Electronegativity is a very useful concept for the explanation or understanding of chemical reactivity throughout the periodic table.
|
|
|
- Mark Goodman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1.6. Review of Electronegativity (χ) CONCEPT: Electronegativity is a very useful concept for the explanation or understanding of chemical reactivity throughout the periodic table. There are many definitions of electronegativity. The resulting numerical values are not interchangeable. Original definition by Linus Pauling: the power of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself Pauling noticed that the bond energies of polar bonds (A-B) were greater than the average of the bond energies of the two homonuclear species (avg. A-A & B-B). (RECALL: the strength of the siloxane linkage -Si-O-Si-O-) Pauling Definition: Derives values for electronegativity χ P by comparing bond energies: A 2 (g) + B 2 (g) 2 AB(g) ΔE (AB) = E (AB)exp ½(E (AA) + E (BB) ) = 23 (χ A χ B ) 2 [kcal/mol] excess energy from ionic contribution χ A - χ B = ΔE 1/2 [ev] χ A - χ B = bond polarity Set χ F = 3.98 and χ H = 2.2, then calculate all other values using experimental data. (See p.31 of your text for actual values.) Mulliken Definition: Derives values for ( absolute ) electronegativity χ M from ionization energy and electron affinity. χ M = ½ (IE + EA) = - µ NOTE: this is the average of IE and EA IE = ionization energy of an atom, EA = Electron Affinity of an atom, µ = chemical potential of the electrons. Pauling and Mulliken scales are very much in line. One reasonably accurate conversion between the two is: χ Pauling = 1.35(χ Mulliken ) 1/
2 Allred + Rochow Definition: Describes χ A electronegativity as a force needed to remove an electron from the atom s ground state. (Note the similarity to Coulomb s Law). Z* A = effective nuclear charge from Slater s rules r A = atomic radius of A (from A-A) in Å NOTE: The larger the effective nuclear charge (Z*), the more electronegative. This implies that electronegativity is different for each orbital of an atom and is dependent on electron filling (i.e., charge). NOTE: The smaller the atomic radius, the more electronegative. Allen Definition: Electronegativity is the average one-electron energy of the valence-shell electrons in ground-state free atoms. i.e., VOIP Valence Orbital Ionization Potential Spectroscopic electronegativity: m, n = number of p and s electrons, respectively ε s, ε p = multiplet averaged ionization potentials of p and s electrons (experimental data). e.g., Consider a carbon atom: C is [He]2s 2 2p 2 valence shell is n = 2 There are 15 possible ways of filling 2 electrons into the three p orbitals: 15 microstates Some of these microstates have the same energy as each other, some have different energies. So the average energy is: Electronegativity is the 3 rd dimension of the periodic table. 37
3 Source: L.C. Allen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1989, 111, The metalloids are the elements roughly along the diagonal from B to Po. Some metalloids have both metallic and non-metallic allotropes. Note the general trends: 1. Elements with n = 2 valence orbitals are significantly more electronegative than the other elements in their respective groups. 2. Hydrogen has approx. same electronegativity as carbon. 3. Noble gases are the most electronegative elements in their period. 4. EN decreases down a group, except: B > Al < Ga and C > Si < Ge This is called the alternation effect. Increased nuclear charge accompanies filling of the 3d orbitals. The 3d electrons shield the 4p electrons poorly, making Ga and Ge more electronegative. 38
4 Consider again: C(s 2 p 2 ) Energy of the groundstate is given by the average of the energy of each microstate (cf. multiplet averaged energies in Allen s definition) Can do the same for C + (s 2 p) and C - (s 2 p 3 ) The resulting Mulliken electronegativity is in fact the electronegativity of the p- orbital of the C-atom! What are the electronegativities of (sp)p 2, (sp 2 )p, and sp 3 hybridized carbons? Source: Purcell & Kotz, Inorganic Chemistry, 1977 need to know the valence state promotion energies to calculate the orbital electronegativities. These energies can be calculated (see Hinze et al., JACS, 85, (1963), 148, and Hinze & Jaffe, J. Phys. Chem., 67, (1963), 1501.) 39
5 Comparison between the various scales: KEY TREND: Within the main group elements, electronegativity increases from left to right across a period and decreases down a group. Orbital electronegativities: Since atomic EN values depend on ionization potentials of individual electrons, EN = f(actual electron configuration) as expressed by the appropriate term symbol: IP(2s 2 2p 2 ) IP(2s 1 2p 3 ) i.e., the EN depends on which orbital an electron is removed from! orbital electronegativity 40
6 The results: Source: Purcell & Kotz, Inorganic Chemistry, 1977 Which is the most acidic? H-C C-H H 2 C=CH 2 H 3 C-CH 3 Take home message: The electronegativity of an atom is (in part) a function of its environment! 41
7 1.7 Hardness: Absolute hardness is the resistance of the chemical potential to change the number of electrons in other words: The harder a chemical species, the more difficult it will be to change its oxidation state. Pearson and Parr have derived the following definition for hardness η. η = ½(IE EA) Q. How does this differ from Mulliken s definition of electronegativity? Lit.: R.G. Parr, R.G. Pearson, JACS, 105, (1983), Absolute electronegativity χ: µ = chemical potential of the electrons 42
8 Absolute hardness η: Absolute softness σ: σ = 1/η Koopman's theorem (recall from CHEM 206): E HOMO -IP E LUMO -EA From these definitions: The larger the energy gap ΔE = E LUMO - E HOMO, the harder the chemical species. Note: Always IP EA for a neutral species Minimum hardness is = 0; maximum softness (achieved for bulk metals: σ ) Source: Tarr & Miessler, Inorganic Chemistry, Prentice-Hall, 1998: 43
9 1.8 Polarizability Polarizability α is an atom s ability to be distorted by an electric field (such as that of a neighboring ion). Atoms (and ions) are highly polarizable if their electron distribution can be distorted readily. High polarizability is most likely to occur when unfilled atomic orbitals lie close in energy to the highest occupied atomic orbital(s), i.e., when there is a small energy difference between highest occupied and lowest unoccupied orbitals. Closely separated frontier orbitals are typically found for large, heavy atoms and ions, whereas small, light atoms typically have widely spaced energy levels. Fajan s rules 1. Small, highly charged cations are able to polarize other atoms (high polarizing ability). 2. Large, highly charged anions are easily polarized. 3. Cations that do not have a noble-gas electron configuration are easily polarized (note that this refers in particular to transition metals, see CHEM365) 1.9 Atomic and ionic radii Atomic radius half the internuclear distance between neighboring atoms of the same element in a metal (metallic radius) or in a molecule (covalent radius). Ionic radius typically determined by assigning the radius of O 2- (in an O h hole of a solid oxide crystal) as 1.40 Å and subsequently determining other ionic radii from experimental data. KEY TREND: Atomic radii increase down a group. Within the main group atomic radii decrease from left to right across a period. 44
