Chemistry std10 ELECTROLYSIS Important terms in Electrolysis
|
|
|
- Benjamin Montgomery
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chemistry std10 ELECTROLYSIS Important terms in Electrolysis 1) Electrolysis: it is the process of decomposition of a chemical compound in aqueous solution or fused state by the passage of a direct electric current resulting in the discharge of ions as neutral atoms at the respective electrodes 2) Electrolyte: it is a compound which either in aqueous solution or molten state allows a current to pass through it. It decomposes into ions and finally neutral atoms at the two electrodes. Electrolytes are: *Ionic compounds in which positive and negative ions are held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction *These compounds conduct electricity in their aqueous or molten state. *Polar covalent compounds conduct electricity in their aqueous state. *Non-conductors in solid state because the ions are not free to conduct electricity. Examples: ACIDS: H2SO4, HNO3, H3PO4, HCl BASES: NaOH, KOH, NH4OH, Ca(OH)2 SALTS: NaCl, CuSO4, PbBr2 Electrolytes are classified into two types Strong electrolyte 1 They allow a large amount of electricity to pass through them Weak electrolyte 1 Allows small amount of electricity to flow through them 2 Good conductors of electricity 2 Poor conductors of electricity 3 Almost completely dissociated in fused or aqueous solution state 4 These solutions contains almost only free mobile ions 5 Strong electrolyte allows a bulb to grow brightly 3 Partially dissociated in fused or aqueous solution state 4 Contains Ions as well as molecules 5 Allow bulb to glow dimly 1
2 ACIDS: H2SO4, HCl, HNO3,HBr BASES: NaOH, KOH, LiOH SALTS: NaCl, CuSO4, PbBr2, CuCl2 ACIDS: Carbonic acid,acetic acid, Oxalic acid BASES: NH4OH, Ca(OH)2 SALTS: Sodium carbonate,potassium bicarbonate Non electrolyte: It is a compound which neither in solution nor in the molten state allows an electric current to pass through it. They do not have ions but only molecules in them Example: Distilled water, alcohol, kerosene, carbon disulphide, Cane sugar, benzene, glucose, urea. Electrolytic cell/ voltameter: it is the vessel in which electrolysis is carried out. Electrochemical Cell: It is a device used to convert chemical energy to electrical energy Examples: Simple voltaic cell, Daniel cell Electrodes: Two metal plates or wires or graphite rods or gas carbon rods immersed in the electrolyte through which the current enters and leaves the cell are called electrodes. Anode: electrode connected to the positive pole of the battery Cathode: Electrode connected to the negative pole of the battery Note: When the current is on, the cathode becomes the negative electrode by which electrons enter the electrolyte and the anode becomes the positive electrode by which electrons leave the electrolyte. Difference between cathode and Anode Anode Cathode 1 Electrode connected to the Positive terminal of the battery 2 1 Electrode connected to the Negative terminal of the battery 2 Anions migrate to anode 2 Cations migrate to cathode 3 Anions are oxidised at the anode 3 Cations are reduced at the cathode Ions: are atom or groups of atoms which carry a positive or negative charge Cations:Ions which carry a positive charge Anions::Ions which are negatively charged Difference between cations and anions Cations Anions 1 Positively charged ions 1 Negatively charged ions 2 Migrate to the cathode 2 Migrate to the Anode
3 3 Gains electrons from the cathode and get reduced 3 Lose electrons to the anode and get oxidised Q. Why do the electrovalent compounds conduct electricity in the fused state or in the aqueous state only? In the electrovalent compounds the ions are held by strong electrostatic forces of attraction between the ions on melting or dissolving the forces of attraction are broken and the ions then can move about conducting electricity Q. How do covalent molecules conduct electricity? Covalent compounds which are polar in nature,eg:hcl,nh3, and H2O ionise in aqueous solution and conduct electricity Q. Why is the process of electrolysis a redox reaction? The reaction at the cathode involves reduction of cations as they gain electrons to become neutral atoms, while at the anode oxidation takes place which involves loss of electrons by the anions to become neutral atoms. Difference between Ionisation and Dissociation Ionisation 1 Formation of positively or negatively charged ions from molecules which are not initially in Ionic state 2 Polar covalent compounds and metals undergo ionisation H2O HCl H + + Cl - or Mg 2e - Mg +2 Dissociation 1 Separation of ions which are already present in an ionic compound 2 Electrovalent compounds show Dissociation KCl K + + Cl - Difference in conduction of electricity in a metal and electrolyte Metal Electrolyte 1 Flow of electricity takes place by flow of electrons Flow of electricity takes place by flow of ions. 2 No decomposition of parent metal. Decomposition of the electrolyte solutions. 3 Good conductors in solid state and in molten state Conduct electricity in the aqueous state or molten state. 4 No transfer of matter takes place Transfer of ions takes place. 3
4 Electrochemical Series of Metals: Based on the ease with which atoms of metals lose electrons to form positively charged ions, the metals are arranged in a series known as the activity series or electrochemical series Increasing each of discharge at the cathode K + Ca +2 Na +2 Mg +2 Increasing ease of reduction Al +3 Zn +2 Fe +3 Ni +2 Sn +4 Increasing ease of discharge at Electrochemical series of Anions: SO4 NO3 Cl Br -2 Increasing 1- ease of discharge -1 at anode I - Pb +2 Cathode OH H + Cu +2 Hg +2 Ag Au +3 Pt +4 Q.Can we store CuSO4 in an Iron vessel? It cannot be stored in an Iron vessel since Cu is below iron in the activity series; Iron displaces copper from copper sulphate Q.What is preferential discharge of ions? 4
5 When two or more ions of the same charge are present in a solution of an electrolyte under identical conditions are competing for discharge at the same electrode, one of them is preferentially discharged this is known as selective discharge of ions Q.What does Selective discharge of ions depends on? Relative positions of ions in the electrochemical series: If all other factors are constant, any ions lower in the electrochemical series gets discharged at the relevant electrode in preference to those above it. Relative concentration of ions: If an electrolyte has a much higher concentration of a particular ion then that ion will be discharged at the relevant electrode in preference to those ions which are lower in the electrochemical series For example: Electrolysis of conc Sodium Chloride (aq) NaCl Na + + Cl - H2O H + +OH - At cathode H + +1e - H2 At Anode Cl - - 1e - Cl + Cl Cl2 Nature of electrode: In the electrolysis of Copper (II) sulphate solution, copper atoms are deposited at the cathode and copper ions are formed at the anode if copper anode and cathode are used, oxygen is formed at the anode if platinum anode is used. Cathode is Copper and Anode are Copper Reaction: CuSO4 Cu +2 +SO4-2 H2O H + + OH - Cathode: Cu +2 +2e - Cu Anode: Cu -2e - Cu +2 Cathode is Copper Anode is Platinum Cathode: Cu +2 +2e - Cu Example of electrolysis: Anode:4OH - - 4e - 2H2O + O2 Electrolysis of Molten lead bromide( PbBr2) 5
