H C C C C H. Secondary halogenoalkane Two carbons attached to the carbon atom adjoining the halogen
|
|
|
- Carol McCoy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3.3 alogenoalkanes Naming alogenoalkanes Based on original alkane, with a prefix indicating atom: Fluoro for F; hloro for l; omo for ; Iodo for I. Substituents are listed alphabetically lassifying oalkanes 1bromopropane l 2chloro2methylbutane aloalkanes can be classified as primary, secondary or tertiary depending on the number of carbon atoms attached to the X functional group. l Primary oalkane One carbon attached to the Reactions of alogenoalkanes Secondary oalkane Two carbons attached to the 1. Nucleophilic substitution reactions alogenoalkanes undergo either substitution or elimination reactions Substitution: swapping a atom for another atom or groups of atoms Tertiary oalkane Three carbons attached to the Organic reactions are classified by their mechanisms Nucleophile: electron pair donator e.g. :O, :N 3, N The Mechanism: We draw (or outline) mechanisms to show in detail how a reaction proceeds :Nu represents any nucleophile they always have a lone pair and act as electron pair donators The nucleophiles attack the positive carbon atom Nu: X δ + δ Nu + X The carbon has a small positive charge because of the electronegativity difference between the carbon and the We use curly arrows in mechanisms (with two line heads) to show the movement of two electrons A curly arrow will always start from a lone pair of electrons or the centre of a bond The rate of these substitution reactions depends on the strength of the X bond The weaker the bond, the easier it is to break and the faster the reaction. The iodoalkanes are the fastest to substitute and the fluoroalkanes are the slowest. The strength of the F bond is such that fluoroalkanes are very unreactive Bond enthalpy / kjmol 1 I l 338 F 484 1
2 omparing the rate of hydrolysis reactions ydrolysis is defined as the splitting of a molecule ( in this case a haloalkane) by a reaction with water 3 2 X + 2 O 3 2 O + X + + Aqueous silver nitrate is added to a haloalkane and the halide leaving group combines with a silver ion to form a SILVER ALIDE PREIPITATE. The precipitate only forms when the halide ion has left the haloalkane and so the rate of formation of the precipitate can be used to compare the reactivity of the different haloalkanes. Water is a poor nucleophile but it can react slowly with haloalkanes in a substitution reaction 3 2 I + 2 O 3 2 O + I + + Ag + (aq) + I (aq) AgI (s) yellow precipitate The iodoalkane forms a precipitate with the silver nitrate first as the I bond is weakest and so it hydrolyses the quickest The quicker the precipitate is formed, the faster the substitution reaction and the more reactive the haloalkane The rate of these substitution reactions depends on the strength of the X bond. The weaker the bond, the easier it is to break and the faster the reaction. AgI (s) yellow precipitate Ag (s) cream precipitate Agl (s) white precipitate forms faster Nucleophilic substitution with aqueous hydroxide ions hange in functional group: oalkane alcohol Reagent: potassium (or sodium) hydroxide onditions: In aqueous solution; eat under reflux Mechanism:Nucleophilic Substitution Type of reagent: Nucleophile, O 1bromopropane + KO O propan1ol + K 3 O: δ + δ 3 O + : The aqueous conditions needed is an important point. If the solvent is changed to ethanol an elimination reaction occurs Alternative mechanism for tertiary oalkanes Tertiary haloalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution in a different way You don t need to learn this but there have been application of understanding questions on this The first breaks away from the haloalkane to form a carbocation intermediate :O The hydroxide nucleophile then attacks the positive carbon O Tertiary oalkanes undergo this mechanism as the tertiary carbocation is stabilised by the electron releasing methyl groups around it. (see alkenes topic for another example of this). Also the bulky methyl groups prevent the hydroxide ion from attacking the oalkane in the same way as the mechanism above 2
3 Nucleophilic substitution with cyanide ions hange in functional group: oalkane nitrile Reagent: KN dissolved in ethanol/water mixture onditions: eating under reflux Mechanism: Nucleophilic Substitution Type of reagent: Nucleophile, :N 1bromopropane + :N N + butanenitrile Note: the mechanism is identical to the above one 3 N: δ + δ 3 N + : This reaction increases the length of the carbon chain (which is reflected in the name) In the above example butanenitrile includes the in the nitrile group Naming Nitriles Nitrile groups have to be at the end of a chain. Start numbering the chain from the in the N 3 2 N : propanenitrile 3 2 N 3methylbutanenitrile Note the naming: butanenitrile and not butannitrile. 3 Nucleophilic substitution with ammonia hange in functional group: oalkane amine Reagent: N 3 dissolved in ethanol onditions: eating under pressure (in a sealed tube) Mechanism: Nucleophilic Substitution Type of reagent: Nucleophile, :N 3 + 2N 3 propylamine N 2 + N 4 Naming amines: δ + δ 3 2 3N: 3 2 N + :N 3 : In the above example propylamine, the propyl shows the 3 s of the carbon chain. Sometimes it is easier to use the IUPA naming for amines e.g. Propan1amine 3 2 N 2 + N 4 Further substitution reactions can occur between the oalkane and the amines formed leading to a lower yield of the amine. Using excess ammonia helps minimise this 3
4 2. Elimination reaction of oalkanes Elimination: removal of small molecule (often water) from the organic molecule Elimination with alcoholic hydroxide ions hange in functional group: oalkane alkene Reagents: Potassium (or sodium) hydroxide onditions: In ethanol ; eat Mechanism: Elimination Type of reagent: Base, O 1bromopropane + KO + K + 2 O propene Note the importance of the solvent to the type of reaction here. Aqueous: substitution Alcoholic: elimination 3 3 :O O Often a mixture of products from both elimination and substitution occurs With unsymmetrical secondary and tertiary oalkanes two (or sometimes three) different structural isomers can be formed l 2methyl 2 chlorobutane can give 2methylbut1ene and 2methylbut2ene The structure of the oalkane also has an effect on the degree to which substitution or elimination occurs in this reaction. Primary tends towards substitution Tertiary tends towards elimination 4
5 Uses of oalkanes chloroalkanes and chlorofluoroalkanes can be used as solvents 3 l 3 was used as the solvent in dry cleaning Many of these uses have now been stopped due to the toxicity of o alkanes and also their detrimental effect on the atmosphere alogenoalkanes have also been used as refrigerants, pesticides and aerosol propellants Ozone hemistry The naturally occurring ozone (O 3 ) layer in the upper atmosphere is beneficial as it filters out much of the sun s harmful UV radiation Ozone in the lower atmosphere is a pollutant and contributes towards the formation of smog Manmade chlorofluorocarbons (F s) caused a hole to form in the ozone layer. hlorine atoms are formed in the upper atmosphere when energy from ultraviolet radiation causes l bonds in chlorofluorocarbons (Fs) to break F 2 l 2 F 2 l + l The chlorine free radical atoms catalyse the decomposition of ozone due to these reactions because they are regenerated. (They provide an alternative route with a lower activation energy) They contributed to the formation of a hole in the ozone layer. l. + O 3 lo. + O 2 lo. + O 3 2O 2 + l. Overall equation 2 O 3 3 O 2 The regenerated l radical means that one l radical could destroy many thousands of ozone molecules Legislation to ban the use of Fs was supported by chemists and that they have now developed alternative chlorinefree compounds Fs (ydro fluoro carbons) e.g.. 2 FF 3 are now used for refrigerators and airconditioners. These are safer as they do not contain the l bond The F bond is stronger than the l bond and is not affected by UV 5
Reaction of alkanes with bromine / chlorine in UV light. This is the overall reaction, but a more complex mixture of products is actually formed
 8. The aloalkanes opyright N Goalby Bancroft's School Synthesis of chloroalkanes Reaction of alkanes with bromine / chlorine in UV light In the presence of UV light alkanes react with chlorine to form
8. The aloalkanes opyright N Goalby Bancroft's School Synthesis of chloroalkanes Reaction of alkanes with bromine / chlorine in UV light In the presence of UV light alkanes react with chlorine to form
Reactions of Haloalkanes
 Reactions of aloalkanes N Goalby chemrevise.org aloalkanes ontain a halogen atom covalently bonded to a carbon atom General formula: R-X where X is a halogen atom (F, l,, I) and R is the carbon chain.
