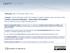
[RNH]SO3CH3 [RNH]SO 4 CH [RNH]I
|
|
|
- Sharyl Singleton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Product bulletin Karl Fischer Tritration The basics of Karl Fischer Tritration Karl Fischer titration is an analytical technique to measure the amount of water contained in various samples, which may be solid, liquid or gaseous. This method was originally developed in the 1930s by a German chemist Karl Fischer. Karl Fischer titration is based on a 1:1 reaction between iodine and water in the presence of sulfur dioxide and a base. Below is the 2-step mechanism of the reaction: CH3OH + SO2 + RH [RNH]SO 3 CH 3 + I 2 + H 2 O + 2 RN [RNH]SO3CH3 [RNH]SO 4 CH [RNH]I From the reaction mechanism, it's evident that the reagent used for the titration needs to contain the following: Alcohol - methanol was used originally, but in different variations of the reagent can be replaced by ethyl carbitol, methoxypropanol, ethanol, etc. Sulfur dioxide Iodine Base - pyridine was used initially, but has since been replaced by imidazole, which assures a higher rate of reaction and is less toxic One of the most important developments in Karl Fischer titration chemistry was the replacement of pyridine with imidazole. Pyridine is a relatively weak base and the equilibrium of the reaction is not completely shifted toward the products. As a result, use of pyridine-based reagents typically resulted in slow reactions and unstable endpoints. This, in turn, negatively impacted reproducibility of measurements. Imidazole is a stronger base and shifts the reaction equilibrium completely to the right, which results in a faster titration rate and more stable endpoints. Order our products online
2 Types of Karl Fischer Titration Karl Fischer titration is based on the stoichiometric reaction of iodine with water. There are two methods of introducing iodine into the sample - addition of molecular iodine in a solution with a volume of a reagent (volumetric titration) and generation of iodine electrochemically within the titration cell (coulometric titration). Volumetric titration has the benefit of speed and generally lower cost, while coulometric titration allows for accurate analysis of samples with low moisture levels. The two main methods have their own variations and both make use of calibration standards to verify accuracy of the measurements. KARL FISCHER TITRATION METRIC TITRATION COULOMETRIC TITRATION ONE-COMPONENT WITH DIAPHRAGM TWO-COMPONENT WITHOUT DIAPHRAGM CALIBRATION STANDARDS
3 Volumetric Karl Fischer Titration Volumetric determination of water can be done with one-component or two-component titration. In one-component titration, all of the reactants needed for the reaction are present in a single solution. Two-component titration uses two solutions - one of them is a solvent that contains sulfur dioxide and the base and the other is the titrant, which is a solution of iodine in methanol or another suitable solvent. In both cases, the sample is dissolved in the solvent/working medium and is contained in the titration cell. The iodine-containing titrant is added, typically by a dosing pump. The water content in the sample is then calculated based on the volume of the reagent. Commercial titrators normally automate the process and integrate all components of the instrument. Alfa Aesar carries the entire line of reagents needed for both the one- and two-component titration methods. Composite T5/T2/T1 Composite K5/K2 Titrant T5/T2 Titrant K5/K2 Methanol, solvent Solvent Solvent KT Solvent CS General one-component titration X X General two-component titration X X Aldehydes & ketones X X Crude oil & petrochemicals X X Biofuels X X X One-component titration is the most common, due to its simplicity and convenience. Two-component titration may still be selected for its high rate of reaction, which produces very sharp endpoints and highly reproducible results. In addition, Titrant T5 (47140) and T2 (47200) have a virtually unlimited shelf life. The titrants for two-component analysis must be used with the Karl Fischer Solvent (47281) to produce the complete reaction medium. Methanol is not the only solvent that can be used as working medium for one-component titration, however the choices are limited. The solvent needs to be sufficiently polar and protic, thus restricting selection to compounds with hydroxyl groups and high overall polarity. In addition, they need to dissolve a variety of samples, which further limits available options. As an example, methoxypropanol can be used as a solvent and it is the basis for Solvent KT (47219). However, the reaction rate is lower than in methanol and the endpoint is not as well defined. These considerations need to be taken into account when attempting to modify the standard solvents to work with difficult to dissolve samples. For instance, chloroform, long-chain alcohols or aromatic solvents may be added. But the fraction of methanol should never be lower than 40% by volume. If the concentration of methanol or similar solvent is too low, reaction stoichiometry may change and produce incorrect results. Composite T5 (47129)/T2 (47137)/T1 (47173) reagents can be used with dry methanol, but Karl Fischer Methanol (47165) is the preferred working medium. It has been formulated to accelerate the reaction rate and produce exceptionally sharp titration endpoints.
4 Volumetric Karl Fischer Reagents: Titer and Reagent Calibration Determination of water content using volumetric Karl Fischer titration is based on the stoichiometric reaction between the components of the reagent and moisture contained in the sample. Capacity of the reagent to react with water is expressed in terms of a titer, or water equivalent (WE). Titer indicates the amount of water that can be consumed by 1 ml of a given reagent. Titer (WE) = Weight of water (mg) / Volume of reagent (ml) For example, if a Composite T2 (47137) reagent has a titer of 2.1, then it indicates that 1 ml of this reagent will neutralize 2.1 mg of water present in a sample. When the titer is known, water content in the sample can be easily calculated from the quantity of reagent used to achieve the endpoint. Alfa Aesar Karl Fischer reagents are manufactured with several standard titers. The Composite series may have titers of 1, 2 and 5, which are indicated by the name of the specific reagent [T1 (47173), T2 (47137) and T5 (47129), respectively]. The general rule is that the greater the anticipated water content in the samples, the higher titer reagent should be used. While theoretically Composite T5 (47129) could be used for any water determination, in practice it may be too coarse for accurate analysis of samples with low moisture content. The titration vessel must be kept as airtight as possible to avoid reagent reacting with ambient moisture contained in the air, which reduces the titer and may cause fading of the endpoint (especially for low titer reagents). It is also recommended that the titration system be flushed with fresh reagent before the analysis, in order to eliminate the accumulated moisture in the tubes and other components of the system. Titer stability and reagent calibration Alfa Aesar Karl Fischer reagents are formulated for maximum stability and maintain their titer within specification for long periods of time. However, once the bottle is opened and the reagent is being used, ambient moisture diffuses into the bulk of the solution and consumes some of the reagent. This process reduces the effective titer and requires a recalibration before use, in order to assure accurate results. There are two main methods of calibration, both based on providing a standard sample with a known water content. The first method uses a water sample dissolved in an organic solvent at a known concentration. The second method makes use of Sodium L-(+)-tartrate dihydrate (33242) crystals that contain 15.66% of water by weight.
5 Titer Determination with Standards Calibration of Alfa Aesar Karl Fischer reagents using Sodium L-(+)-tartrate dihydrate. Sodium L-(+)-tartrate dihydrate (33242) forms a stable complex with water at a known saturation concentration (15.66%) and retains this level even at temperatures over 120 C. Since Sodium L-(+)-tartrate dihydrate (33242) exists as crystals, it is easier to handle and can be weighed with high accuracy using standard analytical balances. The quantity of Sodium L-(+)-tartrate dihydrate (33242) normally depends on the anticipated titer of the reagent, with greater amounts used for higher titers. For example, we recommend using mg of Sodium L-(+)-tartrate dihydrate (33242) to calibrate Composite T5 (47129) reagent. Similarly, mg of Sodium L-(+)-tartrate dihydrate (33242) would be more appropriate for calibration of Composite T2 (47137). Once the crystals are weighed, they are added to the titration vessel. Care must be taken to ensure that the crystals are fully dissolved before beginning the addition of the reagent. At this point, the reagent is added as in a regular titration until the endpoint is reached. The titer (water equivalent) is the calculated as follows: Titer (WE) = Weight of Sodium L-(+)-tartrate dihydrate (mg) * / Volume of KF reagent (ml) Calibration of Alfa Aesar Karl Fischer reagents using liquid water standards Liquid water standards offer the same features as the Sodium L-(+)-tartrate dihydrate (33242). The Sodium L-(+)-tartrate dihydrate (33242) crystals can be weighed easily and do not require any special handling. However, sodium tartrate dihydrate may not fully dissolve in some reagents, such as Solvent KT (47219) and some third-party ethanol-based reagents. To avoid this issue, liquid water standards represent a reliable alternative. Liquid water standards are typically available in sealed glass ampoules and have a known water content, typically 10 mg per 1 g of the standard. The exact value is specified on the Certificate of Analysis supplied with the standard. The standard solution is added to the titration vessel using a syringe in exactly weighed 1g portions. Then the reagent is added and titration is carried out to the endpoint. The titer (water equivalent) is calculated as follows: Titer (WE) = Weight of sample (g) * Water content in CoA (mg/g)/volume of KF reagent (ml) The choice between the two types of standards should be made based on the reagents being calibrated (solubility) and by experimentally comparing results from both methods. Ideally, titer should be verified by titrating a standard water solution (such as SRM 2890 available from NIST) to make sure it has been determined correctly.
