Theoretical approach to the corrosion inhibition efficiency of some pyrimidine derivatives using DFT method
|
|
|
- Logan Price
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Computational Methods in Molecular Design, 2012, 2 (1):1-15 ( ISSN : CODEN (USA): JCMMDA Theoretical approach to the corrosion inhibition efficiency of some pyrimidine derivatives using DFT method P. Udhayakala a*, T. V. Rajendiran b and S. Gunasekaran c a Department of Chemistry, Dr.MGR Educational and Research Institute, Chennai, India b Department of Chemistry, Pachaiyappa s College, Chennai, India c Department of Physics, Spectrophysics Research Laboratory, Pachaiyappa s College, Chennai, India ABSTRACT The adsorption mechanism and inhibition performance of two pyrimidine derivatives 6-methyl-4- phenyl-4,5-dihydropyrimidine-2-thiol (THPT1) and 4,6-diphenyl 4,5-dihydropyrimidine-2-thiol (THPT2) were investigated as corrosion inhibitors using Density functional theory (DFT) at the B3LYP/6-31G(d,p) basis set level. The result showed that the theoretically calculated order of IE was found to be in close agreement with the experimental order. The calculated quantum chemical parameters correlated to the inhibition efficiency are E HOMO (highest occupied molecular orbital energy), E LUMO (lowest unoccupied molecular orbital energy), the energy gap( E), hardness(η), Softness(S), dipole moment(µ), electron affinity(ea), ionization potential(ie), the absolute electronegativity (χ) and the fraction of electron transferred ( N). The local reactivity has been analyzed through the condensed Fukui function and condensed softness indices in order to compare the possible sites for nucleophilic and electrophilic attacks. Keywords: Pyrimidine, reactivity, DFT, Fukui function, softness indices. INTRODUCTION Corrosion of metals is a major industrial problem that has attracted many investigation and researches [1,2]. The use of inhibitors is one of the most practical methods to protect metals against corrosion, especially in acidic media[3]. Most efficient inhibitors are organic compounds containing electronegative functional groups and π-electrons in triple or conjugated double bonds. Researchers conclude that the adsorption on the metal surface depends mainly on the physicochemical properties of the inhibitor group, such as the functional group, molecular electronic structure, electronic density at the donor atom, π orbital character and the molecular 1 Available online at
2 size [4-6]. A number of heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen, oxygen and sulphur either in the aromatic or long chain carbon system have been reported to be effective inhibitors [7,8]. The planarity and the lone electron pairs in the hetero atoms are important features that determine the adsorption of molecules on the metallic surface [9].The inhibition efficiency has been closely related to the inhibitor adsorption abilities and the molecular properties for different kinds of organic compounds [10-14]. The power of the inhibition depends on the molecular structure of the inhibitor. Organic compounds, which can donate electrons to unoccupied d orbital of metal surface to form coordinate covalent bonds and can also accept free electrons from the metal surface by using their anti bonding orbital to form feedback bonds, constitute excellent corrosion inhibitors. Quantum chemical calculations have been widely used to study reaction mechanism. They have been proved to be a very powerful tool for studying corrosion inhibition mechanism [15-20]. Density functional theory (DFT)[21,22] has provided a very useful framework for developing new criteria for rationalizing, predicting, and eventually understanding many aspects of chemical processes [23-27]. A variety of chemical concepts which are now widely used as descriptors of chemical reactivity, e.g., electronegativity [24] hardness or softness quantities etc., appear naturally within DFT [21]. The Fukui function[26] representing the relative local softness of the electron gas, measures the local electron density/population displacements corresponding to the inflow of a single electron. The reactive ability of the inhibitor is closely linked to their frontier molecular orbital (MO), including highest occupied molecular orbital, HOMO, and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital, LUMO, and the other parameters such as hardness and softness. Quantum chemical studies have been successfully performed to link the corrosion inhibition efficiency with molecular orbital (MO) energy levels for some kinds of organic compounds [28,29]. D.G. De Kowalewski et al. have investigated the experimental and DFT study of substituent effects on scalar J(13C, 13C) couplings in pyrimidines [30]. Synthesis and antifungal activities of some novel Pyrimidine derivatives were investigated by Li Sun et al.[31] The pyrimidine derivatives investigated in the present work are: 6-methyl-4-phenyl-4,5-dihydropyrimidine-2-thiol (THPT1) 4,6-diphenyl 4,5-dihydropyrimidine-2-thiol (THPT2) The object of the present study is to carry out a theoretical study on the electronic and structural parameters of two pyrimidine derivatives and the effect of these parameters on their inhibition efficiency of corrosion of mild steel using the quantum chemically calculated parameters. Results obtained showed that THPT1<THPT2. It is well correlated with the experimental results [32]. From the calculations we will try to explain which adsorption site is favoured to bind to the metal surface. Computational calculations were obtained by means of B3LYP/6-31G(d,p) method. Parameters like E HOMO, E LUMO, energy gap( E), dipole moment(µ), global hardness(η), softness(s), the fraction of electron transferred ( N) and total energy change ( E) were calculated. The local reactivity has been analyzed by means of the Fukui indices, since they 2
3 indicate the reactive regions, in the form of the nucleophilic and electrophilic behaviour of each atom in the molecule. MATERIALS AND METHODS Computational Details In computational chemistry tools, the DFT offers the fundamentals for interpreting multiple chemical concept used in different branches of chemistry. In order to explore the theoreticalexperimental consistency, quantum chemical calculations were performed with complete geometry optimizations using Gaussian-03 software package [33]. Geometry optimization were carried out by B3LYP functional at the 6-31G(d,p) basis set and at the density functional theory (DFT) level. Recently, Density functional theory (DFT) has been used to analyze the characteristics of the inhibitor/ surface mechanism and to describe the structural nature of the inhibitor in the corrosion process [34,35]. (THPT1) (THPT2) Figure 1. Names, molecular structure and the abbreviation of the inhibitors investigated 3
4 THPT1 THPT2 Figure 2. Optimized structure of THPT1 and THPT2 calculated with the B3LYP/6-31G(d,p) Density functional theory (DFT) [22] has been quite successful in providing theoretical basis for popular qualitative chemical concepts like electronegativity (χ), hardness (η ), softness(s) and local ones such as Fukui function, F(r) and local softness, s(r). 4
5 The basic relationship of the density functional theory of chemical reactivity is precisely, the one established by Parr, Donnelly, Levy and Palke [36], that links the chemical potential of DFT with the first derivative of the energy with respect to the number of electrons, and therefore with the negative of the electronegativity χ. E µ = = χ N v ( r ) Where µ is the chemical potential, E is the total energy, N is the number of electrons, and ν(r) is the external potential of the system. Hardness (η ) has been defined within the DFT as the second derivative of the E with respect to N as v( r) property which measures both the stability and reactivity of the molecule [37]. 2 E η = 2 N v( r ) where v( r) and µ are, respectively, the external and electronic chemical potentials. From the value of the total electronic energy, the ionization potential (IE) and electron affinity (EA) of the inhibitors are calculated using the following equations and hence χ and η are calculated. IE = E E ( N 1 ) (N) EA = E E ( N ) ( N+ 1) Where E is the total electronic energy, N is the number of electrons, and v(r) is the external electrostatic potential that the electrons feel due to the nuclei. The higher HOMO energy corresponds to the more reactive molecule in the reactions with electrophiles, while lower LUMO energy is essential for molecular reactions with nucleophiles [38]. χ = η = IE + EA 2 IE EA 2 The global softness(s) is the inverse of the global hardness [37] 1 S = η 5
