13.3. Lesson 13.3 The Nature of Solids. Overview
|
|
|
- Hilda Scott
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 13.3 Lesson 13.3 The Nature of Solids Objectives Describe how the structure and properties of solids are related Identify the factors that determine the shape of a crystal. Lesson Links Ch. 13 Lab 21: Allotropic Forms of Sulfur Ch. 13 Core TR: Section 3 Review Chapter 13 Online Student Edition Ch. 13 Concepts in Action: Brick and Mortar Crystal Palaces 13.3 Lesson Overview (PowerPoint file) Study WB Chapter 13 Lesson 3 Overview/Materials Overview In this lesson you will teach students the relationships between the structure of a solid and its properties such as melting point and freezing point. You will also cover how crystal structures are determined. Classroom Materials Standard 1 Block 0.5 Crystal Structure and Unit Cells: samples of wallpaper with repeating patterns, dishwashing detergent, watch glass, overhead projector, drinking straw Standard There are no items. Chemistry & You Engage Have students read the Chemistry & You feature on p Chapter 13 Online Student Edition page 1 of 5
2 Ask What do the number of bonds and bond angles between carbons in fullerenes suggest about its structure? (Some of the carbons are connected by double bonds.) Explain that the double bonds partially explain the strength of the nanotubes. Tell students that they will discover the rest of the explanation as they proceed with the lesson. Activate Prior Knowledge Engage Assess students' knowledge of types of compounds by asking them to compare the structures of molecular and ionic compounds. (Ionic compounds are composed of ions and are usually formed from a metal and a nonmetal. Molecular compounds are composed of molecules formed from two or more nonmetallic elements.) A Model for Solids Explain Explain that this is the third state of matter students will study. Review the kinetic theory and models for liquids and gases introduced in Lessons 13.1 and Have students relate the motion of particles within a gas and liquid to those in a solid. Ask How do the motions and interactions of particles in a solid relate to the melting point of that solid? (Within a solid, the particles are constantly vibrating around a somewhat fixed position. As their kinetic energy increases, so do these vibrations until the particles are no longer in fixed positions and the solid melts.) Compare the melting of a solid with the boiling of a liquid. page 2 of 5
3 Crystal Structure and Unit Cells Explore Use two simple demonstrations to explore analogies for the crystal lattice in solids. Wallpaper patterns often consist of a small group of images that are repeated to obtain the overall effect. The group of images is like a unit cell in a crystal lattice. Show students samples of wallpaper with repeating patterns. Ask students to identify the "unit cells" in the wallpaper samples. Show students how to obtain a set of " lattice points" by choosing the same point in each unit of the repeating pattern. The collection of lattice points shows the fundamental arrangement of the units in the pattern. Ask students if they could arrange the components of each unit differently to produce a different "unit cell." You can use an aqueous solution of detergent to make a model of a crystalline solid. Place the solution in a watch glass on an overhead projector and use a straw to blow bubbles into the solution. The bubbles form a regular, repeating pattern that is analogous to the arrangement of unit cells in a crystalline solid. Materials: samples of wallpaper with repeating patterns, dishwashing detergent, watch glass, overhead projector, drinking straw Crystal Structure and Unit Cells Explain Review basic geometric concepts of threedimensional solids prior to introducing Figure (Figure 13.12_part1, Figure 13.12_part2, Figure 13.12_part3, Figure 13.12_part4, Figure 13.12_part5, Figure 13.12_part6, Figure 13.12_part7, and Figure 13.12_part8). Explain that the properties of the crystals shown in the diagram are based on their geometric construction. Have students describe how a higher degree of organization and stronger intermolecular attractions between particles distinguish solids from gases and liquids. Figure 13.12, part 1 Figure 13.12, part 2 Figure 13.12, part 3 Figure 13.12, part 4 Figure 13.12, part 5 Figure 13.12, part 6 Figure 13.12, part 7 Figure 13.12, part 8 Ask students to determine if any elements besides carbon exist in different allotropic forms. (Elemental oxygen occurs as O2 and page 3 of 5
4 O3, both of which are gases; sulfur can exist as monoclinic or orthorhombic crystals; phosphorus can exist as red or white phosphorus, which are solids at room temperature.) Have students complete the Ch. 13 Concepts in Action: Brick and Mortar Crystal Palaces on PearsonChem.com. Crystal Structure and Unit Cells Extend Explain that scientists can manipulate the crystal structure of various materials to improve certain physical properties. Note that one such method is the production of alloys such as steel, as discussed in Lesson 7.4. Another method is the production of semi-conductors, which led to the development of many important advances in electronics. Have students research the history, structure and uses of key semi-conductors in today's electronics, and report their findings to the class. Assess and Remeditate Evaluate Ask students to describe orally, or in paragraph form, the distinguishing characteristics of crystalline solids and amorphous solids. (Crystalline solids are characterized by an orderly, repeating threedimensional arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules. All crystals have a regular shape that reflects the arrangement of particles in the solid. Amorphous solids lack a well-defined arrangement of particles.) Chapter 13 Online Student Edition Then direct students to complete the 13.3 Lesson Check. Remediate Describe how a higher degree of organization and stronger intermolecular attractions between particles distinguishes solids from gases and liquids. Have students consider how these factors are related to the ability of solids to retain their shape without a container. page 4 of 5
5 Differentiated Instruction Less Proficient Readers Have students create a concept map centered around the term solid. Their maps should highlight the relationship between solids and crystals and amorphous solids. Students should determine where unit cells, allotropes, and amorphous solids fit into their concept map. Ch. 13 Core TR: Section 3 Review Special Needs Students Explain that morphing is a special effect used in films or videos to change the shape or form of an object. Have physically impaired students go online to find an example of morphing. Have them compare their example of morphing to an amorphous solid. Allow class time for them to share their findings. Advanced Students Have students do research on the crystalline structure and formation of natural, synthetic, and simulated diamonds. Have students write a short paper comparing the three kinds of crystalline structures. Focus on ELL Comprehensible Input Briefly review what students learned about crystalline structure with respect to coordinate numbers in ionic crystals and atom arrangement in metallic crystals (see Lessons 7.2 and 7.3). Then preview Figure and 13.13, pointing out the connections to the concepts from Chapter 7. Study WB Chapter 13 Lesson 3 Ch. 13 Core TR: Section 3 Review Figure Figure My Notes Homework page 5 of 5
13.4. Lesson 13.4 Changes of State. Overview
 13.4 Lesson 13.4 Changes of State Objectives 13.4.1 Identify the conditions necessary for sublimation. 13.4.2 Determine how the conditions at which phases are in equilibrium are represented on a phase
13.4 Lesson 13.4 Changes of State Objectives 13.4.1 Identify the conditions necessary for sublimation. 13.4.2 Determine how the conditions at which phases are in equilibrium are represented on a phase
22.3. Lesson 22.3 Isomers. Overview
 22.3 Lesson 22.3 Isomers Objectives 22.3.1 Explain how the properties of constitutional isomers differ. 22.3.2 Identify two types of stereoisomers. Lesson Links Ch. 22 Core TR: Section 3 Review Ch. 22
22.3 Lesson 22.3 Isomers Objectives 22.3.1 Explain how the properties of constitutional isomers differ. 22.3.2 Identify two types of stereoisomers. Lesson Links Ch. 22 Core TR: Section 3 Review Ch. 22
Lesson Links. In this lesson, you will cover the topics of using Hess's Law to find the heat of reaction and the standard heat of formation.
