Where have we been? Lectures 1 and 2 Bohr s Model/ Wave Mechanics/ Radial and Angular Wavefunctions/ Radial Distribution Functions/ s and p orbitals
|
|
|
- Aileen Reed
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Where have we been? Lectures 1 and 2 Bohr s Model/ Wave Mechanics/ Radial and Angular Wavefunctions/ Radial Distribution unctions/ s and p orbitals Where are we going? Lecture 3 Brief wavefunction considerations: d and f orbitals Using wavefunctions and radial distribution functions (RDs) to compare atomic orbitals (AOs) define penetration and shielding explain the aufbau building-up principle Revision - Localised bond pictures - Hybridisation Sylvia Draper smdraper@tcd.ie 40
2 d orbitals wave functions ive d orbitals for each value of n (n 3) l = 2, m l = -2, -1, 0, 1, 2 Wave functions slightly more complicated Radial wave functions same for all 3d orbital R(3d ) = Z a ( ρr) 2 e ( ρr 2) Max probability at r = 9 a 0 AOs with no nodes have max probabilty at same radius as Bohr model 4d orbital has 1 node R(r) in a.u d - R(r) 3d - RD Radius (a.u) πr 2 R(r) 2
3 d orbitals angular functions Angular functions same for d, irrespective of n xy d yz, d xz, d 2, d 2 2 z x same shape for 3d, 4d, 5d orbitals using boundary y surfaces ive different angular functions e.g. Two angular nodes planes orthogonal to s and p e.g. d xy Nodal planes in yz and xz (+ve lobe points between +x and +y axes) Y ( d xz ) 15 16π = 1 2 sin( θ )cos( θ )cos( φ) d xy d z 2
4 f orbitals Almost no covalent bonding because metal orbitals are so contracted shape not really important l = 3 Seven different angular functions for each n (n 4) f block is 14 element wide, same shape for 4f, 5f etc Radial functions same for all nf orbitals Three angular nodes (nodal planes) orthogonal to s, p and d orbitals
5 Penetration RD allow us to directly compare AOs on the same graph The RDs of AOs within a given shell (n) have different maxima Number of nodes n l - 1 n = 3 3s 2 nodes 3p 1 node 3d 0 nodes 3s has a peak very close to the nucleus 3p has a peak close to the nucleus 1.5 3p These close peaks have a very strong interaction with the nucleus 3s is said to be the most penetrating 4πr 2 R(r) d 3s Penetration 3s > 3p > 3d Radius (a.u)
6 Multi-electron Atoms Multi-electron atoms are assumed to have hydrogen-like wave functions. Differences are the increase in atomic number and the effective nuclear charge. In reality the electrons repel each other and shield the nucleus Effective nuclear charge Z eff = Z S S = a screening or shielding constant Li atom why is the electronic configuration 1s 2 2s 1 and not 1s 2 2p 1? 1s electrons shield the valence electron from the nuclear charge 2s penetrates more effectively feels a greater nuclear charge 2p penetrates less effectively 2s is filled first E(1s) < E(2s) < E(2p) E(ns) < E(np) < E(nd) 4πr 2 R(r) s 2p 2s Radius (a.u)
7 Periodic table Shielding and penetration E(ns) < E(np) < E(nd) < E(nf) This gives rise to the electronic configuration of atoms and the order of elements in the periodic table Orbitals are filled in order of increasing energy (Aufbau principle) and electrons fill degenerate (same energy) levels singularly first to give maximum spin (Hund s rule) E(4s) < E(3d) K, Ca 2s 3s 4s 3d 1s 2p 3p 1s E(6s) < E(5d) E(4f) La [Xe] 6s 2 5d 1 Ce [Xe] 6s 2 4f 2 6s 5d 4f
8 More complex results of penetration and shielding Energy levels vs atomic number or H (Z=1) all orbitals within a given n shell have the same energy Penetration follows s > p > d > f 3d shielded very effectively by orbitals of n3 3d almost does not change in energy with Z until Z = 19 4s filled, n = 4 does not shield 3d effectively energy drops Similar pattern for 4d and 4f
9 The Transition Metal Hiccup! or K and Ca the E(3d) > E(4s) so 4s filled first, At Sc the E(3d) < E(4s) (but very close) or Transition metals E(3d) < E(4s) so the 4s electrons are lost first when ionized Energy 4p { 3d 4s { 4p 4s 3d K Ca Sc Ti Increasing Z
10 Drawing representations of AO s Need to be able to draw AOs when considering their interactions i.e. when they form molecular orbitals (MOs). Simple diagrams are all you need!!!!
