MICROBE MISSION SAMPLE 2. (You are given a microscope with a 10 X ocular and 4, 10, and 40 X objectives.)
|
|
|
- Cameron Shelton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PART 1: Microscopy (You are given a microscope with a 10 X ocular and 4, 10, and 40 X objectives.) 1. What is the highest magnification possible with this microscope? 2. What is the range of magnification for this microscope? 3. A student prepares a slide with the letter "d" and positions it on the stage in the normal reading position. When viewed, how will the "d" will appear? Draw it on your answer sheet. 4. Which part of this microscope is used to control the amount of light coming to the image from the light source? (A) objective (B) diaphram (C) ocular (D) fine adjustment 5. What part of this microscope holds and rotates the objectives? (A) stage (B) body tube (C) coarse adjustment (D) nosepiece (E) fine adjustment knob 6. When observing an object under low power and then switching to high power, the image under high power will appear (A.) smaller and brighter (C.) smaller and darker (B.) larger and brighter (D.) larger and darker 7. Using the hands of the clock to describe places on the field of view, if a object appears to be moving toward 1 o clock, what direction is it actually moving? 8. Examine the diagram of the stage with millimeter ruler from a 10X objective. What is the diameter of this field of view (the diagram) in millimeters? in micrometers or mcm? 9. Examine the Photo of Microbe A taken under low power. What type of microbe is Microbe A? (virus, protozoa, algae, fungi, bacteria) 10. What is the approximate length of one of Microbe A cells that is not reproducing in micrometers (mcm)? Diagram of stage with millimeter ruler (10X objective) Microbe A (10X objective) 1
2 PART 2: Types of Microscopes Key: A. Light microscope B. Phase Contrast Microscope C. Florescent Microscope D. Scanning Electron Microscope E. Transmission Electron Microscope Use the above key to identify the type of microscope being described in questions Produces extremely detailed 3-D images. 12. Produces very detailed 2-D images of very thin stained specimens. 13. Can observe live specimens in normal color and background as they move about a slide. 14. Can observe live specimens contrasted against a gray background. 15. Uses dyes to show florescence under UV rays? Use images A-E in answering questions Each image is of yeast taken from a different type of microscope. 16. Which image is from a light microscope? 17. Which image is from a phase contrast microscope? 18. Which image is from a florescent microscope? 19. Which image is from a scanning transmission microscope? 20. Which image is from a transmission electron microscope? A B C D E 2
3 PART 3: Relative Size of Microbes 21. How many micrometers (mcm) are in a millimeter (mm)? 22. How many nanometers (nm) are in a micrometer (cmc)? 23. How many nanometers (nm) are in a millimeter (mm)? Use the microbe images for questions What is the size of a Volvox in nanometers? 25. What is the size of a yeast in nanometers? 26. What is the size of a halobacterium in nanometers? 27. What is the size of a coccus in nanometers? 28. How many viruses would fit across the diameter of a coccus? 29. How many viruses would fit across the diameter of a yeast? 30. How many viruses would fit across the diameter of a Volvox? diatom-200 mcm Volvox-800 mcm yeast-10 mcm halobacterium 2 mcm Coccus 1 mcm Virus 50 nm 3
4 PART 4: Cell Types Use Diagrams A, B, and C to help you answer the following questions 31. Which diagram (A,B,or C) is acellular? 32. Which diagram (A,B,or C) is a prokaryotic cell? 33. Which diagram (A,B,or C) is a eukaryotic cell? For questions 34-39, indicate which cell type (A, B, or C) would fit each of the following microbes 34. fungi 35. virus 36. algae (Plant-like protist) 37. bacteria 38. protozoa (Animal-like protest) 39. Archaea 40. Which of the following would be found in all three diagrams? A. endoplasmic reticulum B. ribosomes C. vacuole D. DNA or RNA 4
5 PART 5: Major Groups of Microbes MICROBE MISSION SAMPLE 2 A. Prion B. Archeae C. Bacteria D. Fungi E. Algae (Plant-like protists) F. Protozoa (Animal-like protists) G. Virus For questions 41-50, use the above key to identify the appropriate group of microbes being described. 41. Important zooplankton 42. Have cell walls and chloroplasts primary producers in many aquatic environments 43. Acellular cluster of DNA or RNA encased in a protein - many types cause diseases 44. Proteinaceous infectious particles cause disease 45. Yeast are examples of these microbes 46. Some species are extremophiles living in extremes of ph, temperature, salinity as well as heat, acid and toxic gases 47. Organized by mode of transportation as cilia, flagella, pseudopods 48. Many are edible and cultivated world wide others are major decomposers in the soil 49. Cause the flu and the common cold 50. Prokaryotic rods, spheres, or spirals- some can cause disease PART 6: Microbes and Food For questions 51-55, use the key of microbes to identify the microbe used in making the following foods some foods may include more than one microbe type. 51. Yogurt 52. Bread 53. Cheese 54. Wine Key: A. yeast B. Bacteria C. mushrooms D. Algae 55. Pepperoni Pizza 5
6 For questions 56-60, determine whether the statement is true or false. 56. When yeast produce alcohol, oxygen is used. 57. Sauerkraut are made by controlled fermentation of cabbage. 58. Bacteria and fungi play a key role in food spoilage. 59. Microbes are used in the production of chocolate. 60. Lowering the temperature of food increases mold growth. PART 7: Important Microbes Use the Key of Microbes to identify the Microbe Group to which each of the important microbes belong A. Bacteria B. Fungi C. Virus D. Algae (Plant-like protists) E. Protozoa (Animal-like protists) 61. Baker s Yeast 62. Diatoms that form diatomaceous earth 63. Oil eating microbes 64. Cheese making Lactobacillus 65. Sporozoa causing Malaria 66. Dinoflagellates that cause red tide 67. Paramecium 68. Zooplankton in the ocean 69. Ruin ¼ to ½ of fruits and vegetables per year 70. Used in sewage treatment plants to breakdown sewage 6