 17.4 Lesson 17.4 Calculating Heats of Reaction Objectives 17.4.1 Identify two ways that the heat of reaction can be determined when it cannot be directly measured. Lesson Links Ch. 17 Lab 35: Heats of
17.4 Lesson 17.4 Calculating Heats of Reaction Objectives 17.4.1 Identify two ways that the heat of reaction can be determined when it cannot be directly measured. Lesson Links Ch. 17 Lab 35: Heats of
Lesson 9.5 The Laws Governing How Compounds Form
 9.5 Lesson 9.5 The Laws Governing How Compounds Form Objectives 9.5.1 how the law of definite proportions is consistent with Dalton's atomic theory. 9.5.2 List the general guidelines that can help you
9.5 Lesson 9.5 The Laws Governing How Compounds Form Objectives 9.5.1 how the law of definite proportions is consistent with Dalton's atomic theory. 9.5.2 List the general guidelines that can help you
4.2. Lesson 4.2 Structure of the Nuclear Atom. Overview
 4.2 Lesson 4.2 Structure of the Nuclear Atom Objectives 4.2.1 Identify three types of subatomic particles. 4.2.2 Describe the structure of atoms according to the Rutherford atomic model. Lesson Links Ch.
4.2 Lesson 4.2 Structure of the Nuclear Atom Objectives 4.2.1 Identify three types of subatomic particles. 4.2.2 Describe the structure of atoms according to the Rutherford atomic model. Lesson Links Ch.
Lesson 9.3 Naming and Writing Formulas for Molecular Compounds
 9.3 Lesson 9.3 Naming and Writing Formulas for Molecular Compounds Objectives 9.3.1 Apply the rules for naming and writing formulas for binary molecular compounds. Lesson Links Ch. 9 Core TR: Section 3
9.3 Lesson 9.3 Naming and Writing Formulas for Molecular Compounds Objectives 9.3.1 Apply the rules for naming and writing formulas for binary molecular compounds. Lesson Links Ch. 9 Core TR: Section 3
Liquids & Solids: Section 12.3
 Liquids & Solids: Section 12.3 MAIN IDEA: The particles in and have a range of motion and are not easily. Why is it more difficult to pour syrup that is stored in the refrigerator than in the cabinet?
Liquids & Solids: Section 12.3 MAIN IDEA: The particles in and have a range of motion and are not easily. Why is it more difficult to pour syrup that is stored in the refrigerator than in the cabinet?
4.2.1 Chemical bonds, ionic, covalent and metallic
 4.2 Bonding, structure, and the properties of matter Chemists use theories of structure and bonding to explain the physical and chemical properties of materials. Analysis of structures shows that atoms
4.2 Bonding, structure, and the properties of matter Chemists use theories of structure and bonding to explain the physical and chemical properties of materials. Analysis of structures shows that atoms
The Liquid and Solid States
 : The Liquid and Solid States 10-1 10.1 Changes of State How do solids, liquids and gases differ? Figure 10.4 10-2 1 10.1 Changes of State : transitions between physical states Vaporization/Condensation
: The Liquid and Solid States 10-1 10.1 Changes of State How do solids, liquids and gases differ? Figure 10.4 10-2 1 10.1 Changes of State : transitions between physical states Vaporization/Condensation
Chemistry States of Matter Lesson 9 Lesson Plan David V. Fansler
 Chemistry States of Matter Lesson 9 Lesson Plan David V. Fansler States of Matter The Nature of Gases Objectives: Describe the motion of gas particles according to the kinetic theory; Interpret gas pressure
Chemistry States of Matter Lesson 9 Lesson Plan David V. Fansler States of Matter The Nature of Gases Objectives: Describe the motion of gas particles according to the kinetic theory; Interpret gas pressure
Chapter 10. Lesson Starter. Why did you not smell the odor of the vapor immediately? Explain this event in terms of the motion of molecules.
 Preview Lesson Starter Objectives The Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases The Kinetic-Molecular Theory and the Nature of Gases Deviations of Real Gases from Ideal Behavior Section 1 The Kinetic-Molecular
Preview Lesson Starter Objectives The Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases The Kinetic-Molecular Theory and the Nature of Gases Deviations of Real Gases from Ideal Behavior Section 1 The Kinetic-Molecular
Chapter 10 States of Matter
 Chapter 10 States of Matter 1 Section 10.1 The Nature of Gases Objectives: Describe the assumptions of the kinetic theory as it applies to gases. Interpret gas pressure in terms of kinetic theory. Define
Chapter 10 States of Matter 1 Section 10.1 The Nature of Gases Objectives: Describe the assumptions of the kinetic theory as it applies to gases. Interpret gas pressure in terms of kinetic theory. Define
The Liquid and Solid States
 : The Liquid and Solid States 10-1 10.1 Changes of State How do solids, liquids and gases differ? Figure 10.4 10-2 10.1 Changes of State : transitions between physical states Vaporization/Condensation
: The Liquid and Solid States 10-1 10.1 Changes of State How do solids, liquids and gases differ? Figure 10.4 10-2 10.1 Changes of State : transitions between physical states Vaporization/Condensation
The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS)
 The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) CHAPTER 2, LESSON 1 HEAT, TEMPERATURE, AND CONDUCTION MS-PS1-4. Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state
The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) CHAPTER 2, LESSON 1 HEAT, TEMPERATURE, AND CONDUCTION MS-PS1-4. Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state
Chapter 8 Notes. Covalent Bonding
 Chapter 8 Notes Covalent Bonding Molecules and Molecular Compounds Helium and Neon are monoatomic, meaning they exist as single atoms Some compounds exist as crystalline solids, such as NaCl Others exist
Chapter 8 Notes Covalent Bonding Molecules and Molecular Compounds Helium and Neon are monoatomic, meaning they exist as single atoms Some compounds exist as crystalline solids, such as NaCl Others exist
4.2 Bonding, structure, and the properties of matter
 4.2 Bonding, structure, and the properties of matter Chemists use theories of structure and bonding to explain the physical and chemical properties of materials. Analysis of structures shows that atoms
4.2 Bonding, structure, and the properties of matter Chemists use theories of structure and bonding to explain the physical and chemical properties of materials. Analysis of structures shows that atoms
The particles in a solid hold relatively fixed positions.