6 Electrolyte: Molten Lead bromide Temperature:Above C Electrolytic Cell: Crucible made of Silica Electrodes: Cathode-Graphite Anode: Graphite Current:12v,3amp battery Electrode Reactions: Cathode: Pb +2 +2e - Pb Anode Br - + 1e - Br Br + Br Br2 Overall Reaction PbBr2 Pb(s) + Br2(g) Observations: Dark reddish fumes of Br2 gas at anode. Greyish black lead metal accumulates at the cathode. Q.Silica is the material used in the electrolytic cell. Why? It can withstand high temperature and almost a non conductor of electricity Q. Solid PbBr2 is a non-conductor. Why? The ions of solid PbBr2 are not free hence it has to be heated to make the ions free from electrostatic forces of attraction. Q. Graphite is preferred over other inert anode. Graphite is preferred since it does not react with the reactive Bromine vapours. Electrolysis of Acidified Water: Electrolyte: Distilled water acidified with Dil H2SO4 6
7 Electrolytic cell: Hoffman s Voltameter Electrodes: Platinum foils Current:12volts Electrode reactions H2SO4 2H + + SO4 2- H2O H + +OH - Cathode: H + +1e - H x 4 2H + 2H 2H2 Anode: OH - -1e - OH 4OH 2H2O + O2 Note: Since OH - is discharged at the anode in preference to SO4 2-. The concentration of sulphate ions increases at the anode and decreases at the cathode but the total concentration of H2SO4 remains since it is the H + and OH - ions that are discharge at the cathode and anode. Q. What is the ratio of hydrogen and oxygen and why? Since the formation of 1 molecule of oxygen at the anode releases 4 electrons and there is no build up of electrons in any part of the circuit,the reaction of the cathode must take up 4 electrons 4H + + 4e - 2H2 This shows the number of molecules of hydrogen is twice that of oxygen molecules. Electrolysis of CuSO4 (aq) CASE 1: Electrolysis of CuSO4 using Platinum anode and Copper cathode Elctrolytic Cell: Glass voltameter Electrolyte: Aq CuSO4 7
8 Electrode: Cathode-Copper Anode-Platinum Electrode Reaction: CuSO4 Cu 2+ + SO4 2- H2O H + + OH - Reaction at Cathode- Cu 2+ +2e - Cu (Reddish brown copper seen at the cathode) Anode- OH - -1e - OH 4OH 2H2O + O2(Bubbles of a colourless gas which rekindles a glowing splinter are seen) The sulphate and hydroxyl ions both travel to the anode but OH - gets discharged.the neutral OH radicals reunite to form water and oxygen Note: The blue colour of the copper ions fade due to the decrease in the number of copper ions and it finally becomes colourless Case II Electrolysis of CuSO4 with copper cathode and anode Electrolytic Cell: Iron crucible Electrolyte: Aqueous Copper Sulphate Electrode: Cathode: Cu Anode: Cu Current: 12 Volt and Current 3 Amps Dissociation of Aqueous copper sulphate : CuSO4 Cu +2 + SO4-2 H2O H + + OH - Reaction at Cathode : Cu e - Cu (Reddish brown copper seen at the cathode the mass of the cathode increases) 8
9 Reaction at Anode : Cu -2e - Cu +2 Obs:The anode decreases in mass as copper ions dissolve and get added to the electrolyte. Q. The blue colour of CuSO4 remains unchanged in the electrolysis. A For every copper ion discharged at the cathode as neutral copper atoms, a copper ion is added to the solution at the anode and hence the total number of copper ions remains the same. Therefore the blue colour does not fade. Applications of Electrolysis: 1. Electroplating with metals. 2. Electro-refining of metals 3. Extractions of metals. I )Def n Electroplating of metals: Electroplating is an electrolytic process of depositing a thin film of a metal like gold, silver, nickel, chromium etc on another inferior metallic article with the help of electricity. Reasons for electroplating:- 1. Decorative purposes; brass objects are plated with silver to give them the appearance of silver article. 2. To protect from rusting and corrosion. Iron articles are often electroplated. Conditions for electroplating:- 1. The article to be electroplated is always the cathode. Why the metal is always deposited at the cathode. 2. The metal to be plated on the article is always made as the anode since the anode continuously dissolves as ions in solution. 3. Electrolyte must have ions of the metal which is to be plated on the article. Electrolyte dissociates into ions of the metals which migrate towards the cathode and are deposited as neutral metallic atoms. 4. A low current for a longer time is used. Longer time and low current initiate a thicker uniform deposition. 5. A (DC) direct current and not a an (AC) alternating current is used. AC current causes discharge and ionisation to alternate at the cathode thus giving no effective coating. 9
10 Electroplating of a brass spoon with Silver:- Electrolyte: Sodium argentocyanide or Potassium argento cyanide Na(Ag(CN)2) Na + + Ag + + 2CN - H2O H + + OH - Cathode: Ag + + 1e - Ag Anode: Ag 1e - Ag + If Silver Nitrate solution is used the deposition of silver is very fast and hence not very smooth and uniform. Electroplating with Nickel Electrolyte: Aqueous solution of NiSO4 Reaction: NiSO4 Ni ++ + SO4-2 H2O H + + OH - Cathode: cleaned article to be electroplated Anode: Block of nickel metal Reaction at Cathode: Ni e - Ni 10
11 Anode: Ni 2e - Ni +2 II )Electro-refining of metals: Electrolysis is the process by which metals containing impurities are purified electrolytically to give a pure metal. Electrorefining of Copper: Electolyte: A solution of CuSO4 Cathode: Thin Strip of pure copper Anode: Impure copper Reaction: CuSO4 Cu +2 + SO4-2 Cathode: Cu e- Cu Anode: Cu 2e- Cu +2 Gradually the impure slabs of copper gets finished and thin strips of pure copper becomes thicker and thicker. The copper deposited has a purity of 99.9% pure. Q.What is electrode mud? Some impurities get dissolved with the acid used, while others namely silver and gold which are insoluble fall down near the anode (anode mud) and are recovered later. Note: Metals like zinc, lead, mercury, silver and copper are refined by electrolysis.the metals extracted by electrolysis are not generally purified. Electrometallurgy: 11
12 Electrolysis of Molten KCl 1. Sodium, potassium, Calcium and magnesium are extracted by electrolysis of their fused chlorides when cathode is made of iron and anode of a graphite rod. For example: CaCl2 Ca Cl - Cathode: Ca e- Ca Anode: Cl- -1e- Cl, Cl + Cl Cl2 2. Aluminium is extracted by electrolysis of Al2O3 Gas carbon lining is cathode and thick carbon rods are made anode. Reaction : Al2O3 2Al + 3O -2 Cathode: gas carbon lining 2Al +3 +6e- 2Al Anode: Thick carbon rods 3O -2-6e- 3 O +3O 12
3. Solids cannot conduct electricity because the ions cannot move freely 4. Electrolytic cell
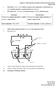 Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
(i) Voltameter consist of a vessel, two electrodes and electrolytic solution.
 Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry which deals with the relationship between electrical energy and chemical changes taking place in redox reactions i.e., how chemical energy produced
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry which deals with the relationship between electrical energy and chemical changes taking place in redox reactions i.e., how chemical energy produced
Lesson on Electrolysis
 Lesson on Electrolysis This lesson package includes a lesson plan, a worksheet for students, and teachers notes on the worksheet. Activity Lesson 1 (50 min-2 Period lesson) Teacher explains (page 1 to
Lesson on Electrolysis This lesson package includes a lesson plan, a worksheet for students, and teachers notes on the worksheet. Activity Lesson 1 (50 min-2 Period lesson) Teacher explains (page 1 to
MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E.
 MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E. GRADE - X (2017-2018) Exam No. : MT/ICSE/SEMI PRELIM - II - SET -A 020 Periodic Table, Chemical bonding, Acid, Bases and Salts, Practical Work, Mole Concept, Electrolysis Chemistry
MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E. GRADE - X (2017-2018) Exam No. : MT/ICSE/SEMI PRELIM - II - SET -A 020 Periodic Table, Chemical bonding, Acid, Bases and Salts, Practical Work, Mole Concept, Electrolysis Chemistry
Chapter 32. Electrolysis
 Chapter 32 Electrolysis 32.1 Electrolysis a type of redox reactions 32.2 Predicting preferential discharge of ions 32.3 Electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid 32.4 Electrolysis of sodium chloride solution
Chapter 32 Electrolysis 32.1 Electrolysis a type of redox reactions 32.2 Predicting preferential discharge of ions 32.3 Electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid 32.4 Electrolysis of sodium chloride solution
Definition 1 An element or compound is oxidized when it gains oxygen atoms
 Oxidation and Reduction Part I Learning Outcomes 1. Introduction to oxidation and reduction: simple examples only, e.g. Na with Cl 2, Mg with O 2, Zn with Cu 2+. 2. Oxidation and reduction in terms of
Oxidation and Reduction Part I Learning Outcomes 1. Introduction to oxidation and reduction: simple examples only, e.g. Na with Cl 2, Mg with O 2, Zn with Cu 2+. 2. Oxidation and reduction in terms of
(c) dilute solution of glucose (d) chloroform 12 Which one of the following represents the same net reaction as the electrolysis of aqueous H2SO4
 1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy (d) none of these 2 Standard hydrogen electrode has an
1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy (d) none of these 2 Standard hydrogen electrode has an
Electrolysis. Question Paper. Cambridge International Examinations. Score: /48. Percentage: /100
 Electrolysis Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International Examinations Electrolysis Question Paper Time llowed: 58 minutes Score: /48 Percentage: /100 1 queous
Electrolysis Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International Examinations Electrolysis Question Paper Time llowed: 58 minutes Score: /48 Percentage: /100 1 queous
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Chemistry 5 - Electricity and Chemistry Electrolysis You need to know that electrolysis is: - The breakdown of ionic substances into their constituent elements
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Chemistry 5 - Electricity and Chemistry Electrolysis You need to know that electrolysis is: - The breakdown of ionic substances into their constituent elements
Electrolytic processes Notes
 Edexcel GCSE Chemistry Topic 3: Chemical changes Electrolytic processes Notes 3.22 Recall that electrolytes are ionic compounds in the molten state or dissolved in water When an ionic substance is melted
Edexcel GCSE Chemistry Topic 3: Chemical changes Electrolytic processes Notes 3.22 Recall that electrolytes are ionic compounds in the molten state or dissolved in water When an ionic substance is melted
MC 17 C SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section.
 Question 1. (a) SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section. Choose from the following list of substances, as to what matches the description from to given below : [Bronze,
Question 1. (a) SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section. Choose from the following list of substances, as to what matches the description from to given below : [Bronze,
CHAPTER 5 REVIEW. C. CO 2 D. Fe 2 O 3. A. Fe B. CO
 CHAPTER 5 REVIEW 1. The following represents the process used to produce iron from iron III oxide: Fe 2 O 3 + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO 2 What is the reducing agent in this process? A. Fe B. CO C. CO 2 D. Fe 2 O 3
CHAPTER 5 REVIEW 1. The following represents the process used to produce iron from iron III oxide: Fe 2 O 3 + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO 2 What is the reducing agent in this process? A. Fe B. CO C. CO 2 D. Fe 2 O 3
Conductivity of Electrolytes in Solution
 Conductivity of Electrolytes in Solution Introduction: Electrical current can be thought of as the movement of electrons or ionic charges from an area of high potential to an area of low potential. Materials
Conductivity of Electrolytes in Solution Introduction: Electrical current can be thought of as the movement of electrons or ionic charges from an area of high potential to an area of low potential. Materials
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry. Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry. Notes.
 Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry Notes Define electrolysis as The breakdown of an ionic compound, molten or in aqueous solution, by the passage of electricity Describe the electrode
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry Notes Define electrolysis as The breakdown of an ionic compound, molten or in aqueous solution, by the passage of electricity Describe the electrode
Topic IV. Electrolysis
 IV. Electrolysis Page 1 Topic IV. Electrolysis Reference Reading Integrated Chemistry Today, L.H.M. Chung, Book 1 pg. 316 335 Objectives 3.4 understand that electrical energy can cause redox reactions
IV. Electrolysis Page 1 Topic IV. Electrolysis Reference Reading Integrated Chemistry Today, L.H.M. Chung, Book 1 pg. 316 335 Objectives 3.4 understand that electrical energy can cause redox reactions
Electrolysis 1 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016
 Electrolysis 1 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Electrolysis 2 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are ionic compounds? 3 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Ionic compounds are made up of positive ions and negative ions. What
Electrolysis 1 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Electrolysis 2 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are ionic compounds? 3 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Ionic compounds are made up of positive ions and negative ions. What
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC TEXT REFERENCE. Electrochemistry. Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18. Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1
 Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
Electrochemistry. Part One: Introduction to Electrolysis and the Electrolysis of Molten Salts
 Part One: Introduction to Electrolysis and the Electrolysis of Molten Salts What do I need to know about electrochemistry? Electrochemistry Learning Outcomes: Candidates should be able to: a) Describe
Part One: Introduction to Electrolysis and the Electrolysis of Molten Salts What do I need to know about electrochemistry? Electrochemistry Learning Outcomes: Candidates should be able to: a) Describe
Electrodes are normally made out of inert (unreactive) materials. Graphite and platinum are common electrode materials.
