HISTORY OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
|
|
|
- Felix Palmer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ITY F GANIC CEMITY Although it is most often taught as a dry subject devoid of major controversy or character, organic chemistry has a truly colorful history. My own interests in the history of organic chemistry are in the contributions of ussian organic chemists to the development of the science. Despite the fact that most students and teachers of organic chemistry tend to credit the major advances in the discipline to the German chemists (Kekulé, Liebig, Wöhler, Baeyer, and their ilk), many major advances were made by ussian organic chemists, whose names have also passed into the vocabulary of the science. ome major ussian contributors to modern organic chemistry include: Aleksandr Erminingel'dovich Arbuzov: the Arbuzov rearrangement of phosphites to phosphonates P ' P ' P ' Aleksandr Porfir'evich Borodin: discovered the Borodin- unsdiecker reaction of silver carboxylates, the aldol addition, and made the first organic fluorine compound (he is the same person as the renowned composer, which is how he usually appears on "Jeopardy!") C 2 Ag 2 Bu Na Bu Pr + Bu Pr
2 Aleksandr Mikhailovich Butlerov: an early champion of structural theory in organic chemistry; first synthesis of a tertiary alcohol and first synthesis (somewhat serendipitous) of a carbohydrate Aleksei Yevgenievich Chichibabin: the Chichibabin reaction of pyridines; Chichibabin pyridine synthesis 1) NaN 2, Δ N 2) 3 N N 2 C C C N 3 NaN 2 N Lev Aleksandrovich Chugaev: the Chugaev elimination of xanthate esters 1) K, C 2 2) I Δ
3 Nikolai Yakovlevich Demyanov: the Demjanov rearrangement of β-aminoalcohols N 2 N 2 N N Aleksei Yevgrafovich Favorskii: the Favorskii rearrangement of α- haloketones; Favorskii-Babayan synthesis of propargylic alcohols 10% K 2 C C C K (powdered) C Vladimir Nikolaevich Ipatieff: pioneer in high-pressure hydrogenation
4 Nikolai Matveyevich Kizhner (Kishner): the Wolff-Kishner reduction of ketones and aldehydes ' 2 NN 2 ' NN 2 K, Δ ' Karl Karlovich Klaus (Carl Ernst Claus): discoverer of ruthenium Vladimir Vasilievich Markovnikov: Markovnikov's ule for addition to alkenes; further exploration of structural theory; first cyclobutane and cycloheptane derivatives C 2 C 2 Cl 2 C Na, Et I, Δ
5 Nikolai Aleksandrovich nshutkin: the nshutkin reaction of tertiary amines; pioneer of physical organic chemistry N ' N ' Ivan Nikolaevich Nazarov: the Nazarov cyclization Nikolai Aleksandrovich Prilezhaev: epoxidation of alkenes with peracids (Prilezhaev reaction) C 6 5 C 2
6 Nikolai Nikolaevich eformatskii: the eformatskii reaction of a- halocarbonyl compounds C 2 Et 1) Zn, Et 2 2) 2 CC C 2 Et Vyacheslav Yevgenievich Tishchenko: the Tishchenko reaction of aromatic aldehydes with aluminum alkoxides Ph C Al(-t-Bu) 3 Ph Ph Egor Egorevich Vagner (Georg Wagner): the Wagner-erwein rearrangement; the Wagner oxidation (permanganate) of alkenes Et EtI Zn Et 2 Zn Kazan' t. Petersburg and Warsaw
7 Aleksandr Mikhailovich Zaitsev (aytzeff): aytzeff's ule for elimination from alkyl halides; the discoverer of sulfoxides; pioneer in organozinc syntheses of alcohols =, Et N 3 I I " ' 'C" Zn I C 2 Et 'CCl ('C) 2 ' ' ' Zn ' Nikolai Dmitrievich Zelinskii: the ell-volhard-zelinskii reaction of carboxylic acids; Zelinskii-tadnikov modification of the trecker amino acid synthesis 1) 2, P 3 2) 2 KCN, N 4 Cl 2 N 2 CN 3 Δ N 2 C 2 Nikolai Nikolaevich Zinin: discoverer of the reduction of nitrobenzene to aniline N 2 N 3, 2 Et, Δ N 2
8 My own special interests are the chemists of the Kazan' chool of Chemistry, among whose luminaries are Zinin, Butlerov, Markovnikov, Zaitsev, Vagner, eformatskii, and Arbuzov.