 Section 3 Solids Key Terms crystalline solid melting crystal structure crystal melting point unit cell amorphous solid supercooled liquid The common expression solid as a rock suggests something that is
Section 3 Solids Key Terms crystalline solid melting crystal structure crystal melting point unit cell amorphous solid supercooled liquid The common expression solid as a rock suggests something that is
GRADE 10A: Chemistry 1. UNIT 10AC.1 11 hours. Structure and bonding in matter. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning.
 GRADE 10A: Chemistry 1 Structure and bonding in matter UNIT 10AC.1 11 hours About this unit This unit is the first of six units on chemistry for Grade 10 advanced. The unit is designed to guide your planning
GRADE 10A: Chemistry 1 Structure and bonding in matter UNIT 10AC.1 11 hours About this unit This unit is the first of six units on chemistry for Grade 10 advanced. The unit is designed to guide your planning
11.2. Lesson Types of Chemical Reactions. Overview
 11.2 Lesson 11. 2 Types of Chemical Reactions Objectives 11.2.1 Identify the five general types of reactions. Lesson Links Ch. 11 Lab 14: Types of Chemical Reactions Ch. 11 Lab 15: Reactivity of Metals
11.2 Lesson 11. 2 Types of Chemical Reactions Objectives 11.2.1 Identify the five general types of reactions. Lesson Links Ch. 11 Lab 14: Types of Chemical Reactions Ch. 11 Lab 15: Reactivity of Metals
Chapter 7: Ionic Compounds and Metals
 Chapter 7: Ionic Compounds and Metals Section 7.1 Section 7.2 Section 7.3 Section 7.4 Ion Formation Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds Names and Formulas for Ionic Compounds Metallic Bonds and the Properties
Chapter 7: Ionic Compounds and Metals Section 7.1 Section 7.2 Section 7.3 Section 7.4 Ion Formation Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds Names and Formulas for Ionic Compounds Metallic Bonds and the Properties
Chem 1075 Chapter 13 Liquids and Solids Lecture Outline
 Chem 1075 Chapter 13 Liquids and Solids Lecture Outline Slide 2-3 Properties of Liquids Unlike gases, liquids respond dramatically to temperature and pressure changes. We can study the liquid state and
Chem 1075 Chapter 13 Liquids and Solids Lecture Outline Slide 2-3 Properties of Liquids Unlike gases, liquids respond dramatically to temperature and pressure changes. We can study the liquid state and
States of Matter Chapter 10 Assignment & Problem Set
 States of Matter Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. States of Matter 2 Study Guide: Things You Must Know Vocabulary (know the definition
States of Matter Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. States of Matter 2 Study Guide: Things You Must Know Vocabulary (know the definition
Chapter 22 States of matter. Section 1 matter Section 2 Changes of State
 Chapter 22 States of matter Section 1 matter Section 2 Changes of State States of Matter is a physical property ***Matter is made of atoms Atoms form chemical bonds to make matter **** Atoms vibrate constantly
Chapter 22 States of matter Section 1 matter Section 2 Changes of State States of Matter is a physical property ***Matter is made of atoms Atoms form chemical bonds to make matter **** Atoms vibrate constantly
Name Date Class THE NATURE OF GASES
 13.1 THE NATURE OF GASES Section Review Objectives Describe the assumptions of the kinetic theory as it applies to gases Interpret gas pressure in terms of kinetic theory Define the relationship between
13.1 THE NATURE OF GASES Section Review Objectives Describe the assumptions of the kinetic theory as it applies to gases Interpret gas pressure in terms of kinetic theory Define the relationship between
Week 11/Th: Lecture Units 28 & 29
 Week 11/Th: Lecture Units 28 & 29 Unit 27: Real Gases Unit 28: Intermolecular forces -- types of forces between molecules -- examples Unit 29: Crystal Structure -- lattice types -- unit cells -- simple
Week 11/Th: Lecture Units 28 & 29 Unit 27: Real Gases Unit 28: Intermolecular forces -- types of forces between molecules -- examples Unit 29: Crystal Structure -- lattice types -- unit cells -- simple
Chapter 10. The Liquid and Solid States. Introduction. Chapter 10 Topics. Liquid-Gas Phase Changes. Physical State of a Substance
 Introduction Chapter 10 The Liquid and Solid States How do the properties of liquid and solid substances differ? How can we predict properties based on molecular- level structure? Glasses Wires Reshaping
Introduction Chapter 10 The Liquid and Solid States How do the properties of liquid and solid substances differ? How can we predict properties based on molecular- level structure? Glasses Wires Reshaping
C2 Quick Revision Questions. C2 for AQA GCSE examination 2018 onwards
 C2 Quick Revision Questions Question 1... of 50 What are the 3 main types of chemical bond? Answer 1... of 50 Ionic, Covalent & Metallic. Question 2... of 50 What force bonds atoms in an ionic bond? Answer
C2 Quick Revision Questions Question 1... of 50 What are the 3 main types of chemical bond? Answer 1... of 50 Ionic, Covalent & Metallic. Question 2... of 50 What force bonds atoms in an ionic bond? Answer
CHAPTER 13. States of Matter. Kinetic = motion. Polar vs. Nonpolar. Gases. Hon Chem 13.notebook
 CHAPTER 13 States of Matter States that the tiny particles in all forms of matter are in constant motion. Kinetic = motion A gas is composed of particles, usually molecules or atoms, with negligible volume
CHAPTER 13 States of Matter States that the tiny particles in all forms of matter are in constant motion. Kinetic = motion A gas is composed of particles, usually molecules or atoms, with negligible volume
Unit 5: Bonding. Place a checkmark next to each item that you can do. If a sample problem is given, complete it as evidence.
