MATRIX TABLETS FORMULATION BASED ON HYDROXYPROPYL AND EVALUATION OF DICLOFENAC SODIUM RELEASE
|
|
|
- Alexina Gray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 74 No. 6 pp. 1901ñ1911, 2017 ISSN Polish Pharmaceutical Society MATRIX TABLETS FORMULATION BASED ON HYDROXYPROPYL METHYLCELLULOSE WITH β-cyclodextrin: CHARACTERIZATION AND EVALUATION OF DICLOFENAC SODIUM RELEASE REGINA KASPEREK 1, UKASZ ZIMMER 1, MARTA GROCHOWICZ 2, AGNIESZKA KIERYS 3 and EWA POLESZAK 1 1 Medical University of Lublin, Faculty of Pharmacy, Department of Applied Pharmacy, 1 Chodzki St., Lublin, Poland 2 Maria Curie-Sk odowska University, Faculty of Chemistry, Department of Polymer Chemistry, 33 Gliniana St., Lublin, Poland 3 Maria Curie-Sk odowska University, Faculty of Chemistry, Department of Adsorption, Pl. M. Curie-Sk odowskiej 3, Lublin, Poland Abstract: The study was conducted to investigate the effect of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose HPMC (K15M, K4M and K100LV) in concentration of 30% with addition of 20% β-cyclodextrin (β-cd), on the tableting, mechanical properties and drug release rates of diclofenac sodium matrix tablets prepared by direct compression. The compressibility indexes indicate that all formulations have acceptable flowability. The DSC and XRD experiments confirm that compressing process does not significantly influence the final structure of the investigated formulations. The release data show that 50% of the drug is released up to 6 h and 4.5 h from tablets with K15M and K4M, respectively. The β-cd addition to these formulations prolongs time of the drug release by about 1 and 1.5 h, respectively. The 80% of the drug is released within h from formulation with K15M and K4M regardless of the β-cd presence. In contrast, tablets with K100LV release 80% of drug within 5.5 h and this process is prolonged up to 7 h after the β-cd addition. Finally, the release data from all formulations present the best fitting to the Higuchi model (R 2 > 0.97) which indicate that the release of drug is predominantly diffusion-controlled. The good fitting of profiles to the Korsmeyer ñ Peppas model suggests that there takes place the drug diffusion within the hydrated matrix and also the polymer relaxation. Swelling and erosion studies reveal that tablets containing both K15M and/or K4M and β-cd uptake significantly greater quantities of water comparing to other tablets. Keywords: matrix tablets, β-cyclodextrin, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, sustained release Matrix tablets can be formulated by using hydrophilic polymers, as an example of the sustained release material. This group includes cellulose derivatives, such as hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), which are selected as carriers due to their swelling properties (1-4). HPMC is available in different form viscosity grades and in four different degrees of substitution (5). An initial letter identifies chemically the type of cellulose ether for example the products marked K are different types of HPMC widely used for controlled-release drug formulations. The number in trademark identifies the viscosity grades. The types K100LV, K4M, K15M are characterized by increasing the apparent viscosity of 2% in water at 20 O C , , cp, respectively (1-5). Different types of HPMC have good compression characteristics, therefore they can be directly compressed to form sustained release swellable matrices (2). Release of drugs from HPMC matrices is influenced by many factors such as the polymer concentration, drug to polymer ratio, size of the polymer particle and polymer degree of substitution (6-8). The β-cyclodextrin (β-cd) is a cyclic oligosaccharide composed of seven dextrose units joined through one to four bonds. This oligosaccharide is the most accessible and useful one on industrial scale. It is commonly used as a filler, in formation of inclusion compounds and taste masking of drug especially in orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs). Moreover, it enhances solubility of poorly soluble compounds (9-11). β-cd has also good * Corresponding author: regina.kasperek@umlub.pl; phone fax:
2 1902 REGINA KASPEREK et al. compression characteristic since it has good compressibility index, which is important in the process of direct tableting (12, 13). Because of its favorable compactibility and dilution potential it is considered to be a promising material for direct compression. It was demonstrated that if β-cd is used it is possible to obtain harder tablets at lower compression force (12, 13). β-cd is also used as a diluent in tablets with the sustained release both in complexes or simply mixed as well as it is incorporated into the hydrophilic matrix tablet (14, 15). β-cd is often added to tablets which are prepared by the direct compression technique to obtain specific release characteristics i.e., ODTs, conventional or sustained release (9-13). It is possible to chemically modify β- CD by hydroxyalkylation, alkylation or sulfoalkylation. Various hydrophobic derivatives of β-cd such as alkylated and acylated have been used to prolong the release rate of drugs. Among them it should be mentioned tablets consisting of chitosan/sulfobutyl ether β-cyclodextrin complex (16). On the other hand, hydrophilic derivatives of β-cd such as hydroxypropyl β-cd has been used to enhance the release rate (17). Selection of an appropriate formulation is essential in the case of matrix tablets, enables analysis of combined effects, such as drug solubility, concentration in the tablet, drug diffusivity, and porosity and tortuosity of the tablet (18, 19). These properties influence the release process of drugs from matrices. The quantitative analysis of the values obtained in dissolution tests is easier when mathematical formulas that express the dissolution results as a function of some of the dosage forms characteristics are used. Therefore, much research is focused on described mathematical models (19).The Higuchi model describes drug release through the diffusion mechanism and it is used to describe drug dissolution from systems such as matrix tablets containing water-soluble drugs (19, 20). The Hixson-Crowell model assumes that drug release is limited by the dissolution rate of the particles rather than by diffusion through the polymer matrix (19). The Korsmeyer-Peppas model can be used to characterize the drug release mechanisms as Fickian diffusion (21). A water-soluble drug incorporated into a hydrophilic matrix is released mainly by a diffusioncontrolled process, whereas for a poorly water-soluble compound, the principal mechanism of release is the function of erosion of the matrix that carries the drug (7, 19). The study discusses influence of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose HPMC (K15M, K4M and K100LV) in concentration of 30% with addition of 20% β- cyclodextrin (β-cd) on the tableting, mechanical properties and drug release rates of matrix tablets prepared by direct compression technique. In our study, diclofenac sodium was chosen as a model drug. It is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug with analgesic and antipyretic properties (22). Solubility of diclofenac sodium depends on the ph of the surrounding solution (23). In acidic solutions the solubility is lower and increases at higher ph values (24). The properties of the drug and its short half-life in plasma (only1-2 h) cause that it is an effective candidate for sustained systems. The study involves the characterization of the prepared formulations by XRD and DSC, the studies on the physical properties of tablets, the evaluation of tablets powders and the in vitro examination of the drug release rate. The drug release data has been analyzed by different models (zero order, first order, Higuchi and Table 1. The composition of tablet /powder mixes formulations. Formulation code Ingredients mg/tablet T1/F1 T2/F2 T3/F3 T4/F4 T5/F5 T6/F6 DIC Avicel PH Lactose HPMC K4M HPMC K15M HPMC K β-cyclodextrin Croscarmellose sodium Magnesium stearate Total
3 Matrix tablets formulation based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose with Table 2. Parameters characterizing the flow properties of investigated powders. Formula Angle of repose ( O ) Bulk density (g/cm 3 ) Tapped density (g/cm 3 ) Compressibility index (%) F ± ± ± ± 1.02 F ± ± ± ± 0.79 F ± ± ± ± 1.12 F ± ± ± ± 1.32 F ± ± ± ± 0.82 F ± ± ± ± 0.93 Table 3. Parameters characterizing the physical properties of tablets. Test T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 Weight (mg), mean SD 301 ± ± ± ± ± ± 0.26 Thickness (mm), SD 5.20 ± ± ± ± ± ± 0.05 Hardness (N), SD 91 ± ± ± ± ± ± 0.10 Friability (%) Drug content: (%) DIC, SD ± ± ± ± ± ± 1.07 HixsonñCrowell) so as to determine the possibility of prolonged drug release and the KorsmeyerñPeppas model in order to get insight into the mechanism of drug release from matrix tablets. MATERIALS AND METHODS Materials Diclofenac sodium (DIC) was purchased from Caesar and Loretz GmbH (Germany). LactopressÆ Spray Dried (lactose) was purchased from DFE Pharma (Germany). Microcrystalline cellulose (Avicel PH-102, MCC) and croscarmellose sodium (AcDiSol) were generously supplied as gift samples from FMC Biopolymer (USA). Hydroxypropyl methylcelluloses (HPMC) i.e., Methocel K15M Premium (K15M), Methocel K4M Premium (K4M), Methocel K100Premium LV (K100) were generous gifts from Colorcon (United Kingdom). Betacyclodextrin (Kleptose, β-cyclodextrin, β-cd) was obtained as a gift from Roquette Lestrem (France). Magnesium stearate used as the internal lubricant was purchased from POCH SA (Poland). The chemicals used were of analytical grade and were used without any further purification. Methods Evaluation of tablets powders The powder mixes F1-F6 were prepared according to the composition given in Table 1, which is the equivalent of the composition of tablet formulations T1-T6, respectively. The flowability of powders F1-F6 was determined and assessed based on the angle of repose and compressibility values (25). Angle of repose The angle of repose was measured by passing investigated powders through a funnel of the internal diameter 10 mm on the horizontal surface. The angle of repose was measured automatically in Apparatus Erweka type GTB in triplicate. Compressibility (Carrís index) The measurements of the compressibility was carried out with the Erweka Apparatus type SVM 222. An accurate weight of tablet formulations formula tablets was poured into a volumetric cylinder to occupy a volume (V 0 ) and then subjected to a standard tapping procedure onto a solid surface until a constant volume was achieved (V f ). The Carrís indexes were calculated from equation (25): Compressibility index = 100 (V 0 ñ V f )/V 0 The parameters characterizing the flow character of powders F1-F6 are presented in Table 2. Preparation of tablets The tablets (T1ñT6) were prepared by the direct compression method. Diclofenac sodium and other components were premixed in a cube mixer
