STEREOELECTRONIC EFFECTS (S.E.) IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
|
|
|
- Marilynn Charles
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 STEREOELECTRONIC EFFECTS (S.E.) IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Pierre Deslongchamps (version du 16 février 2010) Cf. pour le livre: 1
2 SECTION 8 Stereoelectronic Effects (S.E.) and Reactions at Unsaturated Systems 2
3 Reaction on Sp 2 Type Unsaturated System In cyclic ketone, both processes (which leads to a chair) are controlled by steric effects, torsional strain due to the presence of the ring. Stereoelectronic effects are there but does not play a highly discriminating role. The situation is different when the carbonyl group is part of a ring as in oxocarbenium ion 9 where formation of 10 will be always favored. A situation similar with 12 (lactones and lactams) occurs favoring 13. 3
4 Stereoelectronic Control in Iminium Salts Formation of 17 is highly favored. E. TOROMANOFF. Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr 1966, As in the Woodward total synthesis of Reserpine. R.B. WOODWARD et al. Tetrahedron. 1958, 2, 1. 4
5 Other Examples of Iminium Salts Borohydride reductions: (100%) (0%) F. BOHLMANN et al. Chem. Ber. 1963, 96, E. WENKERT et al. Chem. Ber. 1967, 89, G. STORK et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972, 94, (± )-YOHIMBINE 5
6 More on Iminium Salts There are 4 possible pathways in the reduction of 27. Two requires boat-like TS (dotted lines in 29 and 30). Of the two possible chair-like TS (solid arrow in 29 and 30), 30 suffers from severe steric interactions. Thus, the process 29 to 31 is observed. R.V. STEVENS et al. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1982,
7 Strong SE Controlled Despite Severe Steric Effects Organolithium and Grignard reagents add to iminium 60 from the more sterically congested α face yielding 61. Conformation 63 was eliminated because of a strong A 1,2 steric interaction between the N-alkyl group and ring A. L.E. OVERMAN et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102,
8 1,4-Addition in α,β-unaturated Ketone Intermediate 78 is preferred. TOROMANOFF. Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. 1962, 708. One example with the conjugate addition of HCN. Compound 80 is the major product. DJERASSI et al. J. Org. Chem. 1963, 28,
9 Other Examples of HCN 1,4-Addition Compound 81 gives a mixture of 82 and 83 via a chair-like TS. ALEXANDER et al. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans 2, 1972, Compound 93 (R=H or CH 3 ) gave under strickly kinetically controlled conditions only the axial nitrile isomer 96; a result of an attack on the α face of 93 forming 94. C. AGAMI et al. Tetrahedron 1981, 37,
10 10
11 Intramolecular Michael Addition of β-ketoester as a Function of Ring Size 11
12 12
13 13
14 14
15 15
16 16
17 Baldwin Rules for Closure in Trigonal Systems 17
18 Examples of Forbidden Intramolecular Michael No reaction with CH 3 ONa/CH 3 OH But takes place in acidic conditions Due to 18
19 Reduction of Unsaturated Ketone with Metal / NH 3 Metals: Li, Na, K, Ca, etc G. STORK et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1960, 82, 1512; 1964, 86,
20 Stereoelectronic Effects and Chemical Reduction of Bicyclic Unsaturated Ketone 20
21 Reduction of Bicyclic Unsaturated Ketone with Li / NH 3 / EtOH gave only 222 even if it is less stable (~2 kcal/mol) than 223 Because: 226 is electronically destabilized 224 and 225 are both electronically stabilized but 225 is sterically disfavored G. STORK et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1960, 82, 1512; 1964, 86,
22 Hydrogenolysis of a Leaving Group α to Ketone As a consequence, cyclohexanones with axial α substituents must be reduced more readily than analogous compounds with equatorial substituents, especially when the two compounds are essentially conformationally rigid. H.O. HOUSE. «Modern Synthetic Reactions»; 2nd Ed.,; W.A. Benjamin Inc.: Menlo Park, California, 1972; pp C. DJERASSI. «Steroid Reactions»; Holden-Day Inc.: San Francisco, 1963; pp
23 Chemical Reduction of Cyclopropyl Ketone with Li / NH 3 W.S. JOHNSON et al. Tetrahedron Lett. 1968, W.G. DAUBEN et al. J. Org. Chem. 1966, 31,
24 In Chemical Reduction, Two Carbonyl Groups are of Great Help L.A. PAQUETTE et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1978, 100, 1600, 5845; 1981, 103,
25 Double-bond Formation via a Non-concerted Mechanism (E1cB) 284 gives only gives a mixture of 286 (syn mode) and 287 (anti mode) 25
26 Bartsch and Zavada Explanation 284 to 288 to 286 is fine because Ar/ArSO 2 steric repulsion is eliminated. 291 to 287 is difficult because of the Ar/ArSO 2 repulsion. Thus, 285 gives a mixture of 286 and 287. BARTSCH, R.A., ZAVADA, J. Chem. Rev. 1980, 80,
27 Double-bond Formation via a Concerted Mechanism (E2) In conformationally mobile systems, both syn and anti eliminations are theoretically possible. The anti elimination should be favored electronically over the syn elimination because the electron pair of the C- H bond is antiperiplanar to the leaving group. It would appear safe to conclude that where stereoelectronic effects alone are operating, the anti elimination process is favored over the syn. There are however several other parameters which are also important, such as the effects of the nucleophile, the solvent, the alkyl structure of the substrate and the nature of the leaving groups. Any of these variables is capable of completly reversing the stereochemical course of a concerted elimination reaction. BORTSCH, R.A., ZAVADA, J. Chem. Rev. 1980, 80,
28 Julia Method of Homoallylic Bromides by cleavage of cyclopropyl carbinols 302 is obtained with 90-95% stereoselectivities via 304 which is sterically favored JULIA, M. et al. Bull. Soc. Chim. France 1960, 1072; 1961, See also JOHNSON, W.S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1968, 90,
29 1,4-Elimination Reaction Some examples GROB, C.A. et al. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1969, 8,
30 Other Examples of 1,4-Elimination WHARTON et al. J. Org. Chem. 1965, 30,
31 1,4-Elimination in Ryanodol DESLONGCHAMPS et al. Can. J. Chem. 1979, 57,
32 1,4-Elimination by Solvolysis ESCHENMOSER, A. et al. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1979, 18, 634,
