Curriculum Outline for Secondary 1 Science Topic Objectives Worksheets/ Practicals/ Assessments 1. The Scientific
|
|
|
- Kathryn Neal
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 3-5 * 1-2 Sec 1 Orientation Programme Curriculum Outline for Secondary 1 Science 1. The Scientific W1A Endeavour [Chap 1] : K1. show an awareness that that there are many branches of science to find out about the different parts of the world around us. K2. recognize that scientific evidence can be quantitative or qualitative. K3. state the key elements of the processes in science (scientific method). K4. define and explain independent, dependent and control variables K5. state and explain some basic laboratory safety rules while doing experiments. K6. use scientific inquiry skills such as posing questions, observing, measuring, communicating, inferring, predicting, formulating hypotheses, thinking skills (incl. analyzing data, etc). P1A P1B S1. make quantitative or qualitative observations. S2. distinguish between observations and inferences. S3. demonstrate safety consciousness and adopt safe practices when carrying out investigations. S4. light a Bunsen burner to produce luminous and non-luminous flame. S5. distinguish between luminous and non-luminous flame Exploring Diversity of Matter by its Physical Properties [Chap 2] : K1. understand that observable physical properties can be used to classify materials. K2. state some physical properties used to classify materials like strength, hardness, flexibility, density, electrical conductivity, heat (or thermal) conductivity, melting /boiling point. K3. explain the choice of the main classes of materials (plastic, glass metal, ceramic and fibre) in the production of common household items, in terms of their properties. K4. state that physical quantities are physical properties that can be measured. K5. distinguish between base physical quantities and derived physical quantities. K6. state the respective SI units of base physical quantities and hence the SI unit of derived physical quantities. K7. define mass of an object as the amount of matter it has. K8, Define weight and explain the difference between mass and weight. K9. define density of a substance as the mass of substance per unit volume and calculate density using the formula (D = M/V). W2A W2B W2C P2A P2B P2C Assessment 1 1
2 S1. classify a number of common everyday objects and recognize that there are many ways of classifying the same group of objects. S2. communicate findings on classification and justify reasons. S3. display the habit of sustainable use of materials and able to evaluate the environmental impact of excessive use of paper and the disposal of plastics. S4. identify the following physical quantities (length, mass time & temperature) as base physical quantities. S5. Make estimations and measure accurately length, volume and mass (of solids & liquids) using appropriate instruments (meter rule, vernier calipers, measuring cylinder, displacement can, electronic balance) and methods. S6. predict whether an object will sink or float by comparing its density with that of its surrounding medium. S7. demonstrate precision & accuracy in making measurements (taking into consideration parallax error and zero errors) and convert units with one prefix to another Model of Matter The Particulate Nature of Matter [Chap 7] K1. describe the main properties of solids, liquids & gases. K2. show an awareness that matter is made up of small discrete particles which are in constant and random motion. K3. describe diffusion as evidence for the particulate nature of matter. K4. state the particulate theory of matter. K5. show an understanding of the simple models of solids, liquids and gases, in terms of arrangement and movement of the particles. W3.1 P3 Practical Test 1 : S1. Compare the properties of solids, liquids and gases (e.g. volume, shape, density, compressibility) in terms of the arrangement and movement of particles. S2. Use of particle model of matter to explain the following: Expansion and contraction Change of state (melting, freezing, evaporating, boiling, condensing & subliming) a) Exploring Diversity of K1. understand that substances can be classified as elements, compounds W4A W4B 2
3 Matter by its Chemical Composition [Chap 3] b) Model of Matter Atoms & Molecules [Chap 8] and mixtures. K2. distinguish among elements, compounds and mixtures. K3. recognize that elements are the basic building blocks of living and nonliving matter. K4. define elements as substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical methods. K5. recognise that elements are classified according to their properties in the Periodic Table, in groups and periods. K6. recognise the chemical symbols for the first twenty elements and the following elements: Iron, copper, zinc, bromine, silver, iodine, gold, mercury, lead. K7. recognize that elements can be classified into solids, liquids and gases and state mercury and bromine as the only two elements in liquid state at room temperature and pressure. K8. recognize that elements can also be classified into metals and nonmetals by the staircase line in the Periodic Table. K9. describe the general physical properties of metal as solids having high melting and boiling points, malleable, ductile, good conductors of heat and electricity, sonorous. K10. describe the general physical properties of non-metals as elements which are non-malleable, brittle, ductile, poor conductors of heat and electricity, non-sonorous. K11. recognise that an atom is the smallest unit of an element that can take part in the chemical reactions. K12. recognise that a molecule is a group of 2 or more atoms chemically joined together. K13. know that elements are also made up molecules of similar atoms. (E.g. H 2, N 2, O 2, F 2, Cl 2, Br 2, I 2, ) K14. define compounds as substances consisting of two or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions. K15. show an awareness of ways to make and break a compound. (E.g. using heating to make and break compounds and electrolysis to break compounds.) K16. show an awareness of how some common compounds are named according to some general rules. K17. idenitfy the types of elements present in a compound from its chemical name. K18. know that a compound can be represented by a chemical formula. K19. define mixtures as 2 or more substances (elements /compounds) that are not chemically combined. K20. state that pure substances have fixed melting and boiling points. P4A P4B P4C P4D Performance Task Practical Test 2 3
4 K21. show an understanding that solutions and suspensions are mixtures. K22. show an understanding of the terms solute, solvent and solubility. S1. classify elements as metals and non-metals / solids, liquids and gases at room temperature and pressure based on melting /boiling point based on their characteristic properties. S2. be able to represent elements, compounds and mixtures using particle diagrams. S3. use the Bunsen burner correctly to heat small quantities of solids and liquids in a test tube. S4. observe changes in substances caused by heating. S5. use of common laboratory apparatus correctly such as beaker, test tube, dropper, glass rod, crucible. S6. investigate the factors that affect solubility Exploring Diversity of Matter Using Separation Techniques [Chap 4] K1. define a pure substance as a single substance, containing only one type of particles. K2. state that pure substances melt and boil at fixed temperatures. K3. show an understanding that impurity will raise boiling point & lower melting point. K4. recognise that mixtures melt and boil over a range of temperatures. K5. understand that mixtures can be separated by physical methods. K6. show an awareness of basic principles involved in: a) Filtration (state and define key words: residue, filtrate, filter, list the apparatus needed, draw the experimental set up) b) Magnetic attraction c) Evaporation (state that only solutes that do not decompose upon heating can be separated using this method, list the required apparatus and draw experimental set up.) d) Simple distillation (label the apparatus of the experimental set up) e) Separating funnel f) Sublimation g) Paper chromatography K7. describe using filtration, evaporation to separate mixtures. W5 P5A P5B P5C Assessment 2 4