4 1904 REGINA KASPEREK et al. (Erweka, Germany) for 15 min. Next, the mixture was passed through mesh no. 40 and then it was lubricated with the magnesium stearate for another 5 min. A variety of powder mixes were compressed to flat face tablets of 300 mg weight with the use of a Single Pounch Tablet Press ñ EP1 (Erweka, Germany) fitted with 10 mm round-shaped punch. Physical properties of tablets The parameters characterizing physical properties of tablets T1-T6 and the content of DIC are collected in Table 3. All prepared tablets fulfilled pharmacopoeial requirements of European Pharmacopoeia 8 th edition (Ph. Eur.) such as uniformity of weight, hardness, friability and drug content. Physical properties of tablets The tablets were evaluated for weight variation (n = 20) using a weighing balance (Mettler AT 201, Switzerland). From each batch, 20 tablets were randomly selected and weighed together. Their mean weight was calculated and then they were weighed individually. Tablet thickness (n = 20) was measured using a Vernier Caliper (Digital Caliper mm, Comparator). Hardness of tablets (n = 10) was evaluated using a hardness tester (AEG Type AP 56 N2, Germany). Ten tablets were randomly selected from each series. The breaking force needed to crush the tablet was measured. Friability test was conducted using a friabilator (Erweka TAR 120, Germany). Twenty tablets from each series were weighed and placed into the friabilator. The machine was set to 25 rpm for 4 min. After that, the selected tablets were reweighed. Drug content Ten tablets from each batch were randomly selected and crushed together. Then, 300 mg of powder was transferred into a 100 ml volumetric flask and 50 ml phosphate buffer at ph 6.8 was added. The flask was shaken for 10 min in a mixer (Vortex Genius 3). Afterwards, the flask content was diluted with phosphate buffer at ph 6.8. Next, the mixture was filtered through a Whatman filter (0.45 µm pore size) and 2 ml of the solution was transferred into a 50 ml volumetric flask and diluted with phosphate buffer at ph 6.8. The absorbance of this solution was determined spectrophotometrically at 276 nm (Omega UV ñ VIS, Thermo Scientific, England). The DIC concentration in the buffer medium was calculated according to the linear regression equation obtained from a standard curve (A = Conc , R 2 = 0.999). This method obeys Beerís Law within the concentration range of 2.5ñ20 µg/ml for DIC. The experiment was repeated six times (n = 6). Thermal characterization of powders Thermal behavior of substances included in the investigated tablets T1-T6 as well as the reference powder RP1 (i.e., powder prepared without DIC and HPMC) was determined with the Netzsch DSC 204 calorimeter (Germany) operating in the dynamic mode. The dynamic scans were performed at the heating rate of 10 K/min from room temperature to the maximum of 400 O C under argon atmosphere (30 ml/min). The mass of the sample was 5 mg. As a reference an empty aluminium crucible was used. XRD analysis The X-ray diffraction (XRD) analyses were performed on the reference powders RP1 and RP2 (i.e., powder prepared without HPMC and β-cd), powders F1-F6 and powder obtained from the crushed tablet T6 which was randomly selected from the batch. The XRD measurement was conducted on a powder X- ray diffractometer (Empyrean, PANalytical). The diffraction patterns were recorded in the 20 range of 5 O to 25 O at room temperature using Cu Kα radiation (λ = nm) at a step of 0.02 O. Release study The dissolution test was carried out with the Ph Eur. (25) Apparatus 2 (Erweka, Germany) called a paddle apparatus. For the test, 900 ml of phosphate buffer at ph 6.8 maintained at 37 ± 0.5 O C was used as a dissolution medium. Each tablet was placed in each of the six vessels of the paddle apparatus and rotated at 75 rpm. After appropriate intervals of time, 2 ml samples were collected and an equivalent amount of phosphate buffer at ph 6.8 was added to a vessel. Each solution containing the drawn samples was mixed and analyzed spectrophotometrically. In vitro release kinetics The drug release data to the different kinetic models were fitted such as zero-order (Eq. 1), firstorder (Eq. 2), Higuchi (Eq. 3), Hixon and Crowell (Eq. 4) models. Q = K 0 t (1) Log Q= Log Q 0 ñ K 1 t/ (2) Q= K H t 1/2 (3) Q 0 1/3 - Q 1/3 =K HCt (4) where Q and Q 0 are the percent of the drug released at time t and initial amount of drug, respectively. K 0, K 1, K H, K HC are the rate constants of zero-order (26), first-order (27), Higuchi (20) and Hixon-Crowell
5 Matrix tablets formulation based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose with model (19), respectively. The release rate (K) and coefficient of determination (R 2 ) values were calculated from these models. To evaluate the mechanism of the drug release from tablets, the first 60% of the drug release data were plotted in Korsmeyer-Peppas equation (21). Q t /Q = K KP t n (5) where Q t is the percent drug release at time t; Q the percent drug release after infinite time, usually taken as 100; Q t /Q is the fraction of drug released at time t; and K KP is a release constant incorporating the structural and geometric characteristics of the system. In the Korsmeyerís model, n which is the release exponent indicates the drug release mechanism. In addition, for determination of the exponent n, one must use only the initial portion of the release curve (Q t /Q < 0.6). For the cylindrical matrix tablets, if the exponent n = 0.45, then the drug release mechanism is Fickian diffusion, 0.45 < n < 0.89 for non-fickian diffusion, n = 0.89 for Case II transport or typical zero-order release, n > 0.89 for Super Case-II transport (19, 21). Calculated kinetic parameters are collected in Table 4. Quantification of water uptake and erosion determination One tablet from each series was placed in flat dissolution vessel, which contained phosphate buffer at ph 6.8. At time intervals of one hour, the investigated tablets were taken out and weighted after removal of the solution excess from their surface using filter paper. Next, the wetted tablets were dried in an oven at 40 O C up to the constant weight. The increase of the tablets weight (corresponding to the weight of the liquid uptake) was calculated according to Eq. 6 (28,29): Q = 100 (W w ñ W i )/W i (6) where Q is the percentage of liquid uptake, W w and W i are masses of the hydrated samples before drying and the initial starting dry weight, respectively. The degree of erosion (expressed as percentage erosion of the polymer content, E) was determined using Eq. 7: E = 100 (W i ñ W f )/W i (7) where W f is the final mass of the same dried and partially eroded sample. The entire process was repeated to get 3 values for each time point, and the average was calculated. The Vergnaud model was calculated from the equation Eq. 8 (8, 30, 31): M t = kt n (8) where M t is the amount of liquid transferred at time t, and k is the swelling constant which depends on the amount of liquid transferred after infinite time, the porosity of matrix and diffusivity. The exponent n indicates the mechanism of water uptake. A value of n less than 0.5 indicates a diffusioncontrolled mechanism in which the rate of diffusion of the liquid is much less as compared with the rate of relaxation of the polymer. When n equals 1, it suggests that the stress relaxation process is very slow as compared with the rate of diffusion. A value of n between 0.45 and 1 presented an anomalous or complex behavior in which the rate of diffusion of the liquid and that of relaxation are of the same magnitude (8, 30, 31). Statistical analysis Statistical and kinetic analyses were made using Statistica 8.0 software. The obtained data were subjected to statistical analysis using one-way ANOVA and p value of < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Physical properties of powder mixes and prepared tablets Analyzing parameters characterizing the flow properties of powder mixes (F1-F6) presented in Table 2, it can be noticed that the bulk densities for Table 4. Kinetic parameters of DIC release from tablets. Formulation Zero-order model First-order model Higuchi model Korsmeyer-Peppas model K 0 R 2 K 1 R 2 K H R 2 n R 2 T T T T T T
6 1906 REGINA KASPEREK et al. all prepared powders have similar values. It indicates that they do not form larger agglomerates. It is known that value of the compressibility index up to 16-20% indicate a fairly good flow properties, whereas values from 21% to 25% indicate a sufficient flowability (25). The values of compressibility index which are in the range from 18.8% to 22.4% indicate that all formulations have acceptable flowability and compressibility regardless of the β-cd presence and the type of the used HPMC. However, powders containing only HPMC have the compressibility index up to 20%, whereas powders F2, F4 and F6 (with HPMC and β-cd) reach the index at about 21% and above. These results suggest that addition of β-cd slightly reduces the flow properties of the powders. Similar conclusions were previously reported by Ghorab et al. (13). There it was presented that the bulk densities of the prepared granules and their flowability decrease slightly with the increase of the β-cd concentration. The matrix tablets containing DIC were prepared by mixing diluents i.e., lactose and Avicel ph102 in the ratio 1 : 1 and different types of HMPC with and without addition of β-cd. As shown in Table 3, obtained formulations exhibit a good degree of uniformity of weight and thickness. All the tablets have good mechanical properties with regard to both hardness and friability. Only non-significant differences in hardness values exist between formulations, whereas the friability depends on the used HPMC and it decreases for formulations in the following sequence: T1 > T3 > T5. The addition of β-cd to the formulations cause the decrease of friability values of the resulted tablets (T2, T4 and T6). The lowest value of the friability for tablets containing only β-cd (obtained by direct compression) was observed by Ghorab et al. (13). This may be explained by the greater binding strength of β-cd. It is known, that β-cd has crystallization water which helps in binding of the particles; and this, in turn, makes it possible to produce the stronger tablets (32). DSC and XRD studies The DSC and XRD experiments were conducted to indicate the presence of diclofenac sodium as well as to examine crystallinity and possible interactions between drug and the used additives in the prepared formulations. DSC thermograms of the reference sample RP1 and tablets of various compositions (T1-T6) are demonstrated in Figure 1. The DSC curve of the reference sample reveals a large number of complex endothermic events connected with the loss of bounded water (151 O C), melting of lactose (218 O C) and formation of anhydrous microcrystalline cellulose (234 O C). In the thermogram of the intact DIC a significant endothermic peak at 290 O C correspon- Figure 1. DSC thermograms of the investigated matrix tablets
