Single transverse mode control of VCSEL by photonic crystal and trench patterning
|
|
|
- Michael McDaniel
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Available online at Photonics and Nanostructures Fundamentals and Applications 8 (2010) modulation bandwidth, 2D arrays capability, and low cost yet high-yield manufacturing ability (on wafer test and similar microelectronics device processing). Single transverse mode operation of VCSEL is significant for efficient coupling into the central low modal dispersion region of multimode fiber [5] or for coupling into single mode fiber which has a smaller core diameter. Typical commercial multimode VCSEL nowadays used mm oxide aperture technique for index- and current-confinement scheme [6,7]. To achieve single transverse mode operation, the oxide aperture of VCSEL must be less than 4 mm [8]. This stringent condition leads to low power output due to small aperture, high optical losses due to scattering, and introduce high resistance which reduces the high speed capability. Recently, various methods are reported for achieving single transverse mode VCSEL by introduwww.elsevier.com/locate/photonics Single transverse mode control of VCSEL by photonic crystal and trench patterning Mohd Sharizal Alias a, *, Sahbudin Shaari b, Paul O. Leisher c, Kent D. Choquette d a Microelectronics & Nanotechnology Program, Telekom Malaysia Research & Development (TMR&D), Lingkaran Teknokrat Timur, Cyberjaya, Selangor, Malaysia b Institute of Microengineering & Nanoelectronics (IMEN), National University of Malaysia (UKM), Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia c nlight Corporation, 5408 NE 88th St., Bldg. E, Vancouver, WA 98665, USA d Electrical & Computer Engineering Department, University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign (UIUC), Urbana 61801, IL, USA Received 8 December 2009; received in revised form 27 January 2010; accepted 27 January 2010 Available online 4 February 2010 Abstract Single transverse mode control is achieved for multimode GaAs-based VCSEL by utilizing photonic crystal design and etched trench structure. Theoretical analysis is initially performed for photonic crystal design with various lattice constants and air holes diameter. The fabricated photonic crystal VCSEL with etched trench structure exhibits single mode output power of 0.7 mw, threshold current of 3.5 ma, slope efficiency of 0.10 W/A, and continuous single mode output spectrum throughout a wide operating current range. Comparison of typical oxide VCSEL, trench oxide VCSEL, and photonic crystal oxide VCSEL employing trench structure is presented. By combining photonic crystal and trench structure, single transverse mode operation of photonic crystal VCSEL can be much more strictly controlled. # 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. Keywords: VCSEL; Photonic crystal; Semiconductor laser; GaAs 1. Introduction Since the invention of Vertical-Cavity Surface- Emitting (VCSEL) in late 1970s [1], it has dominated the light source market for data communication such as Gigabit Ethernet and Fiber Channel. VCSEL are becoming attractive low cost and high performance light source for long wavelength optical communication, optical interconnect, automotive network, optical mouse, gas spectroscopy, and high definition display [2 4]. These promising developments are due to VCSEL advantages of low operating current and power consumption, high fiber coupling efficiency, high * Corresponding author. address: sharizal@tmrnd.com.my (M.S. Alias) /$ see front matter # 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. doi: /j.photonics
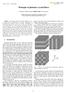
2 M.S. Alias et al. / Photonics and Nanostructures Fundamentals and Applications 8 (2010) cing losses to the higher order modes such as proton implanted structure [9], surface-relief etching [10,11], hybrid oxide-implant VCSEL [12], holey structure [13,14], and photonic crystal air holes [15 18]. In this paper, we report on single transverse mode photonic crystal VCSEL (PhC VCSEL) utilizing trench patterning and fan-pad metallization. VCSEL with trench structure exhibits higher device efficiency and highly confined multimode spectra in comparison to square air post mesa in typical oxide VCSEL [19]. This is due to narrower mode confinement provided for such structure compared with a given square air post mesa VCSEL. Furthermore, the usage of fan-pad metallization can increase high speed operation by reducing current resistance. By combining these advantages of device geometry (trench structure) with photonic crystal (PhC) air holes etched onto the VCSEL top Distributed Bragg Reflector (DBR) mirror, significant control of single transverse mode PhC VCSEL is realized. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive reported work on theoretical analysis and experimental development of this kind of PhC VCSEL (with etched trench). Most of previous reported PhC VCSEL is based on air post mesa structure. 2. Photonic crystal design and device fabrication 2.1. Photonic crystal design Single mode operation in PhC VCSEL can be realized similar to PhC optical fiber concept [20] by creating 2D arrays of air holes onto the top DBR mirror. The PhC structure creates a step refractive index profile across the VCSEL device. In addition, it introduces optical losses to high order modes, allowing only single fundamental mode condition [17]. Detail design of the studied PhC design is shown in Fig. 1, with design parameters consideration of triangular lattice constant, a, and air hole diameter, b. The transverse index around a single defect point can be controlled by the air hole diameter to lattice constant ratio (b/a). We fixed the b/a ratio at 0.5 by varying a and b dimensions; and assuming the VCSEL circular diameter is 43 mm, oxide aperture is 9 mm, average top DBR refractive index of , and oxide layer refractive index of The theoretical analysis is performed using Plane Wave Expansion (PWE) method [21] and Finite Difference Frequency Domain (FDFD) method [22] VCSEL device fabrication The 850 nm oxide VCSEL epiwafer consists of three GaAs quantum wells and four Al 0.3 Ga 0.7 As barriers forming the active region which is sandwiched between 34.5 periods of bottom n-type and 25 periods of top p- type DBR mirrors. The DBR mirrors composed of alternating high- and low-refractive index layers of Al 0.15 Ga 0.85 As/Al 0.9 Ga 0.1 As multilayer. A high aluminum concentration layer of Al 0.98 Ga 0.02 As is introduced in the p-dbr mirror adjacent to the active region for selective oxidation purpose. Three types of oxide VCSEL devices are fabricated which is typical air post mesa VCSEL (sample T1), VCSEL with trench patterning (sample T2), and PhC VCSEL with trench patterning (sample T3). The cross-section for respective device is schematically illustrated in Fig. 2. Fabrication processes for all three 850 nm oxide VCSEL devices (samples T1 T3) are similar with the Fig. 1. PhC design for various b/a ratios of 0.5 mm and 9 mm oxide aperture.
3 40 M.S. Alias et al. / Photonics and Nanostructures Fundamentals and Applications 8 (2010) Fig. 2. The oxide VCSEL devices with (a) air post mesa, (b) trench structure, and (c) PhC and trench structure. only difference in the photomask design used and additional photolithography steps required for VCSEL samples T2 and T3. Detail fabrication is only described for PhC VCSEL with trench patterning since fabrication steps for VCSEL samples of T1 and T2 have been reported previously [19]. The device fabrication started with the metallization of the bottom n- and the top ring p-ohmic contacts by evaporating AuGe/Ni/Au (40/20/ 150 nm) and Ti/Au (15/150 nm), respectively. The bottom n-contact is straightforward deposition; however the top p-contact required photolithography patterning and lift-off process. In order to isolate adjacent devices, the surface of the VCSEL epiwafer is proton implanted. First, SiO 2 mask is deposited by the process of plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD). Then, all VCSEL apertures are protected by thick photoresist pillars (formed on the top ring contact) prior to implantation. After proton implantation, the photoresist pillars are removed and thick SiO 2 mask is re-deposited by PECVD. PhC holes and trench patterning are then transferred (single step photolithography) to SiO 2 mask followed by reactive ion etching (RIE) mask etched. The leftover photoresist is removed and thicker photoresist pillars are formed on the top ring contacts to protect the PhC holes mask patterns prior to trench etching by inductively coupled plasma RIE (ICP- RIE). After trench is partly etched, the thick photoresist pillars are removed. The epiwafer is then exposed to wet oxidation process for forming the oxide aperture. Next, PhC air holes are etched onto the VCSEL aperture by second ICP-RIE process (trench will completely etched at the same time) followed by SiO 2 mask removal by RIE. The PhC VCSEL with trench patterning device fabrication is completed by defining the fan-pad metallization (formed by photolithography, evaporation of Ti/Au of 25/1000 nm and metal lift-off). Fig. 3 shows the scanning electron microscope (SEM) images for all three types of 850 nm oxide VCSEL fabricated devices (samples T1 T3). Each sample is tilted at different angles to effectively demonstrate the air post square mesa structure, the circular mesa and etched trench, and PhC air holes for the respective devices. Fig. 4 displays optical microscope images (top view) for all incorporated PhC designs for b/a ratio of 0.5 fabricated along the PhC VCSEL with trench patterning (prior to fan-pad metallization). The PhC air holes are fabricated exactly as in the computed PhC designs for b/a ratio of 0.5 (refer to Fig. 1). This will ensure that the fabricated PhC VCSEL operates in single mode as expected from the theoretical study. The VCSEL device measurement is performed on wafer probing system at room temperature under continuous wave operation. The light versus current Fig. 3. SEM images for the fabricated (a) air post mesa VCSEL, (b) trench VCSEL, and (c) PhC VCSEL with trench.