Reactions of aloalkanes N Goalby chemrevise.org aloalkanes ontain a halogen atom covalently bonded to a carbon atom General formula: R-X where X is a halogen atom (F, l,, I) and R is the carbon chain.
dihalogenoalkane H 2, Nickel Catalyst KOH alcoholic HBr, HCl Br Cl Elimination KOH aqueous heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution
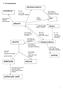 7 AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) Br 2, 2 KO aqueous room temp Electrophilic addition heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
7 AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) Br 2, 2 KO aqueous room temp Electrophilic addition heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
Cl Br H C C C C H. Secondary halogenoalkane Two carbons attached to the carbon atom adjoining the halogen
 alogenoalkanes Naming alogenoalkanes Based on original alkane, with a prefix indicating halogen atom: Fluoro for F; hloro for l; omo for ; Iodo for I. Substituents are listed alphabetically If there are
alogenoalkanes Naming alogenoalkanes Based on original alkane, with a prefix indicating halogen atom: Fluoro for F; hloro for l; omo for ; Iodo for I. Substituents are listed alphabetically If there are
dihalogenoalkane H 2, KOH alcoholic heat under reflux Elimination PCl 5, PBr 3, PI 3 Heat under reflux substitution KOH aqueous heat under reflux
 7. AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) 2, l 2 room temp Electrophilic addition KO aqueous heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
7. AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) 2, l 2 room temp Electrophilic addition KO aqueous heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
FACTFILE: GCE CHEMISTRY
 FATFILE: GE EMISTY 2.5 ALOGENOALKANES Learning Outcomes Students should be able to: 2.5.1 explain the variation in boiling points of halogenoalkanes with different halogen atoms; 2.5.2 explain the variation
FATFILE: GE EMISTY 2.5 ALOGENOALKANES Learning Outcomes Students should be able to: 2.5.1 explain the variation in boiling points of halogenoalkanes with different halogen atoms; 2.5.2 explain the variation
10 Halogenoalkanes. Classifying Halogenoalkanes. Reactions of Halogenoalkanes. Nucleophilic substitution reactions. N Goalby chemrevise.
 10 alogenoalkanes Naming alogenoalkanes Based on original alkane, with a prefix indicating halogen atom: Fluoro for F; hloro for l; Bromo for Br; Iodo for I. Substituents are listed alphabetically lassifying
10 alogenoalkanes Naming alogenoalkanes Based on original alkane, with a prefix indicating halogen atom: Fluoro for F; hloro for l; Bromo for Br; Iodo for I. Substituents are listed alphabetically lassifying
HALOALKANES (HALOGENOALKANES) Structure Contain the functional group C-X where X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br or I)
 alogenoalkanes 1 ALOALKANES (ALOGENOALKANES) Structure ontain the functional group X where X is a halogen (F, l, or I) Types aloalkanes halogen is attached to an aliphatic skeleton alkyl group aloarenes
alogenoalkanes 1 ALOALKANES (ALOGENOALKANES) Structure ontain the functional group X where X is a halogen (F, l, or I) Types aloalkanes halogen is attached to an aliphatic skeleton alkyl group aloarenes
General A haloalkane is a compound in which one or more H atoms of an alkane are replaced by halogen atoms.
 aloalkanes General A haloalkane is a compound in which one or more atoms of an alkane are replaced by halogen atoms. If one hydrogen atom is replaced, the general formula is n 2n+1 X where X = F, l, Br
aloalkanes General A haloalkane is a compound in which one or more atoms of an alkane are replaced by halogen atoms. If one hydrogen atom is replaced, the general formula is n 2n+1 X where X = F, l, Br
HALOGENOALKANES (HALOALKANES) Structure Contain the functional group C-X where X is a halogen (F,Cl,Br or I)
 aloalkanes 2812 1 ALOGENOALKANES (ALOALKANES) Structure ontain the functional group X where X is a halogen (F,l, or I) Types alogenoalkanes halogen is attached to an aliphatic skeleton alkyl group aloarenes
aloalkanes 2812 1 ALOGENOALKANES (ALOALKANES) Structure ontain the functional group X where X is a halogen (F,l, or I) Types alogenoalkanes halogen is attached to an aliphatic skeleton alkyl group aloarenes
HALOGENOALKANES (HALOALKANES) Structure Contain the functional group C-X where X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br or I)
 alogenoalkanes F322 1 ALOGENOALKANES (ALOALKANES) Structure ontain the functional group X where X is a halogen (F, l, or I) Types alogenoalkanes halogen is attached to an aliphatic skeleton alkyl group
alogenoalkanes F322 1 ALOGENOALKANES (ALOALKANES) Structure ontain the functional group X where X is a halogen (F, l, or I) Types alogenoalkanes halogen is attached to an aliphatic skeleton alkyl group
OCR AS Chemistry A H032 for first assessment in Complete Tutor Notes. Section: Boomer Publications
 R AS hemistry A 032 for first assessment in 2016 omplete Tutor Notes www.boomerchemistry.com Section: 4.2.1 Alcohols 4.2.2 aloalkanes 2015 Boomer Publications page 145 page 152 40 Alcohols Page 155 Ethanol
R AS hemistry A 032 for first assessment in 2016 omplete Tutor Notes www.boomerchemistry.com Section: 4.2.1 Alcohols 4.2.2 aloalkanes 2015 Boomer Publications page 145 page 152 40 Alcohols Page 155 Ethanol
HALOALKANES. Structure Contain the functional group C-X where X is a halogen (F,Cl,Br or I)
 aloalkanes AS3 1 ALOALKANES Structure ontain the functional group X where X is a halogen (F,l, or I) Types aloalkanes halogen is attached to an aliphatic skeleton alkyl group aloarenes halogen is attached
aloalkanes AS3 1 ALOALKANES Structure ontain the functional group X where X is a halogen (F,l, or I) Types aloalkanes halogen is attached to an aliphatic skeleton alkyl group aloarenes halogen is attached
Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide.
 Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction? A B C D Electrophilic addition Electrophilic substitution
Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction? A B C D Electrophilic addition Electrophilic substitution
3.2.8 Haloalkanes. Nucleophilic Substitution. 267 minutes. 264 marks. Page 1 of 36
 3.2.8 Haloalkanes Nucleophilic Substitution 267 minutes 264 marks Page 1 of 36 Q1. (a) The equation below shows the reaction of 2-bromopropane with an excess of ammonia. CH 3 CHBrCH 3 + 2NH 3 CH 3 CH(NH
3.2.8 Haloalkanes Nucleophilic Substitution 267 minutes 264 marks Page 1 of 36 Q1. (a) The equation below shows the reaction of 2-bromopropane with an excess of ammonia. CH 3 CHBrCH 3 + 2NH 3 CH 3 CH(NH
F322: Chains, Energy and Resources Halogenoalkanes
 F322: Chains, Energy and Resources Halogenoalkanes 56 Marks 1. Chlorofluoroalkanes, CFCs, were developed from fluoroalkanes and were used in aerosols and as refrigerants. Under the Montreal Protocol, CFCs
F322: Chains, Energy and Resources Halogenoalkanes 56 Marks 1. Chlorofluoroalkanes, CFCs, were developed from fluoroalkanes and were used in aerosols and as refrigerants. Under the Montreal Protocol, CFCs
3.2.8 Haloalkanes. Elimination. 148 minutes. 145 marks. Page 1 of 22
 3.2.8 Haloalkanes Elimination 148 minutes 145 marks Page 1 of 22 Q1. Reaction of 2-bromobutane with potassium hydroxide can produce two types of product depending on the solvent used. In aqueous solution,
3.2.8 Haloalkanes Elimination 148 minutes 145 marks Page 1 of 22 Q1. Reaction of 2-bromobutane with potassium hydroxide can produce two types of product depending on the solvent used. In aqueous solution,
Haloalkanes. Isomers: Draw and name the possible isomers for C 5 H 11 Br
 Haloalkanes The basics: The functional group is a halogen atom: F, Cl, Br or I General formula C n H 2n+1 X Use the prefixes: fluoro, chloro, bromo and iodo. Isomers: Draw and name the possible isomers
Haloalkanes The basics: The functional group is a halogen atom: F, Cl, Br or I General formula C n H 2n+1 X Use the prefixes: fluoro, chloro, bromo and iodo. Isomers: Draw and name the possible isomers
Mechanisms. . CCl2 F + Cl.
 Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
Chemistry of the Halogenoalkanes SN1 and SN2 Reaction Mechanisms
 1 The primary halogenoalkane bromomethane reacts via an SN2 mechanism. Name: lass: Date: / / The tertiary halogenoalkane 2-bromo-2-methylpropane reacts via an SN1 mechanism. hemistry of the alogenoalkanes
1 The primary halogenoalkane bromomethane reacts via an SN2 mechanism. Name: lass: Date: / / The tertiary halogenoalkane 2-bromo-2-methylpropane reacts via an SN1 mechanism. hemistry of the alogenoalkanes
When 2-bromopentane reacts with ethanolic KOH, two structurally isomeric alkenes are formed.
 Q1. Organic reaction mechanisms help chemists to understand how the reactions of organic compounds occur. The following conversions illustrate a number of different types of reaction mechanism. (a) When
Q1. Organic reaction mechanisms help chemists to understand how the reactions of organic compounds occur. The following conversions illustrate a number of different types of reaction mechanism. (a) When
REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION
 REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION Haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes and alkyl halides) are organic compounds where one of the hydrogens of an alkane or cycloalkane has been
REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION Haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes and alkyl halides) are organic compounds where one of the hydrogens of an alkane or cycloalkane has been
2.8 EXTRA QUESTIONS MS. (iii) C 6 H 5 CHCl 2 / C 6 H 5 CCl 3 / C 6 H 5 CHCHC 6 H 5 / other correct possible answer (1) 1
 .8 EXTRA QUESTIONS MS 1. (i) l l / ½ l l 1 (ii) l 6 5 6 5 l 6 5 l l 6 5 l (iii) 6 5 l / 6 5 l / 6 5 6 5 / other correct possible answer 1 [4]. (a) (i) (free)radical substitution 1 (both words required
.8 EXTRA QUESTIONS MS 1. (i) l l / ½ l l 1 (ii) l 6 5 6 5 l 6 5 l l 6 5 l (iii) 6 5 l / 6 5 l / 6 5 6 5 / other correct possible answer 1 [4]. (a) (i) (free)radical substitution 1 (both words required
Q.1 Draw structures for all amines of molecular formula C 4 H 11 N. Classify them as primary, secondary or tertiary amines.
 1 AMIES Structure ontain the 2 group. lassification primary (1 ) amines secondary (2 ) amines tertiary (3 ) amines quarternary (4 ) ammonium salts + 1 2 3 4 Aliphatic Aromatic methylamine, ethylamine,
1 AMIES Structure ontain the 2 group. lassification primary (1 ) amines secondary (2 ) amines tertiary (3 ) amines quarternary (4 ) ammonium salts + 1 2 3 4 Aliphatic Aromatic methylamine, ethylamine,
H H O C C O H Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives C CH 2 C. N Goalby chemrevise.org. Strength of carboxylic acids.
