C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
|
|
|
- Sibyl Bryant
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inherent Difficulties Low bundnce of 13 C (1.1% vs, 99.9% for 1 H) Lower gyromgnetic rtio (1/4 tht of 1 H) - 13 C: vs. 1 H /2 1,000,000 nuclei t 60 MHz E ΔE +1/2 1,000,009 nuclei t 60 MHz mgnetic field (B 0 ) Slow T 1 relxtion times ( sec vs sec for 1 H) 13 C- 1 H coupling complictes spectrum; decreses pek intensity
2 see lso Pvi Tble 6.1; Appendices 7 & 8 Chemicl Shift
3 Chemicl Shift Fctors the Influence Chemicl Shift 1. hybridiztion 2. electronegtivity of element bonded to crbon 3. nisotropy * * * δ 22.6 δ δ 38.2 H * * δ 62.3 δ 202.8
4 Differences Between 1 H nd 13 C NMR 1. rnge of 13 C chemicl shifts is very lrge compred to 1 H C chemicl shifts re more sensitive to smll chnges in chemicl environment 3. Influence of electronegtive toms on chemicl shift greter in 13 C NMR thn 1 H NMR 1 H shifts 13 C shifts CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 H CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 H See Pvi, Appendix 8 for clcultion of 13 C chemicl shifts 4. Homonucler ( 13 C / 13 C) splitting is not observed
5 NMR Spectr of n-butylbenzene
6 Heteronucler Spin-Spin Splitting ( 1 H- 13 C) 3 J = 0-3 Hz CH 2 CH 2 CH 3
7 H H Heteronucler Spin-Spin Splitting H H H cholesterol 1 H coupled spectrum 1 H decoupled spectrum
8 Proton Decoupled 13 C NMR
9 Proton Decoupled 13 C NMR 1 H coupled spectrum CH 3 CH 3 1 H brodbnd decoupled spectrum 1 H off resonnce decoupled spectrum
10 Nucler verhuser Effect & Cross Polriztion of Spin 1 H decoupler 300 MHz B 0 Boltzmn distribution N upper N lower = 1,000,000 1,000,048 = 1,000,000 1,000,000 = C cross polriztion B 0 Boltzmn distribution N upper N lower = 1,000,000 1,000,048 = 1,000,000 1,000,096 Signl Enhncement: CH 3 > CH 2 > CH >> C
11 13 C Pulse Sequence FID:
12 Relxtion Times (T 1 ) in generl 68 s 9.8 s T 1 : C > CH > CH 2 > CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 C CH 2 CH CH 3 CH s 13 s 23 s tumbling H H T 1 = 37 s T 1 = 20 s H H H T 1 = 1-2 s for CH, CH 2, CH 3 T 1 = 4-6 s for quternry C
13 Moleculr Symmetry How Mny Lines? CH 3 H 3 C CH 3 C-CH 2 -CH 3 CH 3 H 3 C CH 3 H H 3 C CH 3 A B C D
14 Integrtion A 2 peks B C 1 D 2 3 4
15 Distortionless Enhncement by Polriztion Trnsfer (DEPT) DEPT-45 DEPT-90 DEPT-135 C CH CH CH
16 Distortionless Enhncement by Polriztion Trnsfer (DEPT) C CH CH 2 CH 3 DEPT DEPT DEPT CH DEPT H H 3 C 8 CH menthol DEPT-90 DEPT C NMR
17 H 13C NH H Nucler Mgnetic Resonnce DEPT-135 CH3 CH32C H CH3 H H
18 Alknes 2-methylpentne R CH 3 R 2 CH 2 R 3 R 4 chemicl shifts CH C 8-30 ppm ppm ppm ppm CH 3 CH 3 CH-CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 3 b c d e c b d e
19 Alkenes C C chemicl shifts ppm cis-2-hexene H H b C C c c b 29.1 d e f H 3 C CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 d e f
20 chemicl shifts Alkenes 1-hexene C C ppm f e d c b CH 3 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH CH b
21 Alkenes C C chemicl shifts ppm dihydropyrn b b
22 Alkenes C C chemicl shifts ppm 4-methyl-2-penten-1-one b H 3 C H 3 C b CH 3
23 Aromtics chemicl shifts C ppm nitrobenzene c b N 2 c b d d
24 Aromtics chemicl shifts C ppm p-cymene CH 3
25 Aromtics chemicl shifts C ppm dichlorobenzenes Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl
26 chemicl shifts Alkynes 2-heptyne C C ppm CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 b C C CH b
27 Alkyl Hlides C C chemicl shifts I Br ppm ppm 1-chloropentne C Cl ppm CH 3 CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 -Cl 45.1
28 Alcohols, Ethers & Amines 2-hexnol C-R C-NR 2 chemicl shifts ppm ppm H CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CHCH
29 Alcohols, Ethers & Amines 1,3-dioxne C-R C-NR 2 chemicl shifts ppm ppm c b b c
30 Alcohols, Ethers & Amines N-methylisobutylmine C-R C-NR 2 chemicl shifts ppm ppm b d N H c d b c
31 Crbonyl Compounds ldehydes & ketones ppm crboxylic cids, esters, mides, etc ppm nitriles ppm
32 Aldehydes & Ketones 2-hexnone R R C H C R' chemicl shifts ppm ppm CH 3 C CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH
33 chemicl shifts 13 R C H ppm Crboxylic Acid Derivtives methcrylic cid R R C C R' NR' ppm ppm H C C CH 2 CH
34 chemicl shifts 13 R C H ppm Crboxylic Acid Derivtives heptyl cette R R C C R' NR' ppm ppm CH 3 C -CH 2 CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 3 b 64.6 b 171.0
35 chemicl shifts 13 R C H ppm Amides N-methyl-6-hexnelctm R R C C R' NR' ppm ppm d 36.9 b b N CH 3 c 51.3 c d 35.7
36 chemicl shifts Nitriles hexnenitrile R C N ppm CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 C N 119.9
37 Heteronucler Coupling to Deuterium multiplicity D C b J b = 45 Hz multiplicity = 2nI + 1 where: n = # of nuclei I = spin reltive intensity
38 Solvent Peks CDCl 3 D 3 C(S=)CD 3
39 Heteronucler Coupling to 19 F fluorotribromomethne F C J F = ~350 Hz F C C b J Fb = ~50 Hz 1 J = 370 Hz
40 Heteronucler Coupling to 19 F 2,2,2-trifluoroethnol (proton decoupled) F C J F = ~350 Hz F C C b J Fb = ~50 Hz 2 J = 35 Hz 1 J = 278 Hz
41 Heteronucler Coupling to 19 F commonly observed systems F C J F = ~350 Hz F C C b J Fb = ~50 Hz F 3 C C R F 3 C S R trifluorocettes trifluoromethnesulfontes (trifltes)
42 P C P C C b Heteronucler Coupling to 31 P J P, J Pb vrible tetrmethylphosphonium chloride (proton decoupled) 1 J = 56 Hz
43 P C P C C b Heteronucler Coupling to 31 P J P, J Pb vrible dimethyl methylphosphonte (proton decoupled) 2 J = 6 Hz 1 J = 144 Hz
44 1 H Nucler Mgnetic Resonnce How to Interpret 13 C NMR Spectrum 1. Get n verview identify ny reference solvents in proton decoupled spectrum 2. Symmetry: count the number of crbons (remember 13 C is not integrted) verify crbon count bsed on the moleculr formul is there ny symmetry? - rrely see overlp of peks in bsence of symmetry - ok to see fewer crbons (if resonble); not oky to hve more! 3. Chemicl Shift: determine the chemicl shift of ech resonnce in the spectrum - wht functionl groups my be present - consider the presence of heterotoms 4. If Needed Collect DEPT Dt determine how mny Hs re on ech crbon 5. Put it ll Together: often helpful to consider 1 H NMR dt simultneously
45 1 H Nucler Mgnetic Resonnce Reporting 13 C NMR Dt (1H decoupled) ppm Int CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 C N 13 C NMR (25 MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ 119.9, 30.9, 25.2, , 13.8.
