Topic 10: Cyanobacteria & Algae
|
|
|
- Cori Norman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany Spring 2009 Topic 10: Cyanobacteria & Algae A. Introduction Plants are not the only organisms that are photosynthetic. In fact, photosynthetic lineages have popped up here and there throughout the tree of life (see the 7 groups in the phylogenetic tree below). In fact, there are even bacteria that are photosynthetic!! Organisms called algae are photosynthetic, but are usually morphologically simpler than higher plants such as mosses, ferns, or angiosperms. Some algae are unicellular, but others are large, multicellular organisms like the kelps. Within the algae you can see the major trend in the evolutionary development of multicellularity reflected in the diversity of organismal forms: i.e., unicellular >> one-dimensional multicellular growth (1D) >> two-dimensional multicellular growth (2D) >> three-dimensional multicellular growth (3D). Algae have been divided into groups based mainly on distinctive plastid accessory pigments. Because of these pigments, many groups of algae have been known by their color: hence red, green, brown, etc. Modern classifications delimit them with many other characters such as cell wall components, reproductive structures, and distinctive food storage molecules. Algae are the dominant producers in aquatic environments, so they are very important ecologically. The materials available in lab today represent the major algal divisions, along with the cyanobacteria Adapted from Fig in Raven et al. (2007). A phylogenetic tree based on DNA sequences, showing 7 major groups of photosynthetic organisms. Topic 10 Cyanobacteria and Algae, page 1 of 15
2 B. Dichotomous Key to Freshwater Algae. Using the detachable key to freshwater algal genera on the last page of this lab, identify the 10 unknown monocultures of algae to their respective genus. See instructor for the answers at the end of class. Important details are viewed at 200X and 400X (or higher) magnifications. Steps: 1. First, inspect the mass of algae in the tube. What color is it? A blue-green color should be indicative of a cyanobacterium, a light green color should indicate a green alga (chlorophyte), etc. VIEW THE CULTURE AGAINST WHITE PAPER IF THAT S EASIER TO DISCERN COLOR. 2. Afterwards, remove a drop and prepare a wet mount on a microscope slide. LABEL THE SLIDE WITH THE NUMBER ON THE TUBE, SO YOU DON T MIX IT UP. 3. Make your observations with the compound microscope, make drawings, and make your identifications. Record the magnification used as well. 4. Make drawings below and label with genus name and other structures such as CHLOROPLAST(S), FLAGELLUM(FLAGELLA), PYRENOID(S), EYESPOT, etc. Also record the color of your algae, as seen with the naked eye. 5. Share your prepared slides with others in your group Topic 10 Cyanobacteria and Algae, page 2 of 15
3 Topic 10 Cyanobacteria and Algae, page 3 of 15
4 Now, go through the next sections on each algal lineage, read, and answer questions pertaining to the algae observed above or additional algal displays in the room. C. Group 1: Cyanobacteria. Also known as blue-green algae, although they are actually bacteria (i.e., prokaryotes). Like algae, these have chlorophyll. Many are unicellular, others are filamentous, while others are colonial. 1. Thought question: If you were to have a unicellular cyanobacterium and a unicellular alga, how might you tell them apart? List at least two ways. 2. You will or did see two species in the freshwater tube cultures from part B. One of Oscillatoria, the other of Anabaena. 2a. Was Oscillatoria unicellular, filamentous, or colonial? 2b. Did you see any movement in Oscillatoria? 2c. Was Anabaena unicellular, filamentous, or colonial? 2d. What color were the masses of algae in the stock culture tubes? Cross reference these answers to your drawings in part B above. Topic 10 Cyanobacteria and Algae, page 4 of 15
5 Figure at left: some cyanobacteria. A-B and D-E are more or less colonial, since the cells and/or filaments stick together in a gelatinous matrix. D. Group 2: Dinoflagellates. Dinoflagellates are not bacteria but protists. What does that mean? Today, you should find some in your collection from Roddy Pond (compare collections from shallow water vs. deeper water). You will know a dinoflagellate by their olive-brown color (due in part to accessory pigments PERIDININ or FUCOXANTHIN) and their elaborate shapes and ornamentation. Interesting phenomena in nature include bioluminescence and red tides caused by some marine species. Topic 10 Cyanobacteria and Algae, page 5 of 15
6 How many cells is each dinoflagellate? How many flagella do these have and how is each arranged to help them move? Read in your book about the armor or plates (p. 334). Are the plates inside or outside the cell(s)? What are they made of? How is this the same or different than a cell wall? Record your drawings here: Topic 10 Cyanobacteria and Algae, page 6 of 15
7 E. Group 3: Euglenoids. Euglena gracilis is represented today in the freshwater algal cultures from part B. It is just one of many (ca ) species. They do not have common names like birds or trees, so we have to refer to them by their scientific name. Euglenoids are interesting because they combine superficial characteristics of both plants and animals. They can make their own food like a plant, but they can also eat other things, like an animal (or, more aptly, an amoeba). They can also swim and move. Scientists argued for years about which Kingdom to put them in, Animalia or Plantae? Right now they are in neither: according to some classifications they are in the Kingdom Protista with other simple (often microscopic) eukaryotes, such as amoeba and paramecium. A euglena's body is only one cell, so they are very small and you must use a microscope to see them. Sometimes, since they live in water, if there are millions of euglena together, they form a mat on the surface of a pond or marsh that you can see. It looks slimy, a lot like algae. Some people say it looks like pea soup. It gets in swimming pools too, if they are not cleaned regularly. If you've ever seen water in a marsh that looks red, it is from many euglena. Some species have chemicals in them that make them red. Euglena gracilis is not one of those species. How many flagella did the euglena from the unknown algal cultures above have? Did the shape of Euglena cells change while you observed them? Or were they rigid? Any unusual behavior? F. Group 4: Brown or Golden-brown Algae. F1. Diatoms Diatoms are unicellular or colonial organisms that are exceedingly important components of phytoplankton of both marine and freshwater systems. The walls of diatoms consist of two halves: known as frustules, the walls are made of opaline silica and consist of two halves that fit together like a Petri dish. These frustules are very ornate and these ornamentations are used to distinguish species. One of the unknowns from the algal culture was a diatom. Was it Synedra or Navicula? In the station in the back, we have a sample of diatomaceous earth (i.e., diatom fossils). What is diatomaceous earth used for by humans? What is the connection between oil and diatoms? It s an important one. Topic 10 Cyanobacteria and Algae, page 7 of 15