Dave and the Dead Russians. Early Contributions by Russian Organic Chemists to the Development of the Discipline
 Dave and the Dead ussians Early Contributions by ussian Organic Chemists to the Development of the Discipline Nikolai Nikolaevich Zinin (1812-1880) kandidat Kazan' 1836 Dr. Chem. St. Petersburg 1841 Study
Dave and the Dead ussians Early Contributions by ussian Organic Chemists to the Development of the Discipline Nikolai Nikolaevich Zinin (1812-1880) kandidat Kazan' 1836 Dr. Chem. St. Petersburg 1841 Study
Chapter 10. Reactions of Alcohols, Amines, Ethers, and Epoxides
 Chapter 10. Reactions of Alcohols, Amines, Ethers, and Epoxides Learning objectives: 1. Provide both IUPAC and common (when applicable) names for alcohols and ethers. 2. Describe the physical properties
Chapter 10. Reactions of Alcohols, Amines, Ethers, and Epoxides Learning objectives: 1. Provide both IUPAC and common (when applicable) names for alcohols and ethers. 2. Describe the physical properties
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 15, 2010 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
Chapter 16. Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group. Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones. Synthesis of Aldehydes
 Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Aldehydes replace the -e of the parent alkane with -al The functional group needs no number Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl
Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Aldehydes replace the -e of the parent alkane with -al The functional group needs no number Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl
Synthetic possibilities Chem 315 Beauchamp 1
 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp Propose reasonable syntheses f the following target molecules (TM-#). You can use the given starting materials and any typical ganic reagents studied in our course
Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp Propose reasonable syntheses f the following target molecules (TM-#). You can use the given starting materials and any typical ganic reagents studied in our course
Page 1 of 9. Sessional Examination (November 2017) Max Marks: 20 Date: Time: One Hour. Model Answers
 Page 1 of 9 Sessional Examination (November 2017) Class: B. Pharm-II yr (III sem) Subject: Pharma Org. Chem-II Max Marks: 20 Date: 14.11.2017 Time: One Hour Model Answers Q. 1. Solve the following (ANY
Page 1 of 9 Sessional Examination (November 2017) Class: B. Pharm-II yr (III sem) Subject: Pharma Org. Chem-II Max Marks: 20 Date: 14.11.2017 Time: One Hour Model Answers Q. 1. Solve the following (ANY
Organic Chemistry 112 A B C - Syllabus Addendum for Prospective Teachers
 Chapter Organic Chemistry 112 A B C - Syllabus Addendum for Prospective Teachers Ch 1-Structure and bonding Ch 2-Polar covalent bonds: Acids and bases McMurry, J. (2004) Organic Chemistry 6 th Edition
Chapter Organic Chemistry 112 A B C - Syllabus Addendum for Prospective Teachers Ch 1-Structure and bonding Ch 2-Polar covalent bonds: Acids and bases McMurry, J. (2004) Organic Chemistry 6 th Edition
Synthesis of Amines Amine Alkylation by SN2 reaction II. Reductive Amination
 Synthesis of Amines I. Amine Alkylation by SN2 reaction Amines can be alkylated in SN2 fashion by alkyl halides; primary halides are best for this purpose. This is not a practical reaction for formation
Synthesis of Amines I. Amine Alkylation by SN2 reaction Amines can be alkylated in SN2 fashion by alkyl halides; primary halides are best for this purpose. This is not a practical reaction for formation
CHEM 203. Midterm Exam 1 October 31, 2008 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Midterm Exam 1 ctober 31, 2008 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This exam contains 8 pages Time: 1h 30 min 1. / 15 2. / 16 3. /
CEM 203 Midterm Exam 1 ctober 31, 2008 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This exam contains 8 pages Time: 1h 30 min 1. / 15 2. / 16 3. /
Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions Dr. Sapna Gupta Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophilic Addition A strong nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion that is then protonated.
Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions Dr. Sapna Gupta Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophilic Addition A strong nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion that is then protonated.
Alcohol Synthesis. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Alcohol Synthesis Dr. Sapna Gupta Synthesis of Alcohols Alcohols can be synthesized from several functional groups. Nucleophilic substitution of O - on alkyl halide ydration of alkenes water in acid solution
Alcohol Synthesis Dr. Sapna Gupta Synthesis of Alcohols Alcohols can be synthesized from several functional groups. Nucleophilic substitution of O - on alkyl halide ydration of alkenes water in acid solution
Naming Organic Halides. Properties of Organic Halides
 Organic Compounds Organic Halides A hydrocarbon in which one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by halogen atoms Freons (chlorofluorocarbons) in refrigeration and air conditioning Teflon (polytetrafluoroethane)
Organic Compounds Organic Halides A hydrocarbon in which one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by halogen atoms Freons (chlorofluorocarbons) in refrigeration and air conditioning Teflon (polytetrafluoroethane)
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 12. Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds Oxidation-Reduction & Organometallic Compounds. Structure
 Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds xidation-eduction & rganometallic Compounds Created by Professor William Tam & Dr. Phillis Chang Structure ~ 120 o ~ 120 o C ~ 120 o Carbonyl carbon: sp 2 hybridized
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds xidation-eduction & rganometallic Compounds Created by Professor William Tam & Dr. Phillis Chang Structure ~ 120 o ~ 120 o C ~ 120 o Carbonyl carbon: sp 2 hybridized
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
REARRANGEMENTS NOTES Mechanistic Aspects of Rearrangements
 - 1 - REARRANGEMENTS NOTES Mechanistic Aspects of Rearrangements Nature of the Rearrangement It can vary from being truly stepwise to migration occurring in concert with initial ionisation. These two situations
- 1 - REARRANGEMENTS NOTES Mechanistic Aspects of Rearrangements Nature of the Rearrangement It can vary from being truly stepwise to migration occurring in concert with initial ionisation. These two situations
FARMINGDALE STATE COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY. CONTACT HOURS: Lecture: 3 Laboratory: 4
 FARMINGDALE STATE COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY COURSE OUTLINE: COURSE TITLE: Prepared by: Dr. M. DeCastro September 2011 Organic Chemistry II COURSE NUMBER: CHM 271 CREDITS: 5 CONTACT HOURS: Lecture:
FARMINGDALE STATE COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY COURSE OUTLINE: COURSE TITLE: Prepared by: Dr. M. DeCastro September 2011 Organic Chemistry II COURSE NUMBER: CHM 271 CREDITS: 5 CONTACT HOURS: Lecture:
Introduction & Definitions Catalytic Hydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of H- and H+ Oxidation of Alcohols Oxidation of
 CEM 241- UNIT 4 xidation/reduction Reactions Redox chemistry 1 utline Introduction & Definitions Catalytic ydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of - and + xidation of Alcohols
CEM 241- UNIT 4 xidation/reduction Reactions Redox chemistry 1 utline Introduction & Definitions Catalytic ydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of - and + xidation of Alcohols
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE
 DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 6 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Oxidation States Easy for inorganic salts: CrO 4 2- reduced to Cr 2 O 3. KMnO 4 reduced to MnO 2. Oxidation: Gain of O,
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 6 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Oxidation States Easy for inorganic salts: CrO 4 2- reduced to Cr 2 O 3. KMnO 4 reduced to MnO 2. Oxidation: Gain of O,
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: PURPOSE OF ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Classical Methods (Wet Chemistry): Chemists needed to run dozens of chemical reactions to determine the type of molecules in a compound.