46 1 H Nucler Mgnetic Resonnce Reporting 13 C NMR Dt (1H decoupled) list chemicl shift of ech pek to 1 deciml plce* 13 C NMR (25 MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ 119.9, 30.9, 25.2, , frequency (1/4 1 H frequency) solvent *if two peks round to sme vlue, cn dd second deciml plce (e.g , 69.89);
47
48 Chemicl Shift
Infrared Spectroscopy: Functional Group Determination
 nfrred pectroscopy: Functionl Group Determintion tch the infrred spectr below with the following compounds. ote tht one of the compounds does not mtch ny of the spectr. dentify ny spectrl fetures tht ssisted
nfrred pectroscopy: Functionl Group Determintion tch the infrred spectr below with the following compounds. ote tht one of the compounds does not mtch ny of the spectr. dentify ny spectrl fetures tht ssisted
Unique Solutions R. Amazing World of Carbon Compounds. C h a p t e r. G l a n c e
 9. C h p t e r t G l n c e Hydrocrbons - The fundmentl orgnic compounds : All orgnic compounds contin hydrogen long with crbon. They re the fundmentl orgnic compounds lso known s "Prent" compounds. These
9. C h p t e r t G l n c e Hydrocrbons - The fundmentl orgnic compounds : All orgnic compounds contin hydrogen long with crbon. They re the fundmentl orgnic compounds lso known s "Prent" compounds. These
Physical Chemistry (II) CHEM Lecture 25. Lecturer: Hanning Chen, Ph.D. 05/01/2018
 Physicl Chemistry (II) CHEM 372-80 Lecture 25 Nucler Overhuser Effect nd Electron Prmgnetic Resonnce Lecturer: Hnning Chen, Ph.D. 05/0/208 Quiz 24 0 minutes Plese stop writing when the timer stops! Spin
Physicl Chemistry (II) CHEM 372-80 Lecture 25 Nucler Overhuser Effect nd Electron Prmgnetic Resonnce Lecturer: Hnning Chen, Ph.D. 05/0/208 Quiz 24 0 minutes Plese stop writing when the timer stops! Spin
Organic Acids - Carboxylic Acids
 Orgnic Acids - rboxylic Acids Orgnic cids - crboxylic cid functionl group rboxylic cids re redily deprotonted by bses such s NO eg 3 O O - + O - + O 3 O O Acid Bse onjugte Bse onjugte Acid This rection
Orgnic Acids - rboxylic Acids Orgnic cids - crboxylic cid functionl group rboxylic cids re redily deprotonted by bses such s NO eg 3 O O - + O - + O 3 O O Acid Bse onjugte Bse onjugte Acid This rection
Unit #9 : Definite Integral Properties; Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 Unit #9 : Definite Integrl Properties; Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus Gols: Identify properties of definite integrls Define odd nd even functions, nd reltionship to integrl vlues Introduce the Fundmentl
Unit #9 : Definite Integrl Properties; Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus Gols: Identify properties of definite integrls Define odd nd even functions, nd reltionship to integrl vlues Introduce the Fundmentl
ORGANIC - EGE 5E CH UV AND INFRARED MASS SPECTROMETRY
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: IR SPECTROSCOPY- FREQUENCIES There are specific absorption frequencies in the functional group region that we should be familiar with EXAMPLE: What are the major IR absorptions
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: IR SPECTROSCOPY- FREQUENCIES There are specific absorption frequencies in the functional group region that we should be familiar with EXAMPLE: What are the major IR absorptions
Using NMR and IR Spectroscopy to Determine Structures Dr. Carl Hoeger, UCSD
 Using NMR and IR Spectroscopy to Determine Structures Dr. Carl Hoeger, UCSD The following guidelines should be helpful in assigning a structure from NMR (both PMR and CMR) and IR data. At the end of this
Using NMR and IR Spectroscopy to Determine Structures Dr. Carl Hoeger, UCSD The following guidelines should be helpful in assigning a structure from NMR (both PMR and CMR) and IR data. At the end of this
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES: IR, NMR, MASS SPECT
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: PURPOSE OF ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Classical Methods (Wet Chemistry): Chemists needed to run dozens of chemical reactions to determine the type of molecules in a compound.
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: PURPOSE OF ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Classical Methods (Wet Chemistry): Chemists needed to run dozens of chemical reactions to determine the type of molecules in a compound.
