Introduction to Chemistry
|
|
|
- Marilynn Andrews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Chemistry CHEMISTRY = the study of the composition of matter, its chemical and physical changes, and the changes that accompany these changes. Scientific law vs. theory: Scientific law- Scientific theory- THE WAY SCIENCE WORKS Science involves critical thinking, or applying logic and reason to observations and conclusions. Observation vs. Inference: Observation- Inference- Variables and Controls: A variable is anything that can in an experiment. Independent variable: The variable being or by the scientist. Dependent variable: The variable being or by the scientist. A tests only one variable at a time. The Scientific Method: A series of logical steps to follow in order to solve problems. FORMULATE A FORM A DESIGN AND CONDUCT AN MAKE AND DATA DRAW FORMULATE and Making Measurements: measurements are made in this class using SI units. : distance between 2 points : space occupied. : the amount of matter in an object. : the force with which gravity pulls on a quantity of matter. Accuracy vs. Precision: Accuracy- Precision- (ex: a scale may be precise to the nearest 100 th of a gram, or +/- 0.01g ) 1
2 precision vs. accuracy increasing precision Density = increasing accuracy Example: What is the mass of 10 ml of a liquid that has a density of 3.76 g/ml? Temperature Conversions Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy in a system. = Kelvin = degree Celsius = degree Fahrenheit =Rankin (we won t use this one in this class K = o F = o C = Percentage Error: Calculate this value in labs where the accepted value is given. % error = ORGANIZING DATA: Data is organized and presented in tables, charts, and graphs. Graph - visual representation of data 1) 2) and axis labeled 3) for both the x and y axis 4) is evenly and correctly spaced for data 5) when appropriate LINE GRAPH: best for displaying data that. Independent Variable: Dependent variable: BAR GRAPH: useful when you want to data for several individual items. PIE CHART: ideal for displaying data that are. 2
3 Matter = anything with mass and volume Classification of Matter: Matter Law of Conservation of Matter (Mass): matter cannot be created or destroyed Law of Conservation of Energy: energy cannot be created or destroyed; it may, however, be transformed Virtually everything that is, is made up of atoms. Currently, we have about kinds of atoms. In the natural world there exists different kinds of atoms. The others have been artificially produced in laboratories. We call each kind of atom an, and we give it a specific name and symbol. Atoms are made up of, &. Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus of atoms. Electrons travel around the nucleus. Different kinds of atoms are different because they have different numbers of. We list elements by their, the # of protons. Physical properties: characteristics that can be observed without changing the identity of the substance. Examples: Physical change: a change in the physical form or properties of a substance that occurs without a change in composition. Examples: Chemical property: describes a substance s ability to change into a different substance. Examples: Chemical change: occurs when a substance changes composition by forming one or more new substances. (bonds are broken and bonds are formed) Example: Indications of a chemical change 3
4 Phases of Matter Kinetic Theory: All matter is made of atoms and molecules that act like tiny particles. These tiny particles are always in motion. The higher the temp., the faster the particles move. At the same temp., more massive (heavier) particles move slower than less massive (lighter) particles Solids: Definite Shape? Definite Volume? Molecules in a solid are and constantly vibrating. Liquids: Definite Shape? Definite Volume? Some liquids flow more easily than others. The resistance of a liquid to flow is called. o Honey has a high viscosity compared to water Gases: Definite Shape? Definite Volume? The particles in a gas are spread, but can be compressed by pumping them into a restricted volume. Changes of State: Energy Transfers: ENERGY is the ability to or move matter. Energy is when substances melt or evaporate. o NOTE: our bodies cool down when our sweat evaporates. Energy is when substances freeze or condense. Melting: Change of state from to Energy (heat) is by the substance that is melting. Freezing: Change of state from to Energy (heat) is by the substance that is undergoing freezing. Evaporation: Change of state at the surface of a as it passes to a Results from random motion of molecules that occasionally escape from the liquid surface. Energy (heat) is by the liquid. (Cooling of the liquid results) Can happen at any time. Condensation: Change of state from to Energy (heat) is by the substance that is melting. (Warming of the liquid results) Boiling: Change of state from to Occurs the liquid. Boiling point/temperature is determined by Energy is by the liquid 4
5 Phase Change Graph *Boiling & freezing points depend on the pressure. Phase Diagrams A phase diagram shows the equilibria pressure-temperature relationship among the different phases of a given substance. H 2O CO 2 AB = AC = AD = triple point = Point The point at which all 3 phases of a substance (solid, liquid, gas) can coexist at equilibrium. critical point = Point The combination of critical temperature and critical pressure. o critical temp = The temperature above which a gas cannot be liquefied. (H 2O=374ºC) o critical pressure = The pressure required to liquefy a gas at its critical temperature. (H 2O=218 atm) 5
6 Significant Figures IS THE LANGUAGE OF! Scientific Notation: scientist use special notation to express VERY LARGE or very small numbers. Ex: 300,000,000 m/sec = Ex: 1,007,000,000 sec = Ex: m = Significant Figures Atlantic - Pacific Rule: Decimal Present: Count from the Pacific side Decimal Absent: Count from the Atlantic side Start counting at the first non-zero number and count until you reach the end of the number Ex. I: Ex. II: 300,700 Significant Figures in Calculations When multiplying and dividing, limit and round to the least number of significant figures in any of the factors. Example: 23.0 x 432 x 19 = When adding and subtracting, limit and round your answer to the least number of decimal places in any of the numbers involved in the calculation. Example: = Determine how many significant figures are in each of the following measurements: L m g 4. 47,900 mm 5. 7,000,000,001 miles Hz 6
7 Round each of the following measurements off so that they each contain 3 significant figures (you may use scientific notation if you prefer): L 8. 9,047,022 mg g J Perform the prescribed operations. Round your answers to the proper number of significant figures. Include the appropriate units in your answer m / 3.21 s = g g g = m x m = 14. (5.83 m / 2.67 s) / 2.1 s = V x 6 = 7
8 Dimensional Analysis Given information: Unit conversion map: Convert 14 gallons to kildurkins: Convert 14 barrels to hogsheads: Convert 3.00 bushels to farkins: 8
Matter & Energy. Objectives: properties and structures of the different states of matter.
