Fabrication and Characterization of Gold Nanoparticles by Femtosecond Laser Ablation in an Aqueous Solution of Cyclodextrins
|
|
|
- Alberta Brown
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, Fabrication and Characterization of Gold Nanoparticles by Femtosecond Laser Ablation in an Aqueous Solution of Cyclodextrins Andrei V. Kabashin, Michel Meunier, Christopher Kingston, and John H. T. Luong*, Laser Processing Laboratory, Department of Engineering Physics, Ecole Polytechnique de Montreal, Montreal, Quebec, Canada H3C 3A7; Steacie Institute of Molecular Sciences, National Research Council Canada, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada K1A 0R6; and Biotechnology Research Institute, National Research Council Canada, Montreal, Quebec, Canada H4P 2R2 ReceiVed: February 10, 2003 Gold nanoparticles were produced by femtosecond laser ablation of a gold metal plate in an aqueous solution of R-cyclodextrin (CD), β-cd, or γ-cd. The gold nanoparticles exhibited the UV-vis absorption spectrum with a maximum absorption band at 520 nm, similar to that of gold nanoparticles chemically prepared in a solution. The size distribution of the nanoparticles measured by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) shifted to a drastically smaller size of nm and narrower size distribution of less than nm fwhm with an increase in the concentration of cyclodextrins. Both the particle size and size distribution were also dependent on the type of cyclodextrins used in aqueous solution. In particular, the gold colloids resulting from ablation in 10 mm β-cd were conspicuously stable under aerobic conditions without any protective agent present. CDs formed an inclusion complex with ablated atoms to reduce the total concentration of embryonic nanoparticles formed in the plume CDs, as evident by Raman spectroscopy. The consecutive particle growth due to the mutual coalescence between nanoclusters and their neighboring free gold atoms was severely limited in the presence of CDs. Introduction Nanomaterials with size-dependent physical properties provide great opportunities for a plethora of novel applications. 1 Among metal nanoparticles, gold nanoparticles possess several appealing features that make them very attractive for intensive research in nanotechnology. For instance, gold nanoparticles with diameters of 3-5 nm show a drastic decrease of the melting point, 2a,b and TiO 2 -supported gold nanoparticles display a highly selective catalytic activity for CO oxidation at -70 C. 2c To exploit the size and quantum confinement effects of nanoparticles and to tailor nanomaterials with new properties, it is of utmost importance to prepare monodispersed nanoparticles with a very narrow size distribution. Wet chemistry techniques have been overwhelmingly used to prepare gold nanoparticles in the nm diameter range by the reduction of a diluted metal salt in aqueous solution with a reducing reagent. 3 The preparation in a micelle or reverse micelle is one of the most successful methods to obtain metal nanoparticles stabilized in solutions. 4 Alternatively, nanosecond laser ablation of a metal surface immersed in a liquid has also been known to produce metal nanoparticles in the liquid. 5 However, the size distribution of the nanoparticles tends to be broadened, as both postablation particle agglomeration and the ejection of large melted fragments from the target usually take place because of the target Joule heating during the nanosecond laser ablation. 6 Several attempts have been made for the size control by combining laser ablation with laser-induced size control, and the preparation is performed in an aqueous solution of surfactant such as sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). 7 Ecole Polytechnique de Montreal. Steacie Institute of Molecular Sciences, National Research Council Canada. Biotechnology Research Institute, National Research Council Canada. In this paper, we present another method to prepare stable nanoparticles by laser ablation of a metal plate in solutions containing neutral R-cyclodextrin (CD), β-cd, or γ-cd. CDs are toruslike macrocycles built up from D-(+)-glucopyranose units, which are linked by R-1-4-linkages (the most common ones are R-, β-, and γ-cds, consisting of six, seven, and eight units, respectively). 8 Experimental Section Materials and Chemicals. R-Cyclodextrin (R-CD), β-cd, and γ-cd were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO) and used without further purification. All solutions were prepared from high-purity deionized water. CD solutions were prepared as stock solutions in appropriate buffers immediately prior to their use. A gold rod (99.99%) with diameter 6 mm and height 6 mm was purchased from Alfa Aesar (Johnson Matthey, Ward Hill, MA). Femtosecond Laser Ablation. Laser ablation was carried out with a Ti/sapphire laser (Hurricane, Spectra Physics Lasers, Mountain View, CA), which provided 110 fs full width at halfmaximum (fwhm) pulses (wavelength 800 nm, maximum energy 1 mj/pulse, repetition rate of 1 khz). The radiation was focused by an objective with the focal distance 7.5 cm onto a gold target, which was placed on the bottom of a 3-mL glass vessel filled with aqueous solutions of cyclodextrins (Figure 1). The depth of the liquid layer above the rod was about 12 mm. Measurements. UV-vis measurements were performed using a spectrophotometer (DU-640, Beckman, CA) and room temperature in the range nm with a 1-cm optimal length curvette. A transmission electron microscope (TEM Philips CM30, Philips, FEI, Hillsboro, OR) with 0.23 nm pointpoint resolution was used to take the electron images of the /jp034345q CCC: $ American Chemical Society Published on Web 04/22/2003
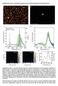
2 4528 J. Phys. Chem. B, Vol. 107, No. 19, 2003 Kabashin et al. Figure 1. Experimental setup: 1, gold target; 2, glass vessel; 3, plasma plume; 4, aqueous solution. nanoparticles in the solution. A drop of a sample solution was placed on a carbon-coated copper grid and dried at room temperature. The grid was washed with deionized water to remove unbound CDs. Typically, the diameters of particles in sight of a given micrograph were measured and the distribution of particle size (diameter) was calculated. In addition, craters on the target surface were also observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Phillips XL20, FEI, Hillsboro, OR) and a profilometer (Dektak 3030, Veeco, Santa Barbara, CA). Solution-phase FT-Raman spectra were recorded using a Bruker FRA 106 spectrometer (Bruker Optics, Milton, ON, Canada) equipped with a liquid nitrogen-cooled germanium detector and a 1064 nm Nd:YAG laser. Samples were mounted inside the instrument using a 0.5 cm quartz cuvette with a mirrored rear surface. The Raman spectrum was collected within the cm -1 interval with 4 cm -1 resolution using 500 mw of excitation laser power. The CD-gold colloids were examined with a triple-quadrupole mass spectrometer (API III LC/MS/MS, Sciex, Thornhill, ON, Canada) to monitor the degradation of CD if any during the course of femtosecond laser ablation. Charged ions were generated by spraying the sample solution through a stainless steel capillary held at 4-6 kv, and the sample solution was delivered to the sprayer by a syringe infusion pump through a fused silica capillary of 100 µm i.d. A gas curtain formed by a continuous flow ( L/min) of N 2 in the interface region served to evaporate the aerosol droplets and to break up the cluster formation from supersonic expansion. The potential on the sampling orifice of the instrument was set at +30 V. Results and Discussion Ablation in Pure Water. We used a femtosecond laser technique, which was anticipated to minimize the average particle size and narrow the size distribution of ablated particles due to both a relatively low ablation threshold and the absence of target heating effects. 6 In pure deionized water, the ablation led to visible changes of the solution color after only several seconds in the experiment. Optical absorption spectra of gold colloids exhibited the characteristic peak of the surface plasmon resonance at nm, similar to those obtained with Sigma gold nanoparticles. TEM micrographs revealed that most of the particles had sizes of nm; however, a rather broad size distribution ranging from 25 to 120 nm was observed (Figure 2). The height and the width of the SPR peak at 520 nm were dependent upon the energy of the laser pulses. At 0.16 mj/pulse the height and width at 520 nm were lower and less broadened in comparison to the case of the ablation performed at 0.8 mj/ Figure 2. TEM micrograph image (right) and corresponding size distribution (left) of gold particles prepared by femtosecond laser ablation in deionized water. pulse. Measuring the diameter of the ablated crater on a target by SEM and a profilometer, and its depth by profilometer (Dektak 3030, Veeco), we were able to determine the volume of ablated gold per pulse. The estimated volume values for 0.8 and 0.16 mj/pulse were (7-8) cm 3 and (1-3) cm 3, respectively. This was consistent with the results of Mafune et al., 7b who have shown that the nanoparticles can only be produced above a threshold laser power and that their number density increases proportionally with the laser power. It should be noted that a 532-nm Nd:YAG laser 5d,7b had significantly larger energy per pulse (90 mj/pulse), which should influence the absolute abundance of the produced particles. The mechanism of laser ablation could be explained in terms of the dynamic formation mechanism postulated by Mafune and co-workers. 