33 Enolization of Carbonyl Group COREY, E.J. Experientia 1953, 9, 329.; J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1954, 76, 175; 1956, 78,
34 Stereochemistry of the Enolization Process Toromanoff and Valls proposed that if stereoelectronic effects are an important parameter, the cyclohexanone enolate should react by two different pathways, one involving a chairlike transition state (443 to 444) and the other a boat-like transition state (443 to 445 to 446). Thus, both of these reactions proceed by perpendicular attack of the electrophile. Their energy difference results from the difference in strain between the chair (444) and the twist-boat (445) forms. VALLS, J., TOROMANOFF, E. Bull. Soc. Chim. France 1961,
35 Experimental Evidence for S.E. in Enolization of Ketone rate of exchange of H 1 / H 2 = 73 / 1 (CH 3 ONa, CH 3 OD) in 449, rate of exchange for H 1 / H 2 = 280 / 1 FRASER, R.R. et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 54, 3809; 1978, 100,
36 H/D Exchange of Tricyclic Ketone only 451 undergoes H/D exchange (CH 3 ONa, CH 3 OD, 25 C) only 451 exists in a boat form, as a result, the bridgehead C 3 -H is appropriatly aligned to overlap with the π orbital of the carbonyl group NICKON et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 93,
37 Decarboxylation of α-keto Acid 456 undergoes decarboxylation, contrary to 458 This is in accord with deuterium incorporation in 459 MEERWEIN, H. et al. Ann. Chem. 1913, 398, 196. BOOTGER, O. Chem. Ber. 1937, 70B, 314. These compounds can undergo enolization because the cyclohexane can take a boat conformation. SCHAEFER and CLARK. J. Org. Chem. Soc. 1965, 30,
38 More About H/D Exchange Conclusion: a boat cyclohexane conformation is needed for H/D exchange YAMADA et al. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn 1979, 52,
39 Selective Exchange of Axial-H at C 6 in Steroid rate of H/D exchange at C 6 is 53 in favor of H 2 RINGOLD et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1966, 88,
40 Reaction of Enolate with Electrophiles (Position of Transition State in Reaction of Enolates) Axial protonation is not strongly favored. They concluded that in practice this type of experiment is complicated by the fact that protonation of an enolate anion can occur either at the carbon (to give 468 or 469) or at at the oxygen atom (to yield the enol). Further reaction of the enol with aqueous acid also yields the two possible ketones 468 and 469. Furthermore, since the protonation steps of this strongly basic anion (either at C or O) are difusioncontrolled, it is possible that the transition state geometries for both reactions resemble the geometry of the enolate anion, so the energy difference between the direction of attack on the enolate is small. HOUSE et al. J. Org. Chem. 1968, 33,
41 Stereochemistry of Alkylation of Enolate Alkylation of the enolate of t-butyl-cyclohexanone with triethyloxonium fluoroborate yielded a mixture of O-alkyl product and approximately equal amounts of the isomeric 2-ethyl-4-t-butyl cyclohexanones. A similar mixture of C-alkylated product was obtained using ethyl iodide. For this reason, they proposed that the corresponding transition state are early resembling the geometry of the enolate (cf. 470). HOUSE, H.O. «Modern Synthetic Organic Reactions». 2 nd Ed.; W.A. Benjamin,
42 More Control on Protonation of Enamine Enamine being less reactive than enolates. TS should be less early leading to more stereoselective reaction on axial position. SCHAEFER, J.P. et al. Tetrahedron Lett. 1965, only JOHNSON et al. Tetrahedron Lett. 1965,
43 Alkylation of Enamine is Also Highly Stereoselective Alkylation proceeds mainly to give 483 [ R = CH 3 (70%), CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 (90%) and CH 2 =CH-CH 2 (93%) ] WOLFF, R.E. et al. Bull. Chem. Soc. France 1965,
44 S.E. Control in α-deprotonation of Iminium Ion using appropriate deuterium labeling, H 1 in 487 is preferentially removed ( OR = OH (factor of 18) OR = CH 3 COO (factor of 110)) using hydroxide ion, H 1 is 486 is preferentially abstracted (factor of 130) en route to yield 489 SPENCER, T.A. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1978,
45 Decarboxylation of C 5 Malonate in 1,3-Dioxane heating 490 (X = O) at 150 C (NaCl, wet DMSO) gave preferentially 491 (9:1 ratio) on the other hand, 493 gave a 1:1 mixture of 494 and 495 Explanation: BANKS, H.D. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46,
46 Stereoselective Alkylation of Functional Groups at C 5 of 1,3-Dioxanes DESLONGCHAMPS, P. et al. Can. J. Chem. 1986, 64,
47 Addition of Electrophiles on Ester Enolate Containing an Oxygen in the β-position DESLONGCHAMPS, P. et al. Can. J. Chem. 1986, 64,
SECTION 3. Antiperiplanar Hypothesis. and Reactions at Unsaturated Systems
 SECTION 3 Antiperiplanar Hypothesis and Reactions at Unsaturated Systems (2016) 1 Reaction on Sp 2 Type Unsaturated System In cyclic ketone, both processes lead to a chair but we will see that C-H and
SECTION 3 Antiperiplanar Hypothesis and Reactions at Unsaturated Systems (2016) 1 Reaction on Sp 2 Type Unsaturated System In cyclic ketone, both processes lead to a chair but we will see that C-H and
Stereochemical Considerations in Planning Synthesis
 Chapter 2 Stereochemical Considerations in Planning Synthesis Chapter 2 Stereochemical Considerations in Planning Syntheses 2.1 Conformational Analysis Molecules that differ from each other by rotation
Chapter 2 Stereochemical Considerations in Planning Synthesis Chapter 2 Stereochemical Considerations in Planning Syntheses 2.1 Conformational Analysis Molecules that differ from each other by rotation
Chapter 8 Alkyl Halides and Elimination Reactions
 Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 8 Alkyl Halides and Elimination Reactions Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 8 Alkyl Halides and Elimination Reactions Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright
1/4/2011. Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds
 Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
STEREOELECTRONIC EFFECTS (S.E.) IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 STEEELECTNIC EFFECTS (S.E.) IN GANIC CEMISTY Pierre Deslongchamps (version du 3 février 2010) Cf. pour le livre: http://pages.usherbrooke.ca/pdeslongchamps/cv.htm 1 SECTIN 5 Stereoelectronic Effects (S.E.)