11 Making Bonds Localised Bond Pictures Revising J Lewis Bonding / VSEPR Localised view of bonding Views bonds between two atoms as covalent (social) Each bond is independent of the others Each single bond is made-up of two shared electrons Each 1 st or 2 nd row atom attains a noble gas configuration Shape obtained by VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Each H has a share in the 2 electrons HH e.g. H 2 H + H H H
12 Lewis bonding Octet rule for main group elements / 18 electron rule for transition metals All atoms have a share of 8 electrons (main group : s + three p orbitals ) or 18 electrons (TM : s + three p + five d orbitals) to fill all their valence atomic orbitals. Diatomics electrons shared bond order = 1 O 2 O + O O O 4 electrons shared bond order = 2 O O
13 Lewis bonding polyatomics (H 2 O) Oxygen (Group 16) has 8 electrons, each hydrogen (Group 1) has 1 electron Oxygen has two lone pairs 2 H + O H O H Shape VSEPR Electrons repel each other (repulsion between lone pair electrons > repulsion between electrons in bonding pairs) Oxygen has 2 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs 4 directions to consider Accommodate 4 directions Tetrahedral shape H 2 O is bent with H-O-H angle of o Compares with a perfect tetrahedral of o lone pair repulsion
14 Lewis bonding polyatomics (ethene) 4 H + 2 C H H C C H H 4 electrons shared between the Carbon atoms bond order = 2 C C Each Carbon hydrogen bond involves the sharing of electrons C H Shape VSEPR Electrons repel each other Carbon atoms have 3 directions bond to C and two bonds to two H Accommodate 3 bond direction 120 o in a plane (molecule is flat)
15 Lewis structures that break the Octet Rule Some structures to not obey the 8 electron rule. These usually contain a 3 rd row element as the central atom e.g P 5 P 90 o P 120 o (only the electrons round the P are shown for clarity) atoms have 3 lone pairs (6 electrons) + 2 in each bond 8 P atom has 5 bond pairs with 2 electrons each 10 electrons! Overall 5 directions to accommodate trigonal bipyrimidal
16 Valence bond theory and hybridisation Valence bond theory (Linus Pauling) Based on localised bonding Hybridisation to give a geometry which is consistent with experiment. Hybridisation constructs new hybrid atomic orbitals from the AOs ON THE SAME ATOM Use Lewis model (number of electron pairs) hybridisation shape. E.g. BeH 2, Be Group 2 H Be H Correctly predicted by VSEPR to be linear can we explain it using Aos Not if we think the Be electrons are in 2s spherical orbitals Mix one s with one p z orbital two sp hybrid orbitals
Lecture January 18, Quantum Numbers Electronic Configurations Ionization Energies Effective Nuclear Charge Slater s Rules
 Lecture 3 362 January 18, 2019 Quantum Numbers Electronic Configurations Ionization Energies Effective Nuclear Charge Slater s Rules Inorganic Chemistry Chapter 1: Figure 1.4 Time independent Schrödinger
Lecture 3 362 January 18, 2019 Quantum Numbers Electronic Configurations Ionization Energies Effective Nuclear Charge Slater s Rules Inorganic Chemistry Chapter 1: Figure 1.4 Time independent Schrödinger
Valence Bond Model and Hybridization
 Valence Bond Model and ybridization APPENDIX 4 1 Concepts The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page reference VSEPR theory 65 More advanced ideas about electronic structure
Valence Bond Model and ybridization APPENDIX 4 1 Concepts The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page reference VSEPR theory 65 More advanced ideas about electronic structure
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories PART I Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories PART I Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
An introduction to. Objectives of the course. Literature. Lecture schedule. 6 Lecture Course
 Objectives of the course An introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory 6 Lecture Course Prof G. W. Watson Lloyd Institute t.36 watsong@tcd.ie Wave mechanics / Atomic orbitals (AOs) The basis for rejecting
Objectives of the course An introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory 6 Lecture Course Prof G. W. Watson Lloyd Institute t.36 watsong@tcd.ie Wave mechanics / Atomic orbitals (AOs) The basis for rejecting
The Electronic Theory of Chemistry
 JF Chemistry CH1101 The Electronic Theory of Chemistry Dr. Baker bakerrj@tcd.ie Module Aims: To provide an introduction to the fundamental concepts of theoretical and practical chemistry, including concepts
JF Chemistry CH1101 The Electronic Theory of Chemistry Dr. Baker bakerrj@tcd.ie Module Aims: To provide an introduction to the fundamental concepts of theoretical and practical chemistry, including concepts
Carbon Compounds. Chemical Bonding Part 1b
 Carbon Compounds Chemical Bonding Part 1b Board Notes Introduction to VSEPR Organic Formulas Various Representations " dimethyl ether C 2 H 6 O " propyl alcohol C 3 H 8 O 3D representations " Wedges and
Carbon Compounds Chemical Bonding Part 1b Board Notes Introduction to VSEPR Organic Formulas Various Representations " dimethyl ether C 2 H 6 O " propyl alcohol C 3 H 8 O 3D representations " Wedges and
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Geometry James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Shapes Lewis Structures show bonding and lone pairs, but do not denote shape. However, we use Lewis Structures to
Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Geometry James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Shapes Lewis Structures show bonding and lone pairs, but do not denote shape. However, we use Lewis Structures to
What Do Molecules Look Like?
 What Do Molecules Look Like? The Lewis Dot Structure approach provides some insight into molecular structure in terms of bonding, but what about 3D geometry? Recall that we have two types of electron pairs:
What Do Molecules Look Like? The Lewis Dot Structure approach provides some insight into molecular structure in terms of bonding, but what about 3D geometry? Recall that we have two types of electron pairs:
VSEPR Theory. Shapes of Molecules. Molecular Structure or Molecular Geometry
 VSEPR Theory VSEPR Theory Shapes of Molecules Molecular Structure or Molecular Geometry The 3-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that make-up a molecule. Determines several properties of a substance,
VSEPR Theory VSEPR Theory Shapes of Molecules Molecular Structure or Molecular Geometry The 3-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that make-up a molecule. Determines several properties of a substance,
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Learning Outcomes: Predict the three-dimensional shapes of molecules using the VSEPR model.
 Chapter 9: Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Learning Outcomes: Predict the three-dimensional shapes of molecules using the VSEPR model. Determine whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar based
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Learning Outcomes: Predict the three-dimensional shapes of molecules using the VSEPR model. Determine whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar based
Covalent Bonding Introduction, 2. Chapter 7 Covalent Bonding. Figure 7.1 The Hydrogen Molecule. Outline. Covalent Bonding Introduction, 1. Figure 7.