4 M.S. Alias et al. / Photonics and Nanostructures Fundamentals and Applications 8 (2010) Fig. 4. Top view optical images for all fabricated PhC designs of b/a = 0.5 for the PhC VCSEL. (L I) and current versus voltage (I V) characteristics are measured with the precise variation of input current (using semiconductor parameter analyzer). The light output is detected by silicon photodetector which is also connected to the semiconductor parameter analyzer. The output spectrum of VCSEL is obtained by coupling the lasing beam into an optical fiber connected to an optical spectrum analyzer. 3. Results and discussion 3.1. Photonic crystal design Fig. 5 shows the out of plane photonic band diagram (PBG) computed using PWE method for all PhC triangular periodic lattice designs of b/a ratio = 0.5 with single point defect and the assumption of infinite holes etched. This is a simplified approximation to describe the optical behavior of the VCSEL top DBR mirror that has been etched with PhC air holes. The area under each linear curve (lower right half) is defined by a line which refers to the lowest order out of plane mode for each PhC air holes design. The slope of this line represents an effective index of the structure formed by the PhC air holes which induced index guiding effect. Higher effective index is obtained as the lattice constant and holes diameter increased. By purposely introduced point defect at centre of the index guiding region (unetched air hole); higher index waveguide confinement is realized. Fig. 6 exhibits the fundamental mode profiles for each of the PhC design for b/a ratio of 0.5 computed using FDFD method. Defect modes can appear inside the index guiding region with proper PhC air holes design. In case of PhC VCSEL, the effective index computed from the PBG diagram corresponds to the refractive index (assumed as n clad ) for area of the top DBR region etched with PhC structure. The refractive index Fig. 5. PBG diagram of PhC structure with out of plane propagation for all PhC designs of b/a = 0.5.
5 42 M.S. Alias et al. / Photonics and Nanostructures Fundamentals and Applications 8 (2010) Fig. 6. Fundamental transverse mode profile for all PhC designs of b/a = 0.5. (assumed as n core ) for the unetched region (no point defect) is obtained by averaging the high- and lowrefractive index multilayer used for the DBR materials. This approach is similar to step index cylindrical waveguide in optical fiber. Due to this similarity, the normalized frequency or V eff parameter [23] as defined in Eq. (1) can be used to determine the number of confined modes (single mode expected if V < 2.405), where D is the defect diameter (2a b), l is the operating wavelength, n clad and n core as described above. V ef f ¼ pd qffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi n l 2 core n2 clad (1) However in PhC fiber, the air holes are etched thoroughly (infinite). In PhC VCSEL, the top DBR mirror is only 50 80% etched with air holes due to the fabrication limitations and to avoid high optical losses inside the VCSEL. Due to this consideration (finite etch depth), Eq. (1) is modified by introducing etch depth factor, g, as calculated in Eq. (2) [24]. V ef f ¼ pd qffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi n l 2 core ½ð1 gþn core þ gn clad Š 2 (2) In order to compute the V eff parameter for all PhC designs of b/a ratio = 0.5, D is calculated from the given a and b dimension in Fig. 1, l is at 850 nm, n core is , n clad is calculated from PBG diagram for every PhC design, and g is assumed as 0.1 (19 DBR pairs etched) [24]. In order to simplify the calculation, the effect of trench structure and optical loss is not taken into account. The trench structure is considered to minimize the number of supported high order modes but not a significant factor in realizing single mode operation (as shown in the experimental result later). Thus the effect of trench structure is neglected and the geometry of the device is assumed like air post mesa in the calculation. The optical loss factor is recently taken into consideration for the V eff parameter calculation [25]. The calculation is simplified in this paper since the purpose is only to provide general analysis of our PhC air holes design. Fig. 7 shows the calculated V eff parameter for all PhC designs of b/a ratio = 0.5. All PhC designs exhibit single mode behavior (V eff < 2.405). By incorporating these PhC designs into the multimode VCSEL, single fundamental mode operation can be achieved Photonic crystal VCSEL experiment Fig. 8 shows the L I characteristic for fabricated 850 nm oxide VCSEL devices of typical air post mesa (sample T1), VCSEL with trench (sample T2), and PhC VCSEL with trench (sample T3). All VCSEL samples have 9 mm diameter of oxide aperture. VCSEL sample T3 is composed of PhC design of b/a ratio = 0.5 with a = 4.0 mm and b = 2.0 mm. VCSEL of samples T1 and T2 exhibits threshold current (I th ) of 0.8 ma, slope efficiency of W/A, and maximum output power (P max ) of 3.5 mw and 3.0 mw, respectively. VCSEL sample T3 achieved I th of 3.5 ma, slope efficiency of 0.10 W/A, and P max of 0.7 mw. The high I th and low slope efficiency in PhC VCSEL is because higher optical threshold gain is required to compensate high order mode loss [17]. In addition, the etched PhC holes increased scattering loss [26] which also results in
6 M.S. Alias et al. / Photonics and Nanostructures Fundamentals and Applications 8 (2010) Fig. 7. V eff parameter for all PhC designs of b/a = 0.5. higher threshold current required to ensure lasing. P max for sample T3 is low compared to others since only fundamental mode is allowed for lasing and modal volume decreased due to the existence of PhC air holes structure. However, the power composed of genuine single mode operation. The output power can be improved by optimizing device parameters such as oxide aperture, etch depth and PhC design. The I V characteristic as depicted in Fig. 9 shows slightly higher series resistance (slope of I V curve) is Fig. 8. L I characteristic for all fabricated VCSEL (typical, trench, and PhC with trench). obtained for both VCSEL samples T2 and T3 compared to sample T1. This is due to the introduction of resistance to the current flow by the PhC air holes and the etched trench structure. In addition, the etching of PhC air holes partially removed the conductive material of p-doped AlGaAs in the top DBR mirror. Fig. 10 exhibits output spectrum for all fabricated VCSEL samples above threshold. Although both samples T1 and T2 are multimode VCSEL, better mode confinement is achieved by VCSEL with trench due to circular device geometry and stringent mode control (less high order modes supported). Almost 70% of the high order modes in the multimode VCSEL are eliminated. By combining the trench structure with etched PhC air holes in VCSEL, highly defined single mode condition is easily realized (as shown in the spectrum). Single mode condition is defined if more than 30 db difference in side mode suppression ratio (SMSR) is achieved from threshold to rollover lasing operation. The PhC VCSEL with trench demonstrated nearly 35 db of SMSR. It is also noticed that the lasing wavelength is blue-shifted when trench and PhC air Fig. 9. I V characteristic for all fabricated VCSEL (typical, trench, and PhC with trench). Fig. 10. Output spectrum for all fabricated VCSEL (typical, trench, and PhC with trench).
7 44 M.S. Alias et al. / Photonics and Nanostructures Fundamentals and Applications 8 (2010) Fig. 11. Output spectrum for (a) typical VCSEL and (b) PhC VCSEL; at various injected currents. holes are incorporated into the VCSEL. This effect could be contributed by the alteration of VCSEL cavity resonance due to the change of refractive index of the top DBR when trench and PhC air holes are introduced. From the experiment measurement, only 50% of the total PhC VCSEL fabricated achieved single mode operation (SMSR > 35 db) for devices with a = mm (b = mm). PhC VCSEL with smallest PhC air holes design (a = 2.0 mm and b = 1.0 mm) did not lase at all. This might be due to the incomplete fabrication of PhC air holes where etching difficulty exists for such small holes diameter. Other PhC VCSEL Fig. 12. Near-field comparison for (a) trench VCSEL and (b) PhC VCSEL with trench.
