212 LSW ALKYNES S04. Alkynes
|
|
|
- Stuart Turner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Alkynes Doubly unsaturated functional group Terminal alkynes, R-- 1) 2) 3) 4) Nomenclature: Functional group suffix = Disubstituted alkynes, R--R' Monosubstituted alkynes, R-- Stability: Substituted alkynes The "extra" bond in an alkyne bond by kj/mol or kcal/mol 171 than the alkene h 1-hexyne = kj/mol or kcal/mol h 1-hexene = kj/mol or kcal/mol - = = kj/mol or kcal/mol = - - = kj/mol or kcal/mol
2 Rank 1-hexyne (terminal) and 3-hexyne(internal) for each of the following properties: eat of eat of hydrogenation formation eat of Stability combustion Structure: ybridization: Shape: Y Y Physical Properties: Polarity: Volatililty: Melting points: Boiling points: Aqueous solubility: rganic solubility: Acidity: pka = 172
3 Reactivity: Alkynes act as nucleophiles. Addition reactions: Terminal alkynes: R-- R B: R Acetylide ion: + -B 173
4 Reactions: Alkyne Preparation ydrogenation Metal Reduction ydrogen alides NaN 2 NaN 2 2 / atalyst Na / N 3 (l) + 1 xs ydration g 2+ alogenation 2 zonolysis + 3 Then 2 + Deprotonation B: R R Alkylation 1. NaN 2 R R 2. R' + -B R' 174
5 Preparation of Alkynes Reaction Type: verall reaction: Leaving groups: Requires: NaN NaN Regioselectivity: Stereospecificity: Mechanism: Leaving Group Base: Selectivity: B: LG + LG 175
6 What is the alkyne product from the reactions of the following with NaN 2 : 1,2-dibromopropane 2,3-dibromooctane 1,2-dibromohexane 2,2-dibromohexane Synthesis: Try it: 2-methyl-4-octene 2-methyl-4-octyne E2 mechanism (For both alkenes and alkynes) Leaving Groups: -LG Base: B 176
7 Stereochemistry E2 reactions 180º 0º Synperiplanar Regioselectivity: Zaitsev's rule: Zaitsev product: offman product: Stereoselectivity: 177
8 Addition Reactions of Alkynes Two factors influence the relative reactivity of alkynes compared to alkenes: ydrogenation of Alkynes 2 / atalyst Reaction type: verall reaction: Regioselectivity: Stereoselectivity: Requirements: Alkanes: Alkenes: Lindlar's catalyst: Pd / a 3 / quinoline Mechanism: ATALYTI YDRGENATIN Step 1: Step 2: Step 3: Step 4: 178
9 Dissolving Metal Reduction of Alkynes Na / N 3 (l) Reaction type: verall reaction: Reactivity order: Regioselectivity: Stereoselectivity: Requirements: Mechanism: Step 1: Step 2: Step 3: Step 4: 3 3 Na 3 + Na 3 N N Na NaN Na 2 Synthesis: ow would you prepare trans 2-pentene from cis 2-pentene? 3 179
10 Reaction of Alkynes with ydrogen alides + 1 Reaction type: verall reaction: Reactivity order: Regioselectivity: 3 Stereoselectivity: Requirements: xs h 3 3 Mechanism: + Br - Br Br Br
11 ydration of Alkynes + 2 Reaction type: verall reaction: Regioselectivity: Stereoselectivity: Requirements: Mechanism: g Tautomerization: enol and keto: N T N N N N A N N N T N N N N G N 181
12 alogenation of Alkynes Reaction type: verall reaction: Reactivity order: Regioselectivity: Stereoselectivity: 2 Requirements: Mechanism: Br Br Br + _ + Br Br Br 182
13 zonolysis of Alkynes Then 2 Reaction type: verall reaction: Requirements: Mechanism: What would be the products of the ozonolysis: ethyne? 1-butyne? 2-butyne? cyclooctyne? 183
14 Acidity of Terminal Alkynes B: R R + -B Terminal alkynes: Stability of the conjugate base (i.e. the carbanion). s character: (sp = %, sp 2 = % and sp 3 = %) Increased s = = onjugate base of alkyne = = Mechanism: B: R R ould you use a Na or NaEt for this reaction? pka 2 = pka 3 2 = pka N 3 = + -B 184
15 Alkylation of Alkynes: Acetylide ion: 1. NaN 2 R R 2. R' Reaction type: verall reaction: Reactivity order: Alkyne: Alkyl halide: alide: Regioselectivity: Stereoselectivity: Requirements: R' Mechanism: _ R 2 Br 3 N N R 185
16 Examples: Ethylene (acetylene): monosubstituted (R--): symmetrical (R = R'): R--R': unsymmetrical (R R') R--R': Problems to try: 1. What is the product of the reactions of with: (a) 2-bromopropane (b) ethanol (c) 1-iodooctane (d) ethyl tosylate (e) (R)-2-bromohexane (f) bromobenzene 2. What would be the product from the reaction of propene with the following reagent sequence: (i) Br 2 (ii) NaN 2, heat (iii) NaN 2 then MeI Final product: 186
17 3. For the reaction 2-butyne with Br: (i) reaction with 1 equivalent gives 2-bromo-2-butene (ii) reaction with excess gives 2,2-dibromobutane (a) What conclusions can you reach about the reactivity of 2-bromo-2-butene compared to 2-butyne? (b) onsider the two possible carbocations that could be formed in the conversion of 2-bromo-2-butene to 2,2-dibromobutane. Suggest a reason for the observed regioselectivity. 5. Show the major products, with stereochemistry where applicable, for the reactions of: With: 1-pentyne 2-pentyne (i) excess 2 / Pd (ii) 2 / Lindlar Pd (iii) Na / N 3 (iv) 1 equiv. l (v) excess l (vi) aq. 2 S 4, gs 4 (vii) excess Br 2 (viii) 3 then 2 187
sp 2 geometry tetrahedral trigonal planar linear ΔH C-C ΔH C-H % s character pk a 464 KJ/mol 33% 44
 hapter 10: Alkynes 10.1 Introduction to Alkynes ~ 111 ~ 122 1.06 Å 180 1.1 Å ~ 116 1.08 Å 1.54 Å 1.34 Å 1.20 Å hybridization of sp 3 sp 2 sp geometry tetrahedral trigonal planar linear 368 KJ/mol 632 KJ/mol
hapter 10: Alkynes 10.1 Introduction to Alkynes ~ 111 ~ 122 1.06 Å 180 1.1 Å ~ 116 1.08 Å 1.54 Å 1.34 Å 1.20 Å hybridization of sp 3 sp 2 sp geometry tetrahedral trigonal planar linear 368 KJ/mol 632 KJ/mol
Lecture 20 Organic Chemistry 1
 CEM 232 rganic Chemistry I at Chicago Lecture 20 rganic Chemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop March 18, 2010 1 Self-Test Question Capnellene (4) is a marine natural product that was isolated from coral