 Matter & Energy Objectives: 1. Use the kinetic theory to describe the properties and structures of the different states of matter. 2. Describe energy transfers involved in changes of state. 3. Describe
Matter & Energy Objectives: 1. Use the kinetic theory to describe the properties and structures of the different states of matter. 2. Describe energy transfers involved in changes of state. 3. Describe
q = m. C p. T q = heat (Joules) m = mass (g) C p = specific heat (J/g.o C) T = change in temp. ( o C) UNIT 11 - SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, & PHASE CHANGES
 HEAT ENERGY NOTES UNIT 11 - SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, & PHASE CHANGES SECTION (A): same temp or change? SECTION (B): same temp or change? temp is called the energy difference at same temp = SECTION (C): same temp
HEAT ENERGY NOTES UNIT 11 - SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, & PHASE CHANGES SECTION (A): same temp or change? SECTION (B): same temp or change? temp is called the energy difference at same temp = SECTION (C): same temp
Chapter 3 Phases of Matter Physical Science
 Chapter 3 Phases of Matter Physical Science CH 3- States of Matter 1 What makes up matter? What is the difference between a solid, a liquid, and a gas? What kind of energy do all particles of matter have?
Chapter 3 Phases of Matter Physical Science CH 3- States of Matter 1 What makes up matter? What is the difference between a solid, a liquid, and a gas? What kind of energy do all particles of matter have?
Section 1 Matter and Energy
 CHAPTER OUTLINE Section 1 Matter and Energy Key Idea questions > What makes up matter? > What is the difference between a solid, a liquid, and a gas? > What kind of energy do all particles of matter have?
CHAPTER OUTLINE Section 1 Matter and Energy Key Idea questions > What makes up matter? > What is the difference between a solid, a liquid, and a gas? > What kind of energy do all particles of matter have?
Pg , Syllabus
 Pg. 169 171, 173-175 Syllabus 5.7 5.14 www.cgrahamphysics.com What do you remember? End www.cgrahamphysics.com How do particles move? 3 of 30 Boardworks Ltd 2012 4 of 30 Boardworks Ltd 2012 States of matter
Pg. 169 171, 173-175 Syllabus 5.7 5.14 www.cgrahamphysics.com What do you remember? End www.cgrahamphysics.com How do particles move? 3 of 30 Boardworks Ltd 2012 4 of 30 Boardworks Ltd 2012 States of matter
Duncan. Q = m. C p. T. Q = heat (Joules) m = mass (g) C p = specific heat capacity (J/g.o C) T = change in temp. ( o C)
 HEAT ENERGY NOTES SECTION (A): phase(s) of matter = SECTION (B): phase(s) of matter = energy difference at same temp = temp is called the SECTION (C): phase(s) of matter = SECTION (D): phase(s) of matter
HEAT ENERGY NOTES SECTION (A): phase(s) of matter = SECTION (B): phase(s) of matter = energy difference at same temp = temp is called the SECTION (C): phase(s) of matter = SECTION (D): phase(s) of matter
Chemistry. The study of matter and the changes it undergoes
 Chemistry. The study of matter and the changes it undergoes 5 Major Areas of Chemistry Analytical Chemistry- composition of substances. Inorganic Chemistry- substances without carbon Organic Chemistry-
Chemistry. The study of matter and the changes it undergoes 5 Major Areas of Chemistry Analytical Chemistry- composition of substances. Inorganic Chemistry- substances without carbon Organic Chemistry-
States of Matter Unit
 Learning Target Notes Section 1: Matter and Energy What makes up matter? Matter is made of atoms and molecules that are in constant motion. Kinetic Theory of Matter A. Particles that make up matter are
Learning Target Notes Section 1: Matter and Energy What makes up matter? Matter is made of atoms and molecules that are in constant motion. Kinetic Theory of Matter A. Particles that make up matter are
EOC review questions I
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ EOC review questions I Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. mixture d. reactant b. product e. heterogeneous mixture c. phase f. vapor 1. gaseous state of
Name: Class: _ Date: _ EOC review questions I Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. mixture d. reactant b. product e. heterogeneous mixture c. phase f. vapor 1. gaseous state of
STATES OF MATTER. The Four States of Ma/er. Four States. Solid Liquid Gas Plasma
 STATES OF MATTER The Four States of Ma/er Solid Liquid Gas Plasma Four States STATES OF MATTER Ø What makes a substance a par:cular state of ma
STATES OF MATTER The Four States of Ma/er Solid Liquid Gas Plasma Four States STATES OF MATTER Ø What makes a substance a par:cular state of ma
Chapter 22 States of matter. Section 1 matter Section 2 Changes of State
 Chapter 22 States of matter Section 1 matter Section 2 Changes of State States of Matter is a physical property ***Matter is made of atoms Atoms form chemical bonds to make matter **** Atoms vibrate constantly
Chapter 22 States of matter Section 1 matter Section 2 Changes of State States of Matter is a physical property ***Matter is made of atoms Atoms form chemical bonds to make matter **** Atoms vibrate constantly
Matter changes phase when energy is added or removed
 Section 12.4 Phase Changes Explain how the addition and removal of energy can cause a phase change. Interpret a phase diagram. Matter changes phase when energy is added or removed Energy Changes Accompanying
Section 12.4 Phase Changes Explain how the addition and removal of energy can cause a phase change. Interpret a phase diagram. Matter changes phase when energy is added or removed Energy Changes Accompanying
Chemistry Day 5. Friday, August 31 st Tuesday, September 4 th, 2018
 Chemistry Day 5 Friday, August 31 st Tuesday, September 4 th, 2018 Do-Now Title: BrainPOP: States of Matter 1. Write down today s FLT 2. List two examples of gases 3. List two examples of things that are
Chemistry Day 5 Friday, August 31 st Tuesday, September 4 th, 2018 Do-Now Title: BrainPOP: States of Matter 1. Write down today s FLT 2. List two examples of gases 3. List two examples of things that are
Thermochemistry. The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state.
