THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY SECTION 1-1 REVIEW. VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank.
|
|
|
- Donald Kelley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SECTION 1-1 REVIEW THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY Define the following terms. 1. development 2. reproduction 3. organ 4. tissue Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. Biology is the study of a. animals. b. plants and animals. 2. A short segment of DNA that contains instructions for the development of a single trait of an organism is known as a a. DNA loop. b. gene. c. library. d. membrane. 3. As the cells in a multicellular organism multiply, they become specialized for different functions in a process called a. sexual reproduction. b. descent with modification. 4. Homeostasis refers to the a. organization of cellular structures. b. stable level of internal conditions in organisms. c. organized structure of crystals. d. destruction of tropical rain forests. c. all living things. d. energy transfer. c. photosynthesis. d. cell differentiation. 5. Photosynthesis is part of a plant s a. metabolism. c. development. b. homeostasis. d. response to stimuli. Modern Biology Study Guide 1
2 Answer the questions in the space provided. 1. Explain why the cell is called the basic unit of life. 2. Give a specific example of homeostasis. 3. Why is it important to study biology? 4. Contrast the reproduction of bacteria with that of frogs. 5. Critical Thinking The organization of a rock is much simpler than that of living things. By what other criteria can a rock be distinguished from living things? Explain how the drawing below illustrates the characteristics of life. 2 Section 1-1 Review
3 SECTION 1-2 REVIEW THEMES IN BIOLOGY Distinguish between the terms in each of the following groups of terms. 1. domain, kingdom 2. diversity of life, unity of life 3. adaptations, evolution 4. ecosystem, ecology Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. A tree of life explains a. how organisms are related to each other. b. how organisms differ from each other. c. the lineages of various organisms. d. All of the above 2. Which of the following is NOT an important unifying theme in biology? a. the diversity and unity of life b. the relationship between organisms and society c. the interdependence of living organisms d. the evolution of life 3. An example of a domain is a. Animalia. b. Protista. c. Fungi. d. Eukarya. 4. A trait that improves an individual s ability to survive and reproduce is a(n) a. mutation. b. natural selection c. adaptation. d. domain. 5. Which of the following statements is true? a. Destruction of rain forests has no effect on living things. b. Destruction of rain forests increases the rate of evolution of rainforest organisms. c. Humans have had no impact on the world s environment. d. Humans have had a large impact on the world s environment. Modern Biology Study Guide 3
4 Answer the questions in the space provided. 1. Give an example of how two organisms are interdependent. 2. Why must an adaptation be inheritable if it is to cause a population to evolve? 3. What is natural selection? 4. If two organisms share the same kingdom, must they also share the same domain? Explain. 5. Critical Thinking A female frog has a genetic trait that prevents it from producing eggs. How likely is it that this trait will spread through the frog population? Explain your answer. Briefly describe the interactions among the panther, the deer, and the grass in the drawing below. 4 Section 1-2 Review
5 SECTION 1-3 REVIEW THE STUDY OF BIOLOGY Define the following terms. 1. prediction 2. control group 3. dependent variable 4. independent variable 5. theory Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. A field biologist who studies the behavior of birds in a rain forest most likely collects data through a. experimenting. b. modeling. c. observing. d. inferring. 2. Constructing a graph is an example of a. measuring. b. organizing data. c. observing. d. predicting. 3. Of the following steps in a scientific investigation, the last to be done is usually a. experimenting. b. observing. c. producing a model. d. hypothesizing. 4. A statement that explains observations and can be tested is called a. a hypothesis. b. an inference. c. a theory. d. a model. 5. A visual, verbal, or mathematical explanation that is supported by data is called a. a hypothesis. b. an inference. c. a theory. d. a model. Modern Biology Study Guide 5
6 Answer the questions in the space provided. 1. What are quantitative data? Give two examples of quantitative data. 2. What is an advantage of a peer review of a scientific paper? 3. How are a hypothesis, a prediction, and an experiment related? 4. What are some of the things scientists might do to analyze data? 5. Critical Thinking A scientist wanted to study the effect of a drug on the blood pressure of rats. She set up an experiment in which the experimental group consisted of rats that were injected with a salt solution containing the drug. What should the control group have consisted of? What were the dependent and independent variables in her experiment? Examine the drawing of the owl. In each space below, provide an observation that would support the inference given or provide an inference that could be derived from the observation given. Observations Inferences Owls live in trees. Owls feed on mice. Owls kill prey with their talons. The owl has wings. Both of the owl s eyes face forward. It is night. 6 Section 1-3 Review
7 SECTION 1-4 REVIEW TOOLS AND TECHNIQUES Circle the term that does not belong in each of the following groups, and briefly explain why it does not belong. 1. compound light, transmission electron, light electron, scanning electron 2. base unit, stage, nosepiece, objective lens 3. magnification, power of magnification, resolution, mass density 4. second, minute, meter, kilogram 5. meter, square meter, cubic meter, kilogram per cubic meter Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. The ability of a microscope to show details clearly is called a. enlargement. b. magnification. c. reduction. d. resolution. 2. One limitation of the scanning electron microscope is that it cannot be used to a. examine specimens smaller than cells. b. view living specimens. c. produce an enlarged image of a specimen. d. produce an image of the surface of a specimen. 3. A microscope with a 10 ocular lens and a 25 objective lens has a total power of magnification equal to a b. 35. c d. 2, The SI base unit for time is the a. second. b. minute. c. hour. d. day. 5. The SI prefix that represents 1,000 times the base unit is a. deci. b. centi. c. kilo. d. micro. Modern Biology Study Guide 7
8 Answer the questions in the space provided. 1. Arrange the following parts in the order that matches the light path through a light microscope: specimen, ocular lens, objective lens, light source. 2. What are the maximum magnifications of the LM, TEM, and SEM? 3. Write the abbreviation for each of the following units: meter, kilometer, centimeter, millimeter, micrometer. What is the mathematical relationship between these units? 4. Critical Thinking A group of scientists want to determine whether the bacteria they are studying have viruses inside them. Which type of microscope should they use? Explain your answer. Label each part of the figure in the spaces provided. a b c d e 8 Section 1-4 Review