 Covalent Bonding Introduction, 2 William L. Masterton Cecile N. Hurley http://academic.cengage.com/chemistry/masterton Chapter 7 Covalent Bonding Electron density Electrons are located between nuclei Electrostatic
Covalent Bonding Introduction, 2 William L. Masterton Cecile N. Hurley http://academic.cengage.com/chemistry/masterton Chapter 7 Covalent Bonding Electron density Electrons are located between nuclei Electrostatic
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories. Chapter 9
 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 Molecular Shapes CCl 4 Lewis structures give atomic connectivity; The shape of a molecule is determined by its bond angles VSEPR Model Valence Shell Electron
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 Molecular Shapes CCl 4 Lewis structures give atomic connectivity; The shape of a molecule is determined by its bond angles VSEPR Model Valence Shell Electron
Hybridization and Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory
 ybridization and Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory Chapter 10 istorical Models G.N.Lewis and I. Langmuir (~1920) laid out foundations Ionic species were formed by electron transfer Covalent molecules arise
ybridization and Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory Chapter 10 istorical Models G.N.Lewis and I. Langmuir (~1920) laid out foundations Ionic species were formed by electron transfer Covalent molecules arise
362 Lecture 6 and 7. Spring 2017 Monday, Jan 30
 362 Lecture 6 and 7 Spring 2017 Monday, Jan 30 Quantum Numbers n is the principal quantum number, indicates the size of the orbital, has all positive integer values of 1 to (infinity) l is the angular
362 Lecture 6 and 7 Spring 2017 Monday, Jan 30 Quantum Numbers n is the principal quantum number, indicates the size of the orbital, has all positive integer values of 1 to (infinity) l is the angular
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Valence Bond Theory. Localized Electron Model. Hybridize the Orbitals! Overlap and Bonding. Atomic Orbitals are. mmmkay. Overlap and Bonding
 Valence Bond Theory Atomic Orbitals are bad mmmkay Overlap and Bonding Lewis taught us to think of covalent bonds forming through the sharing of electrons by adjacent atoms. In such an approach this can
Valence Bond Theory Atomic Orbitals are bad mmmkay Overlap and Bonding Lewis taught us to think of covalent bonds forming through the sharing of electrons by adjacent atoms. In such an approach this can
Topic 2. Structure and Bonding Models of Covalent Compounds of p-block Elements
 Topic 2 2-1 Structure and Bonding Models of Covalent Compounds of p-block Elements Bonding 2-2 Many different approaches to describe bonding: Ionic Bonding: Elements with large electronegativity differences;
Topic 2 2-1 Structure and Bonding Models of Covalent Compounds of p-block Elements Bonding 2-2 Many different approaches to describe bonding: Ionic Bonding: Elements with large electronegativity differences;
Chapter 8. Molecular Shapes. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) What Determines the Shape of a Molecule?
 PowerPoint to accompany Molecular Shapes Chapter 8 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Figure 8.2 The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of bonding
PowerPoint to accompany Molecular Shapes Chapter 8 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Figure 8.2 The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of bonding
Periodic Trends. Homework: Lewis Theory. Elements of his theory:
 Periodic Trends There are various trends on the periodic table that need to be understood to explain chemical bonding. These include: Atomic/Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Electron Affinity
Periodic Trends There are various trends on the periodic table that need to be understood to explain chemical bonding. These include: Atomic/Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Electron Affinity
Review Outline Chemistry 1B, Fall 2012
 Review Outline Chemistry 1B, Fall 2012 -------------------------------------- Chapter 12 -------------------------------------- I. Experiments and findings related to origin of quantum mechanics A. Planck:
Review Outline Chemistry 1B, Fall 2012 -------------------------------------- Chapter 12 -------------------------------------- I. Experiments and findings related to origin of quantum mechanics A. Planck:
5.111 Lecture Summary #7 Wednesday, September 17, 2014
 5.111 Lecture Summary #7 Wednesday, September 17, 2014 Readings for today: Section 1.12 Orbital Energies (of many-electron atoms), Section 1.13 The Building-Up Principle. (Same sections in 5 th and 4 th
5.111 Lecture Summary #7 Wednesday, September 17, 2014 Readings for today: Section 1.12 Orbital Energies (of many-electron atoms), Section 1.13 The Building-Up Principle. (Same sections in 5 th and 4 th
Chemistry: The Central Science. Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory The shape and size of a molecule of a particular substance, together with the strength and polarity of its bonds, largely
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory The shape and size of a molecule of a particular substance, together with the strength and polarity of its bonds, largely
Chemistry 121: Topic 4 - Chemical Bonding Topic 4: Chemical Bonding
 Topic 4: Chemical Bonding 4.0 Ionic and covalent bonds; Properties of covalent and ionic compounds 4.1 Lewis structures, the octet rule. 4.2 Molecular geometry: the VSEPR approach. Molecular polarity.
Topic 4: Chemical Bonding 4.0 Ionic and covalent bonds; Properties of covalent and ionic compounds 4.1 Lewis structures, the octet rule. 4.2 Molecular geometry: the VSEPR approach. Molecular polarity.
Chem 6 Sample Exam 2 Brief Answers
 1 hem 6 Sample Eam 2 Brief Answers 1a. Two possible approaches here to find the energy difference and hence the frequency. Either find the energy of both states and subtract, or use one of the formulas
1 hem 6 Sample Eam 2 Brief Answers 1a. Two possible approaches here to find the energy difference and hence the frequency. Either find the energy of both states and subtract, or use one of the formulas
Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction
 Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent
Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent
Chapter 1 - Basic Concepts: atoms
 Chapter 1 - Basic Concepts: atoms Discovery of atomic structure Rutherford (1910) JJ Thomson (1897) Milliken (1909) Rutherford (1911) 1 Symbol p + e - n 0 Mass (amu) 1.0073 0.000549 1.00870 Discovery 1919,
Chapter 1 - Basic Concepts: atoms Discovery of atomic structure Rutherford (1910) JJ Thomson (1897) Milliken (1909) Rutherford (1911) 1 Symbol p + e - n 0 Mass (amu) 1.0073 0.000549 1.00870 Discovery 1919,
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories. Lecture Presentation. John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of
Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of
Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II. Bonding Theories
 Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II Dr. Chris Kozak Memorial University of Newfoundland, Canada Bonding Theories Previously, we saw how the shapes of molecules can be predicted from the orientation of electron
Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II Dr. Chris Kozak Memorial University of Newfoundland, Canada Bonding Theories Previously, we saw how the shapes of molecules can be predicted from the orientation of electron
B. (i), (iii), and (v) C. (iv) D. (i), (ii), (iii), and (v) E. (i), (iii), (iv), and (v) Answer: B. SO 3, and NO 3 - both have 24 VE and have Lewis
 SCCH 161 Homework 3 1. Give the number of lone pairs around the central atom and the molecular geometry of CBr 4. Answer: Carbon has 4 valence electrons and bonds to four bromine atoms (each has 7 VE s).
