Production of Rubber Seed Pericarp Based Activated Carbon Using Microwave-Induced Different Chemical Activating Agent
|
|
|
- Griselda Ruth Porter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 7, July Production of Rubber Seed Pericarp Based Activated Carbon Using Microwave-Induced Different Chemical Activating Agent D. Anis 1, 2, M.A.M. Ishak 2, A.G. Zaidi, I. Khudzir 1, M.N. Iqbaldin 1,2, Uwaisulqarni M. Osman 3, W.I. Nawawi 2 * * 1 Faculty of Applied Sciences, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah Alam, Selangor, Malaysia. 2 Fossil fuel and Biomass Research Group, Faculty of Applied Sciences, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Arau, Perlis, Malaysia. 3 School of Fundamental Sciences, Universiti Malaysia Terengganu, Kuala Terengganu, Terengganu, Malaysia. Abstract- Microwave assisted activated carbon from rubber seed pericarp (RSP) was successfully produced by using three different chemical activating agents of ZnCl 2, KOH, and H 3 PO 4. The process was carried out at 600W of irradiation power for 20 min. The absorption study was applied for these modified activated carbon samples under cationic methylene blue (MB) dye. The Carbonisation of RSP using ZnCl 2 (RSP-ZnCl) as activating agent was found the best as compared among the rest which high BET surface area, total pore volume and iodine number were m²/g, cc/g and mg/g respectively. The adsorption capacity of RSP-ZnCl under MB was ca mg g -1. This finding showed the feasibility of preparing activated carbon from RSP using ZnCl 2 activating agent via by microwave carbonisation technique. Index Terms- Rubber seed Pericarp, Activated Carbon, Chemical Activation, Microwave irradiation, Methylene Blue, A I. INTRODUCTION ctivated carbon is one of the most important materials that have been widely used in many industrial fields of applications due to its excellent pore structure, high surface area and temperature stability [1, 2]. Yang et al. [3] state that the quality of the resulting activated carbon influenced by the raw material characteristics. Many research and study have been done in the production of activated carbon by using variety of type of starting material. Raw materials for the production of activated carbon include number of carbonaceous material such as wood, peat, brown coal, bituminous coal, lignite, coconut shells, almond shells, pits from peaches and other fruit. Activated carbon from rice husk for example was studied by Kalderis et al. [4], Kumagai et al. [5], Chen et al. [6], and Yan et al. [7]. Various types of nut shell such as pistachio nut shell, almond nut shell, Syzygium jambolanum nut shell and macadamia nut shell were also being used as precursor for activated carbon. The best of our knowledge, no investigations have reported by using Rubber Seed Pericarp (RSP) as precursor to produce activated carbon. Rubber seed pericarp (RSP) is a biomass waste and currently has no commercial value [8]. This carbonaceous material is highly potential to be converted into useful, high-value adsorbent. According to Eka [9], Rubber tree (Havea brasiliensis) starts to bear fruits at four years of age. Normally, each fruit have about three or four seed, which fall to the ground when the fruit ripens and splits. Each tree yields about 800 seeds (1.3 kg) twice a year. A rubber plantation is estimated to be able produced about kg rubber seed per ha per year, and these are normally regarded as waste. Malaysia is known as a one of the main rubber producing country that has 1.7 million hectares of rubber plantation. Therefore, based on estimate average of 1000 kg seed per ha/yr, annually production of rubber seeds in Malaysia would be 1.7 million metric tons. Usually, the pip of rubber seed is sent to oil-mills, but a huge amount of rubber seed pericarp leave as agricultural waste and becomes an environmental problem. Therefore, one of the solutions for this situation is to reuse this waste to produce activated carbon. Currently, high quality activated carbon from biomass is produced by using the conventional slow heating pyrolysis technique. This technique however, consumed much energy and took more than 6 hours to complete [10]. Another new promising technique that can produce equally high quality activated carbon that utilizes relatively less energy in shorter time is by using microwave irradiation. Microwave irradiation uses electromagnetic waves that are directly absorbed within the molecules of a material causing them to vibrate and agitate rapidly that result to an increase in temperature [11]. This microwave irradiation involves volumetric heating since it is possible for the entire volume of bulk material to be heated rapidly [10-12]. Preparation of activated carbons under microwave radiation from materials such as pitch, tobacco stem, waste tea, wood and cotton stalk have been reported in previous studies [13-17] which has evidenced that the microwave heating has the advantages over conventional heat treatment method such as high heating rate easy control of the heating process, and no direct contact between the heating source and the materials. Microwave radiation can heat or cause arcing in many objects, powdered samples can absorb such radiation and be heated efficiently. The main advantage of using microwave heating is that the treatment time can be considerably reduced, which in many cases represents a reduction in the energy consumption. In addition, the consumption of gases (N 2 ) used in the treatment can also be reduced toward % if calculate based on the heating and cooling time during the reaction. In view of the possible advantages associated with the use of microwave heating systems, it was therefore we propose to study the effect of microwave heating combine with three different chemical activating agents i.e. ZnCl 2, KOH, and H 3 PO 4 treatment in more
2 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 7, July detail using a carbon precursor selected (Rubber Seed Pericarp) with a better defined microstructure than that used previously. Matos et al. [18] claimed that the activation process is the most important part in the production of activated carbon. This process creates or increases porosity on the surface carbon materials. Generally, activated carbon can be prepared by one of the following two methods of activation which are by physical or chemical activation. Physical activation is a two-step process and relatively slow. It involves carbonization of a carbonaceous material followed by the activation of the resulting char at elevated temperature in the presence of suitable oxidizing gases such as carbon dioxide, steam, air or their mixtures [19, 20]. In chemical activation carbonization is done after the addition of substances which restrict the formation of tar. This is a single operation of activated carbon preparation. In this method, an activating agent like H 3 PO 4, ZnCl 2, and KOH are applied in large quantities and has to be removed in order to reveal the porous structure and to make the activated carbon to be accessible [21, 22]. Among the available choices of impregnating activating agents, KOH that has been reported to be more suitable for coal based precursors, while ZnCl 2 and H 3 PO 4 are widely used for biomass based lignocellulosic precursors [23, 24]. Although large varieties of precursors have been used to produce activated carbon, the work related to the utilization of rubber seed pericarp as precursor has not been reported in literature. Hence, our study focused on the production of RSP activated carbon using different chemical activating agent. The activated carbon produced was evaluated based on product yield, iodine number, methylene blue adsorption capacity, and surface area development. These findings will be of useful in producing activated carbon from RSP for solid filtration or liquid/gas adsorbent material. II. MATERIALS AND EXPERIMENTAL METHODS A. Sample preparation RSP were collected from the local rubber estate located in Jitra, Kedah, Malaysia. RSP were washed with distilled water to remove foreign materials and dried in an oven at 100 C for 24 hours. The dried RSP were pulverised to a fine powder using grinder and sieved through progressively finer screen to obtain particle size of < 2.0 mm. Sieving were accomplished by shaking the RSP powder in an Endecotts Shaker Model EFL2 for about 30 mins. The fined RSP were stored in an airtight container for further used. The proximate and ultimate analyses of powdered RSP and rubber seed pericarps activated carbon (RSPAC) were measured using thermal gravimetric analyser (TGA) and elemental analyser (EA) respectively [25]. B. Microwave-Carbonization Processes A weight amount (10.0 ± 0.01g) of RSP sample was mixed with 67 ml of different activating agents (KOH, ZnCl 2 and H 3 PO 4 ) solution at various impregnation ratios (0.4 to 2.0 g g -1 ) for 24 hr at room temperature. The impregnated sample was carbonized using a microwave oven at 600W for 20 min of irradiation time in the presence of nitrogen gas. Fig. 1 shows the schematic diagram for microwave irradiation treatment process. The irradiated samples were cooled at room temperature and washed with 0.1M HCl and left for overnight to isolate the residual activator. The samples were then washed with distilled water to remove residual organic matter, and neutralised with base until the ph of filtrate reached 6.5-7, and dried in an oven at 110 C for 24 hours. N 2 gas Gas in Microwave Gas out Quartz reactor Sample Fig. 1. Schematic diagrams of microwave