10 Inorganic Chemistry, 2 nd Ed. Shriver, Atkins and Langford, W. H. Freeman and Co., N.Y., NOTE: O 2- ionic radius is arbitrarily set at 1.40 Å; all others are derived from this. Question: Why is O 2- an obvious choice as a reference ion for radius measurements? Suggested readings: Chapter 9 Note that this is a chapter on periodic trends in general. Much of the content is cross-referenced elsewhere in the textbook. See your textbook for a table of atomic radii, p
11 Atomic Radii: Atomic Volume: Source: Shriver & Atkins, Inorganic Chemistry, 3 rd Edition, Freeman
362 Lecture 6 and 7. Spring 2017 Monday, Jan 30
 362 Lecture 6 and 7 Spring 2017 Monday, Jan 30 Quantum Numbers n is the principal quantum number, indicates the size of the orbital, has all positive integer values of 1 to (infinity) l is the angular
362 Lecture 6 and 7 Spring 2017 Monday, Jan 30 Quantum Numbers n is the principal quantum number, indicates the size of the orbital, has all positive integer values of 1 to (infinity) l is the angular
need another quantum number, m s it is found that atoms, substances with unpaired electrons have a magnetic moment, 2 s(s+1) where {s = m s }
 M polyelectronic atoms need another quantum number, m s it is found that atoms, substances with unpaired electrons have a magnetic moment, 2 s(s+1) where {s = m s } Pauli Exclusion Principle no two electrons
M polyelectronic atoms need another quantum number, m s it is found that atoms, substances with unpaired electrons have a magnetic moment, 2 s(s+1) where {s = m s } Pauli Exclusion Principle no two electrons
Electron Configuration and Periodic Trends - Chapter 5 section 3 Guided Notes
 Electron Configuration and Periodic Trends - Chapter 5 section 3 Guided Notes There are several important atomic characteristics that show predictable that you should know. Atomic Radius The first and
Electron Configuration and Periodic Trends - Chapter 5 section 3 Guided Notes There are several important atomic characteristics that show predictable that you should know. Atomic Radius The first and
Periodic Properties of the Elements
 Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements DEVELOPMENT OF THE PERIODIC TABLE Elements in the same group generally have similar chemical properties. Properties are not identical, however. Brown, LeMay,
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements DEVELOPMENT OF THE PERIODIC TABLE Elements in the same group generally have similar chemical properties. Properties are not identical, however. Brown, LeMay,
Explaining Periodic Trends. Saturday, January 20, 18
 Explaining Periodic Trends Many observable trends in the chemical and physical properties of elements are observable in the periodic table. Let s review a trend that you should already be familiar with,
Explaining Periodic Trends Many observable trends in the chemical and physical properties of elements are observable in the periodic table. Let s review a trend that you should already be familiar with,
Trends in the Periodic Table
 Trends in the Periodic Table A trend is a predictable change in a particular direction. Example: There is a trend in the alkali metals to increase in reactivity as you move down a group. Atomic Radius
Trends in the Periodic Table A trend is a predictable change in a particular direction. Example: There is a trend in the alkali metals to increase in reactivity as you move down a group. Atomic Radius
Journal of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry
 Journal of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry of Islamic Azad University of Iran, 11 (1) 1-13: Spring 214 (J. Phys. Theor. Chem. IAU Iran) ISSN 1735-2126 Investigation of relationship with electron configuration
Journal of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry of Islamic Azad University of Iran, 11 (1) 1-13: Spring 214 (J. Phys. Theor. Chem. IAU Iran) ISSN 1735-2126 Investigation of relationship with electron configuration
Chapter 1 Atomic Structure
 Chapter 1 Atomic Structure CHEM 511 Chapter 1 page 1 of 15 What is inorganic chemistry? The periodic table is made of elements, which are made of...? Define: atomic number (Z): Define: mass number (A):
Chapter 1 Atomic Structure CHEM 511 Chapter 1 page 1 of 15 What is inorganic chemistry? The periodic table is made of elements, which are made of...? Define: atomic number (Z): Define: mass number (A):
CHEMISTRY Topic #1: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercise 5.3
 CHEMISTRY 1000 Topic #1: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercise 5.3 Periodic Trends and Effective Nuclear Charge Imagine four atoms/ions: One has a nucleus with
CHEMISTRY 1000 Topic #1: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercise 5.3 Periodic Trends and Effective Nuclear Charge Imagine four atoms/ions: One has a nucleus with
PowerPoint to accompany. Chapter 6. Periodic Properties of the Elements
 PowerPoint to accompany Chapter 6 Periodic Properties of the Elements Development of the Periodic Table Elements in the same group generally have similar chemical properties. Properties are not identical,
PowerPoint to accompany Chapter 6 Periodic Properties of the Elements Development of the Periodic Table Elements in the same group generally have similar chemical properties. Properties are not identical,
Topic 3: Periodic Trends and Atomic Spectroscopy
 Topic 3: Periodic Trends and Atomic Spectroscopy Introduction Valence Electrons are those in the outer most shell of an element and are responsible for the bonding characteristics of that element. Core
Topic 3: Periodic Trends and Atomic Spectroscopy Introduction Valence Electrons are those in the outer most shell of an element and are responsible for the bonding characteristics of that element. Core
Molecular Orbitals. Based on Inorganic Chemistry, Miessler and Tarr, 4 th edition, 2011, Pearson Prentice Hall
 Molecular Orbitals Based on Inorganic Chemistry, Miessler and Tarr, 4 th edition, 2011, Pearson Prentice Hall Images from Miessler and Tarr Inorganic Chemistry 2011 obtained from Pearson Education, Inc.
Molecular Orbitals Based on Inorganic Chemistry, Miessler and Tarr, 4 th edition, 2011, Pearson Prentice Hall Images from Miessler and Tarr Inorganic Chemistry 2011 obtained from Pearson Education, Inc.
Chapter 7. Generally, the electronic structure of atoms correlates w. the prop. of the elements
 Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements I) Development of the P.T. Generally, the electronic structure of atoms correlates w. the prop. of the elements - reflected by the arrangement of the elements
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements I) Development of the P.T. Generally, the electronic structure of atoms correlates w. the prop. of the elements - reflected by the arrangement of the elements
CHAPTER 6. Chemical Periodicity
 CHAPTER 6 Chemical Periodicity 1 Chapter Goals 1. More About the Periodic Table Periodic Properties of the Elements 2. Atomic Radii 3. Ionization Energy (IE) 4. Electron Affinity (EA) 5. Ionic Radii 6.