CEM 232 rganic Chemistry I at Chicago Lecture 20 rganic Chemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop March 18, 2010 1 Self-Test Question Capnellene (4) is a marine natural product that was isolated from coral
Chapter 8: Chemistry of Alkynes (C n H 2n-2 )
 hapter 8: hemistry of Alkynes ( n 2n-2 ) Bonding & hybridization Both are sp-hybridized Bond angles = 180 o 1 σ + 2 π bonds Linear around lassification R R R' σ bond energy: 88 kcal/mol π bond energy:
hapter 8: hemistry of Alkynes ( n 2n-2 ) Bonding & hybridization Both are sp-hybridized Bond angles = 180 o 1 σ + 2 π bonds Linear around lassification R R R' σ bond energy: 88 kcal/mol π bond energy:
Chapter 9 Alkynes. Introduction
 hapter 9 Alkynes Introduction Alkynes contain a triple bond. General formula is n 2n-2. Two elements of unsaturation for each triple bond. MST reactions are like alkenes: addition and oxidation. Some reactions
hapter 9 Alkynes Introduction Alkynes contain a triple bond. General formula is n 2n-2. Two elements of unsaturation for each triple bond. MST reactions are like alkenes: addition and oxidation. Some reactions
Chapter 3. Alkenes And Alkynes
 Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Learning Guide for Chapter 13 - Alkynes
 Learning Guide for Chapter 13 - Alkynes I. Introduction to Alkynes - p 1 II. Natural ccurrence and Uses of Alkynes - p 5 III. Physical Properties of Alkynes - p 7 IV. Spectroscopy of Alkynes - p 7 V. Nomenclature
Learning Guide for Chapter 13 - Alkynes I. Introduction to Alkynes - p 1 II. Natural ccurrence and Uses of Alkynes - p 5 III. Physical Properties of Alkynes - p 7 IV. Spectroscopy of Alkynes - p 7 V. Nomenclature
Alkynes. Alkynes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon triple bond.
 Alkynes Alkynes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon triple bond. The carbon-carbon triple bond results from the interaction of two sp hybridized carbon atoms. 180 degree angle. Linear. The carbon-carbon
Alkynes Alkynes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon triple bond. The carbon-carbon triple bond results from the interaction of two sp hybridized carbon atoms. 180 degree angle. Linear. The carbon-carbon
Classes of Alkenes. Alkenes and Alkynes. Saturated compounds (alkanes): Have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom.
 Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
Chapter 9 Alkynes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 9 Alkynes Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9.1 Sources of Alkynes Acetylene Industrial preparation of acetylene is by dehydrogenation of
Chapter 9 Alkynes Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9.1 Sources of Alkynes Acetylene Industrial preparation of acetylene is by dehydrogenation of
C h a p t e r T e n : Alkynes. Tazarotene, a synthetic acetylenic retinoid used to treat acne
 C h a p t e r T e n : Alkynes N S Tazarotene, a synthetic acetylenic retinoid used to treat acne CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter 10: Alkynes I. Structure and bonding A. sp-hybridization
C h a p t e r T e n : Alkynes N S Tazarotene, a synthetic acetylenic retinoid used to treat acne CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter 10: Alkynes I. Structure and bonding A. sp-hybridization
CHEM 3013 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I LECTURE NOTES CHAPTER 8
 EM 3013 GANI EMISTY I LETUE NTES 1 1. The Alkyne Functional Group APTE 8 Alkynes are compounds with carbon-carbon triple bonds. ecall that alkanes use sp 3 hybrid orbitals and that alkenes use sp 2 hybrid
EM 3013 GANI EMISTY I LETUE NTES 1 1. The Alkyne Functional Group APTE 8 Alkynes are compounds with carbon-carbon triple bonds. ecall that alkanes use sp 3 hybrid orbitals and that alkenes use sp 2 hybrid
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY- 1
 ORGANIC CEMISTRY- 1 ALKENES Alkenes are also called Olefins (C n 2n ) unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes occur abundantly in nature. Ethylene ( 2 C=C 2 ) is a plant hormone that induces ripening in fruit.
ORGANIC CEMISTRY- 1 ALKENES Alkenes are also called Olefins (C n 2n ) unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes occur abundantly in nature. Ethylene ( 2 C=C 2 ) is a plant hormone that induces ripening in fruit.
Chem 145 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkynes
 Dr. Seham ALTERARY Chem 145 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkynes Chapter 4 1434-1435 2013-2014 2 st semester By the end of this chapter you should be familiar with: Definition for Alkynes. Nomenclature of
Dr. Seham ALTERARY Chem 145 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkynes Chapter 4 1434-1435 2013-2014 2 st semester By the end of this chapter you should be familiar with: Definition for Alkynes. Nomenclature of
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Winter Semester 2001 Dr. Rainer Glaser
 hemistry 210 rganic hemistry I Winter Semester 2001 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Structure, Synthesis and Reactions. Friday, April 20, 2001, 9:00-9:50 Name: Answer Key Question
hemistry 210 rganic hemistry I Winter Semester 2001 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Structure, Synthesis and Reactions. Friday, April 20, 2001, 9:00-9:50 Name: Answer Key Question
This reactivity makes alkenes an important class of organic compounds because they can be used to synthesize a wide variety of other compounds.