8 Above, scanning electron micrographs of a whole diatom (left) and the half of a frustule, showing the inside face (right). Fig a from Raven et al. (2007). An artful representation of many different types of diatoms. Topic 10 Cyanobacteria and Algae, page 8 of 15
9 F2. Brown Algae When marine algae get big (macroscopic), they are called seaweeds. Most browns are relatively big, and none are unicellular or colonial. Only 6 of 265 genera occur in freshwater. Although they have chlorophyll, their special carotenoid fucoxanthin (which they share with diatoms and many dinoflagellates) impart a brown color to them. Well known members include Fucus (rockweed), Laminaria and Macrocystis (the kelps). Common structures will include a HOLDFAST, a STIPE, A BLADDER (for buoyancy; aka pneumatocyst), and BLADES to function like leaves. Holdfast Logic Question: In what way(s) do holdfasts resemble roots, and in which way(s) do they not? HINT: think about function(s). Topic 10 Cyanobacteria and Algae, page 9 of 15
10 Air bladder or receptacle? Air bladder or receptacle? A. Fucus, plant with receptacles and air bladders. B. x-section of receptacle and smaller conceptacles. C. Male conceptacle with antheridia. D. Antheridia with sperm. E. Female conceptacle with oogonia. F. Oogonium with eggs. Above: Fucus, illustrations of the plant, as well as the reproductive parts. There are prepared slides along the side or back of the room that have sections of these parts. From your microscopic observations, label the plant illustration above as to which arrow box points to a receptacle, and which points to an air bladder. Topic 10 Cyanobacteria and Algae, page 10 of 15
11 G. Group 5: Glaucophytes. Extremely small group of algae closely related to red and green algae. Will not be covered in lab. H. Group 6: Red Algae. The red algae are largely marine and multicellular seaweeds. A class of accessory pigments (phycobilins) makes them reddish. OPTIONAL (SEE INSTRUCTOR): Make macroscopic and microscopic observations of the red algae available in lab. Topic 10 Cyanobacteria and Algae, page 11 of 15
12 I. Group 7: Green Algae. The green algae are a very large and diverse group. They range from unicellular organisms such as Chlamydomonas or Chlorella to colonial organisms such as Volvox, to mulicellular organisms such as Ulva (sea-lettuce) and Chara (stonewort). Many of the unlabeled monocultures of algae in the lab were green algae. Presumably, you have now identified them all. I1. Unicellular forms: all three of the algae below were represented in the unknown algal cultures. Which were which? Chlamydomonas Chlorella Closterium (this unicell is bilaterally symmetric, with two equal halves and a single chloroplast; it s known as a desmid ) Which of the algae above is an indicator of polluted fresh or salt waters? I2. Colonial form: e.g., Volvox (also represented in the unknown algal cultures). Can you recognize Volvox on-sight? I3. Filamentous forms: Spirogyra, and Oedogonium were represented in the unknown algal cultures. Why is Spirogyra named as such? Can you spot pyrenoids in Spirogyra chloroplasts? How do you distinguish these two genera? Are there any OOGONIA or ANTHERIDIA present in the Oedogonium material? I4. Macroscopic (seaweed) forms (IF AVAILABLE): drawings. Macroscopic microscopic (paradermal and x-sections; whole many cells thick is Ulva?). Ulva (sea-lettuce) and other species in Ulva Topic 10 Cyanobacteria and Algae, page 12 of 15
13 I5. Life-cycles of some green algal species. Below is that of Chlamydomonas. Next page is that of Oedogonium. Above: Life cycle of Chlamydomonas, a unicellular green alga. Topic 10 Cyanobacteria and Algae, page 13 of 15
14 Above, life-cycle of the green alga Oedogonium. Topic 10 Cyanobacteria and Algae, page 14 of 15
15 Detachable Dichotomous Key to 10 Freshwater Algae ( 2008, MU Botany) 1. Cells single; not grouped in a colony or filament Cells grouped in colony or end to end in a long filament Cells golden-brown, elliptic (football-shaped) or long and thin with pointy tips (i.e., toothpick-shaped)...synedra (Diatom) 2. Cells bright-green and shaped otherwise Cells narrow (longer than wide) Cells round or ovoid Cells apparently not motile; very long, may be slightly crescentshaped; round vacuoles at each tip may be filled with granules; a row of doughnut-shaped bodies (pyrenoids) runs from the tip to a central clear area... Closterium (Desmid) 4. Cells motile (1-flagellate)... Euglena (Euglenoid) 5. Cells ovoid, rather motile, with a groove on the narrower end where two flagella insert; red eye-spot present...chlamydomonas (Green Alga) 5. Cells round, not apparently motile (not flagellate)... Chlorella (Green Alga) 6. Cells grouped into round colonies, bright- or gold-green... Volvox (Green Alga) 6. Cells grouped into filaments, bright-green or blue-green Cells blue-green (Cyanobacteria) Cells bright-green Filament with constrictions between the cells... Anabaena (Cyanobacterium) 8. Filament without constrictions between the cells; moving... Oscillatoria (Cyanobacterium) 9. Cells of filament cylindrical, chloroplast(s) round... Oedogonium (Green Alga) 9. Cells of filament cylindrical, chloroplast(s) spiral or curved... Spirogyra (Green Alga) Topic 10 Cyanobacteria and Algae, page 15 of 15
Kingdom Protista. The following organisms will be examined in the lab today: Volvox, Oedogonium, Spirogyra, Ulva
 Kingdom Protista I. Introduction The protists are a diverse group of organisms. In the past they have been classified as fungi, plants and animals. They can be green, autotrophs or nongreen heterotrophs.
Kingdom Protista I. Introduction The protists are a diverse group of organisms. In the past they have been classified as fungi, plants and animals. They can be green, autotrophs or nongreen heterotrophs.