7 PART 8: Microbes and Ecology Examine the Ocean Food Web and Ocean Energy Pyramid when answering questions Which type of organisms would be the primary producers and carry out photosynthesis? 72. Which of the following types of microbes could be primary producers in the ocean? Cyanobacteria, protozoa, fungi, algae 73. Which of the following types of microbes could be zooplankton? Cyanobacteria, protozoa, fungi, algae 74. Which of the following types of microbes could be decomposers for the ocean ecosystem? bacteria, protozoa, fungi, algae 75. What do carnivorous zooplankton eat? 76. What do herbivorous zooplankton eat? 77. Which types of microbes will eat any dead and decaying material that drops to the bottom of the ocean? bacteria, protozoa, fungi, algae 78. What percent of the energy available to each trophic level will be still available to the next trophic level? 79. If 8000 energy units were produced by the phytoplankton, how many units would be available for the Carnivorous zooplankton? 80. If 8000 energy units were produced by the phytoplankton, how many units would be available for the tuna? Food Web Energy Pyramid 7
8 PART 9: Microbes and Disease Key: MICROBE MISSION SAMPLE 2 A. Fungi B. Virus C. Bacteria D. Protozoan E. Prion Use the above key to indicate which type of microbe causes the disease listed in questions Typhus 82. Herpes 83. Tetanus 84. Ringworm 85. Anthrax 86. Athlete s foot 87. Mad Cow Disease 88. Mononucleosis 89. Lyme Disease 90. Malaria 8
9 PART 10 : Dichotomous Key For questions , identify the specimen & give the name from the key 91. What is specimen A? 92. What is specimen B? 93. What is specimen C? 94. What is specimen D? 95. What is specimen E? 96. What is specimen F? 97. What is specimen G? 98. What is specimen H? 99. What is specimen I? 100. Where would you find these organisms living? Protozoa specimens Dichotomous Key to Selected Protozoa 1. Pseudopods for locomotion Other means for locomotion Dome-shaped shell around cell Difflugia 2. Without shell, many small nuclei Pelomyxa 3. Cell has flagella Cell has cilia One flagellum Peranema 4. Two flagella chilomonas 5. Cilia on stalk vorticella 5. Cilia not on stalk Cilia covering cell Cilia in two bands Didinium 7. Cell is cone-shaped Stentor 7. Cell is elongated Cigar-shaped cell with flattened end Spirostonum 8. Pear-shaped cell Blepharisma 9
10 TEAM NUMBER SCHOOL STUDENT NAMES: (PLEASE PRINT) RAW SCORE 1. RANK 2. BE SURE TO INCLUDE APPROPRIATE UNITS WITH ALL ANSWERS!!! PART 1: Microscopy PART 4: Cell Types PART 2: Microscope Types PART 5: Major Groups PART 3: Relative Size TOTAL PARTS TOTAL PARTS TIE-BREAKER RAW SCORE
11 PART 6: Microbes & Food PART 9: Microbes & Disease PART 7: Important Microbes PART 10: Dichotomous Key PART 8: Microbes & Ecology TOTAL PARTS
12 ANSWER KEY TEAM NUMBER SCHOOL STUDENT NAMES: (PLEASE PRINT) RAW SCORE 1. RANK 2. POINTS BE SURE TO INCLUDE APPROPRIATE UNITS WITH ALL ANSWERS!!! PART 1: Microscopy PART 4: Cell Types X 31. C 2. 40X to 400X 32. A 3. P 33. B 4. B (Diaphram) 34. B 5. D (Nosepiece) 35. C 6. D (larger & darker) 36. B 7. 7 o clock 37. A 8. ~ 1.5 mm ~1500 mcm 38. B 9. protozoa 39. A 10. ~ 500 mcm 40. D PART 2: Microscope Types PART 5: Major Groups 11. D 41. F 12. E 42. E 13. A 43. G 14. B 44. A 15. C 45. D 16. D 46. B 17. C 47. F 18. E 48. D 19. A 49. G 20. B 50. C PART 3: Relative Size mcm nm 23. 1,000,000 nm ,000 nm ,000 nm 26. 2,000 nm 27. 1,000 nm ,000 12
13 Answer Key PART 6: Microbes & Food PART 9: Microbes & Disease 51. B 81. C 52. A 82. B 53. B 83. C 54. A 84. A 55. A,B,C 85. C 56. false 86. A 57. true 87. E 58. true 88. B 59. true 89. C 60. false 90. D PART 7: Important Microbes PART 10: Dichotomous Keys 61. B 91. Pelomyxa 62. D 92. Stentor 63. A 93. Spirostonum 64. A 94. Chilomonas 65. E 95. Didinium 66. D 96. Difflugia 67. E 97. Peranema 68. E 98. Vorticella 69. B 99. Blepharisma 70. A 100. in water (pond) PART 8: Microbes & Ecology 71. phytoplankton 72. cyanobacteria algae 73. protozoa 74. bacteria fungi 75. herbivorous zooplankton 76. phytoplankton 77. bacteria & fungi % energy units energy units 13
MICROBE MISSION - SAMPLE TOURNAMENT #1 by Karen L. Lancour
 MICROBE MISSION - SAMPLE TOURNAMENT #1 by Karen L. Lancour STATION A: MICROSCOPY 1. A microscope has an 10 objective and oculars of 4X, 10X, 40X and 100X. What is the range of magnification for this microscope.
MICROBE MISSION - SAMPLE TOURNAMENT #1 by Karen L. Lancour STATION A: MICROSCOPY 1. A microscope has an 10 objective and oculars of 4X, 10X, 40X and 100X. What is the range of magnification for this microscope.
Have you had a cold, flu, or other infectious disease recently? Do you
 45 The World of Microbes r e a d i n g Have you had a cold, flu, or other infectious disease recently? Do you know what caused your illness? Microbes cause most infectious diseases. Microbes include the
45 The World of Microbes r e a d i n g Have you had a cold, flu, or other infectious disease recently? Do you know what caused your illness? Microbes cause most infectious diseases. Microbes include the
INTRO TO MICROBIOLOGY
 INTRO TO MICROBIOLOGY Spring 2015 Peering through the microscope into a drop of seawater is like looking at stars with a telescope on a clear night. Dr. Gallardo, ocean researcher What will you be studying
INTRO TO MICROBIOLOGY Spring 2015 Peering through the microscope into a drop of seawater is like looking at stars with a telescope on a clear night. Dr. Gallardo, ocean researcher What will you be studying
Chapter 7! Viruses, Bacteria, Protists, & Fungi! p. 208
 Chapter 7! Viruses, Bacteria, Protists, & Fungi! p. 208 1 Vocabulary virus! bacteria! protist! fungi! vaccine! pasteurization! parasite! host! pseudopod! flagellum! cilia! decomposer protozoan!! Viruses
Chapter 7! Viruses, Bacteria, Protists, & Fungi! p. 208 1 Vocabulary virus! bacteria! protist! fungi! vaccine! pasteurization! parasite! host! pseudopod! flagellum! cilia! decomposer protozoan!! Viruses
Objective 1: I can describe protists. Protists are a kingdom of living organisms that CAN NOT be classified as animals plants or fungus.
