|
|
|
- Bethanie Simon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electro Chemistry Part-II 1. Faraday s laws of electrolysis are related to the 1) Molar mass of the electrolyte 2) Equivalent weight of the cation or anion 3) Molecular mass of the electrolyte 4) Atomic mass of the cation or anion 2. The unit of electrochemical equivalent is 1) Gram. Coulomb 2) Gram. Ampere 3) Gram / Coulomb 4) Coulomb / Gram 3. The mass deposited by the passage of 1 amp current for one second is called as 1) A mole 2) Gram equivalent weight 3) Electro chemical equivalent 4) Gram atomic weight. 4. A copper voltameter, a silver voltameter and a water voltameter are connected in series and current is passed for some time. The ratio of the number of moles of copper, silver and hydrogen formed at the cathode is 1) 2:1:1 2) 1:1:1 3) 1:2:1 4) 1:2:2 Hint: when same quantity of electricity is passed through different electrolyte solutions then no. of moles of elements deposited are in the ratio 1/Z 1 :1/Z 2 :1/Z 3 : where Z 1, Z 2, Z 3.are valency of elements. n Cu : n Ag :n H2 =1/2: 1/1:1/2=1:2:1 5. When one faraday of current is passed, which of the following would deposit one gram atomic weight of the metal? 1) BaCl2 2) NaCl 3) AlCl3 4) CuCl2 Hint: For Na +, GEW=GAW
2 6. The charge on 1mole of Mg +2 ions is 1) 96,5 coulombs 2)193coulmbs 3) 4825 coulombs 4) 193 coulombs Hint: The charge on 1mole M n+ or M n- ions=n Faradays. 7. The value of electrochemical equivalent is highest for 1) Al 2) Ag 3) Ca 4) Mg Hint: e α GEW 8. The reaction ½ H2 (g) + AgCl(s) H+ (aq) + Ag(s) can be represented in the galvanic cell as 1) Ag/AgCl(s) KCl(sol) AgNO3 (sol) Ag 2) Pt, H2(g) HCl (sol) AgNO3 (sol) Ag 3) Pt,H2(g) HCl(sol) AgCl(s) Ag 4) H2(g) HCl(sol) AgCl(s) Ag 9. In a Galvanic cell, the electrons flow from 1) Anode to cathode through the solution 2) Cathode to anode through the solution 3) Anode to cathode through the external circuit 4) Cathode to anode through the external circuit. 1. Which of the following statements is wrong about galvanic cells? 1) Cathode is the positive electrode 2) Cathode is the negative electrode 3) In this chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. 4) Reduction occurs at cathode 11. The purpose of the salt bridge in a galvanic cell is to 1) Prevent accumulation of charges around the electrodes 2) Facilitate continuity of the cell reaction
3 3) To produce current at a constant strength 4) All the above 12. A reversible galvanic cell is connected to an external battery. It the EMF of the battery is less than EMF of the galvanic cell, then current 1) Will not pass through the circuit 2) Flows from the battery into the galvanic cell 3) Flows from the galvanic cell into the battery 4) All the three may take place 13. When salt bridge is removed, the voltage of Galvanic cell 1) Drops to zero 2) Increase rapidly 3) Increase slowly. 4) Remains same. 14 The electrolyte used in salt bridge of a galvanic cell is 1) Agar Agar Gel 2) Solid KNO 3 3) Fused KNO 3 4) Saturated aqueous KNO 3 solution. 15. Consider the following E values E Fe 3+ / Fe 2+ = +.77 V and E Sn 2+ / Sn =.14 V. Under standard conditions the potential for the reaction Sn (s) + 2Fe3+ (aq) 2Fe2+ (aq) + Sn2+ (aq) is 1) 1.68 V 2).63 V 3).91 V 4) 1.4 V Solution; E cell = E Fe 3+ / Fe 2+ - E Sn 2+ / Sn 16. E for the reaction Fe + Zn2+ Zn + Fe2+ is.35 V. The given cell reaction is 1) Spontaneous 2) Not feasible 3) Rapid 4) Slow Hint: if EMF of cell is negative then cell reaction is non spontaneous. 17. E.M.F of the cell reaction, 2Ag+ + Cu 2Ag + Cu2+ is.46 V. If E is V then E is Ag / Ag 1).8 V 2).12 V 3).4 V 4) 1.6 V Cu / Cu
4 Hint: EMF of cell= E - 2 Ag / Ag Cu E / Cu 18. The significance of using saturated solution of KNO3 as electrolyte in the Salt Bridge is 1) Velocity of K+ is greater than that of NO 3. 2) Velocity of N O 3 is greater than that of K+. 3) Velocities of both K+ and NO 3 are nearly the same. 4) KNO3 is highly soluble in water. 19 The standard electrode potential of the two half cells are given below Ni+2 + 2e Ni; Eo =.25 Volt Zn+2 + 2e Zn; Eo =.77 volt The voltage of cell formed by combining the two half cells would be 1) 1.2 2) +.52 volt 3) +1.2 volt 4).52 volt Hint: in this Zn acts as anode (lower SRP) and Ni acts as cathode (higher SRP). Emf= E o cathode-e o anode 2) The hydrogen electrode is dipped in a solution of ph = 3 at 25 C. The potential of the cell would be (the value of 2.33 RT/F is.59 V) 1).177 V 2).87 V 3).177 V 4).59 V Hint: R.P of Hydrogen electrode =.59 x P H 21. When 965 amp current is passed through aqueous solution of salt X using platinum electrodes for 1 sec, the volume of gasses liberated at the respective electrodes is in 1:1 ratio. Then X is 1) MgSO4 2) AgCl 3) MgCl2 4) KNO3 Hint: aqueous MgCl2 contains Mg +2,H +.Cl - and OH - ions.on electrolysis it gives H 2 at cathode and Cl 2 at anode. As same quantity of electricity is passed volumes of both are in the ratio 1:1
5 22. Three faradays of electricity are passed through molten Al23, aqueous solution of CuSO4 and molten NaCl taken in three different electrolytic cells. The amount of Al, Cu and Na deposited at the cathodes will be in the ratio of 1) 1 mole :2 mole :3 mole 2) 1 mole:1.5 mole :3 mole 3) 3 mole :2 mole :1 mole 4) 1 mole :1.5 mole :2 mole Hint; Three faradays will deposit three equivalents of each electrolyte. 23. Number of coulombs of current required to convert completely 1 mole of MnO 4 ions in acid medium in to Mn2+ ions is 1) 965 2) 5x965 3) 965x2 4) 965x6 Hint: in acid medium MnO e Mn2+ No. of electrons gained per ion = 5, Current required = 5F 24. How long will a current of 2 ampere take for complete deposition of copper from.5 litre of 1NCuSO4. Solution? 1) 965 sec 2) 2x965sec 3)4825 sec 4) sec Hint: no. of equivalents of Cu +2 =N X Vin lit=1x.5=.5. 1 Equivalent requires 1faraday i.e. 965 coulombs. Thus o.5 equivalents need 4825 coulombs. i.e. Q=c t or t=q/c=4825/2=24125 sec 25. The number of electrons required for deposition of one mole of copper on the cathode during the electrolysis of CuSO4 solution is 1) 6.x123 2) 1.2x124 3) 4.8x124 4) 3x123E Hint: 1 mole of Cu2+ requires 2F (or) 2 N e s i.e. 2X6X1 23 =12X1 23 =1.2X gm of a metal is deposited in 965 seconds by passing a current of 1 amperes through its respective electrolytic solution. The equivalent mass of metal is