6 Volumetric Karl Fischer Titration with Composite T5/T2/T1 Composition Alfa Aesar Karl Fischer Composites are a line of one-component Karl Fischer reagents for volumetric determination of moisture. The reagents include Composit T5 (47129), Composit T2 (47137) and Composit T1 (47173), which differ by titer. Any Alfa Aesar Karl Fischer Composite reagents contain all components required for a stoichiometric reaction of iodine with water in a sample. The components include sulfur dioxide, imidazole and iodine dissolved in diethylene glycol monoethyl ether. Alfa Aesar Karl Fischer Composite reagents are formulated to retain their titer within specification for at least 5 years. The typical loss of titer is less than 3% per year. Recommended Solvents Alfa Aesar Karl Fischer Composite reagents can be used with any methanol-based solvent for a stoichiometric reaction with reproducible results. For best results, Karl Fischer Methanol (47165) should be used, since it produces an exceptionally stable and easily detectable titration end point. In some cases, a specialized solvent is required. For titration of aldehydes and ketones, use Solvent KT (47219). For titration of petrochemicals, biofuels and other samples poorly soluble in methanol, use Solvent CS. Testing Procedure The titration cell must be dry and free of residue from previous measurements. 1. Add Karl Fischer Methanol (47165) or another suitable solvent to the titration cell. The exact volume varies with the model of the instrument and ranges from 30 to 100 ml. 2. Fill the burette or connect the bottle with the Composite reagent to the dosing pump. 3. Add the Composite reagent until the end point is reached and the solution in the titration cell contains no water. 4. Determine the exact titer of the reagent using a water or STD standard. Reach the endpoint. 5. Add a sample of known weight. 6.Titrate the water content with Composites T5/T2/T1 (depending on the anticipated water content and application).
7 Volumetric Titration of Aldehydes and Ketones Alfa Aesar K Series reagent line is formulated for analysis of samples containing aldehydes and ketones. The distinctive characteristic of the K Series is the absence of methanol, which is commonly used in other Karl Fischer reagents. The composition of the reagents is formulated to prevent side reactions that occur in solutions of compounds with carbonyl groups that can undergo a nucleophilic reaction with alcohols with the formation of acetals (Figure 1). One of the products of this reaction is water, which interferes with the results of analysis and causes instability of titration endpoints. Figure 1. Formation of ketals in the reaction of acetone with methanol Alfa Aesar K Series reagents are also designed to prevent bisulfite addition to aldehydes (Figure 2). This second side reaction consumes a portion of the water content in the neat specimen and results in erroneously low water content measurements. Composite K5 (47153) is a variant of Composite T5 (47129), with a formulation for a slightly slower reaction rate to minimize interference from the bisulfite addition side reaction. Figure 2. Bisulfite addition to aldehydes that consumes water. NR+ is a base. Alfa Aesar K Series of reagents for aldehydes and ketones includes solution systems for both onecomponent and two-component KF titration: One-component system includes Composite K5 (47153) and Composite K2 (47159) reagents, as well as Solvent KT (47219). They are methanol-free and include components that inhibit side reactions. Two-component system includes Titrant K5 (47231) and Titrant K2 (47200), with Solvent KT (47219) suitable for use with these reagents. This titration method allows for a more accurate moisture determination with slower side reactions and a more stable titration end point.
8 Titration of Oils, Biofuels and Petroleum Products Methanol is the solvent of choice in the majority of situations. However, some samples have low solubility in methanol, thus requiring a different solvent for volumetric titration. Such samples include heavy hydrocarbons abundant in oil and petrochemical products, components of biofuels and samples that contain oils with long hydrocarbon chains. In these situations, use of Alfa Aesar Solvent CS (47217) is recommended. It's a mixture of methanol with chloroform and xylene, which improves solubility of such samples and retains the stoichiometry of the reaction. Importance of ph Karl Fischer reaction has an optimum ph range between 5 and 7.5. If the ph is below 2, the reaction does not occur at all. In very basic conditions, iodine is consumed in side reactions and leads to false high values. Since increased acidity leads to a drop in the reaction rate, acidic samples need to be neutralized. Weak bases, such as imidazole, can be used to bring ph into a more neutral range. In case of basic samples, weak organic acids are recommended. Benzoic or salicylic acids are good choices. The exact amount will vary depending on the ph of the initial solution, but can be between 5 and 15 g per 60 ml of solvent.
9 Coulometric Karl Fischer Titration In coulometric KF titration, iodine is generated electrochemically and its amount is proportional to the amount of electricity passed through the solution. Once the titration endpoint is achieved, the current is turned off and the final amount of electricity is used to calculate how much iodine was required for the titration. Coulometric titration can be carried out in two types of titration cells - with or without a diaphragm. Cells with a diaphragm were developed first and used a semi-permeable glass diaphragm to separate the volume of the cell into two chambers containing the cathode and the anode, respectively. The separation was used to isolate the individual electrode processes and avoid reduction of iodine back to iodide. Cells without a diaphragm were developed in late 1980s. They allow for a simpler setup and only require one reagent solution. In addition, a diaphragm introduces additional electrical resistance, which can lead to overheating of the solution and limit the maximum current. The specific material of the diaphragm can also impact the drift in the anode and cathode chambers, thus adding a source of error. Currently, cells without a diaphragm are more common. However, cells with a diaphragm have the advantage of separation from the anode chamber where the samples are added. When multiple samples have been added, the composition of the anolyte changes and can impact the reproducibility of consecutive measurements. In cells without a diaphragm, the anolyte reagent has to be changed more frequently to avoid this issue. Cells with a diaphragm help alleviate this problem for samples with very low moisture content that need to be added in large amounts. Reagents of Coulometric Titration The basic reagent used in most of the coulometric titrations is Coulometric AG (47106), which is the general purpose anolyte solution for titration with or without a diaphragm. Different types of samples require different variants of the reagent, mainly to address solubility issues. In cells with a diaphragm, Coulometric CG (47117) is required and can be used with any of the specialized variations of Coulometric AG (47106). Coulometric AG Coulometric AG-Oil Coulometric AG-Oven Coulometric CG General titration with a diaphragm X X General titration without a diaphragm X Titration of biofuels and oils X X Titration of crude oil and petrochemicals X X Titration with oven X The Coulometric CG (47117) reagent has an increased viscosity compared to most existing reagents, which leads to a much lower interference with the anolyte content across the diaphragm. This feature translates into higher accuracy with a lower relative error of measurement. Coulometric CG (47117) is formulated to be non-hygroscopic and allows packaging in 110 ml bottles instead of the traditional single-use ampoules.
10 Coulometric Titration of Petrochemicals and Biofuels Samples containing oils, biofuels and petrochemicals usually have limited solubility in methanol. Specialized reagents have been formulated to dissolve these samples and retain stoichiometry of the reaction. In cases of crude oil or petroleum products, it is recommended to use Coulometric AG-Oil (47195), which contains chloroform and xylene. It should be noted that the addition of non-polar solvents also increases electrical resistance of the solution. Higher electrical resistance may lead to overheating of the solution when titrations take a long time. Therefore, it s important to pay attention to the temperature of the cell and periodically allow it to cool in order to avoid excessive evaporation of the solution. Samples containing crude oil, petrochemicals and biofuels most frequently are titrated in cells with a diaphragm. It prevents the samples from contaminating the cathode and maintains constant composition of the cathode solution. In cells without a diaphragm, these samples can dramatically alter electrochemistry of the cell and negatively impact accuracy. This is especially true for low moisture samples that have to be added in large amounts (up to 10 ml). After only several measurements, the solution becomes so diluted by non-polar components that the current efficiency at the cathode can substantially decrease and lower its performance. Samples containing long-chain hydrocarbons can in some cases be dissolved in Coulometric AG-Oil (47195). However, a specialized reagent for these situations will be added soon to the Alfa Aesar reagent series.