8 M.S. Alias et al. / Photonics and Nanostructures Fundamentals and Applications 8 (2010) with larger PhC air holes designs (a = mm and b = mm) exhibits multimode spectrum. The large PhC air holes designs do not induce highly confined optical confinement (narrow step index profile), thus allowing the existence of high order modes in PhC VCSEL. Fig. 11 demonstrates the output spectrum for both VCSEL samples T1 and T3 at various injected currents. PhC VCSEL with trench achieved single mode condition (SMSR > 30 db) and narrow linewidth throughout the operating current range (above threshold current). No distinguish side modes appear at even high operating current. The typical oxide VCSEL shows multimode spectrum from low to high injection current levels. High number of transverse modes existed within the spectral wavelength range ( nm). The spectrum also exhibits broadening linewidth as the injected current increased. The near-field optical images comparison for both VCSEL samples T2 and T3 are shown in Fig. 12. The PhC VCSEL with trench structure demonstrates superior laser beam confinement at the centre of the PhC structure (no defect point) throughout the operating current range. Higher order modes are discriminated and only fundamental mode is allowed for lasing. As for the trench VCSEL without PhC structure, the laser beam is distributed across the entire VCSEL aperture. Due to this, the trench VCSEL exhibits higher output power compared to PhC VCSEL. 4. Conclusion In this paper, we reported on significant approach to generate single transverse mode operation from a multimode GaAs-based oxide VCSEL by the means of PhC air holes and circular trench structure. The PhC design (in terms of lattice constant and holes diameter) is comprehensively studied using PWE and FDFD methods in order to induce single mode condition. The PhC design is then transferred to VCSEL device for experimental assessment. The fabricated PhC oxide VCSEL with etched trench successfully exhibits single mode output power of 0.7 mw, threshold current of 3.5 ma, slope efficiency of 0.10 W/A, and continuous single mode output spectrum at wide operating current range. Control oxide VCSEL devices in the form of typical air post mesa VCSEL and trench VCSEL (no PhC air holes) are also fabricated for comparison purpose. The PhC VCSEL with etched trench demonstrates an efficient combination approach to generate single transverse mode operation for VCSEL. This method is applicable to longer wavelength VCSEL (GaAs- or InP-based) since the PhC effect in obtaining single mode operation in VCSEL is independent to the laser operating wavelength [27]. Acknowledgements This work is sponsored by Telekom Malaysia Berhad through project number R , R and RDTC/ We would like to acknowledge the Photonics Device Research Group of University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign for their scientific collaboration. Also, we are grateful for the technical support by RSoft Design Group Inc. and Lumerical Solutions Inc. References [1] H. Soda, K. Iga, C. Kitahara, Y. Sumatsu, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 18 (1979) [2] K. Iga, IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 6 (2000) [3] F. Koyama, J. Lightwave Technol. 24 (2006) [4] C.W. Wilmsen, H. Temkin, L.A. Coldren, Vertical-cavity Surface-emitting Lasers: Design, Fabrication, Characterization, and Applications, Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, UK, [5] P. Pepeljugoski, D. Kuchta, Y. Kwark, P. Pleunis, G. Kuyt, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 14 (2002) 717. [6] K.D. Choquette, K.L. Lear, R.P. Schneider, K.M. Geib, J.J. Figiel, R. Hull, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 7 (1995) [7] B. Weigl, M. Grabherr, C. Jung, R. Jager, G. Reiner, R. Michalzik, D. Sowada, K.J. Ebeling, IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 3 (1997) 409. [8] C. Jung, R. Jager, M. Grabherr, P. Schnitzer, R. Michalzik, B. Weigl, S. Muller, K.J. Ebeling, Electron. Lett. 33 (1997) [9] R.A. Morgan, G.D. Guth, M.W. Focht, M.T. Asom, K. Kojima, L.E. Rogers, S.E. Callis, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 4 (1993) 374. [10] H. Martinsson, J.A. Vukusic, M. Grabherr, R. Michalzik, R. Jager, K.J. Ebeling, A. Larsson, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 11 (1999) [11] A. Haglund, J.S. Gustavsson, J. Vukusic, P. Modh, A. Larsson, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 16 (2004) 368. [12] E.W. Young, K.D. Choquette, S.L. Chuang, K.M. Geib, A.J. Fischer, A.A. Allerman, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 13 (2001) 927. [13] A. Furukawa, S. Sasaki, M. Hoshi, A. Matsuzono, K. Moritoh, T. Baba, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85 (2004) [14] H.P.D. Yang, I.-C. Hsu, F.-I. Lai, H.C. Kuo, J.Y. Chi, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 45 (2006) L871. [15] D.S. Song, S.H. Kim, H.G. Park, C.K. Kim, Y.H. Lee, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80 (2002) [16] N. Yokouchi, A.J. Danner, K.D. Choquette, IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 9 (2003) [17] J.H. Baek, D.S. Song, I.K. Hwang, K.H. Lee, Y.H. Lee, Y. Ju, T. Kondo, T. Miyamoto, F. Koyama, Opt. Express 12 (2004) 859. [18] A.J. Danner, J.J. Raftery Jr., P.O. Leisher, K.D. Choquette, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88 (2006) [19] M.S. Alias, S. Shaari, P.K. Choudhury, S.M. Mitani, Laser Phys. 19 (2009) 1. [20] T.A. Birks, J.C. Knight, P.S. Russell, Opt. Lett. 22 (1997) 961.
9 46 M.S. Alias et al. / Photonics and Nanostructures Fundamentals and Applications 8 (2010) [21] A. Ferrando, E. Silvestre, J.J. Miret, P. Andres, M.V. Andres, Opt. Lett. 24 (1999) 276. [22] Z. Zhu, T.G. Brown, Opt. Express 10 (2002) 853. [23] G.P. Agrawal, Fiber-optic Communication Systems, Wiley, New York, USA, [24] N. Yokouchi, A.J. Danner, K.D. Choquette, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82 (2003) [25] D.F. Siriani, P.O. Leisher, K.D. Choquette, IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 45 (2009) 762. [26] P.O. Leisher, A.J. Danner, K.D. Choquette, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 18 (2006) [27] A.M. Kasten, M.P. Tan, J.D. Sulkin, P.O. Leisher, K.D. Choquette, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 20 (2008) 2010.
Highly confined and continuous single-mode operation of self-align photonic crystal oxide VCSEL
 Appl Phys B (2010) 100: 453 459 DOI 10.1007/s00340-010-4062-2 Highly confined and continuous single-mode operation of self-align photonic crystal oxide VCSEL M.S. Alias S. Shaari P.O. Leisher K.D. Choquette
Appl Phys B (2010) 100: 453 459 DOI 10.1007/s00340-010-4062-2 Highly confined and continuous single-mode operation of self-align photonic crystal oxide VCSEL M.S. Alias S. Shaari P.O. Leisher K.D. Choquette
Vectorial analysis of dielectric photonic crystal VCSEL
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 17, 2017 Vectorial analysis of dielectric photonic crystal VCSEL Chung, Il-Sug; Mørk, Jesper Published in: 11th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 17, 2017 Vectorial analysis of dielectric photonic crystal VCSEL Chung, Il-Sug; Mørk, Jesper Published in: 11th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks,
Coupled-Cavity Bottom-Emitting VCSELs a New Laser Design for Increased Single-Transverse-Mode Output Power
 Coupled-Cavity Bottom-Emitting VCSELs a New Laser Design for Increased Single-Transverse-Mode Output Power Morten Stilling Nano-Science Center, University of Copenhagen Universitetsparken 5D, DK-2100 Copenhagen,
Coupled-Cavity Bottom-Emitting VCSELs a New Laser Design for Increased Single-Transverse-Mode Output Power Morten Stilling Nano-Science Center, University of Copenhagen Universitetsparken 5D, DK-2100 Copenhagen,
IMPROVING THE EFFICIENCY AND THRESHOLD CURRENT OF PHOTONIC CRYSTAL VERTICAL-CAVITY SURFACE-EMITTING LASERS MENG PEUN TAN THESIS
 IMPROVING THE EFFICIENCY AND THRESHOLD CURRENT OF PHOTONIC CRYSTAL VERTICAL-CAVITY SURFACE-EMITTING LASERS BY MENG PEUN TAN THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of
IMPROVING THE EFFICIENCY AND THRESHOLD CURRENT OF PHOTONIC CRYSTAL VERTICAL-CAVITY SURFACE-EMITTING LASERS BY MENG PEUN TAN THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of
VERTICAL-CAVITY surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs) Beam Properties of Visible Proton-Implanted Photonic Crystal VCSELs
 1648 IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 17, NO. 6, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2011 Beam Properties of Visible Proton-Implanted Photonic Crystal VCSELs Ansas M. Kasten, Student Member,
1648 IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 17, NO. 6, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2011 Beam Properties of Visible Proton-Implanted Photonic Crystal VCSELs Ansas M. Kasten, Student Member,
Thermal crosstalk in densely packed high power VCSEL arrays
 26 Annual report 1998, Dept. of Optoelectronics, University of Ulm Thermal crosstalk in densely packed high power VCSEL arrays M. Grabherr, M. Miller, H.J. Unold We present detailed investigations on the
26 Annual report 1998, Dept. of Optoelectronics, University of Ulm Thermal crosstalk in densely packed high power VCSEL arrays M. Grabherr, M. Miller, H.J. Unold We present detailed investigations on the
Semiconductor Disk Laser on Microchannel Cooler
 Semiconductor Disk Laser on Microchannel Cooler Eckart Gerster An optically pumped semiconductor disk laser with a double-band Bragg reflector mirror is presented. This mirror not only reflects the laser
Semiconductor Disk Laser on Microchannel Cooler Eckart Gerster An optically pumped semiconductor disk laser with a double-band Bragg reflector mirror is presented. This mirror not only reflects the laser
Optical Feedback in Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers
 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 37, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2001 1643 Optical Feedback in Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers A. Hsu, Student Member, IEEE, J.-F. P. Seurin, S. L. Chuang, Fellow,
IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 37, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2001 1643 Optical Feedback in Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers A. Hsu, Student Member, IEEE, J.-F. P. Seurin, S. L. Chuang, Fellow,