STEEELECTNIC EFFECTS (S.E.) IN GANIC CEMISTY Pierre Deslongchamps (version du 3 février 2010) Cf. pour le livre: http://pages.usherbrooke.ca/pdeslongchamps/cv.htm 1 SECTIN 5 Stereoelectronic Effects (S.E.)
Chapter 19. Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions. ß-dicarbonyl compounds. Why are ß-dicarbonyls useful?
 Chapter 19 Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions ß-dicarbonyl compounds Two carbonyl groups separated by a carbon Three common types ß-diketone ß-ketoester
Chapter 19 Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions ß-dicarbonyl compounds Two carbonyl groups separated by a carbon Three common types ß-diketone ß-ketoester
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320
 Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions I. Reaction of Enols & Enolates with ther Carbonyls Enols and enolates are electron rich nucleophiles that react with a number
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions I. Reaction of Enols & Enolates with ther Carbonyls Enols and enolates are electron rich nucleophiles that react with a number
April 2002 CUME Organic Chemistry Department of Chemistry University of Missouri Columbia Saturday, April 6th, 2002 Dr.
 April 2002 CUME Organic Chemistry Department of Chemistry University of Missouri Columbia Saturday, April 6th, 2002 Dr. Rainer Glaser Announced Reading: Prins Cyclization Reactions 1 Question 1. Aldol-Prins
April 2002 CUME Organic Chemistry Department of Chemistry University of Missouri Columbia Saturday, April 6th, 2002 Dr. Rainer Glaser Announced Reading: Prins Cyclization Reactions 1 Question 1. Aldol-Prins
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions
 Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Suggested solutions for Chapter 32
 s for Chapter 32 32 PBLEM 1 Explain how the stereo- and regio- chemistry of these reactions are controlled. Why is the epoxidation only moderately diastereoselective, and why does the amine attack where
s for Chapter 32 32 PBLEM 1 Explain how the stereo- and regio- chemistry of these reactions are controlled. Why is the epoxidation only moderately diastereoselective, and why does the amine attack where
Reactivity in Organic Chemistry. Mid term test October 31 st 2011, 9:30-12:30. Problem 1 (25p)
 eactivity in rganic Chemistry Mid term test ctober 31 st 2011, 9:30-12:30 Problem 1 (25p) - (+)- Limonone can be epoxidized (using peracetic acid) to give an inseparable mixture of two diastereomeric limonene
eactivity in rganic Chemistry Mid term test ctober 31 st 2011, 9:30-12:30 Problem 1 (25p) - (+)- Limonone can be epoxidized (using peracetic acid) to give an inseparable mixture of two diastereomeric limonene
Chapter 19. Organic Chemistry. Carbonyl Compounds III. Reactions at the a-carbon. 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice
 Organic Chemistry 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 19 Carbonyl Compounds III Reactions at the a-carbon Disampaikan oleh: Dr. Sri Handayani 2013 Irene Lee Case Western Reserve University Cleveland,
Organic Chemistry 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 19 Carbonyl Compounds III Reactions at the a-carbon Disampaikan oleh: Dr. Sri Handayani 2013 Irene Lee Case Western Reserve University Cleveland,
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122)
 Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
CHEM Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (quiz) W25
 CHEM 2425. Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (quiz) W25 Student: 1. Which of the following statements about Aldol reactions with either aldehydes or ketones is true? Equilibrium favors the starting
CHEM 2425. Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (quiz) W25 Student: 1. Which of the following statements about Aldol reactions with either aldehydes or ketones is true? Equilibrium favors the starting
Solution problem 22: Non-Benzoid Aromatic Sytems
 Solution problem 22: on-enzoid Aromatic Sytems 22.1 & 22.2 Each double bond and each heteroatom (, ) with lone pairs donates 2 π- electrons as well as a negative charge. oron or a positive charge does
Solution problem 22: on-enzoid Aromatic Sytems 22.1 & 22.2 Each double bond and each heteroatom (, ) with lone pairs donates 2 π- electrons as well as a negative charge. oron or a positive charge does
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III
 CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon
 Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon There is a basic hydrogen (α hydrogen) on α carbon, which can be removed by a strong base. 19.1 The Acidity of α-hydrogens A hydrogen bonded
Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon There is a basic hydrogen (α hydrogen) on α carbon, which can be removed by a strong base. 19.1 The Acidity of α-hydrogens A hydrogen bonded
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones
 Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions
 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Module No and Title. PAPER No: 5 ; TITLE : Organic Chemistry-II MODULE No: 25 ; TITLE: S E 1 reactions
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 5; Organic Chemistry-II 25; S E 1 reactions CHE_P5_M25 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction 3. S E 1 reactions 3.1
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 5; Organic Chemistry-II 25; S E 1 reactions CHE_P5_M25 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction 3. S E 1 reactions 3.1
Reactions at α-position
 Reactions at α-position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry, a common reaction mechanism observed was a nucleophile reacting at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon site NUC NUC Another reaction that
Reactions at α-position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry, a common reaction mechanism observed was a nucleophile reacting at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon site NUC NUC Another reaction that
Additions to the Carbonyl Groups
 Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups Nucleophilic substitution (S N 2andS N 1) reaction occurs at sp3 hybridized carbons with electronegative leaving groups Why? The carbon is electrophilic! Addition
Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups Nucleophilic substitution (S N 2andS N 1) reaction occurs at sp3 hybridized carbons with electronegative leaving groups Why? The carbon is electrophilic! Addition
Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~ 20
 Enolate Anions Chapter 17 Hydrogen on a carbons a to a carbonyl is unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by resonance to the carbonyl Aldehydes and Ketones II Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~
Enolate Anions Chapter 17 Hydrogen on a carbons a to a carbonyl is unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by resonance to the carbonyl Aldehydes and Ketones II Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~
