent and product alkylcarbenium ions can interact favorably with the micropore wall. 4. Conclusion Figure 4. Carbon number distribution of the cracked products from n-dodecane over Pt-Sn/SAPO-11 catalyst at a cracking yield of catalyst and also found a similar phenomenon. Hydrocracking involves the β-scission of alkylcarbenium ion. In a β-scission, two electrons of a β carbon-carbon bond are transferred toward the positively charged R carbon atom to form an olefin and a smaller alkylcarbenium ion, charged at the γ carbon atom of the parent ion. The rival β-scission modes that exist depend on the nature of the parent ion. β-scission is extremely rapid for a specific tri-branched ion for which both the starting and product ions are tertiary ion (type A). Other β-scission modes can operate also di-branched (B1 and B2) and mono-branched ions (C), which involve secondary ions and are much slower. The rate of β-scission decreases in the order A. B1 ) B2 > C. Type A β-scission generates branched fragments with four and On SAPO-11 base catalysts, n-dodecane can be intensively isomerized with very limited cracking. Hydroisomerization and hydrocracking of n-dodecane in SAPO-11 base catalysts occur in the pore mouth, being governed by shape selectivity imposed by the SAPO-11 structure strongly affecting the product distribution. Preferential formation of mono- or di-branched isododecane is observed. The isomerization selectivity depends on the properties of synthesized zeolite and the balance of acidic vs metallic functions in the catalysts. The addition of Sn improves the isomerization reaction selectivity. On Pt-Sn/SAPO-11 catalysts, the yield of isododecane reaches 81 at 90 n-dodecane, compared to 76 at 90 on Pt/SAPO-11 catalyst. Further investigation on the function of Sn promoter in Sn-modified Pt/SAPO-11 catalysts is made in our laboratory. Acknowledgment. The authors are particularly grateful to the Chinese National Petroleum and Gas Group Corporation for financial support of this work. EF049968X
Catalytic performance of Pt/HY-β in n-octane hydroisomerization
 DOI.7/s12182-9-48-2 299 Catalytic performance of Pt/HY-β in n-octane hydroisomerization Jin Changlei 1, 2, MA Bo 1, Zhang Xiwen 3, Ling Fengxiang 3, Zhang Zhizhi 3 and Qin Bo 3 1 College of Petrochemical
DOI.7/s12182-9-48-2 299 Catalytic performance of Pt/HY-β in n-octane hydroisomerization Jin Changlei 1, 2, MA Bo 1, Zhang Xiwen 3, Ling Fengxiang 3, Zhang Zhizhi 3 and Qin Bo 3 1 College of Petrochemical
Investigation of benzene and cycloparaffin containing hexane fractions skeletal isomerization on Pt/sulphated metal-oxide catalyst
 Investigation of benzene and cycloparaffin containing hexane fractions skeletal isomerization on Pt/sulphated metal-oxide catalyst Zsolt Szoboszlai*, Jenő Hancsók* *University of Pannonia, Institute of
Investigation of benzene and cycloparaffin containing hexane fractions skeletal isomerization on Pt/sulphated metal-oxide catalyst Zsolt Szoboszlai*, Jenő Hancsók* *University of Pannonia, Institute of
Hydroisomerization performance of platinum supported on ZSM-22/ZSM-23 intergrowth zeolite catalyst
 242 Pet.Sci.(13):242-25 DOI.7/s12182-13-273-6 Hydroisomerization performance of platinum supported on ZSM-22/ZSM-23 intergrowth zeolite catalyst Chi Kebin 1, 2, Zhao Zhen 1, Tian Zhijian 3, Hu Sheng 2,
242 Pet.Sci.(13):242-25 DOI.7/s12182-13-273-6 Hydroisomerization performance of platinum supported on ZSM-22/ZSM-23 intergrowth zeolite catalyst Chi Kebin 1, 2, Zhao Zhen 1, Tian Zhijian 3, Hu Sheng 2,
Studies on Mo/HZSM-5 Complex catalyst for Methane Aromatization
 Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)36 40 Studies on Mo/HZSM-5 Complex catalyst for Methane Aromatization Qun Dong 1, Xiaofei Zhao 1, Jian Wang 1, M Ichikawa 2 1. Department of Petrochemical Engineering,
Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)36 40 Studies on Mo/HZSM-5 Complex catalyst for Methane Aromatization Qun Dong 1, Xiaofei Zhao 1, Jian Wang 1, M Ichikawa 2 1. Department of Petrochemical Engineering,
Synthesis of jet fuel range cycloalkanes with diacetone alcohol. from lignocellulose
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Synthesis of jet fuel range cycloalkanes with diacetone alcohol from
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Synthesis of jet fuel range cycloalkanes with diacetone alcohol from
HEXENE CATALYTIC CRACKING OVER 30% SAPO-34 CATALYST FOR PROPYLENE MAXIMIZATION: INFLUENCE OF REACTION CONDITIONS AND REACTION PATHWAY EXPLORATION
 Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering ISSN 14-6632 Printed in Brazil www.abeq.org.br/bjche Vol. 26, No. 4, pp. 75-712, October - December, 29 HEXENE CATALYTIC CRACKING OVER 3% SAPO-34 CATALYST FOR
Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering ISSN 14-6632 Printed in Brazil www.abeq.org.br/bjche Vol. 26, No. 4, pp. 75-712, October - December, 29 HEXENE CATALYTIC CRACKING OVER 3% SAPO-34 CATALYST FOR
Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis over Co/ɣ-Al 2 O 3 Catalyst: Activation by Synthesis Gas
 , July 5-7, 2017, London, U.K. Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis over Co/ɣ-Al 2 O 3 Catalyst: Activation by Synthesis Gas Ditlhobolo Seanokeng, Achtar Iloy, Kalala Jalama Abstract This study aimed at investigating
, July 5-7, 2017, London, U.K. Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis over Co/ɣ-Al 2 O 3 Catalyst: Activation by Synthesis Gas Ditlhobolo Seanokeng, Achtar Iloy, Kalala Jalama Abstract This study aimed at investigating
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using
 Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate
 Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Propylene: key building block for the production of important petrochemicals
 Propylene production from 11-butene and ethylene catalytic cracking: Study of the performance of HZSMHZSM-5 zeolites and silicoaluminophosphates SAPO--34 and SAPOSAPO SAPO-18 E. Epelde Epelde*, *, A.G.
