Heterosis Expression of Hybrid Rice in Natural- and Short-Day Length Conditions
|
|
|
- Trevor Sanders
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Rice Science, 2015, 22(2): Copyright 2015, China National Rice Research Institute Hosting by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved DOI: /S (14) Heterosis Expression of Hybrid Rice in Natural- and Short-Day Length Conditions HUANG Zhi-yuan, ZHAO Bing-ran, LV Qi-ming, FU Xi-qin, XIN Ye-yun, YUAN Long-ping (State Key Laboratory of Hybrid Rice, Hunan Hybrid Rice Research Center, Changsha , China) Abstract: Development of hybrid rice is an important strategy to increase yields of irrigated rice in China. Day length is a highly important environmental factor for hybrid rice adaptability, productivity and quality. Heterosis of hybrid rice has been utilized under natural- (long) day length conditions in the middle and lower reaches plain of Yangtze River Valley in China for a long time. However, whether the hybrid rice can show heterosis under short-day length conditions is unknown. In this study, we analyzed plant height, grain number per panicle, and other yield related traits of hybrid rice Liangyoupeijiu (LYP9) and its parents (Pei ai 64S and 93-11) under natural- and short-day length conditions and compared the respective heterosis. Results showed that earlier heading, reduced plant height, and reduced grain number per panicle were found in these three varieties under short-day length conditions relative to those under natural-day length conditions. In either natural- or short-day length conditions, heterosis of LYP9 was mainly displayed in grain number per panicle and plant height. This study may help in breeding and selecting suitable hybrid rice for different regions with natural- or short-day length. Key words: hybrid rice; heterosis; photoperiod; short-day length Research on hybrid rice in China started in A three-line breeding system composed of a cytoplasmic male sterile (CMS) line, a CMS maintainer, and a CMS restorer line was established in 1973 to generate hybrid rice, and commercial production of hybrid rice began in 1976 (Yuan, 1986). Wild-abortive CMS (CMS-WA) is the first and main type of male sterility used in hybrid rice breeding. The most popular WA-type hybrid, Shanyou 63, with Minghui 63 as the male sterile line, yielded t/hm 2 ; Shanyou 63 was planted on a total acreage of hm 2 between 1984 and 2003, occupying the largest acreage for a single hybrid from 1987 to 2001, and the highest annual acreage of over hm 2 in 1990 because of its good general combining ability. However, some constraints and problems are encountered in such system, such as its genetic vulnerability and plateaued yields, because of insufficient genetic diversity (Cheng and Min, 2000). In 1995, a two-line hybrid rice technology with an environment-sensitive genic male sterile (EGMS) line and a restore line (R line) was successfully commercialized in China and widely used in 1998 (Li and Yuan, 2000; Yuan, 2004). This Received: 2 September 2014; Accepted: 9 December 2014 Corresponding author: HUANG Zhi-yuan (huangzhiyuan@hhrrc.ac.cn) method is designed and developed based on the two new kinds of rice genetic materials, namely photosensitive and thermo-sensitive genic male sterile lines. Male sterility is mainly controlled by one or two pairs of recessive nuclear genes. The advantages of the two-line system over the three-line system include a wider range of germplasm resources used as breeding parents, better grain quality and higher yields, and simpler procedures for breeding and hybrid seed production (Yang et al, 2007). However, the dependency of male sterility on temperature and day length requires more attention from breeders and seed producers. To date, hybrid rice planting area has occupied more than 50% of the total rice planting area in China due to about 10% 20% yield advantage over inbred varieties (Cheng et al, 2007). In recent years, two-line hybrid rice has become an important type in rice production in China, accounting for about 20% of the total planting area of hybrid rice (Si et al, 2011). Thus, the current annual acreage of hybrid rice has increased from hm 2 in 1976 to about hm 2 in China. Heterosis is an important and complex trait of hybrid rice that exhibits superior phenotypes relative to its parents, including enhanced biomass production, development rate, grain yield, and stress tolerance.
2 82 Rice Science, Vol. 22, No. 2, 2015 Thus, it has been effectively utilized to increase rice production from 1970s in China (Zhang et al, 1994; Xiao et al, 1995; Yu et al, 1997; Luo et al, 2001; Hua et al, 2003). Utilization of indica-indica heterosis was a fundamental principle for rice yield improvement during 1970s to 1980s. The heterosis between subspecific varieties is an effective strategy to increase rice yield further (Lu and Zou, 2005). The pioneer super hybrid rice Liangyoupeijiu (LYP9), with the target yield of 10.5 t/hm 2 in 2000 (Yuan, 2006), has been well demonstrated under high-yielding cultivation conditions. LYP9 was developed by a cross of the paternal 93-11, an indica variety widely grown in China (Yu et al, 2002), with the female parent Pei ai 64S (PA64S), a javanica EGMS line with its wide compatibility gene (S n 5 ) from Padi, a cultivar from Indonesia, and its EGMS character from Nongken 58S, a mutant from a japonica cultivar Nongken 58. LYP9 has been widely cultivated for commercial production with 20% to 30% more yield per hectare than its parent lines in the rice growing area between 12 N and 34 N, including southern regions of China and Southeast Asia (Lu et al, 2004). The hybrid has a growth period of 150 ± 24 d with leaves, and an averaged grain yield of 8.4 ± 2.6 t/hm 2 as single seasonal rice. The plant height of LYP9 is 112 ± 19 cm, its tillering ability is strong and the effective tiller number per square meter is usually 260 ± 50, and the 1000-grain weight is 26.2 ± 2.4 g (Lu and Zou, 2005). During 2000 to 2009, the planting area of LYP9 was hm 2, accounting for 26.7% of the total area of two-line hybrid rice. The most suitable region for LYP9 is between 28 N to 30 N. The daily average temperature of 26 C to 28 C at heading is thought to be more favorable for getting a higher seed-setting rate and grain yield (Lu et al, 2004). The growth period of LYP9 is sensitive to day length. The heading promotion rate of LYP9 is 21.0% in the short-day length and high-temperature conditions, and 13.6% in natural- (long) day length and high-temperature conditions. LYP9 is widely cultivated in 28 N, where the day length is longer than 13 h, ensuring a stable stage for its growth and development (Zou et al, 2008). For example, the opportune sowing date of LYP9 is before 21 June in Wenzhou (27 28 N), China, so that when it is sowed after 21 June, the grain number per panicle and seed-setting rate would decrease significantly because the day length is respectively more than 13 h from 21 April to 21 August and 12 h from 1 October to 1 April in N (Bai et al, 2006). Day length, defined as the interval between sunrise and sunset, is known as photoperiod. Rice, according to its subtropical origin, is considered as a short-day plant and can be classified into photoperiod-sensitive and photoperiod-insensitive types, the latter showing a low response or a slight delay in flowering with an increase in photoperiod. Most of the wild species of Oryza and many of the primitive cultivated rice species are photoperiod-sensitive and may be classified as short-day plants. Most of the cultivated rice species may eventually become photoperiodinsensitive ones (Vergara and Chang, 1985). During the process of rice introduction to the regions at high latitudes, rice breeders have selected lines with weak sensitivity to photoperiod to ensure maturity during the period of optimal climatic conditions (Izawa, 2007; Xue et al, 2008; Takahashi et al, 2009; Wei et al, 2010; Ebana et al, 2011). Photoperiod insensitivity plays an important role in expanding the range of rice cultivation to high latitudes (Fujino and Sekiguchi, 2005; Izawa, 2007; Xue et al, 2008). In hybrid rice breeding, most of R lines are insensitive or weakly sensitive to photoperiod, which is suitable for hybrid rice cultivation and extension. Heterosis of hybrid rice has been long utilized under natural-day length conditions in the middle and lower reaches plain of Yangtze River Valley in China. However, whether this hybrid rice can show heterosis in the short-day length conditions is unknown. In this study, we analyzed the heterosis relative phenotypes of LYP9 under natural- and artificial short-day length conditions in Changsha City (28 N) of China to determine the effects of photoperiod on heterosis expression. PA64S, LYP9 and were grown in winter in Sanya City (18 N) for comparison. Results showed that the short-day length treatment affected the development and yielding traits of LYP9 and its parents to some degrees. LYP9 displayed heterosis in plant height and grain number per panicle under the natural- and short-day length conditions, which would help to reveal the mechanisms underlying day length regulation of the rice heterosis. MATERIALS AND METHODS Rice materials and growth conditions The experiment base is in Changsha, which experiences subtropical climate. Super hybrid rice LYP9 and its parental lines (93-11 and PA64S) were grown in the
3 HUANG Zhi-yuan, et al. Heterosis Expression of Hybrid Rice in Different Day Length Conditions 83 rice fields. Approximately 600 kg/hm 2 compound fertilizer (N-P 2 O 5 -K 2 O: ) were applied before seedling transplantation. The 3 4 d germinated seedlings of these varieties were raised in seedling nursery bed for about 25 d in the natural conditions and were transplanted to the paddy fields (spacing of 16.5 cm 20.0 cm) in a randomized block design with three replicates. PA64S was sowed 8 d before LYP9 and to attain simultaneous flowering. In winter, super hybrid rice LYP9 and its parental lines were grown in Sanya, which belongs to tropical climate with the same cultivation method as comparison. Short-day length treatment In Changsha, the short-day length conditions started from 9:00 AM to 6:00 PM at the initial development of the main panicle of plant that was, LYP9, PA64S and began the short-day length 55, 42 and 51 d after sowing. The plants were covered by a box wrapped with shade cloth. Approximately 100% of light was blocked by shade cloth (Fig. 1). No temperature difference existed between inner and outer sides of the box. The light time was 9 h and the dark time was 15 h in the short-day length conditions. By comparison, the light time was about 13 h and the dark time was about 11 h in the natural-day conditions. Thus, the light time was reduced by about 4 h in the short-day length conditions compared with the natural day conditions. In Sanya, the day length increased from 11 h to 12.5 h gradually from 20 December to 20 April. Growth observation and yield component characters examination During rice growth and development, the different growth stages were recorded. Rice yield is dependent on grain number, seed-setting rate, effective panicle number, and 1000-grain weight. Before grain maturity, effective panicle number per plant was examined on the basis of five points per plot, and each point included ten hills. Grain number per panicle, seed-setting rate, and 1000-grain weight of the plants were examined (six hills per plot). Mid-parent heterosis (MPH) and high-parent heterosis (HPH) were calculated according to the following formula: MPH = (F 1 MP) / MP 100%, and HPH = (F 1 HP) / HP 100%, where F 1 is the performance of the hybrid, MP is the average performance of the two parents, and HP is the best performance of the two parents. Hypothesis testing was performed using t-test. Theoretical yield = Effective panicle number per hectare Grain number per panicle Seed-setting rate 1000-grain weight. RESULTS Effects of short-day length on rice plant development The rice plants were treated under short-day length at the stages from initial development to full heading of the main panicle. Particularly, LYP9, PA64S and plants were treated under short-day length for 32, 34 and 37 d, respectively because each variety had different sensitive to day length. The days from sowing to heading of LYP9 in the natural- and short-day length conditions were 94 and 85 d, respectively (Tables 1 and 2). LYP9 headed 9 d earlier in the short-day length conditions than that in the natural-day conditions. The entire growth periods of LYP9 in the natural- and short-day length conditions were 133 and 116 d, respectively. The harvesting of LYP9 in the short-day length conditions was 17 d earlier than that in the natural-day conditions. The days from sowing to heading of the paternal line in the natural- and short-day length conditions were 94 and 87 d, respectively, indicating that the A B C D Fig. 1. Effects of short-day treatment on plant development of hybrid rice Liangyoupeijiu (LYP9) and its parents Pei ai 64S (PA64S) and A, Rice plants were covered by the box wrapped with shade cloth; B, PA64S; C, LYP9; D, Arrows showed that the panicles in the short-day length conditions headed earlier than those in the natural-day length conditions.