7 Matrix tablets formulation based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose with Figure 2. XRD patterns of the investigated samples. The marked points are for XRD reflexes which originate from the drug (stars), matrix (dots) and β-cd (diamonds). Note, Y-scale of all samples has been normalized ding to the melting of drug crystals is visible, and then their immediate decomposition reflected in the following exothermic peak takes place. On DSC curves of RP1 and tablets T1-T6 the broad endothermic peaks are visible in the temperature region about O C (Fig. 1). Although, these peaks are not as sharp and significant as on the drugís thermogram (due to the dilution factor), they are placed in the same temperature region. Thus, it allows to presume that in the investigated formulations, DIC does not interact with the chosen additives. Figure 2 shows the XRD patterns of pure DIC, the reference powders RP1 and RP2 and powder F6. For the comparative purpose the XRD pattern of T6 obtained after compressing F6 into the T6 tablet is presented. Both the intact DIC and formulation without the drug (RP1) possess the distinct sharp peaks which indicate the crystalline nature of the investigated materials. As it follows from the XRD pattern, the introduction of the drug into the various compositions of additives causes only appearing of the additional sharp reflections which originate from DIC (Fig. 3). Similarly, addition of β-cd results only in the appearing of additional XRD peaks at 20 = 8.92 O and 10.5 O (33) for F2, F4 and F6 powders (Fig. 3). Moreover, XRD patterns for T6 confirm that the direct compression of powder mixtures into the tablets neither influence the location of reflections nor cause the appearing of additional patterns. Only decrease of the intensity of the characteristic reflection for DIC (i.e., 20 = 6.6 O by about 31%) is visible in comparison to the F6 powder. This indicates that compressing process does not significantly influence the final structure of the investigated tablets, in principle. Release rate studies The solubility of diclofenac sodium in acidic solutions is poor and increases at higher ph values (7, 18, 24), therefore to assess the influence of excipients on release profiles of DIC only the bufor medium was chosen. The dissolution profiles of prepared tablets (Fig. 4) show that 80% of drug is released within 12 h from the T1 formulation containing K15M, and within 10 h from tablets with K4M both with (T4) and without β-cd (T3) and K15M with β-cd (T2). From tablets with HPMC K100 (T5) 80% of DIC is released up to 5.5 h, but
8 1908 REGINA KASPEREK et al. the dissolution of DIC is longer and continued up to 7 h after addition of β-cd (for the T6 tablet). Taking into account the dissolution of DIC from tablets with K15M and K4M polymers, it can be noticed that 50% DIC is released up to about 6 h and 4.5 h, respectively. The time of the drug release is prolonged by about 1 hours and by about 1.5 hours for matrix tablets containing β-cd (T2 and T4), respectively. However, there are multiple opinions regarding the subject. On the one hand, it has been shown by Ghorab et al. (13) that the increase of the dissolution rate of drug from β-cd/lactose matrix tablets (where β-cd plays the role of diluent) is regardless of the applied production method i.e., the direct compression or the wet granulation technique. On the other hand, Koester et al. (14) have demonstrated that matrix tablets based on HPMC K100 LV and containing carbamazepine/β-cd solid complexes display faster drug release in comparison with the rate of drug release from formulations containing simple physical mixture of carbamazepine and β- CD. Figure 3. XRD patterns of the investigated tablets. The marked points are for XRD reflexes which originate from the drug (stars), matrix (dots) and β-cd (diamonds), respectively. Note, Y-scale of all samples has been normalized Figure 4. Dissolution profiles of DIC from tablets T1-T6 in phosphate buffer at ph 6.8
9 Matrix tablets formulation based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose with Figure 5. Percentage of water uptake for the tablets Figure 6. The curves of the erosion rate of the tablets Release kinetics The obtained drug release data were analyzed with various kinetics models (i.e. zero order, first order, Higuchi and Korsmeyer-Peppas) to understand the mechanism of drug release from matrix tablets. The main parameters i.e., release rate constants and determination coefficients are listed in Table 4. The results indicate that drug release from the tablets prepared in this study was best described by the Higuchi model (R 2 > 0.97) followed by zero order model (R 2 > 0.95). This indicates that the release of drug from investigated matrix tablets is a square root of time dependent process based on diffusion. This explains why the drug diffuses at a comparatively slower rate as the distance of diffusion increases. The zero-order release kinetics indicate that the drug release profile is nearly independent of its concentration. To confirm the release mechanism, the experimental data were fitted into the Korsmeyer ñ Peppas model. The dissolution data for all prepared formulations exhibit a high value of the correlation coefficient (R 2 > 0.993) in the case of this model. The values of the exponent (n) providing the type of release mechanism is in the range of to indicating a coupling of drug diffusion in the hydrated matrix and the polymer relaxation so called anomalous transport (non-fickian), although the diffusion is still the primary mechanism of the drug release. Thus, it can be concluded that this approach to formulation development may be suitable for the controlled delivery of the drug such as diclofenac sodium. Lammoudi et al. (8) have demonstrated that the Higuchi constants are very similar in matrix tablets prepared with the different ratio of HPMC to Acryl and EZE. It indicates that the viscosities of the
10 1910 REGINA KASPEREK et al. Table 5. Kinetic parameters calculated according to the Vergnaud model. Formulation Vergnaud model n R 2 T T T T T T Table 6. Kinetic parameters of erosion data. Formulation a b R 2 T T T T T T a - slope; b - constant; R 2 - correlation coefficient. n - release exponent; R 2 - correlation coefficient. hydrated matrices may be identical, despite the apparent differences in viscosity of the used additives (which is associated with the different ratio of HPMC to Acryl to EZE). Campos-Aldrete and Villafuerte-Robles (34) have pointed out that it is necessary to use the high concentration of HPMC at least 20% in order to eliminate the effect of the viscosity grade on the Higuchi constant. The relaxation and swelling characteristics of HPMC matrices may influence drug release kinetics. It has been shown that HPMC matrices expand predominantly in an axial direction (35). It is commonly known that drug release from swelling matrices depends on the diffusion and the relaxation behavior of the dosage form. The diffusional release is associated with stresses and state transitions involved in the swelling of the hydrophilic polymer. The swelling of the polymer would alter the drug concentration gradient in the gel layer (35). Rate of swelling or water uptake Investigation of the swelling behavior of matrix tablets is very important since it gives insight into the rate of water absorption by the tablet and into the rate of their swelling in the applied dissolution medium (8). As it follows from profiles of water uptake in Figure 5, matrix tablets containing K15M and K4M polymers are characterized by the significantly greater quantities of water uptake than tablets with K100. Furthermore, tablets prepared with addition of β-cd exhibit higher values of water uptake in comparison with tablets without β-cd. Swelling of polymer matrix depends on the rate of penetrant entry into the matrix. The effect of polymer-penetrant interaction enables the release of drug to take place at a constant rate (30, 36). The water uptake data were analyzed using the Vergnaud model (36) to determine the rate and mechanism of water uptake by the polymeric matrices of tablets. The results of kinetic values are presented in Table 5. The water uptake data exhibit a good fit with the Vergnaud model since the coefficients of determination (R 2 > 0.93) present an acceptable fitting to this model for all formulas. The exponents for all formulas are less than 0.5 which suggests that the mechanism is controlled by diffusion of water through the matrix tablet. Thus, it can be concluded that the rate of the polymer relaxation is more important than the molecular diffusion. Polymer erosion The rates of polymer erosion for all matrices are shown in Figure 6 and the kinetic data are presented in Table 6. The results suggest that the weight loss of matrices increases progressively with erosion time and the weight loss versus time is a linear function for all formulations (R 2 > 0.948). The rate of polymer erosion depends on the viscosity of the used HPMC (34). When water penetrates the HPMC matrix, the polymer chains become hydrated and probably disentangle from the matrix. Linear polymeric chains of hydrophilic HPMC form a gelatinous layer on the surface of the tablets which is susceptible to erosion (30). CONCLUSION Matrix tablets containing one of three types of HPMC (K15M, K4M and K100) offer the sustained release of diclofenac sodium in the range of 6 to 12 h, respectively. Addition to the formulation of 20% β-cd causes extension of the drug release time of approximately 2 hours. This is clearly visible in the first 6 h of the release. Flowability and compressibility indexes of powders confirm that the tablets can simply be obtained by direct compression. This process does not significantly influence the final structure of the drug as evidenced by DSC and XRD
