ammonia primary amine secondary amine tertiary amine quaternary ammonium salt (NOT amines) H CH 3 CH 3 CH 2
|
|
|
- Andra Henderson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AMIES 1) TYPES F AMIES Amines can be classed as primary, secondary and tertiary. Amines are related to ammonia ( 3 ). Aromatic amines have the joined directly to the benzene ring. Quaternary ammonium salts contain quaternary ammonium ions and are related to amines, but they are not amines and do T possess a lone pair of electrons on the. There is some hydrogen bonding between molecules and many simple amines are liquids at room temperature, but this is weaker than in alcohols (e.g. 3 2 is a gas). ote that there is no hydrogen bonding between tertiary amine molecules (as there is no attached to the ) ammonia primary amine secondary amine tertiary amine quaternary ammonium salt (T amines) l ethylamine diethylamine trimethylamine tetarmethylammonium chloride 2) PEPAATI F 1 y ALIPATI AMIES a) By reaction of 3 with halogenoalkanes alogenoalkanes are reacted with an excess of concentrated ammonia dissolved in ethanol at pressure in a sealed container e.g. making ethylamine: bromoethane excess conc Br The mechanism is nucleophilic substitution. :3 : 3 This method is not usually used due to make primary amines however as the amine produced can react further with more of the halogenoalkane to form secondary and tertiary amines and quaternary ammonium salts. This problem is minimised by using an excess of concentrated ammonia, but it is still a problem July-2016 hemsheets A2 1078
2 b) By reduction of nitrile compounds This is the commonest way as it only forms one amine rather than a mixture. It is done in two steps. ote that the product has one more atom than the starting material. 1) Formation of a nitrile from a halogenoalkane w arm ethanol K K 2) eduction of the nitrile to form an amine 4 [] LiAl 4 in ethoxyethane 2 2 i catalyst heat e.g. making ethylamine step 1 K KBr step 2 4 [] TASK 1 Give two synthetic paths to making butylamine. Give equations for all reactions. oute 1 oute July-2016 hemsheets A2 1078
3 3) PEPAATI F 1 y AMATI AMIES These are usually prepared by the reduction of nitro compounds using tin and concentrated hydrochloric acid. (this would actually form the ammonium salt and so a is added to give the amine). 6 [] Sn l follow ed by a 2 2 4) BASE STEGT F AMIES Amines are Brønsted-Lowry bases (proton acceptors). They are weak bases, and act as bases because the lone pair on the atom can readily accept a proton. 2 - TASK 2 Write equations for the following reactions of amines as bases. Show the structure of all organic substances 1) Methylamine nitric acid 2) Diethylamine sulfuric acid 16-July-2016 hemsheets A2 1078
4 The ability of ammonia or an amine to act as a base depends on how well the lone pair on the atom can accept. The higher the electron density of the lone pair on the, the better it will be able to accept, so the stronger the base. In general, the order of base strength is: tertiary amine > secondary amine > primary amine > 3 > aromatic amine 3 y, 2 y and 1 y amines compared to ammonia ompared to ammonia, the more alkyl groups that are substituted onto the atom in place of atoms, the more electron density is pushed onto the atom (as the inductive effect of alkyl groups is greater than that of atoms - so alkyl groups push electron density towards the atom better than atoms). So the more alkyl groups, the higher the electron density of the lone pair on the, so the stronger the base. Aromatic amines compared to ammonia The lone pair on this is partially delocalised into the benzene ring, leading to a reduction in the electron density on the atom, so weaker base strength. TASK 3 Draw the structure of the two amines and then identify and explain which is the stronger base. amine amine stronger base reason 1 methylamine diethylamine 2 propylamine phenylamine 3 ammonia phenylmethylamine ( ) 4 ammonia cyclohexylamine 16-July-2016 hemsheets A2 1078
5 5) ULEPILI SUBSTITUTI EATIS 3 reacts with halogenoalkanes to form 1 y amines initially. The overall reaction is nucleophilic substitution, with ammonia acting as a nucleophile through the lone pair on the atom attacking the electron deficient atom of the -halogen bond. verall equation Mechanism : 3 :3 owever, as well as ammonia, the amines produced also have a lone pair on the atom, so they can react with halogenoalkanes. (in fact, the product has a greater electron density on the lone pair and is even better at reacting with halogenoalkane than the original molecule). This means that the 's on the can be successively replaced by the group from the haloalkanes, right through to quaternary ammonium salts. This greatly complicates the reaction, because any amine produced in such a reaction can react with more haloalkane and undergo further substitution. Due to the problems of further substitution in this reaction, it is not often used to prepare amines, as a mixture of amines and ammonium salts is produced which would have to separated. owever, if a large excess of ammonia is used, then a 1 y amine is the main product. Similarly, if a large excess of the haloalkane is used, then the 4 y ammonium salt is the main product. TASK 4 Give two synthetic paths to making butylamine. Give equations for all reactions. 1) Draw the structure of and name the main organic product when ethylamine reacts with a large excess of chloromethane. 2) Draw the structure of and name the main organic product when a large excess of propylamine reacts with a chloromethane July-2016 hemsheets A2 1078
6 3) a) Draw the structure of and name the organic products formed when methylamine reacts with chloroethane. b) Give mechanism for the formation of the tertiary amine in this reaction. 4) Draw the structure of all the organic products formed when diethylamine reacts with 2-bromopropane Use of quaternary ammonium salts Soap and detergent molecules are called surfactants and consist of an ionic "head" this will dissolve in water and is known as being hydrophilic a long alkyl chain ("tail") this dissolves grease (grease is not soluble in water) and is known as being hydrophobic. Micelles are formed as the soap/detergent molecules surround the dirt/grease molecules, with the hydrophobic tails in the centre dissolving the grease, and the hydrophilic heads around the outside dissolving in the water. This is an example of a soap: a This is an example of a detergent: S a Quaternary ammonium salts with some long chain alkyl groups are used as cationic surfactants. Fabric softeners often contain cationic surfactants as the surface of most materials is -ve charged. l e.g. ( 3) 2[( 2) 16 3] 2 l July-2016 hemsheets A2 1078
7 6) ULEPILI ADDITI-ELIMIATI EATIS (AYLATI) Amines react with acyl chlorides and acid anhydrides to replace an on the with the acyl group. This produces an amide and a molecule of l or a carboxylic acid. A second molecule of the amine reacts with the l / carboxylic acid to form a salt. Equation e.g. acylation of an amine (using an acyl chloride) l ' ' l then ' l ' l - overall l 2 ' ' ' l - Mechanism (for acyl chlorides) nucleophilic additionelimination : -.. then 2 3 TASK 5 1) Give balanced equation for: ethylamine propanoic anhydride 2) Give balanced equation and mechanism for: propylamine butanoyl chloride 16-July-2016 hemsheets A2 1078
Amines. Types of Amines. chemrevise.org. N Goalby Chemrevise.org. primary amine (one C attached to N) H. Secondary amine (two C s.