Kingdom Protista. Mr. Krause Edina Public Schools ISD273 EXIT 2/16/2005
 Kingdom Protista Mr. Krause Edina Public Schools ISD273 Kingdom Protista General Characteristics Animal-Like Protists Plant-Like Protists Fungus-Like Protists General Characteristics Protozoa - Greek name
Kingdom Protista Mr. Krause Edina Public Schools ISD273 Kingdom Protista General Characteristics Animal-Like Protists Plant-Like Protists Fungus-Like Protists General Characteristics Protozoa - Greek name
INTRODUCTION prokaryotic eukaryotic pigments
 INTRODUCTION This exercise is intended for you to get familiar and comfortable with using a microscope as well as identifying common microbial groups. Thus, we will observe representatives of all microbes
INTRODUCTION This exercise is intended for you to get familiar and comfortable with using a microscope as well as identifying common microbial groups. Thus, we will observe representatives of all microbes
Name Hour. Section 20-3 Plantlike Protists: Unicellular Algae (pages )
 Name Hour Section 20-3 Plantlike Protists: Unicellular Algae (pages 506-509) Introduction (Page 506) 1. Plantlike protists are commonly called 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Algae include
Name Hour Section 20-3 Plantlike Protists: Unicellular Algae (pages 506-509) Introduction (Page 506) 1. Plantlike protists are commonly called 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Algae include
Biology. Slide 1of 39. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1of 39 2of 39 20-4 Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown, and Green Algae Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown and Green Algae Most of these algae are multicellular, like plants. Their reproductive cycles are
Biology 1of 39 2of 39 20-4 Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown, and Green Algae Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown and Green Algae Most of these algae are multicellular, like plants. Their reproductive cycles are
Topic 20. Protista II: The Stramenopiles
 Topic 20. Protista II: The Stramenopiles The Stramenopiles (heterokonts) are a phylogenetic group within the kingdom, Protista. These organisms were derived from an ancestor with two dissimilar flagella,
Topic 20. Protista II: The Stramenopiles The Stramenopiles (heterokonts) are a phylogenetic group within the kingdom, Protista. These organisms were derived from an ancestor with two dissimilar flagella,
Major groups of algae
 Algae general features. All are protists They require moist environments because they lack a cuticle They lack vascular tissues Algae are photosynthetic and reproduce both sexually and asexually Major
Algae general features. All are protists They require moist environments because they lack a cuticle They lack vascular tissues Algae are photosynthetic and reproduce both sexually and asexually Major
Topic 17 Introduction to Domain Eukarya - Organisms with nucleated cells
 Topic 17 Introduction to Domain Eukarya - Organisms with nucleated cells Domain Eukarya. Eukaryotes have nucleated cells. Endosymbiosis has played an important role in the evolution of the group. Both
Topic 17 Introduction to Domain Eukarya - Organisms with nucleated cells Domain Eukarya. Eukaryotes have nucleated cells. Endosymbiosis has played an important role in the evolution of the group. Both
Biology 11. Day 4 Classification of Algae
 Biology 11 Day 4 Classification of Algae Learning Objectives: Become familiar with biological nomenclature Distinguish between Rhodophyta, Phaeophyta, and Chlorophyta Identify features of each body type
Biology 11 Day 4 Classification of Algae Learning Objectives: Become familiar with biological nomenclature Distinguish between Rhodophyta, Phaeophyta, and Chlorophyta Identify features of each body type
Microscopy and the Diversity of Microorganisms
 Microscopy and the Diversity of Microorganisms Today we will learn how to use one of the most important tools a biologist has, the microscope. We will use the microscope to study organisms throughout the
Microscopy and the Diversity of Microorganisms Today we will learn how to use one of the most important tools a biologist has, the microscope. We will use the microscope to study organisms throughout the
Topic 10 Algae. Chap. 17 (pp ) Chap. 18 (Protista; pp )
 Topic 10 Algae Chap. 17 (pp. 305 309) Chap. 18 (Protista; pp. 319 341) I. What is an alga? A. Any photoautotroph not in Kingdom Plantae. 1. Green algae 2. Red algae 3. Brown algae & Diatoms 4. Dinoflagellates
Topic 10 Algae Chap. 17 (pp. 305 309) Chap. 18 (Protista; pp. 319 341) I. What is an alga? A. Any photoautotroph not in Kingdom Plantae. 1. Green algae 2. Red algae 3. Brown algae & Diatoms 4. Dinoflagellates
Topic 14. Algae. Raven Chap. 12 regarding Cyanobacteria (pp ), Chap 15 regarding algae (pp )
 Topic 14 Algae Raven Chap. 12 regarding Cyanobacteria (pp. 263 266), Chap 15 regarding algae (pp. 317 358) I. What is an alga? A. Any* photoautotroph not in Kingdom Plantae. 1. Green algae 2. Red algae
Topic 14 Algae Raven Chap. 12 regarding Cyanobacteria (pp. 263 266), Chap 15 regarding algae (pp. 317 358) I. What is an alga? A. Any* photoautotroph not in Kingdom Plantae. 1. Green algae 2. Red algae
Structures and Life Functions of Single-Celled Organisms
 Structures and Life Functions of Single-Celled Organisms 7.L.1.1 - Compare the structures and life functions of single-celled organisms that carry out all of the basic functions of life including: Euglena
Structures and Life Functions of Single-Celled Organisms 7.L.1.1 - Compare the structures and life functions of single-celled organisms that carry out all of the basic functions of life including: Euglena
Life Science. Chapter 9 Part 1 Protista
 Life Science Chapter 9 Part 1 Protista Protista Junk drawer kingdom a little bit of everything, some w/ cell walls (composition varies), some w/out. All are Eukaryotes, autotrophs and heterotrophs represented.
Life Science Chapter 9 Part 1 Protista Protista Junk drawer kingdom a little bit of everything, some w/ cell walls (composition varies), some w/out. All are Eukaryotes, autotrophs and heterotrophs represented.
Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor. Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells
 Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells 1 Eukaryotic organelles are odd in many ways Organelles: membrane bound compartments in a cell Nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria
Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells 1 Eukaryotic organelles are odd in many ways Organelles: membrane bound compartments in a cell Nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria
Prokaryotes and Kingdom Protista
 Prokaryotes and Kingdom Protista Domain Eubacteria Domain Archae The Prokaryotes Cell type: Prokaryotes Found in: Domain Bacteria Domain Archae Cell type: Prokaryotes Two Domains: Bacteria and Archae Do
Prokaryotes and Kingdom Protista Domain Eubacteria Domain Archae The Prokaryotes Cell type: Prokaryotes Found in: Domain Bacteria Domain Archae Cell type: Prokaryotes Two Domains: Bacteria and Archae Do
Oceanography Page 1 of 9 Lab: Pond Water M.Sewell rm #70
 Oceanography Page 1 of 9 Pond Water Lab Introduction: Why Study Pond Microlife? Right, what are all those little things really good for? Well, for one thing, without bacteria no fish, no frogs, no birds,
Oceanography Page 1 of 9 Pond Water Lab Introduction: Why Study Pond Microlife? Right, what are all those little things really good for? Well, for one thing, without bacteria no fish, no frogs, no birds,
Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells
 Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells Eukaryotic organelles are odd in many ways Organelles: membrane bound compartments in a cell Nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria
Amoeba hunts and kills paramecia and stentor Eukaryotic photosynthetic cells Eukaryotic organelles are odd in many ways Organelles: membrane bound compartments in a cell Nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria
The Microbial World. Microorganisms of the Sea
 The Microbial World Microorganisms of the Sea Microorganisms Smallest, simplest marine organisms. Very important in evolutionary history of life on Earth. Important primary producers. Include prokaryotes
The Microbial World Microorganisms of the Sea Microorganisms Smallest, simplest marine organisms. Very important in evolutionary history of life on Earth. Important primary producers. Include prokaryotes
Complete the journal below:
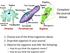 Complete the journal below: 1. Choose one of the three organisms above. 2. Draw that organism in your journal. 3. Observe the organism and infer the following: How do you think the organism moves? How
Complete the journal below: 1. Choose one of the three organisms above. 2. Draw that organism in your journal. 3. Observe the organism and infer the following: How do you think the organism moves? How
Biological Diversity Lab #1 : Domains Eubacteria and Archaea and Protista
 Biological Diversity Lab #1 : Domains Eubacteria and Archaea and Protista Refer to the AP Biology book, Helms Labs 22 and be sure to site other resources used complete this lab in your lab journal. Be
Biological Diversity Lab #1 : Domains Eubacteria and Archaea and Protista Refer to the AP Biology book, Helms Labs 22 and be sure to site other resources used complete this lab in your lab journal. Be
Protists. There are NO typical protists. Protist General Characteristics - usually single cell - eukaryotic - paraphyletic group
 There are NO typical protists. Protist General Characteristics - usually single cell - eukaryotic - paraphyletic group Traditional Classification There are three divisions of the Kingdom Protista: Protozoa,
There are NO typical protists. Protist General Characteristics - usually single cell - eukaryotic - paraphyletic group Traditional Classification There are three divisions of the Kingdom Protista: Protozoa,
Aquatic Ancestors of Land Plants
 Aquatic Ancestors of Land Plants Distinguishing Characteristics: Photosynthetic Live in aqueous environments (ie. In or near water) Lack internal tubes to move water and materials from one part of the
Aquatic Ancestors of Land Plants Distinguishing Characteristics: Photosynthetic Live in aqueous environments (ie. In or near water) Lack internal tubes to move water and materials from one part of the
Algae! b. The basis of most food chains in the ocean. c. Some are so cool, they can live in the snow...and look like blood. d.