 19 arboxylic Acids and Derivatives Naming arboxylic acids These have the ending -oic acid but no number is necessary for the acid group as it must always be at the end of the chain. The numbering always
19 arboxylic Acids and Derivatives Naming arboxylic acids These have the ending -oic acid but no number is necessary for the acid group as it must always be at the end of the chain. The numbering always
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 203/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry
 E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
Organic Chemistry. Unit 10
 Organic Chemistry Unit 10 Halides Primary Carbons Secondary Carbons Tertiary Carbons IMPORTANCE?? REACTIONS!! Benzene C6H6 Aromatic functional group - C6H5 (IUPAC name - phenyl) Substitution Reactions
Organic Chemistry Unit 10 Halides Primary Carbons Secondary Carbons Tertiary Carbons IMPORTANCE?? REACTIONS!! Benzene C6H6 Aromatic functional group - C6H5 (IUPAC name - phenyl) Substitution Reactions
7. Haloalkanes (text )
 2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 7.1 7. aloalkanes (text 7.1 7.10) A. Structure and Nomenclature Like hydrogen, the halogens have a valence of one. Thus, a halogen atom can
2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 7.1 7. aloalkanes (text 7.1 7.10) A. Structure and Nomenclature Like hydrogen, the halogens have a valence of one. Thus, a halogen atom can
Organic Chemistry Review: Topic 10 & Topic 20
 Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
(a) (i) Complete the elimination mechanism by drawing appropriate curly arrows. Draw structures for the E and Z stereoisomers of hex-3-ene
 Q1.Alkenes are useful intermediates in the synthesis of organic compounds. (a) (i) Complete the elimination mechanism by drawing appropriate curly arrows. (3) Draw structures for the E and Z stereoisomers
Q1.Alkenes are useful intermediates in the synthesis of organic compounds. (a) (i) Complete the elimination mechanism by drawing appropriate curly arrows. (3) Draw structures for the E and Z stereoisomers
QUESTIONSHEETS ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS I FREE RADICAL SUBSTITUTION I FREE RADICAL SUBSTITUTION II ELECTROPHILIC ADDITION TO SYMMETRICAL ALKENES
 CHEMISTRY QUESTIONSHEETS AS Level AS TOPIC 14 ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS I Questionsheet 1 Questionsheet 2 Questionsheet 3 Questionsheet 4 Questionsheet 5 Questionsheet 6 Questionsheet 7 Questionsheet
CHEMISTRY QUESTIONSHEETS AS Level AS TOPIC 14 ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS I Questionsheet 1 Questionsheet 2 Questionsheet 3 Questionsheet 4 Questionsheet 5 Questionsheet 6 Questionsheet 7 Questionsheet
Lesmahagow High School CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry
 Lesmahagow High School AHChemistry Organic Chemistry& Instrumental Analysis Lesmahagow High School CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Organic Chemistry and Instrumental Analysis Alkanes, Alkenes and
Lesmahagow High School AHChemistry Organic Chemistry& Instrumental Analysis Lesmahagow High School CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Organic Chemistry and Instrumental Analysis Alkanes, Alkenes and
Mechanism Summary for A-level AQA Chemistry
 Mechanism Summary for Alevel AQA hemistry Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with omine Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with sulphuric acid 3 S 2 3 3 S 2 S 2 Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with hydrogen
Mechanism Summary for Alevel AQA hemistry Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with omine Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with sulphuric acid 3 S 2 3 3 S 2 S 2 Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with hydrogen
UNIT 2 REVISION CHECKLIST. a) understand that reactions are either exothermic or endothermic and apply the sign convention
 UNIT 2 REVISION CHECKLIST Topic 2.1 Energetics a) understand that reactions are either exothermic or endothermic and apply the sign convention b) define the term enthalpy change, recall what standard conditions
UNIT 2 REVISION CHECKLIST Topic 2.1 Energetics a) understand that reactions are either exothermic or endothermic and apply the sign convention b) define the term enthalpy change, recall what standard conditions
TOK: The relationship between a reaction mechanism and the experimental evidence to support it could be discussed. See
 Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours) SL students study the core of these options and HL students study the whole option (the core and the extension material). TOK: The relationship between
Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours) SL students study the core of these options and HL students study the whole option (the core and the extension material). TOK: The relationship between
Classes of Halides. Chapter 6 Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination. Polarity and Reactivity. Classes of Alkyl Halides
 rganic hemistry, 5 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. hapter 6 Alkyl alides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination lasses of alides Alkyl: alogen, X, is directly bonded to sp 3 carbon. Vinyl: X is bonded to
rganic hemistry, 5 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. hapter 6 Alkyl alides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination lasses of alides Alkyl: alogen, X, is directly bonded to sp 3 carbon. Vinyl: X is bonded to
WJEC Eduqas AS Chemistry - Component 2 THERMOCHEMISTRY
 WJEC Eduqas AS Chemistry - Component 2 THERMOCHEMISTRY enthalpy change of reaction, enthalpy change of combustion and standard molar enthalpy change of formation, Δ fh ϴ Hess s law and energy cycles concept
WJEC Eduqas AS Chemistry - Component 2 THERMOCHEMISTRY enthalpy change of reaction, enthalpy change of combustion and standard molar enthalpy change of formation, Δ fh ϴ Hess s law and energy cycles concept
Chapter 10 Free Radicals
 hapter 10 Free Radicals This is an example of a free radical reaction. A radical is a species that has a free unpaired electron. There are several examples of stable radicals, the most common of which
hapter 10 Free Radicals This is an example of a free radical reaction. A radical is a species that has a free unpaired electron. There are several examples of stable radicals, the most common of which
OCR (A) Chemistry A-level. Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis
 OCR (A) Chemistry A-level Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis Organic Synthesis Notes by Adam Robertson DEFINITIONS Heterolytic fission: The breaking of a covalent bond when one of the bonded atoms
OCR (A) Chemistry A-level Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis Organic Synthesis Notes by Adam Robertson DEFINITIONS Heterolytic fission: The breaking of a covalent bond when one of the bonded atoms
Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Chemistry Advanced Paper 2: Advanced Organic and Physical Chemistry
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Centre Number Candidate Number Chemistry Advanced Paper 2: Advanced Organic and Physical Chemistry Specimen Paper for first teaching
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Centre Number Candidate Number Chemistry Advanced Paper 2: Advanced Organic and Physical Chemistry Specimen Paper for first teaching
HYDROCARBONS. Section A
 MCQs Section A Q1The products obtained by cracking an alkane, X, are methane, ethene and propene. The mole fraction of ethene in the products is 0.5. What is the identity of X? A C6H14 B C8H18 C C9H20
MCQs Section A Q1The products obtained by cracking an alkane, X, are methane, ethene and propene. The mole fraction of ethene in the products is 0.5. What is the identity of X? A C6H14 B C8H18 C C9H20
Unit 7 Part 3 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Simple Reactions of Hydrocarbons UNIT 7 INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 Unit 7 Part 3 Introduction to Organic hemistry Simple Reactions of ydrocarbons UNIT 7 INTRODUTION TO ORGANI EMISTRY PART 3 SIMPLE REATIONS OF YDROARBONS ontents 1. Alkanes 2. Alkenes 3. Alkynes 4. Benzene
Unit 7 Part 3 Introduction to Organic hemistry Simple Reactions of ydrocarbons UNIT 7 INTRODUTION TO ORGANI EMISTRY PART 3 SIMPLE REATIONS OF YDROARBONS ontents 1. Alkanes 2. Alkenes 3. Alkynes 4. Benzene
EXTRA QUESTIONS FOR 2.8 HALOALKANES. 1. Methylbenzene is converted into (chloromethyl)benzene in a free radical substitution reaction....