 Energy Thermochemistry The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state. The Nature of Energy Energy - the ability to do work or produce heat Energy is stored in the
Energy Thermochemistry The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state. The Nature of Energy Energy - the ability to do work or produce heat Energy is stored in the
Chapter 1 Matter,Measurement, and Problem Solving
 Chapter 1 Matter,Measurement, and Problem Solving Classification of Matter matter is anything that has mass and occupies space we can classify matter based on whether it s solid, liquid, or gas State Shape
Chapter 1 Matter,Measurement, and Problem Solving Classification of Matter matter is anything that has mass and occupies space we can classify matter based on whether it s solid, liquid, or gas State Shape
Matter: Properties and Change
 Matter: Properties and Change Date: 6.P.2 Understand the structure, classifications and physical properties of matter. 6.P.2.1 Recognize that all matter is made up of atoms and atoms of the same element
Matter: Properties and Change Date: 6.P.2 Understand the structure, classifications and physical properties of matter. 6.P.2.1 Recognize that all matter is made up of atoms and atoms of the same element
Kinetic Theory of Matter
 1 Temperature and Thermal Energy Kinetic Theory of Matter The motion of the particles in matter is described by kinetic theory of matter. Matter is composed of particles that are atoms, molecules, or ions
1 Temperature and Thermal Energy Kinetic Theory of Matter The motion of the particles in matter is described by kinetic theory of matter. Matter is composed of particles that are atoms, molecules, or ions
Matter. Anything that has mass and occupies space. Chemistry. is the study of matter and how it changes.
 Matter Chapter 2.1 Matter Anything that has mass and occupies space. Chemistry is the study of matter and how it changes. PLEASE KEEP YOUR HANDS IN THE BOAT AND PLEASE DON T FEED THE ANIMALS. Pure
Matter Chapter 2.1 Matter Anything that has mass and occupies space. Chemistry is the study of matter and how it changes. PLEASE KEEP YOUR HANDS IN THE BOAT AND PLEASE DON T FEED THE ANIMALS. Pure
WARM-UP. 1. What are the four states of matter? 2. What is melting point? 3. How does water change from a liquid to a gas? 4. Define viscosity.
 WARM-UP 1. What are the four states of matter? 2. What is melting point? 3. How does water change from a liquid to a gas? 4. Define viscosity. STATES OF MATTER: WEB QUEST With your lab partner, you will
WARM-UP 1. What are the four states of matter? 2. What is melting point? 3. How does water change from a liquid to a gas? 4. Define viscosity. STATES OF MATTER: WEB QUEST With your lab partner, you will
Chapter 2 Measurements and Solving Problems
 History of Measurement Chapter 2 Measurements and Solving Problems Humans once used handy items as standards or reference tools for measurement. Ex: foot, cubit, hand, yard. English System the one we use.
History of Measurement Chapter 2 Measurements and Solving Problems Humans once used handy items as standards or reference tools for measurement. Ex: foot, cubit, hand, yard. English System the one we use.
Matter. Gas. Solid Liquid. Both shape and volume are not fixed. It has a fixed shape and a fixed volume.
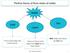 Matter Solid Liquid Gas It has a fixed shape and a fixed volume. It does not have a fixed shape, but it does have a fixed volume. Both shape and volume are not fixed. Felix Yung and John Polias 1 Matter
Matter Solid Liquid Gas It has a fixed shape and a fixed volume. It does not have a fixed shape, but it does have a fixed volume. Both shape and volume are not fixed. Felix Yung and John Polias 1 Matter
Measurement Matter and Density. Name: Period:
 Measurement Matter and Density Name: Period: Studying Physics and Chemistry Physics Tells us how fast objects move or how much it takes to get objects to, turn or stop. Chemistry Explains how different
Measurement Matter and Density Name: Period: Studying Physics and Chemistry Physics Tells us how fast objects move or how much it takes to get objects to, turn or stop. Chemistry Explains how different
Name Date Class STATES OF MATTER. Match the correct state of matter with each description of water by writing a letter on each line.
 10 STATES OF MATTER SECTION 10.1 THE NATURE OF GASES (pages 267 272) This section describes how the kinetic theory applies to gases. It defines gas pressure and explains how temperature is related to the
10 STATES OF MATTER SECTION 10.1 THE NATURE OF GASES (pages 267 272) This section describes how the kinetic theory applies to gases. It defines gas pressure and explains how temperature is related to the
Matter and Energy I. Matter Matter is anything that has mass and volume Mass Amount of matter Measured in grams (g) Volume Space matter occupies
 Matter and Energy I. Matter Matter is anything that has mass and volume Mass Amount of matter Measured in grams (g) Volume Space matter occupies Measured in milliliters (ml), liters (L) or cubic centimeters
Matter and Energy I. Matter Matter is anything that has mass and volume Mass Amount of matter Measured in grams (g) Volume Space matter occupies Measured in milliliters (ml), liters (L) or cubic centimeters
Gilbert Kirss Foster. Chapter 1. Properties of Gases The Air We Breathe
 Gilbert Kirss Foster Chapter 1 Properties of Gases The Air We Breathe Chapter Outline 1.1 States of Matter 1.2 Forms of Energy 1.3 Classes of Matter 1.4 Properties of Matter 1.5 Atomic Theory: The Scientific
Gilbert Kirss Foster Chapter 1 Properties of Gases The Air We Breathe Chapter Outline 1.1 States of Matter 1.2 Forms of Energy 1.3 Classes of Matter 1.4 Properties of Matter 1.5 Atomic Theory: The Scientific
Key Science Vocabulary Scientific Inquiry
 Scientific Inquiry 1. science-- the systematic study of everything 2. scientific method--a system for solving problems or questions 3. P.H.E.O.C.S--problem hypothesis experiment observe conclusion share
Scientific Inquiry 1. science-- the systematic study of everything 2. scientific method--a system for solving problems or questions 3. P.H.E.O.C.S--problem hypothesis experiment observe conclusion share
Ch10.4 Attractive Forces
 Ch10.4 Attractive Forces Intermolecular Forces are the forces holding molecules to each other. Solids have strong forces Gases (vapor) have weak forces Intermolecular forces determine the phase of matter.