Propylene production from 11-butene and ethylene catalytic cracking: Study of the performance of HZSMHZSM-5 zeolites and silicoaluminophosphates SAPO--34 and SAPOSAPO SAPO-18 E. Epelde Epelde*, *, A.G.
Catalysis Science & Technology
 Catalysis Science & Technology PAPER Cite this: Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014, 4, 4045 Received 30th April 2014, Accepted 9th July 2014 DOI: 10.1039/c4cy00561a www.rsc.org/catalysis 1. Introduction To reduce
Catalysis Science & Technology PAPER Cite this: Catal. Sci. Technol., 2014, 4, 4045 Received 30th April 2014, Accepted 9th July 2014 DOI: 10.1039/c4cy00561a www.rsc.org/catalysis 1. Introduction To reduce
Purification Influence of Synthesis Gas Derived from Methanol Cracking on the Performance of Cobalt Catalyst in Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis
 Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 14(2005)193 198 Purification Influence of Synthesis Gas Derived from Methanol Cracking on the Performance of Cobalt Catalyst in Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis Wei Zhou 1,2,
Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 14(2005)193 198 Purification Influence of Synthesis Gas Derived from Methanol Cracking on the Performance of Cobalt Catalyst in Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis Wei Zhou 1,2,
CHAPTER 4 ISOPROPYLATION OF TOLUENE
 9 CHAPTER ISOPROPYLATION OF TOLUENE. INTRODUCTION Zeolites are largely exploited catalysts in industries. They catalyzed both the acid and base catalyzed reactions (Aiello et al 999, Costa et al 009, and
9 CHAPTER ISOPROPYLATION OF TOLUENE. INTRODUCTION Zeolites are largely exploited catalysts in industries. They catalyzed both the acid and base catalyzed reactions (Aiello et al 999, Costa et al 009, and
Supports, Zeolites, Mesoporous Materials - Chapter 9
 Supports, Zeolites, Mesoporous Materials - Chapter 9 Krijn P. de Jong Inorganic Chemistry and Catalysis Utrecht University NIOK CAIA Course, Schiermonnikoog, December 4 th, 2009 1 Overview of lecture Introduction
Supports, Zeolites, Mesoporous Materials - Chapter 9 Krijn P. de Jong Inorganic Chemistry and Catalysis Utrecht University NIOK CAIA Course, Schiermonnikoog, December 4 th, 2009 1 Overview of lecture Introduction
All organic compounds contain carbon, however, not all carbon containing compounds are classified as organic. Organic compounds covalently bonded
 Chapter 20 All organic compounds contain carbon, however, not all carbon containing compounds are classified as organic. Organic compounds covalently bonded compounds containing carbon, excluding carbonates
Chapter 20 All organic compounds contain carbon, however, not all carbon containing compounds are classified as organic. Organic compounds covalently bonded compounds containing carbon, excluding carbonates
Catalysis at the interface of nano-oxides and nanozeolites*
 Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 80, No. 11, pp. 2273 2282, 2008. doi:10.1351/pac200880112273 2008 IUPAC Catalysis at the interface of nano-oxides and nanozeolites* Kyosuke Ito, Hui Jang, Koji Sakashita, and Sachio
Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 80, No. 11, pp. 2273 2282, 2008. doi:10.1351/pac200880112273 2008 IUPAC Catalysis at the interface of nano-oxides and nanozeolites* Kyosuke Ito, Hui Jang, Koji Sakashita, and Sachio
The Effects of Temperature and Hydrogen Partial Pressure on Hydrocracking of Phenanthrene
 www.ccsenet.org/ijc International Journal of Chemistry Vol. 3, No. 2; June 11 The Effects of Temperature and Hydrogen Partial Pressure on Hydrocracking of Phenanthrene Zhaoxiang Yu, Liang Chen, Zhaowang
www.ccsenet.org/ijc International Journal of Chemistry Vol. 3, No. 2; June 11 The Effects of Temperature and Hydrogen Partial Pressure on Hydrocracking of Phenanthrene Zhaoxiang Yu, Liang Chen, Zhaowang
A Brief Catalyst Study on Direct Methane Conversion Using a Dielectric Barrier Discharge
 Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 2007, 54, 823-828 823 Communication A Brief Catalyst Study on Direct Methane Conversion Using a Dielectric Barrier Discharge Antonius Indarto, a,b * Jae-Wook Choi,
Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 2007, 54, 823-828 823 Communication A Brief Catalyst Study on Direct Methane Conversion Using a Dielectric Barrier Discharge Antonius Indarto, a,b * Jae-Wook Choi,
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Catalysis is an important process to improve the production of chemicals. This phenomenon can be employed in a chemical reaction that is favored thermodynamically but is very slow
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Catalysis is an important process to improve the production of chemicals. This phenomenon can be employed in a chemical reaction that is favored thermodynamically but is very slow
TRANSALKYLATION OF HEAVY AROMATICS FOR ENHANCED XYLENE PRODUCTION EFFECT OF METAL TYPE AND CONCENTRATION ON THE C9 CONVERSION AND XYLENE SELECTIVITY
 Proceedings of 15th Saudi-Japan Joint Symposium Dhahran, Saudi Arabia, November 27-28, 2005 TRANSALKYLATION OF HEAVY AROMATICS FOR ENHANCED XYLENE PRODUCTION EFFECT OF METAL TYPE AND CONCENTRATION ON THE
Proceedings of 15th Saudi-Japan Joint Symposium Dhahran, Saudi Arabia, November 27-28, 2005 TRANSALKYLATION OF HEAVY AROMATICS FOR ENHANCED XYLENE PRODUCTION EFFECT OF METAL TYPE AND CONCENTRATION ON THE
Synthesis of renewable diesel with hydroxyacetone and 2-methyl-furan
 Supporting Information Synthesis of renewable diesel with hydroxyacetone and 2-methyl-furan Guangyi Li, a,b Ning Li, a Shanshan Li, a,b Aiqin Wang, a Yu Cong, a Xiaodong Wang a and Tao Zhang a * a State