11 Coulometric Titration with Oven In some cases, samples contain components that do not dissolve in any of the available reagents or cause side reactions that are difficult to prevent. In these situations, titration with an oven can provide a good alternative. A drying oven can also be used for samples that only release water at elevated temperatures, such as plastics and resins. The oven is used to elevate the temperature of the sample and evaporate the moisture, which is then delivered to the titration cell with a carrier gas. Since the moisture is delivered in gas phase and at an elevated temperature, the reagent must be able to dissolve it without boiling. Coulometric AG-Oven (47177) has been designed specifically for this purpose and contains propylene glycol to control the boiling point of the reagent. Technical Support from Alfa Aesar If you have technical questions about the use of Alfa Aesar Karl Fischer reagents or the selection of the appropriate reagent for your application, please contact our Technical Support team: tech@alfa.com Web: We can help you with any of the following: advice on reagent/titrator application custom reagents method development technical literature Safety Data Sheets regulatory questions Order our products online
Analytix. HYDRANAL Product Line Overview
 1 Analytix HYDRANAL Product Line Overview Volumetric Titration with One-Component Reagents Volumetric Titration with Two-Component Reagents Coulometric Titration with Water Standards E Types HYDRANAL Reagents
1 Analytix HYDRANAL Product Line Overview Volumetric Titration with One-Component Reagents Volumetric Titration with Two-Component Reagents Coulometric Titration with Water Standards E Types HYDRANAL Reagents
Aquagent. The Scharlau comprehensive pyridine-free solutions range for a reliable Karl Fischer Titration
 The Scharlau comprehensive pyridine-free solutions range for a reliable Karl Fischer Titration Karl Fischer titration is a well known and globally accepted method for water determination since the beginning
The Scharlau comprehensive pyridine-free solutions range for a reliable Karl Fischer Titration Karl Fischer titration is a well known and globally accepted method for water determination since the beginning
WATER. Brighter. Determination. Aquastar reagents for brilliant Karl Fischer titration results.
 Brighter WATER Determination Aquastar reagents for brilliant Karl Fischer titration results. The life science business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany operates as MilliporeSigma in the U.S. and Canada.
Brighter WATER Determination Aquastar reagents for brilliant Karl Fischer titration results. The life science business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany operates as MilliporeSigma in the U.S. and Canada.
Hy + Hw = Cy + Inv. Discover the perfect formula. Hydranal TM Honeywell Consistency Innovation
 Hy + Hw = Cy + Inv Hydranal TM Honeywell Consistency Innovation Discover the perfect formula HYDRANAL Product Overview Guide Reagents for water determination by Karl Fischer titration HYDRANAL Reagents
Hy + Hw = Cy + Inv Hydranal TM Honeywell Consistency Innovation Discover the perfect formula HYDRANAL Product Overview Guide Reagents for water determination by Karl Fischer titration HYDRANAL Reagents
Hy = KFt Ori x Acy. HYDRANAL Product Overview Guide. Hydranal TM. Karl Fischer titration. Research Chemicals. Discover the perfect formula
 Research Chemicals Hy = KFt Ori x Acy Hydranal TM Karl Fischer titration Original Accuracy Discover the perfect formula HYDRANAL Product Overview Guide Reagents for water determination by Karl Fischer
Research Chemicals Hy = KFt Ori x Acy Hydranal TM Karl Fischer titration Original Accuracy Discover the perfect formula HYDRANAL Product Overview Guide Reagents for water determination by Karl Fischer
á921ñ WATER DETERMINATION
 USP 40 Physical Tests / á921ñ Water Determination 1 á921ñ WATER DETERMINATION Many Pharmacopeial articles either are hydrates or contain water in adsorbed form. As a result, the determination of the water
USP 40 Physical Tests / á921ñ Water Determination 1 á921ñ WATER DETERMINATION Many Pharmacopeial articles either are hydrates or contain water in adsorbed form. As a result, the determination of the water
Karl Fischer Volumetric Titration Theory and Practice
 Karl Fischer Volumetric Titration Theory and Practice - 1 - - when you need to be sure... Table of contents Introduction... 3 Chemical reactions... 3 ph considerations... 4 Volumetric titration... 4 General
Karl Fischer Volumetric Titration Theory and Practice - 1 - - when you need to be sure... Table of contents Introduction... 3 Chemical reactions... 3 ph considerations... 4 Volumetric titration... 4 General
Karl Fischer Titration Of Food : Towards Complete Automation
 Karl Fischer Titration Of Food : Towards Complete Automation Cosimo A. De Caro, A. Aichert, C. Gordon Mettler-Toledo GmbH, Analytical CH-8603 Schwerzenbach, Switzerland Program Introduction Why water determination
Karl Fischer Titration Of Food : Towards Complete Automation Cosimo A. De Caro, A. Aichert, C. Gordon Mettler-Toledo GmbH, Analytical CH-8603 Schwerzenbach, Switzerland Program Introduction Why water determination
Citric Acid Analysis L-6-1. MOISTURE (Karl Fischer)
 Citric Acid Analysis L-6-1 MOISTURE (Karl Fischer) PRINCIPLE SCOPE The sample is dissolved in a mixture of methanol and formamide (50:50 v/v) and then titrated with standardized Karl Fischer reagent. The
Citric Acid Analysis L-6-1 MOISTURE (Karl Fischer) PRINCIPLE SCOPE The sample is dissolved in a mixture of methanol and formamide (50:50 v/v) and then titrated with standardized Karl Fischer reagent. The
Karl Fischer Moisture Determination
 KARL FISCHER MOISTURE DETERMINATION 1 Karl Fischer Moisture Determination Related Articles 13 References 13 Katrin Schöffski Sigma Aldrich Laborchemikalien, Seelze, Germany Dieter Strohm Metrohm Ltd, Herisau,
KARL FISCHER MOISTURE DETERMINATION 1 Karl Fischer Moisture Determination Related Articles 13 References 13 Katrin Schöffski Sigma Aldrich Laborchemikalien, Seelze, Germany Dieter Strohm Metrohm Ltd, Herisau,
J.T.Baker Brand HYDRA-POINT KARL FISCHER REAGENTS. Europe Middle East Africa
 J.T.Baker Brand HYDRA-POINT KARL FISCHER REAGENTS Europe Middle East Africa Lab-Optimized Performance: Function-tested Karl Fischer reagents from the brand that delivers quality and purity. The J.T.Baker
J.T.Baker Brand HYDRA-POINT KARL FISCHER REAGENTS Europe Middle East Africa Lab-Optimized Performance: Function-tested Karl Fischer reagents from the brand that delivers quality and purity. The J.T.Baker
Corn Sugar (crude & refined) Analysis F MOISTURE (Karl Fischer)
 Corn Sugar (crude & refined) Analysis F-32-1 MOISTURE (Karl Fischer) PRINCIPLE SCOPE The sugar sample is dissolved in a mixture of methanol and formamide (50:50 v/v) and then titrated with standardized
Corn Sugar (crude & refined) Analysis F-32-1 MOISTURE (Karl Fischer) PRINCIPLE SCOPE The sugar sample is dissolved in a mixture of methanol and formamide (50:50 v/v) and then titrated with standardized
Karl-Fischer Titration the method for determining water
 Karl-Fischer Titration the method for determining water Quite some experienced analyst will be unpleasantly reminded by the pyridine smell, when hearing the name Karl Fischer. However, modern reagents
Karl-Fischer Titration the method for determining water Quite some experienced analyst will be unpleasantly reminded by the pyridine smell, when hearing the name Karl Fischer. However, modern reagents
Water determination in aldehydes and ketones HYDRANAL Laboratory Report L 676
 Water determination in aldehydes and ketones HYDANA aboratory eport 676 (Extract from HYDANA Manual, chapter 9.6) oth aldehydes and ketones pose problems and erroneously high water content. With with Karl
Water determination in aldehydes and ketones HYDANA aboratory eport 676 (Extract from HYDANA Manual, chapter 9.6) oth aldehydes and ketones pose problems and erroneously high water content. With with Karl
Geavanceerde bepaling van water in poeders en vaste stoffen via geautomatiseerde Karl Fischer titratie. Peter van de Spreng 8 November 2011
 Geavanceerde bepaling van water in poeders en vaste stoffen via geautomatiseerde Karl Fischer titratie Peter van de Spreng 8 November 2011 Mettler Toledo Theory Agenda Types of water Which samples - Karl
Geavanceerde bepaling van water in poeders en vaste stoffen via geautomatiseerde Karl Fischer titratie Peter van de Spreng 8 November 2011 Mettler Toledo Theory Agenda Types of water Which samples - Karl
GTP Brochure. Good Titration Practice in Karl Fischer Titration
 AGC Karl Book Fischer 20% Titration Cyan GTP Brochure Good Titration Practice in Karl Fischer Titration EDITORIAL Dear Reader METTLER TOLEDO has an excellent knowledge in any kind of moisture and water
AGC Karl Book Fischer 20% Titration Cyan GTP Brochure Good Titration Practice in Karl Fischer Titration EDITORIAL Dear Reader METTLER TOLEDO has an excellent knowledge in any kind of moisture and water
Automatic determination of the bromine number and the bromine index in petroleum products
 Application Bulletin 177/5 e Automatic determination of the bromine number and the bromine Branch General analytical chemistry; organic chemistry; petrochemistry, biofuels; trace analysis; paints, lacquers,
Application Bulletin 177/5 e Automatic determination of the bromine number and the bromine Branch General analytical chemistry; organic chemistry; petrochemistry, biofuels; trace analysis; paints, lacquers,
LACTIC ACID. The method is applicable to the determination of lactic acid and lactate salts (Note 2) in light or heavy steepwater.
