10/4/2011. Tells you the number of protons
|
|
|
- Chester Morgan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Atomic Structure The arrangement of the subatomic particles within the atom determines the chemical properties of the elements How they interact with one another The types of ions and structures that they form The periodic table gives you 2 basic pieces of information Atomic number (upper whole number) Atomic mass (lower decimal number) Atomic number Tells you the number of protons Since the overall charge on the atom is neutral, the number of electrons must equal the number of protons 1
2 Atomic mass Weighted average mass that takes into account the mass and abundance in nature of the isotopes of the element Measured in atomic mass units (amu) Mass number Total number of protons and neutrons Isotopes are indicated by including the mass number with the symbol I.e. C- 14 tells you that the mass of carbon is 14, not the more common 12. Atomic mass This number is the mass of the nuclear particles The nucleus is comprised of protons and neutron so the atomic mass is the sum of the protons and neutrons The mass of the electrons is negligible The atomic mass is not a whole number because it is an average of the isotopes of the element Calculating amu Atomic mass units average atomic mass There are 2 isotopes of element X X-10 has a mass of amu and a relative abundance of 19.91% X-11 has a mass of amu and has a relative abundance of 80.09% X-10; x.1991 = amu X-11; x.8009 = amu Element X = amu 2
3 Vocabulary Ion Charged particle Atom that has lost or gained electrons Isotope Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons Nucleus Contains the nucleons Protons and neutrons Where the mass of the atom is located Has an overall positive charge Subatomic Particles Proton The positively charged particle Found in the nucleus Accounts for the mass of the atom, along with the neutrons Determines the identity of the element 3
4 Neutron The neutrally charged particle Located in the nucleus The number of neutrons determines which isotope of an element is present With the proton, accounts for the mass of the atom Mass of a neutron is relatively equivalent to the mass of a proton Electron The negatively charged particle in the atom Located in orbitals around the nucleus When lost or gained determines the type of ion formed from the atom When an atom loses an electron a positive ion (cation) is formed When an atom gains an electron a negative ion (anion) is formed Interact between atoms to form chemical bonds in compounds Arrangement of Electrons Electrons hold the energy in the atom The energy level of an electron is the region around the nucleus where the electron is likely to be moving Electrons move between energy levels based on the energy they possess The energy it takes to move an electron from one level to the next is a quantum 4
5 Waves and electrons Electromagnetic radiation travels at a speed of 3.0 x 10 8 m/s, in a vacuum Amplitude wave height from the origin to the crest Wavelength ( ) distance between the crests Frequency ( ) number of wave cycles to pass a given point per unit of time Calculations Frequency and wavelength are inversely related and can be calculated l The SI unit of frequency (cycles per second) is hertz (Hz) C = Atomic Emission Spectrum When atoms are excited by an electric current passed through its gas or vapor, they first absorb energy, then lose it as they emit light. The light emitted by an atom will consist of a unique set of lines each corresponding to one exact frequency of light Likewise atoms give off a particular color of light when they are burned. 5
6 Max Planck Father of quantum physics Studied the relationship between energy and frequency Showed that the amount of radiant energy absorbed or emitted is proportional to the frequency of the radiation E = h E = energy H = Plancks constant (6.626 x Js) Previously it was thought that there was no limit to how small of an energy change could be in an atom Albert Einstein Proposed that light could be described as quanta of energy that behave like particles Light quanta are called photons Energy of photons is calculated E = h Energy changes in the Atom When energy is added to an atom, the electrons are excited and move to a higher energy level (excited state) The same amount of energy is emitted as a photon when the electron drops back to a lower level (ground state) Only electrons in transition from higher to lower energy levels will emit light 6
Table of Contents Electrons in Atoms > Light and Quantized Energy > Quantum Theory and the Atom > Electron Configuration
 Electrons in Atoms October 20, 2014 Table of Contents Electrons in Atoms > Light and Quantized Energy > Quantum Theory and the Atom > Electron Configuration 1 Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic radiation
Electrons in Atoms October 20, 2014 Table of Contents Electrons in Atoms > Light and Quantized Energy > Quantum Theory and the Atom > Electron Configuration 1 Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic radiation
The ELECTRON: Wave Particle Duality. chapter 4
 The ELECTRON: Wave Particle Duality chapter 4 What do we know about light? Before 1900 s scientists thought light behaved as a wave. This belief changed when it was discovered that light also has particle
The ELECTRON: Wave Particle Duality chapter 4 What do we know about light? Before 1900 s scientists thought light behaved as a wave. This belief changed when it was discovered that light also has particle
Bohr. Electronic Structure. Spectroscope. Spectroscope
 Bohr Electronic Structure Bohr proposed that the atom has only certain allowable energy states. Spectroscope Using a device called a it was found that gaseous elements emitted electromagnetic radiation
Bohr Electronic Structure Bohr proposed that the atom has only certain allowable energy states. Spectroscope Using a device called a it was found that gaseous elements emitted electromagnetic radiation
Chemistry Vocabulary. These vocabulary words appear on the Chemistry CBA in addition to being tested on the Chemistry Vocabulary Test.
 Chemistry Vocabulary These vocabulary words appear on the Chemistry CBA in addition to being tested on the Chemistry Vocabulary Test. atom the smallest unit of an element that still represents that element.
Chemistry Vocabulary These vocabulary words appear on the Chemistry CBA in addition to being tested on the Chemistry Vocabulary Test. atom the smallest unit of an element that still represents that element.
NOTES: 5.3 Light and Atomic Spectra (more Quantum Mechanics!)
 NOTES: 5.3 Light and Atomic Spectra (more Quantum Mechanics!) Light WAVE or PARTICLE? Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation includes: -radio waves -microwaves -infrared waves -visible light
NOTES: 5.3 Light and Atomic Spectra (more Quantum Mechanics!) Light WAVE or PARTICLE? Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation includes: -radio waves -microwaves -infrared waves -visible light
The Bohr Model Bohr proposed that an electron is found only in specific circular paths, or orbits, around the nucleus.