4 84 Rice Science, Vol. 22, No. 2, 2015 Table 1. Treatments in the natural- and short-day length conditions in hybrid rice Liangyoupeijiu (LYP9) and its parents Pei ai 64S (PA64S) and in 2012, Changsha, China. Variety Treatment Days from Sowing to heading (d) Days from sowing to harvest (d) Treatment time (Month-Day) Short day treatment (d) PA64S Natural-day 77 NA a Short-day 70 NA to LYP9 Natural-day Short-day to Natural-day Short-day to a PA64S had no seeds set because of male sterile. heading day of is 7 d earlier in the short-day length conditions than in the natural-day conditions. The entire growth duration of in the naturaland short-day length conditions were 133 and 116 d, respectively, leading to harvesting 17 d earlier in the short-day length conditions than in the natural-day conditions. The days from sowing to heading of PA64S in the natural- and short-day length conditions were 77 and 70 d, respectively. The PA64S was completely male sterile in both conditions and headed 7 d earlier in the short-day length conditions than in the natural-day conditions. These results showed that the short-day length conditions can promote the rice flowering and reduce the entire growth period. The difference between LYP9 and in the short-day length conditions was small, but needed more short-day length conditions time to head fully, thereby shortening the entire growth period. In Sanya, PA64S and LYP9 headed d earlier than (Table 2). The entire growth duration of LYP9 and were 124 and 136 d, respectively. The difference of entire growth period between LYP9 and was considerable. In Sanya, the harvesting of LYP9 was 9 d earlier than in the natural-day conditions in Changsha, but the harvesting day of was only 3 d later than in the natural-day conditions in Changsha, with unremarkable difference. The day length of Sanya is shorter than that of Changsha in the natural-day conditions. The results showed that LYP9 was more sensitive to short-day length than length conditions (Table 3 and Fig. 3-A). Furthermore, LYP9 was the tallest, whereas PA64S was the shortest among the three varieties. These results suggested that the effect of short-day length treatment on the plant height is the largest in LYP9 and relatively smallest in PA64S. The MPH and HPH of plant heights of LYP9 were 22.0% and 3.3% in the natural-day conditions, respectively, and were 20.3% and 1.5% in the short-day length conditions, respectively (Table 3), indicating that MPH of plant height in LYP9 was stronger than HPH. The plant heights of PA64S, LYP9 and were 65.8, 96.4 and 90.8 cm, respectively, in Sanya, which were decreased 18.0, 28.3 and 29.9 cm compared with those in the natural-day conditions in Changsha. The MPH and HPH of plant height of LYP9 were 23.2% and 6.2%, respectively (Table 4). These results suggested that LYP9 displayed stronger heterosis in plant height both under the natural- and short-day length conditions. Effects of short-day length treatment on grain number per panicle Grain number per panicle is a key trait of rice yield. For LYP9, The grain number per panicle was in the natural-day conditions and in the short-day Effects of short-day length treatment on plant height Plant heights of LYP9 in the natural- and short-day length conditions in Changsha were and cm, respectively, whereas the corresponding plant heights of were and cm. Similarly, plant heights of PA64S were 83.8 cm in the natural-day conditions and 80.2 cm in the short-day Fig. 2. Effects of short-day treatment on development of hybrid rice Liangyoupeijiu (LYP9) and its parents Pei ai 64S (PA64S) and ND, Natural-day length conditions; SD, Short-day length conditions.
5 HUANG Zhi-yuan, et al. Heterosis Expression of Hybrid Rice in Different Day Length Conditions 85 Table 2. Growth stages of hybrid rice Liangyoupeijiu (LYP9) and its parents Pei ai 64S (PA64S) and in , Sanya, China. Variety Sowing date (Year-Month-Day) Initial heading date (Year-Month-Day) Full heading date (Year-Month-Day) Days from sowing to full heading (d) Days from sowing to harvest (d) PA64S LYP Table 3. Yield component characters of hybrid rice Liangyoupeijiu (LYP9) and its parents Pei ai 64S (PA64S) and in Changsha, China. Variety and Plant height Effective panicle number Seed-setting rate 1000-grain weight Treatment Grain number per panicle heterosis (cm) per plant (%) (g) PA64S Natural-day 83.8 ± 3.3 Bb 10.6 ± 2.0 Bb ± 18.1 Aa PA64S Short-day 80.2 ± 3.5 Aa 10.6 ± 3.9 Bb ± 24.9 ABab LYP9 Natural-day ± 4.7 Fe 8.2 ± 1.7 Aa ± 23.2 ABb 65.0 Aa ± 0.72 Aa LYP9 Short-day ± 3.8 CDc 7.3 ± 1.6 Aa ± 21.5 Bb 84.0 Bb ± 0.75 Ab Natural-day ± 4.5 Dd 7.3 ± 1.5 Aa ± 41.1 Bb 80.0 BCc ± 1.32 Bc Short-day ± 4.9 Cc 7.3 ± 1.6 Aa ± 41.0 Bb 88.0 Cc ± 0.72 Bc MPH (%) Natural-day HPH (%) Natural-day MPH (%) Short-day HPH (%) Short-day MPH, Mid-parent heterosis; HPH, High-parent heterosis. Values followed by the same lowercase letter and uppercase letters in the same column are not significant at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively. Table 4. Economic characters of hybrid rice Liangyoupeijiu (LYP9) and its parents Pei ai 64S (PA64S) and in , Sanya, China. Variety and heterosis Plant height (cm) Effective panicle number per plant Average grain number per panicle Seed-setting rate (%) 1000-grain weight (g) PA64S 65.8 ± 3. 7 Aa 8.3 ± 3.2 ab ± 21.6 Aa LYP ± 4.0 Cc 10.4 ± 3.7 b ± 21.1 Bb ± 4.9 Bb 7.1 ± 1.8 a ± 4.7 ABa MPH (%) HPH (%) MPH, Mid-parent heterosis; HPH, High-parent heterosis. Values followed by the same lowercase letter and uppercase letters in the same column are not significant at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively. length conditions, whereas for and PA64S, their grain numbers per panicle were and under natural-day conditions and and under short-day length conditions, respectively (Table 3 and Fig. 3-B). These results suggested that the effect of the short-day length treatment on grain number was the largest in and the smallest in LYP9. The MPH and HPH of grain number per panicle of LYP9 were 7.1% and 6.8%, respectively, under natural-day conditions, and 18.2% and 12.3%, respectively, under short-day length conditions (Table 3). The grain numbers per panicle of PA64S, LYP9 and were 153.3, and 156.2, respectively in Sanya, which were decreased 23.8, 7.3 and 22.0 cm compared with those under natural-day conditions in Changsha. The MPH and HPH of plant heights for LYP9 were 18.2% and 17.2% (Table 4). These results suggested that LYP9 exhibited stronger heterosis in grain number per plant under the natural- and short-day length conditions. Effects of short-day length treatment on seed-setting rate and 1000-grain weight The seed-setting rate of LYP9 under natural- and short-day length conditions were 65% and 84%, respectively. The seed-setting rate of under natural- and short-day length conditions were 80% and 88%, respectively. The difference of seed-setting rate of LYP9 between under natural- and short-day length conditions was significant (Table 3 and Fig. 3-C). The results showed that short-day length conditions can improve seed-setting rate. The 1000-grain weights of LYP9 under natural- and short-day length conditions were and g, respectively. The 1000-grain
6 86 Rice Science, Vol. 22, No. 2, 2015 Fig. 3. Effects of short-day treatment on hybrid rice Liangyoupeijiu (LYP9) and its parents Pei ai 64S (PA64S) and A, Plant height; B, Average grain number of per panicle; C, Seed-setting rate. ND, Natural-day length conditions; SD, Short-day length conditions. weights of under natural- and short-day length conditions were and g, respectively. Although the differences between LYP9 and were small, the short-day length conditions were beneficial for 1000-grain weight in both varieties. PA64S was completely male sterile under natural- and short-day length conditions. The seed-setting rates of LYP9 and were 72% and 58%, respectively, in Sanya. And the seed-setting rate of LYP9 was higher than that of The 1000-grain weights of LYP9 and were and g, respectively (Table 4). The 1000-grain weight of was lower under natural-day conditions (Table 3). Effects of short-day length treatment on effective panicle number per plant The effective panicle number per plant of PA64S under natural- and short-day length conditions were both 10.6, and have the highest effective panicle numbers per plant. The effective panicle number per plant of under natural- and short-day length conditions were both 7.3, whereas those of LYP9 were 8.2 and 7.3, respectively. The effective panicle number per plant of LYP9 was between those of PA64S and 93-11, and was higher under natural-day conditions, but the difference was not significant (Table 3). The effective panicle number per plant of PA64S, LYP9 and were 8.3, 10.4 and 7.1, respectively, in Sanya (Table 4). The effective panicle number per plant of LYP9 was larger than those of PA64S and DISCUSSION Hybrid rice has been used in commercial production for four decades, and it is a good choice for resolving food security problem. Currently, approximately 17 million hectares are allotted for hybrid rice production in China and another 4 million hectares in other tropical countries, mainly in Bangladesh, India, Indonesia, Myanmar, the Philippines and Vietnam (Xie et al, 2013). However, the hybrid rice extension area in these countries is still very small compared with that in China. Many Chinese hybrid rice perform poorly in tropical countries because of the environment changes, including day length and temperature. Our study revealed that the heterosis of LYP9 mainly displayed in grain number per panicle and plant height in both natural- and short-day length conditions. Results also showed that the short-day length treatment could not only shorten the flowering time but also reduce the plant height, as described by Ganashan and Whittington (1976) and Craufurd et al (2003). In China, CMS and EGMS lines usually flower earlier than R lines and hybrid rice. PA64S is a typical short-day plant with a short growth period. PA64S and have some similarities in terms of plant development and height under short-day length conditions compared with those under natural-day conditions. They both flowered 7 d earlier, and their plant heights were reduced by 3 4 cm under short-day length conditions compared with those under naturalday conditions. Panicle primordial of rice plants are initialized in response to a short photoperiod and are delayed or inhibited under long photoperiods (Yoshida, 1981). This result also confirmed that rice is sensitive to short-day length when it initiated panicle primordial even in the rice hybrid. Notably, the grain number per panicle of PA64S and were reduced by 17.7 and 34.9 under short-day length conditions compared with those under natural-day conditions, but the grain number per panicle of was more affected under short-day length conditions. The development of LYP9 was tended to under natural- and short-day length conditions. They both flowered 7 9 d earlier and matured 17 d earlier under short-day length conditions. However, flowered and matured later than
