SPECTROPHOTOMETRY/BEER S LAW LECTURE HONORS CHEMISTRY NAME
|
|
|
- Samuel Blair
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SPECTROPHOTOMETRY/BEER S LAW LECTURE HONORS CHEMISTRY NAME Overview: Spectroscopy will be a tool that you will use as you continue in your chemistry, biology and physics courses. Background: We will begin by discussing the relationships between energy, wavelength, frequency, and speed of light waves. The wavelength, (lambda) of any wave is the crest-to-crest distance between waves. The frequency, v (nu) is the number of complete oscillations that a wave makes each second. The speed of a wave is the distance one wave travels in a given time period. The relation between wavelength, frequency, and speed is Speed = wavelength * frequency (1) The speed of light is constant in a given medium. For example, the speed of light in a vacuum is x 10 8 m/s and is symbolized by the letter c. The speed of light decreases in other media such as air or water. In water, the speed of light decreases enough to give illusions such as a spoon appearing bent when it is partially submerged in a glass of water. The decrease in speed is negligible in air so we will consider the speed of light to be 3.00 x 10 8 m/s in air. This leads to the equation c = (2) Where c = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s, = wavelength given in meter units, and = frequency given in Hertz units (Hz, oscillations/second). Each light particle, or photon, carries a discrete amount of energy. This energy is proportional to the frequency of the light, and is therefore inversely proportional to the wavelength of light. This relation was discovered by Max Planck in 1900 when he determined that E photon = hv (3) where E photon = Energy of one photon (not a mole of photons!) given in Joule units and h = Planck s Constant, x Joule*seconds.
2 Extinction Coefficient (cm -1 M -1 x 10-3 ) Visible light: Absorption and Emission of Light: The particle nature of light is most often used to explain absorption and emission properties of atoms and molecules. Molecules absorb or emit energy only in discrete amounts or packets called quanta. Absorption or emission of light by an atom or a molecule can only occur if the energy of the photon is equal to the energy difference between two energy levels in the atom or molecule. For the purposes of Honors Chemistry, we will concern ourselves only with absorption of light for the remainder of this discussion. Molecules can exist only in discrete energy states. This means that they will only absorb photons of specific energies and therefore specific frequencies and wavelengths. This is shown graphically when the amount of light absorbed is plotted as a function of the frequency or wavelength. This graph is called the spectrum of a particular molecule or atom. Figure 1 shows how two molecules that are very similar structurally can have different spectra. We will use this difference in spectra to our advantage during our kinetics laboratory in week NAD + NADH CONH 2 H H CONH N R N R wavelength (nm) NAD NADH Figure 1: Two molecules NAD and NADH have very similar structures but have different spectra in the ultraviolet light range. 2
3 Transmittance and Absorbance: It is difficult, if not impossible, to measure actual absorbance of light. Instead, we measure transmittance or the fraction of light that is able to pass through a solution of molecules. A spectrophotometer measures the intensity of light entering a sample and compares this to the intensity of light emerging from the sample (Figure 2). I O IE Figure 2: Transmittance of light in a spectrophotometer. Transmittance = I 0 /I E. b I O = Intensity of incident light I E = Intensity of exiting light b = path length of sample There are three things that will effect the amount of light emerging from the sample. First, the concentration of molecules in the solution affects the transmittance. Each molecule can absorb light. As you increase the number of molecules in the solution, you also increase the photons absorbed. Therefore, as you increase the concentration of a sample, you decrease the transmittance. Second, the length of the sample path will affect the transmittance. By increasing the pathway that the light must travel through your sample, you are increasing the number of molecules that will interact with the light; in effect, you are increasing the apparent concentration. Third, the transmittance will be affected by specific properties of the molecules. Molecules absorb light at different efficiencies and at different energies. Therefore, the transmittance will be dependent upon the specific molecule in solution and the wavelength of light being passed through the sample. In 1729 Pierre Bouguer discovered that the relationship between transmittance and concentration or sample path length is a logarithmic one. The reason for this can be illustrated if you consider the sample of solution in figure 2 above. The molecules nearest the source of light will experience I O the same as that which was measured by the spectrophotometer. However, molecules nearest the exit point of the sample will experience I O that is less than the original because molecules have absorbed light throughout the sample. In other words, as light travels through the sample, there is a drop in I O in each succeeding layer. The definition of transmittance tells us that that T = I E /I O. Because I O changes throughout the sample, we have a logarithmic, rather than linear, relationship between transmittance and concentration or sample path length. The Lambert-Beer Law: The fact that transmittance of light varies exponentially as it passes through an absorbing medium was rediscovered by Johann Heinrich Lambert in Later, in 1852, August Beer defined absorbance: A = -log 10 (T) (4) When no light is absorbed, I E = I O, T = 1.00 and A = 0. When 90% of the light is absorbed, T = 0.1 and A = 1. Beer then showed that absorbance was linearly related to concentration. These two men are given credit for the Lambert-Beer Law: A = abc (5) 3
4 Absorbance Where a = a constant which takes into account the specific properties of the molecules which are absorbing photons, b = sample path length, usually 1 cm, and c = concentration of solution, M. Note that Absorbance is unitless. It is interesting to note that equations 5 is often referred to as Beer s Law, with no reference to Lambert. Moreover, Pierre Bouguer, who first published the theory upon which this law is based does not get any credit in the name of the equation. Practical Uses of Beer s Law: How does any of this help us in our study of chemistry? Most often we are using Beer s Law to help us determine the concentration of a solution--if we know two of the three variables a, b, or c in equation 5, we can measure the absorbance and determine the unknown variable. Determination of Concentration When a is Known: For many chemicals, the constant a is known and is listed in tables. It is usually listed as its molar absorption coefficient, absorption of solution measures 0.650, then you can solve for c: A = abc = (3600 M -1 cm -1 )(1 cm)c c = 1.80 x 10-4 M -1 cm -1, and the In practice, chemists