Chem 360, Special Topics: Modern Organic Synthesis, Spring 2008
|
|
|
- Elmer Dixon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chem 360, Special Topics: Modern Organic Synthesis, Spring 2008 Instructor Office: HS-446 Course Web Page Office Hours Lecture oratory Dr. Brant Kedrowski Phone: or (Chem. Office) Tues. and Fri. 9:10-11:30 (HS-446), or by appointment M W 10:20-11:20 (HS-456) T 1:50-5:10 (HS-452), lab will also be open at other times Required Materials - Modern Organic Synthesis, An Introduction 1 st Ed., 2007, W. H. Freeman, by G. S. Zweifel and M. H. Nantz - A Bound Notebook Not Spiral. (you can use one from a previous lab if it s in good condition) - An acceptable pair of goggles for lab (Required) Recommended Materials - Advanced Practical Organic Chemsitry 2 nd Ed., 1994, CRC by J. Leonard, B. Lygo, and G. Proctor - Your old text books and model kit from introductory organic chemistry (chem 235 & 335) Introduction to Chem 360 Welcome to Modern Organic Synthesis! This course is a continuation of your education in organic chemistry at an intermediate level, and will focus on organic synthesis. This is the process of building organic target molecules from simpler starting materials through chemical reactions. This is an important subject since organic molecules form the basic fabric of life, and they frequently play a pivotal role in human health, in agriculture, and in biology. Virtually all drugs, vitamins, hormones, food additives, pesticides, herbicides and plastics are organic molecules. We ll learn a variety of new reagents and reactions, synthetic strategies, and laboratory techniques used in modern organic synthesis. The concepts from beginning organic chemistry (chem 235 & 335) will serve as a foundation for this course. From time to time we will review concepts from these previous courses, but the focus of chem 360 this semester will be on new material. Goals for the Course 1. Understand fundamental reactions, mechanisms, and strategies of organic synthesis. 2. Become profecient at reading organic chemistry literature, and learn how to search for this information using modern information resources. 3. Learn standard laboratory techniques in synthetic organic chemistry for carrying out reactions, purifying products, and analyzing these compounds using modern instrumental methods. 4. Develop skills in chemical communication including scientific writing, use of structure drawing programs, and use of presentation software. 1
2 Lecture, and Exam Schedule We ll be covering selected sections in the Zweifel and Nantz text. Sections we ll be covering are listed below. Week Date Chapter - concepts Sec. 1 2/4 2/6 Synthetic Design Exp 1: Intro to chemical literature, information seraching, and drawing software Protecting functional groups: N-H, O-H, diols 1.1, /11 2/13 Protecting functional groups: aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids Exp 2: Synthesis of the insect pheromone frontilin, part 1, tosylate formation Enolate chemistry: 1,3-dicarbonyl enolates /18 2/20 Enolate chemistry: ester and ketone enolates Exp 2: Synthesis of frontilin part 2, acetoacetic ester alkylation Imines, hydrazones and enamines /25 2/27 Aldol reaction, part 1 Exp 2: Synthesis of frontilin part 3, ester hydrolysis/decarboxylation Aldol reaction, part /3 3/5 3/6 Mannich reaction, Michael addition, Robinson Annulation Exp 2: Synthesis of frontilin part 4, alkene epoxidation Review Exam 1: Thursday Evening, 6-8 PM, March 6 th (Chapters 1, 3, and 6) /10 3/12 Reactions of C=C bonds: epoxidation Exp 2: Synthesis of frontilin part 5, epoxide rearrangement to form frontilin Reactions of C=C bonds: dihydroxylation and oxidative cleavage of C=C /17 3/19 Reactions of C=C bonds: hydrogenation and dissolving metal reductions Exp 3: Synthesis of the natural product carpanone part 1, allylation of sesamol Synthesis of carbocyclic systems: ring-closing metathesis (RCM) /22-30 Spring Break 8 3/31 4/2 Claisen rearrangement Exp 3: Synthesis carpanone part 2, Claisen rearrangement Formation of C=C bonds: elminations, reduction of alkynes; carbometallation /7 4/9 Wittig and related olefination reactions Exp 3: Synthesis carpanone part 3, alkene isomerization Synthesis of carbocyclic systems: cation-p cyclizations, Diels-Alder reaction /14 4/16 4/17 Synthesis of carbocyclic systems: Diels-Alder reaction continued Exp 3: Synthesis carpanone part 4, oxidative coupling and hetero Diels-Alder Review Exam 2: Thursday Evening, 6-8 PM, April 17 th (Chapters 5, 8, and 9) 9.3 2
3 Week Date Chapter - concepts Sec. 11 4/21 4/23 Organolithium reagents Exp 4: Synthesis (E)- and (Z)-anethole part 1, boronic acid formation Grignard reagents /28 4/30 Palladium catalyzed coupling reactions Exp 4: Synthesis (E)- and (Z)-anethole part 2, Suzuki reaction Organocopper reagents /5 5/7 Carbonyl reduction, part 1: Exp 5: Synthesis of rasagiline mesylate, a drug for treating Parkinson s disease Carbonyl reduction part 2: distereoselective and enantioselective reductions /12 5/14 5/15 Oxidation of alcohols: to aldehydes and ketones, to carboxylic acids Literature Presentations Review Exam 3: Thursday Evening, 6-8 PM, May 15 th (Chapters 4 and 7) 4.1-3, 6 Evaluation of Performance (1000 points total) Three Exams Graded Homework Assignments 600 points (200 points each) 150 points 250 points In calculating grades, I look for logical breaks in score distributions to set A, AB, B, BC, C, and D cut-offs. Clumps of students that have similar scores are assigned similar grades. As an approximate guide, I use the following percentages: A 90%, B 80%, C 65%, D 50%, with intermediate grades of AB, BC, and CD assigned to people near the boarders. The class will be kept updated on exam performance. Exams There will be three exams throughout the semester worth 200 points each for a total of 600 points. Exams will cover material discussed in lecture, listed in the assigned reading in the textbook, and material from the laboratory portion of the course. The exams will be given in the evening. If you can t attend the evening exams for a valid reason see me (ahead of time) and an early exam will be scheduled for you. Graded Homework I ll be assigning, collecting, and grading homework throughout the semester. The homework will cover material from lecture, the textbook, and the lab. There will be ten homework assignments total, each worth 15 points, for a total of 150 points. Assignments There will be a number of graded assignments associated with the laboratory portion of the course. All written laboratory assignments need to be word-processed and have structures created using an computer drawing program (like ISIS Draw, which is free to download). Also, proper use of written English is required. When you work with a lab partner on an experiment, the two of you should complete lab assignments together and turn them in jointly. A schedule with due dates and specific guidelines for completing each type of assignment are provided on the next page. 3
4 Due date Assignment Points 2/11 Experiment 1 Informal Report 15 2/25 Experiment 2 Progress Report /3 Experiment 2 Progress Report /17 Experiment 2 Full Formal Report 50 4/7 Experiment 3 Progress Report 10 4/21 Experiment 3 Full Formal Report 50 5/5 Experiment 4 Full Formal Report 40 5/12 Experiment 5 Informal Report 15 5/12 Synthesis Article Presentation 50 Total 250 Informal Reports: These reports are similar to those from Chem 235/335. You ll be given a sheet listing the data that you need to report, the questions that you need to answer, and any experimental attachments that need to be provided such as spectra, chromatograms, etc Although the format of these reports is informal, you still need to word process them, computer-generate any sturctures, and use proper written English. Progress Reports: For experiments that span more than two weeks you ll need to turn in progress reports on the dates listed above. These reports will allow me to gauge the progress you have made toward the target molecule, including yields and purity of intermediates. It will also serve to help you catalog your data in preparation for the formal lab report to follow. The information from these progress reports can be cut and pasted into the formal lab report when it comes time to write it. Use the following format: I. Names, Title of Experiment, Date II. For each experimental step report the following: a. Name of the reaction b. Structural equation, in the style of the American Chemical Society (ACS) c. Experimental details of the reaction performed, in the style of the ACS d. Spectral data condensed into text form, in the style of the ACS III. Attach copies of any spectra you were asked to aquire such as NMR, GCMS, IR. Neatly draw structures on each spectrum and assign peaks. 4