OAT Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 19: NMR Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry
 OAT Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 19: NMR Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which statement concerning NMR spectroscopy is incorrect? Question #01 (A) Only nuclei
OAT Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 19: NMR Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which statement concerning NMR spectroscopy is incorrect? Question #01 (A) Only nuclei
To Do s. Read Chapter 3. Complete the end-of-chapter problems, 3-1, 3-3, 3-4, 3-6 and 3-7. Answer Keys are available in CHB204H
 Read Chapter 3. To Do s Complete the end-of-chapter problems, 3-1, 3-3, 3-4, 3-6 and 3-7 Answer Keys are available in CB204 NMR Chemical Shifts Further Discussion A set of spectral data is reported when
Read Chapter 3. To Do s Complete the end-of-chapter problems, 3-1, 3-3, 3-4, 3-6 and 3-7 Answer Keys are available in CB204 NMR Chemical Shifts Further Discussion A set of spectral data is reported when
1. Weak acids. For a weak acid HA, there is less than 100% dissociation to ions. The B-L equilibrium is:
 th 9 Homework: Reding, M&F, ch. 15, pp. 584-598, 602-605 (clcultions of ph, etc., for wek cids, wek bses, polyprotic cids, nd slts; fctors ffecting cid strength). Problems: Nkon, ch. 18, #1-10, 16-18,
th 9 Homework: Reding, M&F, ch. 15, pp. 584-598, 602-605 (clcultions of ph, etc., for wek cids, wek bses, polyprotic cids, nd slts; fctors ffecting cid strength). Problems: Nkon, ch. 18, #1-10, 16-18,
3.15 NMR spectroscopy Different types of NMR There are two main types of NMR 1. C 13 NMR 2. H (proton) NMR
 .5 NMR spetrosopy Different types of NMR There re two min types of NMR. NMR. (proton) NMR There is only round % in orgni moleules ut modern NMR mhines re sensitive enough to give full spetr for The spetr
.5 NMR spetrosopy Different types of NMR There re two min types of NMR. NMR. (proton) NMR There is only round % in orgni moleules ut modern NMR mhines re sensitive enough to give full spetr for The spetr
Read section 3.3, 3.4 Announcements:
 Dte: 3/1/13 Objective: SWBAT pply properties of exponentil functions nd will pply properties of rithms. Bell Ringer: 1. f x = 3x 6, find the inverse, f 1 x., Using your grphing clcultor, Grph 1. f x,f
Dte: 3/1/13 Objective: SWBAT pply properties of exponentil functions nd will pply properties of rithms. Bell Ringer: 1. f x = 3x 6, find the inverse, f 1 x., Using your grphing clcultor, Grph 1. f x,f
Chem 213 Final 2012 Detailed Solution Key for Structures A H
 Chem 213 Final 2012 Detailed Solution Key for Structures A H COMPOUND A on Exam Version A (B on Exam Version B) C 8 H 6 Cl 2 O 2 DBE = 5 (aromatic + 1) IR: 1808 cm 1 suggests an acid chloride since we
Chem 213 Final 2012 Detailed Solution Key for Structures A H COMPOUND A on Exam Version A (B on Exam Version B) C 8 H 6 Cl 2 O 2 DBE = 5 (aromatic + 1) IR: 1808 cm 1 suggests an acid chloride since we
4 7x =250; 5 3x =500; Read section 3.3, 3.4 Announcements: Bell Ringer: Use your calculator to solve
 Dte: 3/14/13 Objective: SWBAT pply properties of exponentil functions nd will pply properties of rithms. Bell Ringer: Use your clcultor to solve 4 7x =250; 5 3x =500; HW Requests: Properties of Log Equtions
Dte: 3/14/13 Objective: SWBAT pply properties of exponentil functions nd will pply properties of rithms. Bell Ringer: Use your clcultor to solve 4 7x =250; 5 3x =500; HW Requests: Properties of Log Equtions
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES: IR, NMR, MASS SPECT
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: PURPOSE OF ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Classical Methods (Wet Chemistry): Chemists needed to run dozens of chemical reactions to determine the type of molecules in a compound.
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: PURPOSE OF ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Classical Methods (Wet Chemistry): Chemists needed to run dozens of chemical reactions to determine the type of molecules in a compound.
Exam I 19 April 2004 Name:
 Chem 317 S04 Page 1 of 7 Kantorowski Exam I 19 April 2004 Name: This exam contains 6 pages of questions confirm this once you begin The last page is a spectral data table that can be removed You will have
Chem 317 S04 Page 1 of 7 Kantorowski Exam I 19 April 2004 Name: This exam contains 6 pages of questions confirm this once you begin The last page is a spectral data table that can be removed You will have
Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry
 Homework Fundmentls of nlyticl hemistry hpter 9 0, 1, 5, 7, 9 cids, Bses, nd hpter 9(b) Definitions cid Releses H ions in wter (rrhenius) Proton donor (Bronsted( Lowry) Electron-pir cceptor (Lewis) hrcteristic
Homework Fundmentls of nlyticl hemistry hpter 9 0, 1, 5, 7, 9 cids, Bses, nd hpter 9(b) Definitions cid Releses H ions in wter (rrhenius) Proton donor (Bronsted( Lowry) Electron-pir cceptor (Lewis) hrcteristic
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: PURPOSE OF ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Classical Methods (Wet Chemistry): Chemists needed to run dozens of chemical reactions to determine the type of molecules in a compound.
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: PURPOSE OF ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Classical Methods (Wet Chemistry): Chemists needed to run dozens of chemical reactions to determine the type of molecules in a compound.
Look for absorption bands in decreasing order of importance:
 1. Match the following to their IR spectra (30 points) Look for absorption bands in decreasing order of importance: a e a 2941 1716 d f b 3333 c b 1466 1.the - absorption(s) between 3100 and 2850 cm-1.
1. Match the following to their IR spectra (30 points) Look for absorption bands in decreasing order of importance: a e a 2941 1716 d f b 3333 c b 1466 1.the - absorption(s) between 3100 and 2850 cm-1.
Cu 3 (PO 4 ) 2 (s) 3 Cu 2+ (aq) + 2 PO 4 3- (aq) circle answer: pure water or Na 3 PO 4 solution This is the common-ion effect.
 CHEM 1122011 NAME: ANSWER KEY Vining, Exm # SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS ============= 4 points ech ============ All work must be shown. 1. Wht re [H O ] nd [OH ] for solution tht hs ph of 9.0? Choose one. ()
CHEM 1122011 NAME: ANSWER KEY Vining, Exm # SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS ============= 4 points ech ============ All work must be shown. 1. Wht re [H O ] nd [OH ] for solution tht hs ph of 9.0? Choose one. ()
22 and Applications of 13 C NMR
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 12 and rganic Spectroscopy 22 and Applications of 13 C NMR CHE_P12_M22 TABLE F CNTENTS 1. Learning utcomes 2. Introduction 3. Structural