 Unit 5: Bonding Place a checkmark next to each item that you can do. If a sample problem is given, complete it as evidence. Intramolecular Forces: forces of attraction within the same molecule. Examples:
Unit 5: Bonding Place a checkmark next to each item that you can do. If a sample problem is given, complete it as evidence. Intramolecular Forces: forces of attraction within the same molecule. Examples:
Chemistry Day 5. Friday, August 31 st Tuesday, September 4 th, 2018
 Chemistry Day 5 Friday, August 31 st Tuesday, September 4 th, 2018 Do-Now Title: BrainPOP: States of Matter 1. Write down today s FLT 2. List two examples of gases 3. List two examples of things that are
Chemistry Day 5 Friday, August 31 st Tuesday, September 4 th, 2018 Do-Now Title: BrainPOP: States of Matter 1. Write down today s FLT 2. List two examples of gases 3. List two examples of things that are
Scientists learned that elements in same group on PT react in a similar way. Why?
 Unit 5: Bonding Scientists learned that elements in same group on PT react in a similar way Why? They all have the same number of valence electrons.which are electrons in the highest occupied energy level
Unit 5: Bonding Scientists learned that elements in same group on PT react in a similar way Why? They all have the same number of valence electrons.which are electrons in the highest occupied energy level
Chemistry 101 Chapter 14 Liquids & Solids
 Chemistry 101 Chapter 14 Liquids & Solids States of matter: the physical state of matter depends on a balance between the kinetic energy of particles, which tends to keep them apart, and the attractive
Chemistry 101 Chapter 14 Liquids & Solids States of matter: the physical state of matter depends on a balance between the kinetic energy of particles, which tends to keep them apart, and the attractive
Chapter 13 - States of Matter. Section 13.1 The nature of Gases
 Chapter 13 - States of Matter Section 13.1 The nature of Gases Kinetic energy and gases Kinetic energy: the energy an object has because of its motion Kinetic theory: all matter is made if particles in
Chapter 13 - States of Matter Section 13.1 The nature of Gases Kinetic energy and gases Kinetic energy: the energy an object has because of its motion Kinetic theory: all matter is made if particles in
IV. How are Atoms held together in a Covalent Bond? (Lesson 3 pages )
 IV. How are Atoms held together in a Covalent Bond? (Lesson 3 pages 139-140) A. Covalent Bond: chemical bond formed when 2 atoms share electrons (e - ) between two or more non-metals B. Electron Sharing
IV. How are Atoms held together in a Covalent Bond? (Lesson 3 pages 139-140) A. Covalent Bond: chemical bond formed when 2 atoms share electrons (e - ) between two or more non-metals B. Electron Sharing
The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS)
 The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) CHAPTER 1, LESSON 1 MOLECULES MATTER MS-PS1-4. Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance
The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) CHAPTER 1, LESSON 1 MOLECULES MATTER MS-PS1-4. Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance
Matter. Gas. Solid Liquid. Both shape and volume are not fixed. It has a fixed shape and a fixed volume.
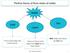 Matter Solid Liquid Gas It has a fixed shape and a fixed volume. It does not have a fixed shape, but it does have a fixed volume. Both shape and volume are not fixed. Felix Yung and John Polias 1 Matter
Matter Solid Liquid Gas It has a fixed shape and a fixed volume. It does not have a fixed shape, but it does have a fixed volume. Both shape and volume are not fixed. Felix Yung and John Polias 1 Matter
Structure of Crystalline Solids
 Structure of Crystalline Solids Solids- Effect of IMF s on Phase Kinetic energy overcome by intermolecular forces C 60 molecule llotropes of Carbon Network-Covalent solid Molecular solid Does not flow
Structure of Crystalline Solids Solids- Effect of IMF s on Phase Kinetic energy overcome by intermolecular forces C 60 molecule llotropes of Carbon Network-Covalent solid Molecular solid Does not flow
States of Matter. Reviewing Vocabulary. Match the definition in Column A with the term in Column B.
 Name Date Class States of Matter Reviewing Vocabulary Match the definition in Column A with the term in Column B. Column A 1. A measure of the resistance of a liquid to flow 2. The energy required to increase
Name Date Class States of Matter Reviewing Vocabulary Match the definition in Column A with the term in Column B. Column A 1. A measure of the resistance of a liquid to flow 2. The energy required to increase
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change. Chapter 12: States of Matter
 CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Chapter 12: States of Matter CHAPTER 12 States of Matter Section 12.1 Section 12.2 Section 12.3 Section 12.4 Gases Forces of Attraction Liquids and Solids Phase Changes Click
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change Chapter 12: States of Matter CHAPTER 12 States of Matter Section 12.1 Section 12.2 Section 12.3 Section 12.4 Gases Forces of Attraction Liquids and Solids Phase Changes Click
Week 13 MO Theory, Solids, & metals
 Week 13 MO Theory, Solids, & metals Q UEST IO N 1 Using the molecular orbital energy diagrams below, which one of the following diatomic molecules is LEAST likely to exist? A. Li2 B. Be2 C. B2 D. C2 E.
Week 13 MO Theory, Solids, & metals Q UEST IO N 1 Using the molecular orbital energy diagrams below, which one of the following diatomic molecules is LEAST likely to exist? A. Li2 B. Be2 C. B2 D. C2 E.