unit for the preparation of RSPAC. C. Analysis of Percent Yield and Iodine Number The efficiency of activated carbon produced from RSP is evaluated based on product yield and iodine number [26]. The percent yield and iodine number of prepared activated carbon were calculated as follows: ( ) (1) ( ) ( ) ( ) (2) Where Wf and Wo are the weight of activated carbon and dried rubber seed pericarp respectively (g). X/M is the iodine absorbed per gram of carbon (mg g -1 ), A is the normality of standard iodine with , B is the normality of sodium thiosulfate with , DF is the dilution factor, S is volume of sodium thiosulfate (ml) and M are the mass of carbon used (g). Iodine number is use to determine the adsorption capacity of activated carbon and it s indicate the porosity of the activated carbon [27]. Iodine number provides an approximation for the surface area and microporosity of actived carbon with good precision. The analysis of iodine was done based on the standard test method ASTM D4607. D. Batch Adsorption studies MB is a strong adsorption onto solid used in a wide variety of application. It was known as a common substances used in dying process due to its potential risk towards the survival aquatic compartment, ecosystem and environmental pollution [28]. Thus, it was chosen in this study. MB is a heterocyclic aromatic chemical component with a chemical formula of C 16 H 18 N 3 and a molecular weight of g mol -1 [29] Fig. 2 shows the chemical structure for MB. MB adsorption experiments were conducted to determine the optimum quality of the adsorbent for
3 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 7, July maximum adsorption [30]. The MB solution for adsorption was prepared by dissolving MB in deionised water without ph adjustment. The adsorption test were carried out in a set of 250 ml conical flask containing 0.2 g of adsorbent and 150 ml dyes solutions with various initial concentrations range of mg L -1. The flask was placed on a shaker setting of 120 rpm for 24 hours to reach equilibrium. Then the samples were filtered to remove carbon and the residual concentration of MB in the filtrate was analyzed using Spectrophotometer at 664 nm wavelength. The MB uptake at equilibrium qₑ (mg g -1 ) was computed using equation 3. Fig. 2. Chemical Structure for Methylene Blue (MB) ( ) Where C o and C e are the initial and equilibrium concentrations of dye (mg L -1 ) in the solution, V is the volume of the solution (L), and W is mass of the adsorbent used (g). While, equation 4 was used to calculate the percentage of MB adsorption based on the initial and equilibrium MB concentration. (3) ( ) (4) The pore size and structure of the activated carbon was determined using N 2 adsorption Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) and scanning electron microscope (SEM) respectively. III. RESULT AND DISCUSSION Table 1 showed that waste RSP material is a carbonaceous material that contained high composition of carbon and high potential to become activated carbon. The percentage of carbon significantly increased after carbonization and activation process due to release of volatile matter during the activation as proven by decreased of volatile content in RSPAC. However, with reference to table 1, the RSPAC treated with ZnCl 2 produced the lowest amount of ash at 4.08% with high percent of fixed carbon at 45.06% in comparison to RSPAC treated with KOH and H 3 PO 4, respectively. Table. 1. Proximate and ultimate analyses of raw rubber seed pericarp (RSP) and rubber seed pericarp activated carbon (RSPAC) with different activating agent Analysis RSP RSPAC KOH H 3 PO 4 ZnCl 2 Proximate Moisture Volatile Matter Fixed Carbon Ash Ultimate Carbon Hydrogen Nitrogen Sulphur Oxygen* Notes : * calculated by difference
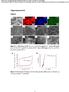
4 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 7, July A. Textural Characteristics of RSPAC Fig. 3 compares the SEM micrographs of RSP and RSPAC treated with three different activating agents. The SEM micrograph of RSP (Figure 3a) shows smooth surface with no pore development. Comparatively, the SEM micrographs of RSPAC treated with different activating agents show pores development as depicted in figures 3 (b), (c) and (d). This phenomenon is mainly due to the released of volatile matter and reaction between activating agent and the carbon atom in the precursor [26, 32]. The SEM micrograph for ZnCl 2 treated RSPAC, however reveals high distribution of pore development. Comparatively, the KOH and H 3 PO 4 treated RSPAC exhibit some porosity with the latter showed development of hollow and rugged surfaces, respectively. Apparently, the mean pore diameter of all the treated RSPAC were about the same in the range of nm. In addition, the effect of pore development was also reflected on the surface area development. The ZnCl 2 treated RSPAC has the highest surface area of 1689 m 2 g -1 in comparison to KOH and H 3 PO 4 treated RSPAC at 392 m 2 g -1 and 1589 m 2 g -1, respectively. Therefore, the ZnCl 2 is found that to be an effective activating agent to produce activated carbon from RSP with high-surface area. a) b) 10µm 10µm Scale 10µm, Mag : 1000x, EHT : 20kV Scale 10µm, Mag : 1000x, EHT : 20kV c) d) 10µm 10µm Scale 10µm, Mag : 1000x, EHT : 20kV Scale 10µm, Mag : 1000x, EHT : 20kV Fig. 3. SEM micrographs (1000x) of a) RSP and RSPAC treated with b) ZnCl 2 c) KOH and d) H 3 PO 4 Table 2. Optimum surface characteristics of rubber seed pericarp activated carbon (RSPAC) treated with different chemical activating agents Analyses RSPAC KOH H 3 PO 4 ZnCl 2 Percent Yield (%) Iodine Number (mg/g) MB Adsorption (mg/g) BET surface area (m 2 /g)
5 Iodine Number (mg/g) Yield ( %) Adsorption capacity (mg/g) International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 7, July B. Percent Yield and Iodine Number The percent yield and iodine number of RSPAC prepared by different activating agents is shown in Fig. 4. Expectedly, the results showed that KOH produced the lowest percent yield of activated carbon followed by ZnCl₂ and H₃PO₄. RSP is a lignocellulosic material, with hemicelluloses, cellulose and lignin as the main components; and this type of material has been reported suitable to be treated with ZnCl 2 and H 3 PO 4 activating agents [24]. It can be seen that the yields of activated carbon decrease with increasing impregnation ratios. The decrease in product yield might due to continuous release of volatile matters from the material creating more pores [26]. Further, it can be seen that the decrease in product yield correlates with increasing in iodine number, indicating an increasing in adsorption capacity of the materials. From fig. 4, it also shows that iodine number increase with increasing the impregnation ratio of activating agent used. This is due to electrolytic action terms as swelling in the molecular structure of cellulose [26]. However, according to Ahmed et al. [26] they claimed that high concentration of activator could also lead to excessive dehydration and destruction of micropores that form larger pores and reduce adsorption efficiency. C. Methylene Blue (MB) Adsorption Analysis MB is a relatively large molecule and often employed as adsorbates to evaluate the efficiency of activated carbon for removal of dyes. Fig. 5 compares the adsorption capacity of treated RSPAC with ZnCl 2, KOH and H 3 PO 4. The MB adsorption capacity was conducted based on the approximation of the highest iodine number to give the highest amount of adsorption. Apparently, the MB adsorption capacity for RSPAC treated with ZnCl 2 produced the highest amount of adsorption capacity with comparison to KOH and H 3 PO 4 treated RSPAC. The amount of MB adsorption increase from about to mg g -1 with increasing ratio of ZnCl 2 from 0.4 to 1.6, and decrease slightly at ratio of 2.0. Similar trend could be observed with KOH and H 3 PO 4. The fact that by increasing the ratio of activating agent, more pores would be created, however as the ratio arrives at the optimum value, the pores would be widened and burnt off [14, 26]. Therefore, the adsorption capacity of activated carbon would increase to a certain value and then decreased with ratio of activating agent a) KOH KOH Zncl₂ H₃PO₄ ZnCl₂ H₃PO₄ Impregnation Ratio (g/g) b) Impregnation Ratio (g/g) KOH ZnCl₂ H₃PO₄ Fig. 5. MB adsorption capacity for RSPAC treated with ZnCl 2, KOH and H 3 PO 4. IV. CONCLUSION A study of the textural and adsorption characteristic of the activated carbon reveals the feasibility to prepare activated carbon from rubber seed pericarp (RSP) via microwave irradiation method using ZnCl 2, as activating agent. The activation process was conducted for 20 mins at the operating power of 600W resulted in a yield of 30.69% and iodine number of mg/g. While the BET surface area, total pore volume and adsorption capacity of MB were m²/g, cc g -1 and mg g -1 respectively. This research would significantly contribute to new findings in term of activated carbon production from abandon biomass waste using new heating technique Impregnation ratio (g/g) Fig. 4. a) Percent yield and b) Iodine number of treated RSPAC with different activating agent. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The authors would like to thank the Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation (MOSTI) for supporting this project under FRGS grant (600-RMI/FRGS/5/3/15/2012). We would like also to acknowledge Ministry of Higher Education (KTP) for My Master fellowship funding Noor Anis Deraman for this research.