 EXTRA QUESTIONS FOR 2.8 HALOALKANES 1. Methylbenzene is converted into (chloromethyl)benzene in a free radical substitution reaction. C 6 H 5 3 + Cl 2 C 6 H 5 2 Cl + HCl Write an equation for the initiation
EXTRA QUESTIONS FOR 2.8 HALOALKANES 1. Methylbenzene is converted into (chloromethyl)benzene in a free radical substitution reaction. C 6 H 5 3 + Cl 2 C 6 H 5 2 Cl + HCl Write an equation for the initiation
Preparation of Alkyl Halides, R-X. Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): R + X X 2.
 Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
3.1 Introduction to Organic Chemistry
 3.1 Introduction to Organic hemistry Organic hemistry is the study of carbon chemistry as carbon has the ability to join together in chains, rings, balls etc. arbon also joins with other elements easily
3.1 Introduction to Organic hemistry Organic hemistry is the study of carbon chemistry as carbon has the ability to join together in chains, rings, balls etc. arbon also joins with other elements easily
Organic Chemistry. Chapter 10
 Organic Chemistry Chapter 10 10.1 Homologous Series Overview We Are Here Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon containing compounds. From the very simple: methane To the very complex:
Organic Chemistry Chapter 10 10.1 Homologous Series Overview We Are Here Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon containing compounds. From the very simple: methane To the very complex:
Which of the following is a correct mechanism for the formation of 2-methylbut-2-ene from 2-bromo-3-methylbutane?
 Which of the following is a correct mechanism for the formation of 2-methylbut-2-ene from 2-bromo-3-methylbutane? A B C D (Total mark) 2 2-bromo-2-methylpentane is heated with potassium hydroxide dissolved
Which of the following is a correct mechanism for the formation of 2-methylbut-2-ene from 2-bromo-3-methylbutane? A B C D (Total mark) 2 2-bromo-2-methylpentane is heated with potassium hydroxide dissolved
Chemical tests to distinguish carbonyl compounds
 R hemistry A 432 arbonyl ompounds arbonyl hemistry arbonyl compounds are those which contain >= - aldehydes - ketones - carboxylic acids - esters You should recall how to name aldehydes and ketones: 3
R hemistry A 432 arbonyl ompounds arbonyl hemistry arbonyl compounds are those which contain >= - aldehydes - ketones - carboxylic acids - esters You should recall how to name aldehydes and ketones: 3
Page (Extra space) (4) Benzene can be converted into amine U by the two-step synthesis shown below.
 Q1. The hydrocarbons benzene and cyclohexene are both unsaturated compounds. Benzene normally undergoes substitution reactions, but cyclohexene normally undergoes addition reactions. (a) The molecule cyclohexatriene
Q1. The hydrocarbons benzene and cyclohexene are both unsaturated compounds. Benzene normally undergoes substitution reactions, but cyclohexene normally undergoes addition reactions. (a) The molecule cyclohexatriene
Overview of Types of Organic Reactions and Basic Concepts of Organic Reaction Mechanisms
 Overview of Types of Organic Reactions and Basic Concepts of Organic Reaction Mechanisms Dr. Solomon Derese 1 A chemical reaction is the transformation of one chemical or collection of chemicals into another
Overview of Types of Organic Reactions and Basic Concepts of Organic Reaction Mechanisms Dr. Solomon Derese 1 A chemical reaction is the transformation of one chemical or collection of chemicals into another
Amines. Types of Amines. chemrevise.org. N Goalby Chemrevise.org. primary amine (one C attached to N) H. Secondary amine (two C s.
 Amines Goalby hemrevise.org Types of Amines primary amine (one attached to ) Secondary amine (two s attached to ) 3 2 2 3 name : diethylamine It is also possible to have aromatic amines 2 phenylamine name:
Amines Goalby hemrevise.org Types of Amines primary amine (one attached to ) Secondary amine (two s attached to ) 3 2 2 3 name : diethylamine It is also possible to have aromatic amines 2 phenylamine name:
Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions
 Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions Halogen compounds are important for several reasons. Simple alkyl and aryl halides, especially chlorides and bromides, are versatile
Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions Halogen compounds are important for several reasons. Simple alkyl and aryl halides, especially chlorides and bromides, are versatile
Alkenes CnH2n Ethene Propene But-2-ene But-1-ene exposed high electron density one sigma (σ) bond and one pi (π) bond.
 Alkenes Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons General formula is n2n Alkenes contain a carboncarbon double bond somewhere in their structure Ethene Propene Numbers need to be added to the name when positional
Alkenes Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons General formula is n2n Alkenes contain a carboncarbon double bond somewhere in their structure Ethene Propene Numbers need to be added to the name when positional
Hydrogen iodide is a strong acid and will drive the reverse reaction, meaning the forward reaction will not occur.