 LACTI.01-1 LACTIC ACID PRINCIPLE SCOPE Lactic acid in steepwater (Note 1) is oxidized to acetaldehyde following treatment with copper sulfate and calcium hydroxide to remove interfering substances. Acetaldehyde
LACTI.01-1 LACTIC ACID PRINCIPLE SCOPE Lactic acid in steepwater (Note 1) is oxidized to acetaldehyde following treatment with copper sulfate and calcium hydroxide to remove interfering substances. Acetaldehyde
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATIONWEWlYHAPOCIHAR OPrAHM3ALlMR l-l0 CTAH~APTbl3ALWl.ORGANlSATlON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION Determination of water - Karl Fischer
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATIONWEWlYHAPOCIHAR OPrAHM3ALlMR l-l0 CTAH~APTbl3ALWl.ORGANlSATlON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION Determination of water - Karl Fischer
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
 Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions Reaction Stoichiometry the numerical relationships between chemical amounts in a reaction is called stoichiometry the coefficients in a balanced chemical
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions Reaction Stoichiometry the numerical relationships between chemical amounts in a reaction is called stoichiometry the coefficients in a balanced chemical
 Chapter No. 2 EXPERIMENTAL TECHNIQUES IN CHEMISTRY SHORT QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS Q.1 Define analytical chemistry? The branch of chemistry which deals with the qualitative and quantitative analyses of sample
Chapter No. 2 EXPERIMENTAL TECHNIQUES IN CHEMISTRY SHORT QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS Q.1 Define analytical chemistry? The branch of chemistry which deals with the qualitative and quantitative analyses of sample
Application Determination of water in petrochemistry products using Titrator TitroLine 7500 KF trace
 Determination of water in petrochemistry products using Titrator TitroLine 7500 KF trace Date: 06.05.2013 Page 1 of 6 Use The application describes the procedure of the coulometric water determination
Determination of water in petrochemistry products using Titrator TitroLine 7500 KF trace Date: 06.05.2013 Page 1 of 6 Use The application describes the procedure of the coulometric water determination
Acid Base Titration Experiment ACID - BASE TITRATION LAB
 ACID - BASE TITRATION LAB MATERIALS and CHEMICALS Burette 50 ml Burette clamp Ring stand Stirring rod Plastic funnel Beakers (50 ml, 100 ml, 400 ml) Graduated cylinder (25 ml, 50 ml) 0.10 M NaOH 0.10 M
ACID - BASE TITRATION LAB MATERIALS and CHEMICALS Burette 50 ml Burette clamp Ring stand Stirring rod Plastic funnel Beakers (50 ml, 100 ml, 400 ml) Graduated cylinder (25 ml, 50 ml) 0.10 M NaOH 0.10 M
Application Note No. 116 / 2013 Nitrogen determination in sodium nitrate
 Application Note No. 116 / 2013 Nitrogen determination in sodium nitrate KjelMaster K-375: Determination of nitrogen in sodium nitrate according the the Devarda method 1. Introduction An easy, quick and
Application Note No. 116 / 2013 Nitrogen determination in sodium nitrate KjelMaster K-375: Determination of nitrogen in sodium nitrate according the the Devarda method 1. Introduction An easy, quick and
Experiment 3. Condensation Reactions of Ketones and Aldehydes: The Aldol Condensation Reaction.
 Experiment 3. Condensation Reactions of Ketones and Aldehydes: The Aldol Condensation Reaction. References: Brown & Foote, Chapters 16, 19, 23 INTRODUCTION: This experiment continues the saga of carbon-carbon
Experiment 3. Condensation Reactions of Ketones and Aldehydes: The Aldol Condensation Reaction. References: Brown & Foote, Chapters 16, 19, 23 INTRODUCTION: This experiment continues the saga of carbon-carbon
Chapter 13. Titrations in Analytical Chemistry
 Chapter 13 Titrations in Analytical Chemistry Titrations in Analytical Chemistry Titration methods are based on determining the quantity of a reagent of known concentration that is required to react completely
Chapter 13 Titrations in Analytical Chemistry Titrations in Analytical Chemistry Titration methods are based on determining the quantity of a reagent of known concentration that is required to react completely
--> Buy True-PDF --> Auto-delivered in 0~10 minutes. NY/T Translated English of Chinese Standard: NY/T
 Translated English of Chinese Standard: NY/T1447-2007 www.chinesestandard.net Buy True-PDF Auto-delivery. Sales@ChineseStandard.net AGRICULTURAL INDUSTRY STANDARD NY OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA ICS
Translated English of Chinese Standard: NY/T1447-2007 www.chinesestandard.net Buy True-PDF Auto-delivery. Sales@ChineseStandard.net AGRICULTURAL INDUSTRY STANDARD NY OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA ICS
Background on Solubility
 CHEM254 01 Open Notebook Science Solubility Challenge 1 For the first laboratory exercise of this semester we are going to participate in the Open Notebook Science (ONS) solubility challenge http://onschallenge.wikispaces.com/.
CHEM254 01 Open Notebook Science Solubility Challenge 1 For the first laboratory exercise of this semester we are going to participate in the Open Notebook Science (ONS) solubility challenge http://onschallenge.wikispaces.com/.
For this lab, you will determine the purity of the aspirin by titration and by spectrophotometric analysis.
 Introduction: ommercially prepared aspirin tablets are not considered 100% pure acetylsalicylic acid. Most aspirin tablets contain a small amount of binder which helps prevent the tablets from crumbling.
Introduction: ommercially prepared aspirin tablets are not considered 100% pure acetylsalicylic acid. Most aspirin tablets contain a small amount of binder which helps prevent the tablets from crumbling.
Limiting Reagent Synthesis of Aspirin Thomas M. Moffett Jr., SUNY Plattsburgh, 2007.