B. A transition state represents a maximum on the reaction path diagram and can be isolated.
 Practice Hour Exam 2, Chemistry 2210, Organic Chemistry I 1. The most stable carbocation is: 2. Which of the following statements is true of transition states? A. A transition state represents a minimum
Practice Hour Exam 2, Chemistry 2210, Organic Chemistry I 1. The most stable carbocation is: 2. Which of the following statements is true of transition states? A. A transition state represents a minimum
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions and Condensation Reactions
 Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
p Bonds as Electrophiles
 Chapter 7 p Bonds as Electrophiles REACTIONS OF CARBONYLS AND RELATED FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 7.2.1 Orbital structure of the carbonyl group Because oxygen is more
Chapter 7 p Bonds as Electrophiles REACTIONS OF CARBONYLS AND RELATED FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 7.2.1 Orbital structure of the carbonyl group Because oxygen is more
Enols and Enolates. A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl)
 Enols and Enolates A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl) E+ E In the preceding chapters, we primarily studied nucleophiles
Enols and Enolates A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl) E+ E In the preceding chapters, we primarily studied nucleophiles
Section Practice Exam II Solutions
 Paul Bracher Chem 30 Section 7 Section Practice Exam II s Whether problems old r problems new, You d better practice, r you ll fail exam II. -- Anonymous TF Problem 1 a) Rank the following series of electrophiles
Paul Bracher Chem 30 Section 7 Section Practice Exam II s Whether problems old r problems new, You d better practice, r you ll fail exam II. -- Anonymous TF Problem 1 a) Rank the following series of electrophiles
Chapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides
 hapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides Overview: The nature of alkyl halides and other groups with electrophilic sp 3 hybridized leads them to react with nucleophiles and
hapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides Overview: The nature of alkyl halides and other groups with electrophilic sp 3 hybridized leads them to react with nucleophiles and
CHEM50002: Orbitals in Organic Chemistry- Stereoelectronics. LECTURE 2 Stereoelectronics of Ground States Conformational Analysis
 CEM50002: rbitals in rganic Chemistry- Stereoelectronics 1 LECTUE 2 Stereoelectronics of Ground States Conformational Analysis Alan C. Spivey a.c.spivey@imperial.ac.uk Feb-Mar 2018 2 Format & scope of
CEM50002: rbitals in rganic Chemistry- Stereoelectronics 1 LECTUE 2 Stereoelectronics of Ground States Conformational Analysis Alan C. Spivey a.c.spivey@imperial.ac.uk Feb-Mar 2018 2 Format & scope of
3. The ring being formed has six members; the breaking C C bond is inside the new ring (endo); the C being attacked is a digonal (sp) atom (dig)
 0. aturated heterocycles and stereoelectronics xyanions add readily to alkynes: see Chapter, p. 000. Br Because the same arguments apply to o for the reaction as a whole (the difference in entropy between
0. aturated heterocycles and stereoelectronics xyanions add readily to alkynes: see Chapter, p. 000. Br Because the same arguments apply to o for the reaction as a whole (the difference in entropy between
Chapter 23. Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds.
 1 Chapter 23. Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds. 1. Enolates. a) Carbonyl compounds are acidic at the α C, can be deprotonated by bases to give enolates. i) Ketones and aldehydes have pk a = 18
1 Chapter 23. Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds. 1. Enolates. a) Carbonyl compounds are acidic at the α C, can be deprotonated by bases to give enolates. i) Ketones and aldehydes have pk a = 18
ORGANIC - BRUICE 8E CH CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III: REACTIONS AT THE ALPHA-CARBON
 !! www.clutchprep.com CNCEPT: ALPHA CARBNS AND TAUTMERIZATIN We have discussed the high reactivity of the carbonyl carbon. However, carbonyls contain another highly reactive component. What is the acidity
!! www.clutchprep.com CNCEPT: ALPHA CARBNS AND TAUTMERIZATIN We have discussed the high reactivity of the carbonyl carbon. However, carbonyls contain another highly reactive component. What is the acidity
A. Loupy, B.Tchoubar. Salt Effects in Organic and Organometallic Chemistry
 A. Loupy, B.Tchoubar Salt Effects in Organic and Organometallic Chemistry 1 Introduction - Classification of Specific Salt Effects 1 1.1 Specific Salt Effects Involving the Salt's Lewis Acid or Base Character
A. Loupy, B.Tchoubar Salt Effects in Organic and Organometallic Chemistry 1 Introduction - Classification of Specific Salt Effects 1 1.1 Specific Salt Effects Involving the Salt's Lewis Acid or Base Character
Lecture 23. Amines. Chemistry 328N. April 12, 2016
 Lecture 23 Amines April 12, 2016 Michael Reaction Michael reaction: conjugate addition of an enolate Arthur Michael anion to an, -unsaturated carbonyl compound!! Following are two examples in the first,
Lecture 23 Amines April 12, 2016 Michael Reaction Michael reaction: conjugate addition of an enolate Arthur Michael anion to an, -unsaturated carbonyl compound!! Following are two examples in the first,
Chem ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I CHEM 221 /4 02 Final Examination April 20, 2005 0900-1200 Dr. Cerrie ROGERS x x periodic table & pk a data table provided non-programmable calculators allowed molecular model kits allowed
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I CHEM 221 /4 02 Final Examination April 20, 2005 0900-1200 Dr. Cerrie ROGERS x x periodic table & pk a data table provided non-programmable calculators allowed molecular model kits allowed
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King. Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; Organometallic Reagents; Oxidation & Reduction
