Research Paper. (1+cos θ)= +
|
|
|
- Adele Bridges
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Research Paper The Utilization of Surface Free Energy for Predicting Flowability of Filler-lubricant or Filler-glidant Mixtures P. TONGLAIROUM, T. NGAWHIRUNPAT, T. ROJANARATA, P. AKKARAMONGKOLPORN, N. NATTAPULWAT 1* AND P. OPANASOPIT* Pharmaceutical Development of Green Innovations Group (PDGIG), Faculty of Pharmacy, 1 Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Silpakorn University, Nakhon Pathom 73000, Thailand Tonglairoum, et al.: Surface Free Energy for Predicting Flowability of Binary Mixtures The aim of this study was to apply the knowledge of surface free energy for the flowability prediction of pharmaceutical excipients. In order to predict the flowability, the spreading coefficient was calculated from the surface free energy of each material using Wu's equation. The resulting spreading coefficient could indicate which material would spread over another in a binary mixture. In this study, the binary mixture consisted of filler (lactose, or dibasic calcium phosphate) and a lubricant (magnesium stearate), talc or silicon dioxide. The flowability of each binary mixture was assessed using angle of repose and compressibility index data. Finally, the resulting spreading behaviour was compared with flowability parameters. The calculated spreading coefficient values revealed that magnesium stearate, talc and silicon dioxide would spread over the surface of lactose and dibasic calcium phosphate. The evaluated flowability from the two methods found that all of the lubricants could improve the flowability of the binary mixtures. Moreover, these results were in accordance with predictions. In conclusion, the spreading coefficient could be a suitable tool for predicting the flowability of powder mixtures. Key words: Surface free energy, tablets, flowability, filler-lubricant mixtures, filler-glidant mixtures In the design of pharmaceutical formulations, an understanding of the surface free energy of pharmaceutical solids is essential [1-3]. This knowledge can support the selection of the excipient used in the formulation when interfacial interactions and compatibility of the formulation components have been established [4]. Previous studies have reported applications of surface free energy and spreading coefficient in the selection of suitable excipients for drug formulation [5], the formation of pellets from 1 to 2 component powder compositions [5] and an investigation of the mucoadhesion of polycarbophil and pig intestinal mucosa [6]. Surface free energy (γ) is an essential physicochemical property of a solid. The technique for calculating the surface free energy from wettability measurements is extensively used [7-9]. Wu and Brzozowski [10] described the surface free energy obtained as the sum of the dispersive and the polar (p) components. The surface free energies of solid materials can be determined using a technique of contact angle measurements, using two liquids with known polarities. They can be calculated according to Eqn. 1. *Address for correspondence opanasopit_p@su.ac.th; nattapulwat_n@su.ac.th d d P P ( γγ s 1) ( γγ s 1 ) 4 4 (1+cos θ)= + γ + γ γ + γ d d P P s 1 s 1 Where, γ s d is the surface free energy of the dispersive component of the solids, γ 1 d is the surface tension of the dispersive component of the liquids, γ s p is the surface free energy of the polar component of the solids, γ 1 p is the surface tension of the polar component of the liquids and θ is the contact angle. After obtaining the surface free energies values, the spreading coefficient can be calculated and the interaction between the two substances may be predicted. Spreading coefficient is defined as the difference between the adhesion work and the cohesion work. The spreading coefficient (S12) of a substance (1) over the surface of another substance (2) can be established according to Eqn. 2 [3,11]. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms Accepted 16 December 2016 Revised 25 October 2016 Received 14 June 2016 Indian J Pharm Sci 2016;78(6): November-December 2016 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 834
2 d d P P γ1ã2 γγ 1 2 γ 1 S12=4 + - d d P P γ1+ γ2 γ1+ γ2 2 Where, S is the spreading coefficient of the liquid over the substrate, γ is the surface free energy, γ p is the polar component and γ d is the dispersive component. Ahfat et al. [12] reported the successful use of surface energy data to predict the adhesion of a binary system onto a third component. The results revealed that there is good correlation between theoretical data and visual observations; spreading coefficients for solid-solid interactions provide good predictions of macroscopic events such as powder mixing. To the best of our knowledge, the use of surface energy data to predict the flowability of drug formulations has not been previously reported. In the present study, the information from the surface free energy and the spreading coefficient was used for the prediction of the flowability of filler-lubricant mixtures. Spreading coefficients (S12 and S21) were calculated from the surface free energy of each material using Wu s equation. The resulting spreading coefficient could indicate which material would spread over the other in the binary mixture and the results were compared with the flowability values obtained from angle of repose and compressibility index from the experiment. MATERIALS AND METHODS The model substances used as received were magnesium stearate (MGST; Glaxo welcome, UK), Talc (HCP, China), colloidal silicon dioxide (SiO 2 ; Evonik industries, Germany), dibasic calcium phosphate (DCP; Budenheim, Germany) and lactose (Carter Holt Harvey, New Zealand), talc or talcum (Talc power-magnesium oxide mining, China). The rest of the chemicals used were of analytical grade. Contact angle measurement on flat surface of the powders: Contact angle measurement was performed using the Wilhelmy plate method which was partially modified from the system used by Afhat et al. [12] Briefly, the powders were stuck to a glass cover slip (26 22 mm) using double-sided adhesive tape. Non-adhering powder was removed by brushing. The contact angles of two different liquids (water and formamide) on the surface of the powders were determined using a drop shape analyser after placing a small drop of each liquid (10 µl) on the surface of each powder using a micropipette. All contact angle measurements were carried out at room temperature. The average of 5 measurements was used for further calculations. The surface free energy and spreading coefficient were calculated according to Eqns. 1 and 2, respectively, using FTA32 software. Preparation of filler-lubricant or filler-glidant mixtures: Powder mixing was performed using a cube mixer (Model PA1540, Yeo Heng factory). The fillers and lubricants or glidants were mixed in various ratios. The compositions of the prepared mixtures are shown in Table 1. The amount of mixture was 120 g and the mixing process was performed for 10 min. Angle of repose: The angle of repose measurements of each filler powder, lubricant powder, glidant powder and the binary mixtures were carried out using a fixed funnel method. Briefly, the material was poured through a funnel to form a cone. The tip of the funnel was held close to the growing cone and slowly raised as the pile grew. The height and width of the cone were measured. The angle TABLE 1: FILLER TO LUBRICANT RATIOS Substance Filler to lubricant ratio Lactose:MGST 99.75: : : :5.00 Lactose:Talc 99.00: : : :10.00 Lactose:SiO : : : :1.00 DCP:MGST 99.75: : : :5.00 DCP:Talc 99.00: : : :10.00 DCP:SiO : : : : Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences November-December 2016
3 of repose was calculated as the inverse tangent of the ratio between the height and half the width of the base of the cone. Carr s compressibility index: The flowability of each filler powder, lubricant powder, glidant powder and the binary mixtures were investigated using Carr s compressibility index. The Carr s compressibility index was calculated from the bulk and tapped densities. The bulk density of each powder was measured by placing the powder (100 mg for talc, DCP and lactose, g for SiO 2 and 70 g for MGST) into a 250 ml cylinder without compaction. The apparent volume of the powder was recorded, and then the bulk density (g/ml) was calculated by dividing the mass by the apparent volume. The tapped densities were determined using the same procedure as the bulk densities, but the apparent volume was recorded after tapping the samples using a tapping machine. The Carr s compressibility index was calculated according Eqn. 3, compressibility index=(tapped density-bulk density)/tapped density) 100. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Applying knowledge of the surface free energy to the selection of excipient used in drug formulation could be very useful. This could save time and cost of the development of drug formulations. It has been reported that the mixing properties of binary and ternary blends can be predicted using surface energy calculations [12,13]. In the experiment, the surface free energies were calculated according to Wu s method using the information obtained from the contact angle of the two reference liquids on the surface of the excipient powders. The surface free energy data were then used to determine the spreading coefficient which was expected to act as a tool to predict the flowability of filler-lubricant or filler-glidant mixtures. The specific surface energy of a solid may possibly be estimated from contact angle measurements using liquids which exhibit different and known polar and dispersive components [14,15]. Therefore, the contact angles of two liquids (water and formamide) on the surface of each excipient were determined using a drop shape analyser and the surface free energies were computed according to Wu s method. The measured contact angle and calculated surface free energy of each excipient were listed in Table 2. The surface free energies of the excipients were used to calculate the spreading coefficients (S12 and S21), and the results were presented in Table 3. The spreading coefficient (S12) can be used to account for the ability of an excipient to spread over another in a binary mixture. Many research studies have shown evidence of the strong relationship between the spreading coefficient of a material and its ability to cover the surface of another material [5,16-19]. When the spreading coefficient is positive, the spreadability of an excipient over the other can be predicted. In fact, positive spreading coefficient values of lubricants or glidants over model fillers enable their adherence to the filler surface and may lead to an increase in the flowability of the mixture powder [3,19]. In contrast, when the spreading coefficient is negative, the excipient cannot spread over another material [3]. From Table 3, the spreading coefficients of lactose over MGST and MGST over lactose were and 10.79, respectively. In this case, lactose could not spread over MGST; however, TABLE 2: CONTACT ANGLE AND SURFACE FREE ENERGY Substances Contact angle of water Contact angle of formamide γ γ d γ p Lactose 35.25± ± DCP 50.40± ± MGST ± ± Talc 96.44± ± SiO ± ± TABLE 3: SPREADING COEFFICIENT OF BINARY MIXTURES Substance 1 Substance 2 Experimental values as measured S (1, 2) S (2, 1) Lactose MGST DCP MGST Lactose Talc DCP Talc Lactose SiO DCP SiO November-December 2016 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 836
4 MGST, which acted as a lubricant, could spread over lactose. Therefore, an increase in flowability could be predicted from the lactose-mgst mixture as per the spreading coefficient results. A similar pattern of results was observed in DCP-MGST, lactose-talc, DCP-talc, lactose-sio 2, and DCP-SiO mixtures. These 2 findings revealed that a rise in flowability may also be expected from these mixtures. To determine the correlation between the theoretical (calculated) data and the experimental data, an assessment of flowability values through angles of repose and compressibility indices of the fillerlubricant mixtures was performed. The angle of repose and compressibility index of each of the fillers and lubricants were also measured and the results were displayed in Table 4. It can be seen from the results that the information obtained from both the angle of repose and the compressibility index provided similar results. Lactose and DCP exhibited quite poor flowability while talc, SiO 2 and MGST presented better flowability. The amount of flowing agent used was also expected to have an effect on the flowability of the filler-lubricant mixtures. In the experiment, various amounts of MGST (0.25, 1.83, 3.41 and 5.00%), talc (1.00, 4.00, 7.00 and 10.00%) or SiO 2 (0.10, 0.40, 0.70 and 1.00%) were mixed with the fillers (lactose or DCP). After mixing lactose or DCP with MGST, the mixture exhibited better flowability as suggested by the angle of repose and compressibility index data (Table 5). Usually, the flowability of the filler-lubricant mixtures increased after raising the amounts of MGST. Table 6 showed the angle of repose and compressibility index data of lactose-talc and DCP-talc mixtures. When lactose or DCP were mixed with talc, small increases in flowability of the mixtures were observed. It can be seen from the results that after increasing the amount of talc, little improvement in the flowability of the filler-lubricant mixtures was observed. This may be because the range of the flowing agents used, which were in normal ranges for tableting, may not have been high enough to distinguish the difference in flowability. The flowability TABLE 4: MEAN ANGLE OF REPOSE AND CARR S COMPRESSIBILITY INDEX OF THE DILUENTS Substance Angle of repose Carr s compressibility index Lactose DCP Talc SiO MGST Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences TABLE 5: MEAN ANGLE OF REPOSE AND CARR S COMPRESSIBILITY INDEX OF LACTOSE OR DCP AFTER BEING MIXED WITH DIFFERENT PERCENTAGES OF MGST MGST (%) Angle of repose (n=10) Compressibility index (n=2) Lactose DCP Lactose DCP TABLE 6: MEAN ANGLE OF REPOSE AND CARR S COMPRESSIBILITY INDEX OF LACTOSE OR DCP AFTER BEING MIXED WITH DIFFERENT PERCENTAGES OF TALC Talc (%) Angle of repose (n=10) Compressibility index (n=2) Lactose DCP Lactose DCP data of lactose-sio 2 and DCP-SiO 2 were presented in Table 7. The angle of repose results revealed an increase in flowability of the mixtures when compared to those of the unmixed fillers. An increase in the SiO 2 amount resulted in an improvement in flowability of the mixtures. In addition, the compressibility index data were in accordance with the angle of repose results except in the case of the DCP-SiO 2 mixture. The improvement in flowability of the filler-lubricant mixtures or filler-glidant mixtures may be because the lubricants or glidants filled the surface cavities of the fillers. This selective adhesion to the surface improved the flowability of the powder by smoothing the surface of the filler particles-the particles became more spherical with a smoother surface and lessened the frictional forces, thus improving flow [20-22]. For lubricants added to a formulation, the most favourable quantity is usually a balance between the lubrication needs for tablet flow or ejection and the negative impacts on the tablet properties. Moreover, it should be noted that the glidant and lubricant used in the formulation are hydrophobic in nature. Higher concentrations may delay the disintegration and dissolution profile. Further research should be carried out to assess the dissolution and disintegration properties of the tablets. The investigation to assess the correlation between the predictions of flowability calculated from the surface free energy and the flowability data from the November-December 2016
5 TABLE 7: MEAN ANGLE OF REPOSE AND CARR S COMPRESSIBILITY INDEX OF LACTOSE OR DCP AFTER BEING MIXED WITH DIFFERENT PERCENTAGES OF SIO 2 SiO 2 (%) Angle of repose (n=10) Compressibility index (n=2) Lactose DCP Lactose DCP experiment revealed that the theoretical data calculated from the surface free energy correlated well with the experimental flowability data. Thus, the surface free energy and spreading coefficient may be used to predict the flowability of filler-lubricant mixtures. These results reveal the importance of knowledge of the surface free energy which can be used as a tool for selecting the excipients for drug formulation. However, other factors should also be taken into account. In this study, we examined the application of surface free energy and spreading coefficient for the prediction of the flowability of filler-lubricant mixtures. The use of surface energy and spreading coefficient data taken from contact angle measurement of the excipients has proved to be a useful tool for predicting the flowability of binary mixtures. A good correlation between theoretical data and the data obtained from the flowability tests was obtained, however other factors such as the properties of excipients should be considered. In addition, the amount and type of flowing agents used were observed to have an effect on the flowability of the mixtures. Acknowledgements: The authors would like to thank the Faculty of Pharmacy, Silpakorn University for financial support and Miss Juthaporn Peantaweeponrung, Miss Suchada Lueamsichan and Miss Suchamon Waradee for their research assistance. Conflict of interest: There are no conflicts of interest mentioned. Financial support and sponsorship: Nil. REFERENCES 1. Fowkes FM. Dispersion force contributions to surface and interfacial tensions, contact angles and heats of immersion. Adv Chem 1964;43: Buckton G, Darcy P. The influence of additives on the recrystallization of amorphous spray dried lactose. Int J Pharm 1995;121: Baki G, Bajdik J, Djuric D, Knop K, Kleinebudde P, Pintye- Hódi K. Role of surface free energy and spreading coefficient in the formulation of active agent-layered pellets. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2010;74: Tüske Z, Regdon Jr G, Erős I, Srčič S, Pintye-Hódi K. The role of the surface free energy in the selection of a suitable excipient in the course of a wet-granulation method. Powder Technol 2005;155: Planinšek O, Pišek R, Trojak A, Srčič S. The utilization of surface free-energy parameters for the selection of a suitable binder in fluidized bed granulation. Int J Pharm 2000;207: Lehr CM, Bouwstra JA, Bodde HE, Junginger HE. A surface energy analysis of mucoadhesion: contact angle measurements on polycarbophil and pig intestinal mucosa in physiologically relevant fluids. Pharm Res 1992;9: Buckton G. Characterization of small changes in the physical properties of powders of significance for dry powder inhaler formulations. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 1997;26: Planinšek O, Trojak A, Srčič S. The dispersive component of the surface free energy of powders assessed using inverse gas chromatography and contact angle measurements. Int J Pharm 2001;221: Bajdik J, Fehér M, Pintye-Hódi K. Effect of plasticizer on surface of free films prepared from aqueous solutions of salts of cationic polymers with different plasticizers. Appl Surf Sci 2007;253: Wu S, Brzozowski KJ. Surface free energy and polarity of organic pigments. J Colloid Interface Sci 1971;37: Rowe RC. Binder-substrate interactions in granulation: a theoretical approach based on surface free energy and polarity. Int J Pharm 1989;52: Ahfat NM, Buckton G, Burrows R, Ticehurst MD. Predicting mixing performance using surface energy measurements. Int J Pharm 1997;156: Steele DF, Moreton RC, Staniforth JN, Young PM, Tobyn MJ, Edge S. Surface energy of microcrystalline cellulose determined by capillary intrusion and inverse gas chromatography. AAPS J 2008;10: Gindl M, Sinn G, Gindl W, Reiterer A, Tschegg S. A comparison of different methods to calculate the surface free energy of wood using contact angle measurements. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 2001;181: Sharma PK, Hanumantha RK. Analysis of different approaches for evaluation of surface energy of microbial cells by contact angle goniometry. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 2002;98: Baki G, Bajdik J, Djuric D, Knop K, Kleinebudde P, Pintye- Hodi K. Role of surface free energy and spreading coefficient in the formulation of active agent-layered pellets. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2010;74: Andersson TM, Mohamed A, Eastoe J. A highly hydrophobic anionic surfactant at oil-water, water polymer and oilpolymer interfaces: Implications for spreading coefficients, polymer interactions and microencapsulation via internal phase separation. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 2013;436: November-December 2016 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 838
6 18. Andrade R, Skurtys O, Osorio F, Zuluaga R, Gañán P, Castro C. Wettability of gelatin coating formulations containing cellulose nanofibers on banana and eggplant epicarps. LWT- Food Sci Technol 2014;58: Shmeis RMA, Alshwwabkeh ID, Alkrad JM, Mohammad MA. Surface free energy data to predict the surface modification ability of force control agents. JJPS 2015;8: Perrault M, Bertrand F, Chaouki J. An investigation of magnesium stearate mixing in a V-blender through gammaray detection. Powder Technol 2010;200: Roblot-Treupel L, Puisieux F. Distribution of magnesium stearate on the surface of lubricated particles. Int J Pharm 1986;31: Morin G, Briens L. The Effect of lubricants on powder flowability for pharmaceutical application. AAPS PharmSciTech 2013;14: Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences November-December 2016
Formulation of Low Dose Medicines - Theory and Practice
 Hashim Ahmed, Ph.D. and Navnit Shah, Ph.D. Pharmaceutical and Analytical R&D, Hoffmann-La Roche Inc., Nutley NJ Formulation of Low Dose Medicines - Theory and Practice Progress in pharmaceutical research
Hashim Ahmed, Ph.D. and Navnit Shah, Ph.D. Pharmaceutical and Analytical R&D, Hoffmann-La Roche Inc., Nutley NJ Formulation of Low Dose Medicines - Theory and Practice Progress in pharmaceutical research
Dynamic Force Measurements in Preformulation of Solid Dosage Forms
 University of Szeged Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutical Technology Summary of PhD Thesis Dynamic Force Measurements in Preformulation of Solid Dosage Forms By András Kelemen Supervisor: Prof.
University of Szeged Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutical Technology Summary of PhD Thesis Dynamic Force Measurements in Preformulation of Solid Dosage Forms By András Kelemen Supervisor: Prof.
A STUDY OF COMPRESSION PROCESS AND PROPERTIES OF TABLETS WITH MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE AND COLLOIDAL SILICON DIOXIDE
 Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 73 No. 5 pp. 1259ñ1265, 2016 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY A STUDY OF COMPRESSION PROCESS AND PROPERTIES OF TABLETS
Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 73 No. 5 pp. 1259ñ1265, 2016 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY A STUDY OF COMPRESSION PROCESS AND PROPERTIES OF TABLETS
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2011/28
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 343 0 A1 (43) Date of publication: 13.07.2011 Bulletin 2011/28 (21) Application number: 196217.3 (1) Int Cl.: A61K 9/16 (2006.01) A61K 9/20 (2006.01) A61K
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 343 0 A1 (43) Date of publication: 13.07.2011 Bulletin 2011/28 (21) Application number: 196217.3 (1) Int Cl.: A61K 9/16 (2006.01) A61K 9/20 (2006.01) A61K
Pharmaceutical Polymers for Tablets and Capsules
 Pharmaceutical Polymers for Tablets and Capsules Edition: March 23, 2010 Wet Granulation Direct compression is not feasible for matrix formulations containing high levels of powder Carbopol polymers (>5%
Pharmaceutical Polymers for Tablets and Capsules Edition: March 23, 2010 Wet Granulation Direct compression is not feasible for matrix formulations containing high levels of powder Carbopol polymers (>5%
Materials for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
 Materials for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing GRACE WHITEPAPER FP Excipients 2-Step Mixing Process Improves API Stability, Flow, and Uniformity Technical Development: Dr. Raghunadha Gupta - Formulation Scientist,
Materials for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing GRACE WHITEPAPER FP Excipients 2-Step Mixing Process Improves API Stability, Flow, and Uniformity Technical Development: Dr. Raghunadha Gupta - Formulation Scientist,
Use of Roller Compaction in the Preparation of Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended Release Matrix Tablets Containing Hydrophilic Polymers
 METHOCEL Application Data Premium Cellulose Ethers Use of Roller Compaction in the Preparation of Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended Release Matrix Tablets Containing Hydrophilic Polymers ABSTRACT SUMMARY
METHOCEL Application Data Premium Cellulose Ethers Use of Roller Compaction in the Preparation of Verapamil Hydrochloride Extended Release Matrix Tablets Containing Hydrophilic Polymers ABSTRACT SUMMARY
HPMC Matrix Granule Formation: Selection of Suitable Granulating Fluid
 Original Article HPMC Matrix Granule Formation: Selection of Suitable Granulating Fluid Wanwilai Darunkaisorn, Jongjan Mahadlek and Thawatchai Phaechamud* Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty
Original Article HPMC Matrix Granule Formation: Selection of Suitable Granulating Fluid Wanwilai Darunkaisorn, Jongjan Mahadlek and Thawatchai Phaechamud* Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty
Investigation of Moisture-Activated Granulation of Hydrophilic Polymer Blends in Verapamil HCl Extended Release Matrices
 METHOCEL Application Data Premium Cellulose Ethers Investigation of Moisture-Activated Granulation of Hydrophilic Polymer Blends in Verapamil HCl Extended Release Matrices ABSTRACT SUMMARY Hydrophilic
METHOCEL Application Data Premium Cellulose Ethers Investigation of Moisture-Activated Granulation of Hydrophilic Polymer Blends in Verapamil HCl Extended Release Matrices ABSTRACT SUMMARY Hydrophilic
Received 25 March, 2010; received in revised form 03 June, 2010; accepted 15 June, 2010
 ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 7 (Research Article) Received 25 March, 2010; received in revised form 03 June, 2010; accepted 15 June, 2010 IMPROVEMENT OF DISSOLUTION BEHAVIOR OF PARACETAMOL
ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 7 (Research Article) Received 25 March, 2010; received in revised form 03 June, 2010; accepted 15 June, 2010 IMPROVEMENT OF DISSOLUTION BEHAVIOR OF PARACETAMOL
Preparation and evaluation of highly drug-loaded fine globular. granules using a multi-functional rotor processor
 Preparation and evaluation of highly drug-loaded fine globular granules using a multi-functional rotor processor 5 Yasunori Iwao a, Shin-ichiro Kimura b, c, Masayuki Ishida a, Ryohei Mise a, Masaki Yamada
Preparation and evaluation of highly drug-loaded fine globular granules using a multi-functional rotor processor 5 Yasunori Iwao a, Shin-ichiro Kimura b, c, Masayuki Ishida a, Ryohei Mise a, Masaki Yamada
Powder. Aulton Chapter 8-10,14,24. Powders
 Powder Aulton Chapter 8-10,14,24 Powders Powders are important in the development of pharmaceutical products since many formulations either is powders or contain powders 1 Pharmaceutical powders Different
Powder Aulton Chapter 8-10,14,24 Powders Powders are important in the development of pharmaceutical products since many formulations either is powders or contain powders 1 Pharmaceutical powders Different
Part ONE. Answer ALL questions. For each questions, there is ONE correct answer. Use the multiple choice reader card provided for ALL your answers.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Pharmacy Main Series UG Examination 2012-2013 PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY PHAN2HGY Time allowed: 2 hours Part ONE. Answer ALL questions. For each questions, there is ONE
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Pharmacy Main Series UG Examination 2012-2013 PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY PHAN2HGY Time allowed: 2 hours Part ONE. Answer ALL questions. For each questions, there is ONE
Applied Surfactants: Principles and Applications
 Applied Surfactants: Principles and Applications Tadros, Tharwat F. ISBN-13: 9783527306299 Table of Contents Preface. 1 Introduction. 1.1 General Classification of Surface Active Agents. 1.2 Anionic Surfactants.