rarely determine concentration in this manner. This method can result in answers that are incorrect due to differences in instrumentation and inherent errors made by the scientist. If the instrument that you are using is not calibrated the same as the instrument used to determine Also, it is possible for you to make consistent mistakes such as pipetting incorrectly or using a cuvette that has a scratch or is dirty. For these reasons, concentrations are most often determined using a standard curve. Determination of Concentration Using a Standard Curve: Standard curves are generated when a is not known and/or to minimize experimental error. In this case, the researcher determines the absorbance of several known concentrations of the solution. These known concentrations are referred to as standard solutions. The standards are then plotted as an absorbance vs concentration graph. This graph is called a standard curve. If you were careful in making the standards and measuring their absorbance, the graph should be a straight line (figure 3). The line should have a y intercept of zero (when the concentration is zero, there should be zero absorbance) and the slope of the line is equal to a in equation Concentration, M Figure 3: Standard curve. 4
5 Absorbance After the standard curve has been plotted, the concentration of experimental solutions can be determined. The absorbance of the experimental solution is measured and compared to the standard curve. A quick, but less precise, method for doing this is to find the absorbance of the experimental solution on the y-axis of the standard curve, draw a line parallel to the x-axis until you reach the line on the graph, then draw a line parallel to the y-axis until you reach the x-axis. The point on the x-axis tells you the concentration of your solution (figure 4) Concentration, M Figure 4: An experimental solution had an absorbance of Using the graphic method, this indicates that the concentration was 0.38 M. A more precise method for determining the concentration of an experimental solution requires you to determine the straight-line equation of your line. This can easily be done by computer. Once you have this equation, you simply put the measured absorbance of your experimental solution in as y, and solve for x. For example, the linear regression of the data in Figures 4 and 5 shows that the straight-line equation for these graphs is y = 1.2x + 0 so, 0.48 = 1.2x x = 0.40 M You will note that the answers from both methods is very similar, but you get a more precise measurement when you use the line equation. Sources of Error in Beer s Law Measurements: Beer s Law is only true for dilute solutions--the exact range of solutions must be determined experimentally. Beyond this range, measurements and calculations using Beer s Law will be erroneous. Other common sources of error include the use of dirty cuvettes, poorly mixed solutions, poor pipetting techniques, and incorrect light source or wavelength. Because you have control over these errors, you must make sure to minimize these problems in your laboratory exercises. 5
Absorption, Emission and Fluorescence Spectroscopies. R. Corn - Chem M3LC
 Absorption, Emission and Fluorescence Spectroscopies R. Corn - Chem M3LC Light behaves like an electromagnetic wave... 2.998 x 10 8 meters/sec λ = the Greek letter lambda ν = the Greek letter nu velocity
Absorption, Emission and Fluorescence Spectroscopies R. Corn - Chem M3LC Light behaves like an electromagnetic wave... 2.998 x 10 8 meters/sec λ = the Greek letter lambda ν = the Greek letter nu velocity
Absorption, Emission and Fluorescence Spectroscopies. Chem M3LC. R. Corn
 Absorption, Emission and Fluorescence Spectroscopies Chem M3LC. R. Corn Review: Light behaves like an electromagnetic wave... 2.998 x 10 8 meters/sec λ = the Greek letter lambda ν = the Greek letter nu
Absorption, Emission and Fluorescence Spectroscopies Chem M3LC. R. Corn Review: Light behaves like an electromagnetic wave... 2.998 x 10 8 meters/sec λ = the Greek letter lambda ν = the Greek letter nu
Spectroscopy Meditsiiniline keemia/medical chemistry LOKT Spectroscopy
 Meditsiiniline keemia/medical chemistry LOKT.00.009 Spectroscopy 04.09.12 http://tera.chem.ut.ee/~koit/arstpr/spe_en.pdf 1 ntroduction Spectroscopy is a general term for methods that investigate interactions
Meditsiiniline keemia/medical chemistry LOKT.00.009 Spectroscopy 04.09.12 http://tera.chem.ut.ee/~koit/arstpr/spe_en.pdf 1 ntroduction Spectroscopy is a general term for methods that investigate interactions
The ELECTRON: Wave Particle Duality. chapter 4
 The ELECTRON: Wave Particle Duality chapter 4 What do we know about light? Before 1900 s scientists thought light behaved as a wave. This belief changed when it was discovered that light also has particle
The ELECTRON: Wave Particle Duality chapter 4 What do we know about light? Before 1900 s scientists thought light behaved as a wave. This belief changed when it was discovered that light also has particle
Beer's- Lambert Law and Standard Curves. BCH 312 [Practical]
![Beer's- Lambert Law and Standard Curves. BCH 312 [Practical] Beer's- Lambert Law and Standard Curves. BCH 312 [Practical]](/thumbs/78/77692425.jpg) Beer's- Lambert Law and Standard Curves BCH 312 [Practical] Spectrophotometer: Spectrophotometer can be used to measure the amount of light absorbed or transmitted by a solution. It consist of two parts:
Beer's- Lambert Law and Standard Curves BCH 312 [Practical] Spectrophotometer: Spectrophotometer can be used to measure the amount of light absorbed or transmitted by a solution. It consist of two parts:
UV-Vis Absorption Experiment 5: Beer- Lambert Law and the Temperature Dependence of the Crystal Violet- Sodium Hydroxide Reaction
 1 UV-Vis Absorption Experiment 5: Beer- Lambert Law and the Temperature Dependence of the Crystal Violet- Sodium Hydroxide Reaction Overview In Part A of this experiment, the absorption behaviour of crystal
1 UV-Vis Absorption Experiment 5: Beer- Lambert Law and the Temperature Dependence of the Crystal Violet- Sodium Hydroxide Reaction Overview In Part A of this experiment, the absorption behaviour of crystal
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 2. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 2 Electromagnetic Radiation Can be described by means of a classical sinusoidal wave model. Oscillating electric and magnetic field. (Wave model) wavelength,
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 2 Electromagnetic Radiation Can be described by means of a classical sinusoidal wave model. Oscillating electric and magnetic field. (Wave model) wavelength,
Chapter 6. Quantum Theory and the Electronic Structure of Atoms Part 1
 Chapter 6 Quantum Theory and the Electronic Structure of Atoms Part 1 The nature of light Quantum theory Topics Bohr s theory of the hydrogen atom Wave properties of matter Quantum mechanics Quantum numbers
Chapter 6 Quantum Theory and the Electronic Structure of Atoms Part 1 The nature of light Quantum theory Topics Bohr s theory of the hydrogen atom Wave properties of matter Quantum mechanics Quantum numbers
NOTES: 5.3 Light and Atomic Spectra (more Quantum Mechanics!)