6 1) 12 2) 24 3) 6 4) 6 Hint; m =Ect/F or E=mF/ct=1.2X965/965X1= On passing a current through a molten aluminium chloride for some time, produced 11.2lit of Cl2 at NTP at anode, the quantity of aluminium deposited at cathode is 1) 27grams 2) 18gram 3) 9gram 4) 36 gram Hint: W Al / W Cl2 = E Al / E Cl2, 11.2 lit Cl2 at STP = 35.5 gm = 1 GEW 1 GEW of Al will be deposited which is 9 gm 28. In the electrolysis of acidulated H2O, 11.2 litres of H2 is liberated at the cathode. The volume of O2 liberated at the anode is 1) 11.2 lit 2) 5.6 lit 3) 2.8lit 4) 22.4 lt Hint; 1 faraday gives 11.2 lit of H 2 or 5.6lit of O 2 at STP i.e 11.2 lit of H 2 = 5.6lit of O How much time is required for a current of 2 amp to decompose 18g of water 1) 965 hours 2) 965 hours 3) 26.8 hours 4) 2.68 hours Hint: for water, GEW=9gm. 9gm water decomposed by 965c 18gm water decomposed by 2X965c, t=q/c= 2X965/2=965sec=965/36=26.8hours 3. When electric current is passed through molten NaCl for 193 sec, 112 ml of Cl 2 is liberated at anode at STP. The current passed in amp is 1).5 2).5 3) 5 4) 5 Hint: i.e 965 coulombs=112ml of Cl ml of Cl 2 is give by 965 coulombs. C=Q/t=965/193=5
7 31. One faraday of electricity is passed separately through one litre of one molar aqueous solution of I) AgNO3, ii) SnCl4 and iii) CuSO4. The number of moles of Ag, Sn and Cu deposited at cathode are respectively 1) 1.,.25,.5 2) 1.,.5,.25 3).5, 1.,.25 4).25,.5, Hint: moles of Ag : Sn : Cu : : 1.,.25, A current of 2amps passing for 5 hours deposits 22.2g of tin (at.wt. = 119), the oxidation state of tin is 1) Zero 2) Three 3) Two 4) Four Hint; m=mct/zf Z=Mct/mF= 119X2X5x36/22, 2x965=1.999 ie; ampere current is passed for 6 seconds into an electrolytic cell. Number of electrons that pass through the solution is. 1) 6.x123 2) 1.2 x 124 3) 3.75 x 12 4) 7.48x121 Hint: 96,5C = 6.23 x 123 e s 6C =6X6.23 x 123 e s/965=3.75 x The STP volume of oxygen liberated by 2 ampere of current when passed through acidulated water for 3 minutes and 13 seconds, is 1) 12cc 2) 22.4cc 3) 11.2cc 4) 44.8 cc Hint: Q=ct=2X193=386coulombs. 965C liberates 56cc of oxygen. 386C liberates 386X56/96 5cc=22.4 of oxygen 35. Total volume of gases evolved at STP when 36g of H2O are completely electrolysed between platinum electrodes 1) 22.4lit 2) 44.8 lit3) 33.6lit 4) 67.2 lit Hint: 2H2O 2H2 + O2 i.e. 36gm of water gives 3 moles of gases. Total volume of gases evolved at STP =3 x 22.4 lit= 67.2 lit
8 36. For a cell the cell reaction is Mg(s) + Cu2+ (aq) Cu(s) + Mg2+(aq). If the S.R.P. values of Mg and Cu are 2.37v and +.34v respectively, the e.m.f. of the cell is 1) +2.3V 2) 2.3V 3) +2.71V 4) 2.71V Hint; E E E 2 2 Cell Sn / Sn Zn / Zn 37. The standard reduction potentials of Ag, Cu, Co and Zn are +.799,+.337,-.277 and-.762v respectively. Which of the following cells will have maximum cell e.m.f.? 1) 2 2 Zn Zn 1 M Cu 1 M Cu 2 2) Zn Zn 1 M Ag 1 M Ag 2 2 3) 1 1 Zn Zn M Co M Co 2 4) Cu Cu 1 M Ag 1 M Ag Hint: emf of the cell is maximum when cathode has highest and anode has lowest SRP values. 38. The standard reduction potentials at 298K for the following half cell reaction are given below: Zn2+ (aq) +2e Zn(s) E=.762 V Cr3+ (aq) +3e Cr(s) E= V 2H+ (aq) + 2e H2 (g) E=+. V Fe3+ (aq) +e Fe2+ (aq) E=+.77 V Which one is the strongest reducing agent? 1) Zn(s) 2) Cr(s) 3) H2 (g) 4) Fe +2 (aq) Hint: lower the SRP value higher is the reducing power
9 39. The standard reduction potential of three metals X, Y, Z are.52, 3.3 and 1.18V respectively. The order of reducing power of the corresponding metals is 1) Y > Z > X 2) X > Y > Z 3) Z > Y > X 4) Z > X > Y Hint: lower the SRP value higher is the reducing power 4. Given: 2 Fe 2 e Fe; E.44V 2 Pb 2 e Pb ; E.13V s 2 Cu 2 e Cu; E.34V Ag e Ag; E.8V Which of the following metals will oxidise iron? a) Ag b) Cu c) Pb d) None of these 1) Only a 2) a,b 3) a,b,c 4) Only b Hint: higher SRP metal oxidizes lower SRP metals.srp values of pb, Ag, Cu are higher than Fe. Pb, Ag, Cu oxidises the Fe 41. When electrons are used in the electrolysis of a metallic salt, 1.9 gm of the metal is deposited at the cathode. The atomic weight of that metal is 57. So oxidation state of the metal in the salt is 1) +2 2) +3 3) +1 4) +4 Hint; Z=Mct/mF 42. The electrochemical equivalent of an element is.1118 gm/coulomb. Its equivalent weight is 1) 1.7 2) ) ) 17 Hint; GEW= ex The charge required to reduce 1mole Cr2O 7 to Cr+3 ions is 1) 3F 2) 2F 3) 6F 4) 12F
10 Hint; Cr2O H + +6e 2Cr3+ +7 H 2 O No. of electrons gained per ion = 6 Charge required = 6F 44. One ampere of current is passed for 965seconds through molten AlCl3. What is the weight in grams of Al deposited at cathode? (Atomic weight of Al=27). 1).9 2) 2.7 3) 9 4) 27 Hint; m= Ect/F, for Al E=27/3=9, m=9x1x965/965=.9gm 45 The E M 3+ /M 2+ values for Cr, Mn, Fe and Co are.14, +1.57, +.77 and V respectively. For which one of these metals the change in oxidation state from +2 to +3 is easiest? 1) Cr 2) Co 3) Fe 4) Mn Hint: lower SRP metal is strong reducing agent i.e. easily oxidized. 46. The cell reaction of the galvanic cell, Cu(s) / Cu2+ (aq) // Hg2+ (aq) / Hg (l) is 1) Hg + Cu2+ Hg2+ + Cu 2) Hg + Cu2+ Hg+ + Cu+ 3) Hg + Cu+ CuHg 4) Cu + Hg2+ Cu2+ + Hg 47. (A): The Daniel cell becomes dead after some time. (R): Oxidation potential of zinc anode increases and that of copper cathode decreases. The correct answer is 1) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A. 2) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A. 3) A is true, but R is false. 4) Both A and R are false.