4.2 Bonding, structure and the properties of matter. GCSE Chemistry
 4.2 Bonding, structure and the properties of matter GCSE Chemistry 4.2.1 Chemical bonds, ionic, covalent and metallic There are three types of strong chemical bond ionic, covalent and metallic. There are
4.2 Bonding, structure and the properties of matter GCSE Chemistry 4.2.1 Chemical bonds, ionic, covalent and metallic There are three types of strong chemical bond ionic, covalent and metallic. There are
UNIT 14 IMFs, LIQUIDS, SOLIDS PACKET. Name: Date: Period: #: BONDING & INTERMOLECULAR FORCES
 Name: Date: Period: #: BONDING & INTERMOLECULAR FORCES p. 1 Name: Date: Period: #: IMF NOTES van der Waals forces: weak attractive forces between molecules. There are 3 types: 1. London Dispersion Forces
Name: Date: Period: #: BONDING & INTERMOLECULAR FORCES p. 1 Name: Date: Period: #: IMF NOTES van der Waals forces: weak attractive forces between molecules. There are 3 types: 1. London Dispersion Forces
Chapter 14. Liquids and Solids
 Chapter 14 Liquids and Solids Section 14.1 Water and Its Phase Changes Reviewing What We Know Gases Low density Highly compressible Fill container Solids High density Slightly compressible Rigid (keeps
Chapter 14 Liquids and Solids Section 14.1 Water and Its Phase Changes Reviewing What We Know Gases Low density Highly compressible Fill container Solids High density Slightly compressible Rigid (keeps
2 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
 Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding 8.1 What information does a molecular formula provide? 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding 8.3 Bonding Theories 8.4 Polar Bonds and Molecules 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc.,
Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding 8.1 What information does a molecular formula provide? 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding 8.3 Bonding Theories 8.4 Polar Bonds and Molecules 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc.,
Unit 3: Chemical Bonding. Section 1: Bond Types and Properties
 Unit 3: Chemical Bonding Section 1: Bond Types and Properties Chemical Bonds Chemical Bond force that holds atoms or ions together to make a molecule or other chemical structure Molecule - two or more
Unit 3: Chemical Bonding Section 1: Bond Types and Properties Chemical Bonds Chemical Bond force that holds atoms or ions together to make a molecule or other chemical structure Molecule - two or more
The OTHER TWO states of matter
 ` The OTHER TWO states of matter LIQUIDS A decrease in the average kinetic energy of gas particles causes the temperature to decrease. As it cools, the particles tend to move more slowly if they slow down
` The OTHER TWO states of matter LIQUIDS A decrease in the average kinetic energy of gas particles causes the temperature to decrease. As it cools, the particles tend to move more slowly if they slow down
Chapter 7 Ionic And Metallic Bonding Answer Key Pearson Education
 Chapter 7 Ionic And Metallic Bonding Answer Key Pearson Education CHAPTER 7 IONIC AND METALLIC BONDING ANSWER KEY PEARSON EDUCATION PDF - Are you looking for chapter 7 ionic and metallic bonding answer
Chapter 7 Ionic And Metallic Bonding Answer Key Pearson Education CHAPTER 7 IONIC AND METALLIC BONDING ANSWER KEY PEARSON EDUCATION PDF - Are you looking for chapter 7 ionic and metallic bonding answer
Classification of Matter. States of Matter Physical and Chemical Properties Physical and Chemical Changes
 1 Classification of Matter States of Matter Physical and Chemical Properties Physical and Chemical Changes 2 Classification of Matter Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. We can classify
1 Classification of Matter States of Matter Physical and Chemical Properties Physical and Chemical Changes 2 Classification of Matter Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. We can classify
States of Matter. Solids Liquids Gases
 States of Matter Solids Liquids Gases 1 Solid vs. Liquid vs. Gas Depends on only two things: What? Attractions Kinetic between particles vs Energy of particles 2 Intermolecular Forces (Molecular Attractions)
States of Matter Solids Liquids Gases 1 Solid vs. Liquid vs. Gas Depends on only two things: What? Attractions Kinetic between particles vs Energy of particles 2 Intermolecular Forces (Molecular Attractions)
A Correlation of. to the. Georgia Standards of Excellence Chemistry
 A Correlation of to the A Correlation of Pearson Introduction The following document demonstrates how Pearson supports the Georgia Standards for Excellence in. Correlation references are to the Student
A Correlation of to the A Correlation of Pearson Introduction The following document demonstrates how Pearson supports the Georgia Standards for Excellence in. Correlation references are to the Student
Allotropes of Carbon Student Study Guide
 Allotropes of Carbon Student Study Guide Name In this lesson you will examine some materials that are composed only of the element carbon. You will be provided models, labeled for identification, as model
Allotropes of Carbon Student Study Guide Name In this lesson you will examine some materials that are composed only of the element carbon. You will be provided models, labeled for identification, as model
Notes: Unit 2: Matter
 Name: Regents Chemistry: Notes: Unit 2: Matter Key Ideas 1. Matter is classified as a pure substance or as a mixture of substances. (3.1q) 2. The three phases of matter (solids, liquids, and gases) have
Name: Regents Chemistry: Notes: Unit 2: Matter Key Ideas 1. Matter is classified as a pure substance or as a mixture of substances. (3.1q) 2. The three phases of matter (solids, liquids, and gases) have
Ionic and Metallic Bonding
 Ionic and Metallic Bonding 7.1 Ions BONDING AND INTERACTIONS Essential Understanding electrically charged. Ions form when atoms gain or lose valence electrons, becoming Lesson Summary Valence Electrons
Ionic and Metallic Bonding 7.1 Ions BONDING AND INTERACTIONS Essential Understanding electrically charged. Ions form when atoms gain or lose valence electrons, becoming Lesson Summary Valence Electrons
IONIC AND METALLIC BONDING
 Name IONIC AND METALLIC BONDING Chem 512 Homework rint this sheet, answer the questions and turn it in as a HARD COY A. Matching Match each description in Column B with the correct term in Column A. Write
Name IONIC AND METALLIC BONDING Chem 512 Homework rint this sheet, answer the questions and turn it in as a HARD COY A. Matching Match each description in Column B with the correct term in Column A. Write
Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page 1. Chemistry A States of Matter Packet
 Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page 1 Chemistry A States of Matter Packet Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page 2 Worksheet #1: States of Matter In this packet we will
Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page 1 Chemistry A States of Matter Packet Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page 2 Worksheet #1: States of Matter In this packet we will
Name Date Class STATES OF MATTER
 13 STATES OF MATTER Chapter Test A A. Matching Match each description in Column B with the correct term in Column A. Write the letter of the correct description on the line. Column A Column B 1. amorphous
13 STATES OF MATTER Chapter Test A A. Matching Match each description in Column B with the correct term in Column A. Write the letter of the correct description on the line. Column A Column B 1. amorphous
Chapter 3. Preview. Section 1 Three States of Matter. Section 2 Behavior of Gases. Section 3 Changes of State. States of Matter.
