Recent Advances in Directed and Intramolecular Transition Metal Catalyzed Oxidative Functionalizations of Carbon- Hydrogen Bonds
|
|
|
- Chastity Andrews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
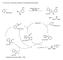
1 Recent Advances in Directed and Intramolecular Transition Metal Catalyzed xidative Functionalizations of Carbon- ydrogen Bonds 1 step R C cat [M] oxidant R X C X = R 2, R, halogen John eemstra Jr. April 18, 2006
2 xidative Functionalization of Alkanes C (g) + 1/2 2 (g) catalyst? C (l) Δ o = kcal/mol owever, two major problems: Chemoselectivity: product more reactive toward oxidant than starting alkene if oxidation involves abstraction of atom, overoxidation to C 2 will be observed C 104 kcal/mol C 93 kcal/mol Regioselectivity: radical and electrophilic reagents oxidize 3 o >2 o >1 o owever, the selectivity is often not high R Me Et i-pr t-bu R- -> R Stahl, S.S.; Labinger, J.A.; Bercaw, J.E. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2180
3 C- Functionalization via the Inner-Sphere Mechanism (alternatively termed organometallic ) kcal/mol ML n C- activation C R oxidative addition functionalization kcal/mol C R or ML n C R ML n + + heterolytic cleavage X X C R X = anything other than Selectivity: kinetic and thermodynamic preference to form the less sterically hindered C-M intermediate (1 o sp 3 > 2 o sp 3 >>> 3 o sp 3 )
4 C- Activation Via Late, ucleophilic Complexes σ* σ-bonding: C- σ -> Md σ π-backbonding: Md π -> C- σ Typically involves coordinatively and electronically unsaturated Rh(I) and Ir(I) intermediate complexes Prone to non-productive reductive elimination in the presence of oxidants and non-productive protonolysis in the presence of protic reagents.
5 C- Activation Via Late, Electrophilic Complexes σ-bonding: C- σ -> Md σ π-backbonding: Md π -> C- σ eterolytic cleavage results in no oxidation state change in metal. Electrophilic complexes in their highest stable oxidation state are typically used (eg. Pt II and Pd II ) Compatible with oxidants (including 2 ) and provide a route to oxidative functionalization.
6 The Shilov System First reported by Shilov and coworkers In 1972.a paradigm shift Pt II 2 - (K + ) 2 (cat.) RC K 2 Pt(IV) 4 (ox.) RC 2 + RC 2 1 o > 2 o > 3 o 120 oc Even though these results were mostly ignored or met with disbelief at first, they are now seen as the origin of the organometallic class of alkene oxidations. Robert Crabtree C "Pt" "Pt" 3 C C C C C Although excellent chemioselectivity is observed, only modest regioselectivities have been obtained for unfunctionalized alkanes. Stahl, S.S.; Labinger, J.A.; Bercaw, J.E. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2180
7 The Shilov System 2 2 C Pt II C 3 Pt IV 2 - (K + ) 2 - K + Pt II 2 Pt II (K + ) 2 C 4 2 Pt II 2 C 3 Pt II 2 C 3 Pt is late soft metal, allowing C- to compete with water for binding to Pt or - K Pt IV 2 C 3 Inversion of stereochem of deuterium labled substrates 2 Pt IV 2 C 3 - K + K2 195 Pt(IV)6 K Pt(II) 4 o oxidation state change to metal Stahl, S.S.; Labinger, J.A.; Bercaw, J.E. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2180
8 Chelate-Directed C- Bond Functionalizations Substrate Product Yield Conditions: 17 mol% K 2 Pt(II) 4, 50 mol% K 2 Pt(IV) 6, D 2, o C, 3 days Kinetic product formed by reductive elim.? Selectivity arises form the tendence to form the metallacycle with the least ring strain For alcohols: α-c << β-c < γ-c δ-c Trend also observed for carboxylic acids, Sulfonic acids, and phosphonic acids Basickes,.; Sen, A. Polyhedron 1995, 14, 202
9 Chelate-Directed C- Bond Functionalizations substrate products γ / δ products isolated yield,% 2 2 dr 2:1 2 + C 2 4 : C : dr 2: : : 3 nd C 2 no reaction conditions: 0.05 equiv K 2 Pt 4, 7 equiv Cu 2, 2, 160 o C, 10h The chelation effect in amino acids can override the inherent selectivity of the C- activation step. Dangel, B.D.; Johnson, J.A.; Sames, D.S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 8149
10 Proposed Catalytic Cycle 2 γ-selective pathway = oxygenation δ-selective pathway = chlorination + alkylation 2 C 2 Alternatively. 3 C 3 C (K + ) or 2 3 C Pt II Dangel, B.D.; Johnson, J.A.; Sames, D.S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 8149 K + - Pt II Pt IV 2 2 C 3 C 3 K + - Cu 2 Pt II C- activation 2 3 C + 2 C Pt II 2 reductive elimination
11 Summary of Platinum Mediated Alkane xidations Pt II 2 - (K + ) 2 (cat.) RC K 2 Pt(IV) 4 (ox.) 120 oc RC 2 + RC 2 as been instrumental in the understanding of mechanistic and selectivity issues related to alkane oxidation by homogeneous transition metal complexes Moderate to excellent regioselectivity can be achieved in the oxidation of functionalized alkanes (eg. alcohols and acids) via the chelate effect owever, the platinum mediated chemistry is plagued by low catatyst turnover numbers. Pt(IV) is not a practical stoichiometric oxidant (cost) and attempts at replacing it with other oxidants have afforded decreased chemoselectivity. Deposition of platinum metal erodes selectivities and the oxidation of Pt(0) tends to be difficult. Palladium on the other hand.. Stahl, S.S.; Labinger, J.A.; Bercaw, J.E. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2180
12 Palladium-Catalyzed xygenation of Unactivated sp 3 C- Bonds Me R 1 R 4 R 2 R 3 5 mol% Pd(Ac) 2 1/1 Ac/ Ac oc, Ac Me Pd R 1 R 2 R equiv PhI(Ac) 2 Me R 1 R 2 R 3 Ac Unlike Pt(II), only 1 0 β-c- bonds undergo functionalization! The chelating group believed to both direct and accelerate unactivated sp 3 C- activation igh reactivity for 1 o β C- likely reflects preference for forming 5-membered palladacycles and strong steric preference for formation less hindered 1 o Pd-alkyls. Desai, L.D.; ull, K.L.; Sanford, M.S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9542
13 Palladium-Catalyzed xygenation of Unactivated sp 3 C- Bonds 1.5 h 5 min Single diastereomer These Pd-catalyzed reactions typically proceed under significantly milder conditions, with higher T (often 50) and with broader substrate scope than those with Pt catalysts Desai, L.D.; ull, K.L.; Sanford, M.S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9542
14 Palladium-Catalyzed xygenation of Unactivated sp 2 C- Bonds X large excess + PhI(Ac) 2 + Pd(Ac) 2 Ac 1 equiv 1 equiv 100 o C, 21h X Ac Substrate yield o:m:p Benzene 39 Anisole 40 44:5:51 Toluene 39 43:26:31 Low levels of regioselectivity observed Yoneyama, T.; Crabtree, R.S. J. Mol. Catal. A 1996, 108, mol% Pd(Ac) Ac 2 Pd o C 2 12 h 1-2 equiv oxidant X Dick, A.R.; ull, K.L.; Sanford, M.S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 2300
15 Chelate-Directed xidation of sp 2 and sp 3 C- Bonds Monooxidation of substrates: Conditions: equiv of PhI(Ac) 2, 1-6 mol% Pd(Ac) 2, 100 o C, h, C 3 C in Me Dioxidation of substrates: Conditions: 2.3 equiv of PhI(Ac) 2, 6-8 mol% Pd(Ac) 2, 100 o C, 12h, C 3 C Dick, A.R.; ull, K.L.; Sanford, M.S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 2300