SCCH 161 Homework 3 1. Give the number of lone pairs around the central atom and the molecular geometry of CBr 4. Answer: Carbon has 4 valence electrons and bonds to four bromine atoms (each has 7 VE s).
Chapters 9&10 Structure and Bonding Theories
 Chapters 9&10 Structure and Bonding Theories Ionic Radii Ions, just like atoms, follow a periodic trend in their radii. The metal ions in a given period are smaller than the non-metal ions in the same
Chapters 9&10 Structure and Bonding Theories Ionic Radii Ions, just like atoms, follow a periodic trend in their radii. The metal ions in a given period are smaller than the non-metal ions in the same
Unit 1 Atomic Theory
 Unit 1 Atomic Theory 1.0 You are expected to be already familiar with. Ionic nomenclature (binary, polyatomic, multivalency) Covalent nomenclature Writing chemical formulas for ionic and covalent compounds
Unit 1 Atomic Theory 1.0 You are expected to be already familiar with. Ionic nomenclature (binary, polyatomic, multivalency) Covalent nomenclature Writing chemical formulas for ionic and covalent compounds
Drawing Good Lewis Structures. Molecular Shape
 3//05 Drawing Good Lewis Structures. # valence e in atoms (± charge) must = # e in structure ; always. determine connectivity: least EN usually central; avoid small rings; always terminal ( e ); work out
3//05 Drawing Good Lewis Structures. # valence e in atoms (± charge) must = # e in structure ; always. determine connectivity: least EN usually central; avoid small rings; always terminal ( e ); work out
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity (which atoms are physically connected). By noting the number of bonding and nonbonding electron
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity (which atoms are physically connected). By noting the number of bonding and nonbonding electron
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories. Lecture Presentation. John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of
Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories molecular shapes the VSEPR model molecular shape and molecular polarity covalent bonding and orbital overlap hybrid orbitals multiple bonds 9.1 Molecular
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories molecular shapes the VSEPR model molecular shape and molecular polarity covalent bonding and orbital overlap hybrid orbitals multiple bonds 9.1 Molecular
Molecular shape is only discussed when there are three or more atoms connected (diatomic shape is obvious).
 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry (Ch9 Jespersen, Ch10 Chang) The arrangement of the atoms of a molecule in space is the molecular geometry. This is what gives the molecules their shape. Molecular shape is
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry (Ch9 Jespersen, Ch10 Chang) The arrangement of the atoms of a molecule in space is the molecular geometry. This is what gives the molecules their shape. Molecular shape is
Experiment 21 Lewis structures and VSEPR Theory
 Experiment 21 Lewis structures and VSEPR Theory Introduction 1. Lewis Structures and Formal Charge LG.N. Lewis, at the University of California at Berkeley devised a simple way to understand the nature
Experiment 21 Lewis structures and VSEPR Theory Introduction 1. Lewis Structures and Formal Charge LG.N. Lewis, at the University of California at Berkeley devised a simple way to understand the nature
25 Mn Ni Co Rh Fe Ru Os Uns (262) Une (266) 195.
 1 Chem 64 Solutions to Problem Set #1, REVIEW 1. AO n l m 1s 1 0 0 2s 2 0 0 2p 2 1 1,0,1 3d 3 2 2, 1,0,1,2 4d 4 2 2, 1,0,1,2 4f 4 3 3, 2, 1,0,1,2,3 2. Penetration relates to the radial probability distribution
1 Chem 64 Solutions to Problem Set #1, REVIEW 1. AO n l m 1s 1 0 0 2s 2 0 0 2p 2 1 1,0,1 3d 3 2 2, 1,0,1,2 4d 4 2 2, 1,0,1,2 4f 4 3 3, 2, 1,0,1,2,3 2. Penetration relates to the radial probability distribution
Chapter Molecules are 3D. Shapes and Bonds. Chapter 9 1. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure 1 Shape 9.1 Molecules are 3D Angle Linear 180 Planar triangular (trigonal planar) 120 Tetrahedral 109.5 2 Shapes and Bonds Imagine a molecule where the
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure 1 Shape 9.1 Molecules are 3D Angle Linear 180 Planar triangular (trigonal planar) 120 Tetrahedral 109.5 2 Shapes and Bonds Imagine a molecule where the
Chem 111 Exam #2 November 8, J h = c E = h E. ΔH = energies of bonds broken - energies of bonds formed SHOW ALL WORK
 General Chemistry I NAME: Answer Key Chem 111 Exam #2 November 8, 2013 Some Equations and Constants for your use: -18-2.18 10 J h = c E = h E n = = 2 n mv o ΔH = energies of bonds broken - energies of
General Chemistry I NAME: Answer Key Chem 111 Exam #2 November 8, 2013 Some Equations and Constants for your use: -18-2.18 10 J h = c E = h E n = = 2 n mv o ΔH = energies of bonds broken - energies of
Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Learning Objective
 Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry 11.1 Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Discuss the atomic trends Metals are located on the left side of the periodic
Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry 11.1 Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Discuss the atomic trends Metals are located on the left side of the periodic
Inorganic Chemistry A. Cl and 37 Cl are and
 S e l f - s t u d y e x e r c i s e s 1 Inorganic Chemistry A Self-study exercises Chapters 1 and 2 1. Calculate the value of A r for naturally occurring chlorine if the distribution of isotopes is 75.77%
S e l f - s t u d y e x e r c i s e s 1 Inorganic Chemistry A Self-study exercises Chapters 1 and 2 1. Calculate the value of A r for naturally occurring chlorine if the distribution of isotopes is 75.77%
like carbon, has fewer than an octet. It is simply less likely but still imperative to draw.