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Advanced Organic Chemistry
 D. A. Evans, G. Lalic Question of the day: Chemistry 530A TBS Me 2 C Me toluene, 130 C 70% TBS C 2 Me H H Advanced rganic Chemistry Me Lecture 16 Cycloaddition Reactions Diels _ Alder Reaction Photochemical
D. A. Evans, G. Lalic Question of the day: Chemistry 530A TBS Me 2 C Me toluene, 130 C 70% TBS C 2 Me H H Advanced rganic Chemistry Me Lecture 16 Cycloaddition Reactions Diels _ Alder Reaction Photochemical
75. A This is a Markovnikov addition reaction. In these reactions, the pielectrons in the alkene act as a nucleophile. The strongest electrophile will
 71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
به نام خدا روشهای سنتز مواد آلی
 به نام خدا روشهای سنتز مواد آلی 1 References: 1. Carey, F. A.; Sundberg, R. J. Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions and Synthesis (Part B), 5th ed., Springer, 2007. 2. Carey, F. A.; Sundberg, R. J. Advanced
به نام خدا روشهای سنتز مواد آلی 1 References: 1. Carey, F. A.; Sundberg, R. J. Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions and Synthesis (Part B), 5th ed., Springer, 2007. 2. Carey, F. A.; Sundberg, R. J. Advanced
CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Text Sections (N0 1.9, 9-11) Homework: Chapter 1:
 CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Atomic Structure - Valence Electrons Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule - Ionic bond - Covalent bond How to write Lewis
CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Atomic Structure - Valence Electrons Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule - Ionic bond - Covalent bond How to write Lewis
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Detailed Course Content
 Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions. Alpha Substitution
 Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Lecture 24 Two Germans and an Englishman
 Lecture 24 Two Germans and an Englishman Robert Robinson 1886-1975 Nobel Laureate 1947 April 17, 2018 tto Paul Hermann Diels 1876-1954 Nobel Laureates 1950 Kurt Alder 1902-1958 Exam III Tomorrow Wed April
Lecture 24 Two Germans and an Englishman Robert Robinson 1886-1975 Nobel Laureate 1947 April 17, 2018 tto Paul Hermann Diels 1876-1954 Nobel Laureates 1950 Kurt Alder 1902-1958 Exam III Tomorrow Wed April
8-3 This exercise is worked out on page 293 as "Working with Concepts".
 Copyright 2009 James K Whitesell 8-1 This exercise combines your knowledge of basic nomenclature rules and concepts of stereochemistry introduced in Chapters 4 and 5. 8-2 Keep in mind that faculty at UCSD
Copyright 2009 James K Whitesell 8-1 This exercise combines your knowledge of basic nomenclature rules and concepts of stereochemistry introduced in Chapters 4 and 5. 8-2 Keep in mind that faculty at UCSD
Suggested solutions for Chapter 28
 s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
MCAT Organic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones
 MCAT rganic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following is not a physical property of aldehydes and ketones? Question #01 (A) Hydrogen bonding
MCAT rganic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following is not a physical property of aldehydes and ketones? Question #01 (A) Hydrogen bonding
Chapter 8 Outline: Alkenes: Structure and Preparation via β-elimination
 Chapter 8 Outline: Alkenes: Structure and Preparation via β-elimination 1. What is β elimination? 2. Alkenes: structure, steroisomerism and stability 3. Elimination Reactions o E2 Mechanism o E1 Mechanism
Chapter 8 Outline: Alkenes: Structure and Preparation via β-elimination 1. What is β elimination? 2. Alkenes: structure, steroisomerism and stability 3. Elimination Reactions o E2 Mechanism o E1 Mechanism
II. Special Topics IIA. Enolate Chemistry & the Aldol Reaction
 P. Wipf - Chem 2320 1 3/20/2006 II. Special Topics IIA. Enolate Chemistry & the Aldol Reaction Boger Notes: p. 147-206 (Chapter VIII) Carey/Sundberg: B p. 57-95 (Chapter B 2.1) Problem of the Day: Wang,
P. Wipf - Chem 2320 1 3/20/2006 II. Special Topics IIA. Enolate Chemistry & the Aldol Reaction Boger Notes: p. 147-206 (Chapter VIII) Carey/Sundberg: B p. 57-95 (Chapter B 2.1) Problem of the Day: Wang,
Chemistry 335 Supplemental Slides: Interlude 2
 Interlude 2: Shapes of Cyclic Molecules Recall from 2 nd year: - Rotation around C C single bonds is generally fast. - This leads to a variety of different conformers for any given molecule. - To evaluate
Interlude 2: Shapes of Cyclic Molecules Recall from 2 nd year: - Rotation around C C single bonds is generally fast. - This leads to a variety of different conformers for any given molecule. - To evaluate
Chem ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I CHEM 221 /2 01 Final Examination December 20, 2005 1400-1700 Dr. Cerrie ROGERS x x molecular model kits (without instructions) programmable calculators must be reset Chem 221 --- ORGANIC
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I CHEM 221 /2 01 Final Examination December 20, 2005 1400-1700 Dr. Cerrie ROGERS x x molecular model kits (without instructions) programmable calculators must be reset Chem 221 --- ORGANIC
SECTION 4. Stereoelectronic Effects (S.E.) and Reactivity of Acetals and Related Functions
 SECTIN 4 Stereoelectronic Effects (S.E.) and Reactivity of Acetals and Related Functions (2018) 1 2 Conformation of acetals 3 STEREELECTRNIC EFFECTS and xygen Basicity, Bond Length and Preferential Cleavage
SECTIN 4 Stereoelectronic Effects (S.E.) and Reactivity of Acetals and Related Functions (2018) 1 2 Conformation of acetals 3 STEREELECTRNIC EFFECTS and xygen Basicity, Bond Length and Preferential Cleavage
CHAPTER 23 HW: ENOLS + ENOLATES
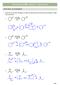 CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
Walden discovered a series of reactions that could interconvert (-)-malic acid and (+)-malic acid.