 EM 261 Oct 18, 2018 Photosynthesis and Related Reactions O 2 2 O 6 12 O 6 2 O N 3, S, Fe, u, o, other Natural Products D-Glucose R O R OR Ionic substitution S N 1 & R X X 2 hv Petroleum/ Alkanes R N 2
EM 261 Oct 18, 2018 Photosynthesis and Related Reactions O 2 2 O 6 12 O 6 2 O N 3, S, Fe, u, o, other Natural Products D-Glucose R O R OR Ionic substitution S N 1 & R X X 2 hv Petroleum/ Alkanes R N 2
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 201/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry CHE1502/201/1/2016
 CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
Organic Chemistry. REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling
 Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
FACTFILE: GCE CHEMISTRY
 FATFILE: GE EMISTRY 2.4 ALKENES Alkenes Students should be able to: 2.4.1 define the term unsaturated hydrocarbon and explain why alkenes are described as unsaturated hydrocarbons; 2.4.2 recall the qualitative
FATFILE: GE EMISTRY 2.4 ALKENES Alkenes Students should be able to: 2.4.1 define the term unsaturated hydrocarbon and explain why alkenes are described as unsaturated hydrocarbons; 2.4.2 recall the qualitative
CHEM2. General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination January Unit 2 Chemistry in Action
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination January 2011 Question 1 2
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination January 2011 Question 1 2
Module 2A Alcohols and halogenoalkanes
 Module 2A Alcohols and halogenoalkanes Making ethanol Ethanol is made in 1 of 2 ways: 1) Hydration of ethene: This is a reversible reaction and only about 5% of ethene is converted to ethanol. Unreacted
Module 2A Alcohols and halogenoalkanes Making ethanol Ethanol is made in 1 of 2 ways: 1) Hydration of ethene: This is a reversible reaction and only about 5% of ethene is converted to ethanol. Unreacted
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 18: Reactions of organic compounds
 hemistry 2000 Lecture 18: Reactions of organic compounds Marc R. Roussel March 6, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Reactions of organic compounds March 6, 2018 1 / 27 Reactions of organic compounds Organic chemists
hemistry 2000 Lecture 18: Reactions of organic compounds Marc R. Roussel March 6, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Reactions of organic compounds March 6, 2018 1 / 27 Reactions of organic compounds Organic chemists
Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours)
 Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/) TOK: The relationship between a reaction mechanism and the experimental evidence to support it could be discussed. See 16... Core material: G1 G8 are core material
Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/) TOK: The relationship between a reaction mechanism and the experimental evidence to support it could be discussed. See 16... Core material: G1 G8 are core material
Module 4 revision guide: Compounds with C=O group
 opyright N Goalby Bancroft's School Module 4 revision guide: ompounds with = group arbonyls: Aldehydes and Ketones arbonyls are compounds with a = bond, they can be either aldehydes or ketones. 3 ethanal
opyright N Goalby Bancroft's School Module 4 revision guide: ompounds with = group arbonyls: Aldehydes and Ketones arbonyls are compounds with a = bond, they can be either aldehydes or ketones. 3 ethanal
3.2.9 Alkenes. Addition Reactions. 271 minutes. 268 marks. Page 1 of 35
 ..9 Alkenes Addition Reactions 71 minutes 68 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Propene reacts with bromine by a mechanism known as electrophilic addition. (a) Explain what is meant by the term electrophile and by
..9 Alkenes Addition Reactions 71 minutes 68 marks Page 1 of 5 Q1. Propene reacts with bromine by a mechanism known as electrophilic addition. (a) Explain what is meant by the term electrophile and by
17 Alcohols H H C C. N Goalby chemrevise.org 1 H H. Bond angles in Alcohols. Boiling points. Different types of alcohols H 2 C CH 2 CH 2
 17 Alcohols General formula alcohols n 2n+1 Naming Alcohols These have the ending -ol and if necessary the position number for the group is added between the name stem and the ol If the compound has an
17 Alcohols General formula alcohols n 2n+1 Naming Alcohols These have the ending -ol and if necessary the position number for the group is added between the name stem and the ol If the compound has an
CHEM2. General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June Unit 2 Chemistry in Action. Friday 27 May pm to 3.
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2011 Question 1 2 Mark
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2011 Question 1 2 Mark
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2
 C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
Carbonyls. Aldehydes and Ketones N Goalby chemrevise.org. chemrevise.org
 arbonyls Aldehydes and Ketones N Goalby chemrevise.org arbonyls are compounds with a = bond, they can be either aldehydes or ketones. 3 ethanal 3 3 propanone If the = is on the end of the chain with an
arbonyls Aldehydes and Ketones N Goalby chemrevise.org arbonyls are compounds with a = bond, they can be either aldehydes or ketones. 3 ethanal 3 3 propanone If the = is on the end of the chain with an
ALKENES. select the longest chain of C atoms containing the double bond; end in ENE
 Alkenes 1 ALKENES Structure form a homologous series of general formula n 2n - non cyclic alkenes only contain a carbon-carbon double bond somewhere in their structure unsaturated hydrocarbons - can still
Alkenes 1 ALKENES Structure form a homologous series of general formula n 2n - non cyclic alkenes only contain a carbon-carbon double bond somewhere in their structure unsaturated hydrocarbons - can still
4.2.1 Alcohols. N Goalby chemrevise.org 1 C O H H C. Reactions of alcohols. General formula alcohols C n H 2n+1 OH
 4.2.1 Alcohols The alcohols have relatively low volatility due to their ability to form hydrogen bond between alcohol molecules. General formula alcohols n 2n+1 The smaller alcohols (up to 3 carbons) are
4.2.1 Alcohols The alcohols have relatively low volatility due to their ability to form hydrogen bond between alcohol molecules. General formula alcohols n 2n+1 The smaller alcohols (up to 3 carbons) are
Unit 2. Answers to examination-style questions. Answers Marks Examiner s tips. 1 (a) heat energy change at constant pressure
 (a) heat energy change at constant pressure This is in the spec but not so well known. Learn it. (b) N 2 (g) + ½O 2 (g) N 2 O(g) (c) (i) D = (bonds broken) (bonds made) = ½(945) + (3/2)(59) 3(278) = 23
(a) heat energy change at constant pressure This is in the spec but not so well known. Learn it. (b) N 2 (g) + ½O 2 (g) N 2 O(g) (c) (i) D = (bonds broken) (bonds made) = ½(945) + (3/2)(59) 3(278) = 23
11. Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
 11. Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions A. Introduction It would be beneficial if you review the chapter on substitution reactions in your textbook prior to lab. This is Ch. 11 in the 9 th edition McMurry
11. Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions A. Introduction It would be beneficial if you review the chapter on substitution reactions in your textbook prior to lab. This is Ch. 11 in the 9 th edition McMurry
Chemistry 2.5 AS WORKBOOK. Working to Excellence Working to Excellence
 Chemistry 2.5 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds WORKBOOK Working to Excellence Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to Cis-Trans
Chemistry 2.5 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds WORKBOOK Working to Excellence Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to Cis-Trans
PMT GCE MARKING SCHEME. CHEMISTRY AS/Advanced SUMMER WJEC CBAC Ltd.