9 Section Development is the process involving cell division and cell differentiation by which an organism becomes a mature adult. 2. Reproduction is the process by which an organism produces new organisms like itself. 3. An organ is a structure that carries out a specialized job inside an organ system. 4. A tissue is a group of cells in an organ that have similar abilities and that allow the organ to function. 1. c 2. b 3. d 4. b 5. a 1. A cell is the smallest unit that can perform all of life s processes. 2. Sample answer: An owl maintains its body temperature by burning fuel to produce body heat and by fluffing up its feathers to trap an insulating layer of air next to its body. 3. Sample answer: By studying biology, you can make informed decisions on issues that impact you and society, such as environmental issues, health, and technology. 4. Bacteria reproduce asexually by splitting in two. Frogs reproduce sexually by producing sperm and eggs. One sperm and one egg combine to form a single cell that divides many times to produce a new frog. 5. Rocks are not composed of cells, do not have internal systems for maintaining homeostasis, and do not contain hereditary information in the form of DNA. The buffaloes and grass are all composed of cells (cells). Different types of cells compose the different tissues in the buffaloes (organization). The grass uses energy from the sun to manufacture food, and the buffaloes consume the grass for their food (energy use). The buffaloes have hair to help maintain their internal environment (homeostasis). The calf will eventually grow into a full-grown buffalo (growth). Buffalo increase their herds through reproduction. Section A domain is one of three major subdivisions of organisms that can be divided into one or more kingdoms. 2. Diversity of life describes the variety of different kinds of living things. Unity of life describes the features that living things have in common. 3. Adaptations are traits that improve an individual s ability to survive and reproduce. Evolution is the process in which a population changes over time due to increased reproduction of organisms with certain adaptations. 4. An ecosystem is a community of living things and their physical environment. Ecology is the branch of biology that studies how organisms interact with each other and with their environments. 1. d 2. b 3. d 4. c 5. d 1. Animals produce carbon dioxide and water, which is needed by plants. Accept all reasonable answers. 2. If an adaptation is not inherited, future generations of organisms will not have the favorable trait and evolution cannot occur. 3. Natural selection is the process by which organisms that have certain favorable traits are better able to survive and reproduce successfully than organisms that lack these traits. 4. Two organisms that share the same kingdom must also share the same domain because kingdoms are subdivisions of domains. 5. This trait will not spread through the population. Since the frog produces no eggs, it will have no offspring to inherit the trait. The deer eat the grass and get energy and nutrients from the grass. The panther kills and eats the deer, getting energy and nutrients from the deer and the grass. Section A prediction is what is expected to happen if a hypothesis were true. 2. A control group is a normal standard against which to compare an experimental group. 3. A dependent variable is a factor that is measured in a controlled experiment. 4. An independent variable is a factor that distinguishes the control and experimental groups in a controlled experiment. 5. A theory is a set of related hypotheses that have been confirmed and that explain a great amount of data. 1. c 2. b 3. c 4. a 5. d 1. Quantitative data are data that can be measured in numbers. Examples include the dimensions of an object, the number of objects in a group, and the duration of an event. 2. The validity of the research is checked by experts in the field. 3. A prediction is a statement made in advance that declares the results that will be obtained from testing a hypothesis in an experiment, if the hypothesis is true. 4. They might use statistics to determine relationships between variables, compare the data with those obtained in other studies, and determine possible sources of experimental error. 5. The control group should have consisted of rats that were injected with the same type of salt solution but without the drug. The dependent variable was blood pressure, and the independent variable was the drug. Observations: Inferences: The owl is sitting Owls can fly. in a tree. The owl has a mouse Owls have binocular in its beak. vision. The owl has Owls hunt at night. sharp talons. Modern Biology Study Guide Answer Key 1
10 Section Light electron does not belong; the other three are types of microscopes. 2. Base unit does not belong; the other three are parts of a light microscope. 3. Mass density does not belong; the other three are characteristics of microscopes. 4. Minute does not belong; the other three are SI base units. 5. Meter does not belong; the other three are SI derived units. 1. d 2. b 3. c 4. a 5. c 1. light source, specimen, objective lens, ocular lens 2. LM, about 2,000 ; TEM, 200,000 ; SEM, 100, m, km, cm, mm, µm. 1 km = 1,000 m; 1 cm = 0.01 m; 1 mm = m; 1 µm = m 4. They should use a TEM, since it has the magnification necessary to view viruses and, unlike an SEM, can reveal structures that are inside cells. a, ocular lens (eyepiece); b, nosepiece; c, objective lenses; d, stage; e, light source Section An atom is the simplest particle of an element that retains all of the properties of that element. 2. A neutron is a nuclear particle that has no electrical charge. 3. A compound is a substance that is made up of atoms of two or more elements in fixed proportions. 4. A covalent bond is an attachment between two atoms that share one or more pairs of electrons. 5. An ion is an atom or molecule with an electrical charge. 1. b 2. a 3. d 4. c 5. a 1. Mass is the quantity of matter an object has, while weight is a measure of the pull of gravity on mass. 2. BO 2, 1 boron and 2 oxygen atoms; C 6 H 12 O 6, 6 carbon, 12 hydrogen, and 6 oxygen atoms; KCl, 1 potassium and 1 chlorine atom; NH 3, 1 nitrogen and 3 hydrogen atoms 3. The oxygen atoms share two pairs of electrons, since each atom needs two more electrons to fill the orbitals of its outermost energy level. 4. Argon will not tend to form bonds with other elements. With an atomic number of 18, argon must have 18 electrons: 2 in the first energy level, 8 in the second, and 8 in the third. Since the orbitals of its outermost energy level is filled, argon is chemically stable. 1. A covalent bond is formed between hydrogen and chlorine atoms. 2. A hydrogen atom and a chlorine atom share one electron. This process gives the hydrogen atom a full orbital of 2 electrons. The chlorine atom will have full orbitals corresponding to its three energy levels of 2, 8, and 8 electrons. Section In a chemical reaction, a reactant is the starting substance and a product is the ending substance. Reactants are shown on the left side of an equation and products are shown on the right side. 2. A catalyst reduces the amount of activation energy needed to start a reaction. An enzyme serves as a catalyst in the reactions of living things. 3. In an oxidation reaction, a reactant loses one or more electrons; in a reduction reaction, a reactant gains one or more electrons. 1. b 2. c 3. d 4. a 5. b 1. Reactants: C 12 H 22 O 11, H 2 O, Products: C 6 H 12 O 6, C 6 H 12 O 6 2. By reducing the activation energy that is needed for a reaction, a catalyst allows the reaction to proceed spontaneously or with the addition of a small amount of energy. 3. It indicates that the reaction can proceed in either the forward or the reverse direction. 4. Cl is reduced; Na is oxidized. 5. The reaction proceeds slowly because the activation energy is high. An enzyme or other catalyst is needed to lower the activation energy and speed up the reaction. 1. energy needed without a catalyst 2. energy needed with a catalyst 3. There is a net release of energy. Energy of the products is less than energy of the reactants. Section A solvent is a substance in which a solute is dissolved. 2. An aqueous solution is a solution in which water is the solvent. 3. A hydroxide ion is a negatively charged ion consisting of one oxygen atom and one hydrogen atom, OH. 4. A base is a solution that contains more hydroxide ions than hydronium ions. 5. A buffer is a chemical substance that neutralizes small amounts of either an acid or a base added to a solution. 1. c 2. b 3. a 4. c 5. d 1. Adhesion allows water to stick to a dry surface. 2. Solutions can be mixtures of liquids, solids, or gases. 3. The solution contains 10 g of sugar, and the solvent is water. 4. Acidic: more H 3 O ions than OH ions. Alkaline: more OH ions than H 3 O ions. Neutral: equal number of H 3 O and OH ions. 5. The solution with a ph of 9 has 10 6, or 1,000,000, times more hydroxide ions. 2 Modern Biology Study Guide Answer Key
THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY SECTION 1-1 REVIEW. VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank.