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: PURPOSE OF ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Classical Methods (Wet Chemistry): Chemists needed to run dozens of chemical reactions to determine the type of molecules in a compound.
ASSIGNMENT BOOKLET Bachelor s Degree Programme (B.Sc.) ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISM. Please Note
 ASSIGNMENT BOOKLET Bachelor s Degree Programme (B.Sc.) ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISM CHE-06 Valid from 1 st January to 31 st December 2014 It is compulsory to submit the Assignment before filling in the Term-End
ASSIGNMENT BOOKLET Bachelor s Degree Programme (B.Sc.) ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISM CHE-06 Valid from 1 st January to 31 st December 2014 It is compulsory to submit the Assignment before filling in the Term-End
b.p.=100 C b.p.=65 C b.p.=-25 C µ=1.69 D µ=2.0 D µ=1.3 D
 Alcohols I eading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10-12 Study Problems: 10-35, 10-37, 10-38, 10-39, 10-40, 10-42, 10-43 Key Concepts and Skills: Show how to convert alkenes, alkyl halides, and and carbonyl
Alcohols I eading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10-12 Study Problems: 10-35, 10-37, 10-38, 10-39, 10-40, 10-42, 10-43 Key Concepts and Skills: Show how to convert alkenes, alkyl halides, and and carbonyl
Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds II
 Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. Recognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. Recognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Loudon Chapter 23 Review: Amines CHEM 3331, Jacquie Richardson, Fall Page 1
 Loudon Chapter 23 eview: Amines CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 This chapter is about the chemistry of nitrogen. We ve seen it before in several places, but now we can look at several reactions
Loudon Chapter 23 eview: Amines CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 This chapter is about the chemistry of nitrogen. We ve seen it before in several places, but now we can look at several reactions
(Neither an oxidation or reduction: Addition or loss of H +, H 2 O, HX).
 eactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. xidation is a
eactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. xidation is a
Alcohols. Have seen many reactions to synthesize alcohols: In this chapter we will study reactions of the alcohols
 Alcohols ave seen many reactions to synthesize alcohols: In this chapter we will study reactions of the alcohols Oxidation Need to understand the nomenclature of organic reduction/oxidation In general
Alcohols ave seen many reactions to synthesize alcohols: In this chapter we will study reactions of the alcohols Oxidation Need to understand the nomenclature of organic reduction/oxidation In general
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions and Condensation Reactions
 Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
20.5 Preparation of Amines
 RGANIC CHEMISTRY 20.5 Preparation of Amines RGANIC CHEMISTRY 20.5A Through Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Alkylation of Ammonia or Amines NaH NH 3 + R X RNH 3 X RNH2 R + R X R 2 X NaH R 2 NH R 2 NH
RGANIC CHEMISTRY 20.5 Preparation of Amines RGANIC CHEMISTRY 20.5A Through Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Alkylation of Ammonia or Amines NaH NH 3 + R X RNH 3 X RNH2 R + R X R 2 X NaH R 2 NH R 2 NH
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds. Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
Chapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols
 Chapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols [ Chapter 9 Sections: 9.10; Chapter 13 Sections: 13.1-13.3, 13.9-13.10] 1. Nomenclature of Alcohols simple alcohols C3 C3C2 Eddie Sachs 1927-1964 larger alcohols find the
Chapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols [ Chapter 9 Sections: 9.10; Chapter 13 Sections: 13.1-13.3, 13.9-13.10] 1. Nomenclature of Alcohols simple alcohols C3 C3C2 Eddie Sachs 1927-1964 larger alcohols find the
2.1. The Main Types of Organic Reactions. Addition, Substitution, and Elimination Reactions
 The Main Types of rganic Reactions Figure 2.1(A) shows raw fruit. The crisp, sharp-tasting fruit becomes soft and sweet when it is cooked. Figure 2.1(B) shows a chemist accelerating the tranformation of
The Main Types of rganic Reactions Figure 2.1(A) shows raw fruit. The crisp, sharp-tasting fruit becomes soft and sweet when it is cooked. Figure 2.1(B) shows a chemist accelerating the tranformation of
NH 2 O O O O OCH (6 pts) Provide an acceptable name for each of the following compounds: NH 2 COOH HOOC COOH. piperidine
 CEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 4 April 1, 2003 Statistics: Average: 87 pts (72%); ighest: 116 pts (97%); Lowest: 49 pts (41%) umber of students performing at or above average: 13 (62%) 1. (9 pts) Mark as true
CEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 4 April 1, 2003 Statistics: Average: 87 pts (72%); ighest: 116 pts (97%); Lowest: 49 pts (41%) umber of students performing at or above average: 13 (62%) 1. (9 pts) Mark as true
SORAN UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF EDUCATION BASIC EDUCATION SCHOOL DEPARTMENT OF GENERAL SCIENCES
 SORAN UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF EDUCATION BASIC EDUCATION SCHOOL DEPARTMENT OF GENERAL SCIENCES SUBJECT OUTLINE 2014-2015 Subject title: Practical organic Chemistry Credit hours: Units: (Practical ) (2)Units
SORAN UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF EDUCATION BASIC EDUCATION SCHOOL DEPARTMENT OF GENERAL SCIENCES SUBJECT OUTLINE 2014-2015 Subject title: Practical organic Chemistry Credit hours: Units: (Practical ) (2)Units