 Kingdom Protista Objective 1: I can describe protists Protists are a kingdom of living organisms that CAN NOT be classified as animals plants or fungus. They are: Eukaryotic they contain a nucleus Can
Kingdom Protista Objective 1: I can describe protists Protists are a kingdom of living organisms that CAN NOT be classified as animals plants or fungus. They are: Eukaryotic they contain a nucleus Can
Biology Test Pack WALCH PUBLISHING
 Biology Test Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher........................................................... v Testing Students Who Do Not Test Well.....................................
Biology Test Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher........................................................... v Testing Students Who Do Not Test Well.....................................
Ladue Microbe Mission Test SCORE: / 90 Name: Date:
 Ladue Microbe Mission Test SCORE: / 90 Name: Date: You may not return to previous stations. However, you can move to another station early if you want to do so. I won t judge you for your grammar/writing
Ladue Microbe Mission Test SCORE: / 90 Name: Date: You may not return to previous stations. However, you can move to another station early if you want to do so. I won t judge you for your grammar/writing
Microbe
 Warm Up 1.) What types of organisms, if any, did you find in the water samples used in the lab? 2.) Which objec@ve lens (4x, 10x, 40x) did you find it easiest to observe small specimens using the microscope?
Warm Up 1.) What types of organisms, if any, did you find in the water samples used in the lab? 2.) Which objec@ve lens (4x, 10x, 40x) did you find it easiest to observe small specimens using the microscope?
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Lab Activity
 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Lab Activity Name: Blk: INTRODUCTION Prokaryotic Cells Cells (the smallest individual units of life) are divided into two basic categories: prokaryotic cells, and eukaryotic
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Lab Activity Name: Blk: INTRODUCTION Prokaryotic Cells Cells (the smallest individual units of life) are divided into two basic categories: prokaryotic cells, and eukaryotic
Lecture 2: Kingdoms Monera, Protoctista and Fungi
 KINGDOM MONERA Bacteria Lecture 2: Kingdoms Monera, Protoctista and Fungi Kingdom Monera Commonly called bacteria All monerans are unicellular All monerans are prokaryotes Prokaryotes: Single-celled organisms
KINGDOM MONERA Bacteria Lecture 2: Kingdoms Monera, Protoctista and Fungi Kingdom Monera Commonly called bacteria All monerans are unicellular All monerans are prokaryotes Prokaryotes: Single-celled organisms
BIOLOGY 1021 UNIT 1: MULTICELLULAR STRUCTURE CHAPTER 15 P AND CHAPTER 16 P
 BIOLOGY 1021 UNIT 1: MULTICELLULAR STRUCTURE CHAPTER 15 P. 307-311 AND CHAPTER 16 P. 328-331 Be sure to know flow chart an understanding from atoms to multicellular organisms. Importance of carbon, hydrogen,
BIOLOGY 1021 UNIT 1: MULTICELLULAR STRUCTURE CHAPTER 15 P. 307-311 AND CHAPTER 16 P. 328-331 Be sure to know flow chart an understanding from atoms to multicellular organisms. Importance of carbon, hydrogen,
Protists - a member of a group of eukaryotic organisms, which have a membrane bound nucleus.
 7ch8 Protists Protists - a member of a group of eukaryotic organisms, which have a membrane bound nucleus. protists are a diverse group with many different adaptations share some characteristics with plants,
7ch8 Protists Protists - a member of a group of eukaryotic organisms, which have a membrane bound nucleus. protists are a diverse group with many different adaptations share some characteristics with plants,
Microscopy and the Diversity of Microorganisms
 Microscopy and the Diversity of Microorganisms Today we will learn how to use one of the most important tools a biologist has, the microscope. We will use the microscope to study organisms throughout the
Microscopy and the Diversity of Microorganisms Today we will learn how to use one of the most important tools a biologist has, the microscope. We will use the microscope to study organisms throughout the
Name: /92 Grade: Microbe Mission regionals test Part A: Microscopy Label all parts. (1 pt each)
 Name: /92 Grade: Microbe Mission regionals test Part A: Microscopy Label all parts. (1 pt each) 15. You are looking at a sample of euglena through a microscope with the x10 objective lens. One specimen
Name: /92 Grade: Microbe Mission regionals test Part A: Microscopy Label all parts. (1 pt each) 15. You are looking at a sample of euglena through a microscope with the x10 objective lens. One specimen
19.1 Diversity of Protists. KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms.
 19.1 Diversity of Protists KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms. 19.1 Diversity of Protists Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. Protists are eukaryotes
19.1 Diversity of Protists KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms. 19.1 Diversity of Protists Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. Protists are eukaryotes
Station 1. View the picture of Volvox on the next slide. Draw a picture of what you see.
 Volvox Station 1 View the picture of Volvox on the next slide Draw a picture of what you see. Why do you think Volvox is green? How do you think Volvox gets its energy? Use the reading on Slide 3 to answer
Volvox Station 1 View the picture of Volvox on the next slide Draw a picture of what you see. Why do you think Volvox is green? How do you think Volvox gets its energy? Use the reading on Slide 3 to answer
2017 MICROBE MISSION(B/C) KAREN LANCOUR NATIONAL SUPERVISOR National Rules Committee Chairman Life Sciences
 2017 MICROBE MISSION(B/C) KAREN LANCOUR NATIONAL SUPERVISOR National Rules Committee Chairman Life Sciences Event Rules 2017 DISCLAIMER This presentation was prepared using draft rules. There may be some
2017 MICROBE MISSION(B/C) KAREN LANCOUR NATIONAL SUPERVISOR National Rules Committee Chairman Life Sciences Event Rules 2017 DISCLAIMER This presentation was prepared using draft rules. There may be some
Observing and Classifying Protozoa
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Observing and Classifying Protozoa Background The name protozoa actually means first animals. This name was given because many protozoa share characteristics with animals. However,
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Observing and Classifying Protozoa Background The name protozoa actually means first animals. This name was given because many protozoa share characteristics with animals. However,
Classification. Classifying Organisms. * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics
 Classification Classifying Organisms * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics Cell Type: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic - No nucleus Eukaryotic
Classification Classifying Organisms * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics Cell Type: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic - No nucleus Eukaryotic
2011 MICROBE MISSION TRAINING HANDOUT