 SECTION 1-1 REVIEW THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. 1. development 2. reproduction 3. organ 4. tissue MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. Biology
SECTION 1-1 REVIEW THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. 1. development 2. reproduction 3. organ 4. tissue MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. Biology
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 1-1 THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY
 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 1-1 THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank. Name Period Date 1. A short segment of DNA that contains instructions for the development of a single
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 1-1 THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank. Name Period Date 1. A short segment of DNA that contains instructions for the development of a single
CHAPTER 1 BIOLOGY THE SCIENCE OF LIFE
 CHAPTER 1 BIOLOGY THE SCIENCE OF LIFE BIOLOGICAL THEMES 1. Cell Structure & Function cell is the basic unit of life all organisms are composed of at least one cell Unicellular single celled ; bacteria,
CHAPTER 1 BIOLOGY THE SCIENCE OF LIFE BIOLOGICAL THEMES 1. Cell Structure & Function cell is the basic unit of life all organisms are composed of at least one cell Unicellular single celled ; bacteria,
The Science of Life. Introduction to Biology
 The Science of Life Introduction to Biology What is Biology Bio = life logos = knowledge many branches - different things to study in biology Botany study of plants all types of plants - trees, flowers,
The Science of Life Introduction to Biology What is Biology Bio = life logos = knowledge many branches - different things to study in biology Botany study of plants all types of plants - trees, flowers,
Introduction to Biology
 Introduction to Biology Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
Introduction to Biology Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
Introduction to Biology
 1 Introduction to Biology 2 Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
1 Introduction to Biology 2 Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
CHAPTER 1 THE SCIENCE OF LIFE
 CHAPTER 1 THE SCIENCE OF LIFE Biology Bio - life Logy- the study of Biology is the study of life or living things Some branches of Biology include- Microbiology, Marine Biology, Botany, Zoology, Ecology
CHAPTER 1 THE SCIENCE OF LIFE Biology Bio - life Logy- the study of Biology is the study of life or living things Some branches of Biology include- Microbiology, Marine Biology, Botany, Zoology, Ecology
Study of Biology. copyright cmassengale
 Study of Biology 1 What is Biology? Biology is the study of all living things Living things are called organisms Organisms include bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, & animals 2 All Living Things Share
Study of Biology 1 What is Biology? Biology is the study of all living things Living things are called organisms Organisms include bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, & animals 2 All Living Things Share
Characteristics of Living Things
 Characteristics of Living Things All Living Things Are made up of units called cells A cell is the smallest unit of an organism that can be considered alive Types of Cellular Organisms Unicellular Uni
Characteristics of Living Things All Living Things Are made up of units called cells A cell is the smallest unit of an organism that can be considered alive Types of Cellular Organisms Unicellular Uni
Chapter 1. Introduction to Biology. The cell is the basic unit of life 1665-Robert Hooke- 1 st discovered cells in cork. The Seven Properties of Life
 The Science of Life Student Learning Goals - Biology Science and Life SC.912.N.1.1 Goal: Define a problem based on a specific body of knowledge, for example: biology, chemistry, physics, & earth/space
The Science of Life Student Learning Goals - Biology Science and Life SC.912.N.1.1 Goal: Define a problem based on a specific body of knowledge, for example: biology, chemistry, physics, & earth/space
 All Living Things Share Common Characteristics 1. Living Things are Composed of Cells: Single-cell organisms have everything they need to be self-sufficient. In multicellular organisms, some cells do only
All Living Things Share Common Characteristics 1. Living Things are Composed of Cells: Single-cell organisms have everything they need to be self-sufficient. In multicellular organisms, some cells do only
1-3 Studying Life. Slide 1 of 45. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 45 2 of 45 Characteristics of Living Things Characteristics of Living Things No single characteristic is enough to describe a living thing. Some nonliving things share one or more traits with living
1 of 45 2 of 45 Characteristics of Living Things Characteristics of Living Things No single characteristic is enough to describe a living thing. Some nonliving things share one or more traits with living
Explain your answer:
 Biology Midterm Exam Review Introduction to Biology and the Scientific Method Name: Date: Hour: 1. Biology is the study of: 2. A living thing is called a(n): 3. All organisms are composed of: 4. The smallest
Biology Midterm Exam Review Introduction to Biology and the Scientific Method Name: Date: Hour: 1. Biology is the study of: 2. A living thing is called a(n): 3. All organisms are composed of: 4. The smallest
7 th Grade Science Curriculum
 (1 st 9 Weeks- 1 st 4.5 9 Weeks) Date Hobbs Science By being embedded throughout the, these Processing Skills will be addressed throughout the year. NM & 1 Scientific Thinking and Practice Understand the
(1 st 9 Weeks- 1 st 4.5 9 Weeks) Date Hobbs Science By being embedded throughout the, these Processing Skills will be addressed throughout the year. NM & 1 Scientific Thinking and Practice Understand the
Chapter 1 The Science of Life
 Chapter 1 The Science of Life (Sect. 1) Biology how living things work how living things interact w/the environment how living things change over time 7 Characteristics of Life 1.Organization & the presence
Chapter 1 The Science of Life (Sect. 1) Biology how living things work how living things interact w/the environment how living things change over time 7 Characteristics of Life 1.Organization & the presence
Performance Level Descriptors. Science
 Performance Level Descriptors Science Grade 5 Content Summary Nature and Application of Science and Technology Distinguish well designed fair tests from flawed fair tests. Distinguish questions that can
Performance Level Descriptors Science Grade 5 Content Summary Nature and Application of Science and Technology Distinguish well designed fair tests from flawed fair tests. Distinguish questions that can
The Science of Biology Chapter 1. Sec. 1-1 What Is Science?