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 12 and rganic Spectroscopy 22 and Applications of 13 C NMR CHE_P12_M22 TABLE F CNTENTS 1. Learning utcomes 2. Introduction 3. Structural
Lecture 11. IR Theory. Next Class: Lecture Problem 4 due Thin-Layer Chromatography
 Lecture 11 IR Theory Next Class: Lecture Problem 4 due Thin-Layer Chromatography This Week In Lab: Ch 6: Procedures 2 & 3 Procedure 4 (outside of lab) Next Week in Lab: Ch 7: PreLab Due Quiz 4 Ch 5 Final
Lecture 11 IR Theory Next Class: Lecture Problem 4 due Thin-Layer Chromatography This Week In Lab: Ch 6: Procedures 2 & 3 Procedure 4 (outside of lab) Next Week in Lab: Ch 7: PreLab Due Quiz 4 Ch 5 Final
2. Match the following NMR spectra with one of the following substances. Write you answer in the box along side the spectrum. (16 points) A B C D E F
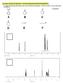 2. Match the following NM spectra with one of the following substances. Write you answer in the box along side the spectrum H H (16 points) A B C H D E F 1. Match the following compounds with their 13
2. Match the following NM spectra with one of the following substances. Write you answer in the box along side the spectrum H H (16 points) A B C H D E F 1. Match the following compounds with their 13
CHEM 203. Midterm Exam 1 October 31, 2008 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Midterm Exam 1 ctober 31, 2008 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This exam contains 8 pages Time: 1h 30 min 1. / 15 2. / 16 3. /
CEM 203 Midterm Exam 1 ctober 31, 2008 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This exam contains 8 pages Time: 1h 30 min 1. / 15 2. / 16 3. /
Chapter 6 Notes, Larson/Hostetler 3e
 Contents 6. Antiderivtives nd the Rules of Integrtion.......................... 6. Are nd the Definite Integrl.................................. 6.. Are............................................ 6. Reimnn
Contents 6. Antiderivtives nd the Rules of Integrtion.......................... 6. Are nd the Definite Integrl.................................. 6.. Are............................................ 6. Reimnn
BOND ORDER (BO): Single bond Þ BO = 1; Double bond Þ BO = 2; Triple bond Þ BO = 3 Bond Order Þ bond strength and bond length
 EMISTRY 104 elp Sheet #1 hem 103 Review (Text: h 6, h 7) Do topics pproprite for your lecture Prepred y Dr. Tony Jco http://www.chem.wisc.edu/res/clc (Resource pge) Nuggets: Electronegtivity (6.7), Bond
EMISTRY 104 elp Sheet #1 hem 103 Review (Text: h 6, h 7) Do topics pproprite for your lecture Prepred y Dr. Tony Jco http://www.chem.wisc.edu/res/clc (Resource pge) Nuggets: Electronegtivity (6.7), Bond
Chem 130 Second Exam
 Nme Chem 130 Second Exm On the following pges you will find questions tht cover the structure of molecules, ions, nd solids, nd the different models we use to explin the nture of chemicl bonding. Red ech
Nme Chem 130 Second Exm On the following pges you will find questions tht cover the structure of molecules, ions, nd solids, nd the different models we use to explin the nture of chemicl bonding. Red ech
Answers to Assignment #5
 Answers to Assignment #5 A. 9 8 l 2 5 DBE (benzene + 1 DBE) ( 9 2(9)+2-9 8+1+1 = 10 ˆ 5 DBE) nmr pattern of two doublets of equal integration at δ7.4 and 7.9 ppm means the group (the δ7.9 shift) IR band
Answers to Assignment #5 A. 9 8 l 2 5 DBE (benzene + 1 DBE) ( 9 2(9)+2-9 8+1+1 = 10 ˆ 5 DBE) nmr pattern of two doublets of equal integration at δ7.4 and 7.9 ppm means the group (the δ7.9 shift) IR band
BASIC NOMENCLATURE. The names of the groups you must be able to recognize and draw are:
 A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: BASIC NOMENCLATURE 1. Give examples of, and recognize when given the structure, representatives of the following classes of compounds. Alkyl halides (1, 2, 3 ) Alcohols (1,
A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO: BASIC NOMENCLATURE 1. Give examples of, and recognize when given the structure, representatives of the following classes of compounds. Alkyl halides (1, 2, 3 ) Alcohols (1,
Proton NMR. Four Questions
 Proton NMR Four Questions How many signals? Equivalence Where on spectrum? Chemical Shift How big? Integration Shape? Splitting (coupling) 1 Proton NMR Shifts Basic Correlation Chart How many 1 H signals?
Proton NMR Four Questions How many signals? Equivalence Where on spectrum? Chemical Shift How big? Integration Shape? Splitting (coupling) 1 Proton NMR Shifts Basic Correlation Chart How many 1 H signals?
The graphs of Rational Functions
 Lecture 4 5A: The its of Rtionl Functions s x nd s x + The grphs of Rtionl Functions The grphs of rtionl functions hve severl differences compred to power functions. One of the differences is the behvior
Lecture 4 5A: The its of Rtionl Functions s x nd s x + The grphs of Rtionl Functions The grphs of rtionl functions hve severl differences compred to power functions. One of the differences is the behvior
ORGANIC - BRUICE 8E CH MASS SPECT AND INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: PURPOSE OF ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Classical Methods (Wet Chemistry): Chemists needed to run dozens of chemical reactions to determine the type of molecules in a compound.
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: PURPOSE OF ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Classical Methods (Wet Chemistry): Chemists needed to run dozens of chemical reactions to determine the type of molecules in a compound.
Chapter 13: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy direct observation of the H s and C s of a molecules
 hapter 13: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy direct observation of the s and s of a molecules Nuclei are positively charged and spin on an axis; they create a tiny magnetic field + + Not all
hapter 13: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy direct observation of the s and s of a molecules Nuclei are positively charged and spin on an axis; they create a tiny magnetic field + + Not all
CHAPTER 08: MONOPROTIC ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIA
 Hrris: Quntittive Chemicl Anlysis, Eight Edition CHAPTER 08: MONOPROTIC ACIDBASE EQUILIBRIA CHAPTER 08: Opener A CHAPTER 08: Opener B CHAPTER 08: Opener C CHAPTER 08: Opener D CHAPTER 08: Opener E Chpter
Hrris: Quntittive Chemicl Anlysis, Eight Edition CHAPTER 08: MONOPROTIC ACIDBASE EQUILIBRIA CHAPTER 08: Opener A CHAPTER 08: Opener B CHAPTER 08: Opener C CHAPTER 08: Opener D CHAPTER 08: Opener E Chpter
Nuclear spin and the splitting of energy levels in a magnetic field
 Nuclear spin and the splitting of energy levels in a magnetic field Top 3 list for 13 C NMR Interpretation 1. Symmetry 2. Chemical Shifts 3. Multiplicity 13 C NMR of C 3 O 1 NMR of C 3 O 13 C NMR of C
Nuclear spin and the splitting of energy levels in a magnetic field Top 3 list for 13 C NMR Interpretation 1. Symmetry 2. Chemical Shifts 3. Multiplicity 13 C NMR of C 3 O 1 NMR of C 3 O 13 C NMR of C