 Andrew Rosen Chapter 1: The Basics - Bonding and Molecular Structure 1.1 - We Are Stardust - Organic chemistry is simply the study of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives, which
Andrew Rosen Chapter 1: The Basics - Bonding and Molecular Structure 1.1 - We Are Stardust - Organic chemistry is simply the study of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives, which
Chapter 1 Basic Concepts: Atoms
 Chapter 1 Basic Concepts: Atoms CHEM 511 chapter 1 page 1 of 12 What is inorganic chemistry? The periodic table is made of elements, which are made of...? Particle Symbol Mass in amu Charge 1.0073 +1e
Chapter 1 Basic Concepts: Atoms CHEM 511 chapter 1 page 1 of 12 What is inorganic chemistry? The periodic table is made of elements, which are made of...? Particle Symbol Mass in amu Charge 1.0073 +1e
The Quantum Mechanical Atom
 The Quantum Mechanical Atom CHAPTER 8 Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter, 6 th edition By Jesperson, Brady, & Hyslop CHAPTER 8: Quantum Mechanical Atom Learning Objectives q Light as Waves, Wavelength
The Quantum Mechanical Atom CHAPTER 8 Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter, 6 th edition By Jesperson, Brady, & Hyslop CHAPTER 8: Quantum Mechanical Atom Learning Objectives q Light as Waves, Wavelength
Development of atomic theory
 Development of atomic theory The chapter presents the fundamentals needed to explain and atomic & molecular structures in qualitative or semiquantitative terms. Li B B C N O F Ne Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni
Development of atomic theory The chapter presents the fundamentals needed to explain and atomic & molecular structures in qualitative or semiquantitative terms. Li B B C N O F Ne Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni
CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING
 CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING Core electrons are found close to the nucleus, whereas valence electrons are found in the most distant s and p energy subshells. The valence electrons are responsible for holding
CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING Core electrons are found close to the nucleus, whereas valence electrons are found in the most distant s and p energy subshells. The valence electrons are responsible for holding
Chapter 1 Atomic Structure
 Chapter 1 Atomic Structure CHEM 511 Chapter 1 page 1 of 15 What is inorganic chemistry? The periodic table is made of elements, which are made of...? Define: atomic number (Z): Define: mass number (A):
Chapter 1 Atomic Structure CHEM 511 Chapter 1 page 1 of 15 What is inorganic chemistry? The periodic table is made of elements, which are made of...? Define: atomic number (Z): Define: mass number (A):
QUANTUM MECHANICS AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
 6 QUANTUM MECHANICS AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 6.1 Quantum Picture of the Chemical Bond 6.2 Exact Molecular Orbital for the Simplest Molecule: H + 2 6.3 Molecular Orbital Theory and the Linear Combination
6 QUANTUM MECHANICS AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 6.1 Quantum Picture of the Chemical Bond 6.2 Exact Molecular Orbital for the Simplest Molecule: H + 2 6.3 Molecular Orbital Theory and the Linear Combination
Valence Bond Theory - Description
 Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 2 - Valence Bond Theory and Hybridization 1. Understand and be able to describe the Valence Bond Theory description of covalent bond formation. 2. Understand and
Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 2 - Valence Bond Theory and Hybridization 1. Understand and be able to describe the Valence Bond Theory description of covalent bond formation. 2. Understand and
Chapter 9. Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Check Your Solution A comparison with the figures in Figure 4.31 on page 234 of the student textbook confirms the results.
 Predicting the Shape of a Molecule (Student textbook page 236) 11. What molecular shape is represented by each of the following VSEPR notations? a. AX 3 b. AX 5 E You need to assign a molecular shape that
Predicting the Shape of a Molecule (Student textbook page 236) 11. What molecular shape is represented by each of the following VSEPR notations? a. AX 3 b. AX 5 E You need to assign a molecular shape that
QUANTUM MECHANICS AND ATOMIC STRUCTURE
 5 CHAPTER QUANTUM MECHANICS AND ATOMIC STRUCTURE 5.1 The Hydrogen Atom 5.2 Shell Model for Many-Electron Atoms 5.3 Aufbau Principle and Electron Configurations 5.4 Shells and the Periodic Table: Photoelectron
5 CHAPTER QUANTUM MECHANICS AND ATOMIC STRUCTURE 5.1 The Hydrogen Atom 5.2 Shell Model for Many-Electron Atoms 5.3 Aufbau Principle and Electron Configurations 5.4 Shells and the Periodic Table: Photoelectron
Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure
 CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
Structure and Bonding of Organic Molecules
 Chem 220 Notes Page 1 Structure and Bonding of Organic Molecules I. Types of Chemical Bonds A. Why do atoms forms bonds? Atoms want to have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas atom (noble
Chem 220 Notes Page 1 Structure and Bonding of Organic Molecules I. Types of Chemical Bonds A. Why do atoms forms bonds? Atoms want to have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas atom (noble
Schrodinger equation
 CH1. Atomic Structure orbitals periodicity 1 Schrodinger equation - (h 2 /2p 2 m e2 ) [d 2 Y/dx 2 +d 2 Y/dy 2 +d 2 Y/dz 2 ] + V Y = E Y h = constant m e = electron mass V = potential E gives quantized
CH1. Atomic Structure orbitals periodicity 1 Schrodinger equation - (h 2 /2p 2 m e2 ) [d 2 Y/dx 2 +d 2 Y/dy 2 +d 2 Y/dz 2 ] + V Y = E Y h = constant m e = electron mass V = potential E gives quantized
Chapter 9. and Bonding Theories
 Chemistry, The Central Science, 11th edition Theodore L. Brown, H. Eugene LeMay, Jr., and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The
Chemistry, The Central Science, 11th edition Theodore L. Brown, H. Eugene LeMay, Jr., and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The
Advanced Theories of Atomic Structure: Atomic Orbitals
 Advanced Theories of Atomic Structure: Atomic Orbitals What are the more advanced theories of atomic structure? Richard Feynman, 1918 1988. Winner of the 1965 Nobel Prize in Physics. The modern scientific
Advanced Theories of Atomic Structure: Atomic Orbitals What are the more advanced theories of atomic structure? Richard Feynman, 1918 1988. Winner of the 1965 Nobel Prize in Physics. The modern scientific
CHEMISTRY - ZUMDAHL 2E CH.4 - MOLECULAR STRUCTURE AND ORBITALS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTRONIC GEOMETRY When drawing a compound you have to take into account two different systems of geometrical shape. The simpler system known as electronic geometry or shape
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTRONIC GEOMETRY When drawing a compound you have to take into account two different systems of geometrical shape. The simpler system known as electronic geometry or shape
Chapter 9. and Bonding Theories. Molecular Shapes. What Determines the Shape of a Molecule? 3/8/2013
 Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown, H. Eugene LeMay, Jr., and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College St. Peters, MO 2006, Prentice-Hall,
Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown, H. Eugene LeMay, Jr., and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College St. Peters, MO 2006, Prentice-Hall,
Chem 1075 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Lecture Outline. Chemical Bond Concept
 Chem 1075 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Lecture Outline Slide 2 Chemical Bond Concept Recall that an atom has and electrons. Core electrons are found to the nucleus. Valence electrons are found in the s
Chem 1075 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Lecture Outline Slide 2 Chemical Bond Concept Recall that an atom has and electrons. Core electrons are found to the nucleus. Valence electrons are found in the s
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Geometries -Bond angles: angles made by the lines joining the nuclei of the atoms in a molecule -Bond angles determine overall shape of
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Geometries -Bond angles: angles made by the lines joining the nuclei of the atoms in a molecule -Bond angles determine overall shape of
Unit One Parts 3 & 4: molecular bonding
 Unit ne Parts 3 & 4: molecular bonding hanging the order we approach this material... gjr- - 1 Locating electrons and drawing Lewis structures Assigning formal charges Describe bonds in terms of orbital
Unit ne Parts 3 & 4: molecular bonding hanging the order we approach this material... gjr- - 1 Locating electrons and drawing Lewis structures Assigning formal charges Describe bonds in terms of orbital
Be H. Delocalized Bonding. Localized Bonding. σ 2. σ 1. Two (sp-1s) Be-H σ bonds. The two σ bonding MO s in BeH 2. MO diagram for BeH 2
 The Delocalized Approach to Bonding: The localized models for bonding we have examined (Lewis and VBT) assume that all electrons are restricted to specific bonds between atoms or in lone pairs. In contrast,
The Delocalized Approach to Bonding: The localized models for bonding we have examined (Lewis and VBT) assume that all electrons are restricted to specific bonds between atoms or in lone pairs. In contrast,
At the end of this lesson, students should be able to :
 At the end of this lesson, students should be able to : (a) Explain Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory (VSEPR) (b) Draw the basic molecular shapes: linear, planar, tetrahedral, and octahedral.
At the end of this lesson, students should be able to : (a) Explain Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory (VSEPR) (b) Draw the basic molecular shapes: linear, planar, tetrahedral, and octahedral.
MOLECULAR MODELS OBJECTIVES
 MOLECULAR MODELS OBJECTIVES 1. To learn to draw Lewis structures for common compounds 2. To identify electron pairs as bonding pairs or lone pairs 3. To use electron pair repulsion theory to predict electronic
MOLECULAR MODELS OBJECTIVES 1. To learn to draw Lewis structures for common compounds 2. To identify electron pairs as bonding pairs or lone pairs 3. To use electron pair repulsion theory to predict electronic
Chapter 10: Modern Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table. How does atomic structure relate to the periodic table? 10.1 Electromagnetic Radiation
 Chapter 10: Modern Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table How does atomic structure relate to the periodic table? 10.1 Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic (EM) radiation is a form of energy that exhibits
Chapter 10: Modern Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table How does atomic structure relate to the periodic table? 10.1 Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic (EM) radiation is a form of energy that exhibits
Shapes of Molecules. Lewis structures are useful but don t allow prediction of the shape of a molecule.
 Shapes of Molecules Lewis structures are useful but don t allow prediction of the shape of a molecule. H O H H O H Can use a simple theory based on electron repulsion to predict structure (for non-transition
Shapes of Molecules Lewis structures are useful but don t allow prediction of the shape of a molecule. H O H H O H Can use a simple theory based on electron repulsion to predict structure (for non-transition
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory The Valence -Shell Electron -Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Model predicts the shapes of the molecules and ions by assuming that the valence shell electron pairs
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory The Valence -Shell Electron -Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Model predicts the shapes of the molecules and ions by assuming that the valence shell electron pairs
Chapter 4 Symmetry and Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 4 Symmetry and Chemical Bonding 4.1 Orbital Symmetries and Overlap 4.2 Valence Bond Theory and Hybrid Orbitals 4.3 Localized and Delocalized Molecular Orbitals 4.4 MX n Molecules with Pi-Bonding
Chapter 4 Symmetry and Chemical Bonding 4.1 Orbital Symmetries and Overlap 4.2 Valence Bond Theory and Hybrid Orbitals 4.3 Localized and Delocalized Molecular Orbitals 4.4 MX n Molecules with Pi-Bonding
Ch 13: Covalent Bonding
 Ch 13: Covalent Bonding Section 13: Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion 1. Recall the rules for drawing Lewis dot structures 2. Remember the special situations: - Resonance structures - ormal charges
Ch 13: Covalent Bonding Section 13: Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion 1. Recall the rules for drawing Lewis dot structures 2. Remember the special situations: - Resonance structures - ormal charges
Chemical Bonding. Chemical Bonding 20/03/2015. The atomic radius increases from right to left. The atomic radius increases from top to bottom
 Chemical Bonding Atomic Radius: This distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron. Chemical Bonding Chemistry 11 Two factors must be taken into consideration in explaining this periodic trend: Increasing
Chemical Bonding Atomic Radius: This distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron. Chemical Bonding Chemistry 11 Two factors must be taken into consideration in explaining this periodic trend: Increasing
Fill in the chart below to determine the valence electrons of elements 3-10
 Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
Loudon Ch. 1 Review: Chemical Structure & Bonds Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 2/8/2018
 Organic chemistry focuses most heavily on the top three rows of the periodic table, plus a few elements from lower rows: H (1) He (2) Li (3) Be (4) B (5) C (6) N (7) O (8) F (9) Ne (10) Na (11) Mg (12)
Organic chemistry focuses most heavily on the top three rows of the periodic table, plus a few elements from lower rows: H (1) He (2) Li (3) Be (4) B (5) C (6) N (7) O (8) F (9) Ne (10) Na (11) Mg (12)
Part 1. Reading: Gray: (4-1), (4-2), and (4-4) OGN: (16.2)
 Part 1 Reading: Gray: (4-1), (4-2), and (4-4) OGN: (16.2) The story so far: MO-LCAO works great for diatomic molecules! But... What about other numbers of atoms? Will MO-LCAO work for polyatomic molecules?