11 Matrix tablets formulation based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose with results. Tablets containing β-cd and K15M and/or K4M and are characterized by the significantly greater uptake of water and extent of swelling in comparison with other tablet formulations. The drug release from the investigated tablets is best described by the Higuchi model. This indicates that the process is based on the diffusion. From the studies it follows that the release mechanism includes the drug diffusion in the hydrated matrix as well as the polymer relaxation. Although diffusion is the primary mechanism of drug release, the drug release data, which exhibit good fitting to the Korsmeyer ñ Peppas model, indicate that the release mechanism also include a coupling of drug diffusion in the hydrated matrix and the polymer relaxation so called anomalous transport. REFERENCES 1. Loh Z.C., Elkordy A.A.: Curr. Drug Deliv. 12, 425 (2015). 2. Nerurkar J., Jun H.W., Price J.C., Park M.O.: Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 61, 56 (2005). 3. Mamani P.L., Ruiz-Caro R., Veiga M.D.: AAPS PharmSciTech. 13, 1073 (2012). 4. Piriyaprasarth S., Sriamornsak P.: Int. J. Pharm. 411, 36 (2011). 5. ViridÈn A., Wittgren B., Larsson A.: Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 36, 297 (2009). 6. Li C.L., Martini L.G., Ford J.L., Roberts M.J.: Pharm. Pharmacol. 57, 533 (2005). 7. Mourão S.C., da Silva C., Bresolin T.M., Serra C.H., Porta V.: Int. J. Pharm. 386, 201 (2010). 8. Lamoudi L., Chaumeil J.C., Daoud K. J.: Drug Deliv. Sci. Tec. 31, 93 (2016). 9. Desai S., Poddar A., Sawant K.: Mater. Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Biol. Appl. 58, 826 (2016). 10. Kaur L., Bala R., Kanojia N., Nagpal M., Dhingra G.A.: ISRN Pharm. 8, (2014). 11. Samprasit W., Akkaramongkolporn P., Ngawhirunpat T., Rojanarata T., Opanasopit P.: Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 41, 1006 (2015). 12. Late S.G., Banga A.K.: AAPS PharmSciTech. 11, 1627 (2010). 13. Ghorab M.M., Abdel-Salam H.M., El-Sayad M.A., Mekhel M.M.: AAPS PharmSciTech. 5, e59 (2004). 14. Koester L.S., Xavier C.R., Mayorga P., Bassani V.L.: Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 55, 85 (2003). 15. Koester L.S., Ortega G.G., Mayorga P., Bassani V.L.: Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 58, 177 (2004). 16. Anraku M., Hiraga A., Iohara D., Pipkin J.D., Uekama K., Hirayama F.: Int. J. Pharm. 487, 142 (2015). 17. Labib G.S.: Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 9, 5135 (2015). 18. Su S.F., Chou C.H., Kung C.F., Huang J.D.: Int. J. Pharm. 260, 39 (2003). 19. Costa P., Lobo J.M.: Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 13, 123 (2001). 20. Higuchi T.: J. Pharm. Sci. 52, 1145 (1963). 21. Siepmann J., Peppas N.A.: Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 48, 139 (2001). 22. Martindale: The complete drug reference, London, The Pharmaceutical Press, 2016, spatch (accessed ). 23. Kincl M., Meleh M., Veber M., VreËer F.: Acta Chim. Slov. 51, 409 (2004). 24. Proikakis C.S., Tarantili P.A., Andreopoulos A.G.: Eur. Polym. J. 42, 3269 (2006). 25. European Pharmacopeia 8.0. Strasbourg, Council of Europe, Hadjiioannou T.P., Christian G.D., Koupparis M.A., Macheras P.E.: Quantitative calculations in pharmaceutical practice and research, VCH Publishers Inc., New York, Bourne D.W.: Pharmacokinetics, in: G.S. Banker, C.T. Rhodes, Eds. Modern Pharmaceutics. 4th ed., p. 67, Marcel Dekker Inc, New York Avachat A., Kotwal V.: AAPS PharmSciTech. 8, E88 (2007). 29. Sahoo J., Murthy P.N., Biswal S., Sahoo S.K., Mahapatra A.K.: AAPS PharmSciTech. 9, 577 (2008). 30. Chaibva F.A., Khamanga S.M., Walker R.B.: Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 36, 1497 (2010). 31. Khamanga S.M., Walker R.B.: Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 32, 1139 (2006). 32. Fenyvesi E., Shirakura O., Szejtli J., Nagai T.: Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo), 32, 665 (1984). 33. Tang L.W., Zhao J.C., Sha B.J., Liu H.: J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 127, 2803 (2013). 34. Campos-Aldrete M.E., Villafuerte-Robles L.: Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 43, 173 (1997). 35. Ford J.L.: Int. J. Pharm. 179, 209 (1999). 36. Vergnaud J.M.: Int. J. Pharm. 90, 89 (1993). Received:
IN VITRO DISSOLUTION KINETIC STUDY OF THEOPHYLLINE FROM HYDROPHILIC AND HYDROPHOBIC MATRICES
 Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 63 No. 1 pp. 63ñ67, 2006 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society IN VITRO DISSOLUTION KINETIC STUDY OF THEOPHYLLINE FROM HYDROPHILIC AND HYDROPHOBIC
Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 63 No. 1 pp. 63ñ67, 2006 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society IN VITRO DISSOLUTION KINETIC STUDY OF THEOPHYLLINE FROM HYDROPHILIC AND HYDROPHOBIC
The Influence of Hydro-Alcoholic Media on Hypromellose Matrix Systems
 METHOCEL Application Data Premium Cellulose Ethers The Influence of Hydro-Alcoholic Media on Hypromellose Matrix Systems OBJECTIVES The hydrophilic matrices (HM) continue to be a popular and widely used
METHOCEL Application Data Premium Cellulose Ethers The Influence of Hydro-Alcoholic Media on Hypromellose Matrix Systems OBJECTIVES The hydrophilic matrices (HM) continue to be a popular and widely used
Research Article. Jafar Akbari 1,2*, Reza Enayatifard 1, Majid Saeedi 1,2 and Massoud Saghafi 1. Abstract. Trop J Pharm Res, October 2011;10(5): 535
 Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research October 2011; 10 (5): 535-541 Pharmacotherapy Group, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Benin, Benin City, 300001 Nigeria. All rights reserved. Research Article
Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research October 2011; 10 (5): 535-541 Pharmacotherapy Group, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Benin, Benin City, 300001 Nigeria. All rights reserved. Research Article
Impact of Granulation and Effect of Polymers on Theophylline Release from Matrix Tablets
 Impact of Granulation and Effect of Polymers on Theophylline Release from Matrix Tablets Kazi Rashidul Azam, Md. Shaikhul Millat Ibn Razzak, Ferdous Khan, Muhammad Shahidul Islam, Md. Ruknuzzaman Rony
Impact of Granulation and Effect of Polymers on Theophylline Release from Matrix Tablets Kazi Rashidul Azam, Md. Shaikhul Millat Ibn Razzak, Ferdous Khan, Muhammad Shahidul Islam, Md. Ruknuzzaman Rony
DISSOLUTION PROFILLING OF NIMESULIDE SOLID DISPERSIONS WITH POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, TALC AND THEIR COMBINATIONS AS DISPERSION CARRIERS
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.2, No.1, pp 480-484, Jan-Mar 2010 DISSOLUTION PROFILLING OF NIMESULIDE SOLID DISPERSIONS WITH POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, TALC
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.2, No.1, pp 480-484, Jan-Mar 2010 DISSOLUTION PROFILLING OF NIMESULIDE SOLID DISPERSIONS WITH POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, TALC
Use of Roller Compaction in the Preparation of Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended Release Matrix Tablets Containing Hydrophilic Polymers
 METHOCEL Application Data Premium Cellulose Ethers Use of Roller Compaction in the Preparation of Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended Release Matrix Tablets Containing Hydrophilic Polymers ABSTRACT SUMMARY
METHOCEL Application Data Premium Cellulose Ethers Use of Roller Compaction in the Preparation of Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended Release Matrix Tablets Containing Hydrophilic Polymers ABSTRACT SUMMARY
IMPROVEMENT OF DISSOLUTION PROFILE OF LORNOXICAM BY SOLID DISPERSION USING SPRAY DRYING TECHNIQUE
 66 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 3(5): September-October 2014 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
66 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 3(5): September-October 2014 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
Chapter 7 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PULSINCAP
 161 Chapter 7 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PULSINCAP 162 Chapter 7 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PULSINCAP S.No. Name of the Sub-Title Page No. 7.1. Optimization of formulations of Pulsincap
161 Chapter 7 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PULSINCAP 162 Chapter 7 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PULSINCAP S.No. Name of the Sub-Title Page No. 7.1. Optimization of formulations of Pulsincap
Formulation and Evaluation of Release-Retardant Matrix Tablets of Diclofenac Sodium
 FABAD J. Pharm. Sci., 31, 119-16, 006 RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Release-Retardant Matrix Tablets of Diclofenac Sodium Sunita DAHIYA*, Formulation and Evaluation of Release-Retardant
FABAD J. Pharm. Sci., 31, 119-16, 006 RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Release-Retardant Matrix Tablets of Diclofenac Sodium Sunita DAHIYA*, Formulation and Evaluation of Release-Retardant
Analysis of Case II drug transport with radial and axial release from cylinders
 International Journal of Pharmaceutics 254 (23) 183 188 Analysis of Case II drug transport with radial and axial release from cylinders Kosmas Kosmidis a, Eleni Rinaki b, Panos Argyrakis a, Panos Macheras
International Journal of Pharmaceutics 254 (23) 183 188 Analysis of Case II drug transport with radial and axial release from cylinders Kosmas Kosmidis a, Eleni Rinaki b, Panos Argyrakis a, Panos Macheras
Effect of Alkaline Excipients on The Release Profile of Gliclazide Extended Release Tablets
 Effect of Alkaline Excipients on The Release Profile of Gliclazide Extended Release Tablets Monika Srivastav 1, B Prabhakar 1, Ashok Omray 2 1 School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, NMIMS University,
Effect of Alkaline Excipients on The Release Profile of Gliclazide Extended Release Tablets Monika Srivastav 1, B Prabhakar 1, Ashok Omray 2 1 School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, NMIMS University,
Available online through ISSN
 Research Article Available online through www.ijrap.net ISSN 2229-3566 COMPARISON OF IN VITRO DISSOLUTION PROFILES OF CEFPODOXIME PROXETIL - PEG SOLID DISPERSIONS WITH CEPODOXIME PROXETIL Madgulkar Ashwini
Research Article Available online through www.ijrap.net ISSN 2229-3566 COMPARISON OF IN VITRO DISSOLUTION PROFILES OF CEFPODOXIME PROXETIL - PEG SOLID DISPERSIONS WITH CEPODOXIME PROXETIL Madgulkar Ashwini
Design and In Vitro Characterization of Dexlansoprazole Controlled Release Tablets
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Design and In Vitro Characterization of Dexlansoprazole Controlled Release Tablets Y. Naveen Kumar 1, J. Sreekanth 2, P. Vijay Chander Reddy 3 1 Drugs Control Administration, Hyderabad,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Design and In Vitro Characterization of Dexlansoprazole Controlled Release Tablets Y. Naveen Kumar 1, J. Sreekanth 2, P. Vijay Chander Reddy 3 1 Drugs Control Administration, Hyderabad,
