Graphene and new 2D materials: Opportunities for High Frequencies applications
|
|
|
- Theodora Phelps
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Graphene and new 2D materials: Opportunities for High Frequencies applications April 21th, 2015 H. Happy, E. Pallecchi, B. Plaçais, D. Jiménez, R. Sordan, D. Neumaier Graphene Flagship WP4 HF electronic
2 Outline Graphene FET: State of the art GFET optimization Gate contact Current saturation exploring velocity saturation Ballistic devices Graphene flagship WP4 High frequency electronic: Some achievements Summary and outlook 2
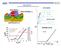
3 3 Progress in fabrication process GFET on SiC substrate Devices on Substrate Optical Microscope Image Full Device SEM Image FIB cross section of the active part of device
4 Study of parametric variation of performances Devices (Number) Gains (db) ft_intr ft_dut fmax / (GHz) frequency (GHz) M.S. Khenissa et al.; EuMIC 2014 Roma Italy, doi: /EuMIC (IEMN) Devices (Number) f max (GHz) 4
5 GFET State of the art 5 Figures of merit: f t, f max f t,: Current gain cut-off frequency f max Maximum oscillation frequency (over this frequency, there is no power gain) F. Schwierz, Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 101, no 7, 2013
6 How these figures of merit (FOM) are defined? Conventional GFET structure RF probes for measurements Top view of dual-gated graphene FET Device under test (DUT) How to extract performances of GFET? (De-embedding procedure) 6
7 Extraction of extrinsic/intrinsic performance 7 50 G R g V GS R GD R GS C GS C GD g m V GS 1 / g d R d C DS D Gains (db) H 21 H f max f t 0-10 f t _Probes_plan -20 Frequency (GHz) R s S f t = 30 GHz f max = 20 GHz F t_probes = 12.5 GHz Pads structures are capacitive f max remains constant with capacitive transform
8 How to define figures of merit (FOM) 8 Small signal equivalent circuit of GFET without access lines c dsp c gdp Source c R g gsp c gdp Gate C gs C gd R s R gs g m V GS R gd Drain R d G c gsp R g V GS R GD R GS C GS C GD g m V GS 1/g d R d C DS D c dsp R s C ds 1 / g d S F t < F t < F t = F c = G m /(2 πc gs ) 17 < 30 < 80 (GHz) F max = F max < F max_intr 23 = 23 < 55 GHz
9 Some drawbacks of GFET o Contact and access resistance o No pinch-off o Lack of current saturation Compare to the typical HEMT devices A v g g m d Low Voltage gain High value of access resistance Main objective: F max # 100 GHz 9
10 Outline Graphene FET for High Frequency (HF): State of the art GFET optimization Gate contact Current saturation exploring velocity saturation Ballistic devices Graphene flagship WP4 High frequency electronic: Some achievements Summary and outlook 10
11 Metal-Graphene Contact Resistance - Modeling Device Components for contact resistance Electrostatics Specific contact resistivity (3Dà 2D) Lateral resistance 11
12 Metal-Graphene Contact Resistance Graphene etched below pure Au contacts R c < 90 Ωµm Au (100 nm) 500 nm R (Ω) R at V 0 (Dirac point) R c W = 86 Ω µm R c W = 87 Ω µm L (µm) R. Sordan (WP4 Flagship) 12
13 Velocity saturation - Requirements Low contact resistance High mobilty graphene layer and low doping (phonon saturation) 50 Ωµm < R c < 150 Ωµm Ft extr = 20 GHz Fmax = 13 GHz (Wg = 2x50 µm, Lg = 1 µm). O. Habibpour et al.; EuMW 2014 Roma Italy (WP4 Flagship) 13
14 Velocity saturation impact of 2D materials 14 G-FET GoBN Y. Wu et al. / Nano Letters 12 (2012) 3062 L=0.6 µm I Meric et al. / IEDM (2011) I Meric et al. IEEE, Vol. 101, No. 7, (2013) " $%& ~34 ()*
15 Towards tunable contact and ballistic GFET 15 Artist view of device SEM picture (L=200 nm) Drain Drain contact gate 16 nm hbn Source SEM Source Channel gate Gated Pd-contacts, 20 nm thick W-gates Contact Contacted graphene contact junctions Free graphene h-bn(20nm) Contacted graphene Contact gate (2) Contact gate (2) Channel gate (1) Contact gate (2) V g2 SiO 2 Si++ Contact Q. Wilmart et al. (unpublished) WP4 Flagship
16 Towards tunable contact and ballistic GFET 16 V cont Drain G2 S D V ds Drain G1 ~ V ch SEM Sourc e 100µm Sourc e Differential resistance Pulsed contact gating RF-gain switching Q. Wilmart thesis High impact of BN good dielectric compared to Al 2 O 3
17 Towards tunable contact and ballistic GFET 17 L=500nm, W=1.5 µm Velocity saturation! Vg=-3...0V Vg=0...3V
18 Outline Graphene FET for High Frequency (HF): State of the art GFET optimization Gate contact Current saturation exploring velocity saturation Ballistic devices Graphene flagship WP4 High frequency electronic: Some achievements Summary and outlook 18
19 From devices to circuits 19 Graphene-based Inverters A v = High voltage gain Av = 11,3 with L = 2 µm
20 From devices to circuits Ring oscillator 20 V DD V DD V DD L = 0.8 µm and W = 5 µm The highest oscillation frequency was f o = 4.3 GHz at the gate length L = 0.9 µm E. Guerriero et al., ACS Nano 7, 5588 (2013) WP4 Flagship
21 Summary and outlook 21 Progress in graphene processing is made H-BN show a great impact on the GFET performances Looking for large scale material Expertise already transfer also to WP8 (Flexible electronics) Recent results using CVD Graphene from Graphenea C. Sire et al, Nano Le0. 12, 1184 (2012) (CEA IEMN - Northwestern U.) f max = 7 GHz and f t = 20 GHz on flex substrate
22 22
23 23
24 WP4 HF electronics 24 Nanostructuration of GFET channel (graphene nanoribbonds) SEM image of nanoribbons and nanomesh obtained by e-beam lithography Nanoribbonds width: from 10 nm to 50 nm
25 Nanostructuration of GFET channel GFET on SiC with Hydrogen intercalation Mobility: 2300 cm 2 /V.s Vds = 300 mv U_ext, U_intr, H21_DUT, H21_ext, H21_intr (db) F t_probes = 17 GHz Frequency 1 (GHz) Lg = 100 nm f max = 30 GHz f t = 50 GHz WP4 Flagship (IEMN) f max = 70 GHz f t = 140 GHz (Without access resistance) 25
26 De-embedding structures Measurement plan Metal Oxide Graphene FET [Y measured ] Pad Extrinsic performance [Y extr ] = [Y measured ] - [Y pad ] open structure «Intrinsic» performance [Y intr ] = [Y measured ] - [Y open ] Only parasitic capacitances are removed 26
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature09979 I. Graphene material growth and transistor fabrication Top-gated graphene RF transistors were fabricated based on chemical vapor deposition (CVD) grown graphene on copper (Cu). Cu foil
doi:.38/nature09979 I. Graphene material growth and transistor fabrication Top-gated graphene RF transistors were fabricated based on chemical vapor deposition (CVD) grown graphene on copper (Cu). Cu foil
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/327/5966/662/dc Supporting Online Material for 00-GHz Transistors from Wafer-Scale Epitaxial Graphene Y.-M. Lin,* C. Dimitrakopoulos, K. A. Jenkins, D. B. Farmer, H.-Y.