 2011 MICROBE MISSION TRAINING HANDOUT KAREN L. LANCOUR National Event Supervisor National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science DISCLAIMER - This presentation was prepared using draft rules. There may
2011 MICROBE MISSION TRAINING HANDOUT KAREN L. LANCOUR National Event Supervisor National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science DISCLAIMER - This presentation was prepared using draft rules. There may
Microbiology. Viruses
 Microbiology Microbiology: The branch of biology that deals with microorganisms and their effects on other living organisms. Typically we study bacteria & protists. Virology studies the impact of viruses
Microbiology Microbiology: The branch of biology that deals with microorganisms and their effects on other living organisms. Typically we study bacteria & protists. Virology studies the impact of viruses
INTRODUCTION prokaryotic eukaryotic pigments
 INTRODUCTION This exercise is intended for you to get familiar and comfortable with using a microscope as well as identifying common microbial groups. Thus, we will observe representatives of all microbes
INTRODUCTION This exercise is intended for you to get familiar and comfortable with using a microscope as well as identifying common microbial groups. Thus, we will observe representatives of all microbes
Ladue Microbe Mission Test SCORE: 90 / 90 Name: Answer Key Date:
 Ladue Microbe Mission Test SCORE: 90 / 90 Name: Answer Key Date: You may not return to previous stations. However, you can move to another station early if you want to do so. I won t judge you for your
Ladue Microbe Mission Test SCORE: 90 / 90 Name: Answer Key Date: You may not return to previous stations. However, you can move to another station early if you want to do so. I won t judge you for your
Protists. Plant Like Animal Like Fungus Like. What are the three main groups of protists?*
 Protists & Fungi Protists Single celled or multi-celled organisms that live in moist areas Eukaryotic organisms Characteristics of plants, animals and fungi Grouped in to three main groups* Plant Like
Protists & Fungi Protists Single celled or multi-celled organisms that live in moist areas Eukaryotic organisms Characteristics of plants, animals and fungi Grouped in to three main groups* Plant Like
Leeuwenhoek s Animacules
 Leeuwenhoek s Animacules Early History of Microbiology: 1668 Francesco Redi disproves spontaneous generation 1676 Antony van Leeuwenhoek first observes microbes 1861 Louis Pasteur disproves spontaneous
Leeuwenhoek s Animacules Early History of Microbiology: 1668 Francesco Redi disproves spontaneous generation 1676 Antony van Leeuwenhoek first observes microbes 1861 Louis Pasteur disproves spontaneous
Leeuwenhoek s Animacules. Early History of Microbiology: Fig. 1.4
 Leeuwenhoek s Animacules Early History of Microbiology: 1668 Francesco Redi disproves spontaneous generation 1676 Antony van Leeuwenhoek first observes microbes 1861 Louis Pasteur disproves spontaneous
Leeuwenhoek s Animacules Early History of Microbiology: 1668 Francesco Redi disproves spontaneous generation 1676 Antony van Leeuwenhoek first observes microbes 1861 Louis Pasteur disproves spontaneous
Investigation: What Are the Different Types of Cells?
 Name: Date: Investigation: What Are the Different Types of Cells? All living organisms are made of cells. The smallest cells are about 0.001 millimeters in diameter and belong to one of two domains: Bacteria
Name: Date: Investigation: What Are the Different Types of Cells? All living organisms are made of cells. The smallest cells are about 0.001 millimeters in diameter and belong to one of two domains: Bacteria
Microbiology 2320 Spring 2017 Dr. Milind Suraokar CRN# 18168
 Microbiology 2320 Spring 2017 Dr. Milind Suraokar CRN# 18168 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 1 A Brief History of Microbiology
Microbiology 2320 Spring 2017 Dr. Milind Suraokar CRN# 18168 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 1 A Brief History of Microbiology
EQ: What are the 3 types of protists? Bellringer: TOD. Week 7 Classification Day 3 & 4 Protista & Fungi.notebook. February 27, 2014.
 Week 7 Classification Day 3 & 4 Protista & Fungi.notebook EQ: What are the 3 types of protists? Bellringer: TOD Assignment: Dichotomous keys Fungi/Protist GO 1 TOD What important characteristics do fungus-like
Week 7 Classification Day 3 & 4 Protista & Fungi.notebook EQ: What are the 3 types of protists? Bellringer: TOD Assignment: Dichotomous keys Fungi/Protist GO 1 TOD What important characteristics do fungus-like
Bio 134. Ch. 19 Protists
 Bio 134 Ch. 19 Protists Main Idea! Protists form a diverse group of organisms that are subdivided based on their method of obtaining nutrients What do all protists have in common?! They are all eukaryotes
Bio 134 Ch. 19 Protists Main Idea! Protists form a diverse group of organisms that are subdivided based on their method of obtaining nutrients What do all protists have in common?! They are all eukaryotes
6 Kingdoms of Life. What is life? How are all living things organized?
 6 Kingdoms of Life What is life? How are all living things organized? Engage List reasons to support why this man is living. List reasons to support why this car is not living. Characteristics of Life
6 Kingdoms of Life What is life? How are all living things organized? Engage List reasons to support why this man is living. List reasons to support why this car is not living. Characteristics of Life
Have cell walls Made of
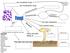 _ are unicellular fungi _ are multicellular fungi And can only Reproduce Using Can also reproduce Can spread using Because they do not make their own food Hyphae Mycelium Fruiting Body Heterotrophs Budding
_ are unicellular fungi _ are multicellular fungi And can only Reproduce Using Can also reproduce Can spread using Because they do not make their own food Hyphae Mycelium Fruiting Body Heterotrophs Budding
General Biology 1004 Chapter 15 Lecture Handout, Summer 2005 Dr. Frisby
 Slide 1 CHAPTER 15 The Evolution of Microbial Life PowerPoint Lecture Slides for Essential Biology, Second Edition & Essential Biology with Physiology Presentation prepared by Chris C. Romero Neil Campbell,
Slide 1 CHAPTER 15 The Evolution of Microbial Life PowerPoint Lecture Slides for Essential Biology, Second Edition & Essential Biology with Physiology Presentation prepared by Chris C. Romero Neil Campbell,
2017 MICROBE MISSION TRAINING HANDOUT KAREN L. LANCOUR National Event Supervisor National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science
 2017 MICROBE MISSION TRAINING HANDOUT KAREN L. LANCOUR National Event Supervisor National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science DISCLAIMER - This presentation was prepared using draft rules. There may
2017 MICROBE MISSION TRAINING HANDOUT KAREN L. LANCOUR National Event Supervisor National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science DISCLAIMER - This presentation was prepared using draft rules. There may
Mastery Objective: The students will explain characteristics of prokaryotic (bacteria) cells by gathering notes from a slideshow.