10 In brief, a dense cloud of gold atoms (plume) was accumulated in the laser spot of the gold target during the course of ablation. This core was made of a number of small gold atoms that were aggregated accidentally due to the density fluctuation to form embryonic nanoparticles. Even when the ablation process had been terminated, the aggregation continued at a significantly slower growth rate until all atoms in the vicinity ( 40 nm) of the embryonic nanoparticles were depleted. 10 As both ablated atoms and embryonic nanoparticles diffuse through the solution toward each other to form larger clusters, this consecutive nanoparticle growth was slow, random, and uncontrollable. Ablation in Aqueous Cyclodextrin Solutions. We were able to effectively ablate the gold target in aqueous solutions of CDs. Ablation in the presence of all three CDs led to a deep red solution, as reflected by a strong absorption band at 520 nm. However, the increase of the CD concentration was accompanied by a certain decrease of the red color intensity. This was especially noticeable for 10 mm β-cd or γ-cd, which had only a weak pink color. It should be noted that the absorption spectra obtained for the Sigma particles (5-, 10-, and 20-nm diameter) indicated that the 520-nm peak height was dependent on the total particle density and the particle size. Therefore, the absorption spectra alone could not be used to estimate the total particle concentration formed during ablation. TEM micrographs revealed that the nanoparticles were nearly spherical and their average sizes decreased with an increase in the CD concentration with a very sharp particle size distribution (Figure 3). Chemical analysis indicated that not even traces of glucose, a possible major degradable product of CDs, was present in the solution. Mass spectrometric data also confirmed that the gold colloids prepared in R-, β-, and γ-cd, respectively, still exhibited molecular masses of 972, 1135, and 1297, the molecular weights of the three CD molecules, and no other peaks were recorded. In view of such data, CDs were considered intact during the course of ablation. The preparation of CD-modified gold
3 Au Nanoparticles in a Solution of Cyclodextrins J. Phys. Chem. B, Vol. 107, No. 19, Figure 3. TEM micrograph image and corresponding size distribution of gold particles prepared by femtosecond laser ablation in (a) 0.1 mm β-cd, (b) 1 mm β-cd, and (c) 10 mm β-cd. The laser energy was 0.8 J/pulse. nanospheres by Rojas et al. 9 by chemical reduction did not report any concern related to CD degradation. β-cd was most effective in reducing the size and dispersion of the gold nanoparticles, followed by γ-cd and R-CD. Ablation in 10 mm β-cd produced particles with the average size nm (Figure 4, top) with a size dispersion less than 1 nm fwhm (Figure 4, bottom). It should be noted that the laser ablation in the presence of 100 mm SDS led to much larger nm particles with the dispersion of 5 nm fwhm. 7a,10 In addition, the surface of gold nanoparticles would be completely covered by SDS, which renders such particles hardly useful for chemical modifications or sensing applications. From the reduction of AuCl - 4 in the presence of perthiolated CD receptors, the nature of the perthiolated CD (R, β, orγ) was also reported to affect the average particle size ranging from 2 to 7 nm. 11 Stability of Gold Colloids. In pure water, the absorbance measured at 520 nm retained only 7% of its original value after 5 days of aging in ambient conditions. Several precipitates were observed in the storage glass vial, and the solution became dark blue, which confirmed that the nanoparticles continued to grow and/or aggregate with time in the solution. In contrast, gold colloids prepared in the presence of CDs exhibited good stability. In β-cd ( mm), the 520-nm peak height remained constant within this time window. The corresponding values for R-CD and γ-cd were 70% and 60%, respectively. Indeed, nanoclusters of β-cd remained well dispersed in 10 mm β-cd for over 45 days with minimal loss of absorption intensity (5-7%). This was very encouraging, since all of the experiments were performed without any precaution taken, such as oxygen-free conditions or use of protective agents, except for CDs. Postulated Mechanism of the CD Effect. As a subject of ongoing research in our laboratory, a mechanism for the formation and/or stabilization of the gold nanoparticles by CDs has not been understood. However, it was evident that CDs
4 4530 J. Phys. Chem. B, Vol. 107, No. 19, 2003 Kabashin et al. Figure 5. FT-Raman spectra of a 10 mm β-cd stock solution (dotted line) and colloidal gold nanoparticles in 10 mm β-cd (solid line). The inset highlights the dampening effect on the low-frequency β-cd vibrational modes due to the presence of gold. Sharp features are laser artifacts. Figure 4. Effect of the CD concentration on the resulting average particle size (top) and the size dispersion at fwhm (bottom). played a critical role in controlling the size as well as the stability of gold nanoparticles. The apolar cavity of the three CDs (internal diameter of 570, 780, and 950 pm, respectively) has been known to form inclusion complexes with various small hydrophobic molecules. 8 With such a dimension, a single and hydrophobic gold atom (288 pm in diameter) and/or small gold nanoclusters would be enclosed in the CD cavity to form an inclusion complex. Indeed, it has been reported that the apolar rhodium nanoparticles are stabilized by hydrophobic cavities of a number of the CDs. 12 FT-Raman measurements were taken in an attempt to probe possible gold-cd interactions. Spectra were recorded for the three 10 mm CD stock solutions and the corresponding colloidal gold solutions. Figure 5 shows the results obtained for the pair of β-cd samples. A small but reproducible reduction in intensity of the low-frequency β-cd modes was observed following the production of gold nanoparticles (see inset Figure 5). Explanations such as concentration differences or inconsistent sample preparation are unlikely, since all other features of the Raman spectra are identical. The effected modes correspond to pyranose ring vibrations along the backbone of the CD. 13 Dampening of these modes suggests an interaction between gold and the primary macrocyclic structure of the CD. This is consistent with the proposed mechanism that single or small numbers of gold atoms are held within the hydrophobic cavity of the CD, removing them as an available feedstock for nanoparticle growth. The magnitude of the observed intensity reduction is not surprising considering the large excess of β-cd compared to the concentration of gold particles. An identical dampening effect was observed in the Raman spectra of the R-CD stock and colloidal gold solutions, but no dampening was observed in the pair of γ-cd spectra. γ-cd possesses the largest internal cavity diameter of the three. Gold atoms included within the γ-cd cavity should be less-strongly coupled to the γ-cd backbone, making any interactions difficult to observe over the large background of free γ-cds in solution. No evidence of Au-O interactions can be obtained from the Raman spectra. The resulting nanoparticles were much smaller and more stable with increase in the CD concentration, implying that hydrophobic interactions between gold nanoparticles and CD molecules were of sufficient strength to prevent agglomeration, as demonstrated by TEM and UV-vis absorption spectroscopy. Consequently, embryonic nanoparticles formed in the plume became limited and had to compete with CD molecules for free ablated gold atoms in the vicinity of this region through diffusion. As CDs could form stable inclusion complexes with free ablated atoms and small nanoparticles as well as exhibit hydrophobic interactions with embryonic nanoparticles, the consecutive particle growth due to the mutual coalescence between such objects was severely limited or terminated, particularly at high CD concentrations. This hypothesis was partly supported by the experimental data to confirm that the nanoparticle size and dispersion decreased with increasing CD concentrations. With the lowest aqueous solubility (18.5 g/l), β-cd should exhibit the strongest hydrophobic interaction with gold compared to those of both R- (145 g/l) and γ-cd (232 g/l). 8 Because both ablation and the formation of inclusion complexes between CD molecules and developing Au particles took place almost simultaneously, the interplay between the kinetics of the two processes was likely the key factor that governed the average size diameter of the gold nanoparticles. Unlike resorcicarenes, 14 there was no evidence to suggest that CD molecules were capable of binding to ablated atoms by chemisorption through Au-O interactions. This point was taken into account, since there are 18, 21, and 24 hydroxyl groups for R-, β-, and γ-cd, respectively. 8 Conclusion Many of the chemical methods involve the use of toxic chemicals and might give rise to toxic side products. In this study, laser ablation has been proven as an environmentally friendly procedure for fabricating monodispersed gold nanoparticles and gold colloid was very stable in high CD concentrations. The laser ablation method can be applied at ambient conditions with no disturbing chemical impurities introduced.