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/327/5966/662/dc Supporting Online Material for 00-GHz Transistors from Wafer-Scale Epitaxial Graphene Y.-M. Lin,* C. Dimitrakopoulos, K. A. Jenkins, D. B. Farmer, H.-Y.
Graphene Field Effect Devices Operating in Differential Circuit Configuration
 Graphene Field Effect Devices Operating in Differential Circuit Configuration C. Nyffeler a,*, M.S. Hanay b,c, D. Sacchetto a, Y. Leblebici a a Institute of Electrical Engineering, EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland
Graphene Field Effect Devices Operating in Differential Circuit Configuration C. Nyffeler a,*, M.S. Hanay b,c, D. Sacchetto a, Y. Leblebici a a Institute of Electrical Engineering, EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland
Fig The electron mobility for a-si and poly-si TFT.
 Fig. 1-1-1 The electron mobility for a-si and poly-si TFT. Fig. 1-1-2 The aperture ratio for a-si and poly-si TFT. 33 Fig. 1-2-1 All kinds defect well. (a) is the Dirac well. (b) is the repulsive Columbic
Fig. 1-1-1 The electron mobility for a-si and poly-si TFT. Fig. 1-1-2 The aperture ratio for a-si and poly-si TFT. 33 Fig. 1-2-1 All kinds defect well. (a) is the Dirac well. (b) is the repulsive Columbic
Graphene devices and integration: A primer on challenges
 Graphene devices and integration: A primer on challenges Archana Venugopal (TI) 8 Nov 2016 Acknowledgments: Luigi Colombo (TI) UT Dallas and UT Austin 1 Outline Where we are Issues o Contact resistance
Graphene devices and integration: A primer on challenges Archana Venugopal (TI) 8 Nov 2016 Acknowledgments: Luigi Colombo (TI) UT Dallas and UT Austin 1 Outline Where we are Issues o Contact resistance
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. 3. MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
MOS Transistor Theory
 CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
Transistori ad effetto di campo con canale in grafene (GFET) aventi risposta fotoelettrica
 Transistori ad effetto di campo con canale in grafene (GFET) aventi risposta fotoelettrica M. A. Giambra, E. Calandra, S. Stivala, A. Busacca DEIM Università di Palermo, via delle Scienze, Edifico 9, 90128,
Transistori ad effetto di campo con canale in grafene (GFET) aventi risposta fotoelettrica M. A. Giambra, E. Calandra, S. Stivala, A. Busacca DEIM Università di Palermo, via delle Scienze, Edifico 9, 90128,
COMPACT GRAPHENE FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR MODELING WITH QUANTUM CAPACITANCE EFFECTS
 COMPACT GRAPHENE FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR MODELING WITH QUANTUM CAPACITANCE EFFECTS Arya Raj K. and Bala Tripura Sundari B. Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Amrita Viswa Vidyapeetham,
COMPACT GRAPHENE FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR MODELING WITH QUANTUM CAPACITANCE EFFECTS Arya Raj K. and Bala Tripura Sundari B. Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Amrita Viswa Vidyapeetham,
EKV MOS Transistor Modelling & RF Application
 HP-RF MOS Modelling Workshop, Munich, February 15-16, 1999 EKV MOS Transistor Modelling & RF Application Matthias Bucher, Wladek Grabinski Electronics Laboratory (LEG) Swiss Federal Institute of Technology,
HP-RF MOS Modelling Workshop, Munich, February 15-16, 1999 EKV MOS Transistor Modelling & RF Application Matthias Bucher, Wladek Grabinski Electronics Laboratory (LEG) Swiss Federal Institute of Technology,
III-V CMOS: What have we learned from HEMTs? J. A. del Alamo, D.-H. Kim 1, T.-W. Kim, D. Jin, and D. A. Antoniadis
 III-V CMOS: What have we learned from HEMTs? J. A. del Alamo, D.-H. Kim 1, T.-W. Kim, D. Jin, and D. A. Antoniadis Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT 1 presently with Teledyne Scientific 23rd International
III-V CMOS: What have we learned from HEMTs? J. A. del Alamo, D.-H. Kim 1, T.-W. Kim, D. Jin, and D. A. Antoniadis Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT 1 presently with Teledyne Scientific 23rd International
H igh frequency and plastic electronics are expected to be among the first industrial entry points for
 OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: ELECTRONIC DEVICES ELECTRONICS, PHOTONICS AND DEVICE PHYSICS ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING ELECTRONIC PROPERTIES AND DEVICES Received 4 July 2013 Accepted 19 August 2013 Published
OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: ELECTRONIC DEVICES ELECTRONICS, PHOTONICS AND DEVICE PHYSICS ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING ELECTRONIC PROPERTIES AND DEVICES Received 4 July 2013 Accepted 19 August 2013 Published
The Devices. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. July 30, 2002
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics
 ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
VLSI Design and Simulation
 VLSI Design and Simulation Performance Characterization Topics Performance Characterization Resistance Estimation Capacitance Estimation Inductance Estimation Performance Characterization Inverter Voltage
VLSI Design and Simulation Performance Characterization Topics Performance Characterization Resistance Estimation Capacitance Estimation Inductance Estimation Performance Characterization Inverter Voltage
RF Performance Projections of Graphene FETs vs. Silicon MOSFETs
 1 RF Performance Projections of Graphene FETs vs. Silicon MOSFETs S. Rodriguez *, S. Vaziri *, M. Ostling *, A. Rusu *, E. Alarcon *,#, M.C. Lemme *1 * KTH Royal Institute of Technology, School of ICT,
1 RF Performance Projections of Graphene FETs vs. Silicon MOSFETs S. Rodriguez *, S. Vaziri *, M. Ostling *, A. Rusu *, E. Alarcon *,#, M.C. Lemme *1 * KTH Royal Institute of Technology, School of ICT,
Electronics with 2D Crystals: Scaling extender, or harbinger of new functions?