 The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Sec. 1-1 What Is Science? 1 What Science Is and Is Not Science a way of using evidence to learn about the natural world. Goals of Science: Investigate and understand the
The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Sec. 1-1 What Is Science? 1 What Science Is and Is Not Science a way of using evidence to learn about the natural world. Goals of Science: Investigate and understand the
Characteristics of Life
 Characteristics of Life All living things share some basic characteristics: 1. Organization 2. Movement 3. Made up of cells 4. Reproduce 5. Grow and / or develop 6. Obtain and use energy 7. Respond to
Characteristics of Life All living things share some basic characteristics: 1. Organization 2. Movement 3. Made up of cells 4. Reproduce 5. Grow and / or develop 6. Obtain and use energy 7. Respond to
1-3 Studying Life. Slide of 45. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Characteristics of Living Things What are some characteristics of living things? Characteristics of Living Things Characteristics of Living Things No single characteristic is enough to describe a living
Characteristics of Living Things What are some characteristics of living things? Characteristics of Living Things Characteristics of Living Things No single characteristic is enough to describe a living
Biology. Slide 1 of 21. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 21 1-1 What Is Science? 2 of 21 1-1 What Is Science? What Science Is and Is Not What Science Is and Is Not What is the goal of science? 3 of 21 1-1 What Is Science? What Science Is and Is
Biology 1 of 21 1-1 What Is Science? 2 of 21 1-1 What Is Science? What Science Is and Is Not What Science Is and Is Not What is the goal of science? 3 of 21 1-1 What Is Science? What Science Is and Is
Studying Life. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 1.3 Studying Life
 Lesson Overview 1.3 Characteristics of Living Things What characteristics do all living things share? Living things are made up of basic units called cells, are based on a universal genetic code, obtain
Lesson Overview 1.3 Characteristics of Living Things What characteristics do all living things share? Living things are made up of basic units called cells, are based on a universal genetic code, obtain
Name Class Date. biosphere biology metabolism biodiversity organism DNA. MAIN IDEA: Earth is home to an incredible diversity of life.
 Section 1: The Study of Life KEY CONCEPT Biologists study life in all its forms. VOCABULARY biosphere biology metabolism biodiversity organism DNA species cell MAIN IDEA: Earth is home to an incredible
Section 1: The Study of Life KEY CONCEPT Biologists study life in all its forms. VOCABULARY biosphere biology metabolism biodiversity organism DNA species cell MAIN IDEA: Earth is home to an incredible
Four elements make up about 90% of the mass of organisms O, C, H, and N
 Chapter 2 Chemistry of Life 2-1 Composition of Matter -Mass- quantity of matter- use a balance to measure mass -Weight- pull of gravity on an object- use a scale Elements -cannot be broken down into simpler
Chapter 2 Chemistry of Life 2-1 Composition of Matter -Mass- quantity of matter- use a balance to measure mass -Weight- pull of gravity on an object- use a scale Elements -cannot be broken down into simpler
Intro. My website is what you should turn to if you lose something or forget what your HW is, OR.if you are absent!!!
 Intro All of my powerpoints, notes, and most handouts can be found on my website at www.bohneoprfhs.weebly.com - please use this website regularly as it is always updated! My website is what you should
Intro All of my powerpoints, notes, and most handouts can be found on my website at www.bohneoprfhs.weebly.com - please use this website regularly as it is always updated! My website is what you should
Growth & Development. Characteristics of Living Things. What is development? Movement. What is a cell?
 Characteristics of Living Things made of cells growth acquire and use energy reproduction movement adaptation respond to stimuli/homeostasis interdependence organization What is development? What are some
Characteristics of Living Things made of cells growth acquire and use energy reproduction movement adaptation respond to stimuli/homeostasis interdependence organization What is development? What are some
8/24/2018. Bio 1101 Lecture 2 (guided) Chapters 2: Essential Chemistry. Chapter 2: Essential Chemistry for Biology
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1101 Lecture 2 (guided) Chapters 2: Essential Chemistry Chapter 2: Essential Chemistry for Biology Levels of biological organization Ecosystem (e.g. savanna) Community (e.g. the organisms
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1101 Lecture 2 (guided) Chapters 2: Essential Chemistry Chapter 2: Essential Chemistry for Biology Levels of biological organization Ecosystem (e.g. savanna) Community (e.g. the organisms
Chapter 1. How Do Biologists Study Life?
 Chapter 1 How Do Biologists Study Life? Biology is the study of life Biologists ask questions about all aspects of living organisms Bios logos means a discourse on life in Greek Biology has many sub-disciplines
Chapter 1 How Do Biologists Study Life? Biology is the study of life Biologists ask questions about all aspects of living organisms Bios logos means a discourse on life in Greek Biology has many sub-disciplines
Let s get started. So, what is science?
 Let s get started So, what is science? Well Science Science is the observation of phenomena and the theoretical explanation of it. Simply, it is the state of knowing. Biology Biology is the study of life.
Let s get started So, what is science? Well Science Science is the observation of phenomena and the theoretical explanation of it. Simply, it is the state of knowing. Biology Biology is the study of life.
The Characteristics of Life. AP Biology Notes: #1
 The Characteristics of Life AP Biology Notes: #1 Life s Diversity & Unity Life has extensive diversity. Despite its diversity, all living things are composed of the same chemical elements that make-up
The Characteristics of Life AP Biology Notes: #1 Life s Diversity & Unity Life has extensive diversity. Despite its diversity, all living things are composed of the same chemical elements that make-up
Grade Seven Science Focus on Life Sciences. Main Ideas in the Study of Cells
 Grade Seven Science Focus on Life Sciences Main Ideas in the Study of Cells Research is an effective way to develop a deeper understanding of challenging content. The following fill-in-the-blanks activity
Grade Seven Science Focus on Life Sciences Main Ideas in the Study of Cells Research is an effective way to develop a deeper understanding of challenging content. The following fill-in-the-blanks activity
Biology Unit Overview and Pacing Guide
 This document provides teachers with an overview of each unit in the Biology curriculum. The Curriculum Engine provides additional information including knowledge and performance learning targets, key
This document provides teachers with an overview of each unit in the Biology curriculum. The Curriculum Engine provides additional information including knowledge and performance learning targets, key
Chapter Two (Chemistry of Life)
 1 Chapter Two (Chemistry of Life) SECTION ONE: THE COMPOSITION OF MATTER MATTER Everything in the universe is made of matter. Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. Mass is the quantity of
1 Chapter Two (Chemistry of Life) SECTION ONE: THE COMPOSITION OF MATTER MATTER Everything in the universe is made of matter. Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. Mass is the quantity of
HA Biology: Practice Quiz 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 HA Biology: Practice Quiz 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements about the properties of life is false?
HA Biology: Practice Quiz 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements about the properties of life is false?