16 Palladium-Catalyzed Acetoxylation of Meta-Substituted Aryl pyridines Conditions: 5 mol% Pd(Ac) 2, equiv PhI(Ac) 2, Ac, C 6 6 or C 6 6 /Ac 2, 100 o C, h Unlike directed ortho-lithiation and Ru-catalyzed C- activation reactions, Me, MM, and F Did not exhibit secondary directing effects Kalyani, D.; Sanford, M.S. rg Lett. 2005, 19, 4149
17 Palladium-Catalyzed Acetoxylation of Aryl Pyrrolidinones Conditions: 5 mol% Pd(Ac) 2, equiv PhI(Ac) 2, Ac, Ac/Ac 2, 100 o C, 3-12 h Selectivity for A may be general over many classes of directing groups in PdII-catalzed C- activation/oxidative functionalizations. Kalyani, D.; Sanford, M.S. rg Lett. 2005, 19, 4149
18 Palladium-Catalyzed Acetoxylation of Substrates with Potential Dual Chelating Groups Conditions: 5 mol% Pd(Ac) 2, equiv PhI(Ac) 2, C 6 6 or C 6 6 /Ac 2, 100 o C Kalyani, D.; Sanford, M.S. rg Lett. 2005, 19, 4149
19 Proposed Catalytic Cycle for Palladium-Catalyzed Acetoxylation of Benzo[h]quinone Ac Pd II 2 equiv PhI(Ac) 2 C 3 C o C Ac 12 h comparible yield? Ac Pd II 2 C 3 C o C 12 h no reaction benzoquinone or Cu(Ac) 2 + Pd(Ac) 2 C 3 C o C no reaction 12 h Dick, A.R.; ull, K.L.; Sanford, M.S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 2300
20 Mechanistic Investigations of C- Bond-Forming Reductive Elimination of Pd(IV) Complexes Stable at rt Expected mechanism A most likely by analogy to C- bond-forming reactions with Pt IV owever. no observed rate acceleration in more polar solvents and no correlation with solvent dielectric constant ΔS = +4.2 ± 1.4 and -1.4 ± 1.9 eu in d 6 DMS and CD 3 respectively (ionic reductive eliminations typically show highly negative values of ΔS). ρ = ± 0.04 (Pt VI C- bond forming reductive elimination ρ = +1.44) Thermolysis in the presence of 5 equiv Bu 4 Ac resulted less than 5% incorporation of the acetate in C 3 or DMS What experiments would you perform to distinguish between Mech. B and C? Dick, A.R.; Kampf, J.W.; Sanford, M.S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12790
21 Mechanistic Investigations of C- Bond-Forming Reductive Elimination of Pd(IV) Complexes Sanford and co-worker currently favor mechanism C
22 Selective C- Activation/alogenation catalyzed by Pd(Ac) 2 Conditions: 1 mol% Pd(Ac) 2, 1.1 equiv of - alosuccinamide, MeC, 100 o C, h Substrate Product Yield (%) Me Me Me Me Me Et Me Et Et t-bu t-bu t-bu Me Me Me Et Et Et I I I Dick, A.R.; ull, K.L.; Sanford, M.S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 2300 t-bu t-bu t-bu (63:37 dr) 88 Conditions: 10 mol% Pd(Ac) 2, I 2 (1 equiv) PhI(Ac) 2 (1 equiv), C 2 2, 24 o C, h Ethanolamine, 2-methyl-2-aminopropanol, or valinol derived oxazolines proceed at much slower rate Giri, R.; Chen, X.; Yu, J.-Q. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 2112
23 Selective C- Activation/alogenation catalyzed by Pd(Ac) 2 Me Me Me t-bu Pd(Ac) 2 C o C, 24h C- activation 60% yield xidative addition/ reductive elimination PdI 2 PhI(Ac) 2 (1 equiv) I 2 (1 equiv) C 2 2, 24 h Pd(Ac) 2 Giri, R.; Chen, X.; Yu, J.-Q. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 2112
24 Summary of the Palladium Catalyzed sp 3 and sp 2 C- bond xidative Functionalization Unactivated sp 3 and sp 2 C- bonds of oximes, pyridine, pyrazole, imine, and azobenzene substrates undergo highly regio- and chemoselective Pd(II) catalyzed oxygenations with PhI(Ac) 2 as a stoichiometric oxidant. C- bonds can also be replaced with ether functionality or halides when reaction are performed in alcohol solvants or in the presence of -halosuccinamides, or I 2. Pd-catalyzed chelate-directed acetoxylation of meta-substituted arene substrates exhibit high regioselectivity for functionalization at the less substituted ortho-position These Pd-catalyzed reactions typically proceed under significantly milder conditions, With higher T (often 50) and with broader substrate scope than those with Pt catalysts. The almost exclusive selectivity for 1 o C- bonds is a could be a limitation if one wanted to develop a stereospecific or enantioselective process.
25 C- Functionalization via the uter-sphere Mechanism (alternatively termed coordination ) C R X ML n C R direct insertion X CR 2 : carbene R: nitrene : oxo LG 2 IPh IPh, R X ML n C R X ML n atom abstraction/ rebound LG X LG=X ML n C R Selectivity: involves buildup of radical and/or cationic character at carbon and shows selectivity for weaker C- bonds: benzylic, allylic, 3 o, or α to heteroatoms.
26 C- Bond Amination via the uter-sphere Mechanism First example of an intermolecular C- amination aryliodinane Breslow. R; Gellman, S.. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1982, 1400 First example of an intramolecular C- amination Tosylamine 89% Cat. Rh 2 (Ac) 4 93% yield Aryliodinane intermediates have poor shelf life First demonstration of the use of the oxidant PhI(Ac) 2 and Rh catalyst system Breslow. R; Gellman, S.. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 6728
27 Rhodium-Catalyzed xidative C- Insertion Reaction for xazolidinone Synthesis R 3 C R C 3 K 2 C 3, Me R 5 mol%rh 2 (R) 4 PhI(Ac) 2 (1.4 equiv ) Mg (2.3 equiv ) R 2 C 2 2, 40 o C A = Rh 2 (Ac) 4 B = Rh 2 (tpa) 4 ne-pot procedure for formation of aryliodinane and insertion of metallonitrenoids in C- bond Espino, C.G.; Du Bois, J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 598
28 Mechanism of xazolidinone Formation Data suggests a concerted, metal-directed -atom insertion process (Ac) 4 Rh 2 2 Me Me PhI(Ac) 2 PhI Me Me Me Me Me Me Rh 2 (Ac) 2 Espino, C.G.; Du Bois, J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 598
29 Rhodium-Catalyzed xidative C- Insertion Reaction for xathiazinane Synthesis S 2 2 R 1 R 2 pyridine, C 2 2 S 2 R 1 R 2 sulfamate 2 mol%rh 2 (R) 4 PhI(Ac) 2 (1.1 equiv ) Mg (2.3 equiv ) R 1 S R 2 A = Rh 2 (Ac) 4 B = Rh 2 (oct) 4 90% (A) 75% (B) single isomer 80% (A) single isomer 91% (B) 13/1 syn/anti 78% (A) 85% (A) 8/1 cis/trans 78% (B) 4/1 cis/anti 60% (A) Espino, C.G.; Wehn P.M.; Chow, J.; Du Bois, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 6935
30 Rhodium-Catalyzed xidative C- Insertion Reaction for xathiazinane Synthesis S- and S- bond lengths of 1.58 A -S- angle of 103 o 2 Ph S C 2 Et sulfamate favored disfavored Ph S C 2 Et oxathiazinane S Ph C 2 Et S- and S- bond lengths of 1.59 A -S- angle of 105 o -S- angle of 95 o sulfamidate Torsional strain induced in developing product Wehn P.M.; Lee, J.; Du Bois, J. rg. Lett. 2003, 5, 4823
31 Rhodium-Catalyzed Amidation of Ethereal C α - Bonds Fleming, J.J.; Fiori, K.W.. Du Bois, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 2028
32 Alkynlzinc Addition Reactions with,-acetals When C6 unsubstituted, 4,5-syn favored When C6 substituted, 4,6-anti favored regardless of C5 configuration Fleming, J.J.; Fiori, K.W.. Du Bois, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 2028