 Electronics with 2D Crystals: Scaling extender, or harbinger of new functions? 1 st Workshop on Data Abundant Systems Technology Stanford, April 2014 Debdeep Jena (djena@nd.edu) Electrical Engineering,
Electronics with 2D Crystals: Scaling extender, or harbinger of new functions? 1 st Workshop on Data Abundant Systems Technology Stanford, April 2014 Debdeep Jena (djena@nd.edu) Electrical Engineering,
ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies
 ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor 2 ρ Source channel charge density
ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor 2 ρ Source channel charge density
MOSFET: Introduction
 E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
MOS Transistor Theory
 MOS Transistor Theory So far, we have viewed a MOS transistor as an ideal switch (digital operation) Reality: less than ideal EE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
MOS Transistor Theory So far, we have viewed a MOS transistor as an ideal switch (digital operation) Reality: less than ideal EE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Field effect = Induction of an electronic charge due to an electric field Example: Planar capacitor
 JFETs AND MESFETs Introduction Field effect = Induction of an electronic charge due to an electric field Example: Planar capacitor Why would an FET made of a planar capacitor with two metal plates, as
JFETs AND MESFETs Introduction Field effect = Induction of an electronic charge due to an electric field Example: Planar capacitor Why would an FET made of a planar capacitor with two metal plates, as
MOS Transistor Properties Review
 MOS Transistor Properties Review 1 VLSI Chip Manufacturing Process Photolithography: transfer of mask patterns to the chip Diffusion or ion implantation: selective doping of Si substrate Oxidation: SiO
MOS Transistor Properties Review 1 VLSI Chip Manufacturing Process Photolithography: transfer of mask patterns to the chip Diffusion or ion implantation: selective doping of Si substrate Oxidation: SiO
Metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistors (2 lectures)
 Metal-ide-semiconductor field effect transistors ( lectures) MOS physics (brief in book) Current-voltage characteristics - pinch-off / channel length modulation - weak inversion - velocity saturation -
Metal-ide-semiconductor field effect transistors ( lectures) MOS physics (brief in book) Current-voltage characteristics - pinch-off / channel length modulation - weak inversion - velocity saturation -
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules
 GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux telligents Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules Mohamad Sawan et al. Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim! http://www.cours.polymtl.ca/gbm8320/! med-amine.miled@polymtl.ca!
GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux telligents Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules Mohamad Sawan et al. Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim! http://www.cours.polymtl.ca/gbm8320/! med-amine.miled@polymtl.ca!
Record Maximum Oscillation Frequency in C-face Epitaxial Graphene Transistors
 Record Maximum Oscillation Frequency in C-face Epitaxial Graphene Transistors Zelei Guo 1, Rui Dong 1, Partha Sarathi Chakraborty 2, Nelson Lourenco 2, James Palmer 1, Yike Hu 1, Ming Ruan 1, John Hankinson
Record Maximum Oscillation Frequency in C-face Epitaxial Graphene Transistors Zelei Guo 1, Rui Dong 1, Partha Sarathi Chakraborty 2, Nelson Lourenco 2, James Palmer 1, Yike Hu 1, Ming Ruan 1, John Hankinson
Normally-Off GaN Field Effect Power Transistors: Device Design and Process Technology Development
 Center for High Performance Power Electronics Normally-Off GaN Field Effect Power Transistors: Device Design and Process Technology Development Dr. Wu Lu (614-292-3462, lu.173@osu.edu) Dr. Siddharth Rajan
Center for High Performance Power Electronics Normally-Off GaN Field Effect Power Transistors: Device Design and Process Technology Development Dr. Wu Lu (614-292-3462, lu.173@osu.edu) Dr. Siddharth Rajan
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits. Lecture 3: MOS RC Model, CMOS Manufacturing
 EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 3: MOS RC Model, CMOS Manufacturing Agenda MOS Transistor: RC Model (pp. 104-113) S R on D CMOS Manufacturing Process (pp. 36-46) S S C GS G G C GD
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 3: MOS RC Model, CMOS Manufacturing Agenda MOS Transistor: RC Model (pp. 104-113) S R on D CMOS Manufacturing Process (pp. 36-46) S S C GS G G C GD
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits. Lecture 03: MOS Transistor
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
NiCl2 Solution concentration. Etching Duration. Aspect ratio. Experiment Atmosphere Temperature. Length(µm) Width (nm) Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa
 Experiment Atmosphere Temperature #1 # 2 # 3 # 4 # 5 # 6 # 7 # 8 # 9 # 10 Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1,
Experiment Atmosphere Temperature #1 # 2 # 3 # 4 # 5 # 6 # 7 # 8 # 9 # 10 Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1,
Explicit drain current, charge and capacitance model of graphene field-effect transistors. David Jiménez
 Explicit drain current, charge and capacitance model of graphene field-effect transistors David Jiménez Departament d'enginyeria Electrònica, Escola d'enginyeria, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, 08193-Bellaterra,
Explicit drain current, charge and capacitance model of graphene field-effect transistors David Jiménez Departament d'enginyeria Electrònica, Escola d'enginyeria, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, 08193-Bellaterra,
Supplementary Figure S1. AFM images of GraNRs grown with standard growth process. Each of these pictures show GraNRs prepared independently,