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry Problem Set 1. Functional Group Transformations Study Guide
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology rganic Chemistry 5.511 Problem Set 1 September, 2007 Prof. Rick L. Danheiser Functional Group Transformations Study Guide The purpose of this three-part study guide
Massachusetts Institute of Technology rganic Chemistry 5.511 Problem Set 1 September, 2007 Prof. Rick L. Danheiser Functional Group Transformations Study Guide The purpose of this three-part study guide
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids
 Teacher Orientation Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids contains following topics: Nomenclature Preparation Properties Student Orientation Preparation and Properties Of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic
Teacher Orientation Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids contains following topics: Nomenclature Preparation Properties Student Orientation Preparation and Properties Of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic
Reducing Agents. Linda M. Sweeting 1998
 Reducing Agents Linda M. Sweeting 1998 Reduction is defined in chemistry as loss of oxygen, gain of hydrogen or gain of electrons; the gain of electrons enables you to calculate an oxidation state. Hydride
Reducing Agents Linda M. Sweeting 1998 Reduction is defined in chemistry as loss of oxygen, gain of hydrogen or gain of electrons; the gain of electrons enables you to calculate an oxidation state. Hydride
MCAT Organic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones
 MCAT rganic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following is not a physical property of aldehydes and ketones? Question #01 (A) Hydrogen bonding
MCAT rganic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following is not a physical property of aldehydes and ketones? Question #01 (A) Hydrogen bonding
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key
 CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
2.222 Practice Problems 2003
 2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
Loudon Chapter 23 Review: Amines Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 4/22/2018
 This chapter is about the chemistry of nitrogen. We ve seen it before in several places, but now we can look at several reactions that are specific to nitrogen. Amines can be subdivided based on how many
This chapter is about the chemistry of nitrogen. We ve seen it before in several places, but now we can look at several reactions that are specific to nitrogen. Amines can be subdivided based on how many
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophile substitutes for a hydrogen on the benzene ring. Chapter 17: Aromatics 2-Reactions Slide 17-2 1 Mechanism Step
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophile substitutes for a hydrogen on the benzene ring. Chapter 17: Aromatics 2-Reactions Slide 17-2 1 Mechanism Step
Exam I 19 April 2004 Name:
 Chem 317 S04 Page 1 of 7 Kantorowski Exam I 19 April 2004 Name: This exam contains 6 pages of questions confirm this once you begin The last page is a spectral data table that can be removed You will have
Chem 317 S04 Page 1 of 7 Kantorowski Exam I 19 April 2004 Name: This exam contains 6 pages of questions confirm this once you begin The last page is a spectral data table that can be removed You will have
Detailed Course Content
 Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
22.7 Reactions of Amines: A Review and a Preview
 22.7 Reactions of Amines: A Review and a Preview Preparation of Amines Two questions to answer: 1) How is the C N C N bond to be formed? 2) How do we obtain the correct oxidation state of nitrogen (and
22.7 Reactions of Amines: A Review and a Preview Preparation of Amines Two questions to answer: 1) How is the C N C N bond to be formed? 2) How do we obtain the correct oxidation state of nitrogen (and
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones
 Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [Chapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ' ketone aldehyde f both aldehydes and ketones, the parent chain is the longest
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [Chapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ' ketone aldehyde f both aldehydes and ketones, the parent chain is the longest
TOK: The relationship between a reaction mechanism and the experimental evidence to support it could be discussed. See
 Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours) SL students study the core of these options and HL students study the whole option (the core and the extension material). TOK: The relationship between
Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours) SL students study the core of these options and HL students study the whole option (the core and the extension material). TOK: The relationship between
Chapter 24. Amines. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition
 Chapter 24. Amines Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Amines Organic Nitrogen Compounds Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH 3, Nitrogen atom with a lone pair of electrons, making amines
Chapter 24. Amines Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Amines Organic Nitrogen Compounds Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH 3, Nitrogen atom with a lone pair of electrons, making amines
Chapter 13 Reactions of Arenes Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 . 13 hapter 13 eactions of Arenes lectrophilic Aromatic ubstitution lectrophiles add to aromatic rings in a fashion somewhat similar to the addition of electrophiles to alkenes. ecall: 3 4 Y 1 4 2 1 δ