Applied Surfactants: Principles and Applications Tadros, Tharwat F. ISBN-13: 9783527306299 Table of Contents Preface. 1 Introduction. 1.1 General Classification of Surface Active Agents. 1.2 Anionic Surfactants.
Keywords: Sustained release matrices, Eudragit, particle size, Aerosil 200, compaction force
 Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences Vol. 1, No. 3, Autumn 7, 197-5 Received: Jun 9, 7; Accepted: Oct 9, 7 Effect of Particle Size, Compaction Force and Presence of Aerosil on the Properties of Matrices
Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences Vol. 1, No. 3, Autumn 7, 197-5 Received: Jun 9, 7; Accepted: Oct 9, 7 Effect of Particle Size, Compaction Force and Presence of Aerosil on the Properties of Matrices
Aqueous Enteric Coating Application on Non-Banded Hard Gelatin Capsules
 ACRYL-EZE Aqueous Acrylic Enteric System Application Data Aqueous Enteric Coating Application on Non-Banded Hard Gelatin Capsules OBJECTIVE To evaluate the application and performance of an aqueous enteric
ACRYL-EZE Aqueous Acrylic Enteric System Application Data Aqueous Enteric Coating Application on Non-Banded Hard Gelatin Capsules OBJECTIVE To evaluate the application and performance of an aqueous enteric
Formulation and Evaluation of Release-Retardant Matrix Tablets of Diclofenac Sodium
 FABAD J. Pharm. Sci., 31, 119-16, 006 RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Release-Retardant Matrix Tablets of Diclofenac Sodium Sunita DAHIYA*, Formulation and Evaluation of Release-Retardant
FABAD J. Pharm. Sci., 31, 119-16, 006 RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Release-Retardant Matrix Tablets of Diclofenac Sodium Sunita DAHIYA*, Formulation and Evaluation of Release-Retardant
Data Sharing Initiatives Dr Andy Teasdale
 Data Sharing Initiatives Dr Andy Teasdale PQRI/USP Workshop on Implementation Status of ICH Q3D Elemental Impurity Requirements - Analytical and Risk Assessment Challenges Overview areas covered Why share
Data Sharing Initiatives Dr Andy Teasdale PQRI/USP Workshop on Implementation Status of ICH Q3D Elemental Impurity Requirements - Analytical and Risk Assessment Challenges Overview areas covered Why share
The Origins of Surface and Interfacial Tension
 The Origins of Surface and Interfacial Tension Imbalance of intermolecular forces exists at the liquid-air interface γ la= the surface tension that exists at the liquid-air interface Suppose we have a
The Origins of Surface and Interfacial Tension Imbalance of intermolecular forces exists at the liquid-air interface γ la= the surface tension that exists at the liquid-air interface Suppose we have a
Pharmaceutics and Pharmaceutical Technology
 Pharmaceutics and Pharmaceutical Technology Pharmaceutics and Pharmaceutical Technology Laboratories Lab Name Location Person in Charge Programs Served Courses Served Pharmaceutics A M12-127 Pharmaceutics
Pharmaceutics and Pharmaceutical Technology Pharmaceutics and Pharmaceutical Technology Laboratories Lab Name Location Person in Charge Programs Served Courses Served Pharmaceutics A M12-127 Pharmaceutics
Understanding Surface Energy
 Understanding Surface Energy Anett Kondor Surface Measurement Systems Ltd. 6 th October 2015 What is the SE; Why it is important to measure and How it can be measured? Basics Atoms in the centre of a material
Understanding Surface Energy Anett Kondor Surface Measurement Systems Ltd. 6 th October 2015 What is the SE; Why it is important to measure and How it can be measured? Basics Atoms in the centre of a material
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLET OF DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE BY MELT GRANULATION TECHNOLOGY
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLET OF DILTIAZEM HYDROCHLORIDE BY MELT GRANULATION TECHNOLOGY
Research Article DEVELOPMENT AND CHARACTERIZATION OF ACECLOFENAC ENTERIC COATED TABLETS
 International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy and Life Sciences Available online at http//www.ijrdpl.com October - November, 2015, Vol. 4, No.6, pp 1861-1866 ISSN (P): 2393-932X, ISSN (E):
International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy and Life Sciences Available online at http//www.ijrdpl.com October - November, 2015, Vol. 4, No.6, pp 1861-1866 ISSN (P): 2393-932X, ISSN (E):
Wettability of CaCO 3 surfaces
 Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 157 (1999) 333 340 www.elsevier.nl/locate/colsurfa Wettability of CaCO 3 surfaces Malvina G. Orkoula a,b, Petros G. Koutsoukos a,b, *, Michel
Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 157 (1999) 333 340 www.elsevier.nl/locate/colsurfa Wettability of CaCO 3 surfaces Malvina G. Orkoula a,b, Petros G. Koutsoukos a,b, *, Michel
A Digital Design Approach to Prediction of Powder Flowability
 A Digital Design Approach to Prediction of Powder Flowability James Elliott, Xizhong Chen ( 陈锡忠 ) and Chunlei Pei ( 裴春雷 ) Macromolecular Materials Laboratory University of Cambridge ADDoPT Work Package
A Digital Design Approach to Prediction of Powder Flowability James Elliott, Xizhong Chen ( 陈锡忠 ) and Chunlei Pei ( 裴春雷 ) Macromolecular Materials Laboratory University of Cambridge ADDoPT Work Package
Solving manufacturing problems for L-carnitine-L-tartrate to improve the likelihood of successful product scale-up
 Acta Pharm. 67 (2017) 511 525 https://doi.org/10.1515/acph-2017-0033 Original research paper Solving manufacturing problems for L-carnitine-L-tartrate to improve the likelihood of successful product scale-up
Acta Pharm. 67 (2017) 511 525 https://doi.org/10.1515/acph-2017-0033 Original research paper Solving manufacturing problems for L-carnitine-L-tartrate to improve the likelihood of successful product scale-up
Mohammad.Zuber. et al. / International Journal of Biopharmaceutics. 2012; 3(1): International Journal of Biopharmaceutics
 44 e- ISSN 0976-1047 Print ISSN 2229-7499 International Journal of Biopharmaceutics Journal homepage: www.ijbonline.com IJB THE EFFECT OF VARIOUS SURFACTANTS ON RELEASE BEHAVIOR OF LIDOCAINE HCL FROM ETHYLCELLULOSE
44 e- ISSN 0976-1047 Print ISSN 2229-7499 International Journal of Biopharmaceutics Journal homepage: www.ijbonline.com IJB THE EFFECT OF VARIOUS SURFACTANTS ON RELEASE BEHAVIOR OF LIDOCAINE HCL FROM ETHYLCELLULOSE
IN VITRO DISSOLUTION KINETIC STUDY OF THEOPHYLLINE FROM HYDROPHILIC AND HYDROPHOBIC MATRICES
 Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 63 No. 1 pp. 63ñ67, 2006 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society IN VITRO DISSOLUTION KINETIC STUDY OF THEOPHYLLINE FROM HYDROPHILIC AND HYDROPHOBIC
Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 63 No. 1 pp. 63ñ67, 2006 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society IN VITRO DISSOLUTION KINETIC STUDY OF THEOPHYLLINE FROM HYDROPHILIC AND HYDROPHOBIC
PHARMACEUTICAL BULLETINS
 PHARMACEUTICAL BULLETINS TABLE OF CONTENTS BULLETIN 1 BULLETIN 2 BULLETIN 3 POLYMERS FOR PHARMACEUTICAL APPLICATIONS Introduction Product Descriptions Typical Properties of Lubrizol s Pharmaceutical Polymers
PHARMACEUTICAL BULLETINS TABLE OF CONTENTS BULLETIN 1 BULLETIN 2 BULLETIN 3 POLYMERS FOR PHARMACEUTICAL APPLICATIONS Introduction Product Descriptions Typical Properties of Lubrizol s Pharmaceutical Polymers
Chapter 7 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PULSINCAP
 161 Chapter 7 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PULSINCAP 162 Chapter 7 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PULSINCAP S.No. Name of the Sub-Title Page No. 7.1. Optimization of formulations of Pulsincap
161 Chapter 7 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PULSINCAP 162 Chapter 7 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PULSINCAP S.No. Name of the Sub-Title Page No. 7.1. Optimization of formulations of Pulsincap