5 S1. explain how the constituents of a mixture can be separated based on their properties (e.g. particle size, solubility, melting /boiling point, density, miscibility) using the appropriate separation techniques. S2. explain the difference between physical and chemical methods of separation. S3. use of common laboratory apparatus correctly such as beaker, evaporating dish, filter funnel, retort stand, separating funnel. S4. draw in proportion, sectional diagrams of apparatus in an experimental set-up for filtration and evaporation Effects of Heat & Its Transmission [Chap 17] K1. know that temperature is a base physical quantity. K2. state the SI unit of temperature is kelvin, K. Another commonly used unit is degree Celsius, o C. K3. use both the Kelvin and Celsius scales at ease, including converting the reading from one scale to another. K4. show understanding that thermal energy is transferred from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature. K5. know why metals are better conductors than non metals highlighting the presence of mobile electrons in metals. K6. Explain how convection currents are set up in a fluid due to density changes, and how heat is thus transferred throughout the fluid. K7. know some effects and applications of expansion and contraction in everyday life. K8. identify and explain applications of heat conduction & convection (e.g. in cooling, heating, insulation & weather patterns) K9. show an understanding that the rate of heat loss or gain by a body through radiation is affected by nature of its surface and temperature difference between the body and its surroundings. K10. explain what radiation (infra red) is and list the factors that affect the rate of radiation (colour, surface area & initial temperature of surface). W6A W6B W6C P6A P6B S1. determine the precision of a liquid-in-glass thermometer and record the readings using a liquid-in-glass thermometer to the correct precision. S2. take the necessary precautions when using a liquid-in-glass thermometer to take measurements. S3. infer that generally, solids, liquids and gases expand when heat is absorbed and contract when heat is given out. S4. explain what is meant by conduction, convection and radiation (Using particulate model of matter to explain conduction) 5
6 S5. identify and explain applications of conduction, convection & radiation (e.g. Styrofoam cups, metal pots, air conditioner, kettle, solar radiation, colour and surface area) S6. explain what radiation (infra red) is and list the factors that affect the rate of radiation (colour, surface area & initial temperature of surface). S7. infer that thermal expansion results in a change in volume of the substance and therefore the density of the substances. S8. infer from experiments that different materials have different rates of conduction Model of Cells The Basic Units of Life [Chap 6] K1. state the functions of the following organelles: (i) chloroplasts, (ii) cell membrane, (iii) cell wall, (iv) cytoplasm, (v) cell vacuoles (large, sap filled in plant cells, small, temporary in animal cells), (vi) nucleus and (vii) mitochondrion. K2. compare the structure of typical animal and plant cells. 3 K3. show an understanding of the functions of the different parts of the cell includes the nucleus (which controls the activities of the cell) and contains genetic materials that determines heredity. 1 K4. recognise that multi-cellular organisms (both plants and animals), cells (e.g. red blood cells, xylem, root hair cell, sperm cell, palisade cell, etc.) of similar structures are organized into tissues (e.g. muscle, xylem, phloem, etc.); several tissues may make up an organ (e.g. heart, skin, leaf, etc.); organ are organized into systems. 1 K5. explain the significance of division of labour, even at the cellular level. 1 K6. briefly describe mitosis as the process in cells that produces daughter cells that are identical to each other and to the parent cell. K7. * identify, with the aid of diagrams, the main stages of mitosis. Optional K8. outline the relationship between genes, chromosomes, and DNA. 4 K9. state the rule of complementary base pairing. 4 K10. state that DNA is used to carry the genetic code (details of translation and transcription are not required). 4 K11. state that each gene is (i) a sequence of nucleotides, as part of a DNA molecule and (ii) controls the production of one polypeptide. 4 W7A W7B P7A P7B P7C S1. identify cell structures (including organelles) of typical plant and animal cells from diagrams, photomicrographs and as seen under the light microscope using prepared slides and fresh material treated with an appropriate temporary staining technique: 3 (i) chloroplasts, (ii) cell membrane, (iii) cell wall, (iv) cytoplasm, (v) cell 6
7 vacuoles (large, sap filled in plant cells, small, temporary in animal cells), (vi) nucleus and (vii) mitochondrion. S2. draw and label typical plant and animal cell (including organelles) S3. prepare specimens (cheek cell and onion epidermal cell) and view them using a typical light microscope Human Digestive System [Chap 11] (Biological Molecules) 9. Transport in Living Things [Chap 10] (Diffusion & Osmosis) *Notes given K1. define and explain the need of a balanced diet. K2. state the roles of water in living organisms. 3 K3. list the chemical elements which make up: (i) carbohydrates (simple sugar, complex sugar & complex carbohydrates), (ii) fats d (iii) proteins. K4. * understand and appreciate the processes of condensation and hydrolysis in the synthesis and digestion of disaccharides. Optional K5. state that large molecules are synthesized from smaller basic units 3 : (i) glycogen from glucose, (ii) polypeptides and proteins from amino acids and (iii) lipids such as fats from glycerol and fatty acids. K6. recognise that a gram of carbohydrates, fats & proteins each supplies a different amount of energy to the body K7. explain why the following food substances are important in the diet Carbohydrates, Vitamins (eg. A, B1, C, D, K, E), Fats, Mineral salts (eg. Fe, Na, Ca, I), Proteins, Water, Fibre. Emphasis to be made on Vitamins C and D and the minerals Fe and Ca. K8. state the sources of all the above nutrients and the deficiency diseases of all vitamins, minerals, proteins and fibre. K9. define diffusion and discuss its importance in nutrient uptake and gaseous exchange in plants and humans. K10. define osmosis and discuss the effects of osmosis on plant and animal tissues. W8 P8A P8B Practical Test 3 Assessment 3 W9A W9B P9A P9B S1. describe and carry out tests for 3 : (i) starch (iodine solution), (ii) reducing sugars (Benedict s solution), (iii) protein (Biuret s test) and(iv) fats (ethanol emulsion) Chemical Changes [Chap 18] (Nutrition & Transport in Plants ) K1. state the word equation for photosynthesis. K2. * state the chemical equation, with symbol for photosynthesis. Optional K3. describe the intake of carbon dioxide and water by plants. K4. * show an understand for the mechanism of stomatal opening. Optional K5. state that chlorophyll traps light energy and converts it into chemical W10A W10B W10C P10A P10B 7
8 energy for the formation of carbohydrates and their subsequent storage. K6. outline the process of photosynthesis by which plant manufacture carbohydrates using raw materials. K7. show an understanding for the conditions (light energy & chlorophyll) and raw materials (carbon dioxide & water) necessary for photosynthesis. K8. show an understanding on how plants take in oxygen and remove carbon dioxide. K9. outline water transport and food translocation in plants via the xylem, with reference to osmosis and transpiration pull) K10. outline food translocation in phloem tissues (sufficient to identify source-sink relationship) S1. identify the cellular and tissue structure of a dicotyledonous leaf, as seen in cross-section under the microscope and state their functions: 3 (i) distribution of chloroplasts photosynthesis, (ii) stomata and mesophyll cells gaseous exchange and (iii) vascular bundles transport S2. describe and carry out tests for the test for starch in leaf. Final Year Exam 8
13. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY)
 PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE O-Level Science (Biology) Examination. Past examination questions have been carefully classified into
PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE O-Level Science (Biology) Examination. Past examination questions have been carefully classified into
Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport
 Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma
Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma
PREFACE. N-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE N-Level Science (Biology) Examination.