 September 26, 2018 Mastery Objective: The students will explain characteristics of prokaryotic (bacteria) cells by gathering notes from a slideshow. Drill Warm-Up: Observe the bacteria and animal cell
September 26, 2018 Mastery Objective: The students will explain characteristics of prokaryotic (bacteria) cells by gathering notes from a slideshow. Drill Warm-Up: Observe the bacteria and animal cell
Chapter 2 Viruses, Bacteria, Protists, and Fungi
 complete petri dishes Chapter 2 Viruses, Bacteria, Protists, and Fungi Viruses Lesson 1 Objectives Name and describe the characteristics of viruses and how they multiply. Discuss both positive and negative
complete petri dishes Chapter 2 Viruses, Bacteria, Protists, and Fungi Viruses Lesson 1 Objectives Name and describe the characteristics of viruses and how they multiply. Discuss both positive and negative
Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2017 Biology
 Grade 08 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2017 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1) Microorganisms that prepares their food from water and carbon dioxide
Grade 08 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2017 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1) Microorganisms that prepares their food from water and carbon dioxide
MICROSCOPY AND CELLS BIO 171 WEEK 3
 MICROSCOPY AND CELLS BIO 171 WEEK 3 MICROSCOPY THE COMPOUND LIGHT MICROSCOPE System of lenses arranged to produce an enlarged, focusable image of a specimen. MICROSCOPY THE MICROSCOPE Illuminating System
MICROSCOPY AND CELLS BIO 171 WEEK 3 MICROSCOPY THE COMPOUND LIGHT MICROSCOPE System of lenses arranged to produce an enlarged, focusable image of a specimen. MICROSCOPY THE MICROSCOPE Illuminating System
VIII. Kingdom Protista- (protists) A. General characteristics of protists:
 VIII. Kingdom Protista- (protists) A. General characteristics of protists: 1. Protists are unicellular organisms that have a nucleus to organize their hereditary material. 2. Some protists help their host
VIII. Kingdom Protista- (protists) A. General characteristics of protists: 1. Protists are unicellular organisms that have a nucleus to organize their hereditary material. 2. Some protists help their host
Study Guide B. Answer Key. Protists and Fungi
 Protists and Fungi Answer Key SECTION 1. DIVERSITY OF PROTISTS 1. eukaryotes 2. protists may be single-celled, colonial, or multicellular 3. No, the size of protists range from microscopic to very large.
Protists and Fungi Answer Key SECTION 1. DIVERSITY OF PROTISTS 1. eukaryotes 2. protists may be single-celled, colonial, or multicellular 3. No, the size of protists range from microscopic to very large.
CH 11 PROTISTS AND FUNGI
 CH 11 PROTISTS AND FUNGI Name Day M T W Th F Weekly Lifeline Period B_ Check Question What is a parasite? KICK-OFF LEARNING LOG KICK-OFF Response (1) A parasite is an organism that feeds off of another
CH 11 PROTISTS AND FUNGI Name Day M T W Th F Weekly Lifeline Period B_ Check Question What is a parasite? KICK-OFF LEARNING LOG KICK-OFF Response (1) A parasite is an organism that feeds off of another
CELLS. Single Celled Organisms. The Building Blocks of Life. Junior Science
 CELLS Single Celled Organisms The Building Blocks of Life Junior Science Lesson Objectives Know what is meant by unicellular and multicellular organisms. List the six kingdoms of life. Explain the difference
CELLS Single Celled Organisms The Building Blocks of Life Junior Science Lesson Objectives Know what is meant by unicellular and multicellular organisms. List the six kingdoms of life. Explain the difference
Structures and Life Functions of Single-Celled Organisms
 Structures and Life Functions of Single-Celled Organisms 7.L.1.1 - Compare the structures and life functions of single-celled organisms that carry out all of the basic functions of life including: Euglena
Structures and Life Functions of Single-Celled Organisms 7.L.1.1 - Compare the structures and life functions of single-celled organisms that carry out all of the basic functions of life including: Euglena
Microscope History Robert Hooke
 1 Microscope History Robert Hooke First described cells in 1665. He viewed thin slices of cork and compared the boxy partitions he observed to the cells (small rooms) in a monastery. (1635 1702) 2 Microscope
1 Microscope History Robert Hooke First described cells in 1665. He viewed thin slices of cork and compared the boxy partitions he observed to the cells (small rooms) in a monastery. (1635 1702) 2 Microscope
Domains and Kingdoms. Images, from left to right: Cholera bacteria, Volvox colony, Strep bacteria
 Domains and Kingdoms Images, from left to right: Cholera bacteria, Volvox colony, Strep bacteria THE DOMAINS A domain is the broadest level in the classification of life. All living organisms belong to
Domains and Kingdoms Images, from left to right: Cholera bacteria, Volvox colony, Strep bacteria THE DOMAINS A domain is the broadest level in the classification of life. All living organisms belong to
Pre-lab Homework Lab 4: The Cell
 Lab Section: Name: Pre-lab Homework After reading over the lab and the cell chapter in your textbook, answer these questions to be turned in at the beginning of the lab! 1. Define organelle : Two examples
Lab Section: Name: Pre-lab Homework After reading over the lab and the cell chapter in your textbook, answer these questions to be turned in at the beginning of the lab! 1. Define organelle : Two examples
1A Review Questions. Matching 6. Class 7. Order 8. Binomial nomenclature 9. Phylum 10. Species
 1A Review Questions 1. What is taxonomy? a. Set of paired statements that are used to identify organisms b. Relationships between organisms c. A science involving naming and categorizing species based
1A Review Questions 1. What is taxonomy? a. Set of paired statements that are used to identify organisms b. Relationships between organisms c. A science involving naming and categorizing species based
Kingdom Protista. Lab Exercise 20. Introduction. Contents. Objectives
 Lab Exercise Kingdom Protista Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Animal-like Protists 2 Activity.2 Fungal-like Protists 3 Activity.3 Plant-like Protists 3 Resutls Section 5 Introduction This
Lab Exercise Kingdom Protista Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Animal-like Protists 2 Activity.2 Fungal-like Protists 3 Activity.3 Plant-like Protists 3 Resutls Section 5 Introduction This
Adding the class. Prerequisites. Welcome to Bio 139 General Microbiology. Syllabus. Amy Rogers, M.D., Ph.D.