5 Full Formal Reports: A formal lab report will be required after each large multi-week experiment is completed. There are three total, and they are worth a signifcant number of points. These will help develop your technical writing abilities. We will be emulating the style used in ACS journals, so you ll be learning to communicate as professional chemists communicate. For good examples of papers written in this style, see any recent issue of the Journal of Organic Chemistry (J. Org. Chem.). A guide to formating formal lab reports is listed on the next page. Grading of the formal reports will be based on technical chemistry-related details, quality of the writing, following ACS conventions, and purity of the final product. Yields will not be graded. However, they do need to be good enough so that you can finish the multi-step synthesis and have a final product to characterize and turn in at the end. (Formal report formatting) Report Title First Author Name and Second Author Name Department of Chemistry, University of Wisconsin, Oshkosh, Oshkosh, WI Graphical abstract In this space place a small 3.5 wide by 1.5 high structural diagram that describes the chemical essence of the report. You have to be very efficeint in your use of this space. Text abstract In 150 words or less, summarize the report. It is intended to present an overview of the experiment and should be as concise as possible. You should explain what was done and why you did it, and summarize your results. Do not include experimental procedures, raw data, spectral information, and/or conclusions in the abstract. Introduction The introduction should include a small amount of background on the molecule you have synthesized. If it was isolated from a plant or animal, report the species and reference literature reports on its isolation and characterization. Use superscript numbers 1 to reference literature. Number references sequentially in the order that they appear in the paper. Include a references section at the end of the report. If there is any known activity associated with the molecule the introduction section is a good place to discuss this. Keep this section brief, including just enough information to give the reader a sense of the nature and significance of the project. Provide a short, simple description of the experiment and describe the synthetic strategy briefly. Results and Discussion In the results and discussion section you present, analyze, and interpret your experimental results. Describe what reactions were run and what functional groups changed during the reaction. Include schemes with structures, and reaction arrows with reagents to graphically show how molecules change structurally. Place a boldface number below each structure in the paper, numbering them sequentially in the order that they appear in the paper, starting with 1. The first time a molecule is referred to in the text, use its chemical name followed by its boldface number in parentheses. Thereafter 5
6 in the paper, refer to the structure by its boldface number. Talk about the mechanism of the reaction, such as which species act as a nucleophiles and which act as electrophiles. Comment on the selectivity of reactions. Does the reaction take place at only one site on the molecule, and if so, explain why. Does the reaction produce stereoisomers such as a racemic mixture? Discuss the yield of each reaction, and mention if you detected or isolated any byproducts produced in the reaction. When reactions don t go perfectly it s helpful to know what s going wrong chemically. Report to what extent each intermediate was purified (by distillation, crystallization, chromatography or used crude in the next step, for example). Report what techniques were used to characterize each intermediate (IR, NMR, GC-MS, for example). Reference any literature reports that describe the synthesis of the same molecules as in your experiment. If other people have synthesized the same molecule before they need to be given credit. Did these syntheses use the same, or essentially the same reaction, or did they use a different synthetic strategy? Are there reports of characterization data for any of the intermediates in your experiment? If so, reference these articles as well. Discuss the key diagnostic features of your spectral results in words. Did your spectral data prove that you actually synthesized the molecule you were after? Comment on this by reporting any peaks that are especially diagnostic. For example, if you were synthesizing an aldehyde this functional group has a very distinctive peak for the H C=O proton at 9 ppm, which would be an important piece of data to discuss. Finally, include a conclusion statement here. Experimental Section Very carefully follow the format of the Journal of Organic Chemistry for reporting experimental details. Each compound gets a paragraph that lists in this order: 1) the chemical name and number you assigned to it, 2) a description of the reagent amounts used, the order of addition of the reagents, temperatures, reaction times, and work up methods, 3) purification methods, 4) actual and % yield, and 5) spectral data reported in tabular form. There are a number of formatting conventions in the way that these items are reported that you need to follow, especially in regards to the spectral data. Look at a few recent synthesis articles in J. Org. Chem. to get these details down. References Citations made in the body of the paper are to be listed in this section using the format found in a current issue of an ACS journal such as J. Org. Chem., or J. Am. Chem. Soc. Again, formatting is very specific and probably different from what you used in your composition courses. Spectra Attach spectra for your final purified product including IR, 1 H NMR, 13 C NMR, GC chromatogram, and mass spectrum. Guide to Writing Style: Scientific writing style makes frequent use of the passive voice and past tense although the active voice and present tense are acceptable at times. The imperative tense is not used. The following generalizations may be helpful to you. Also, remember to write in complete sentences, use proper punctuation and grammar, and spell words correctly. a) In the experimental section use the past tense, passive voice. Don t use the imperative tense. Correct: The reaction was stirred for I h. (Note past tense, passive voice). 6
7 Incorrect: Incorrect: I stirred the reaction for I h. (Note active voice). Stir the reaction for 1 h. (Note imperative voice). b) Be careful in your use of the word reacted Correct: Reagents A and B were mixed and they then reacted to form product C. Incorrect: I reacted reagent A with reagent B to give product C. c) Sentences are not to be started with a number written in numerical form. Correct: Correct: Incorrect: Five grams (0.064 mole) of benzene were placed in the flask. In the flask were placed 5 grams (0.064 mole) of benzene. 5 g (0.064 mole) of benzene were placed in the flask. (Note sentence started with a number written in numerical form). d) Sentences normally are not started with I or We in ACS Journals. Correct: Incorrect: Benzene was put in the flask. [(Use passive voice to avoid starting the sentence with I (We)]. I (we) put benzene in the flask. [(Note sentence started with I (we)]. e) Any current issue of the J. Org. Chem. or J. Am. Chem. Soc. should be reviewed to see how the above suggestions are implemented in a paper. Additionally the format for presenting equations and tables including numbering compounds should be reviewed and followed in your paper. f) The title and abstract pages should be two separate pages. The introductory, experimental, discussion, and reference sections are to follow each other rather than starting new pages for each section. Each section of the report should be headed with the appropriate title. (e.g. Abstract, Discussion, etc.) g) This paper is a formal report of your experimental work and, as such, should be written in a careful, concise, and professional manner. Word processed papers with computer generated structures are required. Synthesis Article Presentation Each pair of students will be given an organic synthesis article near the beginning of the semester. Throughout the semester you and your partner will study paper, learning the reactions, mechanisms, and the strategy employed in the synthesis. The two of you will prepare a minute PowerPoint presentation describing the synthesis in your own words. On the last lab meeting of the semester, 5/12, groups will present to the class, and answer questions for 5 minutes. More details will follow on this assignment. 7