 PREFACE N-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE N-Level Science (Biology) Examination. This book contains: Useful Notes Students are able to revise their
PREFACE N-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE N-Level Science (Biology) Examination. This book contains: Useful Notes Students are able to revise their
Foundation Cell Biology
 Foundation Cell Biology Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution
Foundation Cell Biology Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution
Animal Cell Organelles. Plant Cell. Organelle. Cell Wall. Chloroplasts. Vacuole
 Cell Biology Higher Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution Electron
Cell Biology Higher Electron vs Light Microscope Light use light and lenses to magnify specimen Electron use a beam of electrons to form an image Electron higher magnification and higher resolution Electron
Cell Review. 1. The diagram below represents levels of organization in living things.
 Cell Review 1. The diagram below represents levels of organization in living things. Which term would best represent X? 1) human 2) tissue 3) stomach 4) chloroplast 2. Which statement is not a part of
Cell Review 1. The diagram below represents levels of organization in living things. Which term would best represent X? 1) human 2) tissue 3) stomach 4) chloroplast 2. Which statement is not a part of
Cells. A. The iodine diffused into the bag. B. The starch was changed to sugar.
 Name: Date: 1. A student filled a bag of dialysis tubing with a milky-white starch solution and placed the bag in a beaker of iodine-water as shown in the diagram. An hour later, the student observed that
Name: Date: 1. A student filled a bag of dialysis tubing with a milky-white starch solution and placed the bag in a beaker of iodine-water as shown in the diagram. An hour later, the student observed that
Military High School AL- Ain. Grade 10 &11. Biology Sample Questions. Student Name: Computer #:
 Military High School AL- Ain Grade 10 &11 Biology Sample Questions Student Name: Computer #: Chapter 1: Cells In all multiple choice questions, more than answer could be correct Section : 1 What Is a Cell?
Military High School AL- Ain Grade 10 &11 Biology Sample Questions Student Name: Computer #: Chapter 1: Cells In all multiple choice questions, more than answer could be correct Section : 1 What Is a Cell?
The diagram below represents levels of organization within a cell of a multicellular organism.
 STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
Organelles & Cells Student Edition. A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole
 Name: Date: 1. Which structure is outside the nucleus of a cell and contains DNA? A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole 2. A potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure
Name: Date: 1. Which structure is outside the nucleus of a cell and contains DNA? A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole 2. A potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure
CELL PRACTICE TEST
 Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Biology 4.2 - Plant Nutrition Photosynthesis You need to know the definition of photosynthesis as: the fundamental process by which plants manufacture carbohydrates
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Biology 4.2 - Plant Nutrition Photosynthesis You need to know the definition of photosynthesis as: the fundamental process by which plants manufacture carbohydrates
Quiz 1: Cells and Cell Structures
 Quiz 1: Cells and Cell Structures 1. Identify the structures in the diagram. (3 marks) 2. List the 3 cell structures not found in animal cells but are found in plants cells. (1 mark) 3. Where is DNA found
Quiz 1: Cells and Cell Structures 1. Identify the structures in the diagram. (3 marks) 2. List the 3 cell structures not found in animal cells but are found in plants cells. (1 mark) 3. Where is DNA found
Chapter: Cell Processes
 Table of Contents Chapter: Cell Processes Section 1: Chemistry of Life Section 2: Moving Cellular Materials Section 3: Energy for Life 1 Chemistry of Life The Nature of Matter Matter is anything that has
Table of Contents Chapter: Cell Processes Section 1: Chemistry of Life Section 2: Moving Cellular Materials Section 3: Energy for Life 1 Chemistry of Life The Nature of Matter Matter is anything that has
How many lessons is it?
 Science Unit Learning Summary Content Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes Cells are the basic unit of all life forms. A eukaryotic cell contains genetic material enclosed within a nucleus. Plant and animal cells
Science Unit Learning Summary Content Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes Cells are the basic unit of all life forms. A eukaryotic cell contains genetic material enclosed within a nucleus. Plant and animal cells
2018 Version. Photosynthesis Junior Science
 2018 Version Photosynthesis Junior Science 1 Plants fill the role of Producers in a community Plants are special because they have leaves and are able to produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis
2018 Version Photosynthesis Junior Science 1 Plants fill the role of Producers in a community Plants are special because they have leaves and are able to produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis
Cells: 3 Star. Which row in the chart below best explains the movement of some molecules between the model cell and the solution in the beaker?