 Limiting Reagent Synthesis of Aspirin Thomas M. Moffett Jr., SUNY Plattsburgh, 007. Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is the most common medicinal drug in use today. Aspirin is an analgesic (pain reliever),
Limiting Reagent Synthesis of Aspirin Thomas M. Moffett Jr., SUNY Plattsburgh, 007. Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is the most common medicinal drug in use today. Aspirin is an analgesic (pain reliever),
Experiment 1: Thin Layer Chromatography
 Experiment 1: Thin Layer Chromatography Part A: understanding R f values Part B: R f values & solvent polarity Part C: R f values & compound functionality Part D: identification of commercial food dye
Experiment 1: Thin Layer Chromatography Part A: understanding R f values Part B: R f values & solvent polarity Part C: R f values & compound functionality Part D: identification of commercial food dye
Standard Test Methods for Water in Crude Oils by Coulometric Karl Fischer Titration 1
 Designation: D 4928 00 e1 An American National Standard Designation: Manual of Petroleum Measurement Standards (MPMS), Chapter 10.9 Designation: 386/99 Standard Test Methods for Water in Crude Oils by
Designation: D 4928 00 e1 An American National Standard Designation: Manual of Petroleum Measurement Standards (MPMS), Chapter 10.9 Designation: 386/99 Standard Test Methods for Water in Crude Oils by
From 1 ppm to 100% Karl Fischer water content determination
 METTLER TOLEDO Karl Fischer Titrators DL39 & DL32 Coulometers DL38 & DL31 Volumeters Oven sample changer Stromboli From 1 ppm to 100% Karl Fischer water content determination Karl Fischer water content
METTLER TOLEDO Karl Fischer Titrators DL39 & DL32 Coulometers DL38 & DL31 Volumeters Oven sample changer Stromboli From 1 ppm to 100% Karl Fischer water content determination Karl Fischer water content
Lab 2. Go Their Separate Ways: Separation of an Acid, Base, and Neutral Substance by Acid-Base Extraction
 Lab 2. Go Their Separate Ways: Separation of an Acid, Base, and Neutral Substance by Acid-Base Extraction How can I use an acid-base reaction to separate an acid-base-neutral mixture? Objectives 1. use
Lab 2. Go Their Separate Ways: Separation of an Acid, Base, and Neutral Substance by Acid-Base Extraction How can I use an acid-base reaction to separate an acid-base-neutral mixture? Objectives 1. use
Unit 3 Chemistry - Volumetric Analysis
 Unit 3 Chemistry Volumetric Analysis Volumetric analysis is a quantitative chemical analysis used to determine the unknown concentration of one reactant [the analyte] by measuring the volume of another
Unit 3 Chemistry Volumetric Analysis Volumetric analysis is a quantitative chemical analysis used to determine the unknown concentration of one reactant [the analyte] by measuring the volume of another
OPTION. Karl Fischer Moisture Titrator [Volumetric titration] Karl Fischer Moisture Titrator [Coulometric titration]
![OPTION. Karl Fischer Moisture Titrator [Volumetric titration] Karl Fischer Moisture Titrator [Coulometric titration] OPTION. Karl Fischer Moisture Titrator [Volumetric titration] Karl Fischer Moisture Titrator [Coulometric titration]](/thumbs/74/69733860.jpg) CN073 OPTION Bent-type Sampler for Powder 12-04576 "C" Bent-type Sampler for Powders phi18.5 1/10 Taper Glass Sampler for Light Weight Powder Finger Shaped Sampler 12-04452 12-04184 12-04454 ADP Straight-type
CN073 OPTION Bent-type Sampler for Powder 12-04576 "C" Bent-type Sampler for Powders phi18.5 1/10 Taper Glass Sampler for Light Weight Powder Finger Shaped Sampler 12-04452 12-04184 12-04454 ADP Straight-type
PC Control / Touch Control
 PC Control / Touch Control Version 6.0 / 5.840.0150 New Features Manual 8.840.8007EN Metrohm AG CH-9101 Herisau Switzerland Phone +41 71 353 85 85 Fax +41 71 353 89 01 info@metrohm.com www.metrohm.com
PC Control / Touch Control Version 6.0 / 5.840.0150 New Features Manual 8.840.8007EN Metrohm AG CH-9101 Herisau Switzerland Phone +41 71 353 85 85 Fax +41 71 353 89 01 info@metrohm.com www.metrohm.com
Application Note No. 310/2018
 Application Note No. 310/2018 Nitrogen determination in compound fertilizer according to Devarda KjelFlex K-360 with Devarda Splash Protector, Metrohm Titrino 877 www.buchi.com Quality in your hands 1.
Application Note No. 310/2018 Nitrogen determination in compound fertilizer according to Devarda KjelFlex K-360 with Devarda Splash Protector, Metrohm Titrino 877 www.buchi.com Quality in your hands 1.
Determination of Reducing Sugar Content: Clinitest, Benedict s Solution and the Rebelein Titration
 Determination of Reducing Sugar Content: Clinitest, Benedict s Solution and the Rebelein Titration Chemical Concepts and Techniques: The most important sugars present in wine and fruit juice are the hexoses
Determination of Reducing Sugar Content: Clinitest, Benedict s Solution and the Rebelein Titration Chemical Concepts and Techniques: The most important sugars present in wine and fruit juice are the hexoses
Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 12, page 1] D J Weinkauff - Nerinx Hall High School. Chapter 12 Properties of Solutions
![Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 12, page 1] D J Weinkauff - Nerinx Hall High School. Chapter 12 Properties of Solutions Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 12, page 1] D J Weinkauff - Nerinx Hall High School. Chapter 12 Properties of Solutions](/thumbs/96/127488495.jpg) Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 12, page 1] Chapter 12 Properties of Solutions Section 12 1: The Nature of Aqueous Solutions 1) Sec 12 1.1 Mixtures of Two Liquids When two liquids
Basic Concepts of Chemistry Notes for Students [Chapter 12, page 1] Chapter 12 Properties of Solutions Section 12 1: The Nature of Aqueous Solutions 1) Sec 12 1.1 Mixtures of Two Liquids When two liquids
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): MELO 3D Project Team, 2012 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/
Author(s): MELO 3D Project Team, 2012 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/
In this laboratory exercise we will determine the percentage Acetic Acid (CH 3 CO 2 H) in Vinegar.
 The titration of Acetic Acid in Vinegar In this laboratory exercise we will determine the percentage Acetic Acid (CH CO H) in Vinegar. We will do this by Titrating the Acetic Acid present with a Strong
The titration of Acetic Acid in Vinegar In this laboratory exercise we will determine the percentage Acetic Acid (CH CO H) in Vinegar. We will do this by Titrating the Acetic Acid present with a Strong
Understanding Importance of Water Sorption Isotherm Shape, Hysteresis, and Models on Pharmaceutical Materials
 Understanding Importance of Water Sorption Isotherm Shape, Hysteresis, and Models on Pharmaceutical Materials Dr. Daniel J. Burnett Surface Measurement Systems, Ltd. Dburnett@surfacemeasurementsystems.com
Understanding Importance of Water Sorption Isotherm Shape, Hysteresis, and Models on Pharmaceutical Materials Dr. Daniel J. Burnett Surface Measurement Systems, Ltd. Dburnett@surfacemeasurementsystems.com
The Characteristics of a Soln
 Goal 1 The Characteristics of a Soln Define the term solution, and, given a description of a substance, determine if it is a solution. The Characteristics of a Soln Solution (as used in chemistry) A homogenous
Goal 1 The Characteristics of a Soln Define the term solution, and, given a description of a substance, determine if it is a solution. The Characteristics of a Soln Solution (as used in chemistry) A homogenous
Annex 2 Formaldehyde
 Annex 2 Formaldehyde The 2 methods are analytical procedures for the determination of formaldehyde CH2O, PM/Ref. No 17260, and hexamethylenetetramine (HMTA) C6H12N4, PM/Ref. No 18670, in food simulants
Annex 2 Formaldehyde The 2 methods are analytical procedures for the determination of formaldehyde CH2O, PM/Ref. No 17260, and hexamethylenetetramine (HMTA) C6H12N4, PM/Ref. No 18670, in food simulants
Monograph. Water Determination by Karl Fischer Titration. Peter Bruttel Regina Schlink
 Monograph Water Determination by Karl Fischer Titration Peter Bruttel Regina Schlink Water Determination by Karl Fischer Titration Peter Bruttel Regina Schlink All rights reserved, including translation
Monograph Water Determination by Karl Fischer Titration Peter Bruttel Regina Schlink Water Determination by Karl Fischer Titration Peter Bruttel Regina Schlink All rights reserved, including translation
Easy and reliable KF titrations From 1 ppm to 100%
 AGC Karl Book Fischer 20% Titrators Cyan Volumetric KF Titrators DL31, DL38 Coulometric KF Titrators DL32, DL39 Oven sample changer Stromboli Easy and reliable KF titrations From 1 ppm to 100% Karl Fischer
AGC Karl Book Fischer 20% Titrators Cyan Volumetric KF Titrators DL31, DL38 Coulometric KF Titrators DL32, DL39 Oven sample changer Stromboli Easy and reliable KF titrations From 1 ppm to 100% Karl Fischer
Glossary of Common Laboratory Terms
 Accuracy A measure of how close a measured value is to the true value. Assessed by means of percent recovery of spikes and standards. Aerobic Atmospheric or dissolved oxygen is available. Aliquot A measured
Accuracy A measure of how close a measured value is to the true value. Assessed by means of percent recovery of spikes and standards. Aerobic Atmospheric or dissolved oxygen is available. Aliquot A measured
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS GENERAL PREPARATION
 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS Introduction The Van London-pHoenix Company Ammonium Ion Selective Electrode is used to quickly, simply, accurately, and economically measure potassium in aqueous solutions. Required
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS Introduction The Van London-pHoenix Company Ammonium Ion Selective Electrode is used to quickly, simply, accurately, and economically measure potassium in aqueous solutions. Required
Preparation of an Ester Acetylsalicylic Acid (Aspirin)
 Preparation of an Ester Acetylsalicylic Acid (Aspirin) BJECTIVE: To become familiar with the techniques and principle of esterification. DISCUSSIN: Aspirin is a drug widely used as an antipyretic agent
Preparation of an Ester Acetylsalicylic Acid (Aspirin) BJECTIVE: To become familiar with the techniques and principle of esterification. DISCUSSIN: Aspirin is a drug widely used as an antipyretic agent
METHYL ETHYL KETONE PEROXIDE 3508
 METHYL ETHYL KETONE PEROXIDE 3508 C 8 H 16 O 4 MW: 176.21 CAS: 1338-23-4 RTECS: EL9450000; 21837 METHOD: 3508, Issue 2 EVALUATION: PARTIAL Issue 1: 15 August 1987 Issue 2: 15 August 1994 OSHA : NIOSH:
METHYL ETHYL KETONE PEROXIDE 3508 C 8 H 16 O 4 MW: 176.21 CAS: 1338-23-4 RTECS: EL9450000; 21837 METHOD: 3508, Issue 2 EVALUATION: PARTIAL Issue 1: 15 August 1987 Issue 2: 15 August 1994 OSHA : NIOSH:
TECHNICAL SCIENCE DAS12703 ROZAINITA BT. ROSLEY PUSAT PENGAJIAN DIPLOMA UNVERSITI TUN HUSSEIN ONN MALAYSIA
 TECHNICAL SCIENCE DAS12703 ROZAINITA BT. ROSLEY PUSAT PENGAJIAN DIPLOMA UNVERSITI TUN HUSSEIN ONN MALAYSIA ii TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS... i LIST OF FIGURES... iii Chapter 1... 4 SOLUTIONS...