5 Au Nanoparticles in a Solution of Cyclodextrins J. Phys. Chem. B, Vol. 107, No. 19, This is reproducible, and the reduction is initiated homogeneously; that is, there are no local concentration gradients when reactants are mixed, as encountered in chemical reduction. Polymers in small concentration, such as polyphosphate, polyacrylate, poly(vinyl sulfate), poly(vinyl alcohol), and poly- (ethyleneimine), are often used to stabilize the growing aggregates. 1a Very recently, surfactants such as resorcinarenes 14 and SDS 5d,10 have been used to stabilize gold nanoclusters. To our knowledge, CDs have not been used for size control and stabilization of gold nanoparticles. This CD-mediated size control is a promising technique and can be extended for fabrication of other metal nanoparticles, and work is in progress toward this objective. Acknowledgment. The authors thank Dr. E. Sacher and Mr. J-P. Sylvestre of Ecole Polytechnique for several useful discussions and NSERC Canada for financial assistance. References and Notes (1) (a) Henglein, A. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, (b) Link, S.; El- Sayed, M. A. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, (c) Link, S.; El-Sayed, M. A. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, (d) Hodak, J. H.; Martini, I.; Hartland, G. V.; Link, S.; El-Sayed, M. A. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 108, (2) (a) Takagi, M. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1954, 9, 359. (b) Buffat, D. A.; Borel, J. P. Phys. ReV. 1976, A13, (c) Haruta, M. Catal. Today 1997, 36, 153. (3) (a) Hirai, H.; Wakabayashi, H.; Komiyama, M. Chem. Lett. 1983, (b) Lisiecki, I.; Pileni, M. P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, (c) Ahmadi, T. S.; Wang, Z. L.; Green, T. C.; Hendlein, A.; El-Sayed, M. A. Science 1996, 272, (d) Huang, H. H.; Yan, F. Q.; Kek, Y. M.; Chew, C. H.; Xu, G. Q.; Ji, W.; Oh, P. S.; Tang, S. H. Langmuir 1997, 13, 172. (4) Petit, C.; Lixon, P.; Pileni, M. P. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, (5) (a) Fojtik, A.; Henglein, A. Ber. Bunsen-Ges. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 252. (b) Sibbald, M. S.; Chumanov, G.; Cotton, T. M. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, (c) Yeh, M. S.; Yang, Y. S.; Lee, Y. P.; Lee, H. F.; Yeh, Y. H.; Yeh, C. S. J. Phys. Chem. 1999, 103, (d) Mafune, F.; Kohno, J.-Y.; Takeda, Y.; Kondow, T.; Sawabe, H. J. Phys. Chem. 2000, 104, (6) LIA Handbook of Laser Materials Processing; Ready, J. F, Farson, D. F., Eds.; Springer-Verlag and Heidelberg GmbH & Co.: Berlin, 2001; pp (7) (a) Mafune, F.; Kohno, J.-Y.; Takeda, Y.; Kondow, T.; Sawabe, H. J. Phys. Chem. 2001, 105, (b) Mafune, F.; Kohno, J.-Y.; Takeda, Y.; Kondow, T. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, (c) Mafune, F.; Kohno, J.-Y.; Takeda, Y.; Kondow, T.; Sawabe, H. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, (d) Mafune, F.; Kohno, J.-Y.; Takeda, Y.; Kondow, T. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, (8) Szejtli, J. In ComprehensiVe Supramolecular Chemistry; Atwood, J. L., Davies, J. E. D., Macnicol, D. D., Vogtle, F., Eds.; Pergamon- Elsevier: New York, 1996; Vol. 3, pp (9) Rojas, M. T.; Koniger, R.; Stoddart, J. F.; Kaifer, A. E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 336. (10) Mafune, F.; Kohno, J.-Y.; Takeda, Y.; Kondow, T.; Sawabe, H. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, (11) Liu, J.; Ong, W.; Roman, E.; Lynn, M. J.; Kaifer, A. E. Langmuir 2000, 16, (12) Komiyama, M.; Hirai, H. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1983, 56, (13) Wiedenhof, J. N.; Lammers, J. J.; Van Panthaleon, C. L.; Van Eck, B. Die Stärke 1969, 21, 119. (14) Stavens, K. B.; Pusztay, S. V.; Zou, S.; Andres, R. P.; Wei, A. Langmuir 1999, 15, 24.
LASER PROCESSING LABORATORY
 LASER PROCESSING LABORATORY Michel Meunier Canada Research Chair Department of Engineering Physics École Polytechnique de Montreal http://lpl.phys.polymtl.ca LPL s Research activities Mission: Develop
LASER PROCESSING LABORATORY Michel Meunier Canada Research Chair Department of Engineering Physics École Polytechnique de Montreal http://lpl.phys.polymtl.ca LPL s Research activities Mission: Develop
Nanofabrication and characterization of gold metal by Pulsed Laser. Ablation in SDS solution
 Nanofabrication and characterization of gold metal by Pulsed Laser Ablation in SDS solution Raheem Gaayied Kadhim (Corresponding author) College of the Science - University of Babylon Tel:0964-7801305881
Nanofabrication and characterization of gold metal by Pulsed Laser Ablation in SDS solution Raheem Gaayied Kadhim (Corresponding author) College of the Science - University of Babylon Tel:0964-7801305881
Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles by Pulsed Laser Ablation in NaOH solution
 Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles by Pulsed Laser Ablation in NaOH solution Raheem Gaayied Kadhim Maryam falah noori Babylon university /colloge of the scince Abdulrahman Khalaf Ali School of Applied Sciences
Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles by Pulsed Laser Ablation in NaOH solution Raheem Gaayied Kadhim Maryam falah noori Babylon university /colloge of the scince Abdulrahman Khalaf Ali School of Applied Sciences
Fabrication of Gold Nanoparticles by Pulsed Laser Ablation in Aqueous Media
 Fabrication of Gold Nanoparticles by Pulsed Laser Ablation in Aqueous Media Dongfang YANG, Seongkuk LEE, Bo CHEN and Suwas NIKUMB Industrial Materials Institute, National Research Council Canada 800 Collip
Fabrication of Gold Nanoparticles by Pulsed Laser Ablation in Aqueous Media Dongfang YANG, Seongkuk LEE, Bo CHEN and Suwas NIKUMB Industrial Materials Institute, National Research Council Canada 800 Collip
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Decorating Graphene Sheets with Gold Nanoparticles Ryan Muszynski, Brian Seeger and, Prashant V. Kamat* Radiation Laboratory, Departments of Chemistry & Biochemistry and Chemical
Supporting Information Decorating Graphene Sheets with Gold Nanoparticles Ryan Muszynski, Brian Seeger and, Prashant V. Kamat* Radiation Laboratory, Departments of Chemistry & Biochemistry and Chemical
International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology
 Int. J. Pure Appl. Sci. Technol., 9(1) (2012), pp. 1-8 International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology ISSN 2229-6107 Available online at www.ijopaasat.in Research Paper Preparation,
Int. J. Pure Appl. Sci. Technol., 9(1) (2012), pp. 1-8 International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology ISSN 2229-6107 Available online at www.ijopaasat.in Research Paper Preparation,
HYPER-RAYLEIGH SCATTERING AND SURFACE-ENHANCED RAMAN SCATTERING STUDIES OF PLATINUM NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSIONS
 www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol19issue1/ijrras_19_1_06.pdf HYPER-RAYLEIGH SCATTERING AND SURFACE-ENHANCED RAMAN SCATTERING STUDIES OF PLATINUM NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSIONS M. Eslamifar Physics Department, BehbahanKhatamAl-Anbia
www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol19issue1/ijrras_19_1_06.pdf HYPER-RAYLEIGH SCATTERING AND SURFACE-ENHANCED RAMAN SCATTERING STUDIES OF PLATINUM NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSIONS M. Eslamifar Physics Department, BehbahanKhatamAl-Anbia
On-line characterization of gold nanoparticles generated by laser ablation in liquids
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 41 (2013 ) 531 538 Lasers in Manufacturing Conference 2013 On-line characterization of gold nanoparticles generated by laser ablation in liquids
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 41 (2013 ) 531 538 Lasers in Manufacturing Conference 2013 On-line characterization of gold nanoparticles generated by laser ablation in liquids
Supporting Information s for
 Supporting Information s for # Self-assembling of DNA-templated Au Nanoparticles into Nanowires and their enhanced SERS and Catalytic Applications Subrata Kundu* and M. Jayachandran Electrochemical Materials
Supporting Information s for # Self-assembling of DNA-templated Au Nanoparticles into Nanowires and their enhanced SERS and Catalytic Applications Subrata Kundu* and M. Jayachandran Electrochemical Materials