7 HUANG Zhi-yuan, et al. Heterosis Expression of Hybrid Rice in Different Day Length Conditions 87 LYP9 when they grew in Sanya, owing to reduced day length and temperature change. The grain number per panicle of LYP9 was higher under natural-day conditions than under short-day length conditions, but the seed-setting rate of LYP9 was lower under natural-day conditions than under short-day length conditions. The effective panicle number per plant of LYP9 was PA64S and in both conditions in Changsha, but in Sanya, the seed-setting rate of LYP9 was higher than that of 93-11, and the effective panicle number per plant of LYP9 was higher than those of PA64S and The seed-setting rate and 1000-grain weight of under short-day length conditions were relative higher under natural-day conditions. This result confirmed that the growth duration was shortened, plant height and total grain number per panicle were decreased, and effective panicle number per plant was increased when hybrid rice were grown under short-day length conditions (Mao et al, 2005). Based on the results, we can conclude that the plant height and grain number per panicle are strongly affected by day length. Although the grain numbers per panicle of PA64S, LYP9 and were all decreased under short-day length conditions, LYP9 still showed heterosis with regard to grain number per panicle and plant height. The yield of hybrid rice in short-day length conditions was lower than that in natural-day length conditions because of decreased grain number per panicle. The heterosis expression of LYP9 under natural-day conditions is better than that under short-day length conditions. This finding can provide the clear direction for new hybrid rice breeding under short-day length conditions, which exhibits better heterosis expression than LYP9. So we can develop new hybrid rice with the heterosis expression much better than LYP9 in the short-day length conditions. Given that the heterosis of hybrid rice may have common or different mechanisms under the two day length conditions, the results from the present study may help understand the utilization of rice heterosis in areas with short-day lengths. In future work, we shall distinguish the heterosis expression between the different day length conditions and uncover the genetic and gene regulation mechanisms of heterosis expression in rice. REFERENCES Bai P, Wang Y H, Xiang X, Tao K Z, Wu P X, Yang J Studies on full heading time and optimized sowing dates of hybrid rice Liangyoupeijiu. Acta Agric Zhejiang, 18(3): (in Chinese with English abstract) Cheng S H, Min S K Rice varieties in China: Current status and prospect. China Rice, 6(1): (in Chinese) Cheng S H, Zhuang J Y, Fan Y Y, Du J H, Cao L Y Progress in research and development on hybrid rice: A super-domesticate in China. Ann Bot, 100(5): Craufurd P Q, Hauser I E, Dingkuhn M Photothermal responses of O. sativa and O. glaberrima varieties and interspecific progenies from West Africa. Field Crops Res, 83(3): Ebana K, Shibaya T, Wu J Z, Matsubara K, Kanamori H, Yamane H, Yamanouchi U, Mizubayashi T, Kono I, Shomura A, Ito S, Ando T, Hori K, Matsumoto T, Yano M Uncovering of major genetic factors generating naturally occurring variation in heading date among Asian rice cultivars. Theor Appl Genet, 122: Fujino K, Sekiguchi H Mapping of QTLs conferring extremely early heading in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet, 111(2): Ganashan P, Whittington W J Genetic analysis of the response to day length in rice. Euphytica, 25(1): Hua J P, Xing Y Z, Wu W R, Xu C G, Sun X L, Yu S B, Zhang Q F Single-locus heterotic effects and dominance by dominance interactions can adequately explain the genetic basis of heterosis in an elite rice hybrid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 100(5): Izawa T Adaptation of flowering-time by natural and artificial selection in Arabidopsis and rice. J Exp Bot, 58(12): Li J M, Yuan L P Hybrid rice: Genetics, breeding and seed production. Plant Breeding Rev, 17: Lu C G, Zong S Y, Zou J S Studies on seed setting stability in associated with temperature for a two-line hybrid rice, Liangyoupeijiu. Rice Sci, 11(4): Lu C G, Zou J S Practice and thought on developing hybrid rice for super high yield by exploiting inter-subspecific heterosis. Rice Sci, 12(1): 1 6. Luo L J, Li Z K, Mei H W, Shu Q Y, Tabien R, Zhong D B, Ying C S, Stansel J W, Khush G S, Paterson A H Overdominant epistatic loci are the primary genetic basis of inbreeding depression and heterosis in rice: II. Grain yield components. Genetics, 158(4): Mao C X, Shi Y M, Song Z P, Wei S B, Zhou H, Wei S F, Xie L P Effects of short day length treatment on major traits of photosensitive hybrid rice combination. Guangxi Agric Sci, 36(6): (in Chinese with English abstract) Si H M, Liu W Z, Fu Y P, Sun Z X, Hu G C Current situation and suggestions for development of two-line hybrid rice in China. Chin J Rice Sci, 25(5): (in Chinese with English abstract) Takahashi Y, Teshima K M, Yokoi S, Innan H, Shimamoto K Variations in Hd1 proteins, Hd3a promoters, and Ehd1 expression levels contribute to diversity of flowering time in
8 88 Rice Science, Vol. 22, No. 2, 2015 cultivated rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106: Xie F M, He Z H, Esguerra M Q, Qiu F L, Ramanathan V Determination of heterotic groups for tropical indica hybrid rice germplasm. Theor Appl Genet, 127(2): Xiao J H, Li J M, Yuan L P, Tanksley S D Dominance is the major genetic basis of heterosis in rice as revealed by QTL analysis using molecular markers. Genetics, 140(2): Xue W Y, Xing Y Z, Weng X Y, Zhao Y, Tang W J, Wang L, Zhou H J, Yu S B, Xu C G, Li X H, Zhang Q F Natural variation in Ghd7 is an important regulator of heading date and yield potential in rice. Nat Genet, 40(6): Yang Q K, Liang C Y, Zhuang W, Li J, Deng H B, Deng O Y, Wang B Characterization and identification of the candidate gene of rice thermo-sensitive genic male sterile gene tms5 by mapping. Planta, 225: Yoshida S Fundamentals of Rice Crop Science. Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines: International Rice Research Institute. Yu J, Hu S N, Wang J, Wong G K S, Li S G, Liu B, Deng Y J, Dai L, Zhou Y, Zhang X Q, Cao M L, Liu J, Sun J D, Tang J B, Chen Y J, Huang X G, Lin W J, Ye C, Tong W, Cong L J, Geng J N, Han Y J, Li L, Li W, Hu G Q, Huang X G, Li W J, Li J, Liu Z W, Li L, Liu J P, Qi Q H, Liu J S, Li L, Li T, Wang X G, Lu H, Wu T T, Zhu M, Ni P X, Han H, Dong W, Ren X Y, Feng X L, Cui P, Li X R, Wang H, Xu X, Zhai W X, Xu Z, Zhang J S, He S J, Zhang J G, Xu J C, Zhang K L, Zheng X W, Dong J H, Zeng W Y, Tao L, Ye J, Tan J, Ren X, Chen X W, He J, Liu D F, Tian W, Tian C G, Xia H G, Bao Q Y, Li G, Gao H, Cao T, Wang J, Zhao W M, Li P, Chen W, Wang X D, Zhang Y, Hu J F, Wang J, Liu S, Yang J, Zhang G Y, Xiong Y Q, Li Z J, Mao L, Zhou C S, Zhu Z, Chen R S, Hao B L, Zheng W M, Chen S Y, Guo W, Li G J, Liu S Q, Tao M, Wang J, Zhu L H, Yuan L P, Yang H M A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica). Science, 296(5565): Yu S B, Li J X, Tan Y F, Gao Y J, Li X H, Zhang Q F, Maroof M A S Importance of epistasis as the genetic basis of heterosis in an elite rice hybrid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 94(17): Yuan L P Hybrid rice in China. Chin J Rice Sci, 1: Yuan L P Hybrid rice technology for food security in the world. In: Proceedings of the FAO Rice Conference: Rice is Life. Int Rice Comm Newsl, 53: Yuan L P Super Hybrid Rice Research. Shanghai, China: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publisher. Vergara B S, Chang T T The Flowering Response of the Rice Plant to Photoperiod: A Review of the Literature. Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines: International Rice Research Institute. Wei X J, Xu J F, Guo H N, Jiang L, Chen S H, Yu C Y, Zhou Z L, Hu P S, Zhai H Q, Wan J M DTH8 suppresses flowering in rice, influencing plant height and yield potential simultaneously. Plant Physiol, 153: Zhang Q F, Gao Y J, Yang S H, Ragab R A, Maroof M A S, Li Z B A diallel analysis of heterosis in elite hybrid rice-based on RFLPs and microsatellites. Theor Appl Genet, 89(2/3): Zou J S, Lu C G, Hu N, Li Y Z, Yao K M Studies on ecological adaptability and suitable planting area of a two-line hybrid rice, Liangyoupeijiu. Sci Agric Sin, 41(11): (in Chinese with English abstract)
Combining Ability and Heterosis in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars
 J. Agr. Sci. Tech. (2010) Vol. 12: 223-231 Combining Ability and Heterosis in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars M. Rahimi 1, B. Rabiei 1*, H. Samizadeh 1, and A. Kafi Ghasemi 1 ABSTRACT Quantitative valuations
J. Agr. Sci. Tech. (2010) Vol. 12: 223-231 Combining Ability and Heterosis in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars M. Rahimi 1, B. Rabiei 1*, H. Samizadeh 1, and A. Kafi Ghasemi 1 ABSTRACT Quantitative valuations
Genetic Analysis of Heading Date of Japonica Rice Cultivars in Southwest China
 Rice Science, 2011, 18(4): 287 296 Copyright 2011, China National Rice Research Institute Published by Elsevier BV. All rights reserved Genetic Analysis of Heading Date of Japonica Rice Cultivars in Southwest
Rice Science, 2011, 18(4): 287 296 Copyright 2011, China National Rice Research Institute Published by Elsevier BV. All rights reserved Genetic Analysis of Heading Date of Japonica Rice Cultivars in Southwest
Effects of cytoplasm on the fertility of thermo-sensitive genetic male sterile (TGMS) lines of rice
 AJCS 8(7):999-1004 (2014) ISSN:1835-2707 Effects of cytoplasm on the of thermo-sensitive genetic male sterile (TGMS) lines of rice Gong-Ping Kang 1,2, Xiao-Jun Dai 1, Li-Jun Ou 1, Wen-Jia Li 1, Man-Zhong
AJCS 8(7):999-1004 (2014) ISSN:1835-2707 Effects of cytoplasm on the of thermo-sensitive genetic male sterile (TGMS) lines of rice Gong-Ping Kang 1,2, Xiao-Jun Dai 1, Li-Jun Ou 1, Wen-Jia Li 1, Man-Zhong
IDENTIFICATION OF THERMOSENSITIVE GENIC MALE-STERILE LINES WITH LOW CRITICAL STERILITY POINT FOR HYBRID RICE BREEDING
 Philippine Journal of Crop Science April 2005, 30(1): 19-28 Copyright 2005, Crop Science Society of the Philippines Released 22 April 2005 IDENTIFICATION OF THERMOSENSITIVE GENIC MALE-STERILE LINES WITH
Philippine Journal of Crop Science April 2005, 30(1): 19-28 Copyright 2005, Crop Science Society of the Philippines Released 22 April 2005 IDENTIFICATION OF THERMOSENSITIVE GENIC MALE-STERILE LINES WITH
Source-Sink Relationship in Intersubspecific Hybrid Rice
 250 Rice Science, 2006, 13(4): 250-256 http://www.ricescience.org, http://www.ricesci.cn Source-Sink Relationship in Intersubspecific Hybrid Rice LI Ji-hang 1, 2, 3, XIANG Xun-chao 1, 2, 4, HE Li-bin 1,
250 Rice Science, 2006, 13(4): 250-256 http://www.ricescience.org, http://www.ricesci.cn Source-Sink Relationship in Intersubspecific Hybrid Rice LI Ji-hang 1, 2, 3, XIANG Xun-chao 1, 2, 4, HE Li-bin 1,
RFLP facilitated analysis of tiller and leaf angles in rice (Oryza sativa L.)