 Supplementary Figure S1. AFM images of GraNRs grown with standard growth process. Each of these pictures show GraNRs prepared independently, suggesting that the results is reproducible. Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Figure S1. AFM images of GraNRs grown with standard growth process. Each of these pictures show GraNRs prepared independently, suggesting that the results is reproducible. Supplementary Figure
Graphenea, Avenida de Tolosa 76, Donostia/San Sebastián, Spain 3
 https://doi.org/1.188/5-158/aaab96 OPEN ACCESS RECEIVED 1 November 17 REVISED 1 January 18 ACCEPTED FOR PUBLICATION January 18 PUBLISHED February 18 Original content from this work may be used under the
https://doi.org/1.188/5-158/aaab96 OPEN ACCESS RECEIVED 1 November 17 REVISED 1 January 18 ACCEPTED FOR PUBLICATION January 18 PUBLISHED February 18 Original content from this work may be used under the
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. Lecture 6 MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
BSIM-CMG Model. Berkeley Common-Gate Multi-Gate MOSFET Model
 BSIM-CMG Model Why BSIM-CMG Model When we reach the end of the technology roadmap for the classical CMOS, multigate (MG) CMOS structures will likely take up the baton. Numerous efforts are underway to
BSIM-CMG Model Why BSIM-CMG Model When we reach the end of the technology roadmap for the classical CMOS, multigate (MG) CMOS structures will likely take up the baton. Numerous efforts are underway to
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,5 18, 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,5 18, 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors
Graphene Transistors for Ambipolar Mixing at Microwave Frequencies. University Park, PA 16802, USA. University Park, PA 16802, USA
 Graphene Transistors for Ambipolar Mixing at Microwave Frequencies H. Madan a, M. J. Hollander a, J. A. Robinson b and S. Datta a a Department of Electrical Engineering, The Pennsylvania State University,
Graphene Transistors for Ambipolar Mixing at Microwave Frequencies H. Madan a, M. J. Hollander a, J. A. Robinson b and S. Datta a a Department of Electrical Engineering, The Pennsylvania State University,
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. The Devices. July 30, Devices.
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Beyond silicon electronics-fets with nanostructured graphene channels with high on-off ratio and highmobility
 Beyond silicon electronics-fets with nanostructured graphene channels with high on-off ratio and highmobility M.Dragoman 1, A.Dinescu 1, and D.Dragoman 2 1 National Institute for Research and Development
Beyond silicon electronics-fets with nanostructured graphene channels with high on-off ratio and highmobility M.Dragoman 1, A.Dinescu 1, and D.Dragoman 2 1 National Institute for Research and Development
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 26. MOSFET Small Signal Modelling
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 26 MOSFET Small Signal Modelling Lecture Outline MOSFET small signal behavior will be considered in the same way as for the diode and BJT Capacitances will be considered
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 26 MOSFET Small Signal Modelling Lecture Outline MOSFET small signal behavior will be considered in the same way as for the diode and BJT Capacitances will be considered
Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors
 Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits
 Page 1 of 10 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Exam No. 2 Thursday, November 5, 2009 7:30 to
Page 1 of 10 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Exam No. 2 Thursday, November 5, 2009 7:30 to
Electric Field-Dependent Charge-Carrier Velocity in Semiconducting Carbon. Nanotubes. Yung-Fu Chen and M. S. Fuhrer
 Electric Field-Dependent Charge-Carrier Velocity in Semiconducting Carbon Nanotubes Yung-Fu Chen and M. S. Fuhrer Department of Physics and Center for Superconductivity Research, University of Maryland,
Electric Field-Dependent Charge-Carrier Velocity in Semiconducting Carbon Nanotubes Yung-Fu Chen and M. S. Fuhrer Department of Physics and Center for Superconductivity Research, University of Maryland,
Scaling Issues in Planar FET: Dual Gate FET and FinFETs
 Scaling Issues in Planar FET: Dual Gate FET and FinFETs Lecture 12 Dr. Amr Bayoumi Fall 2014 Advanced Devices (EC760) Arab Academy for Science and Technology - Cairo 1 Outline Scaling Issues for Planar
Scaling Issues in Planar FET: Dual Gate FET and FinFETs Lecture 12 Dr. Amr Bayoumi Fall 2014 Advanced Devices (EC760) Arab Academy for Science and Technology - Cairo 1 Outline Scaling Issues for Planar
Philips Research apple PHILIPS
 c Electronics N.V. 1997 Modelling Compact of Submicron CMOS D.B.M. Klaassen Research Laboratories The Netherlands Eindhoven, contents accuracy and benchmark criteria new applications í RF modelling advanced
c Electronics N.V. 1997 Modelling Compact of Submicron CMOS D.B.M. Klaassen Research Laboratories The Netherlands Eindhoven, contents accuracy and benchmark criteria new applications í RF modelling advanced
Ultra-low noise HEMTs for deep cryogenic lowfrequency and high-impedance readout electronics
 Ultra-low noise HEMTs for deep cryogenic lowfrequency and high-impedance readout electronics Y. Jin, Q. Dong, Y.X. Liang, A. Cavanna, U. Gennser, L Couraud - Why cryoelectronics - Why HEMT - Noise characterization
Ultra-low noise HEMTs for deep cryogenic lowfrequency and high-impedance readout electronics Y. Jin, Q. Dong, Y.X. Liang, A. Cavanna, U. Gennser, L Couraud - Why cryoelectronics - Why HEMT - Noise characterization
GaN based transistors
 GaN based transistors S FP FP dielectric G SiO 2 Al x Ga 1-x N barrier i-gan Buffer i-sic D Transistors "The Transistor was probably the most important invention of the 20th Century The American Institute
GaN based transistors S FP FP dielectric G SiO 2 Al x Ga 1-x N barrier i-gan Buffer i-sic D Transistors "The Transistor was probably the most important invention of the 20th Century The American Institute
30 nm In 0.7 Ga 0.3 As Inverted-type HEMT with Reduced Gate Leakage Current for Logic Applications