 This reactivity makes alkenes an important class of organic compounds because they can be used to synthesize a wide variety of other compounds. Mechanism for the addition of a hydrogen halide What happens
This reactivity makes alkenes an important class of organic compounds because they can be used to synthesize a wide variety of other compounds. Mechanism for the addition of a hydrogen halide What happens
Chapter Name the following compounds: (a) 2,5-dimethyl-3-hexyne (b) 3,3-dimethyl-1-butyne (c) 2,4-octadiene-6-yne (d) 3,3-dimethyl-4-octyne (e)
 hapter 8 8.1 Name the following compounds: 3 3 3 3 2,5-dimethyl-3-hexyne 3 3 3 3,3-dimethyl-1-butyne (c) 3 3 2,4-octadiene-6-yne (d) 3 3 2 2 2 3 3 3,3-dimethyl-4-octyne (e) 3 3 3 2 3 3 2,5,5-trimethyl-3-heptyne
hapter 8 8.1 Name the following compounds: 3 3 3 3 2,5-dimethyl-3-hexyne 3 3 3 3,3-dimethyl-1-butyne (c) 3 3 2,4-octadiene-6-yne (d) 3 3 2 2 2 3 3 3,3-dimethyl-4-octyne (e) 3 3 3 2 3 3 2,5,5-trimethyl-3-heptyne
OCH 3. 3-butyn-2-ol 3-hydroxy-1-butyne
 Alkynes, Part I eading: Wade chapter 9, sections 9-1- 9-8 Study Problems: 9-29, 9-32, 9-36 Key oncepts and Skills: Explain why alkynes are more acidic than alkanes or alkenes; show how to generate nucleophilic
Alkynes, Part I eading: Wade chapter 9, sections 9-1- 9-8 Study Problems: 9-29, 9-32, 9-36 Key oncepts and Skills: Explain why alkynes are more acidic than alkanes or alkenes; show how to generate nucleophilic
Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes
 Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density is symmetric about the internuclear axis) In an alkene,
Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density is symmetric about the internuclear axis) In an alkene,
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Fall Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser
 hemistry 210 rganic hemistry I all Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser xamination #3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Structure, Synthesis and Reactions. riday, November 17, 2000, 9:00-9:50 Name: Answer Key Question 1.
hemistry 210 rganic hemistry I all Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser xamination #3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Structure, Synthesis and Reactions. riday, November 17, 2000, 9:00-9:50 Name: Answer Key Question 1.
CHEM Lecture 7
 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
% % Important Concepts. Problems. Problems C h a p t e r
 Problems C h a p t e r 1 3 599 Important Concepts 1. The rules for naming alkynes are essentially the same as those formulated for alkenes. Molecules with both double and triple bonds are called alkenynes,
Problems C h a p t e r 1 3 599 Important Concepts 1. The rules for naming alkynes are essentially the same as those formulated for alkenes. Molecules with both double and triple bonds are called alkenynes,
Topic 2 Alkenes and alkynes
 Topic 2 Alkenes and alkynes lassification of rganic Reactions Four basic types of organic reaction Acid base reactions Substitution reactions Addition elimination reactions xidation reduction reactions
Topic 2 Alkenes and alkynes lassification of rganic Reactions Four basic types of organic reaction Acid base reactions Substitution reactions Addition elimination reactions xidation reduction reactions
Chem 251 Fall Learning Objectives
 Learning Objectives Chapter 8 (last semester) 1. Write an electron-pushing mechanism for an SN2 reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. 2. Describe the rate law and relative rate of reaction
Learning Objectives Chapter 8 (last semester) 1. Write an electron-pushing mechanism for an SN2 reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. 2. Describe the rate law and relative rate of reaction
CHEM 241 ALKYNES CHAP 9 ASSIGN
 HEM 241 ALKYNES HAP 9 ASSIGN 1. What is the IUPA name of the following compound A. 5-propyl-3-heptyne B. 5-isopropyl-3-heptyne. 5-ethyl-3-octyne D. 4-ethyl-5-octyne 2. What is the correct IUPA name for
HEM 241 ALKYNES HAP 9 ASSIGN 1. What is the IUPA name of the following compound A. 5-propyl-3-heptyne B. 5-isopropyl-3-heptyne. 5-ethyl-3-octyne D. 4-ethyl-5-octyne 2. What is the correct IUPA name for
Organic Chemistry. Alkynes
 For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Alkynes by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Alkynes by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science & Technology seema@ump.edu.my & iezwan@ump.edu.my
Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
 5 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes APTER SUMMARY Addition is the characteristic reaction of alkenes and alkynes. Since the carbons of a double or triple bond do not have the maximum number
5 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes APTER SUMMARY Addition is the characteristic reaction of alkenes and alkynes. Since the carbons of a double or triple bond do not have the maximum number
Name. Department of Chemistry SUNY/Oneonta. Chem Organic Chemistry I. Examination #3 - November 8, 2004 ANSWERS
 Name Department of hemistry SUNY/neonta hem 221 - rganic hemistry I Examination #3 - November 8, 2004 ANSWERS INSTRUTINS --- This examination has two parts. The first part is in multiple choice format;
Name Department of hemistry SUNY/neonta hem 221 - rganic hemistry I Examination #3 - November 8, 2004 ANSWERS INSTRUTINS --- This examination has two parts. The first part is in multiple choice format;
Chapter 4 Electrophilic Addition to Carbon Carbon Multiple Bonds 1. Addition of H X 2. Addition of H OH and addition of Y X 3. Addition to allene and
 Chapter 4 Electrophilic Addition to Carbon Carbon Multiple Bonds 1. Addition of X 2. Addition of and addition of Y X 3. Addition to allene and alkyne 4. Substitution at α-carbon 5. eactions via organoborane
Chapter 4 Electrophilic Addition to Carbon Carbon Multiple Bonds 1. Addition of X 2. Addition of and addition of Y X 3. Addition to allene and alkyne 4. Substitution at α-carbon 5. eactions via organoborane
CHEM 2311 HW1. COMPLETELY FILL THE BOXES IN DARK PENCIL, i.e.:, NOT or or STRUCTURE
 EM 2311 W1 Provide answers to the following multiple choice questions on the Scantron form provided in lecture. Make sure that you put your name and bubble in your GTID # on the answer form. MPLETELY FILL