 Euphytica 109: 79 84, 1999. 1999 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 79 RFLP facilitated analysis of tiller and leaf angles in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Zhikang Li 1,2,3, Andrew H. Paterson
Euphytica 109: 79 84, 1999. 1999 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 79 RFLP facilitated analysis of tiller and leaf angles in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Zhikang Li 1,2,3, Andrew H. Paterson
2008, hm 2. ( Commodity Bundle) [ 6], 25 4 Vol. 25 No JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES Apr., , 2, 3, 1, 2 3*,
![2008, hm 2. ( Commodity Bundle) [ 6], 25 4 Vol. 25 No JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES Apr., , 2, 3, 1, 2 3*, 2008, hm 2. ( Commodity Bundle) [ 6], 25 4 Vol. 25 No JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES Apr., , 2, 3, 1, 2 3*,](/thumbs/93/112700429.jpg) 25 4 Vol. 25 No. 4 2010 4 JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES Apr., 2010 1, 2, 3, 3*, 3, 3, 1, 2 ( 1., 100101; 2., 100049; 3., 100193) :,,,,, ;, 2005, 12 7 5, 2005 :,,, : ; ; ; ; : F301. 21 : A : 1000-3037( 2010)
25 4 Vol. 25 No. 4 2010 4 JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES Apr., 2010 1, 2, 3, 3*, 3, 3, 1, 2 ( 1., 100101; 2., 100049; 3., 100193) :,,,,, ;, 2005, 12 7 5, 2005 :,,, : ; ; ; ; : F301. 21 : A : 1000-3037( 2010)
ACTA AGRONOMICA SINICA SSR. Classification for Some Sterile Lines and Their Restorers of Hybrid Rice with SSR Markers
 32 2 2006 2 169 175 ACTA AGRONOMICA SINICA Vol132, No12 pp1 169-175 Feb1, 2006 SSR 1 1,2, # 1 1 1 1, 3 2 2 Ξ ( 1, 330045 ; 2,,100094) : ( Oryza sativa L. ) 12 36 SSR(simple sequence repeats), 5 7 54 300,
32 2 2006 2 169 175 ACTA AGRONOMICA SINICA Vol132, No12 pp1 169-175 Feb1, 2006 SSR 1 1,2, # 1 1 1 1, 3 2 2 Ξ ( 1, 330045 ; 2,,100094) : ( Oryza sativa L. ) 12 36 SSR(simple sequence repeats), 5 7 54 300,
The Distribution of Japonica
 Journal of Integrative Plant Biology 29 The Distribution of Japonica Rice Cultivars in the Lower Region of the Yangtze River Valley is Determined by Its Photoperiod-sensitivity and Heading Date Genotypes
Journal of Integrative Plant Biology 29 The Distribution of Japonica Rice Cultivars in the Lower Region of the Yangtze River Valley is Determined by Its Photoperiod-sensitivity and Heading Date Genotypes
Pollen fertility Vs Spikelet fertility in F2 of a CMS based hybrids in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Aerobic condition
 Research Article Pollen fertility Vs Spikelet fertility in F of a CMS based hybrids in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Aerobic condition N.Naresh Babu,N.Shivakumar and Shailaja Hittalmani Abstract : Identification
Research Article Pollen fertility Vs Spikelet fertility in F of a CMS based hybrids in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Aerobic condition N.Naresh Babu,N.Shivakumar and Shailaja Hittalmani Abstract : Identification
Mapping QTL for Seedling Root Traits in Common Wheat
 2005,38(10):1951-1957 Scientia Agricultura Sinica 1,2,3 1 1 1 2 1 / / 100081 2 050021 3 100039 DH 10 14 11 15 5A 4B 2D 6D 7D 3 2 3 3 2 2 2 3 2 1 3 1 3 DH Mapping for Seedling Root Traits in Common Wheat
2005,38(10):1951-1957 Scientia Agricultura Sinica 1,2,3 1 1 1 2 1 / / 100081 2 050021 3 100039 DH 10 14 11 15 5A 4B 2D 6D 7D 3 2 3 3 2 2 2 3 2 1 3 1 3 DH Mapping for Seedling Root Traits in Common Wheat
Genetic dissection of chlorophyll content at different growth stages in common wheat
 c Indian Academy of Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE Genetic dissection of chlorophyll content at different growth stages in common wheat KUNPU ZHANG 1,2, ZHIJUN FANG 3, YAN LIANG 1 and JICHUN TIAN 1 1 State
c Indian Academy of Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE Genetic dissection of chlorophyll content at different growth stages in common wheat KUNPU ZHANG 1,2, ZHIJUN FANG 3, YAN LIANG 1 and JICHUN TIAN 1 1 State
Formula for Determining Number of Basic Seedlings at Scattered-Planting with Seedling Dry-Raised on Plastic Trays in Double-Season Rice
 Rice Science, 2006, 13(4): 271-277 271 http://www.ricesci.cn; http://www.ricescience.org Formula for Determining Number of Basic Seedlings at Scattered-Planting with Seedling Dry-Raised on Plastic Trays
Rice Science, 2006, 13(4): 271-277 271 http://www.ricesci.cn; http://www.ricescience.org Formula for Determining Number of Basic Seedlings at Scattered-Planting with Seedling Dry-Raised on Plastic Trays
Case Doc 1059 Filed 11/26/18 Entered 11/26/18 11:05:25 Desc Main Document Page 1 of 9
 Document Page 1 of 9 UNITED STATES BANKRUPTCY COURT DISTRICT OF MASSACHUSETTS ) In Re: ) ) Chapter 11 ) TELEXFREE, LLC, ) Case No. 14-40987-MSH TELEXFREE, INC., ) Case No. 14-40988-MSH TELEXFREE FINANCIAL,
Document Page 1 of 9 UNITED STATES BANKRUPTCY COURT DISTRICT OF MASSACHUSETTS ) In Re: ) ) Chapter 11 ) TELEXFREE, LLC, ) Case No. 14-40987-MSH TELEXFREE, INC., ) Case No. 14-40988-MSH TELEXFREE FINANCIAL,
Case Doc 1061 Filed 11/26/18 Entered 11/26/18 11:07:32 Desc Main Document Page 1 of 8
 Document Page 1 of 8 UNITED STATES BANKRUPTCY COURT DISTRICT OF MASSACHUSETTS ) In Re: ) ) Chapter 11 ) TELEXFREE, LLC, ) Case No. 14-40987-MSH TELEXFREE, INC., ) Case No. 14-40988-MSH TELEXFREE FINANCIAL,
Document Page 1 of 8 UNITED STATES BANKRUPTCY COURT DISTRICT OF MASSACHUSETTS ) In Re: ) ) Chapter 11 ) TELEXFREE, LLC, ) Case No. 14-40987-MSH TELEXFREE, INC., ) Case No. 14-40988-MSH TELEXFREE FINANCIAL,
Main controlling factors of hydrocarbon accumulation in Sujiatun oilfield of Lishu rift and its regularity in enrichment
 35 3 2016 9 GLOBAL GEOLOGY Vol. 35 No. 3 Sept. 2016 1004 5589 2016 03 0785 05 130062 P618. 130. 2 A doi 10. 3969 /j. issn. 1004-5589. 2016. 03. 019 Main controlling factors of hydrocarbon accumulation
35 3 2016 9 GLOBAL GEOLOGY Vol. 35 No. 3 Sept. 2016 1004 5589 2016 03 0785 05 130062 P618. 130. 2 A doi 10. 3969 /j. issn. 1004-5589. 2016. 03. 019 Main controlling factors of hydrocarbon accumulation
Study on form distribution of soil iron in western Jilin and its correlation with soil properties
 35 2 2016 6 GLOBAL GEOLOGY Vol. 35 No. 2 Jun. 2016 1004 5589 2016 02 0593 08 1 1 2 1 1 1. 130061 2. 130012 50 A > B > C > D > E > F > G A A CEC B ph C E A C D G B C D P595 S151. 9 A doi 10. 3969 /j. issn.
35 2 2016 6 GLOBAL GEOLOGY Vol. 35 No. 2 Jun. 2016 1004 5589 2016 02 0593 08 1 1 2 1 1 1. 130061 2. 130012 50 A > B > C > D > E > F > G A A CEC B ph C E A C D G B C D P595 S151. 9 A doi 10. 3969 /j. issn.
Title ghd7, on yield components in rice. Citation Molecular breeding (2014), 33(4): 8.
 Title The effects of the photoperiod-inse ghd7, on yield components in rice. Xu, Quan; Saito, Hiroki; Hirose, Ik Author(s) Yoshitake, Yoshihiro; Yokoo, Takayu Teraishi, Masayoshi; Tanisaka, Taka Citation
Title The effects of the photoperiod-inse ghd7, on yield components in rice. Xu, Quan; Saito, Hiroki; Hirose, Ik Author(s) Yoshitake, Yoshihiro; Yokoo, Takayu Teraishi, Masayoshi; Tanisaka, Taka Citation
Case Doc 1055 Filed 11/26/18 Entered 11/26/18 10:59:37 Desc Main Document Page 1 of 8
 Document Page 1 of 8 UNITED STATES BANKRUPTCY COURT DISTRICT OF MASSACHUSETTS ) In Re: ) ) Chapter 11 ) TELEXFREE, LLC, ) Case No. 14-40987-MSH TELEXFREE, INC., ) Case No. 14-40988-MSH TELEXFREE FINANCIAL,
Document Page 1 of 8 UNITED STATES BANKRUPTCY COURT DISTRICT OF MASSACHUSETTS ) In Re: ) ) Chapter 11 ) TELEXFREE, LLC, ) Case No. 14-40987-MSH TELEXFREE, INC., ) Case No. 14-40988-MSH TELEXFREE FINANCIAL,
HETEROSIS AND COMBINING ABILITY IN HYBRID RICE (Oryza sativa L.)