Probing the Kinetics of Ligand Exchange on Colloidal Gold. Nanoparticles by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering
 -Supporting Information- Probing the Kinetics of Ligand Exchange on Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Yuhua Feng, Shuangxi Xing, Jun Xu, Hong Wang, Jun Wei Lim, and Hongyu
-Supporting Information- Probing the Kinetics of Ligand Exchange on Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Yuhua Feng, Shuangxi Xing, Jun Xu, Hong Wang, Jun Wei Lim, and Hongyu
Permeable Silica Shell through Surface-Protected Etching
 Permeable Silica Shell through Surface-Protected Etching Qiao Zhang, Tierui Zhang, Jianping Ge, Yadong Yin* University of California, Department of Chemistry, Riverside, California 92521 Experimental Chemicals:
Permeable Silica Shell through Surface-Protected Etching Qiao Zhang, Tierui Zhang, Jianping Ge, Yadong Yin* University of California, Department of Chemistry, Riverside, California 92521 Experimental Chemicals:
Novel fluorescent matrix embedded carbon quantum dots enrouting stable gold and silver hydrosols
 Novel fluorescent matrix embedded carbon quantum dots enrouting stable gold and silver hydrosols Shouvik Mitra a, Sourov Chandra b, Prasun Patra a, Panchanan Pramanik b *, Arunava Goswami a * a AERU, Biological
Novel fluorescent matrix embedded carbon quantum dots enrouting stable gold and silver hydrosols Shouvik Mitra a, Sourov Chandra b, Prasun Patra a, Panchanan Pramanik b *, Arunava Goswami a * a AERU, Biological
Size Control of Gold Nanoparticles During Laser Ablation In Liquids With Different Functional Molecules
 Size Control of Gold Nanoparticles During Laser Ablation In Liquids With Different Functional Molecules Aissam Essaidi*1, M`Barek Chakif*1, Benjamin Schöps*1, Andreas Aumman*1, Shizhou Xiao*1, Cemal Esen*1
Size Control of Gold Nanoparticles During Laser Ablation In Liquids With Different Functional Molecules Aissam Essaidi*1, M`Barek Chakif*1, Benjamin Schöps*1, Andreas Aumman*1, Shizhou Xiao*1, Cemal Esen*1
often display a deep green color due to where the SPR occurs (i.e., the wavelength of light that interacts with this specific morphology).
 Synthesis-Dependent Catalytic Properties of Gold Nanoparticles Nanoscience is the study of materials that have dimensions, intuitively, on the nanoscale, typically between 1 100 nm. This field has received
Synthesis-Dependent Catalytic Properties of Gold Nanoparticles Nanoscience is the study of materials that have dimensions, intuitively, on the nanoscale, typically between 1 100 nm. This field has received
Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles through Alcohol Reduction with Organoalkoxysilanes
 Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology 26, 467 471, 2003 c 2003 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles through Alcohol Reduction with Organoalkoxysilanes
Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology 26, 467 471, 2003 c 2003 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles through Alcohol Reduction with Organoalkoxysilanes
Fast ph-assisted functionalization of silver nanoparticles with monothiolated DNA
 Supporting Information for Fast ph-assisted functionalization of silver nanoparticles with monothiolated DNA Xu Zhang ab, Mark R. Servos b, and Juewen Liu* a a Department of Chemistry and Waterloo Institute
Supporting Information for Fast ph-assisted functionalization of silver nanoparticles with monothiolated DNA Xu Zhang ab, Mark R. Servos b, and Juewen Liu* a a Department of Chemistry and Waterloo Institute
Surface-enhanced raman scattering from a layer of gold nanoparticles
 VNU Journal of Science, Mathematics - Physics 26 (2010) 187-192 Surface-enhanced raman scattering from a layer of gold nanoparticles Nguyen The Binh *, Nguyen Thanh Dinh, Nguyen Quang Dong, Vu Thi Khanh
VNU Journal of Science, Mathematics - Physics 26 (2010) 187-192 Surface-enhanced raman scattering from a layer of gold nanoparticles Nguyen The Binh *, Nguyen Thanh Dinh, Nguyen Quang Dong, Vu Thi Khanh
Synthesis of Colloidal Au-Cu 2 S Heterodimers via Chemically Triggered Phase Segregation of AuCu Nanoparticles
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Synthesis of Colloidal Au-Cu 2 S Heterodimers via Chemically Triggered Phase Segregation of AuCu Nanoparticles Nathan E. Motl, James F. Bondi, and Raymond E. Schaak* Department of
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Synthesis of Colloidal Au-Cu 2 S Heterodimers via Chemically Triggered Phase Segregation of AuCu Nanoparticles Nathan E. Motl, James F. Bondi, and Raymond E. Schaak* Department of
High-Purity Separation of Gold Nanoparticle Dimers and Trimers
 -Supporting Information- High-Purity Separation of Gold Nanoparticle Dimers and Trimers Gang Chen, Yong Wang, Li Huey Tan, Miaoxin Yang, Lee Siew Tan, Yuan Chen and Hongyu Chen* Division of Chemistry and
-Supporting Information- High-Purity Separation of Gold Nanoparticle Dimers and Trimers Gang Chen, Yong Wang, Li Huey Tan, Miaoxin Yang, Lee Siew Tan, Yuan Chen and Hongyu Chen* Division of Chemistry and
3D Dendritic Gold Nanostructures: Seeded Growth of Multi-Generation Fractal Architecture
 -Supporting Information- 3D Dendritic Gold Nanostructures: Seeded Growth of Multi-Generation Fractal Architecture Ming Pan, Shuangxi Xing, Ting Sun, Wenwen Zhou, Melinda Sindoro, Hui Hian Teo, Qingyu Yan,
-Supporting Information- 3D Dendritic Gold Nanostructures: Seeded Growth of Multi-Generation Fractal Architecture Ming Pan, Shuangxi Xing, Ting Sun, Wenwen Zhou, Melinda Sindoro, Hui Hian Teo, Qingyu Yan,
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2018. Supporting Information for Small, DOI: 10.1002/smll.201801523 Ultrasensitive Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Detection Based
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2018. Supporting Information for Small, DOI: 10.1002/smll.201801523 Ultrasensitive Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Detection Based
Efficient charge storage in photoexcited TiO 2 nanorod-noble metal nanoparticle composite systems
 Electronic Supplementary Information Efficient charge storage in photoexcited TiO 2 nanorod-noble metal nanoparticle composite systems P. D. Cozzoli, M. L. Curri, and A. Agostiano 1. Synthesis of TiO 2
Electronic Supplementary Information Efficient charge storage in photoexcited TiO 2 nanorod-noble metal nanoparticle composite systems P. D. Cozzoli, M. L. Curri, and A. Agostiano 1. Synthesis of TiO 2
Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylene oxide) templated nickel oxide nanofibers for dye degradation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Environmental Science: Nano. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylene
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Environmental Science: Nano. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylene
CHARACTERIZATION OF SILVER NANOPARTICLES PREPARED BY LASER ABLATION IN DISTILLED WATER
 CHARACTERIZATION OF SILVER NANOPARTICLES PREPARED BY LASER ABLATION IN DISTILLED WATER Alireza HOJABRI *, Fatemeh HAJAKBARI, Maryam DEBASHI SHOREH Department of Physics, College of Basic Sciences, Karaj
CHARACTERIZATION OF SILVER NANOPARTICLES PREPARED BY LASER ABLATION IN DISTILLED WATER Alireza HOJABRI *, Fatemeh HAJAKBARI, Maryam DEBASHI SHOREH Department of Physics, College of Basic Sciences, Karaj
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Precisely Controllable Core-Shell Ag@Carbon Dots Nanoparticles: Application to in Situ Super-Sensitive Monitoring of Catalytic Reactions Jing Jin, Shoujun Zhu, Yubin Song, Hongyue
Supporting Information Precisely Controllable Core-Shell Ag@Carbon Dots Nanoparticles: Application to in Situ Super-Sensitive Monitoring of Catalytic Reactions Jing Jin, Shoujun Zhu, Yubin Song, Hongyue
Solution reduction synthesis of amine terminated carbon quantum dots
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Solution reduction synthesis of amine terminated carbon quantum dots Keith Linehan and Hugh
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Solution reduction synthesis of amine terminated carbon quantum dots Keith Linehan and Hugh
Fluorescent silver nanoparticles via exploding wire technique