 States of Matter Preview Section 1 Three States of Matter Section 2 Behavior of Gases Section 3 Changes of State Concept Mapping Section 1 Three States of Matter Bellringer In the kitchen, you might find
States of Matter Preview Section 1 Three States of Matter Section 2 Behavior of Gases Section 3 Changes of State Concept Mapping Section 1 Three States of Matter Bellringer In the kitchen, you might find
NGSS DCI: Unit Lesson Plan Intermolecular (IM) Forces. Teacher: <Teacher> Time Frame: 9 days. Grade: 10 School: <School>
 Unit Lesson Plan Intermolecular (IM) Forces Teacher: Time Frame: 9 days Grade: 10 School: Subject: PSI Chemistry NGSS DCI: AP Standards: HS-PS1-3 Plan and conduct an investigation to
Unit Lesson Plan Intermolecular (IM) Forces Teacher: Time Frame: 9 days Grade: 10 School: Subject: PSI Chemistry NGSS DCI: AP Standards: HS-PS1-3 Plan and conduct an investigation to
States of Matter. Solids Liquids Gases
 States of Matter Solids Liquids Gases 1 Solid vs. Liquid vs. Gas Depends on only two things: What? Attractions Kinetic between particles vs Energy of particles 2 Intermolecular Forces (Molecular Attractions)
States of Matter Solids Liquids Gases 1 Solid vs. Liquid vs. Gas Depends on only two things: What? Attractions Kinetic between particles vs Energy of particles 2 Intermolecular Forces (Molecular Attractions)
Chapter 11. Kinetic Molecular Theory. Attractive Forces
 Chapter 11 KMT for Solids and Liquids Intermolecular Forces Viscosity & Surface Tension Phase Changes Vapor Pressure Phase Diagrams Solid Structure Kinetic Molecular Theory Liquids and solids will experience
Chapter 11 KMT for Solids and Liquids Intermolecular Forces Viscosity & Surface Tension Phase Changes Vapor Pressure Phase Diagrams Solid Structure Kinetic Molecular Theory Liquids and solids will experience
Question 2 Identify the phase transition that occurs when CO 2 solid turns to CO 2 gas as it is heated.
 For answers, send email to: admin@tutor-homework.com. Include file name: Chemistry_Worksheet_0039 Price: $4 (c) 2012 www.tutor-homework.com: Tutoring, homework help, help with online classes. Chapter 11
For answers, send email to: admin@tutor-homework.com. Include file name: Chemistry_Worksheet_0039 Price: $4 (c) 2012 www.tutor-homework.com: Tutoring, homework help, help with online classes. Chapter 11
CHEMISTRY 20 Formative Assessment Intermolecular Forces
 CHEMISTRY 20 Formative Assessment Intermolecular Forces RECORD ALL RESPONSES IN THIS QUESTION BOOK STUDENTS ARE TO KEEP QUESTION BOOK AND ANSWER KEY AS PART OF THEIR STUDY MATERIALS 1. The high surface
CHEMISTRY 20 Formative Assessment Intermolecular Forces RECORD ALL RESPONSES IN THIS QUESTION BOOK STUDENTS ARE TO KEEP QUESTION BOOK AND ANSWER KEY AS PART OF THEIR STUDY MATERIALS 1. The high surface
Valence Electrons. 1. The electrons responsible for the chemical properties of atoms, and are those in the outer energy level, the valence level.
 Valence Electrons 1. The electrons responsible for the chemical properties of atoms, and are those in the outer energy level, the valence level. 2. Electrons that make bonds are called valence electrons.
Valence Electrons 1. The electrons responsible for the chemical properties of atoms, and are those in the outer energy level, the valence level. 2. Electrons that make bonds are called valence electrons.
Critical Temperature - the temperature above which the liquid state of a substance no longer exists regardless of the pressure.
 Critical Temperature - the temperature above which the liquid state of a substance no longer exists regardless of the pressure. Critical Pressure - the vapor pressure at the critical temperature. Properties
Critical Temperature - the temperature above which the liquid state of a substance no longer exists regardless of the pressure. Critical Pressure - the vapor pressure at the critical temperature. Properties
Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding Learning Objectives Describe the formation of ions by electron loss/gain to obtain the electronic configuration of a noble gas. Describe the formation of ionic bonds between
Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding Learning Objectives Describe the formation of ions by electron loss/gain to obtain the electronic configuration of a noble gas. Describe the formation of ionic bonds between
Covalent Bonding. In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons
 In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
4 States of matter. N Goalby chemrevise.org 1. Ideal Gas Equation
 4 States of matter Ideal Gas Equation The ideal gas equation applies to all gases and mixtures of gases. If a mixture of gases is used the value n will be the total moles of all gases in the mixture. The
4 States of matter Ideal Gas Equation The ideal gas equation applies to all gases and mixtures of gases. If a mixture of gases is used the value n will be the total moles of all gases in the mixture. The
Solids. Adapted from a presentation by Dr. Schroeder, Wayne State University
 Solids Adapted from a presentation by Dr. Schroeder, Wayne State University Properties of Solids Definite shape, definite volume Particles are CLOSE together, so Attractive forces (bonds or IMF s) are
Solids Adapted from a presentation by Dr. Schroeder, Wayne State University Properties of Solids Definite shape, definite volume Particles are CLOSE together, so Attractive forces (bonds or IMF s) are
Name Date Class STATES OF MATTER. Match the correct state of matter with each description of water by writing a letter on each line.
 10 STATES OF MATTER SECTION 10.1 THE NATURE OF GASES (pages 267 272) This section describes how the kinetic theory applies to gases. It defines gas pressure and explains how temperature is related to the
10 STATES OF MATTER SECTION 10.1 THE NATURE OF GASES (pages 267 272) This section describes how the kinetic theory applies to gases. It defines gas pressure and explains how temperature is related to the
AP Chemistry Audit Syllabus Aubrey High School Teacher: Timothy Dean Mooney
 AP Chemistry Audit Syllabus Aubrey High School Teacher: Timothy Dean Mooney Textbook: Chemistry: A Molecular Approach AP Edition, 3 rd Edition, by Nivaldo J. Tro ( 2014) [CR1] Course Description: The purpose
AP Chemistry Audit Syllabus Aubrey High School Teacher: Timothy Dean Mooney Textbook: Chemistry: A Molecular Approach AP Edition, 3 rd Edition, by Nivaldo J. Tro ( 2014) [CR1] Course Description: The purpose
Covalent Bonding. In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons
 In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
THE PHASES OF MATTER. Solid: holds its shape and does not flow. The molecules in a solid vibrate in place, but on average, don t move very far.