 HETEROSIS AND COMBINING ABILITY IN HYBRID RICE (Oryza sativa L.) B. S. Thorat 1, R. L. Kunkerkar 2, B. L. Thaware, M. M. Burondkar 4 and S. G. Bhave 5 1 M.Sc. (Agri.) Scholar, Dept. of Agril. Botany, 2
HETEROSIS AND COMBINING ABILITY IN HYBRID RICE (Oryza sativa L.) B. S. Thorat 1, R. L. Kunkerkar 2, B. L. Thaware, M. M. Burondkar 4 and S. G. Bhave 5 1 M.Sc. (Agri.) Scholar, Dept. of Agril. Botany, 2
Genetic Diversity among Parents of Hybrid Rice Based on Cluster Analysis of Morphological Traits and Simple Sequence Repeat Markers
 Rice Science, 2006, 13(3): 155-160 155 http://www.ricesci.cn; www.ricescience.org Genetic Diversity among Parents of Hybrid Rice Based on Cluster Analysis of Morphological Traits and Simple Sequence Repeat
Rice Science, 2006, 13(3): 155-160 155 http://www.ricesci.cn; www.ricescience.org Genetic Diversity among Parents of Hybrid Rice Based on Cluster Analysis of Morphological Traits and Simple Sequence Repeat
The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2015, VOL. 8, NO. 6, 371 375 The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height HUANG Yan-Yan and
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2015, VOL. 8, NO. 6, 371 375 The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height HUANG Yan-Yan and
ABSTRACT: 54 BREEDING OF HYBRID SOYBEAN ZAYOUDOU NO.1
 ABSTRACT: 54 BREEDING OF HYBRID SOYBEAN ZAYOUDOU NO.1 ZHANG L, DAI O, HUANG Z, LI J, ZHANG L, HU C, YANG J 1.Crop Research Institute of Anhui Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2.Key Laboratory of Crop
ABSTRACT: 54 BREEDING OF HYBRID SOYBEAN ZAYOUDOU NO.1 ZHANG L, DAI O, HUANG Z, LI J, ZHANG L, HU C, YANG J 1.Crop Research Institute of Anhui Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2.Key Laboratory of Crop
Segregation distortion in F 2 and doubled haploid populations of temperate japonica rice
 c Indian Academy of Sciences RESEARCH NOTE Segregation distortion in F 2 and doubled haploid populations of temperate japonica rice MASUMI YAMAGISHI 1,2,6, YOSHINOBU TAKEUCHI 3,7, ISAO TANAKA 4, IZUMI
c Indian Academy of Sciences RESEARCH NOTE Segregation distortion in F 2 and doubled haploid populations of temperate japonica rice MASUMI YAMAGISHI 1,2,6, YOSHINOBU TAKEUCHI 3,7, ISAO TANAKA 4, IZUMI
Relationship Between Coleoptile Length and Drought Resistance and Their QTL Mapping in Rice
 Rice Science, 2007, 14(1): 13-20 Copyright 2007, China National Rice Research Institute. Published by Elsevier BV. All rights reserved Relationship Between Coleoptile Length and Drought Resistance and
Rice Science, 2007, 14(1): 13-20 Copyright 2007, China National Rice Research Institute. Published by Elsevier BV. All rights reserved Relationship Between Coleoptile Length and Drought Resistance and
USING LINE TESTER ANALYSIS TO DEVELOP NEW SOURCE OF CYTOPLASMIC MALE STERILE LINE IN HYBRID RICE
 Plant Archives Vol. 17 No. 1, 2017 pp. 753-759 ISSN 0972-5210 USING LINE TESTER ANALYSIS TO DEVELOP NEW SOURCE OF CYTOPLASMIC MALE STERILE LINE IN HYBRID RICE M. I. Abo Youssef, M. S. Abd El Aty 1, S.
Plant Archives Vol. 17 No. 1, 2017 pp. 753-759 ISSN 0972-5210 USING LINE TESTER ANALYSIS TO DEVELOP NEW SOURCE OF CYTOPLASMIC MALE STERILE LINE IN HYBRID RICE M. I. Abo Youssef, M. S. Abd El Aty 1, S.
Experimental and numerical simulation studies of the squeezing dynamics of the UBVT system with a hole-plug device
 Experimental numerical simulation studies of the squeezing dynamics of the UBVT system with a hole-plug device Wen-bin Gu 1 Yun-hao Hu 2 Zhen-xiong Wang 3 Jian-qing Liu 4 Xiao-hua Yu 5 Jiang-hai Chen 6
Experimental numerical simulation studies of the squeezing dynamics of the UBVT system with a hole-plug device Wen-bin Gu 1 Yun-hao Hu 2 Zhen-xiong Wang 3 Jian-qing Liu 4 Xiao-hua Yu 5 Jiang-hai Chen 6
Evaluation on source rocks and the oil-source correlation in Bayanhushu sag of Hailaer Basin
 30 2 2011 6 GLOBAL GEOLOGY Vol. 30 No. 2 Jun. 2011 1004-5589 2011 02-0231 - 07 163712 3 7 Ⅰ Ⅱ1 3 - - P618. 130 A doi 10. 3969 /j. issn. 1004-5589. 2011. 02. 011 Evaluation on source rocks and the oil-source
30 2 2011 6 GLOBAL GEOLOGY Vol. 30 No. 2 Jun. 2011 1004-5589 2011 02-0231 - 07 163712 3 7 Ⅰ Ⅱ1 3 - - P618. 130 A doi 10. 3969 /j. issn. 1004-5589. 2011. 02. 011 Evaluation on source rocks and the oil-source
Seed production potential of ICRISAT-bred parental lines of two sorghum hybrids in the central Rift-valley of Ethiopia
 Seed production potential of ICRISAT-bred parental lines of two sorghum hybrids in the central Rift-valley of Ethiopia Asfaw Adugna* and Tesfaye Tesso Melkassa Agricultural Research Center, PO Box 436,
Seed production potential of ICRISAT-bred parental lines of two sorghum hybrids in the central Rift-valley of Ethiopia Asfaw Adugna* and Tesfaye Tesso Melkassa Agricultural Research Center, PO Box 436,
Quantitative trait loci mapping of the stigma exertion rate and spikelet number per panicle in rice (Oryza sativa L.)
 Quantitative trait loci mapping of the stigma exertion rate and spikelet number per panicle in rice (Oryza sativa L.) M.H. Rahman, P. Yu, Y.X. Zhang, L.P. Sun, W.X. Wu, X.H. Shen, X.D. Zhan, D.B. Chen,
Quantitative trait loci mapping of the stigma exertion rate and spikelet number per panicle in rice (Oryza sativa L.) M.H. Rahman, P. Yu, Y.X. Zhang, L.P. Sun, W.X. Wu, X.H. Shen, X.D. Zhan, D.B. Chen,
Chemical Research in Chinese Universities
 Chemical Research in Chinese Universities Vol.26 No.3 May 2010 CONTENTS Articles Synthesis and Structure Description of a New Tetradecaborate [H 3 N(CH 2 ) 2 NH 3 ] 2 [B 14 O 20 (OH) 6 ] YANG Miao, ZHANG
Chemical Research in Chinese Universities Vol.26 No.3 May 2010 CONTENTS Articles Synthesis and Structure Description of a New Tetradecaborate [H 3 N(CH 2 ) 2 NH 3 ] 2 [B 14 O 20 (OH) 6 ] YANG Miao, ZHANG
PHOTOPERIOD DRIVEN DAYS TO FLOWERING VARIATION AFFECT VEGETATIVE GROWTH AND YIELD IN SRI LANKAN TRADITIONAL RICE (ORYZA SATIVA L) MA WEE
 Pak. J. Bot., 49(3): 945-954, 7. PHOTOPERIOD DRIVEN DAYS TO FLOWERING VARIATION AFFECT VEGETATIVE GROWTH AND YIELD IN SRI LANKAN TRADITIONAL RICE (ORYZA SATIVA L) MA WEE W.H.D.U. PUSHPAKUMARI, GAMINI SENANAYAKE,
Pak. J. Bot., 49(3): 945-954, 7. PHOTOPERIOD DRIVEN DAYS TO FLOWERING VARIATION AFFECT VEGETATIVE GROWTH AND YIELD IN SRI LANKAN TRADITIONAL RICE (ORYZA SATIVA L) MA WEE W.H.D.U. PUSHPAKUMARI, GAMINI SENANAYAKE,
Genetic analysis of maize kernel thickness by quantitative trait locus identification
 Genetic analysis of maize kernel thickness by quantitative trait locus identification S.S. Wen 1, G.Q. Wen 2, C.M. Liao 3 and X.H. Liu 2 1 Key Laboratory of Southwest Rice Biology and Genetic Breeding,
Genetic analysis of maize kernel thickness by quantitative trait locus identification S.S. Wen 1, G.Q. Wen 2, C.M. Liao 3 and X.H. Liu 2 1 Key Laboratory of Southwest Rice Biology and Genetic Breeding,
Case Doc 1058 Filed 11/26/18 Entered 11/26/18 11:04:24 Desc Main Document Page 1 of 8
 Document Page 1 of 8 UNITED STATES BANKRUPTCY COURT DISTRICT OF MASSACHUSETTS ) In Re: ) ) Chapter 11 ) TELEXFREE, LLC, ) Case No. 14-40987-MSH TELEXFREE, INC., ) Case No. 14-40988-MSH TELEXFREE FINANCIAL,
Document Page 1 of 8 UNITED STATES BANKRUPTCY COURT DISTRICT OF MASSACHUSETTS ) In Re: ) ) Chapter 11 ) TELEXFREE, LLC, ) Case No. 14-40987-MSH TELEXFREE, INC., ) Case No. 14-40988-MSH TELEXFREE FINANCIAL,
Keywords: CGMS, combining ability, fertility restoration, heterosis, pigeonpea. Introduction
 Sri Lanka Journal of Food and Agriculture (2015) Byregowda et al. 1(2): 1-8 ISSN 2424-6913 Research Paper Identification of fertility restorers, stable combiners and heterotic combinations across environments
Sri Lanka Journal of Food and Agriculture (2015) Byregowda et al. 1(2): 1-8 ISSN 2424-6913 Research Paper Identification of fertility restorers, stable combiners and heterotic combinations across environments
Case Doc 1060 Filed 11/26/18 Entered 11/26/18 11:06:29 Desc Main Document Page 1 of 9
 Document Page 1 of 9 UNITED STATES BANKRUPTCY COURT DISTRICT OF MASSACHUSETTS ) In Re: ) ) Chapter 11 ) TELEXFREE, LLC, ) Case No. 14-40987-MSH TELEXFREE, INC., ) Case No. 14-40988-MSH TELEXFREE FINANCIAL,
Document Page 1 of 9 UNITED STATES BANKRUPTCY COURT DISTRICT OF MASSACHUSETTS ) In Re: ) ) Chapter 11 ) TELEXFREE, LLC, ) Case No. 14-40987-MSH TELEXFREE, INC., ) Case No. 14-40988-MSH TELEXFREE FINANCIAL,
Chemical Research in Chinese Universities
 Chemical Research in Chinese Universities Vol.24 No.5 September 2008 CONTENTS Articles Comparison of the Sol-gel Method with the Coprecipitation Technique for Preparation of Hexagonal Barium Ferrite WANG
Chemical Research in Chinese Universities Vol.24 No.5 September 2008 CONTENTS Articles Comparison of the Sol-gel Method with the Coprecipitation Technique for Preparation of Hexagonal Barium Ferrite WANG
General Synthesis of Graphene-Supported. Bicomponent Metal Monoxides as Alternative High- Performance Li-Ion Anodes to Binary Spinel Oxides
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) General Synthesis of Graphene-Supported
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) General Synthesis of Graphene-Supported
Development of a platform for breeding by design of CMS restorer lines based on an SSSL library in rice (Oryza sativa L.)