6 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 7, July REFERENCES [1] W.M.A.W. Daud, A.H. Houshamnd, Textural characteristics, surface chemistry and oxidation of activated carbon, Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry, 19 (2010) [2] M. Rafatullah, O. Sulaiman, R. Hashim, A. Ahmad, Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: A review, J. Hazard. Mater, 177 (2010) [3] K. Yang, J. Peng, C. Srinivasakannan, L. Zhang, H. Xia, X. Duan, Preparation of high surface area activated carbon from coconut shells using microwave heating, Bioresource Technology, 101 (2010) [4] D. Kalderis, S. Bethanis, P. Paraskeva, E. Diamadopoulos, Production of activated carbon from bagasse and rice husk by a single-stage chemical activation method at low retention times, Bioresour. Technol. 99 (2008) [5] S. Kumagai, H. Ishizawa, Y. Aoki, Y. Toida, Molded micro- and mesoporous carbon/silica composite from rice husk and beet sugar, Chem. Eng. J. 156 (2010) [6] C. Liu, Z. Tang, Y. Chen, S. Su, W. Jiang, Characterization of mesoporous activated carbons prepared by pyrolysis of sewage sludge with pyrolusite, Bioresour. Technol. 101 (2010) [7] Y. Liu, Y. Guo, W. Gao, Z. Wang, Y. Ma, Z. Wang, Simultaneous preparation of silica and activated carbon from rice husk ash, Journal of Cleaner Production, 32 (2012) [8] Noorfidza Yub Harun, M.T. Afzal, Mohd Tazli Azizan, TGA Analysis of Rubber Seed Kernel, International Journal of Engineering, 3 (2010) [9] H.D. Eka, Y. Tajul Aris, W.A. Wan Nadiah, Potential use of Malaysian rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) seed as food, feed and biofuel, International Food Research Journal, 17 (2010) [10] M.A. Jamaluddin, K. Ismail, M.A. Mohd Ishak, Z. Ab Ghani, M.F. Abdullah, M.T.-u. Safian, S.S. Idris, S. Tahiruddin, M.F. Mohammed Yunus, N.I.N. Mohd Hakimi, Microwave-assisted pyrolysis of palm kernel shell: Optimization using response surface methodology (RSM), Renewable Energy, 55 (2013) [11] M.I. Mohd Nayai, K. Ismail, M.A. Mohd Ishak, S. Buniran, Z. Zakaria, Properties of Coconut Shell Activated Carbon, Journal of Tropical Forest Chemistry, 25 (2013) [12] F.K. Yuen, B.H. Hameed, Recent developments in the preparation and regeneration of activated carbons by microwaves, Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 149 (2009) [13] Y. Ji, T. Li, L. Zhu, X. Wang, Q. Lin, Preparation of activated carbons by microwave heating KOH activation, Appl. Surf. Sci. 254 (2007) [14] W. Li, L.-b. Zhang, J.-h. Peng, N. Li, X.-y. Zhu, Preparation of high surface area activated carbons from tobacco stems with K2CO3 activation using microwave radiation, Industrial Crops and Products, 27 (2008) [15] E. Yagmur, M. Ozmak, Z. Aktas, A novel method for production of activated carbon from waste tea by chemical activation with microwave energy, Fuel, 87 (2008) [16] H. Deng, L. Yang, G. Tao, J. Dai, Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from cotton stalk by microwave assisted chemical activation Application in methylene blue adsorption from aqueous solution, J. Hazard. Mater. 166 (2009) [17] T. Wang, S. Tan, C. Liang, Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from wood via microwave-induced ZnCl2 activation, Carbon. 47 (2009) [18] J. Matos, C. Nahas, L. Rojas, M. Rosales, Synthesis and characterization of activated carbon from sawdust of Algarroba wood. 1. Physical activation and pyrolysis, J. Hazard. Mater. 196 (2011) [19] K. Sun, J.c. Jiang, Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from rubber-seed shell by physical activation with steam, Biomass and Bioenergy, 34 (2010) [20] T. Kawano, M. Kubota, M.S. Onyango, F. Watanabe, H. Matsuda, Preparation of activated carbon from petroleum coke by KOH chemical activation for adsorption heat pump, Applied Thermal Engineering, 28 (2008) [21] M.L. Martínez, M.M. Torres, C.A. Guzmán, D.M. Maestri, Preparation and characteristics of activated carbon from olive stones and walnut shells, Industrial Crops and Products, 23 (2006) [22] A. Arami-Niya, W.M.A.W. Daud, F.S. Mjalli, Comparative study of the textural characteristics of oil palm shell activated carbon produced by chemical and physical activation for methane adsorption, Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 89 (2011) [23] K. Suresh Kumar Reddy, A. Al Shoaibi, C. Srinivasakannan, A comparison of microstructure and adsorption characteristics of activated carbons by CO2 and H3PO4 activation from date palm pits, Carbon, 52 (2013) 623. [24] S.M. Yakout, G. Sharaf El-Deen, Characterization of activated carbon prepared by phosphoric acid activation of olive stones, Arabian Journal of Chemistry, (2012). [25] S.S. Idris, N.A. Rahman, K. Ismail, Combustion characteristics of Malaysian oil palm biomass, subbituminous coal and their respective blends via thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), Bioresource Technology, 123 (2012) [26] M.J. Ahmed, S.K. Theydan, Microporous activated carbon from Siris seed pods by microwave-induced KOH activation for metronidazole adsorption, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol., 99 (2013) [27] C. Saka, BET, TG DTG, FT-IR, SEM, iodine number analysis and preparation of activated carbon from acorn shell by chemical activation with ZnCl2, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol., 95 (2012) [28] R. Hoseinzadeh Hesas, A. Arami-Niya, W.M.A. Wan Daud, J.N. Sahu, Preparation of granular activated carbon from oil palm shell by microwave-induced chemical activation: Optimisation using surface response methodology, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 91 (2013)
7 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 7, July [29] A. Ahmad, M. Rafatullah, O. Sulaiman, M.H. Ibrahim, R. Hashim, Scavenging behaviour of meranti sawdust in the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution, Journal of Hazardous Materials, 170 (2009) [30] K.Y. Foo, B.H. Hameed, Preparation of activated carbon by microwave heating of langsat (Lansium domesticum) empty fruit bunch waste, Bioresource Technology, 116 (2012) [31] T.C. Chandra, M.M. Mirna, J. Sunarso, Y. Sudaryanto, S. Ismadji, Activated carbon from durian shell: Preparation and characterization, Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 40 (2009) [32] Q.-S. Liu, T. Zheng, P. Wang, L. Guo, Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from bamboo by microwave-induced phosphoric acid activation, Industrial Crops and Products, 31 (2010) AUTHORS First Author - D. Anis, B.Sc, Universiti Teknologi MARA, dnooranis@yahoo.com. Second Author - M.A.M. Ishak, Ph.D, Universiti Teknologi MARA, azlanishak@perlis.uitm.edu.my Third Author - A.Z. Zaidi, M.Sc, University Teknologi MARA Forth Author I. Khudzir, Ph.D, University Teknologi MARA, khudzir@salam.uitm.edu.my Fifth Author M.N. Iqbaldin, M.Sc, University Teknologi MARA, iqbalziana@yahoo.com Sixth Author Uwaisulqarni M. Osman, Ph.D, University Malaysia Terengganu, uwais@umt.edu.my Correspondence Author W.I. Nawawi, address: wi_nawawi@perlis.uitm.edu.my, Tel: ;Fax:
8 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 7, July
C. C. TAY*, M. I. A. KHOSHAR-KHAN, N. S. MD-DESA, Z. AB-GHANI, S. ABDUL-TALIB
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Special Issue on ACEE 2015 Conference August (2015) 40-51 School of Engineering, Taylor s University SUSTAINABLE OPTIMIZATION OF SPENT MUSHROOM COMPOST ACTIVATED
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Special Issue on ACEE 2015 Conference August (2015) 40-51 School of Engineering, Taylor s University SUSTAINABLE OPTIMIZATION OF SPENT MUSHROOM COMPOST ACTIVATED
PRODUCING ACTIVED CARBONS FROM PINECONES VIA CHEMICAL ACTIVATION. Abstract. Introduction. Experimental
 PRODUCING ACTIVED CARBONS FROM PINECONES VIA CHEMICAL ACTIVATION Esin Apaydın Varol, Dept. of Chemical Engineering, Anadolu University, Eskisehir, Turkey Ersan Pütün, Dept. of Material Science and Engineering,
PRODUCING ACTIVED CARBONS FROM PINECONES VIA CHEMICAL ACTIVATION Esin Apaydın Varol, Dept. of Chemical Engineering, Anadolu University, Eskisehir, Turkey Ersan Pütün, Dept. of Material Science and Engineering,
Abstract. Introduction
 REMOVAL OF Pb +2 IONS FROM AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS BY ACTIVATED CARBONS PRODUCED FROM PEANUT SHELLS Ayşe Eren Pütün, Dept. of Chemical Engineering, Anadolu University, Eskisehir, Turkey Esin Apaydın Varol, Dept.
REMOVAL OF Pb +2 IONS FROM AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS BY ACTIVATED CARBONS PRODUCED FROM PEANUT SHELLS Ayşe Eren Pütün, Dept. of Chemical Engineering, Anadolu University, Eskisehir, Turkey Esin Apaydın Varol, Dept.