Sul Ross State University Syllabus for Organic Chemistry II: CHEM 3408 (Spring 2017)
 Sul Ross State University Syllabus for Organic Chemistry II: CHEM 3408 (Spring 2017) Class: Organic Chemistry II Instructor: Dr. David J. Leaver Room: WSB 307 Office: WSB 318 Time: MWF 9:00-9:50am Office
Sul Ross State University Syllabus for Organic Chemistry II: CHEM 3408 (Spring 2017) Class: Organic Chemistry II Instructor: Dr. David J. Leaver Room: WSB 307 Office: WSB 318 Time: MWF 9:00-9:50am Office
Chemistry 204 Organic Chemistry Course Syllabus Spring 2013
 Chemistry 204 Organic Chemistry Course Syllabus Spring 2013 Course Goals: Continue to develop an understanding of the structures and structure-activity relationships of organic molecules. Understand and
Chemistry 204 Organic Chemistry Course Syllabus Spring 2013 Course Goals: Continue to develop an understanding of the structures and structure-activity relationships of organic molecules. Understand and
CHEM2077 HONORS ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SYLLABUS
 CHEM2077 HONORS ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SYLLABUS 1. STRUCTURE AND BONDING a] Atomic structure and bonding b] Hybridization and MO Theory c] Drawing chemical structures 2. POLAR COVALENT BONDS: ACIDS AND BASES
CHEM2077 HONORS ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SYLLABUS 1. STRUCTURE AND BONDING a] Atomic structure and bonding b] Hybridization and MO Theory c] Drawing chemical structures 2. POLAR COVALENT BONDS: ACIDS AND BASES
Spring Term 2012 Dr. Williams (309 Zurn, ex 2386)
 Chemistry 242 Organic Chemistry II Spring Term 2012 Dr. Williams (309 Zurn, ex 2386) Web Page: http://math.mercyhurst.edu/~jwilliams/ jwilliams@mercyhurst.edu (or just visit Department web site and look
Chemistry 242 Organic Chemistry II Spring Term 2012 Dr. Williams (309 Zurn, ex 2386) Web Page: http://math.mercyhurst.edu/~jwilliams/ jwilliams@mercyhurst.edu (or just visit Department web site and look
CHEM 25: Organic Chemistry I https://moodle.drew.edu (2009FA-CHEM )
 CHEM 25: Organic Chemistry I https://moodle.drew.edu (2009FA-CHEM-25-001) Instructor Jane M. Liu, Ph.D. Hall of Sciences S212 jliu3@drew.edu (973-408-3303) Class 9:30-10:35am M, W, F (S244) Laboratory
CHEM 25: Organic Chemistry I https://moodle.drew.edu (2009FA-CHEM-25-001) Instructor Jane M. Liu, Ph.D. Hall of Sciences S212 jliu3@drew.edu (973-408-3303) Class 9:30-10:35am M, W, F (S244) Laboratory
DEPARTMENT: Chemistry
 CODE CHEM 204 TITLE: Organic Chemistry II INSTITUTE: STEM DEPARTMENT: Chemistry COURSE DESCRIPTION: A continuation of CHEM-203, students will extend their studies into topics including aromatic hydrocarbons,
CODE CHEM 204 TITLE: Organic Chemistry II INSTITUTE: STEM DEPARTMENT: Chemistry COURSE DESCRIPTION: A continuation of CHEM-203, students will extend their studies into topics including aromatic hydrocarbons,
Chemistry 20, Section 1204 Fundamentals of Chemistry, 5 Units El Camino College Spring 2008
 Chemistry 20, Section 1204 Fundamentals of Chemistry, 5 Units El Camino College Spring 2008 Instructor: Lida Latifzadeh Masoudipour, Ph.D. Lecture: M, 6:00 PM 9:10 PM, Room Chem. 133 W, 6:00 PM 7:00 PM,
Chemistry 20, Section 1204 Fundamentals of Chemistry, 5 Units El Camino College Spring 2008 Instructor: Lida Latifzadeh Masoudipour, Ph.D. Lecture: M, 6:00 PM 9:10 PM, Room Chem. 133 W, 6:00 PM 7:00 PM,
CHE 325 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II Spring 2017
 Instructor: CHE 325 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II Spring 2017 Professor James Kallmerten 4-014A Center for Science and Technology Phone: 3-2854 Email: jkallmer@syr.edu Office Hours: Monday 11 am -1 pm, Wednesday
Instructor: CHE 325 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II Spring 2017 Professor James Kallmerten 4-014A Center for Science and Technology Phone: 3-2854 Email: jkallmer@syr.edu Office Hours: Monday 11 am -1 pm, Wednesday
Chemistry 12B Organic Chemistry. Spring 2016
 Chemistry 12B Organic Chemistry Spring 2016 Instructor: Nada Khouderchah E-mail: khouderchahnada@fhda.edu Office hours and location: Tuesday from 5:00-5:50 pm and Thursday from 7:20 8:20 pm in the faculty
Chemistry 12B Organic Chemistry Spring 2016 Instructor: Nada Khouderchah E-mail: khouderchahnada@fhda.edu Office hours and location: Tuesday from 5:00-5:50 pm and Thursday from 7:20 8:20 pm in the faculty
Required Materials For complete material(s) information, refer to
 Butler Community College Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math Division Robert Carlson Revised Fall 2017 Implemented Spring 2018 COURSE OUTLINE Organic Chemistry 2 Course Description CH 245. Organic
Butler Community College Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math Division Robert Carlson Revised Fall 2017 Implemented Spring 2018 COURSE OUTLINE Organic Chemistry 2 Course Description CH 245. Organic
Syllabus for Chemistry 12B Spring Semester 2015
 Syllabus for Chemistry 12B Spring Semester 2015 Taught by: Sam Gillette, Ph.D. email: sgillette@peralta.edu Phone: 510-981-5016 Office: BCC 541 Lab: BCC 514 Web Site: http://www.berkeleycitycollege.edu/wp/sgillette/
Syllabus for Chemistry 12B Spring Semester 2015 Taught by: Sam Gillette, Ph.D. email: sgillette@peralta.edu Phone: 510-981-5016 Office: BCC 541 Lab: BCC 514 Web Site: http://www.berkeleycitycollege.edu/wp/sgillette/
CHEM 203. Midterm Exam 1 October 31, 2008 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Midterm Exam 1 ctober 31, 2008 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This exam contains 8 pages Time: 1h 30 min 1. / 15 2. / 16 3. /
CEM 203 Midterm Exam 1 ctober 31, 2008 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This exam contains 8 pages Time: 1h 30 min 1. / 15 2. / 16 3. /
Syllabus for CHEM 241 Organic Chemistry I, 3CR, Great Basin College
 Syllabus for CHEM 241 Organic Chemistry I, 3CR, Great Basin College Instructor: David Freistroffer Office: Lundberg 109 (in the fishbowl) Phone: 753-2018, but please use email for fastest possible response
Syllabus for CHEM 241 Organic Chemistry I, 3CR, Great Basin College Instructor: David Freistroffer Office: Lundberg 109 (in the fishbowl) Phone: 753-2018, but please use email for fastest possible response
CHE 171: Mechanistic Organic Chemistry I
 CHE 171: Mechanistic Organic Chemistry I Syllabus, Autumn Quarter 2003 Instructor: Dr. Matthew R. Dintzner Office hours: Mondays 9:00-11:30 AM, Tuesdays 10:00-12:30, or by appointment Office, Lab: O'Connell
CHE 171: Mechanistic Organic Chemistry I Syllabus, Autumn Quarter 2003 Instructor: Dr. Matthew R. Dintzner Office hours: Mondays 9:00-11:30 AM, Tuesdays 10:00-12:30, or by appointment Office, Lab: O'Connell
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 1
 Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 1 Thursday, February 12, 2015; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 1 Thursday, February 12, 2015; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS CHM201 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II. 5 Credit Hours. Prepared by: Richard A. Pierce
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS CHM201 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Richard A. Pierce Revised Date: January 2008 by Ryan H. Groeneman Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor, Dean
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS CHM201 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Richard A. Pierce Revised Date: January 2008 by Ryan H. Groeneman Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor, Dean
CHE 262 (03): Organic Chemistry II Spring 2018 Syllabus MWF 12:50-1:50 in Phillips Lecture Hall
 CHE 262 (03): Organic Chemistry II Spring 2018 Syllabus MWF 12:50-1:50 in Phillips Lecture Hall Professor: Dr. Mark V. Wilson Office: Hoyt 360 Email: wilsonmv@westminster.edu (Best way to contact me.)