 Breeding Science 66: 768 775 (2016) doi:10.1270/jsbbs.16044 Research Paper Development of a platform for breeding by design of CMS restorer lines based on an SSSL library in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Ziju
Breeding Science 66: 768 775 (2016) doi:10.1270/jsbbs.16044 Research Paper Development of a platform for breeding by design of CMS restorer lines based on an SSSL library in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Ziju
Studies on Fertility Restoration Using Newly Derived Restorers in Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.)
 Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.ci (218) 7(1): 2131-2135 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied ciences IN: 2319-776 Volume 7 Number 1 (218) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.ci (218) 7(1): 2131-2135 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied ciences IN: 2319-776 Volume 7 Number 1 (218) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fe 3 O 4 @Carbon Nanosheets for All-Solid-State Supercapacitor Electrodes Huailin Fan, Ruiting Niu, & Jiaqi Duan, Wei Liu and Wenzhong Shen * State Key Laboratory of Coal Conversion,
Supporting Information Fe 3 O 4 @Carbon Nanosheets for All-Solid-State Supercapacitor Electrodes Huailin Fan, Ruiting Niu, & Jiaqi Duan, Wei Liu and Wenzhong Shen * State Key Laboratory of Coal Conversion,
Decrease of light rain events in summer associated with a warming environment in China during
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L11705, doi:10.1029/2007gl029631, 2007 Decrease of light rain events in summer associated with a warming environment in China during 1961 2005 Weihong Qian, 1 Jiaolan
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L11705, doi:10.1029/2007gl029631, 2007 Decrease of light rain events in summer associated with a warming environment in China during 1961 2005 Weihong Qian, 1 Jiaolan
A STATISTICAL MODEL FOR PREDICTION OF INTENSITY AND FREQUENCY OF TROPICAL CYCLONES MAKING LANDFALL ON CHINA
 Vol.18 No.1 JOURNAL OF TROPICAL METEOROLOGY March 2012 Article ID: 1006-8775(2012) 01-0108-05 A STATISTICAL MODEL FOR PREDICTION OF INTENSITY AND FREQUENCY OF TROPICAL CYCLONES MAKING LANDFALL ON CHINA
Vol.18 No.1 JOURNAL OF TROPICAL METEOROLOGY March 2012 Article ID: 1006-8775(2012) 01-0108-05 A STATISTICAL MODEL FOR PREDICTION OF INTENSITY AND FREQUENCY OF TROPICAL CYCLONES MAKING LANDFALL ON CHINA
Supporting Information. Co 4 N Nanosheets Assembled Mesoporous Sphere as a Matrix for Ultrahigh Sulfur Content Lithium Sulfur Batteries
 Supporting Information Co 4 N Nanosheets Assembled Mesoporous Sphere as a Matrix for Ultrahigh Sulfur Content Lithium Sulfur Batteries Ding-Rong Deng, Fei Xue, Yue-Ju Jia, Jian-Chuan Ye, Cheng-Dong Bai,
Supporting Information Co 4 N Nanosheets Assembled Mesoporous Sphere as a Matrix for Ultrahigh Sulfur Content Lithium Sulfur Batteries Ding-Rong Deng, Fei Xue, Yue-Ju Jia, Jian-Chuan Ye, Cheng-Dong Bai,
Time-delay feedback control in a delayed dynamical chaos system and its applications
 Time-delay feedback control in a delayed dynamical chaos system and its applications Ye Zhi-Yong( ), Yang Guang( ), and Deng Cun-Bing( ) School of Mathematics and Physics, Chongqing University of Technology,
Time-delay feedback control in a delayed dynamical chaos system and its applications Ye Zhi-Yong( ), Yang Guang( ), and Deng Cun-Bing( ) School of Mathematics and Physics, Chongqing University of Technology,
SIGNIFICANCE OF RICE SHEATH PHOTOSYNTHESIS: YIELD DETERMINATION BY 14 C RADIO-AUTOGRAPHY ABSTRACT RÉSUMÉ
 African Crop Science Journal, Vol. 21, No. 3, pp. 185-190 ISSN 1021-9730/2013 $4.00 Printed in Uganda. All rights reserved 2013, African Crop Science Society SIGNIFICANCE OF RICE SHEATH PHOTOSYNTHESIS:
African Crop Science Journal, Vol. 21, No. 3, pp. 185-190 ISSN 1021-9730/2013 $4.00 Printed in Uganda. All rights reserved 2013, African Crop Science Society SIGNIFICANCE OF RICE SHEATH PHOTOSYNTHESIS:
Effects of nitrogen application rate on flag leaf photosynthetic characteristics and grain growth and development of high2quality wheat
 2006,12(1) :49-55 Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science,,,, (, 271018) 3 :,, 8901 N 120 360 kg/ hm 2, SN1391 N 120 240 kg/ hm 2, 360 kg/ hm 2,,, ; ; : ; ; ; : S5121106 : A : 1008-505X(2006) 01-0049- 07
2006,12(1) :49-55 Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science,,,, (, 271018) 3 :,, 8901 N 120 360 kg/ hm 2, SN1391 N 120 240 kg/ hm 2, 360 kg/ hm 2,,, ; ; : ; ; ; : S5121106 : A : 1008-505X(2006) 01-0049- 07
Gene Action and Combining Ability in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Involving Indica and Tropical Japonica Genotypes
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 7 (2017) pp. 8-16 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.002
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 7 (2017) pp. 8-16 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.607.002
EDITORIAL BOARD AND ADVISORY BOARD OF ACTA CHIMICA SINICA
 2018 76 7 Vol. 76 No. 7 0 7 9 770567 735189 EDITORIAL BOARD AND ADVISORY BOARD OF ACTA CHIMICA SINICA (Alphabetically arranged) Editor-in-Chief ZHOU Qi-Lin( ) Nankai University Associate Editors CHEN Xiao-Ming(
2018 76 7 Vol. 76 No. 7 0 7 9 770567 735189 EDITORIAL BOARD AND ADVISORY BOARD OF ACTA CHIMICA SINICA (Alphabetically arranged) Editor-in-Chief ZHOU Qi-Lin( ) Nankai University Associate Editors CHEN Xiao-Ming(
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Cation exchange MOF-derived nitrogen-doped
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Cation exchange MOF-derived nitrogen-doped
Estimation of Heterosis, Heterobeltiosis and Economic Heterosis in Dual Purpose Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]
![Estimation of Heterosis, Heterobeltiosis and Economic Heterosis in Dual Purpose Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] Estimation of Heterosis, Heterobeltiosis and Economic Heterosis in Dual Purpose Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]](/thumbs/85/92593885.jpg) International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 5 (2017) pp. 990-1014 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.109
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 5 (2017) pp. 990-1014 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.109
Chemical Research in Chinese Universities
 Chemical Research in Chinese Universities Vol.26 No.1 January 2010 CONTENTS Articles Primary Organicamine Templated Indium Iodate (H 2 en)kin(io 3 ) 6 2(H 2 O) with Hydrogen-bonded Helices LIU Guo-zong,
Chemical Research in Chinese Universities Vol.26 No.1 January 2010 CONTENTS Articles Primary Organicamine Templated Indium Iodate (H 2 en)kin(io 3 ) 6 2(H 2 O) with Hydrogen-bonded Helices LIU Guo-zong,
Co-vacancy-rich Co 1 x S nanosheets anchored on rgo for high-efficiency oxygen evolution
 Electronic Supplementary Material Co-vacancy-rich Co 1 x S nanosheets anchored on rgo for high-efficiency oxygen evolution Jiaqing Zhu 1, Zhiyu Ren 1 ( ), Shichao Du 1, Ying Xie 1, Jun Wu 1,2, Huiyuan
Electronic Supplementary Material Co-vacancy-rich Co 1 x S nanosheets anchored on rgo for high-efficiency oxygen evolution Jiaqing Zhu 1, Zhiyu Ren 1 ( ), Shichao Du 1, Ying Xie 1, Jun Wu 1,2, Huiyuan
Study on Coal Methane Adsorption Behavior Under Variation Temperature and Pressure-Taking Xia-Yu-Kou Coal for Example
 International Journal of Oil, Gas and Coal Engineering 2018; 6(4): 60-66 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ogce doi: 10.11648/j.ogce.20180604.13 ISSN: 2376-7669 (Print); ISSN: 2376-7677(Online) Study
International Journal of Oil, Gas and Coal Engineering 2018; 6(4): 60-66 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ogce doi: 10.11648/j.ogce.20180604.13 ISSN: 2376-7669 (Print); ISSN: 2376-7677(Online) Study
Characteristics of stratigraphic structure and oil-gas-water distribution by logging data in Arys oilfield
 31 1 2012 3 GLOBAL GEOLOGY Vol. 31 No. 1 Mar. 2012 1004 5589 2012 01 0162 09 100101 4 P618. 130. 2 P631. 8 A doi 10. 3969 /j. issn. 1004-5589. 2012. 01. 020 Characteristics of stratigraphic structure and
31 1 2012 3 GLOBAL GEOLOGY Vol. 31 No. 1 Mar. 2012 1004 5589 2012 01 0162 09 100101 4 P618. 130. 2 P631. 8 A doi 10. 3969 /j. issn. 1004-5589. 2012. 01. 020 Characteristics of stratigraphic structure and
QTL analysis for hybrid sterility and plant height in interspecific populations derived from a wild rice relative, Oryza longistaminata
 Breeding Science 59: 441 445 (2009) Note QTL analysis for hybrid sterility and plant height in interspecific populations derived from a wild rice relative, Oryza longistaminata Zhiwei Chen 1,2), Fengyi
Breeding Science 59: 441 445 (2009) Note QTL analysis for hybrid sterility and plant height in interspecific populations derived from a wild rice relative, Oryza longistaminata Zhiwei Chen 1,2), Fengyi
bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Hierarchical Ni/NiTiO 3 derived from NiTi LDHs: a bifunctional electrocatalyst
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Hierarchical Ni/NiTiO 3 derived from NiTi LDHs: a bifunctional electrocatalyst
Study of Genetic Diversity in Some Newly Developed Rice Genotypes
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 10 (2017) pp. 2693-2698 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.610.317
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 10 (2017) pp. 2693-2698 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.610.317
Pt-like Hydrogen Evolution Electrocatalysis on PANI/CoP Hybrid Nanowires. by Weakening the Shackles of Hydrogen Ions on the Surfaces of Catalysts
 Pt-like Hydrogen Evolution Electrocatalysis on PANI/CoP Hybrid Nanowires by Weakening the Shackles of Hydrogen Ions on the Surfaces of Catalysts Jin-Xian Feng, Si-Yao Tong, Ye-Xiang Tong, and Gao-Ren Li
Pt-like Hydrogen Evolution Electrocatalysis on PANI/CoP Hybrid Nanowires by Weakening the Shackles of Hydrogen Ions on the Surfaces of Catalysts Jin-Xian Feng, Si-Yao Tong, Ye-Xiang Tong, and Gao-Ren Li
Nonlinear Controller Design of the Inverted Pendulum System based on Extended State Observer Limin Du, Fucheng Cao
 International Conference on Automation, Mechanical Control and Computational Engineering (AMCCE 015) Nonlinear Controller Design of the Inverted Pendulum System based on Extended State Observer Limin Du,
International Conference on Automation, Mechanical Control and Computational Engineering (AMCCE 015) Nonlinear Controller Design of the Inverted Pendulum System based on Extended State Observer Limin Du,
Breeding strategy for improvement of flower and seed yields in safflower