6 Electronegativity, hardness and softness have proved to be very useful quantities in the chemical reactivity theory. When two systems, Fe and inhibitor, are brought together, electrons will flow from lower χ (inhibitor) to higher χ (Fe), until the chemical potentials become equal. The number of transferred electrons ( N) was also calculated [39] by using the equation below. N = χfe 2( η Fe χinh + η inh Where χ Fe and χ inh denote the absolute electronegativity of iron and inhibitor molecule respectively η Fe and η inh denote the absolute hardness of iron and the inhibitor molecule respectively. In this study, we use the theoretical value of χ Fe =7.0 ev and η Fe = 0 for the computation of number of transferred electrons[39]. The difference in electronegativity drives the electron transfer, and the sum of the hardness parameters acts as a resistance [40]. The local selectivity of a corrosion inhibitor is best analyzed by means of condensed Fukui function. The global electrophilicity index was introduced by Parr[41] and is given by ω = µ 2 /2η. According to the definition, this index measures the propensity of chemical species to accept electrons. A good, more reactive, nucleophile is characterized by lower value of µ, ω; and conversely a good electrophile is characterized by a high value of µ, ω. This new reactivity index measures the stabilization in energy when the system acquires an additional electronic charge N from the environment. The change in electron density is the nucleophilic f + (r) and electrophilic f - (r) Fukui functions, which can be calculated using the finite difference approximation as follows [42]. f + (r) = ρ N+1 (r) - ρ N (r) (for nucleophilic attack) f - (r) = ρ N (r) - ρ N-1 (r) (for electrophilic attack) where ρ N+1, ρ N and ρ N-1 are the electronic densities of anionic, neutral and cationic species respectively. Condensed softness indices allowing the comparison of reactivity between similar atoms of different molecules can be calculated easily starting from the relation between the Fukui function f (r) and the local softness s(r) [43] ρ( r) N s( r) = = f ( r) S N µ v( r ) v( r ) From this relation, one can infer that local softness and Fukui function are closely related, and they should play an important role in the field of chemical reactivity. 6
7 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The energy of the highest occupied molecular orbital (E HOMO ) measures the tendency towards the donation of electron by a molecule [44]. Therefore, higher values of E HOMO indicate better tendency towards the donation of electron, enhancing the adsorption of the inhibitor on mild steel and therefore better inhibition efficiency. E LUMO indicates the ability of the molecule to accept electrons. The binding ability of the inhibitor to the metal surface increases with increasing of the HOMO and decreasing of the LUMO energy values. Frontier molecular orbital diagrams of THPT1 and THPT2 is represented in figure 3. Table 1. Quantum chemical parameters for THPT1 and THPT2 calculated using B3LYP/6-31G(d,p). Parameters THPT1 THPT2 E HOMO (ev) E LUMO (ev) Energy gap( E) (ev) Dipole moment (Debye) According to the frontier molecular orbital theory(fmo) of chemical reactivity, transition of electron is due to interaction between highest occupied molecular orbital(homo) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) of reacting species[45]. E HOMO is a quantum chemical parameter which is often associated with the electron donating ability of the molecule. High value of E HOMO is likely to a tendency of the molecule to donate electrons to appropriate acceptor molecule of low empty molecular orbital energy[46]. The inhibitor does not only donate electron to the unoccupied d orbital of the metal ion but can also accept electron from the d- orbital of the metal leading to the formation of a feed back bond. The highest value of E HOMO (ev) of THPT2 indicates the better inhibition efficiency than the other compound. The energy gap, ( E = E LUMO E HOMO ) is an important parameter as a function of reactivity of the inhibitor molecule towards the adsorption on the metallic surface. As E decreases the reactivity of the molecule increases leading to increase in the %IE of the molecule. Lower values of the energy difference will render good inhibition efficiency, because the energy to remove an electron from the last occupied orbital will be low [47]. Reportedly, excellent corrosion inhibitors are usually organic compounds which not only offer electrons to unoccupied orbital of the metal but also accept free electrons from the metal [15]. A molecule with a low energy gap is more polarizable and is generally associated with the high chemical activity and low kinetic stability and is termed soft molecule [48]. The results as indicated in table 1 shows that inhibitor THPT2 has the lowest energy gap, this means that the molecule could have better performance as corrosion inhibitor. The dipole moment (µ in Debye) is another important electronic parameter that results from non uniform distribution of charges on the various atoms in the molecule. The high value of dipole moment probably increases the adsorption between chemical compound and metal surface [49]. The energy of the deformability increases with the increase in µ, making the molecule easier to 7
8 adsorb at the Fe surface. The volume of the inhibitor molecules also increases with the increase of µ. This increases the contact area between the molecule and surface of iron and increasing the corrosion inhibition ability of inhibitors. In our study the value (Debye) of THPT2 enumerates its better inhibition efficiency. Ionization energy is a fundamental descriptor of the chemical reactivity of atoms and molecules. High ionization energy indicates high stability and chemical inertness and small ionization energy indicates high reactivity of the atoms and molecules[50]. The low ionization energy (ev) of THPT2 indicates the high inhibition efficiency. Absolute hardness and softness are important properties to measure the molecular stability and reactivity. It is apparent that the chemical hardness fundamentally signifies the resistance towards the deformation or polarization of the electron cloud of the atoms, ions or molecules under small perturbation of chemical reaction. A hard molecule has a large energy gap and a soft molecule has a small energy gap[51]. In our present study THPT2 with low hardness value (ev) compared with other compound have a low energy gap. Normally, the inhibitor with the least value of global hardness(hence the highest value of global softness) is expected to have the highest inhibition efficiency [52]. For the simplest transfer of electron, adsorption could occur at the part of the molecule where softness(s), which is a local property, has a highest value[53]. THPT2 with the softness value of has the highest inhibition efficiency. Table 2. Quantum chemical parameters for THPT1 and THPT2 calculated using B3LYP/6-31G(d,p). Parameters THPT1 THPT2 E N (au) E N-1 (au) E N+1 (au) IE(eV) EA(eV) η (ev) S (ev) χ (ev) ω N The table 2 shows the order of electronegativity as THPT1>THPT2. Hence an increase in the difference of electronegativity between the metal and the inhibitor is observed in the order THPT2>THPT1. According to Sanderson s electronegativity equalization principle [54], THPT1 with a high electronegativity and low difference of electronegativity quickly reaches 8
9 equalization and hence low reactivity is expected which efficiency. in turn indicates low inhibition HOMO of THPT1 LUMO of THPT1 9
10 HOMO of THPT2 LUMO of THPT2 Figure 3. Frontier molecular orbital diagrams of THPT1 and THPT2 by B3LYP/6-31G(d,p) 10
11 Table 3. Fukui and local softness indices for nucleophilic and electrophilic attacks on THPT1 atoms calculated from electron densities Atom No f k + f k - s k + s k - 1 C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 H 6 N 7 N 8 S 9 H 10 C 11 C 12 C 13 C 14 H 15 C 16 H 17 C 18 H 19 H 20 H 21 C 22 H 23 H 24 H The number of electrons transferred ( N) was also calculated and tabulated in Table 2. Values of N show that the inhibition efficiency resulting from electron donation agrees with Lukovits s study [55]. If N < 3.6, the inhibition efficiency increases by increasing electron-donating ability of these inhibitors to donate electrons to the metal surface and it increases in the following order: THPT1<THPT2. The results indicate that N values correlates strongly with experimental inhibition efficiencies. Thus, the highest fraction of electrons transferred is associated with the best inhibitor (THPT2), while the least fraction is associated with the inhibitor that has the least inhibition efficiency (THPT1). There is a general consensus by several authors that the more negatively charged an heteroatom, is the more it can be adsorbed on the metal surface through the donor-acceptor type reaction [15]. It is important to consider the situation corresponding to a molecule that is going to receive a certain amount of charge at some centre and is going to back donate a certain amount of charge 11