 NOTES: 5.3 Light and Atomic Spectra (more Quantum Mechanics!) Light WAVE or PARTICLE? Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation includes: -radio waves -microwaves -infrared waves -visible light
NOTES: 5.3 Light and Atomic Spectra (more Quantum Mechanics!) Light WAVE or PARTICLE? Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation includes: -radio waves -microwaves -infrared waves -visible light
EXPERIMENT 17: Atomic Emission
 EXPERIMENT 17: Atomic Emission PURPOSE: To construct an energy level diagram of the hydrogen atom To identify an element from its line spectrum. PRINCIPLES: White light, such as emitted by the sun or an
EXPERIMENT 17: Atomic Emission PURPOSE: To construct an energy level diagram of the hydrogen atom To identify an element from its line spectrum. PRINCIPLES: White light, such as emitted by the sun or an
Physics and the Quantum Mechanical Model
 chemistry 1 of 38 Mechanical Model Neon advertising signs are formed from glass tubes bent in various shapes. An electric current passing through the gas in each glass tube makes the gas glow with its
chemistry 1 of 38 Mechanical Model Neon advertising signs are formed from glass tubes bent in various shapes. An electric current passing through the gas in each glass tube makes the gas glow with its
Introduction. The amount of radiation absorbed may be measured in a number of ways: Transmittance, T = P / P 0 % Transmittance, %T = 100 T
 Introduction Many compounds absorb ultraviolet (UV) or visible (Vis.) light. The diagram below shows a beam of monochromatic radiation of radiant power P 0, directed at a sample solution. Absorption takes
Introduction Many compounds absorb ultraviolet (UV) or visible (Vis.) light. The diagram below shows a beam of monochromatic radiation of radiant power P 0, directed at a sample solution. Absorption takes
The Sine Wave. You commonly see waves in the environment. Light Sound Electricity Ocean waves
 The Sine Wave Mathematically, a function that represents a smooth oscillation For example, if we drew the motion of how the weight bobs on the spring to the weight we would draw out a sine wave. The Sine
The Sine Wave Mathematically, a function that represents a smooth oscillation For example, if we drew the motion of how the weight bobs on the spring to the weight we would draw out a sine wave. The Sine
Write the electron configuration for Chromium (Cr):
 Write the electron configuration for Chromium (Cr): Energy level Aufbau Principle Atomic orbital Quantum Hund s Rule Atomic number Electron Configuration Whole number Pauli Exlcusion Principle Quantum
Write the electron configuration for Chromium (Cr): Energy level Aufbau Principle Atomic orbital Quantum Hund s Rule Atomic number Electron Configuration Whole number Pauli Exlcusion Principle Quantum
5.3. Physics and the Quantum Mechanical Model
 Chemistry 5-3 Physics and the Quantum Mechanical Model Neon advertising signs are formed from glass tubes bent in various shapes. An electric current passing through the gas in each glass tube makes the
Chemistry 5-3 Physics and the Quantum Mechanical Model Neon advertising signs are formed from glass tubes bent in various shapes. An electric current passing through the gas in each glass tube makes the
Chapter 7 Atomic Structure -1 Quantum Model of Atom. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Chapter 7 Atomic Structure -1 Quantum Model of Atom Dr. Sapna Gupta The Electromagnetic Spectrum The electromagnetic spectrum includes many different types of radiation which travel in waves. Visible light
Chapter 7 Atomic Structure -1 Quantum Model of Atom Dr. Sapna Gupta The Electromagnetic Spectrum The electromagnetic spectrum includes many different types of radiation which travel in waves. Visible light
Experiment 12: SPECTROSCOPY: EMISSION & ABSORPTION
 Sample Experiment 12: SPECTROSCOPY: EMISSION & ABSORPTION Purpose: Emission and absorption spectroscopy is to be explored from different perspectives in a multipart experiment. Part I: Certain elements
Sample Experiment 12: SPECTROSCOPY: EMISSION & ABSORPTION Purpose: Emission and absorption spectroscopy is to be explored from different perspectives in a multipart experiment. Part I: Certain elements
Chemistry 1215 Experiment #11 Spectrophotometric Analysis of an Unknown Brass Sample
 Chemistry 1215 Experiment #11 Spectrophotometric Analysis of an Unknown Brass Sample Objective In this experiment you will use spectrophotometric measurements to determine the copper concentration of a
Chemistry 1215 Experiment #11 Spectrophotometric Analysis of an Unknown Brass Sample Objective In this experiment you will use spectrophotometric measurements to determine the copper concentration of a
Table of Contents Electrons in Atoms > Light and Quantized Energy > Quantum Theory and the Atom > Electron Configuration
 Electrons in Atoms October 20, 2014 Table of Contents Electrons in Atoms > Light and Quantized Energy > Quantum Theory and the Atom > Electron Configuration 1 Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic radiation
Electrons in Atoms October 20, 2014 Table of Contents Electrons in Atoms > Light and Quantized Energy > Quantum Theory and the Atom > Electron Configuration 1 Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic radiation
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms
 Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5.2 Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic Emission Spectra and the Quantum Mechanical Model 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5.2 Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic Emission Spectra and the Quantum Mechanical Model 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
Spectrophotometry. Introduction
 Spectrophotometry Spectrophotometry is a method to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs light by measuring the intensity of light as a beam of light passes through sample solution. The basic principle
Spectrophotometry Spectrophotometry is a method to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs light by measuring the intensity of light as a beam of light passes through sample solution. The basic principle
Lab #12: Determination of a Chemical Equilibrium Constant
 Lab #12: Determination of a Chemical Equilibrium Constant Objectives: 1. Determine the equilibrium constant of the formation of the thiocyanatoiron (III) ions. 2. Understand the application of using a
Lab #12: Determination of a Chemical Equilibrium Constant Objectives: 1. Determine the equilibrium constant of the formation of the thiocyanatoiron (III) ions. 2. Understand the application of using a
Supplemental Activities. Module: Atomic Theory. Section: Electromagnetic Radiation and Matter
 Supplemental Activities Module: Atomic Theory Section: Electromagnetic Radiation and Matter Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation Activity 1 1. What are the two components that make up electromagnetic
Supplemental Activities Module: Atomic Theory Section: Electromagnetic Radiation and Matter Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation Activity 1 1. What are the two components that make up electromagnetic
Lab Investigation 4 - How could you make more of this dye?
 Lab Investigation 4 - How could you make more of this dye? USING SPECTROSCOPY TO DETERMINE SOLUTION CON- CENTRATION Guiding Question How could you make more of this dye? INTRODUCTION A solution is a homogeneous
Lab Investigation 4 - How could you make more of this dye? USING SPECTROSCOPY TO DETERMINE SOLUTION CON- CENTRATION Guiding Question How could you make more of this dye? INTRODUCTION A solution is a homogeneous
Lecture 3: Light absorbance
 Lecture 3: Light absorbance Perturbation Response 1 Light in Chemistry Light Response 0-3 Absorbance spectrum of benzene 2 Absorption Visible Light in Chemistry S 2 S 1 Fluorescence http://www.microscopyu.com
Lecture 3: Light absorbance Perturbation Response 1 Light in Chemistry Light Response 0-3 Absorbance spectrum of benzene 2 Absorption Visible Light in Chemistry S 2 S 1 Fluorescence http://www.microscopyu.com
Background: The Electromagnetic Spectrum
 Background: The Electromagnetic Spectrum Wavelength (λ) in meters wavelength decreasing 10 4 10 2 10 0 10-2 10-4 10-6 10-8 10-10 10-12 10-14 microwaves ultraviolet Gamma rays Radio waves AM 10 4 Shortwave
Background: The Electromagnetic Spectrum Wavelength (λ) in meters wavelength decreasing 10 4 10 2 10 0 10-2 10-4 10-6 10-8 10-10 10-12 10-14 microwaves ultraviolet Gamma rays Radio waves AM 10 4 Shortwave
Concepts, Techniques. Concepts, Techniques 9/11/2012. & Beer s Law. For a simple, transparent, COLORED material, e.g. ROYGBV
 9//22 OBJECTIVES Spectrophotometry of Food Dyes & Beer s Law Last Update: 9//22 9:54 AM What is the quantitative basis for the color of substances? How is the absorption/transmission of light measured?