Synthesis and Characterization of Bio-Based Porous Carbons by Two Step Physical Activation with CO 2
 Jurnal Teknologi Full paper Synthesis and Characterization of Bio-Based Porous Carbons by Two Step Physical Activation with CO 2 Noor Shawal Nasri a, Mohammed Jibril a,b,c*, Muhammad Abbas Ahmad Zaini
Jurnal Teknologi Full paper Synthesis and Characterization of Bio-Based Porous Carbons by Two Step Physical Activation with CO 2 Noor Shawal Nasri a, Mohammed Jibril a,b,c*, Muhammad Abbas Ahmad Zaini
Production of Activated Carbon from Residue of Liquorices Chemical Activation
 Abstract: Production of Activated Carbon from Residue of Liquorices Chemical Activation T.Kaghazchi *, M.Soleimani, M.Madadi Yeganeh, Department of Chemical Engineering, AmirKabir University of Technology,
Abstract: Production of Activated Carbon from Residue of Liquorices Chemical Activation T.Kaghazchi *, M.Soleimani, M.Madadi Yeganeh, Department of Chemical Engineering, AmirKabir University of Technology,
Received: 24 th April-2012 Revised: 07 th May-2012 Accepted: 10 th May-2012 Research article
 Received: 24 th April-2012 Revised: 07 th May-2012 Accepted: 10 th May-2012 Research article EQUILIBRIUM ISOTHERM STUDIES OF METHYLENE BLUE FROM AQUEOUS SOLUTION UNTO ACTIVATED CARBON PREPARED FORM STRYCHNOS
Received: 24 th April-2012 Revised: 07 th May-2012 Accepted: 10 th May-2012 Research article EQUILIBRIUM ISOTHERM STUDIES OF METHYLENE BLUE FROM AQUEOUS SOLUTION UNTO ACTIVATED CARBON PREPARED FORM STRYCHNOS
OPTIMIZATION OF ACTIVATED CARBONS FABRICATED FROM AGRICULTURAL WASTES
 An Open Access, Online International Journal Available at www.cibtech.org/sp.ed/jls/216/1/jls.htm 216 Vol. 6 (S1), pp. 481-493/Sedghi et al. OPTIMIZATION OF ACTIVATED CARBONS FABRICATED FROM AGRICULTURAL
An Open Access, Online International Journal Available at www.cibtech.org/sp.ed/jls/216/1/jls.htm 216 Vol. 6 (S1), pp. 481-493/Sedghi et al. OPTIMIZATION OF ACTIVATED CARBONS FABRICATED FROM AGRICULTURAL
Effect of Process Parameters on Adsorption of Methylene Blue from Synthetic Effluent Using Jack Fruit Seed Powder
 Effect of Process Parameters on Adsorption of Methylene Blue from Synthetic Effluent Using Jack Fruit Seed Powder Anoop Raj J R Anil K Das Aishwarya B S Sruthi Suresh Abstract- Batch sorption experiments
Effect of Process Parameters on Adsorption of Methylene Blue from Synthetic Effluent Using Jack Fruit Seed Powder Anoop Raj J R Anil K Das Aishwarya B S Sruthi Suresh Abstract- Batch sorption experiments
Comparison of the properties of activated carbons produced in a one-stage and a two-stage process
 Communication Comparison of the properties of activated carbons produced in a one-stage and a two-stage process Davide Bergna 1,2, Toni Varila 1,2, Henrik Romar 1 and Ulla Lassi 1,2 1 University of Oulu,
Communication Comparison of the properties of activated carbons produced in a one-stage and a two-stage process Davide Bergna 1,2, Toni Varila 1,2, Henrik Romar 1 and Ulla Lassi 1,2 1 University of Oulu,
Porous structure and adsorptive properties of hide waste activated. carbons prepared via potassium silicate activation
 Porous structure and adsorptive properties of hide waste activated carbons prepared via potassium silicate activation Jiaojiao Kong a, Qinyan Yue a,, Baoyu Gao a, Qian Li a, Yan Wang a, Huu Hao Ngo b,
Porous structure and adsorptive properties of hide waste activated carbons prepared via potassium silicate activation Jiaojiao Kong a, Qinyan Yue a,, Baoyu Gao a, Qian Li a, Yan Wang a, Huu Hao Ngo b,
Effect of Activation Temperature and Heating Duration on Physical Characteristics of Activated Carbon Prepared from Agriculture Waste
 EnvironmentAsia The international journal published by the Thai Society of Higher Education Institutes on Environment Available online at www.tshe.org/ea EnvironmentAsia 3(special issue) (2010) 143-148
EnvironmentAsia The international journal published by the Thai Society of Higher Education Institutes on Environment Available online at www.tshe.org/ea EnvironmentAsia 3(special issue) (2010) 143-148
PREPARATION OF ACTIVATED CARBON FROM PULP AND PAPER MILL WASTES TO BE TESTED FOR THE ADSORPTION OF VOCS
 PREPARATION OF ACTIVATED CARBON FROM PULP AND PAPER MILL WASTES TO BE TESTED FOR THE ADSORPTION OF VOCS A. GREGÓRIO *, A. GARCIA-GARCIA #, D. BOAVIDA *, I. GULYURTLU * AND I. CABRITA * * Department of
PREPARATION OF ACTIVATED CARBON FROM PULP AND PAPER MILL WASTES TO BE TESTED FOR THE ADSORPTION OF VOCS A. GREGÓRIO *, A. GARCIA-GARCIA #, D. BOAVIDA *, I. GULYURTLU * AND I. CABRITA * * Department of
Utilization of Biodiesel Wastes as a Bioresource for the Preparation of Activated Carbon
 Utilization of Biodiesel Wastes as a Bioresource for the Preparation of Activated Carbon A. Buasri, N. Chaiyut, V. Loryuenyong, E. Phakdeepataraphan, S. Watpathomsub, and V. Kunakemakorn, Member, IACSIT
Utilization of Biodiesel Wastes as a Bioresource for the Preparation of Activated Carbon A. Buasri, N. Chaiyut, V. Loryuenyong, E. Phakdeepataraphan, S. Watpathomsub, and V. Kunakemakorn, Member, IACSIT
Characterization of Activated Carbon Prepared from Almond Shells for Scavenging Phenolic Pollutants
 Chem Sci Trans., 2013, 2(3), 835-840 Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2013.358 ISSN/E-ISSN: 2278-3458/2278-3318 RESEARCH ARTICLE Characterization of Activated Carbon Prepared from Almond Shells
Chem Sci Trans., 2013, 2(3), 835-840 Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2013.358 ISSN/E-ISSN: 2278-3458/2278-3318 RESEARCH ARTICLE Characterization of Activated Carbon Prepared from Almond Shells
Waste Palm Shell Converted to High Efficient Activated Carbon by Chemical Activation Method and Its Adsorption Capacity Tested by Water Filtration
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com APCBEE Procedia 1 (2012 ) 293 298 ICESD 2012: 5-7 January 2012, Hong Kong Waste Palm Shell Converted to High Efficient Activated Carbon by Chemical Activation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com APCBEE Procedia 1 (2012 ) 293 298 ICESD 2012: 5-7 January 2012, Hong Kong Waste Palm Shell Converted to High Efficient Activated Carbon by Chemical Activation
Optimization of Preparation Conditions for Corn Cob Based Activated Carbons for the Removal of Remazol Brilliant Blue R dye
 International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol: 11 No: 01 216 Optimization of Preparation Conditions for Corn Cob Based Activated Carbons for the Removal of Remazol Brilliant Blue R dye
International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol: 11 No: 01 216 Optimization of Preparation Conditions for Corn Cob Based Activated Carbons for the Removal of Remazol Brilliant Blue R dye
Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different Proportions
 2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
Physical Characteristics of Activated Carbon Derived from Durian Shell
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 22, No. 1 (2010), 772-780 Physical Characteristics of Activated Carbon Derived from Durian Shell Y.J. THAM, PUZIAH ABDUL LATIF*, A.M. ABDULLAH and Y.H. TAUFIQ-YAP Department
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 22, No. 1 (2010), 772-780 Physical Characteristics of Activated Carbon Derived from Durian Shell Y.J. THAM, PUZIAH ABDUL LATIF*, A.M. ABDULLAH and Y.H. TAUFIQ-YAP Department
PREPARATION AND CHARACTERISTICS OF HIGHLY MICROPOROUS ACTIVATED CARBON DERIVED FROM EMPTY FRUIT BUNCH OF PALM OIL USING KOH ACTIVATION
 Rasayan J. Chem., 11(1), 280-286(2018) http://dx.doi.org/10.7324/rjc.2018.1112000 Vol. 11 No. 1 280-286 January - March 2018 ISSN: 0974-1496 e-issn: 0976-0083 CODEN: RJCABP http://www.rasayanjournal.com
Rasayan J. Chem., 11(1), 280-286(2018) http://dx.doi.org/10.7324/rjc.2018.1112000 Vol. 11 No. 1 280-286 January - March 2018 ISSN: 0974-1496 e-issn: 0976-0083 CODEN: RJCABP http://www.rasayanjournal.com
Production Of Activated Charcoal From Sugar Cane Leaves Using ZnCl 2 Activation For The Adsorption Of Methylene Blue Dye
 Production Of Activated Charcoal From Sugar Cane Leaves Using ZnCl 2 Activation For The Adsorption Of Methylene Blue Dye Deepti Patil 1*, Sanjay Chavan 1, Shrikant Barkade 1 1 Department of Chemical Engineering,
Production Of Activated Charcoal From Sugar Cane Leaves Using ZnCl 2 Activation For The Adsorption Of Methylene Blue Dye Deepti Patil 1*, Sanjay Chavan 1, Shrikant Barkade 1 1 Department of Chemical Engineering,
OIL-PALM SHELL ACTIVATED CARBON PRODUCTION USING CO 2 EMISSION FROM CaCO 3
 Journal of Sustainability Science and Management Volume 8 Number 2, December 2013: 150-160 ISSN: 1823-8556 Penerbit UMT OIL-PALM SHELL ACTIVATED CARBON PRODUCTION USING EMISSION FROM CaCO 3 CALCINATION
Journal of Sustainability Science and Management Volume 8 Number 2, December 2013: 150-160 ISSN: 1823-8556 Penerbit UMT OIL-PALM SHELL ACTIVATED CARBON PRODUCTION USING EMISSION FROM CaCO 3 CALCINATION
TEXTURAL AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISATION OF ACTIVATED CARBONS PREPARED FROM RICE HUSK (ORYZA SATIVA) USING A TWO- STAGE ACTIVATION PROCESS
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 3, No. 3 (2008) 234-242 School of Engineering, Taylor s University College TEXTURAL AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISATION OF ACTIVATED CARBONS PREPARED FROM RICE
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 3, No. 3 (2008) 234-242 School of Engineering, Taylor s University College TEXTURAL AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISATION OF ACTIVATED CARBONS PREPARED FROM RICE
PREPARATION OF ACTIVATED CARBON FROM THE BY-PRODUCTS OF AGRICULTURAL INDUSTRY
 PREPARATION OF ACTIVATED CARBON FROM THE BY-PRODUCTS OF AGRICULTURAL INDUSTRY L. H. NOSZKO, A. BOTA, A. SIMAY and L. Gy. NAGY Department for Applied Chemistry, Technical University, H-1521 Budapest Received
PREPARATION OF ACTIVATED CARBON FROM THE BY-PRODUCTS OF AGRICULTURAL INDUSTRY L. H. NOSZKO, A. BOTA, A. SIMAY and L. Gy. NAGY Department for Applied Chemistry, Technical University, H-1521 Budapest Received
Preparation of Activated Carbon from Palm Shells using KOH and ZnCl2 as the Activating Agent
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Preparation of Activated Carbon from Palm Shells using KOH and ZnCl2 as the Activating Agent To cite this article: Yuliusman et
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Preparation of Activated Carbon from Palm Shells using KOH and ZnCl2 as the Activating Agent To cite this article: Yuliusman et
Methylene Blue Colour Removal Using Physically And Chemically Activated Cashew Nut Shell Activated Carbon
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF TECHNOLOGY ENHANCEMENTS AND EMERGING ENGINEERING RESEARCH, VOL 2, ISSUE 7 64 Methylene Blue Colour Removal Using Physically And Chemically Activated Cashew Nut Shell Activated
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF TECHNOLOGY ENHANCEMENTS AND EMERGING ENGINEERING RESEARCH, VOL 2, ISSUE 7 64 Methylene Blue Colour Removal Using Physically And Chemically Activated Cashew Nut Shell Activated
Preparation and Characterization of Activated Carbon from the Prosopis juliflora Plant
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 20, No. 3 (2008), 1702-1706 Preparation and Characterization of Activated Carbon from the Prosopis juliflora Plant A. JAFAR AHAMED* and K. RIAZ AHAMED Department of Chemistry,
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 20, No. 3 (2008), 1702-1706 Preparation and Characterization of Activated Carbon from the Prosopis juliflora Plant A. JAFAR AHAMED* and K. RIAZ AHAMED Department of Chemistry,
PROCESS VARIABLES OPTIMIZATION FOR PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NOVEL ADSORBENT FROM LIGNOCELLULOSIC WASTE
 PROCESS VARIABLES OPTIMIZATION FOR PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NOVEL ADSORBENT FROM LIGNOCELLULOSIC WASTE Zaira Zaman Chowdhury, a, * Sharifuddin Mohd. Zain, a Arash Arami-Niya, b and Khalisanni
PROCESS VARIABLES OPTIMIZATION FOR PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NOVEL ADSORBENT FROM LIGNOCELLULOSIC WASTE Zaira Zaman Chowdhury, a, * Sharifuddin Mohd. Zain, a Arash Arami-Niya, b and Khalisanni
COMPARATIVE STUDIES ON DIFFERENT KIND OF DURIAN HUSKS AS MICROSTRUCTURE ACTIVATED CARBON
 Journal of Optoelectronics and Biomedical Materials Vol. 7, No. 3, July-September 2015 p. 53-58 COMPARATIVE STUDIES ON DIFFERENT KIND OF DURIAN HUSKS AS MICROSTRUCTURE ACTIVATED CARBON Y. MANICKAM a, M.F.M.