 ells: 3 Star 1. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a model cell setup. The locations of three different substances
ells: 3 Star 1. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a model cell setup. The locations of three different substances
untitled 1. One similarity between cell receptors and antibodies is that both
 Name: ate: 1. One similarity between cell receptors and antibodies is that both. are produced by nerve cells B. are highly specific in their actions. slow the rates of chemical reactions. are involved
Name: ate: 1. One similarity between cell receptors and antibodies is that both. are produced by nerve cells B. are highly specific in their actions. slow the rates of chemical reactions. are involved
Bio Factsheet. Transport in Plants. Number 342
 Number 342 Transport in Plants This Factsheet: Explains why plants need a transport system Describes what plants transport Describes the tissues which carry out transport Outlines the position of the xylem
Number 342 Transport in Plants This Factsheet: Explains why plants need a transport system Describes what plants transport Describes the tissues which carry out transport Outlines the position of the xylem
WANGANUI HIGH SCHOOL
 Year 9 Science Examination 2007 Summary of Topics covered. Skills in Science What lab equipment is used for. Safety rules of the lab Interpreting diagrams, graphs, text etc Parts of a Bunsen burner, how
Year 9 Science Examination 2007 Summary of Topics covered. Skills in Science What lab equipment is used for. Safety rules of the lab Interpreting diagrams, graphs, text etc Parts of a Bunsen burner, how
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Topic 3- Cells and Transport
 Topic 3- Cells and Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma membranes D) All cells can
Topic 3- Cells and Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma membranes D) All cells can
Chemistry is the branch of science that deals with the properties, composition and behavior of matter.
 Chemistry 11 Review Chemistry is the branch of science that deals with the properties, composition and behavior of matter. Chemistry is found all around us in our daily lives: Ex. Plastics, computer chips,
Chemistry 11 Review Chemistry is the branch of science that deals with the properties, composition and behavior of matter. Chemistry is found all around us in our daily lives: Ex. Plastics, computer chips,
3/1/2010. created by Ms Janelle Tay\2010. Learning Objectives
 1 Learning Objectives Define what elements, compounds and mixtures are. Give the names and symbols of common elements. State how elements are classified. State what the building block of an element is.
1 Learning Objectives Define what elements, compounds and mixtures are. Give the names and symbols of common elements. State how elements are classified. State what the building block of an element is.
2012 SECONDARY 1 SCIENCE SCHEME OF WORK
 2012 SECONDARY 1 SCIENCE SCHEME OF WORK Term 1 1 Orientation 2 Introduction to Science Lab Safety 3 Physical Quantities and Units 1. All physical quantities consist of a numerical magnitude and a unit
2012 SECONDARY 1 SCIENCE SCHEME OF WORK Term 1 1 Orientation 2 Introduction to Science Lab Safety 3 Physical Quantities and Units 1. All physical quantities consist of a numerical magnitude and a unit
1. Cell Theory Organelle containing the genetic information of the cell.
 GLOSSARY MATCHING GAME The words and definitions are all mixed up. Cut out each word and definition and glue the correct matches into your workbook. Word Definition 1. Cell Theory Organelle containing
GLOSSARY MATCHING GAME The words and definitions are all mixed up. Cut out each word and definition and glue the correct matches into your workbook. Word Definition 1. Cell Theory Organelle containing
Organs and leaf structure
 Organs and leaf structure Different types of tissues are arranged together to form organs. Structure: 2 parts (Petiole and Leaf Blade) Thin flat blade, large surface area Leaves contain all 3 types of
Organs and leaf structure Different types of tissues are arranged together to form organs. Structure: 2 parts (Petiole and Leaf Blade) Thin flat blade, large surface area Leaves contain all 3 types of
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 1 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 1 2 Number
7. Which letter in the diagram below indicates the structure that is most closely associated with excretion?
 1. Which sequence of terms is in the correct order from simplest to most complex? 1) cells tissues organs organ systems 2) tissues organisms cells organ systems 3) cells tissues organ systems organs 4)
1. Which sequence of terms is in the correct order from simplest to most complex? 1) cells tissues organs organ systems 2) tissues organisms cells organ systems 3) cells tissues organ systems organs 4)
CELLS. Structure and Function
 CELLS Structure and Function Cell Structure All plant and animal tissue consist of cells. Cells are microscopic in size. In general, each cell performs all the characteristics of life and, though in reality
CELLS Structure and Function Cell Structure All plant and animal tissue consist of cells. Cells are microscopic in size. In general, each cell performs all the characteristics of life and, though in reality
Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination April, 2017 Biology
 Grade 09 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination April, 2017 Biology Duration: 2.30 Hours Part 1 Index No:- 1) Choose the correct answer and underline it 1) The diagram shows a high-power
Grade 09 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination April, 2017 Biology Duration: 2.30 Hours Part 1 Index No:- 1) Choose the correct answer and underline it 1) The diagram shows a high-power
Recap. Waxy layer which protects the plant & conserves water. Contains chloroplasts: Specialized for light absorption.
 Recap Contains chloroplasts: Specialized for light absorption Waxy layer which protects the plant & conserves water mesophyll Layer contains air spaces: Specialized for gas exchange Vascular Tissue Exchange
Recap Contains chloroplasts: Specialized for light absorption Waxy layer which protects the plant & conserves water mesophyll Layer contains air spaces: Specialized for gas exchange Vascular Tissue Exchange
Unit B: Cells and Systems
 Unit B: Cells and Systems Topic 4: Fluid Movement in Cells The Cell Membrane A cell membrane allows some to enter or leave the cell, while stopping other substances. It is a selectively membrane. (A permeable
Unit B: Cells and Systems Topic 4: Fluid Movement in Cells The Cell Membrane A cell membrane allows some to enter or leave the cell, while stopping other substances. It is a selectively membrane. (A permeable
Main Topic Sub-topics Students should be able to R O G
 Second Year Science Syllabus Biology Revision Check-list Where is your learning at? Green: I know it all. Orange: I have some idea check the answers. Red: I need to start studying this section. Main Topic
Second Year Science Syllabus Biology Revision Check-list Where is your learning at? Green: I know it all. Orange: I have some idea check the answers. Red: I need to start studying this section. Main Topic
BRAINSTORM ACTIVITY What do we depend on plants for?
 SBI3U1 BRAINSTORM ACTIVITY What do we depend on plants for? STOP! THINK! PAIR! SHARE! With your partner, brainstorm 5 significant uses of plants. Write them down. Now share your ideas with the rest of
SBI3U1 BRAINSTORM ACTIVITY What do we depend on plants for? STOP! THINK! PAIR! SHARE! With your partner, brainstorm 5 significant uses of plants. Write them down. Now share your ideas with the rest of
LEAF STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
 Name Class Date LEAF STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Plants are incredible organisms! They can make all their own food from the simple inputs of: sunlight carbon dioxide water minerals This biological wizardry is
Name Class Date LEAF STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Plants are incredible organisms! They can make all their own food from the simple inputs of: sunlight carbon dioxide water minerals This biological wizardry is
What is the role of the nucleus? What is the role of the cytoplasm? What is the role of the mitochondria? What is the role of the cell wall. membrane?