. 13 hapter 13 eactions of Arenes lectrophilic Aromatic ubstitution lectrophiles add to aromatic rings in a fashion somewhat similar to the addition of electrophiles to alkenes. ecall: 3 4 Y 1 4 2 1 δ
REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW
 REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO PREDICT PRODUCTS, IDENTIFY REACTANTS, GIVE REACTION CONDITIONS, PROPOSE SYNTHESES, AND PROPOSE MECHANISMS (AS LISTED BELOW). REVIEW THE MECHANISM
REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO PREDICT PRODUCTS, IDENTIFY REACTANTS, GIVE REACTION CONDITIONS, PROPOSE SYNTHESES, AND PROPOSE MECHANISMS (AS LISTED BELOW). REVIEW THE MECHANISM
CHEMISTRY Topic #8: Oxidation and Reduction Reactions Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay
 CEMISTRY 2600 Topic #8: xidation and Reduction Reactions Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay xidation States of Carbon Carbon can have any oxidation state from -4 (C 4 ) to +4 (C 2 ). As a general rule, increasing
CEMISTRY 2600 Topic #8: xidation and Reduction Reactions Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay xidation States of Carbon Carbon can have any oxidation state from -4 (C 4 ) to +4 (C 2 ). As a general rule, increasing
acetaldehyde (ethanal)
 hem 263 Nov 2, 2010 Preparation of Ketones and Aldehydes from Alkenes zonolysis 1. 3 2. Zn acetone 1. 3 2. Zn acetone acetaldehyde (ethanal) Mechanism: 3 3 3 + - oncerted reaction 3 3 3 + ozonide (explosive)
hem 263 Nov 2, 2010 Preparation of Ketones and Aldehydes from Alkenes zonolysis 1. 3 2. Zn acetone 1. 3 2. Zn acetone acetaldehyde (ethanal) Mechanism: 3 3 3 + - oncerted reaction 3 3 3 + ozonide (explosive)
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTION
 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTION Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols by various reactions Structure of the Carbonyl
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTION Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols by various reactions Structure of the Carbonyl
KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II
 KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II Course Objectives: 1) To introduce the chemistry of alcohols and ethers. 2) To study the chemistry of functional groups. 3) To learn the chemistry of aromatic compounds and
KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II Course Objectives: 1) To introduce the chemistry of alcohols and ethers. 2) To study the chemistry of functional groups. 3) To learn the chemistry of aromatic compounds and
Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides. Chapter Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry
 Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides Chapter 17-18 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry 1 Introduction Structure and Bonding Alcohols contain a hydroxy group (OH) bonded to an sp 3 hybridized carbon. 2
Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides Chapter 17-18 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry 1 Introduction Structure and Bonding Alcohols contain a hydroxy group (OH) bonded to an sp 3 hybridized carbon. 2
New bond. ph 4.0. Fischer esterification. New bond 2 O * New bond. New bond H 2N. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. O Cl.
 Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY. Wiley STUDY GUIDE AND SOLUTIONS MANUAL TO ACCOMPANY ROBERT G. JOHNSON JON ANTILLA ELEVENTH EDITION. University of South Florida
 STUDY GUIDE AND SOLUTIONS MANUAL TO ACCOMPANY ORGANIC CHEMISTRY ELEVENTH EDITION T. W. GRAHAM SOLOMONS University of South Florida CRAIG B. FRYHLE Pacific Lutheran University SCOTT A. SNYDER Columbia University
STUDY GUIDE AND SOLUTIONS MANUAL TO ACCOMPANY ORGANIC CHEMISTRY ELEVENTH EDITION T. W. GRAHAM SOLOMONS University of South Florida CRAIG B. FRYHLE Pacific Lutheran University SCOTT A. SNYDER Columbia University
Reduction. Boron based reagents. NaBH 4 / NiCl 2. Uses: Zn(BH 4 ) 2. Preparation: Good for base sensitive groups Chelation control model.
 Uses: Ar N 2 Ar N 2 Ar N Ar N 2 eduction Boron based reagents NaB 4 / NiCl 2 2 Ar C N Ar C N 2 Preparation: Zn(B 4 ) 2 ZnCl 2 (Ether) NaB 4 Zn(B 4 ) 2 Good for base sensitive groups Chelation control model
Uses: Ar N 2 Ar N 2 Ar N Ar N 2 eduction Boron based reagents NaB 4 / NiCl 2 2 Ar C N Ar C N 2 Preparation: Zn(B 4 ) 2 ZnCl 2 (Ether) NaB 4 Zn(B 4 ) 2 Good for base sensitive groups Chelation control model
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes. 2. Radical Substitution with Alkenes. 3. Electrophilic Addition
 1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions.
 ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination Chemistry Beauchamp 1 Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions. ources of
ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination Chemistry Beauchamp 1 Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions. ources of
Ketones and Aldehydes Reading Study Problems Key Concepts and Skills Lecture Topics: Structure of Ketones and Aldehydes Structure:
 Ketones and Aldehydes Reading: Wade chapter 18, sections 18-1- 18-21 Study Problems: 18-43, 18-44,18-50, 18-51, 18-52, 18-59, 18-60, 18-62, 18-64, 18-72. Key Concepts and Skills: Interpret the IR, NMR,
Ketones and Aldehydes Reading: Wade chapter 18, sections 18-1- 18-21 Study Problems: 18-43, 18-44,18-50, 18-51, 18-52, 18-59, 18-60, 18-62, 18-64, 18-72. Key Concepts and Skills: Interpret the IR, NMR,
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and How Do They Work?