 Algae! Algae are a large and diverse group of simple, typically organisms, ranging from to multicellular forms. The largest and most complex marine forms are called seaweeds. They are photosynthetic, like
Algae! Algae are a large and diverse group of simple, typically organisms, ranging from to multicellular forms. The largest and most complex marine forms are called seaweeds. They are photosynthetic, like
PROTISTS. Chapter 25 Biology II
 PROTISTS Chapter 25 Biology II Vocabulary- Protists (44 words) 1. Protist 2. binary fission 3. conjugation 4. Multiple fission 5. pseudopodium 6. test 7. Amoeboid movement 8. cilium 9. Pellicle 10. oral
PROTISTS Chapter 25 Biology II Vocabulary- Protists (44 words) 1. Protist 2. binary fission 3. conjugation 4. Multiple fission 5. pseudopodium 6. test 7. Amoeboid movement 8. cilium 9. Pellicle 10. oral
Observing and Classifying Protozoa
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Observing and Classifying Protozoa Background The name protozoa actually means first animals. This name was given because many protozoa share characteristics with animals. However,
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Observing and Classifying Protozoa Background The name protozoa actually means first animals. This name was given because many protozoa share characteristics with animals. However,
Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014
 Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Meet the algae 1 Protist Phylogeny Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular From phytoplankton to kelp forests
Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Meet the algae 1 Protist Phylogeny Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular From phytoplankton to kelp forests
Plankton. -Plankton are almost always at the bottom of the food chain in any marine environment, making them possibly the most important group.
 Plankton -Plankton are almost always at the bottom of the food chain in any marine environment, making them possibly the most important group. -The word plankton isn t necessarily a technical science term,
Plankton -Plankton are almost always at the bottom of the food chain in any marine environment, making them possibly the most important group. -The word plankton isn t necessarily a technical science term,
The Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity
 http://animal.discovery.com/tvshows/monsters-insideme/videos/the-brain-eatingamoeba.htm The Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity Introduction to the protists Kingdom Protista split into as many as 20 kingdoms
http://animal.discovery.com/tvshows/monsters-insideme/videos/the-brain-eatingamoeba.htm The Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity Introduction to the protists Kingdom Protista split into as many as 20 kingdoms
Single Celled Organisms (Uni-Cellular)
 Single Celled Organisms (Uni-Cellular) Learning Goals Compare the structures and life functions of single celled organisms that carry out all the basic functions of life including: Euglena, Amoeba, Paramecium,
Single Celled Organisms (Uni-Cellular) Learning Goals Compare the structures and life functions of single celled organisms that carry out all the basic functions of life including: Euglena, Amoeba, Paramecium,
Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring Protist Phylogeny. Meet the algae. Primary & Secondary Endosymbiosis. Endosymbiosis. Secondary Endosymbiosis
 Meet the algae Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Protist Phylogeny 1 Primary & Secondary Endosymbiosis 2 Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular
Meet the algae Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Protist Phylogeny 1 Primary & Secondary Endosymbiosis 2 Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Lab Activity
 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Lab Activity Name: Blk: INTRODUCTION Prokaryotic Cells Cells (the smallest individual units of life) are divided into two basic categories: prokaryotic cells, and eukaryotic
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Lab Activity Name: Blk: INTRODUCTION Prokaryotic Cells Cells (the smallest individual units of life) are divided into two basic categories: prokaryotic cells, and eukaryotic
Objective 1: I can describe protists. Protists are a kingdom of living organisms that CAN NOT be classified as animals plants or fungus.
 Kingdom Protista Objective 1: I can describe protists Protists are a kingdom of living organisms that CAN NOT be classified as animals plants or fungus. They are: Eukaryotic they contain a nucleus Can
Kingdom Protista Objective 1: I can describe protists Protists are a kingdom of living organisms that CAN NOT be classified as animals plants or fungus. They are: Eukaryotic they contain a nucleus Can
Microbiology and Protista Lab
 Microbiology and Protista Lab Learning Objectives Describe the basic structures of a bacterial cell. Name the three bacterial cell shapes and recognize each under the microscope Recognize and identify
Microbiology and Protista Lab Learning Objectives Describe the basic structures of a bacterial cell. Name the three bacterial cell shapes and recognize each under the microscope Recognize and identify
Kingdom Protista. Lab Exercise 20. Introduction. Contents. Objectives
 Lab Exercise Kingdom Protista Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Animal-like Protists 2 Activity.2 Fungal-like Protists 3 Activity.3 Plant-like Protists 3 Resutls Section 5 Introduction This
Lab Exercise Kingdom Protista Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Animal-like Protists 2 Activity.2 Fungal-like Protists 3 Activity.3 Plant-like Protists 3 Resutls Section 5 Introduction This
ALGAE (L. Seaweed) HABITAT:
 ALGAE (L. Seaweed) SALIENT FEATURES: 1. Algae are autotrophic organisms and they have chlorophyll. 2. They are O2 producing photosynthetic organisms. 3. In algae the plant body shows no differentiation
ALGAE (L. Seaweed) SALIENT FEATURES: 1. Algae are autotrophic organisms and they have chlorophyll. 2. They are O2 producing photosynthetic organisms. 3. In algae the plant body shows no differentiation
Major Events in the History of Earth
 Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
DIVERSITY OF LIFE THE PROTISTS ORIGIN OF EUKARYOTIC CELLS. Diversity of Life Activity #3 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY DIVERSITY OF LIFE ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE PROTISTS ORIGIN OF EUKARYOTIC CELLS Diversity of Life Activity #3 page 1 PROTIST SYSTEMATICS OLD NEW THE PROTIST HUNT The purpose of this activity
AP BIOLOGY DIVERSITY OF LIFE ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE PROTISTS ORIGIN OF EUKARYOTIC CELLS Diversity of Life Activity #3 page 1 PROTIST SYSTEMATICS OLD NEW THE PROTIST HUNT The purpose of this activity
A. Difference between bacteria (Monera) and other algae (Eukaryotes). -normal stuff: circular v. linear DNA; organelles or not; nucleus or not.