Blue-green Emitting Semiconductor Disk Lasers with Intra-Cavity Frequency Doubling
 Blue-green Emitting Semiconductor Disk Lasers with Intra-Cavity Frequency Doubling Eckart Schiehlen and Michael Riedl Diode-pumped semiconductor disk lasers, also referred to as VECSEL (Vertical External
Blue-green Emitting Semiconductor Disk Lasers with Intra-Cavity Frequency Doubling Eckart Schiehlen and Michael Riedl Diode-pumped semiconductor disk lasers, also referred to as VECSEL (Vertical External
Study on Semiconductor Lasers of Circular Structures Fabricated by EB Lithography
 Study on Semiconductor Lasers of Circular Structures Fabricated by EB Lithography Ashim Kumar Saha (D3) Supervisor: Prof. Toshiaki Suhara Doctoral Thesis Defense Quantum Engineering Design Course Graduate
Study on Semiconductor Lasers of Circular Structures Fabricated by EB Lithography Ashim Kumar Saha (D3) Supervisor: Prof. Toshiaki Suhara Doctoral Thesis Defense Quantum Engineering Design Course Graduate
Quantum Dot Lasers. Jose Mayen ECE 355
 Quantum Dot Lasers Jose Mayen ECE 355 Overview of Presentation Quantum Dots Operation Principles Fabrication of Q-dot lasers Advantages over other lasers Characteristics of Q-dot laser Types of Q-dot lasers
Quantum Dot Lasers Jose Mayen ECE 355 Overview of Presentation Quantum Dots Operation Principles Fabrication of Q-dot lasers Advantages over other lasers Characteristics of Q-dot laser Types of Q-dot lasers
Optimum Access Waveguide Width for 1xN Multimode. Interference Couplers on Silicon Nanomembrane
 Optimum Access Waveguide Width for 1xN Multimode Interference Couplers on Silicon Nanomembrane Amir Hosseini 1,*, Harish Subbaraman 2, David Kwong 1, Yang Zhang 1, and Ray T. Chen 1,* 1 Microelectronic
Optimum Access Waveguide Width for 1xN Multimode Interference Couplers on Silicon Nanomembrane Amir Hosseini 1,*, Harish Subbaraman 2, David Kwong 1, Yang Zhang 1, and Ray T. Chen 1,* 1 Microelectronic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12036 We provide in the following additional experimental data and details on our demonstration of an electrically pumped exciton-polariton laser by supplementing optical and electrical
doi:10.1038/nature12036 We provide in the following additional experimental data and details on our demonstration of an electrically pumped exciton-polariton laser by supplementing optical and electrical
An impact of the electrical pumping scheme on some VCSEL performance characteristics
 Optica Applicata, Vol. XXXIX, No. 4, 2009 An impact of the electrical pumping scheme on some VCSEL performance characteristics SEWERYN MORAWIEC, PIOTR KOWALCZEWSKI, ROBERT P. SARZAŁA * Laboratory of Computer
Optica Applicata, Vol. XXXIX, No. 4, 2009 An impact of the electrical pumping scheme on some VCSEL performance characteristics SEWERYN MORAWIEC, PIOTR KOWALCZEWSKI, ROBERT P. SARZAŁA * Laboratory of Computer
Design and simulation of a high power single mode 1550 nm InGaAsP VCSELs
 Design and simulation of a high power single mode 1550 nm InGaAsP VCSELs Rahim Faez 1,AzamMarjani 2, and Saeid Marjani 3a) 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran,
Design and simulation of a high power single mode 1550 nm InGaAsP VCSELs Rahim Faez 1,AzamMarjani 2, and Saeid Marjani 3a) 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran,
Two-Element Phased Array of Anti-Guided Vertical-Cavity Lasers
 Two-Element Phased Array of Anti-Guided Vertical-Cavity Lasers Darwin K. Serkland, K. D. Choquette, G. R. Hadley, K. M. Geib, and A. A. Allerman e - Sandia National Laboratories, P.O. Box 5800, MS 0603,
Two-Element Phased Array of Anti-Guided Vertical-Cavity Lasers Darwin K. Serkland, K. D. Choquette, G. R. Hadley, K. M. Geib, and A. A. Allerman e - Sandia National Laboratories, P.O. Box 5800, MS 0603,
Figure 1: Graphene release, transfer and stacking processes. The graphene stacking began with CVD
 Supplementary figure 1 Graphene Growth and Transfer Graphene PMMA FeCl 3 DI water Copper foil CVD growth Back side etch PMMA coating Copper etch in 0.25M FeCl 3 DI water rinse 1 st transfer DI water 1:10
Supplementary figure 1 Graphene Growth and Transfer Graphene PMMA FeCl 3 DI water Copper foil CVD growth Back side etch PMMA coating Copper etch in 0.25M FeCl 3 DI water rinse 1 st transfer DI water 1:10
Stimulated Emission Devices: LASERS
 Stimulated Emission Devices: LASERS 1. Stimulated Emission and Photon Amplification E 2 E 2 E 2 hυ hυ hυ In hυ Out hυ E 1 E 1 E 1 (a) Absorption (b) Spontaneous emission (c) Stimulated emission The Principle
Stimulated Emission Devices: LASERS 1. Stimulated Emission and Photon Amplification E 2 E 2 E 2 hυ hυ hυ In hυ Out hυ E 1 E 1 E 1 (a) Absorption (b) Spontaneous emission (c) Stimulated emission The Principle
(b) Spontaneous emission. Absorption, spontaneous (random photon) emission and stimulated emission.
 Lecture 10 Stimulated Emission Devices Lasers Stimulated emission and light amplification Einstein coefficients Optical fiber amplifiers Gas laser and He-Ne Laser The output spectrum of a gas laser Laser
Lecture 10 Stimulated Emission Devices Lasers Stimulated emission and light amplification Einstein coefficients Optical fiber amplifiers Gas laser and He-Ne Laser The output spectrum of a gas laser Laser
Segmented 1.55um Laser with 400% Differential Quantum Efficiency J. Getty, E. Skogen, L. Coldren, University of California, Santa Barbara, CA.
 Segmented 1.55um Laser with 400% Differential Quantum Efficiency J. Getty, E. Skogen, L. Coldren, University of California, Santa Barbara, CA. Abstract: By electrically segmenting, and series-connecting
Segmented 1.55um Laser with 400% Differential Quantum Efficiency J. Getty, E. Skogen, L. Coldren, University of California, Santa Barbara, CA. Abstract: By electrically segmenting, and series-connecting
Characteristics of a Designed 1550 nm AlGaInAs/InP MQW VCSEL
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MULTIDISCIPLINARY SCIENCES AND ENGINEERING, VOL. 4, NO. 1, JANUARY 13 Characteristics of a Designed 155 nm AlGaInAs/InP MQW VCSEL Raja Rashidul Hasan and Rinku Basak Abstract The
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MULTIDISCIPLINARY SCIENCES AND ENGINEERING, VOL. 4, NO. 1, JANUARY 13 Characteristics of a Designed 155 nm AlGaInAs/InP MQW VCSEL Raja Rashidul Hasan and Rinku Basak Abstract The
FINITE-DIFFERENCE FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS OF NOVEL PHOTONIC
 FINITE-DIFFERENCE FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS OF NOVEL PHOTONIC WAVEGUIDES Chin-ping Yu (1) and Hung-chun Chang (2) (1) Graduate Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering, National Taiwan University, Taipei,
FINITE-DIFFERENCE FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS OF NOVEL PHOTONIC WAVEGUIDES Chin-ping Yu (1) and Hung-chun Chang (2) (1) Graduate Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering, National Taiwan University, Taipei,
1300nm-Range GaInNAs-Based Quantum Well Lasers with High Characteristic Temperature
 3nm-Range GaInNAs-Based Quantum Well Lasers with High Characteristic Temperature by Hitoshi Shimizu *, Kouji Kumada *, Seiji Uchiyama * and Akihiko Kasukawa * Long wavelength- SQW lasers that include a
3nm-Range GaInNAs-Based Quantum Well Lasers with High Characteristic Temperature by Hitoshi Shimizu *, Kouji Kumada *, Seiji Uchiyama * and Akihiko Kasukawa * Long wavelength- SQW lasers that include a
OPTI510R: Photonics. Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona Meinel building R.626
 OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements HW#3 is assigned due Feb. 20 st Mid-term exam Feb 27, 2PM
OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements HW#3 is assigned due Feb. 20 st Mid-term exam Feb 27, 2PM
MEASUREMENT of gain from amplified spontaneous
 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 40, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2004 123 Fourier Series Expansion Method for Gain Measurement From Amplified Spontaneous Emission Spectra of Fabry Pérot Semiconductor Lasers
IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 40, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2004 123 Fourier Series Expansion Method for Gain Measurement From Amplified Spontaneous Emission Spectra of Fabry Pérot Semiconductor Lasers
VERTICAL-CAVITY surface-emitting lasers (VCSEL s)
 IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 3, NO. 2, APRIL 1997 353 Effects of Optical Feedback on Static and Dynamic Characteristics of Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers Joanne
IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 3, NO. 2, APRIL 1997 353 Effects of Optical Feedback on Static and Dynamic Characteristics of Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers Joanne
A Novel Self-aligned and Maskless Process for Formation of Highly Uniform Arrays of Nanoholes and Nanopillars
 Nanoscale Res Lett (2008) 3: 127 DOI 10.1007/s11671-008-9124-6 NANO EXPRESS A Novel Self-aligned and Maskless Process for Formation of Highly Uniform Arrays of Nanoholes and Nanopillars Wei Wu Æ Dibyendu
Nanoscale Res Lett (2008) 3: 127 DOI 10.1007/s11671-008-9124-6 NANO EXPRESS A Novel Self-aligned and Maskless Process for Formation of Highly Uniform Arrays of Nanoholes and Nanopillars Wei Wu Æ Dibyendu
Analysis and Modeling of Microstructured Fiber Using The Analytical Method Based on The Empirical Equation
 Analysis and Modeling of Microstructured Fiber Using The Analytical Method Based on The Empirical Equation DEBBAL Mohammed 1, CHIKH-BLED Mohammed 2 1 University of Tlemcen, Algeria, Department of electrical
Analysis and Modeling of Microstructured Fiber Using The Analytical Method Based on The Empirical Equation DEBBAL Mohammed 1, CHIKH-BLED Mohammed 2 1 University of Tlemcen, Algeria, Department of electrical
Ge Quantum Well Modulators on Si. D. A. B. Miller, R. K. Schaevitz, J. E. Roth, Shen Ren, and Onur Fidaner
 10.1149/1.2986844 The Electrochemical Society Ge Quantum Well Modulators on Si D. A. B. Miller, R. K. Schaevitz, J. E. Roth, Shen Ren, and Onur Fidaner Ginzton Laboratory, 450 Via Palou, Stanford CA 94305-4088,
10.1149/1.2986844 The Electrochemical Society Ge Quantum Well Modulators on Si D. A. B. Miller, R. K. Schaevitz, J. E. Roth, Shen Ren, and Onur Fidaner Ginzton Laboratory, 450 Via Palou, Stanford CA 94305-4088,