CHAPTER 6 Chemical Periodicity 1 Chapter Goals 1. More About the Periodic Table Periodic Properties of the Elements 2. Atomic Radii 3. Ionization Energy (IE) 4. Electron Affinity (EA) 5. Ionic Radii 6.
Supporting Information for. Predicting the Stability of Fullerene Allotropes Throughout the Periodic Table MA 02139
 Supporting Information for Predicting the Stability of Fullerene Allotropes Throughout the Periodic Table Qing Zhao 1, 2, Stanley S. H. Ng 1, and Heather J. Kulik 1, * 1 Department of Chemical Engineering,
Supporting Information for Predicting the Stability of Fullerene Allotropes Throughout the Periodic Table Qing Zhao 1, 2, Stanley S. H. Ng 1, and Heather J. Kulik 1, * 1 Department of Chemical Engineering,
Lecture 4; January Electrons in Atoms: Magnetism; Term Symbols, Z eff, and Other Properties
 Lecture 4; January 2017 Electrons in Atoms: Magnetism; Term Symbols, Z eff, and Other Properties Three prototypical kinds of Magnetic Behavior Paramagnetism: atoms, molecules, and solids with unpaired
Lecture 4; January 2017 Electrons in Atoms: Magnetism; Term Symbols, Z eff, and Other Properties Three prototypical kinds of Magnetic Behavior Paramagnetism: atoms, molecules, and solids with unpaired
Valence bond theory accounts, at least qualitatively, for the stability of the covalent bond in terms of overlapping atomic orbitals.
 Molecular Orbital Theory Valence bond theory accounts, at least qualitatively, for the stability of the covalent bond in terms of overlapping atomic orbitals. Using the concept of hybridization, valence
Molecular Orbital Theory Valence bond theory accounts, at least qualitatively, for the stability of the covalent bond in terms of overlapping atomic orbitals. Using the concept of hybridization, valence
2011 CHEM 120: CHEMICAL REACTIVITY
 2011 CHEM 120: CHEMICAL REACTIVITY INORGANIC CHEMISTRY SECTION Lecturer: Dr. M.D. Bala Textbook by Petrucci, Harwood, Herring and Madura 15 Lectures (4/10-29/10) 3 Tutorials 1 Quiz 1 Take-home test https://chemintra.ukzn.ac.za/
2011 CHEM 120: CHEMICAL REACTIVITY INORGANIC CHEMISTRY SECTION Lecturer: Dr. M.D. Bala Textbook by Petrucci, Harwood, Herring and Madura 15 Lectures (4/10-29/10) 3 Tutorials 1 Quiz 1 Take-home test https://chemintra.ukzn.ac.za/
Chemical Bonding. Nuclear Charge. Nuclear Charge. Trends of the Periodic Table. Down the Table (from Top to Bottom):
 Trends of the Periodic Table Chemical Bonding TRENDS OF THE PERIODIC TABLE CHEM ISTRY 11 3 factors are usually discussed when explaining trends nuclear charge n value (outer most filled shell) Inter-electron
Trends of the Periodic Table Chemical Bonding TRENDS OF THE PERIODIC TABLE CHEM ISTRY 11 3 factors are usually discussed when explaining trends nuclear charge n value (outer most filled shell) Inter-electron
The wavefunction that describes a bonding pair of electrons:
 4.2. Molecular Properties from VB Theory a) Bonding and Bond distances The wavefunction that describes a bonding pair of electrons: Ψ b = a(h 1 ) + b(h 2 ) where h 1 and h 2 are HAOs on adjacent atoms
4.2. Molecular Properties from VB Theory a) Bonding and Bond distances The wavefunction that describes a bonding pair of electrons: Ψ b = a(h 1 ) + b(h 2 ) where h 1 and h 2 are HAOs on adjacent atoms
1.4 Estimating the effective nuclear charge: Slater Type Orbitals (STO)
 1.4 Estimating the effective nuclear charge: Slater Type Orbitals (STO) NOTE: This section does not appear in your textbook. For further understanding, consult Miessler and Tarr. PREMISE: We can calculate
1.4 Estimating the effective nuclear charge: Slater Type Orbitals (STO) NOTE: This section does not appear in your textbook. For further understanding, consult Miessler and Tarr. PREMISE: We can calculate
sharing or transferring electrons between atoms covalent ionic polar covalent Quantitative description: Quantum mechanics
 Chapter. 3 Chemical Bonding: The Classical Description Two or more atoms approach -> their electrons interact and form new arrangements of electrons with lower total potential energy than isolated atoms
Chapter. 3 Chemical Bonding: The Classical Description Two or more atoms approach -> their electrons interact and form new arrangements of electrons with lower total potential energy than isolated atoms
Chemical Bonding. Chemical Bonding 20/03/2015. The atomic radius increases from right to left. The atomic radius increases from top to bottom
 Chemical Bonding Atomic Radius: This distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron. Chemical Bonding Chemistry 11 Two factors must be taken into consideration in explaining this periodic trend: Increasing
Chemical Bonding Atomic Radius: This distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron. Chemical Bonding Chemistry 11 Two factors must be taken into consideration in explaining this periodic trend: Increasing
Why is it called a periodic table?
 The Periodic Table Why is it called a periodic table? The properties of the elements in the table repeat in a "periodic" way (specific pattern). Periodic law: There is a periodic repetition of chemical
The Periodic Table Why is it called a periodic table? The properties of the elements in the table repeat in a "periodic" way (specific pattern). Periodic law: There is a periodic repetition of chemical
Earth Solid Earth Rocks Minerals Atoms. How to make a mineral from the start of atoms?