Ch10.4 Attractive Forces Intermolecular Forces are the forces holding molecules to each other. Solids have strong forces Gases (vapor) have weak forces Intermolecular forces determine the phase of matter.
States of Matter. What physical changes and energy changes occur as matter goes from one state to another?
 Name States of Matter Date What physical changes and energy changes occur as matter goes from one state to another? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about states of
Name States of Matter Date What physical changes and energy changes occur as matter goes from one state to another? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about states of
Notes: Unit 1: Math and Measurement
 Name: Regents Chemistry: Notes: Unit 1: Math and Measurement www.chempride.weebly.com Key Ideas Major Understandings: o Chemistry is the study of matter: Matter takes up space and has mass. (K- 4, 3.1a)
Name: Regents Chemistry: Notes: Unit 1: Math and Measurement www.chempride.weebly.com Key Ideas Major Understandings: o Chemistry is the study of matter: Matter takes up space and has mass. (K- 4, 3.1a)
Notes: Unit 1: Math and Measurement
 Name: Regents Chemistry: Notes: Unit 1: Math and Measurement www.chempride.weebly.com Key Ideas Major Understandings: o Chemistry is the study of matter: Matter takes up space and has mass. (K- 4, 3.1a)
Name: Regents Chemistry: Notes: Unit 1: Math and Measurement www.chempride.weebly.com Key Ideas Major Understandings: o Chemistry is the study of matter: Matter takes up space and has mass. (K- 4, 3.1a)
Matter: Properties & Change
 Matter: Properties & Change Essential Vocabulary 6.P.2.1 Recognize that all matter is made up of atoms and atoms of the same element are all alike, but are different from the atoms of other elements. 6.P.2.2
Matter: Properties & Change Essential Vocabulary 6.P.2.1 Recognize that all matter is made up of atoms and atoms of the same element are all alike, but are different from the atoms of other elements. 6.P.2.2
Name Date Class STATES OF MATTER. SECTION 13.1 THE NATURE OF GASES (pages )
 Name Date Class 13 STATES OF MATTER SECTION 13.1 THE NATURE OF GASES (pages 385 389) This section introduces the kinetic theory and describes how it applies to gases. It defines gas pressure and explains
Name Date Class 13 STATES OF MATTER SECTION 13.1 THE NATURE OF GASES (pages 385 389) This section introduces the kinetic theory and describes how it applies to gases. It defines gas pressure and explains
Notes for: How Can You Describe Matter, Mixtures, and Solutions? A. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space
 Notes for: How Can You Describe Matter, Mixtures, and Solutions? I. Properties of Matter A. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space 1. scientists describe and compare matter based on properties,
Notes for: How Can You Describe Matter, Mixtures, and Solutions? I. Properties of Matter A. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space 1. scientists describe and compare matter based on properties,
Kinetic Theory of Matter notes 2012
 Kinetic Theory of Matter notes 2012 Kinetic Theory of Matter 3 parts: 1) All matter is made up of and that act as tiny 2) These tiny particles are always in. State of matter depends on its molecular motion
Kinetic Theory of Matter notes 2012 Kinetic Theory of Matter 3 parts: 1) All matter is made up of and that act as tiny 2) These tiny particles are always in. State of matter depends on its molecular motion
10/12/10. Chapter 16. A Macroscopic Description of Matter. Chapter 16. A Macroscopic Description of Matter. State Variables.
 Chapter 16. A Macroscopic Description of Matter Macroscopic systems are characterized as being either solid, liquid, or gas. These are called the phases of matter, and in this chapter we ll be interested
Chapter 16. A Macroscopic Description of Matter Macroscopic systems are characterized as being either solid, liquid, or gas. These are called the phases of matter, and in this chapter we ll be interested
Ch Kinetic Theory. 1.All matter is made of atoms and molecules that act like tiny particles.
 Ch. 15.1 Kinetic Theory 1.All matter is made of atoms and molecules that act like tiny particles. Kinetic Theory 2.These tiny particles are always in motion. The higher the temperature, the faster the
Ch. 15.1 Kinetic Theory 1.All matter is made of atoms and molecules that act like tiny particles. Kinetic Theory 2.These tiny particles are always in motion. The higher the temperature, the faster the
Chapter 1 Introduction: Matter and Measurement
 Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 1 Introduction: and Chemistry: The study of matter and the changes it undergoes. Scientific
Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 1 Introduction: and Chemistry: The study of matter and the changes it undergoes. Scientific
Gases and States of Matter: Unit 8
 Gases and States of Matter: Unit 8 States of Matter There are three states (also called phases) of matter. The picture represents the same chemical substance, just in different states. There are three
Gases and States of Matter: Unit 8 States of Matter There are three states (also called phases) of matter. The picture represents the same chemical substance, just in different states. There are three
13.1 The Nature of Gases (refer to pg )
 13.1 The Nature of Gases (refer to pg. 420-424) Essential Understanding any other state of matter. Temperature and pressure affect gases much more than they affect Lesson Summary Kinetic Theory and a Model
13.1 The Nature of Gases (refer to pg. 420-424) Essential Understanding any other state of matter. Temperature and pressure affect gases much more than they affect Lesson Summary Kinetic Theory and a Model
BRCC CHM 101 Class Notes Chapter 1 Page 1 of 7
 BRCC CHM 101 Class Notes Chapter 1 Page 1 of 7 Chemistry - the study of matter, its behavior and interactions. matter - anything that takes up space and has mass mass - the substance which makes up the
BRCC CHM 101 Class Notes Chapter 1 Page 1 of 7 Chemistry - the study of matter, its behavior and interactions. matter - anything that takes up space and has mass mass - the substance which makes up the
Chapter 14: Liquids and Solids
 I. Phases of matter and phase changes a. Recall the three main phases of matter: Chapter 14: Liquids and Solids Energy is involved during the transition from one phase of matter to another. You should
I. Phases of matter and phase changes a. Recall the three main phases of matter: Chapter 14: Liquids and Solids Energy is involved during the transition from one phase of matter to another. You should
Chapter 3 Metric Units and Conversions
 Chapter 3 Metric Units and Conversions 3.1 The Metric System and Prefixes Metric system: a simple decimal system of measurement that uses the following basic units: Quantity Basic Unit Symbol length meter
Chapter 3 Metric Units and Conversions 3.1 The Metric System and Prefixes Metric system: a simple decimal system of measurement that uses the following basic units: Quantity Basic Unit Symbol length meter
Chemistry 104 Chapter Two PowerPoint Notes
 Measurements in Chemistry Chapter 2 Physical Quantities Measurable physical properties such as height, volume, and temperature are called Physical quantity. A number and a unit of defined size is required
Measurements in Chemistry Chapter 2 Physical Quantities Measurable physical properties such as height, volume, and temperature are called Physical quantity. A number and a unit of defined size is required
2 Standards for Measurement. Careful and accurate measurements of ingredients are important both when cooking and in the chemistry laboratory!