 Amines Goalby hemrevise.org Types of Amines primary amine (one attached to ) Secondary amine (two s attached to ) 3 2 2 3 name : diethylamine It is also possible to have aromatic amines 2 phenylamine name:
Amines Goalby hemrevise.org Types of Amines primary amine (one attached to ) Secondary amine (two s attached to ) 3 2 2 3 name : diethylamine It is also possible to have aromatic amines 2 phenylamine name:
6.10 Amines. Naming. N Goalby chemrevise.org 1 CH2 CH2
 6.10 Amines aming Amines These end in amine. There is, however, rather confusingly two ways of using this suffix. The exam board tend to use the common version where the name stem ends in -yl propylamine.
6.10 Amines aming Amines These end in amine. There is, however, rather confusingly two ways of using this suffix. The exam board tend to use the common version where the name stem ends in -yl propylamine.
Q.1 Draw structures for all amines of molecular formula C 4 H 11 N. Classify them as primary, secondary or tertiary amines.
 1 AMIES Structure ontain the 2 group. lassification primary (1 ) amines secondary (2 ) amines tertiary (3 ) amines quarternary (4 ) ammonium salts + 1 2 3 4 Aliphatic Aromatic methylamine, ethylamine,
1 AMIES Structure ontain the 2 group. lassification primary (1 ) amines secondary (2 ) amines tertiary (3 ) amines quarternary (4 ) ammonium salts + 1 2 3 4 Aliphatic Aromatic methylamine, ethylamine,
OCR Chemistry A H432. Amines are described as primary, secondary or tertiary depending on how many carbons are bonded to the N atom.
 OCR Chemistry A 432 About amines: can be considered as derivatives of ammonia, with one or more of the atoms replaced by alkyl groups. They are noted for their unpleasant, often fishy odours. We classify
OCR Chemistry A 432 About amines: can be considered as derivatives of ammonia, with one or more of the atoms replaced by alkyl groups. They are noted for their unpleasant, often fishy odours. We classify
Some..(A) Describe the synthesis of azo dyes and the full chemical equations for each step.
 A2 Chemistry: F324 Rings, Polymers and Analysis Amines Learning Outcomes: All.. (E) Most.. (C) Explain why amines are basic Draw the structure of a primary secondary and tertiary amine Describe the reactions
A2 Chemistry: F324 Rings, Polymers and Analysis Amines Learning Outcomes: All.. (E) Most.. (C) Explain why amines are basic Draw the structure of a primary secondary and tertiary amine Describe the reactions
Mechanism Summary for A-level AQA Chemistry
 Mechanism Summary for Alevel AQA hemistry Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with omine Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with sulphuric acid 3 S 2 3 3 S 2 S 2 Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with hydrogen
Mechanism Summary for Alevel AQA hemistry Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with omine Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with sulphuric acid 3 S 2 3 3 S 2 S 2 Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with hydrogen
AMINES HYDROXYNITRILES
 AMINES ACYL CHLORIDES HYDROXYNITRILES ALDEHYDE/KETONE REDUCTION Amines are nitrogen- containing organic compounds derived from ammonia, where one or more of the hydrogen atoms has been replaced by an alkyl
AMINES ACYL CHLORIDES HYDROXYNITRILES ALDEHYDE/KETONE REDUCTION Amines are nitrogen- containing organic compounds derived from ammonia, where one or more of the hydrogen atoms has been replaced by an alkyl
AQA A2 CHEMISTRY TOPIC 4.6 AROMATIC CHEMISTRY TOPIC 4.7 AMINES BOOKLET OF PAST EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
 AQA A2 CHEMISTRY TOPIC 4.6 AROMATIC CHEMISTRY TOPIC 4.7 AMINES BOOKLET OF PAST EXAMINATION QUESTIONS 1 1. (a) Benzene reacts with nitric acid in the presence of a catalyst to form nitrobenzene. This is
AQA A2 CHEMISTRY TOPIC 4.6 AROMATIC CHEMISTRY TOPIC 4.7 AMINES BOOKLET OF PAST EXAMINATION QUESTIONS 1 1. (a) Benzene reacts with nitric acid in the presence of a catalyst to form nitrobenzene. This is
3.10 Benzene : Aromatic Hydrocarbons / Arenes
 3.10 Benzene : Aromatic ydrocarbons / Arenes There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six
3.10 Benzene : Aromatic ydrocarbons / Arenes There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six
Name/CG: 2012 Term 2 Organic Chemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question
 Name/G: 2012 Term 2 rganic hemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question 1(a) A yellow liquid A, 7 7 N 2, reacts with alkaline potassium manganate (VII) and on acidification gives a yellow solid B,
Name/G: 2012 Term 2 rganic hemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question 1(a) A yellow liquid A, 7 7 N 2, reacts with alkaline potassium manganate (VII) and on acidification gives a yellow solid B,
Summary of mechanisms. Type of reaction: Nucleophilic subsitution/hydrolysis
 S Summary of mechanisms S Summary of mechanisms electrophilic addition Electrophiles: H δ in H (Ni catalyst needed), H δ in H-X; X δ in X ; H δ in H O (g) (conc H 3 PO 4 cat needed); H δ in NH 3 ; H δ
S Summary of mechanisms S Summary of mechanisms electrophilic addition Electrophiles: H δ in H (Ni catalyst needed), H δ in H-X; X δ in X ; H δ in H O (g) (conc H 3 PO 4 cat needed); H δ in NH 3 ; H δ
Class XII: Chemistry Chapter 13: Amines Top concepts
 Class XII: Chemistry Chapter 13: Amines Top concepts 1. Amines are regarded as derivatives of ammonia in which one, two or all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl or aryl group 2. Classification
Class XII: Chemistry Chapter 13: Amines Top concepts 1. Amines are regarded as derivatives of ammonia in which one, two or all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl or aryl group 2. Classification
H H O C C O H Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives C CH 2 C. N Goalby chemrevise.org. Strength of carboxylic acids.