Supporting Information Synthesis of renewable diesel with hydroxyacetone and 2-methyl-furan Guangyi Li, a,b Ning Li, a Shanshan Li, a,b Aiqin Wang, a Yu Cong, a Xiaodong Wang a and Tao Zhang a * a State
ROLE OF HETEROGENEOUS CATALYSTS IN CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES- A REVIEW
 ROLE OF HETEROGENEOUS CATALYSTS IN CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES- A REVIEW Priya Das 1, Yagnesh Joshi 2, Darshan Sarang 3, Dr. Yogesh Rotliwala 4 Student, Chemical Engg. Dept., SNPITRC, Bardoli, Gujarat, India 1
ROLE OF HETEROGENEOUS CATALYSTS IN CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES- A REVIEW Priya Das 1, Yagnesh Joshi 2, Darshan Sarang 3, Dr. Yogesh Rotliwala 4 Student, Chemical Engg. Dept., SNPITRC, Bardoli, Gujarat, India 1
University of Bucharest, Faculty of Chemistry, Regina Elisabeta Blvd. 4-12, Bucharest, Romania
 AROMATIZATION OF C 6 HYDROCARBONS ON ZN /H-ZSM-5 CATALYST Adriana Urd, Rodica Z voianu and I. S ndulescu abstract: The distribution of reaction products in the aromatization of C 6 hydrocarbons depends
AROMATIZATION OF C 6 HYDROCARBONS ON ZN /H-ZSM-5 CATALYST Adriana Urd, Rodica Z voianu and I. S ndulescu abstract: The distribution of reaction products in the aromatization of C 6 hydrocarbons depends
Effect of ZSM-5 on the aromatization performance in cracking catalyst
 Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical 215 (2004) 195 199 Effect of ZSM-5 on the aromatization performance in cracking catalyst Conghua Liu a,b,, Youquan Deng a, Yuanqing Pan b, Yusheng Gu b, Botao
Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical 215 (2004) 195 199 Effect of ZSM-5 on the aromatization performance in cracking catalyst Conghua Liu a,b,, Youquan Deng a, Yuanqing Pan b, Yusheng Gu b, Botao
Method and process for combustion synthesized supported cobalt catalysts for fixed bed Fischer Tropsch reaction
 Method and process for combustion synthesized supported cobalt catalysts for fixed bed Fischer Tropsch reaction Center for Sustainable Technologies Indian Institute of Science Bangalore IDF presentation
Method and process for combustion synthesized supported cobalt catalysts for fixed bed Fischer Tropsch reaction Center for Sustainable Technologies Indian Institute of Science Bangalore IDF presentation
A method for the Regeneration of used Fe-ZSM5 Catalyst in Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis
 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Volume 21, 2010 Editor J. J. Klemeš, H. L. Lam, P. S. Varbanov Copyright 2010, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-05-1 ISSN 1974-9791 DOI: 10.3303/CET1021175 1045
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Volume 21, 2010 Editor J. J. Klemeš, H. L. Lam, P. S. Varbanov Copyright 2010, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-05-1 ISSN 1974-9791 DOI: 10.3303/CET1021175 1045
Catalytic Aromatization of Methane
 Catalytic Aromatization of Methane N.I.FAYZULLAYEV* 1, S.M.TUROBJONOV 2 1 Department of Natural Sciences, Division of Chemistry, Samarkand State University, Samarkand, Uzbekistan 2 Tashkent chemistry-technology
Catalytic Aromatization of Methane N.I.FAYZULLAYEV* 1, S.M.TUROBJONOV 2 1 Department of Natural Sciences, Division of Chemistry, Samarkand State University, Samarkand, Uzbekistan 2 Tashkent chemistry-technology
Asian Journal on Energy and Environment
 As. J. Energy Env. 2006, 7(01), 241-245 Asian Journal on Energy and Environment ISSN 1513-4121 Available online at www.asian-energy-journal.info Hydrogen Production from Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane
As. J. Energy Env. 2006, 7(01), 241-245 Asian Journal on Energy and Environment ISSN 1513-4121 Available online at www.asian-energy-journal.info Hydrogen Production from Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane
2. Hydrocarbons. 2.1 Composition of Petroleum
 2. Hydrocarbons 2.1 Composition of Petroleum Naturally occurring petroleum is composed of organic chemicals: approximately 11 to 13% hydrogen and 84 to 87% carbon. Traces of oxygen, sulfur, nitrogen and
2. Hydrocarbons 2.1 Composition of Petroleum Naturally occurring petroleum is composed of organic chemicals: approximately 11 to 13% hydrogen and 84 to 87% carbon. Traces of oxygen, sulfur, nitrogen and
Selective Hydrogenation of 1-Hexyne Using Pd-Cu and Pd- W Supported on Alumina Catalysts
 847 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERINGTRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 13 Chief Editors:SauroPierucci, JiříJ. Klemeš Copyright 13, AIDIC ServiziS.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian Association
847 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERINGTRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 13 Chief Editors:SauroPierucci, JiříJ. Klemeš Copyright 13, AIDIC ServiziS.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian Association
Fischer-Tropsch Waxes Upgrading via Hydrocracking and Selective Hydroisomerization
 Oil & Gas Science and Technology Rev. IFP, Vol. 64 (29), No. 1, pp. 91-112 Copyright 29, Institut français du pétrole DOI: 1.2516/ogst/2847 Dossier The Fischer-Tropsch Process Le procédé Fischer-Tropsch
Oil & Gas Science and Technology Rev. IFP, Vol. 64 (29), No. 1, pp. 91-112 Copyright 29, Institut français du pétrole DOI: 1.2516/ogst/2847 Dossier The Fischer-Tropsch Process Le procédé Fischer-Tropsch
ON THE POSSIBLE MECHANISMS OF HIGHER N-ALKANES ISOMERISATION
 Petroleum & Coal ISSN 1337-727 Available online at www,vurup,sk/pc Petroleum & Coal 5 (2), 25-29, 8 ON THE POSSIBLE MECHANISMS OF HIGHER N-ALKANES ISOMERISATION Dobromir Ivanov Yordanov*, Petko Stoyanov