 THE QUESTIONS What are the phases of matter? What makes these phases different from each other? What is the difference between melting, freezing, boiling and condensation? How do you interpret a Temperature
THE QUESTIONS What are the phases of matter? What makes these phases different from each other? What is the difference between melting, freezing, boiling and condensation? How do you interpret a Temperature
Chapter 2, Lesson 5: Changing State Melting
 Chapter 2, Lesson 5: Changing State Melting Key Concepts Melting is a process that causes a substance to change from a solid to a liquid. Melting occurs when the molecules of a solid speed up enough that
Chapter 2, Lesson 5: Changing State Melting Key Concepts Melting is a process that causes a substance to change from a solid to a liquid. Melting occurs when the molecules of a solid speed up enough that
Ch. 12 Section 1: Introduction to Chemical Bonding
 Name Period Date Chemical Bonding & Intermolecular Forces (Chapter 12, 13 &14) Fill-in the blanks during the PowerPoint presentation in class. Ch. 12 Section 1: Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical
Name Period Date Chemical Bonding & Intermolecular Forces (Chapter 12, 13 &14) Fill-in the blanks during the PowerPoint presentation in class. Ch. 12 Section 1: Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical
ionic or molecular? Ionic and Molecular Compounds
 ionic or molecular? Ionic and Molecular Compounds There are two major classes of compounds: Ionic compounds are formed by the attractions between oppositely charged ions. (metal + nonmetal or complex ion)
ionic or molecular? Ionic and Molecular Compounds There are two major classes of compounds: Ionic compounds are formed by the attractions between oppositely charged ions. (metal + nonmetal or complex ion)
Name: Period: ELEMENTS AND ATOMS Chapter 1. The Building Blocks of matter pages L6-11
 Name: Period: ELEMENTS AND ATOMS Chapter 1 The Building Blocks of matter pages L6-11 1. The simplest pure substances are called. 2. Why are elements often called the building blocks of matter? 3. Is the
Name: Period: ELEMENTS AND ATOMS Chapter 1 The Building Blocks of matter pages L6-11 1. The simplest pure substances are called. 2. Why are elements often called the building blocks of matter? 3. Is the
Chapter 13 States of Matter Forces of Attraction 13.3 Liquids and Solids 13.4 Phase Changes
 Chapter 13 States of Matter 13.2 Forces of Attraction 13.3 Liquids and Solids 13.4 Phase Changes I. Forces of Attraction (13.2) Intramolecular forces? (forces within) Covalent Bonds, Ionic Bonds, and metallic
Chapter 13 States of Matter 13.2 Forces of Attraction 13.3 Liquids and Solids 13.4 Phase Changes I. Forces of Attraction (13.2) Intramolecular forces? (forces within) Covalent Bonds, Ionic Bonds, and metallic
Chemistry Final Study Guide KEY. 3. Define physical changes. A change in any physical property of a substance, not in the substance itself.
 Chemistry Final Study Guide KEY Unit 2: Matter & Its Properties, Lesson 1: Physical and Chemical Properties & Changes 1. Define physical properties. The characteristics of a substance that can be observed
Chemistry Final Study Guide KEY Unit 2: Matter & Its Properties, Lesson 1: Physical and Chemical Properties & Changes 1. Define physical properties. The characteristics of a substance that can be observed
Part 4- Chemistry Paper 1 Bonding Knowledge Questions
 Part 4- Chemistry Paper 1 Bonding Knowledge Questions How bonding and structure are related to the properties of substances A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge
Part 4- Chemistry Paper 1 Bonding Knowledge Questions How bonding and structure are related to the properties of substances A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge
Chapter 8. Chapter 8. Preview. Bellringer. Chapter 8. Particles of Matter. Objectives. Chapter 8. Particles of Matter, continued
 States of Matter Preview Bellringer Section 2 Behavior of Gases In the kitchen, you might find three different forms of water. What are these three forms of water, and where exactly in the kitchen would
States of Matter Preview Bellringer Section 2 Behavior of Gases In the kitchen, you might find three different forms of water. What are these three forms of water, and where exactly in the kitchen would
Rationale: Phase diagrams are standard in all high school chemistry textbooks and therefore are considered prior knowledge.
 Big Idea 2: Chemical and physical properties of materials can be explained by the structure and the arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules and the forces between them. Material Covered (Y or N) and Location
Big Idea 2: Chemical and physical properties of materials can be explained by the structure and the arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules and the forces between them. Material Covered (Y or N) and Location
4 Discuss and evaluate the 5th state of matter. 3 - Differentiate among the four states of matter in terms of energy,
 Goal: Differentiate among the four states of matter in terms of energy, particle motion, and phase transitions. 4 States of Mater Sections 3.1, 3.2 4 Discuss and evaluate the 5 th state of matter. 3 -
Goal: Differentiate among the four states of matter in terms of energy, particle motion, and phase transitions. 4 States of Mater Sections 3.1, 3.2 4 Discuss and evaluate the 5 th state of matter. 3 -
Elements,Compounds and Mixtures
 BASIC CONCEPTS: Elements,s and s 1. The smallest fundamental particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of the element is called an atom. 2. A pure substance that cannot be split up into
BASIC CONCEPTS: Elements,s and s 1. The smallest fundamental particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of the element is called an atom. 2. A pure substance that cannot be split up into
Ch 6 Chemical Bonding
 Ch 6 Chemical Bonding What you should learn in this section (objectives): Define chemical bond Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds Describe ionic and covalent bonding Explain why most chemical bonding
Ch 6 Chemical Bonding What you should learn in this section (objectives): Define chemical bond Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds Describe ionic and covalent bonding Explain why most chemical bonding
SG 4 Elements and Chemical Bonds 5 States of Matter
 Name Date Period SG 4 Elements and Chemical Bonds 5 States of Matter 4.1 Electrons and Energy Levels Directions: On the line before each definition, write the term that matches it correctly. Each term
Name Date Period SG 4 Elements and Chemical Bonds 5 States of Matter 4.1 Electrons and Energy Levels Directions: On the line before each definition, write the term that matches it correctly. Each term
Learning Objectives: Visualize in three dimensions the structure of covalently-bonded compounds
 Covalent Bonds With all humility and mildness, with patience, support one another in charity. Careful to keep the unity of the Spirit in the bond of peace Ephesians 4:2-3 Introduction A covalent bond is
Covalent Bonds With all humility and mildness, with patience, support one another in charity. Careful to keep the unity of the Spirit in the bond of peace Ephesians 4:2-3 Introduction A covalent bond is
ObjecGve. Class Work 1/4/ Properties of Ionic/Covalent SPARK 1. What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonding?