TECHNICAL SCIENCE DAS12703 ROZAINITA BT. ROSLEY PUSAT PENGAJIAN DIPLOMA UNVERSITI TUN HUSSEIN ONN MALAYSIA ii TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS... i LIST OF FIGURES... iii Chapter 1... 4 SOLUTIONS...
METHANOL REFERENCE SPECIFICATIONS
 IMPCA INTERNATIONAL METHANOL PRODUCERS & CONSUMERS ASSOCIATION Avenue de Tervuren 149 1150 Brussels, Belgium Tel : (32/2) 7418683 Fax : (32/2) 7418684 e-mail : impca@epca.be IMPCA METHANOL REFERENCE SPECIFICATIONS
IMPCA INTERNATIONAL METHANOL PRODUCERS & CONSUMERS ASSOCIATION Avenue de Tervuren 149 1150 Brussels, Belgium Tel : (32/2) 7418683 Fax : (32/2) 7418684 e-mail : impca@epca.be IMPCA METHANOL REFERENCE SPECIFICATIONS
To see how this data can be used, follow the titration of hydrofluoric acid against sodium hydroxide:
 Weak Acid Titration v010516 You are encouraged to carefully read the following sections in Tro (3 rd ed.) to prepare for this experiment: Sec 4.8, pp 168-174 (Acid/Base Titrations), Sec 16.4, pp 769-783
Weak Acid Titration v010516 You are encouraged to carefully read the following sections in Tro (3 rd ed.) to prepare for this experiment: Sec 4.8, pp 168-174 (Acid/Base Titrations), Sec 16.4, pp 769-783
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS GENERAL PREPARATION
 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS Introduction The Van London-pHoenix Company Fluoroborate Ion Selective Electrode is used to quickly, simply, accurately, and economically measure Fluoroborate in aqueous solutions.
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS Introduction The Van London-pHoenix Company Fluoroborate Ion Selective Electrode is used to quickly, simply, accurately, and economically measure Fluoroborate in aqueous solutions.
Redox Titration. Properties of Umass Boston
 Redox Titration Redox Titration Ce 4+ + Fe 2+ Ce 3+ + Fe 3+ Redox titration is based on the redox reaction (oxidation-reduction) between analyte and titrant. Position of the end point Determine the end
Redox Titration Redox Titration Ce 4+ + Fe 2+ Ce 3+ + Fe 3+ Redox titration is based on the redox reaction (oxidation-reduction) between analyte and titrant. Position of the end point Determine the end
I Write the reference number of the correct answer in the Answer Sheet below.
 (2016) Nationality No. CHEMISTRY Name (Please print full name, underlining family name) Marks I Write the reference number of the correct answer in the Answer Sheet below. (1) Which of the atoms 1) to
(2016) Nationality No. CHEMISTRY Name (Please print full name, underlining family name) Marks I Write the reference number of the correct answer in the Answer Sheet below. (1) Which of the atoms 1) to
Experiment 2: Analysis of Commercial Bleach Solutions
 Experiment 2: Analysis of Commercial Bleach Solutions I. Introduction The ability of household bleach to remove stains is related to the amount of oxidizing agent in it. The oxidizing agent in bleach is
Experiment 2: Analysis of Commercial Bleach Solutions I. Introduction The ability of household bleach to remove stains is related to the amount of oxidizing agent in it. The oxidizing agent in bleach is
Sodium Borohydride Reduction of Benzoin
 Sodium Borohydride Reduction of Benzoin Introduction The most common and useful reducing agents for reducing aldehydes, ketones, and other functional groups are metal hydride reagents. The two most common
Sodium Borohydride Reduction of Benzoin Introduction The most common and useful reducing agents for reducing aldehydes, ketones, and other functional groups are metal hydride reagents. The two most common
MERCAPTAN SULFUR IN GASOLINE & KEROSENE AVIATION TURBINE & DISTILLATE FUELS USING ASTM D3227
 MERCAPTAN SULFUR IN GASOLINE & KEROSENE AVIATION TURBINE & DISTILLATE FUELS USING ASTM D3227 Titration Application Use For the determination of mercaptan sulfur in a range from 3 mg/kg 100 mg/kg. Required
MERCAPTAN SULFUR IN GASOLINE & KEROSENE AVIATION TURBINE & DISTILLATE FUELS USING ASTM D3227 Titration Application Use For the determination of mercaptan sulfur in a range from 3 mg/kg 100 mg/kg. Required
Mercaptan Sulfur in Gasoline and Kerosene Aviation Turbine and Distillate Fuels
 Application Note Mercaptan Sulfur in Gasoline and Kerosene Aviation Turbine and Distillate Fuels USING ASTM D 3227 Introduction For the determination of mercaptan sulfur in a range from 3 mg/kg 100 mg/kg.
Application Note Mercaptan Sulfur in Gasoline and Kerosene Aviation Turbine and Distillate Fuels USING ASTM D 3227 Introduction For the determination of mercaptan sulfur in a range from 3 mg/kg 100 mg/kg.
Titer determination in potentiometry
 Branch General analytical chemistry Keywords Titration; potentiometric titration; titer; branch 1 Summary This Bulletin provides an overview of the potentiometric titer determination in common volumetric
Branch General analytical chemistry Keywords Titration; potentiometric titration; titer; branch 1 Summary This Bulletin provides an overview of the potentiometric titer determination in common volumetric
EXPERIMENT NINE Part I - The Standardization of Thiosulfate Solutions
 EXPERIMENT NINE Part I - The Standardization of Thiosulfate Solutions In general, thiosulfate solutions are standardized by indirect methods, Primary-standard oxidizing agents such as KIO 3, As 2 O 3,
EXPERIMENT NINE Part I - The Standardization of Thiosulfate Solutions In general, thiosulfate solutions are standardized by indirect methods, Primary-standard oxidizing agents such as KIO 3, As 2 O 3,
Authors: Philippe Lam, Sr. Engineer. Genentech, Inc., Pharmaceutical Process R&D, 1 DNA Way, South San Francisco, CA 94080
 Authors: Philippe Lam, Sr. Engineer. Genentech, Inc., Pharmaceutical Process R&D, 1 DNA Way, South San Francisco, CA 94080 Mike Nariman, AB Control, Inc., Irvine, CA, www.abcontrols.com. Abstract Genentech
Authors: Philippe Lam, Sr. Engineer. Genentech, Inc., Pharmaceutical Process R&D, 1 DNA Way, South San Francisco, CA 94080 Mike Nariman, AB Control, Inc., Irvine, CA, www.abcontrols.com. Abstract Genentech
Application Determination of isocyanate (NCO-) content
 Determination of isocyanate (NCO-) content date: 20.06.2013 page 1 from 10 Use This method is applicable for material containing reactive isocyanate groups.the isocyanate is reacted with di-n-butyl amine
Determination of isocyanate (NCO-) content date: 20.06.2013 page 1 from 10 Use This method is applicable for material containing reactive isocyanate groups.the isocyanate is reacted with di-n-butyl amine
Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Molarity of Acetic Acid in Vinegar A Titration Experiment
 Molarity of Acetic Acid in Vinegar A Titration Experiment Introduction Vinegar is prepared commercially in two steps, both requiring microorganisms. The first step is the production of ethyl alcohol, C
Molarity of Acetic Acid in Vinegar A Titration Experiment Introduction Vinegar is prepared commercially in two steps, both requiring microorganisms. The first step is the production of ethyl alcohol, C
The Atom, The Mole & Stoichiometry. Chapter 2 I. The Atomic Theory A. proposed the modern atomic model to explain the laws of chemical combination.