CHE 262 (03): Organic Chemistry II Spring 2018 Syllabus MWF 12:50-1:50 in Phillips Lecture Hall Professor: Dr. Mark V. Wilson Office: Hoyt 360 Email: wilsonmv@westminster.edu (Best way to contact me.)
General Chemistry 201 Section ABC Harry S. Truman College Spring Semester 2014
 Instructor: Michael Davis Office: 3226 Phone: 773 907 4718 Office Hours: Tues 9:00 12:00 Wed 1:00 3:00 Thurs 9:00 12:00 Email: mdavis@ccc.edu Website: http://faradaysclub.com http://ccc.blackboard.com
Instructor: Michael Davis Office: 3226 Phone: 773 907 4718 Office Hours: Tues 9:00 12:00 Wed 1:00 3:00 Thurs 9:00 12:00 Email: mdavis@ccc.edu Website: http://faradaysclub.com http://ccc.blackboard.com
CHEM ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 BRAZOSPORT COLLEGE LAKE JACKSON, TEXAS SYLLABUS CHEM 2423 - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY CATALOG DESCRIPTION: CHEM 2423 Organic Chemistry I. CIP 4005045203 A study of the nomenclature, classification and reactions
BRAZOSPORT COLLEGE LAKE JACKSON, TEXAS SYLLABUS CHEM 2423 - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY CATALOG DESCRIPTION: CHEM 2423 Organic Chemistry I. CIP 4005045203 A study of the nomenclature, classification and reactions
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions
 Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Chemistry 883 Computational Quantum Chemistry
 Chemistry 883 Computational Quantum Chemistry Instructor Contact Information Professor Benjamin G. Levine levine@chemistry.msu.edu 215 Chemistry Building 517-353-1113 Office Hours Tuesday 9:00-11:00 am
Chemistry 883 Computational Quantum Chemistry Instructor Contact Information Professor Benjamin G. Levine levine@chemistry.msu.edu 215 Chemistry Building 517-353-1113 Office Hours Tuesday 9:00-11:00 am
The lecture schedule is only a rough guide and will be likely changed as needed.
 CEHM 239 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Hyun-Soon Chong Chemistry Division, BCPS Dept, IIT, LS 398, Chong@iit.edu, 312-567-3235 Course Hours: TR 1:50pm-3:05pm in LS 111 Office Hours:
CEHM 239 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Hyun-Soon Chong Chemistry Division, BCPS Dept, IIT, LS 398, Chong@iit.edu, 312-567-3235 Course Hours: TR 1:50pm-3:05pm in LS 111 Office Hours:
PELLISSIPPI STATE TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS APPLIED ORGANIC CHEMISTRY W/ LAB CHT 2210
 PELLISSIPPI STATE TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS APPLIED ORGANIC CHEMISTRY W/ LAB CHT 2210 Class Hours: 3.0 Credit Hours: 4.0 Laboratory Hours: 3.0 Date Revised: Fall 2001 NOTE: This course
PELLISSIPPI STATE TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS APPLIED ORGANIC CHEMISTRY W/ LAB CHT 2210 Class Hours: 3.0 Credit Hours: 4.0 Laboratory Hours: 3.0 Date Revised: Fall 2001 NOTE: This course
X UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF THE FRASER VALLEY COURSE INFORMATION. DISCIPLINE/DEPARTMENT: Chemistry IMPLEMENTATION DATE: Fall 1993
 X UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF THE FRASER VALLEY COURSE INFORMATION DISCIPLINE/DEPARTMENT: Chemistry IMPLEMENTATION DATE: Fall 1993 Course Revised Implementation Date: May 2006 Course to be Reviewed: December
X UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF THE FRASER VALLEY COURSE INFORMATION DISCIPLINE/DEPARTMENT: Chemistry IMPLEMENTATION DATE: Fall 1993 Course Revised Implementation Date: May 2006 Course to be Reviewed: December
Cape Cod Community College
 Cape Cod Community College Departmental Syllabus Prepared by the Department of Natural Sciences & Applied Technology Date of Departmental Approval: February 3, 2014 Date Approved by Curriculum and Programs:
Cape Cod Community College Departmental Syllabus Prepared by the Department of Natural Sciences & Applied Technology Date of Departmental Approval: February 3, 2014 Date Approved by Curriculum and Programs:
CHEMISTRY 413 Spring 2014
 Instructor: Office: Dr. Alan J. Jircitano 33 Hammermill Phone: 898-6400 CHEMISTRY 413 Spring 2014 Internet: e-mail: jircitano@psu.edu web site: http://chemistry.bd.psu.edu/jircitano/ Office Hours: M 11
Instructor: Office: Dr. Alan J. Jircitano 33 Hammermill Phone: 898-6400 CHEMISTRY 413 Spring 2014 Internet: e-mail: jircitano@psu.edu web site: http://chemistry.bd.psu.edu/jircitano/ Office Hours: M 11
CHEM 333 Spring 2016 Organic Chemistry I California State University Northridge
 CHEM 333 Spring 2016 Organic Chemistry I California State University Northridge Lecture: Instructor: Thomas Minehan Office: Science 2314 Office hours: MW 12:00-1:00 pm E.mail: thomas.minehan@csun.edu Class
CHEM 333 Spring 2016 Organic Chemistry I California State University Northridge Lecture: Instructor: Thomas Minehan Office: Science 2314 Office hours: MW 12:00-1:00 pm E.mail: thomas.minehan@csun.edu Class
Georgia Gwinnett College CHEM 2212 Organic Chemistry II Course Syllabus Summer MTWR, 9-11am, A1640 (class); MTW, pm, A1290 (lab)
 Georgia Gwinnett College CHEM 2212 Organic Chemistry II Course Syllabus Summer 2008 Class Meetings: Instructor: Office: E-Mail: Phone Number: Wiki page: MTWR, 9-11am, A1640 (class); MTW, 1.15-4pm, A1290
Georgia Gwinnett College CHEM 2212 Organic Chemistry II Course Syllabus Summer 2008 Class Meetings: Instructor: Office: E-Mail: Phone Number: Wiki page: MTWR, 9-11am, A1640 (class); MTW, 1.15-4pm, A1290
Los Angeles Mission College Chemistry 65 Syllabus Spring Semester 2012
 Lecture Instructor: Dr. R. W. Gellert Section: # Los Angeles Mission College Chemistry 6 Syllabus Spring Semester 0 Tel: (88) 6-7600 x8 (Use email!) Office Hours: MW 8:-9:00 PM INST 00 Lec. MW 7:00-8:
Lecture Instructor: Dr. R. W. Gellert Section: # Los Angeles Mission College Chemistry 6 Syllabus Spring Semester 0 Tel: (88) 6-7600 x8 (Use email!) Office Hours: MW 8:-9:00 PM INST 00 Lec. MW 7:00-8:
Chemistry Syllabus Fall Term 2017
 Chemistry 9 - Syllabus Fall Term 17 Date Lecture Number - General Subject Chapter W 8/30 F 9/1 1 - Introduction and orgo I review X - Review, friendly diagnostic exam M 9/4 2 - Orgo I review, exam highlights
Chemistry 9 - Syllabus Fall Term 17 Date Lecture Number - General Subject Chapter W 8/30 F 9/1 1 - Introduction and orgo I review X - Review, friendly diagnostic exam M 9/4 2 - Orgo I review, exam highlights
Syllabus for Chemistry 12A Spring Semester 2015
 Syllabus for Chemistry 12A Spring Semester 2015 Taught by: Sam Gillette, Ph.D. email: sgillette@peralta.edu Phone: 510-981-5016 Office: BCC 541 Lab: BCC 514 Web Site: http://www.berkeleycitycollege.edu/wp/sgillette/
Syllabus for Chemistry 12A Spring Semester 2015 Taught by: Sam Gillette, Ph.D. email: sgillette@peralta.edu Phone: 510-981-5016 Office: BCC 541 Lab: BCC 514 Web Site: http://www.berkeleycitycollege.edu/wp/sgillette/
Strategies for Organic Synthesis
 Strategies for rganic Synthesis ne of the things that makes chemistry unique among the sciences is synthesis. Chemists make things. New pharmaceuticals, food additives, materials, agricultural chemicals,
Strategies for rganic Synthesis ne of the things that makes chemistry unique among the sciences is synthesis. Chemists make things. New pharmaceuticals, food additives, materials, agricultural chemicals,