Petroleum & Coal ISSN 1337-727 Available online at www,vurup,sk/pc Petroleum & Coal 5 (2), 25-29, 8 ON THE POSSIBLE MECHANISMS OF HIGHER N-ALKANES ISOMERISATION Dobromir Ivanov Yordanov*, Petko Stoyanov
PETE 203: Properties of oil
 PETE 203: Properties of oil Prepared by: Mr. Brosk Frya Ali Koya University, Faculty of Engineering, Petroleum Engineering Department 2013 2014 Lecture no. (2): Crude oil chemistry and composition 5. Crude
PETE 203: Properties of oil Prepared by: Mr. Brosk Frya Ali Koya University, Faculty of Engineering, Petroleum Engineering Department 2013 2014 Lecture no. (2): Crude oil chemistry and composition 5. Crude
RKCL5155 PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF AMMONIA DECOMPOSITION CATALYSTS BY HIGH-THROUGHPUT TECHNIQUE
 Jointly published by React.Kinet.Catal.Lett. Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest Vol. 93, No. 1, 11 17 (2008) and Springer, Dordrecht 10.1007/s11144-008-5155-3 RKCL5155 PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF AMMONIA DECOMPOSITION
Jointly published by React.Kinet.Catal.Lett. Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest Vol. 93, No. 1, 11 17 (2008) and Springer, Dordrecht 10.1007/s11144-008-5155-3 RKCL5155 PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF AMMONIA DECOMPOSITION
RKCL4616. CATALYTIC PROPERTIES OF HZSM-12 ZEOLITE IN n-heptane CATALYTIC CRACKING
 Jointly published by React.Kinet.Catal.Lett. Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest Vol. 84, No. 2, 287-293 and Springer, Dordrecht (2005) RKCL4616 CATALYTIC PROPERTIES OF HZSM-12 ZEOLITE IN n-heptane CATALYTIC CRACKING
Jointly published by React.Kinet.Catal.Lett. Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest Vol. 84, No. 2, 287-293 and Springer, Dordrecht (2005) RKCL4616 CATALYTIC PROPERTIES OF HZSM-12 ZEOLITE IN n-heptane CATALYTIC CRACKING
Chemical Technology Prof. Indra D. Mall Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee
 Chemical Technology Prof. Indra D. Mall Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Module - 6 Petroleum Refinery Lecture - 7 Alkylation Isomerisation and Polymerization
Chemical Technology Prof. Indra D. Mall Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Module - 6 Petroleum Refinery Lecture - 7 Alkylation Isomerisation and Polymerization
Research and Development of Novel Heavy Oil Catalytic Cracking Catalyst RCC-1
 Catalyst Research China Petroleum Processing and Petrochemical Technology 2014, Vol. 16, No. 4, pp 7-11 December 31, 2014 Research and Development of Novel Heavy Oil Catalytic Cracking Catalyst RCC-1 Zhang
Catalyst Research China Petroleum Processing and Petrochemical Technology 2014, Vol. 16, No. 4, pp 7-11 December 31, 2014 Research and Development of Novel Heavy Oil Catalytic Cracking Catalyst RCC-1 Zhang
Dehydrogenation of Propane to Propylene Over Pt-Sn/Al 2 O 3 Catalysts: The influence of operating conditions on product selectivity
 Iranian Journal of Chemical Engineering Vol. 7, No. (Spring), 1, IAChE Dehydrogenation of Propane to Propylene Over Pt-Sn/Al O 3 Catalysts: The influence of operating conditions on product selectivity
Iranian Journal of Chemical Engineering Vol. 7, No. (Spring), 1, IAChE Dehydrogenation of Propane to Propylene Over Pt-Sn/Al O 3 Catalysts: The influence of operating conditions on product selectivity
PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 11, No. 1, January - March 2016, p. 271-276 PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 11, No. 1, January - March 2016, p. 271-276 PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL
Chapter 12 Alkanes Based on Material Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette
 Chapter 12 Alkanes Based on Material Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Introduction
Chapter 12 Alkanes Based on Material Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Introduction
Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite) catalyst
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
One-Pot Conversion of Methane to Light Olefins or Higher Hydrocarbons through H-SAPO-34 Catalyzed in-situ Halogenation
 S1 Supporting Information One-Pot Conversion of Methane to Light Olefins or Higher Hydrocarbons through H-SAPO-34 Catalyzed in-situ Halogenation Patrice T. D. Batamack, Thomas Mathew, G. K. Surya Prakash*
S1 Supporting Information One-Pot Conversion of Methane to Light Olefins or Higher Hydrocarbons through H-SAPO-34 Catalyzed in-situ Halogenation Patrice T. D. Batamack, Thomas Mathew, G. K. Surya Prakash*
Effect of Strontium Addition to Platinum Catalyst for Propane Dehydrogenation
 Catalyst Research China Petroleum Processing and Petrochemical Technology 2012,Vol. 14, No. 3, pp 75-82 September 30, 2012 Effect of Strontium Addition to Platinum Catalyst for Propane Dehydrogenation
Catalyst Research China Petroleum Processing and Petrochemical Technology 2012,Vol. 14, No. 3, pp 75-82 September 30, 2012 Effect of Strontium Addition to Platinum Catalyst for Propane Dehydrogenation
The Simplest Alkanes. Physical Properties 2/16/2012. Butanes are still gases. bp -160 C bp -89 C bp -42 C. CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 n-pentane.
 The Simplest Alkanes Butanes are still gases Methane (CH 4 ) Ethane (C 2 H 6 ) Propane (C 3 H 8 ) n-butane CH 2 CH 2 Isobutane ( ) 3 CH bp -160 C bp -89 C bp -42 C bp -0.4 C bp -10.2 C Branched isomer
The Simplest Alkanes Butanes are still gases Methane (CH 4 ) Ethane (C 2 H 6 ) Propane (C 3 H 8 ) n-butane CH 2 CH 2 Isobutane ( ) 3 CH bp -160 C bp -89 C bp -42 C bp -0.4 C bp -10.2 C Branched isomer
DEVELOPMENT OF CATALYSTS FOR ETHANE EPOXIDATION REACTION. Keywords: Ethylene oxide, Partial oxidation, Ethane epoxidation, Second metal.