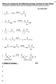 What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
Mechanisms. . CCl2 F + Cl.
 Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions. Alpha Substitution
 Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Chemistry 254 Lab Experiment 1: Qualitative Organic Analysis Summer 2004
 Chemistry 254 Lab Experiment 1: Qualitative Organic Analysis Summer 2004 Introduction: Qualitative organic analysis, the identification and characterization of unknown compounds, in an important part of
Chemistry 254 Lab Experiment 1: Qualitative Organic Analysis Summer 2004 Introduction: Qualitative organic analysis, the identification and characterization of unknown compounds, in an important part of
Ethers can be symmetrical or not:
 Chapter 14: Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides 175 Physical Properties Ethers can be symmetrical or not: linear or cyclic. Ethers are inert and make excellent solvents for organic reactions. Epoxides are very
Chapter 14: Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides 175 Physical Properties Ethers can be symmetrical or not: linear or cyclic. Ethers are inert and make excellent solvents for organic reactions. Epoxides are very
Synthesis and Structure of Alcohols Alcohols can be considered organic analogues of water.
 Synthesis and Structure of Alcohols Alcohols can be considered organic analogues of water. Alcohols are usually classified as primary, secondary and tertiary. Alcohols with the hydroxyl bound directly
Synthesis and Structure of Alcohols Alcohols can be considered organic analogues of water. Alcohols are usually classified as primary, secondary and tertiary. Alcohols with the hydroxyl bound directly
Exam 1 (Monday, July 6, 2015)
 Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Cape Cod Community College
 Cape Cod Community College Departmental Syllabus Prepared by the Department of Natural Sciences & Applied Technology Date of Departmental Approval: February 3, 2014 Date Approved by Curriculum and Programs:
Cape Cod Community College Departmental Syllabus Prepared by the Department of Natural Sciences & Applied Technology Date of Departmental Approval: February 3, 2014 Date Approved by Curriculum and Programs:
Hyperlearning MCAT Instructor Qualifying Exam Organic Chemistry
 Hyperlearning MCAT Instructor Qualifying Exam Organic Chemistry 30 Questions (5 pages); Time limit = 45 minutes Use of books or notes is not permitted. 1. When analyzed with a polarimeter, which of the
Hyperlearning MCAT Instructor Qualifying Exam Organic Chemistry 30 Questions (5 pages); Time limit = 45 minutes Use of books or notes is not permitted. 1. When analyzed with a polarimeter, which of the
Suggested solutions for Chapter 28
 s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
Spring Term 2012 Dr. Williams (309 Zurn, ex 2386)
 Chemistry 242 Organic Chemistry II Spring Term 2012 Dr. Williams (309 Zurn, ex 2386) Web Page: http://math.mercyhurst.edu/~jwilliams/ jwilliams@mercyhurst.edu (or just visit Department web site and look
Chemistry 242 Organic Chemistry II Spring Term 2012 Dr. Williams (309 Zurn, ex 2386) Web Page: http://math.mercyhurst.edu/~jwilliams/ jwilliams@mercyhurst.edu (or just visit Department web site and look
ROADMAP FOR REACTIONS Chapter 6
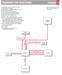 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapter 6 (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L) (M) (N) () Regiochemistry: Markovnikov addition to a bond Stereochemistry: anti-addition Regiochemistry: non-markovnikov addition
RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapter 6 (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L) (M) (N) () Regiochemistry: Markovnikov addition to a bond Stereochemistry: anti-addition Regiochemistry: non-markovnikov addition
Chapter 18: Ketones and Aldehydes. I. Introduction
 1 Chapter 18: Ketones and Aldehydes I. Introduction We have already encountered numerous examples of this functional group (ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, acid chlorides, etc). The three-dimensional
1 Chapter 18: Ketones and Aldehydes I. Introduction We have already encountered numerous examples of this functional group (ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, acid chlorides, etc). The three-dimensional
Chapter 17: Carbonyl Compounds II
 Chapter 17: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. ecognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chapter 17: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. ecognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Look for absorption bands in decreasing order of importance:
 1. Match the following to their IR spectra (30 points) Look for absorption bands in decreasing order of importance: a e a 2941 1716 d f b 3333 c b 1466 1.the - absorption(s) between 3100 and 2850 cm-1.
1. Match the following to their IR spectra (30 points) Look for absorption bands in decreasing order of importance: a e a 2941 1716 d f b 3333 c b 1466 1.the - absorption(s) between 3100 and 2850 cm-1.