EM 2311 W1 Provide answers to the following multiple choice questions on the Scantron form provided in lecture. Make sure that you put your name and bubble in your GTID # on the answer form. MPLETELY FILL
HOMEWORK PROBLEMS: ALKYNES. 1. Provide the complete IUPAC name for the following compounds:
 CEM 31 MEWRK PRBLEMS: ALKYNES 1. Provide the complete IUPAC name for the following compounds: 2. When the compound below is treated with one equivalent of B 3, where does it react Explain. Where would
CEM 31 MEWRK PRBLEMS: ALKYNES 1. Provide the complete IUPAC name for the following compounds: 2. When the compound below is treated with one equivalent of B 3, where does it react Explain. Where would
Chapter 12 Alkenes and Alkynes
 BR M 102 lass Notes hapter 12 Page 1 of 8 hapter 12 Alkenes and Alkynes * alkenes = double bonds * alkynes triple bonds * aromatics or arenes alternating double and single bonds such as in benzene * saturated
BR M 102 lass Notes hapter 12 Page 1 of 8 hapter 12 Alkenes and Alkynes * alkenes = double bonds * alkynes triple bonds * aromatics or arenes alternating double and single bonds such as in benzene * saturated
Time Allowed: 60 minutes MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC AND BIOCHEMISTRY QUIZ 5 Time Allowed: 60 minutes MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What is the IUPAC name
INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC AND BIOCHEMISTRY QUIZ 5 Time Allowed: 60 minutes MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What is the IUPAC name
Lecture 11 Organic Chemistry 1
 EM 232 rganic hemistry I at hicago Lecture 11 rganic hemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop February 16, 2010 1 Self Test Question What is the product(s) of the following reaction? 3 K( 3 ) 3 A 3 ( 3 ) 3
EM 232 rganic hemistry I at hicago Lecture 11 rganic hemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop February 16, 2010 1 Self Test Question What is the product(s) of the following reaction? 3 K( 3 ) 3 A 3 ( 3 ) 3
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds Chapter Outline 13.1 Alkenes and Alkynes 13.2 Nomenclature of Alkenes and Alkynes 13.3 Cis Trans Isomers 13.4 Alkenes in Food and Medicine 13.6 Reactions
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds Chapter Outline 13.1 Alkenes and Alkynes 13.2 Nomenclature of Alkenes and Alkynes 13.3 Cis Trans Isomers 13.4 Alkenes in Food and Medicine 13.6 Reactions
台灣大學開放式課程 有機化學乙 蔡蘊明教授 本著作除另有註明, 作者皆為蔡蘊明教授, 所有內容皆採用創用 CC 姓名標示 - 非商業使用 - 相同方式分享 3.0 台灣授權條款釋出
 台灣大學開放式課程 有機化學乙 蔡蘊明教授 本著作除另有註明, 作者皆為蔡蘊明教授, 所有內容皆採用創用 姓名標示 - 非商業使用 - 相同方式分享 3.0 台灣授權條款釋出 hapter 7 Alkenes and alkynes: synthesis alkenes also called olefins alkynes common name: acetylenes Nomenclature
台灣大學開放式課程 有機化學乙 蔡蘊明教授 本著作除另有註明, 作者皆為蔡蘊明教授, 所有內容皆採用創用 姓名標示 - 非商業使用 - 相同方式分享 3.0 台灣授權條款釋出 hapter 7 Alkenes and alkynes: synthesis alkenes also called olefins alkynes common name: acetylenes Nomenclature
11/5/ Conjugated Dienes. Conjugated Dienes. Conjugated Dienes. Heats of Hydrogenation
 8.12 Sites of unsaturation Many compounds have numerous sites of unsaturation If sites are well separated in molecule they react independently If sites are close together they may interact with one another
8.12 Sites of unsaturation Many compounds have numerous sites of unsaturation If sites are well separated in molecule they react independently If sites are close together they may interact with one another
1. What is the letter designation given to dumbbell shaped orbitals like the one depicted below?
 1. What is the letter designation given to dumbbell shaped orbitals like the one depicted below? 2. Which of the following does not have an octet of electrons surrounding the central atom? A. B 3 B. C
1. What is the letter designation given to dumbbell shaped orbitals like the one depicted below? 2. Which of the following does not have an octet of electrons surrounding the central atom? A. B 3 B. C
N.b. A catalyst is a species which speeds up a chemical reaction but which remains chemically unchanged. Reverse process of dehydration of an alcohol
 An Introduction to Organic hemistry N.b. A catalyst is a species which speeds up a chemical reaction but which remains chemically unchanged. ydration (Addition) Reverse process of dehydration of an alcohol
An Introduction to Organic hemistry N.b. A catalyst is a species which speeds up a chemical reaction but which remains chemically unchanged. ydration (Addition) Reverse process of dehydration of an alcohol
Departmental Final Examination. Organic Chemistry I Caffein
 Departmental Final Examination rganic Chemistry I 2423 Caffein Name CEMISTRY 2423 FINAL EXAM FALL, 2005 DIRECTINS: A periodic table is attached at the end of this exam. Please answer all questions as completely
Departmental Final Examination rganic Chemistry I 2423 Caffein Name CEMISTRY 2423 FINAL EXAM FALL, 2005 DIRECTINS: A periodic table is attached at the end of this exam. Please answer all questions as completely
Loudon Chapter 14 Review: Reactions of Alkynes Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 1/16/2018
 An alkyne is any molecule with a triple bond between two carbon atoms. This triple bond consists of one σ bond and two π bonds: the σ bond exists on a straight line between carbon atoms, while one π bond
An alkyne is any molecule with a triple bond between two carbon atoms. This triple bond consists of one σ bond and two π bonds: the σ bond exists on a straight line between carbon atoms, while one π bond
When H and OH add to the alkyne, an enol is formed, which rearranges to form a carbonyl (C=O) group:
 Next Up: Addition of, : The next two reactions are the Markovnikov and non-markovnikov additions of and to an alkyne But you will not see alcohols form in this reaction! When and add to the alkyne, an
Next Up: Addition of, : The next two reactions are the Markovnikov and non-markovnikov additions of and to an alkyne But you will not see alcohols form in this reaction! When and add to the alkyne, an
ADDITION REACTIONS OF ALKYNES
 ADDITIN REATINS F ALKYNES ADDITIN REATINS F ALKYNES two pi bonds A carbon-carbon triple bond is like two carbon-carbon double bonds. Most double bond reagents will react twice. ALKYNES ARE LESS REATIVE
ADDITIN REATINS F ALKYNES ADDITIN REATINS F ALKYNES two pi bonds A carbon-carbon triple bond is like two carbon-carbon double bonds. Most double bond reagents will react twice. ALKYNES ARE LESS REATIVE
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions "
 Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The π
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The π
Organic Chemistry. M. R. Naimi-Jamal. Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology
 Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 4-3: Continue Alkynes: An Introduction to Organic Synthesis Based on: McMurry s Organic Chemistry,
Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 4-3: Continue Alkynes: An Introduction to Organic Synthesis Based on: McMurry s Organic Chemistry,
Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Excluded sections 3.15&3.16
 Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes Excluded sections 3.15&3.16 3.1 Definition and Classification Alkene: a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboncarbon double bonds. ethylene is the simplest alkene. Alkyne:
Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes Excluded sections 3.15&3.16 3.1 Definition and Classification Alkene: a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboncarbon double bonds. ethylene is the simplest alkene. Alkyne:
Part C- section 1 p-bonds as nucleophiles
 Part C- section 1 p-bonds as nucleophiles Chemistry of Alkenes (Ch 8, 9, 10) - the double bond prevents free rotation - isomerism cis and trans - nomenclature E and Z (3 or 4 different substituents around
Part C- section 1 p-bonds as nucleophiles Chemistry of Alkenes (Ch 8, 9, 10) - the double bond prevents free rotation - isomerism cis and trans - nomenclature E and Z (3 or 4 different substituents around
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Fall Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser
 Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Fall Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Structure, Synthesis and Reactions. Friday, November 17, 2000, 9:00-9:50 Name: Question 1. Alkenes
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Fall Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Structure, Synthesis and Reactions. Friday, November 17, 2000, 9:00-9:50 Name: Question 1. Alkenes
Final Exam Professor R. Hoenigman
 I pledge to uphold the CU onor Code: CEM 3311-200 Fall 2006 Final Exam Professor. oenigman Average Score = 145 igh Score = 235 Low Score = 27 Signature Name (printed) Last four digits of your student ID
I pledge to uphold the CU onor Code: CEM 3311-200 Fall 2006 Final Exam Professor. oenigman Average Score = 145 igh Score = 235 Low Score = 27 Signature Name (printed) Last four digits of your student ID
CHAPTER 3 ALKENES, ALKYNES & CONJUGATE DIENES
 CHEM 244 PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PRE-REQUISITES COURSE; CHEM 101 CREDIT HOURS; 2 (2+0) Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College
CHEM 244 PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PRE-REQUISITES COURSE; CHEM 101 CREDIT HOURS; 2 (2+0) Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College
As time allows, additional practice questions for Exam 2 follow. This is an incomplete collection. Content & emphasis will vary.
 Chem 226 Exam 2 Fall 2005: will cover Bruice, Chaps 3 through 6; Note: review e-mail & inclass quizzes and Worksheets, suggest on-line practice questions and quizzes plus ACS rganic Chemistry Guide As
Chem 226 Exam 2 Fall 2005: will cover Bruice, Chaps 3 through 6; Note: review e-mail & inclass quizzes and Worksheets, suggest on-line practice questions and quizzes plus ACS rganic Chemistry Guide As
Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkenes
 Dr. Seham ALTERARY Chem 145 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkenes Chapter 3 1434-1435 2013-2014 2 nd semester By the end of this chapter you should be familiar with: Definition of Alkenes. Nomenclature of Alkenes.
Dr. Seham ALTERARY Chem 145 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkenes Chapter 3 1434-1435 2013-2014 2 nd semester By the end of this chapter you should be familiar with: Definition of Alkenes. Nomenclature of Alkenes.
CHAPTER 9. ALKYNES: AN INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC SYNTHESIS
 CAPTER 9. ALKYNES: AN INTRDUCTIN T RGANIC SYNTESIS Alkyne Nomenclature. Like alkenes, number so the alkyne gets the lowest number. Name the following two molecules: 3 C C CC 2 C 2 C(C 3 ) 2 Cl If, however,
CAPTER 9. ALKYNES: AN INTRDUCTIN T RGANIC SYNTESIS Alkyne Nomenclature. Like alkenes, number so the alkyne gets the lowest number. Name the following two molecules: 3 C C CC 2 C 2 C(C 3 ) 2 Cl If, however,
Chem101 General Chemistry. Lecture 11 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 hem101 General hemistry Lecture 11 Unsaturated ydrocarbons Unsaturated ydrocarbons ontain one or more double or triple carbon-carbon bond. University of Wisconsin-Eau laire hem101 - Lecture 11 2 Unsaturated
hem101 General hemistry Lecture 11 Unsaturated ydrocarbons Unsaturated ydrocarbons ontain one or more double or triple carbon-carbon bond. University of Wisconsin-Eau laire hem101 - Lecture 11 2 Unsaturated
HONORS ORGANIC CHEM. HAHS MRS. RICHARDS
 NRS RGANIC CEM. AS MRS. RICARDS RGANIC CEMISTRY: FINAL EXAM REVIEW List of Topics: While the exam will specifically focus on material from Quarter 2, an understanding of several important concepts from
NRS RGANIC CEM. AS MRS. RICARDS RGANIC CEMISTRY: FINAL EXAM REVIEW List of Topics: While the exam will specifically focus on material from Quarter 2, an understanding of several important concepts from
Alkynes Nomenclature of Alkynes
 Chapter 7 Alkynes Alkynes - hydrocarbons containing a carbon-carbon triple bond (2 bonds) Acyclic alkanes = C n H 2n+2 Alkenes and cyclic alkanes = C n H 2n Alkynes (and cyclic alkenes) = C n H 2n-2 The
Chapter 7 Alkynes Alkynes - hydrocarbons containing a carbon-carbon triple bond (2 bonds) Acyclic alkanes = C n H 2n+2 Alkenes and cyclic alkanes = C n H 2n Alkynes (and cyclic alkenes) = C n H 2n-2 The
CHEM120 - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY WORKSHEET 1
 EM120 - RGANI EMISTRY WRKSEET 1 Some of the objectives To understand and know the hybridization concept Be able to distinguish different geometries, including basic bond lengths and angles within organic
EM120 - RGANI EMISTRY WRKSEET 1 Some of the objectives To understand and know the hybridization concept Be able to distinguish different geometries, including basic bond lengths and angles within organic
Chemistry 2541, Fall 2017 Midterm Exam 3 (100 points)