 Earth Solid Earth Rocks Minerals Atoms How to make a mineral from the start of atoms? Formation of ions Ions excess or deficit of electrons relative to protons Anions net negative charge Cations net
Earth Solid Earth Rocks Minerals Atoms How to make a mineral from the start of atoms? Formation of ions Ions excess or deficit of electrons relative to protons Anions net negative charge Cations net
Periodic Trends (Section 5.3)
 Periodic Trends (Section 5.3) Periodic Trends (Section 5.3) 1. Atomic Radius: Periodic Trends (Section 5.3) 1. Atomic Radius: The distance from the nucleus to the outermost electrons. (See Figure 3.2,
Periodic Trends (Section 5.3) Periodic Trends (Section 5.3) 1. Atomic Radius: Periodic Trends (Section 5.3) 1. Atomic Radius: The distance from the nucleus to the outermost electrons. (See Figure 3.2,
Periodic Table trends
 2017/2018 Periodic Table trends Mohamed Ahmed Abdelbari Atomic Radius The size of an atom is defined by the edge of its orbital. However, orbital boundaries are fuzzy and in fact are variable under different
2017/2018 Periodic Table trends Mohamed Ahmed Abdelbari Atomic Radius The size of an atom is defined by the edge of its orbital. However, orbital boundaries are fuzzy and in fact are variable under different
Periodic Trends in Properties of Homonuclear
 Chapter 8 Periodic Trends in Properties of Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules Up to now, we have discussed various physical properties of nanostructures, namely, two-dimensional - graphene-like structures:
Chapter 8 Periodic Trends in Properties of Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules Up to now, we have discussed various physical properties of nanostructures, namely, two-dimensional - graphene-like structures:
Chem 115: Chapter 9 Dr. Babb
 Periodic Properties of the Atom Properties that depend on position of element in the periodic table. Factors that affect the periodic properties: 1. Principal quantum number of valence shell (n valence
Periodic Properties of the Atom Properties that depend on position of element in the periodic table. Factors that affect the periodic properties: 1. Principal quantum number of valence shell (n valence
CHEM 103 Quantum Mechanics and Periodic Trends
 CHEM 103 Quantum Mechanics and Periodic Trends Lecture Notes April 11, 2006 Prof. Sevian Agenda Predicting electronic configurations using the QM model Group similarities Interpreting measured properties
CHEM 103 Quantum Mechanics and Periodic Trends Lecture Notes April 11, 2006 Prof. Sevian Agenda Predicting electronic configurations using the QM model Group similarities Interpreting measured properties
MOLECULAR STRUCTURE. Molecular Structure - B. Molecular Structure - B. Molecular Structure - B. Molecular Structure - B. Molecular Structure - B
 MOLECULAR STRUCTURE Molecular Orbital all orbitals of the appropriate symmetry contribute to a molecular orbital. Bundet Boekfa Chem Div, Faculty Lib Arts & Sci Kasetsart University Kamphaeng Saen Campus
MOLECULAR STRUCTURE Molecular Orbital all orbitals of the appropriate symmetry contribute to a molecular orbital. Bundet Boekfa Chem Div, Faculty Lib Arts & Sci Kasetsart University Kamphaeng Saen Campus
Periodic Table. Metalloids diagonal between metals and nonmetals. Have metallic and non-metallic properties
 Chapter 6 Periodic Table Most elements are metals Metals are shiny, malleable, ductile, and good conductors of heat and electricity Most metals are solid at room temperature Non-metals in upper right corner,
Chapter 6 Periodic Table Most elements are metals Metals are shiny, malleable, ductile, and good conductors of heat and electricity Most metals are solid at room temperature Non-metals in upper right corner,
4 Periodic Trends. 1.Atomic Radii (AR) 2.Ionization Energy (IE) 3.Ionic Radii (IR) 4.Electronegativity (EN) Periodic Trends > Types of Periodic Trends
 Periodic Trends > Types of Periodic Trends 4 Periodic Trends 1.Atomic Radii (AR) 2.Ionization Energy (IE) 3.Ionic Radii (IR) 4.Electronegativity (EN) 1 of 31 Periodic Trends > Trends in Atomic Size The
Periodic Trends > Types of Periodic Trends 4 Periodic Trends 1.Atomic Radii (AR) 2.Ionization Energy (IE) 3.Ionic Radii (IR) 4.Electronegativity (EN) 1 of 31 Periodic Trends > Trends in Atomic Size The
Trends in Atomic Size. Atomic Radius-one half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms of the same element when the atoms are joined
 Periodic trends Trends in Atomic Size Atomic Radius-one half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms of the same element when the atoms are joined Trends in Atomic Size Group Trend: Atomic radii of
Periodic trends Trends in Atomic Size Atomic Radius-one half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms of the same element when the atoms are joined Trends in Atomic Size Group Trend: Atomic radii of
The Electronic Theory of Chemistry
 JF Chemistry CH1101 The Electronic Theory of Chemistry Dr. Baker bakerrj@tcd.ie Module Aims: To provide an introduction to the fundamental concepts of theoretical and practical chemistry, including concepts
JF Chemistry CH1101 The Electronic Theory of Chemistry Dr. Baker bakerrj@tcd.ie Module Aims: To provide an introduction to the fundamental concepts of theoretical and practical chemistry, including concepts
- Chapter 7 - Periodic Properties of the Elements
 - Chapter 7 - Periodic Properties of the Elements Summary 7.1 Development of the periodic table 7.2 Effective nuclear charge 7.3 Size of atoms and ions 7.4 Ionization energy 7.5 Electron affinities 7.6
- Chapter 7 - Periodic Properties of the Elements Summary 7.1 Development of the periodic table 7.2 Effective nuclear charge 7.3 Size of atoms and ions 7.4 Ionization energy 7.5 Electron affinities 7.6
1. Atomic and Ionic radius 2. Ionization energy 3. Electronegativity 4. Electron Affinity PERIODIC TRENDS
 PERIODIC TRENDS Nov 11 9:05 PM Periodic trends that change in a predictable way: 1. Atomic and Ionic radius 2. Ionization energy 3. Electronegativity 4. Electron Affinity Nov 11 8:20 PM 1 Atomic Radius
PERIODIC TRENDS Nov 11 9:05 PM Periodic trends that change in a predictable way: 1. Atomic and Ionic radius 2. Ionization energy 3. Electronegativity 4. Electron Affinity Nov 11 8:20 PM 1 Atomic Radius
Electron configurations follow the order of sublevels on the periodic table.
 Electron configurations follow the order of sublevels on the periodic table. 1 The periodic table consists of sublevel blocks arranged in order of increasing energy. Groups 1A(1)-2A(2) = s level Groups
Electron configurations follow the order of sublevels on the periodic table. 1 The periodic table consists of sublevel blocks arranged in order of increasing energy. Groups 1A(1)-2A(2) = s level Groups
Lecture 2: Bonding in solids
 Lecture 2: Bonding in solids Electronegativity Van Arkel-Ketalaar Triangles Atomic and ionic radii Band theory of solids Molecules vs. solids Band structures Analysis of chemical bonds in Reciprocal space
Lecture 2: Bonding in solids Electronegativity Van Arkel-Ketalaar Triangles Atomic and ionic radii Band theory of solids Molecules vs. solids Band structures Analysis of chemical bonds in Reciprocal space
Periods: horizontal rows (# 1-7) 2. Periodicity the of the elements in the same group is explained by the arrangement of the around the nucleus.