 30 nm In 0.7 Ga 0.3 As Inverted-type HEMT with Reduced Gate Leakage Current for Logic Applications T.-W. Kim, D.-H. Kim* and J. A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories MIT Presently with Teledyne
30 nm In 0.7 Ga 0.3 As Inverted-type HEMT with Reduced Gate Leakage Current for Logic Applications T.-W. Kim, D.-H. Kim* and J. A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories MIT Presently with Teledyne
Supporting information
 Supporting information Design, Modeling and Fabrication of CVD Grown MoS 2 Circuits with E-Mode FETs for Large-Area Electronics Lili Yu 1*, Dina El-Damak 1*, Ujwal Radhakrishna 1, Xi Ling 1, Ahmad Zubair
Supporting information Design, Modeling and Fabrication of CVD Grown MoS 2 Circuits with E-Mode FETs for Large-Area Electronics Lili Yu 1*, Dina El-Damak 1*, Ujwal Radhakrishna 1, Xi Ling 1, Ahmad Zubair
MOSFET. Id-Vd curve. I DS Transfer curve V G. Lec. 8. Vd=1V. Saturation region. V Th
 MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT. Teledyne Scientific Company (TSC)
 Extraction of Virtual-Source Injection Velocity in sub-100 nm III-V HFETs 1,2) D.-H. Kim, 1) J. A. del Alamo, 1) D. A. Antoniadis and 2) B. Brar 1) Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT 2) Teledyne
Extraction of Virtual-Source Injection Velocity in sub-100 nm III-V HFETs 1,2) D.-H. Kim, 1) J. A. del Alamo, 1) D. A. Antoniadis and 2) B. Brar 1) Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT 2) Teledyne
ECE-305: Spring 2016 MOSFET IV
 ECE-305: Spring 2016 MOSFET IV Professor Mark Lundstrom Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA lundstro@purdue.edu Lundstrom s lecture notes: Lecture 4 4/7/16 outline
ECE-305: Spring 2016 MOSFET IV Professor Mark Lundstrom Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA lundstro@purdue.edu Lundstrom s lecture notes: Lecture 4 4/7/16 outline
L ECE 4211 UConn F. Jain Scaling Laws for NanoFETs Chapter 10 Logic Gate Scaling
 L13 04202017 ECE 4211 UConn F. Jain Scaling Laws for NanoFETs Chapter 10 Logic Gate Scaling Scaling laws: Generalized scaling (GS) p. 610 Design steps p.613 Nanotransistor issues (page 626) Degradation
L13 04202017 ECE 4211 UConn F. Jain Scaling Laws for NanoFETs Chapter 10 Logic Gate Scaling Scaling laws: Generalized scaling (GS) p. 610 Design steps p.613 Nanotransistor issues (page 626) Degradation
Scaling up Chemical Vapor Deposition Graphene to 300 mm Si substrates
 Scaling up Chemical Vapor Deposition Graphene to 300 mm Si substrates Co- Authors Aixtron Alex Jouvray Simon Buttress Gavin Dodge Ken Teo The work shown here has received partial funding from the European
Scaling up Chemical Vapor Deposition Graphene to 300 mm Si substrates Co- Authors Aixtron Alex Jouvray Simon Buttress Gavin Dodge Ken Teo The work shown here has received partial funding from the European
THE high-speed electronic properties of graphene, including
 94 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NANOTECHNOLOGY, VOL. 16, NO. 1, JANUARY 2017 Impact of Contact Resistance on the f T and f max of Graphene Versus MoS 2 Transistors Kyle D. Holland, Member, IEEE, Ahsan U. Alam,
94 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NANOTECHNOLOGY, VOL. 16, NO. 1, JANUARY 2017 Impact of Contact Resistance on the f T and f max of Graphene Versus MoS 2 Transistors Kyle D. Holland, Member, IEEE, Ahsan U. Alam,
Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET
 ECE 541/ME 541 Microelectronic Fabrication Techniques Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) What is a Transistor? A Switch! An MOS Transistor V GS V T V GS S Ron D
ECE 541/ME 541 Microelectronic Fabrication Techniques Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) What is a Transistor? A Switch! An MOS Transistor V GS V T V GS S Ron D
Introduction and Background
 Analog CMOS Integrated Circuit Design Introduction and Background Dr. Jawdat Abu-Taha Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Islamic University of Gaza jtaha@iugaza.edu.ps 1 Marking Assignments
Analog CMOS Integrated Circuit Design Introduction and Background Dr. Jawdat Abu-Taha Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Islamic University of Gaza jtaha@iugaza.edu.ps 1 Marking Assignments
ECE-305: Fall 2017 MOS Capacitors and Transistors
 ECE-305: Fall 2017 MOS Capacitors and Transistors Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals (SDF) Chapters 15+16 (pp. 525-530, 563-599) Professor Peter Bermel Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue
ECE-305: Fall 2017 MOS Capacitors and Transistors Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals (SDF) Chapters 15+16 (pp. 525-530, 563-599) Professor Peter Bermel Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices
 EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 10/30/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 17, 19 Announcements The next HW set is due on Thursday. Midterm 2 is next week!!!! Threshold and Subthreshold
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 10/30/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 17, 19 Announcements The next HW set is due on Thursday. Midterm 2 is next week!!!! Threshold and Subthreshold
Manufacture of Nanostructures for Power Electronics Applications
 Manufacture of Nanostructures for Power Electronics Applications Brian Hunt and Jon Lai Etamota Corporation 2672 E. Walnut St. Pasadena, CA 91107 APEC, Palm Springs Feb. 23rd, 2010 1 Background Outline
Manufacture of Nanostructures for Power Electronics Applications Brian Hunt and Jon Lai Etamota Corporation 2672 E. Walnut St. Pasadena, CA 91107 APEC, Palm Springs Feb. 23rd, 2010 1 Background Outline
Section 12: Intro to Devices
 Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals EE143 Ali Javey Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals EE143 Ali Javey Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
ENEE 359a Digital VLSI Design
 SLIDE 1 ENEE 359a Digital VLSI Design & Logical Effort Prof. blj@ece.umd.edu Credit where credit is due: Slides contain original artwork ( Jacob 2004) as well as material taken liberally from Irwin & Vijay