 2 Standards for Measurement Careful and accurate measurements of ingredients are important both when cooking and in the chemistry laboratory! Chapter Outline 2.1 Scientific Notation 2.2 Measurement and
2 Standards for Measurement Careful and accurate measurements of ingredients are important both when cooking and in the chemistry laboratory! Chapter Outline 2.1 Scientific Notation 2.2 Measurement and
Matter: Properties and Change
 Matter: Properties and Change 6.P.2 Understand the structure, classifications and physical properties of matter. 6.P.2.1 Recognize that all matter is made up of atoms and atoms of the same element are
Matter: Properties and Change 6.P.2 Understand the structure, classifications and physical properties of matter. 6.P.2.1 Recognize that all matter is made up of atoms and atoms of the same element are
Most substances can be in three states: solid, liquid, and gas.
 States of Matter Most substances can be in three states: solid, liquid, and gas. Solid Particles Have Fixed Positions The particles in a solid are very close together and have an orderly, fixed arrangement.
States of Matter Most substances can be in three states: solid, liquid, and gas. Solid Particles Have Fixed Positions The particles in a solid are very close together and have an orderly, fixed arrangement.
Name Date Class THE NATURE OF GASES
 13.1 THE NATURE OF GASES Section Review Objectives Describe the assumptions of the kinetic theory as it applies to gases Interpret gas pressure in terms of kinetic theory Define the relationship between
13.1 THE NATURE OF GASES Section Review Objectives Describe the assumptions of the kinetic theory as it applies to gases Interpret gas pressure in terms of kinetic theory Define the relationship between
0 o K is called absolute zero. Water Freezes: 273 o K Water Boils: 373 o K
 Part I Notes Temperature and Heat The terms at the right all mean the same thing. The heat energy of a substance is the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of all of the atoms and molecules in the
Part I Notes Temperature and Heat The terms at the right all mean the same thing. The heat energy of a substance is the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of all of the atoms and molecules in the
Dimensional Analysis, SI Units & Significant figures
 Dimensional Analysis, SI Units & Significant figures WHAT IS CHEMISTRY The study of matter, its composition, structure, properties, and the changes it undergoes & energy changes associated with it. Scientific
Dimensional Analysis, SI Units & Significant figures WHAT IS CHEMISTRY The study of matter, its composition, structure, properties, and the changes it undergoes & energy changes associated with it. Scientific
CHAPTER ONE. The Foundations of Chemistry
 CHAPTER ONE The Foundations of Chemistry Why is Chemistry Important? Materials for our homes Components for computers and other electronic devices Cooking Fuel Body functions 2 Some definitions / Vocabulary
CHAPTER ONE The Foundations of Chemistry Why is Chemistry Important? Materials for our homes Components for computers and other electronic devices Cooking Fuel Body functions 2 Some definitions / Vocabulary
Activities for chapter 13: States of matter
 Activities for chapter 13: States of matter What do I already know about states of matter? (index card) and Vocabulary table Chapter 13 reading guide (feb break assignment) and Powerpoints POGIL activities:
Activities for chapter 13: States of matter What do I already know about states of matter? (index card) and Vocabulary table Chapter 13 reading guide (feb break assignment) and Powerpoints POGIL activities:
PRACTICE TEST Topic 5: Heating, Cooling, and Phase Diagrams
 PRACTICE TEST Topic 5: Heating, Cooling, and Phase Diagrams Directions: Use the heating graph below to answer the following questions. Known Melting Point Data Name of Chemical Lauric Acid Naphthalene
PRACTICE TEST Topic 5: Heating, Cooling, and Phase Diagrams Directions: Use the heating graph below to answer the following questions. Known Melting Point Data Name of Chemical Lauric Acid Naphthalene
Unit 2. Phases of Matter and Density
 Name Pd Unit 2 Phases of Matter and Density Name Pd Name Pd Homework for Unit 2 1. Vocab for Unit 2; due: 2. Pg 17 (1-5), pg 19 (1-5), pg21 (1-5) complete sentences; due: 3. Pg 23 (1-6), pg 27 (1-6) complete
Name Pd Unit 2 Phases of Matter and Density Name Pd Name Pd Homework for Unit 2 1. Vocab for Unit 2; due: 2. Pg 17 (1-5), pg 19 (1-5), pg21 (1-5) complete sentences; due: 3. Pg 23 (1-6), pg 27 (1-6) complete
CHAPTER 2 Data Analysis
 CHAPTER 2 Data Analysis 2.1 Units of Measurement The standard of measurement used in science are those of the metric system. All the units are based on 10 or multiples of 10. SI Units: The International
CHAPTER 2 Data Analysis 2.1 Units of Measurement The standard of measurement used in science are those of the metric system. All the units are based on 10 or multiples of 10. SI Units: The International
UNIT 1: The Scientific Method Chapter 1: The Nature of Science (pages 5-35)
 CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
relatively narrow range of temperature and pressure.