 19 arboxylic Acids and Derivatives Naming arboxylic acids These have the ending -oic acid but no number is necessary for the acid group as it must always be at the end of the chain. The numbering always
19 arboxylic Acids and Derivatives Naming arboxylic acids These have the ending -oic acid but no number is necessary for the acid group as it must always be at the end of the chain. The numbering always
OCR (A) Chemistry A-level. Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis
 OCR (A) Chemistry A-level Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis Organic Synthesis Notes by Adam Robertson DEFINITIONS Heterolytic fission: The breaking of a covalent bond when one of the bonded atoms
OCR (A) Chemistry A-level Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis Organic Synthesis Notes by Adam Robertson DEFINITIONS Heterolytic fission: The breaking of a covalent bond when one of the bonded atoms
ORGANIC - EGE 5E CH. 2 - COVALENT BONDING AND CHEMICAL REACTIVITY
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HYBRID ORBITAL THEORY The Aufbau Principle states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy. If carbon has only two unfilled orbitals, why does it like to
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HYBRID ORBITAL THEORY The Aufbau Principle states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy. If carbon has only two unfilled orbitals, why does it like to
UNIT 4 REVISION CHECKLIST CHEM 4 AS Chemistry
 UNIT 4 REVISION CHECKLIST CHEM 4 AS Chemistry Topic 4.1 Kinetics a) Define the terms: rate of a reaction, rate constant, order of reaction and overall order of reaction b) Deduce the orders of reaction
UNIT 4 REVISION CHECKLIST CHEM 4 AS Chemistry Topic 4.1 Kinetics a) Define the terms: rate of a reaction, rate constant, order of reaction and overall order of reaction b) Deduce the orders of reaction
HALOGENOALKANES (HALOALKANES) Structure Contain the functional group C-X where X is a halogen (F,Cl,Br or I)
 aloalkanes 2812 1 ALOGENOALKANES (ALOALKANES) Structure ontain the functional group X where X is a halogen (F,l, or I) Types alogenoalkanes halogen is attached to an aliphatic skeleton alkyl group aloarenes
aloalkanes 2812 1 ALOGENOALKANES (ALOALKANES) Structure ontain the functional group X where X is a halogen (F,l, or I) Types alogenoalkanes halogen is attached to an aliphatic skeleton alkyl group aloarenes
HALOALKANES. Structure Contain the functional group C-X where X is a halogen (F,Cl,Br or I)
 aloalkanes AS3 1 ALOALKANES Structure ontain the functional group X where X is a halogen (F,l, or I) Types aloalkanes halogen is attached to an aliphatic skeleton alkyl group aloarenes halogen is attached
aloalkanes AS3 1 ALOALKANES Structure ontain the functional group X where X is a halogen (F,l, or I) Types aloalkanes halogen is attached to an aliphatic skeleton alkyl group aloarenes halogen is attached
Theoretically because there are 3 double bonds one might expect the amount of energy to be 3 times as much.
 18. Arenes There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six carbon ams with delocalised bonding.
18. Arenes There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six carbon ams with delocalised bonding.
AMINES. 3. Secondary When two hydrogen atoms are replaced by two alkyl or aryl groups.
 AMINES Amine may be regarded as derivative of ammonia formed by replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by corresponding number of alkyl or aryl group CLASSIFICATION 1. Ammonia 2. Primary amine 3. Secondary
AMINES Amine may be regarded as derivative of ammonia formed by replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by corresponding number of alkyl or aryl group CLASSIFICATION 1. Ammonia 2. Primary amine 3. Secondary
HALOGENOALKANES (HALOALKANES) Structure Contain the functional group C-X where X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br or I)
 alogenoalkanes F322 1 ALOGENOALKANES (ALOALKANES) Structure ontain the functional group X where X is a halogen (F, l, or I) Types alogenoalkanes halogen is attached to an aliphatic skeleton alkyl group
alogenoalkanes F322 1 ALOGENOALKANES (ALOALKANES) Structure ontain the functional group X where X is a halogen (F, l, or I) Types alogenoalkanes halogen is attached to an aliphatic skeleton alkyl group
FACTFILE: GCE CHEMISTRY
 FATFILE: GE EMISTY 2.5 ALOGENOALKANES Learning Outcomes Students should be able to: 2.5.1 explain the variation in boiling points of halogenoalkanes with different halogen atoms; 2.5.2 explain the variation
FATFILE: GE EMISTY 2.5 ALOGENOALKANES Learning Outcomes Students should be able to: 2.5.1 explain the variation in boiling points of halogenoalkanes with different halogen atoms; 2.5.2 explain the variation
Mechanisms. . CCl2 F + Cl.
 Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
2A - Amines. 2 H atoms replaced: 2 attached C's to N. 3 H atom replaced: 3 attached C's to N Ammonia, NH3 Primary amine Secondary amine Tertiary amine
 2A - Amines Something fishy about amines: Have an NH 2, amine group. Amines are derivatives of ammonia: 3 H atoms 1 H atom replaced: 1 attached C to N 2 H atoms replaced: 2 attached C's to N 3 H atom replaced:
2A - Amines Something fishy about amines: Have an NH 2, amine group. Amines are derivatives of ammonia: 3 H atoms 1 H atom replaced: 1 attached C to N 2 H atoms replaced: 2 attached C's to N 3 H atom replaced:
Organic Mechanisms 1
 Organic Mechanisms 1 Concepts The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Chemical properties of alkanes 314 Chemical properties of alkenes 318 Bonding in alkenes 320 Bonding
Organic Mechanisms 1 Concepts The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Chemical properties of alkanes 314 Chemical properties of alkenes 318 Bonding in alkenes 320 Bonding
TOK: The relationship between a reaction mechanism and the experimental evidence to support it could be discussed. See
 Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours) SL students study the core of these options and HL students study the whole option (the core and the extension material). TOK: The relationship between
Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours) SL students study the core of these options and HL students study the whole option (the core and the extension material). TOK: The relationship between
Haloalkanes. Isomers: Draw and name the possible isomers for C 5 H 11 Br
 Haloalkanes The basics: The functional group is a halogen atom: F, Cl, Br or I General formula C n H 2n+1 X Use the prefixes: fluoro, chloro, bromo and iodo. Isomers: Draw and name the possible isomers
Haloalkanes The basics: The functional group is a halogen atom: F, Cl, Br or I General formula C n H 2n+1 X Use the prefixes: fluoro, chloro, bromo and iodo. Isomers: Draw and name the possible isomers
 Top concepts Chapter: Amines 1. Amines are regarded as derivatives of ammonia in which one, two or all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl or aryl group 2. Classification of amines: 3. Preparation
Top concepts Chapter: Amines 1. Amines are regarded as derivatives of ammonia in which one, two or all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by alkyl or aryl group 2. Classification of amines: 3. Preparation
Downloaded from
 Page 1 of 6 AMINES Amines are derivatives of ammonia (NH3), obtained by replacement of 1, 2 or all the 3 hydrogen atoms by alkyl and/or aryl groups. In nature amines are present in - proteins, vitamins,
Page 1 of 6 AMINES Amines are derivatives of ammonia (NH3), obtained by replacement of 1, 2 or all the 3 hydrogen atoms by alkyl and/or aryl groups. In nature amines are present in - proteins, vitamins,
Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy
 By Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College of Science, King Saud University http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/melnewehy Amines 1 Classification and Structure of Amines -The relation between ammonia and
By Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College of Science, King Saud University http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/melnewehy Amines 1 Classification and Structure of Amines -The relation between ammonia and
Chapter 17. Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic system, they are available to attack a strong electrophile to give
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic system, they are available to attack a strong electrophile to give
Synthesis of Nitriles a. dehydration of 1 amides using POCl 3 : b. SN2 reaction of cyanide ion on halides:
 I. Nitriles Nitriles consist of the CN functional group, and are linear with sp hybridization on C and N. Nitriles are non-basic at nitrogen, since the lone pair exists in an sp orbital (50% s character
I. Nitriles Nitriles consist of the CN functional group, and are linear with sp hybridization on C and N. Nitriles are non-basic at nitrogen, since the lone pair exists in an sp orbital (50% s character
6.1.1 Aromatic Compounds
 6.1.1 Aromatic ompounds There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six carbon ams with delocalised
6.1.1 Aromatic ompounds There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six carbon ams with delocalised
Aromatic Hydrocarbons / Arenes
 Aromatic ydrocarbons / Arenes There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six carbon atoms
Aromatic ydrocarbons / Arenes There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six carbon atoms
Amines Reading Study Problems Key Concepts and Skills Lecture Topics: Amines: structure and nomenclature
 Amines Reading: Wade chapter 19, sections 19-1-19-19 Study Problems: 19-37, 19-39, 19-40, 19-41, 19-44, 19-46, 19-47, 19-48, 19-51, 19-54 Key Concepts and Skills: Explain how the basicity of amines varies
Amines Reading: Wade chapter 19, sections 19-1-19-19 Study Problems: 19-37, 19-39, 19-40, 19-41, 19-44, 19-46, 19-47, 19-48, 19-51, 19-54 Key Concepts and Skills: Explain how the basicity of amines varies
Organic Chemistry Review: Topic 10 & Topic 20
 Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
Organic Chemistry. Unit 10
 Organic Chemistry Unit 10 Halides Primary Carbons Secondary Carbons Tertiary Carbons IMPORTANCE?? REACTIONS!! Benzene C6H6 Aromatic functional group - C6H5 (IUPAC name - phenyl) Substitution Reactions
Organic Chemistry Unit 10 Halides Primary Carbons Secondary Carbons Tertiary Carbons IMPORTANCE?? REACTIONS!! Benzene C6H6 Aromatic functional group - C6H5 (IUPAC name - phenyl) Substitution Reactions
Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours)
 Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/) TOK: The relationship between a reaction mechanism and the experimental evidence to support it could be discussed. See 16... Core material: G1 G8 are core material
Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/) TOK: The relationship between a reaction mechanism and the experimental evidence to support it could be discussed. See 16... Core material: G1 G8 are core material
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds. Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
CHEMISTRY OF AMINES. There many organic nitrogen containing compounds, among which is amines. Organic nitrogen compounds are:
 CHEMISTRY OF AMINES There many organic nitrogen containing compounds, among which is amines. Organic nitrogen compounds are: Amines RNH 2 Amide RCONH 2 Imine R R C=NR Nitrile RC N Generally amines are
CHEMISTRY OF AMINES There many organic nitrogen containing compounds, among which is amines. Organic nitrogen compounds are: Amines RNH 2 Amide RCONH 2 Imine R R C=NR Nitrile RC N Generally amines are
6. Compounds with amine groups
 6. ompounds with amine groups 6.1. lassifying amines and amides 6.2 Properties of amines 6.3 Amine mechanisms 6.4 Amino acids 6.5 Amino acids and p 6.6 Amine preparation Answers ompounds with amine groups
6. ompounds with amine groups 6.1. lassifying amines and amides 6.2 Properties of amines 6.3 Amine mechanisms 6.4 Amino acids 6.5 Amino acids and p 6.6 Amine preparation Answers ompounds with amine groups