Journal of Optoelectronics and Biomedical Materials Vol. 7, No. 3, July-September 2015 p. 53-58 COMPARATIVE STUDIES ON DIFFERENT KIND OF DURIAN HUSKS AS MICROSTRUCTURE ACTIVATED CARBON Y. MANICKAM a, M.F.M.
Removal of heavy metals onto KOH-activated ash-rich sludge
 Removal of heavy metals onto KOH-activated ash-rich sludge adsorbent Muhammad Abbas Ahmad Zaini et al. Centre of Lipids Engineering g and Applied Research (CLEAR) UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA www.utm.my
Removal of heavy metals onto KOH-activated ash-rich sludge adsorbent Muhammad Abbas Ahmad Zaini et al. Centre of Lipids Engineering g and Applied Research (CLEAR) UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA www.utm.my
Validation of Adsorption Efficiency of Activated Carbons through Surface Morphological Characterization Using Scanning Electron Microscopy Technique
 Carbon Science Vol. 5, No. 2 June 2004 pp. 75-80 Validation of Adsorption Efficiency of Activated Carbons through Surface Morphological Characterization Using Scanning Electron Microscopy Technique Ruchi
Carbon Science Vol. 5, No. 2 June 2004 pp. 75-80 Validation of Adsorption Efficiency of Activated Carbons through Surface Morphological Characterization Using Scanning Electron Microscopy Technique Ruchi
CARBONIZATION KINETICS OF COCONUT SHELL AND PLUM STONE
 CARBONIZATION KINETICS OF COCONUT SHELL AND PLUM STONE Benoît CAGNON, Xavier PY, André GUILLOT I.M.P.-C.N.R.S., Institut de Science et Génie des Matériaux et Procédés, Rambla de la Thermodynamique, Tecnosud,
CARBONIZATION KINETICS OF COCONUT SHELL AND PLUM STONE Benoît CAGNON, Xavier PY, André GUILLOT I.M.P.-C.N.R.S., Institut de Science et Génie des Matériaux et Procédés, Rambla de la Thermodynamique, Tecnosud,
Thermal degradation of Shredded Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunches (SOPEFB) embedded with Cobalt catalyst by Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Thermal degradation of Shredded Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunches (SOPEFB) embedded with Cobalt catalyst by Thermogravimetric Analysis
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Thermal degradation of Shredded Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunches (SOPEFB) embedded with Cobalt catalyst by Thermogravimetric Analysis
The Study of Natural Nano-Composite Filter for Industrial Wastewater Treatment
 The Study of Natural Nano-Composite Filter for Industrial Wastewater Treatment Chin-Ya Kuo, Hsiao-Han Liu * Department of Biological Science & Technology, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung 824, Taiwan, ROC
The Study of Natural Nano-Composite Filter for Industrial Wastewater Treatment Chin-Ya Kuo, Hsiao-Han Liu * Department of Biological Science & Technology, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung 824, Taiwan, ROC
a, * b University, Muang, Phitsanulok 65000, Thailand. *Corresponding author. address: (R. Sananmuang)
 Naresuan University Journal 2007; 15(1): 9-16 9 ก ก ก ก ก ก a, * b Physical Characteristics and Adsorption Properties for Reactive Dyes of Char and Activated Carbon Prepared from Mangosteen Peel and Tamarind
Naresuan University Journal 2007; 15(1): 9-16 9 ก ก ก ก ก ก a, * b Physical Characteristics and Adsorption Properties for Reactive Dyes of Char and Activated Carbon Prepared from Mangosteen Peel and Tamarind
Response Surface Methodology Optimization of Methylene Blue Removal by Activated Carbon Derived from Foxtail Palm Tree Empty Fruit Bunch
 J. Trop. Resour. Sustain. Sci. 4 (206): 25-30 Response Surface Methodology Optimization of Methylene Blue Removal by Activated Carbon Derived from Foxtail Palm Tree Empty Fruit Bunch Farah Amni Daud, Norhisyam
J. Trop. Resour. Sustain. Sci. 4 (206): 25-30 Response Surface Methodology Optimization of Methylene Blue Removal by Activated Carbon Derived from Foxtail Palm Tree Empty Fruit Bunch Farah Amni Daud, Norhisyam
Production of Mesoporous Carbon from Waste Tire
 Production of Mesoporous Carbon from Waste Tire E.L.K. Mui and G. M c Kay Department of Chemical Engineering Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Clear Water Bay, Kowloon, Hong Kong Corresponding
Production of Mesoporous Carbon from Waste Tire E.L.K. Mui and G. M c Kay Department of Chemical Engineering Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Clear Water Bay, Kowloon, Hong Kong Corresponding
Efficient removal of typical dye and Cr(VI) reduction using N-doped
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Efficient removal of typical dye and Cr(VI) reduction using N-doped magnetic porous carbon
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Efficient removal of typical dye and Cr(VI) reduction using N-doped magnetic porous carbon
Adsorption of phenol from diluted aqueous solutions by activated carbons obtained from bagasse, oil palm shell and pericarp of rubber fruit
 Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 30 (2), 185-189, Mar. - Apr. 2008 http://www.sjst.psu.ac.th Original Article Adsorption of phenol from diluted aqueous solutions by activated carbons obtained from bagasse,
Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 30 (2), 185-189, Mar. - Apr. 2008 http://www.sjst.psu.ac.th Original Article Adsorption of phenol from diluted aqueous solutions by activated carbons obtained from bagasse,
Adsorption Studies on Activated Carbon Derived from Steam Activation of Jute Stick Char
 Vol-23-1&2 1 J. Surface Sci. Technol., Vol 23, No. 1-2, pp. 73-80, 2007 2007 Indian Society for Surface Science and Technology, India. Adsorption Studies on Activated Carbon Derived from Steam Activation
Vol-23-1&2 1 J. Surface Sci. Technol., Vol 23, No. 1-2, pp. 73-80, 2007 2007 Indian Society for Surface Science and Technology, India. Adsorption Studies on Activated Carbon Derived from Steam Activation
Advances in Environmental Technology 3 (2016) Advances in Environmental Technology. journal homepage:
 Advances in Environmental Technology 3 (216) 137-141 Advances in Environmental Technology journal homepage: http://aet.irost.ir Desorption of reactive red 198 from activated Carbon prepared from walnut
Advances in Environmental Technology 3 (216) 137-141 Advances in Environmental Technology journal homepage: http://aet.irost.ir Desorption of reactive red 198 from activated Carbon prepared from walnut
International Journal of Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences
 V. Nandhakumar et al IJCPS, 2014, Vol.2(8): 1032-1039 Research Article ISSN: 2321-3132 International Journal of Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijcps Kinetics of Adsorption
V. Nandhakumar et al IJCPS, 2014, Vol.2(8): 1032-1039 Research Article ISSN: 2321-3132 International Journal of Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijcps Kinetics of Adsorption
REMOVAL OF SYNTHETIC DYE ACID RED 186 FROM WATER BY ACTIVATED CARBON. Libya
 REMOVAL OF SYNTHETIC DYE ACID RED 186 FROM WATER BY ACTIVATED CARBON Ezzedein Mohamed Aboushloa 1 and Abdunnaser Mohamed Etorki 2 1 Department of chemistry, school of Basic sciences, Libyan Academy, Tripoli,Libya
REMOVAL OF SYNTHETIC DYE ACID RED 186 FROM WATER BY ACTIVATED CARBON Ezzedein Mohamed Aboushloa 1 and Abdunnaser Mohamed Etorki 2 1 Department of chemistry, school of Basic sciences, Libyan Academy, Tripoli,Libya
Activated Carbon from Sugar Waste Bagasse is used for Removal of Colour from Dye Solution
 International Journal of Research in Advent Technology, Vol.2, No.11, November214 Activated Carbon from Sugar Waste Bagasse is used for Removal of Colour from Dye Solution Amish B. Patel 1 *, Mehul H.