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University. ECE 5330: Semiconductor Optoelectronics. Fall Due on Nov 20, 2014 by 5:00 PM
 School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University ECE 533: Semiconductor Optoelectronics Fall 14 Homewor 8 Due on Nov, 14 by 5: PM This is a long -wee homewor (start early). It will count
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University ECE 533: Semiconductor Optoelectronics Fall 14 Homewor 8 Due on Nov, 14 by 5: PM This is a long -wee homewor (start early). It will count
Resonator Fabrication for Cavity Enhanced, Tunable Si/Ge Quantum Cascade Detectors
 Resonator Fabrication for Cavity Enhanced, Tunable Si/Ge Quantum Cascade Detectors M. Grydlik 1, P. Rauter 1, T. Fromherz 1, G. Bauer 1, L. Diehl 2, C. Falub 2, G. Dehlinger 2, H. Sigg 2, D. Grützmacher
Resonator Fabrication for Cavity Enhanced, Tunable Si/Ge Quantum Cascade Detectors M. Grydlik 1, P. Rauter 1, T. Fromherz 1, G. Bauer 1, L. Diehl 2, C. Falub 2, G. Dehlinger 2, H. Sigg 2, D. Grützmacher
Ultra-Slow Light Propagation in Room Temperature Solids. Robert W. Boyd
 Ultra-Slow Light Propagation in Room Temperature Solids Robert W. Boyd The Institute of Optics and Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Rochester, Rochester, NY USA http://www.optics.rochester.edu
Ultra-Slow Light Propagation in Room Temperature Solids Robert W. Boyd The Institute of Optics and Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Rochester, Rochester, NY USA http://www.optics.rochester.edu
Emission Spectra of the typical DH laser
 Emission Spectra of the typical DH laser Emission spectra of a perfect laser above the threshold, the laser may approach near-perfect monochromatic emission with a spectra width in the order of 1 to 10
Emission Spectra of the typical DH laser Emission spectra of a perfect laser above the threshold, the laser may approach near-perfect monochromatic emission with a spectra width in the order of 1 to 10
Fabrication and optical measurements of silicon on insulator photonic nanostructures
 Microelectronic Engineering 61 62 (2002) 529 536 www.elsevier.com/ locate/ mee Fabrication and optical measurements of silicon on insulator photonic nanostructures * M. Agio, L.C. Andreani, E. Silberstein,
Microelectronic Engineering 61 62 (2002) 529 536 www.elsevier.com/ locate/ mee Fabrication and optical measurements of silicon on insulator photonic nanostructures * M. Agio, L.C. Andreani, E. Silberstein,
Implant isolation of AlGaAs multilayer DBR
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 218 (2004) 381 385 www.elsevier.com/locate/nimb Implant isolation of AlGaAs multilayer DBR A.V.P. Coelho a, *, H. Boudinov a, T. v. Lippen b, H.H.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 218 (2004) 381 385 www.elsevier.com/locate/nimb Implant isolation of AlGaAs multilayer DBR A.V.P. Coelho a, *, H. Boudinov a, T. v. Lippen b, H.H.
Continuous room-temperature operation of optically pumped InGaAs/InGaAsP microdisk lasers
 Continuous room-temperature operation of optically pumped InGaAs/InGaAsP microdisk lasers S. M. K. Thiyagarajan, A. F. J. Levi, C. K. Lin, I. Kim, P. D. Dapkus, and S. J. Pearton + Department of Electrical
Continuous room-temperature operation of optically pumped InGaAs/InGaAsP microdisk lasers S. M. K. Thiyagarajan, A. F. J. Levi, C. K. Lin, I. Kim, P. D. Dapkus, and S. J. Pearton + Department of Electrical
Diode Lasers and Photonic Integrated Circuits
 Diode Lasers and Photonic Integrated Circuits L. A. COLDREN S. W. CORZINE University of California Santa Barbara, California A WILEY-INTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. NEW YORK / CHICHESTER
Diode Lasers and Photonic Integrated Circuits L. A. COLDREN S. W. CORZINE University of California Santa Barbara, California A WILEY-INTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. NEW YORK / CHICHESTER
Oscillateur paramétrique optique en
 C. Ozanam 1, X. Lafosse 2, I. Favero 1, S. Ducci 1, G. Leo 1 1 Université Paris Diderot, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Laboratoire MPQ, CNRS-UMR 7162, Paris, France, 2 Laboratoire de Photonique et Nanostructures,
C. Ozanam 1, X. Lafosse 2, I. Favero 1, S. Ducci 1, G. Leo 1 1 Université Paris Diderot, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Laboratoire MPQ, CNRS-UMR 7162, Paris, France, 2 Laboratoire de Photonique et Nanostructures,
3-1-2 GaSb Quantum Cascade Laser
 3-1-2 GaSb Quantum Cascade Laser A terahertz quantum cascade laser (THz-QCL) using a resonant longitudinal optical (LO) phonon depopulation scheme was successfully demonstrated from a GaSb/AlSb material
3-1-2 GaSb Quantum Cascade Laser A terahertz quantum cascade laser (THz-QCL) using a resonant longitudinal optical (LO) phonon depopulation scheme was successfully demonstrated from a GaSb/AlSb material
Investigation on Mode Splitting and Degeneracy in the L3 Photonic Crystal Nanocavity via Unsymmetrical Displacement of Air-Holes
 The International Journal Of Engineering And Science (Ijes) Volume 2 Issue 2 Pages 146-150 2013 Issn: 2319 1813 Isbn: 2319 1805 Investigation on Mode Splitting and Degeneracy in the L3 Photonic Crystal
The International Journal Of Engineering And Science (Ijes) Volume 2 Issue 2 Pages 146-150 2013 Issn: 2319 1813 Isbn: 2319 1805 Investigation on Mode Splitting and Degeneracy in the L3 Photonic Crystal
Abnormal PL spectrum in InGaN MQW surface emitting cavity
 Abnormal PL spectrum in InGaN MQW surface emitting cavity J. T. Chu a, Y.-J. Cheng b, H. C. Kuo a, T. C. Lu a, and S. C. Wang a a Department of Photonics & Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering, National
Abnormal PL spectrum in InGaN MQW surface emitting cavity J. T. Chu a, Y.-J. Cheng b, H. C. Kuo a, T. C. Lu a, and S. C. Wang a a Department of Photonics & Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering, National
Fabrication of Efficient Blue Light-Emitting Diodes with InGaN/GaN Triangular Multiple Quantum Wells. Abstract
 Fabrication of Efficient Blue Light-Emitting Diodes with InGaN/GaN Triangular Multiple Quantum Wells R. J. Choi, H. W. Shim 2, E. K. Suh 2, H. J. Lee 2, and Y. B. Hahn,2, *. School of Chemical Engineering
Fabrication of Efficient Blue Light-Emitting Diodes with InGaN/GaN Triangular Multiple Quantum Wells R. J. Choi, H. W. Shim 2, E. K. Suh 2, H. J. Lee 2, and Y. B. Hahn,2, *. School of Chemical Engineering
Modelling and design of complete photonic band gaps in two-dimensional photonic crystals
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 70, No. 1 journal of January 2008 physics pp. 153 161 Modelling and design of complete photonic band gaps in two-dimensional photonic crystals YOGITA KALRA and
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 70, No. 1 journal of January 2008 physics pp. 153 161 Modelling and design of complete photonic band gaps in two-dimensional photonic crystals YOGITA KALRA and
Two-dimensional Bragg grating lasers defined by electron-beam lithography
 Two-dimensional Bragg grating lasers defined by electron-beam lithography Guy A. DeRose a Pasadena, California 91125 and Department of Applied Physics, California Institute of Technology, 1200 E. California
Two-dimensional Bragg grating lasers defined by electron-beam lithography Guy A. DeRose a Pasadena, California 91125 and Department of Applied Physics, California Institute of Technology, 1200 E. California
Cavity Solitons positioning and drift in presence of a phase gradient
 Cavity Solitons positioning and drift in presence of a phase gradient F. Pedaci, S. Barland, E. Caboche, P. Genevet, M. Giudici, J. Tredicce Institut non linéaire de Nice Acknowledge: FunFACS CEE project
Cavity Solitons positioning and drift in presence of a phase gradient F. Pedaci, S. Barland, E. Caboche, P. Genevet, M. Giudici, J. Tredicce Institut non linéaire de Nice Acknowledge: FunFACS CEE project
ECE 484 Semiconductor Lasers
 ECE 484 Semiconductor Lasers Dr. Lukas Chrostowski Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia January, 2013 Module Learning Objectives: Understand the importance of
ECE 484 Semiconductor Lasers Dr. Lukas Chrostowski Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia January, 2013 Module Learning Objectives: Understand the importance of
Polarization-Resolved Output Characteristics of InAlGaAs VCSELs under Anisotropic Strain
 Polarization-Resolved Output Characteristics of InAlGaAs VCSELs under Anisotropic Strain Andrea Kroner and Johannes Michael Ostermann We present a setup that enables direct examination of the correlation
Polarization-Resolved Output Characteristics of InAlGaAs VCSELs under Anisotropic Strain Andrea Kroner and Johannes Michael Ostermann We present a setup that enables direct examination of the correlation
Study on Quantum Dot Lasers and their advantages
 Study on Quantum Dot Lasers and their advantages Tae Woo Kim Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Illinois, Urbana Champaign Abstract Basic ideas for understanding a Quantum Dot Laser were
Study on Quantum Dot Lasers and their advantages Tae Woo Kim Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Illinois, Urbana Champaign Abstract Basic ideas for understanding a Quantum Dot Laser were
Step index planar waveguide
 N. Dubreuil S. Lebrun Exam without document Pocket calculator permitted Duration of the exam: 2 hours The exam takes the form of a multiple choice test. Annexes are given at the end of the text. **********************************************************************************
N. Dubreuil S. Lebrun Exam without document Pocket calculator permitted Duration of the exam: 2 hours The exam takes the form of a multiple choice test. Annexes are given at the end of the text. **********************************************************************************
Photonic Crystal Nanocavities for Efficient Light Confinement and Emission
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 42, No., February 2003, pp. 768 773 Photonic Crystal Nanocavities for Efficient Light Confinement and Emission Axel Scherer, T. Yoshie, M. Lončar, J. Vučković
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 42, No., February 2003, pp. 768 773 Photonic Crystal Nanocavities for Efficient Light Confinement and Emission Axel Scherer, T. Yoshie, M. Lončar, J. Vučković
Low threshold and room-temperature lasing of electrically pumped red-emitting InP/(Al Ga 0.80 ) In 0.49.