Electrophilic substitution Both words needed Ignore minor misspellings 1
 M.(a) Electrophilic substitution Both words needed Ignore minor misspellings (b) (i) Sn / HCl H 2 / Ni H 2 / Pt Fe / HCl Zn / HCl SnCl 2 / HCl Ignore conc or dil with HCl, Allow (dil) H 2 SO 4 but not
M.(a) Electrophilic substitution Both words needed Ignore minor misspellings (b) (i) Sn / HCl H 2 / Ni H 2 / Pt Fe / HCl Zn / HCl SnCl 2 / HCl Ignore conc or dil with HCl, Allow (dil) H 2 SO 4 but not
N.b. A catalyst is a species which speeds up a chemical reaction but which remains chemically unchanged. Reverse process of dehydration of an alcohol
 An Introduction to Organic hemistry N.b. A catalyst is a species which speeds up a chemical reaction but which remains chemically unchanged. ydration (Addition) Reverse process of dehydration of an alcohol
An Introduction to Organic hemistry N.b. A catalyst is a species which speeds up a chemical reaction but which remains chemically unchanged. ydration (Addition) Reverse process of dehydration of an alcohol
H 2 SO 4 Ar-NO 2 + H2O
 Phenyl group: Shorthand for phenyl: Ph, C 6 5,. An aryl group is an aromatic group: phenyl, substituted phenyl, or other aromatic group. Shorthand: Ar Generalized electrophilic aromatic substitution: E
Phenyl group: Shorthand for phenyl: Ph, C 6 5,. An aryl group is an aromatic group: phenyl, substituted phenyl, or other aromatic group. Shorthand: Ar Generalized electrophilic aromatic substitution: E
Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Thiols
 Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Thiols 45 -Alcohols have the general formula R-OH and are characterized by the presence of a hydroxyl group, -OH. -Phenols have a hydroxyl group attached directly to an
Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Thiols 45 -Alcohols have the general formula R-OH and are characterized by the presence of a hydroxyl group, -OH. -Phenols have a hydroxyl group attached directly to an
٢
 Amines ١ ٢ ٣ ٤ ٥ ٦ ٧ ٨ ٩ ١٠ ١١ Physical Properties of Amines - Amines are moderately polar. For this reason the low formula weight amines are readily soluble in water due to the formation of hydrogen bonds
Amines ١ ٢ ٣ ٤ ٥ ٦ ٧ ٨ ٩ ١٠ ١١ Physical Properties of Amines - Amines are moderately polar. For this reason the low formula weight amines are readily soluble in water due to the formation of hydrogen bonds
Aromatic Hydrocarbons / Arenes
 Aromatic ydrocarbons / Arenes There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six carbon atoms
Aromatic ydrocarbons / Arenes There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six carbon atoms
Lecture Notes Chemistry 342 Mukund P. Sibi Lecture 33 Amines
 Lecture otes Chemistry 342 Mukund P. Sibi Amines Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia. The nitrogen in amines contains a lone pair of electrons. The presence of this lone pair of electrons
Lecture otes Chemistry 342 Mukund P. Sibi Amines Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia. The nitrogen in amines contains a lone pair of electrons. The presence of this lone pair of electrons
Chapter 22: Amines. Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH 3. Nitrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the amine both basic and nucleophilic
 hapter 22: Amines. rganic derivatives of ammonia, 3. itrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the amine both basic and nucleophilic 22.1: Amines omenclature. (please read) sp 3 Amines are classified
hapter 22: Amines. rganic derivatives of ammonia, 3. itrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the amine both basic and nucleophilic 22.1: Amines omenclature. (please read) sp 3 Amines are classified
Chapter 20. Amines. Nomenclature for amines. Aryl amines
 Nomenclature for amines Chapter 20 Common names are widely used, named as alkylamines Systematic (IUPAC) nomenclature replaces the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -amine Amines Simple secondary
Nomenclature for amines Chapter 20 Common names are widely used, named as alkylamines Systematic (IUPAC) nomenclature replaces the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -amine Amines Simple secondary
Carboxylic acid derivatives
 arboxylic acid derivatives Acyl hlorides and Acid Anhydrides N Goalby hemrevise.org arboxylic acid derivatives carboxylic acid (ethanoic acid) 3 l Acyl hloride (ethanoyl chloride) key 3 3 Acid Anhydride
arboxylic acid derivatives Acyl hlorides and Acid Anhydrides N Goalby hemrevise.org arboxylic acid derivatives carboxylic acid (ethanoic acid) 3 l Acyl hloride (ethanoyl chloride) key 3 3 Acid Anhydride
Chapter 2 Acids and Bases. Arrhenius Acid and Base Theory. Brønsted-Lowry Acid and Base Theory
 hapter 2 Acids and Bases A significant amount of chemistry can be described using different theories of acids and bases. We ll consider three different acid-base theories (listed in order of increasing
hapter 2 Acids and Bases A significant amount of chemistry can be described using different theories of acids and bases. We ll consider three different acid-base theories (listed in order of increasing
Chemistry 343- Spring 2008
 Chemistry 343- Spring 2008 27 Chapter 2- Representative Carbon Compounds: Functional Groups, Intermolecular Forces and IR Spectroscopy A. ydrocarbons: Compounds composed of only C and Four Basic Types:
Chemistry 343- Spring 2008 27 Chapter 2- Representative Carbon Compounds: Functional Groups, Intermolecular Forces and IR Spectroscopy A. ydrocarbons: Compounds composed of only C and Four Basic Types:
Reactions of Haloalkanes
 Reactions of aloalkanes N Goalby chemrevise.org aloalkanes ontain a halogen atom covalently bonded to a carbon atom General formula: R-X where X is a halogen atom (F, l,, I) and R is the carbon chain.
Reactions of aloalkanes N Goalby chemrevise.org aloalkanes ontain a halogen atom covalently bonded to a carbon atom General formula: R-X where X is a halogen atom (F, l,, I) and R is the carbon chain.
Aromatic Compounds II
 2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 2 Aromatic Compounds II Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 17 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 2 Aromatic Compounds II Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 17 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
Topic 4.8 AMINO ACIDS. Structure Acid-Base Properties Condensation Reactions Proteins
 Topic 4.8 AMI AIDS Structure Acid-Base Properties ondensation eactions Proteins STUTUE F AMI AIDS Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group and a carboxylic acid group. aturally occurring amino
Topic 4.8 AMI AIDS Structure Acid-Base Properties ondensation eactions Proteins STUTUE F AMI AIDS Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group and a carboxylic acid group. aturally occurring amino
Chapter 22 Amines. Nomenclature Amines are classified according to the degree of substitution at nitrogen.
 CH. 22 Chapter 22 Amines Amines are very important in biological chemistry. Most of the bases in biological acid-base reactions are amines. They are also very important nucleophiles in biochemical reactions.
CH. 22 Chapter 22 Amines Amines are very important in biological chemistry. Most of the bases in biological acid-base reactions are amines. They are also very important nucleophiles in biochemical reactions.