 The Modern Periodic Table 1. An arrangement of the elements in order of their numbers so that elements with properties fall in the same column (or group). Groups: vertical columns (#1-18) Periods: horizontal
The Modern Periodic Table 1. An arrangement of the elements in order of their numbers so that elements with properties fall in the same column (or group). Groups: vertical columns (#1-18) Periods: horizontal
Periodic Relationships
 Periodic Relationships 1 Tabulation of Elements Mendeleev (1869) Arranged by mass Tabulation by chem.& physical properties Predicted missing elements and properties 2 Modern Periodic Table Argon vs. potassium
Periodic Relationships 1 Tabulation of Elements Mendeleev (1869) Arranged by mass Tabulation by chem.& physical properties Predicted missing elements and properties 2 Modern Periodic Table Argon vs. potassium
Lectures in Advanced Inorganic Chemistry
 Republic of Iraq The Ministry of Higher Education & Scientific Research University:Karbala College:Science Department:Chemistry Stage:M.Sc Lectures in Advanced Inorganic Chemistry By Assist.Prof. Dr. Hayder
Republic of Iraq The Ministry of Higher Education & Scientific Research University:Karbala College:Science Department:Chemistry Stage:M.Sc Lectures in Advanced Inorganic Chemistry By Assist.Prof. Dr. Hayder
CHEM 115 Electron Configurations and
 CHEM 115 Electron Configurations and Periodic Trends Lecture 20 Prof. Sevian 1 Agenda Electron configurations Ground state vs. excited state Periodic properties Ionization energy Atomic radius Others Interpreting
CHEM 115 Electron Configurations and Periodic Trends Lecture 20 Prof. Sevian 1 Agenda Electron configurations Ground state vs. excited state Periodic properties Ionization energy Atomic radius Others Interpreting
2.Ionization Energies
 2.Ionization Energies Ionization energy, IE, is the energy required to remove one electron from an atom or ion; an endothermic process that is, A A + + 1 e - H = +ve The energy, in kj mol -1, required
2.Ionization Energies Ionization energy, IE, is the energy required to remove one electron from an atom or ion; an endothermic process that is, A A + + 1 e - H = +ve The energy, in kj mol -1, required
Interactive Periodic Trends: A Graphical Experience
 CHM 101 Name Interactive Periodic Trends: A Graphical Experience This activity explores a variety of properties of the chemical elements as they vary based on position on the periodic table. You should
CHM 101 Name Interactive Periodic Trends: A Graphical Experience This activity explores a variety of properties of the chemical elements as they vary based on position on the periodic table. You should
8.1 Early Periodic Tables CHAPTER 8. Modern Periodic Table. Mendeleev s 1871 Table
 8.1 Early Periodic Tables CHAPTER 8 Periodic Relationships Among the Elements 1772: de Morveau table of chemically simple substances 1803: Dalton atomic theory, simple table of atomic masses 1817: Döbreiner's
8.1 Early Periodic Tables CHAPTER 8 Periodic Relationships Among the Elements 1772: de Morveau table of chemically simple substances 1803: Dalton atomic theory, simple table of atomic masses 1817: Döbreiner's
Periodic Trends. Homework: Lewis Theory. Elements of his theory:
 Periodic Trends There are various trends on the periodic table that need to be understood to explain chemical bonding. These include: Atomic/Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Electron Affinity
Periodic Trends There are various trends on the periodic table that need to be understood to explain chemical bonding. These include: Atomic/Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Electron Affinity
Chemical symbols. Know names and symbols of elements #1 30, plus. Rb, Cs, Sr, Ba, Ag, Au, Cd, Hg, Pt, Ga, Ge, As, Sn, Pb, Se, Br, I, and U
 Chemical symbols Know names and symbols of elements #1 30, plus Rb, Cs, Sr, Ba, Ag, Au, Cd, Hg, Pt, Ga, Ge, As, Sn, Pb, Se, Br, I, and U Coulomb s Law F = attractive/repulsive force Q 1, Q 2 = charges
Chemical symbols Know names and symbols of elements #1 30, plus Rb, Cs, Sr, Ba, Ag, Au, Cd, Hg, Pt, Ga, Ge, As, Sn, Pb, Se, Br, I, and U Coulomb s Law F = attractive/repulsive force Q 1, Q 2 = charges
Chapter 3 Atoms and Ionic Bonds
 Chapter 3 Atoms and Ionic Bonds LEARNING OBJECTIVES SUMMARIES 1. Periodic trends: Know how each of the following are affected by the size of the valence shell (n), the nuclear charge (# of protons), and
Chapter 3 Atoms and Ionic Bonds LEARNING OBJECTIVES SUMMARIES 1. Periodic trends: Know how each of the following are affected by the size of the valence shell (n), the nuclear charge (# of protons), and
Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table
 Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table The periodic table can be used as a guide for electron configurations. The period number is the value of n. Groups 1A and 2A have the s-orbital filled. Groups
Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table The periodic table can be used as a guide for electron configurations. The period number is the value of n. Groups 1A and 2A have the s-orbital filled. Groups
Ionic Bonding. Example: Atomic Radius: Na (r = 0.192nm) Cl (r = 0.099nm) Ionic Radius : Na (r = 0.095nm) Cl (r = 0.181nm)
 Ionic Bonding Ion: an atom or molecule that gains or loses electrons (acquires an electrical charge). Atoms form cations (+charge), when they lose electrons, or anions (- charge), when they gain electrons.
Ionic Bonding Ion: an atom or molecule that gains or loses electrons (acquires an electrical charge). Atoms form cations (+charge), when they lose electrons, or anions (- charge), when they gain electrons.