 DEVELOPMENT OF CATALYSTS FOR ETHANE EPOXIDATION REACTION Kingsuda Mahunee a, Krittiya Pornmai a, Sitthiphong Pengpanich c, Sumaeth Chavade j* a,b a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn
DEVELOPMENT OF CATALYSTS FOR ETHANE EPOXIDATION REACTION Kingsuda Mahunee a, Krittiya Pornmai a, Sitthiphong Pengpanich c, Sumaeth Chavade j* a,b a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn
Manganese promotion in cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch catalysis
 Manganese promotion in cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch catalysis F. Morales Cano, O.L.J. Gijzeman, F.M.F. de Groot and B.M. Weckhuysen Department of Inorganic Chemistry and Catalysis, Debye Institute, Utrecht
Manganese promotion in cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch catalysis F. Morales Cano, O.L.J. Gijzeman, F.M.F. de Groot and B.M. Weckhuysen Department of Inorganic Chemistry and Catalysis, Debye Institute, Utrecht
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Families of Organic Compounds Organic compounds can be grouped into families by their common structural features We shall survey the nature of the compounds in a tour of the families
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Families of Organic Compounds Organic compounds can be grouped into families by their common structural features We shall survey the nature of the compounds in a tour of the families
Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Substituted Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves with AEL Structure
 Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)231 237 Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Substituted Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves with AEL Structure Benjing Xu, Ling Qian, Xinmei Liu, Chunmin
Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)231 237 Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Substituted Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves with AEL Structure Benjing Xu, Ling Qian, Xinmei Liu, Chunmin
OBTAINING OF LIQUID FUEL FROM COAL IN THE PRESENCE OF THE POLYMERS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 14(1), 2016, 261-268 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com OBTAINING OF LIQUID FUEL FROM COAL IN THE PRESENCE OF THE POLYMERS D. A. BAISEITOV, SH. E. GABDRASHOVA, A. K. AKYLBAI,
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 14(1), 2016, 261-268 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com OBTAINING OF LIQUID FUEL FROM COAL IN THE PRESENCE OF THE POLYMERS D. A. BAISEITOV, SH. E. GABDRASHOVA, A. K. AKYLBAI,
QUESTION 1 The boiling temperature of hydrocarbons making up crude oil depends on the strength of intermolecular forces known as:
 QUESTION 1 The boiling temperature of hydrocarbons making up crude oil depends on the strength of intermolecular forces known as: B C D Hydrogen bonding. Dipole-dipole interactions. Dispersion forces.
QUESTION 1 The boiling temperature of hydrocarbons making up crude oil depends on the strength of intermolecular forces known as: B C D Hydrogen bonding. Dipole-dipole interactions. Dispersion forces.
5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Hangzhou , PR China
 5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Influence of Ni based catalysts on CH 4 -CO 2 reforming reaction Hangjie Li 1, Dongming Shen 2, Xikun Gai 3,
5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Influence of Ni based catalysts on CH 4 -CO 2 reforming reaction Hangjie Li 1, Dongming Shen 2, Xikun Gai 3,
DRASTIC ENHANCEMENT OF PROPENE YIELD FROM 1-HEXENE CATALYTIC CRACKING USING A SHAPE INTENSIFIED MESO-SAPO-34 CATALYST
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 4, No. 4 (2009) 409-418 School of Engineering, Taylor s University College DRASTIC ENHANCEMENT OF PROPENE YIELD FROM 1-HEXENE CATALYTIC CRACKING USING
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 4, No. 4 (2009) 409-418 School of Engineering, Taylor s University College DRASTIC ENHANCEMENT OF PROPENE YIELD FROM 1-HEXENE CATALYTIC CRACKING USING
Effect of Ni Loading and Reaction Conditions on Partial Oxidation of Methane to Syngas
 Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 12(2003)205 209 Effect of Ni Loading and Reaction Conditions on Partial Oxidation of Methane to Syngas Haitao Wang, Zhenhua Li, Shuxun Tian School of Chemical Engineering
Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 12(2003)205 209 Effect of Ni Loading and Reaction Conditions on Partial Oxidation of Methane to Syngas Haitao Wang, Zhenhua Li, Shuxun Tian School of Chemical Engineering
Adsorption Processes. Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad
 Adsorption Processes Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Contents Introduction Principles of adsorption Types of adsorption Definitions Brief history Adsorption isotherms Mechanism
Adsorption Processes Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Contents Introduction Principles of adsorption Types of adsorption Definitions Brief history Adsorption isotherms Mechanism
NOBLE METAL CATALYSTS FOR THE HYDROCRACKING OF FISCHER-TROPSCH WAXES
 NOBLE METAL CATALYSTS FOR THE HYDROCRACKING OF FISCHER-TROPSCH WAXES Characterization and Testing Ibone Elorriaga de la Fuente Stockholm, June 2012 Thesis supervisors: Francesco Regali PhD Student Magali
NOBLE METAL CATALYSTS FOR THE HYDROCRACKING OF FISCHER-TROPSCH WAXES Characterization and Testing Ibone Elorriaga de la Fuente Stockholm, June 2012 Thesis supervisors: Francesco Regali PhD Student Magali
KMUTNB Int J Appl Sci Technol, Vol. 9, No. 4, pp , 2016
 KMUTNB Int J Appl Sci Technol, Vol. 9, No. 4, pp. 255 259, 216 Research Article Effect of Strong Metal Support Interactions of Supported Ni and Ni-Co Catalyst on Metal Dispersion and Catalytic Activity
KMUTNB Int J Appl Sci Technol, Vol. 9, No. 4, pp. 255 259, 216 Research Article Effect of Strong Metal Support Interactions of Supported Ni and Ni-Co Catalyst on Metal Dispersion and Catalytic Activity
Catalytic Chemistry. Bruce C. Gates. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore. University of Delaware ^.'-'.
 : s / ; '.... ;. : : ^.'-'. Catalytic Chemistry Bruce C. Gates University of Delaware John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore Contents List of Notation xix 1 INTRODUCTION
: s / ; '.... ;. : : ^.'-'. Catalytic Chemistry Bruce C. Gates University of Delaware John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore Contents List of Notation xix 1 INTRODUCTION
Aliphatic Hydrocarbones : Alkanes
 Dr. Salam Ghafour Taher https://sites.google.com/a/koyauniversity.org/salam-taher/ Aliphatic Hydrocarbones : Alkanes Alkanes are fully saturated hydrocarbons, have only C s and H s. Contains single bonds
Dr. Salam Ghafour Taher https://sites.google.com/a/koyauniversity.org/salam-taher/ Aliphatic Hydrocarbones : Alkanes Alkanes are fully saturated hydrocarbons, have only C s and H s. Contains single bonds
2CH3OH + H2CO = CH2(OCH3) 2 + H20.