17 Alcohols H H C C. N Goalby chemrevise.org 1 H H. Bond angles in Alcohols. Boiling points. Different types of alcohols H 2 C CH 2 CH 2
 17 Alcohols General formula alcohols n 2n+1 Naming Alcohols These have the ending -ol and if necessary the position number for the group is added between the name stem and the ol If the compound has an
17 Alcohols General formula alcohols n 2n+1 Naming Alcohols These have the ending -ol and if necessary the position number for the group is added between the name stem and the ol If the compound has an
HALOALKANES (HALOGENOALKANES) Structure Contain the functional group C-X where X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br or I)
 alogenoalkanes 1 ALOALKANES (ALOGENOALKANES) Structure ontain the functional group X where X is a halogen (F, l, or I) Types aloalkanes halogen is attached to an aliphatic skeleton alkyl group aloarenes
alogenoalkanes 1 ALOALKANES (ALOGENOALKANES) Structure ontain the functional group X where X is a halogen (F, l, or I) Types aloalkanes halogen is attached to an aliphatic skeleton alkyl group aloarenes
Lecture Notes Chemistry Mukund P. Sibi Lecture 36 Synthesis of Amines
 Lecture otes hemistry 42-2008 Mukund P. Sibi Synthesis of Amines Amines can be prepared from a variety of starting materials. All of these methods involve functional group transformations. The main methods
Lecture otes hemistry 42-2008 Mukund P. Sibi Synthesis of Amines Amines can be prepared from a variety of starting materials. All of these methods involve functional group transformations. The main methods
CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer Instructor: Paul J. Bracher. Quiz # 3. Monday, July 21 st, :30 a.m.
 CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer 2014 Quiz # 3 Solutions Key Page 1 of 9 CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer 2014 Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Quiz # 3 Monday, July 21 st,
CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer 2014 Quiz # 3 Solutions Key Page 1 of 9 CHEM 343 Principles of Organic Chemistry II Summer 2014 Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Quiz # 3 Monday, July 21 st,
Chapter 15. Reactions of Aromatic Compounds. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Arenes. The first step is the slow, rate-determining step
 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Arenes Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds The characteristic reaction of aromatic rings is substitution initiated by an electrophile halogenation nitration
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Arenes Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds The characteristic reaction of aromatic rings is substitution initiated by an electrophile halogenation nitration
dihalogenoalkane H 2, Nickel Catalyst KOH alcoholic HBr, HCl Br Cl Elimination KOH aqueous heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution
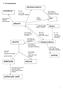 7 AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) Br 2, 2 KO aqueous room temp Electrophilic addition heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
7 AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) Br 2, 2 KO aqueous room temp Electrophilic addition heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
Chapter 19: Amines. Introduction
 Chapter 19: Amines Chap 19 HW: (be able to name amines); 37, 39, 41, 42, 44, 46, 47, 48, 53-55, 57, 58 Introduction Organic derivatives of ammonia. Many are biologically active. Chap 19: Amines Slide 19-2
Chapter 19: Amines Chap 19 HW: (be able to name amines); 37, 39, 41, 42, 44, 46, 47, 48, 53-55, 57, 58 Introduction Organic derivatives of ammonia. Many are biologically active. Chap 19: Amines Slide 19-2
Chemistry Questions ans Answers BASED ON HIGH ORDER THINKING SKILL (HOTS) UNIT- 13 ORGANIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING NITROGEN
 Chemistry Questions ans Answers BASED N HIGH RDER THINKING SKILL (HTS) UNIT- 13 RGANIC CMPUNDS CNTAINING NITRGEN 1 MARK QUESTINS Q. 1. Why the presence of a base is essential in the ammonolysis of alkyl
Chemistry Questions ans Answers BASED N HIGH RDER THINKING SKILL (HTS) UNIT- 13 RGANIC CMPUNDS CNTAINING NITRGEN 1 MARK QUESTINS Q. 1. Why the presence of a base is essential in the ammonolysis of alkyl
Electrophilic substitution Both words needed Ignore minor misspellings 1
 M.(a) Electrophilic substitution Both words needed Ignore minor misspellings (b) (i) Sn / HCl OR H 2 / Ni OR H 2 / Pt OR Fe / HCl OR Zn / HCl OR SnCl 2 / HCl Ignore conc or dil with HCl, Allow (dil) H
M.(a) Electrophilic substitution Both words needed Ignore minor misspellings (b) (i) Sn / HCl OR H 2 / Ni OR H 2 / Pt OR Fe / HCl OR Zn / HCl OR SnCl 2 / HCl Ignore conc or dil with HCl, Allow (dil) H
Amines and Related Nitrogen Compounds
 11 Amines and Related itrogen ompounds hapter Summary Amines are organic derivatives of ammonia. They may be primary, secondary, or tertiary, depending on whether one, two, or three organic groups are
11 Amines and Related itrogen ompounds hapter Summary Amines are organic derivatives of ammonia. They may be primary, secondary, or tertiary, depending on whether one, two, or three organic groups are
R N R N R N. primary secondary tertiary
 Chapter 19 Amines omenclature o assification of amines Amines are classified as 1, 2, or 3 based on how many R groups are attached to the nitrogen R R R R R R primary secondary tertiary When there are
Chapter 19 Amines omenclature o assification of amines Amines are classified as 1, 2, or 3 based on how many R groups are attached to the nitrogen R R R R R R primary secondary tertiary When there are
Ch 20 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
 Ch 20 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Carboxylic Acids (RCO 2 H) are compounds with an OH attached to a carbonyl. Nitriles (RC N) are compounds a carbon-nitrogen triple bond. Naming Carboxylic Acids 1. Replace