Chapter 19: Amines. Introduction
 Chapter 19: Amines Chap 19 HW: (be able to name amines); 37, 39, 41, 42, 44, 46, 47, 48, 53-55, 57, 58 Introduction Organic derivatives of ammonia. Many are biologically active. Chap 19: Amines Slide 19-2
Chapter 19: Amines Chap 19 HW: (be able to name amines); 37, 39, 41, 42, 44, 46, 47, 48, 53-55, 57, 58 Introduction Organic derivatives of ammonia. Many are biologically active. Chap 19: Amines Slide 19-2
Course Outline. TERM EFFECTIVE: Fall 2016 CURRICULUM APPROVAL DATE: 03/14/2016
 5055 Santa Teresa Blvd Gilroy, CA 95023 Course Outline COURSE: CHEM 12B DIVISION: 10 ALSO LISTED AS: TERM EFFECTIVE: Fall 2016 CURRICULUM APPROVAL DATE: 03/14/2016 SHORT TITLE: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LONG TITLE:
5055 Santa Teresa Blvd Gilroy, CA 95023 Course Outline COURSE: CHEM 12B DIVISION: 10 ALSO LISTED AS: TERM EFFECTIVE: Fall 2016 CURRICULUM APPROVAL DATE: 03/14/2016 SHORT TITLE: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LONG TITLE:
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction and Organometallic Compounds
 Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction and Organometallic Compounds Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction and Organometallic Compounds Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols
Chemistry 2030, FS17, Dr. Rainer Glaser Introduction to Organic Chemistry
 Chemistry 2030, FS17, Dr. Rainer Glaser Introduction to Organic Chemistry Examination #4 Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Carboxylic Acid Derivatives, Lipids & Detergents, and Amines. Handout: Tuesday,
Chemistry 2030, FS17, Dr. Rainer Glaser Introduction to Organic Chemistry Examination #4 Aldehydes & Ketones, Carboxylic Acids & Carboxylic Acid Derivatives, Lipids & Detergents, and Amines. Handout: Tuesday,
Practice Synthetic Problems: CHEM 235 Page 2
 Practice Synthetic Problems: CM 235 Page 2 Syntheses based on diethyl malonate, ethyl acetoacetate, etc. Using diethyl malonate and any other necessary organic reagents, show a synthesis of: a) 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propanediamine
Practice Synthetic Problems: CM 235 Page 2 Syntheses based on diethyl malonate, ethyl acetoacetate, etc. Using diethyl malonate and any other necessary organic reagents, show a synthesis of: a) 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propanediamine
18.8 Oxidation. Oxidation by silver ion requires an alkaline medium
 18.8 Oxidation Oxidation by silver ion requires an alkaline medium Test for detecting aldehydes Tollens reagent to prevent precipitation of the insoluble silver oxide, a complexing agent is added: ammonia
18.8 Oxidation Oxidation by silver ion requires an alkaline medium Test for detecting aldehydes Tollens reagent to prevent precipitation of the insoluble silver oxide, a complexing agent is added: ammonia
Reactions at α-position
 Reactions at α-position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry, a common reaction mechanism observed was a nucleophile reacting at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon site NUC NUC Another reaction that
Reactions at α-position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry, a common reaction mechanism observed was a nucleophile reacting at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon site NUC NUC Another reaction that
Chapter 11 Reaction of Alcohols
 Chapter 11 eaction of Alcohols xidation of alcohols Alcohols are at the same oxidation level as alkenes Therefore alkenes can be converted to alcohols with acidic water PDC or PCC 2 C C 2 3 + X 3 C 3 C
Chapter 11 eaction of Alcohols xidation of alcohols Alcohols are at the same oxidation level as alkenes Therefore alkenes can be converted to alcohols with acidic water PDC or PCC 2 C C 2 3 + X 3 C 3 C
Loudon Chapter 19 Review: Aldehydes and Ketones CHEM 3331, Jacquie Richardson, Fall Page 1
 Loudon Chapter 19 eview: Aldehydes and Ketones CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 Beginning with this chapter, we re looking at a very important functional group: the carbonyl. We ve seen
Loudon Chapter 19 eview: Aldehydes and Ketones CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 Beginning with this chapter, we re looking at a very important functional group: the carbonyl. We ve seen
Chapter 18: Carbonyl Compounds II
 Chapter 18: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. ecognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chapter 18: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. ecognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chem 315/316 Reactions. Bromo organic compounds C1 & C2 carbon skeletons C3 carbon skeletons C4 carbon skeletons. Alcohols. Chem 316 / Beauchamp 1
 hem 316 / Beauchamp 1 hem 315/316 eactions Name available sources of carbon 4 3 NaN methyl 3 2 ethyl 3 2 2 n-propyl 3 3 isopropyl 2 3 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 3 n-butyl sec butyl t-butyl phenyl available until topic
hem 316 / Beauchamp 1 hem 315/316 eactions Name available sources of carbon 4 3 NaN methyl 3 2 ethyl 3 2 2 n-propyl 3 3 isopropyl 2 3 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 3 n-butyl sec butyl t-butyl phenyl available until topic
Chem 22 Final Exam Practice
 Chem 22 Final Exam Practice Questions taken from regular tests given during the previous semesters. Only one answer is correct unless the question says otherwise. The questions are somewhat scrambled with
Chem 22 Final Exam Practice Questions taken from regular tests given during the previous semesters. Only one answer is correct unless the question says otherwise. The questions are somewhat scrambled with
CHEMISTRY MIDTERM # 2 November 02, The total number of points in this midterm is 100. The total exam time is 120 min (2 h). Good luck!
 CEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 2 November 02, 2009 Name... The total number of points in this midterm is 100. The total exam time is 120 min (2 h). Good luck! 1. (8 pts) Mark as true (T) or false (F) the following
CEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 2 November 02, 2009 Name... The total number of points in this midterm is 100. The total exam time is 120 min (2 h). Good luck! 1. (8 pts) Mark as true (T) or false (F) the following
Homework Problem Set 9 Iverson CH320M/328M Due Friday, November 30
 omework Problem Set 9 Iverson C0M/8M Due Friday, November 0 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 0M/8M Dr. ent Iverson 9th omework November 9, 08 Please print the first three letters of your last name in
omework Problem Set 9 Iverson C0M/8M Due Friday, November 0 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 0M/8M Dr. ent Iverson 9th omework November 9, 08 Please print the first three letters of your last name in
Chapter 12. Reactions of Arenes: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution. Class Notes. A. The method by which substituted benzenes are synthesized
 Chapter 12 Reactions of Arenes: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Chapter 12 suggested problems: 22, 23, 26, 27, 32, 33 Class Notes I. Electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions A. The method by which
Chapter 12 Reactions of Arenes: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Chapter 12 suggested problems: 22, 23, 26, 27, 32, 33 Class Notes I. Electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions A. The method by which
A. Loupy, B.Tchoubar. Salt Effects in Organic and Organometallic Chemistry
 A. Loupy, B.Tchoubar Salt Effects in Organic and Organometallic Chemistry 1 Introduction - Classification of Specific Salt Effects 1 1.1 Specific Salt Effects Involving the Salt's Lewis Acid or Base Character
A. Loupy, B.Tchoubar Salt Effects in Organic and Organometallic Chemistry 1 Introduction - Classification of Specific Salt Effects 1 1.1 Specific Salt Effects Involving the Salt's Lewis Acid or Base Character
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III
 CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
Physical Properties. Alcohols can be: CH CH 2 OH CH 2 CH 3 C OH CH 3. Secondary alcohol. Primary alcohol. Tertiary alcohol
 Chapter 10: Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols 100 Physical Properties Alcohols can be: CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 OH * Primary alcohol CH 3 OH CH * CH 2 CH 3 Secondary alcohol CH 3 CH 3 * C OH CH 3 Tertiary alcohol
Chapter 10: Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols 100 Physical Properties Alcohols can be: CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 OH * Primary alcohol CH 3 OH CH * CH 2 CH 3 Secondary alcohol CH 3 CH 3 * C OH CH 3 Tertiary alcohol
CH Organic Chemistry I (Katz) Practice Exam #3- Fall 2013
 C2710 - rganic Chemistry I (Katz) Practice Exam #3- all 2013 Name: Score: Part I - Choose the best answer and write the letter of your choice in the space provided. (32 pts) 1. f the following, which reaction
C2710 - rganic Chemistry I (Katz) Practice Exam #3- all 2013 Name: Score: Part I - Choose the best answer and write the letter of your choice in the space provided. (32 pts) 1. f the following, which reaction
Classification Tests
 3CLASFIC.DC 10/23/2008 Classification Tests 1. Classification Tests For Alcohols a) Sodium Metal: RH Na RNa H2(g) Positive Test: evolution of gas the rate is highly variable and depends upon the alcohol
3CLASFIC.DC 10/23/2008 Classification Tests 1. Classification Tests For Alcohols a) Sodium Metal: RH Na RNa H2(g) Positive Test: evolution of gas the rate is highly variable and depends upon the alcohol
HOMEWORK PROBLEMS: ALKYNES. 1. Provide the complete IUPAC name for the following compounds:
 CEM 31 MEWRK PRBLEMS: ALKYNES 1. Provide the complete IUPAC name for the following compounds: 2. When the compound below is treated with one equivalent of B 3, where does it react Explain. Where would
CEM 31 MEWRK PRBLEMS: ALKYNES 1. Provide the complete IUPAC name for the following compounds: 2. When the compound below is treated with one equivalent of B 3, where does it react Explain. Where would
Suggested solutions for Chapter 30
 s for Chapter 30 30 PRBLEM 1 uggest a mechanism for this synthesis of a tricyclic aromatic heterocycle. 2 Cl base A simple exercise in the synthesis of a pyridine fused to a pyrrole (or an indole with
s for Chapter 30 30 PRBLEM 1 uggest a mechanism for this synthesis of a tricyclic aromatic heterocycle. 2 Cl base A simple exercise in the synthesis of a pyridine fused to a pyrrole (or an indole with
Retrosynthetic Analysis & Synthesis Problems
 Chem 232 D. J. Wardrop wardropd@uic.edu Retrosynthetic Analysis & Synthesis Problems As we draw towards the end of the semester, we will be paying more attention to questions regarding synthesis, which
Chem 232 D. J. Wardrop wardropd@uic.edu Retrosynthetic Analysis & Synthesis Problems As we draw towards the end of the semester, we will be paying more attention to questions regarding synthesis, which
When planning an organic synthesis there are usually different questions that one must ask.
 CE 132 Work Shop Exercise Strategies for rganic Synthesis ne of the things that makes chemistry unique among the sciences is synthesis. Chemists make things. New pharmaceuticals, food additives, materials,
CE 132 Work Shop Exercise Strategies for rganic Synthesis ne of the things that makes chemistry unique among the sciences is synthesis. Chemists make things. New pharmaceuticals, food additives, materials,
12.1 The Nature of Organic molecules
 12.1 The Nature of Organic molecules Organic chemistry: : The chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon is tetravalent; it always form four bonds. Prentice Hall 2003 Chapter One 2 Organic molecules have covalent
12.1 The Nature of Organic molecules Organic chemistry: : The chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon is tetravalent; it always form four bonds. Prentice Hall 2003 Chapter One 2 Organic molecules have covalent