 5.1 The Development of Atomic Models Rutherford s atomic model could not explain the chemical properties of elements. Rutherford s atomic model could not explain why objects change color when heated. The
5.1 The Development of Atomic Models Rutherford s atomic model could not explain the chemical properties of elements. Rutherford s atomic model could not explain why objects change color when heated. The
CVB102 Lecture 1 - Chemical Structure and Reactivity. Contact Information: Dr. Bill Lot Electronic Structure of Atoms
 CVB102 Lecture 1 - Chemical Structure and Reactivity Contact Information: Dr. Bill Lot b.lott@qut.edu.au Electronic Structure of Atoms Text: Blackman, et al Pp. 127-147 (Pp. 148-159 recommended) The periodic
CVB102 Lecture 1 - Chemical Structure and Reactivity Contact Information: Dr. Bill Lot b.lott@qut.edu.au Electronic Structure of Atoms Text: Blackman, et al Pp. 127-147 (Pp. 148-159 recommended) The periodic
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms
 Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5.2 Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic Emission Spectra and the Quantum Mechanical Model 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5.2 Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic Emission Spectra and the Quantum Mechanical Model 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
The Bohr Model of the Atom
 Unit 4: The Bohr Model of the Atom Properties of light Before the 1900 s, light was thought to behave only as a wave. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation - a form of energy that exhibits wave
Unit 4: The Bohr Model of the Atom Properties of light Before the 1900 s, light was thought to behave only as a wave. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation - a form of energy that exhibits wave
Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements. 2.4 The Atom
 Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements 2.4 The Atom Atoms Dalton s Atomic Theory Are tiny particles of matter. Of an element are similar and different from other elements. Of two or more different elements combine
Chapter 2 Atoms and Elements 2.4 The Atom Atoms Dalton s Atomic Theory Are tiny particles of matter. Of an element are similar and different from other elements. Of two or more different elements combine
i. This is the best evidence for the fact that electrons in an atom surround the nucleus in certain allowed energy levels or orbitals ii.
 Atomic Structure I. The Atom A. Atomic theory: Devised in 1807 by John Dalton, states that all matter is made up of a small number of different kinds of atoms that are indivisible and indestructible but
Atomic Structure I. The Atom A. Atomic theory: Devised in 1807 by John Dalton, states that all matter is made up of a small number of different kinds of atoms that are indivisible and indestructible but
UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY
 UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY VOCABULARY: Allotrope Electron Configuration Nuclear Charge Anion Element Nucleons Atom Excited state Nucleus Atomic Mass Ground state Orbital Atomic Mass unit (a.m.u.) Ion Proton
UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY VOCABULARY: Allotrope Electron Configuration Nuclear Charge Anion Element Nucleons Atom Excited state Nucleus Atomic Mass Ground state Orbital Atomic Mass unit (a.m.u.) Ion Proton
Name Class Date ELECTRONS AND THE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS
 Electrons in Atoms ELECTRONS AND THE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model Essential Understanding of an atom. An electron s energy depends on its location around the nucleus Reading Strategy
Electrons in Atoms ELECTRONS AND THE STRUCTURE OF ATOMS 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model Essential Understanding of an atom. An electron s energy depends on its location around the nucleus Reading Strategy
UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY
 UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY VOCABULARY: Allotrope Electron Configuration Nuclear Charge Anion Element Nucleons Atom Excited state Nucleus Atomic Mass Ground state Orbital Atomic Mass unit (a.m.u.) Ion Proton
UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY VOCABULARY: Allotrope Electron Configuration Nuclear Charge Anion Element Nucleons Atom Excited state Nucleus Atomic Mass Ground state Orbital Atomic Mass unit (a.m.u.) Ion Proton
Electrons in Atoms. Before You Read. Chapter 4. Review the structure of the atom by completing the following table.
 Electrons in Atoms Before You Read Chapter 4 Review the structure of the atom by completing the following table. Part of the Atom Description proton centrally located part of the atom that contains protons
Electrons in Atoms Before You Read Chapter 4 Review the structure of the atom by completing the following table. Part of the Atom Description proton centrally located part of the atom that contains protons
Physics and the Quantum Mechanical Model
 chemistry 1 of 38 Mechanical Model Neon advertising signs are formed from glass tubes bent in various shapes. An electric current passing through the gas in each glass tube makes the gas glow with its
chemistry 1 of 38 Mechanical Model Neon advertising signs are formed from glass tubes bent in various shapes. An electric current passing through the gas in each glass tube makes the gas glow with its
Do Now: Bohr Diagram, Lewis Structures, Valence Electrons 1. What is the maximum number of electrons you can fit in each shell?
 Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Do Now: Bohr Diagram, Lewis Structures, Valence Electrons 1. What is the maximum number of electrons you can fit in each shell? 1 st shell 2 nd shell 3 rd shell 4 th shell
Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Do Now: Bohr Diagram, Lewis Structures, Valence Electrons 1. What is the maximum number of electrons you can fit in each shell? 1 st shell 2 nd shell 3 rd shell 4 th shell
Energy and the Quantum Theory
 Energy and the Quantum Theory Light electrons are understood by comparing them to light 1. radiant energy 2. travels through space 3. makes you feel warm Light has properties of waves and particles Amplitude:
Energy and the Quantum Theory Light electrons are understood by comparing them to light 1. radiant energy 2. travels through space 3. makes you feel warm Light has properties of waves and particles Amplitude:
Atomic Theory. Contribution to Modern Atomic Theory
 Alief High School Chemistry STAAR Review Reporting Category 2: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry C.6.A Understand the experimental design and conclusions used in the development of modern atomic theory,
Alief High School Chemistry STAAR Review Reporting Category 2: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry C.6.A Understand the experimental design and conclusions used in the development of modern atomic theory,
Atomic Structure Early Theories Democritus: 4 B.C.: atom Dalton: atoms cannot Thomson: Cathode Ray Tubes Rutherford:
 Atomic Structure n a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world; n an organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances to explain a specific set
Atomic Structure n a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world; n an organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances to explain a specific set
a. According to Dalton, what is inside the atom? Nothing, the atom it the smallest
 Unit 3: Review SCIENTIFIC THEORIES Dalton theorized that atoms were the smallest particle and could not be divided. Atoms can bond with one another in whole number ratios to form compounds but cannot be
Unit 3: Review SCIENTIFIC THEORIES Dalton theorized that atoms were the smallest particle and could not be divided. Atoms can bond with one another in whole number ratios to form compounds but cannot be
What is a theory? An organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances to explain a specific set of phenomena
 Atomic Structure What is a theory? An organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances to explain a specific set of phenomena Early Theories Democritus: 4 B.C.: atom He
Atomic Structure What is a theory? An organized system of accepted knowledge that applies in a variety of circumstances to explain a specific set of phenomena Early Theories Democritus: 4 B.C.: atom He
5.3. Physics and the Quantum Mechanical Model
 Chemistry 5-3 Physics and the Quantum Mechanical Model Neon advertising signs are formed from glass tubes bent in various shapes. An electric current passing through the gas in each glass tube makes the
Chemistry 5-3 Physics and the Quantum Mechanical Model Neon advertising signs are formed from glass tubes bent in various shapes. An electric current passing through the gas in each glass tube makes the
Unit 3: Electron configuration and periodicity
 Unit 3: Electron configuration and periodicity Group 1 BOHR MODELS Group 18 H Group 2 Group 13 Group 14 Group 15 Group 16 Group 17 He Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar K Ca His theory couldn t
Unit 3: Electron configuration and periodicity Group 1 BOHR MODELS Group 18 H Group 2 Group 13 Group 14 Group 15 Group 16 Group 17 He Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar K Ca His theory couldn t
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms
 Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5.2 Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic Emission Spectra and the Quantum Mechanical Model 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5.2 Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic Emission Spectra and the Quantum Mechanical Model 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates.
The structure of the Atom. Chemistry chapter 4
 The structure of the Atom Chemistry chapter 4 Rutherford-Bohr Model Niels Bohr (1922) Proposed improvements to Rutherford Atomic Model. For this reason the planetary model of the atoms is sometimes called
The structure of the Atom Chemistry chapter 4 Rutherford-Bohr Model Niels Bohr (1922) Proposed improvements to Rutherford Atomic Model. For this reason the planetary model of the atoms is sometimes called
Chapter Test B. Chapter: Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms. possible angular momentum quantum numbers? energy level? a. 4 b. 8 c. 16 d.
 Assessment Chapter Test B Chapter: Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms PART I In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question
Assessment Chapter Test B Chapter: Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms PART I In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question
The ELECTRON: Wave Particle Duality
 The ELECTRON: Wave Particle Duality No familiar conceptions can be woven around the electron. Something unknown is doing we don t know what. -Sir Arthur Eddington The Nature of the Physical World (1934)
The ELECTRON: Wave Particle Duality No familiar conceptions can be woven around the electron. Something unknown is doing we don t know what. -Sir Arthur Eddington The Nature of the Physical World (1934)
Name Date Class MODELS OF THE ATOM
 Name Date Class 5.1 MODELS OF THE ATOM Section Review Objectives Identify inadequacies in the Rutherford atomic model Identify the new assumption in the Bohr model of the atom Describe the energies and
Name Date Class 5.1 MODELS OF THE ATOM Section Review Objectives Identify inadequacies in the Rutherford atomic model Identify the new assumption in the Bohr model of the atom Describe the energies and
Atomic Structure Notes: Parts of the atom:
 Day 1 Atomic Structure Notes: Parts of the atom: Protons: Positively charged particles found in the Neutrons: Neutral charged particle found in the Electrons: Negatively charged particle found in the.
Day 1 Atomic Structure Notes: Parts of the atom: Protons: Positively charged particles found in the Neutrons: Neutral charged particle found in the Electrons: Negatively charged particle found in the.
Electrons in Atoms. Section 5.1 Light and Quantized Energy
 Name Date Class 5 Electrons in Atoms Section 5.1 Light and Quantized Energy In your textbook, read about the wave nature of light. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. amplitude
Name Date Class 5 Electrons in Atoms Section 5.1 Light and Quantized Energy In your textbook, read about the wave nature of light. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. amplitude
Notes:&&Unit&4:&Atomics& & & & & & & & & & & & & & & & &
 Name: RegentsChemistry:Mr.Palermo Notes:Unit4:Atomics! www.mrpalermo.com Name: $ Key$Ideas$ Themodernmodeloftheatomhasevolvedoveralongperiodoftimethroughtheworkofmany scientists.(3.1a) Eachatomhasanucleus,withanoverallpositivecharge,surroundedbyoneormorenegatively
Name: RegentsChemistry:Mr.Palermo Notes:Unit4:Atomics! www.mrpalermo.com Name: $ Key$Ideas$ Themodernmodeloftheatomhasevolvedoveralongperiodoftimethroughtheworkofmany scientists.(3.1a) Eachatomhasanucleus,withanoverallpositivecharge,surroundedbyoneormorenegatively
LIGHT AND THE QUANTUM MODEL
 LIGHT AND THE QUANTUM MODEL WAVES Wavelength ( ) - length of one complete wave Frequency ( ) - # of waves that pass a point during a certain time period hertz (Hz) = 1/s Amplitude (A) - distance from the
LIGHT AND THE QUANTUM MODEL WAVES Wavelength ( ) - length of one complete wave Frequency ( ) - # of waves that pass a point during a certain time period hertz (Hz) = 1/s Amplitude (A) - distance from the
UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY
 *KEY* *KEY* UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY *KEY* *KEY* VOCABULARY: Allotrope Anion Atom Atomic Mass Atomic Mass unit (a.m.u.) Atomic number Bohr model Cation Compound Electron Electron Configuration Element Excited
*KEY* *KEY* UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY *KEY* *KEY* VOCABULARY: Allotrope Anion Atom Atomic Mass Atomic Mass unit (a.m.u.) Atomic number Bohr model Cation Compound Electron Electron Configuration Element Excited
Chem 1075 Chapter 5 Models of the Atom Lecture Outline
 Chem 1075 Chapter 5 Models of the Atom Lecture Outline Slide 2 Dalton Model of the Atom John Dalton proposed that is made up of The particles are or can be broken down into by chemical processes. cannot
Chem 1075 Chapter 5 Models of the Atom Lecture Outline Slide 2 Dalton Model of the Atom John Dalton proposed that is made up of The particles are or can be broken down into by chemical processes. cannot
UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY
 UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY VOCABULARY: Allotrope Anion Atom Atomic Mass Atomic Mass unit (a.m.u.) Atomic number Bohr model Cation Compound Electron Electron Configuration Element Excited state Ground state
UNIT 2 - ATOMIC THEORY VOCABULARY: Allotrope Anion Atom Atomic Mass Atomic Mass unit (a.m.u.) Atomic number Bohr model Cation Compound Electron Electron Configuration Element Excited state Ground state
Bohr Diagram, Lewis Structures, Valence Electrons Review 1. What is the maximum number of electrons you can fit in each energy level or shell?