 1) Of solids, liquids, and gases, the least common state of matter is the liquid state. a) Liquids can exist only within a relatively narrow range of temperature and pressure. 2) The kinetic-molecular
1) Of solids, liquids, and gases, the least common state of matter is the liquid state. a) Liquids can exist only within a relatively narrow range of temperature and pressure. 2) The kinetic-molecular
Unit 1 Lesson 6 Changes of State. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 The Fact of the Matter What happens when matter changes state? The three most familiar states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. A change of state is the change of a substance from one physical form
The Fact of the Matter What happens when matter changes state? The three most familiar states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. A change of state is the change of a substance from one physical form
solid IMF>liquid IMF>gas IMF Draw a diagram to represent the 3 common states of matter of a given substance: solid liquid gas
 Thermochemistry Part 1 Notes States of Matter and Intermolecular Forces (IMF) Chemistry HP At the end of this unit, students should be able to: Describe the various states of matter in terms of kinetic
Thermochemistry Part 1 Notes States of Matter and Intermolecular Forces (IMF) Chemistry HP At the end of this unit, students should be able to: Describe the various states of matter in terms of kinetic
Interactive Chalkboard
 1 Interactive Chalkboard 1 Table of Contents Unit 1: Energy and Motion Chapter 1: The Nature of Science 1.1: The Methods of Science 1.2: Standards of Measurement 1.3: Communicating with Graphs 1.1 The
1 Interactive Chalkboard 1 Table of Contents Unit 1: Energy and Motion Chapter 1: The Nature of Science 1.1: The Methods of Science 1.2: Standards of Measurement 1.3: Communicating with Graphs 1.1 The
Chapter 1 Introduction: Matter and Measurement
 23/07/2014 Chemistry Chapter 1 Introduction: and AP Chemistry 2014-15 North Nova Education Centre Mr. Gauthier In this science we study matter and the changes it undergoes. Scientific Method The scientific
23/07/2014 Chemistry Chapter 1 Introduction: and AP Chemistry 2014-15 North Nova Education Centre Mr. Gauthier In this science we study matter and the changes it undergoes. Scientific Method The scientific
Matter & Energy. Kinetic Theory of Matter. Kinetic Theory of Matter. Kinetic Theory of Matter. Kinetic Theory of Matter. Temperature.
 Matter & Energy 1) All matter is made up of atoms and molecules that act as tiny particles. 1 2 2) These tiny particles are always in motion. State of matter depends on its molecular motion as measured
Matter & Energy 1) All matter is made up of atoms and molecules that act as tiny particles. 1 2 2) These tiny particles are always in motion. State of matter depends on its molecular motion as measured
Lecture Notes: Chem 110 Chapter 1
 1 Lecture Notes: Chem 110 Chapter 1 Overview of syllabus: e-mail: vtc101@psu.edu What is chemistry? Some definitions of chemistry (p. 2): Chemistry has been called the central science. This is due to it
1 Lecture Notes: Chem 110 Chapter 1 Overview of syllabus: e-mail: vtc101@psu.edu What is chemistry? Some definitions of chemistry (p. 2): Chemistry has been called the central science. This is due to it
Thermodynamics and States of Matter
 Thermodynamics and States of Matter There are three states (also called phases) ) of matter. The picture to the side represents the same chemical substance, just in different states. There are three states
Thermodynamics and States of Matter There are three states (also called phases) ) of matter. The picture to the side represents the same chemical substance, just in different states. There are three states
Section 16.3 Phase Changes
 Section 16.3 Phase Changes Solid Liquid Gas 3 Phases of Matter Density of Matter How packed matter is (The amount of matter in a given space) Solid: Liquid: Gas: High Density Medium Density Low Density
Section 16.3 Phase Changes Solid Liquid Gas 3 Phases of Matter Density of Matter How packed matter is (The amount of matter in a given space) Solid: Liquid: Gas: High Density Medium Density Low Density
Chapter 3 - Measurements
 Chapter 3 - Measurements You ll learn it in the summer, If not, it ll be a bummer. You ll need to know conversions, For units, Euro version. Metrics are powers of ten, And you might cry when, You re forced
Chapter 3 - Measurements You ll learn it in the summer, If not, it ll be a bummer. You ll need to know conversions, For units, Euro version. Metrics are powers of ten, And you might cry when, You re forced
* Defining Temperature * Temperature is proportional to the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. * Temperature * Internal energy
 * Defining Temperature * We associate temperature with how hot or cold an object feels. * Our sense of touch serves as a qualitative indicator of temperature. * Energy must be either added or removed from
* Defining Temperature * We associate temperature with how hot or cold an object feels. * Our sense of touch serves as a qualitative indicator of temperature. * Energy must be either added or removed from
Unit 8 Kinetic Theory of Gases. Chapter 13-14
 Unit 8 Kinetic Theory of Gases Chapter 13-14 This tutorial is designed to help students understand scientific measurements. Objectives for this unit appear on the next slide. Each objective is linked to
Unit 8 Kinetic Theory of Gases Chapter 13-14 This tutorial is designed to help students understand scientific measurements. Objectives for this unit appear on the next slide. Each objective is linked to
Silent Card Shuffle. Dump out the word strips onto your desk.
 Silent Card Shuffle Dump out the word strips onto your desk. With a partner, silently work to arrange the strips into 8 groups. Each group should have a term (purple paper), its definition (white paper),
Silent Card Shuffle Dump out the word strips onto your desk. With a partner, silently work to arrange the strips into 8 groups. Each group should have a term (purple paper), its definition (white paper),
Unit 4: Gas Laws. Matter and Phase Changes
 Unit 4: Gas Laws Matter and Phase Changes ENERGY and matter What is 에너지 A fundamental property of the universe that cannot be easily defined. Energy No one knows what energy is, only what it does or has
Unit 4: Gas Laws Matter and Phase Changes ENERGY and matter What is 에너지 A fundamental property of the universe that cannot be easily defined. Energy No one knows what energy is, only what it does or has
Name Date Class. N 10 n. Thus, the temperature of the Sun, 15 million kelvins, is written as K in scientific notation.