 Theoretical and Experimental ChemistD', VoL 36. No. 2. 200( EFFECT OF CRYSTALLNTY N ZSM-5-AMORPOUS ALUMOSLCA SYSTEMS ON TER CATALYTC PROPERTES N TE SYNTESS OF DMETOXYMETANE N. V. Pavlenko, Yu. N. Kochkin,
Theoretical and Experimental ChemistD', VoL 36. No. 2. 200( EFFECT OF CRYSTALLNTY N ZSM-5-AMORPOUS ALUMOSLCA SYSTEMS ON TER CATALYTC PROPERTES N TE SYNTESS OF DMETOXYMETANE N. V. Pavlenko, Yu. N. Kochkin,
Synthesis, characterization and catalytic properties of Y-β zeolite composites
 224 Pet.Sci.(2011)8:224-228 DOI 10.1007/s12182-011-0139-8 Synthesis, characterization and catalytic properties of Y-β zeolite composites Qin Bo, Zhang Xiwen, Zhang Zhizhi, Ling Fengxiang and Sun Wanfu
224 Pet.Sci.(2011)8:224-228 DOI 10.1007/s12182-011-0139-8 Synthesis, characterization and catalytic properties of Y-β zeolite composites Qin Bo, Zhang Xiwen, Zhang Zhizhi, Ling Fengxiang and Sun Wanfu
Catalyst of Palladium Supported on H-Beta Zeolite with Nanosized Al2O3 for Isomerization of n-heptane
 Journal of the Japan Petroleum Institute, 55, (2), 99-107 (2012) 99 [Regular Paper] Catalyst of Palladium Supported on H-Beta Zeolite with Nanosized Al2O3 for Isomerization of n-heptane Toshiyuki KIMURA,
Journal of the Japan Petroleum Institute, 55, (2), 99-107 (2012) 99 [Regular Paper] Catalyst of Palladium Supported on H-Beta Zeolite with Nanosized Al2O3 for Isomerization of n-heptane Toshiyuki KIMURA,
H 22. (a) Give the general formula of alkanes. (1) (b) Carbon monoxide, CO, is formed during the incomplete combustion of decane.
 1 Crude oil is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons. Initial separation is achieved by fractional distillation of the crude oil. The separate fractions are further refined to produce hydrocarbons such as
1 Crude oil is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons. Initial separation is achieved by fractional distillation of the crude oil. The separate fractions are further refined to produce hydrocarbons such as
Studies on the Kinetics of Heavy Oil Catalytic Pyrolysis
 60 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 00, 4, 60-609 Studies on the Kinetics of Heavy Oil Catalytic Pyrolysis Meng Xiang-hai,* Xu Chun-ming, Li Li, and Gao Jin-sen State Key Laboratory of Heavy Oil Processing, University
60 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 00, 4, 60-609 Studies on the Kinetics of Heavy Oil Catalytic Pyrolysis Meng Xiang-hai,* Xu Chun-ming, Li Li, and Gao Jin-sen State Key Laboratory of Heavy Oil Processing, University
A test reaction for titanium silicalite catalysts
 A test reaction for titanium silicalite catalysts Kraushaar, B.; van Hooff, J.H.C. Published in: Catalysis Letters DOI: 10.1007/BF00765329 Published: 01/01/1989 Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known
A test reaction for titanium silicalite catalysts Kraushaar, B.; van Hooff, J.H.C. Published in: Catalysis Letters DOI: 10.1007/BF00765329 Published: 01/01/1989 Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known
Selective O-Alkylation Reaction of Hydroquinone with Methanol over Cs Ion-Exchanged Zeolites
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 19(3), 406-410 (2002) Selective O-Alkylation Reaction of Hydroquinone with Methanol over Cs Ion-Exchanged Zeolites Sang Sung Lee, Soo Chool Lee and Jae Chang Kim Department of Chemical
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 19(3), 406-410 (2002) Selective O-Alkylation Reaction of Hydroquinone with Methanol over Cs Ion-Exchanged Zeolites Sang Sung Lee, Soo Chool Lee and Jae Chang Kim Department of Chemical
Supporting information
 Supporting information Hierarchical Macro-meso-microporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Hollow Fibers With Highly Efficient Catalytic Cracking Capability Jia Liu, a Guiyuan Jiang,* a Ying Liu, a Jiancheng Di, b Yajun
Supporting information Hierarchical Macro-meso-microporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Hollow Fibers With Highly Efficient Catalytic Cracking Capability Jia Liu, a Guiyuan Jiang,* a Ying Liu, a Jiancheng Di, b Yajun
Supplementary Information. Synthesis and Characterization of Fibrous Silica ZSM-5 for Cumene Hydrocracking
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 1 Supplementary Information Synthesis and Characterization of Fibrous Silica
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 1 Supplementary Information Synthesis and Characterization of Fibrous Silica
EFFECTS OF POST-TREATMENT STEAMING ON CATALYTIC PERFORMANCE OF MODIFIED HZSM-5 CATALYSTS FOR THE CONVERSION OF n-pentane TO AROMATICS
 EFFECTS OF POST-TREATMENT STEAMING ON CATALYTIC PERFORMANCE OF MODIFIED HZSM-5 CATALYSTS FOR THE CONVERSION OF n-pentane TO AROMATICS Chaninwut Kalajuck a, Siriporn Jongpatiwut*,a,b, Thirasak Rirksomboon
EFFECTS OF POST-TREATMENT STEAMING ON CATALYTIC PERFORMANCE OF MODIFIED HZSM-5 CATALYSTS FOR THE CONVERSION OF n-pentane TO AROMATICS Chaninwut Kalajuck a, Siriporn Jongpatiwut*,a,b, Thirasak Rirksomboon
Chapter 21: Hydrocarbons Section 21.3 Alkenes and Alkynes
 Section 21.1 Introduction to Hydrocarbons Section 1 Objectives: Explain the terms organic compound and organic chemistry. Section 21.2 Alkanes Chapter 21: Hydrocarbons Section 21.3 Alkenes and Alkynes
Section 21.1 Introduction to Hydrocarbons Section 1 Objectives: Explain the terms organic compound and organic chemistry. Section 21.2 Alkanes Chapter 21: Hydrocarbons Section 21.3 Alkenes and Alkynes
Alkanes. The reaction is initiated by the formation of chlorine radicals from chlorine. ...