 Cyanophyta (Cyanobacteria; blue-green algae). A. Difference between bacteria (Monera) and other algae (Eukaryotes). -normal stuff: circular v. linear DNA; organelles or not; nucleus or not. B. Differences
Cyanophyta (Cyanobacteria; blue-green algae). A. Difference between bacteria (Monera) and other algae (Eukaryotes). -normal stuff: circular v. linear DNA; organelles or not; nucleus or not. B. Differences
5/10/2013. Protists. Kingdom Protista. Called the Junk Drawer. 3 Subkingdoms of Protists. Protozoans Algae Slime molds
 Protists Kingdom Protista Called the Junk Drawer 3 Subkingdoms of Protists Protozoans Algae Slime molds 1 Protozoans Animal-like Superphyla: Sarcodines ( Sarcodina ) Ciliates ( Ciliophora ) Flagellates
Protists Kingdom Protista Called the Junk Drawer 3 Subkingdoms of Protists Protozoans Algae Slime molds 1 Protozoans Animal-like Superphyla: Sarcodines ( Sarcodina ) Ciliates ( Ciliophora ) Flagellates
Kingdom Protista. The world of Protists: Animal-like Protists Plant-like Protists Fungus-like Protists
 Kingdom Protista The world of Protists: Animal-like Protists Plant-like Protists Fungus-like Protists DOMAIN EUKARYA PROTISTS KINGDOM PROTISTA Any eukaryote that is not classified as a fungus, plant, or
Kingdom Protista The world of Protists: Animal-like Protists Plant-like Protists Fungus-like Protists DOMAIN EUKARYA PROTISTS KINGDOM PROTISTA Any eukaryote that is not classified as a fungus, plant, or
Chapter 20 Protists Section Review 20-1
 Chapter 20 Protists Section Review 20-1 1. What are protists? 2. Why is it easier to define protists by what they are not, rather than by what they are? Completion On the lines provided, complete the following
Chapter 20 Protists Section Review 20-1 1. What are protists? 2. Why is it easier to define protists by what they are not, rather than by what they are? Completion On the lines provided, complete the following
KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM. Dr. Urvashi Sinha, Asst. Prof., Department of Botany Patna Women s College, Patna
 KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM Dr. Urvashi Sinha, Asst. Prof., Department of Botany Patna Women s College, Patna THE CONCEPT Carl Linnaeus introduced the rank-based system of nomenclature
KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM Dr. Urvashi Sinha, Asst. Prof., Department of Botany Patna Women s College, Patna THE CONCEPT Carl Linnaeus introduced the rank-based system of nomenclature
Lab #5 Multicellular Marine Primary Producers. Part 1: Photosynthesis and Photosynthetic Pigments
 Lab #5 Multicellular Marine Primary Producers Part 1: Photosynthesis and Photosynthetic Pigments Introduction Photosynthesis is a fundamental life process upon which all living things depend. Organisms
Lab #5 Multicellular Marine Primary Producers Part 1: Photosynthesis and Photosynthetic Pigments Introduction Photosynthesis is a fundamental life process upon which all living things depend. Organisms
Frequently asked questions (FAQs).
 Frequently asked questions (FAQs). Q.1. What is The term algae (singular: alga), has been derived from a Latin word algere, meaning seaweeds. Algae include a diverse group of mostly autotrophic, eukaryotic
Frequently asked questions (FAQs). Q.1. What is The term algae (singular: alga), has been derived from a Latin word algere, meaning seaweeds. Algae include a diverse group of mostly autotrophic, eukaryotic
Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants. Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR
 Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR In single cell organisms (protists) all life functions are performed by specialized organelles within one cell (a.k.a.
Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR In single cell organisms (protists) all life functions are performed by specialized organelles within one cell (a.k.a.
METHODS OF CLASSIFYING INTO A CERTAIN KINGDOM: 1. prokaryote OR eukaryote 2. single OR multi celled 3. autotroph OR heterotroph
 CH. 22 PROTISTS METHODS OF CLASSIFYING INTO A CERTAIN KINGDOM: 1. prokaryote OR eukaryote 2. single OR multi celled 3. autotroph OR heterotroph 6 Kingdoms 1. Eubacteria prokaryotes; single cell; heterotroph
CH. 22 PROTISTS METHODS OF CLASSIFYING INTO A CERTAIN KINGDOM: 1. prokaryote OR eukaryote 2. single OR multi celled 3. autotroph OR heterotroph 6 Kingdoms 1. Eubacteria prokaryotes; single cell; heterotroph
biology Slide 1of 33 End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 biology 1of 33 2of 33 General characteristics of Plantlike Protists Commonly called algae Found in ponds and lakes Lack true roots, true leaves and stems (differ from true plants) Most are autotrophic
biology 1of 33 2of 33 General characteristics of Plantlike Protists Commonly called algae Found in ponds and lakes Lack true roots, true leaves and stems (differ from true plants) Most are autotrophic
Protists are in the Eukaryote Domain
 Protista Protists are in the Eukaryote Domain All protists are eukaryotic (cells with a nucleus) Euglena Paramecium Amoeba Protists are really just all of the Eukaryotes that don t fit into the Animal,
Protista Protists are in the Eukaryote Domain All protists are eukaryotic (cells with a nucleus) Euglena Paramecium Amoeba Protists are really just all of the Eukaryotes that don t fit into the Animal,
Primary Productivity. Global Net PP. Chapter 5- The Microbial World. Fill in the blank. Bacteria Unicellular algae Protists The Microbial Loop
 Chapter 5- The Microbial World Bacteria Unicellular algae Protists The Microbial Loop Megaplankton Macroplankton Mesoplankton Microplankton Nanoplankton Picoplankton Fill in the blank A. Femtoplankton
Chapter 5- The Microbial World Bacteria Unicellular algae Protists The Microbial Loop Megaplankton Macroplankton Mesoplankton Microplankton Nanoplankton Picoplankton Fill in the blank A. Femtoplankton
Station 1. View the picture of Volvox on the next slide. Draw a picture of what you see.