12 through the same centre or another one [56]. Parr and Yang proposed that larger value of Fukui function indicate more reactivity [26]. Hence greater the value of condensed Fukui function, the more reactive is the particular atomic centre in the molecule. The f k +,measures the changes of density when the molecules gains electrons and it corresponds to reactivity with respect to nucleophilic attack. On the other hand, f k - corresponds to reactivity with respect to electrophilic attack or when the molecule loss electrons. Table 4. Fukui and local softness indices for nucleophilic and electrophilic attacks in THPT2 atoms calculated from electron densities. Atom No f k + f k - s k + s k - C 1 C 2 C 3 C 4 H 5 N 6 N 7 S 8 H 9 C 10 C 11 C 12 C 13 H 14 C 15 H 16 C 17 H 18 H 19 H 20 C 21 C 22 C 23 C 24 H 25 C 26 H 27 C 28 H 29 H 30 H
13 The FMO diagram of THPT1 and THPT2 indicates the lack of electron cloud in LUMO near the thiol group in C1 showing the nucleophilic attack at the C1 site which is confirmed by the fukui function f k +. In case of HOMO of THPT1 the dense electron cloud around N6 indicates the site of electrophilic attack. The same is the case around S8 in THPT2 as confirmed by the Fukui function f k - too. CONCLUSION The following conclusions can be drawn from this study: 1. The inhibition efficiency of pyrimidine derivatives obtained Quantum chemically increase with the increase in E HOMO, and decrease in E LUMO and energy gap ( E). THPT2 has the highest inhibition efficiency because it had the highest HOMO energy and N values and it was most capable of offering electrons. 2. The parameters like hardness(η), Softness(S), dipole moment(µ), electron affinity(ea) ionization potential(ie), electronegativity(χ) and the fraction of electron transferred ( N) confirms the inhibition efficiency in the order of THPT2>THPT1. 3. Fukui function shows the nucleophilic and electrophilic attacking sites in the pyrimidine derivatives. REFERENCES [1] S.Tarab, A.M.Al.Turkustani, Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta,2006, 24, 53. [2] N.O.Eddy, E.E.Ebenso, Pigment and Resin Tech, 2010, 39, 77. [3] S.A.Umoren, I.B.Obot, and N.O. Obi-Egbedi, Mater. Sci. 2009, 44(1), 274. [4] I.B.Obot and N.O.Obi-Egbedi, Surface Review and Letters, 2008, 15(6), 903. [5] I.B.Obot and N.O. Obi-Egbedi, Colloids and surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 2008, 330, 207. [6] H.Ju, Z.P.Kai and Y. Li, Corros. Sci., 2008, 50, 865. [7] N.O.Eddy and S.A.Odoemelam, Adv. Nat. & Appl. Sci. 2008, 2(1), 35. [8] S.A.Umoren, I.B.Obot, E.E.Ebenso and N.O.Obi-Egbedi, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci, 2008,3, [9] S.S. Abd El-Rehim, M.A.M. Ibrahim and F.F.J. Khaled, Appl. Electrochem., 1999, 29, 593. [10] H.L.Wang, R.B.Liu and J.Xin, Corros. Sci., 2004, 46, [11] S.Rengamati, S.Muralidharan, M.Anbu Kulamdainathan, S.Venkatakrishna Iyer. J Appl Electrochem., 1994, 24, 355 [12] E.E.Ebenso, Bull. Electrochem., 2003,19, 209. [13] N.Khalil, Electrochim. Acta., 2003, 48, [14] S.L. Granese, Corros., 1988,44, 322. [15] G.Breket, E.Hur and C.Ogretir, J.Mol.stru(THEOCHEM),2002,578,79. [16] J. Vosta and J. Eliasek, Corros. Sci., 1971, 11, 223. [17] P.Choa, Q.Liang and Y. Li, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2005, 252, [18] Y.Xiao-Ci, Z.Hong, L.Ming-Dao, R.Hong-Xuang and Y. Lu- An, Corros. Sci., 2000,42, 645. [19] F.Bentiss, M.Lebrini and M.Lagrenee, Corros. Sci., 2005,47, [20] R.M.Issa, M.K.Awad and F.M. Atlam, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2008,255,
14 [21] P.Hohenberg and W. Kohn, Phys. Rev., 1964,136B, 864. [22] R.G.Parr and W. Yang, Density Functional Theory of Atoms and Molecules; Oxford University Press: New York, [23] M.H.Cohen, In Topics in Current Chemistry; R.F.Nalewajski, Ed.; Springer-Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 1996, 183, 143. [24] R.T.Sanderson, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1952, [25] M.K.Awad, J.Electroanal.Chem, 2004,,567,219 [26] R.G.Parr and W. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1984, 106, [27] R.G.Pearson, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1963, 85, [28] J.Fang and J.Li, J.Mol. Struct. (THEOCHEM), 2002, 593, 179. [29] T.Arslan, F.Kandemirli, E.E.Ebenso, I. Love and H. Alemu, Corros Sci., 2009, 51, 35. [30] D.G.De Kowalewski, E.Díez, A.LEsteban, V.Barone, J.E.Peralta and R.H. Contreras, Magn. Reson Chem. 2004, 42(11),938. [31] Li Sun, Jie Wu, Lingzi Zhang, Min Luo and Dequn Sun, Molecules 2011, 16, [32] P.Sathya, K.Parameswari, S.Chitra and A.Selvaraj, E-Journal of Chemistry, 2009, 6(S1), S65-S-74. [33] M.J.Frisch, G.W.Trucks and H.B.Schlegel et al. Gaussian 03, Gaussian, Inc.: Pittsburgh PA, [34] L.Rodriguez-Valdez, A.Martinez-Villafane and D.Glossman- Mitnik, J.Mol.Struct. (THEO CHEM). 2005,716, 61. [35] M.Lashkari and M.R. Arshadi, Chem. Phys., 2004, 299, 131. [36] R.G. Parr, R.A. Donnelly, M. Levy, W.E. Palke, J. Chem. Phys. 1978, 68, [37] R.G. Parr, R.G. Pearson, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1983, 105, [38] A.Rauk, Orbital interaction Theory of Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edn John Wiley & Sons: Newyork, 2001,34 [39] R.G.Pearson, Inorg.Chem., 1988, 27,734. [40] H.Chermette, J. Comput. Chem., 1999, 20, 129. [41] R.G.Parr, L.Szentpaly and S.Liu, J.Am.Che.Soc, 1999, 121,1922. [42] Nnabuk O Eddy, Stanislav R. Stoyanov and Eno.E.Ebenso, Int.J.Electro Chem.Sci., 2010, 5, [43] H.Wang, X.Wang, H.Wang, L.Wang and A. Liu, J. Mol. Model., 2007, 13, 147. [44] H.E.El Ashry, A.El Nemr, S.A.Esawy and S.Ragab, Electrochimica Acta, 2006,51, [45] A.Y.Musa, A.H.Kadhum, A.B.Mohamad, A.b.Rohoma and H.Mesmari, J.Mol.Struct, 2010,969,233. [46] G.Gece and S.Bilgic, Corros.Sci, 2009, 51, [47] I.B.Obot, N.O.Obi-Egbedi ans S.A.Umoren, Int. J. Electro Chem. Sci., 2009,4,863. [48] I. Fleming, Frontier Orbitals and Organic Chemical Reactions, John Wiley and Sons, New York, [49] X. Li, S. Deng, H. Fu, T. Li, Electrochim. Acta. 2009, 54, [50] Sandip K.Rajak, Nazmul Islam and Dulal C.Ghosh, J.Quantum information Science, 2011, 1, 87. [51] N.O. Obi-Egbedi, I.B. Obot, M.I. El-Khaiary, S.A. Umoren and E.E. Ebenso, Int. J. Electro Chem. Sci., 2011, [52] E.E. Ebenso, D.A. Isabirye, N.O. Eddy, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, [53] R. Hasanov, M. Sadikglu, S. Bilgic, Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, [54] P. Geerlings and F. De Proft, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2002, 3,
15 [55] I. Lukovits, E. Kalman, F. Zucchi, Corrosion, 2001,57, 3. [56] B.Gomez, N.V.Likhanova, M.A.Dominguez-Aguilar, R.Martinez-Palou, A.Vela and J.Gasquez, J.Phy.Chem B, 2006,110,
A theoretical study of some barbiturates as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(4):1027-1039 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 A theoretical study of some barbiturates as corrosion
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(4):1027-1039 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 A theoretical study of some barbiturates as corrosion
Journal of Advanced Scientific Research DFT APPROACH ON CORROSION INHIBITION PERFORMANCE OF THIOSEMICARBAZONE DERIVATIVES ON METALLIC IRON
 Rajendran et al., J Adv Sci Res, 2016, 7(1): 32-37 32 Journal of Advanced Scientific Research Available online through http://www.sciensage.info/jasr ISSN 0976-9595 Research Article DFT APPROACH ON CORROSION
Rajendran et al., J Adv Sci Res, 2016, 7(1): 32-37 32 Journal of Advanced Scientific Research Available online through http://www.sciensage.info/jasr ISSN 0976-9595 Research Article DFT APPROACH ON CORROSION
Density functional theory calculations on corrosion inhibitory action of five azlactones on mild steel
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(7):117-127 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Density functional theory calculations on corrosion
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(7):117-127 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Density functional theory calculations on corrosion
DFT study on the adsorption mechanism of some phenyltetrazole substituted compounds as effective corrosion inhibitors for mild steel
 Available online at www.derpharmachemica.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharma Chemica, 2013, 5(6):111-124 (http://derpharmachemica.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-413X CODEN (USA): PCHHAX DFT study on
Available online at www.derpharmachemica.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharma Chemica, 2013, 5(6):111-124 (http://derpharmachemica.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-413X CODEN (USA): PCHHAX DFT study on
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences
 AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences ISSN:1991-8178 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Theoretical Study for the Effect of Hydroxyl Radical on the Electronic Properties of Cyclobutadiene
AENSI Journals Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences ISSN:1991-8178 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Theoretical Study for the Effect of Hydroxyl Radical on the Electronic Properties of Cyclobutadiene
New Hydrazine Derivatives as Corrosion for mild steel in phosphoric acid medium. Part B: Theoretical investigation.