 Page 1 What is the role of the nucleus? What is the role of the cytoplasm? What is the role of the cell membrane? What is the role of the mitochondria? What is the role of ribosomes? What is the role of
Page 1 What is the role of the nucleus? What is the role of the cytoplasm? What is the role of the cell membrane? What is the role of the mitochondria? What is the role of ribosomes? What is the role of
Ark Elvin Academy Year 10 Science Study Pack Spring assessment 2018 Cumulative content part 1
 Ark Elvin Academy Year 10 Science Study Pack Spring assessment 2018 Cumulative content part 1 Name Biology Cell Biology: structure and transport Part 1: Glossary 1. active transport the movement of substances
Ark Elvin Academy Year 10 Science Study Pack Spring assessment 2018 Cumulative content part 1 Name Biology Cell Biology: structure and transport Part 1: Glossary 1. active transport the movement of substances
GRADE 5. Units of Study: Using Variables in the Inquiry Process Astronomy: Earth, Sun, Moon, Planets (Solar System) and Beyond Elements and Compounds
 GRADE 5 Course Overview In fifth grade, students use the inquiry process more independently throughout the year with teacher support, as needed. Students practice designing, conducting, evaluating, and
GRADE 5 Course Overview In fifth grade, students use the inquiry process more independently throughout the year with teacher support, as needed. Students practice designing, conducting, evaluating, and
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology. 5. Which letter corresponds to that of the endoplasmic reticulum?
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology. 5. Which letter corresponds to that of the endoplasmic reticulum?
Page 1 / 12. Chemistry Exam. Name: Matter Properties, Structure. Question 1 (1 point) The atomic number of an atom is. A. The mass of the atom.
 Chemistry Exam Matter Properties, Structure Name: Question 1 (1 point) The atomic number of an atom is A. The mass of the atom. B. The number of protons added to the number of neutrons in the nucleus.
Chemistry Exam Matter Properties, Structure Name: Question 1 (1 point) The atomic number of an atom is A. The mass of the atom. B. The number of protons added to the number of neutrons in the nucleus.
Cells. B. the development of advanced techniques to determine the chemical composition of substances
 ells Name: ate: 1. Which factor contributed most to the development of the cell theory? 1.. the discovery of many new species during the last century. the development of advanced techniques to determine
ells Name: ate: 1. Which factor contributed most to the development of the cell theory? 1.. the discovery of many new species during the last century. the development of advanced techniques to determine
6 Plant Nutrition. Question Paper. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Plant Nutrition Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Unit ooklet IGSE iology ambridge International Examinations 6 Plant Nutrition
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Plant Nutrition Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Unit ooklet IGSE iology ambridge International Examinations 6 Plant Nutrition
Which row in the chart below identifies the lettered substances in this process?
 1. A biological process that occurs in both plants and animals is shown below. Which row in the chart below identifies the lettered substances in this process? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 2. All life depends on
1. A biological process that occurs in both plants and animals is shown below. Which row in the chart below identifies the lettered substances in this process? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 2. All life depends on
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
 4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
Matter has many different phases (sometimes called states) which depend on the temperature and/or pressure.
 Matter Phases of Matter Matter has many different phases (sometimes called states) which depend on the temperature and/or pressure. Some non common sates of matter include (but are not limited to): - Plasma,
Matter Phases of Matter Matter has many different phases (sometimes called states) which depend on the temperature and/or pressure. Some non common sates of matter include (but are not limited to): - Plasma,
How is matter classified?
 Matter How is matter classified? AP Chemistry (1 of 45) AP Chemistry (2 of 45) Solids Liquids AP Chemistry (3 of 45) AP Chemistry (4 of 45) Gases Classification Scheme for Matter AP Chemistry (5 of 45)
Matter How is matter classified? AP Chemistry (1 of 45) AP Chemistry (2 of 45) Solids Liquids AP Chemistry (3 of 45) AP Chemistry (4 of 45) Gases Classification Scheme for Matter AP Chemistry (5 of 45)
Mid-Unit 1 Study Guide
 Mid- Study Guide Lessons 1, 3, & 4 1.1 Essential Questions: What are living things made of? What term describes the smallest unit that can perform all of the functions necessary for life? Eukaryotic cells
Mid- Study Guide Lessons 1, 3, & 4 1.1 Essential Questions: What are living things made of? What term describes the smallest unit that can perform all of the functions necessary for life? Eukaryotic cells
SPECIFIC OUTCOMES METHODOLOGY SUGGESTED EXPERIMENTS. Discuss the personal and general laboratory safety. Introduce the apparatus used in the lab.
 MINISTRY OF GENERAL EDUCATION PROVINCIAL SCHEMES OF WORK FOR SCIENCE 5124 Subject: INTEGRATED SCIENCE Grade: 8 Term: ONE Year: 20. Teacher: ---------------------- WEEK TOPIC GENERAL LABORATORY SAFETY PROCEDURE
MINISTRY OF GENERAL EDUCATION PROVINCIAL SCHEMES OF WORK FOR SCIENCE 5124 Subject: INTEGRATED SCIENCE Grade: 8 Term: ONE Year: 20. Teacher: ---------------------- WEEK TOPIC GENERAL LABORATORY SAFETY PROCEDURE
Midterm Study Guide Major Concepts
 Midterm Study Guide Name 7 th Grade PSI Major Concepts 1. What is an atom? 2. What is a molecule? 3. What is an element? 4. What is a compound? 5. What are physical properties? Describe a few examples.
Midterm Study Guide Name 7 th Grade PSI Major Concepts 1. What is an atom? 2. What is a molecule? 3. What is an element? 4. What is a compound? 5. What are physical properties? Describe a few examples.
active transport active transport support
 1 Which row matches the cell membrane and cell wall of a palisade cell to their functions? cell membrane active transport active transport support support cell wall active transport support active transport
1 Which row matches the cell membrane and cell wall of a palisade cell to their functions? cell membrane active transport active transport support support cell wall active transport support active transport
1. The drawings below show three healthy young plants. A B C. The drawings below show the three plants after two weeks.
 1. The drawings below show three healthy young plants. A B C The drawings below show the three plants after two weeks. A C B (a) (i) Plant B did not have enough light. How can you tell this from the drawing?....