International Journal of Research in Advent Technology, Vol.2, No.11, November214 Activated Carbon from Sugar Waste Bagasse is used for Removal of Colour from Dye Solution Amish B. Patel 1 *, Mehul H.
1997 P a g e. Keywords: Adsorption, banana peel, Colour removal, orange peel
 Removal of Colour (dyes) from textile effluent by adsorption using Orange and Banana peel R.S.Mane*, V.N.Bhusari** *(M.Tech Environmental Engineering, G.H.Raisoni College of Engineering, NAGPUR, (India)
Removal of Colour (dyes) from textile effluent by adsorption using Orange and Banana peel R.S.Mane*, V.N.Bhusari** *(M.Tech Environmental Engineering, G.H.Raisoni College of Engineering, NAGPUR, (India)
Optimization of preparation conditions of activated carbon from the residue of desilicated rice husk using response surface methodology
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 31(10), 1810-1817 (2014) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-014-0103-6 INVITED REVIEW PAPER INVITED REVIEW PAPER pissn: 0256-1115 eissn: 1975-7220 Optimization of preparation conditions of activated
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 31(10), 1810-1817 (2014) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-014-0103-6 INVITED REVIEW PAPER INVITED REVIEW PAPER pissn: 0256-1115 eissn: 1975-7220 Optimization of preparation conditions of activated
PRODUCTION OF ACTIVATED CARBON FROM SOLID WASTE RICE PEEL (HUSK) USING CHEMICAL ACTIVATION
 Jr. of Industrial Pollution Control 33(2)(2017) pp 1132-1139 www.icontrolpollution.com Research Article PRODUCTION OF ACTIVATED CARBON FROM SOLID WASTE RICE PEEL (HUSK) USING CHEMICAL ACTIVATION D. SHARATH
Jr. of Industrial Pollution Control 33(2)(2017) pp 1132-1139 www.icontrolpollution.com Research Article PRODUCTION OF ACTIVATED CARBON FROM SOLID WASTE RICE PEEL (HUSK) USING CHEMICAL ACTIVATION D. SHARATH
STUDIES ON THE REMOVAL OF CATIONIC DYES FROM AQUEOUS SOLUTION BY MIXED ADSORBENTS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 12(4), 2014, 1550-1556 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com STUDIES ON THE REMOVAL OF CATIONIC DYES FROM AQUEOUS SOLUTION BY MIXED ADSORBENTS AMITA SHARMA * Chemistry Department,
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 12(4), 2014, 1550-1556 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com STUDIES ON THE REMOVAL OF CATIONIC DYES FROM AQUEOUS SOLUTION BY MIXED ADSORBENTS AMITA SHARMA * Chemistry Department,
Jurnal Teknologi CHARACTERIZATION OF PHOSPHORIC ACID IMPREGNATED ACTIVATED CARBON PRODUCED FROM HONEYDEW PEEL. Full Paper
 Jurnal Teknologi CHARACTERIZATION OF PHOSPHORIC ACID IMPREGNATED ACTIVATED CARBON PRODUCED FROM HONEYDEW PEEL Zalilah Murni Yunus a*, Norzila Othman b, R. Hamdan a, N. N. Ruslan b a Dept. Of Sci., Fac.
Jurnal Teknologi CHARACTERIZATION OF PHOSPHORIC ACID IMPREGNATED ACTIVATED CARBON PRODUCED FROM HONEYDEW PEEL Zalilah Murni Yunus a*, Norzila Othman b, R. Hamdan a, N. N. Ruslan b a Dept. Of Sci., Fac.
Water Extractable Organic Carbon in Fresh and Treated Biochars
 Water Extractable Organic Carbon in Fresh and Treated Biochars Yun Lin a, Paul Munroe a, Stephen Joseph a, Rita Henderson b, Artur. Ziolkowski c a School of Materials Science and Engineering, The University
Water Extractable Organic Carbon in Fresh and Treated Biochars Yun Lin a, Paul Munroe a, Stephen Joseph a, Rita Henderson b, Artur. Ziolkowski c a School of Materials Science and Engineering, The University
Dielectric Properties of Sodium Hydroxide-Impregnated and Activated Cempedak Peel Samples at Microwave Frequencies
 931 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 56, 2017 Guest Editors: Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Wai Shin Ho, Jeng Shiun Lim Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-47-1;
931 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 56, 2017 Guest Editors: Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Wai Shin Ho, Jeng Shiun Lim Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-47-1;
Utilization of Rice Husk Ash Silica in Controlled Releasing Application
 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol.9 No.2 pp.6-65, 29 Utilization of Rice Husk Ash Silica in Controlled Releasing Application Piyawan PRAWINGWONG, Chaiyan CHAIYA 2, Prasert REUBROYCHAROEN 3
Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol.9 No.2 pp.6-65, 29 Utilization of Rice Husk Ash Silica in Controlled Releasing Application Piyawan PRAWINGWONG, Chaiyan CHAIYA 2, Prasert REUBROYCHAROEN 3
Production and characterization of activated carbon derived from brewer s yeast
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 27(5), 1476-1482 (2010) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-010-0227-2 RAPID COMMUNICATION Production and characterization of activated carbon derived from brewer s yeast Guiping Wu*, Tae-seop Jeong**,
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 27(5), 1476-1482 (2010) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-010-0227-2 RAPID COMMUNICATION Production and characterization of activated carbon derived from brewer s yeast Guiping Wu*, Tae-seop Jeong**,
Adsorption Studies of Organic Pollutants onto Activated Carbon
 Adsorption Studies of Organic Pollutants onto Activated Carbon K.BALASUBRAMANI 1, N.SIVARAJASEKAR 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of Chemical Engineering, Kongu Engineering College, Perundurai, Erode 63852,
Adsorption Studies of Organic Pollutants onto Activated Carbon K.BALASUBRAMANI 1, N.SIVARAJASEKAR 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of Chemical Engineering, Kongu Engineering College, Perundurai, Erode 63852,
15 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology
 15 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 31 August to 2 September 2017 The removal of reactive dyestuff from aqueous solutions using activated carbon prepared
15 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 31 August to 2 September 2017 The removal of reactive dyestuff from aqueous solutions using activated carbon prepared
Study of some Effecting Factors on the Removal of Phenol from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption onto Activated Carbon
 J. Int. Environmental Application & Science, Vol. 11(2): 148-153 (2016) Study of some Effecting Factors on the Removal of Phenol from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption onto Activated Carbon M. R. Mohammad
J. Int. Environmental Application & Science, Vol. 11(2): 148-153 (2016) Study of some Effecting Factors on the Removal of Phenol from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption onto Activated Carbon M. R. Mohammad
Preparation and Adsorption Studies of High Specific Surface Area Activated Carbons Obtained from the Chemical Activation of Jute Stick
 761 Preparation and Adsorption Studies of High Specific Surface Area Activated Carbons Obtained from the Chemical Activation of Jute Stick Mohammad Asadullah *, Muhammad A. Rahman, Mohammad A. Motin and
761 Preparation and Adsorption Studies of High Specific Surface Area Activated Carbons Obtained from the Chemical Activation of Jute Stick Mohammad Asadullah *, Muhammad A. Rahman, Mohammad A. Motin and
Research in Chemistry and Environment
 International Journal of Research in Chemistry and Environment Available online at: www.ijrce.org ISSN 2248-9649 Research Paper Adsorption of Eosin Dyes Onto Activated Carbon Prepared from Wood of Adina
International Journal of Research in Chemistry and Environment Available online at: www.ijrce.org ISSN 2248-9649 Research Paper Adsorption of Eosin Dyes Onto Activated Carbon Prepared from Wood of Adina
STUDY ON THE IMPROVEMENT OF THE REDUCTION CAPACITY OF ACTIVATED CARBON FIBER
 STUDY ON THE IMPROVEMENT OF THE REDUCTION CAPACITY OF ACTIVATED CARBON FIBER Chen Shuixia, Zeng Hanmin Materials Science Institute, Zhongshan University, Guangzhou 51275, China Key Laboratory for Polymeric
STUDY ON THE IMPROVEMENT OF THE REDUCTION CAPACITY OF ACTIVATED CARBON FIBER Chen Shuixia, Zeng Hanmin Materials Science Institute, Zhongshan University, Guangzhou 51275, China Key Laboratory for Polymeric
ABSTRACT. Keywords: Cadmium Removal, sawdust, adsorption. Corresponding Author: P. Akhila Swathanthra 1. INTRODUCTION:
 International Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering and Development Issue 4, Vol.5 (Aug.- Sep. 214) Removal of Cadmium Ions by adsorption onto Sawdust as adsorbent from aqueous solutions P.AKHILA SWATHANTHRA
International Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering and Development Issue 4, Vol.5 (Aug.- Sep. 214) Removal of Cadmium Ions by adsorption onto Sawdust as adsorbent from aqueous solutions P.AKHILA SWATHANTHRA
Supporting information A Porous Zr-cluster-based Cationic Metal-Organic Framework for Highly Efficient Cr 2 O 7
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information A Porous Zr-cluster-based Cationic Metal-Organic Framework for Highly Efficient
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information A Porous Zr-cluster-based Cationic Metal-Organic Framework for Highly Efficient
Adsorption of metal ions by pecan shell-based granular activated carbons