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Low threshold and room-temperature lasing of electrically pumped red-emitting InP/(Al 0.20 Ga 0.80 ) 0.51 In 0.49 P quantum dots To cite this article: Marcus Eichfelder
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Low threshold and room-temperature lasing of electrically pumped red-emitting InP/(Al 0.20 Ga 0.80 ) 0.51 In 0.49 P quantum dots To cite this article: Marcus Eichfelder
Title. Author(s)Nagasaki, Akira; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori. CitationOptics Express, 19(4): Issue Date Doc URL.
 Title Polarization characteristics of photonic crystal fib Author(s)Nagasaki, Akira; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Express, 19(4): 3799-3808 Issue Date 2011-02-14 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/45257
Title Polarization characteristics of photonic crystal fib Author(s)Nagasaki, Akira; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Express, 19(4): 3799-3808 Issue Date 2011-02-14 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/45257
Principle of photonic crystal fibers
 Principle of photonic crystal fibers Jan Sporik 1, Miloslav Filka 1, Vladimír Tejkal 1, Pavel Reichert 1 1 Fakulta elektrotechniky a komunikačních technologií VUT v Brně Email: {xspori1, filka, xtejka,
Principle of photonic crystal fibers Jan Sporik 1, Miloslav Filka 1, Vladimír Tejkal 1, Pavel Reichert 1 1 Fakulta elektrotechniky a komunikačních technologií VUT v Brně Email: {xspori1, filka, xtejka,
Demonstration of ultra-flattened dispersion in photonic crystal fibers
 Demonstration of ultra-flattened dispersion in photonic crystal fibers W.H. Reeves, J.C. Knight, and P.St.J. Russell Optoelectronics Group, School of Physics, University of Bath, Claverton Down, Bath,
Demonstration of ultra-flattened dispersion in photonic crystal fibers W.H. Reeves, J.C. Knight, and P.St.J. Russell Optoelectronics Group, School of Physics, University of Bath, Claverton Down, Bath,
Quantum cascade lasers with an integrated polarization mode converter
 Quantum cascade lasers with an integrated polarization mode converter D. Dhirhe, 1,* T. J. Slight, 2 B. M. Holmes, 1 D. C. Hutchings, 1 and C. N. Ironside 1 1 School of Engineering, University of Glasgow,
Quantum cascade lasers with an integrated polarization mode converter D. Dhirhe, 1,* T. J. Slight, 2 B. M. Holmes, 1 D. C. Hutchings, 1 and C. N. Ironside 1 1 School of Engineering, University of Glasgow,
Laser Basics. What happens when light (or photon) interact with a matter? Assume photon energy is compatible with energy transition levels.
 What happens when light (or photon) interact with a matter? Assume photon energy is compatible with energy transition levels. Electron energy levels in an hydrogen atom n=5 n=4 - + n=3 n=2 13.6 = [ev]
What happens when light (or photon) interact with a matter? Assume photon energy is compatible with energy transition levels. Electron energy levels in an hydrogen atom n=5 n=4 - + n=3 n=2 13.6 = [ev]
A COMPACT POLARIZATION BEAM SPLITTER BASED ON A MULTIMODE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL WAVEGUIDE WITH AN INTERNAL PHOTONIC CRYSTAL SECTION
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 103, 393 401, 2010 A COMPACT POLARIZATION BEAM SPLITTER BASED ON A MULTIMODE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL WAVEGUIDE WITH AN INTERNAL PHOTONIC CRYSTAL SECTION Y. C. Shi Centre
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 103, 393 401, 2010 A COMPACT POLARIZATION BEAM SPLITTER BASED ON A MULTIMODE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL WAVEGUIDE WITH AN INTERNAL PHOTONIC CRYSTAL SECTION Y. C. Shi Centre
Semiconductor Lasers II
 Semiconductor Lasers II Materials and Structures Edited by Eli Kapon Institute of Micro and Optoelectronics Department of Physics Swiss Federal Institute oftechnology, Lausanne OPTICS AND PHOTONICS ACADEMIC
Semiconductor Lasers II Materials and Structures Edited by Eli Kapon Institute of Micro and Optoelectronics Department of Physics Swiss Federal Institute oftechnology, Lausanne OPTICS AND PHOTONICS ACADEMIC
Room-temperature continuous-wave lasing from monolayer molybdenum ditelluride integrated with a silicon nanobeam cavity
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2017.128 Room-temperature continuous-wave lasing from monolayer molybdenum ditelluride integrated with a silicon nanobeam cavity Yongzhuo
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2017.128 Room-temperature continuous-wave lasing from monolayer molybdenum ditelluride integrated with a silicon nanobeam cavity Yongzhuo
Low-Threshold Lasing and Purcell Effect in Microdisk Lasers at Room Temperature
 1340 IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 9, NO. 5, SEPTEMBER/OCTOBER 2003 Low-Threshold Lasing and Purcell Effect in Microdisk Lasers at Room Temperature Toshihiko Baba, Member,
1340 IEEE JOURNAL OF SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 9, NO. 5, SEPTEMBER/OCTOBER 2003 Low-Threshold Lasing and Purcell Effect in Microdisk Lasers at Room Temperature Toshihiko Baba, Member,
Influence of Temperature on Steady-State Performance of VCSEL
 P P P Department International Journal of Scientific Engineering Applied Science (IJSEAS) - Volume-, Issue-4, June 05 Influence of Temperature on Steady-State Performance of VCSEL Ashraful ArefinP P, Nusrat
P P P Department International Journal of Scientific Engineering Applied Science (IJSEAS) - Volume-, Issue-4, June 05 Influence of Temperature on Steady-State Performance of VCSEL Ashraful ArefinP P, Nusrat
Reflectivity and photoluminescence studies in Bragg reflectors with absorbing layers
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING SEMICONDUCTOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Semicond. Sci. Technol. 16 (2001) 548 552 www.iop.org/journals/ss PII: S0268-1242(01)16119-5 Reflectivity and photoluminescence studies
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING SEMICONDUCTOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Semicond. Sci. Technol. 16 (2001) 548 552 www.iop.org/journals/ss PII: S0268-1242(01)16119-5 Reflectivity and photoluminescence studies
Dielectric Meta-Reflectarray for Broadband Linear Polarization Conversion and Optical Vortex Generation
 Supporting Information Dielectric Meta-Reflectarray for Broadband Linear Polarization Conversion and Optical Vortex Generation Yuanmu Yang, Wenyi Wang, Parikshit Moitra, Ivan I. Kravchenko, Dayrl P. Briggs,
Supporting Information Dielectric Meta-Reflectarray for Broadband Linear Polarization Conversion and Optical Vortex Generation Yuanmu Yang, Wenyi Wang, Parikshit Moitra, Ivan I. Kravchenko, Dayrl P. Briggs,
Design of a Multi-Mode Interference Crossing Structure for Three Periodic Dielectric Waveguides
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 75, 47 52, 2018 Design of a Multi-Mode Interference Crossing Structure for Three Periodic Dielectric Waveguides Haibin Chen 1, Zhongjiao He 2,andWeiWang
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 75, 47 52, 2018 Design of a Multi-Mode Interference Crossing Structure for Three Periodic Dielectric Waveguides Haibin Chen 1, Zhongjiao He 2,andWeiWang
Dmitriy Churin. Designing high power single frequency fiber lasers
 Dmitriy Churin Tutorial for: Designing high power single frequency fiber lasers Single frequency lasers with narrow linewidth have long coherence length and this is an essential property for many applications
Dmitriy Churin Tutorial for: Designing high power single frequency fiber lasers Single frequency lasers with narrow linewidth have long coherence length and this is an essential property for many applications
High Speed VCSELs With Separated Quantum Wells
 High Speed VCSELs With Separated Quantum Wells V. V. Lysak 1,2, I. M. Safonov 2, Y. M. Song 1, I. A. Sukhoivanov 1,3, Yong Tak Lee 1 1 Department of Information and Communications, Gwangju Institute of
High Speed VCSELs With Separated Quantum Wells V. V. Lysak 1,2, I. M. Safonov 2, Y. M. Song 1, I. A. Sukhoivanov 1,3, Yong Tak Lee 1 1 Department of Information and Communications, Gwangju Institute of
Appendix. Photonic crystal lasers: future integrated devices
 91 Appendix Photonic crystal lasers: future integrated devices 5.1 Introduction The technology of photonic crystals has produced a large variety of new devices. However, photonic crystals have not been