 AP Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Bohr Diagram, Lewis Structures, Valence Electrons Review 1. What is the maximum number of electrons you can fit in each energy level or shell? 1 st shell 2 nd shell
AP Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Bohr Diagram, Lewis Structures, Valence Electrons Review 1. What is the maximum number of electrons you can fit in each energy level or shell? 1 st shell 2 nd shell
Q1 and Q2 Review large CHEMISTRY
 Q1 and Q2 Review large CHEMISTRY Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. E = hv relates the following a. Energy to Planck s constant & wavelength
Q1 and Q2 Review large CHEMISTRY Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. E = hv relates the following a. Energy to Planck s constant & wavelength
Democritus & Leucippus (~400 BC) Greek philosophers: first to propose that matter is made up of particles called atomos, the Greek word for atoms
 Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block The Evolution of the Atomic Model Since atoms are too small to see even with a very powerful microscope, scientists rely upon indirect evidence and models to help them
Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block The Evolution of the Atomic Model Since atoms are too small to see even with a very powerful microscope, scientists rely upon indirect evidence and models to help them
Write the electron configuration for Chromium (Cr):
 Write the electron configuration for Chromium (Cr): Energy level Aufbau Principle Atomic orbital Quantum Hund s Rule Atomic number Electron Configuration Whole number Pauli Exlcusion Principle Quantum
Write the electron configuration for Chromium (Cr): Energy level Aufbau Principle Atomic orbital Quantum Hund s Rule Atomic number Electron Configuration Whole number Pauli Exlcusion Principle Quantum
Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT.
 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Chapter Quiz Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. The orbitals of a principal energy level are lower in energy than the orbitals
ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Chapter Quiz Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. The orbitals of a principal energy level are lower in energy than the orbitals
Electromagnetic spectrum Electromagnetic radiation
 Chapter 4 Section 1 Electromagnetic spectrum includes all the different wave lengths of radiation. Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave like behavior as it travels through space.
Chapter 4 Section 1 Electromagnetic spectrum includes all the different wave lengths of radiation. Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave like behavior as it travels through space.
CHEMISTRY - TRO 4E CH.7 - THE QUANTUM-MECHANICAL MODEL OF THE ATOM
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: THE NATURE OF LIGHT Visible light represents a small portion of the continuum of radiant energy known as. The visible light spectrum ranges from to. Its wave properties of
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: THE NATURE OF LIGHT Visible light represents a small portion of the continuum of radiant energy known as. The visible light spectrum ranges from to. Its wave properties of
c = λν 10/23/13 What gives gas-filled lights their colors? Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms
 CHEMISTRY & YOU What gives gas-filled lights their colors? Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5. Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic and the Quantum Mechanical Model An electric
CHEMISTRY & YOU What gives gas-filled lights their colors? Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5. Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic and the Quantum Mechanical Model An electric
Chapter 6. Quantum Theory and the Electronic Structure of Atoms Part 1
 Chapter 6 Quantum Theory and the Electronic Structure of Atoms Part 1 The nature of light Quantum theory Topics Bohr s theory of the hydrogen atom Wave properties of matter Quantum mechanics Quantum numbers
Chapter 6 Quantum Theory and the Electronic Structure of Atoms Part 1 The nature of light Quantum theory Topics Bohr s theory of the hydrogen atom Wave properties of matter Quantum mechanics Quantum numbers
Ch. 4 Sec. 1-2, Ch. 3 sec.6-8 ENERGY CHANGES AND THE QUANTUM THEORY THE PERIODIC TABLE
 Ch. 4 Sec. 1-2, Ch. 3 sec.6-8 ENERGY CHANGES AND THE QUANTUM THEORY THE PERIODIC TABLE What Makes Red Light Red? (4.1) Electromagnetic Radiation: energy that travels in waves (light) Waves Amplitude: height
Ch. 4 Sec. 1-2, Ch. 3 sec.6-8 ENERGY CHANGES AND THE QUANTUM THEORY THE PERIODIC TABLE What Makes Red Light Red? (4.1) Electromagnetic Radiation: energy that travels in waves (light) Waves Amplitude: height
Atoms and Isotopes 1 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016
 Atoms and Isotopes 1 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Atoms and Isotopes 2 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are atoms made of? 3 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Atoms are made up of three smaller particles: protons neutrons
Atoms and Isotopes 1 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Atoms and Isotopes 2 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are atoms made of? 3 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Atoms are made up of three smaller particles: protons neutrons
10/27/2017 [pgs ]
![10/27/2017 [pgs ] 10/27/2017 [pgs ]](/thumbs/82/85139288.jpg) Objectives SWBAT explain the relationship between energy and frequency. SWBAT predict the behavior of and/or calculate quantum and photon energy from frequency. SWBAT explain how the quantization of energy
Objectives SWBAT explain the relationship between energy and frequency. SWBAT predict the behavior of and/or calculate quantum and photon energy from frequency. SWBAT explain how the quantization of energy
CP/Honors Chemistry Unit 3: Atomic Theory Sections 4.1, 4.2, 4.3
 CP/Honors Chemistry Unit 3: Atomic Theory Sections 4.1, 4.2, 4.3 Subatomic Particles Warm-Up Quiz 1. What are the three subatomic particles? 2. Where are the particles located in the atom? 3. What are
CP/Honors Chemistry Unit 3: Atomic Theory Sections 4.1, 4.2, 4.3 Subatomic Particles Warm-Up Quiz 1. What are the three subatomic particles? 2. Where are the particles located in the atom? 3. What are
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change
 CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Chapter 5: Electrons in Atoms 5 Section 5.1 Section Section 5.3 Table Of Contents Light and Quantized Energy Electron Configuration Compare the wave and particle natures of
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Chapter 5: Electrons in Atoms 5 Section 5.1 Section Section 5.3 Table Of Contents Light and Quantized Energy Electron Configuration Compare the wave and particle natures of
Electrons! Chapter 5
 Electrons! Chapter 5 I.Light & Quantized Energy A.Background 1. Rutherford s nuclear model: nucleus surrounded by fast-moving electrons; no info on how electrons move, how they re arranged, or differences
Electrons! Chapter 5 I.Light & Quantized Energy A.Background 1. Rutherford s nuclear model: nucleus surrounded by fast-moving electrons; no info on how electrons move, how they re arranged, or differences
Properties of Light. Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms. The Development of a New Atomic Model. Electromagnetic Radiation CHAPTER 4
 CHAPTER 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms The Development of a New Atomic Model The Rutherford model was a great improvement over the Thomson model of the atom. But, there was one major question that
CHAPTER 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms The Development of a New Atomic Model The Rutherford model was a great improvement over the Thomson model of the atom. But, there was one major question that
Properties of Light and Atomic Structure. Chapter 7. So Where are the Electrons? Electronic Structure of Atoms. The Wave Nature of Light!