Periodic Relationships
 Periodic Relationships 1 Tabulation of Elements Mendeleev (1869) Arranged by mass Tabulation by chem.& physical properties Predicted missing elements and properties 2 Modern Periodic Table Argon vs. potassium
Periodic Relationships 1 Tabulation of Elements Mendeleev (1869) Arranged by mass Tabulation by chem.& physical properties Predicted missing elements and properties 2 Modern Periodic Table Argon vs. potassium
Schrodinger equation
 CH1. Atomic Structure orbitals periodicity 1 Schrodinger equation - (h 2 /2p 2 m e2 ) [d 2 Y/dx 2 +d 2 Y/dy 2 +d 2 Y/dz 2 ] + V Y = E Y h = constant m e = electron mass V = potential E gives quantized
CH1. Atomic Structure orbitals periodicity 1 Schrodinger equation - (h 2 /2p 2 m e2 ) [d 2 Y/dx 2 +d 2 Y/dy 2 +d 2 Y/dz 2 ] + V Y = E Y h = constant m e = electron mass V = potential E gives quantized
Unit 2 Part 2: Periodic Trends
 Unit 2 Part 2: Periodic Trends Outline Classification of elements using properties Representative elements, transition elements Metals, nonmetals and metalloids Classification of elements using electron
Unit 2 Part 2: Periodic Trends Outline Classification of elements using properties Representative elements, transition elements Metals, nonmetals and metalloids Classification of elements using electron
THE PERIODIC LAW. History of the Periodic Table
 THE PERIODIC LAW History of the Periodic Table CHAPTER 5 Mendeleev & Chemical Periodicity Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev accepts atomic mass values discussed at the First International Congress of Chemists
THE PERIODIC LAW History of the Periodic Table CHAPTER 5 Mendeleev & Chemical Periodicity Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev accepts atomic mass values discussed at the First International Congress of Chemists
THE PERIODIC LAW CHAPTER 5
 THE PERIODIC LAW CHAPTER 5 History of the Periodic Table In September 1860, scientists gathered together for the First International Congress of Chemists to settle the issue of atomic mass. Italian scientist
THE PERIODIC LAW CHAPTER 5 History of the Periodic Table In September 1860, scientists gathered together for the First International Congress of Chemists to settle the issue of atomic mass. Italian scientist
Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry
 Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry Lecture No. 4 Date :25/10 /2012 Dr. Mohammed Hamed --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry Lecture No. 4 Date :25/10 /2012 Dr. Mohammed Hamed --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[3.4] The Periodic Table and Periodic Trends
![[3.4] The Periodic Table and Periodic Trends [3.4] The Periodic Table and Periodic Trends](/thumbs/83/87323071.jpg) [3.4] The Periodic Table and Periodic Trends Father of the Periodic Table Dmitri Mendeleev: Scientist who did a lot of work in the development of the modern periodic table Early periodic tables were arranged
[3.4] The Periodic Table and Periodic Trends Father of the Periodic Table Dmitri Mendeleev: Scientist who did a lot of work in the development of the modern periodic table Early periodic tables were arranged
Explaining Periodic Trends
 Explaining Periodic Trends! Many observable trends in the chemical and physical properties of elements are observable in the periodic table.! On trends you may be familiar with is reactivity, which is
Explaining Periodic Trends! Many observable trends in the chemical and physical properties of elements are observable in the periodic table.! On trends you may be familiar with is reactivity, which is
POGIL 6 Key Periodic Table Trends (Part 2)
 Honors Chem Block Name POGIL 6 Key Periodic Table Trends (Part 2) is a measure of the ability of an atom s nucleus to attract electrons from a different atom within a covalent bond. A higher electronegativity
Honors Chem Block Name POGIL 6 Key Periodic Table Trends (Part 2) is a measure of the ability of an atom s nucleus to attract electrons from a different atom within a covalent bond. A higher electronegativity
SCH3U- R. H. KING ACADEMY ATOMIC STRUCTURE HANDOUT NAME:
 Particle Theory of Matter Matter is anything that has and takes up. All matter is made up of very small. Each pure substance has its of particle, from the particles of other pure substances. Particles
Particle Theory of Matter Matter is anything that has and takes up. All matter is made up of very small. Each pure substance has its of particle, from the particles of other pure substances. Particles
Trends in the Periodic Table revisited! SCH4U1 SP04
 Trends in the Periodic Table revisited! SCH4U1 SP04 Factors Affecting the Properties Many of the properties of the elements are related to the force of attraction between the nucleus and the electrons.
Trends in the Periodic Table revisited! SCH4U1 SP04 Factors Affecting the Properties Many of the properties of the elements are related to the force of attraction between the nucleus and the electrons.
The Periodic Law Notes (Chapter 5)
 The Periodic Law Notes (Chapter 5) I. History of the Periodic Table About 70 elements were known by 1850 (no noble gases) but there didn t appear to be a good way of arranging or relating them to study.
The Periodic Law Notes (Chapter 5) I. History of the Periodic Table About 70 elements were known by 1850 (no noble gases) but there didn t appear to be a good way of arranging or relating them to study.
Big Idea: Ionic Bonds: Ionic Bonds: Metals: Nonmetals: Covalent Bonds: Ionic Solids: What ions do atoms form? Electron Electron
 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
CHEMISTRY XL-14A CHEMICAL BONDS
 CHEMISTRY XL-14A CHEMICAL BONDS July 16, 2011 Robert Iafe Office Hours 2 July 18-July 22 Monday: 2:00pm in Room MS-B 3114 Tuesday-Thursday: 3:00pm in Room MS-B 3114 Chapter 2 Overview 3 Ionic Bonds Covalent
CHEMISTRY XL-14A CHEMICAL BONDS July 16, 2011 Robert Iafe Office Hours 2 July 18-July 22 Monday: 2:00pm in Room MS-B 3114 Tuesday-Thursday: 3:00pm in Room MS-B 3114 Chapter 2 Overview 3 Ionic Bonds Covalent
Valence electron- Energy sublevel- Transition element- Period 10. Electronegativity- Alkaline earth metal- 11. Ion- Halogen- 12.
 Mrs. Hilliard 1. Valence electron 2. Period 3. Alkaline earth metal 4. Halogen 5. Metalloid 6. Hund s Rule 7. Representative element 8. Energy sublevel 9. Transition element 10. Electronegativity 11. Ion
Mrs. Hilliard 1. Valence electron 2. Period 3. Alkaline earth metal 4. Halogen 5. Metalloid 6. Hund s Rule 7. Representative element 8. Energy sublevel 9. Transition element 10. Electronegativity 11. Ion
Periodic Properties (Booklet Solution)
 Periodic Properties (Booklet Solution) Foundation Builders (Objective). (B) Law of triads states that in the set of three elements arranged in increasing order of atomic weight, having similar properties,
Periodic Properties (Booklet Solution) Foundation Builders (Objective). (B) Law of triads states that in the set of three elements arranged in increasing order of atomic weight, having similar properties,
Topic 3 Periodicity 3.2 Physical Properties. IB Chemistry T03D02
 Topic 3 Periodicity 3.2 Physical Properties IB Chemistry T03D02 3.1 Physical Properties hrs 3.2.1 Define the terms first ionization energy and electronegativity. (1) 3.2.2 Describe and explain the trends
Topic 3 Periodicity 3.2 Physical Properties IB Chemistry T03D02 3.1 Physical Properties hrs 3.2.1 Define the terms first ionization energy and electronegativity. (1) 3.2.2 Describe and explain the trends
Periodicity SL (answers) IB CHEMISTRY SL
 (answers) IB CHEMISTRY SL Syllabus objectives 3.1 Periodic table Understandings: The periodic table is arranged into four blocks associated with the four sublevels s, p, d, and f. The periodic table consists
(answers) IB CHEMISTRY SL Syllabus objectives 3.1 Periodic table Understandings: The periodic table is arranged into four blocks associated with the four sublevels s, p, d, and f. The periodic table consists
Worksheet 5 - Chemical Bonding
 Worksheet 5 - Chemical Bonding The concept of electron configurations allowed chemists to explain why chemical molecules are formed from the elements. In 1916 the American chemist Gilbert Lewis proposed
Worksheet 5 - Chemical Bonding The concept of electron configurations allowed chemists to explain why chemical molecules are formed from the elements. In 1916 the American chemist Gilbert Lewis proposed
Chapter 5 Notes Chemistry; The Periodic Law The Periodic Table The periodic table is used to organize the elements in a meaningful way.