Module 2: Rate Law & Stoichiomtery (Chapter 3, Fogler)
 CHE 309: Chemicl Rection Engineering Lecture-8 Module 2: Rte Lw & Stoichiomtery (Chpter 3, Fogler) Topics to be covered in tody s lecture Thermodynmics nd Kinetics Rection rtes for reversible rections
CHE 309: Chemicl Rection Engineering Lecture-8 Module 2: Rte Lw & Stoichiomtery (Chpter 3, Fogler) Topics to be covered in tody s lecture Thermodynmics nd Kinetics Rection rtes for reversible rections
7a. Structure Elucidation: IR and 13 C-NMR Spectroscopies (text , , 12.10)
 2009, Department of Chemistry, The University of Western Ontario 7a.1 7a. Structure Elucidation: IR and 13 C-NMR Spectroscopies (text 11.1 11.5, 12.1 12.5, 12.10) A. Electromagnetic Radiation Energy is
2009, Department of Chemistry, The University of Western Ontario 7a.1 7a. Structure Elucidation: IR and 13 C-NMR Spectroscopies (text 11.1 11.5, 12.1 12.5, 12.10) A. Electromagnetic Radiation Energy is
CHEM Chapter 13. Nuclear Magnetic Spectroscopy (Homework) W
 CHEM 2423. Chapter 13. Nuclear Magnetic Spectroscopy (Homework) W Short Answer 1. For a nucleus to exhibit the nuclear magnetic resonance phenomenon, it must be magnetic. Magnetic nuclei include: a. all
CHEM 2423. Chapter 13. Nuclear Magnetic Spectroscopy (Homework) W Short Answer 1. For a nucleus to exhibit the nuclear magnetic resonance phenomenon, it must be magnetic. Magnetic nuclei include: a. all
Tuesday, January 13, NMR Spectroscopy
 NMR Spectroscopy NMR Phenomenon Nuclear Magnetic Resonance µ A spinning charged particle generates a magnetic field. A nucleus with a spin angular momentum will generate a magnetic moment (μ). If these
NMR Spectroscopy NMR Phenomenon Nuclear Magnetic Resonance µ A spinning charged particle generates a magnetic field. A nucleus with a spin angular momentum will generate a magnetic moment (μ). If these
Chem 130 Second Exam
 Nme Chem 130 Second Exm On the following pges you will find seven questions covering vries topics rnging from the structure of molecules, ions, nd solids to different models for explining bonding. Red
Nme Chem 130 Second Exm On the following pges you will find seven questions covering vries topics rnging from the structure of molecules, ions, nd solids to different models for explining bonding. Red
Carbon Compounds. Chemical Bonding Part 2
 Carbon Compounds Chemical Bonding Part 2 Introduction to Functional Groups: Alkanes! Alkanes Compounds that contain only carbons and hydrogens, with no double or triple bonds.! Alkyl Groups A part of a
Carbon Compounds Chemical Bonding Part 2 Introduction to Functional Groups: Alkanes! Alkanes Compounds that contain only carbons and hydrogens, with no double or triple bonds.! Alkyl Groups A part of a
CHEM 213 FALL 2016 MIDTERM EXAM 2 - VERSION A
 CHEM 213 FALL 2016 MIDTERM EXAM 2 - VERSIN A Answer multiple choice questions on the green computer sheet provided with a PENCIL. Be sure to encode both your NAME and Registration Number (V#). You will
CHEM 213 FALL 2016 MIDTERM EXAM 2 - VERSIN A Answer multiple choice questions on the green computer sheet provided with a PENCIL. Be sure to encode both your NAME and Registration Number (V#). You will
13: Diffusion in 2 Energy Groups
 3: Diffusion in Energy Groups B. Rouben McMster University Course EP 4D3/6D3 Nucler Rector Anlysis (Rector Physics) 5 Sept.-Dec. 5 September Contents We study the diffusion eqution in two energy groups
3: Diffusion in Energy Groups B. Rouben McMster University Course EP 4D3/6D3 Nucler Rector Anlysis (Rector Physics) 5 Sept.-Dec. 5 September Contents We study the diffusion eqution in two energy groups
SPECTROSCOPY MEASURES THE INTERACTION BETWEEN LIGHT AND MATTER
 SPECTROSCOPY MEASURES THE INTERACTION BETWEEN LIGHT AND MATTER c = c: speed of light 3.00 x 10 8 m/s (lamda): wavelength (m) (nu): frequency (Hz) Increasing E (J) Increasing (Hz) E = h h - Planck s constant
SPECTROSCOPY MEASURES THE INTERACTION BETWEEN LIGHT AND MATTER c = c: speed of light 3.00 x 10 8 m/s (lamda): wavelength (m) (nu): frequency (Hz) Increasing E (J) Increasing (Hz) E = h h - Planck s constant
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 1
 Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 1 Thursday, February 11, 2016; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 1 Thursday, February 11, 2016; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out
video 14.4 isomers isomers Isomers have the molecular formula but are rearranged in a structure with different properties. Example: Both C 4 H 10
 video 14.4 isomers isomers Isomers have the molecular formula but are rearranged in a structure with different properties. Example: Both C 4 H 10 Butane Methylpropane 1 match the isomers drawing an isomer
video 14.4 isomers isomers Isomers have the molecular formula but are rearranged in a structure with different properties. Example: Both C 4 H 10 Butane Methylpropane 1 match the isomers drawing an isomer
C NMR Spectroscopy
 13.14 13 C NMR Spectroscopy 1 H and 13 C NMR compared: both give us information about the number of chemically nonequivalent nuclei (nonequivalent hydrogens or nonequivalent carbons) both give us information
13.14 13 C NMR Spectroscopy 1 H and 13 C NMR compared: both give us information about the number of chemically nonequivalent nuclei (nonequivalent hydrogens or nonequivalent carbons) both give us information
CHEMICAL KINETICS
 CHEMICAL KINETICS Long Answer Questions: 1. Explin the following terms with suitble exmples ) Averge rte of Rection b) Slow nd Fst Rections c) Order of Rection d) Moleculrity of Rection e) Activtion Energy
CHEMICAL KINETICS Long Answer Questions: 1. Explin the following terms with suitble exmples ) Averge rte of Rection b) Slow nd Fst Rections c) Order of Rection d) Moleculrity of Rection e) Activtion Energy
SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE
 SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Indices & Logrithms 2 Contents Indices.2 Frctionl Indices.4 Logrithms 6 Exponentil equtions. Simplifying Surds 13 Opertions on Surds..16 Scientific Nottion..18
SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Indices & Logrithms 2 Contents Indices.2 Frctionl Indices.4 Logrithms 6 Exponentil equtions. Simplifying Surds 13 Opertions on Surds..16 Scientific Nottion..18
More information can be found in Chapter 12 in your textbook for CHEM 3750/ 3770 and on pages in your laboratory manual.
 CHEM 3780 rganic Chemistry II Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry Review More information can be found in Chapter 12 in your textbook for CHEM 3750/ 3770 and on pages 13-28 in your laboratory manual.
CHEM 3780 rganic Chemistry II Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry Review More information can be found in Chapter 12 in your textbook for CHEM 3750/ 3770 and on pages 13-28 in your laboratory manual.
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and How Do They Work?