 Unit 2: The Atom, The Mole & Stoichiometry Chapter 2 I. The Atomic Theory A. proposed the modern atomic model to explain the laws of chemical combination. Postulates of the atomic theory: 1. All matter
Unit 2: The Atom, The Mole & Stoichiometry Chapter 2 I. The Atomic Theory A. proposed the modern atomic model to explain the laws of chemical combination. Postulates of the atomic theory: 1. All matter
Experiment 12: Grignard Synthesis of Triphenylmethanol
 1 Experiment 12: Grignard Synthesis of Triphenylmethanol Reactions that form carbon-carbon bonds are among the most useful to the synthetic organic chemist. In 1912, Victor Grignard received the Nobel
1 Experiment 12: Grignard Synthesis of Triphenylmethanol Reactions that form carbon-carbon bonds are among the most useful to the synthetic organic chemist. In 1912, Victor Grignard received the Nobel
18 Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments
 360465-P01[01-024] 10/17/02 16:16 Page 18 Sahuja Ahuja_QXP_03:Desktop Folder:17/10/02: 18 Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments Preparing a Laboratory Record Use the following steps to prepare
360465-P01[01-024] 10/17/02 16:16 Page 18 Sahuja Ahuja_QXP_03:Desktop Folder:17/10/02: 18 Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments Preparing a Laboratory Record Use the following steps to prepare
Name Date Class PROPERTIES OF SOLUTIONS
 16.1 PROPERTIES OF SOLUTIONS Section Review Objectives Identify the factors that determine the rate at which a solute dissolves Identify the units usually used to express the solubility of a solute Calculate
16.1 PROPERTIES OF SOLUTIONS Section Review Objectives Identify the factors that determine the rate at which a solute dissolves Identify the units usually used to express the solubility of a solute Calculate
Some Reactions of Hydrocarbons Experiment #2
 Some Reactions of Hydrocarbons Experiment #2 Objective: To distinguish alkanes, alkenes and aromatic hydrocarbons by their chemical reactions and reactivity. Introduction Hydrocarbons are organic compounds
Some Reactions of Hydrocarbons Experiment #2 Objective: To distinguish alkanes, alkenes and aromatic hydrocarbons by their chemical reactions and reactivity. Introduction Hydrocarbons are organic compounds
MEASURING H 2 S IN CRUDE OIL FOR QUALITY CONTROL & TRANSPORTATION SAFETY
 MEASURING IN CRUDE OIL FOR QUALITY CONTROL & TRANSPORTATION SAFETY COQA Meeting 2015 Marriott West Loop, Houston Wesley Kimbell Analytical Systems Keco www.h2sanalyzer.com Why measure in crude oil? Safety
MEASURING IN CRUDE OIL FOR QUALITY CONTROL & TRANSPORTATION SAFETY COQA Meeting 2015 Marriott West Loop, Houston Wesley Kimbell Analytical Systems Keco www.h2sanalyzer.com Why measure in crude oil? Safety
Butyldiglycol. Diethylene glycol monobutyl ether, 2-(2-butoxyethoxy)ethanol. Molecular formula C 8 H 18 O 3. CAS-No EC-No.
 Technical Information Petrochemicals M 2161 e August 2016 Page 1 of 5 Supersedes edition of July 2014 Butyldiglycol Low-volatility, high-boiling, clear liquid with a mild odor. Solvent for numerous natural
Technical Information Petrochemicals M 2161 e August 2016 Page 1 of 5 Supersedes edition of July 2014 Butyldiglycol Low-volatility, high-boiling, clear liquid with a mild odor. Solvent for numerous natural
KEM SET. for FOOD. Salinity. Brix Density Concentration. Acid Value POV. Water Content
 Salinity for FOOD Brix Density Concentration Acid Value POV Water Content Vitamin C Acid Value / POV Salinity Vitamin C for FOOD A Automatic Potentiometric Titrator B Automatic Potentiometric Titrator
Salinity for FOOD Brix Density Concentration Acid Value POV Water Content Vitamin C Acid Value / POV Salinity Vitamin C for FOOD A Automatic Potentiometric Titrator B Automatic Potentiometric Titrator
Experiment 7: Titration of an Antacid
 1 Experiment 7: Titration of an Antacid Objective: In this experiment, you will standardize a solution of base using the analytical technique known as titration. Using this standardized solution, you will
1 Experiment 7: Titration of an Antacid Objective: In this experiment, you will standardize a solution of base using the analytical technique known as titration. Using this standardized solution, you will
Experiment 8 and 9 Weak Acids and Bases: Exploring the Nature of Buffers
 Experiment 8 and 9 Weak Acids and Bases: Exploring the Nature of Buffers Pre-Laboratory Assignments Reading: Textbook Chapter 16 Chapter 17:1-3 This Laboratory Handout Pre-Laboratory Assignments: Complete
Experiment 8 and 9 Weak Acids and Bases: Exploring the Nature of Buffers Pre-Laboratory Assignments Reading: Textbook Chapter 16 Chapter 17:1-3 This Laboratory Handout Pre-Laboratory Assignments: Complete
Acidimetry in Non-Aqueous Titrations
 Acidimetry in Non-Aqueous Titrations 1. In order to perform feasible titrations of weak bases, the solvent system should be selected specifically in such a fashion so as to eliminate as far as possible
Acidimetry in Non-Aqueous Titrations 1. In order to perform feasible titrations of weak bases, the solvent system should be selected specifically in such a fashion so as to eliminate as far as possible
Rule 2. Rule 1. Rule 4. Rule 3. Rule 5. Rule 6. Rule 7. Rule 8
 Rule 1 Follow the directions in your course reader, of your teaching assistant and of your instructor. They are usually much more experienced doing chemistry. Rule 3 When in doubt, ask. This will make
Rule 1 Follow the directions in your course reader, of your teaching assistant and of your instructor. They are usually much more experienced doing chemistry. Rule 3 When in doubt, ask. This will make
IMPCA METHANOL REFERENCE SPECIFICATIONS
 IMPCA INTERNATIONAL METHANOL PRODUCERS & CONSUMERS ASSOCIATION IMPCA METHANOL REFERENCE SPECIFICATIONS a.i.s.b.l. International Methanol Producers & Consumers Association i.v.z.w. Avenue de Tervueren 270
IMPCA INTERNATIONAL METHANOL PRODUCERS & CONSUMERS ASSOCIATION IMPCA METHANOL REFERENCE SPECIFICATIONS a.i.s.b.l. International Methanol Producers & Consumers Association i.v.z.w. Avenue de Tervueren 270
--> Buy True-PDF --> Auto-delivered in 0~10 minutes. GB Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB
 Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB18350-2013 www.chinesestandard.net Sales@ChineseStandard.net ICS 75.160.20 NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB E 31 Replacing GB 18350-2001
Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB18350-2013 www.chinesestandard.net Sales@ChineseStandard.net ICS 75.160.20 NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB E 31 Replacing GB 18350-2001
To understand concept of limiting reagents. To learn how to do a vacuum filtration. To understand the concept of recrystallization.
 E x p e r i m e n t Synthesis of Aspirin Experiment : http://genchemlab.wordpress.com/-aspirin/ objectives To synthesize aspirin. To understand concept of limiting reagents. To determine percent yield.
E x p e r i m e n t Synthesis of Aspirin Experiment : http://genchemlab.wordpress.com/-aspirin/ objectives To synthesize aspirin. To understand concept of limiting reagents. To determine percent yield.