 Bioresource Technology 89 (23) 115 119 Adsorption of metal ions by pecan shell-based granular activated carbons R.R. Bansode a, J.N. Losso a, W.E. Marshall b, R.M. Rao a, *, R.J. Portier c a Department
Bioresource Technology 89 (23) 115 119 Adsorption of metal ions by pecan shell-based granular activated carbons R.R. Bansode a, J.N. Losso a, W.E. Marshall b, R.M. Rao a, *, R.J. Portier c a Department
Sulphur Dioxide and Oxygen Adsorption Isotherm Breakthrough Time on Surface Porous Palm Shell Activated Carbon
 211 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 56 2017 Guest Editors: Jiří Jaromír Klemeš Peng Yen Liew Wai Shin Ho Jeng Shiun Lim Copyright 2017 AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-47-1;
211 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 56 2017 Guest Editors: Jiří Jaromír Klemeš Peng Yen Liew Wai Shin Ho Jeng Shiun Lim Copyright 2017 AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-47-1;
Easy synthesis of hollow core, bimodal mesoporous shell carbon nanospheres and their. application in supercapacitor
 Electronic Electronic Supplementary Information Easy synthesis of hollow core, bimodal mesoporous shell carbon nanospheres and their application in supercapacitor Bo You, Jun Yang,* Yingqiang Sun and Qingde
Electronic Electronic Supplementary Information Easy synthesis of hollow core, bimodal mesoporous shell carbon nanospheres and their application in supercapacitor Bo You, Jun Yang,* Yingqiang Sun and Qingde
Treatment of Battery Waste Water Using Meranti Wood Sawdust as Adsorbent
 Treatment of Battery Waste Water Using Meranti Wood Sawdust as Adsorbent Hind Hamed Al-Riyami, Shah Jahan, and Priy Brat Dwivedi Abstract The release of heavy metals into the environment is a worldwide
Treatment of Battery Waste Water Using Meranti Wood Sawdust as Adsorbent Hind Hamed Al-Riyami, Shah Jahan, and Priy Brat Dwivedi Abstract The release of heavy metals into the environment is a worldwide
Developing a Low Cost Activated Carbon from Agricultural Waste for the Removal of Heavy Metal from Contaminated Water
 International Journal of Applied Chemistry. ISSN 0973-1792 Volume 13, Number 3 (2017) pp. 453-460 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Developing a Low Cost Activated Carbon from Agricultural
International Journal of Applied Chemistry. ISSN 0973-1792 Volume 13, Number 3 (2017) pp. 453-460 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Developing a Low Cost Activated Carbon from Agricultural
Experimental study on biochar modified characteristics
 2nd Annual International Conference on Energy, Environmental & Sustainable Ecosystem Development (EESED 2016) Experimental study on biochar modified characteristics Yan-Ru Ma, Li-Ming Wang, Wen-Yang Sun,
2nd Annual International Conference on Energy, Environmental & Sustainable Ecosystem Development (EESED 2016) Experimental study on biochar modified characteristics Yan-Ru Ma, Li-Ming Wang, Wen-Yang Sun,
Adsorption behavior of methylene blue onto gellan gum-bentonite composite beads for bioremediation application
 World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
AN ADSORPTION ISOTHERM MODEL FOR ADSORPTION PERFORMANCE OF SILVER-LOADED ACTIVATED CARBON
 THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 2017, Vol. 21, No. 4, pp. 1645-1649 1645 AN ADSORPTION ISOTHERM MODEL FOR ADSORPTION PERFORMANCE OF SILVER-LOADED ACTIVATED CARBON by a, Xue-Feng YAN b, Xue-Rong FAN a*, Qiang WANG
THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 2017, Vol. 21, No. 4, pp. 1645-1649 1645 AN ADSORPTION ISOTHERM MODEL FOR ADSORPTION PERFORMANCE OF SILVER-LOADED ACTIVATED CARBON by a, Xue-Feng YAN b, Xue-Rong FAN a*, Qiang WANG
Methylene blue adsorption by pyrolytic tyre char
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Division of Environmental Science and Engineering Division of Environmental Science and Engineering EG2605 UROP Report Methylene blue adsorption by pyrolytic tyre char
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Division of Environmental Science and Engineering Division of Environmental Science and Engineering EG2605 UROP Report Methylene blue adsorption by pyrolytic tyre char
Physical Characterization of Activated Carbon Derived from Mangosteen Peel
 Asian Journal of Chemistry; Vol. 24, No. 2 (212), 579-583 Physical Characterization of Activated Carbon Derived from Mangosteen Peel A. SHAMALA DEVI 1, PUZIAH ABDUL LATIF 1,*, Y.J. THAM 1 and Y.H. TAUFIQ-YAP
Asian Journal of Chemistry; Vol. 24, No. 2 (212), 579-583 Physical Characterization of Activated Carbon Derived from Mangosteen Peel A. SHAMALA DEVI 1, PUZIAH ABDUL LATIF 1,*, Y.J. THAM 1 and Y.H. TAUFIQ-YAP
BARIUM CHLORIDE MODIFICATION OF DIATOMITE FOR REMOVAL OF METHYLENE BLUE AND LEAD ION AQUEOUS SOLUTION
 ISSN: 974-1496 e-issn: 976-83 CODEN: RJCABP http://www.rasayanjournal.com http://www.rasayanjournal.co.in BARIUM CHLORIDE MODIFICATION OF DIATOMITE FOR FROM AQUEOUS SOLUTION Le Van Tan * and Le Thiet Hung
ISSN: 974-1496 e-issn: 976-83 CODEN: RJCABP http://www.rasayanjournal.com http://www.rasayanjournal.co.in BARIUM CHLORIDE MODIFICATION OF DIATOMITE FOR FROM AQUEOUS SOLUTION Le Van Tan * and Le Thiet Hung
Removal of Cd (II) and Cr (VI) from Electroplating Wastewater by Coconut Shell
 International Journal of Environmental Engineering and Management ISSN 2231-1319, Volume 4, Number 4 (213), pp. 273-28 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ ijeem.htm Removal of Cd
International Journal of Environmental Engineering and Management ISSN 2231-1319, Volume 4, Number 4 (213), pp. 273-28 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ ijeem.htm Removal of Cd
Supporting material. Figures
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2018 Supporting material Figures
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2018 Supporting material Figures
Research Article Effect of CO 2 Flow Rate on the Pinang Frond-Based Activated Carbon for Methylene Blue Removal
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 545948, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/545948 Research Article Effect of CO 2 Flow Rate on the Pinang Frond-Based
Hindawi Publishing Corporation The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 545948, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/545948 Research Article Effect of CO 2 Flow Rate on the Pinang Frond-Based
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Removal of Basic Dyes from Aqueous Solutions by Sugar Can Stalks
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2011, 2 (4):283-290 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Removal of Basic Dyes from Aqueous Solutions by Sugar Can
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2011, 2 (4):283-290 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Removal of Basic Dyes from Aqueous Solutions by Sugar Can
A novel Ag 3 AsO 4 visible-light-responsive photocatalyst: facile synthesis and exceptional photocatalytic performance
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Supporting Information A novel Ag 3 AsO 4 visible-light-responsive photocatalyst: facile synthesis and exceptional photocatalytic performance
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Supporting Information A novel Ag 3 AsO 4 visible-light-responsive photocatalyst: facile synthesis and exceptional photocatalytic performance
Adsorption of chromium from aqueous solution by activated alumina and activated charcoal
 Adsorption of chromium from aqueous solution by activated alumina and activated charcoal Suman Mor a,b*, Khaiwal Ravindra c and N. R. Bishnoi b a Department of Energy and Environmental Science, Chaudhary
Adsorption of chromium from aqueous solution by activated alumina and activated charcoal Suman Mor a,b*, Khaiwal Ravindra c and N. R. Bishnoi b a Department of Energy and Environmental Science, Chaudhary
Utilization of Chemically Modified Rice Hull for the Treatment of Industrial Wastewater
 2012 3rd International Conference on Chemistry and Chemical Engineering IPCBEE vol.38 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Utilization of Chemically Modified Rice Hull for the Treatment of Industrial
2012 3rd International Conference on Chemistry and Chemical Engineering IPCBEE vol.38 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Utilization of Chemically Modified Rice Hull for the Treatment of Industrial
ACTIVATION OF BIOMASS FIBRES USING ALKALI METAL SALTS
 SUMMARY ACTIVATION OF BIOMASS FIBRES USING ALKALI METAL SALTS James Illingworth, Aidan Westwood*, Brian Rand and Paul Williams School of Process Environmental and Materials Engineering University of Leeds,
SUMMARY ACTIVATION OF BIOMASS FIBRES USING ALKALI METAL SALTS James Illingworth, Aidan Westwood*, Brian Rand and Paul Williams School of Process Environmental and Materials Engineering University of Leeds,
R&D on adsorption processing technology using pitch activated carbon fiber
 1999D.4.1.1 R&D on adsorption processing technology using pitch activated carbon fiber 1. Contents of empirical research With respect to waste water, exhausts and other emissions in the petroleum refining
1999D.4.1.1 R&D on adsorption processing technology using pitch activated carbon fiber 1. Contents of empirical research With respect to waste water, exhausts and other emissions in the petroleum refining