 GE MARKING SEME EMISTRY AS/Advanced SUMMER 2013 GE EMISTRY - 2 SUMMER 2013 MARK SEME Section A Q.1 Q.2 B Q.3 (a) alcium chloride (b) (c) Magnesium carbonate Sodium sulfate Q.4 Species l N 3 lassification
GE MARKING SEME EMISTRY AS/Advanced SUMMER 2013 GE EMISTRY - 2 SUMMER 2013 MARK SEME Section A Q.1 Q.2 B Q.3 (a) alcium chloride (b) (c) Magnesium carbonate Sodium sulfate Q.4 Species l N 3 lassification
Organic Halogen Compounds
 8 Organic alogen ompounds APTER SUMMARY 8.1 Introduction Although organic halogen compounds are rarely found in nature, they do have a variety of commercial applications including use as insecticides,
8 Organic alogen ompounds APTER SUMMARY 8.1 Introduction Although organic halogen compounds are rarely found in nature, they do have a variety of commercial applications including use as insecticides,
Page 2. Q1.Consider the following scheme of reactions. (a) Give the IUPAC name for compound P and that for compound Q. P... Q...
 Q1.Consider the following scheme of reactions. (a) Give the IUPAC name for compound P and that for compound Q. P... Q... (2) (b) The conversion of P into Q in Reaction 1 uses HCl Name and outline a mechanism
Q1.Consider the following scheme of reactions. (a) Give the IUPAC name for compound P and that for compound Q. P... Q... (2) (b) The conversion of P into Q in Reaction 1 uses HCl Name and outline a mechanism
CHAPTER 7. Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination
 CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
TOPIC 13 ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES QUESTIONSHEET 1 ALKANES
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 ALKANES a) (i) UV light / temperatures > 500 ºC (ii) CH 4 (g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl(g) + HCl(g) Cl(g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl 2 (l) + HCl(g) Cl 2 (l) + Cl 2 (g) CHCl 3 (l) + HCl(g) CHCl 3 (l) + Cl 2 (g)
QUESTIONSHEET 1 ALKANES a) (i) UV light / temperatures > 500 ºC (ii) CH 4 (g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl(g) + HCl(g) Cl(g) + Cl 2 (g) Cl 2 (l) + HCl(g) Cl 2 (l) + Cl 2 (g) CHCl 3 (l) + HCl(g) CHCl 3 (l) + Cl 2 (g)
Chapter 5. Nucleophilic aliphatic substitution mechanism. by G.DEEPA
 Chapter 5 Nucleophilic aliphatic substitution mechanism by G.DEEPA 1 Introduction The polarity of a carbon halogen bond leads to the carbon having a partial positive charge In alkyl halides this polarity
Chapter 5 Nucleophilic aliphatic substitution mechanism by G.DEEPA 1 Introduction The polarity of a carbon halogen bond leads to the carbon having a partial positive charge In alkyl halides this polarity
Halo Alkanes and Halo Arenes
 alo Alkanes and alo Arenes Short Answer Questions: **1. Write the isomers of the compound having formula C 4 9 Br? Sol. There are five isomers of C 4 9 Br. These are: 2-bromobutane is expected to exhibit
alo Alkanes and alo Arenes Short Answer Questions: **1. Write the isomers of the compound having formula C 4 9 Br? Sol. There are five isomers of C 4 9 Br. These are: 2-bromobutane is expected to exhibit
Physical Properties: Structure:
 Nomenclature: Functional group suffix = -ol Functional group prefix = hydroxy- Primary, secondary or tertiary? Alcohols are described as primary (1 o ), secondary (2 o ) or tertiary (3 o ) depending on
Nomenclature: Functional group suffix = -ol Functional group prefix = hydroxy- Primary, secondary or tertiary? Alcohols are described as primary (1 o ), secondary (2 o ) or tertiary (3 o ) depending on
ammonia primary amine secondary amine tertiary amine quaternary ammonium salt (NOT amines) H CH 3 CH 3 CH 2
 AMIES 1) TYPES F AMIES Amines can be classed as primary, secondary and tertiary. Amines are related to ammonia ( 3 ). Aromatic amines have the joined directly to the benzene ring. Quaternary ammonium salts
AMIES 1) TYPES F AMIES Amines can be classed as primary, secondary and tertiary. Amines are related to ammonia ( 3 ). Aromatic amines have the joined directly to the benzene ring. Quaternary ammonium salts
Topic 2 Alkenes and alkynes
 Topic 2 Alkenes and alkynes lassification of rganic Reactions Four basic types of organic reaction Acid base reactions Substitution reactions Addition elimination reactions xidation reduction reactions
Topic 2 Alkenes and alkynes lassification of rganic Reactions Four basic types of organic reaction Acid base reactions Substitution reactions Addition elimination reactions xidation reduction reactions
Homework problems Chapters 6 and Give the curved-arrow formalism for the following reaction: CH 3 OH + H 2 C CH +
 omework problems hapters 6 and 7 1. Give the curved-arrow formalism for the following reaction: : 3 - : 2 : 3 2-3 3 2. In each of the following sets, arrange the compounds in order of decreasing pka and
omework problems hapters 6 and 7 1. Give the curved-arrow formalism for the following reaction: : 3 - : 2 : 3 2-3 3 2. In each of the following sets, arrange the compounds in order of decreasing pka and
Organic Chemistry HL IB CHEMISTRY HL
 Organic Chemistry HL IB CHEMISTRY HL Understandings: Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions: SN1 represents a nucleophilic unimolecular substitution reaction and SN2 represents a nucleophilic bimolecular
Organic Chemistry HL IB CHEMISTRY HL Understandings: Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions: SN1 represents a nucleophilic unimolecular substitution reaction and SN2 represents a nucleophilic bimolecular
Elimination Reactions Heating an alkyl halide with a strong base causes elimination of a. molecule of HX
 Elimination eactions eating an alkyl halide with a strong base causes elimination of a molecule of X 1. Potassium hydroxide dissolved in ethanol and the sodium salts of alcohols (such as sodium ethoxide)
Elimination eactions eating an alkyl halide with a strong base causes elimination of a molecule of X 1. Potassium hydroxide dissolved in ethanol and the sodium salts of alcohols (such as sodium ethoxide)
3.10 Benzene : Aromatic Hydrocarbons / Arenes
 3.10 Benzene : Aromatic ydrocarbons / Arenes There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six
3.10 Benzene : Aromatic ydrocarbons / Arenes There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six
A Level Chemistry A H432/02 Synthesis and analytical techniques. Practice paper Set 1 Time allowed: 2 hours 15 minutes
 A Level hemistry A 432/02 Synthesis and analytical techniques Practice paper Set 1 Time allowed: 2 hours 15 minutes You must have: the Data Sheet for hemistry A You may use: a scientific calculator a ruler