 New Hydrazine Derivatives as Corrosion for mild steel in phosphoric acid medium. Part B: Theoretical investigation. M.E. Belghiti 1, Y. Karzazi 1,, S. Tighadouini 1, A. Dafali *1, C. Jama 3, I. Warad 4,
New Hydrazine Derivatives as Corrosion for mild steel in phosphoric acid medium. Part B: Theoretical investigation. M.E. Belghiti 1, Y. Karzazi 1,, S. Tighadouini 1, A. Dafali *1, C. Jama 3, I. Warad 4,
Quantum Chemical Studies on the Inhibiting Effect of Bipyrazoles on Steel Corrosion in HCl
 ISS: 0973-4945; CODE ECJHAO E- Chemistry http://www.e-journals.net 2010, 7(2), 419-424 Quantum Chemical Studies on the Inhibiting Effect of Bipyrazoles on Steel Corrosion in HCl K. LAAREJ, M. BOUACHRIE
ISS: 0973-4945; CODE ECJHAO E- Chemistry http://www.e-journals.net 2010, 7(2), 419-424 Quantum Chemical Studies on the Inhibiting Effect of Bipyrazoles on Steel Corrosion in HCl K. LAAREJ, M. BOUACHRIE
Research Article. DFT calculations for corrosion inhibition of copper by tetrazole derivatives
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(1):763-773 Research Article ISS : 0975-7384 CODE(USA) : JCPRC5 DFT calculations for corrosion inhibition of copper
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(1):763-773 Research Article ISS : 0975-7384 CODE(USA) : JCPRC5 DFT calculations for corrosion inhibition of copper
Thiamine Hydrochloride as a Potential Inhibitor for Aluminium Corrosion in 1.0 M HCl: Mass Loss and DFT Studies
 Journal of Computational Methods in Molecular Design, 2018, 8 (1):13-25 ISSN : 2231-3176 CODEN (USA): JCMMD Thiamine Hydrochloride as a Potential Inhibitor for Aluminium Corrosion in 1.0 M HCl: Mass Loss
Journal of Computational Methods in Molecular Design, 2018, 8 (1):13-25 ISSN : 2231-3176 CODEN (USA): JCMMD Thiamine Hydrochloride as a Potential Inhibitor for Aluminium Corrosion in 1.0 M HCl: Mass Loss
Structure-Corrosion Inhibition Performance Relationship: Application to Some Natural Free Acids and Antioxidants
 Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 2018, 36(1), 23-34 DOI: 10.4152/pea.201801023 PORTUGALIAE ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA ISSN 1647-1571 Structure-Corrosion Inhibition Performance Relationship: Application to Some
Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 2018, 36(1), 23-34 DOI: 10.4152/pea.201801023 PORTUGALIAE ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA ISSN 1647-1571 Structure-Corrosion Inhibition Performance Relationship: Application to Some
Elshafie A. M. GadP0F
 P Jabir International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 10, October-015 570 Adsorpitivity and corrosion inhibtion performance of -(alkyloxy)-n,n,n-tris(-hydroxyethyl)--oxoethanaminium
P Jabir International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 10, October-015 570 Adsorpitivity and corrosion inhibtion performance of -(alkyloxy)-n,n,n-tris(-hydroxyethyl)--oxoethanaminium
Computational Studies for Inhibitory Action of 2-Mercapto-1-Methylimidazole Tautomers on Steel Using of Density Functional Theory Method (DFT)
 International Journal of Computational and Theoretical Chemistry 2016; 4(1): 1-6 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijctc doi: 10.11648/j.ijctc.20160401.11 ISSN: 2376-7286 (Print); ISSN: 2376-7308
International Journal of Computational and Theoretical Chemistry 2016; 4(1): 1-6 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijctc doi: 10.11648/j.ijctc.20160401.11 ISSN: 2376-7286 (Print); ISSN: 2376-7308
Journal of Computational Methods in Molecular Design, 2013, 3 (1):1-8. Scholars Research Library (
 Journal of Computational Methods in Molecular Design, 2013, 3 (1):1-8 Scholars Research Library (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN : 2231-3176 CODEN (USA): JCMMDA Theoretical study
Journal of Computational Methods in Molecular Design, 2013, 3 (1):1-8 Scholars Research Library (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN : 2231-3176 CODEN (USA): JCMMDA Theoretical study
Quantum Mechanical Study on the Adsorption of Drug Gentamicin onto γ-fe 2
 ORIENTAL JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal www.orientjchem.org ISSN: 0970-00 X CODEN: OJCHEG 015, Vol. 31, No. (3): Pg. 1509-1513 Quantum Mechanical
ORIENTAL JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal www.orientjchem.org ISSN: 0970-00 X CODEN: OJCHEG 015, Vol. 31, No. (3): Pg. 1509-1513 Quantum Mechanical
Theoretical Study of the Mechanism of Corrosion Inhibition of Carbon Steel in Acidic Solution by 2-aminobenzothaizole and 2- Mercatobenzothiazole
 Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 13 (2018) 3535 3554, doi: 10.20964/2018.04.50 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Theoretical Study of the Mechanism of Corrosion Inhibition
Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 13 (2018) 3535 3554, doi: 10.20964/2018.04.50 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Theoretical Study of the Mechanism of Corrosion Inhibition
Additional Halogen Group (F, Cl, and Br) to 2-Phenylimidazole[1,2α]pyridine. Computational Study
![Additional Halogen Group (F, Cl, and Br) to 2-Phenylimidazole[1,2α]pyridine. Computational Study Additional Halogen Group (F, Cl, and Br) to 2-Phenylimidazole[1,2α]pyridine. Computational Study](/thumbs/82/86257742.jpg) IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Additional Halogen Group (F, Cl, and Br) to 2-Phenylimidazole[1,2α]pyridine on Corrosion Inhibition Properties: A Computational
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Additional Halogen Group (F, Cl, and Br) to 2-Phenylimidazole[1,2α]pyridine on Corrosion Inhibition Properties: A Computational
Global and Reactivity Descriptors Studies of Cyanuric Acid Tautomers in Different Solvents by using of Density Functional Theory (DFT)
 Global and Reactivity Descriptors Studies of Cyanuric Acid Tautomers in Different Solvents by using of Density Functional Theory (DFT) Numbury Surendra Babu 1, Didugu Jayaprakash 1 Department of Chemistry,
Global and Reactivity Descriptors Studies of Cyanuric Acid Tautomers in Different Solvents by using of Density Functional Theory (DFT) Numbury Surendra Babu 1, Didugu Jayaprakash 1 Department of Chemistry,
DFT based Study of interaction between Frontier Orbitals of Transition Metal Halides and Thioamides
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol. 3, No.3, pp 1571-1579, July-Sept 2011 DFT based Study of interaction between Frontier Orbitals of Transition Metal Halides
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol. 3, No.3, pp 1571-1579, July-Sept 2011 DFT based Study of interaction between Frontier Orbitals of Transition Metal Halides
Inhibition of Aluminium Corrosion in Hydrochloric Acid Using Nizoral and the Effect of Iodide Ion Addition
 ISSN: 0973-4945; CODEN ECJHAO E- Chemistry http://www.e-journals.net 2010, 7(3), 837-843 Inhibition of Aluminium Corrosion in Hydrochloric Acid Using Nizoral and the Effect of Iodide Ion Addition I.B.
ISSN: 0973-4945; CODEN ECJHAO E- Chemistry http://www.e-journals.net 2010, 7(3), 837-843 Inhibition of Aluminium Corrosion in Hydrochloric Acid Using Nizoral and the Effect of Iodide Ion Addition I.B.
Computational Investigations on Curcumin and Demethoxycurcumin as Corrosion Inhibitors: A Comparative Analysis
 Computational Investigations on Curcumin and Demethoxycurcumin as Corrosion Inhibitors: A Comparative Analysis 1 V. Kavitha, 2 N. Gunavathy 1 Research scholar, 2 Assistant professor, Department of Chemistry,
Computational Investigations on Curcumin and Demethoxycurcumin as Corrosion Inhibitors: A Comparative Analysis 1 V. Kavitha, 2 N. Gunavathy 1 Research scholar, 2 Assistant professor, Department of Chemistry,
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(2): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(2):641-645 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Synthesis, characterization and theoretical study
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(2):641-645 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Synthesis, characterization and theoretical study
Quantum Chemical Assessment of Two Natural Compounds: Vasicine and Vasicinone as Green Corrosion Inhibitors.
 Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 13 (2018) 3200 3209, doi: 10.20964/2018.04.57 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Quantum Chemical Assessment of Two Natural Compounds: Vasicine
Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 13 (2018) 3200 3209, doi: 10.20964/2018.04.57 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org Quantum Chemical Assessment of Two Natural Compounds: Vasicine
Journal of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry
 Journal of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry of Islamic Azad University of Iran, 11 (1) 1-13: Spring 214 (J. Phys. Theor. Chem. IAU Iran) ISSN 1735-2126 Investigation of relationship with electron configuration
Journal of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry of Islamic Azad University of Iran, 11 (1) 1-13: Spring 214 (J. Phys. Theor. Chem. IAU Iran) ISSN 1735-2126 Investigation of relationship with electron configuration
QUANTITATIVE STRUCTURE ACTIVITY RELATIONSHIPSOFSOME ATENOLOL AND PROPRANOLOLDERIVATIVES
 Vol. 9 No. 2 189 202 April June 2016 ISSN: 09741496 eissn: 09760083 CODEN: RJCABP http://www.rasayanjournal.com http://www.rasayanjournal.co.in QUANTITATIVE STRUCTURE ACTIVITY RELATIONSHIPSOFSOME ATENOLOL
Vol. 9 No. 2 189 202 April June 2016 ISSN: 09741496 eissn: 09760083 CODEN: RJCABP http://www.rasayanjournal.com http://www.rasayanjournal.co.in QUANTITATIVE STRUCTURE ACTIVITY RELATIONSHIPSOFSOME ATENOLOL
Chemistry Research Journal, 2018, 3(2): Research Article
 , 2018, 3(2):120-124 Available online www.chemrj.org Research Article ISSN: 2455-8990 CODEN(USA): CRJHA5 The First Calculation to the Proton (H + ) Absolute Hardness Robson Fernandes de Farias Universidade
, 2018, 3(2):120-124 Available online www.chemrj.org Research Article ISSN: 2455-8990 CODEN(USA): CRJHA5 The First Calculation to the Proton (H + ) Absolute Hardness Robson Fernandes de Farias Universidade
Bincy Joseph, Sam John, K K Aravindakshan & Abraham Joseph*
 Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 17, November 2010, pp. 425-430 Inhibition of mild steel corrosion in 1 M hydrochloric acid using (E)-4-(2- chlorobenzylideneamino)-6-methyl-3-thioxo-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-triazin-5(2h)-one
Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 17, November 2010, pp. 425-430 Inhibition of mild steel corrosion in 1 M hydrochloric acid using (E)-4-(2- chlorobenzylideneamino)-6-methyl-3-thioxo-3,4-dihydro-1,2,4-triazin-5(2h)-one
Quantum chemical studies on the structures of some heterocyclic azo disperse dyes
 Quantum chemical studies on the structures of some heterocyclic azo disperse dyes Nesrin Tokay, a* Zeynel Seferoğlu, b Cemil Öğretir, c and Nermin Ertan b a Hacettepe University, Faculty of Science, Chemistry
Quantum chemical studies on the structures of some heterocyclic azo disperse dyes Nesrin Tokay, a* Zeynel Seferoğlu, b Cemil Öğretir, c and Nermin Ertan b a Hacettepe University, Faculty of Science, Chemistry
International Journal of Pure and Applied Researches; Volume 1(1)/2015
 Computational tudies and Multivariate Analysis of Global and Local Reactivity Descriptors of Five Membered Heterocycles Molecules by Density Functional Theory (DFT). urendra Babu Department of Chemistry
Computational tudies and Multivariate Analysis of Global and Local Reactivity Descriptors of Five Membered Heterocycles Molecules by Density Functional Theory (DFT). urendra Babu Department of Chemistry
DFT calculations of effective reactive sites of inositol
 Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 56A, July 2017, pp. 786-790 DFT calculations of effective reactive sites of inositol D Jeevitha a, K Sadasivam a, * & R Praveena b a Department of Physics, b Department
Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 56A, July 2017, pp. 786-790 DFT calculations of effective reactive sites of inositol D Jeevitha a, K Sadasivam a, * & R Praveena b a Department of Physics, b Department
Introduction. Loutfy H. Madkour 1 S. K. Elroby. bonding the metal iron surface by donating electrons to the metal.