 Volvox Station 1 View the picture of Volvox on the next slide Draw a picture of what you see. Why do you think Volvox is green? How do you think Volvox gets its energy? Use the reading on Slide 3 to answer
Volvox Station 1 View the picture of Volvox on the next slide Draw a picture of what you see. Why do you think Volvox is green? How do you think Volvox gets its energy? Use the reading on Slide 3 to answer
Protist any organism that is NOT a plant, animal, fungi, prokaryote. grouping for organisms that don't fit into other kingdoms
 Chapter 20 Protists 20 1 What are protists? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ln69k7lytsu (20 Minutes) Protist any organism that is NOT a plant, animal, fungi, prokaryote grouping for organisms that don't
Chapter 20 Protists 20 1 What are protists? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ln69k7lytsu (20 Minutes) Protist any organism that is NOT a plant, animal, fungi, prokaryote grouping for organisms that don't
Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta
 Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 3 types of algae Why we believe land plants developed from algae Lifecycle of a bryophyte
Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 3 types of algae Why we believe land plants developed from algae Lifecycle of a bryophyte
Purpose (1 point) Investigate differences to cell size and shape across various kingdoms
 Living Cells Lab 61 points total As will be seen through this lab, there is no such thing as a typical cell. Though both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are often shown as general cells (p. 206), rarely
Living Cells Lab 61 points total As will be seen through this lab, there is no such thing as a typical cell. Though both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are often shown as general cells (p. 206), rarely
Building the Tree of Life
 18.3 Building the Tree of Life Changing Ideas About Kingdoms This diagram shows some of the ways in which organisms have been classified into kingdoms since the 1700s. Three Domains Genetic analysis has
18.3 Building the Tree of Life Changing Ideas About Kingdoms This diagram shows some of the ways in which organisms have been classified into kingdoms since the 1700s. Three Domains Genetic analysis has
Ch. 19: Protists & Fungi
 Ch. 19: Protists & Fungi Ch. 19: Protists Major Concepts 1. Protists make up a diverse catch-all kingdom of organisms. 2. Algae are photosynthetic protists that are major producers in the biosphere. 3.
Ch. 19: Protists & Fungi Ch. 19: Protists Major Concepts 1. Protists make up a diverse catch-all kingdom of organisms. 2. Algae are photosynthetic protists that are major producers in the biosphere. 3.
Polyphyletic group: multiple genealogies Prokaryotic algae (cyanobacteria) and Eukaryotic algae (protistans; not true plants) Autotrophy Body form:
 Algae Seaweeds Polyphyletic group: multiple genealogies Prokaryotic algae (cyanobacteria) and Eukaryotic algae (protistans; not true plants) Autotrophy Body form: unicellular, filamentous, and multicellular
Algae Seaweeds Polyphyletic group: multiple genealogies Prokaryotic algae (cyanobacteria) and Eukaryotic algae (protistans; not true plants) Autotrophy Body form: unicellular, filamentous, and multicellular
Protists 9/11/2017. Endosymbiosis
 Protists Chapter 28 Most eukaryotes are single-celled organisms Protists are eukaryotes Eukaryotic cells have organelles and are more complex than prokaryotic cells Most protists are unicellular, but there
Protists Chapter 28 Most eukaryotes are single-celled organisms Protists are eukaryotes Eukaryotic cells have organelles and are more complex than prokaryotic cells Most protists are unicellular, but there
Protists. Protists. Protist Feeding Strategies. Protist Body Plans. Endosymbiosis. Protist Reproduction 3/3/2011. Eukaryotes Not a monophyletic group
 Protists Protists Eukaryotes Not a monophyletic group Paraphyletic March 3 rd, 2011 Still use the term protist All eukaryotes except Plants, Fungi, Animals Most unicellular Some colonial Some multicelled
Protists Protists Eukaryotes Not a monophyletic group Paraphyletic March 3 rd, 2011 Still use the term protist All eukaryotes except Plants, Fungi, Animals Most unicellular Some colonial Some multicelled
Name Class Date. 1. What three groups can scientists use to organize protists based on shared traits?
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Kinds of Protists 1. What three groups can scientists use to organize protists based on shared traits? PROTIST PRODUCERS 2. What is the name for protists that
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Kinds of Protists 1. What three groups can scientists use to organize protists based on shared traits? PROTIST PRODUCERS 2. What is the name for protists that
ALGAE. Biol 165: Diversity of Life :24 PM
 Biol 165: Diversity of Life 2013-04-21 9:24 PM ALGAE Introduction Eukaryotic Algae are members of the Kingdom Protoctista Cyanobacteria is a Prokaryotic bacterial Algae, and part of the Domain Bacteria,
Biol 165: Diversity of Life 2013-04-21 9:24 PM ALGAE Introduction Eukaryotic Algae are members of the Kingdom Protoctista Cyanobacteria is a Prokaryotic bacterial Algae, and part of the Domain Bacteria,
19.1 Diversity of Protists. KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms.
 19.1 Diversity of Protists KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms. 19.1 Diversity of Protists Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. Protists are eukaryotes
19.1 Diversity of Protists KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms. 19.1 Diversity of Protists Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. Protists are eukaryotes
Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists
 Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists This organism consists of a single cell with several flagella. Is it a prokaryote, such as a bacterium? Actually, it s larger than a prokaryotic cell, and it also has
Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists This organism consists of a single cell with several flagella. Is it a prokaryote, such as a bacterium? Actually, it s larger than a prokaryotic cell, and it also has
The Microbial World. Chapter 5
 The Microbial World Chapter 5 Viruses Non-cellular infectious agents that have two basic characteristics: Not capable of reproduction without a host cell Structure: Nucleic acid core- can be DNA or RNA
The Microbial World Chapter 5 Viruses Non-cellular infectious agents that have two basic characteristics: Not capable of reproduction without a host cell Structure: Nucleic acid core- can be DNA or RNA
SG 9.2 notes Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants
 Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
What Are the Protists?