 Important notes: Chemistry 2541, Fall 2017 Midterm Exam 3 (100 points) - Please use the provided Scantron form for your answers; you can keep the sheet with the questions and can use it as scratch paper
Important notes: Chemistry 2541, Fall 2017 Midterm Exam 3 (100 points) - Please use the provided Scantron form for your answers; you can keep the sheet with the questions and can use it as scratch paper
Practice Multiple-Choice Questions for Ending Chem 21 and/or Starting Chem 22
 Practice Multiple-Choice Questions for Ending Chem 21 and/or Starting Chem 22 Includes information from chapters 5-10 of the third edition of Klein s Organic Chemistry text. 1. Which of the following compounds
Practice Multiple-Choice Questions for Ending Chem 21 and/or Starting Chem 22 Includes information from chapters 5-10 of the third edition of Klein s Organic Chemistry text. 1. Which of the following compounds
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 Unsaturated ydrocarbons hemical Formulas and Unsaturation n n 2n n 2n+2 n 2n+2 hemical Formulas and Unsaturation n n n n 2n n 2n hemical Formulas and Unsaturation ydrocarbons Saturated ydrocarbons Unsaturated
Unsaturated ydrocarbons hemical Formulas and Unsaturation n n 2n n 2n+2 n 2n+2 hemical Formulas and Unsaturation n n n n 2n n 2n hemical Formulas and Unsaturation ydrocarbons Saturated ydrocarbons Unsaturated
Química Orgânica I. alkynes 2008/09. w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 ALKYNE 1. w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 ALKYNE 2
 Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 ALKYNE 1 alkynes w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 ALKYNE 2 1 Name these: 3 propyne 3 2 2 Br 5-bromo-2-pentyne 5-bromopent-2-yne 3 3 3 2 3 2,6-dimethyl-3-heptyne
Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 ALKYNE 1 alkynes w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 ALKYNE 2 1 Name these: 3 propyne 3 2 2 Br 5-bromo-2-pentyne 5-bromopent-2-yne 3 3 3 2 3 2,6-dimethyl-3-heptyne
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
 11 R R R ALDEYDES AND KETNES APTER SUMMARY 111 Structure of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones both have a carbonyl group (carbonoxygen double bond); aldehydes have at least one carbon bonded
11 R R R ALDEYDES AND KETNES APTER SUMMARY 111 Structure of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones both have a carbonyl group (carbonoxygen double bond); aldehydes have at least one carbon bonded
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Winter Semester 2002 Dr. Rainer Glaser
 hemistry 210 rganic hemistry I Winter Semester 2002 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #6 Reactions of Alkenes & Alkyne hemistry. Friday, March 26, 2002, 9 9:50 am Name: Answer Key Question 1. alogenation Reactions.
hemistry 210 rganic hemistry I Winter Semester 2002 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #6 Reactions of Alkenes & Alkyne hemistry. Friday, March 26, 2002, 9 9:50 am Name: Answer Key Question 1. alogenation Reactions.
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions. Alkenes are electron rich. Additions to Alkenes
 Additions to Alkenes hapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition eactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Additions to Alkenes hapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition eactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Chapter 20 (part 2) Organic Chemistry
 Chapter 20 (part 2) Organic Chemistry Section 20.7 Alkenes and Alkynes Alkenes: hydrocarbons that contain a carbon carbon double bond. [C n H 2n ] CH 3 CH=CH 2 propene Alkynes: hydrocarbons containing
Chapter 20 (part 2) Organic Chemistry Section 20.7 Alkenes and Alkynes Alkenes: hydrocarbons that contain a carbon carbon double bond. [C n H 2n ] CH 3 CH=CH 2 propene Alkynes: hydrocarbons containing
Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones
 Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones 9.1 Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al The aldehyde functional group is always carbon
Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones 9.1 Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al The aldehyde functional group is always carbon
CHEM 2312 practice final. Version - II
 EM 2312 practice final Version - II The following standardized final examination covers the entire introductory year of organic chemistry (EM 2311 and 2312 at Georgia Tech). The exam consists of 70 multiple
EM 2312 practice final Version - II The following standardized final examination covers the entire introductory year of organic chemistry (EM 2311 and 2312 at Georgia Tech). The exam consists of 70 multiple
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes. 2. Radical Substitution with Alkenes. 3. Electrophilic Addition
 1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
350 Organic Chemistry I Winona State University
 350 Organic Chemistry I Winona State University Exam #4B, December 9, 2013 Professor T. Nalli Name General Instructions: Write your name in the space provided above and on the provided Scan-tron form.
350 Organic Chemistry I Winona State University Exam #4B, December 9, 2013 Professor T. Nalli Name General Instructions: Write your name in the space provided above and on the provided Scan-tron form.
Chapter 8 Addition Reactions to Alkenes
 . 8 hapter 8 Addition eactions to Alkenes In this chapter will we study the addition reactions of alkenes. We will see that the π electrons of the double bond are loosely held and that their maximum electron
. 8 hapter 8 Addition eactions to Alkenes In this chapter will we study the addition reactions of alkenes. We will see that the π electrons of the double bond are loosely held and that their maximum electron
Alkenes. Alkenes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes have the formula C n H 2n. Nomenclature
 Alkenes Alkenes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes have the formula n 2n. Nomenclature Alkenes are named in the same manner as alkanes with the following adjustments. 1. Find the longest
Alkenes Alkenes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes have the formula n 2n. Nomenclature Alkenes are named in the same manner as alkanes with the following adjustments. 1. Find the longest
Hydrogen iodide is a strong acid and will drive the reverse reaction, meaning the forward reaction will not occur.