Inverse Gas Chromatography
 Inverse Gas Chromatography David R.Merrifield Presentation to iprd Industrialists Club Weetwood Hall, 26 th November 2010. Inverse Gas Chromatography What is it? - with respect to chromatography? Chromatography
Inverse Gas Chromatography David R.Merrifield Presentation to iprd Industrialists Club Weetwood Hall, 26 th November 2010. Inverse Gas Chromatography What is it? - with respect to chromatography? Chromatography
QbD QUANTITATIVE MEASUREMENTS OF CQAS IN SOLID DOSAGE FORM UNIT OPERATIONS
 QbD QUANTITATIVE MEASUREMENTS OF CQAS IN SOLID DOSAGE FORM UNIT OPERATIONS Particle Size Material Segregation-Flow USP USP USP Ph. Eur. 2.9.31 Ph. Eur. 2.9.36 JP 1 JP 18 Light Diffraction
QbD QUANTITATIVE MEASUREMENTS OF CQAS IN SOLID DOSAGE FORM UNIT OPERATIONS Particle Size Material Segregation-Flow USP USP USP Ph. Eur. 2.9.31 Ph. Eur. 2.9.36 JP 1 JP 18 Light Diffraction
Application of Ring Shear Testing to Optimize Pharmaceutical Formulation and Process Development of Solid Dosage Forms
 ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 21, 2013 Application of Ring Shear Testing to Optimize Pharmaceutical Formulation and Process Development of Solid Dosage Forms Søren V. Søgaard
ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 21, 2013 Application of Ring Shear Testing to Optimize Pharmaceutical Formulation and Process Development of Solid Dosage Forms Søren V. Søgaard
Mouth Disintegrating Tablets of Taste-Masked Ondansetron HCl
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 19, No. 5 (2007), 3455-3460 Mouth Disintegrating Tablets of Taste-Masked Ondansetron HCl V.K. CHATAP, D.K. SHARMA*, ANIL MIDDHA, R.D. GUPTA, VIPIN SAINI, MAHENDRA SHIRADKAR
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 19, No. 5 (2007), 3455-3460 Mouth Disintegrating Tablets of Taste-Masked Ondansetron HCl V.K. CHATAP, D.K. SHARMA*, ANIL MIDDHA, R.D. GUPTA, VIPIN SAINI, MAHENDRA SHIRADKAR
Effect of Alkaline Excipients on The Release Profile of Gliclazide Extended Release Tablets
 Effect of Alkaline Excipients on The Release Profile of Gliclazide Extended Release Tablets Monika Srivastav 1, B Prabhakar 1, Ashok Omray 2 1 School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, NMIMS University,
Effect of Alkaline Excipients on The Release Profile of Gliclazide Extended Release Tablets Monika Srivastav 1, B Prabhakar 1, Ashok Omray 2 1 School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, NMIMS University,
Solid-liquid interface
 Lecture Note #9 (Spring, 2017) Solid-liquid interface Reading: Shaw, ch. 6 Contact angles and wetting Wetting: the displacement from a surface of one fluid by another. A gas is displaced by a liquid at
Lecture Note #9 (Spring, 2017) Solid-liquid interface Reading: Shaw, ch. 6 Contact angles and wetting Wetting: the displacement from a surface of one fluid by another. A gas is displaced by a liquid at
Application of a Fully Formulated Aqueous Enteric Coating System on Rabeprazole Sodium Tablets (20 mg)
 ACRYL-EZE Aqueous Acrylic Enteric System Application Data Application of a Fully Formulated Aqueous Enteric Coating System on Rabeprazole Sodium Tablets (20 mg) OBJECTIVES Rabeprazole sodium is a proton
ACRYL-EZE Aqueous Acrylic Enteric System Application Data Application of a Fully Formulated Aqueous Enteric Coating System on Rabeprazole Sodium Tablets (20 mg) OBJECTIVES Rabeprazole sodium is a proton
Formulation and in vitro evaluation of candesartan liquid solid compacts to enhance drug solubility
 IJPAR Vol.5 Issue 1 Jan- Mar -2016 Journal Home page: ISSN:2320-2831 Research article Open Access Formulation and in vitro evaluation of candesartan liquid solid compacts to enhance drug solubility Sai
IJPAR Vol.5 Issue 1 Jan- Mar -2016 Journal Home page: ISSN:2320-2831 Research article Open Access Formulation and in vitro evaluation of candesartan liquid solid compacts to enhance drug solubility Sai
Design and In Vitro Characterization of Dexlansoprazole Controlled Release Tablets
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Design and In Vitro Characterization of Dexlansoprazole Controlled Release Tablets Y. Naveen Kumar 1, J. Sreekanth 2, P. Vijay Chander Reddy 3 1 Drugs Control Administration, Hyderabad,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Design and In Vitro Characterization of Dexlansoprazole Controlled Release Tablets Y. Naveen Kumar 1, J. Sreekanth 2, P. Vijay Chander Reddy 3 1 Drugs Control Administration, Hyderabad,
Technical Paper. Spray Granulation Gives Solid Materials Customized. The properties of spray-granulated products can be as varied as their appearance
 03/17/15 page 1 of 7 Weimar, March / 17 / 2015 Flowability, dustlessness and easy dosing - these are some of the plus points of granulates produced by fluidized or spouted bed technology. The product design
03/17/15 page 1 of 7 Weimar, March / 17 / 2015 Flowability, dustlessness and easy dosing - these are some of the plus points of granulates produced by fluidized or spouted bed technology. The product design
FACULTY OF PHARMACY. M. Pharmacy I Semester (Suppl.) Examination, November 2015 (Common To All) Subject: Pharmaceutical Analytical Techniques
 M. Pharmacy I Semester (Suppl.) Examination, November 2015 (Common To All) Subject: Pharmaceutical Analytical Techniques Code No. 6001 / S Note: Answer any Five questions. All questions carry equal marks.
M. Pharmacy I Semester (Suppl.) Examination, November 2015 (Common To All) Subject: Pharmaceutical Analytical Techniques Code No. 6001 / S Note: Answer any Five questions. All questions carry equal marks.
AEROSIL Colloidal Silicon Dioxide for Pharmaceuticals
 AEROSIL Colloidal Silicon Dioxide for Pharmaceuticals Product Quality and Product Safety Customer Proximity R & D, Applied Technology Technical Literature Technical Service Logistics Concepts Supply Security
AEROSIL Colloidal Silicon Dioxide for Pharmaceuticals Product Quality and Product Safety Customer Proximity R & D, Applied Technology Technical Literature Technical Service Logistics Concepts Supply Security
3.0 APPARATUS : Capsule Machine, Analytical balance, Spatula, Beaker, Pestle and mortar, Powder paper.
 1.0 TITLE OF EXPERIMENT : - Herbal Capsule 2.0 OBJECTIVE OF EXPERIMENT : - To understand how to prepare capsule. 3.0 APPARATUS : Capsule Machine, Analytical balance, Spatula, Beaker, Pestle and mortar,
1.0 TITLE OF EXPERIMENT : - Herbal Capsule 2.0 OBJECTIVE OF EXPERIMENT : - To understand how to prepare capsule. 3.0 APPARATUS : Capsule Machine, Analytical balance, Spatula, Beaker, Pestle and mortar,
Research Article Surface Characterization of Phenylpropanolamine Drug by Inverse Gas Chromatography
 ISRN Physical Chemistry Volume 2013, Article ID 142687, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/142687 Research Article Surface Characterization of Phenylpropanolamine Drug by Inverse Gas Chromatography
ISRN Physical Chemistry Volume 2013, Article ID 142687, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/142687 Research Article Surface Characterization of Phenylpropanolamine Drug by Inverse Gas Chromatography
Technical brochure DuraLac H TABLETING DIRECT COMPRESSION ANHYDROUS LACTOSE
 U A AC Technical brochure TABLETING DIRECT COMPRESSION ANHYDROUS LACTOSE MEGGLE anhydrous lactose grade for direct compression: General information Direct compression (DC) tablet manufacture is a popular
U A AC Technical brochure TABLETING DIRECT COMPRESSION ANHYDROUS LACTOSE MEGGLE anhydrous lactose grade for direct compression: General information Direct compression (DC) tablet manufacture is a popular
Particle Size and Shape Analysis in PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY.