 Unit 5 NAME Class Work 1/4/14 5.7 Properties of Ionic/Covalent SPARK 1. What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonding? ObjecGve SWBAT identify the type of bond based on the properties Agenda:
Unit 5 NAME Class Work 1/4/14 5.7 Properties of Ionic/Covalent SPARK 1. What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonding? ObjecGve SWBAT identify the type of bond based on the properties Agenda:
(for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes)
 www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) Question 1 An atom loses an electron to another atom. Is this an example of a physical or chemical change? Question 2 Physical
www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) Question 1 An atom loses an electron to another atom. Is this an example of a physical or chemical change? Question 2 Physical
554 Chapter 10 Liquids and Solids
 554 Chapter 10 Liquids and Solids above 7376 kpa, CO 2 is a supercritical fluid, with properties of both gas and liquid. Like a gas, it penetrates deep into the coffee beans; like a liquid, it effectively
554 Chapter 10 Liquids and Solids above 7376 kpa, CO 2 is a supercritical fluid, with properties of both gas and liquid. Like a gas, it penetrates deep into the coffee beans; like a liquid, it effectively
States of Matter. The Solid State. Particles are tightly packed, very close together (strong cohesive forces) Low kinetic energy (energy of motion)
 States of Matter The Solid State Particles are tightly packed, very close together (strong cohesive forces) Low kinetic energy (energy of motion) Fixed shape and volume Crystalline or amorphous structure
States of Matter The Solid State Particles are tightly packed, very close together (strong cohesive forces) Low kinetic energy (energy of motion) Fixed shape and volume Crystalline or amorphous structure
CHAPTER ELEVEN KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS
 CHAPTER ELEVEN AND LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS Differences between condensed states and gases? KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS Phase Homogeneous part
CHAPTER ELEVEN AND LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS Differences between condensed states and gases? KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS Phase Homogeneous part
Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT.
 Chapter 11 THE NATURE OF GASES States of Matter Describe the motion of gas particles according to the kinetic theory Interpret gas pressure in terms of kinetic theory Key Terms: 1. kinetic energy 2. gas
Chapter 11 THE NATURE OF GASES States of Matter Describe the motion of gas particles according to the kinetic theory Interpret gas pressure in terms of kinetic theory Key Terms: 1. kinetic energy 2. gas
Properties of Solutions
 Properties of Solutions The States of Matter The state a substance is in at a particular temperature and pressure depends on two antagonistic entities: The kinetic energy of the particles The strength
Properties of Solutions The States of Matter The state a substance is in at a particular temperature and pressure depends on two antagonistic entities: The kinetic energy of the particles The strength
Unit 2 Chapters 5 and 6 Atoms/Periodic Table/ NOMENCLATURE NAMING AND FORMING COMPOUNDS
 Unit 2 Chapters 5 and 6 Atoms/Periodic Table/ NOMENCLATURE NAMING AND FORMING COMPOUNDS Review of Atomic Structure What is an atom? The smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that
Unit 2 Chapters 5 and 6 Atoms/Periodic Table/ NOMENCLATURE NAMING AND FORMING COMPOUNDS Review of Atomic Structure What is an atom? The smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that
Third Quarter Cumulative Review Questions. 1. Which factor distinguishes a metallic bond from an ionic bond or a covalent bond?
 Name: Thursday, March 27, 2008 Third Quarter Cumulative Review Questions 1. Which factor distinguishes a metallic bond from an ionic bond or a covalent bond? 1. the mobility of electrons 3. the equal sharing
Name: Thursday, March 27, 2008 Third Quarter Cumulative Review Questions 1. Which factor distinguishes a metallic bond from an ionic bond or a covalent bond? 1. the mobility of electrons 3. the equal sharing
Unit 3 Lesson 4 Ionic, Covalent, and Metallic Bonding. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Opposites Attract What is an ion? An atom has a neutral charge because it has an equal number of electrons and protons. An ion is a particle with a positive or negative charge. An ion forms when an atom
Opposites Attract What is an ion? An atom has a neutral charge because it has an equal number of electrons and protons. An ion is a particle with a positive or negative charge. An ion forms when an atom
GRADE 8: Materials 1. UNIT 8M.1 7 hours. Atoms and molecules. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning. Expectations
 GRADE 8: Materials 1 Atoms and molecules UNIT 8M.1 7 hours About this unit This is the first of four units on materials for Grade 8. This unit builds on all the units in Grade 7, providing a theoretical
GRADE 8: Materials 1 Atoms and molecules UNIT 8M.1 7 hours About this unit This is the first of four units on materials for Grade 8. This unit builds on all the units in Grade 7, providing a theoretical
M7 Question 1 Higher
 M7 Question 1 Higher Explain why carbon dioxide is a compound by oxygen is an element Carbon dioxide contains two elements carbon and oxygen. Oxygen contains only one type of atom. M7 Question 2 Higher
M7 Question 1 Higher Explain why carbon dioxide is a compound by oxygen is an element Carbon dioxide contains two elements carbon and oxygen. Oxygen contains only one type of atom. M7 Question 2 Higher
National 5 Chemistry
 St Ninian s High School Chemistry Department National 5 Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes & Structure Section 3: Bonding & Properties of Substances Summary Notes Name Learning Outcomes After completing
St Ninian s High School Chemistry Department National 5 Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes & Structure Section 3: Bonding & Properties of Substances Summary Notes Name Learning Outcomes After completing
Good Morning. Please take out your notebook and something to write with. In your notes: Write the balanced equation for Beryllium Iodide.
 Good Morning Please take out your notebook and something to write with. In your notes: Write the balanced equation for Beryllium Iodide. Homework Due Wednesday From Monday s Class: 3-7, 10, 11, 14, 16,
Good Morning Please take out your notebook and something to write with. In your notes: Write the balanced equation for Beryllium Iodide. Homework Due Wednesday From Monday s Class: 3-7, 10, 11, 14, 16,