Acid-Base Titration. M M V a
 Acid-Base Titration Pre-Lab Discussion In the chemistry laboratory, it is sometimes necessary to experimentally determine the concentration of an acid solution or a base solution. A procedure for making
Acid-Base Titration Pre-Lab Discussion In the chemistry laboratory, it is sometimes necessary to experimentally determine the concentration of an acid solution or a base solution. A procedure for making
O H 3 O 1 1 A. O 1 1 OH (K w
 CHAPTER 8 Acid Base Titration Curves Objectives The objectives of this experiment are to: Understand the titration curves for the following solutions: a strong acid: hydrochloric acid, HCl. a weak acid:
CHAPTER 8 Acid Base Titration Curves Objectives The objectives of this experiment are to: Understand the titration curves for the following solutions: a strong acid: hydrochloric acid, HCl. a weak acid:
SVENSK STANDARD SS-ISO Plast Polyoler för användning vid produktion av polyuretan Bestämning av vatteninnehåll
 SVENSK STANDARD SS-ISO 14897 Fastställd 2003-10-31 Utgåva 1 Plast Polyoler för användning vid produktion av polyuretan Bestämning av vatteninnehåll Plastics Polyols for use in the production of polyurethane
SVENSK STANDARD SS-ISO 14897 Fastställd 2003-10-31 Utgåva 1 Plast Polyoler för användning vid produktion av polyuretan Bestämning av vatteninnehåll Plastics Polyols for use in the production of polyurethane
Determination of Carbonyl Compounds In Water by Dinitrophenylhydrazine Derivatization and HPLC/UV*
 Determination of Carbonyl Compounds In Water by Dinitrophenylhydrazine Derivatization and HPLC/UV* EPA Method 8315A UCT Part Number: EUC1812M15 (Unendcapped C18-2000 mg/15 ml cartridge) March 2013 Method
Determination of Carbonyl Compounds In Water by Dinitrophenylhydrazine Derivatization and HPLC/UV* EPA Method 8315A UCT Part Number: EUC1812M15 (Unendcapped C18-2000 mg/15 ml cartridge) March 2013 Method
1.8K: Define a buffer as relatively large amounts of a weak acid or base and its conjugate in equilibrium that maintain a relatively constant ph when
 1.8K: Define a buffer as relatively large amounts of a weak acid or base and its conjugate in equilibrium that maintain a relatively constant ph when small amounts of acid or base are added. 1 Chem 20
1.8K: Define a buffer as relatively large amounts of a weak acid or base and its conjugate in equilibrium that maintain a relatively constant ph when small amounts of acid or base are added. 1 Chem 20
Ch. 10: Acid-Base Titrations
 Ch. 10: Acid-Base Titrations Outline: 10-1 Titration of Strong Base with Strong Acid 10-2 Titration of Weak Acid with Strong Base 10-3 Titration of Weak Base with Strong Acid 10-4 Titrations in Diprotic
Ch. 10: Acid-Base Titrations Outline: 10-1 Titration of Strong Base with Strong Acid 10-2 Titration of Weak Acid with Strong Base 10-3 Titration of Weak Base with Strong Acid 10-4 Titrations in Diprotic
GCSE Chemistry. Module C7 Further Chemistry: What you should know. Name: Science Group: Teacher:
 GCSE Chemistry Module C7 Further Chemistry: What you should know Name: Science Group: Teacher: R.A.G. each of the statements to help focus your revision: R = Red: I don t know this A = Amber: I partly
GCSE Chemistry Module C7 Further Chemistry: What you should know Name: Science Group: Teacher: R.A.G. each of the statements to help focus your revision: R = Red: I don t know this A = Amber: I partly
TWO ENZYME CATALYSIS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION
 TWO ENZYME CATALYSS OVERVEW n this lab you will: 1. observe the conversion of hydrogen peroxide (H 2 0 2 ) to water and oxygen gas by the enzyme catalase, and 2. measure the amount of oxygen generated
TWO ENZYME CATALYSS OVERVEW n this lab you will: 1. observe the conversion of hydrogen peroxide (H 2 0 2 ) to water and oxygen gas by the enzyme catalase, and 2. measure the amount of oxygen generated
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
 Aromatic Hydrocarbons Aromatic hydrocarbons contain six-membered rings of carbon atoms with alternating single and double carbon-carbon bonds. The ring is sometimes shown with a circle in the center instead
Aromatic Hydrocarbons Aromatic hydrocarbons contain six-membered rings of carbon atoms with alternating single and double carbon-carbon bonds. The ring is sometimes shown with a circle in the center instead
IMPCA METHANOL REFERENCE SPECIFICATIONS
 IMPCA INTERNATIONAL METHANOL PRODUCERS & CONSUMERS ASSOCIATION IMPCA METHANOL REFERENCE SPECIFICATIONS a.i.s.b.l. International Methanol Producers & Consumers Association i.v.z.w. Avenue de Tervueren 270
IMPCA INTERNATIONAL METHANOL PRODUCERS & CONSUMERS ASSOCIATION IMPCA METHANOL REFERENCE SPECIFICATIONS a.i.s.b.l. International Methanol Producers & Consumers Association i.v.z.w. Avenue de Tervueren 270
2012 AP CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS
 01 AP CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS. A sample of a pure, gaseous hydrocarbon is introduced into a previously evacuated rigid 1.00 L vessel. The pressure of the gas is 0.00 atm at a temperature of 17C.
01 AP CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS. A sample of a pure, gaseous hydrocarbon is introduced into a previously evacuated rigid 1.00 L vessel. The pressure of the gas is 0.00 atm at a temperature of 17C.
OH [H + ] KMnO 4 DME OH
![OH [H + ] KMnO 4 DME OH OH [H + ] KMnO 4 DME OH](/thumbs/87/95833877.jpg) 1.a. Reaction 1 is an elimination reaction which includes a rearrangement via a hydride shift. Reaction 2 is an oxidation reaction that leads to a cis-diol. This reaction was used to qualitatively confirm
1.a. Reaction 1 is an elimination reaction which includes a rearrangement via a hydride shift. Reaction 2 is an oxidation reaction that leads to a cis-diol. This reaction was used to qualitatively confirm
Scope and application: For water, wastewater and seawater. Distillation is required for wastewater and seawater.
 Nitrogen, Ammonia DOC316.53.01078 USEPA 1 Nessler Method 2 Method 8038 0.02 to 2.50 mg/l NH 3 N Reagent Solution Scope and application: For water, wastewater and seawater. Distillation is required for
Nitrogen, Ammonia DOC316.53.01078 USEPA 1 Nessler Method 2 Method 8038 0.02 to 2.50 mg/l NH 3 N Reagent Solution Scope and application: For water, wastewater and seawater. Distillation is required for
12A Lab Activity Notes
 12A Lab Activity Notes Lab Activity 12 In this experiment, RX reacts with a base. The methoxide ion (CH 3 O - ) is a small, strong base. The tert-butoxide ion ((CH 3 ) 3 CO - ) is a large, strong base.
12A Lab Activity Notes Lab Activity 12 In this experiment, RX reacts with a base. The methoxide ion (CH 3 O - ) is a small, strong base. The tert-butoxide ion ((CH 3 ) 3 CO - ) is a large, strong base.
Alcohols. Contents. Structure. structure
 Page 1 of 9 Alcohols Contents structure Physical Properties Classification of Alcohols Nomenclature of Alcohols Preparation of Alcohols Oxidation of Alcohols oxidation of aldehydes Structure Alcohols can
Page 1 of 9 Alcohols Contents structure Physical Properties Classification of Alcohols Nomenclature of Alcohols Preparation of Alcohols Oxidation of Alcohols oxidation of aldehydes Structure Alcohols can
Application Note #97 Alkalinity and Hardness by Potentiometric Titration Using TRIS Buffer
 Application Note #97 Alkalinity and Hardness by Potentiometric Titration Using TRIS Buffer Updated July 2017 Introduction: Alkalinity refers to the acid-neutralizing or buffering capacity of a solution.
Application Note #97 Alkalinity and Hardness by Potentiometric Titration Using TRIS Buffer Updated July 2017 Introduction: Alkalinity refers to the acid-neutralizing or buffering capacity of a solution.
Teacher Resource and Assessment Book Exercises Unit 3 answers
 Teacher Resource and Assessment Book Exercises Unit 3 answers 2. Exercise: Gravimetric analysis of chicken soup Part A 1. n(agcl) = 0.246 143.3 = 1.72 x 10 3 mole 2. Amount of NaCl in 20.00 ml aliquot
Teacher Resource and Assessment Book Exercises Unit 3 answers 2. Exercise: Gravimetric analysis of chicken soup Part A 1. n(agcl) = 0.246 143.3 = 1.72 x 10 3 mole 2. Amount of NaCl in 20.00 ml aliquot
Aldol Condensation Notes
 Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace, the laboratory manual. Aldol Condensation Notes History and Application Condensation reactions are molecular transformations that join together
Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace, the laboratory manual. Aldol Condensation Notes History and Application Condensation reactions are molecular transformations that join together