Chemistry Organic Chemistry II, Spring 2018
 Chemistry 2320 Organic Chemistry II, Spring 2018 Instructor: Dr. Tom Chang Office: Widtsoe 337 Phone: 797-3545 Email: tom.chang@usu.edu Meeting Time/Place: MWF 10:30-11:20 am, Eccles Business Building
Chemistry 2320 Organic Chemistry II, Spring 2018 Instructor: Dr. Tom Chang Office: Widtsoe 337 Phone: 797-3545 Email: tom.chang@usu.edu Meeting Time/Place: MWF 10:30-11:20 am, Eccles Business Building
Chemistry 2332, Honors Organic Chemistry II Spring Semester 2013
 Chemistry 2332, Honors Organic Chemistry II Spring Semester 2013 Instructor: Professor Jane E. Wissinger, Kolthoff 455, 612-625-9586, jwiss@umn.edu Office Hours: Mon. 10:30-11:30 a.m. Wed. 3:30-4:30 p.m.,
Chemistry 2332, Honors Organic Chemistry II Spring Semester 2013 Instructor: Professor Jane E. Wissinger, Kolthoff 455, 612-625-9586, jwiss@umn.edu Office Hours: Mon. 10:30-11:30 a.m. Wed. 3:30-4:30 p.m.,
COURSE UNIT DESCRIPTION. Dept. Organic Chemistry, Vilnius University. Type of the course unit
 Course unit title Organic Chemistry II Lecturer(s) Rimantas Vaitkus COURSE UNIT DESCRIPTION Department Dept. Organic Chemistry, Vilnius University Cycle First Type of the course unit Mode of delivery Period
Course unit title Organic Chemistry II Lecturer(s) Rimantas Vaitkus COURSE UNIT DESCRIPTION Department Dept. Organic Chemistry, Vilnius University Cycle First Type of the course unit Mode of delivery Period
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE General Organic Chemistry I
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE General Organic Chemistry I Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number CHM 235 (SUN# CHM 2235) Title General Organic Chemistry I Credits 4 Developed
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE General Organic Chemistry I Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number CHM 235 (SUN# CHM 2235) Title General Organic Chemistry I Credits 4 Developed
Molecular Graphics. Molecular Graphics Expt. 1 1
 Molecular Graphics Expt. 1 1 Molecular Graphics The study of organic chemistry has for more than a century and a half focussed on the relationship between the structure of an organic molecule (its three-dimensional
Molecular Graphics Expt. 1 1 Molecular Graphics The study of organic chemistry has for more than a century and a half focussed on the relationship between the structure of an organic molecule (its three-dimensional
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS CHM201 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II. 5 Credit Hours. Prepared by: Richard A. Pierce. Revised by: Sean Birke October, 2013
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS CHM201 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Richard A. Pierce Revised by: Sean Birke October, 2013 Ms. Linda Abernathy, Math, Science & Business Division Chair
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS CHM201 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Richard A. Pierce Revised by: Sean Birke October, 2013 Ms. Linda Abernathy, Math, Science & Business Division Chair
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School
 COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in the sophomore year. Catalog Description: CHM4250 - ORGANIC
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in the sophomore year. Catalog Description: CHM4250 - ORGANIC
Welcome to Chem 36!! Organic Chem Lab. Dr. Katie Masters
 Welcome to Chem 36!! Organic Chem Lab Dr. Katie Masters Chem 36 Info Section 101: Monday/Wednesday 1:25-4:25 pm Section 102: Tuesday/Thursday 1:25-4:25 pm Section 103: Tuesday/Thursday 6:30-9:30 pm Faculty
Welcome to Chem 36!! Organic Chem Lab Dr. Katie Masters Chem 36 Info Section 101: Monday/Wednesday 1:25-4:25 pm Section 102: Tuesday/Thursday 1:25-4:25 pm Section 103: Tuesday/Thursday 6:30-9:30 pm Faculty
Hour Examination # 2
 CHEM 347 Hour Examination # 2 Spring 2014 Page 1 of 8 CHEM 347 rganic Chemistry II (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Hour Examination # 2 Wednesday, March 5 th, 2014 5:30 8:30 p.m. Student Name
CHEM 347 Hour Examination # 2 Spring 2014 Page 1 of 8 CHEM 347 rganic Chemistry II (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Hour Examination # 2 Wednesday, March 5 th, 2014 5:30 8:30 p.m. Student Name
A SURVEY OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY 1315 TuTr 9:35-10:55 am, Boggs B6
 GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY School of Chemistry and Biochemistry Spring 2004 A SURVEY OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY 1315 TuTr 9:35-10:55 am, Boggs B6 Instructor: Marcus Weck Office: Boggs 3-85 Phone:
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY School of Chemistry and Biochemistry Spring 2004 A SURVEY OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY 1315 TuTr 9:35-10:55 am, Boggs B6 Instructor: Marcus Weck Office: Boggs 3-85 Phone:
Prerequisites: CHEM 1312 and CHEM 1112, or CHEM 1412 General Chemistry II (Lecture and Laboratory)
 Course Syllabus CHEM 2423 Organic Chemistry I Revision Date: 8/19/2013 Catalog Description: Fundamental principles of organic chemistry will be studied, including the structure, bonding, properties, and
Course Syllabus CHEM 2423 Organic Chemistry I Revision Date: 8/19/2013 Catalog Description: Fundamental principles of organic chemistry will be studied, including the structure, bonding, properties, and
Suggested solutions for Chapter 28
 s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
CHEM 2240L Final Exam Review Topics
 CHEM 2240L Final Exam Review Topics Many students do not adequately prepare for the final exam in 2240L.The average grade is typically in the mid 60 s. Each semester, some students score in the 90 s, and
CHEM 2240L Final Exam Review Topics Many students do not adequately prepare for the final exam in 2240L.The average grade is typically in the mid 60 s. Each semester, some students score in the 90 s, and
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key
 CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
4. Prerequisites Grade of C or better in Chemistry 201 & Chem. 203 or consent of the department chairperson
 1 Harry S Truman College Master Syllabus Chemistry 205 Organic Chemistry I Active IAI Code CHM 914 1. Title, Number, and Classification Organic Chemistry I 073-0205-1 2. Course Term 16 week Semester or
1 Harry S Truman College Master Syllabus Chemistry 205 Organic Chemistry I Active IAI Code CHM 914 1. Title, Number, and Classification Organic Chemistry I 073-0205-1 2. Course Term 16 week Semester or
Chemistry 3720 Old Exams. Practice Exams & Keys
 Chemistry 3720 ld Exams Practice Exams & Keys 2015-17 Spring 2017 Page File 3 Spring 2017 Exam 1 10 Spring 2017 Exam 1 Key 16 Spring 2017 Exam 2 23 Spring 2017 Exam 2 Key 29 Spring 2017 Exam 3 36 Spring
Chemistry 3720 ld Exams Practice Exams & Keys 2015-17 Spring 2017 Page File 3 Spring 2017 Exam 1 10 Spring 2017 Exam 1 Key 16 Spring 2017 Exam 2 23 Spring 2017 Exam 2 Key 29 Spring 2017 Exam 3 36 Spring