Characterization Of Activated Carbon Prepared From Coconut Shell Using Various Reagents For A Low Cost Water- Filter
 Characterization Of Activated Carbon Prepared From Coconut Shell Using Various Reagents For A Low Cost Water- Filter Sohan Ahmed 1, Vaibhav V Mada 1, Vaibhav Kamath 1, Gautham P Jeppu 2 1 UG Student. Chemical
Characterization Of Activated Carbon Prepared From Coconut Shell Using Various Reagents For A Low Cost Water- Filter Sohan Ahmed 1, Vaibhav V Mada 1, Vaibhav Kamath 1, Gautham P Jeppu 2 1 UG Student. Chemical
Modification of Activated Carbon from Biomass Nypa and Amine Functional Groups as Carbon Dioxide Adsorbent
 Journal of Physical Science, Vol. 28(Supp. 1), 227 240, 2017 Modification of Activated Carbon from Biomass Nypa and Amine Functional Groups as Carbon Dioxide Adsorbent Nur 'Izzati A. Ghani, 1 Nur Yusra
Journal of Physical Science, Vol. 28(Supp. 1), 227 240, 2017 Modification of Activated Carbon from Biomass Nypa and Amine Functional Groups as Carbon Dioxide Adsorbent Nur 'Izzati A. Ghani, 1 Nur Yusra
CO 2 ADSORPTION BY SURFACE MODIFIED CARBON SORBENTS
 CO 2 ADSORPTION BY SURFACE MODIFIED CARBON SORBENTS Mercedes Maroto-Valer*, Zhong Tang and Yinzhi Zhang The Energy Institute and The Department of Energy and Geo-Environmental Engineering, The Pennsylvania
CO 2 ADSORPTION BY SURFACE MODIFIED CARBON SORBENTS Mercedes Maroto-Valer*, Zhong Tang and Yinzhi Zhang The Energy Institute and The Department of Energy and Geo-Environmental Engineering, The Pennsylvania
CHAPTER - 3 ADSORBENT CHARACTERISTICS
 CHAPTER - 3 ADSORBENT CHARACTERISTICS In the present work five categories of activated carbon were prepared from Ananas Comosus L by different methods. Out of five activated carbons, one superior quality
CHAPTER - 3 ADSORBENT CHARACTERISTICS In the present work five categories of activated carbon were prepared from Ananas Comosus L by different methods. Out of five activated carbons, one superior quality
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: Vol.7, No.7, pp , 2015
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: 0974-4290 Vol.7, No.7, pp 3095-3099, 2015 ICEWEST-2015 [05 th - 06 th Feb 2015] International Conference on Energy, Water and Environmental
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: 0974-4290 Vol.7, No.7, pp 3095-3099, 2015 ICEWEST-2015 [05 th - 06 th Feb 2015] International Conference on Energy, Water and Environmental
Please do not adjust margins. Flower stamen-like porous boron carbon nitride nanoscrolls for water cleaning
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2017 not adjust margins Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Flower stamen-like porous
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2017 not adjust margins Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Flower stamen-like porous
Adsorption of Free Fatty Acid from Crude Palm Oil on Magnesium Silicate Derived From Rice Husk
 Adsorption of Free Fatty Acid from Crude Palm Oil on Magnesium Silicate Derived From Rice Husk Weerawat Clowutimon, Prakob Kitchaiya, and Pornsawan Assawasaengrat* Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty
Adsorption of Free Fatty Acid from Crude Palm Oil on Magnesium Silicate Derived From Rice Husk Weerawat Clowutimon, Prakob Kitchaiya, and Pornsawan Assawasaengrat* Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information A honeycomb-like porous carbon derived from pomelo peel for use in high-performance
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information A honeycomb-like porous carbon derived from pomelo peel for use in high-performance
N. F. N. Yah 1, H. A. Rahim 1*, Y. S. Lee 2, F. H. Wee 1, and H. H. Zainal 1. Abstract. 1. Introduction
 ADVANCED ELECTROMAGNETICS, VOL. 7, NO. 1, JANUARY 018 Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties of Novel Green Composites Coconut Fiber and Powder over X-band Frequency for Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing
ADVANCED ELECTROMAGNETICS, VOL. 7, NO. 1, JANUARY 018 Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties of Novel Green Composites Coconut Fiber and Powder over X-band Frequency for Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE
 EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE The present experimentation is carried out on biosorption of chromium and lead from aqueous solutions by biosorbents Ageratum conyzoides leaf and Anacardium occidentale testa powder.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE The present experimentation is carried out on biosorption of chromium and lead from aqueous solutions by biosorbents Ageratum conyzoides leaf and Anacardium occidentale testa powder.
Kuala Lumpur 50603, Malaysia 2 Department of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, Faculty of Engineering,
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences Engineering and Technology 4(5): 458-465, 01 ISSN: 040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 01 Submitted: October 05, 011 Accepted: October 3, 011 Published: March
Research Journal of Applied Sciences Engineering and Technology 4(5): 458-465, 01 ISSN: 040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 01 Submitted: October 05, 011 Accepted: October 3, 011 Published: March
Comparative Analysis of Adsorption of Methylene Blue Dye Using Carbon from Palmkernel Shell Activated by Different Activating Agents
 Comparative Analysis of Adsorption of Methylene Blue Dye Using Carbon from Palmkernel Shell Activated by Different Activating Agents Sann S. E., Adeeyo O. A., Efeovbokhan V., Ojewumi M., Ayoola A., Ogunbiyi
Comparative Analysis of Adsorption of Methylene Blue Dye Using Carbon from Palmkernel Shell Activated by Different Activating Agents Sann S. E., Adeeyo O. A., Efeovbokhan V., Ojewumi M., Ayoola A., Ogunbiyi
Extraction Behaviour of Cu 2+ Ions with Used Cooking Oil-Based Organic Solvent
 International Proceedings of Chemical, Biological and Environmental Engineering, V0l. 96 (2016) DOI: 10.7763/IPCBEE. 2016. V96. 4 Extraction Behaviour of Cu 2+ Ions with Used Cooking Oil-Based Organic
International Proceedings of Chemical, Biological and Environmental Engineering, V0l. 96 (2016) DOI: 10.7763/IPCBEE. 2016. V96. 4 Extraction Behaviour of Cu 2+ Ions with Used Cooking Oil-Based Organic
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Au nanoparticles supported on magnetically separable Fe 2 O 3 - graphene
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Au nanoparticles supported on magnetically separable Fe 2 O 3 - graphene
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL 17 19, July ENGINEERING. COLOR REMOVAL FROM TEXTILE WASTEWATER USING CuO NANO- PARTICLE COATED ON SAND, CINDER AND GAC
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL 17 19, July ENGINEERING 2014, Mysore, Karnataka, India AND TECHNOLOGY (IJCIET) ISSN 0976 6308 (Print) ISSN 0976 6316(Online) Volume 5, Issue 9, September (2014), pp. 79-84
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL 17 19, July ENGINEERING 2014, Mysore, Karnataka, India AND TECHNOLOGY (IJCIET) ISSN 0976 6308 (Print) ISSN 0976 6316(Online) Volume 5, Issue 9, September (2014), pp. 79-84
Preparation of Activated Carbon Using the Copyrolysis of Agricultural and Municipal Solid Wastes at a Low Carbonization Temperature
 2011 International Conference on Biology, Environment and Chemistry IPCBEE vol.24 (2011) (2011)IACSIT Press, Singapoore Preparation of Activated Carbon Using the Copyrolysis of Agricultural and Municipal
2011 International Conference on Biology, Environment and Chemistry IPCBEE vol.24 (2011) (2011)IACSIT Press, Singapoore Preparation of Activated Carbon Using the Copyrolysis of Agricultural and Municipal
The Effect of Coal Fly Ash Treatment with NaOH on the Characters and Adsorption Mechanism toward Methyl Violet in The Solution
 2012 3rd International Conference on Chemistry and Chemical Engineering IPCBEE vol.38 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore The Effect of Coal Fly Ash Treatment with Na on the Characters and Adsorption
2012 3rd International Conference on Chemistry and Chemical Engineering IPCBEE vol.38 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore The Effect of Coal Fly Ash Treatment with Na on the Characters and Adsorption
Preparation and Characterization of Soybean Straw Activated Carbon by Zinc Chloride Xu Zhong, Zhao Dan
 2nd International Conference on Machinery, Materials Engineering, Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology (MMECEB 215) Preparation and Characterization of Soybean Straw Activated Carbon by Zinc Chloride
2nd International Conference on Machinery, Materials Engineering, Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology (MMECEB 215) Preparation and Characterization of Soybean Straw Activated Carbon by Zinc Chloride
Kinetics of adsorption of methylene blue onto activated carbon prepared from palm kernel shell
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Archives of Applied Science Research, 211, 3 (1):154-164 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 975-58X CODEN
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Archives of Applied Science Research, 211, 3 (1):154-164 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 975-58X CODEN