 Adding the class Welcome to Bio 139 General Microbiology Amy Rogers, M.D., Ph.D. Lectures MW 12:00-1:15 PM (section 8) Labs: MW 1:30-2:45 PM or MW 3:00 PM-4:15 PM I anticipate a large number of students
Adding the class Welcome to Bio 139 General Microbiology Amy Rogers, M.D., Ph.D. Lectures MW 12:00-1:15 PM (section 8) Labs: MW 1:30-2:45 PM or MW 3:00 PM-4:15 PM I anticipate a large number of students
copyright cmassengale Kingdoms and Classification
 1 Kingdoms and Classification 2 Domains Broadest, most inclusive taxon Three domains Archaea and Eubacteria are unicellular prokaryotes (no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles) Eukarya are more complex
1 Kingdoms and Classification 2 Domains Broadest, most inclusive taxon Three domains Archaea and Eubacteria are unicellular prokaryotes (no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles) Eukarya are more complex
Bio 134 PRACTICE TEST Ch. 19, 20 (Protist and Fungi)
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Bio 134 PRACTICE TEST Ch. 19, 20 (Protist and Fungi) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A protist is any organism
Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Bio 134 PRACTICE TEST Ch. 19, 20 (Protist and Fungi) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A protist is any organism
MAJOR GROUPS OF MICROBES
 MAJOR GROUPS OF MICROBES MICROBES The term microbe is short for microorganism which means small organism observed with a microscope Over 99% of microbes contribute to the quality of human life A small
MAJOR GROUPS OF MICROBES MICROBES The term microbe is short for microorganism which means small organism observed with a microscope Over 99% of microbes contribute to the quality of human life A small
Protista and Fungi. Fungi. Protista
 Protista and Fungi Protista -eukaryotic -multi and single cellular many singular -consumers, producers, and decomposers -some movement -algae like protists, plant like protists, and animal like protists
Protista and Fungi Protista -eukaryotic -multi and single cellular many singular -consumers, producers, and decomposers -some movement -algae like protists, plant like protists, and animal like protists
2. Cell surface proteins or receptors, that help cells communicate, are embedded within the cell membrane s phospholipid bilayer.
 UNIT 3 TEST BIOLOGY: 1.1.1, 1.1.2, 1.1.3 Cells, Cell Structures, Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic, Bacteria & Protists, Microscopes, Cell Communication, & Stem Cells True/False Indicate whether the statement
UNIT 3 TEST BIOLOGY: 1.1.1, 1.1.2, 1.1.3 Cells, Cell Structures, Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic, Bacteria & Protists, Microscopes, Cell Communication, & Stem Cells True/False Indicate whether the statement
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function 7.1: Life is Cellular
 Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function 7.1: Life is Cellular Key Questions: 1) What is the cell theory? 2) How do microscopes work? 3) How are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells different? THINK ABOUT IT
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function 7.1: Life is Cellular Key Questions: 1) What is the cell theory? 2) How do microscopes work? 3) How are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells different? THINK ABOUT IT
Unit 10: The simplest living beings
 Unit 10: The simplest living beings 1. Fungi 2. Protoctists 2.1. Protozoa 2.2. Algae 3. Bacteria 4. Viruses Think and answer? a. What type of organism can you see in the photograph? b. What type of cells
Unit 10: The simplest living beings 1. Fungi 2. Protoctists 2.1. Protozoa 2.2. Algae 3. Bacteria 4. Viruses Think and answer? a. What type of organism can you see in the photograph? b. What type of cells
Major Events in the History of Earth
 Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
Unit3L.3: Micro-organisms
 Unit3L.3: Bacteria Viruses Fungi Science skills: Classification Observing Predicting Comparing 37 3.8.1 Life Science Bacteria Why should I keep myself clean? Germs! Germs! Germs! Germs can be too tiny
Unit3L.3: Bacteria Viruses Fungi Science skills: Classification Observing Predicting Comparing 37 3.8.1 Life Science Bacteria Why should I keep myself clean? Germs! Germs! Germs! Germs can be too tiny
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites
 Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites Date: Sized Extra-Small What is a prokaryote? All living things are either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are made up of one or many cells, each of which has
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites Date: Sized Extra-Small What is a prokaryote? All living things are either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are made up of one or many cells, each of which has
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites. 8th grade
 Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites 8th grade Sized Extra-Small What is a prokaryote? All living things are either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. What is a prokaryote? Eukaryotes are made up of one or many
Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi & Parasites 8th grade Sized Extra-Small What is a prokaryote? All living things are either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. What is a prokaryote? Eukaryotes are made up of one or many
Kingdom Monera - The Bacteria
 Chapter 8 The World of Microbes Kingdom Monera - The Bacteria Bio-significance- The down side: Disease of plants crop loss Disease of animals loss of livestock and herds Human disease cavities to The Plague
Chapter 8 The World of Microbes Kingdom Monera - The Bacteria Bio-significance- The down side: Disease of plants crop loss Disease of animals loss of livestock and herds Human disease cavities to The Plague
- A virus is a short piece of DNA or RNA, sometimes with some associated enzymes.
 Viruses, bacteria, protists & fungi (just the basics!) I. Viruses: - parasites postponed until we discuss them in class. - A virus is a short piece of DNA or RNA, sometimes with some associated enzymes.
Viruses, bacteria, protists & fungi (just the basics!) I. Viruses: - parasites postponed until we discuss them in class. - A virus is a short piece of DNA or RNA, sometimes with some associated enzymes.
KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS SKILLS. 2. Most infectious diseases are caused by microbes.
 Who s Who? 44 40- to 1 50-minute session ACTIVITY OVERVIEW I N V E S T I O N I G AT SUMMARY Cards with images of the major groups of disease-causing microbes (s, bacteria, and es) are presented. Students
Who s Who? 44 40- to 1 50-minute session ACTIVITY OVERVIEW I N V E S T I O N I G AT SUMMARY Cards with images of the major groups of disease-causing microbes (s, bacteria, and es) are presented. Students
Golden Gopher Invitational. Microbe Mission. *Please do not write on these tests.
 Golden Gopher Invitational Microbe Mission *Please do not write on these tests. Part A: Multiple Choice (1 pt each) 1. What objective magnification on a compound light microscope would use immersion oil?
Golden Gopher Invitational Microbe Mission *Please do not write on these tests. Part A: Multiple Choice (1 pt each) 1. What objective magnification on a compound light microscope would use immersion oil?
Cells Under the Microscope Measuring Cell Structures
 Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher Chapter 3 Cell Structure Section 1: Looking at Cells Objectives Describe how scientists measure the length of objects. Relate magnification and resolution in
Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher Chapter 3 Cell Structure Section 1: Looking at Cells Objectives Describe how scientists measure the length of objects. Relate magnification and resolution in
Period: Date: Marine Science Midyear Exam Study Guide & Review This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES.
 Marine Science Midyear Exam Study Guide & Review This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Intro: the water planet; scientific method Properties of Water Tides,
Marine Science Midyear Exam Study Guide & Review This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Intro: the water planet; scientific method Properties of Water Tides,
Biology Test 2 The Cell. For questions 1 15, choose ONLY ONE correct answer and fill in that choice on your Scantron form.