 Chapter 11: Reactions of alkyl halides: nucleophilic substitutions and eliminations Alkyl halides are polarized in the C-X bond, making carbon δ+ (electrophilic). A nucleophilecan attack this carbon, displacing
Chapter 11: Reactions of alkyl halides: nucleophilic substitutions and eliminations Alkyl halides are polarized in the C-X bond, making carbon δ+ (electrophilic). A nucleophilecan attack this carbon, displacing
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2
 C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
Chapter 9. Nucleophilic Substitution and ß-Elimination
 Chapter 9 Nucleophilic Substitution and ß-Elimination Nucleophilic Substitution Nucleophile: From the Greek meaning nucleus loving. A molecule or ion that donates a pair of electrons to another atom or
Chapter 9 Nucleophilic Substitution and ß-Elimination Nucleophilic Substitution Nucleophile: From the Greek meaning nucleus loving. A molecule or ion that donates a pair of electrons to another atom or
2.339 Practice Problems
 2.339 Practice Problems Basics of Structure and Mechanism 1. What is the expected site of protonation in an enol ether (C=C)? Justify your choice using resonance structures. 2. ank the following molecules
2.339 Practice Problems Basics of Structure and Mechanism 1. What is the expected site of protonation in an enol ether (C=C)? Justify your choice using resonance structures. 2. ank the following molecules
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes
 Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
20.3 Alkylation of Enolate Anions
 864 APTER 20 ELATE AD TER ARB ULEPILES which precipitates as a yellow solid, provides a positive test for the presence of a methyl ketone The reaction can also be used in synthesis to convert a methyl
864 APTER 20 ELATE AD TER ARB ULEPILES which precipitates as a yellow solid, provides a positive test for the presence of a methyl ketone The reaction can also be used in synthesis to convert a methyl
REARRANGEMENTS NOTES Mechanistic Aspects of Rearrangements
 - 1 - REARRANGEMENTS NOTES Mechanistic Aspects of Rearrangements Nature of the Rearrangement It can vary from being truly stepwise to migration occurring in concert with initial ionisation. These two situations
- 1 - REARRANGEMENTS NOTES Mechanistic Aspects of Rearrangements Nature of the Rearrangement It can vary from being truly stepwise to migration occurring in concert with initial ionisation. These two situations
(5) a. b. (6) N H CH 3 N H O H O (7) CH 3 O (8) OCH 3 2. explanation:
 ame Key 15 W1-Exam o. Page I. (16 points) For each of the following pairs of compounds, predict which compound is more acidic. Compare the two underlined s for each pair and circle the compound that is
ame Key 15 W1-Exam o. Page I. (16 points) For each of the following pairs of compounds, predict which compound is more acidic. Compare the two underlined s for each pair and circle the compound that is
Classes of Alkenes. Alkenes and Alkynes. Saturated compounds (alkanes): Have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom.
 Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
CHEMISTRY. Module No and Title Module-7, Nucleophilic and Free Radical Addition. Reactions of Alkenes
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Paper-9, Organic Chemistry-III (Reaction Mechanism-2) Module No and Title Module-7, Nucleophilic and Free Radical Addition Module Tag CHE_P9_M7 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Paper-9, Organic Chemistry-III (Reaction Mechanism-2) Module No and Title Module-7, Nucleophilic and Free Radical Addition Module Tag CHE_P9_M7 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.
Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides E2 and E1 Reactions in Detail
 Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides E2 and E1 Reactions in Detail b-elimination Reactions Overview dehydration of alcohols: X = H; Y = OH dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides: X = H; Y = Br, etc. X C
Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides E2 and E1 Reactions in Detail b-elimination Reactions Overview dehydration of alcohols: X = H; Y = OH dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides: X = H; Y = Br, etc. X C
Reversible Additions to carbonyls: Weak Nucleophiles Relative Reactivity of carbonyls: Hydration of Ketones and Aldehydes
 Reversible Additions to carbonyls: Weak Nucleophiles Weak nucleophiles, such as water, alcohols, and amines, require acid or base catalysis to undergo addition to carbonyl compounds Relative Reactivity
Reversible Additions to carbonyls: Weak Nucleophiles Weak nucleophiles, such as water, alcohols, and amines, require acid or base catalysis to undergo addition to carbonyl compounds Relative Reactivity
CHEM 330. Topics Discussed on Oct 5. Irreversible nature of the reaction of carbonyl enolates with the electrophiles discussed on Oct 2
 CEM 330 Topics Discussed on ct 5 Irreversible nature of the reaction of carbonyl enolates with the electrophiles discussed on ct 2 Kinetic control in an irreversible reaction: the product that is obtained
CEM 330 Topics Discussed on ct 5 Irreversible nature of the reaction of carbonyl enolates with the electrophiles discussed on ct 2 Kinetic control in an irreversible reaction: the product that is obtained
Chem 263 March 7, 2006
 Chem 263 March 7, 2006 Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group, in which the carbon atom is doubly bonded to an oxygen atom. The carbonyl group is highly polarized, with a
Chem 263 March 7, 2006 Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group, in which the carbon atom is doubly bonded to an oxygen atom. The carbonyl group is highly polarized, with a
CHAPTER 7. Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination
 CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
Chapter 7 Alkenes; Elimination Reactions
 hapter 7 Alkenes; Elimination Reactions Alkenes Alkenes contain a carbon-carbon double bond. They are named as derivatives of alkanes with the suffix -ane changed to -ene. The parent alkane is the longest
hapter 7 Alkenes; Elimination Reactions Alkenes Alkenes contain a carbon-carbon double bond. They are named as derivatives of alkanes with the suffix -ane changed to -ene. The parent alkane is the longest
2.222 Practice Problems 2003
 2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
OChem1 Old Exams. Chemistry 3719 Practice Exams
 OChem1 Old Exams Chemistry 3719 Practice Exams Fall 2017 Chemistry 3719 Practice Exam A1 This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 600 points for Chemistry 3719/3719L. You have 50 minutes to complete