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 65, No. 5 journal of November 2005 physics pp. 815 819 Fluorescent silver nanoparticles via exploding wire technique ALQUDAMI ABDULLAH and S ANNAPOORNI Department
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 65, No. 5 journal of November 2005 physics pp. 815 819 Fluorescent silver nanoparticles via exploding wire technique ALQUDAMI ABDULLAH and S ANNAPOORNI Department
CHAPTER 3. OPTICAL STUDIES ON SnS NANOPARTICLES
 42 CHAPTER 3 OPTICAL STUDIES ON SnS NANOPARTICLES 3.1 INTRODUCTION In recent years, considerable interest has been shown on semiconducting nanostructures owing to their enhanced optical and electrical
42 CHAPTER 3 OPTICAL STUDIES ON SnS NANOPARTICLES 3.1 INTRODUCTION In recent years, considerable interest has been shown on semiconducting nanostructures owing to their enhanced optical and electrical
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 3, March-2014 ISSN
 156 Copper Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis Characterization Y.Suresh*1, S.Annapurna*2, G.Bhikshamaiah*3, A.K.Singh#4 Abstract Present work describes the synthesis nanoparticles using papaya extract as a
156 Copper Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis Characterization Y.Suresh*1, S.Annapurna*2, G.Bhikshamaiah*3, A.K.Singh#4 Abstract Present work describes the synthesis nanoparticles using papaya extract as a
Supplementary Information:
 Supplementary Information: One-Step and Rapid Synthesis of Clean and Monodisperse Dendritic Pt Nanoparticles and Their High Performance Toward Methanol Oxidation and p-nitrophenol Reduction Jun Wang, Xin-Bo
Supplementary Information: One-Step and Rapid Synthesis of Clean and Monodisperse Dendritic Pt Nanoparticles and Their High Performance Toward Methanol Oxidation and p-nitrophenol Reduction Jun Wang, Xin-Bo
Biodegradable Hollow Silica Nanospheres Containing Gold Nanoparticle Arrays
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Biodegradable Hollow Silica Nanospheres Containing Gold Nanoparticle Arrays Domenico Cassano a,b,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Biodegradable Hollow Silica Nanospheres Containing Gold Nanoparticle Arrays Domenico Cassano a,b,
Magnetically-driven selective synthesis of Au clusters on Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Magnetically-driven selective synthesis of Au clusters on Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles Víctor Sebastian, M. Pilar Calatayud, Gerardo F. Goya
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Magnetically-driven selective synthesis of Au clusters on Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles Víctor Sebastian, M. Pilar Calatayud, Gerardo F. Goya
- Supporting Information - Controlled Assembly of Eccentrically Encapsulated Gold Nanoparticles
 - Supporting Information - S1 Controlled Assembly of Eccentrically Encapsulated Gold Nanoparticles Tao Chen, Miaoxin Yang, Xinjiao Wang, Li Huey Tan, Hongyu Chen* Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry,
- Supporting Information - S1 Controlled Assembly of Eccentrically Encapsulated Gold Nanoparticles Tao Chen, Miaoxin Yang, Xinjiao Wang, Li Huey Tan, Hongyu Chen* Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry,
Exploiting the Interaction of Pyranine-3 with Poly(L-Lysine) to Mediate Nanoparticle Assembly: Fabrication of Dynamic ph-responsive Nanocontainers
 Exploiting the Interaction of Pyranine-3 with Poly(L-Lysine) to Mediate Nanoparticle Assembly: Fabrication of Dynamic ph-responsive Nanocontainers Arlin Jose Amali, a Shashi Singh, b Nandini Rangaraj,
Exploiting the Interaction of Pyranine-3 with Poly(L-Lysine) to Mediate Nanoparticle Assembly: Fabrication of Dynamic ph-responsive Nanocontainers Arlin Jose Amali, a Shashi Singh, b Nandini Rangaraj,
Interaction of Gold Nanoparticle with Proteins
 Chapter 7 Interaction of Gold Nanoparticle with Proteins 7.1. Introduction The interfacing of nanoparticle with biomolecules such as protein is useful for applications ranging from nano-biotechnology (molecular
Chapter 7 Interaction of Gold Nanoparticle with Proteins 7.1. Introduction The interfacing of nanoparticle with biomolecules such as protein is useful for applications ranging from nano-biotechnology (molecular
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Direct Synthesis of a Macroscopic Array of Naked Ag Nanoparticles Omar Ayyad,* a,b,c David Muñoz-Rojas, a Pedro Gómez-Romero* a,c Experimental details Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP40T-500G,
Supplementary Information Direct Synthesis of a Macroscopic Array of Naked Ag Nanoparticles Omar Ayyad,* a,b,c David Muñoz-Rojas, a Pedro Gómez-Romero* a,c Experimental details Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP40T-500G,
Physisorption of Antibodies using BioReady Bare Nanoparticles
 TECHNICAL RESOURCE Lateral Flow Immunoassays Physisorption of Antibodies using BioReady Bare Nanoparticles Introduction For more than 20 years, lateral flow immunoassay diagnostic tests have provided a
TECHNICAL RESOURCE Lateral Flow Immunoassays Physisorption of Antibodies using BioReady Bare Nanoparticles Introduction For more than 20 years, lateral flow immunoassay diagnostic tests have provided a
Laser Dissociation of Protonated PAHs
 100 Chapter 5 Laser Dissociation of Protonated PAHs 5.1 Experiments The photodissociation experiments were performed with protonated PAHs using different laser sources. The calculations from Chapter 3
100 Chapter 5 Laser Dissociation of Protonated PAHs 5.1 Experiments The photodissociation experiments were performed with protonated PAHs using different laser sources. The calculations from Chapter 3
Modify morphology of colloidal Ag 2 Se nanostructures by laser irradiation
 Supporting information for Modify morphology of colloidal Ag 2 Se nanostructures by laser irradiation Ling-Ling Zhao a, Zhi-Ming Gao a, Hui Liu a, Jing Yang a, Shi-Zhang Qiao a,b, Xi-Wen Du a a School
Supporting information for Modify morphology of colloidal Ag 2 Se nanostructures by laser irradiation Ling-Ling Zhao a, Zhi-Ming Gao a, Hui Liu a, Jing Yang a, Shi-Zhang Qiao a,b, Xi-Wen Du a a School
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2011 69451 Weinheim, Germany Silver Nanocrystals with Concave Surfaces and Their Optical and Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Properties** Xiaohu Xia, Jie Zeng, Brenden
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2011 69451 Weinheim, Germany Silver Nanocrystals with Concave Surfaces and Their Optical and Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Properties** Xiaohu Xia, Jie Zeng, Brenden
Synthesis of Nanoparticles using Atmospheric Microplasma Discharge
 Synthesis of Nanoparticles using Atmospheric Microplasma Discharge Ankit Bisht, G. Roshan Deen, Usman Ilyas, Y. Wang, Alireza Talebitaher, P. Lee, R.S. Rawat NSSE, National Institute of Education, Nanyang
Synthesis of Nanoparticles using Atmospheric Microplasma Discharge Ankit Bisht, G. Roshan Deen, Usman Ilyas, Y. Wang, Alireza Talebitaher, P. Lee, R.S. Rawat NSSE, National Institute of Education, Nanyang
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Synthesis of Circular and Triangular Gold Nanorings with
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Synthesis of Circular and Triangular Gold Nanorings with
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Time-dependent growth of zinc hydroxide nanostrands and their crystal structure Xinsheng Peng, ab Jian Jin, a Noriko Kobayashi, a Wolfgang Schmitt, c and Izumi Ichinose* a a Organic
Supplementary Information Time-dependent growth of zinc hydroxide nanostrands and their crystal structure Xinsheng Peng, ab Jian Jin, a Noriko Kobayashi, a Wolfgang Schmitt, c and Izumi Ichinose* a a Organic
arxiv: v1 [physics.bio-ph] 11 Sep 2015
![arxiv: v1 [physics.bio-ph] 11 Sep 2015 arxiv: v1 [physics.bio-ph] 11 Sep 2015](/thumbs/87/97055193.jpg) arxiv:1509.04625v1 [physics.bio-ph] 11 Sep 2015 IR-Laser Welding and Ablation of Biotissue Stained with Metal Nanoparticles A. A. Lalayan, S. S. Israelyan Centre of Strong Fields Physics, Yerevan State
arxiv:1509.04625v1 [physics.bio-ph] 11 Sep 2015 IR-Laser Welding and Ablation of Biotissue Stained with Metal Nanoparticles A. A. Lalayan, S. S. Israelyan Centre of Strong Fields Physics, Yerevan State