 Particle Size and Shape Analysis in PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY Generalities Many analytical methods exist for the characterization of products manufactured in the pharmaceutical industry. Measuring the size
Particle Size and Shape Analysis in PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY Generalities Many analytical methods exist for the characterization of products manufactured in the pharmaceutical industry. Measuring the size
Study of processing parameters affecting dissolution profile of highly water soluble drug
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2013, 5 (3):211-222 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2013, 5 (3):211-222 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
ADDITIVES. HIGH SOLIDS AND WATER- BORNE COATINGS Werner J. Blank Rudy Berndlmaier & Dan Miller King Industries Inc.
 You are now at www.wernerblank.com HOME NEWS PUBLICATIONS LECTURES PATENTS DOWNLOADS ADDITIVES FOR HIGH SOLIDS AND WATER- BORNE COATINGS Werner J. Blank Rudy Berndlmaier & Dan Miller King Industries Inc.
You are now at www.wernerblank.com HOME NEWS PUBLICATIONS LECTURES PATENTS DOWNLOADS ADDITIVES FOR HIGH SOLIDS AND WATER- BORNE COATINGS Werner J. Blank Rudy Berndlmaier & Dan Miller King Industries Inc.
Interfacial forces and friction on the nanometer scale: A tutorial
 Interfacial forces and friction on the nanometer scale: A tutorial M. Ruths Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Lowell Presented at the Nanotribology Tutorial/Panel Session, STLE/ASME International
Interfacial forces and friction on the nanometer scale: A tutorial M. Ruths Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Lowell Presented at the Nanotribology Tutorial/Panel Session, STLE/ASME International
Measuring the flow properties of powders. FT4 Powder Rheometer. freemantechnology
 Measuring the flow properties of powders FT4 Powder Rheometer freemantechnology Efficiency, quality and productivity Successful powder processing requires the ability to reliably and repeatably predict
Measuring the flow properties of powders FT4 Powder Rheometer freemantechnology Efficiency, quality and productivity Successful powder processing requires the ability to reliably and repeatably predict
COMPARISON OF WETTABILITY AND CAPILLARY EFFECT EVALUATED BY DIFFERENT CHARACTERIZING METHODS
 18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS COMPARISON OF WETTABILITY AND CAPILLARY EFFECT EVALUATED BY DIFFERENT CHARACTERIZING METHODS S.K. Wang*, M. Li*, Y.Z. Gu, Y.X. Li and Z.G. Zhang Key
18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS COMPARISON OF WETTABILITY AND CAPILLARY EFFECT EVALUATED BY DIFFERENT CHARACTERIZING METHODS S.K. Wang*, M. Li*, Y.Z. Gu, Y.X. Li and Z.G. Zhang Key
Tendency of blends for segregation
 Tendency of blends for segregation How to study it? Methods for measuring the segregation potential Louk Peffer 1 Outline/Themes Blends unmix Theory or reality Visual inspection Segregation mechanisms
Tendency of blends for segregation How to study it? Methods for measuring the segregation potential Louk Peffer 1 Outline/Themes Blends unmix Theory or reality Visual inspection Segregation mechanisms
Changes of polymer material wettability by surface discharge
 Changes of polymer material wettability by surface discharge Surface discharge and material treatment Surface treatment of materials in low temperature plasma belongs to the modern and very perspective
Changes of polymer material wettability by surface discharge Surface discharge and material treatment Surface treatment of materials in low temperature plasma belongs to the modern and very perspective
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Visualization of equilibrium position of colloidal particles at fluid-water
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Visualization of equilibrium position of colloidal particles at fluid-water
Critical Micellization Concentration Determination using Surface Tension Phenomenon
 Critical Micellization Concentration Determination using Phenomenon 1. Introduction Surface-active agents (surfactants) were already known in ancient times, when their properties were used in everyday
Critical Micellization Concentration Determination using Phenomenon 1. Introduction Surface-active agents (surfactants) were already known in ancient times, when their properties were used in everyday
Determination of Design Space for Oral Pharmaceutical Drugs
 Determination of Design Space for Oral Pharmaceutical Drugs Kalliopi Chatzizaharia and Dimitris Hatziavramidis School of Chemical Engineering National Technical University of Athens, Greece Design Space
Determination of Design Space for Oral Pharmaceutical Drugs Kalliopi Chatzizaharia and Dimitris Hatziavramidis School of Chemical Engineering National Technical University of Athens, Greece Design Space
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE DISSOLUTION CHARACTERISTICS OF CAPSULE AND TABLET DOSAGE FORMS OF MELT GRANULATIONS OF PARACETAMOL ñ DILUENT EFFECTS
 Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 64 No. 1 pp. 73ñ79, 2007 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE DISSOLUTION CHARACTERISTICS OF CAPSULE AND TABLET DOSAGE
Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 64 No. 1 pp. 73ñ79, 2007 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE DISSOLUTION CHARACTERISTICS OF CAPSULE AND TABLET DOSAGE
BIO & PHARMA ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES. Chapter 5 Particle Size Analysis
 BIO & PHARMA ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Chapter 5 by Dr Siti Umairah Mokhtar Faculty of Engineering Technology umairah@ump.edu.my Chapter Description Aims Discuss theory, principles and application of analytical
BIO & PHARMA ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Chapter 5 by Dr Siti Umairah Mokhtar Faculty of Engineering Technology umairah@ump.edu.my Chapter Description Aims Discuss theory, principles and application of analytical
THE INTRODUCTION OF PROCESS ANALYTICAL TECHNOLOGY, USING NEAR INFRARED ANALYSIS, TO A PHARMACEUTICAL BLENDING PROCESS
 THE INTRODUCTION OF PROCESS ANALYTICAL TECHNOLOGY, USING NEAR INFRARED ANALYSIS, TO A PHARMACEUTICAL BLENDING PROCESS Krishel Naicker a, Gareth Kilian a * and Johan Olivier b a Nelson Mandela Metropolitan
THE INTRODUCTION OF PROCESS ANALYTICAL TECHNOLOGY, USING NEAR INFRARED ANALYSIS, TO A PHARMACEUTICAL BLENDING PROCESS Krishel Naicker a, Gareth Kilian a * and Johan Olivier b a Nelson Mandela Metropolitan
Technological Excipients of Tablets: Study of Flow Properties and Compaction Behavior
 American Journal of Medical Sciences and Medicine, 2014, Vol. 2, No. 4, 71-76 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmsm/2/4/2 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmsm-2-4-2 Technological
American Journal of Medical Sciences and Medicine, 2014, Vol. 2, No. 4, 71-76 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmsm/2/4/2 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmsm-2-4-2 Technological
General Chemistry I CHEM-1030 Laboratory Experiment No. 2 Physical Separation Techniques
 General Chemistry I CHEM-1030 Laboratory Experiment No. 2 Physical Separation Techniques Introduction When two or more substances that do not react chemically are blended together, the components of the
General Chemistry I CHEM-1030 Laboratory Experiment No. 2 Physical Separation Techniques Introduction When two or more substances that do not react chemically are blended together, the components of the
S.Janakidevi et al. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2014, 5 (7) INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF CEFIXIME TRIHYDRATE SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS USING DIFFERENT POLYMERS S.Janakidevi*,
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF CEFIXIME TRIHYDRATE SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS USING DIFFERENT POLYMERS S.Janakidevi*,
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/42
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 10 922 A1 (43) Date of publication: 17.10.2012 Bulletin 2012/42 (1) Int Cl.: A61K 9/20 (2006.01) A61K 31/4 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 12163907.4
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 10 922 A1 (43) Date of publication: 17.10.2012 Bulletin 2012/42 (1) Int Cl.: A61K 9/20 (2006.01) A61K 31/4 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 12163907.4
Microfluidics 2 Surface tension, contact angle, capillary flow
 MT-0.6081 Microfluidics and BioMEMS Microfluidics 2 Surface tension, contact angle, capillary flow 28.1.2017 Ville Jokinen Surface tension & Surface energy Work required to create new surface = surface
MT-0.6081 Microfluidics and BioMEMS Microfluidics 2 Surface tension, contact angle, capillary flow 28.1.2017 Ville Jokinen Surface tension & Surface energy Work required to create new surface = surface
An Experimental Investigation of EOR Mechanisms for Nanoparticles Fluid in Glass Micromodel
 1 / 12 An Experimental Investigation of EOR Mechanisms for Nanoparticles Fluid in Glass Micromodel Shidong Li and Ole Torsæter, Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) This paper was prepared
1 / 12 An Experimental Investigation of EOR Mechanisms for Nanoparticles Fluid in Glass Micromodel Shidong Li and Ole Torsæter, Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) This paper was prepared
DISSOLUTION PROFILLING OF NIMESULIDE SOLID DISPERSIONS WITH POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, TALC AND THEIR COMBINATIONS AS DISPERSION CARRIERS
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.2, No.1, pp 480-484, Jan-Mar 2010 DISSOLUTION PROFILLING OF NIMESULIDE SOLID DISPERSIONS WITH POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, TALC
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.2, No.1, pp 480-484, Jan-Mar 2010 DISSOLUTION PROFILLING OF NIMESULIDE SOLID DISPERSIONS WITH POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, TALC
Chapter 7 Mixing and Granulation
 Chapter 7 Mixing and Granulation 7.1 Mixing and Segregation (Chapter 9) Mixing vs. segregation (1) Types of Mixture * Perfect mixing Random mixing Segregating mixing Figure 9.1 (2) Segregation 1) Causes
Chapter 7 Mixing and Granulation 7.1 Mixing and Segregation (Chapter 9) Mixing vs. segregation (1) Types of Mixture * Perfect mixing Random mixing Segregating mixing Figure 9.1 (2) Segregation 1) Causes
Pharmaceutical Characterisation. Dr. Lidia Tajber and Dr. Krzysztof Paluch School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Trinity College Dublin
 Pharmaceutical Characterisation Dr. Lidia Tajber and Dr. Krzysztof Paluch School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Trinity College Dublin Characterisation for Pharma Active pharmaceutical ingredients
Pharmaceutical Characterisation Dr. Lidia Tajber and Dr. Krzysztof Paluch School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Trinity College Dublin Characterisation for Pharma Active pharmaceutical ingredients
ICH Q3D: Practical implementation and the role of excipient data in a risk based approach. Dr Andrew Teasdale
 ICH Q3D: Practical implementation and the role of excipient data in a risk based approach Dr Andrew Teasdale Andrew.Teasdale@astrazeneca.com Overview areas covered Why share data? What data already exists?