9//22 OBJECTIVES Spectrophotometry of Food Dyes & Beer s Law Last Update: 9//22 9:54 AM What is the quantitative basis for the color of substances? How is the absorption/transmission of light measured?
The relationship between these aspects is described by the following equation: E = hν =
 1 Learning Outcomes EXPERIMENT A10: LINE SPECTRUM Upon completion of this lab, the student will be able to: 1) Examine the line spectrum of the hydrogen atom. 2) Calculate the frequency and energy of the
1 Learning Outcomes EXPERIMENT A10: LINE SPECTRUM Upon completion of this lab, the student will be able to: 1) Examine the line spectrum of the hydrogen atom. 2) Calculate the frequency and energy of the
Chem 321 Lecture 18 - Spectrophotometry 10/31/13
 Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 18 - Spectrophotometry 10/31/13 In the lab you will use spectrophotometric techniques to determine the amount of iron, calcium and magnesium in unknowns. Although
Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 18 - Spectrophotometry 10/31/13 In the lab you will use spectrophotometric techniques to determine the amount of iron, calcium and magnesium in unknowns. Although
Atomic Spectroscopy and Energy Levels
 Activity 18 Atomic Spectroscopy and Energy Levels Why? The emission of light by the hydrogen atom and other atoms played a key role in helping scientists to understand the electronic structure of atoms.
Activity 18 Atomic Spectroscopy and Energy Levels Why? The emission of light by the hydrogen atom and other atoms played a key role in helping scientists to understand the electronic structure of atoms.
Spectroscopy Primer. for ultraviolet and visible absorbance spectroscopy. by Stephanie Myers Summer 2015
 Spectroscopy Primer for ultraviolet and visible absorbance spectroscopy by Stephanie Myers Summer 2015 Abstract: An overview of uv vis absorbance spectroscopy including Beer s Law, calibration curves,
Spectroscopy Primer for ultraviolet and visible absorbance spectroscopy by Stephanie Myers Summer 2015 Abstract: An overview of uv vis absorbance spectroscopy including Beer s Law, calibration curves,
Wave - Particle Duality of Light
 Properties of Light Objectives Explain wave-particle duality State the speed of light Describe electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum Explain how light interacts with transparent and opaque
Properties of Light Objectives Explain wave-particle duality State the speed of light Describe electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum Explain how light interacts with transparent and opaque
Experiment#1 Beer s Law: Absorption Spectroscopy of Cobalt(II)
 : Absorption Spectroscopy of Cobalt(II) OBJECTIVES In successfully completing this lab you will: prepare a stock solution using a volumetric flask; use a UV/Visible spectrometer to measure an absorption
: Absorption Spectroscopy of Cobalt(II) OBJECTIVES In successfully completing this lab you will: prepare a stock solution using a volumetric flask; use a UV/Visible spectrometer to measure an absorption
Supplemental Activities. Module: Atomic Theory. Section: Electromagnetic Radiation and Matter - Key
 Supplemental Activities Module: Atomic Theory Section: Electromagnetic Radiation and Matter - Key Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation Activity 1 1. What are the two components that make up electromagnetic
Supplemental Activities Module: Atomic Theory Section: Electromagnetic Radiation and Matter - Key Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation Activity 1 1. What are the two components that make up electromagnetic
Determining the Concentration of a Solution: Beer s Law
 Determining the Concentration of a Solution: Beer s Law The primary objective of this experiment is to determine the concentration of an unknown cobalt (II) chloride solution. You will use a Vernier SpectroVis
Determining the Concentration of a Solution: Beer s Law The primary objective of this experiment is to determine the concentration of an unknown cobalt (II) chloride solution. You will use a Vernier SpectroVis
This activity has been password protected to prevent modification. In order to request an unprotected version of this activity, contact
 This activity has been password protected to prevent modification. In order to request an unprotected version of this activity, contact pogil@pogil.org The BEER-LAMBERT LAW Learning Objectives Students
This activity has been password protected to prevent modification. In order to request an unprotected version of this activity, contact pogil@pogil.org The BEER-LAMBERT LAW Learning Objectives Students
Chemistry 141 Laboratory Spectrometric Determination of Iron Concentration Lab Lecture Notes 8/29/2011 Dr. Abrash
 Chemistry 141 Laboratory Spectrometric Determination of Iron Concentration Lab Lecture Notes 8/29/2011 Dr. Abrash What is the purpose of this experiment? We re going to learn a way to quantify the amount
Chemistry 141 Laboratory Spectrometric Determination of Iron Concentration Lab Lecture Notes 8/29/2011 Dr. Abrash What is the purpose of this experiment? We re going to learn a way to quantify the amount
DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT
 DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT In this experiment the equilibrium properties of the reaction between the iron(iii) ion and the thiocyanate ion will be studied. The relevant chemical equation
DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT In this experiment the equilibrium properties of the reaction between the iron(iii) ion and the thiocyanate ion will be studied. The relevant chemical equation
Electrons, Energy, & the Electromagnetic Spectrum Notes Simplified, 2-D Bohr Model: Figure 2. Figure 3 UNIT 4 - ELECTRONS & ELECTRON ARRANGEMENT
 Electrons, Energy, & the Electromagnetic Spectrum Notes Simplified, 2-D Bohr Model: Figure 1 UNIT 4 - ELECTRONS & ELECTRON ARRANGEMENT Figure 2 Figure 3 The energy is released as electromagnetic radiation.
Electrons, Energy, & the Electromagnetic Spectrum Notes Simplified, 2-D Bohr Model: Figure 1 UNIT 4 - ELECTRONS & ELECTRON ARRANGEMENT Figure 2 Figure 3 The energy is released as electromagnetic radiation.