SLIDE 1 ENEE 359a Digital VLSI Design & Logical Effort Prof. blj@ece.umd.edu Credit where credit is due: Slides contain original artwork ( Jacob 2004) as well as material taken liberally from Irwin & Vijay
Electrical Degradation of InAlAs/InGaAs Metamorphic High-Electron Mobility Transistors
 Electrical Degradation of InAlAs/InGaAs Metamorphic High-Electron Mobility Transistors S. D. Mertens and J.A. del Alamo Massachusetts Institute of Technology Sponsor: Agilent Technologies Outline Introduction
Electrical Degradation of InAlAs/InGaAs Metamorphic High-Electron Mobility Transistors S. D. Mertens and J.A. del Alamo Massachusetts Institute of Technology Sponsor: Agilent Technologies Outline Introduction
EE 230 Lecture 31. THE MOS TRANSISTOR Model Simplifcations THE Bipolar Junction TRANSISTOR
 EE 23 Lecture 3 THE MOS TRANSISTOR Model Simplifcations THE Bipolar Junction TRANSISTOR Quiz 3 Determine I X. Assume W=u, L=2u, V T =V, uc OX = - 4 A/V 2, λ= And the number is? 3 8 5 2? 6 4 9 7 Quiz 3
EE 23 Lecture 3 THE MOS TRANSISTOR Model Simplifcations THE Bipolar Junction TRANSISTOR Quiz 3 Determine I X. Assume W=u, L=2u, V T =V, uc OX = - 4 A/V 2, λ= And the number is? 3 8 5 2? 6 4 9 7 Quiz 3
Self-Aligned InGaAs FinFETs with 5-nm Fin-Width and 5-nm Gate-Contact Separation
 Self-Aligned InGaAs FinFETs with 5-nm Fin-Width and 5-nm Gate-Contact Separation Alon Vardi, Lisa Kong, Wenjie Lu, Xiaowei Cai, Xin Zhao, Jesús Grajal* and Jesús A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories,
Self-Aligned InGaAs FinFETs with 5-nm Fin-Width and 5-nm Gate-Contact Separation Alon Vardi, Lisa Kong, Wenjie Lu, Xiaowei Cai, Xin Zhao, Jesús Grajal* and Jesús A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories,
Contact Engineering of Two-Dimensional Layered Semiconductors beyond Graphene
 Contact Engineering of Two-Dimensional Layered Semiconductors beyond Graphene Zhixian Zhou Department of Physics and Astronomy Wayne State University Detroit, Michigan Outline Introduction Ionic liquid
Contact Engineering of Two-Dimensional Layered Semiconductors beyond Graphene Zhixian Zhou Department of Physics and Astronomy Wayne State University Detroit, Michigan Outline Introduction Ionic liquid
CMOS INVERTER. Last Lecture. Metrics for qualifying digital circuits. »Cost» Reliability» Speed (delay)»performance
 CMOS INVERTER Last Lecture Metrics for qualifying digital circuits»cost» Reliability» Speed (delay)»performance 1 Today s lecture The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis
CMOS INVERTER Last Lecture Metrics for qualifying digital circuits»cost» Reliability» Speed (delay)»performance 1 Today s lecture The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis
The Critical Role of Quantum Capacitance in Compact Modeling of Nano-Scaled and Nanoelectronic Devices
 The Critical Role of Quantum Capacitance in Compact Modeling of Nano-Scaled and Nanoelectronic Devices Zhiping Yu and Jinyu Zhang Institute of Microelectronics Tsinghua University, Beijing, China yuzhip@tsinghua.edu.cn
The Critical Role of Quantum Capacitance in Compact Modeling of Nano-Scaled and Nanoelectronic Devices Zhiping Yu and Jinyu Zhang Institute of Microelectronics Tsinghua University, Beijing, China yuzhip@tsinghua.edu.cn
Technology Development for InGaAs/InP-channel MOSFETs
 MRS Spring Symposium, Tutorial: Advanced CMOS Substrates, Devices, Reliability, and Characterization, April 13, 2009, San Francisco Technology Development for InGaAs/InP-channel MOSFETs Mark Rodwell University
MRS Spring Symposium, Tutorial: Advanced CMOS Substrates, Devices, Reliability, and Characterization, April 13, 2009, San Francisco Technology Development for InGaAs/InP-channel MOSFETs Mark Rodwell University
R. Ludwig and G. Bogdanov RF Circuit Design: Theory and Applications 2 nd edition. Figures for Chapter 6
 R. Ludwig and G. Bogdanov RF Circuit Design: Theory and Applications 2 nd edition Figures for Chapter 6 Free electron Conduction band Hole W g W C Forbidden Band or Bandgap W V Electron energy Hole Valence
R. Ludwig and G. Bogdanov RF Circuit Design: Theory and Applications 2 nd edition Figures for Chapter 6 Free electron Conduction band Hole W g W C Forbidden Band or Bandgap W V Electron energy Hole Valence
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
Understanding the effect of n-type and p-type doping in the channel of graphene nanoribbon transistor
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 39, No. 5, September 2016, pp. 1303 1309. DOI 10.1007/s12034-016-1277-9 c Indian Academy of Sciences. Understanding the effect of n-type and p-type doping in the channel of graphene
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 39, No. 5, September 2016, pp. 1303 1309. DOI 10.1007/s12034-016-1277-9 c Indian Academy of Sciences. Understanding the effect of n-type and p-type doping in the channel of graphene
Introduction to CMOS VLSI. Chapter 2: CMOS Transistor Theory. Harris, 2004 Updated by Li Chen, Outline
 Introduction to MOS VLSI Design hapter : MOS Transistor Theory copyright@david Harris, 004 Updated by Li hen, 010 Outline Introduction MOS apacitor nmos IV haracteristics pmos IV haracteristics Gate and
Introduction to MOS VLSI Design hapter : MOS Transistor Theory copyright@david Harris, 004 Updated by Li hen, 010 Outline Introduction MOS apacitor nmos IV haracteristics pmos IV haracteristics Gate and
Self-heat Modeling of Multi-finger n-mosfets for RF-CMOS Applications
 Self-heat Modeling of Multi-finger n-mosfets for RF-CMOS Applications Hitoshi Aoki and Haruo Kobayashi Faculty of Science and Technology, Gunma University (RMO2D-3) Outline Research Background Purposes
Self-heat Modeling of Multi-finger n-mosfets for RF-CMOS Applications Hitoshi Aoki and Haruo Kobayashi Faculty of Science and Technology, Gunma University (RMO2D-3) Outline Research Background Purposes
Carbon Nanotube Electronics
 Carbon Nanotube Electronics Jeorg Appenzeller, Phaedon Avouris, Vincent Derycke, Stefan Heinz, Richard Martel, Marko Radosavljevic, Jerry Tersoff, Shalom Wind H.-S. Philip Wong hspwong@us.ibm.com IBM T.J.