1. The drawings below show three healthy young plants. A B C The drawings below show the three plants after two weeks. A C B (a) (i) Plant B did not have enough light. How can you tell this from the drawing?....
Chapter 3 Cell Processes and Energy
 Chapter 3 Cell Processes and Energy 1 Chapter 3 Objectives Section 1: Chemical Compounds in Cells 1. Define elements and compounds 2. Explain how water is important to the function of cells 3. Identify
Chapter 3 Cell Processes and Energy 1 Chapter 3 Objectives Section 1: Chemical Compounds in Cells 1. Define elements and compounds 2. Explain how water is important to the function of cells 3. Identify
September Mid-September
 September Mid-September Lab Safety Advanced Lab Skills (calibrating equipment, making solutions for lab experiments, etc.) Advanced Study Skills Solving problems through experimentation Advanced Metric
September Mid-September Lab Safety Advanced Lab Skills (calibrating equipment, making solutions for lab experiments, etc.) Advanced Study Skills Solving problems through experimentation Advanced Metric
CORE CONCEPTS & TERMINOLOGY FALL 2010
 CORE CONCEPTS & TERMINOLOGY FALL 2010 The following concepts and terms will be covered by all BIO 120 lecture instructors. Presentation of additional concepts is left to the discretion of the individual
CORE CONCEPTS & TERMINOLOGY FALL 2010 The following concepts and terms will be covered by all BIO 120 lecture instructors. Presentation of additional concepts is left to the discretion of the individual
Page 1. Name: UNIT: PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION TOPIC: PHOTOSYNTHESIS
 Name: 4667-1 - Page 1 UNIT: PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION TOPIC: PHOTOSYNTHESIS 1) The diagram below illustrates the movement of materials involved in a process that is vital for the energy needs of organisms.
Name: 4667-1 - Page 1 UNIT: PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION TOPIC: PHOTOSYNTHESIS 1) The diagram below illustrates the movement of materials involved in a process that is vital for the energy needs of organisms.
Chemistry. Animal Health Technology Student Development Program
 Chemistry Animal Health Technology Student Development Program Chemistry Chemistry is a fundamental component in all of us. Chemical reactions are happening in our bodies constantly. In the Animal Health
Chemistry Animal Health Technology Student Development Program Chemistry Chemistry is a fundamental component in all of us. Chemical reactions are happening in our bodies constantly. In the Animal Health
PAF Chapter Prep Section Science Class 7 Worksheets for Intervention Classes
 The City School PAF Chapter Prep Section Science Class 7 Worksheets for Intervention Classes From cells to organisms Q1. Encircle the best answer from the given options. 1. Size of an animal cell is a.
The City School PAF Chapter Prep Section Science Class 7 Worksheets for Intervention Classes From cells to organisms Q1. Encircle the best answer from the given options. 1. Size of an animal cell is a.
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 chapter 7 Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells? a. Anton van
chapter 7 Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells? a. Anton van
- know that in multi-cellular organisms cells are massed together to form tissues, and tissues can be massed together to form organs
 Science Age 12-13 (A) BIOLOGY: ORGANISMS, THEIR BEHAVIOUR AND THE ENVIRONMENT 1. Cells and their functions - know that in multi-cellular organisms cells are massed together to form tissues, and tissues
Science Age 12-13 (A) BIOLOGY: ORGANISMS, THEIR BEHAVIOUR AND THE ENVIRONMENT 1. Cells and their functions - know that in multi-cellular organisms cells are massed together to form tissues, and tissues
CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant
 Name: Date: Period: CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant Plants are incredible organisms! They can make all their own food from the simple inputs of: Sunlight air (carbon dioxide) water minerals
Name: Date: Period: CELERY LAB - Structure and Function of a Plant Plants are incredible organisms! They can make all their own food from the simple inputs of: Sunlight air (carbon dioxide) water minerals
Biology 2 Chapter 21 Review
 Biology 2 Chapter 21 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is not a tissue system of vascular plants? a. vascular
Biology 2 Chapter 21 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is not a tissue system of vascular plants? a. vascular
Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
 L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION - 2016-17 CHEMISTRY - GRADE: VIII Elements, Compounds and Mixtures ELEMENTS An element is a pure substance which cannot be converted into anything simpler
L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION - 2016-17 CHEMISTRY - GRADE: VIII Elements, Compounds and Mixtures ELEMENTS An element is a pure substance which cannot be converted into anything simpler
BIOCHEMISTRY 10/9/17 CHEMISTRY OF LIFE. Elements: simplest form of a substance - cannot be broken down any further without changing what it is
 BIOCHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY OF LIFE Elements: simplest form of a substance - cannot be broken down any further without changing what it is THE ATOM Just like cells are the basic unit of life, the ATOM is the
BIOCHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY OF LIFE Elements: simplest form of a substance - cannot be broken down any further without changing what it is THE ATOM Just like cells are the basic unit of life, the ATOM is the
Unit 1 Cell Biology Topic 1: Cell Structure
 Unit 1 Cell Biology Topic 1: Cell Structure Lesson 1.1.1 I will know I am successful if I can: 1. Label all parts of plant and animal cells and state their functions 2. State the differences between plant
Unit 1 Cell Biology Topic 1: Cell Structure Lesson 1.1.1 I will know I am successful if I can: 1. Label all parts of plant and animal cells and state their functions 2. State the differences between plant
PHOTOSYNTHESIS GR 11 LIFE SCIENCES
 PHOTOSYNTHESIS GR 11 LIFE SCIENCES Definition: Photosynthesis is the process where the energy of the sunlight is used by green plants (and some animals) to bond molecules together to form carbohydrates
PHOTOSYNTHESIS GR 11 LIFE SCIENCES Definition: Photosynthesis is the process where the energy of the sunlight is used by green plants (and some animals) to bond molecules together to form carbohydrates
Cells: 2 Star. 7. The diagram below represents a cell.
 ells: 2 Star 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a cell and its changes as a result of two laboratory procedures,
ells: 2 Star 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a cell and its changes as a result of two laboratory procedures,
BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES
 BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES A1 A1. Basic Biological Principles 1. Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms 2. Compare cellular structures and their function
BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES A1 A1. Basic Biological Principles 1. Describe the characteristics of life shared by all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms 2. Compare cellular structures and their function
Transport of substances in plants
 Transport of substances in plants We have already looked at why many organisms need transport systems with special reference to surface area and volume. The larger the volume : surface area ratio, the
Transport of substances in plants We have already looked at why many organisms need transport systems with special reference to surface area and volume. The larger the volume : surface area ratio, the
Chapter C3: Multicellular Organisms Plants
 Chapter C3: Multicellular Organisms Plants Multicellular Organisms Multicellular organisms have specialized cells of many different types that allow them to grow to a larger size than single-celled organisms.