 Properties of Light and Atomic Structure Chapter 7 So Where are the Electrons? We know where the protons and neutrons are Nuclear structure of atoms (Chapter 2) The interaction of light and matter helps
Properties of Light and Atomic Structure Chapter 7 So Where are the Electrons? We know where the protons and neutrons are Nuclear structure of atoms (Chapter 2) The interaction of light and matter helps
Name: Electrons in Atoms Chemical Periodicity Chapters 13 and 14
 Name: Electrons in Atoms Chemical Periodicity Chapters 13 and 14 1 Chapter 13 Electrons in Atoms We need to further develop our understanding of atomic structure to help us understand how atoms bond to
Name: Electrons in Atoms Chemical Periodicity Chapters 13 and 14 1 Chapter 13 Electrons in Atoms We need to further develop our understanding of atomic structure to help us understand how atoms bond to
[3.2] The Atom. p in Textbook
![[3.2] The Atom. p in Textbook [3.2] The Atom. p in Textbook](/thumbs/83/88700013.jpg) [3.2] The Atom p. 145 149 in Textbook We will be learning about three different parts of the atom today 1. What makes up an atom 2. Where an atom s mass is found 3. What are isotopes What does the atom
[3.2] The Atom p. 145 149 in Textbook We will be learning about three different parts of the atom today 1. What makes up an atom 2. Where an atom s mass is found 3. What are isotopes What does the atom
Observation information obtained through the senses; observation in science often involves measurement
 Review Sheet Unit 1: The Atom Chemistry the study of the composition of matter and the changes matter undergoes Scientific Method Scientific method a logical, systematic approach to the solution of a scientific
Review Sheet Unit 1: The Atom Chemistry the study of the composition of matter and the changes matter undergoes Scientific Method Scientific method a logical, systematic approach to the solution of a scientific
Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos Pearson Education, Inc.
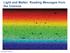 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos Light and Color Light is a form of energy (think of the warmth of sunlight or a lightbulb) White light is actually made up of many different colors. How
Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos Light and Color Light is a form of energy (think of the warmth of sunlight or a lightbulb) White light is actually made up of many different colors. How
I understand the relationship between energy and a quanta I understand the difference between an electron s ground state and an electron s excited
 NCCS 1.1.2 & 1.1.3 I understand the relationship between energy and a quanta I understand the difference between an electron s ground state and an electron s excited state I will describe how an electron
NCCS 1.1.2 & 1.1.3 I understand the relationship between energy and a quanta I understand the difference between an electron s ground state and an electron s excited state I will describe how an electron
Wavelength (λ)- Frequency (ν)- Which of the following has a higher frequency?
 Name: Unit 5- Light and Energy Electromagnetic Spectrum Notes Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that emits wave-like behavior as it travels through space. Amplitude (a)- Wavelength (λ)- Which
Name: Unit 5- Light and Energy Electromagnetic Spectrum Notes Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that emits wave-like behavior as it travels through space. Amplitude (a)- Wavelength (λ)- Which
Chapter 4 The Structure of the Atom
 Chapter 4 The Structure of the Atom Read pg. 86-97 4.1 Early Theories of Matter The Philosophers Democritus Artistotle - Artistotle s influence so great and the science so primitive (lacking!) his denial
Chapter 4 The Structure of the Atom Read pg. 86-97 4.1 Early Theories of Matter The Philosophers Democritus Artistotle - Artistotle s influence so great and the science so primitive (lacking!) his denial
Name Date Class MODELS OF THE ATOM
 5.1 MODELS OF THE ATOM Section Review Objectives Identify inadequacies in the Rutherford atomic model Identify the new assumption in the Bohr model of the atom Describe the energies and positions of electrons
5.1 MODELS OF THE ATOM Section Review Objectives Identify inadequacies in the Rutherford atomic model Identify the new assumption in the Bohr model of the atom Describe the energies and positions of electrons
Chapter 5. Electrons in Atoms
 Chapter 5 Electrons in Atoms Warm - Up What kind of light causes you to sunburn? Why does only this type of light burn your skin and not other light? What does sunscreen do on a chemical level? Today s
Chapter 5 Electrons in Atoms Warm - Up What kind of light causes you to sunburn? Why does only this type of light burn your skin and not other light? What does sunscreen do on a chemical level? Today s
Chapter 7 QUANTUM THEORY & ATOMIC STRUCTURE Brooks/Cole - Thomson
 Chapter 7 QUANTUM THEORY & ATOMIC STRUCTURE 1 7.1 The Nature of Light 2 Most subatomic particles behave as PARTICLES and obey the physics of waves. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation Light consists
Chapter 7 QUANTUM THEORY & ATOMIC STRUCTURE 1 7.1 The Nature of Light 2 Most subatomic particles behave as PARTICLES and obey the physics of waves. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation Light consists
Energy of Waves. What is the relationship between l, n and Energy?!