91 Appendix Photonic crystal lasers: future integrated devices 5.1 Introduction The technology of photonic crystals has produced a large variety of new devices. However, photonic crystals have not been
MODELING OF ABOVE-THRESHOLD SINGLE-MODE OPERATION OF EDGE- EMITTING DIODE LASERS
 MODELING OF ABOVE-THRESHOLD SINGLE-MODE OPERATION OF EDGE- EMITTING DIODE LASERS A. P. Napartovich, N. N. Elkin, A. G. Sukharev, V. N. Troshchieva, and D. V. Vysotsky Troitsk Institute for Innovation and
MODELING OF ABOVE-THRESHOLD SINGLE-MODE OPERATION OF EDGE- EMITTING DIODE LASERS A. P. Napartovich, N. N. Elkin, A. G. Sukharev, V. N. Troshchieva, and D. V. Vysotsky Troitsk Institute for Innovation and
Refractive Index Measurement by Gain- or Loss-Induced Resonance
 Refractive Index Measurement by Gain- or Loss-Induced Resonance 59 Refractive Index Measurement by Gain- or Loss-Induced Resonance Markus Miller Using a semiconductor optical resonator consisting of a
Refractive Index Measurement by Gain- or Loss-Induced Resonance 59 Refractive Index Measurement by Gain- or Loss-Induced Resonance Markus Miller Using a semiconductor optical resonator consisting of a
Distributed feedback semiconductor lasers
 Distributed feedback semiconductor lasers John Carroll, James Whiteaway & Dick Plumb The Institution of Electrical Engineers SPIE Optical Engineering Press 1 Preface Acknowledgments Principal abbreviations
Distributed feedback semiconductor lasers John Carroll, James Whiteaway & Dick Plumb The Institution of Electrical Engineers SPIE Optical Engineering Press 1 Preface Acknowledgments Principal abbreviations
Gold Nanoparticles Floating Gate MISFET for Non-Volatile Memory Applications
 Gold Nanoparticles Floating Gate MISFET for Non-Volatile Memory Applications D. Tsoukalas, S. Kolliopoulou, P. Dimitrakis, P. Normand Institute of Microelectronics, NCSR Demokritos, Athens, Greece S. Paul,
Gold Nanoparticles Floating Gate MISFET for Non-Volatile Memory Applications D. Tsoukalas, S. Kolliopoulou, P. Dimitrakis, P. Normand Institute of Microelectronics, NCSR Demokritos, Athens, Greece S. Paul,
IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 45, NO. 12, DECEMBER /$ IEEE
 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 45, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2009 1529 Mode Analysis for Equilateral-Triangle-Resonator Microlasers with Metal Confinement Layers Yue-De Yang, Yong-Zhen Huang, Senior
IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 45, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2009 1529 Mode Analysis for Equilateral-Triangle-Resonator Microlasers with Metal Confinement Layers Yue-De Yang, Yong-Zhen Huang, Senior
Polarization control and sensing with two-dimensional coupled photonic crystal microcavity arrays. Hatice Altug * and Jelena Vučković
 Polarization control and sensing with two-dimensional coupled photonic crystal microcavity arrays Hatice Altug * and Jelena Vučković Edward L. Ginzton Laboratory, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305-4088
Polarization control and sensing with two-dimensional coupled photonic crystal microcavity arrays Hatice Altug * and Jelena Vučković Edward L. Ginzton Laboratory, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305-4088
A normal-incident quantum well infrared photodetector enhanced by surface plasmon resonance
 Best Student Paper Award A normal-incident quantum well infrared photodetector enhanced by surface plasmon resonance Wei Wu a, Alireza Bonakdar, Ryan Gelfand, and Hooman Mohseni Bio-inspired Sensors and
Best Student Paper Award A normal-incident quantum well infrared photodetector enhanced by surface plasmon resonance Wei Wu a, Alireza Bonakdar, Ryan Gelfand, and Hooman Mohseni Bio-inspired Sensors and
Angular and polarization properties of a photonic crystal slab mirror
 Angular and polarization properties of a photonic crystal slab mirror Virginie Lousse 1,2, Wonjoo Suh 1, Onur Kilic 1, Sora Kim 1, Olav Solgaard 1, and Shanhui Fan 1 1 Department of Electrical Engineering,
Angular and polarization properties of a photonic crystal slab mirror Virginie Lousse 1,2, Wonjoo Suh 1, Onur Kilic 1, Sora Kim 1, Olav Solgaard 1, and Shanhui Fan 1 1 Department of Electrical Engineering,
GaInNAs: A new Material in the Race for Long Wavelength VCSELs. Outline
 GaInNAs: A new Material in the Race for Long Wavelength VCSELs J. S. Harris S. Spruytte, C. Coldren, M. Larson, M. Wistey, V. Gambin, W. Ha Stanford University Agilent Seminar, Palo Alto, CA 14 February
GaInNAs: A new Material in the Race for Long Wavelength VCSELs J. S. Harris S. Spruytte, C. Coldren, M. Larson, M. Wistey, V. Gambin, W. Ha Stanford University Agilent Seminar, Palo Alto, CA 14 February
Supplementary Information Our InGaN/GaN multiple quantum wells (MQWs) based one-dimensional (1D) grating structures
 Polarized white light from hybrid organic/iii-nitrides grating structures M. Athanasiou, R. M. Smith, S. Ghataora and T. Wang* Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, University of Sheffield,
Polarized white light from hybrid organic/iii-nitrides grating structures M. Athanasiou, R. M. Smith, S. Ghataora and T. Wang* Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, University of Sheffield,
Optical and Photonic Glasses. Lecture 30. Femtosecond Laser Irradiation and Acoustooptic. Professor Rui Almeida
 Optical and Photonic Glasses : Femtosecond Laser Irradiation and Acoustooptic Effects Professor Rui Almeida International Materials Institute For New Functionality in Glass Lehigh University Femto second
Optical and Photonic Glasses : Femtosecond Laser Irradiation and Acoustooptic Effects Professor Rui Almeida International Materials Institute For New Functionality in Glass Lehigh University Femto second
INSTITUTE BECKMAN. K. Hess, Y. Liu, F. Oyafuso, W.C. Ng and B.D. Klein. The Beckman Institute University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 BECKMAN INSTITUTE K. Hess, Y. Liu, F. Oyafuso, W.C. Ng and B.D. Klein. The Beckman Institute University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Photo by Don Hamerman Typical VCSEL Structure and Electronic Mesh
BECKMAN INSTITUTE K. Hess, Y. Liu, F. Oyafuso, W.C. Ng and B.D. Klein. The Beckman Institute University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Photo by Don Hamerman Typical VCSEL Structure and Electronic Mesh
Introduction to Semiconductor Integrated Optics
 Introduction to Semiconductor Integrated Optics Hans P. Zappe Artech House Boston London Contents acknowledgments reface itroduction Chapter 1 Basic Electromagnetics 1 1.1 General Relationships 1 1.1.1
Introduction to Semiconductor Integrated Optics Hans P. Zappe Artech House Boston London Contents acknowledgments reface itroduction Chapter 1 Basic Electromagnetics 1 1.1 General Relationships 1 1.1.1
NONLINEAR TRANSITIONS IN SINGLE, DOUBLE, AND TRIPLE δ-doped GaAs STRUCTURES
 NONLINEAR TRANSITIONS IN SINGLE, DOUBLE, AND TRIPLE δ-doped GaAs STRUCTURES E. OZTURK Cumhuriyet University, Faculty of Science, Physics Department, 58140 Sivas-Turkey E-mail: eozturk@cumhuriyet.edu.tr
NONLINEAR TRANSITIONS IN SINGLE, DOUBLE, AND TRIPLE δ-doped GaAs STRUCTURES E. OZTURK Cumhuriyet University, Faculty of Science, Physics Department, 58140 Sivas-Turkey E-mail: eozturk@cumhuriyet.edu.tr
MQW design parameter variation in a 1.5 μm wavelength InP-based LW-VCSEL
 MQW design parameter variation in a.5 μm wavelength InP-based LW-VCSEL K. Kumarajah, Menon, P. S., Ismail, M., Yeop, B. Y. & Shaari, S. Institute of Microengineering and Nanoelectronics, Department of
MQW design parameter variation in a.5 μm wavelength InP-based LW-VCSEL K. Kumarajah, Menon, P. S., Ismail, M., Yeop, B. Y. & Shaari, S. Institute of Microengineering and Nanoelectronics, Department of
Polarization Properties of Photonic Crystal Fibers Considering Thermal and External Stress Effects
 Polarization Properties of Photonic Crystal Fibers Considering Thermal and External Stress Effects Md. Afzal Hossain*, M. Shah Alam** * Department of Computer Science and Engineering Military Institute
Polarization Properties of Photonic Crystal Fibers Considering Thermal and External Stress Effects Md. Afzal Hossain*, M. Shah Alam** * Department of Computer Science and Engineering Military Institute
White light generation and amplification using a soliton pulse within a nano-waveguide