11 48. The reaction, 1/2H2 (g)+agcl(s) H+ (aq) +Cl (aq) + Ag(s) occurs in the galvanic cell : 1) Ag AgCl( s) KCl( aq) AgNO3( aq) Ag 2), 2( s) ( aq) 3( aq) Pt H HCl AgNO Ag 3), 2( g) ( aq) ( s) Pt H HCl AgCl Ag 4), 2( g) ( aq) ( s) Pt H KCl AgCl Ag 49. Which metal will dissolve if the cell works Cu Cu 1) Cu 2) Ag 3) Both (1) and (2) 4) None of these Hint: at anode metal is dissolved. 5. Given standard electrode potentials Fe3+ + 3e Fe; E =.36V Fe2+ + 2e Fe; E =.44V The standard electrode potential E for 2 Ag Fe3+ + e Fe2+ is 1).476V 2).44V 3).4V 4) +.772V Hint: required equations obtained by subtracting eq 2 from eq1. =3[-.36]-2[-.44]/1 =+.772V Ag E n E n E n 3
12 Key 1) 2 2) 3 3) 3 4) 3 5) 2 6) 2 7) 2 8) 3 9) 3 1) 2 11) 4 12)3 13) 1 14) 4 15)3 16)2 17)1 18)3 19)2 2)3 21) 3 22) 2 23) 2 24) 4 25) 2 26)1 27)3 28) ) 3 31)1 32) 3 33)3 34)2 35) 4 36)3 37)2 38)1 39)1 4)3 41)2 42)4 43)3 44)1 45)1 46)4 47)3 48)3 49)1 5)4
Solved Examples On Electrochemistry
 Solved Examples On Electrochemistry Example 1. Find the charge in coulomb on 1 g-ion of Charge on one ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 coulomb Thus, charge on one g-ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 6.02 10 23 = 2.89
Solved Examples On Electrochemistry Example 1. Find the charge in coulomb on 1 g-ion of Charge on one ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 coulomb Thus, charge on one g-ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 6.02 10 23 = 2.89
(i) Voltameter consist of a vessel, two electrodes and electrolytic solution.
 Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry which deals with the relationship between electrical energy and chemical changes taking place in redox reactions i.e., how chemical energy produced
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry which deals with the relationship between electrical energy and chemical changes taking place in redox reactions i.e., how chemical energy produced
CHEMISTRY 13 Electrochemistry Supplementary Problems
 1. When the redox equation CHEMISTRY 13 Electrochemistry Supplementary Problems MnO 4 (aq) + H + (aq) + H 3 AsO 3 (aq) Mn 2+ (aq) + H 3 AsO 4 (aq) + H 2 O(l) is properly balanced, the coefficients will
1. When the redox equation CHEMISTRY 13 Electrochemistry Supplementary Problems MnO 4 (aq) + H + (aq) + H 3 AsO 3 (aq) Mn 2+ (aq) + H 3 AsO 4 (aq) + H 2 O(l) is properly balanced, the coefficients will
Ch 11 Practice Problems
 Ch 11 Practice Problems 1. How many electrons are transferred in the following reaction? 2Cr 2O 7 2- + 14H + + 6Cl 2Cr 3+ + 3Cl 2 + 7H 2O A) 2 B) 4 C) 6 D) 8 2. Which metal, Al or Ni, could reduce Zn 2+
Ch 11 Practice Problems 1. How many electrons are transferred in the following reaction? 2Cr 2O 7 2- + 14H + + 6Cl 2Cr 3+ + 3Cl 2 + 7H 2O A) 2 B) 4 C) 6 D) 8 2. Which metal, Al or Ni, could reduce Zn 2+
Option 4 Standard hydrogen electrode Correct Answer 4 Explanation Standard hydrogen electrode
 Q. No. 1 Which of the following has been universally accepted as a reference electrode at all temperatures and has been assigned a value of zero volt? Platinum electrode Copper electrode Graphite electrode
Q. No. 1 Which of the following has been universally accepted as a reference electrode at all temperatures and has been assigned a value of zero volt? Platinum electrode Copper electrode Graphite electrode
AP Questions: Electrochemistry
 AP Questions: Electrochemistry I 2 + 2 S 2O 2-3 2 I - + S 4O 2-6 How many moles of I 2 was produced during the electrolysis? The hydrogen gas produced at the cathode during the electrolysis was collected
AP Questions: Electrochemistry I 2 + 2 S 2O 2-3 2 I - + S 4O 2-6 How many moles of I 2 was produced during the electrolysis? The hydrogen gas produced at the cathode during the electrolysis was collected
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry. Electrochemical Cells
 Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Chapter 18 1 Electrochemical Cells Electrochemical Cells are of two basic types: Galvanic Cells a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current Electrolytic Cells
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Chapter 18 1 Electrochemical Cells Electrochemical Cells are of two basic types: Galvanic Cells a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current Electrolytic Cells
A voltaic cell using the following reaction is in operation: 2 Ag + (lm) + Cd(s) 2 Ag(s) + Cd 2+ (l M)
 0. Cu (s) + 2Ag + Cu 2+ + 2Ag (s) If the equilibrium constant for the reaction above is 3.7x10 15, which of the following correctly describes the standard voltage, E o and the standard free energy change,
0. Cu (s) + 2Ag + Cu 2+ + 2Ag (s) If the equilibrium constant for the reaction above is 3.7x10 15, which of the following correctly describes the standard voltage, E o and the standard free energy change,
1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number
 General Chemistry II Exam 4 Practice Problems 1 1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number a. K 2 Cr 2 O 7 +6 b. NaAl(OH) 4 +3 c.
General Chemistry II Exam 4 Practice Problems 1 1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number a. K 2 Cr 2 O 7 +6 b. NaAl(OH) 4 +3 c.
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17
 Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
Electrochemistry. A. Na B. Ba C. S D. N E. Al. 2. What is the oxidation state of Xe in XeO 4? A +8 B +6 C +4 D +2 E 0
 Electrochemistry 1. Element M reacts with oxygen to from an oxide with the formula MO. When MO is dissolved in water, the resulting solution is basic. Element M is most likely: A. Na B. Ba C. S D. N E.
Electrochemistry 1. Element M reacts with oxygen to from an oxide with the formula MO. When MO is dissolved in water, the resulting solution is basic. Element M is most likely: A. Na B. Ba C. S D. N E.
Class 12 Important Questions for Chemistry Electrochemistry
 Class 12 Important Questions for Chemistry Electrochemistry Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Which cell will measure standard electrode potential of copper electrode? o (i) Pt (s) H2 (g,0.1 bar) H
Class 12 Important Questions for Chemistry Electrochemistry Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Which cell will measure standard electrode potential of copper electrode? o (i) Pt (s) H2 (g,0.1 bar) H
ELECTROCHEMISTRY OXIDATION-REDUCTION
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrochemistry involves the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy. OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SPONTANEOUS REACTIONS Can extract electrical energy from these.
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrochemistry involves the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy. OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SPONTANEOUS REACTIONS Can extract electrical energy from these.