1. List the steps of the scientific method in order:.
 Name: Period: Biology: 1 st Semester Final Review Scientific Method, Tools of Science 1. List the steps of the scientific method in order:. 2. The use of the five senses to gather data is called:. 3. A
Name: Period: Biology: 1 st Semester Final Review Scientific Method, Tools of Science 1. List the steps of the scientific method in order:. 2. The use of the five senses to gather data is called:. 3. A
Biology Assessment. Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
 Biology Assessment Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills STAAR Biology Assessment Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function The student will demonstrate an understanding of biomolecules
Biology Assessment Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills STAAR Biology Assessment Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function The student will demonstrate an understanding of biomolecules
STAAR Biology Assessment
 STAAR Biology Assessment Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function The student will demonstrate an understanding of biomolecules as building blocks of cells, and that cells are the basic unit of
STAAR Biology Assessment Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function The student will demonstrate an understanding of biomolecules as building blocks of cells, and that cells are the basic unit of
Unit 1 ~ Scientific Reasoning & Logic
 Unit 1 ~ Scientific Reasoning & Logic A) An Introduction to Biology What is the study of Biology? Every thing can be classified into one of 3 groups... o _ o _ o _ Why do people study it?... Or better
Unit 1 ~ Scientific Reasoning & Logic A) An Introduction to Biology What is the study of Biology? Every thing can be classified into one of 3 groups... o _ o _ o _ Why do people study it?... Or better
Name: Date: Answer: Answer:
 Name: Date: 5 6 7 8 9 0 Scoring Guide: Scoring Guide: 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 6 7 8 9 0 Scoring Guide: Scoring Guide: 5 Scoring Guide: 6 7 8 9 0 5 6 7 8 9 50 Scoring Guide: 5 Scoring Guide: Standard(s):..0.F,...F,..0.D,...D,..0.C,...C,..0.E,...E,.5.0.F,.5..F
Name: Date: 5 6 7 8 9 0 Scoring Guide: Scoring Guide: 5 6 7 8 9 0 5 6 7 8 9 0 Scoring Guide: Scoring Guide: 5 Scoring Guide: 6 7 8 9 0 5 6 7 8 9 50 Scoring Guide: 5 Scoring Guide: Standard(s):..0.F,...F,..0.D,...D,..0.C,...C,..0.E,...E,.5.0.F,.5..F
Chapter: Cell Processes
 Table of Contents Chapter: Cell Processes Section 1: Chemistry of Life Section 2: Moving Cellular Materials Section 3: Energy for Life 1 Chemistry of Life The Nature of Matter Matter is anything that has
Table of Contents Chapter: Cell Processes Section 1: Chemistry of Life Section 2: Moving Cellular Materials Section 3: Energy for Life 1 Chemistry of Life The Nature of Matter Matter is anything that has
Biology. The study of life
 Biology The study of life Genesis 1:11 Then God said, Let the land produce vegetation: seed-bearing plants and trees on the land that bear fruit with seed in it, according to their various kinds. Genesis
Biology The study of life Genesis 1:11 Then God said, Let the land produce vegetation: seed-bearing plants and trees on the land that bear fruit with seed in it, according to their various kinds. Genesis
WHAT IS SCIENCE? Chapter 1. Key concept: What is the goal of science?
 WHAT IS SCIENCE? Chapter 1 Key concept: What is the goal of science? SCIENCE: Is an Uses to events Collects and organizes Deals only with Looks for patterns and organized method evidence connections explain
WHAT IS SCIENCE? Chapter 1 Key concept: What is the goal of science? SCIENCE: Is an Uses to events Collects and organizes Deals only with Looks for patterns and organized method evidence connections explain
Chapter 1 Biology 103
 Chapter 1 Biology 103 Properties of Life Living organisms: are composed of cells are complex and ordered respond to their environment can grow and reproduce obtain and use energy maintain internal balance
Chapter 1 Biology 103 Properties of Life Living organisms: are composed of cells are complex and ordered respond to their environment can grow and reproduce obtain and use energy maintain internal balance
The Science of Biology. Chapter 1
 The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Warm Up Exercise Please complete the pretest that you picked up when you came in. Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary.
The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Warm Up Exercise Please complete the pretest that you picked up when you came in. Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary.
CHAPTER 6--- CHEMISTRY IN BIOLOGY. Miss Queen
 CHAPTER 6--- CHEMISTRY IN BIOLOGY Miss Queen SECTION 6.1 Atoms, Elements, Compounds COMPOSITION OF MATTER Matter - Everything in universe is composed of matter Matter is anything that occupies space or
CHAPTER 6--- CHEMISTRY IN BIOLOGY Miss Queen SECTION 6.1 Atoms, Elements, Compounds COMPOSITION OF MATTER Matter - Everything in universe is composed of matter Matter is anything that occupies space or
6-12. Grades. Great extension activities for biology topics. Correlated to standards. Comprehensive biology vocabulary study
 Grades 6-12 CD-104643 Great extension activities for biology topics Correlated to standards Comprehensive biology vocabulary study Fascinating true-tolife illustrations 10 20 30 40 50 70 80 90 100 110
Grades 6-12 CD-104643 Great extension activities for biology topics Correlated to standards Comprehensive biology vocabulary study Fascinating true-tolife illustrations 10 20 30 40 50 70 80 90 100 110
The Science of Biology
 The Science of Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary l Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms l Science-
The Science of Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary l Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms l Science-
Warm Up: Vocabulary. Unit 1 Introduction to Biology. Defining Key Terms. Defining Key Terms. Defining Key Terms (continued) Think About It
 Unit 1 Introduction to Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms Science-
Unit 1 Introduction to Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms Science-
INTRO TO BIOLOGY -GUIDED NOTES-
 INTRO TO BIOLOGY -GUIDED NOTES- DEFINING KEY SCIENCE TERMS - an organized way of using evidence to learn about the natural world. Biology-. Observation- the process of. Data- the information gathered from
INTRO TO BIOLOGY -GUIDED NOTES- DEFINING KEY SCIENCE TERMS - an organized way of using evidence to learn about the natural world. Biology-. Observation- the process of. Data- the information gathered from
Chapter Test A. It s Alive!! Or Is It? MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Assessment Chapter Test A It s Alive!! Or Is It? MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic that all organisms share?
Assessment Chapter Test A It s Alive!! Or Is It? MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic that all organisms share?
THINGS I NEED TO KNOW:
 THINGS I NEED TO KNOW: 1. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus. In eukaryotic cells, the DNA is surrounded by a membrane. Both types of cells have ribosomes. Some
THINGS I NEED TO KNOW: 1. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus. In eukaryotic cells, the DNA is surrounded by a membrane. Both types of cells have ribosomes. Some
Exploring Life Content Assessment 1
 Exploring Life Content Assessment 1 INSTRUCTIONS: Below you will find 42 questions that explore your understanding of science. Each question is numbered in the left-hand column and has only one correct
Exploring Life Content Assessment 1 INSTRUCTIONS: Below you will find 42 questions that explore your understanding of science. Each question is numbered in the left-hand column and has only one correct
Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life
 Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Seventh Edition Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Figure 1.0_1 Chapter 1:
Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Seventh Edition Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Figure 1.0_1 Chapter 1:
Biology Test 2 BIO.2c-d: Metabolic Processes. For questions 1 16, choose the best answer. Indicate your answer on the Scantron and on the test.