Electronic supplementary information for:
 Electronic supplementary information for: Charge-transfer-induced suppression of galvanic replacement and synthesis of (Au@Ag)@Au double shell nanoparticles for highly uniform, robust and sensitive bioprobes
Electronic supplementary information for: Charge-transfer-induced suppression of galvanic replacement and synthesis of (Au@Ag)@Au double shell nanoparticles for highly uniform, robust and sensitive bioprobes
Hybrid Gold Superstructures: Synthesis and. Specific Cell Surface Protein Imaging Applications
 Supporting Information Hybrid Gold Nanocube@Silica@Graphene-Quantum-Dot Superstructures: Synthesis and Specific Cell Surface Protein Imaging Applications Liu Deng, Ling Liu, Chengzhou Zhu, Dan Li and Shaojun
Supporting Information Hybrid Gold Nanocube@Silica@Graphene-Quantum-Dot Superstructures: Synthesis and Specific Cell Surface Protein Imaging Applications Liu Deng, Ling Liu, Chengzhou Zhu, Dan Li and Shaojun
Dual-Wavelength Lasing from Organic Dye Encapsulated Metal-Organic Framework Microcrystals
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Electronic Supplementary Information Dual-Wavelength Lasing from Organic Dye Encapsulated Metal-Organic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Electronic Supplementary Information Dual-Wavelength Lasing from Organic Dye Encapsulated Metal-Organic
ph-depending Enhancement of Electron Transfer by {001} Facet-Dominating TiO 2 Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution under Visible Irradiation
 S1 ph-depending Enhancement of Electron Transfer by {001} Facet-Dominating TiO 2 Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution under Visible Irradiation Masato M. Maitani a *, Zhan Conghong a,b, Dai Mochizuki
S1 ph-depending Enhancement of Electron Transfer by {001} Facet-Dominating TiO 2 Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution under Visible Irradiation Masato M. Maitani a *, Zhan Conghong a,b, Dai Mochizuki
Quantitative Evaluation of Proteins with Bicinchoninic Acid (BCA): Resonance Raman and Surface-enhanced Resonance Raman Scatteringbased
 Supporting Information Quantitative Evaluation of Proteins with Bicinchoninic Acid (BCA): Resonance Raman and Surface-enhanced Resonance Raman Scatteringbased Methods Lei Chen, a,b Zhi Yu, b Youngju Lee,
Supporting Information Quantitative Evaluation of Proteins with Bicinchoninic Acid (BCA): Resonance Raman and Surface-enhanced Resonance Raman Scatteringbased Methods Lei Chen, a,b Zhi Yu, b Youngju Lee,
Supporting Information for:
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information for: Hydroxyl-Triggered Fluorescence for Location of Inorganic Materials
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information for: Hydroxyl-Triggered Fluorescence for Location of Inorganic Materials
Instantaneous and Quantitative Functionalization of Gold Nanoparticles with Thiolated DNA Using a ph-assisted and Surfactant-Free Route
 Supporting Information Instantaneous and Quantitative Functionalization of Gold Nanoparticles with Thiolated DNA Using a ph-assisted and Surfactant-Free Route Xu Zhang,, Mark R. Servos and Juewen Liu *
Supporting Information Instantaneous and Quantitative Functionalization of Gold Nanoparticles with Thiolated DNA Using a ph-assisted and Surfactant-Free Route Xu Zhang,, Mark R. Servos and Juewen Liu *
SUPPORTING INFORMATION. A New Approach for the Surface Enhanced Resonance Raman Scattering (SERRS)
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION A New Approach for the Surface Enhanced Resonance Raman Scattering (SERRS) Detection of Dopamine at Picomolar (pm) Levels in the Presence of Ascorbic Acid Murat Kaya, Mürvet Volkan
SUPPORTING INFORMATION A New Approach for the Surface Enhanced Resonance Raman Scattering (SERRS) Detection of Dopamine at Picomolar (pm) Levels in the Presence of Ascorbic Acid Murat Kaya, Mürvet Volkan
Surfactant-free exfoliation of graphite in aqueous solutions
 Surfactant-free exfoliation of graphite in aqueous solutions Karen B. Ricardo, Anne Sendecki, and Haitao Liu * Department of Chemistry, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA 15260, U.S.A 1. Materials
Surfactant-free exfoliation of graphite in aqueous solutions Karen B. Ricardo, Anne Sendecki, and Haitao Liu * Department of Chemistry, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA 15260, U.S.A 1. Materials
Catalytic Decomposition of Formaldehyde on Nanometer Manganese Dioxide
 Modern Applied Science April, 29 Catalytic Decomposition of Formaldehyde on Nanometer Manganese Dioxide Xiujuan Chu & Hua Zhang (Corresponding author) Tianjin Municipal Key Lab of Fibres Modification and
Modern Applied Science April, 29 Catalytic Decomposition of Formaldehyde on Nanometer Manganese Dioxide Xiujuan Chu & Hua Zhang (Corresponding author) Tianjin Municipal Key Lab of Fibres Modification and
Department of Chemistry of The College of Staten Island and The Graduate Center, The City University of
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Fe 3 O 4 /Carbon quantum dots hybrid nanoflowers for highly active and
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Fe 3 O 4 /Carbon quantum dots hybrid nanoflowers for highly active and
Studying the Chemical, Optical and Catalytic Properties of Noble Metal (Pt, Pd, Ag, Au)/Cu 2 O Core-Shell Nanostructures Grown via General Approach
 Studying the Chemical, Optical and Catalytic Properties of Noble Metal (Pt, Pd, Ag, Au)/Cu 2 O Core-Shell Nanostructures Grown via General Approach Noga Meir, Ilan Jen-La Plante, Kobi Flomin, Elina Chockler,
Studying the Chemical, Optical and Catalytic Properties of Noble Metal (Pt, Pd, Ag, Au)/Cu 2 O Core-Shell Nanostructures Grown via General Approach Noga Meir, Ilan Jen-La Plante, Kobi Flomin, Elina Chockler,
Highly Sensitive and Selective Colorimetric Visualization of Streptomycin in Raw Milk Using Au Nanoparticles Supramolecular Assembly
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Highly Sensitive and Selective Colorimetric Visualization of Streptomycin in Raw Milk Using Au Nanoparticles Supramolecular Assembly Jiayu Sun, Jiechao Ge, Weimin Liu, Zhiyuan Fan,
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Highly Sensitive and Selective Colorimetric Visualization of Streptomycin in Raw Milk Using Au Nanoparticles Supramolecular Assembly Jiayu Sun, Jiechao Ge, Weimin Liu, Zhiyuan Fan,
A General Synthesis of Discrete Mesoporous Carbon Microspheres through a Confined Self- Assembly Process in Inverse Opals
 A General Synthesis of Discrete Mesoporous Carbon Microspheres through a Confined Self- Assembly Process in Inverse Opals Zhenkun Sun,, Yong Liu, Bin Li, Jing Wei, Minghong Wang, Qin Yue, Yonghui Deng,
A General Synthesis of Discrete Mesoporous Carbon Microspheres through a Confined Self- Assembly Process in Inverse Opals Zhenkun Sun,, Yong Liu, Bin Li, Jing Wei, Minghong Wang, Qin Yue, Yonghui Deng,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Dynamic Interaction between Methylammonium Lead Iodide and TiO 2 Nanocrystals Leads to Enhanced Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution from HI Splitting Xiaomei Wang,, Hong Wang,, Hefeng Zhang,,
Supporting Information Dynamic Interaction between Methylammonium Lead Iodide and TiO 2 Nanocrystals Leads to Enhanced Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution from HI Splitting Xiaomei Wang,, Hong Wang,, Hefeng Zhang,,
Laser-assisted methods for nanofabrication
 Laser-assisted methods for nanofabrication Andrei V. Kabashin, Michel Meunier Laser Processing Laboratory, Department of Engineering Physics, Ecole Polytechnique de Montreal, Case Postale 679, Succ. Centre-ville,
Laser-assisted methods for nanofabrication Andrei V. Kabashin, Michel Meunier Laser Processing Laboratory, Department of Engineering Physics, Ecole Polytechnique de Montreal, Case Postale 679, Succ. Centre-ville,
Supporting Information for. Chad A. Mirkin* Department of Chemistry and Institute for Nanotechnology, Northwestern University,
 S1 Supporting Information for Observation of a Quadrupole Plasmon Mode for a Colloidal Solution of Gold Nanoprisms Jill E. Millstone, Sungho Park, Kevin L. Shuford, Lidong Qin, George C. Schatz, and Chad
S1 Supporting Information for Observation of a Quadrupole Plasmon Mode for a Colloidal Solution of Gold Nanoprisms Jill E. Millstone, Sungho Park, Kevin L. Shuford, Lidong Qin, George C. Schatz, and Chad
Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy
 Supporting Information Core/Shell to Yolk/Shell Nanostructures by a Novel Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy Jie Han, Rong Chen and Rong Guo* School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University,
Supporting Information Core/Shell to Yolk/Shell Nanostructures by a Novel Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy Jie Han, Rong Chen and Rong Guo* School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University,
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Supporting Information for Halide-assisted activation of atomic hydrogen for photoreduction on
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Supporting Information for Halide-assisted activation of atomic hydrogen for photoreduction on
Supplementary Note 1: Dark field measurements and Scattering properties of NPoM geometries
 Supplementary Note 1: Dark field measurements and Scattering properties of NPoM geometries Supplementary Figure 1: Dark field scattering properties of individual nanoparticle on mirror geometries separated
Supplementary Note 1: Dark field measurements and Scattering properties of NPoM geometries Supplementary Figure 1: Dark field scattering properties of individual nanoparticle on mirror geometries separated
Special Properties of Au Nanoparticles
 Special Properties of Au Nanoparticles Maryam Ebrahimi Chem 7500/750 March 28 th, 2007 1 Outline Introduction The importance of unexpected electronic, geometric, and chemical properties of nanoparticles
Special Properties of Au Nanoparticles Maryam Ebrahimi Chem 7500/750 March 28 th, 2007 1 Outline Introduction The importance of unexpected electronic, geometric, and chemical properties of nanoparticles
One-pot Solvent-free Synthesis of Sodium Benzoate from the Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol over Novel Efficient AuAg/TiO 2 Catalysts
 Electronic Supplementary Information One-pot Solvent-free Synthesis of Sodium Benzoate from the Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol over Novel Efficient AuAg/TiO 2 Catalysts Ying Wang, Jia-Min Zheng, Kangnian
Electronic Supplementary Information One-pot Solvent-free Synthesis of Sodium Benzoate from the Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol over Novel Efficient AuAg/TiO 2 Catalysts Ying Wang, Jia-Min Zheng, Kangnian
Electronic supplementary information
 Electronic supplementary information Surface plasmon resonance enhanced upconversion luminescence in aqueous media for TNT selective detection Nina Tu and Leyu Wang* State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource
Electronic supplementary information Surface plasmon resonance enhanced upconversion luminescence in aqueous media for TNT selective detection Nina Tu and Leyu Wang* State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource
Synthesis and Characterization of Polymeric Composites Embeded with Silver Nanoparticles
 World Journal of Nano Science and Engineering, 2012, 2, 19-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/wjnse.2012.21004 Published Online March 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjnse) 19 Synthesis and Characterization
World Journal of Nano Science and Engineering, 2012, 2, 19-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/wjnse.2012.21004 Published Online March 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjnse) 19 Synthesis and Characterization
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Formation of MS-Ag and MS (M=Pb, Cd, Zn) nanotubes via microwave-assisted cation exchange and their enhanced photocatalytic activities Yanrong Wang, a Wenlong Yang,
Electronic Supplementary Information Formation of MS-Ag and MS (M=Pb, Cd, Zn) nanotubes via microwave-assisted cation exchange and their enhanced photocatalytic activities Yanrong Wang, a Wenlong Yang,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Polyoxometalate-based crystalline tubular microreactor: redox-active inorganic-organic hybrid materials producing gold nanoparticles and catalytic properties Dong-Ying Du, Jun-Sheng
Supporting Information Polyoxometalate-based crystalline tubular microreactor: redox-active inorganic-organic hybrid materials producing gold nanoparticles and catalytic properties Dong-Ying Du, Jun-Sheng
Electrolessly deposited electrospun metal nanowire transparent
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION FOR Electrolessly deposited electrospun metal nanowire transparent electrodes Po-Chun Hsu 1, Desheng Kong 1, Shuang Wang 2, Haotian Wang 3, Alex J. Welch 1, Hui Wu 1,, Yi Cui 1,4,*
SUPPORTING INFORMATION FOR Electrolessly deposited electrospun metal nanowire transparent electrodes Po-Chun Hsu 1, Desheng Kong 1, Shuang Wang 2, Haotian Wang 3, Alex J. Welch 1, Hui Wu 1,, Yi Cui 1,4,*
Experimental details. General
 Experimental details General TiO 2 P25 was purchased from Degussa; methyl methacrylate (MMA, 99%), 2,2 -azobis(2- methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride (97%), titanium (IV) isopropoxide (97%), concentrated
Experimental details General TiO 2 P25 was purchased from Degussa; methyl methacrylate (MMA, 99%), 2,2 -azobis(2- methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride (97%), titanium (IV) isopropoxide (97%), concentrated
Supporting Information. Synthesis, Structural and Photophysical Properties of. Pentacene Alkanethiolate Monolayer-Protected Gold
 Supporting Information Synthesis, Structural and Photophysical Properties of Pentacene Alkanethiolate Monolayer-Protected Gold Nanoclusters and Nanorods: Supramolecular Intercalation and Photoinduced Electron
Supporting Information Synthesis, Structural and Photophysical Properties of Pentacene Alkanethiolate Monolayer-Protected Gold Nanoclusters and Nanorods: Supramolecular Intercalation and Photoinduced Electron
UV-light induced shape changes of gold nanoparticles
 June 2008 Volume 2 Issue 1 Trade Science Inc. NSNTAIJ, 2(1), 2008 [20-24] S.A.M.Al-Sherbini*, Y.Atiaa, M.M.Baker National Institute of Laser Enhanced Science (NILES), Cairo University, Cairo, P.O. Box
June 2008 Volume 2 Issue 1 Trade Science Inc. NSNTAIJ, 2(1), 2008 [20-24] S.A.M.Al-Sherbini*, Y.Atiaa, M.M.Baker National Institute of Laser Enhanced Science (NILES), Cairo University, Cairo, P.O. Box
An Unconventional Role of Ligand in Continuously. Tuning of Metal-Metal Interfacial Strain
 -Supporting Information- An Unconventional Role of Ligand in Continuously Tuning of Metal-Metal Interfacial Strain Yuhua Feng, Jiating He, Hong Wang, Yee Yan Tay, Hang Sun, Liangfang Zhu, and Hongyu Chen*,
-Supporting Information- An Unconventional Role of Ligand in Continuously Tuning of Metal-Metal Interfacial Strain Yuhua Feng, Jiating He, Hong Wang, Yee Yan Tay, Hang Sun, Liangfang Zhu, and Hongyu Chen*,
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012179 TITLE: Salt-Induced Block Copolymer Micelles as Nanoreactors for the Formation of CdS Nanoparticles DISTRIBUTION: Approved
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012179 TITLE: Salt-Induced Block Copolymer Micelles as Nanoreactors for the Formation of CdS Nanoparticles DISTRIBUTION: Approved
FEMTOSECOND MID-INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY OF HYDROGEN-BONDED LIQUIDS
 Laser Chem., 1999, Vol. 19, pp. 83-90 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1999 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published by license under
Laser Chem., 1999, Vol. 19, pp. 83-90 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1999 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published by license under
Chiral nematic mesoporous silica films enabling. multi-colour and On-Off switchable circularly polarized. luminescence
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2019 Electronic Supplementary Information
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2019 Electronic Supplementary Information
Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Characterization
 Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Characterization Abstract The preparation of stable, uniform silver nanoparticles by reduction of silver ions by ethanol is reported in the present paper.
Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Characterization Abstract The preparation of stable, uniform silver nanoparticles by reduction of silver ions by ethanol is reported in the present paper.
Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh
 Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh hierarchical superstructures for greatly fast removal of heavy metal ions with high efficiency Yong-Xing Zhang, a,b Yong
Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh hierarchical superstructures for greatly fast removal of heavy metal ions with high efficiency Yong-Xing Zhang, a,b Yong
Supplementary Information for
 Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Kinetically Controlled Seeded Growth Synthesis of Citrate Stabilized Gold. Nanoparticles up to 200 nm: Size Focusing versus.
 Kinetically Controlled Seeded Growth Synthesis of Citrate Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles up to 200 nm: Size Focusing versus. Ostwald Ripening Neus G. Bastús, Joan Comenge and Víctor Puntes Additional Results
Kinetically Controlled Seeded Growth Synthesis of Citrate Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles up to 200 nm: Size Focusing versus. Ostwald Ripening Neus G. Bastús, Joan Comenge and Víctor Puntes Additional Results
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Materials Graphite powder (SP-1 graphite) was obtained from Bay carbon.
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Materials Graphite powder (SP-1 graphite) was obtained from Bay carbon.
Supplementary Information. Core-Shell Silver/Polymeric Nanoparticles-Based Combinatorial Therapy against Breast Cancer In-vitro
 Supplementary Information Core-Shell Silver/Polymeric Nanoparticles-Based Combinatorial Therapy against Breast Cancer In-vitro Nancy M. El-Baz 1,2, Laila Ziko 1,3, Rania Siam 1,3, Wael Mamdouh 1,2 * 1
Supplementary Information Core-Shell Silver/Polymeric Nanoparticles-Based Combinatorial Therapy against Breast Cancer In-vitro Nancy M. El-Baz 1,2, Laila Ziko 1,3, Rania Siam 1,3, Wael Mamdouh 1,2 * 1
Supporting Information for. Photoactive PANI/TiO 2 /Si Composite Coatings With 3D Bio-inspired. Structures
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2017 Supporting Information for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2017 Supporting Information for
Growth of silver nanocrystals on graphene by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and silver ions with a rapid and efficient one-step approach
 Growth of silver nanocrystals on graphene by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and silver ions with a rapid and efficient one-step approach Xiu-Zhi Tang, a Zongwei Cao, b Hao-Bin Zhang, a Jing Liu
Growth of silver nanocrystals on graphene by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and silver ions with a rapid and efficient one-step approach Xiu-Zhi Tang, a Zongwei Cao, b Hao-Bin Zhang, a Jing Liu
Richard Miles and Arthur Dogariu. Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08540, USA
 Richard Miles and Arthur Dogariu Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08540, USA Workshop on Oxygen Plasma Kinetics Sept 20, 2016 Financial support: ONR and MetroLaser
Richard Miles and Arthur Dogariu Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08540, USA Workshop on Oxygen Plasma Kinetics Sept 20, 2016 Financial support: ONR and MetroLaser
Electronic Supplementary Information. Low-temperature Benchtop-synthesis of All-inorganic Perovskite Nanowires
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Low-temperature Benchtop-synthesis of All-inorganic Perovskite
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Low-temperature Benchtop-synthesis of All-inorganic Perovskite
Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different Proportions
 2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
Continuous-wave biexciton lasing at room temperature using solution-processed quantum wells
 CORRECTION NOTICE Continuous-wave bieciton lasing at room temperature using solution-processed quantum wells Joel Q. Grim, Sotirios Christodoulou, Francesco Di Stasio, Roman Krahne, Roberto Cingolani,
CORRECTION NOTICE Continuous-wave bieciton lasing at room temperature using solution-processed quantum wells Joel Q. Grim, Sotirios Christodoulou, Francesco Di Stasio, Roman Krahne, Roberto Cingolani,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Phenyl-Modified Carbon Nitride Quantum Dots with Distinct Photoluminescence Behavior Qianling Cui, Jingsan Xu,* Xiaoyu Wang, Lidong Li,* Markus Antonietti, and Menny Shalom anie_201511217_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf
Supporting Information Phenyl-Modified Carbon Nitride Quantum Dots with Distinct Photoluminescence Behavior Qianling Cui, Jingsan Xu,* Xiaoyu Wang, Lidong Li,* Markus Antonietti, and Menny Shalom anie_201511217_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf
Laser matter interaction
 Laser matter interaction PH413 Lasers & Photonics Lecture 26 Why study laser matter interaction? Fundamental physics Chemical analysis Material processing Biomedical applications Deposition of novel structures
Laser matter interaction PH413 Lasers & Photonics Lecture 26 Why study laser matter interaction? Fundamental physics Chemical analysis Material processing Biomedical applications Deposition of novel structures
Three Dimensional Nano-assemblies of Noble Metal. Nanoparticles-Infinite Coordination Polymers as a Specific
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Three Dimensional Nano-assemblies of Noble Metal Nanoparticles-Infinite
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Three Dimensional Nano-assemblies of Noble Metal Nanoparticles-Infinite
Synthesis of 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted Nucleation for Plasmon-Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Electronic Supplementary Information. Facile synthesis of polypyrrole coated copper nanowire: new concept to engineered core-shell structures
 Electronic Supplementary Information Facile synthesis of polypyrrole coated copper nanowire: new concept to engineered core-shell structures Yang Liu, a Zhen Liu, a Ning Lu, b Elisabeth Preiss, a Selcuk
Electronic Supplementary Information Facile synthesis of polypyrrole coated copper nanowire: new concept to engineered core-shell structures Yang Liu, a Zhen Liu, a Ning Lu, b Elisabeth Preiss, a Selcuk
Formation mechanism and Coulomb blockade effect in self-assembled gold quantum dots
 Formation mechanism and Coulomb blockade effect in self-assembled gold quantum dots S. F. Hu a) National Nano Device Laboratories, Hsinchu 300, Taiwan R. L. Yeh and R. S. Liu Department of Chemistry, National
Formation mechanism and Coulomb blockade effect in self-assembled gold quantum dots S. F. Hu a) National Nano Device Laboratories, Hsinchu 300, Taiwan R. L. Yeh and R. S. Liu Department of Chemistry, National
Synthesis and characterization of silica titania core shell particles
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 65, No. 5 journal of November 2005 physics pp. 787 791 Synthesis and characterization of silica titania core shell particles SUCHITA KALELE 1, RAVI DEY 1, NEHA
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 65, No. 5 journal of November 2005 physics pp. 787 791 Synthesis and characterization of silica titania core shell particles SUCHITA KALELE 1, RAVI DEY 1, NEHA
Biosensing based on slow plasmon nanocavities
 iosensing based on slow plasmon nanocavities. Sepulveda, 1, Y. Alaverdyan,. rian, M. Käll 1 Nanobiosensors and Molecular Nanobiophysics Group Research Center on Nanoscience and Nanotechnolog (CIN)CSIC-ICN
iosensing based on slow plasmon nanocavities. Sepulveda, 1, Y. Alaverdyan,. rian, M. Käll 1 Nanobiosensors and Molecular Nanobiophysics Group Research Center on Nanoscience and Nanotechnolog (CIN)CSIC-ICN
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information A Generic Method for Rational Scalable Synthesis of Monodisperse Metal Sulfide Nanocrystals Haitao Zhang, Byung-Ryool Hyun, Frank W. Wise, Richard D. Robinson * Department of Materials
Supporting Information A Generic Method for Rational Scalable Synthesis of Monodisperse Metal Sulfide Nanocrystals Haitao Zhang, Byung-Ryool Hyun, Frank W. Wise, Richard D. Robinson * Department of Materials
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Visualization of equilibrium position of colloidal particles at fluid-water
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Visualization of equilibrium position of colloidal particles at fluid-water