 Protists 1 What Are the Protists? 2 Protists are all the eukaryotes that are not fungi, plants, or animals. Protists are a paraphyletic group. Protists exhibit wide variation in morphology, size, and nutritional
Protists 1 What Are the Protists? 2 Protists are all the eukaryotes that are not fungi, plants, or animals. Protists are a paraphyletic group. Protists exhibit wide variation in morphology, size, and nutritional
Importance of Protists
 Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
The Domain Eukarya is a large, diverse and complex group or organisms that consist of one or more Eukaryotic Cells
 The Domain Eukarya is a large, diverse and complex group or organisms that consist of one or more Eukaryotic Cells This domain is divided into four fairly distinct kingdoms: - Protists (Protista) - Plants
The Domain Eukarya is a large, diverse and complex group or organisms that consist of one or more Eukaryotic Cells This domain is divided into four fairly distinct kingdoms: - Protists (Protista) - Plants
There are two commonly accepted theories for how eukaryotic cells evolved: infolding and endosymbiosis. Infolding
 Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
29/11/2012. Characteristics. Protist Diversity. Characteristics. Kingdom Protista. Examples of Plant-like Protists
 Kingdom Protista Learning Outcome B1 Characteristics Appeared in the fossil record 1.5 billion years ago have an evolutionary advancement over bacteria, because they have a membranebound nucleus. also
Kingdom Protista Learning Outcome B1 Characteristics Appeared in the fossil record 1.5 billion years ago have an evolutionary advancement over bacteria, because they have a membranebound nucleus. also
Lecture #9-2/8 Dr. Kopeny
 Lecture #9-2/8 Dr. Kopeny Protistans, Part 1 Lecture VIII Protistans Lecture Themes structure and function; recurring evolutionary themes and unifying features the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts
Lecture #9-2/8 Dr. Kopeny Protistans, Part 1 Lecture VIII Protistans Lecture Themes structure and function; recurring evolutionary themes and unifying features the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts
Mid-Year Exam Review
 Biology 504 Mid-Year Exam Review Name: Spontaneous Generation Ch. 2 Heath Biology 1. What is meant by spontaneous generation? Give 3 examples of the appearance of living things that people believed were
Biology 504 Mid-Year Exam Review Name: Spontaneous Generation Ch. 2 Heath Biology 1. What is meant by spontaneous generation? Give 3 examples of the appearance of living things that people believed were
Kingdom Protista. Protista
 Kingdom Protista Protista Traditionally a kingdom level taxon Current evidence places organisms in as many as 3-5 kingdoms We will classify all: Unicellular or simple colonial Eukaryotic Organisms that
Kingdom Protista Protista Traditionally a kingdom level taxon Current evidence places organisms in as many as 3-5 kingdoms We will classify all: Unicellular or simple colonial Eukaryotic Organisms that
Biology 2. Lab Packet. For. Practical 1
 Biology 2: LAB PRACTICUM 1 1 Biology 2 Lab Packet For Practical 1 Diplomonads Excavata Parabaslids Euglenozoans Dinoflagellates Alveolates Apicomplexans Ciliates Chromalveo Diatoms Golden Algae Stramenopiles
Biology 2: LAB PRACTICUM 1 1 Biology 2 Lab Packet For Practical 1 Diplomonads Excavata Parabaslids Euglenozoans Dinoflagellates Alveolates Apicomplexans Ciliates Chromalveo Diatoms Golden Algae Stramenopiles
Vocab Check. How many words were familiar to you? Botany Pre-Test
 Vocab Check How many words were familiar to you? Botany Pre-Test Homework Chapter 4 Section 1 in textbook Read and complete questions on socrative.com same room number/set up PELOQUINSCIENCE Learning Targets
Vocab Check How many words were familiar to you? Botany Pre-Test Homework Chapter 4 Section 1 in textbook Read and complete questions on socrative.com same room number/set up PELOQUINSCIENCE Learning Targets
Comparing Kingdoms Lab
 Comparing Kingdoms Lab Name: Introduction: Living things are all around us. In der to identify ganisms effectively, scientists have developed methods of classifying ganisms into six maj groups called Kingdoms.
Comparing Kingdoms Lab Name: Introduction: Living things are all around us. In der to identify ganisms effectively, scientists have developed methods of classifying ganisms into six maj groups called Kingdoms.
MICROSCOPY AND CELLS BIO 171 WEEK 3
 MICROSCOPY AND CELLS BIO 171 WEEK 3 MICROSCOPY THE COMPOUND LIGHT MICROSCOPE System of lenses arranged to produce an enlarged, focusable image of a specimen. MICROSCOPY THE MICROSCOPE Illuminating System
MICROSCOPY AND CELLS BIO 171 WEEK 3 MICROSCOPY THE COMPOUND LIGHT MICROSCOPE System of lenses arranged to produce an enlarged, focusable image of a specimen. MICROSCOPY THE MICROSCOPE Illuminating System
Life is Cellular. Discovery of the Cell. Chapter 7 Cell Structure & Function. Exploring the Cell. Introduction. The Discovery of the Cell
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure & Function Life is Cellular Discovery of the Cell As is usually the case, it was the discovery of new technology that led to an important scientific advance Early microscopes led
Chapter 7 Cell Structure & Function Life is Cellular Discovery of the Cell As is usually the case, it was the discovery of new technology that led to an important scientific advance Early microscopes led
Biology 2015 Evolution and Diversity
 Biology 2015 Evolution and Diversity Lab 3: Protista, part II Algae The term "algae" refers to eukaryotic, photosynthetic organisms that are mostly aquatic and lack the characters that are found in plants.
Biology 2015 Evolution and Diversity Lab 3: Protista, part II Algae The term "algae" refers to eukaryotic, photosynthetic organisms that are mostly aquatic and lack the characters that are found in plants.
Name Date Class CHAPTER 19
 Name Date Class Study Guide CHAPTER 19 Section 1: Introduction to Protists In your textbook, read about protists. Match the definition in Column A with the term in Column B. Column A Column B 1. protist
Name Date Class Study Guide CHAPTER 19 Section 1: Introduction to Protists In your textbook, read about protists. Match the definition in Column A with the term in Column B. Column A Column B 1. protist
Domains and Kingdoms
 Domains and Kingdoms Archaea Ancient Bacteria Bacteria Regular Bacteria Eukaryota Organisms with a nucleus DOMAIN: Archaea KINGDOM: Archaebacteria Cell Type Structural Organization Cell Wall Mode of Nutrition
Domains and Kingdoms Archaea Ancient Bacteria Bacteria Regular Bacteria Eukaryota Organisms with a nucleus DOMAIN: Archaea KINGDOM: Archaebacteria Cell Type Structural Organization Cell Wall Mode of Nutrition
Biology 160 Cell Lab. Name Lab Section: 1:00pm 3:00 pm. Student Learning Outcomes:
 Biology 160 Cell Lab Name Lab Section: 1:00pm 3:00 pm Student Learning Outcomes: Upon completion of today s lab you will be able to do the following: Properly use a compound light microscope Discuss the
Biology 160 Cell Lab Name Lab Section: 1:00pm 3:00 pm Student Learning Outcomes: Upon completion of today s lab you will be able to do the following: Properly use a compound light microscope Discuss the
Period: Date: Marine Science Midyear Exam Study Guide & Review This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES.