Carbon Nanotube Electronics Jeorg Appenzeller, Phaedon Avouris, Vincent Derycke, Stefan Heinz, Richard Martel, Marko Radosavljevic, Jerry Tersoff, Shalom Wind H.-S. Philip Wong hspwong@us.ibm.com IBM T.J.
Extensive reading materials on reserve, including
 Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals EE143 Ali Javey Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals EE143 Ali Javey Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
crystals were phase-pure as determined by x-ray diffraction. Atomically thin MoS 2 flakes were
 Nano Letters (214) Supplementary Information for High Mobility WSe 2 p- and n-type Field Effect Transistors Contacted by Highly Doped Graphene for Low-Resistance Contacts Hsun-Jen Chuang, Xuebin Tan, Nirmal
Nano Letters (214) Supplementary Information for High Mobility WSe 2 p- and n-type Field Effect Transistors Contacted by Highly Doped Graphene for Low-Resistance Contacts Hsun-Jen Chuang, Xuebin Tan, Nirmal
A. Optimizing the growth conditions of large-scale graphene films
 1 A. Optimizing the growth conditions of large-scale graphene films Figure S1. Optical microscope images of graphene films transferred on 300 nm SiO 2 /Si substrates. a, Images of the graphene films grown
1 A. Optimizing the growth conditions of large-scale graphene films Figure S1. Optical microscope images of graphene films transferred on 300 nm SiO 2 /Si substrates. a, Images of the graphene films grown
The Prospects for III-Vs
 10 nm CMOS: The Prospects for III-Vs J. A. del Alamo, Dae-Hyun Kim 1, Donghyun Jin, and Taewoo Kim Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT 1 Presently with Teledyne Scientific 2010 European Materials
10 nm CMOS: The Prospects for III-Vs J. A. del Alamo, Dae-Hyun Kim 1, Donghyun Jin, and Taewoo Kim Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT 1 Presently with Teledyne Scientific 2010 European Materials
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Controllable Atmospheric Pressure Growth of Mono-layer, Bi-layer and Tri-layer
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Controllable Atmospheric Pressure Growth of Mono-layer, Bi-layer and Tri-layer
Operation and Modeling of. The MOS Transistor. Second Edition. Yannis Tsividis Columbia University. New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Operation and Modeling of The MOS Transistor Second Edition Yannis Tsividis Columbia University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Chapter 1 l.l 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Chapter 2 2.1 2.2
Operation and Modeling of The MOS Transistor Second Edition Yannis Tsividis Columbia University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Chapter 1 l.l 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Chapter 2 2.1 2.2
EE410 vs. Advanced CMOS Structures
 EE410 vs. Advanced CMOS Structures Prof. Krishna S Department of Electrical Engineering S 1 EE410 CMOS Structure P + poly-si N + poly-si Al/Si alloy LPCVD PSG P + P + N + N + PMOS N-substrate NMOS P-well
EE410 vs. Advanced CMOS Structures Prof. Krishna S Department of Electrical Engineering S 1 EE410 CMOS Structure P + poly-si N + poly-si Al/Si alloy LPCVD PSG P + P + N + N + PMOS N-substrate NMOS P-well
The Physical Structure (NMOS)
 The Physical Structure (NMOS) Al SiO2 Field Oxide Gate oxide S n+ Polysilicon Gate Al SiO2 SiO2 D n+ L channel P Substrate Field Oxide contact Metal (S) n+ (G) L W n+ (D) Poly 1 Transistor Resistance Two
The Physical Structure (NMOS) Al SiO2 Field Oxide Gate oxide S n+ Polysilicon Gate Al SiO2 SiO2 D n+ L channel P Substrate Field Oxide contact Metal (S) n+ (G) L W n+ (D) Poly 1 Transistor Resistance Two
ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors
 ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors Spring 2018 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu NMOS Transistor NMOS Transistor N-Channel MOSFET Built on p-type
ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors Spring 2018 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu NMOS Transistor NMOS Transistor N-Channel MOSFET Built on p-type
Research Article Fabrication of Self-Aligned Graphene FETs with Low Fringing Capacitance and Series Resistance
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Electronics Volume 212, Article ID 89148, 7 pages doi:1.542/212/89148 Research Article Fabrication of Self-Aligned raphene FETs with Low Fringing Capacitance
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Electronics Volume 212, Article ID 89148, 7 pages doi:1.542/212/89148 Research Article Fabrication of Self-Aligned raphene FETs with Low Fringing Capacitance
EE 330 Lecture 17. MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow
 EE 330 Lecture 17 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Lecture Limitations of Existing Models V DD V OUT V OUT V DD?? V IN V OUT V IN V IN V DD Switch-Level Models V DD Simple square-law
EE 330 Lecture 17 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Lecture Limitations of Existing Models V DD V OUT V OUT V DD?? V IN V OUT V IN V IN V DD Switch-Level Models V DD Simple square-law
Supplementary Methods A. Sample fabrication