33 Tandem Rhodium C- Amination, Iminium Ion Coupling Reactions R = Me a a b a R = Me b R = CPh 3 Ketene acetals can also be employed ne-pot procedure: rxn mixture filtered to remove Mg and then treated with either 1.5 equiv BF 3 Et 2 and 4 equiv allyltrimethyl silane or 0.1 equiv Sc(Tf) 3 and 4 equiv of silyl enol ether Fiori, K.W.; Fleming, J.J. Du Bois, J.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 4349
34 Stereochemical Models for Iminium Ion Additions Model for alkylzinc Reagents Model for allylsilanes and silyl enol ethers Fiori, K.W.; Fleming, J.J. Du Bois, J.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 4349
35 Stereochemical Models for Iminium Ion Additions ighly selective additions to 5,6-syn-substituted iminium ions 78% 20:1 72% 20:1 Selectivity erodes with 5,6-anti-configured substrates 81% 1.5:1 82% 2.5:1 Fiori, K.W.; Fleming, J.J. Du Bois, J.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 4349
36 A Silver-Catalyzed xidative C- Insertion Reaction for xazolidinone and xathiazinane Synthesis Both ligand and Ag Salt commercially available Carbamate C- insertions sulfamate C- insertions Similar yields; however, Rh-catalyzed process proceeds at 40 o C stereospecific Cui, Y.; e, C. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 5, 4210
37 Intramolecular C- Bond Formations Reactions Catalyzed By a Ruthenium Porphyrin 1.5 mol% 1 2 equiv PhI(Ac) equiv Al 2 3 C 2 2, 40 o C Fe and Mn metalloporphyrins afforded lower yields Single isomer* ighly robust catalyst featuring up to 59 catalytic turnovers at 1.5 mol%, and up to 300 at 0.1 mol% catalyst loadings *Dirhodium complex afforded 8:1 cis:trans Liang, J.-L.; Yuan, S.-X.; uang, J.S.; Yu, W.Y.; Che, C.-M. J. rg. Chem. 2004, 69, 3610
38 Intramolecular C- Bond Formations Reactions Catalyzed By Ruthenium Porphyrins owever, intramolecular C- amination is stereospecific! a) Carboradical is too shortlived to undergo configuration inversion b) onsynchronous concerted mechanism bearing significant hydrogen abstraction character Data for intermolecular reaction supports -atom abstraction mechanism Liang, J.-L.; Yuan, S.-X.; uang, J.S.; Yu, W.Y.; Che, C.-M. J. rg. Chem. 2004, 69, 3610
39 Expanding the Scope of C- Amination Through Catalyst Design Chelate effect should disfavor complete ligand dissociation from metal center and confer added stability to complex Espino, C.G.; Fiori,K.W.; Du Bois, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15378
40 Intramolecular C- Bond Formations Reactions Catalyzed By a Chiral Ruthenium 1.5 mol% equiv PhI(Ac) equiv Al 2 3 * [d] in C 2 2 at 40 o C [e] in C 2 2 at 5 o C [f] in toluene at 0 o C Chiral porphyrin ligand is both expensive and difficult to synthesize Liang, J.-L.; Yuan, S.-X.; uang, J.S.; Yu, W.Y.; Che, C.-M. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 3465
41 Intramolecular C- Bond Formations Reactions Catalyzed By a Chiral Ruthenium Porphyrin Imido phenyl group points toward the smaller methano-bridge X-ray structure of the major enantiomer Liang, J.-L.; Yuan, S.-X.; uang, J.S.; Yu, W.Y.; Che, C.-M. J. rg. Chem. 2004, 69, 3610
42 Intramolecular C- Bond Formations Reactions Catalyzed By Rhodium and Manganese complexes L = A B Catalyst yield er A 55% 65:35 B 48% 76:24 JR1 More readily accessible and cheaper owever low selectivity obtained Fruit, C.; Muller, P. elv. Chim. Acta 2004, 87, 1607 Zhang, J.; Chan, P.W..; Che, C.-M. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 5403
43 Slide 42 JR1 John R eemstra Jr, 4/17/2006
44 Summary of Intramolecular C- Aminations via the uter-sphere Mechanism The intramolecular C- amination reaction is now a highly dependable and predictable transformation and has found application in the preparation of a variety of natural products. The intramolecular insertion of metallonitrenoids (M = Ag, Rh, Ru) into C- bond is a stereospecific process. The new Rh 2 (esp) 2 catalysts now allows very low catalyst loadings and extremely high catalyst T (>600) Enantioselective methods are still in their infancy and a method that provides high selectivity is still lacking
Palladium-Catalyzed Oxygenation of Unactivated sp 3 C-H Bonds
 Palladium-Catalyzed xygenation of Unactivated sp 3 C- Bonds Pd(Ac) 2 5 mol% PhI(Ac) 2 1.1 eq. Pd 2 Ac Desai, L. P.; ull, K. L.; Sanford *, M. S. University of Michigan J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, ASAP
Palladium-Catalyzed xygenation of Unactivated sp 3 C- Bonds Pd(Ac) 2 5 mol% PhI(Ac) 2 1.1 eq. Pd 2 Ac Desai, L. P.; ull, K. L.; Sanford *, M. S. University of Michigan J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, ASAP
Reductive Elimination from High-Valent Palladium. Kazunori Nagao MacMillan Group Meeting
 Reductive Elimination from igh-valent Palladium Kazunori agao MacMillan Group eting Why do people focus on rging with C activation Facile reductive elimination DG C palladacycle oxidant complex C etero
Reductive Elimination from igh-valent Palladium Kazunori agao MacMillan Group eting Why do people focus on rging with C activation Facile reductive elimination DG C palladacycle oxidant complex C etero
Rhodium Catalyzed Alkyl C-H Insertion Reactions
 Rhodium Catalyzed Alkyl C-H Insertion Reactions Rh Rh Jeff Kallemeyn 5/17/05 1. Cyclopropanation The Versatile and Reactive Rhodium Carbene R + Et Rh 2 (Ac) 4 R C 2 Et N 2 2. [2,3] sigmatropic rearrangement
Rhodium Catalyzed Alkyl C-H Insertion Reactions Rh Rh Jeff Kallemeyn 5/17/05 1. Cyclopropanation The Versatile and Reactive Rhodium Carbene R + Et Rh 2 (Ac) 4 R C 2 Et N 2 2. [2,3] sigmatropic rearrangement
Organometallic Chemistry and Homogeneous Catalysis
 rganometallic hemistry and omogeneous atalysis Dr. Alexey Zazybin Lecture N8 Kashiwa ampus, December 11, 2009 Types of reactions in the coordination sphere of T 3. Reductive elimination X-L n -Y L n +
rganometallic hemistry and omogeneous atalysis Dr. Alexey Zazybin Lecture N8 Kashiwa ampus, December 11, 2009 Types of reactions in the coordination sphere of T 3. Reductive elimination X-L n -Y L n +
Palladium-catalyzed sp 3 C H activation. Yan Xu Dong Group Meeting Apr. 2, 2014
 Palladium-catalyzed sp 3 C H activation, Yan Xu Dong Group Meeting Apr. 2, 2014 Content 1 Allylic C H activation 2 Benzylic C H activation Palladiumcatalyzed sp 3 C H activation 3 4 Common sp 3 C H activation:
Palladium-catalyzed sp 3 C H activation, Yan Xu Dong Group Meeting Apr. 2, 2014 Content 1 Allylic C H activation 2 Benzylic C H activation Palladiumcatalyzed sp 3 C H activation 3 4 Common sp 3 C H activation:
Additions to Metal-Alkene and -Alkyne Complexes
 Additions to tal-alkene and -Alkyne Complexes ecal that alkenes, alkynes and other π-systems can be excellent ligands for transition metals. As a consequence of this binding, the nature of the π-system
Additions to tal-alkene and -Alkyne Complexes ecal that alkenes, alkynes and other π-systems can be excellent ligands for transition metals. As a consequence of this binding, the nature of the π-system
Transition Metal-Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Cleavage (C-C Activation) Group Meeting Timothy Chang