 Wht is in Common for the Following Rections, nd ow Do They Work? You should eventully be ble to drw the mechnism for these (nd other) rections 13 Key Intermedite 1 Br-Br N Br 2 C 3 -I Me NMe Me Me C 3
Wht is in Common for the Following Rections, nd ow Do They Work? You should eventully be ble to drw the mechnism for these (nd other) rections 13 Key Intermedite 1 Br-Br N Br 2 C 3 -I Me NMe Me Me C 3
Consolidation Worksheet
 Cmbridge Essentils Mthemtics Core 8 NConsolidtion Worksheet N Consolidtion Worksheet Work these out. 8 b 7 + 0 c 6 + 7 5 Use the number line to help. 2 Remember + 2 2 +2 2 2 + 2 Adding negtive number is
Cmbridge Essentils Mthemtics Core 8 NConsolidtion Worksheet N Consolidtion Worksheet Work these out. 8 b 7 + 0 c 6 + 7 5 Use the number line to help. 2 Remember + 2 2 +2 2 2 + 2 Adding negtive number is
FAMILIES of ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
 1 SCH4U October 2016 Organic Chemistry Chemistry of compounds that contain carbon (except: CO, CO 2, HCN, CO 3 - ) Carbon is covalently bonded to another carbon, hydrogen and possibly to oxygen, a halogen
1 SCH4U October 2016 Organic Chemistry Chemistry of compounds that contain carbon (except: CO, CO 2, HCN, CO 3 - ) Carbon is covalently bonded to another carbon, hydrogen and possibly to oxygen, a halogen
Polynomial Approximations for the Natural Logarithm and Arctangent Functions. Math 230
 Polynomil Approimtions for the Nturl Logrithm nd Arctngent Functions Mth 23 You recll from first semester clculus how one cn use the derivtive to find n eqution for the tngent line to function t given
Polynomil Approimtions for the Nturl Logrithm nd Arctngent Functions Mth 23 You recll from first semester clculus how one cn use the derivtive to find n eqution for the tngent line to function t given
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy II. 13 C NMR. Reading: Pavia Chapter , 6.7, 6.11, 6.13
 Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy II. 13 NMR Reading: Pavia hapter 6.1-6.5, 6.7, 6.11, 6.13 1. General - more/better/additional structural information for larger compounds -problems: a) isotopes
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy II. 13 NMR Reading: Pavia hapter 6.1-6.5, 6.7, 6.11, 6.13 1. General - more/better/additional structural information for larger compounds -problems: a) isotopes
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Solutions to In-Text Problems 13.1 (b) Apply Eq. 13.2b with = 360 MHz. chemical shift in Hz = δ = (4.40)(360) = 1584 Hz 13.2 (b) Follow the same procedure used
13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Solutions to In-Text Problems 13.1 (b) Apply Eq. 13.2b with = 360 MHz. chemical shift in Hz = δ = (4.40)(360) = 1584 Hz 13.2 (b) Follow the same procedure used
7.2 Riemann Integrable Functions
 7.2 Riemnn Integrble Functions Theorem 1. If f : [, b] R is step function, then f R[, b]. Theorem 2. If f : [, b] R is continuous on [, b], then f R[, b]. Theorem 3. If f : [, b] R is bounded nd continuous
7.2 Riemnn Integrble Functions Theorem 1. If f : [, b] R is step function, then f R[, b]. Theorem 2. If f : [, b] R is continuous on [, b], then f R[, b]. Theorem 3. If f : [, b] R is bounded nd continuous
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds. Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 15, 2010 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
CH 320/328 N Summer II 2018
 CH 320/328 N Summer II 2018 HW 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. (5 pts each) 1. Which
CH 320/328 N Summer II 2018 HW 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. (5 pts each) 1. Which
Properties of Integrals, Indefinite Integrals. Goals: Definition of the Definite Integral Integral Calculations using Antiderivatives
 Block #6: Properties of Integrls, Indefinite Integrls Gols: Definition of the Definite Integrl Integrl Clcultions using Antiderivtives Properties of Integrls The Indefinite Integrl 1 Riemnn Sums - 1 Riemnn
Block #6: Properties of Integrls, Indefinite Integrls Gols: Definition of the Definite Integrl Integrl Clcultions using Antiderivtives Properties of Integrls The Indefinite Integrl 1 Riemnn Sums - 1 Riemnn
CHAPTER 24 Organic Chemistry
 CHAPTER 24 rganic Chemistry 1. The general formula for alkenes is A. C n H 2n+2 B. C 2n H 2n C. C n H n+2 D. C n H 2n E. C n H 2n 2 2. The general formula of an alkane is A. C n H 2n B. C n H 2n+2 C. C
CHAPTER 24 rganic Chemistry 1. The general formula for alkenes is A. C n H 2n+2 B. C 2n H 2n C. C n H n+2 D. C n H 2n E. C n H 2n 2 2. The general formula of an alkane is A. C n H 2n B. C n H 2n+2 C. C
Lesson 1: Quadratic Equations
 Lesson 1: Qudrtic Equtions Qudrtic Eqution: The qudrtic eqution in form is. In this section, we will review 4 methods of qudrtic equtions, nd when it is most to use ech method. 1. 3.. 4. Method 1: Fctoring
Lesson 1: Qudrtic Equtions Qudrtic Eqution: The qudrtic eqution in form is. In this section, we will review 4 methods of qudrtic equtions, nd when it is most to use ech method. 1. 3.. 4. Method 1: Fctoring
Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes
 Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons generally fall into 2 general groupings, aliphatic hydrocarbons and aromatic hydrocarbons. Aliphatic hydrocarbons contain chains and rings of hydrocarbons,
Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons generally fall into 2 general groupings, aliphatic hydrocarbons and aromatic hydrocarbons. Aliphatic hydrocarbons contain chains and rings of hydrocarbons,
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance H-NMR Part 1 Introduction to NMR, Instrumentation, Sample Prep, Chemical Shift. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance H-NMR Part 1 Introduction to NMR, Instrumentation, Sample Prep, Chemical Shift Dr. Sapna Gupta Introduction NMR is the most powerful tool available for organic structure determination.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance H-NMR Part 1 Introduction to NMR, Instrumentation, Sample Prep, Chemical Shift Dr. Sapna Gupta Introduction NMR is the most powerful tool available for organic structure determination.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry Hour Exam #1. Name. Official Recitation Instructor
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology rganic Chemistry. Friday, September 0, 00 Prof. Timothy F. Jamison Hour Exam # Name (please both print and sign your name) fficial Recitation Instructor Directions:
Massachusetts Institute of Technology rganic Chemistry. Friday, September 0, 00 Prof. Timothy F. Jamison Hour Exam # Name (please both print and sign your name) fficial Recitation Instructor Directions:
Chemistry 14C Winter 2017 Exam 2 Solutions Page 1
 Chemistry 14C Winter 2017 Exam 2 Solutions Page 1 Statistics: High score, average, and low score will be posted on the course web site after exam grading is complete. Some questions have more than one
Chemistry 14C Winter 2017 Exam 2 Solutions Page 1 Statistics: High score, average, and low score will be posted on the course web site after exam grading is complete. Some questions have more than one
Table 8.2 Detailed Table of Characteristic Infrared Absorption Frequencies
 Table 8.2 Detailed Table of Characteristic Infrared Absorption Frequencies The hydrogen stretch region (3600 2500 cm 1 ). Absorption in this region is associated with the stretching vibration of hydrogen
Table 8.2 Detailed Table of Characteristic Infrared Absorption Frequencies The hydrogen stretch region (3600 2500 cm 1 ). Absorption in this region is associated with the stretching vibration of hydrogen
AP Calculus Multiple Choice: BC Edition Solutions
 AP Clculus Multiple Choice: BC Edition Solutions J. Slon Mrch 8, 04 ) 0 dx ( x) is A) B) C) D) E) Divergent This function inside the integrl hs verticl symptotes t x =, nd the integrl bounds contin this
AP Clculus Multiple Choice: BC Edition Solutions J. Slon Mrch 8, 04 ) 0 dx ( x) is A) B) C) D) E) Divergent This function inside the integrl hs verticl symptotes t x =, nd the integrl bounds contin this
MASS SPECTROMETRY: BASIC EXPERIMENT
 http://science.widener.edu/svb/massspec/ei.html relative abundance Pavia 8.1-8.5 MASS SPECTROMETRY: BASIC EXPERIMENT scienceaid.co.uk -e Molecule Molecule +. + 2e base peak [Fragments] +. fragment peaks