 Name Date Class 53 MATH HANDBOOK TRANSPARENCY MASTER Scientific Notation 1 Use with Appendix B, Scientific Notation Scientists need to express small measurements, such as the mass of the proton at the
Name Date Class 53 MATH HANDBOOK TRANSPARENCY MASTER Scientific Notation 1 Use with Appendix B, Scientific Notation Scientists need to express small measurements, such as the mass of the proton at the
Ch 1 Chemistry and Measurement
 Ch 1 Chemistry and Measurement Matter - Matter is anything that has substance and occupies space. Matter also has mass and volume. - A material is any particular type of matter. - An atom is the smallest
Ch 1 Chemistry and Measurement Matter - Matter is anything that has substance and occupies space. Matter also has mass and volume. - A material is any particular type of matter. - An atom is the smallest
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 13 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 13 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 13 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Chapter 1 Reading Guide Introduction: Matter and Measurement. 1. Chemistry is the study of matter and the it undergoes.
 Chapter 1 Reading Guide Introduction: Matter and Measurement Name Section 1.1 The Study of Chemistry 1. Chemistry is the study of matter and the it undergoes. 2. Matter is characterized as anything that
Chapter 1 Reading Guide Introduction: Matter and Measurement Name Section 1.1 The Study of Chemistry 1. Chemistry is the study of matter and the it undergoes. 2. Matter is characterized as anything that
Study Guide for Chapters 2, 3, and 10
 Study Guide for Chapters 2, 3, and 10 1. What is matter? Where can it be found? Anything that has mass and takes up space. 2. What units are used to measure volume? Liters and meters cubed 3. How would
Study Guide for Chapters 2, 3, and 10 1. What is matter? Where can it be found? Anything that has mass and takes up space. 2. What units are used to measure volume? Liters and meters cubed 3. How would
Example 3: 4000: 1 significant digit Example 4: : 4 significant digits
 Notes: Measurement and Math 1 Accuracy and Precision Precision depends on the precision of the measuring device o For example a device that can measure to the ten thousands place (1.6829 grams) is a more
Notes: Measurement and Math 1 Accuracy and Precision Precision depends on the precision of the measuring device o For example a device that can measure to the ten thousands place (1.6829 grams) is a more
Solids (cont.) Describe the movement of particles in a solid and the forces between them.
 Solids A solid is matter that has a definite shape and a definite volume. The attractive forces between the particles in a solid are strong and pull them close together. Solids (cont.) Describe the movement
Solids A solid is matter that has a definite shape and a definite volume. The attractive forces between the particles in a solid are strong and pull them close together. Solids (cont.) Describe the movement
PHASE CHANGES. * melting * boiling * sublimation. * freezing * condensation * deposition. vs.
 PHASE CHANGES endothermic * melting * boiling * sublimation vs. vs. exothermic * freezing * condensation * deposition H enthalpy: heat content of a system under constant pressure HEATING CURVE: Where is
PHASE CHANGES endothermic * melting * boiling * sublimation vs. vs. exothermic * freezing * condensation * deposition H enthalpy: heat content of a system under constant pressure HEATING CURVE: Where is
Study guide for AP test on TOPIC 1 Matter & Measurement
 Study guide for AP test on TOPIC 1 Matter & Measurement The following list is a GUIDE to what you should study in order to be prepared for the AP test on TOPIC 1 ALL students should: Recall a definition
Study guide for AP test on TOPIC 1 Matter & Measurement The following list is a GUIDE to what you should study in order to be prepared for the AP test on TOPIC 1 ALL students should: Recall a definition
The Methods of Science
 1 The Methods of Science What is Science? Science is a method for studying the natural world. It is a process that uses observation and investigation to gain knowledge about events in nature. 1 The Methods
1 The Methods of Science What is Science? Science is a method for studying the natural world. It is a process that uses observation and investigation to gain knowledge about events in nature. 1 The Methods
Part 1: Matter. Chapter 1: Matter, Measurements, and Calculations. Sections MATTER Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space.
 Part 1: Matter Chapter 1: Matter, Measurements, and Calculations Sections 1.1-1.4 1 2 MATTER Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. MASS Mass is a measurement of the amount of matter in an
Part 1: Matter Chapter 1: Matter, Measurements, and Calculations Sections 1.1-1.4 1 2 MATTER Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. MASS Mass is a measurement of the amount of matter in an
Matter, Atoms & Molecules
 Matter, Atoms & Molecules Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. All matter is made of tiny particles called atoms, which are too small to see with the naked eye. Matter Matter is anything
Matter, Atoms & Molecules Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. All matter is made of tiny particles called atoms, which are too small to see with the naked eye. Matter Matter is anything
Thermal energy 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 Thermal energy 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE Temperature There s more to temperature than the idea of hot and cold. Remember that all matter is made up of tiny particles that are constantly moving even in solid objects.
Thermal energy 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE Temperature There s more to temperature than the idea of hot and cold. Remember that all matter is made up of tiny particles that are constantly moving even in solid objects.
Changes in Matter. Introduction to Chemistry
 Changes in Matter Introduction to Chemistry Classifying Matter Matter: is anything that has mass and volume. Volume: the amount of space that something takes up Property: a characteristic of a material
Changes in Matter Introduction to Chemistry Classifying Matter Matter: is anything that has mass and volume. Volume: the amount of space that something takes up Property: a characteristic of a material
CHEMISTRY. Chapter 11 Intermolecular Forces Liquids and Solids
 CHEMISTRY The Central Science 8 th Edition Chapter 11 Liquids and Solids Kozet YAPSAKLI States of Matter difference between states of matter is the distance between particles. In the solid and liquid states
CHEMISTRY The Central Science 8 th Edition Chapter 11 Liquids and Solids Kozet YAPSAKLI States of Matter difference between states of matter is the distance between particles. In the solid and liquid states
Analytical chemistry concerned with the composition of matter development of advanced equipment
 Chemistry Unit #1 Matter Chemistry the scientific study of matter, its properties, and interactions with other matter and with energy a general term for many specialized fields Analytical chemistry concerned
Chemistry Unit #1 Matter Chemistry the scientific study of matter, its properties, and interactions with other matter and with energy a general term for many specialized fields Analytical chemistry concerned
Physical Science Final Examination-Review Sheet (14-15) KEY. 1. A process used to answer questions or solve problems is called scientific inquiry.
 Physical Science Final Examination-Review Sheet (14-15) KEY 1. A process used to answer questions or solve problems is called scientific inquiry. 2. Anything that has mass and takes up space is matter.