Chapter C3: Multicellular Organisms Plants Multicellular Organisms Multicellular organisms have specialized cells of many different types that allow them to grow to a larger size than single-celled organisms.
PURE SUBSTANCES AND MIXTURES. Substance = form of a matter consisting of a great number of elementary particles: atoms, ions and...
 PURE SUBSTANCES AND MIXTURES Substance = form of a matter consisting of a great number of elementary particles: atoms, ions and... Substances differ in the kind of the particles they consist of. The type
PURE SUBSTANCES AND MIXTURES Substance = form of a matter consisting of a great number of elementary particles: atoms, ions and... Substances differ in the kind of the particles they consist of. The type
Fifth Grade: FOSS Life Science - Living Systems
 Fifth Grade: FOSS Life Science - Living Systems Investigation Title and Synopsis Concepts Assessments and TE Page Numbers 1. Living Cells Students study four related human/body transport systems that provide
Fifth Grade: FOSS Life Science - Living Systems Investigation Title and Synopsis Concepts Assessments and TE Page Numbers 1. Living Cells Students study four related human/body transport systems that provide
Chapter 6 Chemistry in Biology
 Section 1: Atoms, Elements, and Compounds Section 2: Chemical Reactions Section 3: Water and Solutions Section 4: The Building Blocks of Life Click on a lesson name to select. 6.1 Atoms, Elements, and
Section 1: Atoms, Elements, and Compounds Section 2: Chemical Reactions Section 3: Water and Solutions Section 4: The Building Blocks of Life Click on a lesson name to select. 6.1 Atoms, Elements, and
Which row in the chart correctly identifies the functions of structures A, B, and C? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4
 1. What is a similarity between all bacteria and plants? A) They both have a nucleus B) They are both composed of cells C) They both have chloroplasts D) They both lack a cell wall 2. Which statement is
1. What is a similarity between all bacteria and plants? A) They both have a nucleus B) They are both composed of cells C) They both have chloroplasts D) They both lack a cell wall 2. Which statement is
Downloaded from
 Science For Class IX Is Matter Around Us Pure (Q.1) Name the process which can be used to recover sugar from an aqueous sugar solution. (Q.2) What happens when a saturated solution is heated?
Science For Class IX Is Matter Around Us Pure (Q.1) Name the process which can be used to recover sugar from an aqueous sugar solution. (Q.2) What happens when a saturated solution is heated?
the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together Chemical structure Covalent bond Ionic bond
 Chemical structure the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together Covalent bond bond formed by the sharing of valence electrons between atoms Ionic bond
Chemical structure the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together Covalent bond bond formed by the sharing of valence electrons between atoms Ionic bond
IGCSE (9-1) Edexcel - Chemistry
 IGCSE (9-1) Edexcel - Chemistry Principles of Chemistry Element, Compounds and Mixtures NOTES 1.8: Understand how to classify a substance as an element, compound or mixture Classifications: S Class Element
IGCSE (9-1) Edexcel - Chemistry Principles of Chemistry Element, Compounds and Mixtures NOTES 1.8: Understand how to classify a substance as an element, compound or mixture Classifications: S Class Element
Cell Types. Prokaryotes
 Cell Types Prokaryotes before nucleus no membrane-bound nucleus only organelle present is the ribosome all other reactions occur in the cytoplasm not very efficient Ex.: bacteria 1 Cell Types Eukaryotes
Cell Types Prokaryotes before nucleus no membrane-bound nucleus only organelle present is the ribosome all other reactions occur in the cytoplasm not very efficient Ex.: bacteria 1 Cell Types Eukaryotes
The Chemistry of Life
 The Chemistry of Life Things you should be able to do 1. Describe how the unique properties of water support life on Earth. 2. Explain how carbon is uniquely suited to form biological macromolecules. 3.
The Chemistry of Life Things you should be able to do 1. Describe how the unique properties of water support life on Earth. 2. Explain how carbon is uniquely suited to form biological macromolecules. 3.
Dushan [δβ] BOODHENA 1
![Dushan [δβ] BOODHENA 1 Dushan [δβ] BOODHENA 1](/thumbs/80/82205169.jpg) CHEMISTRY SUMMARY FOR THE FORM 3 NATIONAL ASSESSMENT 1. Define the term element. An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by any ordinary chemical process. 2. Define
CHEMISTRY SUMMARY FOR THE FORM 3 NATIONAL ASSESSMENT 1. Define the term element. An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by any ordinary chemical process. 2. Define
Grade 7 Science Curriculum Maps
 Grade 7 Science Curriculum Maps Unit 1: Cells The Basic Unit of Life Unit 2: The Cell in Action Unit 3: Genes and DNA Unit 4: Heredity Unit 5: Evolution Unit 6: It s Alive! Or is it?! Unit 7: Bacteria
Grade 7 Science Curriculum Maps Unit 1: Cells The Basic Unit of Life Unit 2: The Cell in Action Unit 3: Genes and DNA Unit 4: Heredity Unit 5: Evolution Unit 6: It s Alive! Or is it?! Unit 7: Bacteria
Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology
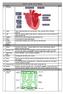 Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Tissues and organs PART 2
 Tissues and organs PART 2 The structure and function of the mesophytic leaf (a plant organ) The mesopyhtic leaf (lives in a moderately moist environment) contains 7 layers of tissue: 1. Upper epidermis
Tissues and organs PART 2 The structure and function of the mesophytic leaf (a plant organ) The mesopyhtic leaf (lives in a moderately moist environment) contains 7 layers of tissue: 1. Upper epidermis
B05 comparison of plant and animal cells.notebook. November 22, 2012
 Worksheet:List of Cell Organelles and Functions Instructions: After watching the video, complete the following table http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o1gqycijata&feature=related Organelle Location Function
Worksheet:List of Cell Organelles and Functions Instructions: After watching the video, complete the following table http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o1gqycijata&feature=related Organelle Location Function
Chapter-2: IS MATTER AROUND US PURE
 1 Chapter-2: IS MATTER AROUND US PURE Revision Notes: # A pure substance consists of a single type of particles. # A mixture contains more than one substance (element and/or compound) mixed in any proportion.