http://science.widener.edu/svb/massspec/ei.html relative abundance Pavia 8.1-8.5 MASS SPECTROMETRY: BASIC EXPERIMENT scienceaid.co.uk -e Molecule Molecule +. + 2e base peak [Fragments] +. fragment peaks
Hydronium or hydroxide ions can also be produced by a reaction of certain substances with water:
 Chpter 14 1 ACIDS/BASES Acids hve tste, rect with most metls to produce, rect with most crbontes to produce, turn litmus nd phenolphthlein. Bses hve tste rect very well well with most metls or crbontes,
Chpter 14 1 ACIDS/BASES Acids hve tste, rect with most metls to produce, rect with most crbontes to produce, turn litmus nd phenolphthlein. Bses hve tste rect very well well with most metls or crbontes,
State space systems analysis (continued) Stability. A. Definitions A system is said to be Asymptotically Stable (AS) when it satisfies
 Stte spce systems nlysis (continued) Stbility A. Definitions A system is sid to be Asymptoticlly Stble (AS) when it stisfies ut () = 0, t > 0 lim xt () 0. t A system is AS if nd only if the impulse response
Stte spce systems nlysis (continued) Stbility A. Definitions A system is sid to be Asymptoticlly Stble (AS) when it stisfies ut () = 0, t > 0 lim xt () 0. t A system is AS if nd only if the impulse response
Instrumental Chemical Analysis
 L15 Page1 Instrumental Chemical Analysis Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Dr. Ahmad Najjar Philadelphia University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences 1 st semester, 2017/2018 Nuclear Magnetic
L15 Page1 Instrumental Chemical Analysis Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Dr. Ahmad Najjar Philadelphia University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences 1 st semester, 2017/2018 Nuclear Magnetic
Numerical Analysis: Trapezoidal and Simpson s Rule
 nd Simpson s Mthemticl question we re interested in numericlly nswering How to we evlute I = f (x) dx? Clculus tells us tht if F(x) is the ntiderivtive of function f (x) on the intervl [, b], then I =
nd Simpson s Mthemticl question we re interested in numericlly nswering How to we evlute I = f (x) dx? Clculus tells us tht if F(x) is the ntiderivtive of function f (x) on the intervl [, b], then I =
Chapter 1: Fundamentals
 Chpter 1: Fundmentls 1.1 Rel Numbers Types of Rel Numbers: Nturl Numbers: {1, 2, 3,...}; These re the counting numbers. Integers: {... 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,...}; These re ll the nturl numbers, their negtives,
Chpter 1: Fundmentls 1.1 Rel Numbers Types of Rel Numbers: Nturl Numbers: {1, 2, 3,...}; These re the counting numbers. Integers: {... 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,...}; These re ll the nturl numbers, their negtives,
NMRis the most valuable spectroscopic technique for organic chemists because it maps the carbon-hydrogen framework of a molecule.
 Chapter 13: Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy NMRis the most valuable spectroscopic technique for organic chemists because it maps the carbon-hydrogen framework of a molecule. 13.2 The nature of
Chapter 13: Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy NMRis the most valuable spectroscopic technique for organic chemists because it maps the carbon-hydrogen framework of a molecule. 13.2 The nature of
UNIT 1 FUNCTIONS AND THEIR INVERSES Lesson 1.4: Logarithmic Functions as Inverses Instruction
 Lesson : Logrithmic Functions s Inverses Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: determining the dependent nd independent vribles in n exponentil function bsed on dt from
Lesson : Logrithmic Functions s Inverses Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: determining the dependent nd independent vribles in n exponentil function bsed on dt from
IUPAC Nomenclature Chem12A, Organic Chemistry I
 IUPAC Nomenclature ChemA, rganic Chemistry I IUPAC PEFIXES Prefix Substituent Group Number of Carbons meth- methyl eth- ethyl prop- propyl but- butyl pent- pentyl hex- hexyl hept- heptyl 7 oct- octyl 8
IUPAC Nomenclature ChemA, rganic Chemistry I IUPAC PEFIXES Prefix Substituent Group Number of Carbons meth- methyl eth- ethyl prop- propyl but- butyl pent- pentyl hex- hexyl hept- heptyl 7 oct- octyl 8
A-Level Mathematics Transition Task (compulsory for all maths students and all further maths student)
 A-Level Mthemtics Trnsition Tsk (compulsory for ll mths students nd ll further mths student) Due: st Lesson of the yer. Length: - hours work (depending on prior knowledge) This trnsition tsk provides revision
A-Level Mthemtics Trnsition Tsk (compulsory for ll mths students nd ll further mths student) Due: st Lesson of the yer. Length: - hours work (depending on prior knowledge) This trnsition tsk provides revision
Closed book exam, no books, notebooks, notes, etc. allowed. However, calculators, rulers, and molecular model sets are permitted.
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13 Friday, September 26, 2003 Prof. Timothy F. Jamison Hour Exam #1 Name (please both print and sign your name) Official Recitation Instructor
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13 Friday, September 26, 2003 Prof. Timothy F. Jamison Hour Exam #1 Name (please both print and sign your name) Official Recitation Instructor
x = b a n x 2 e x dx. cdx = c(b a), where c is any constant. a b
 CHAPTER 5. INTEGRALS 61 where nd x = b n x i = 1 (x i 1 + x i ) = midpoint of [x i 1, x i ]. Problem 168 (Exercise 1, pge 377). Use the Midpoint Rule with the n = 4 to pproximte 5 1 x e x dx. Some quick
CHAPTER 5. INTEGRALS 61 where nd x = b n x i = 1 (x i 1 + x i ) = midpoint of [x i 1, x i ]. Problem 168 (Exercise 1, pge 377). Use the Midpoint Rule with the n = 4 to pproximte 5 1 x e x dx. Some quick
n f(x i ) x. i=1 In section 4.2, we defined the definite integral of f from x = a to x = b as n f(x i ) x; f(x) dx = lim i=1
 The Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus As we continue to study the re problem, let s think bck to wht we know bout computing res of regions enclosed by curves. If we wnt to find the re of the region below the
The Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus As we continue to study the re problem, let s think bck to wht we know bout computing res of regions enclosed by curves. If we wnt to find the re of the region below the
Construction of Gauss Quadrature Rules
 Jim Lmbers MAT 772 Fll Semester 2010-11 Lecture 15 Notes These notes correspond to Sections 10.2 nd 10.3 in the text. Construction of Guss Qudrture Rules Previously, we lerned tht Newton-Cotes qudrture
Jim Lmbers MAT 772 Fll Semester 2010-11 Lecture 15 Notes These notes correspond to Sections 10.2 nd 10.3 in the text. Construction of Guss Qudrture Rules Previously, we lerned tht Newton-Cotes qudrture
Please write neatly!
 Nme Chem 130 Second Exm On the following pges re eight questions tht consider the structure of molecules, ions, nd solids, nd the different models we use to explin the nture of chemicl bonding. Red ech
Nme Chem 130 Second Exm On the following pges re eight questions tht consider the structure of molecules, ions, nd solids, nd the different models we use to explin the nture of chemicl bonding. Red ech
William H. Brown & Christopher S. Foote
 Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to:permissions Department, Harcourt Brace & Company, 6277 Sea Harbor Drive, Orlando, Florida 32887-6777 William H. Brown
Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to:permissions Department, Harcourt Brace & Company, 6277 Sea Harbor Drive, Orlando, Florida 32887-6777 William H. Brown
Infrared Spectroscopy An Instrumental Method for Detecting Functional Groups
 Infrared Spectroscopy An Instrumental Method for Detecting Functional Groups 1 The Electromagnetic Spectrum Infrared Spectroscopy I. Physics Review Frequency, υ (nu), is the number of wave cycles that
Infrared Spectroscopy An Instrumental Method for Detecting Functional Groups 1 The Electromagnetic Spectrum Infrared Spectroscopy I. Physics Review Frequency, υ (nu), is the number of wave cycles that
1.2. Linear Variable Coefficient Equations. y + b "! = a y + b " Remark: The case b = 0 and a non-constant can be solved with the same idea as above.