 Marine Science Midyear Exam Study Guide & Review This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Intro: the water planet; scientific method Properties of Water Tides,
Marine Science Midyear Exam Study Guide & Review This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Intro: the water planet; scientific method Properties of Water Tides,
Plantae. Rhodophyta Chlorophytes Charophytes Land Plants. II. Algal taxonomy. Division: Chlorophyta (green algae)
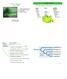 Division: Chlorophyta (green algae) I. General Characteristics II. Distinguishing Classes III. Morphology IV. Classes in Detail II. Algal taxonomy Hierarchical system of classification: Level: suffix:
Division: Chlorophyta (green algae) I. General Characteristics II. Distinguishing Classes III. Morphology IV. Classes in Detail II. Algal taxonomy Hierarchical system of classification: Level: suffix:
Biology 2201 Unit 2 Chapter 5
 Biology 2201 Unit 2 Chapter 5 5.2 Kingdom Protista (pp. 140-151) Kingdom Protista general characterisitcs and groups Protists are a very diverse kingdom of living things that do not fit into any other
Biology 2201 Unit 2 Chapter 5 5.2 Kingdom Protista (pp. 140-151) Kingdom Protista general characterisitcs and groups Protists are a very diverse kingdom of living things that do not fit into any other
Protist any organism that is NOT a plant, animal, fungi, prokaryote. grouping for organisms that don't fit into other kingdoms
 Chapter 20 Protists 20 1 What are protists? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ln69k7lytsu (20 Minutes) Protist any organism that is NOT a plant, animal, fungi, prokaryote include more than 200,000 species
Chapter 20 Protists 20 1 What are protists? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ln69k7lytsu (20 Minutes) Protist any organism that is NOT a plant, animal, fungi, prokaryote include more than 200,000 species
4 Marine Biology Notes. Multi-cellular Primary Producers: Seaweeds and Plants
 4 Marine Biology Notes Multi-cellular Primary Producers: Seaweeds and Plants Marine Algae Marine algae are important primary producers (photosynthetic) These algae are called by a generic term seaweeds
4 Marine Biology Notes Multi-cellular Primary Producers: Seaweeds and Plants Marine Algae Marine algae are important primary producers (photosynthetic) These algae are called by a generic term seaweeds
Station A: #3. If two organisms belong to the same order, they must also belong to the same
 Station A: #1. Write your mnemonic for remembering the order of the taxa (from the broadest, most generic taxon to the most specific). Out to the side of each, write the name of each taxon the mnemonic
Station A: #1. Write your mnemonic for remembering the order of the taxa (from the broadest, most generic taxon to the most specific). Out to the side of each, write the name of each taxon the mnemonic
Classification of organisms. The grouping of objects or information based on similarities Taxonomy: branch of biology that classifies organisms
 Bell Work: Think about your CD, video game, DVD or book collection at home. How would you separate this collection into different groups? What would the groups be? Try to come up with 4 or 5. Classification
Bell Work: Think about your CD, video game, DVD or book collection at home. How would you separate this collection into different groups? What would the groups be? Try to come up with 4 or 5. Classification
BIOLOGY 1021 UNIT 1: MULTICELLULAR STRUCTURE CHAPTER 15 P AND CHAPTER 16 P
 BIOLOGY 1021 UNIT 1: MULTICELLULAR STRUCTURE CHAPTER 15 P. 307-311 AND CHAPTER 16 P. 328-331 Be sure to know flow chart an understanding from atoms to multicellular organisms. Importance of carbon, hydrogen,
BIOLOGY 1021 UNIT 1: MULTICELLULAR STRUCTURE CHAPTER 15 P. 307-311 AND CHAPTER 16 P. 328-331 Be sure to know flow chart an understanding from atoms to multicellular organisms. Importance of carbon, hydrogen,
Objectives. Classification. Activity. Scientists classify millions of species
 Objectives Classification Notes 8.1 Summarize classification Describe the evidence used to classify organisms. List the seven levels of classification. Describe and list the six kingdoms of living organisms
Objectives Classification Notes 8.1 Summarize classification Describe the evidence used to classify organisms. List the seven levels of classification. Describe and list the six kingdoms of living organisms
Protists - a member of a group of eukaryotic organisms, which have a membrane bound nucleus.
 7ch8 Protists Protists - a member of a group of eukaryotic organisms, which have a membrane bound nucleus. protists are a diverse group with many different adaptations share some characteristics with plants,
7ch8 Protists Protists - a member of a group of eukaryotic organisms, which have a membrane bound nucleus. protists are a diverse group with many different adaptations share some characteristics with plants,
1. General Features of Protists
 Chapter 28: Protists 1. General Features of Protists 2. Survey of the Protista A. The Excavata B. The SAR Clade C. The Archaeplastida D. The Unikonta 1. General Features of Protists All Protists are Eukaryotes
Chapter 28: Protists 1. General Features of Protists 2. Survey of the Protista A. The Excavata B. The SAR Clade C. The Archaeplastida D. The Unikonta 1. General Features of Protists All Protists are Eukaryotes
Unicellular Marine Organisms. Chapter 4
 Unicellular Marine Organisms Chapter 4 The Cellular Structure of Life: Review Cell wall: firm, fairly rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, most bacteria, and some protists;
Unicellular Marine Organisms Chapter 4 The Cellular Structure of Life: Review Cell wall: firm, fairly rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, most bacteria, and some protists;
CLASSIFICATION. Why Classify? 2/18/2013. History of Taxonomy Biodiversity: variety of organisms at all levels from populations to ecosystems.
 Why Classify? Classification has been around ever since people paid attention to organisms. CLASSIFICATION One primeval system was based on harmful and non-harmful organisms. Life is easier when we organize
Why Classify? Classification has been around ever since people paid attention to organisms. CLASSIFICATION One primeval system was based on harmful and non-harmful organisms. Life is easier when we organize
Bio 134. Ch. 19 Protists
 Bio 134 Ch. 19 Protists Main Idea! Protists form a diverse group of organisms that are subdivided based on their method of obtaining nutrients What do all protists have in common?! They are all eukaryotes
Bio 134 Ch. 19 Protists Main Idea! Protists form a diverse group of organisms that are subdivided based on their method of obtaining nutrients What do all protists have in common?! They are all eukaryotes
Protists & Fungi. Words to Know: Chapters 19 & 20. Label the paramecium diagram above. (pg. 548)
 Words to Know: Protozoan Chapters 19 & 20 Protists & Fungi Microsporidium Contractile vacuole Pseudopod Bioluminescent Colony Plasmodium Chitin Hypha Septum Spore Sporangium Rhizoid Lichen Mycorrhiza Label
Words to Know: Protozoan Chapters 19 & 20 Protists & Fungi Microsporidium Contractile vacuole Pseudopod Bioluminescent Colony Plasmodium Chitin Hypha Septum Spore Sporangium Rhizoid Lichen Mycorrhiza Label
Prokaryotes. Prokaryotes. Chapter 15: Prokaryotes and Protists. Major episodes in the history of life. Major episodes in the history of life
 Chapter 15: Prokaryotes and Protists The book lumps these VERY DIFFERENT organsims together, simply because they are small, or microscopic Bacteria Archae Protista Major episodes in the history of life
Chapter 15: Prokaryotes and Protists The book lumps these VERY DIFFERENT organsims together, simply because they are small, or microscopic Bacteria Archae Protista Major episodes in the history of life
EXERCISE 3 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC ORGANISMS
 EXERCISE 3 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC ORGANISMS 3.1 INTRODUCTION In the previous exercise you studied the ultrastructure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells with the help of electron
EXERCISE 3 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC ORGANISMS 3.1 INTRODUCTION In the previous exercise you studied the ultrastructure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells with the help of electron
Cells and Microscopes Biology Concepts of Biology 2.1
 Cells and Microscopes Biology 100 - Concepts of Biology 2.1 Name Instructor Lab Section Objectives: To gain an understanding of how to: Correctly use the compound light microscope Differentiate between
Cells and Microscopes Biology 100 - Concepts of Biology 2.1 Name Instructor Lab Section Objectives: To gain an understanding of how to: Correctly use the compound light microscope Differentiate between