 Name Block Date Biology Test 2 BIO.2c-d: Metabolic Processes For questions 1 16, choose the best answer. Indicate your answer on the Scantron and on the test. 1. Scientists hypothesize that oxygen began
Name Block Date Biology Test 2 BIO.2c-d: Metabolic Processes For questions 1 16, choose the best answer. Indicate your answer on the Scantron and on the test. 1. Scientists hypothesize that oxygen began
Name Date Class. W What I Want to Learn. Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3. NEW binomial nomenclature species genus dichotomous key cladogram
 Name Date Class Chapter 9 1 The Practice of Science 2 The Characteristics of Scientific Knowledge 14 Organization and Development of Living Organisms 15 Diversity and Evolution of Living Organisms THINK
Name Date Class Chapter 9 1 The Practice of Science 2 The Characteristics of Scientific Knowledge 14 Organization and Development of Living Organisms 15 Diversity and Evolution of Living Organisms THINK
The Science of Biology. Chapter 1
 The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Properties of Life Living organisms: are composed of cells are complex and ordered respond to their environment can grow and reproduce obtain and use energy maintain internal
The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Properties of Life Living organisms: are composed of cells are complex and ordered respond to their environment can grow and reproduce obtain and use energy maintain internal
Chapter 1. Scientific Process and Themes of Biology
 Chapter 1 Scientific Process and Themes of Biology What is Science? u Scientific knowledge is acquired using a rigorous process u Science is an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the
Chapter 1 Scientific Process and Themes of Biology What is Science? u Scientific knowledge is acquired using a rigorous process u Science is an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the
FINAL VERSION_ Secondary Preservice Teacher Standards -- Life Science AFK12SE/NGSS Strand Disciplinary Core Idea
 Secondary Preservice Teacher Standards -- Life Science AFK12SE/NGSS Strand Disciplinary Core Idea LS1: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes LS1.A: Structure and Function How do the structures
Secondary Preservice Teacher Standards -- Life Science AFK12SE/NGSS Strand Disciplinary Core Idea LS1: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes LS1.A: Structure and Function How do the structures
BSC 1010C Biology I. Themes in the Study of Life Chapter 1
 BSC 1010C Biology I Themes in the Study of Life Chapter 1 Objectives Distinguish among the three domains of life. Distinguish between the Levels of Biological Organization. Note the differences in the
BSC 1010C Biology I Themes in the Study of Life Chapter 1 Objectives Distinguish among the three domains of life. Distinguish between the Levels of Biological Organization. Note the differences in the
1.1. KEY CONCEPT Biologists study life in all its forms. 4 Reinforcement Unit 1 Resource Book. Biology in the 21st Century CHAPTER 1
 1.1 THE STUDY OF LIFE KEY CONCEPT Biologists study life in all its forms. Biology is the scientific study of all forms of life. Living things are found almost everywhere on Earth, from very hot environments
1.1 THE STUDY OF LIFE KEY CONCEPT Biologists study life in all its forms. Biology is the scientific study of all forms of life. Living things are found almost everywhere on Earth, from very hot environments
Chapter Chemical Elements Matter solid, liquid, and gas elements atoms. atomic symbol protons, neutrons, electrons. atomic mass atomic number
 Chapter 2 2.1 Chemical Elements 1. Matter is defined as anything that takes up space and has mass. 2. Matter exists in three states: solid, liquid, and gas. A. Elements 1. All matter (both living and non-living)
Chapter 2 2.1 Chemical Elements 1. Matter is defined as anything that takes up space and has mass. 2. Matter exists in three states: solid, liquid, and gas. A. Elements 1. All matter (both living and non-living)
2.1 The Nature of Matter
 2.1 The Nature of Matter Lesson Objectives Identify the three subatomic particles found in atoms. Explain how all of the isotopes of an element are similar and how they are different. Explain how compounds
2.1 The Nature of Matter Lesson Objectives Identify the three subatomic particles found in atoms. Explain how all of the isotopes of an element are similar and how they are different. Explain how compounds
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser Middle School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser Middle School Science 7 Units and s Science 7A Unit 1 Nature of Science Scientific Explanations (12 days) s 1. I can make an informed decision using a scientific decision-making model
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser Middle School Science 7 Units and s Science 7A Unit 1 Nature of Science Scientific Explanations (12 days) s 1. I can make an informed decision using a scientific decision-making model
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms (LS1)
 EALR 4: Big Idea: Core Content: Life Science Structures and Functions of Living Organisms (LS1) Processes Within Cells In prior grades students learned that all living systems are composed of cells which
EALR 4: Big Idea: Core Content: Life Science Structures and Functions of Living Organisms (LS1) Processes Within Cells In prior grades students learned that all living systems are composed of cells which
The Chemistry of Biology
 The Chemistry of Biology Life depends on chemistry. Living things are composed of chemical compounds. If order to understand biology, one must first understand the chemistry of life. I. The Nature of Matter
The Chemistry of Biology Life depends on chemistry. Living things are composed of chemical compounds. If order to understand biology, one must first understand the chemistry of life. I. The Nature of Matter
Grade 7 Science Curriculum Maps
 Grade 7 Science Curriculum Maps Unit 1: Cells The Basic Unit of Life Unit 2: The Cell in Action Unit 3: Genes and DNA Unit 4: Heredity Unit 5: Evolution Unit 6: It s Alive! Or is it?! Unit 7: Bacteria
Grade 7 Science Curriculum Maps Unit 1: Cells The Basic Unit of Life Unit 2: The Cell in Action Unit 3: Genes and DNA Unit 4: Heredity Unit 5: Evolution Unit 6: It s Alive! Or is it?! Unit 7: Bacteria
Unit 1 Introduction Chapter 1 The Nature of Life watch?v=vyuokb3go7e
 Unit 1 Introduction Chapter 1 The Nature of Life https://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=vyuokb3go7e Unit 1: Standards 1. Explain how events in the natural world are discovered. 2. Distinguish how the scientific
Unit 1 Introduction Chapter 1 The Nature of Life https://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=vyuokb3go7e Unit 1: Standards 1. Explain how events in the natural world are discovered. 2. Distinguish how the scientific
The Science of Biology
 The Science of Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms Science- an
The Science of Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms Science- an
Biology EOC Review Study Questions
 Biology EOC Review Study Questions Microscopes and Characteristics of Life 1. How do you calculate total magnification on a compound light microscope? 2. What is the basic building block of all living
Biology EOC Review Study Questions Microscopes and Characteristics of Life 1. How do you calculate total magnification on a compound light microscope? 2. What is the basic building block of all living
Chapter 1. An Introduction To Life On Earth
 Chapter 1 An Introduction To Life On Earth John Klock, MA, MS 16 th year teaching life sciences 5 colleges (LBCC, OSU, Univ. of Maryland,..) Two children 15 years abroad, climbing (Mt.Mckinley) traveling
Chapter 1 An Introduction To Life On Earth John Klock, MA, MS 16 th year teaching life sciences 5 colleges (LBCC, OSU, Univ. of Maryland,..) Two children 15 years abroad, climbing (Mt.Mckinley) traveling
1. Ecosystems are made up of both living and non-living things. True False. 2. Ecosystems can be very large or very small.