(c) Na is deposited at the cathode (d) Na appears at the anode
 year chemiry n0tes new CHAPTER 10 ELECTROCHEMISTRY MCQS Q.1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy
year chemiry n0tes new CHAPTER 10 ELECTROCHEMISTRY MCQS Q.1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy
AP Chemistry: Electrochemistry Multiple Choice Answers
 AP Chemistry: Electrochemistry Multiple Choice Answers 14. Questions 14-17 The spontaneous reaction that occurs when the cell in the picture operates is as follows: 2Ag + + Cd (s) à 2 Ag (s) + Cd 2+ (A)
AP Chemistry: Electrochemistry Multiple Choice Answers 14. Questions 14-17 The spontaneous reaction that occurs when the cell in the picture operates is as follows: 2Ag + + Cd (s) à 2 Ag (s) + Cd 2+ (A)
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC TEXT REFERENCE. Electrochemistry. Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18. Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1
 Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
Redox reactions & electrochemistry
 Redox reactions & electrochemistry Electrochemistry Electrical energy ; Chemical energy oxidation/reduction = redox reactions Electrochemistry Zn + Cu 2+ º Zn 2+ + Cu Oxidation-reduction reactions always
Redox reactions & electrochemistry Electrochemistry Electrical energy ; Chemical energy oxidation/reduction = redox reactions Electrochemistry Zn + Cu 2+ º Zn 2+ + Cu Oxidation-reduction reactions always
Chemistry 102 Chapter 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS
 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS Some of the most important reaction in chemistry are oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. In these reactions, electrons transfer from one reactant to the other. The rusting
OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS Some of the most important reaction in chemistry are oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. In these reactions, electrons transfer from one reactant to the other. The rusting
(c) dilute solution of glucose (d) chloroform 12 Which one of the following represents the same net reaction as the electrolysis of aqueous H2SO4
 1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy (d) none of these 2 Standard hydrogen electrode has an
1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy (d) none of these 2 Standard hydrogen electrode has an
Guide to Chapter 18. Electrochemistry
 Guide to Chapter 18. Electrochemistry We will spend three lecture days on this chapter. During the first class meeting we will review oxidation and reduction. We will introduce balancing redox equations
Guide to Chapter 18. Electrochemistry We will spend three lecture days on this chapter. During the first class meeting we will review oxidation and reduction. We will introduce balancing redox equations
Chapter 20. Electrochemistry
 Chapter 20. Electrochemistry 20.1 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Oxidation-reduction reactions = chemical reactions in which the oxidation state of one or more substance changes (redox reactions). Recall:
Chapter 20. Electrochemistry 20.1 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Oxidation-reduction reactions = chemical reactions in which the oxidation state of one or more substance changes (redox reactions). Recall:
CHAPTER ELECTROCHEMISTRY
 149 CHAPTER ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. On electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid using platinum electrodes, the product obtained at the anode will be hydrogen oxygen hydrogen sulphide sulphur dioxide 2. Which
149 CHAPTER ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. On electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid using platinum electrodes, the product obtained at the anode will be hydrogen oxygen hydrogen sulphide sulphur dioxide 2. Which
CHAPTER 12. Practice exercises
 CHAPTER 12 Practice exercises 12.1 2Al(s) + 3Cl 2 (g) 2AlCl 3 (aq) Aluminium is oxidised and is therefore the reducing agent. Chlorine is reduced and is therefore the oxidising agent. 12.3 First the oxidation
CHAPTER 12 Practice exercises 12.1 2Al(s) + 3Cl 2 (g) 2AlCl 3 (aq) Aluminium is oxidised and is therefore the reducing agent. Chlorine is reduced and is therefore the oxidising agent. 12.3 First the oxidation
Electrochem: It s Got Potential!
 Electrochem: It s Got Potential! Presented by: Denise DeMartino Westlake High School, Eanes ISD Pre-AP, AP, and Advanced Placement are registered trademarks of the College Board, which was not involved
Electrochem: It s Got Potential! Presented by: Denise DeMartino Westlake High School, Eanes ISD Pre-AP, AP, and Advanced Placement are registered trademarks of the College Board, which was not involved
Electrochemistry (Galvanic and Electrolytic Cells) Exchange of energy in chemical cells
 Electrochemistry (Galvanic and Electrolytic Cells) Exchange of energy in chemical cells Oxidation loss of electrons (oxidation number increases) OIL RIG Reduction gain of electrons (oxidation number decreases)
Electrochemistry (Galvanic and Electrolytic Cells) Exchange of energy in chemical cells Oxidation loss of electrons (oxidation number increases) OIL RIG Reduction gain of electrons (oxidation number decreases)
CET Q UESTIONS QUESTIONS
 CET QUESTIONS ON ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance differs from 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance increases with increase of temperature 2. Electrolytic conductance increases
CET QUESTIONS ON ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance differs from 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance increases with increase of temperature 2. Electrolytic conductance increases
DO NOT USE A CALCULATOR.
 Practice Test 20.1 (va pg 1 of 5) This is practice - Do NOT cheat yourself of finding out what you are capable of doing. Be sure you follow the testing conditions outlined below. DO NOT USE A CALCULATOR.
Practice Test 20.1 (va pg 1 of 5) This is practice - Do NOT cheat yourself of finding out what you are capable of doing. Be sure you follow the testing conditions outlined below. DO NOT USE A CALCULATOR.
Practice Exam Topic 9: Oxidation & Reduction
 Name Practice Exam Topic 9: Oxidation & Reduction 1. What are the oxidation numbers of the elements in sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4? Hydrogen Sulfur Oxygen A. +1 +6 2 B. +1 +4 2 C. +2 +1 +4 D. +2 +6 8 2. Consider
Name Practice Exam Topic 9: Oxidation & Reduction 1. What are the oxidation numbers of the elements in sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4? Hydrogen Sulfur Oxygen A. +1 +6 2 B. +1 +4 2 C. +2 +1 +4 D. +2 +6 8 2. Consider
Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species.
 Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species. The species that loses the electron is oxidized. The species that gains the electron is reduced.
Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species. The species that loses the electron is oxidized. The species that gains the electron is reduced.
Unit - 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 3. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells of a galvanic cell?
 Unit - 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. What is a galvanic cell? VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 2. Give the cell representation for Daniell Cell. 3. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells
Unit - 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. What is a galvanic cell? VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 2. Give the cell representation for Daniell Cell. 3. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells
CHAPTER 5 REVIEW. C. CO 2 D. Fe 2 O 3. A. Fe B. CO
 CHAPTER 5 REVIEW 1. The following represents the process used to produce iron from iron III oxide: Fe 2 O 3 + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO 2 What is the reducing agent in this process? A. Fe B. CO C. CO 2 D. Fe 2 O 3
CHAPTER 5 REVIEW 1. The following represents the process used to produce iron from iron III oxide: Fe 2 O 3 + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO 2 What is the reducing agent in this process? A. Fe B. CO C. CO 2 D. Fe 2 O 3
Oxidation & Reduction (Redox) Notes
 Oxidation & Reduction (Redox) Notes Chemical Activity (or Chemical Reactivity) is the measure of the reactivity of elements. If an element has high activity, then it means that the element is willing to
Oxidation & Reduction (Redox) Notes Chemical Activity (or Chemical Reactivity) is the measure of the reactivity of elements. If an element has high activity, then it means that the element is willing to
CET Q UESTIONS QUESTIONS
 CET QUESTIONS ON ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance differs from 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance increases with increase of temperature 2. Electrolytic conductance increases
CET QUESTIONS ON ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance differs from 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance increases with increase of temperature 2. Electrolytic conductance increases
Oxidation-Reduction Review. Electrochemistry. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions. Sample Problem.
 1 Electrochemistry Oxidation-Reduction Review Topics Covered Oxidation-reduction reactions Balancing oxidationreduction equations Voltaic cells Cell EMF Spontaneity of redox reactions Batteries Electrolysis
1 Electrochemistry Oxidation-Reduction Review Topics Covered Oxidation-reduction reactions Balancing oxidationreduction equations Voltaic cells Cell EMF Spontaneity of redox reactions Batteries Electrolysis
CHEM N-12 November In the electrolytic production of Al, what mass of Al can be deposited in 2.00 hours by a current of 1.8 A?