 Transition Metal-Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Cleavage (C-C Activation) Group Meeting 01-15-2008 Timothy Chang Outlines - Fundamental considerations, C-H versus C-C activation - Orbital interactions -
Transition Metal-Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Cleavage (C-C Activation) Group Meeting 01-15-2008 Timothy Chang Outlines - Fundamental considerations, C-H versus C-C activation - Orbital interactions -
Wilkinson s other (ruthenium) catalyst
 Wilkinson s other (ruthenium) catalyst Cl 3 ; 2 h 3, reflux 3h h 3 Cl h 3 h Cl 3 Good catalyst especially for 2 1-alkenes 2, base toluene Cl h 3 h 3 h 3 Et 3 Cl h 3 Cl h 3 h 3 R h 3 h 3 Cl h 3 R RC 2 C
Wilkinson s other (ruthenium) catalyst Cl 3 ; 2 h 3, reflux 3h h 3 Cl h 3 h Cl 3 Good catalyst especially for 2 1-alkenes 2, base toluene Cl h 3 h 3 h 3 Et 3 Cl h 3 Cl h 3 h 3 R h 3 h 3 Cl h 3 R RC 2 C
Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation
 Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation X MoL n u u * Tommy Bui 9/14/04 Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation from a Synthetic Viewpoint X X M u u * and/or u form a C-C bond with the creation of a new
Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation X MoL n u u * Tommy Bui 9/14/04 Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation from a Synthetic Viewpoint X X M u u * and/or u form a C-C bond with the creation of a new
CH 3 TMG, DMF N H 3 CO 2 S. (PPh 3 ) 2 Pd 0
 1. (a) rovide a reasonable mechanism for the following transformation. I S 2 C 3 C 3 ( 3 ) 2 2, CuI C 3 TMG, DMF 3 C 2 S TMG = Me 2 Me 2 ICu ( 3 ) 2 0 I S 2 C 3 S 2 C 3 Cu I 3 3 3 C 2 S I 3 3 3 C 2 S 3
1. (a) rovide a reasonable mechanism for the following transformation. I S 2 C 3 C 3 ( 3 ) 2 2, CuI C 3 TMG, DMF 3 C 2 S TMG = Me 2 Me 2 ICu ( 3 ) 2 0 I S 2 C 3 S 2 C 3 Cu I 3 3 3 C 2 S I 3 3 3 C 2 S 3
Copper-catalyzed cleavage of benzyl ethers with diacetoxyiodobenzene and p-toluenesulfonamide
 General Papers ARKIVC 2008 (xii) 103-108 Copper-catalyzed cleavage of benzyl ethers with diacetoxyiodobenzene and p-toluenesulfonamide Ling He a,b, Qin Wang a, Guo-Chuan Zhou b, Lei Guo b, and Xiao-Qi
General Papers ARKIVC 2008 (xii) 103-108 Copper-catalyzed cleavage of benzyl ethers with diacetoxyiodobenzene and p-toluenesulfonamide Ling He a,b, Qin Wang a, Guo-Chuan Zhou b, Lei Guo b, and Xiao-Qi
Electrophilic Carbenes
 Electrophilic Carbenes The reaction of so-called stabilized diazo compounds with late transition metals produces a metal carbene intermediate that is electrophilic. The most common catalysts are Cu(I)
Electrophilic Carbenes The reaction of so-called stabilized diazo compounds with late transition metals produces a metal carbene intermediate that is electrophilic. The most common catalysts are Cu(I)
CO 2 and CO activation
 2 and activation Most organic chemicals are currently made commercially from ethylene, a product of oil refining. It is possible that in the next several decades we may have to shift toward other carbon
2 and activation Most organic chemicals are currently made commercially from ethylene, a product of oil refining. It is possible that in the next several decades we may have to shift toward other carbon
Reductive Elimination
 Reductive Elimination Reductive elimination, the reverse of oxidative addition, is most often seen in higher oxidation states because the formal oxidation state of the metal is reduced by two units in
Reductive Elimination Reductive elimination, the reverse of oxidative addition, is most often seen in higher oxidation states because the formal oxidation state of the metal is reduced by two units in
INTRODUCING FUNCTIONALITY THROUGH C-H BOND ACTIVATIONS
 ITRDUCIG FUCTIALITY TRUG C- BD ACTIVATIS Reported by Rachel S. ector September 4, 001 ITRDUCTI Carbon-hydrogen (C-) bond activation reactions, those that replace hydrogen in a carbon-hydrogen bond with
ITRDUCIG FUCTIALITY TRUG C- BD ACTIVATIS Reported by Rachel S. ector September 4, 001 ITRDUCTI Carbon-hydrogen (C-) bond activation reactions, those that replace hydrogen in a carbon-hydrogen bond with
Direct Oxidative Heck Cyclizations: Intramolecular Fujiwara-Moritani Arylations for the Synthesis of Functionalized Benzofurans and Dihydrobenzofurans
 Direct xidative eck Cyclizations: Intramolecular Fujiwara-Moritani Arylations for the Synthesis of Functionalized Benzofurans and Dihydrobenzofurans by Zhang,.; Ferreira, E. M.; Stoltz, B. M. Angewandte
Direct xidative eck Cyclizations: Intramolecular Fujiwara-Moritani Arylations for the Synthesis of Functionalized Benzofurans and Dihydrobenzofurans by Zhang,.; Ferreira, E. M.; Stoltz, B. M. Angewandte
Highlights of Schmidt Reaction in the Last Ten Years
 ighlights of Schmidt eaction in the Last Ten Years Dendrobates histrionicus Jack Liu ov. 18, 2003 Introduction Classical Schmidt reaction of aldehydes and carboxylic acids Classical Schmidt reaction of
ighlights of Schmidt eaction in the Last Ten Years Dendrobates histrionicus Jack Liu ov. 18, 2003 Introduction Classical Schmidt reaction of aldehydes and carboxylic acids Classical Schmidt reaction of
Copper-Catalyzed Reaction of Alkyl Halides with Cyclopentadienylmagnesium Reagent
 Copper-Catalyzed eaction of Alkyl Halides with Cyclopentadienylmagnesium eagent Mg 1) cat. Cu(Tf) 2 i Pr 2, 25 o C, 3 h 2) H 2, Pt 2 Masahiro Sai, Hidenori Someya, Hideki Yorimitsu, and Koichiro shima
Copper-Catalyzed eaction of Alkyl Halides with Cyclopentadienylmagnesium eagent Mg 1) cat. Cu(Tf) 2 i Pr 2, 25 o C, 3 h 2) H 2, Pt 2 Masahiro Sai, Hidenori Someya, Hideki Yorimitsu, and Koichiro shima
O + k 2. H(D) Ar. MeO H(D) rate-determining. step?
 ame: CEM 633: Advanced rganic Chem: ysical Problem Set 6 (Due Thurs, 12/8/16) Please do not look up references until after you turn in the problem set unless otherwise noted. For the following problems,
ame: CEM 633: Advanced rganic Chem: ysical Problem Set 6 (Due Thurs, 12/8/16) Please do not look up references until after you turn in the problem set unless otherwise noted. For the following problems,
ummary Manipulating Radicals
 Manipulating Radicals ummary Modern catalysis research tries to address issues such as material scarcity, sustainability or process costs. One solution is to replace expensive and scarce noble metal catalysts
Manipulating Radicals ummary Modern catalysis research tries to address issues such as material scarcity, sustainability or process costs. One solution is to replace expensive and scarce noble metal catalysts
Palladium-Catalyzed Electrophilic Aromatic C H Fluorination
 Palladium-Catalyzed Electrophilic Aromatic C luorination +2 Pd II 2 B 4 C (5 mol %) SI (2 eq) MeC, rt 61%, 69:31 o:p C Yamamoto, K; Li, J.; Garber, J. A..; Rolfes, J. D.; Boursalian, G. B.; Borghs, J.
Palladium-Catalyzed Electrophilic Aromatic C luorination +2 Pd II 2 B 4 C (5 mol %) SI (2 eq) MeC, rt 61%, 69:31 o:p C Yamamoto, K; Li, J.; Garber, J. A..; Rolfes, J. D.; Boursalian, G. B.; Borghs, J.