 Electrolysis Electrolysis is using an electric current to break up an ionic compound to form elements. Covalent compounds can t be split up by electrolysis. Terms used in electrolysis: Electrolyte - the
Electrolysis Electrolysis is using an electric current to break up an ionic compound to form elements. Covalent compounds can t be split up by electrolysis. Terms used in electrolysis: Electrolyte - the
CHEMISTRY 13 Electrochemistry Supplementary Problems
 1. When the redox equation CHEMISTRY 13 Electrochemistry Supplementary Problems MnO 4 (aq) + H + (aq) + H 3 AsO 3 (aq) Mn 2+ (aq) + H 3 AsO 4 (aq) + H 2 O(l) is properly balanced, the coefficients will
1. When the redox equation CHEMISTRY 13 Electrochemistry Supplementary Problems MnO 4 (aq) + H + (aq) + H 3 AsO 3 (aq) Mn 2+ (aq) + H 3 AsO 4 (aq) + H 2 O(l) is properly balanced, the coefficients will
Electrochemistry Worksheets
 Electrochemistry Worksheets Donald Calbreath, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive
Electrochemistry Worksheets Donald Calbreath, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive
IB Topics 9 & 19 Multiple Choice Practice
 IB Topics 9 & 19 Multiple Choice Practice 1. What are the oxidation states of chromium in (NH 4) 2Cr 2O 7 (s) and Cr 2O 3 (s)? 2. Which of the following is a redox reaction? 3Mg (s) + 2AlCl 3 (aq) 2Al
IB Topics 9 & 19 Multiple Choice Practice 1. What are the oxidation states of chromium in (NH 4) 2Cr 2O 7 (s) and Cr 2O 3 (s)? 2. Which of the following is a redox reaction? 3Mg (s) + 2AlCl 3 (aq) 2Al
ELECTROCHEMISTRY. Electrons are transferred from Al to Cu 2+. We can re write this equation as two separate half reactions:
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY A. INTRODUCTION 1. Electrochemistry is the branch of chemistry which is concerned with the conversion of chemical energy to electrical energy, and vice versa. Electrochemical reactions
ELECTROCHEMISTRY A. INTRODUCTION 1. Electrochemistry is the branch of chemistry which is concerned with the conversion of chemical energy to electrical energy, and vice versa. Electrochemical reactions
11.3. Electrolytic Cells. Electrolysis of Molten Salts. 524 MHR Unit 5 Electrochemistry
 11.3 Electrolytic Cells Section Preview/ Specific Expectations In this section, you will identify the components of an electrolytic cell, and describe how they work describe electrolytic cells using oxidation
11.3 Electrolytic Cells Section Preview/ Specific Expectations In this section, you will identify the components of an electrolytic cell, and describe how they work describe electrolytic cells using oxidation
Chapter 19: Oxidation - Reduction Reactions
 Chapter 19: Oxidation - Reduction Reactions 19-1 Oxidation and Reduction I. Oxidation States A. The oxidation rules (as summarized by Mr. Allan) 1. In compounds, hydrogen has an oxidation # of +1. In compounds,
Chapter 19: Oxidation - Reduction Reactions 19-1 Oxidation and Reduction I. Oxidation States A. The oxidation rules (as summarized by Mr. Allan) 1. In compounds, hydrogen has an oxidation # of +1. In compounds,
Oxidation & Reduction (Redox) Notes
 Oxidation & Reduction (Redox) Notes Chemical Activity (or Chemical Reactivity) is the measure of the reactivity of elements. If an element has high activity, then it means that the element is willing to
Oxidation & Reduction (Redox) Notes Chemical Activity (or Chemical Reactivity) is the measure of the reactivity of elements. If an element has high activity, then it means that the element is willing to
CET Q UESTIONS QUESTIONS
 CET QUESTIONS ON ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance differs from 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance increases with increase of temperature 2. Electrolytic conductance increases
CET QUESTIONS ON ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance differs from 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance increases with increase of temperature 2. Electrolytic conductance increases
Chemistry 102 Chapter 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS
 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS Some of the most important reaction in chemistry are oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. In these reactions, electrons transfer from one reactant to the other. The rusting
OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS Some of the most important reaction in chemistry are oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. In these reactions, electrons transfer from one reactant to the other. The rusting
(c) Na is deposited at the cathode (d) Na appears at the anode
 year chemiry n0tes new CHAPTER 10 ELECTROCHEMISTRY MCQS Q.1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy
year chemiry n0tes new CHAPTER 10 ELECTROCHEMISTRY MCQS Q.1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy
Regents review Electrochemistry(redox)
 2011-2012 1. Chlorine has an oxidation state of +3 in the compound A) HClO B) HClO2 C) HClO3 D) HClO4 2. What is the oxidation number of iodine in KIO4? A) +1 B) 1 C) +7 D) 7 3. What is the oxidation number
2011-2012 1. Chlorine has an oxidation state of +3 in the compound A) HClO B) HClO2 C) HClO3 D) HClO4 2. What is the oxidation number of iodine in KIO4? A) +1 B) 1 C) +7 D) 7 3. What is the oxidation number
Practice Exam Topic 9: Oxidation & Reduction
 Name Practice Exam Topic 9: Oxidation & Reduction 1. What are the oxidation numbers of the elements in sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4? Hydrogen Sulfur Oxygen A. +1 +6 2 B. +1 +4 2 C. +2 +1 +4 D. +2 +6 8 2. Consider
Name Practice Exam Topic 9: Oxidation & Reduction 1. What are the oxidation numbers of the elements in sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4? Hydrogen Sulfur Oxygen A. +1 +6 2 B. +1 +4 2 C. +2 +1 +4 D. +2 +6 8 2. Consider
ICSE QUESTION PAPER Class X Chemistry (2016) Solution
 ICSE QUESTION PAPER Class X Chemistry (016) Solution Section I 1. Metals are good reducing agents because they are electron donors. Electrovalent compounds have high melting points. (iii) Higher the ph
ICSE QUESTION PAPER Class X Chemistry (016) Solution Section I 1. Metals are good reducing agents because they are electron donors. Electrovalent compounds have high melting points. (iii) Higher the ph
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes
 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
YEAR 10 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min
 YEAR 10 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min NAME: CLASS: Useful data: Q = It. Faraday Constant = 96,500 C mol -1. Use the Periodic table, given below, where necessary. Marks Grid [For Examiners use only] Question