OChem1 Old Exams Chemistry 3719 Practice Exams Fall 2017 Chemistry 3719 Practice Exam A1 This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 600 points for Chemistry 3719/3719L. You have 50 minutes to complete
Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of Alkyl Halides
 Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of Alkyl Halides There are two types of possible reaction in organic compounds in which sp 3 carbon is bonded to an electronegative atom or group (ex, halides) 1. Substitution
Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of Alkyl Halides There are two types of possible reaction in organic compounds in which sp 3 carbon is bonded to an electronegative atom or group (ex, halides) 1. Substitution
Synthetic Organic Chemistry Final Exam Resit (6KM33) Thursday, 26th June, 2014, 9:00 12:00 (3 h)
 Synthetic rganic Chemistry Final Exam Resit (6KM33) Thursday, 26th June, 2014, 9:00 12:00 (3 h) This is an open-book written exam. The course textbooks (Warren & Wyatt, 2 nd Ed.) with personal notes and
Synthetic rganic Chemistry Final Exam Resit (6KM33) Thursday, 26th June, 2014, 9:00 12:00 (3 h) This is an open-book written exam. The course textbooks (Warren & Wyatt, 2 nd Ed.) with personal notes and
20.10 Conjugate Additions
 894 APTER 20 ELATE AD THER CARB UCLEPHILES 2010 Conjugate Additions The conjugate addition of nucleophiles to,-unsaturated carbonyl compounds at the -position was described in Section 1810 Enolate and
894 APTER 20 ELATE AD THER CARB UCLEPHILES 2010 Conjugate Additions The conjugate addition of nucleophiles to,-unsaturated carbonyl compounds at the -position was described in Section 1810 Enolate and
Ch 22 Carbonyl Alpha ( ) Substitution
 Ch 22 Carbonyl Alpha () Substitution The overall reaction replaces an H with an E + The acid-catalyzed reaction has an enol intermediate The base-catalyzed reaction has an enolate intermediate Keto-Enol
Ch 22 Carbonyl Alpha () Substitution The overall reaction replaces an H with an E + The acid-catalyzed reaction has an enol intermediate The base-catalyzed reaction has an enolate intermediate Keto-Enol
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes. 2. Radical Substitution with Alkenes. 3. Electrophilic Addition
 1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
Substitution α to a carbonyl center: Enol and enolate chemistry
 Chapter 11 Organic Reaction Mechanisms, Part 2: Substitutions at Aliphatic Centers and Thermal Isomerizations/Rearrangements 11.1 Tautomerization Substitution α to a carbonyl center: Enol and enolate chemistry
Chapter 11 Organic Reaction Mechanisms, Part 2: Substitutions at Aliphatic Centers and Thermal Isomerizations/Rearrangements 11.1 Tautomerization Substitution α to a carbonyl center: Enol and enolate chemistry
New bond. ph 4.0. Fischer esterification. New bond 2 O * New bond. New bond H 2N. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. O Cl.
 Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination
 Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Alkyl halides react with a nucleophile in one of two ways. Either they eliminate an X to form an alkene, or they undergo a substitution with the nucleophile, Nu,
Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Alkyl halides react with a nucleophile in one of two ways. Either they eliminate an X to form an alkene, or they undergo a substitution with the nucleophile, Nu,
Ethers. Synthesis of Ethers. Chemical Properties of Ethers
 Page 1 of 6 like alcohols are organic derivatives of water, but lack the labile -OH group. As a result, ethers, except for epoxides, are usually not very reactive and are often used as solvents for organic
Page 1 of 6 like alcohols are organic derivatives of water, but lack the labile -OH group. As a result, ethers, except for epoxides, are usually not very reactive and are often used as solvents for organic
ENOLATES IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS
 ENLATES IN RGANIC SYNTHESIS 1 ENLATES IN RGANIC SYNTHESIS Recall Enolate alkylation, Aldol addition and condensation can provide access to a wide variety of multi-functional compounds, which can lend themselves
ENLATES IN RGANIC SYNTHESIS 1 ENLATES IN RGANIC SYNTHESIS Recall Enolate alkylation, Aldol addition and condensation can provide access to a wide variety of multi-functional compounds, which can lend themselves
11. Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations
 11. Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition 2003 Ronald Kluger Department of Chemistry University of Toronto Alkyl Halides
11. Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition 2003 Ronald Kluger Department of Chemistry University of Toronto Alkyl Halides
Course Goals for CHEM 202
 Course Goals for CHEM 202 Students will use their understanding of chemical bonding and energetics to predict and explain changes in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy for a variety of processes and reactions.
Course Goals for CHEM 202 Students will use their understanding of chemical bonding and energetics to predict and explain changes in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy for a variety of processes and reactions.
Page 1 of 9. Sessional Examination (November 2017) Max Marks: 20 Date: Time: One Hour. Model Answers
 Page 1 of 9 Sessional Examination (November 2017) Class: B. Pharm-II yr (III sem) Subject: Pharma Org. Chem-II Max Marks: 20 Date: 14.11.2017 Time: One Hour Model Answers Q. 1. Solve the following (ANY
Page 1 of 9 Sessional Examination (November 2017) Class: B. Pharm-II yr (III sem) Subject: Pharma Org. Chem-II Max Marks: 20 Date: 14.11.2017 Time: One Hour Model Answers Q. 1. Solve the following (ANY
Organic Chemistry, Third Edition. Chapter 24 Carbonyl condensations
 rganic Chemistry, Third Edition Chapter 24 Carbonyl condensations 1 Review: enolates LDA, -78 C TF kinetic RX R = Me, 1 alkyl R Na TF, RT RX R = Me, 1 alkyl thermodynamic R enolates = nucleophiles React
rganic Chemistry, Third Edition Chapter 24 Carbonyl condensations 1 Review: enolates LDA, -78 C TF kinetic RX R = Me, 1 alkyl R Na TF, RT RX R = Me, 1 alkyl thermodynamic R enolates = nucleophiles React
Chapter 2: An Introduction to Organic Compounds
 Chapter : An Introduction to Organic Compounds I. FUNCTIONAL GROUPS: Functional groups with similar structure/reactivity may be "grouped" together. A. Functional Groups With Carbon-Carbon Multiple Bonds.