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences
 Research Article Bioinformatics International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 MODEL DEPENDANT AND STATISTICAL APPROACHES TO STUDY RELEASE KINETICS OF MELOXICAM RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS
Research Article Bioinformatics International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 MODEL DEPENDANT AND STATISTICAL APPROACHES TO STUDY RELEASE KINETICS OF MELOXICAM RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS
Investigation of Moisture-Activated Granulation of Hydrophilic Polymer Blends in Verapamil HCl Extended Release Matrices
 METHOCEL Application Data Premium Cellulose Ethers Investigation of Moisture-Activated Granulation of Hydrophilic Polymer Blends in Verapamil HCl Extended Release Matrices ABSTRACT SUMMARY Hydrophilic
METHOCEL Application Data Premium Cellulose Ethers Investigation of Moisture-Activated Granulation of Hydrophilic Polymer Blends in Verapamil HCl Extended Release Matrices ABSTRACT SUMMARY Hydrophilic
Research Article. Development of Controlled Release Tablets of Nisoldipine with Improved Pharmaceutical Properties
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2013, 5(7):112-120 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Development of Controlled Release Tablets of Nisoldipine
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2013, 5(7):112-120 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Development of Controlled Release Tablets of Nisoldipine
CHAPTER-3 MATERIALS AND METHODS
 75 CHAPTER-3 MATERIALS AND METHODS 76 3.1 MATERIALS 3.1.1 Drugs used in the present study Lamivudine Zidovudine Stavudine Drug name Source Alchem laboratories, Mumbai, India 3.1.2 Excipients and chemicals
75 CHAPTER-3 MATERIALS AND METHODS 76 3.1 MATERIALS 3.1.1 Drugs used in the present study Lamivudine Zidovudine Stavudine Drug name Source Alchem laboratories, Mumbai, India 3.1.2 Excipients and chemicals
ph-independent release of propranolol hydrochloride from HPMCbased matrices using organic acids
 DARU Vol. 16, No. 3 8 136 ph-independent release of propranolol hydrochloride from HPMCbased matrices using organic acids * Bolourchian N., Dadashzadeh S. School of Pharmacy, Pharmaceutical Sciences Research
DARU Vol. 16, No. 3 8 136 ph-independent release of propranolol hydrochloride from HPMCbased matrices using organic acids * Bolourchian N., Dadashzadeh S. School of Pharmacy, Pharmaceutical Sciences Research
ASSESSMENT OF XANTHAN GUM BASED SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS CONTAINING HIGHLY WATER-SOLUBLE PROPRANOLOL HCL
 Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 70 No. 2 pp. 283ñ289, 2013 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society ASSESSMENT OF XANTHAN GUM BASED SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS CONTAINING HIGHLY
Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 70 No. 2 pp. 283ñ289, 2013 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society ASSESSMENT OF XANTHAN GUM BASED SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS CONTAINING HIGHLY
POLYOX. Application Data. Formulation of POLYOX ER Matrices for a Highly Soluble Active APPLICATIONS DATA SUMMARY INTRODUCTION POLYOX - 1 -
 POLYOX Application Data Water Soluble Resins Formulation of POLYOX ER Matrices for a Highly Soluble Active APPLICATIONS DATA SUMMARY POLYOX, water soluble resins (WSR), can be used as an alternative to
POLYOX Application Data Water Soluble Resins Formulation of POLYOX ER Matrices for a Highly Soluble Active APPLICATIONS DATA SUMMARY POLYOX, water soluble resins (WSR), can be used as an alternative to
Formulation of Low Dose Medicines - Theory and Practice
 Hashim Ahmed, Ph.D. and Navnit Shah, Ph.D. Pharmaceutical and Analytical R&D, Hoffmann-La Roche Inc., Nutley NJ Formulation of Low Dose Medicines - Theory and Practice Progress in pharmaceutical research
Hashim Ahmed, Ph.D. and Navnit Shah, Ph.D. Pharmaceutical and Analytical R&D, Hoffmann-La Roche Inc., Nutley NJ Formulation of Low Dose Medicines - Theory and Practice Progress in pharmaceutical research
International Journal of Advanced Chemical Science and Applications (IJACSA)
 Water-sorption behavior of some commonly used pharmaceutical excipients: Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and Croscarmellose Sodium 1 A Ravikiran, 2 M Arthanareeswari,
Water-sorption behavior of some commonly used pharmaceutical excipients: Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and Croscarmellose Sodium 1 A Ravikiran, 2 M Arthanareeswari,
A STUDY OF COMPRESSION PROCESS AND PROPERTIES OF TABLETS WITH MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE AND COLLOIDAL SILICON DIOXIDE
 Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 73 No. 5 pp. 1259ñ1265, 2016 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY A STUDY OF COMPRESSION PROCESS AND PROPERTIES OF TABLETS
Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 73 No. 5 pp. 1259ñ1265, 2016 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY A STUDY OF COMPRESSION PROCESS AND PROPERTIES OF TABLETS
S.Janakidevi et al. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2014, 5 (7) INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF CEFIXIME TRIHYDRATE SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS USING DIFFERENT POLYMERS S.Janakidevi*,
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF CEFIXIME TRIHYDRATE SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS USING DIFFERENT POLYMERS S.Janakidevi*,
Influence of different grades and concentrations of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose on the release of metformin hydrochloride
 World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
Mohammad.Zuber. et al. / International Journal of Biopharmaceutics. 2012; 3(1): International Journal of Biopharmaceutics
 44 e- ISSN 0976-1047 Print ISSN 2229-7499 International Journal of Biopharmaceutics Journal homepage: www.ijbonline.com IJB THE EFFECT OF VARIOUS SURFACTANTS ON RELEASE BEHAVIOR OF LIDOCAINE HCL FROM ETHYLCELLULOSE
44 e- ISSN 0976-1047 Print ISSN 2229-7499 International Journal of Biopharmaceutics Journal homepage: www.ijbonline.com IJB THE EFFECT OF VARIOUS SURFACTANTS ON RELEASE BEHAVIOR OF LIDOCAINE HCL FROM ETHYLCELLULOSE
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(3): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(3):1573-1579 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 In vitro release kinetic study of ambroxol hydrochloride
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(3):1573-1579 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 In vitro release kinetic study of ambroxol hydrochloride
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences
 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Kinetics and Mechanisms of Drug Release from Swellable and Non Swellable Matrices: A Review Chime Salome A*, Onunkwo Godswill C and
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Kinetics and Mechanisms of Drug Release from Swellable and Non Swellable Matrices: A Review Chime Salome A*, Onunkwo Godswill C and
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INSTITUTIONAL PHARMACY AND LIFE SCIENCES
 International Journal of Institutional Pharmacy and Life Sciences 6(2): March-April 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INSTITUTIONAL PHARMACY AND LIFE SCIENCES Pharmaceutical Sciences Research Article!!! Received:
International Journal of Institutional Pharmacy and Life Sciences 6(2): March-April 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INSTITUTIONAL PHARMACY AND LIFE SCIENCES Pharmaceutical Sciences Research Article!!! Received:
Preparation And Characterization Of Simvastatin Nanosuspension By Homogenization Method
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.5, No.1, pp 193-197, Jan-Mar 2013 Preparation And Characterization Of Simvastatin Nanosuspension By Homogenization Method
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.5, No.1, pp 193-197, Jan-Mar 2013 Preparation And Characterization Of Simvastatin Nanosuspension By Homogenization Method
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FAST DISSOLVING TABLETS OF GLICLAZIDE
 ISSN 976 44X Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FAST DISSOLVING TABLETS OF GLICLAZIDE Ch.T.Lalitha kumari*, Dr.M.Mohan Varma, P.Satish Kumar, N. Jahnavi Shri Vishnu College of Pharmacy, Vishnupur,
ISSN 976 44X Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FAST DISSOLVING TABLETS OF GLICLAZIDE Ch.T.Lalitha kumari*, Dr.M.Mohan Varma, P.Satish Kumar, N. Jahnavi Shri Vishnu College of Pharmacy, Vishnupur,
Formulation and evaluation of matrix tablets of Famotidine using hydrophilic polymer
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Archives of Applied Science Research, 2010, 2 (3):212-220 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Archives of Applied Science Research, 2010, 2 (3):212-220 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X
Received 25 March, 2010; received in revised form 03 June, 2010; accepted 15 June, 2010
 ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 7 (Research Article) Received 25 March, 2010; received in revised form 03 June, 2010; accepted 15 June, 2010 IMPROVEMENT OF DISSOLUTION BEHAVIOR OF PARACETAMOL
ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 7 (Research Article) Received 25 March, 2010; received in revised form 03 June, 2010; accepted 15 June, 2010 IMPROVEMENT OF DISSOLUTION BEHAVIOR OF PARACETAMOL
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences
 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Formulation and Development of ph Independent Once Daily Matrix Tablet of Quetiapine Fumarate R Mohapatra* 1, S Senapati 1, C Sahoo
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Formulation and Development of ph Independent Once Daily Matrix Tablet of Quetiapine Fumarate R Mohapatra* 1, S Senapati 1, C Sahoo
CHAPTER 7 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS. constitutes the objective of many a research project in the field of pharmaceutical
 CHAPTER 7 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS Taste masking and development of palatable dosage forms of bitter drugs constitutes the objective of many a research project in the field of pharmaceutical technology.
CHAPTER 7 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS Taste masking and development of palatable dosage forms of bitter drugs constitutes the objective of many a research project in the field of pharmaceutical technology.