YEAR 10 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min NAME: CLASS: Useful data: Q = It. Faraday Constant = 96,500 C mol -1. Use the Periodic table, given below, where necessary. Marks Grid [For Examiners use only] Question
Solved Examples On Electrochemistry
 Solved Examples On Electrochemistry Example 1. Find the charge in coulomb on 1 g-ion of Charge on one ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 coulomb Thus, charge on one g-ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 6.02 10 23 = 2.89
Solved Examples On Electrochemistry Example 1. Find the charge in coulomb on 1 g-ion of Charge on one ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 coulomb Thus, charge on one g-ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 6.02 10 23 = 2.89
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes
 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
Electrolysis. Introduction. Electrolysis APPENDIX. The key ideas required to understand this section are:
 Electrolysis APPENDIX 7 1 Introduction The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Redox reactions 100 Writings and balancing redox equations 104 Standard electrode potentials
Electrolysis APPENDIX 7 1 Introduction The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Redox reactions 100 Writings and balancing redox equations 104 Standard electrode potentials
What is the importance of redox reactions? Their importance lies in the fact that we can use the transfer of electrons between species to do useful
 What is the importance of redox reactions? Their importance lies in the fact that we can use the transfer of electrons between species to do useful work. This is accomplished by constructing a voltaic
What is the importance of redox reactions? Their importance lies in the fact that we can use the transfer of electrons between species to do useful work. This is accomplished by constructing a voltaic
CET Q UESTIONS QUESTIONS
 CET QUESTIONS ON ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance differs from 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance increases with increase of temperature 2. Electrolytic conductance increases
CET QUESTIONS ON ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance differs from 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance increases with increase of temperature 2. Electrolytic conductance increases
1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number
 General Chemistry II Exam 4 Practice Problems 1 1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number a. K 2 Cr 2 O 7 +6 b. NaAl(OH) 4 +3 c.
General Chemistry II Exam 4 Practice Problems 1 1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number a. K 2 Cr 2 O 7 +6 b. NaAl(OH) 4 +3 c.
Electrochemistry. A. Na B. Ba C. S D. N E. Al. 2. What is the oxidation state of Xe in XeO 4? A +8 B +6 C +4 D +2 E 0
 Electrochemistry 1. Element M reacts with oxygen to from an oxide with the formula MO. When MO is dissolved in water, the resulting solution is basic. Element M is most likely: A. Na B. Ba C. S D. N E.
Electrochemistry 1. Element M reacts with oxygen to from an oxide with the formula MO. When MO is dissolved in water, the resulting solution is basic. Element M is most likely: A. Na B. Ba C. S D. N E.
SCHOOL YEAR CH- 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY GRADE: 12
 SCHOOL YEAR 2017-18 NAME: CH- 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY GRADE: 12 TEST A Choose the best answer from the options that follow each question. 1. During oxidation, one or more electrons
SCHOOL YEAR 2017-18 NAME: CH- 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SUBJECT: CHEMISTRY GRADE: 12 TEST A Choose the best answer from the options that follow each question. 1. During oxidation, one or more electrons
UNIT 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY
 95414101 UNIT 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1 MARK QUESTIONS Q. 1. Which solution will allow greater conductance of electricity, 1 M NaCl at 93 K or 1 M NaCl at 33 K and why? Ans. 1 M NaCl at 33 K as the ionic mobilities
95414101 UNIT 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1 MARK QUESTIONS Q. 1. Which solution will allow greater conductance of electricity, 1 M NaCl at 93 K or 1 M NaCl at 33 K and why? Ans. 1 M NaCl at 33 K as the ionic mobilities
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS NAME ROW PD
 4-26-12 NAME ROW PD (1) Which statement describes the redox reaction that occurs when an object is electroplated? The diagram below shows the electrolysis of fused KCl. A) It is spontaneous and requires
4-26-12 NAME ROW PD (1) Which statement describes the redox reaction that occurs when an object is electroplated? The diagram below shows the electrolysis of fused KCl. A) It is spontaneous and requires
Unit - 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 3. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells of a galvanic cell?
 Unit - 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. What is a galvanic cell? VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 2. Give the cell representation for Daniell Cell. 3. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells
Unit - 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. What is a galvanic cell? VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 2. Give the cell representation for Daniell Cell. 3. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells
Reactions in aqueous solutions Redox reactions
 Reactions in aqueous solutions Redox reactions Redox reactions In precipitation reactions, cations and anions come together to form an insoluble ionic compound. In neutralization reactions, H + ions and
Reactions in aqueous solutions Redox reactions Redox reactions In precipitation reactions, cations and anions come together to form an insoluble ionic compound. In neutralization reactions, H + ions and
(Q.) By which process, we can easily obtain gold ornaments at cheaper costs? (1 Mark)
 Science Class 8 (CBSE) Page: 1 (Q.) Define electrolysis. (1 Mark) (Ans) The chemical reaction (decomposition) of an electrolyte (conducting liquid) into its componentswhen electricity is passed through
Science Class 8 (CBSE) Page: 1 (Q.) Define electrolysis. (1 Mark) (Ans) The chemical reaction (decomposition) of an electrolyte (conducting liquid) into its componentswhen electricity is passed through
Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species.
 Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species. The species that loses the electron is oxidized. The species that gains the electron is reduced.
Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species. The species that loses the electron is oxidized. The species that gains the electron is reduced.