 1 12 Liner Vrible Coefficient Equtions Section Objective(s): Review: Constnt Coefficient Equtions Solving Vrible Coefficient Equtions The Integrting Fctor Method The Bernoulli Eqution 121 Review: Constnt
1 12 Liner Vrible Coefficient Equtions Section Objective(s): Review: Constnt Coefficient Equtions Solving Vrible Coefficient Equtions The Integrting Fctor Method The Bernoulli Eqution 121 Review: Constnt
Numerical Integration
 Chpter 5 Numericl Integrtion Numericl integrtion is the study of how the numericl vlue of n integrl cn be found. Methods of function pproximtion discussed in Chpter??, i.e., function pproximtion vi the
Chpter 5 Numericl Integrtion Numericl integrtion is the study of how the numericl vlue of n integrl cn be found. Methods of function pproximtion discussed in Chpter??, i.e., function pproximtion vi the
N_HW1 N_HW1. 1. What is the purpose of the H 2 O in this sequence?
 N_HW1 N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. 1. What is the purpose of the H 2 O in this
N_HW1 N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. 1. What is the purpose of the H 2 O in this
Problem Set 3 Solutions
 Chemistry 36 Dr Jen M Stndrd Problem Set 3 Solutions 1 Verify for the prticle in one-dimensionl box by explicit integrtion tht the wvefunction ψ ( x) π x is normlized To verify tht ψ ( x) is normlized,
Chemistry 36 Dr Jen M Stndrd Problem Set 3 Solutions 1 Verify for the prticle in one-dimensionl box by explicit integrtion tht the wvefunction ψ ( x) π x is normlized To verify tht ψ ( x) is normlized,
MATH SS124 Sec 39 Concepts summary with examples
 This note is mde for students in MTH124 Section 39 to review most(not ll) topics I think we covered in this semester, nd there s exmples fter these concepts, go over this note nd try to solve those exmples
This note is mde for students in MTH124 Section 39 to review most(not ll) topics I think we covered in this semester, nd there s exmples fter these concepts, go over this note nd try to solve those exmples
Organic Chemistry 1 CHM 2210 Exam 4 (December 10, 2001)
 Exam 4 (December 10, 2001) Name (print): Signature: Student ID Number: There are 12 multiple choice problems (4 points each) on this exam. Record the answers to the multiple choice questions on THIS PAGE.
Exam 4 (December 10, 2001) Name (print): Signature: Student ID Number: There are 12 multiple choice problems (4 points each) on this exam. Record the answers to the multiple choice questions on THIS PAGE.
Electronegativity Scale F > O > Cl, N > Br > C, H
 Organic Chem Chapter 12 Alkanes Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds. Carbon has several properties that are worth discussing: Tetravalent Always forms 4 bonds Can form multiple bonds (double
Organic Chem Chapter 12 Alkanes Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds. Carbon has several properties that are worth discussing: Tetravalent Always forms 4 bonds Can form multiple bonds (double
Chem 130 Third Exam. Total /100
 Nme Chem 130 Third Exm On the following pges you will find eight questions covering vries topics rnging from precipittion solubility, cid bse, nd oxidtion reduction rections to metl lignd complexes nd
Nme Chem 130 Third Exm On the following pges you will find eight questions covering vries topics rnging from precipittion solubility, cid bse, nd oxidtion reduction rections to metl lignd complexes nd
2008 Mathematical Methods (CAS) GA 3: Examination 2
 Mthemticl Methods (CAS) GA : Exmintion GENERAL COMMENTS There were 406 students who st the Mthemticl Methods (CAS) exmintion in. Mrks rnged from to 79 out of possible score of 80. Student responses showed
Mthemticl Methods (CAS) GA : Exmintion GENERAL COMMENTS There were 406 students who st the Mthemticl Methods (CAS) exmintion in. Mrks rnged from to 79 out of possible score of 80. Student responses showed
The resonance frequency of the H b protons is dependent upon the orientation of the H a protons with respect to the external magnetic field:
 Spin-Spin Splitting in Alkanes The signal arising from a proton or set of protons is split into (N+1) lines by the presence of N adjacent nuclei Example 1: Bromoethane The resonance frequency of the H
Spin-Spin Splitting in Alkanes The signal arising from a proton or set of protons is split into (N+1) lines by the presence of N adjacent nuclei Example 1: Bromoethane The resonance frequency of the H
Section 5.1 #7, 10, 16, 21, 25; Section 5.2 #8, 9, 15, 20, 27, 30; Section 5.3 #4, 6, 9, 13, 16, 28, 31; Section 5.4 #7, 18, 21, 23, 25, 29, 40
 Mth B Prof. Audrey Terrs HW # Solutions by Alex Eustis Due Tuesdy, Oct. 9 Section 5. #7,, 6,, 5; Section 5. #8, 9, 5,, 7, 3; Section 5.3 #4, 6, 9, 3, 6, 8, 3; Section 5.4 #7, 8,, 3, 5, 9, 4 5..7 Since
Mth B Prof. Audrey Terrs HW # Solutions by Alex Eustis Due Tuesdy, Oct. 9 Section 5. #7,, 6,, 5; Section 5. #8, 9, 5,, 7, 3; Section 5.3 #4, 6, 9, 3, 6, 8, 3; Section 5.4 #7, 8,, 3, 5, 9, 4 5..7 Since
Química Orgânica I. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (II) Ciências Farmacêuticas Bioquímica Química AFB QO I 2007/08 1 AFB QO I 2007/08 2
 Química Orgânica I Ciências Farmacêuticas Bioquímica Química AFB QO I 2007/08 1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (II) AFB QO I 2007/08 2 1 Adaptado de Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition; L.G. Wade,
Química Orgânica I Ciências Farmacêuticas Bioquímica Química AFB QO I 2007/08 1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (II) AFB QO I 2007/08 2 1 Adaptado de Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition; L.G. Wade,
To Do s. Answer Keys are available in CHB204H
 To Do s Read Chapters 2, 3 & 4. Complete the end-of-chapter problems, 2-1, 2-2, 2-3 and 2-4 Complete the end-of-chapter problems, 3-1, 3-3, 3-4, 3-6 and 3-7 Complete the end-of-chapter problems, 4-1, 4-2,
To Do s Read Chapters 2, 3 & 4. Complete the end-of-chapter problems, 2-1, 2-2, 2-3 and 2-4 Complete the end-of-chapter problems, 3-1, 3-3, 3-4, 3-6 and 3-7 Complete the end-of-chapter problems, 4-1, 4-2,