Chapter : An Introduction to Organic Compounds I. FUNCTIONAL GROUPS: Functional groups with similar structure/reactivity may be "grouped" together. A. Functional Groups With Carbon-Carbon Multiple Bonds.
Grob Fr agmentations. Dan Tao Overman Group Meeting 9/24/12
 : Grob Fr agmentations Dan Tao Overman Group Meeting 9/24/12 What is a Grob Fragmentation? Heterolytic fragmentation is certain combinations of carbon and hetero atoms which undergo a regulated cleavage
: Grob Fr agmentations Dan Tao Overman Group Meeting 9/24/12 What is a Grob Fragmentation? Heterolytic fragmentation is certain combinations of carbon and hetero atoms which undergo a regulated cleavage
B X A X. In this case the star denotes a chiral center.
 Lecture 13 Chirality III October 29, 2013 We can also access chiral molecules through the use of something called chiral auxiliaries, which basically is a chiral attachment that you add to your molecule
Lecture 13 Chirality III October 29, 2013 We can also access chiral molecules through the use of something called chiral auxiliaries, which basically is a chiral attachment that you add to your molecule
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Why this Chapter? Carboxylic acids present in many industrial processes and most biological processes They are the starting materials from which other acyl derivatives are
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Why this Chapter? Carboxylic acids present in many industrial processes and most biological processes They are the starting materials from which other acyl derivatives are
Tautomerism and Keto Enol Equilibrium
 Tautomerism and Keto Enol Equilibrium Enols & enolates are important nucleophiles in organic & biochemistry. Keto-Enol Equilibrium: Tautomerisation can be catalyzed by either acids or bases. Relative stability
Tautomerism and Keto Enol Equilibrium Enols & enolates are important nucleophiles in organic & biochemistry. Keto-Enol Equilibrium: Tautomerisation can be catalyzed by either acids or bases. Relative stability
A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation:
 1 Chapter 22: Reactions of Enols and Enolates I. Alpha Substitution verview: A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation: Recall that the
1 Chapter 22: Reactions of Enols and Enolates I. Alpha Substitution verview: A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation: Recall that the
Points: 1 / 15 / Total: 100 points /
 Chemistry 6372 Fall 2002 omework #6 Answer Key Name Points: 1 / 15 / 2 / 10 / 3 / 10 / 4 / 10 / 5 / 10 / 6 / 10 / 7 / 35 / Total: 100 points / Average: 73 1) Answer the following questions from our book:
Chemistry 6372 Fall 2002 omework #6 Answer Key Name Points: 1 / 15 / 2 / 10 / 3 / 10 / 4 / 10 / 5 / 10 / 6 / 10 / 7 / 35 / Total: 100 points / Average: 73 1) Answer the following questions from our book:
Organic Chemistry Lecture 2 - Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Substitutions
 ALKANES Water-insoluble, low density C-C single bonds Higher MW -> higher BP, higher MP Branching -> lower BP, higher MP Forms cycloalkanes which can have ring strain Cyclohexane: chair vs. boat configuration
ALKANES Water-insoluble, low density C-C single bonds Higher MW -> higher BP, higher MP Branching -> lower BP, higher MP Forms cycloalkanes which can have ring strain Cyclohexane: chair vs. boat configuration
STEREOELECTRONIC EFFECTS (S.E.) IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 STEEELECTNIC EFFECTS (S.E.) IN GANIC CEMISTY Pierre Deslongchamps (version du 5 février 2010) Cf. pour le livre: http://pages.usherbrooke.ca/pdeslongchamps/cv.htm 1 SECTIN 2 Stereoelectronic Effects (S.E.)
STEEELECTNIC EFFECTS (S.E.) IN GANIC CEMISTY Pierre Deslongchamps (version du 5 février 2010) Cf. pour le livre: http://pages.usherbrooke.ca/pdeslongchamps/cv.htm 1 SECTIN 2 Stereoelectronic Effects (S.E.)
CHAPTER 8 HW SOLUTIONS: ELIMINATIONS REACTIONS
 APTER 8 W SLUTNS: ELMNATNS REATNS S-TRANS SMERSM 1. Use a discussion and drawing of orbitals to help explain why it is generally easy to rotate around single bonds at room temperature, while it is difficult
APTER 8 W SLUTNS: ELMNATNS REATNS S-TRANS SMERSM 1. Use a discussion and drawing of orbitals to help explain why it is generally easy to rotate around single bonds at room temperature, while it is difficult
Multistep Synthesis of 5-isopropyl-1,3-cyclohexanedione
 Multistep Synthesis of 5-isopropyl-1,3-cyclohexanedione The purpose of this experiment was to synthesize 5-isopropyl-1,3-cyclohexanedione from commercially available compounds. To do this, acetone and
Multistep Synthesis of 5-isopropyl-1,3-cyclohexanedione The purpose of this experiment was to synthesize 5-isopropyl-1,3-cyclohexanedione from commercially available compounds. To do this, acetone and
Important Concepts. Problems. Chapter Problems. Cuprate additions followed by enolate alkylations. 15. Michael Addition (Section 18-11)
 Problems hapter 18 861 uprate additions followed by enolate alkylations P 1. R 2uLi, TF 2. RX A A R R N 15. Michael Addition (Section 18-11) D P D R P R A RR 16. Robinson Annulation (Section 18-11) Important
Problems hapter 18 861 uprate additions followed by enolate alkylations P 1. R 2uLi, TF 2. RX A A R R N 15. Michael Addition (Section 18-11) D P D R P R A RR 16. Robinson Annulation (Section 18-11) Important
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key
 CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