Electrochemistry. Electrochemical Process. The Galvanic Cell or Voltaic Cell
 Electrochemistry Electrochemical Process The conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and the conversion of electrical energy into chemical energy are electrochemical process. Recall that an
Electrochemistry Electrochemical Process The conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and the conversion of electrical energy into chemical energy are electrochemical process. Recall that an
Redox Reactions, Chemical Cells and Electrolysis
 Topic 5 Redox Reactions, Chemical Cells and Electrolysis Part A Unit-based exercise Unit 19 Chemical cells in daily life Fill in the blanks 1 chemical; electrical 2 electrolyte 3 voltmeter; multimeter
Topic 5 Redox Reactions, Chemical Cells and Electrolysis Part A Unit-based exercise Unit 19 Chemical cells in daily life Fill in the blanks 1 chemical; electrical 2 electrolyte 3 voltmeter; multimeter
Unit 4: Chemical Changes (Higher Content)
 Metals react with oxygen to produce metal oxides. E.g. Copper + Oxygen > Copper Oxide The reactions are oxidation reactions because the metals gain oxygen. Reactivity of Metals Metal Extraction Metals
Metals react with oxygen to produce metal oxides. E.g. Copper + Oxygen > Copper Oxide The reactions are oxidation reactions because the metals gain oxygen. Reactivity of Metals Metal Extraction Metals
 CHAPTER 10 ELECTROCHEMISTRY TEXT BOOK EXERCISE Q1. Multiple choice questions. (i) The cathode reaction in the electrolysis of dill. H2SO4 with Pt electrode is (a) Reduction (b) Oxidation (c) Both oxidation
CHAPTER 10 ELECTROCHEMISTRY TEXT BOOK EXERCISE Q1. Multiple choice questions. (i) The cathode reaction in the electrolysis of dill. H2SO4 with Pt electrode is (a) Reduction (b) Oxidation (c) Both oxidation
One mole of electrons carries a charge of 96500C or 1 Faraday Q=It One mole of any gas occupies 22.4dm 3 at standard temperature and pressure (s.t.p.
 1 One mole of electrons carries a charge of 96500C or 1 Faraday Q=It One mole of any gas occupies 22.4dm 3 at standard temperature and pressure (s.t.p.) Standard temperature is 0 0 C or 273K and standard
1 One mole of electrons carries a charge of 96500C or 1 Faraday Q=It One mole of any gas occupies 22.4dm 3 at standard temperature and pressure (s.t.p.) Standard temperature is 0 0 C or 273K and standard
Electrolytes non electrolytes. Types of Electrolytes
 Electrochemistry Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred between molecules are called oxidation/reduction (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry deals with situations where oxidation
Electrochemistry Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred between molecules are called oxidation/reduction (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry deals with situations where oxidation
Unit 8 Redox 8-1. At the end of this unit, you ll be able to
 8-1 Unit 8 Redox At the end of this unit, you ll be able to Define and identify oxidation reactions Define and identify reduction reactions Assign oxidation numbers to elements in a compound Write and
8-1 Unit 8 Redox At the end of this unit, you ll be able to Define and identify oxidation reactions Define and identify reduction reactions Assign oxidation numbers to elements in a compound Write and
Electrochemistry Pulling the Plug on the Power Grid
 Electrochemistry 18.1 Pulling the Plug on the Power Grid 18.3 Voltaic (or Galvanic) Cells: Generating Electricity from Spontaneous Chemical Reactions 18.4 Standard Electrode Potentials 18.7 Batteries:
Electrochemistry 18.1 Pulling the Plug on the Power Grid 18.3 Voltaic (or Galvanic) Cells: Generating Electricity from Spontaneous Chemical Reactions 18.4 Standard Electrode Potentials 18.7 Batteries:
1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
 1 Intext Questions On Page 6 Question 1. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air? Magnesium ribbon reacts with CO present in air to form a protective and inert layer of magnesium
1 Intext Questions On Page 6 Question 1. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air? Magnesium ribbon reacts with CO present in air to form a protective and inert layer of magnesium
The electrolysis of sodium chloride solution produces useful substances. covalent ionic non-metallic
 1 The electrolysis of sodium chloride solution produces useful substances. (a) (i) Choose a word from the box to complete the sentence. covalent ionic non-metallic Electrolysis takes place when electricity
1 The electrolysis of sodium chloride solution produces useful substances. (a) (i) Choose a word from the box to complete the sentence. covalent ionic non-metallic Electrolysis takes place when electricity
Worked solutions. Chapter 9. Exercises O 3
 Worked solutions Chapter 9 Exercises 1 The numbers are assigned following the strategy on page 408. In most of these it is best to assign the values for [2] and H [+1] first, and then assign values to
Worked solutions Chapter 9 Exercises 1 The numbers are assigned following the strategy on page 408. In most of these it is best to assign the values for [2] and H [+1] first, and then assign values to
Name: Regents Chemistry Date:
 Name: Date: 1. The reaction CuO + CO CO 2 + Cu is an example of (A) reduction, only (B) oxidation, only (C) both oxidation and reduction (D) neither oxidation nor reduction 6. In which compound does chlorine
Name: Date: 1. The reaction CuO + CO CO 2 + Cu is an example of (A) reduction, only (B) oxidation, only (C) both oxidation and reduction (D) neither oxidation nor reduction 6. In which compound does chlorine
Section A: Summary Notes
 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS 25 AUGUST 2015 Section A: Summary Notes Important definitions: Oxidation: the loss of electrons by a substance during a chemical reaction Reduction: the gain of electrons by a substance
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS 25 AUGUST 2015 Section A: Summary Notes Important definitions: Oxidation: the loss of electrons by a substance during a chemical reaction Reduction: the gain of electrons by a substance
Introduction to electrochemistry
 Introduction to electrochemistry Oxidation reduction reactions involve energy changes. Because these reactions involve electronic transfer, the net release or net absorption of energy can occur in the
Introduction to electrochemistry Oxidation reduction reactions involve energy changes. Because these reactions involve electronic transfer, the net release or net absorption of energy can occur in the
Electrolysis. Specification points. Year 11 Electrolysis
 Electrolysis Specification points Year Electrolysis The process of electrolysis When an ionic compound is melted or dissolved in water, the ions are free to move about within the liquid or solution (the
Electrolysis Specification points Year Electrolysis The process of electrolysis When an ionic compound is melted or dissolved in water, the ions are free to move about within the liquid or solution (the
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 18. Electrochemistry. Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University Harnessing the Power in Nature The goal of scientific research is to understand nature. Once we understand the
Lecture Presentation Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University Harnessing the Power in Nature The goal of scientific research is to understand nature. Once we understand the
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2013 Solution SECTION I
 ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2013 Solution SECTION I 1) i. Hydronium ii. Hydroxide iii. Salt iv. Water v. Hydrogen 2) i. C 2 H 6 gas Reaction: ii. Sulphur dioxide gas is evolved. K 2 SO 3 +
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2013 Solution SECTION I 1) i. Hydronium ii. Hydroxide iii. Salt iv. Water v. Hydrogen 2) i. C 2 H 6 gas Reaction: ii. Sulphur dioxide gas is evolved. K 2 SO 3 +
CHEMISTRY. SCIENCE Paper 2
 CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
5.0 Electricity and Chemistry
 5.0 Electricity and hemistry Question Paper Level IGSE Subject hemistry (0620) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic Electricity and hemistry Sub-Topic 5.0 Electricity and hemistry ooklet
5.0 Electricity and hemistry Question Paper Level IGSE Subject hemistry (0620) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic Electricity and hemistry Sub-Topic 5.0 Electricity and hemistry ooklet
Chem II. Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq)
 Redox Review Chem II 1. What is the sum of the oxidation numbers of the atoms in the compound CO2? A) 0 B) 2 C) 4 D) +4 2. In which substance does phosphorus have a +3 oxidation state? A) P4O10 B) PCl5
Redox Review Chem II 1. What is the sum of the oxidation numbers of the atoms in the compound CO2? A) 0 B) 2 C) 4 D) +4 2. In which substance does phosphorus have a +3 oxidation state? A) P4O10 B) PCl5
Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination April, 2017 Chemistry
 Grade 09 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination April, 2017 Chemistry Duration: 2.30 Hours Index No:- Part -1 1) Select most suitable answers and underline them. 1) The diagram shows
Grade 09 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination April, 2017 Chemistry Duration: 2.30 Hours Index No:- Part -1 1) Select most suitable answers and underline them. 1) The diagram shows
ELECTROCHEMISTRY OXIDATION-REDUCTION
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrochemistry involves the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy. OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SPONTANEOUS REACTIONS Can extract electrical energy from these.