INSTRUCTOR (Lec): Mike Fenton OFFICE PHONE: (818) OFFICE: CMS 243
 LOS ANGELES MISSION COLLEGE-SPRING 2017 CHEMISTRY 101-SECTIONS 3162 & 3163 LEC: T TH 5:15 PM-6:40 PM (CMS-236) LAB (3162): T TH 1:50 PM-5:00 PM (CMS-210) LAB (3163): T TH 6:50 PM-10:00 PM (CMS-210) INSTRUCTOR
LOS ANGELES MISSION COLLEGE-SPRING 2017 CHEMISTRY 101-SECTIONS 3162 & 3163 LEC: T TH 5:15 PM-6:40 PM (CMS-236) LAB (3162): T TH 1:50 PM-5:00 PM (CMS-210) LAB (3163): T TH 6:50 PM-10:00 PM (CMS-210) INSTRUCTOR
Course Syllabus. Department: Science & Technology. Date: April I. Course Prefix and Number: CHM 211. Course Name: Organic Chemistry I
 Department: Science & Technology Date: April 2012 I. Course Prefix and Number: CHM 211 Course Name: Organic Chemistry I Course Syllabus Credit Hours and Contact Hours: 5 credit hours and 7 (3:3:1) contact
Department: Science & Technology Date: April 2012 I. Course Prefix and Number: CHM 211 Course Name: Organic Chemistry I Course Syllabus Credit Hours and Contact Hours: 5 credit hours and 7 (3:3:1) contact
CHEMISTRY 3A INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY SPRING
 CHEMISTRY 3A INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY SPRING ---- 2007 INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Phil Reedy Office: Cunningham 321 Telephone: 954-5671 email: preedy@deltacollege.edu WEBSITES: www.deltacollege.edu/emp/preedy www.preparatorychemistry.com
CHEMISTRY 3A INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY SPRING ---- 2007 INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Phil Reedy Office: Cunningham 321 Telephone: 954-5671 email: preedy@deltacollege.edu WEBSITES: www.deltacollege.edu/emp/preedy www.preparatorychemistry.com
Dr. LeGrande M. Slaughter Chemistry Building Rm. 307E Office phone: ; Tues, Thurs 11:00 am-12:20 pm, CHEM 331D
 Syllabus: CHEM 5620 Selected Topics in Inorganic Chemistry: Transition Metal Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis Spring Semester 2017 (3 credit hours) Instructor: Lecture: Required Text: Office Hours:
Syllabus: CHEM 5620 Selected Topics in Inorganic Chemistry: Transition Metal Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis Spring Semester 2017 (3 credit hours) Instructor: Lecture: Required Text: Office Hours:
Name The Following Alkene Sapling
 Name The Following Alkene Sapling Free PDF ebook Download: Name The Following Alkene Sapling Download or Read Online ebook name the following alkene sapling in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database
Name The Following Alkene Sapling Free PDF ebook Download: Name The Following Alkene Sapling Download or Read Online ebook name the following alkene sapling in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database
Chemistry 7A Fall 2009
 Chemistry 7A Fall 2009 Instructor: A. Tontcheva, Ph.D. e-mail: atontcheva@elcamino.edu Office: Chemistry 112 Phone ext. 6010 Office Hours: M 12:30-1:30, T 12:30-1:00, W 12:30-1:55 Required Materials: Vollhardt
Chemistry 7A Fall 2009 Instructor: A. Tontcheva, Ph.D. e-mail: atontcheva@elcamino.edu Office: Chemistry 112 Phone ext. 6010 Office Hours: M 12:30-1:30, T 12:30-1:00, W 12:30-1:55 Required Materials: Vollhardt
Ventura College COURSE OUTLINE OF RECORD
 Today's Date: 01/26/2016 Course ID: CHEM V12BL CC Approval: 04/02/2013 Effective Term: Fall 2013 I. Course Information (Printed catalog data elements) A. Discipline: Chemistry B. Course ID: CHEM V12BL
Today's Date: 01/26/2016 Course ID: CHEM V12BL CC Approval: 04/02/2013 Effective Term: Fall 2013 I. Course Information (Printed catalog data elements) A. Discipline: Chemistry B. Course ID: CHEM V12BL
Chemistry 8 Principles of Organic Chemistry Spring Semester, 2013
 Chemistry 8 Principles of Organic Chemistry Spring Semester, 2013 Instructor: Office Hours: At the Lantern Prof. Jason Hein Mon 2:30 3:30 Email: jhein2@ucmerced.edu Tue 1:30 2:30 Phone: 683-4650 Office:
Chemistry 8 Principles of Organic Chemistry Spring Semester, 2013 Instructor: Office Hours: At the Lantern Prof. Jason Hein Mon 2:30 3:30 Email: jhein2@ucmerced.edu Tue 1:30 2:30 Phone: 683-4650 Office:
2.222 Practice Problems 2003
 2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
20.10 Conjugate Additions
 894 APTER 20 ELATE AD THER CARB UCLEPHILES 2010 Conjugate Additions The conjugate addition of nucleophiles to,-unsaturated carbonyl compounds at the -position was described in Section 1810 Enolate and
894 APTER 20 ELATE AD THER CARB UCLEPHILES 2010 Conjugate Additions The conjugate addition of nucleophiles to,-unsaturated carbonyl compounds at the -position was described in Section 1810 Enolate and
CHEM*2700 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (Spring/Summer Semester 2009) Information Sheet and Course Outline
 CHEM*2700 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (Spring/Summer Semester 2009) Information Sheet and Course Outline Instructor: Professor William Tam Office: MacN 332 Phone: 824-4120 (Ext.52268) E-mail: wtam@uoguelph.ca
CHEM*2700 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (Spring/Summer Semester 2009) Information Sheet and Course Outline Instructor: Professor William Tam Office: MacN 332 Phone: 824-4120 (Ext.52268) E-mail: wtam@uoguelph.ca
Chemistry 20: Fundamentals of Chemistry
 Chemistry 20: Fundamentals of Chemistry Instructor: Valerie Baggett Office: Chem 132 Office Hours: M/W 10:10 am to 10:25 am, or by appointment Telephone: 310-660-6131 Email: vbaggett@elcamino.edu Course
Chemistry 20: Fundamentals of Chemistry Instructor: Valerie Baggett Office: Chem 132 Office Hours: M/W 10:10 am to 10:25 am, or by appointment Telephone: 310-660-6131 Email: vbaggett@elcamino.edu Course
II. Special Topics IIA. Enolate Chemistry & the Aldol Reaction
 P. Wipf - Chem 2320 1 3/20/2006 II. Special Topics IIA. Enolate Chemistry & the Aldol Reaction Boger Notes: p. 147-206 (Chapter VIII) Carey/Sundberg: B p. 57-95 (Chapter B 2.1) Problem of the Day: Wang,
P. Wipf - Chem 2320 1 3/20/2006 II. Special Topics IIA. Enolate Chemistry & the Aldol Reaction Boger Notes: p. 147-206 (Chapter VIII) Carey/Sundberg: B p. 57-95 (Chapter B 2.1) Problem of the Day: Wang,
Aldehydes and Ketones 2. Based on Organic Chemistry, J. G. Smith 3rde.
 Aldehydes and Ketones 2 Based on Organic Chemistry, J. G. Smith 3rde. The Wittig Reaction Wittig reaction, named for German chemist Georg Wittig, who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1979 for
Aldehydes and Ketones 2 Based on Organic Chemistry, J. G. Smith 3rde. The Wittig Reaction Wittig reaction, named for German chemist Georg Wittig, who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1979 for
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 1
 Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 1 Thursday, February 11, 2016; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 1 Thursday, February 11, 2016; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 1. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 1 Syllabus Chemistry 4631 Spring 2018 Lecture: MWF 9:00 9:50 a.m. Chem 352 Attendance is expected. Instructor: Dr. Teresa D. Golden Chem 279, 565-2888, tgolden@unt.edu.