Determining Riboflavin Content in a Multivitamin: Things to do before the lab
 Determining Riboflavin Content in a Multivitamin: Things to do before the lab Calculate everything you can that you can in advance Step 1: Calculate the dilution of a 4.0 M solution to 1 L of a 0.02 M
Determining Riboflavin Content in a Multivitamin: Things to do before the lab Calculate everything you can that you can in advance Step 1: Calculate the dilution of a 4.0 M solution to 1 L of a 0.02 M
The Fundamentals of Spectroscopy: Theory BUILDING BETTER SCIENCE AGILENT AND YOU
 The Fundamentals of Spectroscopy: Theory BUILDING BETTER SCIENCE AGILENT AND YOU 1 Agilent is committed to the educational community and is willing to provide access to company-owned material. This slide
The Fundamentals of Spectroscopy: Theory BUILDING BETTER SCIENCE AGILENT AND YOU 1 Agilent is committed to the educational community and is willing to provide access to company-owned material. This slide
Skill Building Activity 2 Determining the Concentration of a Species using a Vernier Spectrometer
 Skill Building Activity 2 Determining the Concentration of a Species using a Vernier Spectrometer Purpose To use spectroscopy to prepare a Beer s Law plot of known dilutions of copper(ii) sulfate so that
Skill Building Activity 2 Determining the Concentration of a Species using a Vernier Spectrometer Purpose To use spectroscopy to prepare a Beer s Law plot of known dilutions of copper(ii) sulfate so that
Lesmahagow High School AHChemistry Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Lesmahagow High School CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry
 Lesmahagow High School CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 1 Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Electromagnetic Radiation and Atomic Spectra 1 Electromagnetic Radiation Radiation such as light, microwaves,
Lesmahagow High School CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 1 Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Electromagnetic Radiation and Atomic Spectra 1 Electromagnetic Radiation Radiation such as light, microwaves,
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
 Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table The electronic structure of an atom determines its characteristics Studying atoms by analyzing light emissions/absorptions Spectroscopy: analysis of light emitted
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table The electronic structure of an atom determines its characteristics Studying atoms by analyzing light emissions/absorptions Spectroscopy: analysis of light emitted
Unit 3: Electron configuration and periodicity
 Unit 3: Electron configuration and periodicity Group 1 BOHR MODELS Group 18 H Group 2 Group 13 Group 14 Group 15 Group 16 Group 17 He Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar K Ca His theory couldn t
Unit 3: Electron configuration and periodicity Group 1 BOHR MODELS Group 18 H Group 2 Group 13 Group 14 Group 15 Group 16 Group 17 He Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar K Ca His theory couldn t
Atomic Theory: Spectroscopy and Flame Tests
 Atomic Theory: Spectroscopy and Flame Tests Introduction Light energy is also known as electromagnetic (EM) radiation. The light that we observe with our eyes, visible light, is just a small portion of
Atomic Theory: Spectroscopy and Flame Tests Introduction Light energy is also known as electromagnetic (EM) radiation. The light that we observe with our eyes, visible light, is just a small portion of
10/4/2011. Tells you the number of protons
 Atomic Structure The arrangement of the subatomic particles within the atom determines the chemical properties of the elements How they interact with one another The types of ions and structures that they
Atomic Structure The arrangement of the subatomic particles within the atom determines the chemical properties of the elements How they interact with one another The types of ions and structures that they
AH Chemistry Unit 1. Electromagnetic Radiation and Atomic Spectra
 AH Chemistry Unit 1 Electromagnetic Radiation and Atomic Spectra Introduction This topic describes the Electromagnetic Spectrum and how it can interact with atoms, Spectroscopy. Much information about
AH Chemistry Unit 1 Electromagnetic Radiation and Atomic Spectra Introduction This topic describes the Electromagnetic Spectrum and how it can interact with atoms, Spectroscopy. Much information about
The Bohr Model of the Atom
 Unit 4: The Bohr Model of the Atom Properties of light Before the 1900 s, light was thought to behave only as a wave. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation - a form of energy that exhibits wave
Unit 4: The Bohr Model of the Atom Properties of light Before the 1900 s, light was thought to behave only as a wave. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation - a form of energy that exhibits wave
CHEMICAL KINETICS E + 2B 2C + D (1)
 CHEMICAL KINETICS Chemical kinetics is the branch of chemistry that is concerned with the study of the rates and mechanisms of chemical reactions. The rate of a reaction is a measure of its speed. Consider
CHEMICAL KINETICS Chemical kinetics is the branch of chemistry that is concerned with the study of the rates and mechanisms of chemical reactions. The rate of a reaction is a measure of its speed. Consider
Chem 105 Fri 22 Oct 2010
 Chem 105 Fri 22 Oct 2010 1) Chapter 6 - Atomic Structure Hour Exam 2 will be returned Monday 10/22/2010 1 Mark your calendar: Hour Exam 3 (Ch 6, 7, 8) is Friday, Nov. 12. 10/22/2010 2 10/22/2010 3 Chap.
Chem 105 Fri 22 Oct 2010 1) Chapter 6 - Atomic Structure Hour Exam 2 will be returned Monday 10/22/2010 1 Mark your calendar: Hour Exam 3 (Ch 6, 7, 8) is Friday, Nov. 12. 10/22/2010 2 10/22/2010 3 Chap.