A. Loupy, B.Tchoubar. Salt Effects in Organic and Organometallic Chemistry
 A. Loupy, B.Tchoubar Salt Effects in Organic and Organometallic Chemistry 1 Introduction - Classification of Specific Salt Effects 1 1.1 Specific Salt Effects Involving the Salt's Lewis Acid or Base Character
A. Loupy, B.Tchoubar Salt Effects in Organic and Organometallic Chemistry 1 Introduction - Classification of Specific Salt Effects 1 1.1 Specific Salt Effects Involving the Salt's Lewis Acid or Base Character
Lecture Topics: I. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS)
 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
Enantioselective Borylations. David Kornfilt Denmark Group Meeting Sept. 14 th 2010
 Enantioselective Borylations David Kornfilt Denmark Group Meeting Sept. 14 th 2010 30.000-foot View Enantioenriched Organoboranes What to do with them Crudden C. M. et. al., Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 46
Enantioselective Borylations David Kornfilt Denmark Group Meeting Sept. 14 th 2010 30.000-foot View Enantioenriched Organoboranes What to do with them Crudden C. M. et. al., Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 46
Chiral Brønsted Acid Catalysis
 Chiral Brønsted Acid Catalysis Aryl Aryl Aryl Aryl S CF 3 2 P Fe CF 3 CF 3 2 Jack Liu ov. 16, 2004 CF 3 Introduction Chiral Brønsted acid catalysis in nature: enzymes and peptides Chiral Brønsted acid
Chiral Brønsted Acid Catalysis Aryl Aryl Aryl Aryl S CF 3 2 P Fe CF 3 CF 3 2 Jack Liu ov. 16, 2004 CF 3 Introduction Chiral Brønsted acid catalysis in nature: enzymes and peptides Chiral Brønsted acid
CHAPTER 7. Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination
 CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
Palladium-Catalyzed Alkylation of sp2 and sp3 C-H Bonds with Methylboroxine and Alkylboronic Acids: Two Distinct C-H Activation Pathways
 Palladium-Catalyzed Alkylation of sp2 and sp3 C-H Bonds with Methylboroxine and Alkylboronic Acids: Two Distinct C-H Activation Pathways Xiao Cheng, Charles Goodhue, and Jin-Quan Yu Brandeis University
Palladium-Catalyzed Alkylation of sp2 and sp3 C-H Bonds with Methylboroxine and Alkylboronic Acids: Two Distinct C-H Activation Pathways Xiao Cheng, Charles Goodhue, and Jin-Quan Yu Brandeis University
Functionalization of C(sp 3 ) H Bonds Using a Transient Directing Group
 Literature eport Functionalization of C(sp 3 ) Bonds Using a Transient Directing Group eporter: Mu-Wang Chen Checker: Yue Ji Date: 2016-04-05 Yu, J.-Q. et al. Science 2016, 351, 252-256. Scripps esearch
Literature eport Functionalization of C(sp 3 ) Bonds Using a Transient Directing Group eporter: Mu-Wang Chen Checker: Yue Ji Date: 2016-04-05 Yu, J.-Q. et al. Science 2016, 351, 252-256. Scripps esearch
Oxidative Addition and Reductive Elimination
 xidative Addition and Reductive Elimination red elim coord 2 ox add ins Peter.. Budzelaar xidative Addition Basic reaction: n + X Y n X Y The new -X and -Y bonds are formed using: the electron pair of
xidative Addition and Reductive Elimination red elim coord 2 ox add ins Peter.. Budzelaar xidative Addition Basic reaction: n + X Y n X Y The new -X and -Y bonds are formed using: the electron pair of
Amines. Amines are organic compounds containing a nitrogen functionality. primary secondary tertiary quaternary
 Amines Amines are organic compounds containing a nitrogen functionality Depending upon the number of alkyl, or aryl, groups attached to nitrogen determines its classification, or order 2 primary secondary
Amines Amines are organic compounds containing a nitrogen functionality Depending upon the number of alkyl, or aryl, groups attached to nitrogen determines its classification, or order 2 primary secondary
Transition Metal Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Activation
 literature seminar 2 H. Mitsunuma(M1) 2010/09/08 Transition tal Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Activation 0. Introduction Currently, selective C-H and C-C bond activation by transition metal complexes has
literature seminar 2 H. Mitsunuma(M1) 2010/09/08 Transition tal Catalyzed Carbon-Carbon Bond Activation 0. Introduction Currently, selective C-H and C-C bond activation by transition metal complexes has
The Mechanistic Studies of the Wacker Oxidation. Tyler W. Wilson SED Group Meeting
 The Mechanistic Studies of the Wacker xidation Tyler W. Wilson SE Group Meeting 11.27.2007 Introduction xidation of ethene by (II) chloride solutions (Phillips, 1894) -First used as a test for alkenes
The Mechanistic Studies of the Wacker xidation Tyler W. Wilson SE Group Meeting 11.27.2007 Introduction xidation of ethene by (II) chloride solutions (Phillips, 1894) -First used as a test for alkenes
Chapter 15. Reactions of Aromatic Compounds. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Arenes. The first step is the slow, rate-determining step
 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Arenes Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds The characteristic reaction of aromatic rings is substitution initiated by an electrophile halogenation nitration
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Arenes Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds The characteristic reaction of aromatic rings is substitution initiated by an electrophile halogenation nitration
Reactivity within Confined Nano-spaces
 Reactivity within Confined Nano-spaces Larry Wolf Group Meeting 11-17-09 Encapsulating Cyclobutadiene hemicarcerand Anslyn, E. V; Dougherty, D. A. Modern Physical Organic Chemistry Cram. D. J. et. al.
Reactivity within Confined Nano-spaces Larry Wolf Group Meeting 11-17-09 Encapsulating Cyclobutadiene hemicarcerand Anslyn, E. V; Dougherty, D. A. Modern Physical Organic Chemistry Cram. D. J. et. al.
Enantioselective 1,1-Arylborylation of. Transfer with Pd Catalysis
 Enantioselective 1,1-Arylborylation of Alkenes: Merging Chiral Anion Phase Transfer with Pd Catalysis Reporter: Lian-Jin Liu Checker: Wen-Xue Huang Date: 12/05/2015 F. Dean Toste University of California,
Enantioselective 1,1-Arylborylation of Alkenes: Merging Chiral Anion Phase Transfer with Pd Catalysis Reporter: Lian-Jin Liu Checker: Wen-Xue Huang Date: 12/05/2015 F. Dean Toste University of California,
Direct, Catalytic Hydroaminoalkylation of Unactivated Olefins with N-Alkyl Arylamines
 Current Literature - May 12, 2007 Direct, Catalytic ydroaminoalkylation of Unactivated lefins with -Alkyl ylamines ' '' Ta[ 2 ] 5 (4-8 mol%), 160-165 o C 24-67h 66-95% ' '' S. B. erzon and J. F. artwig,
Current Literature - May 12, 2007 Direct, Catalytic ydroaminoalkylation of Unactivated lefins with -Alkyl ylamines ' '' Ta[ 2 ] 5 (4-8 mol%), 160-165 o C 24-67h 66-95% ' '' S. B. erzon and J. F. artwig,
Organometallic Catalysis
 Organometallic Catalysis The catalysts we will study are termed homogeneous catalysts as they are dissolved in th e same solvent as the substrate. In contrast, heterogeneous catalysts, such as palladium
Organometallic Catalysis The catalysts we will study are termed homogeneous catalysts as they are dissolved in th e same solvent as the substrate. In contrast, heterogeneous catalysts, such as palladium
Suggested solutions for Chapter 40
 s for Chapter 40 40 PBLEM 1 Suggest mechanisms for these reactions, explaining the role of palladium in the first step. Ac Et Et BS () 4 2 1. 2. K 2 C 3 evision of enol ethers and bromination, the Wittig
s for Chapter 40 40 PBLEM 1 Suggest mechanisms for these reactions, explaining the role of palladium in the first step. Ac Et Et BS () 4 2 1. 2. K 2 C 3 evision of enol ethers and bromination, the Wittig
Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions.
 ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination Chemistry Beauchamp 1 Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions. ources of
ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination Chemistry Beauchamp 1 Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions. ources of
A Stereoselective Synthesis of (+)-Gonyautoxin 3
 A Stereoselective Synthesis of (+)-Gonyautoxin 3 Mulcahy, J. V.; Du Bois, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12630-12631 Total Synthesis of (+)-Lithospermic Acid by Asymmetric Intramolecular Alkylation via
A Stereoselective Synthesis of (+)-Gonyautoxin 3 Mulcahy, J. V.; Du Bois, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12630-12631 Total Synthesis of (+)-Lithospermic Acid by Asymmetric Intramolecular Alkylation via
ACTIVATION OF C H BONDS BY LOW-VALENT METAL COMPLEXES ( THE ORGANOMETALLIC CHEMISTRY )
 CHAPTER IV ACTIVATION OF C H BONDS BY LOW-VALENT METAL COMPLEXES ( THE ORGANOMETALLIC CHEMISTRY ) n the end of the 1960s the leading specialist in homogeneous catalysis Jack Halpern wrote [1]: to develop
CHAPTER IV ACTIVATION OF C H BONDS BY LOW-VALENT METAL COMPLEXES ( THE ORGANOMETALLIC CHEMISTRY ) n the end of the 1960s the leading specialist in homogeneous catalysis Jack Halpern wrote [1]: to develop
1/4/2011. Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds
 Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
Tips for taking exams in 852
 Comprehensive Tactical Methods in rganic Synthesis W. D. Wulff 1) Know the relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds Tips for taking exams in 852 Cl > > ' > > ' N2 eg: 'Mg Et ' 1equiv. 1equiv. ' ' Et 50%
Comprehensive Tactical Methods in rganic Synthesis W. D. Wulff 1) Know the relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds Tips for taking exams in 852 Cl > > ' > > ' N2 eg: 'Mg Et ' 1equiv. 1equiv. ' ' Et 50%
Intramolecular Ene Reactions Utilizing Oxazolones and Enol Ethers Fisk, J.S. and Tepe, J..J J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129,
 Intramolecular Ene Reactions Utilizing xazolones and Enol Ethers Fisk, J.S. and Tepe, J..J J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 3058-3059 - versus -Arylation of Aminoalcohols: rthogonal Selectivity in Copper-Based