 Int J Ind Chem (2015) 6:165 184 DI 10.1007/s40090-015-0039-7 RESEARC Inhibitive properties, thermodynamic, kinetics and quantum chemical calculations of polydentate Schiff base compounds as corrosion inhibitors
Int J Ind Chem (2015) 6:165 184 DI 10.1007/s40090-015-0039-7 RESEARC Inhibitive properties, thermodynamic, kinetics and quantum chemical calculations of polydentate Schiff base compounds as corrosion inhibitors
DFT STUDY OF Co 2+ AND Fe 2+ - URACIL COMPLEXES IN THE GAS PHASE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DFT STUDY OF Co 2+ AND Fe 2+ - URACIL COMPLEXES IN THE GAS PHASE Raghab Parajuli* Department
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DFT STUDY OF Co 2+ AND Fe 2+ - URACIL COMPLEXES IN THE GAS PHASE Raghab Parajuli* Department
AB INITIO MODELING OF THE STRUCTURAL DEFECTS IN AMIDES
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 9(4), 2011, 1564-1568 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com AB INITIO MODELING OF THE STRUCTURAL DEFECTS IN AMIDES M. FATHIMA BEGUM, HEMA TRESA VARGHESE a, Y. SHEENA MARY a, C.
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 9(4), 2011, 1564-1568 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com AB INITIO MODELING OF THE STRUCTURAL DEFECTS IN AMIDES M. FATHIMA BEGUM, HEMA TRESA VARGHESE a, Y. SHEENA MARY a, C.
First Order Hyperpolarizability and Homo-Lumo Analysis of L-Arginine Maleate (LArM) by Density Functional Theory Methods
 51 Sciencia Acta Xaveriana An International Science Journal ISSN. 0976-1152 Volume 4 No. 2 pp. 51-58 September 2013 First Order Hyperpolarizability and Homo-Lumo Analysis of L-Arginine Maleate (LArM) by
51 Sciencia Acta Xaveriana An International Science Journal ISSN. 0976-1152 Volume 4 No. 2 pp. 51-58 September 2013 First Order Hyperpolarizability and Homo-Lumo Analysis of L-Arginine Maleate (LArM) by
Molecular Orbitals of Ethene
 Molecular Orbitals of Ethene 1 Molecular Orbital Analysis of Ethene Dimerisation the reaction is said to be a "symmetry forbidden" interestingly, this reaction is rare and very slow! Molecular Orbitals
Molecular Orbitals of Ethene 1 Molecular Orbital Analysis of Ethene Dimerisation the reaction is said to be a "symmetry forbidden" interestingly, this reaction is rare and very slow! Molecular Orbitals
Theoretical Study on the Structural Effect of Sulfur Containing Amino Acids As Corrosion Inhibitors On Brass In HClO 4
 Theoretical Study on the Structural Effect of Sulfur Containing Amino Acids As Corrosion Inhibitors On Brass In HClO 4 Musa E. Mohamed 1,*, Kamal K. Taha 2 1, 2 Department of Chemistry, College of Applied
Theoretical Study on the Structural Effect of Sulfur Containing Amino Acids As Corrosion Inhibitors On Brass In HClO 4 Musa E. Mohamed 1,*, Kamal K. Taha 2 1, 2 Department of Chemistry, College of Applied
Density Functional Theory Investigation of The Physical Properties of Dicyano Pyridazine Molecules
 Density Functional Theory Investigation of The Physical Properties of Dicyano Pyridazine Molecules Fouad N. Ajeel 1, Alaa M. Khudhair 2, Anees A. Mohammed 3 1,2,3 Department of Physics, College of Sciences,
Density Functional Theory Investigation of The Physical Properties of Dicyano Pyridazine Molecules Fouad N. Ajeel 1, Alaa M. Khudhair 2, Anees A. Mohammed 3 1,2,3 Department of Physics, College of Sciences,
Electronegativity is a very useful concept for the explanation or understanding of chemical reactivity throughout the periodic table.
 1.6. Review of Electronegativity (χ) CONCEPT: Electronegativity is a very useful concept for the explanation or understanding of chemical reactivity throughout the periodic table. There are many definitions
1.6. Review of Electronegativity (χ) CONCEPT: Electronegativity is a very useful concept for the explanation or understanding of chemical reactivity throughout the periodic table. There are many definitions
Structure, Electronic and Nonlinear Optical Properties of Furyloxazoles and Thienyloxazoles
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structure, Electronic and Nonlinear Optical Properties of Furyls and Thienyls To cite this article: Ozlem Dagli et al 6 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 77 View
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structure, Electronic and Nonlinear Optical Properties of Furyls and Thienyls To cite this article: Ozlem Dagli et al 6 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 77 View
Molecular Orbital Theory. Molecular Orbital Theory: Electrons are located in the molecule, not held in discrete regions between two bonded atoms
 Molecular Orbital Theory Valence Bond Theory: Electrons are located in discrete pairs between specific atoms Molecular Orbital Theory: Electrons are located in the molecule, not held in discrete regions
Molecular Orbital Theory Valence Bond Theory: Electrons are located in discrete pairs between specific atoms Molecular Orbital Theory: Electrons are located in the molecule, not held in discrete regions
Andrew Zahrt Denmark Group Meeting
 Andrew Zahrt Denmark Group Meeting 4.28.15 Introduction Early Publications/Hypotheses: Thermodynamic Product Stability Ground State Destabilization Transition State Stabilization Solvent Effects Gas Phase
Andrew Zahrt Denmark Group Meeting 4.28.15 Introduction Early Publications/Hypotheses: Thermodynamic Product Stability Ground State Destabilization Transition State Stabilization Solvent Effects Gas Phase
Pericyclic reactions
 Pericyclic reactions In pericyclic reactions the breaking and making of bonds occur simultaneously by the way of a single cyclic transition state (concerted reaction). There are no intermediates formed
Pericyclic reactions In pericyclic reactions the breaking and making of bonds occur simultaneously by the way of a single cyclic transition state (concerted reaction). There are no intermediates formed
PM3 Based Calculation of Interaction Energy between Metal Halides and Organic Bases and its Comparison with DFT
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.3, No.1, pp 253-266, Jan-Mar 2011 PM3 Based Calculation of Interaction Energy between Metal Halides and Organic Bases
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.3, No.1, pp 253-266, Jan-Mar 2011 PM3 Based Calculation of Interaction Energy between Metal Halides and Organic Bases
International Journal of Materials Science ISSN Volume 12, Number 2 (2017) Research India Publications
 HF, DFT Computations and Spectroscopic study of Vibrational frequency, HOMO-LUMO Analysis and Thermodynamic Properties of Alpha Bromo Gamma Butyrolactone K. Rajalakshmi 1 and A.Susila 2 1 Department of
HF, DFT Computations and Spectroscopic study of Vibrational frequency, HOMO-LUMO Analysis and Thermodynamic Properties of Alpha Bromo Gamma Butyrolactone K. Rajalakshmi 1 and A.Susila 2 1 Department of
Competition between Alkalide Characteristics and Nonlinear Optical Properties in OLi 3 M Li 3 O (M = Li, Na, and K) Complexes
 Competition between Alkalide Characteristics and Nonlinear Optical Properties in OLi 3 M Li 3 O (M = Li, Na, and K) Complexes Ambrish Kumar Srivastava and Neeraj Misra * Department of Physics, University
Competition between Alkalide Characteristics and Nonlinear Optical Properties in OLi 3 M Li 3 O (M = Li, Na, and K) Complexes Ambrish Kumar Srivastava and Neeraj Misra * Department of Physics, University
An electrochemical and quantum chemical investigation of some corrosion inhibitors on aluminium alloy in 0.6 M aqueous sodium chloride solution
 Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 18, July 2011, pp. 309-313 An electrochemical and quantum chemical investigation of some corrosion inhibitors on aluminium alloy in 0.6 M aqueous sodium chloride
Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 18, July 2011, pp. 309-313 An electrochemical and quantum chemical investigation of some corrosion inhibitors on aluminium alloy in 0.6 M aqueous sodium chloride
Corrosion Inhibition of Steel in Acidic Medium by Eugenol Derivatives: Insight from Density Functional Calculation
 Hadisaputra et al. /J Applied Chem. Sci. 4 (2017) 312-317 312 Corrosion Inhibition of Steel in Acidic Medium by Eugenol Derivatives: Insight from Density Functional Calculation Saprizal Hadisaputra*, Saprini
Hadisaputra et al. /J Applied Chem. Sci. 4 (2017) 312-317 312 Corrosion Inhibition of Steel in Acidic Medium by Eugenol Derivatives: Insight from Density Functional Calculation Saprizal Hadisaputra*, Saprini
 CHAPTER 6 CHEMICAL BONDING SHORT QUESTION WITH ANSWERS Q.1 Dipole moments of chlorobenzene is 1.70 D and of chlorobenzene is 2.5 D while that of paradichlorbenzene is zero; why? Benzene has zero dipole
CHAPTER 6 CHEMICAL BONDING SHORT QUESTION WITH ANSWERS Q.1 Dipole moments of chlorobenzene is 1.70 D and of chlorobenzene is 2.5 D while that of paradichlorbenzene is zero; why? Benzene has zero dipole
The Ag x Si y (x=1-5, y=1-5) Clusters with Electronegativity, Molecular Orbitals and SCF Density
 International Journal of Computational and Theoretical Chemistry 2015; 3(3-1): 1-18 Published online March 9, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijctc) doi: 10.11648/j.ijctc.s.2015030301.11
International Journal of Computational and Theoretical Chemistry 2015; 3(3-1): 1-18 Published online March 9, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijctc) doi: 10.11648/j.ijctc.s.2015030301.11
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(1):572-583 Ground state properties: Gross orbital charges,
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(1):572-583 Ground state properties: Gross orbital charges,
Organic Chemistry 6 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice. Chapter 1. Electronic Structure and Bonding. Acids and Bases Pearson Education, Inc.
 Organic Chemistry 6 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 1 Electronic Structure and Bonding Acids and Bases 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Organic Chemistry Carbon-containing compounds were once considered
Organic Chemistry 6 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 1 Electronic Structure and Bonding Acids and Bases 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Organic Chemistry Carbon-containing compounds were once considered
INVESTIGATION OF INHIBITION EFFECT OF NAPHTHYL CHALCONES ON MILD STEEL CORROSION IN SULPHURIC ACID MEDIUM
 ISSN: 0974-1496 e-issn: 0976-0083 DEN: RJABP http://www.rasayanjournal.com http://www.rasayanjournal.co.in INVESTIGATIN F INHIBITIN EFFET F NAPHTHYL HALNES N MILD STEEL RRSIN IN SULPHURI AID MEDIUM S.
ISSN: 0974-1496 e-issn: 0976-0083 DEN: RJABP http://www.rasayanjournal.com http://www.rasayanjournal.co.in INVESTIGATIN F INHIBITIN EFFET F NAPHTHYL HALNES N MILD STEEL RRSIN IN SULPHURI AID MEDIUM S.
Hanane HAMANI 1, Tahar DOUADI 2
 Third International Conference on Energy, Materials, Applied Energetics and Pollution ICEMAEP2016, October30-31, 2016, Constantine,Algeria A QUATUM CHEMICAL CALCULATIO (DFT) : 1-(4-ITRPHEYLO- IMIO) -1
Third International Conference on Energy, Materials, Applied Energetics and Pollution ICEMAEP2016, October30-31, 2016, Constantine,Algeria A QUATUM CHEMICAL CALCULATIO (DFT) : 1-(4-ITRPHEYLO- IMIO) -1
Quantum Chemical Study of Some Benzimidazole Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors of Copper in 1M HNO 3.
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(11): 309-317, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Quantum Chemical Study of Some Benzimidazole Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors of Copper in 1M HNO 3. 1 P.M. Niamien,
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(11): 309-317, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Quantum Chemical Study of Some Benzimidazole Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors of Copper in 1M HNO 3. 1 P.M. Niamien,
CHAPTER IV MATERIALS AND METHODS FOR CORROSION INHIBITION STUDIES 4.1 MATERIALS 4.2 METHODS FOR STUDYING CORROSION 4.3 REFERENCES
 CHAPTER IV MATERIALS AND METHODS FOR CORROSION INHIBITION STUDIES 4.1 MATERIALS 4.2 METHODS FOR STUDYING CORROSION 4.3 REFERENCES 4.1 MATERIALS The metals used for the corrosion studies are copper and
CHAPTER IV MATERIALS AND METHODS FOR CORROSION INHIBITION STUDIES 4.1 MATERIALS 4.2 METHODS FOR STUDYING CORROSION 4.3 REFERENCES 4.1 MATERIALS The metals used for the corrosion studies are copper and
Advances in Physics Theories and Applications ISSN X (Paper) ISSN (Online) Vol.25, 2013
 Theoretical Study of the Effect of Hydroxy Subgroup on the Electronic and Spectroscopic Properties of Azulene Molecule: As a Nano Structure DFT Calculations Maan Abd-Al Ameer Saleh Physics department,
Theoretical Study of the Effect of Hydroxy Subgroup on the Electronic and Spectroscopic Properties of Azulene Molecule: As a Nano Structure DFT Calculations Maan Abd-Al Ameer Saleh Physics department,
Chemical Bonding Petrucci, Harwood and Herring: Chapters 10 and 11
 Chemical Bonding Petrucci, Harwood and Herring: Chapters 10 and 11 Aims: To look at bonding and possible shapes of molecules We will mainly do this through Lewis structures To look at ionic and covalent
Chemical Bonding Petrucci, Harwood and Herring: Chapters 10 and 11 Aims: To look at bonding and possible shapes of molecules We will mainly do this through Lewis structures To look at ionic and covalent
A density functional study on equilibrium geometries, stabilities and electronic properties of Au 5 Li binary clusters
 Appl Nanosci (2012) 2:359 364 DOI 10.1007/s13204-012-0092-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE A density functional study on equilibrium geometries, stabilities and electronic properties of Au 5 Li binary clusters Ajanta
Appl Nanosci (2012) 2:359 364 DOI 10.1007/s13204-012-0092-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE A density functional study on equilibrium geometries, stabilities and electronic properties of Au 5 Li binary clusters Ajanta
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Uniformly Sized (112) Facet Co 2 P on Graphene for Highly Effective Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Bin Tian, a, b Zhen Li, a, b Wenlong Zhen c and Gongxuan Lu *a a State Key Laboratory
Supporting Information Uniformly Sized (112) Facet Co 2 P on Graphene for Highly Effective Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Bin Tian, a, b Zhen Li, a, b Wenlong Zhen c and Gongxuan Lu *a a State Key Laboratory
Reaction Mechanism of Polar Diels-Alder Reactions between 3-Nitrofuran and different Dienes. A Theoretical Study.
 Reaction Mechanism of Polar Diels-Alder Reactions between 3-Nitrofuran and different Dienes. A Theoretical Study. MAUR CAINELLI, CARLA RMACHEA, PEDR MANCINI, MARÍA KNEETEMAN* Área Química rgánica Departamento
Reaction Mechanism of Polar Diels-Alder Reactions between 3-Nitrofuran and different Dienes. A Theoretical Study. MAUR CAINELLI, CARLA RMACHEA, PEDR MANCINI, MARÍA KNEETEMAN* Área Química rgánica Departamento
Reaction mechanisms offer us insights into how reactions work / how molecules react with one another.