A Level hemistry A 432/02 Synthesis and analytical techniques Practice paper Set 1 Time allowed: 2 hours 15 minutes You must have: the Data Sheet for hemistry A You may use: a scientific calculator a ruler
Cherry Hill Tuition A Level Chemistry OCR (A) Paper 11
 ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE CEMISTRY A Chains, Energy and Resources F322 *OCE/23212* Candidates answer on the question paper. OCR Supplied Materials: Data Sheet for Chemistry A (inserted) Other Materials Required:
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE CEMISTRY A Chains, Energy and Resources F322 *OCE/23212* Candidates answer on the question paper. OCR Supplied Materials: Data Sheet for Chemistry A (inserted) Other Materials Required:
N.b. A catalyst is a species which speeds up a chemical reaction but which remains chemically unchanged. Reverse process of dehydration of an alcohol
 An Introduction to Organic hemistry N.b. A catalyst is a species which speeds up a chemical reaction but which remains chemically unchanged. ydration (Addition) Reverse process of dehydration of an alcohol
An Introduction to Organic hemistry N.b. A catalyst is a species which speeds up a chemical reaction but which remains chemically unchanged. ydration (Addition) Reverse process of dehydration of an alcohol
CHEM J-10 June The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below.
 CEM1102 2014-J-10 June 2014 The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below. 4 What is the molecular formula of ( )-linalool? C 10 18 O Which of the following best describes
CEM1102 2014-J-10 June 2014 The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below. 4 What is the molecular formula of ( )-linalool? C 10 18 O Which of the following best describes
Chapter 5. 3-Chloro-2-methylpentane. Cl 2. 2-Chloro-2-methylpentane. 1-Chloro-2-methylpentane. Cl 2-Chloro-4-methylpentane. 1-Chloro-4-methylpentane
 hapter 5 5.1 lassify each of the following reactions as an addition, elimination, substitution, or rearrangement: (a) 3Br K 3 KBr (b) 3 2 2 2 2 (c) 2 2 2 3 3 a. substitution b. elimination c. addition
hapter 5 5.1 lassify each of the following reactions as an addition, elimination, substitution, or rearrangement: (a) 3Br K 3 KBr (b) 3 2 2 2 2 (c) 2 2 2 3 3 a. substitution b. elimination c. addition
OCR Chemistry A H432. Amines are described as primary, secondary or tertiary depending on how many carbons are bonded to the N atom.
 OCR Chemistry A 432 About amines: can be considered as derivatives of ammonia, with one or more of the atoms replaced by alkyl groups. They are noted for their unpleasant, often fishy odours. We classify
OCR Chemistry A 432 About amines: can be considered as derivatives of ammonia, with one or more of the atoms replaced by alkyl groups. They are noted for their unpleasant, often fishy odours. We classify
AS Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds
 No Brain Too Small EMISTRY AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds ollated Flow hart Type Questions / types of reaction (2017) (a) (i) omplete the following reaction
No Brain Too Small EMISTRY AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds ollated Flow hart Type Questions / types of reaction (2017) (a) (i) omplete the following reaction
Model 1 Homolysis Reactions are Highly Endothermic
 Chem 201 Activity 24: Radical chain mechanisms (What do radicals do? What does a radical chain mechanism look like) Model 1 Homolysis Reactions are Highly Endothermic Heterolysis Homolysis Y Z Y + Z Y
Chem 201 Activity 24: Radical chain mechanisms (What do radicals do? What does a radical chain mechanism look like) Model 1 Homolysis Reactions are Highly Endothermic Heterolysis Homolysis Y Z Y + Z Y
Aromatic Compounds II
 2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 2 Aromatic Compounds II Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 17 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 2 Aromatic Compounds II Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 17 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
This reactivity makes alkenes an important class of organic compounds because they can be used to synthesize a wide variety of other compounds.
 This reactivity makes alkenes an important class of organic compounds because they can be used to synthesize a wide variety of other compounds. Mechanism for the addition of a hydrogen halide What happens
This reactivity makes alkenes an important class of organic compounds because they can be used to synthesize a wide variety of other compounds. Mechanism for the addition of a hydrogen halide What happens
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds. Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
Name/CG: 2012 Term 2 Organic Chemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question
 Name/G: 2012 Term 2 rganic hemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question 1(a) A yellow liquid A, 7 7 N 2, reacts with alkaline potassium manganate (VII) and on acidification gives a yellow solid B,
Name/G: 2012 Term 2 rganic hemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question 1(a) A yellow liquid A, 7 7 N 2, reacts with alkaline potassium manganate (VII) and on acidification gives a yellow solid B,
(a) Which test always gives a positive result with carbonyl compounds? (b) Which test would give a positive result with ethane-1,2-diol?
 1 Some chemical tests are described below. Warm with Fehling s (or enedict s) solution Warm with acidified potassium dichromate(vi) solution dd sodium carbonate solution dd 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine solution
1 Some chemical tests are described below. Warm with Fehling s (or enedict s) solution Warm with acidified potassium dichromate(vi) solution dd sodium carbonate solution dd 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine solution
The rate of reaction is defined as the change in concentration of a substance in unit time Its usual unit is mol dm -3 s -1
 11. Kinetics The rate of reaction is defined as the change in concentration of a substance in unit time Its usual unit is mol dm -3 s -1 When a graph of concentration of reactant is plotted vs time, the
11. Kinetics The rate of reaction is defined as the change in concentration of a substance in unit time Its usual unit is mol dm -3 s -1 When a graph of concentration of reactant is plotted vs time, the