1 Chapter-2: IS MATTER AROUND US PURE Revision Notes: # A pure substance consists of a single type of particles. # A mixture contains more than one substance (element and/or compound) mixed in any proportion.
Science and Technology/Engineering Standards that May Be Assessed on the 2018 MCAS Grades 8STE Test
 Science and Technology/Engineering Standards that May Be Assessed on the 2018 MCAS Grades 8STE Test Earth and Space Science Earth s Layers 2. Describe the layers of the earth, including the lithosphere,
Science and Technology/Engineering Standards that May Be Assessed on the 2018 MCAS Grades 8STE Test Earth and Space Science Earth s Layers 2. Describe the layers of the earth, including the lithosphere,
8.L.5.1 Practice Questions
 Name: ate: 1. The diagram below represents a series of events that occur in living cells. Which molecule is indicated by X?. glucose. TP. carbon dioxide. protein 2. The diagram represents one metabolic
Name: ate: 1. The diagram below represents a series of events that occur in living cells. Which molecule is indicated by X?. glucose. TP. carbon dioxide. protein 2. The diagram represents one metabolic
KS3 Science Levelness Posters
 KS Science Levelness Posters Contents Year Year 8 Year 9 A. Cells 8A. Food and digestion 9A. Inheritance and selection B. Reproduction 8B. Respiration 9B. Fit and healthy C. Environment and feeding 8C.
KS Science Levelness Posters Contents Year Year 8 Year 9 A. Cells 8A. Food and digestion 9A. Inheritance and selection B. Reproduction 8B. Respiration 9B. Fit and healthy C. Environment and feeding 8C.
Mixtures 1 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016
 Mixtures 1 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Mixtures 2 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Pure and impure substances 3 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016 All materials can be classified as either a pure substance or an impure
Mixtures 1 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Mixtures 2 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Pure and impure substances 3 of 38 Boardworks Ltd 2016 All materials can be classified as either a pure substance or an impure
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
 4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
Chapter Life Is Cellular
 Chapter 7 7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell Anton van Leeuwenhoek used a single-lens microscope to observe tiny little organisms in pond water. The Discovery of the Cell In 1665, Robert Hooke
Chapter 7 7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell Anton van Leeuwenhoek used a single-lens microscope to observe tiny little organisms in pond water. The Discovery of the Cell In 1665, Robert Hooke
Science Scheme of Work
 Cherry Tree Hill Primary School Science Scheme of Work Essential characteristics: High-quality science education provides the foundations for understanding the world through the specific disciplines of
Cherry Tree Hill Primary School Science Scheme of Work Essential characteristics: High-quality science education provides the foundations for understanding the world through the specific disciplines of
7.1.2 Cell Functions. 104 minutes. 137 marks. Page 1 of 30
 7.1.2 Cell Functions 104 minutes 137 marks Page 1 of 30 ## Most pollen grains are transferred from one flower to another either by wind or by insects. Look at the drawings below which show pollen grains
7.1.2 Cell Functions 104 minutes 137 marks Page 1 of 30 ## Most pollen grains are transferred from one flower to another either by wind or by insects. Look at the drawings below which show pollen grains
Review_Unit 2 Biochemistry
 Review_Unit 2 Biochemistry Basic Chemistry 1. What is an element? A substance that cannot be broken down into smaller particles. 2. What are atoms? The smallest part of an element that still maintains
Review_Unit 2 Biochemistry Basic Chemistry 1. What is an element? A substance that cannot be broken down into smaller particles. 2. What are atoms? The smallest part of an element that still maintains
Reason... (2) Reason... (2) Reason... (2)
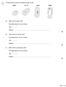 1 The figure below shows four different types of cell. (a) Which cell is a plant cell? Give one reason for your answer. Cell... Reason... (b) Which cell is an animal cell? Give one reason for your answer.
1 The figure below shows four different types of cell. (a) Which cell is a plant cell? Give one reason for your answer. Cell... Reason... (b) Which cell is an animal cell? Give one reason for your answer.
Fifth Grade Science Curriculum
 Fifth Grade Science Curriculum Science Content Standard 1. Students, through the inquiry process, demonstrate the ability to design, conduct, evaluate, and communicate results and reasonable conclusions
Fifth Grade Science Curriculum Science Content Standard 1. Students, through the inquiry process, demonstrate the ability to design, conduct, evaluate, and communicate results and reasonable conclusions
Science Home Learning Task. Year 9. GCSE Cell structure and transport
 Science Home Learning Task Year 9 GCSE Cell structure and transport Name Tutor Group Teacher Given out: Monday 23 April Hand in: Monday 30 April Parent/Carer Comment Staff Comment GCSE level Target Investigating
Science Home Learning Task Year 9 GCSE Cell structure and transport Name Tutor Group Teacher Given out: Monday 23 April Hand in: Monday 30 April Parent/Carer Comment Staff Comment GCSE level Target Investigating
It helps scientists understand the workings of the human body and of other animals and plants
 Science 8 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 1 Cells Online resources: Click on Chapter 1 at the site below. http://www.nelson.com/bcscienceprobe8/student/weblinks.html Chapter 1.1 1. Organism is another word used
Science 8 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 1 Cells Online resources: Click on Chapter 1 at the site below. http://www.nelson.com/bcscienceprobe8/student/weblinks.html Chapter 1.1 1. Organism is another word used
What in the Cell is Going On?
 What in the Cell is Going On? Robert Hooke naturalist, philosopher, inventor, architect... (July 18, 1635 - March 3, 1703) In 1665 Robert Hooke publishes his book, Micrographia, which contains his drawings
What in the Cell is Going On? Robert Hooke naturalist, philosopher, inventor, architect... (July 18, 1635 - March 3, 1703) In 1665 Robert Hooke publishes his book, Micrographia, which contains his drawings
Year 8 Tracking Document. Year 8 Science National Curriculum. Health and Lifestyle
 Health and Lifestyle Describe the components of a healthy diet Explain the role of each food group in the body Describe the test for starch, lipids, sugar and proteins Describe the positive test for each
Health and Lifestyle Describe the components of a healthy diet Explain the role of each food group in the body Describe the test for starch, lipids, sugar and proteins Describe the positive test for each