 Alkanes 1. Butane, 4 10, reacts with chlorine to produce a chloroalkane with molecular formula 4 9 l. The reaction is initiated by the formation of chlorine radicals from chlorine. What is meant by the
Alkanes 1. Butane, 4 10, reacts with chlorine to produce a chloroalkane with molecular formula 4 9 l. The reaction is initiated by the formation of chlorine radicals from chlorine. What is meant by the
Zn/H-ZSM-5 zeolite as catalyst for benzene alkylation with isobutane
 Prog. Catal, Vol. 13, No. 1-2, pp. 35-41 (24) Prog. Catal. Zn/H-ZSM-5 zeolite as catalyst for benzene alkylation with isobutane Adriana Urdă *, Ioan Săndulescu, Ioan-Cezar Marcu University of Bucharest,
Prog. Catal, Vol. 13, No. 1-2, pp. 35-41 (24) Prog. Catal. Zn/H-ZSM-5 zeolite as catalyst for benzene alkylation with isobutane Adriana Urdă *, Ioan Săndulescu, Ioan-Cezar Marcu University of Bucharest,
Organic Chemistry. A brief introduction
 Organic Chemistry A brief introduction Organic Chemistry the study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties excluding: CO, CO 2, CS 2, carbonates and cyanides eight million known organic compounds
Organic Chemistry A brief introduction Organic Chemistry the study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties excluding: CO, CO 2, CS 2, carbonates and cyanides eight million known organic compounds
Cracking. 191 minutes. 186 marks. Page 1 of 27
 3.1.6.2 Cracking 191 minutes 186 marks Page 1 of 27 Q1. (a) Gas oil (diesel), kerosine (paraffin), mineral oil (lubricating oil) and petrol (gasoline) are four of the five fractions obtained by the fractional
3.1.6.2 Cracking 191 minutes 186 marks Page 1 of 27 Q1. (a) Gas oil (diesel), kerosine (paraffin), mineral oil (lubricating oil) and petrol (gasoline) are four of the five fractions obtained by the fractional
Mesostructured Zeolite Y - High Hydrothermal Stability and Superior FCC Catalytic Performance
 Supporting Information Mesostructured Zeolite Y - High Hydrothermal Stability and Superior FCC Catalytic Performance Javier García-Martínez,* Marvin Johnson, Julia Valla, Kunhao Li, and Jackie Y. Ying*
Supporting Information Mesostructured Zeolite Y - High Hydrothermal Stability and Superior FCC Catalytic Performance Javier García-Martínez,* Marvin Johnson, Julia Valla, Kunhao Li, and Jackie Y. Ying*
Compound A [1]... have different boiling points.
![Compound A [1]... have different boiling points. Compound A [1]... have different boiling points.](/thumbs/78/77084916.jpg) 1 This question is about different alkanes present in crude oil (a) Compound A, shown below, is one of the structural isomers of C 7 H 16 Compound A What is meant by the term structural isomers? Name compound
1 This question is about different alkanes present in crude oil (a) Compound A, shown below, is one of the structural isomers of C 7 H 16 Compound A What is meant by the term structural isomers? Name compound
Saturated: Alkanes only single, covalent C-C and C-H bonds, no rings Cycloalkanes same, but contain rings
 Hydrocarbons Compounds that contain only Carbon and Hydrogen Types of hydrocarbons: Saturated: Alkanes only single, covalent C-C and C-H bonds, no rings Cycloalkanes same, but contain rings Unsaturated:
Hydrocarbons Compounds that contain only Carbon and Hydrogen Types of hydrocarbons: Saturated: Alkanes only single, covalent C-C and C-H bonds, no rings Cycloalkanes same, but contain rings Unsaturated:
A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with. Aliphatic Alcohols in the Presence of Molecular Oxygen. Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with Aliphatic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with Aliphatic
Firewood? Chapter 22. Formulas and Models for Methane and Ethane. One carbon atom can form a single covalent bond with four hydrogen atoms.
 Chapter 22 Gasoline, diesel fuel, and kerosene are examples of liquid fuels. A solid fuel, coal, produced the steam for the locomotives that pulled old-time trains. These fuels are mixtures of compounds
Chapter 22 Gasoline, diesel fuel, and kerosene are examples of liquid fuels. A solid fuel, coal, produced the steam for the locomotives that pulled old-time trains. These fuels are mixtures of compounds
Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR
 a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
Transformation of Lower Alkanes into Aromatic. Hydrocarbons over ZSM-5 Zeolites
 Transformation of Lower Alkanes into Aromatic Hydrocarbons over ZSM-5 Zeolites Yoshio ONO*, Hiroyoshi KITAGAWA, and Yoko SENDODA Department of Chemical Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology Ookayama,
Transformation of Lower Alkanes into Aromatic Hydrocarbons over ZSM-5 Zeolites Yoshio ONO*, Hiroyoshi KITAGAWA, and Yoko SENDODA Department of Chemical Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology Ookayama,
Comparison of acid catalysts for the dehydration of methanol to dimethyl ether
 Proceedings of European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE-6) Copenhagen, 16-2 September 27 Comparison of acid catalysts for the dehydration of methanol to dimethyl ether I. Sierra, J. Ereña, A. T.
Proceedings of European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE-6) Copenhagen, 16-2 September 27 Comparison of acid catalysts for the dehydration of methanol to dimethyl ether I. Sierra, J. Ereña, A. T.
Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite from
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite from
3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 3 2003 Ronald Kluger Department of Chemistry University of Toronto 1 Families of Organic Compounds!
3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 3 2003 Ronald Kluger Department of Chemistry University of Toronto 1 Families of Organic Compounds!
Differences between MFI- and MEL-Type Zeolites in Paraffin Hydrocracking
 Journal of Catalysis 203, 281 291 (2001) doi:10.1006/jcat.2001.3332, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Differences between MFI- and MEL-Type Zeolites in Paraffin Hydrocracking Th. L. M.
Journal of Catalysis 203, 281 291 (2001) doi:10.1006/jcat.2001.3332, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Differences between MFI- and MEL-Type Zeolites in Paraffin Hydrocracking Th. L. M.