Intramolecular Ene Reactions Utilizing xazolones and Enol Ethers Fisk, J.S. and Tepe, J..J J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 3058-3059 - versus -Arylation of Aminoalcohols: rthogonal Selectivity in Copper-Based
Functionalization of terminal olefins via H migratory insertion /reductive elimination sequence Hydrogenation
 M.C. White, Chem 153 verview -282- Week of ovember 11, 2002 Functionalization of terminal olefins via migratory insertion /reductive elimination sequence ydrogenation ML n E ydrosilylation Si 3 Si 3 ML
M.C. White, Chem 153 verview -282- Week of ovember 11, 2002 Functionalization of terminal olefins via migratory insertion /reductive elimination sequence ydrogenation ML n E ydrosilylation Si 3 Si 3 ML
Module9. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy - Chemical shift - Integration of signal area
 1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
Chem 634. Introduction to Transition Metal Catalysis. Reading: Heg Ch 1 2 CS-B 7.1, , 11.3 Grossman Ch 6
 Chem 634 Introduction to Transition etal Catalysis eading: eg Ch 1 2 CS-B 7.1, 8.2 8.3, 11.3 Grossman Ch 6 Announcements Problem Set 1 due Thurs, 9/24 at beginning of class ffice our: Wed, 10:30-12, 220
Chem 634 Introduction to Transition etal Catalysis eading: eg Ch 1 2 CS-B 7.1, 8.2 8.3, 11.3 Grossman Ch 6 Announcements Problem Set 1 due Thurs, 9/24 at beginning of class ffice our: Wed, 10:30-12, 220
Direct Catalytic Cross-Coupling of Organolithium
 Literature report Direct Catalytic Cross-Coupling of Organolithium Compounds Reporter: Zhang-Pei Chen Checker: Mu-Wang Chen Date: 02/07/2013 Feringa, B.L.et al. Feringa, B. L. et al. Nature Chem. 2013,
Literature report Direct Catalytic Cross-Coupling of Organolithium Compounds Reporter: Zhang-Pei Chen Checker: Mu-Wang Chen Date: 02/07/2013 Feringa, B.L.et al. Feringa, B. L. et al. Nature Chem. 2013,
Metal Hydrides, Alkyls, Aryls, and their Reactions
 Metal Hydrides, Alkyls, Aryls, and their Reactions A Primer on MO Theory σ-bonding in Organotransition Metal Complexes M-C Bond Energies in Organotransition Metal Complexes Thermodynamic Predictions
Metal Hydrides, Alkyls, Aryls, and their Reactions A Primer on MO Theory σ-bonding in Organotransition Metal Complexes M-C Bond Energies in Organotransition Metal Complexes Thermodynamic Predictions
Zr-Catalyzed Carbometallation
 -Catalyzed Carbometallation C C C C ML n C C ML n ML n C C C C ML n ML n C C ML n Wipf Group esearch Topic Seminar Juan Arredondo November 13, 2004 Juan Arredondo @ Wipf Group 1 11/14/2004 Carbometallation
-Catalyzed Carbometallation C C C C ML n C C ML n ML n C C C C ML n ML n C C ML n Wipf Group esearch Topic Seminar Juan Arredondo November 13, 2004 Juan Arredondo @ Wipf Group 1 11/14/2004 Carbometallation
Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation
 Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation Chiral dioxirane strategy: R 3 + 1 xone, ph 10.5, K 2 C 3, H 2, C R 3 formed in situ catalyst (10-20 mol%) is prepared from D-fructose, and its enantiomer from L-sorbose oxone,
Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation Chiral dioxirane strategy: R 3 + 1 xone, ph 10.5, K 2 C 3, H 2, C R 3 formed in situ catalyst (10-20 mol%) is prepared from D-fructose, and its enantiomer from L-sorbose oxone,
Facile preparation of α-amino ketones from oxidative ring-opening of aziridines by pyridine N-oxide
 Facile preparation of α-amino ketones from oxidative ring-opening of aziridines by pyridine -oxide rg. Biomol. Chem., 2007, 5, 3428 Luo, Z.-B.; Wu, J.-Y.; ou, X.-L.; Dai, L.-X. Ts toluene Ts 80 o C John
Facile preparation of α-amino ketones from oxidative ring-opening of aziridines by pyridine -oxide rg. Biomol. Chem., 2007, 5, 3428 Luo, Z.-B.; Wu, J.-Y.; ou, X.-L.; Dai, L.-X. Ts toluene Ts 80 o C John
Manganese-Catalyzed Late- Stage Aliphatic C H Azidation
 Wipf group current literature Manganese-Catalyzed Late- Stage Aliphatic C H Azidation J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5300 5303 Xiongyi Huang, Tova M. Bergsten, and John T. Groves Department of Chemistry,
Wipf group current literature Manganese-Catalyzed Late- Stage Aliphatic C H Azidation J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5300 5303 Xiongyi Huang, Tova M. Bergsten, and John T. Groves Department of Chemistry,
Preparation of alkenes
 Lecture 11 אלקנים הכנה ותגובות של אלקנים: הידרוגנציה, סיפוח הידרוהלוגנים )כלל מארקובניקוב(, סיפוח הלוגנים והסטראוכימיה של תוצרי הסיפוח, הידרובורציה, אפוקסידציה, אוזונוליזה. 1 Preparation of alkenes 1.
Lecture 11 אלקנים הכנה ותגובות של אלקנים: הידרוגנציה, סיפוח הידרוהלוגנים )כלל מארקובניקוב(, סיפוח הלוגנים והסטראוכימיה של תוצרי הסיפוח, הידרובורציה, אפוקסידציה, אוזונוליזה. 1 Preparation of alkenes 1.
Olefin Metathesis ROMP. L n Ru= ROMP n RCM. dilute
 lefin Metathesis MP: ing-opening metathesis polymerization Thermodynamically favored for 3,4, 8, larger ring systems Bridging groups (bicyclic olefins) make ΔG polymerization more favorable as a result
lefin Metathesis MP: ing-opening metathesis polymerization Thermodynamically favored for 3,4, 8, larger ring systems Bridging groups (bicyclic olefins) make ΔG polymerization more favorable as a result
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122)
 Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
Chapter 7 Substitution Reactions 7.1 Introduction to Substitution Reactions Substitution Reactions: two reactants exchange parts to give new products
 hapter 7 Substitution eactions 7.1 Introduction to Substitution eactions Substitution eactions: two reactants exchange parts to give new products A-B + -D A-D + B- 3 2 + Br 3 2 Br + Elimination eaction:
hapter 7 Substitution eactions 7.1 Introduction to Substitution eactions Substitution eactions: two reactants exchange parts to give new products A-B + -D A-D + B- 3 2 + Br 3 2 Br + Elimination eaction:
12/27/2010. Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen atom
Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen atom
Highly Efficient, Convergent, and Enantioselective Synthesis of Phthioceranic Acid
 Highly Efficient, Convergent, and Enantioselective Synthesis of Phthioceranic Acid Shiqing Xu, Akimichi Oda, Thomas Bobinski, Haijun Li, Yohei Matsueda, and Ei-ichi Negishi Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015,
Highly Efficient, Convergent, and Enantioselective Synthesis of Phthioceranic Acid Shiqing Xu, Akimichi Oda, Thomas Bobinski, Haijun Li, Yohei Matsueda, and Ei-ichi Negishi Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015,
Chapter 7: Alkene reactions conversion to new functional groups
 hapter 7: Alkene reactions conversion to new functional groups Preparation of alkenes: two common elimination reactions 1. Dehydration of alcohols Dehydration is a common biochemical reaction in carbohydrate
hapter 7: Alkene reactions conversion to new functional groups Preparation of alkenes: two common elimination reactions 1. Dehydration of alcohols Dehydration is a common biochemical reaction in carbohydrate
Chapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides
 hapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides Overview: The nature of alkyl halides and other groups with electrophilic sp 3 hybridized leads them to react with nucleophiles and
hapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides Overview: The nature of alkyl halides and other groups with electrophilic sp 3 hybridized leads them to react with nucleophiles and
C H activation of aliphatic amines without unnecessary mask M2 Takaya Togo
 C H activation of aliphatic amines without unnecessary mask 2017.11.25 M2 Takaya Togo 1 Outline 1.Introduction 2.Free amines as DG Discovery of new activation mode Mechanistic studies Application of the
C H activation of aliphatic amines without unnecessary mask 2017.11.25 M2 Takaya Togo 1 Outline 1.Introduction 2.Free amines as DG Discovery of new activation mode Mechanistic studies Application of the
1. Theoretical Investigation of Mechanisms and Stereoselectivities of Synthetic Organic Reactions
 1. Theoretical Investigation of Mechanisms and Stereoselectivities of Synthetic Organic Reactions 2. Copper Catalyzed One-Pot Synthesis of Multisubstituted Quinolinones Hao Wang Denmark Group Presentation
1. Theoretical Investigation of Mechanisms and Stereoselectivities of Synthetic Organic Reactions 2. Copper Catalyzed One-Pot Synthesis of Multisubstituted Quinolinones Hao Wang Denmark Group Presentation
Investigation of the Role and Form. Formation. Michael Enright
 Investigation of the Role and Form of Silver Catalysts in C N Bond Formation Michael Enright Ripon College Importance Carbon Nitrogen Bonds Medicine Biological compounds Make C N bonds whenever we want
Investigation of the Role and Form of Silver Catalysts in C N Bond Formation Michael Enright Ripon College Importance Carbon Nitrogen Bonds Medicine Biological compounds Make C N bonds whenever we want
sp 3 C-H insertion by α-oxo Gold Carbene B4 Kei Ito
 1 sp 3 C-H insertion by α-oxo Gold Carbene B4 Kei Ito 2016. 1. 30 1. Introduction 2 About Carbene 3 Brief history of carbene (~2000) Carbene Neutral compounds featuring a divalent carbon atom with only
1 sp 3 C-H insertion by α-oxo Gold Carbene B4 Kei Ito 2016. 1. 30 1. Introduction 2 About Carbene 3 Brief history of carbene (~2000) Carbene Neutral compounds featuring a divalent carbon atom with only
Recent advances in transition metal-catalyzed or -mediated cyclization of 2,3-allenoic acids: New methodologies for the synthesis of butenolides*
 Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 76, No. 3, pp. 651 656, 2004. 2004 IUPAC Recent advances in transition metal-catalyzed or -mediated cyclization of 2,3-allenoic acids: New methodologies for the synthesis of butenolides*
Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 76, No. 3, pp. 651 656, 2004. 2004 IUPAC Recent advances in transition metal-catalyzed or -mediated cyclization of 2,3-allenoic acids: New methodologies for the synthesis of butenolides*
Reaction chemistry of complexes Three general forms: 1. Reactions involving the gain and loss of ligands a. Ligand Dissoc. and Assoc. (Bala) b.