 Breeding strategy for improvement of flower and seed yields in safflower Vrijendra Singh, N. M. Kolekar and N. Nimbkar Nimbkar Agricultural Research Institute, Lonand Road, Phaltan 415523, Maharashtra,
Breeding strategy for improvement of flower and seed yields in safflower Vrijendra Singh, N. M. Kolekar and N. Nimbkar Nimbkar Agricultural Research Institute, Lonand Road, Phaltan 415523, Maharashtra,
BREEDING, GENETICS, AND PHYSIOLOGY. Phenotypic Analysis of the 2006 MY2 Mapping Population in Arkansas
 BREEDING, GENETICS, AND PHYSIOLOGY Phenotypic Analysis of the 2006 MY2 Mapping Population in Arkansas E.J. Boza, K.A.K. Moldenhauer, R.D. Cartwright, S. Linscombe, J.H. Oard, and M.M. Blocker ABSTRACT
BREEDING, GENETICS, AND PHYSIOLOGY Phenotypic Analysis of the 2006 MY2 Mapping Population in Arkansas E.J. Boza, K.A.K. Moldenhauer, R.D. Cartwright, S. Linscombe, J.H. Oard, and M.M. Blocker ABSTRACT
2016 International Conference on Modern Economic Development and Environment Protection (ICMED 2016) ISBN:
 2016 International Conference on Modern Economic Development and Environment Protection (ICMED 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-355-7 Difference in FVC Changes between Desert Grasslands with Different Stocking
2016 International Conference on Modern Economic Development and Environment Protection (ICMED 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-355-7 Difference in FVC Changes between Desert Grasslands with Different Stocking
EDITORIAL BOARD AND ADVISORY BOARD OF ACTA CHIMICA SINICA
 2017 75 3 Vol. 75 No. 3 Editor-in-Chief ZHOU Qi-Lin( ) Nankai University Associate Editors EDITORIAL BOARD AND ADVISORY BOARD OF ACTA CHIMICA SINICA DING Kui-Ling( ) Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemisry,
2017 75 3 Vol. 75 No. 3 Editor-in-Chief ZHOU Qi-Lin( ) Nankai University Associate Editors EDITORIAL BOARD AND ADVISORY BOARD OF ACTA CHIMICA SINICA DING Kui-Ling( ) Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemisry,
Supporting Information. Engineering Two-Dimensional Mass-Transport Channels
 Supporting Information Engineering Two-Dimensional Mass-Transport Channels of MoS 2 Nanocatalyst towards Improved Hydrogen Evolution Performance Ge Wang a, Jingying Tao a, Yijie Zhang a, Shengping Wang
Supporting Information Engineering Two-Dimensional Mass-Transport Channels of MoS 2 Nanocatalyst towards Improved Hydrogen Evolution Performance Ge Wang a, Jingying Tao a, Yijie Zhang a, Shengping Wang
Assessment Model of Set Pair Analysis for Flood Loss Based on Triangular Fuzzy Intervals under α-cut
 Assessment Model of Set Pair Analysis for Flood Loss Based on Triangular Fuzzy Intervals under -Cut PAN Zheng-wei WU Kai-ya 2 JIN Ju-liang 3 LIU Xiao-wei. College of Natural Resources and Environmental
Assessment Model of Set Pair Analysis for Flood Loss Based on Triangular Fuzzy Intervals under -Cut PAN Zheng-wei WU Kai-ya 2 JIN Ju-liang 3 LIU Xiao-wei. College of Natural Resources and Environmental
Abstract. Song-Ping Hu 1,2, Ying Zhou 1, Lin Zhang 1, Xiu-Dong Zhu 3,LinLi 3, Li-Jun Luo 2, Guo-Lan Liu 2 and Qing-Ming Zhou 3
 Journal of Integrative Plant Biology 2009 Correlation and Quantitative Trait Loci Analyses of Total Chlorophyll Content and Photosynthetic Rate of Rice (Oryza sativa) under Water Stress and Well-watered
Journal of Integrative Plant Biology 2009 Correlation and Quantitative Trait Loci Analyses of Total Chlorophyll Content and Photosynthetic Rate of Rice (Oryza sativa) under Water Stress and Well-watered
EDITORIAL BOARD AND ADVISORY BOARD OF ACTA CHIMICA SINICA
 2018 76 2 Vol. 76 No. 2 Editor-in-Chief ZHOU Qi-Lin( ) Nankai University Associate Editors EDITORIAL BOARD AND ADVISORY BOARD OF ACTA CHIMICA SINICA DING Kui-Ling( ) Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemisry,
2018 76 2 Vol. 76 No. 2 Editor-in-Chief ZHOU Qi-Lin( ) Nankai University Associate Editors EDITORIAL BOARD AND ADVISORY BOARD OF ACTA CHIMICA SINICA DING Kui-Ling( ) Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemisry,
EVIDENCE FOR THE EXISTENCE OF THE MEDIEVAL WARM PERIOD IN CHINA
 EVIDENCE FOR THE EXISTENCE OF THE MEDIEVAL WARM PERIOD IN CHINA ZHANG DE'ER Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, Baishiqiaolu No. 46 Beijing 100081, China 1. Introduction Abstract. The collected
EVIDENCE FOR THE EXISTENCE OF THE MEDIEVAL WARM PERIOD IN CHINA ZHANG DE'ER Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, Baishiqiaolu No. 46 Beijing 100081, China 1. Introduction Abstract. The collected
Supporting information
 a Supporting information Core-Shell Nanocomposites Based on Gold Nanoparticle@Zinc-Iron- Embedded Porous Carbons Derived from Metal Organic Frameworks as Efficient Dual Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction and
a Supporting information Core-Shell Nanocomposites Based on Gold Nanoparticle@Zinc-Iron- Embedded Porous Carbons Derived from Metal Organic Frameworks as Efficient Dual Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction and
Genetic and physiological approach to elucidation of Cd absorption mechanism by rice plants
 Genetic and physiological approach to elucidation of Cd absorption mechanism by rice plants Satoru Ishikawa National Institute for Agro-Environmental Sciences, 3-1-3, Kannondai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, 305-8604,
Genetic and physiological approach to elucidation of Cd absorption mechanism by rice plants Satoru Ishikawa National Institute for Agro-Environmental Sciences, 3-1-3, Kannondai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, 305-8604,
Quantitative trait locus analysis for ear height in maize based on a recombinant inbred line population
 Quantitative trait locus analysis for ear height in maize based on a recombinant inbred line population Z.Q. Li 4,5, H.M. Zhang 1,4, X.P. Wu 1,4, Y. Sun 3,4 and X.H. Liu 2 1 Maize Research Institute, Shanxi
Quantitative trait locus analysis for ear height in maize based on a recombinant inbred line population Z.Q. Li 4,5, H.M. Zhang 1,4, X.P. Wu 1,4, Y. Sun 3,4 and X.H. Liu 2 1 Maize Research Institute, Shanxi
ARX System identification of a positioning stage based on theoretical modeling and an ARX model WANG Jing-shu 1 GUO Jie 2 ZHU Chang-an 2
 DOI:10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2013.13.026 32 13 JOURNAL OF VIBRATION AND SHOCK Vol. 32 No. 13 2013 ARX 1 2 2 1. 400054 2. 230027 ARX ARX ARX TH113 A System identification of a positioning stage based on theoretical
DOI:10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2013.13.026 32 13 JOURNAL OF VIBRATION AND SHOCK Vol. 32 No. 13 2013 ARX 1 2 2 1. 400054 2. 230027 ARX ARX ARX TH113 A System identification of a positioning stage based on theoretical
Metal-Organic Framework Derived Iron Sulfide-Carbon Core-Shell Nanorods as a Conversion-Type Battery Material
 Supporting Information Metal-Organic Framework Derived Iron Sulfide-Carbon Core-Shell Nanorods as a Conversion-Type Battery Material Wei Huang,, Shuo Li, Xianyi Cao, Chengyi Hou, Zhen Zhang, Jinkui Feng,
Supporting Information Metal-Organic Framework Derived Iron Sulfide-Carbon Core-Shell Nanorods as a Conversion-Type Battery Material Wei Huang,, Shuo Li, Xianyi Cao, Chengyi Hou, Zhen Zhang, Jinkui Feng,
Genetic Analysis for Heterotic Traits in Bread Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Using Six Parameters Model
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.029
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.029
Response of leaf dark respiration of winter wheat to changes in CO 2 concentration and temperature
 Article Atmospheric Science May 2013 Vol.58 No.15: 1795 1800 doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5605-1 Response of leaf dark respiration of winter wheat to changes in CO 2 concentration and temperature TAN KaiYan
Article Atmospheric Science May 2013 Vol.58 No.15: 1795 1800 doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5605-1 Response of leaf dark respiration of winter wheat to changes in CO 2 concentration and temperature TAN KaiYan
Exploration of combining ability for yield and morpholo-physical traits in hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.)
 2017; SP1: 644648 EISS: 22784136 PISS: 23498234 JPP 2017; SP1: 644648 Madhru Grace Minz Deepak Sharma Exploration of combining ability for yield and morpholophysical traits in hybrid rice (Oryza sativa
2017; SP1: 644648 EISS: 22784136 PISS: 23498234 JPP 2017; SP1: 644648 Madhru Grace Minz Deepak Sharma Exploration of combining ability for yield and morpholophysical traits in hybrid rice (Oryza sativa
RESPONSE DIFFERENCES OF PHOTOSYNTHETIC CHARACTERISTICS OF A SUPER HYBRID RICE CULTIVAR UNDER TRANSPLANTED AND DIRECT-SEEDED CONDITIONS TO NO-TILLAGE
 RESPONSE DIFFERENCES OF PHOTOSYNTHETIC CHARACTERISTICS OF A SUPER HYBRID RICE CULTIVAR UNDER TRANSPLANTED AND DIRECT-SEEDED CONDITIONS TO NO-TILLAGE Xiaohong Yin, Min Huang*, Yingbin Zou ABSTRACT Southern
RESPONSE DIFFERENCES OF PHOTOSYNTHETIC CHARACTERISTICS OF A SUPER HYBRID RICE CULTIVAR UNDER TRANSPLANTED AND DIRECT-SEEDED CONDITIONS TO NO-TILLAGE Xiaohong Yin, Min Huang*, Yingbin Zou ABSTRACT Southern
Program & Abstracts. On The Occasion of Jun-Zhi Cui s 70 TH Birthday. International Workshop on Scientific Computing
 International Workshop on Scientific Computing On The Occasion of Jun-Zhi Cui s 70 TH Birthday June 7-8, 2008 Institute of Computational Mathematics, Beijing Program & Abstracts Sponsors: Institute of
International Workshop on Scientific Computing On The Occasion of Jun-Zhi Cui s 70 TH Birthday June 7-8, 2008 Institute of Computational Mathematics, Beijing Program & Abstracts Sponsors: Institute of
Journal of Agriculture and Ecology Research International 4(2): 43-52, 2015; Article no.jaeri ISSN:
 Journal of Agriculture and Ecology Research International 4(2): 43-52, 2015; Article no.jaeri.2015.051 ISSN: 2394-1073 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org Effects of the Two-early-flowering-time
Journal of Agriculture and Ecology Research International 4(2): 43-52, 2015; Article no.jaeri.2015.051 ISSN: 2394-1073 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org Effects of the Two-early-flowering-time
Proceedings of 2005 International Conference On Machine Learning and Cybernetics. Volume 2 of 9
 4/rx ' rvernational IEEE ii/liversity 4 Hi K * A f f Proceedings of 2005 International Conference On Machine Learning and Cybernetics Volume 2 of 9 August 18-21, 2005 Ramada Hotel Guangzhou, China IEEE
4/rx ' rvernational IEEE ii/liversity 4 Hi K * A f f Proceedings of 2005 International Conference On Machine Learning and Cybernetics Volume 2 of 9 August 18-21, 2005 Ramada Hotel Guangzhou, China IEEE
Submergence Escape in Oryza glaberrima Steud.