One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene Peipei Zhang,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene Peipei Zhang,
Investigation of Hydrogen Influence on n-hexane Aromatization over Pt/Al O Catalyst
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(8): 3835-3842, 2010 ISSN 1991-8178 Investigation of Hydrogen Influence on n-hexane Aromatization over Pt/Al O Catalyst D.O. Agbajelola and F. Aberuagba
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(8): 3835-3842, 2010 ISSN 1991-8178 Investigation of Hydrogen Influence on n-hexane Aromatization over Pt/Al O Catalyst D.O. Agbajelola and F. Aberuagba
HYDROISOMERIZATION OF 1-PENTENE TO ISO- PENTANE IN A SINGLE REACTOR
 Chemical Engineering Communications ISSN: 0098-6445 (Print) 1563-5201 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/gcec20 HYDROISOMERIZATION OF 1-PENTENE TO ISO- PENTANE IN A SINGLE REACTOR
Chemical Engineering Communications ISSN: 0098-6445 (Print) 1563-5201 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/gcec20 HYDROISOMERIZATION OF 1-PENTENE TO ISO- PENTANE IN A SINGLE REACTOR
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 28. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 28 Two types in general use: -packed (stationary phase) -open tubular or capillary determine selectivity and efficiency of the sample. Column Materials Column
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 28 Two types in general use: -packed (stationary phase) -open tubular or capillary determine selectivity and efficiency of the sample. Column Materials Column
Alkylation of benzene with ethanol over ZSM-5 catalyst with different SiO 2 /Al 2 O 3 ratios
 Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 11, May 2004, pp 337-345 Alkylation of benzene with ethanol over ZSM-5 catalyst with different SiO 2 /Al 2 O 3 ratios Jun-Jun Yuan & Börje S Gevert* Department
Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 11, May 2004, pp 337-345 Alkylation of benzene with ethanol over ZSM-5 catalyst with different SiO 2 /Al 2 O 3 ratios Jun-Jun Yuan & Börje S Gevert* Department
Synthesis of a Zeolite Column with a Monolithic Microhoneycomb Structure Using the Ice Template Method
 Synthesis of a Zeolite Column with a Monolithic Microhoneycomb Structure Using the Ice Template Method Shin R. Mukai, Shinya Murata, Kazufusa Onodera and Izumi Yamada *1 Graduate School of Engineering,
Synthesis of a Zeolite Column with a Monolithic Microhoneycomb Structure Using the Ice Template Method Shin R. Mukai, Shinya Murata, Kazufusa Onodera and Izumi Yamada *1 Graduate School of Engineering,
Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known as Version of Record (includes final page, issue and volume numbers)
 On the temperature dependence of the Arrhenius activation energy for hydroisomerization catalyzed by Pt/Mordenite Runstraat, van de, A.; van Grondelle, J.; van Santen, R.A. Published in: Journal of Catalysis
On the temperature dependence of the Arrhenius activation energy for hydroisomerization catalyzed by Pt/Mordenite Runstraat, van de, A.; van Grondelle, J.; van Santen, R.A. Published in: Journal of Catalysis
The time-on-stream stability of some selected bifunctional nanoporous-based catalysts in n-heptane hydroisomerisation
 Appl Petrochem Res (214) 4:189 27 DOI 1.17/s1323-13-38-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The time-on-stream stability of some selected bifunctional nanoporous-based catalysts in n-heptane hydroisomerisation Faisal M.
Appl Petrochem Res (214) 4:189 27 DOI 1.17/s1323-13-38-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The time-on-stream stability of some selected bifunctional nanoporous-based catalysts in n-heptane hydroisomerisation Faisal M.
Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons
 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Chapter 12 Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds 12.2 Alkanes 12.3 Alkanes with Substituents 12.4 Properties of Alkanes 12.5 Alkenes and Alkynes 12.6 Cis-Trans
Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Chapter 12 Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds 12.2 Alkanes 12.3 Alkanes with Substituents 12.4 Properties of Alkanes 12.5 Alkenes and Alkynes 12.6 Cis-Trans
Organic Compounds. Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons. also contain other nonmetals such as oxygen, nitrogen,
 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds Identify properties characteristic of organic or inorganic compounds. Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds 12.2 Alkanes 12.3
Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds Identify properties characteristic of organic or inorganic compounds. Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds 12.2 Alkanes 12.3
(a) (i) What is represented by... (ii) What is represented by... (2) (b) What is the symbol for lithium?... (1) (Total 3 marks)
 1 The diagram shows the structure of a lithium atom. (a) (i) What is represented by... (ii) What is represented by... (b) What is the symbol for lithium?... (Total 3 marks) 2 (a) Balance these chemical
1 The diagram shows the structure of a lithium atom. (a) (i) What is represented by... (ii) What is represented by... (b) What is the symbol for lithium?... (Total 3 marks) 2 (a) Balance these chemical
Kinetic Characterisation of Zeolite Catalysts Using Cracking, Alkylation and Other Chemical Reactions
 Haldor Topsøe Catalysis Forum Munkerupgaard, 27-28 August 2015 Kinetic Characterisation of Zeolite Catalysts Using Cracking, Alkylation and Other Chemical Reactions Dmitry B. Lukyanov Catalysis & Reaction
Haldor Topsøe Catalysis Forum Munkerupgaard, 27-28 August 2015 Kinetic Characterisation of Zeolite Catalysts Using Cracking, Alkylation and Other Chemical Reactions Dmitry B. Lukyanov Catalysis & Reaction
The effect of phase transition of methanol on the reaction rate in the alkylation of hydroquinone
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 26(3), 649-653 (2009) SHORT COMMUNICATION The effect of phase transition of methanol on the reaction rate in the alkylation of hydroquinone Jung Je Park*, Soo Chool Lee*, Sang Sung
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 26(3), 649-653 (2009) SHORT COMMUNICATION The effect of phase transition of methanol on the reaction rate in the alkylation of hydroquinone Jung Je Park*, Soo Chool Lee*, Sang Sung
A mini review on the chemistry and catalysis of the water gas shift reaction
 A mini review on the chemistry and catalysis of the water gas shift reaction Abstract: Bifunctional/bimetallic catalysts are a set of important catalytic materials that find their applications in many
A mini review on the chemistry and catalysis of the water gas shift reaction Abstract: Bifunctional/bimetallic catalysts are a set of important catalytic materials that find their applications in many
Organic Chemistry. REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling
 Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Alkanes molecules consisting of carbons and hydrogens in the following ratio: C n H 2n+2 Therefore, an alkane having 4 carbons would have 2(4) + 2 hydrogens, which equals 10 hydrogens.
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Alkanes molecules consisting of carbons and hydrogens in the following ratio: C n H 2n+2 Therefore, an alkane having 4 carbons would have 2(4) + 2 hydrogens, which equals 10 hydrogens.