 1 Pre-Test Directions: Answer each of the following either true or false. 1. Ecosystems are made up of both living and non-living things. True False 2. Ecosystems can be very large or very small. True
1 Pre-Test Directions: Answer each of the following either true or false. 1. Ecosystems are made up of both living and non-living things. True False 2. Ecosystems can be very large or very small. True
Grade 7 Science Learning Standards
 Grrade 7 Sciience Currrriicullum Overrviiew Middle School Science Hands-on, Minds-On, Science is the primary focus of the middle school science program, and includes content from Earth and Space Science,
Grrade 7 Sciience Currrriicullum Overrviiew Middle School Science Hands-on, Minds-On, Science is the primary focus of the middle school science program, and includes content from Earth and Space Science,
Learning Objective. Chapter 1: Introduction to Biology. Class Exercise: What does it mean to be living? Properties of Life
 1 2 Introduction to Biology Learning Objective Chapter 1: Introduction to Biology Describe the properties and levels of organization of living things 1.1: Themes and Concepts of Biology 1.2: The Process
1 2 Introduction to Biology Learning Objective Chapter 1: Introduction to Biology Describe the properties and levels of organization of living things 1.1: Themes and Concepts of Biology 1.2: The Process
NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE. Honors Biology I
 NOTE/STUDY GUIDE: Unit 1-2, Biochemistry Honors Biology I, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: Period: Seat #: Date: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE Honors Biology I Unit
NOTE/STUDY GUIDE: Unit 1-2, Biochemistry Honors Biology I, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: Period: Seat #: Date: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE Honors Biology I Unit
Use evidence of characteristics of life to differentiate between living and nonliving things.
 Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards All living things have a common set characteristic needs and functions that separate them from nonliving things such as:
Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards All living things have a common set characteristic needs and functions that separate them from nonliving things such as:
Biology/Honors Biology Benchmark #2 Review Guide Fall 2016
 Biology/Honors Biology Benchmark #2 Review Guide Fall 2016 Name CH 1: Science of Biology 1. Fill in the following table with parts of the scientific process. 2. What is the difference between an observation
Biology/Honors Biology Benchmark #2 Review Guide Fall 2016 Name CH 1: Science of Biology 1. Fill in the following table with parts of the scientific process. 2. What is the difference between an observation
Scientific Method. Chapter 1.3. Copyright Cmassengale
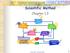 Scientific Method Chapter 1.3 1 Observation STEP 1 Employing your five senses to perceive objects or events 2 3 Asking a Question Based on observations; one or more questions are generated 4 Forming a
Scientific Method Chapter 1.3 1 Observation STEP 1 Employing your five senses to perceive objects or events 2 3 Asking a Question Based on observations; one or more questions are generated 4 Forming a
An Introduction to the Science of Botany. Chapter 1
 An Introduction to the Science of Botany Chapter 1 TTU MS 43131 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Briefly describe the field of botany, and give short definitions of at least five subdisciplines of plant biology Summarize
An Introduction to the Science of Botany Chapter 1 TTU MS 43131 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Briefly describe the field of botany, and give short definitions of at least five subdisciplines of plant biology Summarize
Section Objectives: Section Objectives: Distinguish mixtures and solutions. Define acids and bases and relate their importance to biological systems.
 Section Objectives: Relate the structure of an atom to the identity of elements. Relate the formation of covalent and ionic chemical bonds to the stability of atoms. Section Objectives: Distinguish mixtures
Section Objectives: Relate the structure of an atom to the identity of elements. Relate the formation of covalent and ionic chemical bonds to the stability of atoms. Section Objectives: Distinguish mixtures
1. The basic structural and physiological unit of all living organisms is the A) aggregate. B) organelle. C) organism. D) membrane. E) cell.
 Name: Date: Test File Questions 1. The basic structural and physiological unit of all living organisms is the A) aggregate. B) organelle. C) organism. D) membrane. E) cell. 2. A cell A) can be composed
Name: Date: Test File Questions 1. The basic structural and physiological unit of all living organisms is the A) aggregate. B) organelle. C) organism. D) membrane. E) cell. 2. A cell A) can be composed
7 th Grade Life Science Review Packet
 7 th Grade Life Science Review Packet Ms. Shirreffs Name: Introduction and Characteristics of Life 1. This year we studied life science, another word for life science is 2. Which term describes an organism
7 th Grade Life Science Review Packet Ms. Shirreffs Name: Introduction and Characteristics of Life 1. This year we studied life science, another word for life science is 2. Which term describes an organism
Campbell Essential Biology, 5e (Simon/Yeh) Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today. Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell Essential Biology, 5e (Simon/Yeh) Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today Multiple-Choice Questions 1) In what way(s) is the science of biology influencing and changing our culture? A) by helping
Campbell Essential Biology, 5e (Simon/Yeh) Chapter 1 Introduction: Biology Today Multiple-Choice Questions 1) In what way(s) is the science of biology influencing and changing our culture? A) by helping
Need to Know. How do you conduct science? What are the characteristics of life?
 Science and Biology Need to Know How do you conduct science? What is biology? What are the characteristics of life? Science Science is an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the natural
Science and Biology Need to Know How do you conduct science? What is biology? What are the characteristics of life? Science Science is an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the natural
Bio10 Practice Lab Exam 1
 Bio10 Practice Lab Exam 1 Instructions: Answer the following questions using the concepts pertaining to laboratory exercises. This information is in your textbook, lab manual, or instructor provided handouts.
Bio10 Practice Lab Exam 1 Instructions: Answer the following questions using the concepts pertaining to laboratory exercises. This information is in your textbook, lab manual, or instructor provided handouts.