 Introduction 1) Lewis Structures 2) Representing Organic Structures 3) Geometry and Hybridization 4) Electronegativities and Dipoles 5) Resonance Structures (a) Drawing Them (b) Rules for Resonance 6)
Introduction 1) Lewis Structures 2) Representing Organic Structures 3) Geometry and Hybridization 4) Electronegativities and Dipoles 5) Resonance Structures (a) Drawing Them (b) Rules for Resonance 6)
one ν im: transition state saddle point
 Hypothetical Potential Energy Surface Ethane conformations Hartree-Fock theory, basis set stationary points all ν s >0: minimum eclipsed one ν im: transition state saddle point multiple ν im: hilltop 1
Hypothetical Potential Energy Surface Ethane conformations Hartree-Fock theory, basis set stationary points all ν s >0: minimum eclipsed one ν im: transition state saddle point multiple ν im: hilltop 1
FT-IR, FT-Raman, NMR and FMO Analysis of 3-(2- Furyl) Propionic Acid By Quantum Chemical Calculations
 FT-IR, FT-Raman, NMR and FMO Analysis of 3-(2- Furyl) Propionic Acid By Quantum Chemical Calculations G. Velraj, S. Ramachandran, and T. Kavitha* Department of Physics, Periyar University Salem-636 011,
FT-IR, FT-Raman, NMR and FMO Analysis of 3-(2- Furyl) Propionic Acid By Quantum Chemical Calculations G. Velraj, S. Ramachandran, and T. Kavitha* Department of Physics, Periyar University Salem-636 011,
Doctor of Philosophy
 STUDIES ON THE CORROSION INHIBITION BEHAVIOUR OF SOME AMINO ACID SURFACTANT ADDITIVES ABSTRACT SUBMITTED FOR THE AWARD OF THE DEGREE OF Doctor of Philosophy IN APPLIED CHEMISTRY By MOSARRAT PARVEEN UNDER
STUDIES ON THE CORROSION INHIBITION BEHAVIOUR OF SOME AMINO ACID SURFACTANT ADDITIVES ABSTRACT SUBMITTED FOR THE AWARD OF THE DEGREE OF Doctor of Philosophy IN APPLIED CHEMISTRY By MOSARRAT PARVEEN UNDER
For more info visit Chemical bond is the attractive force which holds various constituents together in a molecule.
 Chemical bond:- Chemical bond is the attractive force which holds various constituents together in a molecule. There are three types of chemical bonds: Ionic Bond, Covalent Bond, Coordinate Bond. Octet
Chemical bond:- Chemical bond is the attractive force which holds various constituents together in a molecule. There are three types of chemical bonds: Ionic Bond, Covalent Bond, Coordinate Bond. Octet
1,2,3 BENZOTRIAZOLE AS CORROSION INHIBITOR
 CHAPTER - V 1,2,3 BENZOTRIAZOLE AS CORROSION INHIBITOR In general, organic corrosion inhibitors have reactive functional groups which are the sites for the adsorption process. Electron density of the organic
CHAPTER - V 1,2,3 BENZOTRIAZOLE AS CORROSION INHIBITOR In general, organic corrosion inhibitors have reactive functional groups which are the sites for the adsorption process. Electron density of the organic
How Partial Atomic Charges and Bonding. Orbitals Affect the Reactivity of Aluminum
 Supporting Information for: How Partial Atomic Charges and Bonding Orbitals Affect the Reactivity of Aluminum Clusters with Water? Anthony M.S Pembere ξ, Xianhu Liu ξ, Weihua Ding, Zhixun Luo * State Key
Supporting Information for: How Partial Atomic Charges and Bonding Orbitals Affect the Reactivity of Aluminum Clusters with Water? Anthony M.S Pembere ξ, Xianhu Liu ξ, Weihua Ding, Zhixun Luo * State Key
need another quantum number, m s it is found that atoms, substances with unpaired electrons have a magnetic moment, 2 s(s+1) where {s = m s }
 M polyelectronic atoms need another quantum number, m s it is found that atoms, substances with unpaired electrons have a magnetic moment, 2 s(s+1) where {s = m s } Pauli Exclusion Principle no two electrons
M polyelectronic atoms need another quantum number, m s it is found that atoms, substances with unpaired electrons have a magnetic moment, 2 s(s+1) where {s = m s } Pauli Exclusion Principle no two electrons
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(4): 589-595 Altering the electronic properties of adamantane
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(4): 589-595 Altering the electronic properties of adamantane
Corrosion inhibition effect of hydroxy pyrazoline derivatives on mild steel in sulphuric acid solution together with Quantum chemical studies
 Corrosion inhibition effect of hydroxy pyrazoline derivatives on mild steel in sulphuric acid solution together with Quantum chemical studies N. Anusuya 1, P. Sounthari 2, J. Saranya 2, K. Parameswari
Corrosion inhibition effect of hydroxy pyrazoline derivatives on mild steel in sulphuric acid solution together with Quantum chemical studies N. Anusuya 1, P. Sounthari 2, J. Saranya 2, K. Parameswari
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer. Lecture 31, April 12, 2006
 Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 31, April 12, 2006 (Some material in this lecture has been adapted from Cramer, C.
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 31, April 12, 2006 (Some material in this lecture has been adapted from Cramer, C.
 Organic Chemistry I Dr Alex Roche Organic chemistry is the chemistry of Carbon and its compounds. Organic molecules constitute the essence of life (fats, sugars, proteins, DNA), and also permeate our everyday
Organic Chemistry I Dr Alex Roche Organic chemistry is the chemistry of Carbon and its compounds. Organic molecules constitute the essence of life (fats, sugars, proteins, DNA), and also permeate our everyday
DFT Study of the Interaction of Cu(II), Zn(II), Sn(II) with Carbohydrates in Aqueous Solution
 J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 8 (2014) 1009-1017 doi: 10.17265/1934-7375/2014.11.001 D DAVID PUBLISHING DFT Study of the Interaction of Cu(II), Zn(II), Sn(II) with Carbohydrates in Aqueous Solution Faiza Boukli-Hacene,
J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 8 (2014) 1009-1017 doi: 10.17265/1934-7375/2014.11.001 D DAVID PUBLISHING DFT Study of the Interaction of Cu(II), Zn(II), Sn(II) with Carbohydrates in Aqueous Solution Faiza Boukli-Hacene,
Chemical hardness and density functional theory
 J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 117, No. 5, September 005, pp. 369 377. Indian Academy of Sciences. Chemical hardness and density functional theory RALPH G PEARSON Chemistry Department, University of California, Santa
J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 117, No. 5, September 005, pp. 369 377. Indian Academy of Sciences. Chemical hardness and density functional theory RALPH G PEARSON Chemistry Department, University of California, Santa
Periodic Trends in Properties of Homonuclear
 Chapter 8 Periodic Trends in Properties of Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules Up to now, we have discussed various physical properties of nanostructures, namely, two-dimensional - graphene-like structures:
Chapter 8 Periodic Trends in Properties of Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules Up to now, we have discussed various physical properties of nanostructures, namely, two-dimensional - graphene-like structures:
Visualization in Chemistry. Giovanni Morelli
 Visualization in Chemistry Giovanni Morelli What is Chemistry? If we provide a good answer to this question maybe we can understand what graphics can do for chemistry and chemists What is Chemistry? A
Visualization in Chemistry Giovanni Morelli What is Chemistry? If we provide a good answer to this question maybe we can understand what graphics can do for chemistry and chemists What is Chemistry? A
CHEM 344 Molecular Modeling
 CHEM 344 Molecular Modeling The Use of Computational Chemistry to Support Experimental Organic Chemistry Part 1: Molecular Orbital Theory, Hybridization, & Formal Charge * all calculation data obtained
CHEM 344 Molecular Modeling The Use of Computational Chemistry to Support Experimental Organic Chemistry Part 1: Molecular Orbital Theory, Hybridization, & Formal Charge * all calculation data obtained
Copper Corrosion Inhibition by Cefuroxime Drug in 1M Nitric Acid
 Research Article Copper Corrosion Inhibition by Cefuroxime Drug in 1M Nitric Acid OUEDRAOGO Augustin 1, DIKI N guessan Yao Silvère 1 *, BOHOUSSOU Kouadio Valery 2, SORO Doh 2 and TROKOUREY Albert 1 1 Laboratoire
Research Article Copper Corrosion Inhibition by Cefuroxime Drug in 1M Nitric Acid OUEDRAOGO Augustin 1, DIKI N guessan Yao Silvère 1 *, BOHOUSSOU Kouadio Valery 2, SORO Doh 2 and TROKOUREY Albert 1 1 Laboratoire
Experimental and Theoretical Study of Some N- pyridinium Salt Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors for Mild-steel in 1 M H 2 SO 4
 Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 2017, 35(1), 39-51 DOI: 10.4152/pea.201701039 PORTUGALIAE ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA ISSN 1647-1571 Experimental and Theoretical Study of Some N- pyridinium Salt Derivatives as
Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 2017, 35(1), 39-51 DOI: 10.4152/pea.201701039 PORTUGALIAE ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA ISSN 1647-1571 Experimental and Theoretical Study of Some N- pyridinium Salt Derivatives as
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid
![Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid](/thumbs/95/123929992.jpg) Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Congo Red Dye As A Novel Corrosion Inhibitor for Zinc in Hydrochloric Acid Solution