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 00 (009) 000 000 53 57 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia Frontier Research in Nanoscale Science and Technology White light generation and amplification
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 00 (009) 000 000 53 57 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia Frontier Research in Nanoscale Science and Technology White light generation and amplification
Semiconductor Lasers for Optical Communication
 Semiconductor Lasers for Optical Communication Claudio Coriasso Manager claudio.coriasso@avagotech.com Turin Technology Centre 10Gb/s DFB Laser MQW 1 Outline 1) Background and Motivation Communication
Semiconductor Lasers for Optical Communication Claudio Coriasso Manager claudio.coriasso@avagotech.com Turin Technology Centre 10Gb/s DFB Laser MQW 1 Outline 1) Background and Motivation Communication
nmos IC Design Report Module: EEE 112
 nmos IC Design Report Author: 1302509 Zhao Ruimin Module: EEE 112 Lecturer: Date: Dr.Zhao Ce Zhou June/5/2015 Abstract This lab intended to train the experimental skills of the layout designing of the
nmos IC Design Report Author: 1302509 Zhao Ruimin Module: EEE 112 Lecturer: Date: Dr.Zhao Ce Zhou June/5/2015 Abstract This lab intended to train the experimental skills of the layout designing of the
Optical sensor based on hybrid LPG/FBG in D-fiber for simultaneous refractive index and temperature measurement
 Optical sensor based on hybrid G/FBG in D-fiber for simultaneous refractive index and temperature measurement Xianfeng Chen*, Kaiming Zhou, Lin Zhang, Ian Bennion Photonics Research Group, Aston University,
Optical sensor based on hybrid G/FBG in D-fiber for simultaneous refractive index and temperature measurement Xianfeng Chen*, Kaiming Zhou, Lin Zhang, Ian Bennion Photonics Research Group, Aston University,
Size Scaling of Photonic Crystal Surface Emitting Lasers on Silicon Substrates
 Size Scaling of Photonic Crystal Surface Emitting Lasers on Silicon Substrates Volume 10, Number 3, June 2018 Open Access Shih-Chia Liu Deyin Zhao Xiaochen Ge Carl Reuterskiöld-Hedlund Mattias Hammar Shanhui
Size Scaling of Photonic Crystal Surface Emitting Lasers on Silicon Substrates Volume 10, Number 3, June 2018 Open Access Shih-Chia Liu Deyin Zhao Xiaochen Ge Carl Reuterskiöld-Hedlund Mattias Hammar Shanhui
Gain Apodization in Highly Doped, Distributed-Feedback (DFB) Fiber Lasers
 Gain Apodization in Highly Doped Distributed- Feedback (DFB) Fiber Lasers Introduction Fiber lasers have been the subect of much research over the past ten years. They can provide high reliability fiber
Gain Apodization in Highly Doped Distributed- Feedback (DFB) Fiber Lasers Introduction Fiber lasers have been the subect of much research over the past ten years. They can provide high reliability fiber
Nanosphere Lithography
 Nanosphere Lithography Derec Ciafre 1, Lingyun Miao 2, and Keita Oka 1 1 Institute of Optics / 2 ECE Dept. University of Rochester Abstract Nanosphere Lithography is quickly emerging as an efficient, low
Nanosphere Lithography Derec Ciafre 1, Lingyun Miao 2, and Keita Oka 1 1 Institute of Optics / 2 ECE Dept. University of Rochester Abstract Nanosphere Lithography is quickly emerging as an efficient, low
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 22, 39 52, 2010
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 22, 39 52, 2010 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF HIGH BIREFRINGENCE AND LOW CONFINEMENT LOSS PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER EMPLOYING ELLIPTICAL AIR HOLES IN FIBER CLADDING
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 22, 39 52, 2010 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF HIGH BIREFRINGENCE AND LOW CONFINEMENT LOSS PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER EMPLOYING ELLIPTICAL AIR HOLES IN FIBER CLADDING
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 33, 27 35, 2012
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 33, 27 35, 2012 TUNABLE WAVELENGTH DEMULTIPLEXER FOR DWDM APPLICATION USING 1-D PHOTONIC CRYSTAL A. Kumar 1, B. Suthar 2, *, V. Kumar 3, Kh. S. Singh
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 33, 27 35, 2012 TUNABLE WAVELENGTH DEMULTIPLEXER FOR DWDM APPLICATION USING 1-D PHOTONIC CRYSTAL A. Kumar 1, B. Suthar 2, *, V. Kumar 3, Kh. S. Singh
MICRODISK lasers supported by a pedestal to form strong
 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 26, NO. 11, JUNE 1, 2008 1411 Mode Coupling and Vertical Radiation Loss for Whispering-Gallery Modes in 3-D Microcavities Yong-Zhen Huang, Senior Member, IEEE, and
JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 26, NO. 11, JUNE 1, 2008 1411 Mode Coupling and Vertical Radiation Loss for Whispering-Gallery Modes in 3-D Microcavities Yong-Zhen Huang, Senior Member, IEEE, and
THEIR sophisticated structure make vertical-cavity surface-emitting
 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 43, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2007 1227 Spatiotemporal Turn-On Dynamics of Grating Relief VCSELs Christian Fuchs, Tobias Gensty, Pierluigi Debernardi, Gian Paolo Bava,
IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 43, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2007 1227 Spatiotemporal Turn-On Dynamics of Grating Relief VCSELs Christian Fuchs, Tobias Gensty, Pierluigi Debernardi, Gian Paolo Bava,
Fabrication-tolerant high quality factor photonic crystal microcavities
 Fabrication-tolerant high quality factor photonic crystal microcavities Kartik Srinivasan, Paul E. Barclay, and Oskar Painter Department of Applied Physics, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena,
Fabrication-tolerant high quality factor photonic crystal microcavities Kartik Srinivasan, Paul E. Barclay, and Oskar Painter Department of Applied Physics, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena,
Study of Propagating Modes and Reflectivity in Bragg Filters with AlxGa1-xN/GaN Material Composition
 Study of Propagating Modes and Reflectivity in Bragg Filters with AlxGa1-xN/GaN Material Composition Sourangsu Banerji Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, RCC Institute of Information
Study of Propagating Modes and Reflectivity in Bragg Filters with AlxGa1-xN/GaN Material Composition Sourangsu Banerji Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, RCC Institute of Information
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. fabrication. A schematic of the experimental setup used for graphene Supplementary Figure 2. Emission spectrum of the plasma: Negative peaks indicate an
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. fabrication. A schematic of the experimental setup used for graphene Supplementary Figure 2. Emission spectrum of the plasma: Negative peaks indicate an
SUPER-LATTICE STRUCTURE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 11, 53 64, 2010 SUPER-LATTICE STRUCTURE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER D. Chen, M.-L. V. Tse, and H. Y. Tam Photonics Research Centre, Department of Electrical Engineering
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 11, 53 64, 2010 SUPER-LATTICE STRUCTURE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL FIBER D. Chen, M.-L. V. Tse, and H. Y. Tam Photonics Research Centre, Department of Electrical Engineering
ACTIVE WDM FILTER ON DILUTE NITRIDE QUAN- TUM WELL PHOTONIC BAND GAP WAVEGUIDE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 35, 37 49, 2012 ACTIVE WDM FILTER ON DILUTE NITRIDE QUAN- TUM WELL PHOTONIC BAND GAP WAVEGUIDE G. Calò 1, D. Alexandropoulos 2, and V. Petruzzelli 1,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 35, 37 49, 2012 ACTIVE WDM FILTER ON DILUTE NITRIDE QUAN- TUM WELL PHOTONIC BAND GAP WAVEGUIDE G. Calò 1, D. Alexandropoulos 2, and V. Petruzzelli 1,
Transverse modes in thermally detuned oxide-confined vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers
 PHYSICAL REVIEW A, VOLUME 63, 023817 Transverse modes in thermally detuned oxide-confined vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers C. Degen, I. Fischer, and W. Elsäßer Institute of Applied Physics, Darmstadt
PHYSICAL REVIEW A, VOLUME 63, 023817 Transverse modes in thermally detuned oxide-confined vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers C. Degen, I. Fischer, and W. Elsäßer Institute of Applied Physics, Darmstadt