ICH Q3D: Practical implementation and the role of excipient data in a risk based approach Dr Andrew Teasdale Andrew.Teasdale@astrazeneca.com Overview areas covered Why share data? What data already exists?
Particle interactions in dry and suspension based formulations
 Finnish Society of Physical Pharmacy, 9 th Feb 2012 Particle interactions in dry and suspension based formulations Pharmaceutical Surface Science Research Group, Department of Pharmacy and Pharmacology,
Finnish Society of Physical Pharmacy, 9 th Feb 2012 Particle interactions in dry and suspension based formulations Pharmaceutical Surface Science Research Group, Department of Pharmacy and Pharmacology,
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN Research Article
 Margret Chandira R et al. IRJP 212, 3 (2) INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 223 847 Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF ISONIAZID AND ETHAMBUTOL HYDROCHLORIDE
Margret Chandira R et al. IRJP 212, 3 (2) INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 223 847 Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF ISONIAZID AND ETHAMBUTOL HYDROCHLORIDE
Formulation and evaluation of doxycycline hydrochloride delayed release enteric coated tablets
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2012, 4 (1): 249-255 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2012, 4 (1): 249-255 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Nano Sciences Journal homepage:
 Research Article CODEN: IJRPJK ISSN: 2319 9563 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Nano Sciences Journal homepage: www.ijrpns.com FORMULATION, OPTIMIZATION AND INVITRO EVALUATION OF
Research Article CODEN: IJRPJK ISSN: 2319 9563 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Nano Sciences Journal homepage: www.ijrpns.com FORMULATION, OPTIMIZATION AND INVITRO EVALUATION OF
Research Article Validation of Methods for the Optical Characterisation of the Wettability of Polymeric Films for Food Packaging
 Industrial Engineering, Article ID 6235, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.1155/14/6235 Research Article Validation of Methods for the Optical Characterisation of the Wettability of Polymeric Films for Food Packaging
Industrial Engineering, Article ID 6235, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.1155/14/6235 Research Article Validation of Methods for the Optical Characterisation of the Wettability of Polymeric Films for Food Packaging
Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Development
 African Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Development Vol. 4 No.1 pp. 19-24 (2012) Some Physicochemical Properties of Crosslinked Acacia Gum Mbah CC*, Ogah JA, Builders PF, Kunle OO Department of Pharmaceutical
African Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Development Vol. 4 No.1 pp. 19-24 (2012) Some Physicochemical Properties of Crosslinked Acacia Gum Mbah CC*, Ogah JA, Builders PF, Kunle OO Department of Pharmaceutical
Application Report. Textile cleaning, washing, rewetting, surfactant, cotton, interfacial tension
 Application Report Cleaning of textiles Application report: AR231e Industry section: Textiles Author: C. Bilke-Krause Date: 01/2003 Method: Force Tensiometer K100 Drop Shape Analysis System DSA10 Keywords:
Application Report Cleaning of textiles Application report: AR231e Industry section: Textiles Author: C. Bilke-Krause Date: 01/2003 Method: Force Tensiometer K100 Drop Shape Analysis System DSA10 Keywords:
Multivariate statistical modelling of the pharmaceutical process of wet granulation and tableting Westerhuis, Johannes Arnold
 University of Groningen Multivariate statistical modelling of the pharmaceutical process of wet granulation and tableting Westerhuis, Johannes Arnold IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's
University of Groningen Multivariate statistical modelling of the pharmaceutical process of wet granulation and tableting Westerhuis, Johannes Arnold IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's
Implementing Fundamental Pharmaceutical Science and Materials/Engineer Expertise in Scale-up
 Implementing Fundamental Pharmaceutical Science and Materials/Engineer Expertise in Scale-up 2 nd FDA/PQRI Conference on Advancing Product Quality Session: The Science of Tech Transfer/Scale-up North Bethesda,
Implementing Fundamental Pharmaceutical Science and Materials/Engineer Expertise in Scale-up 2 nd FDA/PQRI Conference on Advancing Product Quality Session: The Science of Tech Transfer/Scale-up North Bethesda,
Fabrication of calcium pectinate microparticles from pomelo pectin by ionotropic gelation
 RESEARCH PAPER Fabrication of calcium pectinate microparticles from pomelo pectin by ionotropic gelation Pornsak Sriamornsak 1,2, Srisuda Konthong 2 and Jurairat Nunthanid 1,2 1 Department of Pharmaceutical
RESEARCH PAPER Fabrication of calcium pectinate microparticles from pomelo pectin by ionotropic gelation Pornsak Sriamornsak 1,2, Srisuda Konthong 2 and Jurairat Nunthanid 1,2 1 Department of Pharmaceutical
FORCE TENSIOMETER K100 THE HIGH-END SOLUTION FOR MEASURING SURFACE AND INTERFACIAL TENSION
 FORCE TENSIOMETER K100 THE HIGH-END SOLUTION FOR MEASURING SURFACE AND INTERFACIAL TENSION MAXIMIZING THE VARIETY OF SURFACE AND INTERFACIAL TENSION MEASURING METHODS Determines surface and interfacial
FORCE TENSIOMETER K100 THE HIGH-END SOLUTION FOR MEASURING SURFACE AND INTERFACIAL TENSION MAXIMIZING THE VARIETY OF SURFACE AND INTERFACIAL TENSION MEASURING METHODS Determines surface and interfacial
Multivariate statistical modelling of the pharmaceutical process of wet granulation and tableting
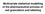 Multivariate statistical modelling of the pharmaceutical process of wet granulation and tableting RIJKSUNIVERSITEIT GRONINGEN Multivariate statistical modelling of the pharmaceutical process of wet granulation
Multivariate statistical modelling of the pharmaceutical process of wet granulation and tableting RIJKSUNIVERSITEIT GRONINGEN Multivariate statistical modelling of the pharmaceutical process of wet granulation
A MECHANISTIC STUDY OF FLOW AND COMPRESSION BEHAVIOR OF PHARMACEUTICAL POWDERS
 University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Open Access Dissertations 2001 A MECHANISTIC STUDY OF FLOW AND COMPRESSION BEHAVIOR OF PHARMACEUTICAL POWDERS Yogita Desai University of Rhode Island Follow
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Open Access Dissertations 2001 A MECHANISTIC STUDY OF FLOW AND COMPRESSION BEHAVIOR OF PHARMACEUTICAL POWDERS Yogita Desai University of Rhode Island Follow
Particle Characterization of Pharmaceutical Products by Dynamic Image Analysis
 WHITE PAPER Particle Characterization of Pharmaceutical Products by Dynamic Image Analysis Retsch Technology GmbH Retsch-Allee 1-5 42781 Haan, Germany Phone: +49 24/2333-0 E-Mail: technology@retsch.com
WHITE PAPER Particle Characterization of Pharmaceutical Products by Dynamic Image Analysis Retsch Technology GmbH Retsch-Allee 1-5 42781 Haan, Germany Phone: +49 24/2333-0 E-Mail: technology@retsch.com
PAINT COATINGS WITH HIGHER HYDROPHOBICITY FOR PROTECTION AGAINST ICE ACCRETION
 17th International Symposium on Ice Saint Petersburg, Russia, 21-25 June 2004 International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research Session A PAINT COATINGS WITH HIGHER HYDROPHOBICITY FOR PROTECTION