 CHEM161 014-N-1 November 014 In the electrolytic production of Al, what mass of Al can be deposited in.00 hours by a current of 1.8 A? What products would you expect at the anode and the cathode on electrolysis
CHEM161 014-N-1 November 014 In the electrolytic production of Al, what mass of Al can be deposited in.00 hours by a current of 1.8 A? What products would you expect at the anode and the cathode on electrolysis
Dr. Anand Gupta
 By Dr Anand Gupta Mr. Mahesh Kapil Dr. Anand Gupta 09356511518 09888711209 anandu71@yahoo.com mkapil_foru@yahoo.com Electrochemistry Electrolysis Electric energy Chemical energy Galvanic cell 2 Electrochemistry
By Dr Anand Gupta Mr. Mahesh Kapil Dr. Anand Gupta 09356511518 09888711209 anandu71@yahoo.com mkapil_foru@yahoo.com Electrochemistry Electrolysis Electric energy Chemical energy Galvanic cell 2 Electrochemistry
We can use chemistry to generate electricity... this is termed a Voltaic (or sometimes) Galvanic Cell
 Unit 6 Electrochemistry Chemistry 020, R. R. Martin Electrochemistry Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy. We can use chemistry to generate electricity...
Unit 6 Electrochemistry Chemistry 020, R. R. Martin Electrochemistry Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy. We can use chemistry to generate electricity...
Electrochemistry Pearson Education, Inc. Mr. Matthew Totaro Legacy High School AP Chemistry
 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Mr. Matthew Totaro Legacy High School AP Chemistry Electricity from Chemistry Many chemical reactions involve the transfer of electrons between atoms or ions electron transfer
2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Mr. Matthew Totaro Legacy High School AP Chemistry Electricity from Chemistry Many chemical reactions involve the transfer of electrons between atoms or ions electron transfer
Chapter 18 problems (with solutions)
 Chapter 18 problems (with solutions) 1) Assign oxidation numbers for the following species (for review see section 9.4) a) H2SO3 H = +1 S = +4 O = -2 b) Ca(ClO3)2 Ca = +2 Cl = +5 O = -2 c) C2H4 C = -2
Chapter 18 problems (with solutions) 1) Assign oxidation numbers for the following species (for review see section 9.4) a) H2SO3 H = +1 S = +4 O = -2 b) Ca(ClO3)2 Ca = +2 Cl = +5 O = -2 c) C2H4 C = -2
Chapter 19: Redox & Electrochemistry
 Chapter 19: Redox & Electrochemistry 1. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Definitions Oxidation - refers to the of electrons by a molecule, atom or ion Reduction - refers to the of electrons by an molecule,
Chapter 19: Redox & Electrochemistry 1. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Definitions Oxidation - refers to the of electrons by a molecule, atom or ion Reduction - refers to the of electrons by an molecule,
Q1. Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution?
 Q1. Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution? A1. Conductivity of a solution is the conductance of ions present in a unit volume of the solution. On dilution the number of ions per
Q1. Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution? A1. Conductivity of a solution is the conductance of ions present in a unit volume of the solution. On dilution the number of ions per
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam of General Chemistry :ch.18-19 Name ID MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) When the following half-reaction is balanced, the number
Exam of General Chemistry :ch.18-19 Name ID MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) When the following half-reaction is balanced, the number
(for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes)
 www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) 1. chem10b 20.4-3 In a voltaic cell electrons flow from the anode to the cathode. Value 2. chem10b 20.1-35 How many grams
www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) 1. chem10b 20.4-3 In a voltaic cell electrons flow from the anode to the cathode. Value 2. chem10b 20.1-35 How many grams
CHEMISTRY CET ELEC ELE TROCHEMIS
 CHEMISTRY CET ELECTROCHEMISTRY LET US BRIEFLY DISCUSS WHAT WE STUDIED IN ELECTROCHEMISTRY CHAPTER BEFORE WE LOOK INTO C.E.T QUESTIONS. WHAT IS ELECTROCHEMISTRY? IT IS A BRANCH OF CHEMISTRY WHICH DEALS
CHEMISTRY CET ELECTROCHEMISTRY LET US BRIEFLY DISCUSS WHAT WE STUDIED IN ELECTROCHEMISTRY CHAPTER BEFORE WE LOOK INTO C.E.T QUESTIONS. WHAT IS ELECTROCHEMISTRY? IT IS A BRANCH OF CHEMISTRY WHICH DEALS
IB Topics 9 & 19 Multiple Choice Practice
 IB Topics 9 & 19 Multiple Choice Practice 1. What are the oxidation states of chromium in (NH 4) 2Cr 2O 7 (s) and Cr 2O 3 (s)? 2. Which of the following is a redox reaction? 3Mg (s) + 2AlCl 3 (aq) 2Al
IB Topics 9 & 19 Multiple Choice Practice 1. What are the oxidation states of chromium in (NH 4) 2Cr 2O 7 (s) and Cr 2O 3 (s)? 2. Which of the following is a redox reaction? 3Mg (s) + 2AlCl 3 (aq) 2Al
Redox and Electrochemistry
 Redox and Electrochemistry 1 Electrochemistry in Action! 2 Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers The oxidation number of any uncombined element is 0. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the
Redox and Electrochemistry 1 Electrochemistry in Action! 2 Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers The oxidation number of any uncombined element is 0. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the
18.3 Electrolysis. Dr. Fred Omega Garces. Chemistry 201. Driving a non-spontaneous Oxidation-Reduction Reaction. Miramar College.
 18.3 Electrolysis Driving a non-spontaneous Oxidation-Reduction Reaction Dr. Fred Omega Garces Chemistry 201 Miramar College 1 Electrolysis Voltaic Vs. Electrolytic Cells Voltaic Cell Energy is released
18.3 Electrolysis Driving a non-spontaneous Oxidation-Reduction Reaction Dr. Fred Omega Garces Chemistry 201 Miramar College 1 Electrolysis Voltaic Vs. Electrolytic Cells Voltaic Cell Energy is released
Electrochemical Reactions
 1 of 20 4/11/2016 1:00 PM Electrochemical Reactions Electrochemical Reactions Electrical Work From Spontaneous Oxidation- Reduction Reactions Predicting Spontaneous Redox Reactions from the Sign of E Line
1 of 20 4/11/2016 1:00 PM Electrochemical Reactions Electrochemical Reactions Electrical Work From Spontaneous Oxidation- Reduction Reactions Predicting Spontaneous Redox Reactions from the Sign of E Line
Electrochemistry : Electrochemistry is a branch of science which deals with the production of electricity from energy released during spontaneous
 Electrochemistry : Electrochemistry is a branch of science which deals with the production of electricity from energy released during spontaneous chemical reactions and the use of electric energy to bring
Electrochemistry : Electrochemistry is a branch of science which deals with the production of electricity from energy released during spontaneous chemical reactions and the use of electric energy to bring
Ch : Electrochemistry and Radiochemistry AP Review Questions
 Ch. 17-21: Electrochemistry and Radiochemistry AP Review Questions Radioactivity: Zone of Stability All nuclides with 84 or more protons are unstable (radioactive). Light elements like the neutron to proton
Ch. 17-21: Electrochemistry and Radiochemistry AP Review Questions Radioactivity: Zone of Stability All nuclides with 84 or more protons are unstable (radioactive). Light elements like the neutron to proton
 CHAPTER 10 ELECTROCHEMISTRY TEXT BOOK EXERCISE Q1. Multiple choice questions. (i) The cathode reaction in the electrolysis of dill. H2SO4 with Pt electrode is (a) Reduction (b) Oxidation (c) Both oxidation
CHAPTER 10 ELECTROCHEMISTRY TEXT BOOK EXERCISE Q1. Multiple choice questions. (i) The cathode reaction in the electrolysis of dill. H2SO4 with Pt electrode is (a) Reduction (b) Oxidation (c) Both oxidation
Electrochemistry. 1. Determine the oxidation states of each element in the following compounds. (Reference: Ex. 4:16) a. N 2 N: b.