Ch 20 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Carboxylic Acids (RCO 2 H) are compounds with an OH attached to a carbonyl. Nitriles (RC N) are compounds a carbon-nitrogen triple bond. Naming Carboxylic Acids 1. Replace
Ammonia Primary Secondary Tertiary Quarternary Ammonium Ion
 1 Chapter 19: Amines I. Introduction: Classification: NH 3 RNH 2 R 2 NH R 3 N R 4 N + Ammonia Primary Secondary Tertiary Quarternary Ammonium Ion Amines are a very common functional group in organic chemistry,
1 Chapter 19: Amines I. Introduction: Classification: NH 3 RNH 2 R 2 NH R 3 N R 4 N + Ammonia Primary Secondary Tertiary Quarternary Ammonium Ion Amines are a very common functional group in organic chemistry,
All Classes of Organic Compounds
 Amines All Classes of Organic Compounds ydrocarbons Functionalized ydrocarbons F,Cl,Br O,S, Alkanes Alkenes Alkynes Aromatics alides -O- -S- -- Alcohols Phenols Ethers Thiols Dissulfides Amines O C O C
Amines All Classes of Organic Compounds ydrocarbons Functionalized ydrocarbons F,Cl,Br O,S, Alkanes Alkenes Alkynes Aromatics alides -O- -S- -- Alcohols Phenols Ethers Thiols Dissulfides Amines O C O C
Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Chapter 24. Amines. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition
 Chapter 24. Amines Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Amines Organic Nitrogen Compounds Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH 3, Nitrogen atom with a lone pair of electrons, making amines
Chapter 24. Amines Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Amines Organic Nitrogen Compounds Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH 3, Nitrogen atom with a lone pair of electrons, making amines
REASONING QUESTIONS FROM ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (CH. 1 & 2)
 REASONING QUESTIONS FROM ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (CH. 1 & 2) 1.) Why do haloalkenes under go nucleophillic substitution whereas haloarenes under go electophillic substitution. Ans. Due to more electro negative
REASONING QUESTIONS FROM ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (CH. 1 & 2) 1.) Why do haloalkenes under go nucleophillic substitution whereas haloarenes under go electophillic substitution. Ans. Due to more electro negative
H C C C C H. Secondary halogenoalkane Two carbons attached to the carbon atom adjoining the halogen
 3.3 alogenoalkanes Naming alogenoalkanes Based on original alkane, with a prefix indicating atom: Fluoro for F; hloro for l; omo for ; Iodo for I. Substituents are listed alphabetically lassifying oalkanes
3.3 alogenoalkanes Naming alogenoalkanes Based on original alkane, with a prefix indicating atom: Fluoro for F; hloro for l; omo for ; Iodo for I. Substituents are listed alphabetically lassifying oalkanes
Module 4 revision guide: Compounds with C=O group
 opyright N Goalby Bancroft's School Module 4 revision guide: ompounds with = group arbonyls: Aldehydes and Ketones arbonyls are compounds with a = bond, they can be either aldehydes or ketones. 3 ethanal
opyright N Goalby Bancroft's School Module 4 revision guide: ompounds with = group arbonyls: Aldehydes and Ketones arbonyls are compounds with a = bond, they can be either aldehydes or ketones. 3 ethanal
Chapter 2: Acids and Bases
 hapter 2: Acids and Bases 32 hapter 2: Acids and Bases Problems 2.1 Write each acid- reaction as a proton-transfer reaction. Label which reactant is the acid and which the, as well as which product is
hapter 2: Acids and Bases 32 hapter 2: Acids and Bases Problems 2.1 Write each acid- reaction as a proton-transfer reaction. Label which reactant is the acid and which the, as well as which product is
 Question 13.1: Classify the following amines as primary, secondary or tertiary: (i) (ii) (iii) (C 2 H 5 ) 2 CHNH 2 (iv) (C 2 H 5 ) 2 NH Primary: (i) and (iii) Secondary: (iv) Tertiary: (ii) Question 13.2:
Question 13.1: Classify the following amines as primary, secondary or tertiary: (i) (ii) (iii) (C 2 H 5 ) 2 CHNH 2 (iv) (C 2 H 5 ) 2 NH Primary: (i) and (iii) Secondary: (iv) Tertiary: (ii) Question 13.2:
AMINES. 3. From your knowledge of the effects involved, predict or explain experimental results. Important areas include:
 AMINES A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Name given the structure, and draw the structure given the name of amines and common nitrogen heterocycles (pyrrole and pyridine). Also, give the classification of
AMINES A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Name given the structure, and draw the structure given the name of amines and common nitrogen heterocycles (pyrrole and pyridine). Also, give the classification of
Reaction of alkanes with bromine / chlorine in UV light. This is the overall reaction, but a more complex mixture of products is actually formed
 8. The aloalkanes opyright N Goalby Bancroft's School Synthesis of chloroalkanes Reaction of alkanes with bromine / chlorine in UV light In the presence of UV light alkanes react with chlorine to form
8. The aloalkanes opyright N Goalby Bancroft's School Synthesis of chloroalkanes Reaction of alkanes with bromine / chlorine in UV light In the presence of UV light alkanes react with chlorine to form
Benzylamine reacts with nitrous acid to form unstable diazonium salt, which in turn gives alcohol with the evolution of nitrogen gas.
 Benzylamine reacts with nitrous acid to form unstable diazonium salt, which in turn gives alcohol with the evolution of nitrogen gas. On the other hand, aniline reacts with HNO2 at a low temperature to
Benzylamine reacts with nitrous acid to form unstable diazonium salt, which in turn gives alcohol with the evolution of nitrogen gas. On the other hand, aniline reacts with HNO2 at a low temperature to
EXTRA QUESTIONS FOR 2.8 HALOALKANES. 1. Methylbenzene is converted into (chloromethyl)benzene in a free radical substitution reaction....