 eaction chemistry of complexes Three general forms: 1. eactions involving the gain and loss of ligands a. Ligand Dissoc. and Assoc. (Bala) b. Oxidative Addition c. eductive Elimination d. Nucleophillic
eaction chemistry of complexes Three general forms: 1. eactions involving the gain and loss of ligands a. Ligand Dissoc. and Assoc. (Bala) b. Oxidative Addition c. eductive Elimination d. Nucleophillic
Chemistry 335 Supplemental Slides: Interlude 1. Reduction: addition of hydrogen to the substrate. Oxidation: addition of oxygen to the substrate
 Interlude 1: Oxidations, Reductions & Other Functional Group Interconversions (FGI) 1. Definition of Oxidation and Reduction For practical purposes in organic chemistry, oxidation and reduction are defined
Interlude 1: Oxidations, Reductions & Other Functional Group Interconversions (FGI) 1. Definition of Oxidation and Reduction For practical purposes in organic chemistry, oxidation and reduction are defined
A Simple Introduction of the Mizoroki-Heck Reaction
 A Simple Introduction of the Mizoroki-Heck Reaction Reporter: Supervisor: Zhe Niu Prof. Yang Prof. Chen Prof. Tang 2016/2/3 Content Introduction Intermolecular Mizoroki-Heck Reaction Intramolecular Mizoroki-Heck
A Simple Introduction of the Mizoroki-Heck Reaction Reporter: Supervisor: Zhe Niu Prof. Yang Prof. Chen Prof. Tang 2016/2/3 Content Introduction Intermolecular Mizoroki-Heck Reaction Intramolecular Mizoroki-Heck
C H Activated Trifluoromethylation
 Literature report C H Activated Trifluoromethylation Reporter:Yan Fang Superior:Prof. Yong Huang Jun. 17 th 2013 Contents Background Trifluoromethylation of sp-hybridized C-H Bonds Trifluoromethylation
Literature report C H Activated Trifluoromethylation Reporter:Yan Fang Superior:Prof. Yong Huang Jun. 17 th 2013 Contents Background Trifluoromethylation of sp-hybridized C-H Bonds Trifluoromethylation
σ Bonded ligands: Transition Metal Alkyls and Hydrides
 σ Bonded ligands: Transition Metal Alkyls and Hydrides Simplest of organo-transitionmetal species Rare until and understanding of their stability in the 60 s and 70 s Metal alkyls can be considered as
σ Bonded ligands: Transition Metal Alkyls and Hydrides Simplest of organo-transitionmetal species Rare until and understanding of their stability in the 60 s and 70 s Metal alkyls can be considered as
Ch.16 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Ch.16 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophilic aromatic substitution: E + E + + Some electrophilic aromatic substitution: X N 2 S 3 R C R alogenation Nitration Sulfonation
Ch.16 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophilic aromatic substitution: E + E + + Some electrophilic aromatic substitution: X N 2 S 3 R C R alogenation Nitration Sulfonation
Advanced Organic Chemistry
 D. A. Evans, G. Lalic Question of the day: Chemistry 530A TBS Me 2 C Me toluene, 130 C 70% TBS C 2 Me H H Advanced rganic Chemistry Me Lecture 16 Cycloaddition Reactions Diels _ Alder Reaction Photochemical
D. A. Evans, G. Lalic Question of the day: Chemistry 530A TBS Me 2 C Me toluene, 130 C 70% TBS C 2 Me H H Advanced rganic Chemistry Me Lecture 16 Cycloaddition Reactions Diels _ Alder Reaction Photochemical
ELECTROPHILIC ADDITIONS OF ALKENES AS THE COUNTERPART OF ELIMINATIONS
 ELECTRPHILIC ADDITINS F ALKENES AS THE CUNTERPART F ELIMINATINS INTRDUCTIN - Chapter 8 is mostly about alkene reactions. That is, how one can transform alkenes into other functional groups. Most of these
ELECTRPHILIC ADDITINS F ALKENES AS THE CUNTERPART F ELIMINATINS INTRDUCTIN - Chapter 8 is mostly about alkene reactions. That is, how one can transform alkenes into other functional groups. Most of these
π-alkyne metal complex and vinylidene metal complex in organic synthesis
 Literature Seminar 080220 Kenzo YAMATSUGU (D1) π-alkyne metal complex and vinylidene metal complex in organic synthesis 0. Introduction ' ' = π-alkyne metal complex vinylidene metal complex ecently, electrophilic
Literature Seminar 080220 Kenzo YAMATSUGU (D1) π-alkyne metal complex and vinylidene metal complex in organic synthesis 0. Introduction ' ' = π-alkyne metal complex vinylidene metal complex ecently, electrophilic
Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 15 1 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen
Chapter 15 1 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen
Organic Chemistry Laboratory Summer Lecture 6 Transition metal organometallic chemistry and catalysis July
 344 Organic Chemistry Laboratory Summer 2013 Lecture 6 Transition metal organometallic chemistry and catalysis July 30 2013 Summary of Grignard lecture Organometallic chemistry - the chemistry of compounds
344 Organic Chemistry Laboratory Summer 2013 Lecture 6 Transition metal organometallic chemistry and catalysis July 30 2013 Summary of Grignard lecture Organometallic chemistry - the chemistry of compounds
CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK
 Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
H Organometallic Catalysis in Industry
 H Organometallic Catalysis in Industry Some terminology: Catalytic cycles: a circular path meant to show productive reactions, in order, that lead from the catalytically active species and its reaction
H Organometallic Catalysis in Industry Some terminology: Catalytic cycles: a circular path meant to show productive reactions, in order, that lead from the catalytically active species and its reaction
Amphoteric Molecules < Chemistry of Andrei K. Yudin > Hyung Min Chi 17 JUNE 2014
 Amphoteric Molecules < Chemistry of Andrei K. Yudin > Hyung Min Chi 17 JUNE 2014 1 Amphoteric molecules Amphoteric? Greek word amphoteros (both of two) Amphoterism in acid/base chemistry Amino acids (thermodynatic
Amphoteric Molecules < Chemistry of Andrei K. Yudin > Hyung Min Chi 17 JUNE 2014 1 Amphoteric molecules Amphoteric? Greek word amphoteros (both of two) Amphoterism in acid/base chemistry Amino acids (thermodynatic
CHAPTER 16 - CHEMISTRY OF BENZENE: ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION
 CAPTR 16 - CMISTRY F BNZN: LCTRPILIC ARMATIC SUBSTITUTIN As stated in the previous chapter, benzene and other aromatic rings do not undergo electrophilic addition reactions of the simple alkenes but rather
CAPTR 16 - CMISTRY F BNZN: LCTRPILIC ARMATIC SUBSTITUTIN As stated in the previous chapter, benzene and other aromatic rings do not undergo electrophilic addition reactions of the simple alkenes but rather
CHEM 153 PRACTICE TEST #1 ANSWER KEY
 CEM 153 PACTICE TEST #1 ASWE KEY Provide a mechanism for the following transformation, indicating the electron count and oxidation state of each organometallic intermediate: u 3 (C) 12 (5 mol%) TF, 135
CEM 153 PACTICE TEST #1 ASWE KEY Provide a mechanism for the following transformation, indicating the electron count and oxidation state of each organometallic intermediate: u 3 (C) 12 (5 mol%) TF, 135
Lecture 6: Transition-Metal Catalysed C-C Bond Formation
 Lecture 6: Transition-Metal Catalysed C-C Bond Formation (a) Asymmetric allylic substitution 1 u - d u (b) Asymmetric eck reaction 2 3 Ar- d (0) Ar 2 3 (c) Asymmetric olefin metathesis alladium π-allyl