Part 1 Reading: Gray: (4-1), (4-2), and (4-4) OGN: (16.2) The story so far: MO-LCAO works great for diatomic molecules! But... What about other numbers of atoms? Will MO-LCAO work for polyatomic molecules?
Example: Write the Lewis structure of XeF 4. Example: Write the Lewis structure of I 3-. Example: Select the favored resonance structure of the PO 4
 Expanded valence shells (extended octets) more than 8e - around a central atom Extended octets are formed only by atoms with vacant d-orbitals in the valence shell (p-elements from the third or later periods)
Expanded valence shells (extended octets) more than 8e - around a central atom Extended octets are formed only by atoms with vacant d-orbitals in the valence shell (p-elements from the third or later periods)
Name: Period: Date: What Is VSEPR? Now explore the Compare Two Structures link. Try changing the display to explore different combinations.
 Name: Period: Date: What Is VSEPR? Exploring The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model. Go to the Purdue University website to explore VSEPR theory. http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/vsepr/structur2.html
Name: Period: Date: What Is VSEPR? Exploring The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model. Go to the Purdue University website to explore VSEPR theory. http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/vsepr/structur2.html
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories. Molecular Shapes. Molecular Shapes. Chapter 9 Part 2 November 16 th, 2004
 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 Part 2 November 16 th, 2004 8 Molecular Shapes When considering the geometry about the central atom, we consider all electrons (lone pairs and bonding
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 Part 2 November 16 th, 2004 8 Molecular Shapes When considering the geometry about the central atom, we consider all electrons (lone pairs and bonding
CHAPTER TEN MOLECULAR GEOMETRY MOLECULAR GEOMETRY V S E P R CHEMICAL BONDING II: MOLECULAR GEOMETRY AND HYBRIDIZATION OF ATOMIC ORBITALS
 CHAPTER TEN CHEMICAL BONDING II: AND HYBRIDIZATION O ATOMIC ORBITALS V S E P R VSEPR Theory In VSEPR theory, multiple bonds behave like a single electron pair Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR)
CHAPTER TEN CHEMICAL BONDING II: AND HYBRIDIZATION O ATOMIC ORBITALS V S E P R VSEPR Theory In VSEPR theory, multiple bonds behave like a single electron pair Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR)
Chapter 8: Periodic Properties of the Elements
 C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 8 P a g e 1 Chapter 8: Periodic Properties of the Elements Homework: Read Chapter 8. Work out sample/practice exercises Check for the MasteringChemistry.com assignment
C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 8 P a g e 1 Chapter 8: Periodic Properties of the Elements Homework: Read Chapter 8. Work out sample/practice exercises Check for the MasteringChemistry.com assignment
Quantum Numbers. principal quantum number: n. angular momentum quantum number: l (azimuthal) magnetic quantum number: m l
 Quantum Numbers Quantum Numbers principal quantum number: n angular momentum quantum number: l (azimuthal) magnetic quantum number: m l Principal quantum number: n related to size and energy of orbital
Quantum Numbers Quantum Numbers principal quantum number: n angular momentum quantum number: l (azimuthal) magnetic quantum number: m l Principal quantum number: n related to size and energy of orbital
Lecture B6 Molecular Orbital Theory. Sometimes it's good to be alone.
 Lecture B6 Molecular Orbital Theory Sometimes it's good to be alone. Covalent Bond Theories 1. VSEPR (valence shell electron pair repulsion model). A set of empirical rules for predicting a molecular geometry
Lecture B6 Molecular Orbital Theory Sometimes it's good to be alone. Covalent Bond Theories 1. VSEPR (valence shell electron pair repulsion model). A set of empirical rules for predicting a molecular geometry
Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, Valence Bond Theory, and Molecular Orbital Theory
 10.1 Artificial Sweeteners: Fooled by Molecular Shape 425 10.2 VSEPR Theory: The Five Basic Shapes 426 10.3 VSEPR Theory: The Effect of Lone Pairs 430 10.4 VSEPR Theory: Predicting Molecular Geometries
10.1 Artificial Sweeteners: Fooled by Molecular Shape 425 10.2 VSEPR Theory: The Five Basic Shapes 426 10.3 VSEPR Theory: The Effect of Lone Pairs 430 10.4 VSEPR Theory: Predicting Molecular Geometries
Survey of Elements. 1s - very small atom All noble gases have very high first I.E. s which is in line with their chemical inertness
 Survey of Elements 354 Hydrogen 1s 1 Naturally, loss of one e - dominates 1s Helium 1s 2 - closed shell 1s - very small atom All noble gases have very high first I.E. s which is in line with their chemical
Survey of Elements 354 Hydrogen 1s 1 Naturally, loss of one e - dominates 1s Helium 1s 2 - closed shell 1s - very small atom All noble gases have very high first I.E. s which is in line with their chemical
Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms.