Experiment 7: Adsorption Spectroscopy I, Determination of Iron with 1,10 Phenanthroline
 Procedure Experiment 7: Adsorption Spectroscopy I, Determination of Iron with 1,10 Phenanthroline John Smith CHE226.001 4/10/95 In this experiment, we aim to determine the Na concentration of an unknown
Procedure Experiment 7: Adsorption Spectroscopy I, Determination of Iron with 1,10 Phenanthroline John Smith CHE226.001 4/10/95 In this experiment, we aim to determine the Na concentration of an unknown
Atomic Theory: Spectroscopy and Flame Tests
 Atomic Theory: Spectroscopy and Flame Tests Introduction Light energy is also known as electromagnetic (EM) radiation. The light that we observe with our eyes, visible light, is just a small portion of
Atomic Theory: Spectroscopy and Flame Tests Introduction Light energy is also known as electromagnetic (EM) radiation. The light that we observe with our eyes, visible light, is just a small portion of
Experiment 18 - Absorption Spectroscopy and Beer s Law: Analysis of Cu 2+
 Experiment 18 - Absorption Spectroscopy and Beer s Law: Analysis of Cu 2+ Many substances absorb light. When light is absorbed, electrons in the ground state are excited to higher energy levels. Colored
Experiment 18 - Absorption Spectroscopy and Beer s Law: Analysis of Cu 2+ Many substances absorb light. When light is absorbed, electrons in the ground state are excited to higher energy levels. Colored
Unit 3. Chapter 4 Electrons in the Atom. Niels Bohr s Model. Recall the Evolution of the Atom. Bohr s planetary model
 Unit 3 Chapter 4 Electrons in the Atom Electrons in the Atom (Chapter 4) & The Periodic Table/Trends (Chapter 5) Niels Bohr s Model Recall the Evolution of the Atom He had a question: Why don t the electrons
Unit 3 Chapter 4 Electrons in the Atom Electrons in the Atom (Chapter 4) & The Periodic Table/Trends (Chapter 5) Niels Bohr s Model Recall the Evolution of the Atom He had a question: Why don t the electrons
Beers Law Instructor s Guide David T. Harvey
 Beers Law Instructor s Guide David T. Harvey Introduction This learning module provides an introduction to Beer s law that is designed for an introductory course in analytical chemistry. The module consists
Beers Law Instructor s Guide David T. Harvey Introduction This learning module provides an introduction to Beer s law that is designed for an introductory course in analytical chemistry. The module consists
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms
 Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5.2 Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic Emission Spectra and the Quantum Mechanical Model 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5.2 Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic Emission Spectra and the Quantum Mechanical Model 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
Chapter 4 Ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy Molecular Spectrophotometry
 Chapter 4 Ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy Molecular Spectrophotometry Properties of light Electromagnetic radiation and electromagnetic spectrum Absorption of light Beer s law Limitation of Beer s
Chapter 4 Ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy Molecular Spectrophotometry Properties of light Electromagnetic radiation and electromagnetic spectrum Absorption of light Beer s law Limitation of Beer s
Spectroscopy Chapter 13
 Spectroscopy Chapter 13 Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic spectrum in terms of wavelength, frequency and Energy c=λν c= speed of light in a vacuum 3x108 m/s v= frequency in Hertz (Hz s-1 ) λ= wavelength
Spectroscopy Chapter 13 Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic spectrum in terms of wavelength, frequency and Energy c=λν c= speed of light in a vacuum 3x108 m/s v= frequency in Hertz (Hz s-1 ) λ= wavelength
Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back
 Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back Incident ray θ 1 θ 2 Reflected ray Medium 1 (air) η = 1.00 Medium 2 (glass) η = 1.50 Specular reflection = situation
Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back Incident ray θ 1 θ 2 Reflected ray Medium 1 (air) η = 1.00 Medium 2 (glass) η = 1.50 Specular reflection = situation
CHM 152 updated May 2011 Lab 6: Experimentally Determining an Equilibrium Constant using Spectrophotometry
 CHM 152 updated May 2011 Lab 6: Experimentally Determining an Equilibrium Constant using Spectrophotometry Introduction In this lab you will experimentally determine the equilibrium constant with respect
CHM 152 updated May 2011 Lab 6: Experimentally Determining an Equilibrium Constant using Spectrophotometry Introduction In this lab you will experimentally determine the equilibrium constant with respect
ATOMIC STRUCTURE ELECTRON CONFIGURATION 10/13/15 PROJECT DATE. Tuesday, October 13, 15
 PROJECT DATE ATOMIC STRUCTURE ELECTRON CONFIGURATION 10/13/15 Agenda Begin Topic 2.2 Electron Configuration Homework: Energy of waves calculations Due tomorrow! Yes - tomorrow Atomic Structure The nuclear
PROJECT DATE ATOMIC STRUCTURE ELECTRON CONFIGURATION 10/13/15 Agenda Begin Topic 2.2 Electron Configuration Homework: Energy of waves calculations Due tomorrow! Yes - tomorrow Atomic Structure The nuclear
Today is Thursday, March (!) 1 st, 2018
 In This Lesson: Atomic Emissions (Lesson 2 of 4) Stuff You Need: Calculator Today is Thursday, March (!) 1 st, 2018 Pre-Class: [choose one] What is white light? How are fireworks made to be different colors?
In This Lesson: Atomic Emissions (Lesson 2 of 4) Stuff You Need: Calculator Today is Thursday, March (!) 1 st, 2018 Pre-Class: [choose one] What is white light? How are fireworks made to be different colors?
Ch 7 Quantum Theory of the Atom (light and atomic structure)
 Ch 7 Quantum Theory of the Atom (light and atomic structure) Electromagnetic Radiation - Electromagnetic radiation consists of oscillations in electric and magnetic fields. The oscillations can be described
Ch 7 Quantum Theory of the Atom (light and atomic structure) Electromagnetic Radiation - Electromagnetic radiation consists of oscillations in electric and magnetic fields. The oscillations can be described
PH300 Spring Homework 06
 PH300 Spring 2011 Homework 06 Total Points: 30 1. (1 Point) Each week you should review both your answers and the solutions for the previous week's homework to make sure that you understand all the questions
PH300 Spring 2011 Homework 06 Total Points: 30 1. (1 Point) Each week you should review both your answers and the solutions for the previous week's homework to make sure that you understand all the questions
Rate law Determination of the Crystal Violet Reaction Using the Isolation Method
 Rate law Determination of the Crystal Violet Reaction Using the Isolation Method Introduction A common challenge in chemical kinetics is to determine the rate law for a reaction with multiple reactants.
Rate law Determination of the Crystal Violet Reaction Using the Isolation Method Introduction A common challenge in chemical kinetics is to determine the rate law for a reaction with multiple reactants.
Atomic Theory: Spectroscopy and Flame Tests
 Atomic Theory: Spectroscopy and Flame Tests Introduction Light energy is also known as electromagnetic (EM) radiation. The light that we observe with our eyes, visible light, is just a small portion of
Atomic Theory: Spectroscopy and Flame Tests Introduction Light energy is also known as electromagnetic (EM) radiation. The light that we observe with our eyes, visible light, is just a small portion of
ANALYSIS OF ZINC IN HAIR USING FLAME ATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY
 ANALYSIS OF ZINC IN HAIR USING FLAME ATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY Introduction The purpose of this experiment is to determine the concentration of zinc in a sample of hair. You will use both the calibration
ANALYSIS OF ZINC IN HAIR USING FLAME ATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY Introduction The purpose of this experiment is to determine the concentration of zinc in a sample of hair. You will use both the calibration
Spectroscopy. Page 1 of 8 L.Pillay (2012)
 Spectroscopy Electromagnetic radiation is widely used in analytical chemistry. The identification and quantification of samples using electromagnetic radiation (light) is called spectroscopy. Light has
Spectroscopy Electromagnetic radiation is widely used in analytical chemistry. The identification and quantification of samples using electromagnetic radiation (light) is called spectroscopy. Light has
CHEMISTRY 135 General Chemistry II. Determination of an Equilibrium Constant
 CHEMISTRY 135 General Chemistry II Determination of an Equilibrium Constant Show above is a laboratory sample from chemistry, not phlebotomy. [1] Is the bloody-looking product the main component of this
CHEMISTRY 135 General Chemistry II Determination of an Equilibrium Constant Show above is a laboratory sample from chemistry, not phlebotomy. [1] Is the bloody-looking product the main component of this
CHEM Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy
 CHEM 21112 Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy References: 1. Fundamentals of Molecular Spectroscopy by C.N. Banwell 2. Physical Chemistry by P.W. Atkins Dr. Sujeewa De Silva Sub topics Light and matter
CHEM 21112 Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy References: 1. Fundamentals of Molecular Spectroscopy by C.N. Banwell 2. Physical Chemistry by P.W. Atkins Dr. Sujeewa De Silva Sub topics Light and matter
Chapter 18. Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry. Properties of Light
 Chapter 18 Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Properties of Light Electromagnetic Radiation energy radiated in the form of a WAVE caused by an electric field interacting with a magnetic field result of
Chapter 18 Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Properties of Light Electromagnetic Radiation energy radiated in the form of a WAVE caused by an electric field interacting with a magnetic field result of
Electromagnetic spectrum Electromagnetic radiation
 Chapter 4 Section 1 Electromagnetic spectrum includes all the different wave lengths of radiation. Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave like behavior as it travels through space.