 Name: Electrochemistry Two of the most common types of chemical reactions are acid-base reactions in which protons are transferred between two reactants and oxidation-reduction reactions in which electrons
Name: Electrochemistry Two of the most common types of chemical reactions are acid-base reactions in which protons are transferred between two reactants and oxidation-reduction reactions in which electrons
Electrolysis and Faraday's laws of Electrolysis
 Electrolysis and Faraday's laws of Electrolysis Electrolysis is defined as the passage of an electric current through an electrolyte with subsequent migration of positively and negatively charged ions
Electrolysis and Faraday's laws of Electrolysis Electrolysis is defined as the passage of an electric current through an electrolyte with subsequent migration of positively and negatively charged ions
Electrochemical Cells
 Electrochemical Cells There are two types: Galvanic and Electrolytic Galvanic Cell: a cell in which a is used to produce electrical energy, i.e., Chemical energy is transformed into Electrical energy.
Electrochemical Cells There are two types: Galvanic and Electrolytic Galvanic Cell: a cell in which a is used to produce electrical energy, i.e., Chemical energy is transformed into Electrical energy.
Electrochemical Cells
 Electrochemistry Electrochemical Cells The Voltaic Cell Electrochemical Cell = device that generates electricity through redox rxns 1 Voltaic (Galvanic) Cell An electrochemical cell that produces an electrical
Electrochemistry Electrochemical Cells The Voltaic Cell Electrochemical Cell = device that generates electricity through redox rxns 1 Voltaic (Galvanic) Cell An electrochemical cell that produces an electrical
Chapter 18. Electrochemistry
 Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 http://www.bozemanscience.com/ap-chemistry/ Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 http://www.bozemanscience.com/ap-chemistry/ Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes
Chapter 19 ElectroChemistry
 Chem 1046 General Chemistry by Ebbing and Gammon, 9th Edition George W.J. Kenney, Jr, Professor of Chemistry Last Update: 11July2009 Chapter 19 ElectroChemistry These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text,
Chem 1046 General Chemistry by Ebbing and Gammon, 9th Edition George W.J. Kenney, Jr, Professor of Chemistry Last Update: 11July2009 Chapter 19 ElectroChemistry These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text,
1.11 Electrochemistry
 1.11 Electrochemistry Recap from 1.7: Oxidation and Reduction: Oxidation and Reduction: Oxidation and reduction reactions can be identified by looking at the reaction in terms of electron transfer: Definitions:
1.11 Electrochemistry Recap from 1.7: Oxidation and Reduction: Oxidation and Reduction: Oxidation and reduction reactions can be identified by looking at the reaction in terms of electron transfer: Definitions:
mccord (pmccord) HW11 Electrochemistry I mccord (51520) 1
 mccord (pmccord) HW11 Electrochemistry I mccord (51520) 1 This print-out should have 27 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. 001
mccord (pmccord) HW11 Electrochemistry I mccord (51520) 1 This print-out should have 27 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. 001
ELECTROCHEMISTRY. these are systems involving oxidation or reduction there are several types METALS IN CONTACT WITH SOLUTIONS OF THEIR IONS
 Electrochemistry 1 ELECTROCHEMISTRY REDOX Reduction gain of electrons Cu 2+ (aq) + 2e > Cu(s) Oxidation removal of electrons Zn(s) > Zn 2+ (aq) + 2e HALF CELLS these are systems involving oxidation or
Electrochemistry 1 ELECTROCHEMISTRY REDOX Reduction gain of electrons Cu 2+ (aq) + 2e > Cu(s) Oxidation removal of electrons Zn(s) > Zn 2+ (aq) + 2e HALF CELLS these are systems involving oxidation or
Electrolytes non electrolytes. Types of Electrolytes
 Electrochemistry Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred between molecules are called oxidation/reduction (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry deals with situations where oxidation
Electrochemistry Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred between molecules are called oxidation/reduction (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry deals with situations where oxidation
CHEMISTRY 102 EXAM 4 FORM 4D
 CHEMISTRY 102 EXAM 4 SECTIONS 529-537 Dr. Joy Heising Directions: FORM 4D April 22, 2002 1. This examination consists of two parts: 12 multiple choice questions (5 points each) in Part 1 and 3 free response
CHEMISTRY 102 EXAM 4 SECTIONS 529-537 Dr. Joy Heising Directions: FORM 4D April 22, 2002 1. This examination consists of two parts: 12 multiple choice questions (5 points each) in Part 1 and 3 free response
Electrochemistry. Slide 1 / 144. Slide 2 / 144. Slide 3 / 144. Electrochemistry. Electrochemical Reactions
 Slide 1 / 144 Electrochemistry Electrochemistry Slide 2 / 144 Electrochemistry deals with relationships between reactions and electricity In electrochemical reactions, electrons are transferred from one
Slide 1 / 144 Electrochemistry Electrochemistry Slide 2 / 144 Electrochemistry deals with relationships between reactions and electricity In electrochemical reactions, electrons are transferred from one
ELECTROCHEMISTRY. these are systems involving oxidation or reduction there are several types METALS IN CONTACT WITH SOLUTIONS OF THEIR IONS
 Electrochemistry 1 ELECTROCHEMISTRY REDOX Reduction gain of electrons Cu 2+ (aq) + 2e > Cu(s) Oxidation removal of electrons Zn(s) > Zn 2+ (aq) + 2e HALF CELLS these are systems involving oxidation or
Electrochemistry 1 ELECTROCHEMISTRY REDOX Reduction gain of electrons Cu 2+ (aq) + 2e > Cu(s) Oxidation removal of electrons Zn(s) > Zn 2+ (aq) + 2e HALF CELLS these are systems involving oxidation or
UNIT 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY
 95414101 UNIT 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1 MARK QUESTIONS Q. 1. Which solution will allow greater conductance of electricity, 1 M NaCl at 93 K or 1 M NaCl at 33 K and why? Ans. 1 M NaCl at 33 K as the ionic mobilities
95414101 UNIT 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1 MARK QUESTIONS Q. 1. Which solution will allow greater conductance of electricity, 1 M NaCl at 93 K or 1 M NaCl at 33 K and why? Ans. 1 M NaCl at 33 K as the ionic mobilities
Date Topics Problems Video(s) Due One Review tests, introduce red-ox, identify oxidizing and reducing agents
 Chapter 20: Electrochemistry. Tentative Schedule Date Topics Problems Video(s) Due One Review tests, introduce redox, identify oxidizing and reducing agents Oxidation numbers / oxidizing and reducing agents
Chapter 20: Electrochemistry. Tentative Schedule Date Topics Problems Video(s) Due One Review tests, introduce redox, identify oxidizing and reducing agents Oxidation numbers / oxidizing and reducing agents
UNIT-3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY CONCEPTS
 UNIT-3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY CONCEPTS Electrochemistry may be defined as the branch of chemistry which deals with the quantitative study of interrelation ship between chemical energy and electrical energy and
UNIT-3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY CONCEPTS Electrochemistry may be defined as the branch of chemistry which deals with the quantitative study of interrelation ship between chemical energy and electrical energy and