 Chapter 9 CH 180 Major Concepts: Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms. Sublevels (s, p, d, & f) of separate atoms may overlap and result in hybrid orbitals
Chapter 9 CH 180 Major Concepts: Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms. Sublevels (s, p, d, & f) of separate atoms may overlap and result in hybrid orbitals
Please pass in only this completed answer sheet on the day of the test. LATE SUBMISSIONS WILL NOT BE ACCEPTED
 CHM-201 General Chemistry and Laboratory I Unit #4 Take Home Test Due December 13, 2018 Please pass in only this completed answer sheet on the day of the test. LATE SUBMISSIONS WILL NOT BE ACCEPTED CHM-201
CHM-201 General Chemistry and Laboratory I Unit #4 Take Home Test Due December 13, 2018 Please pass in only this completed answer sheet on the day of the test. LATE SUBMISSIONS WILL NOT BE ACCEPTED CHM-201
Bonding in Molecules Covalent Bonding
 Bonding in Molecules Covalent Bonding The term covalent implies sharing of electrons between atoms. Valence electrons and valence shell orbitals - nly valence electrons are used for bonding: ns, np, nd
Bonding in Molecules Covalent Bonding The term covalent implies sharing of electrons between atoms. Valence electrons and valence shell orbitals - nly valence electrons are used for bonding: ns, np, nd
Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds
 Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds Introduction Organic Chemistry The chemistry of the compounds of carbon The human body is largely composed of organic compounds Organic chemistry plays a central role
Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds Introduction Organic Chemistry The chemistry of the compounds of carbon The human body is largely composed of organic compounds Organic chemistry plays a central role
The symmetry properties & relative energies of atomic orbitals determine how they react to form molecular orbitals. These molecular orbitals are then
 1 The symmetry properties & relative energies of atomic orbitals determine how they react to form molecular orbitals. These molecular orbitals are then filled with the available electrons according to
1 The symmetry properties & relative energies of atomic orbitals determine how they react to form molecular orbitals. These molecular orbitals are then filled with the available electrons according to
Chapter 4 Lecture Outline. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 4 Lecture Outline 1 Copyright McGraw-ill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 4.1 Introduction to Covalent Bonding Covalent bonds result from the sharing of electrons between
Chapter 4 Lecture Outline 1 Copyright McGraw-ill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 4.1 Introduction to Covalent Bonding Covalent bonds result from the sharing of electrons between
Ionic and Covalent Bonding
 1. Define the following terms: a) valence electrons Ionic and Covalent Bonding the electrons in the highest occupied energy level always electrons in the s and p orbitals maximum of 8 valence electrons
1. Define the following terms: a) valence electrons Ionic and Covalent Bonding the electrons in the highest occupied energy level always electrons in the s and p orbitals maximum of 8 valence electrons
Valence Shell Electron Pair repulsion
 Molecular Geometry Valence Shell Electron Pair repulsion The valence shell electron pair repulsion model (VSEPR model) assumes that electron pairs repel one another. (VSEPR) model gives helps determine
Molecular Geometry Valence Shell Electron Pair repulsion The valence shell electron pair repulsion model (VSEPR model) assumes that electron pairs repel one another. (VSEPR) model gives helps determine
Chemistry 1B Fall 2013
 Chemistry 1B Fall 2013 lectures 5-6 Chapter 12 pp. 557-569 th 7 *(569-571) 7th 4 2012 Nobel in QUANTUM physics 5 many-electron atoms and Schrödinger Equation (ppn557-558) Although the Schrödinger equation
Chemistry 1B Fall 2013 lectures 5-6 Chapter 12 pp. 557-569 th 7 *(569-571) 7th 4 2012 Nobel in QUANTUM physics 5 many-electron atoms and Schrödinger Equation (ppn557-558) Although the Schrödinger equation
Chapter 13: Phenomena
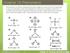 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
CHEMISTRY - MCMURRY 7E CH.7 - COVALENT BONDING AND ELECTRON DOT STRUCTURES
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTRONIC GEOMETRY When drawing a compound you have to take into account two different systems of geometrical shape. The simpler system known as electronic geometry or shape
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTRONIC GEOMETRY When drawing a compound you have to take into account two different systems of geometrical shape. The simpler system known as electronic geometry or shape
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin
 Lecture INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin Chemical Bonding by Christopher G. Hamaker Illinois State University Chemical Bond Concept Recall that
Lecture INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin Chemical Bonding by Christopher G. Hamaker Illinois State University Chemical Bond Concept Recall that
For more info visit Chemical bond is the attractive force which holds various constituents together in a molecule.
 Chemical bond:- Chemical bond is the attractive force which holds various constituents together in a molecule. There are three types of chemical bonds: Ionic Bond, Covalent Bond, Coordinate Bond. Octet
Chemical bond:- Chemical bond is the attractive force which holds various constituents together in a molecule. There are three types of chemical bonds: Ionic Bond, Covalent Bond, Coordinate Bond. Octet
Practice Final # Jim and Tim s Excellent Adventure s in Final Exam Preparation. Practice Final
 Jim and Tim s Excellent Adventure s in Final Exam Preparation Practice Final 1 2013 1. What type of orbital is designated by the quantum numbers n = 3, l = 1, and m l = 0? A. 4p B. 1f C. 3s D. 3p E. 3d
Jim and Tim s Excellent Adventure s in Final Exam Preparation Practice Final 1 2013 1. What type of orbital is designated by the quantum numbers n = 3, l = 1, and m l = 0? A. 4p B. 1f C. 3s D. 3p E. 3d
Chemistry- Unit 3. Section II - Chapter 7 ( , 7.11) Quantum Mechanics
 Chemistry- Unit 3 Section II - Chapter 7 (7.6-7.8, 7.11) Quantum Mechanics Atomic Review What subatomic particles do you get to play with? Protons Neutrons Electrons NO! It would change the element Don
Chemistry- Unit 3 Section II - Chapter 7 (7.6-7.8, 7.11) Quantum Mechanics Atomic Review What subatomic particles do you get to play with? Protons Neutrons Electrons NO! It would change the element Don
Contour Plots Electron assignments and Configurations Screening by inner and common electrons Effective Nuclear Charge Slater s Rules
 Lecture 4 362 January 23, 2019 Contour Plots Electron assignments and Configurations Screening by inner and common electrons Effective Nuclear Charge Slater s Rules How to handle atoms larger than H? Effective
Lecture 4 362 January 23, 2019 Contour Plots Electron assignments and Configurations Screening by inner and common electrons Effective Nuclear Charge Slater s Rules How to handle atoms larger than H? Effective