Chapter 4 Section 1 Electromagnetic spectrum includes all the different wave lengths of radiation. Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave like behavior as it travels through space.
Bioengineering Laboratory I. Enzyme Assays. Part II: Determination of Kinetic Parameters Fall Semester
 Bioengineering Laboratory I Enzyme Assays Part II: Determination of Kinetic Parameters 2016-2017 Fall Semester 1. Theoretical background There are several mathematical models to determine the kinetic constants
Bioengineering Laboratory I Enzyme Assays Part II: Determination of Kinetic Parameters 2016-2017 Fall Semester 1. Theoretical background There are several mathematical models to determine the kinetic constants
Democritus and Leucippus Matter is made up of indivisible particles Dalton - one type of atom for each element. Greek Idea
 Electrons in Atoms Democritus and Leucippus Matter is made up of indivisible particles Dalton - one type of atom for each element Greek Idea Thomson s Model Discovered electrons Atoms were made of positive
Electrons in Atoms Democritus and Leucippus Matter is made up of indivisible particles Dalton - one type of atom for each element Greek Idea Thomson s Model Discovered electrons Atoms were made of positive
MORE LIGHTS, COLOR, ABSORPTION!
 Name Partner(s) Section Date MORE LIGHTS, COLOR, ABSORPTION! PRE-LAB QUERIES 1. The terms absorption and transmittance are often used when describing the interaction of light with matter. Explain what
Name Partner(s) Section Date MORE LIGHTS, COLOR, ABSORPTION! PRE-LAB QUERIES 1. The terms absorption and transmittance are often used when describing the interaction of light with matter. Explain what
Beer's Law and Data Analysis *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m15131 1 Beer's Law and Data Analysis * Mary McHale This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0 1 Beer's Law and Data Analysis
OpenStax-CNX module: m15131 1 Beer's Law and Data Analysis * Mary McHale This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0 1 Beer's Law and Data Analysis
5.1 Light & Quantized Energy
 5.1 Light & Quantized Energy Objectives: 1. Describe electromagnetic (EM) wave properties & measures 2. Relate visible light to areas of the EM spectrum with higher & lower energy 3. Know the relationship
5.1 Light & Quantized Energy Objectives: 1. Describe electromagnetic (EM) wave properties & measures 2. Relate visible light to areas of the EM spectrum with higher & lower energy 3. Know the relationship
PART SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC STUDIES
 PART SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC STUDIES CHAPTER General Principles of Spectrophotometry 123 In absorption spectroscopy, absorption measurements based upon ultraviolet light and visible radiation find application
PART SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC STUDIES CHAPTER General Principles of Spectrophotometry 123 In absorption spectroscopy, absorption measurements based upon ultraviolet light and visible radiation find application
The Bohr Model Bohr proposed that an electron is found only in specific circular paths, or orbits, around the nucleus.
 5.1 The Development of Atomic Models Rutherford s atomic model could not explain the chemical properties of elements. Rutherford s atomic model could not explain why objects change color when heated. The
5.1 The Development of Atomic Models Rutherford s atomic model could not explain the chemical properties of elements. Rutherford s atomic model could not explain why objects change color when heated. The
R O Y G B V. Spin States. Outer Shell Electrons. Molecular Rotations. Inner Shell Electrons. Molecular Vibrations. Nuclear Transitions
 Spin States Molecular Rotations Molecular Vibrations Outer Shell Electrons Inner Shell Electrons Nuclear Transitions NMR EPR Microwave Absorption Spectroscopy Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy UV-vis Absorption,
Spin States Molecular Rotations Molecular Vibrations Outer Shell Electrons Inner Shell Electrons Nuclear Transitions NMR EPR Microwave Absorption Spectroscopy Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy UV-vis Absorption,
November 06, Chapter 7 Atomic Struture. CHAPTER 7 Atomic Structure. Oct 27 9:34 AM ATOMIC STRUCTURE. Oct 27 9:34 AM
 CHAPTER 7 Atomic Structure ATOMIC STRUCTURE 1 The Wave Nature of Light Most subatomic particles behave as PARTICLES and obey the physics of waves. Visible light Ultravioletlight Wavelength Frequency (Hertz
CHAPTER 7 Atomic Structure ATOMIC STRUCTURE 1 The Wave Nature of Light Most subatomic particles behave as PARTICLES and obey the physics of waves. Visible light Ultravioletlight Wavelength Frequency (Hertz
CHEM Lab 7: Determination of an Equilibrium Constant using Spectroscopy
 CHEM 0012 Lab 7: Determination of an Equilibrium Constant using Spectroscopy 1 Determination of the equilibrium constant of the following equilibrium system at room temperature. Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN- (aq)
CHEM 0012 Lab 7: Determination of an Equilibrium Constant using Spectroscopy 1 Determination of the equilibrium constant of the following equilibrium system at room temperature. Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN- (aq)
Experimental Procedure Overview
 Lab 4: Determination of an Equilibrium Constant using Spectroscopy Determination of the equilibrium constant of the following equilibrium system at room temperature. Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN (aq) Fe(SCN) 2+ (aq)
Lab 4: Determination of an Equilibrium Constant using Spectroscopy Determination of the equilibrium constant of the following equilibrium system at room temperature. Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN (aq) Fe(SCN) 2+ (aq)
CHEMISTRY SEMESTER ONE
 BEER-LAMBERT LAW Lab format: this lab is a remote lab activity Relationship to theory: This activity quantitatively relates the concentration of a lightabsorbing substance to the absorbance of light. LEARNING
BEER-LAMBERT LAW Lab format: this lab is a remote lab activity Relationship to theory: This activity quantitatively relates the concentration of a lightabsorbing substance to the absorbance of light. LEARNING
The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law.