Semester 1 Review Questions for Exam
 Semester 1 Review Questions for Exam Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 1. The part of an ecosystem where an organism lives and feeds is called the organism s 2. All the biotic and abiotic
Semester 1 Review Questions for Exam Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 1. The part of an ecosystem where an organism lives and feeds is called the organism s 2. All the biotic and abiotic
98 Washington State K-12 Science Learning Standards Version 1.2
 EALR 4: Big Idea: Core Content: Life Science Structures and Functions of Living Organisms (LS1) Processes Within Cells In prior grades students learned that all living systems are composed of cells which
EALR 4: Big Idea: Core Content: Life Science Structures and Functions of Living Organisms (LS1) Processes Within Cells In prior grades students learned that all living systems are composed of cells which
Contents. Chapter 5 Elements and Compounds 129. Chapter 1 Living Cells 1. Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes 161. Chapter 2 Organ Systems 25
 Contents Words to Watch iv Chapter 5 Elements and Compounds 129 1 1.1 Plant, animal and fungal cells 3 1.2 Structures within cells 7 1.3 Examining cells 9 1.4 Single-celled organisms 15 1.5 Cell division
Contents Words to Watch iv Chapter 5 Elements and Compounds 129 1 1.1 Plant, animal and fungal cells 3 1.2 Structures within cells 7 1.3 Examining cells 9 1.4 Single-celled organisms 15 1.5 Cell division
McDougal Littell Science, Cells and Heredity MAZER PDF. IL Essential Lesson. IL Extend Lesson. Program Planning Guide LP page.
 s7an-ppg-pc-il-002-012.indd 2 7/18/05 2:46:40 PM 2 McDougal Littell Science, Cells and Heredity Chapter 1: The Cell, pp. 6 37 1.1 The cell is the basic unit of living things. pp. 9 17 Explore: Activity
s7an-ppg-pc-il-002-012.indd 2 7/18/05 2:46:40 PM 2 McDougal Littell Science, Cells and Heredity Chapter 1: The Cell, pp. 6 37 1.1 The cell is the basic unit of living things. pp. 9 17 Explore: Activity
BIOCHEMISTRY 10/9/17 CHEMISTRY OF LIFE. Elements: simplest form of a substance - cannot be broken down any further without changing what it is
 BIOCHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY OF LIFE Elements: simplest form of a substance - cannot be broken down any further without changing what it is THE ATOM Just like cells are the basic unit of life, the ATOM is the
BIOCHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY OF LIFE Elements: simplest form of a substance - cannot be broken down any further without changing what it is THE ATOM Just like cells are the basic unit of life, the ATOM is the
Name Date Period Handout A: Characteristics of Life
 Name Date Period Handout A: Characteristics of Life Directions: 1. Read and highlight the main ideas in each passage. 2. Circle Key vocabulary 3. Answer the questions below each passage. Most people feel
Name Date Period Handout A: Characteristics of Life Directions: 1. Read and highlight the main ideas in each passage. 2. Circle Key vocabulary 3. Answer the questions below each passage. Most people feel
2. The development of revolutionized the of life.
 Science 10 Unit 7 Worksheet Chapter 15, Part 1. 1. Briefly describe the three main parts of cell theory: 2. The development of revolutionized the of life. 3. Individual cells need to take in to build and
Science 10 Unit 7 Worksheet Chapter 15, Part 1. 1. Briefly describe the three main parts of cell theory: 2. The development of revolutionized the of life. 3. Individual cells need to take in to build and
B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M Science 7 th grade
 B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M Science 7 th grade ORGANIZING THEME/TOPIC UNIT 1: CELLS Structure and Function of Cells MS-LS1-1. Conduct an investigation to provide evidence that
B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M Science 7 th grade ORGANIZING THEME/TOPIC UNIT 1: CELLS Structure and Function of Cells MS-LS1-1. Conduct an investigation to provide evidence that
Case study: spider mimicry
 Pounce rate (% of trials in which spider jumped on fly) Case study: spider mimicry Control group (untreated flies) Experimental group (wing markings masked) Pounce rate (% of trials in which spider jumped
Pounce rate (% of trials in which spider jumped on fly) Case study: spider mimicry Control group (untreated flies) Experimental group (wing markings masked) Pounce rate (% of trials in which spider jumped
Organizing Diversity Taxonomy is the discipline of biology that identifies, names, and classifies organisms according to certain rules.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Outline 1.1 Introduction to AP Biology 1.2 Big Idea 1: Evolution 1.3 Big Idea 2: Energy and Molecular Building Blocks 1.4 Big Idea 3: Information Storage, Transmission, and Response
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Outline 1.1 Introduction to AP Biology 1.2 Big Idea 1: Evolution 1.3 Big Idea 2: Energy and Molecular Building Blocks 1.4 Big Idea 3: Information Storage, Transmission, and Response
1.1. Biology in the 21st Century CHAPTER 1. Biologists study life in all its forms. Earth is home to an incredible diversity of life.
 SECTION 1.1 KEY CONCEPT THE STUDY OF LIFE Study Guide Biologists study life in all its forms. VOCABULARY biosphere biology metabolism biodiversity organism DNA species MAIN IDEA: Earth is home to an incredible
SECTION 1.1 KEY CONCEPT THE STUDY OF LIFE Study Guide Biologists study life in all its forms. VOCABULARY biosphere biology metabolism biodiversity organism DNA species MAIN IDEA: Earth is home to an incredible
CELL AND MICROBIOLOGY Nadia Iskandarani
 7Course Title: Head of Department: Teacher(s) + e-mail: Cycle/Division: Biology IA: CELL AND MICROBIOLOGY Nadia Iskandarani Ms.Ibtessam: ibtissam.h@greenwood.sch.ae High School Grade Level: Grade 10 Credit
7Course Title: Head of Department: Teacher(s) + e-mail: Cycle/Division: Biology IA: CELL AND MICROBIOLOGY Nadia Iskandarani Ms.Ibtessam: ibtissam.h@greenwood.sch.ae High School Grade Level: Grade 10 Credit
13. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Study Guide Exam 1 BIO 301L Chinnery Spring 2013
 Study Guide Exam 1 BIO 301L Chinnery Spring 2013 Lecture 1: Biology and Life What are the big picture messages from this lecture? How can you associate the contents of this lecture with those of the other
Study Guide Exam 1 BIO 301L Chinnery Spring 2013 Lecture 1: Biology and Life What are the big picture messages from this lecture? How can you associate the contents of this lecture with those of the other
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTERS 1 and 2: Introduction, and The Chemical Context of Life:
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTERS 1 and 2: Introduction, and The Chemical Context of Life: BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 1: Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life Natural Selection and change: Focus What is science, and what
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTERS 1 and 2: Introduction, and The Chemical Context of Life: BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 1: Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life Natural Selection and change: Focus What is science, and what
Cells. Unit Review: Cells MEIOSIS. TECHBOOK UNIT 0 Views. Essential Questions and Answers for Review Sheet. What is meiosis?
 Cells TECHBOOK UNIT 0 Views Unit Review: Cells MEIOSIS Essential Questions and Answers for Review Sheet What is meiosis? Answer: Meiosis is the process by which specialized cells called gametes form in
Cells TECHBOOK UNIT 0 Views Unit Review: Cells MEIOSIS Essential Questions and Answers for Review Sheet What is meiosis? Answer: Meiosis is the process by which specialized cells called gametes form in
BIOLOGY NOTES - CHAPTER 1
 BIOLOGY NOTES - CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1 and 2 Biology is the study of life Bio = life Logy = study of The scientific study of all forms of life, or all types of organisms Science means to know Science is a
BIOLOGY NOTES - CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1 and 2 Biology is the study of life Bio = life Logy = study of The scientific study of all forms of life, or all types of organisms Science means to know Science is a