Lecture 6: Transition-Metal Catalysed C-C Bond Formation (a) Asymmetric allylic substitution 1 u - d u (b) Asymmetric eck reaction 2 3 Ar- d (0) Ar 2 3 (c) Asymmetric olefin metathesis alladium π-allyl
Insertion Reactions. 1) 1,1 insertion in which the metal and the X ligand end up bound to the same (1,1) atom
 Insertion Reactions xidative addition and substitution allow us to assemble 1e and 2e ligands on the metal, respectively. With insertion, and its reverse reaction, elimination, we can now combine and transform
Insertion Reactions xidative addition and substitution allow us to assemble 1e and 2e ligands on the metal, respectively. With insertion, and its reverse reaction, elimination, we can now combine and transform
Metal Catalyzed Outer Sphere Alkylations of Unactivated Olefins and Alkynes
 Metal Catalyzed uter Sphere Alkylations of Unactivated lefins and Alkynes Stephen Goble rganic Super-Group Meeting Literature Presentation ctober 6, 2004 1 utline I. Background Introduction to Carbometallation
Metal Catalyzed uter Sphere Alkylations of Unactivated lefins and Alkynes Stephen Goble rganic Super-Group Meeting Literature Presentation ctober 6, 2004 1 utline I. Background Introduction to Carbometallation
The aldol reaction with metal enolates proceeds by a chair-like, pericyclic process: favored. disfavored. favored. disfavored
 The aldol reaction with metal enolates proceeds by a chair-like, pericyclic process: Z-enolates: M 2 M 2 syn 2 C 2 favored 2 M 2 anti disfavored E-enolates: M 2 2 C 3 C 3 C 2 favored 2 M M disfavored In
The aldol reaction with metal enolates proceeds by a chair-like, pericyclic process: Z-enolates: M 2 M 2 syn 2 C 2 favored 2 M 2 anti disfavored E-enolates: M 2 2 C 3 C 3 C 2 favored 2 M M disfavored In
Introduction & Definitions Catalytic Hydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of H- and H+ Oxidation of Alcohols Oxidation of
 CEM 241- UNIT 4 xidation/reduction Reactions Redox chemistry 1 utline Introduction & Definitions Catalytic ydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of - and + xidation of Alcohols
CEM 241- UNIT 4 xidation/reduction Reactions Redox chemistry 1 utline Introduction & Definitions Catalytic ydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of - and + xidation of Alcohols
Stable gold(iii) catalysts by oxidative addition of a carboncarbon
 Stable gold(iii) catalysts by oxidative addition of a carboncarbon bond Chung-Yeh Wu, Takahiro oribe, Christian Borch Jacobsen & F. Dean Toste ature, 517, 449-454 (2015) presented by Ian Crouch Literature
Stable gold(iii) catalysts by oxidative addition of a carboncarbon bond Chung-Yeh Wu, Takahiro oribe, Christian Borch Jacobsen & F. Dean Toste ature, 517, 449-454 (2015) presented by Ian Crouch Literature
S N 1 Displacement Reactions
 S N 1 Displacement Reactions Tertiary alkyl halides cannot undergo S N 2 reactions because of the severe steric hindrance blocking a backside approach of the nucleophile. They can, however, react via an
S N 1 Displacement Reactions Tertiary alkyl halides cannot undergo S N 2 reactions because of the severe steric hindrance blocking a backside approach of the nucleophile. They can, however, react via an
11. Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations
 11. Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition 2003 Ronald Kluger Department of Chemistry University of Toronto Alkyl Halides
11. Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition 2003 Ronald Kluger Department of Chemistry University of Toronto Alkyl Halides
sp 3 C-H Alkylation with Olefins Yan Xu Dec. 3, 2014
 sp 3 C-H Alkylation with Olefins, Yan Xu Dec. 3, 2014 1) sp 3 C-H Alkylation via Directed C-H activation 2) Hydroaminoalkylation (still via C-H activation) 3) Hydrohydroxyalkylation (via radical chemistry)
sp 3 C-H Alkylation with Olefins, Yan Xu Dec. 3, 2014 1) sp 3 C-H Alkylation via Directed C-H activation 2) Hydroaminoalkylation (still via C-H activation) 3) Hydrohydroxyalkylation (via radical chemistry)
Classes of Alkenes. Alkenes and Alkynes. Saturated compounds (alkanes): Have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom.
 Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
Oxidative couplings of two nucleophiles
 Oxidative Couplings of Hydrocarbons Oxidative couplings of two nucleophiles Oxidants involved: O 2 H 2 O 2 high h valent metals(copper salts) halides(iodine(Ⅲ) oxidants) Lei, A. W. Chem. Rev., 2011, 111,
Oxidative Couplings of Hydrocarbons Oxidative couplings of two nucleophiles Oxidants involved: O 2 H 2 O 2 high h valent metals(copper salts) halides(iodine(Ⅲ) oxidants) Lei, A. W. Chem. Rev., 2011, 111,
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophile substitutes for a hydrogen on the benzene ring. Chapter 17: Aromatics 2-Reactions Slide 17-2 1 Mechanism Step
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophile substitutes for a hydrogen on the benzene ring. Chapter 17: Aromatics 2-Reactions Slide 17-2 1 Mechanism Step
O CH 3. Mn CH 3 OC C. 16eelimination
 igratory Insertion igratory Insertion/Elimination 1 A migratory insertion reaction is when a cisoidal anionic and neutral ligand on a metal complex couple together to generate a new coordinated anionic
igratory Insertion igratory Insertion/Elimination 1 A migratory insertion reaction is when a cisoidal anionic and neutral ligand on a metal complex couple together to generate a new coordinated anionic
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King. Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; Organometallic Reagents; Oxidation & Reduction
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
BSc. II 3 rd Semester. Submitted By Dr. Sangita Nohria Associate Professor PGGCG-11 Chandigarh 1
 BSc. II 3 rd Semester Submitted By Dr. Sangita Nohria Associate Professor PGGCG-11 Chandigarh 1 Introduction to Alkyl Halides Alkyl halides are organic molecules containing a halogen atom bonded to an
BSc. II 3 rd Semester Submitted By Dr. Sangita Nohria Associate Professor PGGCG-11 Chandigarh 1 Introduction to Alkyl Halides Alkyl halides are organic molecules containing a halogen atom bonded to an
Preparation of Alkyl Halides, R-X. Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): R + X X 2.
 Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Denmark Group Meeting. & Electrophilic rearrangement of amides
 Denmark Group Meeting Palladium catalyzed Dearomatizationeaction & Electrophilic rearrangement of amides 11 th Bo Peng th Feb. 2014 1 https://maps.google.com 2 Palladium catalyzed Dearomatization eaction
Denmark Group Meeting Palladium catalyzed Dearomatizationeaction & Electrophilic rearrangement of amides 11 th Bo Peng th Feb. 2014 1 https://maps.google.com 2 Palladium catalyzed Dearomatization eaction
Reversible Interaction between Substrate and Ligand
 Reversible Interaction between Substrate and Ligand 2010.6.9.YoheiShimizu(D3) is is is Ser 271 P Lys 229-2 3 P Zn 2+ Tyr P 3 2- + 3 Lys 107 P 3 2- class 1 aldolase class 2 aldolase Glu 185 Asp 211 C 2
Reversible Interaction between Substrate and Ligand 2010.6.9.YoheiShimizu(D3) is is is Ser 271 P Lys 229-2 3 P Zn 2+ Tyr P 3 2- + 3 Lys 107 P 3 2- class 1 aldolase class 2 aldolase Glu 185 Asp 211 C 2