Scholars Research Library. Innovation on Development and Evaluation of Gastric Oral Floating Capsules Containing Captopril
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(3): 103-109 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4 Innovation on Development
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(3): 103-109 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4 Innovation on Development
Pharmaceutical Polymers for Tablets and Capsules
 Pharmaceutical Polymers for Tablets and Capsules Edition: March 23, 2010 Wet Granulation Direct compression is not feasible for matrix formulations containing high levels of powder Carbopol polymers (>5%
Pharmaceutical Polymers for Tablets and Capsules Edition: March 23, 2010 Wet Granulation Direct compression is not feasible for matrix formulations containing high levels of powder Carbopol polymers (>5%
Keywords: Sustained release matrices, Eudragit, particle size, Aerosil 200, compaction force
 Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences Vol. 1, No. 3, Autumn 7, 197-5 Received: Jun 9, 7; Accepted: Oct 9, 7 Effect of Particle Size, Compaction Force and Presence of Aerosil on the Properties of Matrices
Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences Vol. 1, No. 3, Autumn 7, 197-5 Received: Jun 9, 7; Accepted: Oct 9, 7 Effect of Particle Size, Compaction Force and Presence of Aerosil on the Properties of Matrices
Physicochemical Characterization of Binary Ionic Polymer Blends: Polyvinyl Acetate Phthalate and Eudragit E PO
 OPADRY Enteric Acrylic-Based Coating System Poster Reprint Physicochemical Characterization of Binary Ionic Polymer Blends: Polyvinyl Acetate Phthalate and Eudragit E PO PURPOSES Polymer complexes, such
OPADRY Enteric Acrylic-Based Coating System Poster Reprint Physicochemical Characterization of Binary Ionic Polymer Blends: Polyvinyl Acetate Phthalate and Eudragit E PO PURPOSES Polymer complexes, such
Study of processing parameters affecting dissolution profile of highly water soluble drug
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2013, 5 (3):211-222 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2013, 5 (3):211-222 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLET OF DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE BY MELT GRANULATION TECHNOLOGY
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLET OF DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE BY MELT GRANULATION TECHNOLOGY
Scholars Research Library
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2010, 2(4): 509-519 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2010, 2(4): 509-519 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Cronicon PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCE. Research Article The Impact of the Polymer Content on the Kinetics of Propranolol HCl from Buccal Adhesive Tablets
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Majid Saeedi 1 * and Katayoun Morteza-Semnani 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Mazandaran University of Medical Science, Iran 2 Department of Medicinal Chemistry, Mazandaran University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Majid Saeedi 1 * and Katayoun Morteza-Semnani 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Mazandaran University of Medical Science, Iran 2 Department of Medicinal Chemistry, Mazandaran University
Polymer Percolation Threshold in Multi-Component HPMC Matrices Tablets
 Advanced Pharmaceutical Bulletin,2011, 1(1), 27-33 doi: 10.5681/apb.2011.004 http://apb.tbzmed.ac.ir/ Polymer Percolation Threshold in Multi-Component HPMC Matrices Tablets Maryam Maghsoodi*, Leila Barghi
Advanced Pharmaceutical Bulletin,2011, 1(1), 27-33 doi: 10.5681/apb.2011.004 http://apb.tbzmed.ac.ir/ Polymer Percolation Threshold in Multi-Component HPMC Matrices Tablets Maryam Maghsoodi*, Leila Barghi
Biomaterials 23 (2002)
 Biomaterials 23 (2002) 1113 1119 Dissolution behaviour of hydrophilic matrix tablets containing two different polyethylene oxides (PEOs) for the controlled release of a water-soluble drug. Dimensionality
Biomaterials 23 (2002) 1113 1119 Dissolution behaviour of hydrophilic matrix tablets containing two different polyethylene oxides (PEOs) for the controlled release of a water-soluble drug. Dimensionality
CHAPTER - 5 DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF ALFUZOSIN ER TABLETS
 55 CHAPTER - 5 DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF ALFUZOSIN ER TABLETS 5.1 MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENTS Table 5.1: List of materials used in research work Name of the Material Manufacturer Alfuzosin Hydrochloride
55 CHAPTER - 5 DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF ALFUZOSIN ER TABLETS 5.1 MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENTS Table 5.1: List of materials used in research work Name of the Material Manufacturer Alfuzosin Hydrochloride
Research Article DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE FORMULATIONS OF THEOPHYLLINE USING NATURAL POLYMERS
 International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy and Life Sciences Available online at http//www.ijrdpl.com October - November, 2013, Vol. 2, No.6, pp 721-725 ISSN: 2278-0238 Research Article
International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy and Life Sciences Available online at http//www.ijrdpl.com October - November, 2013, Vol. 2, No.6, pp 721-725 ISSN: 2278-0238 Research Article
International Journal of Medicine and Health Profession Research
 Research Article ISSN: 2394 7403 International Journal of Medicine and Health Profession Research Journal home page: www.ijmhpr.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING SUSTAINED RELEASED
Research Article ISSN: 2394 7403 International Journal of Medicine and Health Profession Research Journal home page: www.ijmhpr.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING SUSTAINED RELEASED
Practical Pharmaceutical Technology I USP Dissolution Method for PARACETAMOL 500 mg Tablets Section No. 6 Group D
 University of Jordan Faculty of Pharmacy Practical Pharmaceutical Technology I USP Dissolution Method for PARACETAMOL 500 mg Tablets Section No. 6 Group D USP Dissolution Method for PARACETAMOL 500 mg
University of Jordan Faculty of Pharmacy Practical Pharmaceutical Technology I USP Dissolution Method for PARACETAMOL 500 mg Tablets Section No. 6 Group D USP Dissolution Method for PARACETAMOL 500 mg
Jacek Balcerzak, Maria Mucha
 ANALYSIS OF MODEL DRUG RELEASE KINETICS FROM COMPLEX MATRICES OF POLYLACTIDE-CHITOSAN Jacek Balcerzak, Maria Mucha Technical University of Lodz, Faculty of Process and Environmental Engineering Wolczanska
ANALYSIS OF MODEL DRUG RELEASE KINETICS FROM COMPLEX MATRICES OF POLYLACTIDE-CHITOSAN Jacek Balcerzak, Maria Mucha Technical University of Lodz, Faculty of Process and Environmental Engineering Wolczanska
Formulation development and evaluation of sustained release matrix tablets of quetiapine fumarate
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(4):628-632 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Formulation development and evaluation of sustained
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(4):628-632 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Formulation development and evaluation of sustained
Mouth Disintegrating Tablets of Taste-Masked Ondansetron HCl
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 19, No. 5 (2007), 3455-3460 Mouth Disintegrating Tablets of Taste-Masked Ondansetron HCl V.K. CHATAP, D.K. SHARMA*, ANIL MIDDHA, R.D. GUPTA, VIPIN SAINI, MAHENDRA SHIRADKAR
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 19, No. 5 (2007), 3455-3460 Mouth Disintegrating Tablets of Taste-Masked Ondansetron HCl V.K. CHATAP, D.K. SHARMA*, ANIL MIDDHA, R.D. GUPTA, VIPIN SAINI, MAHENDRA SHIRADKAR
Calculation of the required size and shape of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose matrices to achieve desired drug release profiles
 International Journal of Pharmaceutics 201 (2000) 151 164 www.elsevier.com/locate/ijpharm Calculation of the required size and shape of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose matrices to achieve desired drug release
International Journal of Pharmaceutics 201 (2000) 151 164 www.elsevier.com/locate/ijpharm Calculation of the required size and shape of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose matrices to achieve desired drug release
Noveon AA1 as enhancer of HPMC as a direct compression matrix for controlled release
 .. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science Vol. 4 (11), pp. 62-68, November, 214 Available online at http://www.japsonline.com DOI: 1.7324/JAPS.214.41111 ISSN 2231-3354 Noveon AA1 as enhancer of HPMC
.. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science Vol. 4 (11), pp. 62-68, November, 214 Available online at http://www.japsonline.com DOI: 1.7324/JAPS.214.41111 ISSN 2231-3354 Noveon AA1 as enhancer of HPMC
Comparison of US Pharmacopeia Simulated Intestinal Fluid TS (without pancreatin)
 dx.doi.org/10.14227/dt110204p6 Comparison of US Pharmacopeia Simulated Intestinal Fluid TS (without pancreatin) and Phosphate Standard Buffer ph 6.8, TS of the International Pharmacopoeia with Respect
dx.doi.org/10.14227/dt110204p6 Comparison of US Pharmacopeia Simulated Intestinal Fluid TS (without pancreatin) and Phosphate Standard Buffer ph 6.8, TS of the International Pharmacopoeia with Respect
Quality by design (QbD) is an intelligent
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Quality by Design-based Formulation and Evaluation of Fast Dissolving Tablet of Aspirin R. N. Mali, S. R. Desai, J.I. Disouza Department of Quality Assurance, Tatyasaheb Kore College of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Quality by Design-based Formulation and Evaluation of Fast Dissolving Tablet of Aspirin R. N. Mali, S. R. Desai, J.I. Disouza Department of Quality Assurance, Tatyasaheb Kore College of
Formulation and evaluation of sustained release matrix tablets of nifedipine
 IJPAR Vol.4 Issue 3 Jul-Sep-2015 Journal Home page: ISSN: 2320-2831 Research article Open Access Formulation and evaluation of sustained release matrix tablets of nifedipine Eswar kumar.a 1*, A.Vaishnavi,