 Chapter 5 Notes Chemistry; The Periodic Law The Periodic Table The periodic table is used to organize the elements in a meaningful way. As a consequence of this organization, there are periodic properties
Chapter 5 Notes Chemistry; The Periodic Law The Periodic Table The periodic table is used to organize the elements in a meaningful way. As a consequence of this organization, there are periodic properties
Lecture B6 Molecular Orbital Theory. Sometimes it's good to be alone.
 Lecture B6 Molecular Orbital Theory Sometimes it's good to be alone. Covalent Bond Theories 1. VSEPR (valence shell electron pair repulsion model). A set of empirical rules for predicting a molecular geometry
Lecture B6 Molecular Orbital Theory Sometimes it's good to be alone. Covalent Bond Theories 1. VSEPR (valence shell electron pair repulsion model). A set of empirical rules for predicting a molecular geometry
CHAPTER 2: BONDING AND PROPERTIES
 CHAPTER 2: BONDING AND PROPERTIES ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What promotes bonding? What types of bonds are there? What properties are inferred from bonding? Chapter 2-1 Atomic Structure (Freshman Chem.) atom
CHAPTER 2: BONDING AND PROPERTIES ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What promotes bonding? What types of bonds are there? What properties are inferred from bonding? Chapter 2-1 Atomic Structure (Freshman Chem.) atom
Chapter 8: Periodic Properties of the Elements
 C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 8 P a g e 1 Chapter 8: Periodic Properties of the Elements Homework: Read Chapter 8. Work out sample/practice exercises Check for the MasteringChemistry.com assignment
C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 8 P a g e 1 Chapter 8: Periodic Properties of the Elements Homework: Read Chapter 8. Work out sample/practice exercises Check for the MasteringChemistry.com assignment
List how many protons, neutrons, and electrons in the following isotopes
 List how many protons, neutrons, and electrons in the following isotopes Silver 109 47 p + and e ; 62 n 0 Molybdenum 96 42 p + and e ; 54 n 0 Scandium 45 21 p + and e ; 24 n 0 1of 26 2of 26 Review: Which
List how many protons, neutrons, and electrons in the following isotopes Silver 109 47 p + and e ; 62 n 0 Molybdenum 96 42 p + and e ; 54 n 0 Scandium 45 21 p + and e ; 24 n 0 1of 26 2of 26 Review: Which
3-1 Lewis Electron-Dot Diagram
 3-1 Lewis Electron-Dot Diagram Lewis-dot diagrams, are diagrams that show the bonding between atoms of a molecule, & the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule. Duet rule Octet rule beyond
3-1 Lewis Electron-Dot Diagram Lewis-dot diagrams, are diagrams that show the bonding between atoms of a molecule, & the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule. Duet rule Octet rule beyond
Studying the properties of substances and the reactions that transform substances into other substances.
 3 CHEMISTRY Studying the properties of substances and the reactions that transform substances into other substances. Improving agricultural production, curing many diseases, increasing the efficiency of
3 CHEMISTRY Studying the properties of substances and the reactions that transform substances into other substances. Improving agricultural production, curing many diseases, increasing the efficiency of
CHEM 101: CHAPTER 11: CHEMICAL BONDS: THE FORMATION OF COMPOUNDS FROM ATOMS
 1 CHEM 101: CHAPTER 11: CHEMICAL BONDS: THE FORMATION OF COMPOUNDS FROM ATOMS PERIODIC TRENDS: See pages 214-216, 221 Table 11.3, and 227 + 228 of text. Lewis Structures of Atoms: The Lewis Dot Diagram
1 CHEM 101: CHAPTER 11: CHEMICAL BONDS: THE FORMATION OF COMPOUNDS FROM ATOMS PERIODIC TRENDS: See pages 214-216, 221 Table 11.3, and 227 + 228 of text. Lewis Structures of Atoms: The Lewis Dot Diagram
Genesis of Periodic Classification and Mendeleev Periodic Table:
 Genesis of Periodic Classification and Mendeleev Periodic Table: Classification of elements and periodicity in properties: Periodic table helps in the systematic study of most of the elements found in
Genesis of Periodic Classification and Mendeleev Periodic Table: Classification of elements and periodicity in properties: Periodic table helps in the systematic study of most of the elements found in
The Periodic Table and Chemical Reactivity
 The and Chemical Reactivity Noble gases Less electronegative elements More electronegative elements Then what is electronegativity? The tendency of an atom to attract an electron (or electron density)
The and Chemical Reactivity Noble gases Less electronegative elements More electronegative elements Then what is electronegativity? The tendency of an atom to attract an electron (or electron density)
Discovery of Elements. Dmitri Mendeleev Stanislao Canizzaro (1860) Modern Periodic Table. Henry Moseley. PT Background Information
 Discovery of Elements Development of the Periodic Table Chapter 5 Honors Chemistry 412 At the end of the 1700 s, only 30 elements had been isolated Included most currency metals and some nonmetals New
Discovery of Elements Development of the Periodic Table Chapter 5 Honors Chemistry 412 At the end of the 1700 s, only 30 elements had been isolated Included most currency metals and some nonmetals New
Trends in the Periodic Table
 Trends in the Periodic Table Effective nuclear charge: < effective nuclear charge is the attraction felt by the valence electrons from the nucleus < increases across a period : increases across because
Trends in the Periodic Table Effective nuclear charge: < effective nuclear charge is the attraction felt by the valence electrons from the nucleus < increases across a period : increases across because
6.3 Periodic Trends > Chapter 6 The Periodic Table. 6.3 Periodic Trends. 6.1 Organizing the Elements. 6.2 Classifying the Elements
 1 63 Periodic Trends > Chapter 6 The Periodic Table 61 Organizing the Elements 62 Classifying the Elements 63 Periodic Trends 2 63 Periodic Trends > CHEMISTRY & YOU How are trends in the weather similar
1 63 Periodic Trends > Chapter 6 The Periodic Table 61 Organizing the Elements 62 Classifying the Elements 63 Periodic Trends 2 63 Periodic Trends > CHEMISTRY & YOU How are trends in the weather similar
Chapter 9 Bonding - 1. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Chapter 9 Bonding - 1 Dr. Sapna Gupta Lewis Dot Symbol Lewis dot symbols is a notation where valence electrons are shown as dots. Draw the electrons symmetrically around the sides (top, bottom, left and
Chapter 9 Bonding - 1 Dr. Sapna Gupta Lewis Dot Symbol Lewis dot symbols is a notation where valence electrons are shown as dots. Draw the electrons symmetrically around the sides (top, bottom, left and
Trends in Atomic Size. What are the trends among the elements for atomic size? The distances between atoms in a molecule are extremely small.