 Chapter 5 Part 2 c = ln Practice! What is the wavelength of a microwave that has a frequency of 1.56 x 10 9 Hz? The red-colored light in a fireworks display might be produced when Strontium salts are heated.
Chapter 5 Part 2 c = ln Practice! What is the wavelength of a microwave that has a frequency of 1.56 x 10 9 Hz? The red-colored light in a fireworks display might be produced when Strontium salts are heated.
Contents. Atomic Structure. 2(a) The Periodic Table. 2(b) Amount of Substance. 2(c) 2(d) Bonding and Structure. Enthalpy Changes.
 1 C h e m i s t r y Contents 2(a) 2(b) 2(c) 2(d) 2(e) Atomic Structure The Periodic Table Amount of Substance Bonding and Structure Enthalpy Changes 3 14 18 28 42 2 C h e m i s t r y 2(a) Atomic Structure
1 C h e m i s t r y Contents 2(a) 2(b) 2(c) 2(d) 2(e) Atomic Structure The Periodic Table Amount of Substance Bonding and Structure Enthalpy Changes 3 14 18 28 42 2 C h e m i s t r y 2(a) Atomic Structure
CHAPTER 4 10/11/2016. Properties of Light. Anatomy of a Wave. Components of a Wave. Components of a Wave
 Properties of Light CHAPTER 4 Light is a form of Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) Form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior and travels at the speed of light. Together, all
Properties of Light CHAPTER 4 Light is a form of Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) Form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior and travels at the speed of light. Together, all
A. 24 B. 27 C. 30 D. 32 E. 33. A. It is impossible to tell from the information given. B. 294 mm C. 122 mm D. 10 mm E. 60 mm A. 1 H B. C. D. 19 F " E.
 CHEMISTRY 110 EXAM 1 Sept. 24, 2012 FORM A 1. A microwave oven uses 2.45! 10 9 Hz electromagnetic waves to heat food. What is the wavelength of this radiation in mm? A. It is impossible to tell from the
CHEMISTRY 110 EXAM 1 Sept. 24, 2012 FORM A 1. A microwave oven uses 2.45! 10 9 Hz electromagnetic waves to heat food. What is the wavelength of this radiation in mm? A. It is impossible to tell from the
I. History and Development of the Atom
 Unit 3: The Atom I. History and Development of the Atom A. Democritus (around 400 B.C.) Based on his observations of the natural world around him, Democritus was the first to suggest that all matter was
Unit 3: The Atom I. History and Development of the Atom A. Democritus (around 400 B.C.) Based on his observations of the natural world around him, Democritus was the first to suggest that all matter was
Chapter 4. Models of the Atom
 Chapter 4 Models of the Atom Dalton Model of the Atom John Dalton proposed that all matter is made up of tiny particles. These particles are molecules or atoms. Molecules can be broken down into atoms
Chapter 4 Models of the Atom Dalton Model of the Atom John Dalton proposed that all matter is made up of tiny particles. These particles are molecules or atoms. Molecules can be broken down into atoms
Electrons in Atoms. Section 5.1 Light and Quantized Energy Section 5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom Section 5.3 Electron Configuration
 Electrons in Atoms Section 5.1 Light and Quantized Energy Section 5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom Section 5.3 Electron Configuration Click a hyperlink or folder tab to view the corresponding slides. Exit
Electrons in Atoms Section 5.1 Light and Quantized Energy Section 5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom Section 5.3 Electron Configuration Click a hyperlink or folder tab to view the corresponding slides. Exit
Chapter 4 Electron Configurations
 Chapter 4 Electron Configurations Waves Today scientists recognize light has properties of waves and particles Waves: light is electromagnetic radiation and travels in electromagnetic waves. 4 Characteristics
Chapter 4 Electron Configurations Waves Today scientists recognize light has properties of waves and particles Waves: light is electromagnetic radiation and travels in electromagnetic waves. 4 Characteristics
ATOMIC STRUCTURE, ELECTRONS, AND PERIODICITY
 ATOMIC STRUCTURE, ELECTRONS, AND PERIODICITY All matter is made of atoms. There are a limited number of types of atoms; these are the elements. (EU 1.A) Development of Atomic Theory Atoms are so small
ATOMIC STRUCTURE, ELECTRONS, AND PERIODICITY All matter is made of atoms. There are a limited number of types of atoms; these are the elements. (EU 1.A) Development of Atomic Theory Atoms are so small
Name Period Date Engage-Atoms 1. What does Bill cut in half?
 Name Period Date Engage-Atoms https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fmuskig2exi 1. What does Bill cut in half? 2. By cutting this item in half he tries to prove that there are pieces that are uncut- table called
Name Period Date Engage-Atoms https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fmuskig2exi 1. What does Bill cut in half? 2. By cutting this item in half he tries to prove that there are pieces that are uncut- table called
Honors Ch3 and Ch4. Atomic History and the Atom
 Honors Ch3 and Ch4 Atomic History and the Atom Ch. 3.1 The Atom is Defined 400 B.C. the Greek philosopher Democritus said that the world was made of two things: Empty space and tiny particles called atoms
Honors Ch3 and Ch4 Atomic History and the Atom Ch. 3.1 The Atom is Defined 400 B.C. the Greek philosopher Democritus said that the world was made of two things: Empty space and tiny particles called atoms
CHEMISTRY - ZUMDAHL 8E CH.7 - ATOMIC STRUCTURE & PERIODICITY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: THE NATURE OF LIGHT Visible light represents a small portion of the continuum of radiant energy known as. The visible light spectrum ranges from to. Its wave properties of
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: THE NATURE OF LIGHT Visible light represents a small portion of the continuum of radiant energy known as. The visible light spectrum ranges from to. Its wave properties of
Warm-up For sulfur: 1. How many valence electrons does it have? 2. What ion does this typically form? 3. Write the electron configuration for the ion.
 Warm-up For sulfur: 1. How many valence electrons does it have? 2. What ion does this typically form? 3. Write the electron configuration for the ion. Nucleus Contains 99.9% of the mass of an atom Found
Warm-up For sulfur: 1. How many valence electrons does it have? 2. What ion does this typically form? 3. Write the electron configuration for the ion. Nucleus Contains 99.9% of the mass of an atom Found
ATOMIC STRUCTURE, ELECTRONS, AND PERIODICITY
 ATOMIC STRUCTURE, ELECTRONS, AND PERIODICITY All matter is made of atoms. There are a limited number of types of atoms; these are the elements. (EU 1.A) Development of Atomic Theory Atoms are so small
ATOMIC STRUCTURE, ELECTRONS, AND PERIODICITY All matter is made of atoms. There are a limited number of types of atoms; these are the elements. (EU 1.A) Development of Atomic Theory Atoms are so small
CHEMISTRY - KIRSS 2E CH.3 - ATOMIC STRUCTURE: EXPLAINING THE PROPERTIES OF ELEMENTS
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: THE NATURE OF LIGHT Visible light represents a small portion of the continuum of radiant energy known as. The visible light spectrum ranges from to. Its wave properties of
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: THE NATURE OF LIGHT Visible light represents a small portion of the continuum of radiant energy known as. The visible light spectrum ranges from to. Its wave properties of
Greek Philosophers (cont.)
 Greek Philosophers (cont.) Many ancient scholars believed matter was composed of such things as earth, water, air, and fire. Many believed matter could be endlessly divided into smaller and smaller pieces.
Greek Philosophers (cont.) Many ancient scholars believed matter was composed of such things as earth, water, air, and fire. Many believed matter could be endlessly divided into smaller and smaller pieces.
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos. What is light? Properties of Waves. Waves. The Electromagnetic Spectrum
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos What is light? Light is a form of radiant energy Light can act either like a wave or like a particle (photon) Spectrum of the Sun 1 2 Waves
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos What is light? Light is a form of radiant energy Light can act either like a wave or like a particle (photon) Spectrum of the Sun 1 2 Waves
CHAPTER 4. Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
 CHAPTER 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms 4.1 Part I Development of a New Atomic Model 4.1 Objectives 1. Explain the mathematical relationship among the speed, wavelength, and frequency of electromagnetic
CHAPTER 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms 4.1 Part I Development of a New Atomic Model 4.1 Objectives 1. Explain the mathematical relationship among the speed, wavelength, and frequency of electromagnetic
Basic science. Atomic structure. Electrons. The Rutherford-Bohr model of an atom. Electron shells. Types of Electrons. Describing an Atom
 Basic science A knowledge of basic physics is essential to understanding how radiation originates and behaves. This chapter works through what an atom is; what keeps it stable vs. radioactive and unstable;
Basic science A knowledge of basic physics is essential to understanding how radiation originates and behaves. This chapter works through what an atom is; what keeps it stable vs. radioactive and unstable;
The Development of Atomic Theory
 The Development of Atomic Theory Democritus (400 BC) John Dalton (1803) J.J. Thomson (1897) Ernest Rutherford (1911) James Chadwick (1932) - suggested that matter is composed of indivisible particles called
The Development of Atomic Theory Democritus (400 BC) John Dalton (1803) J.J. Thomson (1897) Ernest Rutherford (1911) James Chadwick (1932) - suggested that matter is composed of indivisible particles called
Collegiate Institute for Math and Science Day 57: December 9, 2016 Room 427
 Unit 2: Atomic Concepts Outline Name: Period: Date: 1. The modern model of the atom has evolved over a long period of time through the work of many scientists. Dalton s Model: Elements are made of atoms
Unit 2: Atomic Concepts Outline Name: Period: Date: 1. The modern model of the atom has evolved over a long period of time through the work of many scientists. Dalton s Model: Elements are made of atoms
Regents Chemistry Unit 1 Atomic Concepts. Textbook Chapters 3 & 4
 Regents Chemistry Unit 1 Atomic Concepts Textbook Chapters 3 & 4 Atomic Theory- Atoms are the building blocks of matter Atomic Models Democritus ~440 BC a Greek Philosopher suggested that matter is made
Regents Chemistry Unit 1 Atomic Concepts Textbook Chapters 3 & 4 Atomic Theory- Atoms are the building blocks of matter Atomic Models Democritus ~440 BC a Greek Philosopher suggested that matter is made
WAVE NATURE OF LIGHT
 WAVE NATURE OF LIGHT Light is electromagnetic radiation, a type of energy composed of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. The fields oscillate perpendicular to each other. In vacuum, these waves
WAVE NATURE OF LIGHT Light is electromagnetic radiation, a type of energy composed of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. The fields oscillate perpendicular to each other. In vacuum, these waves
Unit 1, Lesson 01: Summary of Atomic Structure so far
 Unit 1, Lesson 01: Summary of Atomic Structure so far Atoms are made of sub-atomic particles: Protons: found in the nucleus, charge of 1+, mass of 1 amu (u) Neutrons: found in nucleus, no charge, mass
Unit 1, Lesson 01: Summary of Atomic Structure so far Atoms are made of sub-atomic particles: Protons: found in the nucleus, charge of 1+, mass of 1 amu (u) Neutrons: found in nucleus, no charge, mass
UNIT TWO TEST HISTORY OF ATOM, STRUCTURE OF ATOM, ATOMIC MASS CARBON-12
 KEY Review Sheet: UNIT TWO TEST HISTORY OF ATOM, STRUCTURE OF ATOM, ATOMIC MASS 1. Know which isotope is the standard for the atomic mass unit. CARBON-12 2. Know what the difference in masses of isotopes
KEY Review Sheet: UNIT TWO TEST HISTORY OF ATOM, STRUCTURE OF ATOM, ATOMIC MASS 1. Know which isotope is the standard for the atomic mass unit. CARBON-12 2. Know what the difference in masses of isotopes
The Structure of the Atom
 CHAPTER 5 The Structure of the Atom 5.4 Light and Spectroscopy 460 370 BC 1808 1870 1897 1910 1925 Today Democritus Atomism Dalton Modern atomic theory Crookes Cathode rays Thomson Discovery of the electron
CHAPTER 5 The Structure of the Atom 5.4 Light and Spectroscopy 460 370 BC 1808 1870 1897 1910 1925 Today Democritus Atomism Dalton Modern atomic theory Crookes Cathode rays Thomson Discovery of the electron
November 06, Chapter 7 Atomic Struture. CHAPTER 7 Atomic Structure. Oct 27 9:34 AM ATOMIC STRUCTURE. Oct 27 9:34 AM
 CHAPTER 7 Atomic Structure ATOMIC STRUCTURE 1 The Wave Nature of Light Most subatomic particles behave as PARTICLES and obey the physics of waves. Visible light Ultravioletlight Wavelength Frequency (Hertz
CHAPTER 7 Atomic Structure ATOMIC STRUCTURE 1 The Wave Nature of Light Most subatomic particles behave as PARTICLES and obey the physics of waves. Visible light Ultravioletlight Wavelength Frequency (Hertz
Name Date Class ELECTRONS IN ATOMS
 Name _ Date Class 5 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS SECTION 5.1 MODELS OF THE ATOM (pages 127 132) This section summarizes the development of atomic theory. It also explains the significance of quantized energies of
Name _ Date Class 5 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS SECTION 5.1 MODELS OF THE ATOM (pages 127 132) This section summarizes the development of atomic theory. It also explains the significance of quantized energies of
CHAPTER 5 Electrons in Atoms
 CHAPTER 5 Electrons in Atoms 5.1 Light & Quantized Energy Was the Nuclear Atomic model incomplete? To most scientists, the answer was yes. The arrangement of electrons was not determined > Remember...the
CHAPTER 5 Electrons in Atoms 5.1 Light & Quantized Energy Was the Nuclear Atomic model incomplete? To most scientists, the answer was yes. The arrangement of electrons was not determined > Remember...the
: the smallest particle that has the properties of an element. In, this Greek philosopher suggested that the universe was made of.
 Notes: ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE Atomic Structure: : the smallest particle that has the properties of an element. From the early concept of the atom to the modern atomic theory, scientists have built
Notes: ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE Atomic Structure: : the smallest particle that has the properties of an element. From the early concept of the atom to the modern atomic theory, scientists have built
2) The energy of a photon of light is proportional to its frequency and proportional to its wavelength.
 Advanced Chemistry Chapter 13 Review Name Per Show all work Wave Properties 1) Which one of the following is correct? A) ν + λ = c B) ν λ = c C) ν = cλ D) λ = c ν E) νλ = c 2) The energy of a photon of
Advanced Chemistry Chapter 13 Review Name Per Show all work Wave Properties 1) Which one of the following is correct? A) ν + λ = c B) ν λ = c C) ν = cλ D) λ = c ν E) νλ = c 2) The energy of a photon of
CHEMISTRY 110 EXAM 1 SEPTEMBER 20, 2010 FORM A
 CHEMISTRY 110 EXAM 1 SEPTEMBER 20, 2010 FORM A 1. What are the correct numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons in a 39 K + ion? p n e A. 20 19 18 B. 20 19 19 C. 19 20 18 D. 19 20 19 E. 20 19 20 2. Which
CHEMISTRY 110 EXAM 1 SEPTEMBER 20, 2010 FORM A 1. What are the correct numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons in a 39 K + ion? p n e A. 20 19 18 B. 20 19 19 C. 19 20 18 D. 19 20 19 E. 20 19 20 2. Which
Lecture 6: The Physics of Light, Part 1. Astronomy 111 Wednesday September 13, 2017
 Lecture 6: The Physics of Light, Part 1 Astronomy 111 Wednesday September 13, 2017 Reminders Star party tonight! Homework #3 due Monday Exam #1 Monday, September 25 The nature of light Look, but don t
Lecture 6: The Physics of Light, Part 1 Astronomy 111 Wednesday September 13, 2017 Reminders Star party tonight! Homework #3 due Monday Exam #1 Monday, September 25 The nature of light Look, but don t
Atomic Theory Review
 Atomic Theory Review Fill in the Blank mass number 1. The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is the. isotopes 2. Atoms possessing the same number of protons but a different number
Atomic Theory Review Fill in the Blank mass number 1. The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is the. isotopes 2. Atoms possessing the same number of protons but a different number
Calendar. October 23, Chapter 5 Notes Waves.notebook Waves vocab waves ws. quiz PSAT. Blank. elements test. demo day
 Calendar Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday 13 14 Waves vocab waves ws 20 PSAT make notecards 7th 15 21 22 quiz 16 23 17 24 27 28 29 30 31 elements test demo day Blank 1 The Nature
Calendar Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday 13 14 Waves vocab waves ws 20 PSAT make notecards 7th 15 21 22 quiz 16 23 17 24 27 28 29 30 31 elements test demo day Blank 1 The Nature
Atomic Structure. Chemistry Mr. McKenzie
 Atomic Structure Chemistry Mr. McKenzie How was the understanding of the atom developed? John Dalton (1766-1844) - developed a model to explain observations made at the time 1. Elements are made of tiny
Atomic Structure Chemistry Mr. McKenzie How was the understanding of the atom developed? John Dalton (1766-1844) - developed a model to explain observations made at the time 1. Elements are made of tiny
Atomic Structure Practice Questions
 Atomic Structure Practice Questions 1. Experiments performed to reveal the structure of atoms led scientists to conclude that an atom s (1) positive charge is evenly distributed throughout its volume (2)
Atomic Structure Practice Questions 1. Experiments performed to reveal the structure of atoms led scientists to conclude that an atom s (1) positive charge is evenly distributed throughout its volume (2)