 EXTRA QUESTIONS FOR 2.8 HALOALKANES 1. Methylbenzene is converted into (chloromethyl)benzene in a free radical substitution reaction. C 6 H 5 3 + Cl 2 C 6 H 5 2 Cl + HCl Write an equation for the initiation
EXTRA QUESTIONS FOR 2.8 HALOALKANES 1. Methylbenzene is converted into (chloromethyl)benzene in a free radical substitution reaction. C 6 H 5 3 + Cl 2 C 6 H 5 2 Cl + HCl Write an equation for the initiation
abc Mark Scheme Chemistry 6421 General Certificate of Education 2006 examination - January series CHM4 Further Physical and Organic Chemistry
 General ertificate of Education abc hemistry 642 M4 Further Physical and rganic hemistry Mark Scheme 2006 examination - January series Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and considered,
General ertificate of Education abc hemistry 642 M4 Further Physical and rganic hemistry Mark Scheme 2006 examination - January series Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and considered,
Q.1 Draw out suitable structures which fit the molecular formula C 6 H 6
 Aromatic compounds 2814 1 BENZENE Structure Primary analysis revealed benzene had an... empirical formula of and a molecular formula of 6 6 Q.1 Draw out suitable structures which fit the molecular formula
Aromatic compounds 2814 1 BENZENE Structure Primary analysis revealed benzene had an... empirical formula of and a molecular formula of 6 6 Q.1 Draw out suitable structures which fit the molecular formula
AMINES. 4. From your knowledge of the effects involved, predict or explain experimental results. Important areas include:
 AMINES A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Give the IUPAC or common name given the structure, and draw the structure given the name of amines and common nitrogen heterocycles (pyrrole, pyridine, purine, pyrimidine,
AMINES A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Give the IUPAC or common name given the structure, and draw the structure given the name of amines and common nitrogen heterocycles (pyrrole, pyridine, purine, pyrimidine,
Topic 4.10 ORGANIC SYNTHESIS AND ANALYSIS. Organic analysis Organic synthesis
 Topic 4.10 ORGANIC SYNTHESIS AND ANALYSIS Organic analysis Organic synthesis DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN DIFFERENT ORGANIC COMPOUNDS Many of the organic compounds prepared in AS Unit 2 and in A2 Unit 4 can
Topic 4.10 ORGANIC SYNTHESIS AND ANALYSIS Organic analysis Organic synthesis DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN DIFFERENT ORGANIC COMPOUNDS Many of the organic compounds prepared in AS Unit 2 and in A2 Unit 4 can
Downloaded from
 1 Class XII Chemistry Chapter: Alcohols, Phenols And Ethers Top concepts: 1. Structure of alcohols, phenols and ethers: 2. Preparation of alcohols: 3. Preparation of phenols: 2 4. Physical properties of
1 Class XII Chemistry Chapter: Alcohols, Phenols And Ethers Top concepts: 1. Structure of alcohols, phenols and ethers: 2. Preparation of alcohols: 3. Preparation of phenols: 2 4. Physical properties of
CHAPTER 2. Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules
 CHAPTER 2 Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules 2-1 Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Simple Chemical Processes Chemical thermodynamics: Is concerned with the extent that
CHAPTER 2 Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules 2-1 Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Simple Chemical Processes Chemical thermodynamics: Is concerned with the extent that
Aryl Halides. Structure
 Aryl Halides Structure Aryl halides are compounds containing halogen attached directly to an aromatic ring. They have the general formula ArX, where Ar is phenyl, substituted phenyl. X= F,Cl,Br,I An aryl
Aryl Halides Structure Aryl halides are compounds containing halogen attached directly to an aromatic ring. They have the general formula ArX, where Ar is phenyl, substituted phenyl. X= F,Cl,Br,I An aryl
I5 ELECTROPHILIC SUBSTITUTIONS OF
 Section I Aromatic chemistry I5 ELECTPILIC SUBSTITUTINS F MN-SUBSTITUTED AMATIC INGS Key Notes ortho, meta and para substitution Substituent effect eaction profile Activating groups inductive o/p Deactivating
Section I Aromatic chemistry I5 ELECTPILIC SUBSTITUTINS F MN-SUBSTITUTED AMATIC INGS Key Notes ortho, meta and para substitution Substituent effect eaction profile Activating groups inductive o/p Deactivating
Chapter 10: Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
 Chapter 10: Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives The back of the white willow tree (Salix alba) is a source of salicylic acid which is used to make aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) The functional group
Chapter 10: Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives The back of the white willow tree (Salix alba) is a source of salicylic acid which is used to make aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) The functional group
12/27/2010. Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen atom
Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen atom
Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 15 1 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen
Chapter 15 1 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen
.. Amines CHAPTER SUMMARY
 10 N.. N.. CHAPTER SUMMARY 10.1 Structure of are derivatives of ammonia in which one or more hydrogens have been replaced by organic groups. Replacement of one hydrogen results in a primary amine. In a
10 N.. N.. CHAPTER SUMMARY 10.1 Structure of are derivatives of ammonia in which one or more hydrogens have been replaced by organic groups. Replacement of one hydrogen results in a primary amine. In a
Organic Chemistry SL IB CHEMISTRY SL
 Organic Chemistry SL IB CHEMISTRY SL 10.1 Fundamentals of organic chemistry Understandings: A homologous series is a series of compounds of the same family, with the same general formula, which differ
Organic Chemistry SL IB CHEMISTRY SL 10.1 Fundamentals of organic chemistry Understandings: A homologous series is a series of compounds of the same family, with the same general formula, which differ
Page 2. Q1.Consider the following scheme of reactions. (a) Give the IUPAC name for compound P and that for compound Q. P... Q...
 Q1.Consider the following scheme of reactions. (a) Give the IUPAC name for compound P and that for compound Q. P... Q... (2) (b) The conversion of P into Q in Reaction 1 uses HCl Name and outline a mechanism
Q1.Consider the following scheme of reactions. (a) Give the IUPAC name for compound P and that for compound Q. P... Q... (2) (b) The conversion of P into Q in Reaction 1 uses HCl Name and outline a mechanism
Ammonia and Amines. Four sp 3 hybridized orbitals. Three used for bonding and one for the lone pair of electrons. secondary 2. Et Me.
 Ammonia and Amines threefold axis of rotation 111 107 Four sp 3 hybridized orbitals. Three used for bonding and one for the lone pair of electrons. trigonal pyramidal primary 1 secondary 2 tertiary 3 quaternary
Ammonia and Amines threefold axis of rotation 111 107 Four sp 3 hybridized orbitals. Three used for bonding and one for the lone pair of electrons. trigonal pyramidal primary 1 secondary 2 tertiary 3 quaternary
Amines - Derivatives of Ammonia
 Amines - Derivatives of Ammonia lassification by the number of attached groups ethylamine diethylamine triethylamine Amines - Derivatives of Ammonia lassification by the type of attached groups 2 2 aromatic
Amines - Derivatives of Ammonia lassification by the number of attached groups ethylamine diethylamine triethylamine Amines - Derivatives of Ammonia lassification by the type of attached groups 2 2 aromatic
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
 Aromatic Hydrocarbons Aromatic hydrocarbons contain six-membered rings of carbon atoms with alternating single and double carbon-carbon bonds. The ring is sometimes shown with a circle in the center instead
Aromatic Hydrocarbons Aromatic hydrocarbons contain six-membered rings of carbon atoms with alternating single and double carbon-carbon bonds. The ring is sometimes shown with a circle in the center instead
CHEM1902/ N-8 November Consider the following reaction sequences beginning with the carboxylic acid, E.
 CEM1902/4 2014--8 ovember 2014 Consider the following reaction sequences beginning with the carboxylic acid, E. 6 ame compounds E and G. E: propionic acid G: methyl propionate Propose structures for compounds
CEM1902/4 2014--8 ovember 2014 Consider the following reaction sequences beginning with the carboxylic acid, E. 6 ame compounds E and G. E: propionic acid G: methyl propionate Propose structures for compounds