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrochemistry involves the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy. OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SPONTANEOUS REACTIONS Can extract electrical energy from these.
Unit 13 Electrochemistry Review
 1. What is the oxidation state of nitrogen in NaNO2? A) +1 B) +2 C) +3 D) +4 2. Given the reaction that occurs in an electrochemical cell: Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) During this reaction, the
1. What is the oxidation state of nitrogen in NaNO2? A) +1 B) +2 C) +3 D) +4 2. Given the reaction that occurs in an electrochemical cell: Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) During this reaction, the
CHEMISTRY PAPER 1999
 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1999 (One and a half hours) Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will NOT be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent
CHEMISTRY PAPER 1999 (One and a half hours) Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will NOT be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent
Redox and Voltaic Cells
 Name: Redox and Voltaic Cells Period: 1. Which half-reaction equation represents the reduction of an iron(ii) ion? 1) Fe 2+ Fe 3+ + e 2) Fe 2+ + 2e Fe 1) 1 to +2 2) 1 to 2 3) Fe 3+ + e Fe 2+ 4) Fe Fe 2+
Name: Redox and Voltaic Cells Period: 1. Which half-reaction equation represents the reduction of an iron(ii) ion? 1) Fe 2+ Fe 3+ + e 2) Fe 2+ + 2e Fe 1) 1 to +2 2) 1 to 2 3) Fe 3+ + e Fe 2+ 4) Fe Fe 2+
Electrochemical Cells
 Electrochemical Cells There are two types: Galvanic and Electrolytic Galvanic Cell: a cell in which a is used to produce electrical energy, i.e., Chemical energy is transformed into Electrical energy.
Electrochemical Cells There are two types: Galvanic and Electrolytic Galvanic Cell: a cell in which a is used to produce electrical energy, i.e., Chemical energy is transformed into Electrical energy.
12.05 Galvanic Cells. Zn(s) + 2 Ag + (aq) Zn 2+ (aq) + 2 Ag(s) Ni(s) + Pb 2+ (aq) «Ni 2+ (aq) + Pb(s)
 12.05 Galvanic Cells 1. In an operating voltaic cell, reduction occurs A) at the anode B) at the cathode C) in the salt bridge D) in the wire 2. Which process occurs in an operating voltaic cell? A) Electrical
12.05 Galvanic Cells 1. In an operating voltaic cell, reduction occurs A) at the anode B) at the cathode C) in the salt bridge D) in the wire 2. Which process occurs in an operating voltaic cell? A) Electrical
CHEMISTRY. SCIENCE Paper 2
 CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015
 Grade 11B Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Chemistry - I Duration: 1.00 Hour Part 1 1) A liquid boils at a temperature of 100 o C. Which other property of the liquid
Grade 11B Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Chemistry - I Duration: 1.00 Hour Part 1 1) A liquid boils at a temperature of 100 o C. Which other property of the liquid
Ch 11 Practice Problems
 Ch 11 Practice Problems 1. How many electrons are transferred in the following reaction? 2Cr 2O 7 2- + 14H + + 6Cl 2Cr 3+ + 3Cl 2 + 7H 2O A) 2 B) 4 C) 6 D) 8 2. Which metal, Al or Ni, could reduce Zn 2+
Ch 11 Practice Problems 1. How many electrons are transferred in the following reaction? 2Cr 2O 7 2- + 14H + + 6Cl 2Cr 3+ + 3Cl 2 + 7H 2O A) 2 B) 4 C) 6 D) 8 2. Which metal, Al or Ni, could reduce Zn 2+
Class 12 Important Questions for Chemistry Electrochemistry
 Class 12 Important Questions for Chemistry Electrochemistry Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Which cell will measure standard electrode potential of copper electrode? o (i) Pt (s) H2 (g,0.1 bar) H
Class 12 Important Questions for Chemistry Electrochemistry Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Which cell will measure standard electrode potential of copper electrode? o (i) Pt (s) H2 (g,0.1 bar) H
In the exam, you will be asked to tackle questions such as the one below. 6 volt d.c. power supply
 Get started AO1, AO2 3 Electrolysis Electrolysis is the decomposition (breakdown) of a compound using electricity. This unit will help you to explain what happens in electrolysis and to predict and explain
Get started AO1, AO2 3 Electrolysis Electrolysis is the decomposition (breakdown) of a compound using electricity. This unit will help you to explain what happens in electrolysis and to predict and explain
ICSE Chemistry Model Paper-9
 ICSE Chemistry Model Paper-9 Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading the
ICSE Chemistry Model Paper-9 Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading the
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions and Introduction to Electrochemistry
 ADVANCED PLACEMENT CHEMISTRY Oxidation-Reduction Reactions and Introduction to Electrochemistry Students will be able to: identify oxidation and reduction of chemical species; identify oxidants and reductants
ADVANCED PLACEMENT CHEMISTRY Oxidation-Reduction Reactions and Introduction to Electrochemistry Students will be able to: identify oxidation and reduction of chemical species; identify oxidants and reductants
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17
 Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2014 Solution SECTION I
 ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2014 Solution SECTION I Answer 1 1) D 2) B 3) C 4) A 5) C 6) A 7) D 8) C 9) A 10) D 11) 1 12) Sodium ethoxide 13) CaO is alkaline 14) Downward displacement of air
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2014 Solution SECTION I Answer 1 1) D 2) B 3) C 4) A 5) C 6) A 7) D 8) C 9) A 10) D 11) 1 12) Sodium ethoxide 13) CaO is alkaline 14) Downward displacement of air
Today s Objectives: and an electrolytic cell. standard cell potentials. Section 14.3 (pp )
 Today s Objectives: 1. Identify the similarities and differences between a voltaic cell and an electrolytic cell 2. Predict the spontaneity of REDOX reactions based on standard cell potentials. 3. Recognize
Today s Objectives: 1. Identify the similarities and differences between a voltaic cell and an electrolytic cell 2. Predict the spontaneity of REDOX reactions based on standard cell potentials. 3. Recognize
Page 1 Name: 2Al 3+ (aq) + 3Mg(s) 3Mg 2+ (aq) + 2Al(s) Fe 2 O 3 + 2Al Al 2 O 3 + 2Fe
 9666-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) What is the oxidation number of chromium in the chromate ion, CrO 2-4? A) +8 B) +3 C) +2 D) +6 2) What is the oxidation number of sulfur in Na 2 S 2 O 3? A) +6 B) +4 C) +2 D) -1
9666-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) What is the oxidation number of chromium in the chromate ion, CrO 2-4? A) +8 B) +3 C) +2 D) +6 2) What is the oxidation number of sulfur in Na 2 S 2 O 3? A) +6 B) +4 C) +2 D) -1
Chemistry. Electrochemistry.