17th International Symposium on Ice Saint Petersburg, Russia, 21-25 June 2004 International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research Session A PAINT COATINGS WITH HIGHER HYDROPHOBICITY FOR PROTECTION
Recovery of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory. drugs from wastes using ionic liquid-based. three-phase partitioning systems
 Supporting Information Recovery of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from wastes using ionic liquid-based three-phase partitioning systems Francisca A. e Silva 1, Magda Caban 2, Mariam Kholany 1, Piotr
Supporting Information Recovery of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from wastes using ionic liquid-based three-phase partitioning systems Francisca A. e Silva 1, Magda Caban 2, Mariam Kholany 1, Piotr
Influence of different grades and concentrations of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose on the release of metformin hydrochloride
 World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
OPTIMIZATION OF FUROSEMIDE LIQUISOLID TABLETS PREPARATION PROCESS LEADING TO THEIR MASS AND SIZE REDUCTION
 Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 73 No. 5 pp. 1325ñ1331, 2016 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society OPTIMIZATION OF FUROSEMIDE LIQUISOLID TABLETS PREPARATION PROCESS LEADING TO
Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 73 No. 5 pp. 1325ñ1331, 2016 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society OPTIMIZATION OF FUROSEMIDE LIQUISOLID TABLETS PREPARATION PROCESS LEADING TO
SOLID DISPERSION OF POORLY WATER SOLUBLE DRUGS EARLY PROMISES SUBSEQUENT ELECTROSPUN AMORPHOUS SOLID DISPERSIONS OF POORLY WATER
 PROBLEMS AND RECENT BREAKTHROUGHS SOLID DISPERSION OF POORLY PDF ELECTROSPUN AMORPHOUS SOLID DISPERSIONS OF POORLY WATER EVALUATION OF AMORPHOUS SOLID DISPERSION PROPERTIES USING 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 solid
PROBLEMS AND RECENT BREAKTHROUGHS SOLID DISPERSION OF POORLY PDF ELECTROSPUN AMORPHOUS SOLID DISPERSIONS OF POORLY WATER EVALUATION OF AMORPHOUS SOLID DISPERSION PROPERTIES USING 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 solid
International Journal of Medicine and Health Profession Research
 Research Article ISSN: 2394 7403 International Journal of Medicine and Health Profession Research Journal home page: www.ijmhpr.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING SUSTAINED RELEASED
Research Article ISSN: 2394 7403 International Journal of Medicine and Health Profession Research Journal home page: www.ijmhpr.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING SUSTAINED RELEASED
Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification
 Chemical Engineering and Processing 48 (2009) 859 863 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/cep
Chemical Engineering and Processing 48 (2009) 859 863 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/cep
Influence of Surface Energy of Polymer Films on Spreading and Adhesion of UV-Flexo Inks
 acta graphica 219 short communication received: 08-04-2013. accepted: 17-07-2013. Influence of Surface Energy of Polymer Films on Spreading and Adhesion of UV-Flexo Inks Authors Vyacheslav Repeta Ukrainian
acta graphica 219 short communication received: 08-04-2013. accepted: 17-07-2013. Influence of Surface Energy of Polymer Films on Spreading and Adhesion of UV-Flexo Inks Authors Vyacheslav Repeta Ukrainian
POWDER TECHNOLOGY AND PHARMACEUTICAL PROCESSES
 POWDER TECHNOLOGY AND PHARMACEUTICAL PROCESSES ' fe Edited by DOMINIQUE CHULIA Laboratoire de Pharmacie Galenique, UFR de Pharmacie, Limoges, France MICHEL DELEUIL Rhone-Poulenc Rorer, Antony, France YVETTE
POWDER TECHNOLOGY AND PHARMACEUTICAL PROCESSES ' fe Edited by DOMINIQUE CHULIA Laboratoire de Pharmacie Galenique, UFR de Pharmacie, Limoges, France MICHEL DELEUIL Rhone-Poulenc Rorer, Antony, France YVETTE
Physicochemical Characterization of Binary Ionic Polymer Blends: Polyvinyl Acetate Phthalate and Eudragit E PO
 OPADRY Enteric Acrylic-Based Coating System Poster Reprint Physicochemical Characterization of Binary Ionic Polymer Blends: Polyvinyl Acetate Phthalate and Eudragit E PO PURPOSES Polymer complexes, such
OPADRY Enteric Acrylic-Based Coating System Poster Reprint Physicochemical Characterization of Binary Ionic Polymer Blends: Polyvinyl Acetate Phthalate and Eudragit E PO PURPOSES Polymer complexes, such
FORCE TENSIOMETER K100 THE HIGH-END SOLUTION FOR MEASURING SURFACE AND INTERFACIAL TENSION
 FORCE TENSIOMETER K100 THE HIGH-END SOLUTION FOR MEASURING SURFACE AND INTERFACIAL TENSION MAXIMIZING THE VARIETY OF SURFACE AND INTERFACIAL TENSION MEASURING METHODS Determines surface and interfacial
FORCE TENSIOMETER K100 THE HIGH-END SOLUTION FOR MEASURING SURFACE AND INTERFACIAL TENSION MAXIMIZING THE VARIETY OF SURFACE AND INTERFACIAL TENSION MEASURING METHODS Determines surface and interfacial
Hydrophilization of Fluoropolymers and Silicones
 2017 Adhesive and Sealant Council Spring Meeting Hydrophilization of Fluoropolymers and Silicones Aknowledgements: Wei Chen Mount Holyoke College NSF, NIH, Dreyfus, ACS-RF, MHC Bryony Coupe, Mamle Quarmyne,
2017 Adhesive and Sealant Council Spring Meeting Hydrophilization of Fluoropolymers and Silicones Aknowledgements: Wei Chen Mount Holyoke College NSF, NIH, Dreyfus, ACS-RF, MHC Bryony Coupe, Mamle Quarmyne,
Pelagia Research Library
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Der Pharmacia Sinica, 2012, 3 (1):111-116 ISSN: 0976-8688 CODEN (USA): PSHIBD Formulation and Evaluation of Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride Extended Release
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Der Pharmacia Sinica, 2012, 3 (1):111-116 ISSN: 0976-8688 CODEN (USA): PSHIBD Formulation and Evaluation of Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride Extended Release
Influence of Functionalized Silanes on Mechanical Properties of Wood Sawdust Reinforced ABS Composites
 Influence of Functionalized Silanes on Mechanical Properties of Wood Sawdust Reinforced ABS Composites Pichaya Kimchiang Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Faculty of Engineering and Industrial
Influence of Functionalized Silanes on Mechanical Properties of Wood Sawdust Reinforced ABS Composites Pichaya Kimchiang Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Faculty of Engineering and Industrial
Electrostatics and cohesion: Cause or effect?
 Electrostatics and cohesion: Cause or effect? Fernando Muzzio Rutgers University Department of Chemical and Biochemical Engineering, 98 Brett Road, Piscataway, NJ 08854 Powder Flow 2009 16 December ENGINEERING
Electrostatics and cohesion: Cause or effect? Fernando Muzzio Rutgers University Department of Chemical and Biochemical Engineering, 98 Brett Road, Piscataway, NJ 08854 Powder Flow 2009 16 December ENGINEERING
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
 B05D PROCESSES FOR APPLYING LIQUIDS OR OTHER FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL (apparatus for applying liquids or other fluent materials to surfaces B05B, B05C; {coating of foodstuffs A23P 20/17,
B05D PROCESSES FOR APPLYING LIQUIDS OR OTHER FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL (apparatus for applying liquids or other fluent materials to surfaces B05B, B05C; {coating of foodstuffs A23P 20/17,