ELECTROCHEMISTRY (SUMMER VACATION WORKSHEET)
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY (SUMMER VACATION WORKSHEET) QUESTION CARRYING 1 MARK 1. What is the effect of temperature on molar conductivity? 2. Why is it not possible to measure single electrode potential? 3. Name
ELECTROCHEMISTRY (SUMMER VACATION WORKSHEET) QUESTION CARRYING 1 MARK 1. What is the effect of temperature on molar conductivity? 2. Why is it not possible to measure single electrode potential? 3. Name
CHEM 1423 Chapter 21 Homework Questions TEXTBOOK HOMEWORK
 CHEM 1423 Chapter 21 Homework Questions TEXTBOOK HOMEWORK 21.5 Consider the following balanced redox reaction: 16 H + (aq) + 2 MnO 4- (aq) + 10 Cl - (aq) 2 Mn 2+ (aq) + 5 Cl 2 (g) + 8 H 2 O(l) (a) Which
CHEM 1423 Chapter 21 Homework Questions TEXTBOOK HOMEWORK 21.5 Consider the following balanced redox reaction: 16 H + (aq) + 2 MnO 4- (aq) + 10 Cl - (aq) 2 Mn 2+ (aq) + 5 Cl 2 (g) + 8 H 2 O(l) (a) Which
Chapter 20. Electrochemistry Recommendation: Review Sec. 4.4 (oxidation-reduction reactions) in your textbook
 Chapter 20. Electrochemistry Recommendation: Review Sec. 4.4 (oxidation-reduction reactions) in your textbook 20.1 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Oxidation-reduction reactions = chemical reactions in which
Chapter 20. Electrochemistry Recommendation: Review Sec. 4.4 (oxidation-reduction reactions) in your textbook 20.1 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Oxidation-reduction reactions = chemical reactions in which
Regents review Electrochemistry(redox)
 2011-2012 1. Chlorine has an oxidation state of +3 in the compound A) HClO B) HClO2 C) HClO3 D) HClO4 2. What is the oxidation number of iodine in KIO4? A) +1 B) 1 C) +7 D) 7 3. What is the oxidation number
2011-2012 1. Chlorine has an oxidation state of +3 in the compound A) HClO B) HClO2 C) HClO3 D) HClO4 2. What is the oxidation number of iodine in KIO4? A) +1 B) 1 C) +7 D) 7 3. What is the oxidation number
Chemistry 112 Name Exam III Form A Section April 2,
 Chemistry 112 Name Exam III Form A Section April 2, 2013 email IMPORTANT: On the scantron (answer sheet), you MUST clearly fill your name, your student number, section number, and test form (white cover
Chemistry 112 Name Exam III Form A Section April 2, 2013 email IMPORTANT: On the scantron (answer sheet), you MUST clearly fill your name, your student number, section number, and test form (white cover
Chemistry. Electrochemistry.
 Chemistry Electrochemistry www.testprepkart.com Table of Content 1. Electrolytes and Electrolysis.. Faraday s laws of electrolysis. 3. Metallic and Electrolytic conductors. 4. Electrolytic conduction.
Chemistry Electrochemistry www.testprepkart.com Table of Content 1. Electrolytes and Electrolysis.. Faraday s laws of electrolysis. 3. Metallic and Electrolytic conductors. 4. Electrolytic conduction.
Faraday s Law. Current (Amperes)
 Faraday s Law How can one predict the amount of product made in an electrolytic reaction? Why? In an electrolytic reaction, an electrical current is used to run a nonspontaneous redox reaction. This might
Faraday s Law How can one predict the amount of product made in an electrolytic reaction? Why? In an electrolytic reaction, an electrical current is used to run a nonspontaneous redox reaction. This might
Part One: Introduction. a. Chemical reactions produced by electric current. (electrolysis)
 CHAPTER 19: ELECTROCHEMISTRY Part One: Introduction A. Terminology. 1. Electrochemistry deals with: a. Chemical reactions produced by electric current. (electrolysis) b. Production of electric current
CHAPTER 19: ELECTROCHEMISTRY Part One: Introduction A. Terminology. 1. Electrochemistry deals with: a. Chemical reactions produced by electric current. (electrolysis) b. Production of electric current
3. Solids cannot conduct electricity because the ions cannot move freely 4. Electrolytic cell
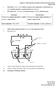 Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
Homework 11. Electrochemical Potential, Free Energy, and Applications
 HW11 Electrochemical Poten!al, Free Energy, and Applica!ons Homework 11 Electrochemical Potential, Free Energy, and Applications Question 1 What is the E for Zn(s) Zn (aq) Ce (aq) Ce (aq) + cell + 4+ 3+
HW11 Electrochemical Poten!al, Free Energy, and Applica!ons Homework 11 Electrochemical Potential, Free Energy, and Applications Question 1 What is the E for Zn(s) Zn (aq) Ce (aq) Ce (aq) + cell + 4+ 3+
Page 1 Name: 2Al 3+ (aq) + 3Mg(s) 3Mg 2+ (aq) + 2Al(s) Fe 2 O 3 + 2Al Al 2 O 3 + 2Fe
 9666-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) What is the oxidation number of chromium in the chromate ion, CrO 2-4? A) +8 B) +3 C) +2 D) +6 2) What is the oxidation number of sulfur in Na 2 S 2 O 3? A) +6 B) +4 C) +2 D) -1
9666-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) What is the oxidation number of chromium in the chromate ion, CrO 2-4? A) +8 B) +3 C) +2 D) +6 2) What is the oxidation number of sulfur in Na 2 S 2 O 3? A) +6 B) +4 C) +2 D) -1
Chemistry 12. Resource Exam B. Exam Booklet
 Chemistry 12 Resource Exam B Exam Booklet Contents: 21 pages Examination: 2 hours 50 multiple-choice questions in the Exam Booklet Additional Time Permitted: 60 minutes Province of British Columbia PART
Chemistry 12 Resource Exam B Exam Booklet Contents: 21 pages Examination: 2 hours 50 multiple-choice questions in the Exam Booklet Additional Time Permitted: 60 minutes Province of British Columbia PART
Chapter 20. Electrochemistry
 Chapter 20. Electrochemistry 20.1 OxidationReduction Reactions Oxidationreduction reactions = chemical reactions in which the oxidation state of one or more substance changes (redox reactions). Recall:
Chapter 20. Electrochemistry 20.1 OxidationReduction Reactions Oxidationreduction reactions = chemical reactions in which the oxidation state of one or more substance changes (redox reactions). Recall:
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 A.P. Chemistry Practice Test - Ch. 17: Electochemistry MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The gain of electrons by an element is called.
A.P. Chemistry Practice Test - Ch. 17: Electochemistry MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The gain of electrons by an element is called.
Study Guide for Module 17 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions and Electrochemistry
 Chemistry 1020, Module 17 Name Study Guide for Module 17 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions and Electrochemistry Reading Assignment: Chapter 17 in Chemistry, 6th Edition by Zumdahl. Guide for Your Lecturer:
Chemistry 1020, Module 17 Name Study Guide for Module 17 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions and Electrochemistry Reading Assignment: Chapter 17 in Chemistry, 6th Edition by Zumdahl. Guide for Your Lecturer:
Chapter 20. Electrochemistry
 Chapter 20. Electrochemistry Sample Exercise 20.1 (p. 845) The nickelcadmium (nicad) battery, a rechargeable dry cell used in batteryoperated devices, uses the following redox reaction to generate electricity:
Chapter 20. Electrochemistry Sample Exercise 20.1 (p. 845) The nickelcadmium (nicad) battery, a rechargeable dry cell used in batteryoperated devices, uses the following redox reaction to generate electricity:
Standard reduction potentials are established by comparison to the potential of which half reaction?