 63 Periodic Trends > 63 Periodic Trends > CHEMISTRY & YOU Chapter 6 The Periodic Table 61 Organizing the Elements 62 Classifying the Elements 63 Periodic Trends How are trends in the weather similar to
63 Periodic Trends > 63 Periodic Trends > CHEMISTRY & YOU Chapter 6 The Periodic Table 61 Organizing the Elements 62 Classifying the Elements 63 Periodic Trends How are trends in the weather similar to
 CHAPTER 6 CHEMICAL BONDING SHORT QUESTION WITH ANSWERS Q.1 Dipole moments of chlorobenzene is 1.70 D and of chlorobenzene is 2.5 D while that of paradichlorbenzene is zero; why? Benzene has zero dipole
CHAPTER 6 CHEMICAL BONDING SHORT QUESTION WITH ANSWERS Q.1 Dipole moments of chlorobenzene is 1.70 D and of chlorobenzene is 2.5 D while that of paradichlorbenzene is zero; why? Benzene has zero dipole
CHEMGGURU.ORG YOUTUBE: CHEMGGURU
 Modern Periodic Law: Properties of elements are the periodic function to their atomic numbers. The periodicity in properties is due to repetition of similar outer shell electronic configuration at a certain
Modern Periodic Law: Properties of elements are the periodic function to their atomic numbers. The periodicity in properties is due to repetition of similar outer shell electronic configuration at a certain
Chapter 8. Periodic Properties of the Element
 Chapter 8 Periodic Properties of the Element Mendeleev (1834 1907) Ordered elements by atomic mass Saw a repeating pattern of properties Periodic law when the elements are arranged in order of increasing
Chapter 8 Periodic Properties of the Element Mendeleev (1834 1907) Ordered elements by atomic mass Saw a repeating pattern of properties Periodic law when the elements are arranged in order of increasing
Chapter 13: Phenomena
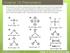 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 7 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table
 Chapter 7 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009 1 7.1 Development of the Periodic Table 1864 - John Newlands - Law of Octaves- every 8th element had similar properties
Chapter 7 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table Copyright McGraw-Hill 2009 1 7.1 Development of the Periodic Table 1864 - John Newlands - Law of Octaves- every 8th element had similar properties
Electronegativity Trends
 Ashley Robison My Preferences Site Tools Popular pages MindTouch User Guide FAQ Sign Out If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it
Ashley Robison My Preferences Site Tools Popular pages MindTouch User Guide FAQ Sign Out If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it
Periodic Relationships Among the Elements
 Periodic Relationships Among the Elements Chapter 8 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. When the Elements Were Discovered 2 ns 1 Ground State Electron
Periodic Relationships Among the Elements Chapter 8 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. When the Elements Were Discovered 2 ns 1 Ground State Electron
Getting to know the Periodic Table: Recall: Elements are organized based on atomic number and similar properties
 Getting to know the Periodic Table: Recall: Elements are organized based on atomic number and similar properties 1. Find your staircase on the right side of the periodic table. Feel free to make the lines
Getting to know the Periodic Table: Recall: Elements are organized based on atomic number and similar properties 1. Find your staircase on the right side of the periodic table. Feel free to make the lines
"My name is Bond." N2 (Double 07)
 "My name is Bond." N2 (Double 07) "Metallic Bond." Element 3: Lithium [He]2s 1 "My name is Bond." In the last lecture we identified three types of molecular bonding: van der Waals Interactions (Ar) Covalent
"My name is Bond." N2 (Double 07) "Metallic Bond." Element 3: Lithium [He]2s 1 "My name is Bond." In the last lecture we identified three types of molecular bonding: van der Waals Interactions (Ar) Covalent
Chapter 9 Bonding. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Chapter 9 Bonding Dr. Sapna Gupta Lewis Dot Symbol Lewis dot symbols is a notation where valence electrons are shown as dots. Draw the electrons symmetrically around the sides (top, bottom, left and right)
Chapter 9 Bonding Dr. Sapna Gupta Lewis Dot Symbol Lewis dot symbols is a notation where valence electrons are shown as dots. Draw the electrons symmetrically around the sides (top, bottom, left and right)
Chapter 10: Modern Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table. How does atomic structure relate to the periodic table? 10.1 Electromagnetic Radiation
 Chapter 10: Modern Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table How does atomic structure relate to the periodic table? 10.1 Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic (EM) radiation is a form of energy that exhibits
Chapter 10: Modern Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table How does atomic structure relate to the periodic table? 10.1 Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic (EM) radiation is a form of energy that exhibits
Chapter 7. Periodic Properties of the Elements
 Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements periodic table the most significant tool that chemist use for organizing and remembering chemical facts 7.1 Development of the periodic table discovery of
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements periodic table the most significant tool that chemist use for organizing and remembering chemical facts 7.1 Development of the periodic table discovery of
4/4/2013. Covalent Bonds a bond that results in the sharing of electron pairs between two atoms.
 A chemical bond is a mutual electrical attraction between the nucleus and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together. Why bond? As independent particles, atoms have a high potential
A chemical bond is a mutual electrical attraction between the nucleus and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together. Why bond? As independent particles, atoms have a high potential
Unit 2 Structures and Properties. Chapter 5 Chemical Bonding
 Section 5.1 Elements and Compounds Unit 2 Structures and Properties Chapter 5 Chemical Bonding LEWIS DOT DIAGRAMS (electron dot) show only the valence electrons (Group Number) around the chemical symbol.
Section 5.1 Elements and Compounds Unit 2 Structures and Properties Chapter 5 Chemical Bonding LEWIS DOT DIAGRAMS (electron dot) show only the valence electrons (Group Number) around the chemical symbol.
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH
 C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE The Ionic Bond Formation of Ions The
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE The Ionic Bond Formation of Ions The