 EM 261 Oct 18, 2018 Photosynthesis and Related Reactions O 2 2 O 6 12 O 6 2 O N 3, S, Fe, u, o, other Natural Products D-Glucose R O R OR Ionic substitution S N 1 & R X X 2 hv Petroleum/ Alkanes R N 2
EM 261 Oct 18, 2018 Photosynthesis and Related Reactions O 2 2 O 6 12 O 6 2 O N 3, S, Fe, u, o, other Natural Products D-Glucose R O R OR Ionic substitution S N 1 & R X X 2 hv Petroleum/ Alkanes R N 2
Chapter 7: Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis
 hapter 7: Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis alcohol alkane halohydrin 1,2-diol 1,2-dihalide carbonyl halide halide Addition Y Y Elimination Electrophilic Addition Dehydrohalogenation: loss of from an alkyl
hapter 7: Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis alcohol alkane halohydrin 1,2-diol 1,2-dihalide carbonyl halide halide Addition Y Y Elimination Electrophilic Addition Dehydrohalogenation: loss of from an alkyl
Vision. Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. How rods work H 3 C CH 3. Protein opsin. 11-cis-retinal. Opsin. Rhodopsin.
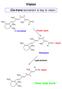 Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
به نام خدا. Organic Chemistry 1. Dr Morteza Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran
 به نام خدا 8 Organic Chemistry 1 Dr Morteza Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir 8 Alkynes: An Introduction to Organic Synthesis آلکین ها: مقدمه ای
به نام خدا 8 Organic Chemistry 1 Dr Morteza Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir 8 Alkynes: An Introduction to Organic Synthesis آلکین ها: مقدمه ای
Chapter 7 Alkenes; Elimination Reactions
 hapter 7 Alkenes; Elimination Reactions Alkenes Alkenes contain a carbon-carbon double bond. They are named as derivatives of alkanes with the suffix -ane changed to -ene. The parent alkane is the longest
hapter 7 Alkenes; Elimination Reactions Alkenes Alkenes contain a carbon-carbon double bond. They are named as derivatives of alkanes with the suffix -ane changed to -ene. The parent alkane is the longest
Homework Problem Set 9 Iverson CH320M/328M Due Friday, November 30
 omework Problem Set 9 Iverson C0M/8M Due Friday, November 0 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 0M/8M Dr. ent Iverson 9th omework November 9, 08 Please print the first three letters of your last name in
omework Problem Set 9 Iverson C0M/8M Due Friday, November 0 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 0M/8M Dr. ent Iverson 9th omework November 9, 08 Please print the first three letters of your last name in
Alkenes. Alkenes are unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons.
 Alkenes Alkenes Each member contains one double covalent bond between two C atoms. Draw condensed structural formulas of first three members of alkenes family. Alkenes are unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons.
Alkenes Alkenes Each member contains one double covalent bond between two C atoms. Draw condensed structural formulas of first three members of alkenes family. Alkenes are unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons.
1.8. Organic Chemistry. Practice Exam Organic Chem. System LENGTH: VOLUME MASS Temperature. 1 gal = 4 qt. 1 lb = 16 oz.
 rganic hemistry Practice Exam rganic hem Name (last) (First) Read all questions before you start. Show all work and explain your answers to receive full credit. Report all numerical answers to the proper
rganic hemistry Practice Exam rganic hem Name (last) (First) Read all questions before you start. Show all work and explain your answers to receive full credit. Report all numerical answers to the proper
ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE (AUTONOMOUS) ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE ROAD, CUDDALORE CH101T ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (SEMESTER-I)
 UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
Introduction to Organic Chemistry. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Copyright The McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Common Elements in Organic Compounds 2 Classification of ydrocarbons ydrocarbons
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Copyright The McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Common Elements in Organic Compounds 2 Classification of ydrocarbons ydrocarbons
Chapter 5. Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
 Chapter 5. Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes Learning objectives: 1. Identify the followings from a reaction coordinate diagram when applicable: endothermic or exothermic reactions, activation energy, heat
Chapter 5. Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes Learning objectives: 1. Identify the followings from a reaction coordinate diagram when applicable: endothermic or exothermic reactions, activation energy, heat
1.13 Acid-Base Reactions: Lone-Pair Donors & Acceptors
 1.13 Acid-Base Reactions: Lone-Pair Donors & Acceptors I, Cl, N 3, 3 P 4 pka 10 to 5 Super strong acids 3 + pka 1.7 RC 2 pka ~ 5 acids Ph pka ~ 10 get 2, R pka ~ 16 weaker RCC (alkynes) pka ~ 26 RN 2 pka
1.13 Acid-Base Reactions: Lone-Pair Donors & Acceptors I, Cl, N 3, 3 P 4 pka 10 to 5 Super strong acids 3 + pka 1.7 RC 2 pka ~ 5 acids Ph pka ~ 10 get 2, R pka ~ 16 weaker RCC (alkynes) pka ~ 26 RN 2 pka
and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
 Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy 2010, Prentice all Conjugated Systems Conjugated double bonds are separated
Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy 2010, Prentice all Conjugated Systems Conjugated double bonds are separated
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Organic Chemistry, Fifth Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Lecture Outline Modified by Dr. Juliet Hahn Copyright 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction
Organic Chemistry, Fifth Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Lecture Outline Modified by Dr. Juliet Hahn Copyright 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction
Chemistry 2321 OLD TEST QUESTIONS
 hemistry 2321 Test No. 3 Professor M. Pomerantz LD TEST QUESTINS Select the best name for the compounds shown. 1. l 2 3 2 2-chloro-4-ethyl-5-heptyne 6-chloro-4-ethyl-2-heptyne 4-(2-chloropropyl)-2-hexyne
hemistry 2321 Test No. 3 Professor M. Pomerantz LD TEST QUESTINS Select the best name for the compounds shown. 1. l 2 3 2 2-chloro-4-ethyl-5-heptyne 6-chloro-4-ethyl-2-heptyne 4-(2-chloropropyl)-2-hexyne
(c) The intermediate carbocation resulting from 3-bromobut-1-ene is resonance stabilized.
 KT121 Sem II 09/10 SETIN B: 1.(a) Name of mechanism: E1 elimination. 7 marks (b) (i) + 3 3 3 (ii) + 3 (iii) l 8 marks (c) The intermediate carbocation resulting from 3-bromobut-1-ene is resonance stabilized.