 Supplementary Methods A. Sample fabrication Supplementary Figure 1(a) shows the SEM photograph of a typical sample, with three suspended graphene resonators in an array. The cross-section schematic is
Supplementary Methods A. Sample fabrication Supplementary Figure 1(a) shows the SEM photograph of a typical sample, with three suspended graphene resonators in an array. The cross-section schematic is
Graphene Canada Montreal Oct. 16, 2015 (International Year of Light)
 Luminescence Properties of Graphene A. Beltaos 1,2,3, A. Bergren 1, K. Bosnick 1, N. Pekas 1, A. Matković 4, A. Meldrum 2 1 National Institute for Nanotechnology (NINT), 11421 Saskatchewan Drive, Edmonton,
Luminescence Properties of Graphene A. Beltaos 1,2,3, A. Bergren 1, K. Bosnick 1, N. Pekas 1, A. Matković 4, A. Meldrum 2 1 National Institute for Nanotechnology (NINT), 11421 Saskatchewan Drive, Edmonton,
EE105 - Fall 2005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE105 - Fall 005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits ecture 7 MOS Transistor Announcements Homework 3, due today Homework 4 due next week ab this week Reading: Chapter 4 1 ecture Material ast lecture
EE105 - Fall 005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits ecture 7 MOS Transistor Announcements Homework 3, due today Homework 4 due next week ab this week Reading: Chapter 4 1 ecture Material ast lecture
SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom. ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: Spring 2016 April 18, 2016 M. A. Alam and M.S. Lundstrom Purdue University
 NAME: PUID: SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 18, 2016 M A Alam and MS Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam You may use a calculator and the formula
NAME: PUID: SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 18, 2016 M A Alam and MS Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam You may use a calculator and the formula
Supporting Information. by Hexagonal Boron Nitride
 Supporting Information High Velocity Saturation in Graphene Encapsulated by Hexagonal Boron Nitride Megan A. Yamoah 1,2,, Wenmin Yang 1,3, Eric Pop 4,5,6, David Goldhaber-Gordon 1 * 1 Department of Physics,
Supporting Information High Velocity Saturation in Graphene Encapsulated by Hexagonal Boron Nitride Megan A. Yamoah 1,2,, Wenmin Yang 1,3, Eric Pop 4,5,6, David Goldhaber-Gordon 1 * 1 Department of Physics,
Layout-Optimization of Power-Devices. Frederik Vanaverbeke, J. Das, H. Oprins, J. Derluyn, M. Germain, W. De Raedt
 Layout-Optimization of Power-Devices Frederik Vanaverbeke, J. Das, H. Oprins, J. Derluyn, M. Germain, W. De Raedt Outline 1. Problem + Nomenclature 2. Unit gatewidth 3. Thermal 4. Number of unit cells
Layout-Optimization of Power-Devices Frederik Vanaverbeke, J. Das, H. Oprins, J. Derluyn, M. Germain, W. De Raedt Outline 1. Problem + Nomenclature 2. Unit gatewidth 3. Thermal 4. Number of unit cells
Erik Lind
 High-Speed Devices, 2011 Erik Lind (Erik.Lind@ftf.lth.se) Course consists of: 30 h Lectures (H322, and Fys B check schedule) 8h Excercises 2x2h+4h Lab Excercises (2 Computer simulations, 4 RF measurment
High-Speed Devices, 2011 Erik Lind (Erik.Lind@ftf.lth.se) Course consists of: 30 h Lectures (H322, and Fys B check schedule) 8h Excercises 2x2h+4h Lab Excercises (2 Computer simulations, 4 RF measurment
Investigation of the Thermal Noise of MOS Transistors under Analog and RF Operating Conditions
 Investigation of the Thermal Noise of MOS Transistors under Analog and RF Operating Conditions Ralf Brederlow 1, Georg Wenig 2, and Roland Thewes 1 1 Infineon Technologies, Corporate Research, 2 Technical
Investigation of the Thermal Noise of MOS Transistors under Analog and RF Operating Conditions Ralf Brederlow 1, Georg Wenig 2, and Roland Thewes 1 1 Infineon Technologies, Corporate Research, 2 Technical
Digital Microelectronic Circuits ( )
 Digital Microelectronic ircuits (361-1-3021 ) Presented by: Dr. Alex Fish Lecture 5: Parasitic apacitance and Driving a Load 1 Motivation Thus far, we have learned how to model our essential building block,
Digital Microelectronic ircuits (361-1-3021 ) Presented by: Dr. Alex Fish Lecture 5: Parasitic apacitance and Driving a Load 1 Motivation Thus far, we have learned how to model our essential building block,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Molecular structures of functional materials involved in our SGOTFT devices. Supplementary Figure 2 Capacitance measurements of a SGOTFT device. (a) Capacitance
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Molecular structures of functional materials involved in our SGOTFT devices. Supplementary Figure 2 Capacitance measurements of a SGOTFT device. (a) Capacitance
GHZ ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF CARBON NANOTUBES ON SILICON DIOXIDE MICRO BRIDGES
 GHZ ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF CARBON NANOTUBES ON SILICON DIOXIDE MICRO BRIDGES SHENG F. YEN 1, HAROON LAIS 1, ZHEN YU 1, SHENGDONG LI 1, WILLIAM C. TANG 1,2, AND PETER J. BURKE 1,2 1 Electrical Engineering
GHZ ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF CARBON NANOTUBES ON SILICON DIOXIDE MICRO BRIDGES SHENG F. YEN 1, HAROON LAIS 1, ZHEN YU 1, SHENGDONG LI 1, WILLIAM C. TANG 1,2, AND PETER J. BURKE 1,2 1 Electrical Engineering