 Name Block Date Biology Test 2 The Cell For questions 1 15, choose ONLY ONE correct answer and fill in that choice on your Scantron form. 1. Which pair of structures best shows that plant cells have functions
Name Block Date Biology Test 2 The Cell For questions 1 15, choose ONLY ONE correct answer and fill in that choice on your Scantron form. 1. Which pair of structures best shows that plant cells have functions
Lab 1: Using the Microscope & Cell Biology
 Name Lab 1: Using the Microscope & Cell Biology The anatomy of the compound microscope Review or learn the following parts of the compound microscope and their functions. Eyepieces Objectives Arm Stage
Name Lab 1: Using the Microscope & Cell Biology The anatomy of the compound microscope Review or learn the following parts of the compound microscope and their functions. Eyepieces Objectives Arm Stage
Life is Cellular. At the cellular level, what is the difference between animal cells and bacterial cells? How do microscopes work?
 Life is Cellular At the cellular level, what is the difference between animal cells and bacterial cells? How do microscopes work? Objectives 8a) I can state the cell theory and distinguish between prokaryotes
Life is Cellular At the cellular level, what is the difference between animal cells and bacterial cells? How do microscopes work? Objectives 8a) I can state the cell theory and distinguish between prokaryotes
Notes - Microbiology Protista
 Notes - Microbiology Protista Part 1 Animal like Protists - Kingdom Protista is a very diverse group of organisms. There are over 115 000 different kinds, with traits that fit with fungi, plants, and animals.
Notes - Microbiology Protista Part 1 Animal like Protists - Kingdom Protista is a very diverse group of organisms. There are over 115 000 different kinds, with traits that fit with fungi, plants, and animals.
The Microbial World. Chapter 5
 The Microbial World Chapter 5 Viruses Non-cellular infectious agents that have two basic characteristics: Not capable of reproduction without a host cell Structure: Nucleic acid core- can be DNA or RNA
The Microbial World Chapter 5 Viruses Non-cellular infectious agents that have two basic characteristics: Not capable of reproduction without a host cell Structure: Nucleic acid core- can be DNA or RNA
Introductory Microbiology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Introductory Microbiology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Why Study Microbes? Microbiology is the branch of biological sciences concerned with the study of the microbes. 1. Microbes and Man in Sickness and Health
Introductory Microbiology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Why Study Microbes? Microbiology is the branch of biological sciences concerned with the study of the microbes. 1. Microbes and Man in Sickness and Health
Protists are in the Eukaryote Domain
 Protista Protists are in the Eukaryote Domain All protists are eukaryotic (cells with a nucleus) Euglena Paramecium Amoeba Protists are really just all of the Eukaryotes that don t fit into the Animal,
Protista Protists are in the Eukaryote Domain All protists are eukaryotic (cells with a nucleus) Euglena Paramecium Amoeba Protists are really just all of the Eukaryotes that don t fit into the Animal,
Kingdom Protista. Mr. Krause Edina Public Schools ISD273 EXIT 2/16/2005
 Kingdom Protista Mr. Krause Edina Public Schools ISD273 Kingdom Protista General Characteristics Animal-Like Protists Plant-Like Protists Fungus-Like Protists General Characteristics Protozoa - Greek name
Kingdom Protista Mr. Krause Edina Public Schools ISD273 Kingdom Protista General Characteristics Animal-Like Protists Plant-Like Protists Fungus-Like Protists General Characteristics Protozoa - Greek name
Unit 2 Benchmark Review. Disease Review:
 Match the term with the definition: Unit 2 Benchmark Review Disease Review: 1. Caused by tiny organisms called pathogens B 2. This is responsible for distinguishing between the different kinds of pathogens
Match the term with the definition: Unit 2 Benchmark Review Disease Review: 1. Caused by tiny organisms called pathogens B 2. This is responsible for distinguishing between the different kinds of pathogens
5/10/2013. Protists. Kingdom Protista. Called the Junk Drawer. 3 Subkingdoms of Protists. Protozoans Algae Slime molds
 Protists Kingdom Protista Called the Junk Drawer 3 Subkingdoms of Protists Protozoans Algae Slime molds 1 Protozoans Animal-like Superphyla: Sarcodines ( Sarcodina ) Ciliates ( Ciliophora ) Flagellates
Protists Kingdom Protista Called the Junk Drawer 3 Subkingdoms of Protists Protozoans Algae Slime molds 1 Protozoans Animal-like Superphyla: Sarcodines ( Sarcodina ) Ciliates ( Ciliophora ) Flagellates
Most are autotrophic. Heterotrophic Some autotrophic. animal- like = heterotrophs plant- like = autotrophs fungi- like = heterotrophs.
 Earth Science Exam 2 Review Energy and Nutrient Flow in Ecosystems Vocabulary to know: ecosystem biotic abiotic organism species population community producers consumers decomposers food chain food web
Earth Science Exam 2 Review Energy and Nutrient Flow in Ecosystems Vocabulary to know: ecosystem biotic abiotic organism species population community producers consumers decomposers food chain food web
Classification. Old 5 Kingdom system. New 3 Domain system. reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence
 Classification Old 5 Kingdom system Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals New 3 Domain system reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence Prokaryote: Bacteria Prokaryote: Archaebacteria
Classification Old 5 Kingdom system Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals New 3 Domain system reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence Prokaryote: Bacteria Prokaryote: Archaebacteria
The Microbial World. Microorganisms of the Sea
 The Microbial World Microorganisms of the Sea Microorganisms Smallest, simplest marine organisms. Very important in evolutionary history of life on Earth. Important primary producers. Include prokaryotes
The Microbial World Microorganisms of the Sea Microorganisms Smallest, simplest marine organisms. Very important in evolutionary history of life on Earth. Important primary producers. Include prokaryotes
Eukarya. Eukarya includes all organisms with eukaryotic cells Examples: plants animals fungi algae single-celled animal-like protozoa
 Eukarya Eukarya includes all organisms with eukaryotic cells Examples: plants animals fungi algae single-celled animal-like protozoa Protists Eukaryotic; but comprises its own Kingdom Protista Algae -
Eukarya Eukarya includes all organisms with eukaryotic cells Examples: plants animals fungi algae single-celled animal-like protozoa Protists Eukaryotic; but comprises its own Kingdom Protista Algae -
Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike.
 SECTION 19.1 DIVERSITY OF PROTISTS Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms. VOCABULARY protist Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. 1. Are protists
SECTION 19.1 DIVERSITY OF PROTISTS Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms. VOCABULARY protist Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. 1. Are protists
Some history. Now, we know that Robert Hooke was not looking at living cells, but the remains of dead cell walls.
 The Life of a Cell Some history In 1665, Robert Hooke examined the bark of an oak tree under an early microscope. He thought he was looking at something similar to the small rooms of dormitories and prisons;
The Life of a Cell Some history In 1665, Robert Hooke examined the bark of an oak tree under an early microscope. He thought he was looking at something similar to the small rooms of dormitories and prisons;
Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria
 Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria All bacteria are Prokaryotic. This means that they are organisms that are one-celled and do not contain a nucleus or other membrane bound organelles.
Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria All bacteria are Prokaryotic. This means that they are organisms that are one-celled and do not contain a nucleus or other membrane bound organelles.
The Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity
 http://animal.discovery.com/tvshows/monsters-insideme/videos/the-brain-eatingamoeba.htm The Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity Introduction to the protists Kingdom Protista split into as many as 20 kingdoms
http://animal.discovery.com/tvshows/monsters-insideme/videos/the-brain-eatingamoeba.htm The Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity Introduction to the protists Kingdom Protista split into as many as 20 kingdoms
Life Science. Chapter 9 Part 1 Protista
 Life Science Chapter 9 Part 1 Protista Protista Junk drawer kingdom a little bit of everything, some w/ cell walls (composition varies), some w/out. All are Eukaryotes, autotrophs and heterotrophs represented.
Life Science Chapter 9 Part 1 Protista Protista Junk drawer kingdom a little bit of everything, some w/ cell walls (composition varies), some w/out. All are Eukaryotes, autotrophs and heterotrophs represented.
Plants Week 3 Booklet
 Plants Week 3 Booklet Living vs. Non-Living Foss Investigation #2 The Microscope Part 3: Microscopic Life: Brine Shrimp Foss Investigation #3 The Cell Part 1: Discovering Cells-Elodea Protists, Fungi &
Plants Week 3 Booklet Living vs. Non-Living Foss Investigation #2 The Microscope Part 3: Microscopic Life: Brine Shrimp Foss Investigation #3 The Cell Part 1: Discovering Cells-Elodea Protists, Fungi &
WHAT DO CELLS DO? CHALLENGE QUESTION. What are the functions of the structures inside of cells?
 WHAT DO CELLS DO? CHALLENGE QUESTION What are the functions of the structures inside of cells? WHAT DO CELLS DO? Understanding normal cell structures and their functions help scientists understand how
WHAT DO CELLS DO? CHALLENGE QUESTION What are the functions of the structures inside of cells? WHAT DO CELLS DO? Understanding normal cell structures and their functions help scientists understand how
Comparing Cells from Different Biological Kingdoms
 Comparing Cells from Different Biological Kingdoms I. Introduction to Cells In 1655, the English scientist Robert Hooke made an observation that would change biological theory and research forever. While
Comparing Cells from Different Biological Kingdoms I. Introduction to Cells In 1655, the English scientist Robert Hooke made an observation that would change biological theory and research forever. While
Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor. Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells
 Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells 1 Eukaryotic organelles are odd in many ways Organelles: membrane bound compartments in a cell Nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria
Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells 1 Eukaryotic organelles are odd in many ways Organelles: membrane bound compartments in a cell Nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria
29/11/2012. Characteristics. Protist Diversity. Characteristics. Kingdom Protista. Examples of Plant-like Protists
 Kingdom Protista Learning Outcome B1 Characteristics Appeared in the fossil record 1.5 billion years ago have an evolutionary advancement over bacteria, because they have a membranebound nucleus. also
Kingdom Protista Learning Outcome B1 Characteristics Appeared in the fossil record 1.5 billion years ago have an evolutionary advancement over bacteria, because they have a membranebound nucleus. also
Biology Lab Practical Review Biology 1110 Instructor: Kate Blinka
 Biology Lab Practical Review Biology 1110 Instructor: Kate Blinka 1. Know and be able to label the parts of a microscope. Including: Eyepiece, arm, base, optical lens, stage, iris diaphram, coarse focus,
Biology Lab Practical Review Biology 1110 Instructor: Kate Blinka 1. Know and be able to label the parts of a microscope. Including: Eyepiece, arm, base, optical lens, stage, iris diaphram, coarse focus,
Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes
 The Microbial World Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes Mircrobes of the Ocean Primary Producers Are the organisms that produce bio-mass from inorganic compounds (autotrophs). -Photosynthetic autotrophs Phytoplankton
The Microbial World Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes Mircrobes of the Ocean Primary Producers Are the organisms that produce bio-mass from inorganic compounds (autotrophs). -Photosynthetic autotrophs Phytoplankton
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Karyotic- from Greek karyon meaning nut or kernel (referring to the nucleus here) Pro- Latin meaning for before Eu- Greek meaning for true Prokaryotic
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Karyotic- from Greek karyon meaning nut or kernel (referring to the nucleus here) Pro- Latin meaning for before Eu- Greek meaning for true Prokaryotic
Importance of Protists
 Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Oceanography Page 1 of 9 Lab: Pond Water M.Sewell rm #70
 Oceanography Page 1 of 9 Pond Water Lab Introduction: Why Study Pond Microlife? Right, what are all those little things really good for? Well, for one thing, without bacteria no fish, no frogs, no birds,
Oceanography Page 1 of 9 Pond Water Lab Introduction: Why Study Pond Microlife? Right, what are all those little things really good for? Well, for one thing, without bacteria no fish, no frogs, no birds,
CHAPTER 1 BIOLOGY THE SCIENCE OF LIFE
 CHAPTER 1 BIOLOGY THE SCIENCE OF LIFE BIOLOGICAL THEMES 1. Cell Structure & Function cell is the basic unit of life all organisms are composed of at least one cell Unicellular single celled ; bacteria,
CHAPTER 1 BIOLOGY THE SCIENCE OF LIFE BIOLOGICAL THEMES 1. Cell Structure & Function cell is the basic unit of life all organisms are composed of at least one cell Unicellular single celled ; bacteria,
CHAPTER 7 VIRUSES BACTERIA PROTISTS FUNGI
 CHAPTER 7 VIRUSES BACTERIA PROTISTS FUNGI 1 Chapter 7 Objectives: Section 1: 1. List characteristics of viruses and start reasons why viruses are considered to be nonliving 2. Describe the components of
CHAPTER 7 VIRUSES BACTERIA PROTISTS FUNGI 1 Chapter 7 Objectives: Section 1: 1. List characteristics of viruses and start reasons why viruses are considered to be nonliving 2. Describe the components of
Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells
 Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells Eukaryotic organelles are odd in many ways Organelles: membrane bound compartments in a cell Nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria
Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells Eukaryotic organelles are odd in many ways Organelles: membrane bound compartments in a cell Nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria
Name Class Date. 1. What three groups can scientists use to organize protists based on shared traits?
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Kinds of Protists 1. What three groups can scientists use to organize protists based on shared traits? PROTIST PRODUCERS 2. What is the name for protists that
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Kinds of Protists 1. What three groups can scientists use to organize protists based on shared traits? PROTIST PRODUCERS 2. What is the name for protists that