IJPAR Vol.4 Issue 3 Jul-Sep-2015 Journal Home page: ISSN: 2320-2831 Research article Open Access Formulation and evaluation of sustained release matrix tablets of nifedipine Eswar kumar.a 1*, A.Vaishnavi,
A theoretical approach to evaluate the release rate of. acetaminophen from erosive wax matrix dosage forms
 1 2 A theoretical approach to evaluate the release rate of acetaminophen from erosive wax matrix dosage forms 3 4 Yasuyoshi Agata, Yasunori Iwao, Kai Shiino, Atsuo Miyagishima, Shigeru Itai* 5 6 7 8 9
1 2 A theoretical approach to evaluate the release rate of acetaminophen from erosive wax matrix dosage forms 3 4 Yasuyoshi Agata, Yasunori Iwao, Kai Shiino, Atsuo Miyagishima, Shigeru Itai* 5 6 7 8 9
International Journal of Innovative Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research
 International Journal of Innovative Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research www.ijipsr.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF MONTLUKAST SODIUM EXTENDED RELEASE MATRIX TABLET 1 G.Rajini*, 2 Dr N. Srinivas Malla
International Journal of Innovative Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research www.ijipsr.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF MONTLUKAST SODIUM EXTENDED RELEASE MATRIX TABLET 1 G.Rajini*, 2 Dr N. Srinivas Malla
Formulation and in-vitro Evaluation of Captopril Floating Matrix Tablets Using HPMC 50cps
 Formulation and in-vitro Evaluation of Captopril Floating Matrix Tablets Using HPMC 50cps Basawaraj S.Patil*, Sandeep J. Sonawane, Upendra Kulkarni, Hariprasanna R.C. PG Department of Pharmaceutics, R.M.E.S
Formulation and in-vitro Evaluation of Captopril Floating Matrix Tablets Using HPMC 50cps Basawaraj S.Patil*, Sandeep J. Sonawane, Upendra Kulkarni, Hariprasanna R.C. PG Department of Pharmaceutics, R.M.E.S
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FAST DISSOLVING CHLORTHALIDONE TABLETS
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vol. 1, Suppl 1, Nov.-Dec. 2009 Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FAST DISSOLVING CHLORTHALIDONE TABLETS RAGHAVENDRA RAO N.G
International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Vol. 1, Suppl 1, Nov.-Dec. 2009 Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FAST DISSOLVING CHLORTHALIDONE TABLETS RAGHAVENDRA RAO N.G
Formulation & Evaluation of Mucoadhesive Drug Delivery System of Nifedipine
 Formulation & Evaluation of Mucoadhesive Drug Delivery System of Nifedipine Vipul*, Ashish Singh Research and Development Department, Phyto Ingredients Biopharma Pvt. Ltd., Yamunanagar, Haryana, India
Formulation & Evaluation of Mucoadhesive Drug Delivery System of Nifedipine Vipul*, Ashish Singh Research and Development Department, Phyto Ingredients Biopharma Pvt. Ltd., Yamunanagar, Haryana, India
Preparation and Evaluation of Matrix Tablets Containing Ambroxol Hydrochloride
 139 Research Article Preparation and Evaluation of Matrix Tablets Containing Ambroxol Hydrochloride Soma Vinisha*, Sajida Akhtari Begum, Nikhat Tabassum, Soma Anusha Department of pharmaceutical science,
139 Research Article Preparation and Evaluation of Matrix Tablets Containing Ambroxol Hydrochloride Soma Vinisha*, Sajida Akhtari Begum, Nikhat Tabassum, Soma Anusha Department of pharmaceutical science,
Determination of Design Space for Oral Pharmaceutical Drugs
 Determination of Design Space for Oral Pharmaceutical Drugs Kalliopi Chatzizaharia and Dimitris Hatziavramidis School of Chemical Engineering National Technical University of Athens, Greece Design Space
Determination of Design Space for Oral Pharmaceutical Drugs Kalliopi Chatzizaharia and Dimitris Hatziavramidis School of Chemical Engineering National Technical University of Athens, Greece Design Space
Formulation and in-vitro evaluation of sustained release matrix tablets of gliclazide
 Research Article S.Shanmugamet al. /BioMedRx 2013,1(4), Available online through http://jprsolutions.info Formulation and in-vitro evaluation of sustained release matrix tablets of gliclazide S.Shanmugam,
Research Article S.Shanmugamet al. /BioMedRx 2013,1(4), Available online through http://jprsolutions.info Formulation and in-vitro evaluation of sustained release matrix tablets of gliclazide S.Shanmugam,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF REPAGLINIDE FAST DISSOLVING TABLETS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF REPAGLINIDE FAST DISSOLVING TABLETS Chirravuri S Phani Kumar
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF REPAGLINIDE FAST DISSOLVING TABLETS Chirravuri S Phani Kumar
Improvement of the Dissolution Rate of Piroxicam by Surface Solid Dispersion
 CMU. Journal (24) Vol. 3(2) 77 Improvement of the Dissolution Rate of Piroxicam by Surface Solid Dispersion Suporn Charumanee*, Siriporn Okonoki and Jakkapan Sirithunyalug Department of Pharmaceutical
CMU. Journal (24) Vol. 3(2) 77 Improvement of the Dissolution Rate of Piroxicam by Surface Solid Dispersion Suporn Charumanee*, Siriporn Okonoki and Jakkapan Sirithunyalug Department of Pharmaceutical
CHAPTER - 3 ANALYTICAL PROFILE. 3.1 Estimation of Drug in Pharmaceutical Formulation Estimation of Drugs
 CHAPTER - 3 ANALYTICAL PROFILE 3.1 Estimation of Drug in Pharmaceutical Formulation 3.1.1 Estimation of Drugs ANALYTICAL PROFILE 84 3.1 ESTIMATION OF DRUG IN PHARMACEUTICAL FORMULATION. Agrawal A et al
CHAPTER - 3 ANALYTICAL PROFILE 3.1 Estimation of Drug in Pharmaceutical Formulation 3.1.1 Estimation of Drugs ANALYTICAL PROFILE 84 3.1 ESTIMATION OF DRUG IN PHARMACEUTICAL FORMULATION. Agrawal A et al
Improvement of Dissolution Properties of Furosemide by Complexation with p=c yclodextrin
 Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 24( l), 19-25 (1998) RESEARCH PAPER Improvement of Dissolution Properties of Furosemide by Complexation with p=c yclodextrin Nurten Ozdemir and Sefika Ordu Department
Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 24( l), 19-25 (1998) RESEARCH PAPER Improvement of Dissolution Properties of Furosemide by Complexation with p=c yclodextrin Nurten Ozdemir and Sefika Ordu Department
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE PELLETS OF BOSENTAN HCl SIDDHI V. PATEL 1,2, DR. MUKESH S. PATEL 2 1. Research scholar,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE PELLETS OF BOSENTAN HCl SIDDHI V. PATEL 1,2, DR. MUKESH S. PATEL 2 1. Research scholar,
Research Article. Dissolution Study of Oxolamine Citrate by UV Spectrophotometric Method in Pharmaceutical Dosage Form
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(7):108-112 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Dissolution Study of Oxolamine Citrate by UV Spectrophotometric
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(7):108-112 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Dissolution Study of Oxolamine Citrate by UV Spectrophotometric
OPTIMIZATION OF FUROSEMIDE LIQUISOLID TABLETS PREPARATION PROCESS LEADING TO THEIR MASS AND SIZE REDUCTION
 Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 73 No. 5 pp. 1325ñ1331, 2016 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society OPTIMIZATION OF FUROSEMIDE LIQUISOLID TABLETS PREPARATION PROCESS LEADING TO
Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 73 No. 5 pp. 1325ñ1331, 2016 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society OPTIMIZATION OF FUROSEMIDE LIQUISOLID TABLETS PREPARATION PROCESS LEADING TO
Enhancement of Dissolution of Valsartan by Surface Solid Dispersion Technique
 Research Article ISSN: 0974-6943 Janika Garg et al. / Journal of Pharmacy Research 2012,5(8), Available online through http://jprsolutions.info Enhancement of Dissolution of Valsartan by Surface Solid
Research Article ISSN: 0974-6943 Janika Garg et al. / Journal of Pharmacy Research 2012,5(8), Available online through http://jprsolutions.info Enhancement of Dissolution of Valsartan by Surface Solid
Atenolol Press Coated (HE) Tablet
 CHAPTER 6: FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF ATENOLOL PULSATILE PRESS COATED TABLETS USING RUPTURABLE AND ERODIBLE POLYMERS 6.1. INTRODUCTION AND AIM OF THE STUDY In order to achieve the chronopharmaceutical
CHAPTER 6: FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF ATENOLOL PULSATILE PRESS COATED TABLETS USING RUPTURABLE AND ERODIBLE POLYMERS 6.1. INTRODUCTION AND AIM OF THE STUDY In order to achieve the chronopharmaceutical
Spectrophotometric estimation and validation of hydrochlorothiazide in tablet dosage forms by using different solvents
 Available online at www.derpharmachemica.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharma Chemica, 2012, 4 (1):10-14 (http://derpharmachemica.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-413X CODEN (USA): PCHHAX Spectrophotometric
Available online at www.derpharmachemica.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharma Chemica, 2012, 4 (1):10-14 (http://derpharmachemica.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-413X CODEN (USA): PCHHAX Spectrophotometric
Md.Khairul Alam et al / Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Vol. 3 (6), 2011,
 STUDY OF DISSOLUTION IMPROVEMENT OF VARIOUS POORLY WATER SOLUBLE DRUGS BY SOLID DISPERSION MIXING WITH HPMC 6CPS AND PEG 6 Md. Khairul Alam 1 *, Reza-ul Jalil 2, Nazia Zaman 1, Md. SM Ashraful Islam 3
STUDY OF DISSOLUTION IMPROVEMENT OF VARIOUS POORLY WATER SOLUBLE DRUGS BY SOLID DISPERSION MIXING WITH HPMC 6CPS AND PEG 6 Md. Khairul Alam 1 *, Reza-ul Jalil 2, Nazia Zaman 1, Md. SM Ashraful Islam 3
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF PIOGLITAZONE HYDROCHLORIDE GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING MATRIX TABLET
 Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol 5, Issue 4, 12 ISSN - 974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF PIOGLITAZONE HYDROCHLORIDE GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING
Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol 5, Issue 4, 12 ISSN - 974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF PIOGLITAZONE HYDROCHLORIDE GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING
PRACTICAL APPROACH FOR THE ESTIMATION OF ALCOHOL DRUG RELEASE FROM THE SUSTAINED RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS OF VERAPAMIL HYDROCHLORIDE
 295 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 4(6): November-December 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY
295 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 4(6): November-December 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY
Research Article DEVELOPMENT AND CHARACTERIZATION OF ACECLOFENAC ENTERIC COATED TABLETS
 International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy and Life Sciences Available online at http//www.ijrdpl.com October - November, 2015, Vol. 4, No.6, pp 1861-1866 ISSN (P): 2393-932X, ISSN (E):
International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy and Life Sciences Available online at http//www.ijrdpl.com October - November, 2015, Vol. 4, No.6, pp 1861-1866 ISSN (P): 2393-932X, ISSN (E):
HPMC Matrix Granule Formation: Selection of Suitable Granulating Fluid
 Original Article HPMC Matrix Granule Formation: Selection of Suitable Granulating Fluid Wanwilai Darunkaisorn, Jongjan Mahadlek and Thawatchai Phaechamud* Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty
Original Article HPMC Matrix Granule Formation: Selection of Suitable Granulating Fluid Wanwilai Darunkaisorn, Jongjan Mahadlek and Thawatchai Phaechamud* Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty
Application of a Fully Formulated Aqueous Enteric Coating System on Rabeprazole Sodium Tablets (20 mg)
 ACRYL-EZE Aqueous Acrylic Enteric System Application Data Application of a Fully Formulated Aqueous Enteric Coating System on Rabeprazole Sodium Tablets (20 mg) OBJECTIVES Rabeprazole sodium is a proton
ACRYL-EZE Aqueous Acrylic Enteric System Application Data Application of a Fully Formulated Aqueous Enteric Coating System on Rabeprazole Sodium Tablets (20 mg) OBJECTIVES Rabeprazole sodium is a proton
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND CHEMICAL SCIENCES
 Research Article An In-Vitro Evaluation for the Effect of Β-Cyclodextrin and PVP-K 3 on Drug Release Pattern of Sertraline Hydrochloride Deepa Warrier 1, Aanna Zagade 1, Amir Shaikh 2*, Yogesh Pawar 2
Research Article An In-Vitro Evaluation for the Effect of Β-Cyclodextrin and PVP-K 3 on Drug Release Pattern of Sertraline Hydrochloride Deepa Warrier 1, Aanna Zagade 1, Amir Shaikh 2*, Yogesh Pawar 2
Asian Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences 1 (3) 2011, 13-19
 Asian Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences 1 (3) 2011, 13-19 RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN 2249-622X Formulation and Evaluation of Extended Release Solid Dispersions Conatining Simvastatin Prasad
Asian Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences 1 (3) 2011, 13-19 RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN 2249-622X Formulation and Evaluation of Extended Release Solid Dispersions Conatining Simvastatin Prasad
FORMULATION, DEVELOPMENT AND CHARACTERIZATION OF ORAL DISINTEGRAING TABLET OF CIMITIDINE HCL
 wjpmr, 2018,4(12), 233-237 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.639 Marabathuni et al. Research Article WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH ISSN 2455-3301 www.wjpmr.com WJPMR FORMULATION, DEVELOPMENT
wjpmr, 2018,4(12), 233-237 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.639 Marabathuni et al. Research Article WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH ISSN 2455-3301 www.wjpmr.com WJPMR FORMULATION, DEVELOPMENT
International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Nano Sciences Journal homepage:
 Research Article CODEN: IJRPJK ISSN: 2319 9563 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Nano Sciences Journal homepage: www.ijrpns.com FORMULATION, OPTIMIZATION AND INVITRO EVALUATION OF
Research Article CODEN: IJRPJK ISSN: 2319 9563 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Nano Sciences Journal homepage: www.ijrpns.com FORMULATION, OPTIMIZATION AND INVITRO EVALUATION OF
Investigation of Solid Dispersion Technique in Improvement of Physicochemical Characteristics of Ibuprofen Powder
 R Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Spring 2007: 3(2): 69-76 www.ijps.ir Original Article Investigation of Solid Dispersion Technique in Improvement of Physicochemical Characteristics of Ibuprofen
R Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Spring 2007: 3(2): 69-76 www.ijps.ir Original Article Investigation of Solid Dispersion Technique in Improvement of Physicochemical Characteristics of Ibuprofen
Simultaneously enhancing the solubility and permeability of
 Supporting information for Simultaneously enhancing the solubility and permeability of acyclovir by crystal engineering approach Yan Yan, Jia-Mei Chen*, and Tong-Bu Lu* Experimental section General remarks:
Supporting information for Simultaneously enhancing the solubility and permeability of acyclovir by crystal engineering approach Yan Yan, Jia-Mei Chen*, and Tong-Bu Lu* Experimental section General remarks:
Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets of Esomeprazole Using Natural and Synthetic Polymers
 ISSN 2395-3411 Available online at www.ijpacr.com 415 Research Article Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets of Esomeprazole Using Natural and Synthetic Polymers Rama Rao Nadendla and
ISSN 2395-3411 Available online at www.ijpacr.com 415 Research Article Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets of Esomeprazole Using Natural and Synthetic Polymers Rama Rao Nadendla and
The Efficiency Of Glyceryl Behenate As Sustained-Release Agent Compared With Hydroxypropylcellulose In Tablets
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.5, No.2, pp 622-628, April-June 2013 The Efficiency Of Glyceryl Behenate As Sustained-Release Agent Compared With Hydroxypropylcellulose
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.5, No.2, pp 622-628, April-June 2013 The Efficiency Of Glyceryl Behenate As Sustained-Release Agent Compared With Hydroxypropylcellulose
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 31(2), March April 2015; Article No. 26, Pages:
 Research Article Y. Ganesh Kumar* 1, J. Sreekanth 2, D. Satyavati 3 1 Research Scholar, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, JNTU, Kukatpally, Hyderabad, Telangana, India. 2 Sr. General Manager, R&D Center,
Research Article Y. Ganesh Kumar* 1, J. Sreekanth 2, D. Satyavati 3 1 Research Scholar, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, JNTU, Kukatpally, Hyderabad, Telangana, India. 2 Sr. General Manager, R&D Center,
Development and Statistical Validation of Spectrophotometric Methods for the Estimation of Nabumetone in Tablet Dosage Form
 ISSN: 0973-4945; CODEN ECJHAO E- Chemistry http://www.e-journals.net 2010, 7(4), 1463-1467 Development and Statistical Validation of Spectrophotometric Methods for the Estimation of Nabumetone in Tablet
ISSN: 0973-4945; CODEN ECJHAO E- Chemistry http://www.e-journals.net 2010, 7(4), 1463-1467 Development and Statistical Validation of Spectrophotometric Methods for the Estimation of Nabumetone in Tablet
Formulation and Evaluation of Immediate Release Tablets of Nevirapine Solid Dispersions
 ARC Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (AJPS) Volume 4, Issue 3, 2018, PP 13-20 ISSN No.: 2455-1538 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2455-1538.0404003 www.arcjournals.org Formulation and Evaluation of Immediate
ARC Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (AJPS) Volume 4, Issue 3, 2018, PP 13-20 ISSN No.: 2455-1538 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2455-1538.0404003 www.arcjournals.org Formulation and Evaluation of Immediate
Development and Validation of UV Spectrophotometric Estimation of Diclofenac Sodium Bulk and Tablet Dosage form using Area under Curve Method
 21 Article Development and Validation of UV Spectrophotometric Estimation of Diclofenac Sodium Bulk and Tablet Dosage form using Area under Curve Method Mali Audumbar Digambar*, Jadhav Santosh, Mane Pandurang,
21 Article Development and Validation of UV Spectrophotometric Estimation of Diclofenac Sodium Bulk and Tablet Dosage form using Area under Curve Method Mali Audumbar Digambar*, Jadhav Santosh, Mane Pandurang,
Controlled-release carbamazepine matrix granules and tablets comprising lipophilic and hydrophilic
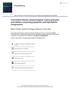 Drug Delivery ISSN: 171-7544 (Print) 1521-464 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/idrd2 Controlled-release carbamazepine matrix granules and tablets comprising lipophilic and hydrophilic
Drug Delivery ISSN: 171-7544 (Print) 1521-464 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/idrd2 Controlled-release carbamazepine matrix granules and tablets comprising lipophilic and hydrophilic
Ondansetron hydrochloride (OSH) is an effective
 dx.doi.org/10.14227/dt200413p34 In Vitro Dissolution Enhancement of Ondansetron by Solid Dispersion in Superdisintegrants e-mail: rkpharma26@yahoo.co.in Rajnikant M. Suthar 1, *, Narendra P. Chotai 1,
dx.doi.org/10.14227/dt200413p34 In Vitro Dissolution Enhancement of Ondansetron by Solid Dispersion in Superdisintegrants e-mail: rkpharma26@yahoo.co.in Rajnikant M. Suthar 1, *, Narendra P. Chotai 1,
Comparative study of formulations of ondansetron hydrochloride orodispersible tablets by effervescent and sublimation methods
 World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
CHAPTER.6 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FAST DISSOLVING TABLET OF ONDANSETRON HCl
 CHAPTER.6 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FAST DISSOLVING TABLET OF ONDANSETRON HCl 6.1 Taste making of ondansetron HCl 6.1.1 Development and characterization of taste masked granules of ondansetron HCl
CHAPTER.6 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FAST DISSOLVING TABLET OF ONDANSETRON HCl 6.1 Taste making of ondansetron HCl 6.1.1 Development and characterization of taste masked granules of ondansetron HCl
8. FORMULATION OF LANSOPRAZOLE NANOPARTICLES
 8. FORMULATION OF LANSOPRAZOLE NANOPARTICLES FORMULATION OF LANSOPRAZOLE NANOPARTICLES Preparation of capsule of modified solubility to protect the drug from degradation To protect the drug from degradation
8. FORMULATION OF LANSOPRAZOLE NANOPARTICLES FORMULATION OF LANSOPRAZOLE NANOPARTICLES Preparation of capsule of modified solubility to protect the drug from degradation To protect the drug from degradation
Scholars Research Library
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2010, 2(5): 412-427 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2010, 2(5): 412-427 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