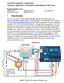 The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law. Required Supplies & Costs: RGB LED; $1.95 Light Sensors; $3.95 ea 3-way switch; $6.54 3 ohm resistor;
The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law. Required Supplies & Costs: RGB LED; $1.95 Light Sensors; $3.95 ea 3-way switch; $6.54 3 ohm resistor;
EXPERIMENT 6 INTRODUCTION TO SPECTROSCOPY
 EXPERIMENT 6 INTRODUCTION TO SPECTROSCOPY INTRODUCTION Much of what we know about the structures of atoms and molecules has been learned through experiments in which photons (electromagnetic radiation
EXPERIMENT 6 INTRODUCTION TO SPECTROSCOPY INTRODUCTION Much of what we know about the structures of atoms and molecules has been learned through experiments in which photons (electromagnetic radiation
Lambert s law. Beer s law. di x / I x = -kdx (-di x = k I x dx) = - a c dx. I/I 0 = e -kl T = A = - log (T) = - log (I/I 0 )
 di x / I x = -kdx (-di x = k I x dx) Integrating this equation from x=0 ~ l (I x =I 0 ~I) gives ; ln I ln I 0 = -kl ln I/I 0 = -kl Expressing the number of photons absorbed by the slab as di x, and the
di x / I x = -kdx (-di x = k I x dx) Integrating this equation from x=0 ~ l (I x =I 0 ~I) gives ; ln I ln I 0 = -kl ln I/I 0 = -kl Expressing the number of photons absorbed by the slab as di x, and the
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE NOTES
 CHAPTER 13 LECTURE NOTES Spectroscopy is concerned with the measurement of (a) the wavelengths (or frequencies) at which molecules absorb/emit energy, and (b) the amount of radiation absorbed at these
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE NOTES Spectroscopy is concerned with the measurement of (a) the wavelengths (or frequencies) at which molecules absorb/emit energy, and (b) the amount of radiation absorbed at these
2 SPECTROSCOPIC ANALYSIS
 2 SPECTROSCOPIC ANALYSIS 2.1 Introduction Chemical analysis falls into two basic categories: qualitative what is present quantitative how much is present Spectroscopy is capable of both types of analysis,
2 SPECTROSCOPIC ANALYSIS 2.1 Introduction Chemical analysis falls into two basic categories: qualitative what is present quantitative how much is present Spectroscopy is capable of both types of analysis,
Spectroscopy II Introduction: Spectrophotometry and Fluorometry
 Introduction: Spectrophotometry and Fluorometry In this experiment you will use the SpectroVis Plus (a small computer controlled Spectrophotometer + Fluorometer) to: Measure the Transmission and Absorbance
Introduction: Spectrophotometry and Fluorometry In this experiment you will use the SpectroVis Plus (a small computer controlled Spectrophotometer + Fluorometer) to: Measure the Transmission and Absorbance
Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5. What is light? What is a wave? Radiation carries information
 Concepts: Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5 Electromagnetic waves Types of spectra Temperature Blackbody radiation Dual nature of radiation Atomic structure Interaction of light and matter
Concepts: Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5 Electromagnetic waves Types of spectra Temperature Blackbody radiation Dual nature of radiation Atomic structure Interaction of light and matter
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter-I
 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter-I Physics Without Fear CONTENTS ELECTRON EMISSION PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT; HERTZ S OBSERVATIONS HALLWACHS AND LENARD S OBSERVATIONS EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF PHOTOELECTRIC
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter-I Physics Without Fear CONTENTS ELECTRON EMISSION PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT; HERTZ S OBSERVATIONS HALLWACHS AND LENARD S OBSERVATIONS EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF PHOTOELECTRIC
Chemistry 213. A KINETIC STUDY: REACTION OF CRYSTAL VIOLET WITH NaOH LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 Chemistry 213 A KINETIC STUDY: REACTION OF CRYSTAL VIOLET WITH NaOH The objectives of this experiment are to... LEARNING OBJECTIVES study the reaction rate of crystal violet with NaOH using a Spectronic
Chemistry 213 A KINETIC STUDY: REACTION OF CRYSTAL VIOLET WITH NaOH The objectives of this experiment are to... LEARNING OBJECTIVES study the reaction rate of crystal violet with NaOH using a Spectronic
4.3A: Electronic transitions
 Ashley Robison My Preferences Site Tools Popular pages MindTouch User Guide FAQ Sign Out If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it
Ashley Robison My Preferences Site Tools Popular pages MindTouch User Guide FAQ Sign Out If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it
ElectroMagnetic Radiation (EMR) Lecture 2-3 August 29 and 31, 2005
 ElectroMagnetic Radiation (EMR) Lecture 2-3 August 29 and 31, 2005 Jensen, Jensen, Ways of of Energy Transfer Energy is is the the ability to to do do work. In In the the process of of doing work, energy
ElectroMagnetic Radiation (EMR) Lecture 2-3 August 29 and 31, 2005 Jensen, Jensen, Ways of of Energy Transfer Energy is is the the ability to to do do work. In In the the process of of doing work, energy
Lecture 5. More on UV-visible Spectrophotometry: Beer s Law and Measuring Protein Concentration
 Biological Chemistry Laboratory Biology 3515/Chemistry 3515 Spring 2018 Lecture 5 More on UV-visible Spectrophotometry: Beer s Law and Measuring Protein Concentration 23 January 2018 c David P. Goldenberg
Biological Chemistry Laboratory Biology 3515/Chemistry 3515 Spring 2018 Lecture 5 More on UV-visible Spectrophotometry: Beer s Law and Measuring Protein Concentration 23 January 2018 c David P. Goldenberg
Clinical Chemistry (CHE221) Professor Hicks Week 1. Statistics Made Slightly Less Boring and Introduction to Spectrophotometry. Accuracy vs Precision
 Clinical Chemistry (CHE221) Professor Hicks Week 1 Statistics Made Slightly Less Boring and Introduction to Spectrophotometry 3 Accuracy vs Precision Precision is the consistency of a measurement made
Clinical Chemistry (CHE221) Professor Hicks Week 1 Statistics Made Slightly Less Boring and Introduction to Spectrophotometry 3 Accuracy vs Precision Precision is the consistency of a measurement made
I understand the relationship between energy and a quanta I understand the difference between an electron s ground state and an electron s excited
 NCCS 1.1.2 & 1.1.3 I understand the relationship between energy and a quanta I understand the difference between an electron s ground state and an electron s excited state I will describe how an electron
NCCS 1.1.2 & 1.1.3 I understand the relationship between energy and a quanta I understand the difference between an electron s ground state and an electron s excited state I will describe how an electron
1 WHAT IS SPECTROSCOPY?
 1 WHAT IS SPECTROSCOPY? 1.1 The Nature Of Electromagnetic Radiation Anyone who has been sunburnt will know that light packs a punch: in scientific terms, it contains considerable amounts of energy. All
1 WHAT IS SPECTROSCOPY? 1.1 The Nature Of Electromagnetic Radiation Anyone who has been sunburnt will know that light packs a punch: in scientific terms, it contains considerable amounts of energy. All