 HW10 Electrochemical Poten al, Free Energy, and Applica ons This is a preview of the draft version of the quiz Started: Nov 8 at 5:51pm Quiz Instruc ons Question 1 What is the E for cell + 4+ 3+ Zn(s)
HW10 Electrochemical Poten al, Free Energy, and Applica ons This is a preview of the draft version of the quiz Started: Nov 8 at 5:51pm Quiz Instruc ons Question 1 What is the E for cell + 4+ 3+ Zn(s)
Electrochemistry Pulling the Plug on the Power Grid
 Electrochemistry 18.1 Pulling the Plug on the Power Grid 18.3 Voltaic (or Galvanic) Cells: Generating Electricity from Spontaneous Chemical Reactions 18.4 Standard Electrode Potentials 18.7 Batteries:
Electrochemistry 18.1 Pulling the Plug on the Power Grid 18.3 Voltaic (or Galvanic) Cells: Generating Electricity from Spontaneous Chemical Reactions 18.4 Standard Electrode Potentials 18.7 Batteries:
Chemistry 201: General Chemistry II - Lecture
 Name Date Chemistry 201: General Chemistry II - Lecture Short-Answer Exam #3, 70 Points Total Form: A Read all directions carefully. Answers not conforming to the directions will be marked as incorrect!
Name Date Chemistry 201: General Chemistry II - Lecture Short-Answer Exam #3, 70 Points Total Form: A Read all directions carefully. Answers not conforming to the directions will be marked as incorrect!
REDUCTION - OXIDATION TITRATION REDOX TITRATION
 References REDUCTION OXIDATION TITRATION REDOX TITRATION 1 Fundamentals of analytical chemistry, Skoog. 2 Analytical chemistry, Gary D. Christian. الكيمياء التحليلية الجامعية تأليف د.هادي حسن جاسم 3 Oxidation
References REDUCTION OXIDATION TITRATION REDOX TITRATION 1 Fundamentals of analytical chemistry, Skoog. 2 Analytical chemistry, Gary D. Christian. الكيمياء التحليلية الجامعية تأليف د.هادي حسن جاسم 3 Oxidation
Module-1: Electrode Potential And Cells 2015
 Lecture-2 Standard Electrode potential Standard electrode potential is the electrode potential when the metal is in contact with a solution of its own ions of unit concentration (1M) at 298K. If the electrode
Lecture-2 Standard Electrode potential Standard electrode potential is the electrode potential when the metal is in contact with a solution of its own ions of unit concentration (1M) at 298K. If the electrode
Electrochemistry. Outline
 Electrochemistry Outline 1. Oxidation Numbers 2. Voltaic Cells 3. Calculating emf or Standard Cell Potential using Half-Reactions 4. Relationships to Thermo, Equilibrium, and Q 5. Stoichiometry 6. Balancing
Electrochemistry Outline 1. Oxidation Numbers 2. Voltaic Cells 3. Calculating emf or Standard Cell Potential using Half-Reactions 4. Relationships to Thermo, Equilibrium, and Q 5. Stoichiometry 6. Balancing
 Electrochem 1 Electrochemistry Some Key Topics Conduction metallic electrolytic Electrolysis effect and stoichiometry Galvanic cell Electrolytic cell Electromotive Force (potential in volts) Electrode
Electrochem 1 Electrochemistry Some Key Topics Conduction metallic electrolytic Electrolysis effect and stoichiometry Galvanic cell Electrolytic cell Electromotive Force (potential in volts) Electrode
Electrochemistry C020. Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy
 Electrochemistry C020 Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy Using chemistry to generate electricity involves using a Voltaic Cell or Galvanic Cell (battery)
Electrochemistry C020 Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy Using chemistry to generate electricity involves using a Voltaic Cell or Galvanic Cell (battery)
Section A: Summary Notes
 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS 25 AUGUST 2015 Section A: Summary Notes Important definitions: Oxidation: the loss of electrons by a substance during a chemical reaction Reduction: the gain of electrons by a substance
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS 25 AUGUST 2015 Section A: Summary Notes Important definitions: Oxidation: the loss of electrons by a substance during a chemical reaction Reduction: the gain of electrons by a substance
Ch 18 Electrochemistry OIL-RIG Reactions
 Ch 18 Electrochemistry OIL-RIG Reactions Alessandro Volta s Invention Modified by Dr. Cheng-Yu Lai Daily Electrochemistry Appliactions Electrochemistry: The area of chemistry that examines the transformations
Ch 18 Electrochemistry OIL-RIG Reactions Alessandro Volta s Invention Modified by Dr. Cheng-Yu Lai Daily Electrochemistry Appliactions Electrochemistry: The area of chemistry that examines the transformations
Unit 8 Redox 8-1. At the end of this unit, you ll be able to
 8-1 Unit 8 Redox At the end of this unit, you ll be able to Define and identify oxidation reactions Define and identify reduction reactions Assign oxidation numbers to elements in a compound Write and
8-1 Unit 8 Redox At the end of this unit, you ll be able to Define and identify oxidation reactions Define and identify reduction reactions Assign oxidation numbers to elements in a compound Write and
Electrical Conduction. Electrical conduction is the flow of electric charge produced by the movement of electrons in a conductor. I = Q/t.
 Electrical Conduction e- in wire e- out Electrical conduction is the flow of electric charge produced by the movement of electrons in a conductor. The rate of electron flow (called the current, I, in amperes)
Electrical Conduction e- in wire e- out Electrical conduction is the flow of electric charge produced by the movement of electrons in a conductor. The rate of electron flow (called the current, I, in amperes)
Electrochemistry. Galvanic Cell. Page 1. Applications of Redox
 Electrochemistry Applications of Redox Review Oxidation reduction reactions involve a transfer of electrons. OIL- RIG Oxidation Involves Loss Reduction Involves Gain LEO-GER Lose Electrons Oxidation Gain
Electrochemistry Applications of Redox Review Oxidation reduction reactions involve a transfer of electrons. OIL- RIG Oxidation Involves Loss Reduction Involves Gain LEO-GER Lose Electrons Oxidation Gain
Oxidation Numbers, ox #
 Oxidation Numbers, ox # are or numbers assigned to each or assuming that the are transferred from the electronegative element to the electronegative element. now mimic systems. ox # are written followed
Oxidation Numbers, ox # are or numbers assigned to each or assuming that the are transferred from the electronegative element to the electronegative element. now mimic systems. ox # are written followed
ELECTROCHEMISTRY. Electrons are transferred from Al to Cu 2+. We can re write this equation as two separate half reactions:
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY A. INTRODUCTION 1. Electrochemistry is the branch of chemistry which is concerned with the conversion of chemical energy to electrical energy, and vice versa. Electrochemical reactions
ELECTROCHEMISTRY A. INTRODUCTION 1. Electrochemistry is the branch of chemistry which is concerned with the conversion of chemical energy to electrical energy, and vice versa. Electrochemical reactions
SHOCK TO THE SYSTEM! ELECTROCHEMISTRY
 SHOCK TO THE SYSTEM! ELECTROCHEMISTRY REVIEW I. Re: Balancing Redox Reactions. A. Every redox reaction requires a substance to be... 1. oxidized (loses electrons). a.k.a. reducing agent 2. reduced (gains
SHOCK TO THE SYSTEM! ELECTROCHEMISTRY REVIEW I. Re: Balancing Redox Reactions. A. Every redox reaction requires a substance to be... 1. oxidized (loses electrons). a.k.a. reducing agent 2. reduced (gains
Chapter 19: Oxidation - Reduction Reactions
 Chapter 19: Oxidation - Reduction Reactions 19-1 Oxidation and Reduction I. Oxidation States A. The oxidation rules (as summarized by Mr. Allan) 1. In compounds, hydrogen has an oxidation # of +1. In compounds,
Chapter 19: Oxidation - Reduction Reactions 19-1 Oxidation and Reduction I. Oxidation States A. The oxidation rules (as summarized by Mr. Allan) 1. In compounds, hydrogen has an oxidation # of +1. In compounds,