Physical Science Final Examination-Review Sheet (14-15) KEY 1. A process used to answer questions or solve problems is called scientific inquiry. 2. Anything that has mass and takes up space is matter.
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Physics 5 - Thermal Properties of Matter Thermal Expansion You need to know thermal expansions for solids, liquids, and gases, and their applications. Thermal
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Physics 5 - Thermal Properties of Matter Thermal Expansion You need to know thermal expansions for solids, liquids, and gases, and their applications. Thermal
Properties and Structure of Matter
 Properties and Structure of Matter Chapter 10 You can use a spider map to organize the main ideas and supporting details of a topic such as properties of matter. Look at the example shown below. The central
Properties and Structure of Matter Chapter 10 You can use a spider map to organize the main ideas and supporting details of a topic such as properties of matter. Look at the example shown below. The central
Chapter 1. Introduction: Matter and Measurement. Chemistry. In this science we study matter, its properties, and its behavior. Matter And Measurement
 Chapter 1 Introduction: and Chemistry 2 In this science we study matter, its properties, and its behavior. We define matter as anything that has mass and takes up space. 3 4 Atoms are the building blocks
Chapter 1 Introduction: and Chemistry 2 In this science we study matter, its properties, and its behavior. We define matter as anything that has mass and takes up space. 3 4 Atoms are the building blocks
C L A S S I F I C AT I O N O F M AT T E R
 UNIT 2: C L A S S I F I C AT I O N O F M AT T E R MATTER Reflect: What is matter? MATTER Matter: Anything that has mass and occupies space. You can describe matter in terms of quantity by mass NOT weight.
UNIT 2: C L A S S I F I C AT I O N O F M AT T E R MATTER Reflect: What is matter? MATTER Matter: Anything that has mass and occupies space. You can describe matter in terms of quantity by mass NOT weight.
Welcome to General Chemistry I
 Welcome to General Chemistry I Chemistry Chemistry is a branch of science that studies the composition and properties of matter and the changes it undergoes H 2 O http://theresilientearth.com/?q=content/climate-models-blown-away-water-vapor
Welcome to General Chemistry I Chemistry Chemistry is a branch of science that studies the composition and properties of matter and the changes it undergoes H 2 O http://theresilientearth.com/?q=content/climate-models-blown-away-water-vapor
Unit 2 review for finals
 Unit 2 review for finals These are the topics you should know and be able to answer questions about: 1. Heating/cooling curve (phase change diagram) a. Draw a heating curve showing a solid melting to a
Unit 2 review for finals These are the topics you should know and be able to answer questions about: 1. Heating/cooling curve (phase change diagram) a. Draw a heating curve showing a solid melting to a
AlCl3(aq) + 3 NaOH(aq) Al(OH)3(s) + 3 NaCl(aq)
 1. Under which conditions does a real gas behave most like an ideal gas? A) at low temperatures and high pressures B) at low temperatures and low pressures C) at high temperatures and high pressures D)
1. Under which conditions does a real gas behave most like an ideal gas? A) at low temperatures and high pressures B) at low temperatures and low pressures C) at high temperatures and high pressures D)
Chapter 13 - States of Matter. Section 13.1 The nature of Gases
 Chapter 13 - States of Matter Section 13.1 The nature of Gases Kinetic energy and gases Kinetic energy: the energy an object has because of its motion Kinetic theory: all matter is made if particles in
Chapter 13 - States of Matter Section 13.1 The nature of Gases Kinetic energy and gases Kinetic energy: the energy an object has because of its motion Kinetic theory: all matter is made if particles in
1) Of solids, liquids, and gases, the common state of matter is the liquid state.
 I. Properties of LIQUIDS: 1) Of solids, liquids, and gases, the common state of matter is the liquid state. a) can exist only within a relatively narrow range of temperature and pressure. 2) The kinetic-molecular
I. Properties of LIQUIDS: 1) Of solids, liquids, and gases, the common state of matter is the liquid state. a) can exist only within a relatively narrow range of temperature and pressure. 2) The kinetic-molecular
Atom - the smallest unit of an element that has the properties of that element From the Greek word for indivisible
 Matter Atom - the smallest unit of an element that has the properties of that element From the Greek word for indivisible 3 subatomic particles Proton - positively charged particle in the nucleus of an
Matter Atom - the smallest unit of an element that has the properties of that element From the Greek word for indivisible 3 subatomic particles Proton - positively charged particle in the nucleus of an
Name: Date: Chemistry ~ Ms. Hart Class: Anions or Cations. Station Review Midterm January 2014 STATION 1: Chemical/physical properties and change
 Name: Date: STATION 1: Chemical/physical properties and change Physical changes are changes in matter in which the appearance of a substance changes but the identity of the compound remains the same Chemical
Name: Date: STATION 1: Chemical/physical properties and change Physical changes are changes in matter in which the appearance of a substance changes but the identity of the compound remains the same Chemical
CH.1 Matter & Measurements
 CH.1 Matter & Measurements Chemistry- the study of matter and its behavior and properties. Matter- anything with mass and takes up space. If you can find it on the periodic table its matter. Atom- Building
CH.1 Matter & Measurements Chemistry- the study of matter and its behavior and properties. Matter- anything with mass and takes up space. If you can find it on the periodic table its matter. Atom- Building
Name. Objective 1: Describe, at the molecular level, the difference between a gas, liquid, and solid phase.
 Unit 6 Notepack States of Matter Name Unit 4 Objectives 1. Describe, at the molecular level, the difference between a gas, liquid, and solid phase. (CH 10) 2. Describe states of matter using the kinetic
Unit 6 Notepack States of Matter Name Unit 4 Objectives 1. Describe, at the molecular level, the difference between a gas, liquid, and solid phase. (CH 10) 2. Describe states of matter using the kinetic
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 1. Introduction: Matter and Measurement. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 1 Introduction: Matter and Measurement James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Why do we study chemistry? My parents want me to study chemistry. I need to graduate.
Lecture Presentation Chapter 1 Introduction: Matter and Measurement James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Why do we study chemistry? My parents want me to study chemistry. I need to graduate.