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 12, December 2013 1 Congo Red Dye As A ovel Corrosion Inhibitor for Zinc in Hydrochloric Acid Solution A.Pasupathy 1 *, S.irmala
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 12, December 2013 1 Congo Red Dye As A ovel Corrosion Inhibitor for Zinc in Hydrochloric Acid Solution A.Pasupathy 1 *, S.irmala
Exchange Correlation Functional Investigation of RT-TDDFT on a Sodium Chloride. Dimer. Philip Straughn
 Exchange Correlation Functional Investigation of RT-TDDFT on a Sodium Chloride Dimer Philip Straughn Abstract Charge transfer between Na and Cl ions is an important problem in physical chemistry. However,
Exchange Correlation Functional Investigation of RT-TDDFT on a Sodium Chloride Dimer Philip Straughn Abstract Charge transfer between Na and Cl ions is an important problem in physical chemistry. However,
Ch 2 Polar Covalent Bonds
 h 2 Polar ovalent Bonds Two primary bond types: ovalent (shared e -1 s) and Ionic (transferred e -1 s) Ionic bonds can have covalent character, such as with Na:l. An e -1 pair on l -1 can fill the 3s orbital
h 2 Polar ovalent Bonds Two primary bond types: ovalent (shared e -1 s) and Ionic (transferred e -1 s) Ionic bonds can have covalent character, such as with Na:l. An e -1 pair on l -1 can fill the 3s orbital
1. Following Dalton s Atomic Theory, 2. In 1869 Russian chemist published a method. of organizing the elements. Mendeleev showed that
 20 CHEMISTRY 11 D. Organizing the Elements The Periodic Table 1. Following Dalton s Atomic Theory, By 1817, chemists had discovered 52 elements and by 1863 that number had risen to 62. 2. In 1869 Russian
20 CHEMISTRY 11 D. Organizing the Elements The Periodic Table 1. Following Dalton s Atomic Theory, By 1817, chemists had discovered 52 elements and by 1863 that number had risen to 62. 2. In 1869 Russian
All chemical bonding is based on the following relationships of electrostatics: 2. Each period on the periodic table
 UNIT VIII ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE 25 E. Chemical Bonding 1. An ELECTROSTATIC FORCE is All chemical bonding is based on the following relationships of electrostatics: The greater the distance between
UNIT VIII ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE 25 E. Chemical Bonding 1. An ELECTROSTATIC FORCE is All chemical bonding is based on the following relationships of electrostatics: The greater the distance between
General Physical Chemistry II
 General Physical Chemistry II Lecture 13 Aleksey Kocherzhenko October 16, 2014" Last time " The Hückel method" Ø Used to study π systems of conjugated molecules" Ø π orbitals are treated separately from
General Physical Chemistry II Lecture 13 Aleksey Kocherzhenko October 16, 2014" Last time " The Hückel method" Ø Used to study π systems of conjugated molecules" Ø π orbitals are treated separately from
First-Principle Studies on Adsorption of Cu + and Hydrated Cu + Cations on Clean Si(111) Surface
 CHEM. RES. CHINESE UNIVERSITIES 2010, 26(3), 472 478 First-Principle Studies on Adsorption of Cu + and Hydrated Cu + Cations on Clean Si(111) Surface CHENG Feng-ming 1,2, SHENG Yong-li 1,3, LI Meng-hua
CHEM. RES. CHINESE UNIVERSITIES 2010, 26(3), 472 478 First-Principle Studies on Adsorption of Cu + and Hydrated Cu + Cations on Clean Si(111) Surface CHENG Feng-ming 1,2, SHENG Yong-li 1,3, LI Meng-hua
Solution problem 22: Non-Benzoid Aromatic Sytems
 Solution problem 22: on-enzoid Aromatic Sytems 22.1 & 22.2 Each double bond and each heteroatom (, ) with lone pairs donates 2 π- electrons as well as a negative charge. oron or a positive charge does
Solution problem 22: on-enzoid Aromatic Sytems 22.1 & 22.2 Each double bond and each heteroatom (, ) with lone pairs donates 2 π- electrons as well as a negative charge. oron or a positive charge does
2. Polar Covalent Bonds: Acids and Bases
 2. Polar Covalent Bonds: Acids and Bases Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 2 2003 Ronald Kluger Department of Chemistry University of Toronto 2.1 Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity!
2. Polar Covalent Bonds: Acids and Bases Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 2 2003 Ronald Kluger Department of Chemistry University of Toronto 2.1 Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity!
Why Is Molecular Interaction Important in Our Life
 Why Is Molecular Interaction Important in ur Life QuLiS and Graduate School of Science iroshima University http://www.nabit.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/iwatasue/indexe.htm Suehiro Iwata Sept. 29, 2007 Department
Why Is Molecular Interaction Important in ur Life QuLiS and Graduate School of Science iroshima University http://www.nabit.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/iwatasue/indexe.htm Suehiro Iwata Sept. 29, 2007 Department
MOLECULAR STRUCTURE. Molecular Structure - B. Molecular Structure - B. Molecular Structure - B. Molecular Structure - B. Molecular Structure - B
 MOLECULAR STRUCTURE Molecular Orbital all orbitals of the appropriate symmetry contribute to a molecular orbital. Bundet Boekfa Chem Div, Faculty Lib Arts & Sci Kasetsart University Kamphaeng Saen Campus
MOLECULAR STRUCTURE Molecular Orbital all orbitals of the appropriate symmetry contribute to a molecular orbital. Bundet Boekfa Chem Div, Faculty Lib Arts & Sci Kasetsart University Kamphaeng Saen Campus
CHEM1901/ J-5 June 2013
 CHEM1901/3 2013-J-5 June 2013 Oxygen exists in the troposphere as a diatomic molecule. 4 (a) Using arrows to indicate relative electron spin, fill the left-most valence orbital energy diagram for O 2,
CHEM1901/3 2013-J-5 June 2013 Oxygen exists in the troposphere as a diatomic molecule. 4 (a) Using arrows to indicate relative electron spin, fill the left-most valence orbital energy diagram for O 2,
Class XI: Chemistry Chapter 4: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Top Concepts
 1 Class XI: Chemistry Chapter 4: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Top Concepts 1. The attractive force which holds together the constituent particles (atoms, ions or molecules) in chemical species
1 Class XI: Chemistry Chapter 4: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Top Concepts 1. The attractive force which holds together the constituent particles (atoms, ions or molecules) in chemical species
Fundamental Interactions: 6 Forces
 Fundamental Interactions: 6 Forces In nuclear and high-energy physics 6 fundamental forces are recognized, which describe the structure of matter. - the strong interaction - the weak interaction act inside
Fundamental Interactions: 6 Forces In nuclear and high-energy physics 6 fundamental forces are recognized, which describe the structure of matter. - the strong interaction - the weak interaction act inside
Chapter 8: Bonding. Section 8.1: Lewis Dot Symbols
 Chapter 8: Bonding Section 8.1: Lewis Dot Symbols The Lewis electron dot symbol is named after Gilbert Lewis. In the Lewis dot symbol, the element symbol represents the nucleus and the inner electrons.
Chapter 8: Bonding Section 8.1: Lewis Dot Symbols The Lewis electron dot symbol is named after Gilbert Lewis. In the Lewis dot symbol, the element symbol represents the nucleus and the inner electrons.
Oxidative Addition/Reductive Elimination 1. Oxidative Addition
 Oxidative Addition Oxidative Addition/Reductive Elimination 1 An oxidative addition reaction is one in which (usually) a neutral ligand adds to a metal center and in doing so oxidizes the metal, typically
Oxidative Addition Oxidative Addition/Reductive Elimination 1 An oxidative addition reaction is one in which (usually) a neutral ligand adds to a metal center and in doing so oxidizes the metal, typically
The Inhibition of Mild Steel Corrosion in Acidic Solution by Amine Melamine Chloral Resin
 Abdel-Amir Hussain Taobi The Inhibition of Mild. The Inhibition of Mild Steel Corrosion in Acidic Solution by Amine Melamine Chloral Resin Abdel-Amir Hussain Taobi Chemistry Department, College of Science,
Abdel-Amir Hussain Taobi The Inhibition of Mild. The Inhibition of Mild Steel Corrosion in Acidic Solution by Amine Melamine Chloral Resin Abdel-Amir Hussain Taobi Chemistry Department, College of Science,
Chapter 5. Molecular Orbitals
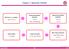 Chapter 5. Molecular Orbitals MO from s, p, d, orbitals: - Fig.5.1, 5.2, 5.3 Homonuclear diatomic molecules: - Fig. 5.7 - Para- vs. Diamagnetic Heteronuclear diatomic molecules: - Fig. 5.14 - ex. CO Hybrid
Chapter 5. Molecular Orbitals MO from s, p, d, orbitals: - Fig.5.1, 5.2, 5.3 Homonuclear diatomic molecules: - Fig. 5.7 - Para- vs. Diamagnetic Heteronuclear diatomic molecules: - Fig. 5.14 - ex. CO Hybrid
Conjugated Systems. With conjugated double bonds resonance structures can be drawn
 Conjugated Systems Double bonds in conjugation behave differently than isolated double bonds With conjugated double bonds resonance structures can be drawn With isolated double bonds cannot draw resonance
Conjugated Systems Double bonds in conjugation behave differently than isolated double bonds With conjugated double bonds resonance structures can be drawn With isolated double bonds cannot draw resonance
Chapter 13: Phenomena
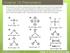 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