 Submergence Escape in Oryza glaberrima Steud. Jun-Ichi Sakagami a, *, Chiharu Sone a, Naoyoshi Kawano b a Crop, Livestock and Environment Division, Japan International Research Center for Agricultural
Submergence Escape in Oryza glaberrima Steud. Jun-Ichi Sakagami a, *, Chiharu Sone a, Naoyoshi Kawano b a Crop, Livestock and Environment Division, Japan International Research Center for Agricultural
Principles of QTL Mapping. M.Imtiaz
 Principles of QTL Mapping M.Imtiaz Introduction Definitions of terminology Reasons for QTL mapping Principles of QTL mapping Requirements For QTL Mapping Demonstration with experimental data Merit of QTL
Principles of QTL Mapping M.Imtiaz Introduction Definitions of terminology Reasons for QTL mapping Principles of QTL mapping Requirements For QTL Mapping Demonstration with experimental data Merit of QTL
PRODUCTION OF HYBRID BASMATI RICE IN KENYA: PROGRESS AND CHALLENGES
 International Journal of Innovations in Bio-Sciences Vol. 3 (4), 2013 pp. 115-124 http://www.parees.co.in/ijibs.htm PRODUCTION OF HYBRID BASMATI RICE IN KENYA: PROGRESS AND CHALLENGES Njiruh P.N., J.I.
International Journal of Innovations in Bio-Sciences Vol. 3 (4), 2013 pp. 115-124 http://www.parees.co.in/ijibs.htm PRODUCTION OF HYBRID BASMATI RICE IN KENYA: PROGRESS AND CHALLENGES Njiruh P.N., J.I.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Nest-like NiCoP for Highly Efficient Overall Water Splitting Cheng Du, a Lan Yang, a Fulin Yang, a Gongzhen Cheng a and Wei Luo a,b* a College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences,
Supporting Information Nest-like NiCoP for Highly Efficient Overall Water Splitting Cheng Du, a Lan Yang, a Fulin Yang, a Gongzhen Cheng a and Wei Luo a,b* a College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences,
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 154 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 154 (2016 ) 574 581 12th International Conference on Hydroinformatics, HIC 2016 Research on the Strength and Space-time Distribution
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 154 (2016 ) 574 581 12th International Conference on Hydroinformatics, HIC 2016 Research on the Strength and Space-time Distribution
Identification of interspecific grain yield heterosis between two cultivated rice species Oryza sativa L. and Oryza glaberrima Steud.
 AJCS 6(11):1558-1564 (2012) ISSN:1835-2707 Identification of interspecific grain yield heterosis between two cultivated rice species Oryza sativa L. and Oryza glaberrima Steud. Adedze Y.M. Nevame 1, Efisue
AJCS 6(11):1558-1564 (2012) ISSN:1835-2707 Identification of interspecific grain yield heterosis between two cultivated rice species Oryza sativa L. and Oryza glaberrima Steud. Adedze Y.M. Nevame 1, Efisue
Development of specific simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers for non-pollen type thermo-sensitive genic male sterile gene in rice (Oryza sativa L.
 African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 10(73), pp. 16437-16442, 21 November, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.2401 ISSN 1684 5315 2011 Academic Journals Full
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 10(73), pp. 16437-16442, 21 November, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.2401 ISSN 1684 5315 2011 Academic Journals Full
New Feedback Control Model in the Lattice Hydrodynamic Model Considering the Historic Optimal Velocity Difference Effect
 Commun. Theor. Phys. 70 (2018) 803 807 Vol. 70, No. 6, December 1, 2018 New Feedback Control Model in the Lattice Hydrodynamic Model Considering the Historic Optimal Velocity Difference Effect Guang-Han
Commun. Theor. Phys. 70 (2018) 803 807 Vol. 70, No. 6, December 1, 2018 New Feedback Control Model in the Lattice Hydrodynamic Model Considering the Historic Optimal Velocity Difference Effect Guang-Han
Raghavendra P and S. Hittalmani * Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, University of Agricultural Sciences GKVK, Bangalore , India
 SAARC J. Agri., 13(2): 198-213 (2015) GENETIC PARAMETERS OF TWO BC 2 F 1 POPULATIONS FOR DEVELOPMENT OF SUPERIOR MALE STERILE LINES PERTAINING TO MORPHO-FLORAL TRAITS FOR AEROBIC RICE (Oryza sativa L.)
SAARC J. Agri., 13(2): 198-213 (2015) GENETIC PARAMETERS OF TWO BC 2 F 1 POPULATIONS FOR DEVELOPMENT OF SUPERIOR MALE STERILE LINES PERTAINING TO MORPHO-FLORAL TRAITS FOR AEROBIC RICE (Oryza sativa L.)
Supporting material. Figures
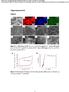 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2018 Supporting material Figures
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2018 Supporting material Figures
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Ultrasensitive Label-Free Resonance Rayleigh Scattering Aptasensor for Hg 2+ Using Hg 2+ -Triggered Exonuclease III-Assisted Target Recycling and Growth of G-Wires for Signal Amplification
Supporting Information Ultrasensitive Label-Free Resonance Rayleigh Scattering Aptasensor for Hg 2+ Using Hg 2+ -Triggered Exonuclease III-Assisted Target Recycling and Growth of G-Wires for Signal Amplification
Self-floating nanostructural Ni-NiO x /Ni foam for solar thermal water evaporation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 The supporting information for Self-floating nanostructural Ni-NiO x /Ni
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 The supporting information for Self-floating nanostructural Ni-NiO x /Ni
Partial diallel analysis of agronomic characters in rice (Oryza sativa L.)
 Research Article Genetics and Molecular Biology, 30, 3, 605-613 (2007) Copyright by the Brazilian Society of Genetics. Printed in Brazil www.sbg.org.br Partial diallel analysis of agronomic characters
Research Article Genetics and Molecular Biology, 30, 3, 605-613 (2007) Copyright by the Brazilian Society of Genetics. Printed in Brazil www.sbg.org.br Partial diallel analysis of agronomic characters
Supporting Information. Metal-Organic Frameworks Mediated Synthesis of One-Dimensional Molybdenum-Based/Carbon Composites for Enhanced Lithium Storage
 Supporting Information Metal-Organic Frameworks Mediated Synthesis of One-Dimensional Molybdenum-Based/Carbon Composites for Enhanced Lithium Storage Wei Tian a, Han Hu b, Yixian Wang a, Peng Li c, Jingyan
Supporting Information Metal-Organic Frameworks Mediated Synthesis of One-Dimensional Molybdenum-Based/Carbon Composites for Enhanced Lithium Storage Wei Tian a, Han Hu b, Yixian Wang a, Peng Li c, Jingyan
A Preliminary Analysis of the Relationship between Precipitation Variation Trends and Altitude in China
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2011, VOL. 4, NO. 1, 41 46 A Preliminary Analysis of the Relationship between Precipitation Variation Trends and Altitude in China YANG Qing 1, 2, MA Zhu-Guo 1,
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2011, VOL. 4, NO. 1, 41 46 A Preliminary Analysis of the Relationship between Precipitation Variation Trends and Altitude in China YANG Qing 1, 2, MA Zhu-Guo 1,
EDITORIAL BOARD AND ADVISORY BOARD OF ACTA CHIMICA SINICA
 EDITORIAL BOARD AND ADVISORY BOARD OF ACTA CHIMICA SINICA (Alphabetically arranged) Editor-in-Chief ZHOU Qi-Lin( ) Nankai University Associate Editors CHEN Xiao-Ming( ) Sun Yat-sen University DING Kui-Ling(
EDITORIAL BOARD AND ADVISORY BOARD OF ACTA CHIMICA SINICA (Alphabetically arranged) Editor-in-Chief ZHOU Qi-Lin( ) Nankai University Associate Editors CHEN Xiao-Ming( ) Sun Yat-sen University DING Kui-Ling(
Effects of Exogenous Melatonin on Photosynthetic Characteristics. of Eggplant Seedlings under Low Temperature and Weak Light Stress
 International Conference on Manufacturing Science and Engineering (ICMSE 2015) Effects of Exogenous Melatonin on Photosynthetic Characteristics of Eggplant Seedlings under Low Temperature and Weak Light
International Conference on Manufacturing Science and Engineering (ICMSE 2015) Effects of Exogenous Melatonin on Photosynthetic Characteristics of Eggplant Seedlings under Low Temperature and Weak Light
Hydrothermally Activated Graphene Fiber Fabrics for Textile. Electrodes of Supercapacitors
 Supporting Information for Hydrothermally Activated Graphene Fiber Fabrics for Textile Electrodes of Supercapacitors Zheng Li, Tieqi Huang, Weiwei Gao*, Zhen Xu, Dan Chang, Chunxiao Zhang, and Chao Gao*
Supporting Information for Hydrothermally Activated Graphene Fiber Fabrics for Textile Electrodes of Supercapacitors Zheng Li, Tieqi Huang, Weiwei Gao*, Zhen Xu, Dan Chang, Chunxiao Zhang, and Chao Gao*
Supporting Information. Bi-functional Catalyst with Enhanced Activity and Cycle Stability for. Rechargeable Lithium Oxygen Batteries
 Supporting Information Hierarchical Mesoporous/Macroporous Perovskite La 0.5 Sr 0.5 CoO 3-x Nanotubes: a Bi-functional Catalyst with Enhanced Activity and Cycle Stability for Rechargeable Lithium Oxygen
Supporting Information Hierarchical Mesoporous/Macroporous Perovskite La 0.5 Sr 0.5 CoO 3-x Nanotubes: a Bi-functional Catalyst with Enhanced Activity and Cycle Stability for Rechargeable Lithium Oxygen