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 1 Syllabus Chemistry 4631 Spring 2018 Lecture: MWF 9:00 9:50 a.m. Chem 352 Attendance is expected. Instructor: Dr. Teresa D. Golden Chem 279, 565-2888, tgolden@unt.edu.
Synthesis of Tetraphenylcyclopentadienone. Becky Ortiz
 Synthesis of Tetraphenylcyclopentadienone Becky Ortiz Introduction An aldol reaction is a reaction in which aldehydes or ketones undergo a base- catalyzed carbonyl condensation reaction to form a beta-
Synthesis of Tetraphenylcyclopentadienone Becky Ortiz Introduction An aldol reaction is a reaction in which aldehydes or ketones undergo a base- catalyzed carbonyl condensation reaction to form a beta-
Title of experiment and short description of the purpose of the experiment.
 The Laboratory Notebook for Chem 267 and 268. Use only the required notebook, one that allows a copy of each page to be made and torn out. The copy is given to the TA for grading and the original is kept
The Laboratory Notebook for Chem 267 and 268. Use only the required notebook, one that allows a copy of each page to be made and torn out. The copy is given to the TA for grading and the original is kept
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 15, 2010 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
Exam 1 (Monday, July 6, 2015)
 Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
(available at the Rutgers bookstore)
 Spring 2016 Chem 316 Overview Instructor: Prof. Lawrence Williams Room: WL Auditorium Day/Time: Monday/Wednesday 3:20 4:40 pm Office hours: Monday/Wednesday 4:40 5:30 pm (Rm. 276) Student Mentors: Matt,
Spring 2016 Chem 316 Overview Instructor: Prof. Lawrence Williams Room: WL Auditorium Day/Time: Monday/Wednesday 3:20 4:40 pm Office hours: Monday/Wednesday 4:40 5:30 pm (Rm. 276) Student Mentors: Matt,
Lecture 24 Two Germans and an Englishman
 Lecture 24 Two Germans and an Englishman Robert Robinson 1886-1975 Nobel Laureate 1947 April 17, 2018 tto Paul Hermann Diels 1876-1954 Nobel Laureates 1950 Kurt Alder 1902-1958 Exam III Tomorrow Wed April
Lecture 24 Two Germans and an Englishman Robert Robinson 1886-1975 Nobel Laureate 1947 April 17, 2018 tto Paul Hermann Diels 1876-1954 Nobel Laureates 1950 Kurt Alder 1902-1958 Exam III Tomorrow Wed April
Hunan University. CHEM32: Organic Chemistry
 Academic Inquiries: Hunan University Email: iss@hnu.edu.cn Hunan University CHEM32: Organic Chemistry Professor: To be announced Total contact hours: 54 hours Credit: 4 Course Description Topics covered
Academic Inquiries: Hunan University Email: iss@hnu.edu.cn Hunan University CHEM32: Organic Chemistry Professor: To be announced Total contact hours: 54 hours Credit: 4 Course Description Topics covered
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions I. Reaction of Enols & Enolates with ther Carbonyls Enols and enolates are electron rich nucleophiles that react with a number
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions I. Reaction of Enols & Enolates with ther Carbonyls Enols and enolates are electron rich nucleophiles that react with a number
Organic Chemistry Syllabus
 Organic Chemistry Syllabus 2017-2018 Instructor Information: Teacher: James Poindexter Room: Belle Vernon Area High School, Room 412 Contact: Phone: 724-808-2500; ext.2412 Email: james.poindexter@bellevernonarea.net
Organic Chemistry Syllabus 2017-2018 Instructor Information: Teacher: James Poindexter Room: Belle Vernon Area High School, Room 412 Contact: Phone: 724-808-2500; ext.2412 Email: james.poindexter@bellevernonarea.net
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and How Do They Work?
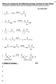 What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK
 Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
EMA 3011 Fundamental Principles of Materials, Section 9765 Spring, 2014
 EMA 3011 Fundamental Principles of Materials, Section 9765 Spring, 2014 1. Catalog Description: The fundamental principles of structure, reactivity and energies describing materials systems will be covered,
EMA 3011 Fundamental Principles of Materials, Section 9765 Spring, 2014 1. Catalog Description: The fundamental principles of structure, reactivity and energies describing materials systems will be covered,
DEPARTMENT: Chemistry
 CODE: CHEM 203 TITLE: Organic Chemistry I INSTITUTE: STEM DEPARTMENT: Chemistry COURSE DESCRIPTION: Students will apply many concepts from general chemistry to a study of organic chemistry. They will be
CODE: CHEM 203 TITLE: Organic Chemistry I INSTITUTE: STEM DEPARTMENT: Chemistry COURSE DESCRIPTION: Students will apply many concepts from general chemistry to a study of organic chemistry. They will be
WAYNE STATE UNIVERSITY CHEM 1410 CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES I: General /Organic Chemistry FALL 1998
 WAYNE STATE UNIVERSITY CHEM 1410 CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES I: General /Organic Chemistry FALL 1998 STAFF Instructor: Dr. Mary T. Office: 33 Chemistry 577-2431 Lab: 20 Chemistry 577-0780 Office Hours: MWF 9:30A
WAYNE STATE UNIVERSITY CHEM 1410 CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES I: General /Organic Chemistry FALL 1998 STAFF Instructor: Dr. Mary T. Office: 33 Chemistry 577-2431 Lab: 20 Chemistry 577-0780 Office Hours: MWF 9:30A
FIRST EXAMINATION. Name: CHM 332
 ame: CM 332 FIRST EXAMIATI All answers should be written on the exam in the spaces provided. Clearly indicate your answers in the spaces provided; if I have to guess as to what or where your answer is,
ame: CM 332 FIRST EXAMIATI All answers should be written on the exam in the spaces provided. Clearly indicate your answers in the spaces provided; if I have to guess as to what or where your answer is,
Figure 1. Structures of compounds to be analyzed by IR.
 Experiment 4 IR Exercise Reading Assignment Mohrig Chapter 21 and watch IR videos online In this experiment, students will study the infrared (IR) spectra of compounds with different functional groups.
Experiment 4 IR Exercise Reading Assignment Mohrig Chapter 21 and watch IR videos online In this experiment, students will study the infrared (IR) spectra of compounds with different functional groups.
Study Time: You should plan to spend about 2 hours studying for each hour of class lecture.
 Mercyhurst College Organic Chemistry I ( Sec.1) Winter Term 2013 Chemistry 240 Dr. J. Williams (ex. 2386, 309 Zurn) Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry http://math.mercyhurst.edu/~jwilliams/ Lecture:
Mercyhurst College Organic Chemistry I ( Sec.1) Winter Term 2013 Chemistry 240 Dr. J. Williams (ex. 2386, 309 Zurn) Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry http://math.mercyhurst.edu/~jwilliams/ Lecture:
Don t Trust Atoms, they Make Up Everything High School Chemistry
 Don t Trust Atoms, they Make Up Everything High School Chemistry Grades: 9 th 12 th Day of Week: Thursday Time of Class: 1:00 pm 2:30 pm EST Length of Class: 30 weeks Semester: Fall 2019, Winter 2020,
Don t Trust Atoms, they Make Up Everything High School Chemistry Grades: 9 th 12 th Day of Week: Thursday Time of Class: 1:00 pm 2:30 pm EST Length of Class: 30 weeks Semester: Fall 2019, Winter 2020,
Score: Homework Problem Set 9 Iverson CH320N Due Monday, April 17. NAME (Print): Chemistry 320N Dr. Brent Iverson 9th Homework April 10, 2017
 omework Problem Set 9 Iverson C0N Due Monday, April 7 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 0N Dr. ent Iverson 9th omework April 0, 07 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes
omework Problem Set 9 Iverson C0N Due Monday, April 7 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 0N Dr. ent Iverson 9th omework April 0, 07 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes
Enols and Enolates. A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl)
 Enols and Enolates A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl) E+ E In the preceding chapters, we primarily studied nucleophiles
Enols and Enolates A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl) E+ E In the preceding chapters, we primarily studied nucleophiles
CHEMISTRY 101 DETAILED WEEKLY TEXTBOOK HOMEWORK & READING SCHEDULE*
 CHEMISTRY 101 COURSE POLICIES 15 CHEMISTRY 101 DETAILED WEEKLY TEXTBOOK HOMEWORK & READING SCHEDULE* *Refer to textbook homework assignment and pre-lecture assignment for corresponding chapters to read.