 Chemistry Electrochemistry www.testprepkart.com Table of Content 1. Electrolytes and Electrolysis.. Faraday s laws of electrolysis. 3. Metallic and Electrolytic conductors. 4. Electrolytic conduction.
Chemistry Electrochemistry www.testprepkart.com Table of Content 1. Electrolytes and Electrolysis.. Faraday s laws of electrolysis. 3. Metallic and Electrolytic conductors. 4. Electrolytic conduction.
Sindh Text Book Board, Jamshoro. ELECTROCHEMISTRY
 Chapter # 8 ELECTROCHEMISTRY You will learn in this chapter about: Electrolytes and non-electrolytes. Electrolysis. Electrolysis of molten NaCl. Electrolysis of water. Faraday's laws of electrolysis. Electrochemical
Chapter # 8 ELECTROCHEMISTRY You will learn in this chapter about: Electrolytes and non-electrolytes. Electrolysis. Electrolysis of molten NaCl. Electrolysis of water. Faraday's laws of electrolysis. Electrochemical
 CHAPTER No. 1 CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS HOTS: (High Order Thinking Skill) Questions with Answers: 1 A compound `X` is used for drinking, has ph =7.Its acidified solution undergoes decomposition
CHAPTER No. 1 CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS HOTS: (High Order Thinking Skill) Questions with Answers: 1 A compound `X` is used for drinking, has ph =7.Its acidified solution undergoes decomposition
(for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes)
 www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) 1. chem10b 20.4-3 In a voltaic cell electrons flow from the anode to the cathode. Value 2. chem10b 20.1-35 How many grams
www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) 1. chem10b 20.4-3 In a voltaic cell electrons flow from the anode to the cathode. Value 2. chem10b 20.1-35 How many grams
Redox and Electrochemistry
 Redox and Electrochemistry 1 Electrochemistry in Action! 2 Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers The oxidation number of any uncombined element is 0. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the
Redox and Electrochemistry 1 Electrochemistry in Action! 2 Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers The oxidation number of any uncombined element is 0. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the
We can use chemistry to generate electricity... this is termed a Voltaic (or sometimes) Galvanic Cell
 Unit 6 Electrochemistry Chemistry 020, R. R. Martin Electrochemistry Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy. We can use chemistry to generate electricity...
Unit 6 Electrochemistry Chemistry 020, R. R. Martin Electrochemistry Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy. We can use chemistry to generate electricity...
Chapter 19 ElectroChemistry
 Chem 1046 General Chemistry by Ebbing and Gammon, 9th Edition George W.J. Kenney, Jr, Professor of Chemistry Last Update: 11July2009 Chapter 19 ElectroChemistry These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text,
Chem 1046 General Chemistry by Ebbing and Gammon, 9th Edition George W.J. Kenney, Jr, Professor of Chemistry Last Update: 11July2009 Chapter 19 ElectroChemistry These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text,
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry. Electrochemical Cells
 Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Chapter 18 1 Electrochemical Cells Electrochemical Cells are of two basic types: Galvanic Cells a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current Electrolytic Cells
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Chapter 18 1 Electrochemical Cells Electrochemical Cells are of two basic types: Galvanic Cells a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current Electrolytic Cells
Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions & Equations
 CBSE Class 10th NCERT Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions & Equations Intext Questions On Page 6 Question 1: Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air? Magnesium is an extremely reactive
CBSE Class 10th NCERT Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions & Equations Intext Questions On Page 6 Question 1: Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air? Magnesium is an extremely reactive
CHAPTER ELECTROCHEMISTRY
 149 CHAPTER ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. On electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid using platinum electrodes, the product obtained at the anode will be hydrogen oxygen hydrogen sulphide sulphur dioxide 2. Which
149 CHAPTER ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. On electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid using platinum electrodes, the product obtained at the anode will be hydrogen oxygen hydrogen sulphide sulphur dioxide 2. Which
Oxidation-Reduction Review. Electrochemistry. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions. Sample Problem.
 1 Electrochemistry Oxidation-Reduction Review Topics Covered Oxidation-reduction reactions Balancing oxidationreduction equations Voltaic cells Cell EMF Spontaneity of redox reactions Batteries Electrolysis
1 Electrochemistry Oxidation-Reduction Review Topics Covered Oxidation-reduction reactions Balancing oxidationreduction equations Voltaic cells Cell EMF Spontaneity of redox reactions Batteries Electrolysis
ELECTROLYSIS The Divorcing of a Compound PART ONE
 ELECTROLYSIS The Divorcing of a Compound PART ONE ADEng. PROGRAMME Chemistry for Engineers Department of Pure and Applied Sciences Portmore Community College Prepared by M. J. McNeil, MPhil. 1 SPECIFIC
ELECTROLYSIS The Divorcing of a Compound PART ONE ADEng. PROGRAMME Chemistry for Engineers Department of Pure and Applied Sciences Portmore Community College Prepared by M. J. McNeil, MPhil. 1 SPECIFIC