KT121 Sem II 09/10 SETIN B: 1.(a) Name of mechanism: E1 elimination. 7 marks (b) (i) + 3 3 3 (ii) + 3 (iii) l 8 marks (c) The intermediate carbocation resulting from 3-bromobut-1-ene is resonance stabilized.
1. Introduction. Cis-Trans System Useful for 1,2-disubstituted alkenes Examples: Alkynes Hydrocarbons containing C C Common name: acetylenes
 hapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I: Properties and Synthesis. Elimination eactions of Alkyl alides reated by Professor William Tam & Dr. illis hang h. 7-1 About The Authors These PowerPoint Lecture Slides
hapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I: Properties and Synthesis. Elimination eactions of Alkyl alides reated by Professor William Tam & Dr. illis hang h. 7-1 About The Authors These PowerPoint Lecture Slides
Chapter 7: Alkenes and Alkynes
 Chapter 7: Alkenes and Alkynes ydrocarbons Containing Double and Triple Bonds Unsaturated Compounds (Less than Maximum Atoms) Alkenes also Referred to as Olefins Properties Similar to those of Corresponding
Chapter 7: Alkenes and Alkynes ydrocarbons Containing Double and Triple Bonds Unsaturated Compounds (Less than Maximum Atoms) Alkenes also Referred to as Olefins Properties Similar to those of Corresponding
Unsaturated hydrocarbons. Chapter 13
 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Chapter 13 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons which contain at least one C-C multiple (double or triple) bond. The multiple bond is a site for chemical reactions in these molecules.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons Chapter 13 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons which contain at least one C-C multiple (double or triple) bond. The multiple bond is a site for chemical reactions in these molecules.
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
LEVEL I. 1. Electrolysis of concentrated solution of sodium propanate produces the hydrocarbon
 QUESTIN BANK--1 ydrocarbons LEVEL I 1. Electrolysis of concentrated solution of sodium propanate produces the hydrocarbon methane ethane propane butane. The reactivity of hydrogen atom in an alkane towards
QUESTIN BANK--1 ydrocarbons LEVEL I 1. Electrolysis of concentrated solution of sodium propanate produces the hydrocarbon methane ethane propane butane. The reactivity of hydrogen atom in an alkane towards
1. Which of the following compounds is the weakest base?
 I. Multiple-choice Questions Fall 2018 1. Which of the following compounds is the weakest base? a. C3C2 b. C3C2 c. N3 d. C3 e. N2 2. Which of the following functional groups is indicated by a strong and
I. Multiple-choice Questions Fall 2018 1. Which of the following compounds is the weakest base? a. C3C2 b. C3C2 c. N3 d. C3 e. N2 2. Which of the following functional groups is indicated by a strong and
Ch.6 Alkenes: Structure and Reactivity
 alkene = olefin 2 2 Ethylene α-pinene 3 β-arotene (orange pigment and vitamin A precursor) 6.1 Industrial Preparation and Use of Alkenes ompounds derived industrially from ethylene 2 2 Ethylene (26 million
alkene = olefin 2 2 Ethylene α-pinene 3 β-arotene (orange pigment and vitamin A precursor) 6.1 Industrial Preparation and Use of Alkenes ompounds derived industrially from ethylene 2 2 Ethylene (26 million
Alkane and Alkene Reactions
 Name: Date: Pd: Alkane and Alkene Reactions 1. Give the structure (structural fmula and condensed structural fmula) of the maj ganic product of the following reactions. a. hexane and chline Reaction Type:
Name: Date: Pd: Alkane and Alkene Reactions 1. Give the structure (structural fmula and condensed structural fmula) of the maj ganic product of the following reactions. a. hexane and chline Reaction Type:
There are 19 problems on 22 pages. Please make sure that you have them all.
 EMISTRY 222, Spring 2001 Review Problems Page 1 There are 19 problems on 22 pages. Please make sure that you have them all. 1) Give an unambiguous name for the following compounds. e sure to use cis/trans,
EMISTRY 222, Spring 2001 Review Problems Page 1 There are 19 problems on 22 pages. Please make sure that you have them all. 1) Give an unambiguous name for the following compounds. e sure to use cis/trans,
Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions. Alpha Substitution
 Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Lecture 22 Organic Chemistry 1
 CEM 232 rganic Chemistry I at Chicago Lecture 22 rganic Chemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop April 1, 2010 1 Self Test Question Which starting material could not be used to prepare the tribromide below?
CEM 232 rganic Chemistry I at Chicago Lecture 22 rganic Chemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop April 1, 2010 1 Self Test Question Which starting material could not be used to prepare the tribromide below?
Chapter 6: Alkenes: Structure and Reactivity
 hapter 6: Alkenes: Structure and eactivity overage: 1. Degrees of Unsaturation 2. Nomenclature cis/trans E/Z 3. Alkene Stability 4. Electrophilic Addition eactions/markovinikov s ule 5. The ammond Postulate
hapter 6: Alkenes: Structure and eactivity overage: 1. Degrees of Unsaturation 2. Nomenclature cis/trans E/Z 3. Alkene Stability 4. Electrophilic Addition eactions/markovinikov s ule 5. The ammond Postulate
Alkynes Are Found in Natural Products
 Objective 13 Apply Reactivity Principles to Electrophilic Addition Reactions 2: Alkynes Identify structural features (pi bond) and electrophiles Use curved arrows to predict product Alkynes Are Found in
Objective 13 Apply Reactivity Principles to Electrophilic Addition Reactions 2: Alkynes Identify structural features (pi bond) and electrophiles Use curved arrows to predict product Alkynes Are Found in
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Summer Semester 1999 Dr. Somnath Sarkar
 Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Summer Semester 1999 Dr. Somnath Sarkar Examination #3 Elimination Reactions Structure, Synthesis and Reactions of Alkenes and alkynes. Friday, July 23, 1999, 8:40 9:40
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Summer Semester 1999 Dr. Somnath Sarkar Examination #3 Elimination Reactions Structure, Synthesis and Reactions of Alkenes and alkynes. Friday, July 23, 1999, 8:40 9:40