CHEMISTRY 101 COURSE POLICIES 15 CHEMISTRY 101 DETAILED WEEKLY TEXTBOOK HOMEWORK & READING SCHEDULE* *Refer to textbook homework assignment and pre-lecture assignment for corresponding chapters to read.
Organic Chemistry Semester II 1st unit specialty reactions (mechanisms not emphasized)
 rganic Chemistry Semester II 1st unit specialty reactions (mechanisms not emphasized) 1. X addition to an alkyne powerful method to add halogens (Cl,, I) to an alkyne to create geminal dihalides (pages
rganic Chemistry Semester II 1st unit specialty reactions (mechanisms not emphasized) 1. X addition to an alkyne powerful method to add halogens (Cl,, I) to an alkyne to create geminal dihalides (pages
CHEMISTRY Organic Chemistry Laboratory II Spring 2019 Lab #1: Oxidation of Alcohols to Ketones - Borneol Oxidation (2 weeks)
 CHEMISTRY 244 - Organic Chemistry Laboratory II Spring 2019 Lab #1: Oxidation of Alcohols to Ketones - Borneol Oxidation (2 weeks) Purpose. In this lab you will learn about oxidation reactions in organic
CHEMISTRY 244 - Organic Chemistry Laboratory II Spring 2019 Lab #1: Oxidation of Alcohols to Ketones - Borneol Oxidation (2 weeks) Purpose. In this lab you will learn about oxidation reactions in organic
CHEMISTRY INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY
 BRAZOSPORT COLLEGE LAKE JACKSON, TEXAS SYLLABUS CHEMISTRY 1405 - INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY CATALOG DESCRIPTION: CHEM 1405 Introductory Chemistry. CIP 4005015103 A study of basic organic and inorganic chemistry
BRAZOSPORT COLLEGE LAKE JACKSON, TEXAS SYLLABUS CHEMISTRY 1405 - INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY CATALOG DESCRIPTION: CHEM 1405 Introductory Chemistry. CIP 4005015103 A study of basic organic and inorganic chemistry
Enolates, Enols, and Enamines Part 3
 Enolates, Enols, and Enamines Part 3 Guanine Tautomerize 2 2 Thymine C 3 Tautomerize C 3 Thursday March 21, 8:00-11:00 AM Final Exam Topics Part A: Carbonyl Fundamentals Carbonyl Survey Enolates, Enols,
Enolates, Enols, and Enamines Part 3 Guanine Tautomerize 2 2 Thymine C 3 Tautomerize C 3 Thursday March 21, 8:00-11:00 AM Final Exam Topics Part A: Carbonyl Fundamentals Carbonyl Survey Enolates, Enols,
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 2
 Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 2 Thursday, March 12, 2015; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out of
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 2 Thursday, March 12, 2015; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out of
Chapter 22 Enols and Enolates
 Chapter Enols and Enolates Acidity of the α hydrogen o The position next door to a carbonyl is called the α position o When an α proton is abstracted, the resulting carbanion is resonancestabilized. This
Chapter Enols and Enolates Acidity of the α hydrogen o The position next door to a carbonyl is called the α position o When an α proton is abstracted, the resulting carbanion is resonancestabilized. This
Course Syllabus. Department: Science & Technology. Date: April I. Course Prefix and Number: CHM 212. Course Name: Organic Chemistry II
 Department: Science & Technology Date: April 2012 I. Course Prefix and Number: CHM 212 Course Name: Organic Chemistry II Course Syllabus Credit Hours and Contact Hours: 5 credit hours and 7 (3:3:1) contact
Department: Science & Technology Date: April 2012 I. Course Prefix and Number: CHM 212 Course Name: Organic Chemistry II Course Syllabus Credit Hours and Contact Hours: 5 credit hours and 7 (3:3:1) contact
Chapter 19. Organic Chemistry. Carbonyl Compounds III. Reactions at the a-carbon. 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice
 Organic Chemistry 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 19 Carbonyl Compounds III Reactions at the a-carbon Disampaikan oleh: Dr. Sri Handayani 2013 Irene Lee Case Western Reserve University Cleveland,
Organic Chemistry 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 19 Carbonyl Compounds III Reactions at the a-carbon Disampaikan oleh: Dr. Sri Handayani 2013 Irene Lee Case Western Reserve University Cleveland,
Modern Organic Synthesis an Introduction
 Modern Organic Synthesis an Introduction G. S. Zweifel M. H. Nantz W.H. Freeman and Company Chapter 1 Synthetic Design 1 What is an ideal or viable synthesis, and how does one approach a synthetic project?
Modern Organic Synthesis an Introduction G. S. Zweifel M. H. Nantz W.H. Freeman and Company Chapter 1 Synthetic Design 1 What is an ideal or viable synthesis, and how does one approach a synthetic project?
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School
 COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II CHM 4251 5 Credit Hours Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in the sophomore
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II CHM 4251 5 Credit Hours Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in the sophomore
CHEM Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (quiz) W25
 CHEM 2425. Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (quiz) W25 Student: 1. Which of the following statements about Aldol reactions with either aldehydes or ketones is true? Equilibrium favors the starting
CHEM 2425. Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (quiz) W25 Student: 1. Which of the following statements about Aldol reactions with either aldehydes or ketones is true? Equilibrium favors the starting
WITTIG REACTION. Solo Experiment 2 Individual Lab Report (due at 12:00 pm one week after the lab is performed)
 WITTIG REACTION Solo Experiment 2 Individual Lab Report (due at 2:00 pm one week after the lab is performed) Last Name: Atique First Name: Anika TA Name: Davin Date Lab Performed: 2/26/204 Date Lab Submitted:
WITTIG REACTION Solo Experiment 2 Individual Lab Report (due at 2:00 pm one week after the lab is performed) Last Name: Atique First Name: Anika TA Name: Davin Date Lab Performed: 2/26/204 Date Lab Submitted:
CHEM*2700 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (Winter Semester 2007) Information Sheet and Course Outline-Revised
 CHEM*2700 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (Winter Semester 2007) Information Sheet and Course Outline-Revised Instructor: Professor William Tam Office: MacN 332 Phone: 824-4120 (Ext.52268) E-mail: wtam@uoguelph.ca
CHEM*2700 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (Winter Semester 2007) Information Sheet and Course Outline-Revised Instructor: Professor William Tam Office: MacN 332 Phone: 824-4120 (Ext.52268) E-mail: wtam@uoguelph.ca
KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II
 KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II Course Objectives: 1) To introduce the chemistry of alcohols and ethers. 2) To study the chemistry of functional groups. 3) To learn the chemistry of aromatic compounds and
KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II Course Objectives: 1) To introduce the chemistry of alcohols and ethers. 2) To study the chemistry of functional groups. 3) To learn the chemistry of aromatic compounds and
CHEM 344 Fall 2015 Final Exam (100 pts)
 CHEM 344 Fall 2015 Final Exam (100 pts) Name: TA Name: DO NOT REMOVE ANY PAGES FROM THIS EXAM PACKET. Have a swell winter break. Directions for drawing molecules, reactions, and electron-pushing mechanisms:
CHEM 344 Fall 2015 Final Exam (100 pts) Name: TA Name: DO NOT REMOVE ANY PAGES FROM THIS EXAM PACKET. Have a swell winter break. Directions for drawing molecules, reactions, and electron-pushing mechanisms:
